Page 1

Service Manual
Colour Television
Models:
CE28FN1-E
CE25FN1-E
CE21FN1-E
CRT 28” A59EAK071X11
CRT 25” A66EAK071X11
CRT 21” A51EAL155X10
CRT 21” A51EAL155X11
CHASSIS No 2103
EB5-A
Index
1. Safety instructions..................................................................................................................................................................................................1
2. WARNING.............................................................................................................................................................................................................1
3. Precaution against X-Rays.....................................................................................................................................................................................1
4. Technical characteristics........................................................................................................................................................................................2
5. Safety.....................................................................................................................................................................................................................2
6. EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility).....................................................................................................................................................................2
7. Factory special mode..............................................................................................................................................................................................3
8. “HOTEL” and “RENTAL” modes............................................................................................................................................................................3
9. Automatic channel search reactivating...................................................................................................................................................................3
10. Block diagram.......................................................................................................................................................................................................4
11. Power supply........................................................................................................................................................................................................5
12. Microprocessor and Teletext ................................................................................................................................................................................5
13. Video processor/Comb filter.................................................................................................................................................................................5
13.1 Video Intermediate Frequency Section ..........................................................................................................................................................5
13.2 Horizontal and vertical synchronisation..........................................................................................................................................................5
13.3 Geometry.......................................................................................................................................................................................................6
13.4 Filters and video switches..............................................................................................................................................................................6
13.5 Colour decoder ..............................................................................................................................................................................................6
13.6 RGB Processing............................................................................................................................................................................................6
13.7 RGB Control..................................................................................................................................................................................................7
13.8 Supply and bandgap decoupling....................................................................................................................................................................7
14. Audio processor/A3D Surround/Output amplifiers/Sound IF................................................................................................................................7
15. Service menu........................................................................................................................................................................................................8
16. Adjustment and repair procedures .....................................................................................................................................................................10
16.1 Notes about the adjustment:........................................................................................................................................................................10
16.2 Switch-on sequence. ...................................................................................................................................................................................11
16.3 Protect modes and failure indication............................................................................................................................................................11
16.4 Protect mode inhibition ................................................................................................................................................................................11
16.5 Power supply repair procedure....................................................................................................................................................................11
16.6 Non-volatile memory (NVM) replacement, IC125.........................................................................................................................................11
17. Failure location flow-charts.................................................................................................................................................................................12
18. Complete PCB codes for after sales service......................................................................................................................................................15
19. CHASSIS ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST CE21FN1-E / CE25FN1-E / CE28FN1-E ...........................................................................................16
20. CE21FN1-E CABINET PARTS LIST ................................................................................................................................................................17
21. CE25FN1-E CABINET PARTS LIST ................................................................................................................................................................18
22. CE28FN1-E CABINET PARTS LIST ................................................................................................................................................................19
23. Parts List............................................................................................................................................................................................................20
Give complete “SERVICE PART No” for parts order or
servicing, it is shown on the rating sheet on the cabinet
back of the TV set.
16-11-1998
Note
This TV receiver will not work properly in foreign
countries where the television transmission system and
power source differ from the design specifications. Refer
to the specifications for the design specifications.
Ref. Nº
MS CE25FN1-E
Page 2
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
1. Safety instructions
Read this page before doing any operation of adjustment, maintenance or repair the TV set described.
Only skilled personnel of Sanyo Technical Service should do the adjustment, maintenance or repair of TV set.
2. WARNING
For the correct and safe use of the TV set, it is essential that the service personnel follow the process of safety
generally accepted and the safety precautions specified in this manual.
An isolation transformer should be connected in the power line between the receiver and the AC line when a
service is performed on the primary side of the converter transformer of the set.
3. Precaution against X-Rays
The primary source of X-RADIATION in the television receiver is the picture tube. The picture tube is specially
constructed to limit X-RADIATION emissions. For continued X-RADIATION protection, the replacement tube
must be the same type as the original including suffix letter. Excessive high voltage may produce potentially
hazardous X-RADIATION. To avoid such hazards, the high voltage must be maintained within specified limit. If
high voltage exceeds specified limits, take necessary corrective action. Follow the instructions carefully for +B1
volt power supply adjustment, and high voltage adjustment to maintain the high voltage within the specified
limits.
COMPLIANCE TO STANDARDS
All of those marked with X or must be
replaced with original parts
WARNING! This TV set contains components which
are particularly sensitive to static electricity (ESD).
It is recommended that all due precaution be taken
handling integrated circuits and semiconductors.
1
Page 3
4. Technical characteristics
Cathode-ray tubes 21” (54 cm) Model CE21FN1-E
25” (65 cm) Model CE25FN1-E
28” (70 cm) Model CE28FN1-E
In-Line gun type. Black Matrix.
Tuning system
Program selection
Receiving channels
(Cable and Aerial)
TV system
Colour system
Audio power
Speakers
Aerial
Headphones
AV connectors
Power source
Power consumption
CE25FN1-E and CE28FN1-E
Power consumption
CE21FN1-E
STEREO Systems
Sound effects
Comb Filter Models CE25FN1-E and CE28FN1-E
Clock function
Alarm function
Timer function
Teletext
Hotel mode
Voltage synthesis, 100 programs in non volatile memory, AFT, fine tuning (first
10 programs), automatic, semiautomatic and manual channel search.
Sequential selection from the controls on the set. Direct selection of any
program from the remote-control device.
Band I channels E2 ... E4; S1 ... S10;
Band III channels E5 ... E12; S11 ... S41;
Band IV-V channels E21 ... E69.
B/G and D/K systems
PAL, NTSC 4.43
2 x 8 W rms, 10% distortion
2 x 8 Ω, full range
External aerial-socket 75 Ω IEC.
Jack stereo 3,5 mm (with independent control).
1 SCART connector 21-pin, standard CENELEC AV and RGB.
1 SCART connector 21-pin, standard CENELEC AV and S-video.
1 RCA type Video input (front).
2 RCA type Audio R/L input (front).
220 Vac ... 240 Vac, 50 Hz.
108 W (maximum).
72 W (IEC 107-1)
2.5 W (stand-by).
87 W (maximum).
65 W (IEC 107-1)
2.3 W (stand-by).
Nicam and A2.
Active 3D Surround. Pseudo Stereo. Bass boost. Auto volume
Auto capture from teletext.
Programmable over 24 hours.
Switch on and off are programmable over 24 hours.
Level 1.5 Flof, Top and List. 10 teletext pages memory.
East european TXT included.
Can be programmed in Hotel and Hotel Rental mode.
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
5. Safety
It fulfils the safety requirements established in the regulation:
• EN 60065:93
6. EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
It fulfils the EMC requirements established in the regulation:
• EN 55013:1990/A12:1994
• EN 55020:1994
• EN 60555-2:1987
2
Page 4

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
7. Factory special mode
The factory mode is a special TV working mode intended to help in the manufacturing process and it is
identified on the screen with the message “FAC”. This mode is never suited for customer use.
The main differences respect to normal mode are:
1- The standby mode is always disabled.
2- The Blue-back (no sync. signal present) is disabled.
3- The customer adjustments ( volume, contrast …) work faster.
In case of finding the TV set in Factory mode, it must be taken out of this state. To do so, enter the clock
setting menu on the customer OSD and then exit.
8. “HOTEL” and “RENTAL” modes
The TV set has a special mode of operation that is adapted for use in hotels, hospitals… Its main purpose is to
avoid the manipulation of the basic TV settings. This mode is stored in NVM, so it is maintained even though
the TV set is disconnected from the mains.
Its main features are:
1. The maximum volume level is limited to the volume chosen when the mode is entered.
2. Channel searching and fine tuning are disabled.
3. The TV set always switches on with the normalisation settings and users can not memorise any of their
personal preferences.
4. Language selection and child lock are disabled.
5. It is possible to force the TV set to always switch-on in a selected program between the 1st and 8th or AV1.
To activate this mode, hold down the “VOL -” front key and simultaneously, press the “RECALL” remote control
key. A message like “ HOTEL: 00 “ will appear waiting for two digits entry.
The most significant digit indicates the selected mode:
‘0’: normal mode ‘1’: HOTEL mode ‘2’: RENTAL mode
The second digit indicates the programme in which the set will switch on:
‘0’: the same as it was selected when the TV set was switched off (normal mode)
‘1’ to ‘8’: always this programme selection (1 to 8).
‘9’: always AV1 mode
The ‘RENTAL’ mode has the same features as the ‘HOTEL’ mode and additionally the front keys are inhibited
so it is only possible to change the program with the remote control. In order to exit from this mode, the colour
saturation level must be set to zero.
9. Automatic channel search reactivating
In order to reset the initial automatic channel search function, start a channel search in AUTO mode from the
user tuning menu and switch-off the TV set before any station is found. The next time the TV set is switched
on, it will start an automatic channel-search.
3
Page 5
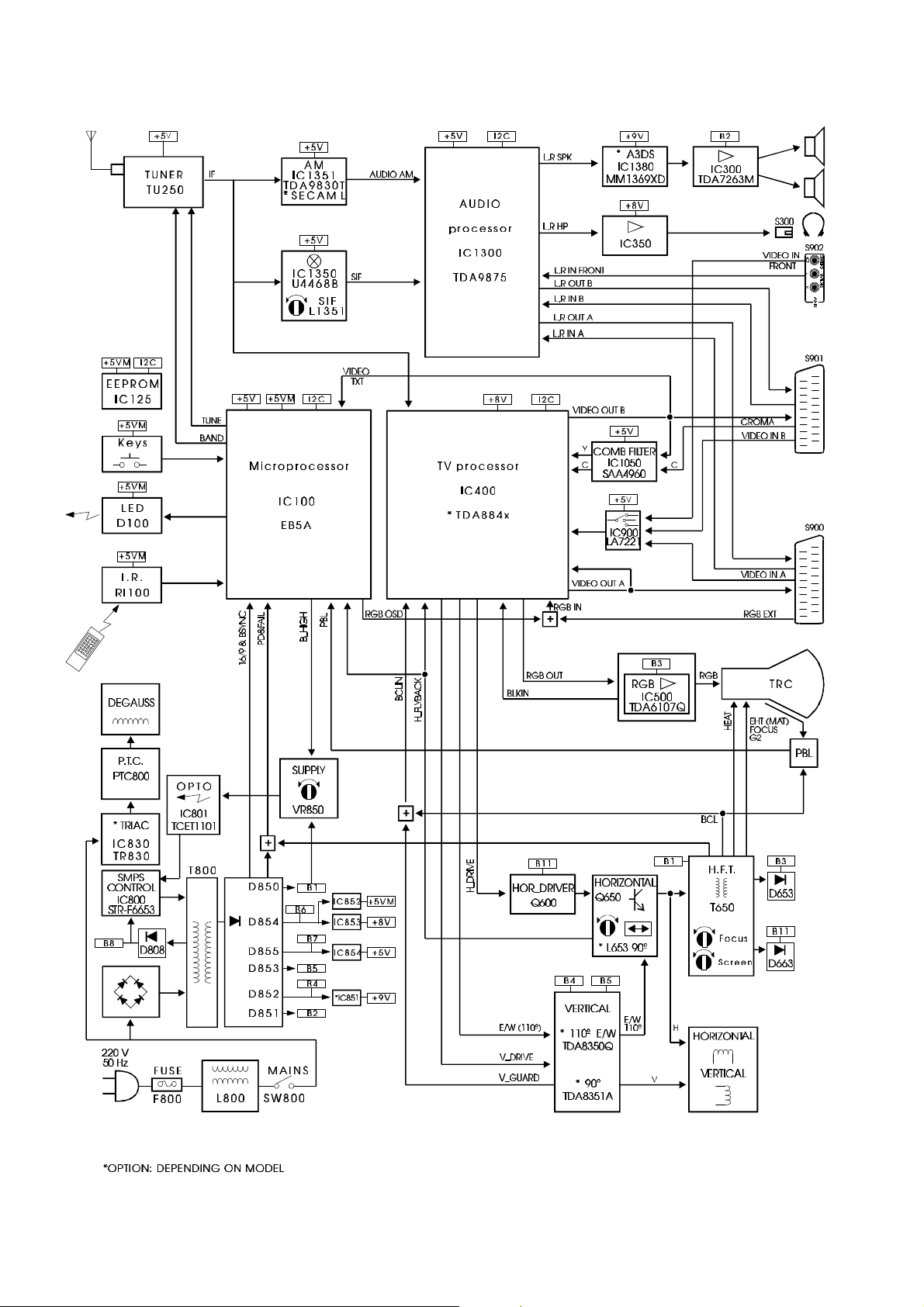
10. Block diagram
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
4
Page 6

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
11. Power supply
First, let’s define some TV states or working modes to clarify later explanations:
State Description
SMPS_B_LOW The power supply is in low consumption (low voltage). The deflection is stopped.
SMPS_B_HIGH The power supply works at nominal voltage. The deflection can be on or off.
STANDBY The micro stops “B_HIGH” port oscillation and the power supply is on “SMPS_B_LOW”.
ON The power supply is on “SMPS_B_HIGH” and deflections are on.
ERROR_N Protect situation. The power supply is on SMPS_B_LOW and the micro shows the error by
the led indicator. The TV is not allowed to switch-on (except ERROR_5).
The power supply works in switched mode with “flyback” self oscillating topology and with control in current
mode. The outputs of the source are shown in the block diagram. Also there are:
• B8: feeds the power supply controller. The initial source in switch-on situation is extracted through
R803+R816.
• B9: feeds the optocoupler primary part.
The power supply sends two signals to the micro processor:
• -PD&FAIL: Switch-off immediately (mains off).
• 16/9&BSYNC: Mains pulses synchronism and 16/9 control. The micro analyses this line in order to switch
correctly from SMPS_B_LOW to SMPS_B_HIGH.
In STAND-BY mode all the voltage outputs are reduced except the microprocessor supply (it remains at 5
volts). The triac TR830 disconnects the PTC800 supply.
12. Microprocessor and Teletext
The microprocessor (IC100) main tasks are the following:
• video processor control
• audio processor control
• NVM access
• IR decoding
• Teletext processing and display
• OSD generation
• tuning and AFT
• failure checking
• …
13. Video processor/Comb filter
The video processor (IC400) has the following functional blocks: video Intermediate frequency, mono sound
(not used), vertical and horizontal synchronism, geometry processor, video switching and filtering, colour
decoder and RGB processing. All the adjustments are performed by the microprocessor via the I2C bus.
13.1 Video Intermediate Frequency Section
• I.F Amplifier: The input signal comes from the tuner (TU250) through the S.A.W. filter SF200 (band pass
filter of the video information and the picture carrier.
• PLL Demodulator and VCO: The VCO does not need any adjust neither external coil. The frequency
adjustment is performed through the I2C bus. The components associated with the PLL are connected to
the pin 5 (PLLLF).
• Video buffer: The demodulated video signal is present at pin 6 (IFVO) with a typical level of 2Vpp.
• AGC: It controls the IF amplifier gain in order to maintain its amplitude constant. The capacitor connected to
the pin 53 (DECAGC) determines the AGC time constant.
• Tuner AGC: It reduces the gain when a high level aerial signal is received. The level at which this reduction
is performed is I2C bus adjusted (AGC in the service menu).
• AFC: The AFC information is accessible via I2C bus.
• Video identification: The video identification information is accessible via I2C bus.
13.2 Horizontal and vertical synchronisation
• Horizontal sync separator
• Horizontal oscillator: it is internal and only needs the crystal oscillator X400 as a reference frequency.
• PHI-1 detector: It is a PLL that synchronises the horizontal oscillator with the video signal. The components
associated with the PHI-1 are connected to the pin 43 (PH1LF). The PHI-1 time constant and the noise
5
Page 7

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
detector are controlled via I2C bus.
• PHI-2 detector and Sandcastle generator: The PHI-2 detector performs a stable picture. It synchronises the
horizontal oscillator with the horizontal flyback signal (pin 41, FBISO) to generate the horizontal output (pin
40, HOUT). . The components associated with the PHI-2 are connected to the pin 42 (PH2LF). The picture
phase is adjusted via I2C (HOR SHIFT in the service menu). The flyback input pin 41 (FBISO) is combined
with the sandcastle output and provides a three level sandcastle signal. The levels are: 2V à vertical
retrace; 3Và horizontal retrace; 5.3V àBurstkey.
• Horizontal output (pin 40, HOUT): It is a open collector type and the duty cycle in normal condition is 45%
high and 55% low. A built in slow start/stop circuit ensures a smooth start/stop behaviour of the line
deflection. Also during switching off via stand by the RGB drive is set to maximum to discharge the EHT
CRT capacitance.
• Coincidence detector
• Vertical sync separator
• Vertical divider
13.3 Geometry
• Vertical sawtooth generator: it delivers the reference signals for vertical and horizontal geometry processor.
An accurate reference current is used to charge the external capacitor during vertical scan. The resistor
R426 in pin 52 (IREF) determines this reference current. It is a Metal Film resistor with 1% tolerance in
order to provide a temperature stabilisation and lower dispersion. The ramp capacitor (C425) is connected
to pin 51 (VCS). It is a polycarbon one in order to provide temperature stabilisation.
• Vertical geometry processor: it performs the sawtooth signal and it has a differential current output in pins
47 (VDRA) and 46 (VDRB) for a DC coupled vertical output stage (drive). Control functions accessible via
I2C are VERT SLOPE, VERT AMPL, S-CORREC, VERT SHIFT (see service menu).
• Horizontal geometry processor (E/W drive): it has a single-ended current output for E-W drive (pin 45
EWD). This current is amplified and applied to the diode modulator of the horizontal deflection. The
adjustments are accessible via I2C (EW AMPLIT, PARABOLA, CORNER PAR, TRAPEZIUM in the service
menu).
• EHT tracking (pin 50, EHTO): this tracking makes the picture size independent of EHT variations due to the
beam current.
13.4 Filters and video switches
• Video signal selection: the input selector has CVBS_INT(pin 13), CVBS_EXT (pin 17), CVBS/Y (pin11) and
CHROMA (pin 10) as inputs which can be selected via I2C bus. The selected video signal is present at pin
38 (CVBSO).
• Filter calibration: it is an auto-tuning loop which calibrates every field retrace. The filters are the
chrominance bandpass and the chrominance trap.
• Chrominance signal processing: this circuit keeps constant the colour saturation level.
• Luminance signal processing: the selected video signal is supplied to the chrominance trap. The output
signal is supplied to the peaking and coring stages. Both are controlled via I2C bus. The output (pin 28
LUMOUT) is fed through a band pass filter (L409, R439 and C440) as internal luminance signal (pin 27
LUMIN).
13.5 Colour decoder
• PLL/VCXO: The PLL operates during the burstkey period. In the lock condition the VCXO reference signal
(X400 in pin 35) and the burstkey become synchronous. An optimum transient response can be chosen with
the loop filter connected to pin 36 (DET). The reference output (4,43MHz in pin 33) can be used for comb
filter applications.
• PAL/NTSC Demodulation: The reference signals from the VCXO are supplied to the HUE phase rotator; its
outputs are supplied to the (R-Y) and (B-Y) demodulators. The (B-Y)/(R-Y) baseband signals are filtered and
supplied via the PAL/SECAM switch to the internal baseband delay line. The signals from the delay line are
RYO (pin 30) and BYO (pin 29).
• SECAM Demodulation: It is realised with a PLL type demodulator. The SECAM reference voltage is
generated at pin 16 (SECPLL). The demodulated signal is distributed to the (R-Y) and (B-Y) amplifiers and
via de PAL/SECAM switch to the baseband delay line.
• Automatic system manager: it can identify PAL/SECAM/NTSC colour standards. The different possibilities
are controlled by the I2C bus.
13.6 RGB Processing
• (R-Y)/(B-Y) processing/matrixing: The amplitude of this signals (pins 32 (RYI) and 31 (BYI)) is controlled via
the I2C bus (colour saturation) and also this signals are supplied to dynamic skin control. After the R-Y and
6
Page 8

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
B-Y matrixing, the output signals are added with the luminance signal in order to generate the internal RGB
signals.
• RGB selector: it is controlled by the FB signal in signal 26 (RGBIN). The external RGB signals are present
in pins 23 (RI), 24 (GI) and 25 (BI). The RGB selector output is fed to then RGB control.
13.7 RGB Control
• Contrast and brightness control: There are I2C bus controlled. These adjustments can be reduced by the
beam current limiter stage. Furthermore, contrast is affected by the Peak Beam Limiter (Q670 and Q671
circuitry). This circuit’s output is the PBL signal to microprocessor’s pin 11 and must be 5V with a black
pattern on the screen.
• Beam current limiter/vertical guard: The BCLIN (pin 22) input circuit functions as an average beam current
limiter as well as a peak white limiter. The vertical deflection works correctly when there is a pulse level
above 3.7V during the vertical retrace. The vertical guard function can be I2C controlled. The contrast and
brightness reduction begins when BCLIN level is below 3.0V and 2.0V respectively.
• Continuous cathode calibration (AKB): it is divided into two loops: a black level stabilisation and a cathode
drive stabilisation. Each gun of the CRT is stabilised sequentially and independently and a feedback current
flows to the black current input (pin 18 BLKIN) supplied by the RGB amplifier (IC500). In order to change the
cathode levels at the picture tube three I2C bits are available.
• White point adjust and blue stretcher.
13.8 Supply and bandgap decoupling
The IC400 has two supply pins 12 and 37. Both pins must be supplied simultaneously. The nominal supply
voltage is 8V. The pins 14 and 44 must be connected to ground.
The bandgap circuit provides a very stable and temperature independent reference voltage that ensures
optimal performance of the video processor. Short decoupling (pin 9 DECBG) to pin 14 of the external
capacitor is important for stable horizontal drive.
The comb-filter (IC1050) is only performed with a PAL signal. To enhance the image quality its main features
are: cross colour reduction (only at vertical frequencies), cross luminance reduction and improved video
bandwidth.
The input signal is composite video. It comes from the IC400 (pin 38 CVBSO) to the pin 17 (YEXT/CVBS). It is
processed internally and the resultant signals are Luminance (pin 14 Y0) and chrominance (pin 12 C0). These
signals return to the colour decoder in the video processor. The comb-filter is switched on through the I2C bus
by writing a bit in the video processor. This one outputs a 4,43MHz signal on the REF0 port superposed to a
high level one.
With SECAM, NTSC or S-VHS signals the comb-filter is disabled. It bypasses the luminance (pin 17 YEXT/CVBS- to pin 14 -YO-) and chrominance (pin 10 -CEXT- to pin 12 -CO-) signals. The video processor
outputs a low level on pin 33.
In the models without the comb-filter, the jumpers JO1050 and JO1051 bypass the signals.
14. Audio processor/A3D Surround/Output amplifiers/Sound IF
The audio processor (IC1300) is controlled via I2C bus. It has 3 main sections: analog, digital and DSP (digital
signal processing).
• The analog part takes: audio input and output switching, A/D and D/A conversion of input/output sound
signals.
• The digital part: demodulates FM (multistandard) and decodes the two carrier signals, controls the sound IF
AGC, demodulates DQPSK (multistandard) and decodes NICAM.
• The DSP section takes: sound controls, sound effects for loudspeakers, mute for loudspeakers and
headphones, beeper (alarm function) and digital audio switching matrix.
The IC1380 produces the Active 3D Surround (A3DS) effect. The models without A3DS effect use the jumpers
JO1381 and JO1382 to bypass the audio signals to the audio amplifier for loudspeakers.
IC300 is the stereo audio amplifier for loudspeakers, it has a variable gain through the resistive dividers
R303/R304 and R305/R306 (for channels L and R respectively). The power driven is approximately 8W rms. at
10% of distortion (each channel). The input pins (1 and 5) are connected to the audio processor (IC1300) or to
the Active 3D Surround in models that have this feature. Pins 10 and 8 are the loudspeakers power outputs
(channels L and R respectively). The microprocessor can mute the audio by setting high the MUTE signal. This
pin is used only at TV set switch-on and off and in case of bad aerial reception. In all other situations the mute
function is performed by the IC1300.
A fixed gain stereo amplifier is used for headphones (IC350). The input pins (7 and 6 for channels L and R)
come from the audio processor headphones outputs. The headphones connector outputs are the pins 1 and 3.
7
Page 9
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
The microprocessor detects the headphones presence via the HP_SW signal. The MUTE signal also affects
the headphones audio.
The FM or NICAM-modulated sound IF signal, which inputs the audio processor, is produced by the sound IF
circuit, IC1350. This IC takes the signal from the tuner and converts it to the intercarrier frequency. The internal
VCO frequency is adjusted by means of L1351.
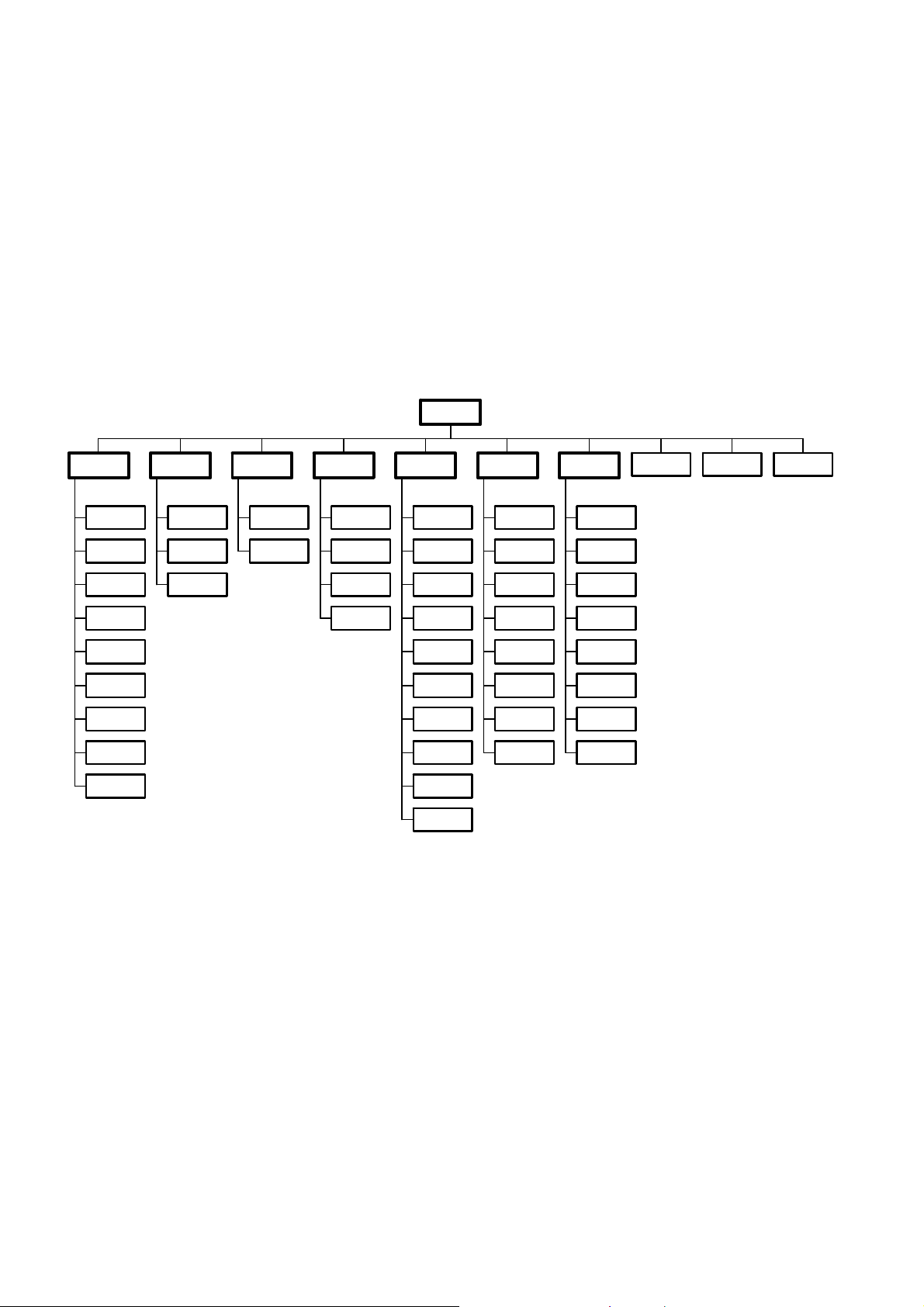
15. Service menu
The service menu is accessed by holding down the front key “VOL-“ and simultaneously pressing the teletext
green key from the remote control. The service menu is a two level structure as shown in the diagram below.
The active keys (local or remote) in service mode are: VOL-, VOL+, P-, P+, MENU and the digits. The
navigation through this menu works the same than in the user menu.
* The P+ and P- keys allow to navigate through the options in the active menu.
* The VOL+ key opens the second level menu if available. If there is a highlighted adjustment, the VOL- and
VOL+ keys allow to change it.
* The MENU key goes back one level menu. If the active menu is the main one, it exits the service mode.
* The digit keys allow direct entry for adjustments.
* The SERVICE mode is exited by pressing any other key.
SERVICE
GEOMET
HOR SHIFT
EW AMPLIT
PARABOLA
CORNER PAR
TRAPEZIUM
VERT SLOPE
VERT AMPL
S-CORREC
VERT SHIFT
VIF
PLL
PLL L'
AGC
WHITE
GREEN
BLUE
G2
BRI
ADJ
AKB
K-DRV
MORE
Y/C PAL
Y/C SECAM
Y/C NTSC
Y/C AV
PBL SPEED
CONTR OSD
CONTR TXT
CENTR TXT
SEMI MUTE
INI NVM
CONFIG
TXEAST
FFI
SCS
CMB
DSA
OSO
OEM
16:9
STANDARD
PAL BG
PAL DK
PAL I
SECAM BG
SECAM DK
SECAM L
NTSC BG
NTSC M
V-STAT S-STAT I2C BUS
8
Page 10

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Adjustment Meaning Range Initial
value
HOR SHIFT Horizontal phase 0 to 63 37 EW AMPLIT Horizontal width 0 to 63 57 -
Irrelevant in 90º deflection models
PARABOLA E/W correction 0 to 63 38 -
Irrelevant in 90º deflection models
CORNER PAR E/W corner correction 0 to 63 30 -
Irrelevant in 90º deflection models
TRAPEZIUM Trapezium correction 0 to 63 21 -
Irrelevant in 90º deflection models
VERT SLOPE Ramp generator amplitude 0 to 63 36 VERT AMPL Vertical amplitude 0 to 63 40 S-CORREC Vertical S-correction 0 to 63 18 VERT SHIFT Vertical centre 0 to 63 36 PLL PLL of video IF 0 to 127 80 80 (imperative)
PLL L’ PLL of video IF in L’ system 0 to 127 80 80 (imperative)
AGC Automatic gain control 0 to 63 16 GREEN White point, green gain 0 to 63 40 BLUE White point, blue gain 0 to 63 36 BRI G2 adjust brightness level 0 to 63 32 0 if cut-off = 160V
5 if cut-off = 150V
32 if cut-off = 130V
ADJ Service Line Adjust - - AKB Enable/Disable AKB servo ON/OFF ON ON
K-DRV RGB Drive 0 to 7 5 5 in Ph110º
4 in 90º
Y/C PAL PAL Phase luma-croma 0 to 15 03 03 in models PAL B/G 110º
Irrelevant in 90º models
Y/C SECAM SECAM Phase luma-croma 0 to 15 00 00
Irrelevant in 90º models
Y/C NTSC NTSC Phase luma-croma 0 to 15 03 03
Irrelevant in 90º models
Y/C AV AV inputs Phase luma-croma 0 to 15 10 10
Irrelevant in 90º models
PBL SPEED Contrast reduction speed when PBL acts 0 to 63 9 9 in 100º models
18 in 90º models
CONTR OSD OSD Contrast 0 to 63 25 25
CONTR TXT TXT Contrast 0 to 63 18 18
CENTR TXT OSD and TXT Centre 0 to 3 1 0
SEMI MUTE Attenuation (dB) by pushing Mute once 0 to 63 15 15
INI NVM Non volatile memory initialisation - - FFI PLL constant time of IF ON/OFF OFF OFF
SCS SCART connectors interchange ON/OFF OFF Equals the OSD with the back cover label
CMB Enable/Disable the Comb Filter ON/OFF OFF ON in models with Comb-Filter
OFF in models without Comb-Filter
TXEAST Eastern characters set ON/OFF OFF OFF
DSA Skin tone correction angle ON/OFF OFF OFF
OSO HV discharge mode ON/OFF OFF ON
OEM TV set trade-mark ON/OFF OFF OFF in SANYO models
ON in SONITRON models
16:9 16:9 picture configuration ON/OFF OFF OFF
PAL B/G PAL B/G Configuration ON/OFF ON ON
PAL D/K PAL D/K Configuration ON/OFF ON OFF
PAL I PAL I Configuration ON/OFF OFF OFF
SECAM B/G SECAM B/G Configuration ON/OFF OFF OFF in PAL models
ON in SECAM models
SECAM D/K SECAM D/K Configuration ON/OFF OFF OFF
SECAM L SECAM L Configuration ON/OFF OFF OFF
NTSC BG NTSC 4.43MHz Configuration ON/OFF ON ON
NTSC M NTSC 3,58MHz Configuration ON/OFF OFF OFF (imperative)
V-STAT Video processor status - - S-STAT Sound processor status - - I2C BUS I2C Bus stop - - -
Suggested value
9
Page 11

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
16. Adjustment and repair procedures
ADJUSTMENT SIGNAL CONDITIONS TEST POINTS ADJUSTMENT POINT ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE INSTRUMENTS
Power supply Philips pattern Picture: Normalised
AGC. UHF Band - mid
Sound IF Any picture Pin 5 of IC1350 L1351
Vertical slope Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/GEOMETRY/VERT SLOPE Adjust to achieve that the centre line of the Philips pattern matches the
Vertical centre Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/GEOMETRY/VERT SHIFT Adjust to centre the picture in vertical direction Visual adjustment
Vertical size Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/ GEOMETRY/VERT AMPLIT Adjust just to get the checked board hidden Visual adjustment
Horizontal centre Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/ GEOMETRY/HOR SHIFT Adjust to centre the picture in horizontal direction Visual adjustment
Width (90º) Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen L653 Adjust just to get the checked board hidden Visual adjustment
Width (110º) Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/ GEOMETRY/EW AMPLIT Adjust just to get the checked board hidden Visual adjustment
Pin Cushion
(110º)
Corner Pin
Cushion (110º)
Trapezium (110º) Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/ GEOMETRY/TRAPEZIUM Adjust to obtain the lateral vertical lines parallel Visual adjustment
G2 Philips pattern Before SERVICE/G2/BRI must be:
White point Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/WHITE/GREEN
channel (e.g.CH25)
Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/ GEOMETRY/PARABOLA Adjust to correct the pin cushion distortion in the way that vertical lateral
Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/ GEOMETRY/CORNER PAR Adjust to correct the pin cushion distortion in the corner in the way that
Sound: Minimum volume
Aerial signal level: 60dBuV (1mVrms) Pin 1 of TU250
32 en CRTs Philips A59/A66EAK071X11
0 en CRTs Philips A51EAL155X10/X11
B1
Cathode D850
(AGC)
CRT Screen SERVICE/G2/ADJ
VR800 Adjust to obtain:
SERVICE/VIF/AGC
SCREEN potentiometer
SERVICE/WHITE/RED
Voltmeter DC
150V ± 0.5V in CRTs Philips A59/A66EAK071X11 if C651 = 12 nF
148V ± 0.5V in CRTs Philips A59/A66EAK071X11 if C651 = 11 nF
148V ± 0.5V in CRTs Videocolor A59/A66EHJ43X38
150V ± 0.5V in CRTs Panasonic A59/A66ECF50X05
118V ± 0.5V in CRTs Philips A51EAL155X10/X11
Adjust to obtain 3,3V ±0,2V
Adjust to obtain 2,3V ±0,15V
beginning of the service blanking
lines become straight
vertical lateral lines become straight
Adjust just to see the service line Visual adjustment
Adjust to obtain a white tone acceptable Visual adjustment
Resolution >0,1V
Voltmeter DC
Resolution >0,1V
Voltmeter DC
Resolution >0,1V
Visual adjustment
Visual adjustment
Visual adjustment
Focus Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen FOCUS potentiometer Adjust to obtain the best possible focusing in the centre of screen Visual adjustment
TXT centre Philips pattern Picture: Normalised CRT Screen SERVICE/MORE/CENTR TXT Adjust to centre the OSD in the screen Visual adjustment
Common condition to all adjustments (except AGC): The aerial signal level must be acceptable (the picture doesn’t present snow degradation)
16.1 Notes about the adjustment:
Normalised: Factory picture control normal has the following OSD positions:
• Brightness: 32 (Push key “+” 32 times starting at minimum position)
• Contrast: 58
• Colour: 30
10
Page 12

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
16.2 Switch-on sequence.
In case of malfunction it is very important to know the switch-on procedure:
1. When the reset is at low level the microprocessor begins to work.
2. It recalls from NVM the last state before the switch-off.
3. If it is STAND BY, it remains in STAND BY. If it is ON, it continues the switch-on procedure.
4. It waits until a falling edge in the 16/9&BSYNC signal occurs.
5. The port B_HIGH is set (B_HIGH oscillating).
6. It waits until a rising edge in the 16/9&BSYNC signal occurs.
7. It reads the CTL1 signal. If this signal doesn’t rise before 160mS the process is stopped indicating
ERROR_4.
8. The Video processor is started via I2C bus. If there isn’t any answer the process is stopped indicating
ERROR_1.
9. There is a 1 second delay.
10. The deflections start. If there are failures the process is stopped indicating ERROR_2 or ERROR_3.
11. It waits until the cathode heater is warm by inspection of the video processor register bit AKB.
12. The picture and the sound are switched on and the procedure is finished.
16.3 Protect modes and failure indication
The microprocessor checks periodically the different parts of the circuit and if it detects any fault in a safety
defined part then it puts the TV set in PROTECTED mode. The found error code is indicated by the red LED.
The red indicator lamp flashes every 0,3 seconds and stops during 0,7 seconds. The number of flashes
depends on the error code (see table below).
Error indication Meaning
ERROR_1 The Video Processor does not answer
ERROR_2 Vertical Deflection Fault
ERROR_3 Horizontal Deflection Fault
ERROR_4 Power Supply Short-circuit.
ERROR_5 The Sound Processor does not answer
ERROR_6 The non volatile memory does not answer
The 1, 2, 5 and 6 error codes are read via the I2C Bus.
The 3 and 4 error codes are read through the CTL1, CTL2 and -PD&FAIL signals.
In all cases except ERROR_5 the power supply is set in SMPS_B_LOW state.
16.4 Protect mode inhibition
In order to facilitate the TV set repair it is possible to disable the protect mode. By pushing the M key (PL100)
in a fault detection situation, the microprocessor resumes normal execution flow except in ERROR_4 state
(Power Supply Short-circuit). In this case the microprocessor keeps the power supply in SMPS_B_LOW state
(the M key does not act).
16.5 Power supply repair procedure
• When it is necessary to replace the IC800, it is strongly recommended to replace also the current sensor
resistors R804 and R805 (they may be also damaged or altered).
• Keep in mind that when the power supply is forced to SMPS_B_HIGH state and without current
consumption at the main output (deflection stopped), B6 is the stabilised output. The minimum voltage
circuit is working and B6 can go down from the nominal 10 volts to 7,5 volts approximately. Also, in this
situation B1 goes up until 160 - 180 volts in TV sets with 110º CRT.
16.6 Non-volatile memory (NVM) replacement, IC125
When the TV set starts up, the microprocessor checks the non volatile memory in order to know if it has been
initialised. Even if it detects no initialisation it will continue the start up procedure with a minimum default
adjustment values stored in ROM. Then, in case of NVM replacement, it is necessary to initialise the non
volatile memory from the SERVICE menu (it will load a complete set of default values) and afterwards adjust
all the controls to its correct value.
11
Page 13

17. Failure location flow-charts
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
ERROR_1
Switch on the TV set with PL100
pushed (protect mode disabled)
Check the +8V supply
in pins 12 and 37 of IC400
OK
Check I2C bus path to
pins 7 and 8 of IC400
OK
Replace IC400
Check +B5
in pin 8 IC701
Replace IC701
Are the retrace
lines visible?
*Check +B3 at IC500
*R506 is possibly fused
*IC500 is possibly damaged
NG Yes
Check TO478
(Output of IC701)
OK
Check the path of
V_GUARD signal
Probably:
*C425 failure
*IC400 failure
No
Switch on the TV set with PL100
pushed (protect mode disabled)
Adjust G2 just to see the picture
NG
ERROR_2
Does it happen quickly
after switch on?
Yes
Check the vertical deflection
path to IC701
OK
Is the vertical
size OK?
No
Check TO047
(Ramp generator)
OK
ERROR_5
Check +5Vin L1304 (audio PCB)
OK
Check I2C bus path to
pins 4 and 5 of IC1300 (audio PCB)
OK
Check +5V in pins
7, 15, 38, 59 and 64 of IC1300 (audio PCB)
OK
Check the crystal oscillador of IC1300
OK
Replace IC1300
ERROR_6
Check the path
of +V_DRIVE and -V_DRIVE
signals in IC400
OK
Replace IC400
NG
Check B4 in
pin 4 IC701
OK
Open the pins 1 and 2 of
IC701 and check the
+V_DRIVE and -V_DRIVE signals
OK
Replace IC701
12
Check +5VM in pin 8 of IC125
OK
Check I2C bus track continuity
in pins 5 and 6 of IC125
OK
Replace IC125
Page 14

ERROR_3
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Are retrace lines visible ?
*Check +B3 at IC500
*R506 posibly fused
*IC500 posibly damaged
Does it happen quickly
No
after switch on?
Yes
Switch on the TV set with PL100
pushed (protect mode disabled)
Does it sound line
stage abnormal?
No
Is there picture ?
No
* Possible failure of T650
Yes
Yes Yes
E/W output to the diode modulator
With the TV set switched off
and the tester in ohms, does
it measure shortcircuit between
* Possible shortcircuit in
secondary of T650
* Check B10
Is the E/W
correction OK?
No
Check the path from the
OK
pins 11 and 7 of IC701?
No
Possible failure in protect circuits
(Q750, Q751, Q653, Q651, Q652)
Check that the voltage level
in -PD&FAIL is 5V.
OK
Probably:
Leakage in C402 or C403
(Bandgap capacitance)
Probably:
* IC701failure
Yes
* D750 failure
Check the E/W signal
from the IC400 output
to the IC701 input
Check +B1 in
pin 2 of T650
OK
Check D663 and the
path of +B10
OK
Check the path of the
horizontal deflector
yoke to the circuit
OK
Check the horizontal
deflection path
OK
Probably:
*X400 damaged
*T650 failure
The pulses level
is low
There is an H_FLY
abnormal positive polarization
of H_FLY or H_SYNC signals
(Collector of Q600)
The pulses are OK
generator circuit
failure. There is an
Check TO585
Possible
heater shortcircuit
Connect the D660
anode to ground
Is there horizontal
Yes
drive?
There are not pulses
No
Probably:
*X400 damaged
*IC400 failure
*There is not +8V at R418
*R418 opened
Check R701
OK
Check +B5 in
D600 cathode
OK
Check TO270
NG
(H_OUT)
OK
Check the Q600
signal at the base
OK
Probably:
*Primary T600 opened
*There is not B11 at T600
*Q600 damaged
NG
Probably IC701
is damaged
13
Page 15

ERROR_4
Put a jumper between B-E of Q850 (N.1)
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Check +B4
(cathode of D852)
OK
In models with Active 3D Surround: Check +9V
In models without Active 3D Surround:Skip this step
OK
Check +8V
(N.2)
OK
Check +5V
OK
NG OK
NG Yes
NG
Check the rectifier
diodes
Is the voltage level
at pin 4 of IC853
greater than 2V?
No
Check the path of
Q853, Q854 and Q856.
Is the voltage level
at pin 4 of IC854
greater than 2V?
No
Check D875 and R869
Yes
Probably:
* IC701failure
* Shortcircuit or over consumptiom
* IC850 does not work OK
Probably:
*There is not +B6 at IC853
*Shortcircuit in +8V
*IC853 failure
Probably:
*There is not +B7at IC854
*Shortcircuit in +5V
*IC854 failure
* Check the B_HIGH signal and his path until Q850
* Check the pull-up of the pin 52 of IC100
OK
Check with the oscilloscope that the rise time of B1 in the stand-by
to "ON" sequence is less than 160 ms (without the jumper in Q850)
OK
Check that the rise time of +8V is less than 20 ms
NG
Check Q856 and its components at the base
N.1: Once the power supply is repaired, remove the jumper. Without it, the deflection does not start
N.2: Consider in this situation that the +8V source could be at 7,5 volts
NG
Check C809 and B8 source
14
Page 16

THE TV SET DOES NOT START
AND THERE IS NOT
AN ERROR INDICATION
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Does the LED flash
only one time?
No
- Verify SCR850 and its control circuit
Does the LED remain highlighted?
Yes
Put the TV set "ON" by pushing
front keys (P+ or P-)
The TV set remains stopped
The power supply
powers on and then stops
Yes
oscillation (the over voltage
protection is working)
- Force a B_LOW situation (put a jumper between C-E of Q850)
-SCR850 failure
Is the power supply in
No No
Check:
*Q650
*Shortcircuits in secundary windings
protect mode?
(it sounds like a "grig"?)
Yes
OK
Check the winding continuity of
the B1generator
OK
Check D856
OK
- Connect A-K of SCR850
Check B6 (15 volts aprox.)
Is there a voltage
level in secondary
windings?
No
NG
Yes
Check:
*IC100 oscillator (X100, C108, C109)
*IC100 reset circuit (Q106 and perifery)
Probably there is a
failure in the control loop
Check +5VM
OK
(16/9&BSYNC in Stand_By mode)
Check TO396
OK
Check the path of
+5VM at pin 44 of IC100
- N.1: If there is an IC800 failure, and R810 was openned, it is strongly recommended to replace also the resistors R804 and R805
NG
Check that the power supply
is working in burst mode
OK
Check the 16/9&BSYNC
signal generator circuit
Probably:
- IC800 failure (N.1)
- secondary diode failure
Yes No
Is R810 fused?
18. Complete PCB codes for after sales service
CE28FN1-E CE25FN1-E CE21FN1-E
CRT (PHILIPS) A66EAK071X11 A59EAK071X11 A51EAL155X10
A51EAL155X11
General PCB
+ Socket CRT
+ Audio PCB
Socket PCB 7040002409 7040002409 7040002508
General PCB 7110015000 7110015000 7110014904
Audio PCB 7140001301 7140001301 7140001301
6110369201 6110369201 6110369102
OK
Replace IC100
Check:
*Main power supply (+BM)
*IC800 power supply (B8)
OK
Probably IC800 failure
15
Page 17

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
19. CHASSIS ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST CE21FN1-E / CE25FN1-E / CE28FN1-E
Position Part No. Description
YG 1 0200826402 LED Holder
YG 4 ¬ 0080112501 COMP. Side IF Shield EB5-A
YG 5 ¬ 0080112600 Copper Side IF Shield EB5-A
YG 6 0200627305 AUDIO MODULE Holder
Assy PA (Audio)
IC300 0360512206 TDA 7263 M
YR300 0200224319 HEARSINK 'Z' 56,6X126,5
YR300A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
YR301 0970200804 Silicon Grease YG6260
YR302 0890005200 Screw M3X0,5X10
YR303 0990010316 HEXAGONAL NUT M3X0,5
YR304 0050709104 Washer
YR305 0050203207 SAFETY Washer M3
Assy PD (Deflection)
IC701 25”/28” 0360514608 TDA 8350Q N5
IC701 21” 0360514707 TDA 8351AQ N5
Q650 0360306708 S 2055 N
YR650 0200224608 Heatsink Deflection EB5-A
YR650A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
YR651 0970200804 Silicon Grease YG6260
YR652 0010106300 Spring CLIP 56379
Position Part No. Description
Assy PF(Power Supply)
IC800 0360467609 STR-F6653
YR800 0200224707 Heatsink SOURCE EB5-A
YR800A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
YR801 0970200804 Silicon Grease YG6260
YR802 0010106300 Spring CLIP 56379
Assy PL
IC854 0360472807 KA78R05-STU
YR854 0200224905 Heatsink TO-220-F
Assy PC (Socket TRC)
IC500 0360514202 TDA 6107 Q N1
YR500 0200224806 Heatsink RGB EB5-A
YR500A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
YR501 0970200804 Silicon Grease YG6260
YR502 0050709104 Washer
YR503 0890121106 Screw M3X6 FE/ZN DIN 7985
16
Page 18

20. CE21FN1-E CABINET PARTS LIST
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description
17
YP 4 0020125209 SANYO Badge 46,2X13,5 L46
YP 5 0340207000 TRANS. DEC BOARD F3SCM
YF 1 2700047315 Front Cabinet Assy 21"
YF 2 0590265617 Back Cover 21"
YF 3 0130214000 Power BUTTON F3SCM
YF 4 0010106607 Key Spring
YF 6 0390242006 Rating Plate CE21FN1-E
YF 8-1 0590265765 DOOR 21”
YF 9 0020128708 DEC SHEET 21/25/28 EB-5A
YF14 0200819910 AC Cord Holder
YF15 0050709005 Washer
YF18 0010108231 Cover CLIP
YF23 0890161318 Screw HI-LO 5,8X27 W/Washer
YF24 0890191315 Screw AR 4X15
YF25 0890190903 Screw 4X13
YF30 0970136008 Adhesive Tape PS
Page 19

21. CE25FN1-E CABINET PARTS LIST
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
18
Location Part No. Description
YP 4 0020125209 SANYO Badge 46,2X13,5 L46
YP 5 0340207000 TRANS. DEC BOARD F3SCM
YF 1 2700046713 Front Cabinet Assy 25" A F3PC
YF 2 0590264719 Back Cover 25" A-F3PAM
YF 3 0130214000 Power BUTTON F3SCM
YF 4 0010106607 Key Spring
YF 6 0390242105 Rating Plate CE25FN1-E
YF 8-1 0590264867 DOOR 25/28 F3SC EB-5A
YF 9 0020128708 DEC SHEET 21/25/28 EB-5A
YF14 0200819910 AC Cord Holder
YF15 0050708718 Washer
YF18 0010108231 Cover CLIP
YF23 0890161326 Screw HI-LO 5,8X27 W/Washer
YF24 0890191315 Screw AR 4X15
YF25 0890190903 Screw 4X13
YF30 0970136008 Adhesive Tape PS
Page 20

22. CE28FN1-E CABINET PARTS LIST
Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
19
Location Part No. Description
YP 4 0020125209 SANYO Badge 46,2X13,5 L46
YP 5 0340207000 TRANS. DEC BOARD F3SCM
YF 1 2700046812 Front Cabinet Assy 28"
YF 2 0590265013 Back Cover 25" A-F3PAM
YF 3 0130214000 Power BUTTON F3SCM
YF 4 0010106607 Key Spring
YF 6 0390242204 Rating Plate CE28FN1-E
YF 8-1 0590264867 DOOR 25/28 F3SC EB-5A
YF 9 0020128708 DEC SHEET 21/25/28 EB-5A
YF14 0200819910 AC Cord Holder
YF15 0050708718 Washer
YF18 0010108231 Cover CLIP
YF23 0890161326 Screw HI-LO 5,8X27 W/Washer
YF24 0890191315 Screw AR 4X15
YF25 0890190903 Screw 4X13
YF30 0970136008 Adhesive Tape PS
Page 21

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
C1053 25”/28” 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
23. Parts List
PCB SOCKET TRC
CONNECTORS
CON FD 0330144205 Ribbon Wire Holder 4 P.
CON FH 0330144304 Ribbon Wire Holder 5 P.
CON.FD 0160220711 Polarised Band Grey 4P. 520+6+6
CON.FH 0160230819 Polarised Band Grey 5P. 450+6+6
CON.FK 0640202610 Earth Wire 270 mm.
CAPACITORS
C500 0270341324 Polyester 100 nF. 10% 250V.
C501 0250322849 Electrolytic 10 µF. 250V.
C503 0240590901 Ceramic 2200pF +80-20% 2KV.
DIODES
D500 0360007215 BAV21 DIODE
D501 0360007215 BAV21 DIODE
D502 0360007215 BAV21 DIODE
INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
IC500 0360514202 TDA 6107 Q N1
COILS
L503 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
L504 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
L505 0090304924 Choke R.F. 470 µH. 10%
PCB04 0750151029 Socket PCB EB5-A
RESISTORS
R500 0790741409 Solid 1,5 KΩ 10% 1/2W.
R501 0790741409 Solid 1,5 KΩ 10% 1/2W.
R502 0790741409 Solid 1,5 KΩ 10% 1/2W.
R503 0790741409 Solid 1,5 KΩ 10% 1/2W.
R504 0790741409 Solid 1,5 KΩ 10% 1/2W.
R506 25”/28” 0790539704 Fuse 22 Ω 5% 0,3W.
R506 21” 0790535702 Fuse 10 Ω 5% 0,33W.
R507 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R508 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R509 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R510 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R511 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R512 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
ZOCALO 0330162009 CRT Socket DIAMETER 22,5 mm.
MAIN PCB
CF200 0090412701 Ceramic TRAP Filter 5,5/6,5 MHz
CONNECTORS
CN FB 0330193608 4P. Connector
CN FC 0330115106 2P. Socket X RTM 1/6/8
CN FD 0330144205 Ribbon Wire Holder 4 P.
CN FE 0330115106 2P. Socket X RTM 1/6/8
CN FF1 0330190000 2P. Connector
CN FF2 0330270109 2 P. Socket
CN FH 0330144304 Ribbon Wire Holder 5 P.
CN G2 25”/28” 0640706503 Blue G2 Wire with two Terminals
CAPACITORS
C100 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C101 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C102 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C103 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C104 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C105 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1050 25”/28” 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C1051 25”/28” 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1052 25”/28” 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1054 25”/28” 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C1055 25”/28” 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C1056 25”/28” 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1057 25”/28” 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1058 25”/28” 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
C1059 25”/28” 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C106 0270101231 Polyester 1000pF. 5% 63V.
C1060 25”/28” 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1061 25”/28” 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1062 X25”/28” 0230190308 Ceramic SMD 39 pF. 5% 50V.
C1063 X25”/28” 0230190308 Ceramic SMD 39 pF. 5% 50V.
C107 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C108 0230160327 Ceramic SMD 22 pF. 1% 50V.
C109 0230160327 Ceramic SMD 22 pF. 1% 50V.
C110 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C111 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C112 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C113 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C114 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C115 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C116 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C117 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C118 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C1351 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1352 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1353 0250280864 Electrolytic 4,7 µF. 25V.
C1354 0250280864 Electrolytic 4,7 µF. 25V.
C1355 0230680308 Ceramic SMD 470 nF. 10% 16V.
C1356 0230190704 Ceramic SMD. 8 pF. +/-0,5pF. 50V.
C1358 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1359 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C200 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C201 0230190308 Ceramic SMD 39 pF. 5% 50V.
C202 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C203 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C204 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C205 0230740003 Ceramic SMD 2,2 µF. 10V. +80-20%
C206 X 0230190308 Ceramic SMD 39 pF. 5% 50V.
C207 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C250 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C251 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
C252 0270341480 Polyester 100 nF. 10% 63V.
C256 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C257 0270341480 Polyester 100 nF. 10% 63V.
C258 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C259 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C260 0250360468 Electrolytic 22 µF. 16V.
C261 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C300 0250601069 Electrolytic 2200 µF. 35V. R-7,5
C301 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C303 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C304 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C305 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C306 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C307 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C308 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C309 0250240462 Electrolytic 2,2 µF. 63V.
C310 0250240462 Electrolytic 2,2 µF. 63V.
C311 0250601663 Electrolytic 2200 µF. 16V.
C312 0250601663 Electrolytic 2200 µF. 16V.
C313 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C314 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C315 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C316 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C319 0250360468 Electrolytic 22 µF. 16V.
C320 0250360468 Electrolytic 22 µF. 16V.
C350 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C351 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C352 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C353 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C354 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C355 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C356 0250500667 Electrolytic 220 µF. 16V.
C357 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
C359 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C361 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
20
Page 22

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
C364 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C400 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
C401 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C402 0230740003 Ceramic SMD 2,2 µF. 10V. +80-20%
C403 0230520405 Ceramic SMD 22 nF. 10% 50V.
C405 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C406 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C408 0230520405 Ceramic SMD 22 nF. 10% 50V.
C409 0230520405 Ceramic SMD 22 nF. 10% 50V.
C410 0230520405 Ceramic SMD 22 nF. 10% 50V.
C411 0230150229 Ceramic SMD 18 pF. 1% 50V.
C412 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C413 0230420119 Ceramic SMD 3300 pF.10% 63V.0805
C414 0230520405 Ceramic SMD 22 nF. 10% 50V.
C415 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
C416 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C417 0230400103 Ceramic SMD 2200 pF. 10% 50V.
C418 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C420 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C421 0230440125 Ceramic SMD 4700 pF.10% 50V.0805
C423 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C424 X 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C425 0270342603 Policarbonate 100 nF. 5% 63V.
C426 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C427 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C428 X 0230240327 Ceramic SMD 100 pF. 5% 50V.
C432 25”/28” 0230390205 Ceramic SMD 1800 pF. 10% 50V.
C432 21” 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C433 0230240327 Ceramic SMD 100 pF. 5% 50V.
C435 0230440125 Ceramic SMD 4700 pF.10% 50V.
C437 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C439 X 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C440 0230180226 Ceramic SMD 33 pF. 1% 50V.
C600 25”/28” 0250248267 Electrolytic 2,2 µF. 160V.
C600 21” 0250220464 Electrolytic 1 µF. 100V.
C601 0270140122 Polyester 2200 pF. 10% 400V.
C603 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C604 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C650 25”/28” 0260125273 Polypropylene 27 nF. 5% 1KV.
C651 25”/28” 0260011374 Polypropylene 12 nF. 5% 1,6KV
C651 21” 0260217179 Polypropylene 9100 pF. 5% 1,6KV
C651A 0640850210 Eyelet 1,6-3
C652 25”/28” 0260420278 Polypropylene 470nF. 5% 400V.
C652A 25”/28” 0640850210 Eyelet 1,6-3
C653 25”/28” 0260433073 Polypropylene 820 nF. 5% 250V.
C653 21” 0260420278 Polypropilene 470 nF. 5% 400V.
C653A 0640850210 Eyelet 1,6-3
C654 0260120472 Polypropylene 1000pF. 5% 2KV
C655 25”/28” 0270261720 Polyester 22 nF. 10% 100V.
C655 21” 0270250582 Polyester 18 nF. 10% 250V.
C656 0250248267 Electrolytic 2,2 µF. 160V.
C657 0240132035 Ceramic 470 pF. 10% 1KV.
C659 25”/28” 0250132743 Electrolytic 100 µF. 200V.
C660 0230340408 Ceramic SMD 680 pF. 10% 630V.
C661 0250283868 Electrolytic 4,7 µF. 250V.
C663 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C664 0230200305 Ceramic SMD 47 pF. 5% 50V.
C666 21” 0270450216 Polyester 820 nF. 5% 250V.
C667 0270100522 Polyester 1000 pF. 10% 400V.
C668 0250116761 Electrolytic 4,7 µF. 160V.
C669 0230340408 Ceramic SMD 680 pF. 10% 630V.
C670 0270341324 Polyester 100 nF. 10% 250V.
C671 0270220726 Polyester 10 nF. 10% 250V.
C672 25”/28” 0230360505 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF 5% 100V.
C673 0270220726 Polyester 10 nF. 10% 250V.
C674 0230520405 Ceramic SMD 22 nF. 10% 50V.
C675 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C676 0270381080 Polyester 220 nF. 10% 63V.
C677 21” 0230260705 Ceramic SMD 150 pF. 10% 630V.
C679 0250210861 Electrolytic 0,47 µF. 50V.
C680 0230680308 Ceramic SMD 470 nF. 10% 16V.
C700 0250321064 Electrolytic 10 µF. 63V.
C701 0250412962 Electrolytic 47 µF. 50V.
C702 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C703 25”/28” 0270381080 Polyester 220 nF. 10% 63V.
C703 21” 0270341480 Polyester 100 nF. 10% 63V.
C705 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C706 X 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C710 0270220726 Polyester 10 nF. 10% 250V.
C712 0270220726 Polyester 10 nF. 10% 250V.
C750 25”/28” 0270320732 Polyester 68 nF. 10% 63V.
C751 X25”/28” 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C752 X25”/28” 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C753 25”/28” 0250116761 Electrolytic 4,7 µF. 160V.
C800 X 0270342702 Polyester 100 nF. 20% 275V.AC
C801 X 0270342702 Polyester 100 nF. 20% 275V.AC
C802 0240134767 Ceramic 1000 pF. +-20% 1KV.
C803 0240134767 Ceramic 1000 pF. +-20% 1KV.
C804 0240134767 Ceramic 1000 pF. +-20% 1KV.
C805 0240134767 Ceramic 1000 pF. +-20% 1KV.
C807 0230560302 Ceramic SMD 47 nF. 10% 50V.
C809 0250362308 Electrolytic 22 µF. 20% 50V.
C810 0250503604 Electrolytic. 220 µF. 385V.
C810A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
C811 0230320525 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 5% 50V.
C812 X 25”/28” 0240136135 Ceramic 1000 pF. 20% 4KV
C812 X 21” 0240590133 Ceramic 2200 pF. 20% 4KV
C814 0230340309 Ceramic SMD 680 pF.10% 50V.
C815 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C816 X 25”/28” 0240136135 Ceramic 1000 pF. 20% 4KV
C817 0230300303 Ceramic SMD 330 pF. 10% 630V.
C818 X 0230300303 Ceramic SMD 330 pF. 10% 630V.
C819 0230300402 Ceramic SMD 330 pF. 10% 1KV.1206
C830 0250362308 Electrolytic 22 µF. 20% 50V.
C833 0230720302 Ceramic SMD 1µF. +80-20% 25V.
C850 25”/28” 0240460501 Ceramic 180 pF. 5% 1KV.
C850 21” 0240470708 Ceramic 220 pF. 5% 1KV.
C852 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C853 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C854 0250220464 Electrolytic 1 µF. 100V.
C855 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C856 25”/28” 0250132743 Electrolytic 100 µF. 200V.
C856 21” 0250465044 Electrolytic 100 µF. 160V.
C857 0250572260 Electrolytic 1000 µF. 35V.
C858 0250572369 Electrolytic 1000 µF. 25V.
C859 0250463767 Electrolytic 100 µF. 50V.
C860 0250150240 Electrolytic 3300 µF. 16V.
C861 0250141462 Electrolytic 470 µF. 16V.
C862 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C863 0230360406 Ceramic SMD 1000 pF. 10% 50V.
C865 0240391102 Ceramic 47 pF. 5% 500V. SL
C866 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C867 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C868 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C869 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C870 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C872 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C873 0250141462 Electrolytic 470 µF. 16V.
C874 0250461266 Electrolytic 100 µF. 16V.
C875 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C876 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C877 0250141462 Electrolytic 470 µF. 16V.
C900 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C901 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C902 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C903 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C904 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C905 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C906 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C907 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C908 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C909 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C910 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C911 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C913 X 0230240327 Ceramic SMD 100 pF. 5% 50V.
C914 X 0230240327 Ceramic SMD 100 pF. 5% 50V.
C917 X 0230240327 Ceramic SMD 100 pF. 5% 50V.
C918 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C920 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C921 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C922 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C923 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C924 X 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
21
Page 23

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
C925 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C926 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C927 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C928 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C929 0250220464 Electrolytic 1 µF. 100V.
C930 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C931 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C932 0250220464 Electrolytic 1 µF. 100V.
C933 0250220464 Electrolytic 1 µF. 100V.
C934 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C935 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C936 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C937 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C938 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C939 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C940 X 0230240327 Ceramic SMD 100 pF. 5% 50V.
DIODES
D100 0360126205 Red/Green 3 mm.
D101 0360602403 Zener SMD BZM55C6V2
D103 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D104 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D105 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D106 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D107 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D250 0360706014 HZT33-02 RE
D300 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D301 0360602106 Zener SMD BZM55C4V7
D350 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D400 0360130819 1N 4148
D600 0360130819 1N 4148
D650 25”/28” 0360011316 BY 228/40
D651 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D652 25”/28” 0360376404 ERB44-06
D652 21” 0470040007 Jumper Lead 0,6 mm.
D653 0360376909 ERB44-02
D654 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D655 0360603906 Zener SMD BZM55C33
D656 0360603302 Zener SMD BZM55C15
D657 0360130819 1N 4148
D658 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D659 0360130819 1N 4148
D660 0360130819 1N 4148
D661 0360007215 BAV21 DIODE
D663 0360376909 ERB44-02
D665 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
D670 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D671 0360377006 ERB44-04
D672 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D673 25”/28” 0360005805 Zener BZX79C4V7
D674 25”/28” 0360602304 Zener SMD BZM55C8V2
D674 21” 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D675 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D676 0360602304 Zener SMD BZM55C8V2
D677 0360130819 1N 4148
D678 0360130819 1N 4148
D679 0360603005 Zener SMD BZM55C12
D680 0360603005 Zener SMD BZM55C12
D681 0360130819 1N 4148
D700 0360130819 1N 4148
D701 0360130819 1N 4148
D702 0360130819 1N 4148
D703 0360134902 Zener BXZ79C33
D704 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D705 25”/28” 0360602304 Zener SMD BZM55C8V2
D705 21” 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D750 25”/28” 0360603906 Zener SMD BZM55C33
D751 25”/28” 0360603302 Zener SMD BZM55C15
D752 25”/28” 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D800 0360372411 ERC05-10B
D801 0360372411 ERC05-10B
D802 0360372411 ERC05-10B
D803 0360372411 ERC05-10B
D807 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D808 0360376909 ERB44-02
D809 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D811 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D812 0360377501 Schottky AK 03 V1 30V 1A
D830 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D831 0360376909 ERB44-02
D832 0360604508 Zener SMD BZM55C10
D850 25”/28” 0360374409 RU4B LF-T3
D850 21” 0360378103 ERB44-08 800V 1A
D851 0360376008 RN4Z LF-T3
D852 0360377303 Schottky ERB84-009 90V 2A
D853 0360377204 AU01 V1 400V 0,5A
D854 0360376909 ERB44-02
D855 0360377303 Schottky ERB84-009 90V 2A
D856 0360376404 ERB44-06
D857 0360604508 Zener SMD BZM55C10
D858 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D859 0360130819 1N 4148
D860 0360103204 Zener BZX79C5V1
D861 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D863 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D864 0360605109 Zener SMD BZM55C18
D865 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D866 0360603609 Zener SMD BZM55C5V6
D868 0360130819 1N 4148
D869 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D870 0360130819 1N 4148
D871 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D872 0360605406 Zener SMD BZM55C9V1
D873 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D874 0360601504 SMD MCL4148
D875 0360103204 Zener BZX79C5V1
D900 0360602403 Zener SMD BZM55C6V2
D901 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D902 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D903 0360602403 Zener SMD BZM55C6V2
D905 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D906 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D907 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D908 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D909 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D910 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D911 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
FUSES
F-800 0760100701 Fuse Terminal Taped
F800 0330119819 Fuse T 1.6 A./250V. TIME-LAG
INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
IC100 0360514400 SAA 5297 PS/208
IC1050 25”/28” 0360472401 SAA 4960 V3
IC125 0360711303 SMD SLA 24C08-SR
IC1350 0360472203 U4468B - M
IC300 0360512206 TDA 7263 M
IC350 0360472609 KA2209B
IC400 25”/28” 0360514301 TDA8843 N2
IC400 21” 0360514509 TDA8841 N2
IC701 25”/28” 0360514608 TDA 8350Q N5
IC701 21” 0360514707 TDA 8351AQ N5
IC800 0360467609 STR-F6653
IC801 0360491203 OPTO TCET1101G
IC830 0360711204 SMD TLP 165J
IC850 0360378715 KA431AZTA TO-92
IC851 0360472500 KA78L09AZTA TO92
IC852 0360472906 KA7805TU
IC853 0360472708 KA78R08TU
IC854 0360472807 KA78R05-STU
IC900 0360708804 LA 7221
J-115 25”/28” 0470040007 Jumper Lead 0,6 mm.
J-121 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-140 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-142 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-143 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-144 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-147 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-152 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-156 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-158 25”/28” 0470040007 Jumper Lead 0,6 mm.
J-240 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-246 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-250 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
22
Page 24

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
J-251 25”/28” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-252 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-264 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-265 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
J-266 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
JO1050 21” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
JO1051 21” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
JO650 21” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
K9A 0330330002 8P. Connector
K9B 0330380007 12P. Female Connector
K9C 0330490004 Connector Assy 10P W/Wires 260 MM
COILS
L100 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L101 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L102 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L103 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L1050 25”/28” 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L1051 25”/28” 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L1052 25”/28” 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L1053 X25”/28” 0790131908 Carbon 220 Ω 5% 1/6W.
L1054 X25”/28” 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L1054 21” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
L1055 X25”/28” 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L1055 21” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
L1350 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L1351 0090206806 Adjustable Coil 292XNS-4051Z
L1352 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L201 0090315029 Peaking Coil 10 µH. 10%
L250 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L251 0090318668 Peaking Coil 1 µH. 20% I MAX=270MA
L300 0090817016 Choke Coil 12 µH. 1,2 A. 4X10
L301 X 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L302 X 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L303 X 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L304 X 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L350 X 0090319765 Peaking Coil 22 µH. 10% I MAX=130MA
L351 X 0090319765 Peaking Coil 22 µH. 10% I MAX=130MA
L400 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L401 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L402 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L403 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L404 X 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L405 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L406 X 0090316605 Peaking Coil 10 µH. 10%
L407 X 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
L408 X25”/28” 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
L409 0090319765 Peaking Coil 22 µH. 10% I MAX=130MA
L600 25”/28” 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L600 21” 0090305269 Peaking Coil 6,8 µH 10% I MAX=860MA
L651 25”/28” 0090502709 Dynamic Correction Coil 0,85 MH.
L652 25”/28” 0090816828 Linearity Coil BDL-1415-039
L652 21” 0090816711 Linearity LH11J70SH-T10
L652A1 25”/28” 0640850210 Eyelet 1,6-3
L652A2 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
L652A3 21” 0640850210 Eyelet 1,6-3
L653 21” 0090310806 Adjustable Width Coil 27/130 µH.
L653A 21” 0640850210 Eyelet 1,6-3
L654 25”/28” 0090817016 Choke Coil 12 µH. 1,2 A. 4X10
L655 0090304924 Choke R.F. 470 µH. 10%
L700 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L701 X 0090305020 Choke R.F. 2,2 µH. 10%
L702 X 0090305020 Choke R.F. 2,2 µH. 10%
L750 25”/28” 0090502600 E/W Coil 5,5 MH. 10%
L800 X 0090412206 Mains Filter 2X27 MH 250VAC 1A
L802 X 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L804 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L805 0620005504 Ferrite Bead 3,5X6 80 Ω/100 MHz
L850 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L851 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L852 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L853 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L854 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L855 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L856 0620005116 Pipe Core 3,5X4,5
L857 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L858 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L859 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L860 0090305665 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH 10% I MAX=930MA
L861 0090315763 Peaking Coil 100 µH 10%
L900 X 0090315029 Peaking Coil 10 µH. 10%
L901 X 0090315029 Peaking Coil 10 µH. 10%
L902 X 0090315029 Peaking Coil 10 µH. 10%
L903 0090319229 Peaking Coil 4,7 µH. 10%
L904 X 0090315029 Peaking Coil 10 µH. 10%
L905 X 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
PCB11 0750150823 MAIN PCB EB-5A
PL100 0130209109 Push Switch L-8,35MM
PL101 0130209109 Push Switch L-8,35MM
PL102 0130209109 Push Switch L-8,35MM
PL103 0130209109 Push Switch L-8,35MM
PL104 0130209109 Push Switch L-8,35MM
PL105 0130209109 Push Switch L-8,35MM
PTC800 0810101212 Dual PTC 18 Ω +-25%
TRANSISTORS
Q100 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q101 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q102 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q104 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q105 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q106 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q1354 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q200 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q201 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q202 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q203 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q250 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q251 0360189112 PH2369
Q252 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q253 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q254 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q255 0360161400 BF 370
Q256 0360320600 BRT SMD PDTC124ET SOT-23
Q300 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q350 0360320600 BRT SMD PDTC124ET SOT-23
Q351 0360320600 BRT SMD PDTC124ET SOT-23
Q400 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q600 0360308506 KSP 42 TO-92
Q601 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q650 0360306708 S 2055 N
Q650A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
Q651 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q652 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q653 0360308605 KSP 92 TO-92
Q670 0360308605 KSP 92 TO-92
Q671 0360308506 KSP 42 TO-92
Q672 25”/28” 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q673 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q700 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q750 25”/28” 0360308605 KSP 92 TO-92
Q751 25”/28” 0360320600 BRT SMD PDTC124ET SOT-23
Q830 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q831 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q832 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q850 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q851 0360320600 BRT SMD PDTC124ET SOT-23
Q852 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q853 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q854 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
Q855 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q856 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q857 0360320501 BRT SMD PDTA124ET SOT-23
Q858 0360320600 BRT SMD PDTC124ET SOT-23
Q900 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q901 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q902 0360320022 SMD BC 848 B
Q903 0360320121 SMD BC 858 B
RI100 0600122204 Infrared Receiver SBX8030-F
23
Page 25

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
RESISTORS
R100 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R101 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R102 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R103 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R104 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R1050 25”/28” 0790223002 R.M.G. SMD 47 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R106 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R107 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R108 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R109 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R110 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R111 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R112 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R113 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R114 0790256002 R.M.G. SMD 27 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R115 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R116 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R117 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R118 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R120 0790233001 R.M.G. SMD 330 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R121 0790233001 R.M.G. SMD 330 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R122 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R123 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R124 0790864102 R.M.G. SMD 1,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R125 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R126 0790230007 R.M.G. SMD 180 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R127 0790155600 Carbon 22 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R129 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R130 0790741805 R.M.G. SMD 1,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R131 0790580328 Metal Film 23,7 KΩ 1% 0,4W.
R132 0790256002 R.M.G. SMD 27 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R133 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R134 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R135 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R1356 0790229009 R.M.G. SMD 150 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R136 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R1360 0790133607 Carbon 330 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R1361 0790233001 R.M.G. SMD 330 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R1362 0790235006 R.M.G. SMD 470 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R137 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R138 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R139 0790151500 Carbon 10 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R140 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R141 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R142 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R143 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R144 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R145 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R146 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R147 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R148 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R149 0790133607 Carbon 330 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R151 0790027502 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R152 0790138804 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R153 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R154 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R155 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R156 0790741805 R.M.G. SMD 1,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R157 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R158 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R159 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R160 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R162 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R163 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R165 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R166 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R167 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R168 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R170 0790741805 R.M.G. SMD 1,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R172 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R173 0790749402 R.M.G. SMD 6,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R200 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R201 0790128201 Carbon 120 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R202 0790235006 R.M.G. SMD 470 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R203 0790846109 R.M.G. SMD 220 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R204 0790846109 R.M.G. SMD 220 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R205 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R206 0790846109 R.M.G. SMD 220 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R207 X 0790223002 R.M.G. SMD 47 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R208 X 0790223002 R.M.G. SMD 47 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R211 0790138804 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R212 0790234009 R.M.G. SMD 390 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R213 0790235006 R.M.G. SMD 470 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R214 0790235006 R.M.G. SMD 470 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R215 0790131908 Carbon 220 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R216 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R250 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R251 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R252 0790235006 R.M.G. SMD 470 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R253 0790263008 R.M.G. SMD 100 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R254 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R255 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R256 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R257 0790564009 Metal Film 1,8 KΩ 5% 2W.
R258 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R259 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R262 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R263 0790246003 R.M.G. SMD 3,9 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R264 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R265 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R266 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R267 0790874101 R.M.G. SMD 2,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R268 0790123400 Carbon 47 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R269 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R270 0790223002 R.M.G. SMD 47 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R271 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R300 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R301 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R302 0790243000 R.M.G. SMD 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R303 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R304 0790131908 Carbon 220 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R305 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R306 0790131908 Carbon 220 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R307 0790111413 Carbon 4,7 Ω 5% 1/2W.
R308 0790111413 Carbon 4,7 Ω 5% 1/2W.
R309 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R310 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R311 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R312 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R313 0470040007 Jumper Lead 0,6 mm.
R350 0790123103 Carbon 47 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R351 0790123103 Carbon 47 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R352 0790711204 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R353 0790711204 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R354 0790535702 Fuse 10 Ω 5% 0,33W.
R355 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R356 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R359 0790741805 R.M.G. SMD 1,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R360 0790757603 R.M.G. SMD 33 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R361 0790741805 R.M.G. SMD 1,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R362 0790757603 R.M.G. SMD 33 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R363 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R364 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R400 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R401 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R402 0790151500 Carbon 10 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R403 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R404 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R405 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R407 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R408 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R409 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R410 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R411 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R412 0790263008 R.M.G. SMD 100 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R413 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R414 0790256002 R.M.G. SMD 27 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R415 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
24
Page 26

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
R416 0790784201 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 MΩ 5% 1/10W.
R417 0790784201 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 MΩ 5% 1/10W.
R418 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R419 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R423 0790263008 R.M.G. SMD 100 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R424 0790256002 R.M.G. SMD 27 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R425 0790773303 R.M.G. SMD 680 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R426 0790758304 R.M.G. SMD 39 KΩ 1% 1/8W.
R427 0790137707 Carbon 680 Ω 5% 1/6W
R428 0790123400 Carbon 47 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R429 0790127104 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R436 0790135701 Carbon 470 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R437 0790151500 Carbon 10 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R438 0790180509 Carbon 2,2 MΩ 5% 1/4W.
R439 0790237002 R.M.G. SMD 680 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R600 25”/28” 0790569636 Metal Film 4,64 KΩ 1% 0,6W.
R600 21” 0790350508 Metal Film 2,7 KΩ 1% 0,6W.
R601 0790148100 Carbon 5,6 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R602 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R603 25”/28” 0790349005 Metal Film 2,2 KΩ 5% 2W.
R603 21” 0470040007 Jumper Lead 0,6 mm.
R604 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R605 0790741805 R.M.G. SMD 1,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R606 25”/28” 0790343008 Metal Film 1 KΩ 5% 1W
R606 21” 0790133102 Carbon 330 Ω 5% 1/4W
R607 0790123400 Carbon 47 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R650 25”/28” 0790578140 Metal Oxide 15 KΩ 5% 2W.
R651 25”/28” 0790578140 Metal Oxide 15 KΩ 5% 2W.
R651 21” 0790577142 Metal Oxide 12 KΩ 5% 2W.
R652 25”/28” 0790559223 Metal Film 820 Ω 5% 1W
R653 0790151104 Carbon 10 KΩ 2% 1/4W.
R655 25”/28” 0790310015 Metal Film 3,9 Ω 5% 2W.
R655 21” 0790532402 Metal Oxide 4,7 Ω 5% 1,5W.
R656 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R657 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R658 0790766406 R.M.G. SMD 180 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R659 0790138804 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R660 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R661 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R662 0790131908 Carbon 220 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R663 0790048607 Carbon 10 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R664 21” 0780163309 Wirewound Resistor 8,2 Ω 10% 5W.
R665 21” 0780559223 Metal Film 820 Ω 5% 1W.
R666 25”/28” 0790516702 Fuse 0,47 Ω 5% 0,5W.
R666 21” 0790512313 Metal Film 0,33 Ω 5% 1W.
R667 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R668 0790163109 Carbon 100 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R669 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R670 0790846109 R.M.G. SMD 220 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R671 25”/28” 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R671 21” 0790766307 Carbon SMD 180 KΩ 5% 0,25W.
R672 0790238000 R.M.G. SMD 820 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R673 0790131106 Carbon 220 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R674 25”/28” 0790157408 Carbon 33 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R674 21” 0790588529 Metal Film 100 KΩ 1% 0,4W.
R675 0470040007 Jumper Lead 0,6 mm.
R676 25”/28” 0790753909 R.M.G. SMD 15 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R676 21” 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R677 0790749402 R.M.G. SMD 6,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R678 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R679 25”/28” 0790261002 R.M.G. SMD 68 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R680 0790263008 R.M.G. SMD 100 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R681 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R682 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R683 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R684 0790143606 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R685 25”/28” 0790363105 R.M.G. SMD 18 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R686 25”/28” 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R686 21” 0790232003 R.M.G. SMD 270 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R687 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R688 0790767503 R.M.G. SMD 220 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R700 0790351100 Metal Film 3 KΩ 1% 0,4W.
R701 0790538706 Fuse 15 Ω 5% 0,5W.
R702 25”/28” 0790520407 Metal Film 0,68 Ω 5% 0,61W.
R702 21” 0790303408 Metal Film 1,33 Ω 1% 0,6W.
R703 25”/28” 0790119200 Carbon 22 Ω 5% 1/2W.
R703 21” 0790122303 Carbon 39 Ω 5% 1/2W.
R704 0790864102 R.M.G. SMD 1,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R705 0790554828 Power Metal Film 330 Ω 5% 1W.
R706 0790243000 R.M.G. SMD 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R707 0790539001 Metal Film 18 Ω 5% 1W.
R708 0790135701 Carbon 470 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R750 25”/28” 0790542518 Metal Film 33 Ω 5% 2W.
R753 25”/28” 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R754 25”/28” 0790586309 Metal Film 68 KΩ 1% 0,6W
R755 25”/28” 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R756 25”/28” 0790233001 R.M.G. SMD 330 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R757 25”/28” 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R758 25”/28” 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R759 25”/28” 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R800 0790180111 Carbon 2,2 MΩ 5% 1/2W.
R801 0790184113 Carbon 4,7 MΩ 5% 1/2W.
R802 0780145504 Wirewound 2,7 Ω 10% 5W.
R803 0790579411 Power Metal Film 18 KΩ 5% 2W.
R804 25”/28” 0790514202 Metal Film 0,43 Ω 5% 1,2W.
R804 21” 0790516819 Metal Film 0,51 Ω 5% 1W.
R805 25”/28” 0790514202 Metal Film 0,43 Ω 5% 1,2W.
R805 21” 0790516819 Metal Film 0,51 Ω 5% 1W.
R806 0790237002 R.M.G. SMD 680 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R807 0790115505 Carbon 10 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R808 25”/28” 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R808 21” 0790243000 R.M.G. SMD 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R809 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R810 0790513014 Fuse 0,33 Ω 5% 0,5W.
R811 0790185524 Solid 5,6 MΩ 10% 1/2W.
R812 0790185524 Solid 5,6 MΩ 10% 1/2W.
R815 0790127104 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R816 0790362107 Metal Film 15 KΩ 5% 1W.
R830 0790339105 Fuse 390 Ω 5% 0,5W.
R831 0790757603 R.M.G. SMD 33 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R832 0790259006 R.M.G. SMD 47 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R833 0790136402 Carbon 560 Ω 5% 1/2W.
R834 0790248009 R.M.G. SMD 5,6 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R835 0790545404 Fuse 56 Ω 5% 0,5W.
R836 0790246003 R.M.G. SMD 3,9 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R837 0790749402 R.M.G. SMD 6,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R838 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R839 0790248009 R.M.G. SMD 5,6 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R850 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R851 0790363105 R.M.G. SMD 18 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R852 0790237002 R.M.G. SMD 680 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R853 0790238000 R.M.G. SMD 820 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R854 0790233001 R.M.G. SMD 330 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R855 25”/28” 0790588602 Metal Film 110 KΩ 1% 0,6W.
R855 21” 0790588701 Metal Film 100 KΩ 1% 0,6W.
R856 25”/28” 0790347009 R.M.G. SMD 1,78 KΩ 1% 1/8W
R856 21” 0790348106 R.M.G. SMD 2,05 KΩ 1% 1/8W
R857 0790766406 R.M.G. SMD 180 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R858 0790135206 Carbon 470 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R859 0790159503 Carbon 47 KΩ 5% 1/6W
R861 0790583603 Metal Film 62 KΩ 5% 2W.
R862 0790245005 R.M.G. SMD 3,3 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R863 0790229009 R.M.G. SMD 150 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R864 0790242002 R.M.G. SMD 1,8 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R865 0790243000 R.M.G. SMD 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R867 0790256002 R.M.G. SMD 27 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R868 0790260004 R.M.G. SMD 56 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R869 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R870 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R871 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R872 25”/28” 0790157408 Carbon 33 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R872 21” 0790758007 Carbon 36 KΩ 5% 1/6W.
R873 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R875 0790135206 Carbon 470 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R876 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R877 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R900 0790026207 Carbon 560 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R901 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
25
Page 27

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
R902 0790036305 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R903 0790026207 Carbon 560 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R904 0790126700 Carbon 100 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R905 0790036305 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R906 0790046403 Carbon 12 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R907 0790888101 R.M.G. SMD 9,1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R908 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R909 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R910 0790046403 Carbon 12 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R911 0790888101 R.M.G. SMD 9,1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R912 0790026207 Carbon 560 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R913 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R914 0790026207 Carbon 560 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R915 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R916 0790036305 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R917 0790036305 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R918 0790027502 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R919 0790027502 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R920 0790027502 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R921 0790027502 Carbon 1 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R922 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R923 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R924 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R925 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R926 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R927 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R928 0790036305 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R929 0790036305 Carbon 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/4W.
R930 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R931 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R932 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R933 X 0790234009 R.M.G. SMD 390 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R934 0790135701 Carbon 470 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R935 0790128201 Carbon 120 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R936 0790135701 Carbon 470 Ω 5% 1/6W.
R937 0790255004 R.M.G. SMD 22 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R940 0790125702 Carbon 75 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R941 0790128201 Carbon 120 Ω 5% 1/4W.
R942 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R943 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R944 0790247001 R.M.G. SMD 4,7 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R945 0790243000 R.M.G. SMD 2,2 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R946 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R947 0790235006 R.M.G. SMD 470 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R948 X 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
SCR850 0360306807 Thyristor MCR22-6 400V/1,5A TO-92
SF1350 X 0090410507 SAW Filter K9260M
SF200 X 0090410408 SAW Filter G3964M
SW800 0140204108 Power Switch S-95 WITHOUT WIPER
S300 0330729807 Phone Jack Stereo W/Disconnection
S900 0330161407 Scart Connector 21 PIN BLACK
S901 0330161506 Scart Connector 21 PIN BLUE
S902 0330159708 3 RCA'S ASSEMBLY
TR830 0360306906 Triac BT 137-600 Lead Form 78-05W
TUNER
TU250 X 0850102609 Tuner UV1315AS/IEC
TRANSFORMER
T600 0940200801 Driver Transformer 800T/20T
T650 25”/28” 0940108707 FBT 25"/28" HFT426M
T650 21” 0940108202 FBT 21" HFT867M
T650A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
T650CF 0330160508 FOCUS Wire FBT SANYO
T650CG 21” 0330160607 G2 Wire FBT
T800 25”/28” 0930107008 Switch Transf. 110DG EB5-A 10592330
T800 21” 0930107206 Switch Transf. 90 DG EB5-A 10603970
T800A 0640705117 Eyelet 2,5-3
VR850 0770511152 VR 220 Ω
X100 0090121708 Quartz Crystal 12 MHz
X400 0090121104 Quartz Crystal, 4,4336190 MHz.
DIGITAL AUDIO PCB
CAPACITORS
C1301 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1302 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1303 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C1304 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1305 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1306 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1307 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C1308 0230180226 Ceramic SMD 33 pF. 1% 50V.
C1309 0230180226 Ceramic SMD 33 pF. 1% 50V.
C1310 0230540205 Ceramic SMD 33 nF. 10% 50V.
C1311 0270381080 Polyester 220 nF. 10% 63V.
C1319 0230600504 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. 10% 25V.
C1320 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C1321 0230280307 Ceramic SMD 220 pF. 5% 50V.
C1322 0230280307 Ceramic SMD 220 pF. 5% 50V.
C1323 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C1324 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C1326 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C1328 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C1330 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C1332 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C1333 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1334 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1335 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1336 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1338 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1339 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1340 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1341 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1342 0230480600 Ceramic SMD 10 nF. +80-20% 50V
C1343 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C1344 0230720203 Ceramic SMD 1 µF. 16V. +80-20%
C1380 0230600603 Ceramic SMD 100 nF. +80-20% 25V.
C1381 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1382 0230740003 Ceramic SMD 2,2 µF. 10V. +80-20%
C1383 0270222037 Polyester 10 nF. 5% 63V.
C1384 0270342835 Polyester 100 nF. 5% 63V.
C1385 0270101231 Polyester 1000 pF. 5% 63V.
C1386 0270222037 Polyester 10 nF. 5% 63V.
C1387 0270222037 Polyester 10 nF. 5% 63V.
C1388 0270222037 Polyester 10 nF. 5% 63V.
C1389 0270222037 Polyester 10 nF. 5% 63V.
C1390 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1391 0250320769 Electrolytic 10 µF. 16V.
C1392 0230740003 Ceramic SMD 2,2 µF. 10V. +80-20%
C1393 0250410867 Electrolytic 47 µF. 16V.
C1394 0270101231 Polyester 1000 pF. 5% 63V.
C1395 0270342835 Polyester 100 nF. 5% 63V.
C1396 0270222037 Polyester 10 nF. 5% 63V.
C1397 0230740003 Ceramic SMD 2,2 µF. 10V. +80-20%
C1398 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
C1399 X 0230320301 Ceramic SMD 470 pF. 10% 50V.
DIODES
D1300 0360111405 Varicap SMD BB 135
D1301 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D1302 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D1303 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
D1304 0360602205 Zener SMD BZM55C5V1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
IC1300 0360513808 TDA 9875 V1
IC1380 0360513907 MM 1369BD
K1300A 0330330101 8P. Connector
K1300B 0330380106 12P. Male Connector
K1300C 0330198706 10 P. Connector
COILS
L1300 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
26
Page 28

Service Manual MS CE25FN1-E
Location Part No. Description Location Part No. Description
L1301 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L1302 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L1303 0620011502 Ferrite SMD 0603 600 Ω/20 MHz
L1304 0090316506 Peaking Coil 2,2 µH.10% RADIAL
L1305 0090318924 Peaking Coil 3,3 µH.10% IMAX=210 MA
L1306 0090316506 Peaking Coil 2,2 µH.10% RADIAL
L1308 0090316506 Peaking Coil 2,2 µH.10% RADIAL
PCB14 0750150914 AUDIO PCB EB5-A
RESISTORS
R1300 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R1301 0790227003 R.M.G. 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R1302 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1303 0790239008 R.M.G. SMD 1 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1304 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R1305 0790258008 R.M.G. SMD 39 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1306 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1307 0790754600 R.M.G. SMD 20 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1310 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1311 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1312 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1313 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1314 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1315 0790752208 R.M.G. SMD 12 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1316 0790232003 R.M.G. SMD 270 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R1317 0790232003 R.M.G. SMD 270 Ω 5% 1/10W.
R1318 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1319 0790701106 SMD 0 Ω 1/10W.
R1381 0790749808 R.M.G. SMD 7,5 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1382 0790227003 R.M.G. SMD 100 Ω 5% 1/10W
R1383 0790251003 R.M.G. SMD 10 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
R1384 0790258008 R.M.G. SMD 39 KΩ 5% 1/10W.
BAT 0660100603 Dry Battery 1,5V. SUM-3F
EM 1 25” 0190204107 Packing Carton 25" F3PC
EM 1 28” 0190204206 Packing Carton 28"
EM 1 21” 0190204008 Packing Carton 21"
EM 2 25” 0190177006 Upper Cushion Assy 25" F3PAM
EM 2 28” 0190177204 Upper Cushion Assy 28"
EM 2 21” 0190177501 Upper Cushion Assy 21"
EM 3 25” 0190177113 Bottom Cushion Assy 25" F3PAM-A
EM 3 28” 0190177311 Bottom Cushion Assy 28"
EM 3 21” 0190177410 Bottom Cushion Assy 21"
EM10 0600122808 Remote Control EB-5A SANYO
EM13 0390238418 Electrostatic LABEL EB5-A
All information in this manual is correct at the start of
production. Sanyo reserves its right to modify
components and procedures in order to comply with
their continuous improvement policy.
X1300 0090121906 Quartz Crystal 24.576 MHz
ELECTRICAL ASSY
AM 1 0010203917 Insulanting Ring HV CABLE
BRDEFL 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
BRDG 25”/28” 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
BRDGI 25”/28” 0010203313 Holder DC GBR-HBZ
BRDGI 21” 0010203404 Wire Band 430/4,8
BRDGS 0010203313 Holder DC GBR-HBZ
BRDY 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
BRFEFC 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
BRFH 0200099406 Wire Holding HOOK G
BRK9C 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
BRSPK1 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
BRSPK2 0010203503 Wire Band 98/2.5 Natural
CN.FB 0330256629 4P CONNEC. W/WireS 770+33/630+33 MM
CN.FE 0330208208 Power Cord Assy 17-212 L=2500 MM
CN.FF1 0330246901 2 WAY Connector CASE W/LEAD
CN.FF2 0330246802 2 WAY Connector CASE W/LEAD
L-800 25” 0090257205 Degaussing Coil 25"
L-800 28” 0090257304 Degaussing Coil 28"
L-800 21” 0090257106 Degaussing Coil 21"
SC001 0170200406 Shield Mesh 2 mm.
SC1000 0330100009 AM SPLICE
SC1001 0010001311 Spring Ground CRT
SPK 1 0030701916 Speaker 8 Ω 12W. 120X60
SPK 2 0030701916 Speaker 8 Ω 12W. 120X60
TRC 25” 1000107118 C.R.T. 25" A59EAK071X11 PHILIPS
TRC 28” 1000107217 C.R.T. 28" A66EAK071X11 PHILIPS
TRC 21” 1000107605 C.R.T. 21" A51EAL155X10 PHILIPS
TRC 21” 1000107605 C.R.T. 21" A51EAL155X11 PHILIPS
PACKING
27
Page 29

Page 30

 Loading...
Loading...