Page 1

SERVICE & OPERATING MANUAL
II 2GD T5
Original Instructions
Model HDB2 Type 3
See pages 18 & 19
for ATEX ratings
Table of Contents
Engineering Data and Performance Curve............................................................ 1
Explanation of Pump Nomenclature and Temperature Limitations ........................ 2
Dimensions ............................................................................................................ 3
Principle of Operation ............................................................................................ 4
Installation and Start-Up ........................................................................................ 4
Air Supply .............................................................................................................. 4
Installation Guide ................................................................................................... 5
Air Inlet & Priming .................................................................................................. 6
Air Exhaust ............................................................................................................ 6
Between Uses ....................................................................................................... 6
Check Valve Servicing ........................................................................................... 6
Diaphragm Servicing ............................................................................................. 6
Air Valve Lubrication .............................................................................................. 7
ESADS+Plus
®
:
Externally Serviceable Air Distribution System ................................ 7
Pilot Valve .............................................................................................................. 8
Pilot Valve Actuator ................................................................................................8
Service Instructions: Troubleshooting ................................................................... 9
Warranty ................................................................................................................ 9
Recommended Accessories, Available Service Kits .............................................. 9
Important Safety Information ............................................................................... 10
Recycling ............................................................................................................. 10
Grounding The Pump .......................................................................................... 11
Material Codes .................................................................................................... 12
Composite Repair Parts List ........................................................................... 13-15
Composite Repair Drawing.................................................................................. 16
CE Declaration of Conformity - Machinery .......................................................... 17
CE Declaration fo Conformity - ATEX .................................................................. 18
Explanation of ATEX Certication ........................................................................ 19
Warren Rupp, Inc. • A Unit of IDEX Corporation • 800 N. Main St., Manseld, Ohio 44902 USA
Telephone (419) 524-8388 • Fax (419) 522-7867 • warrenrupp.com
hdb2dl3sm-rev0614
©Copyright 2014 Warren Rupp, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Page 3
Quality System
II 2GD T5
ISO9001 Certied
Environmental
Management System
ISO14001 Certied
Bottom Discharge Porting
Top Discharge Porting
See pages 18 & 19
for ATEX ratings
HDB2 Type 3
Heavy Duty Ball Valve
Air-Operated
Double Diaphragm Pump
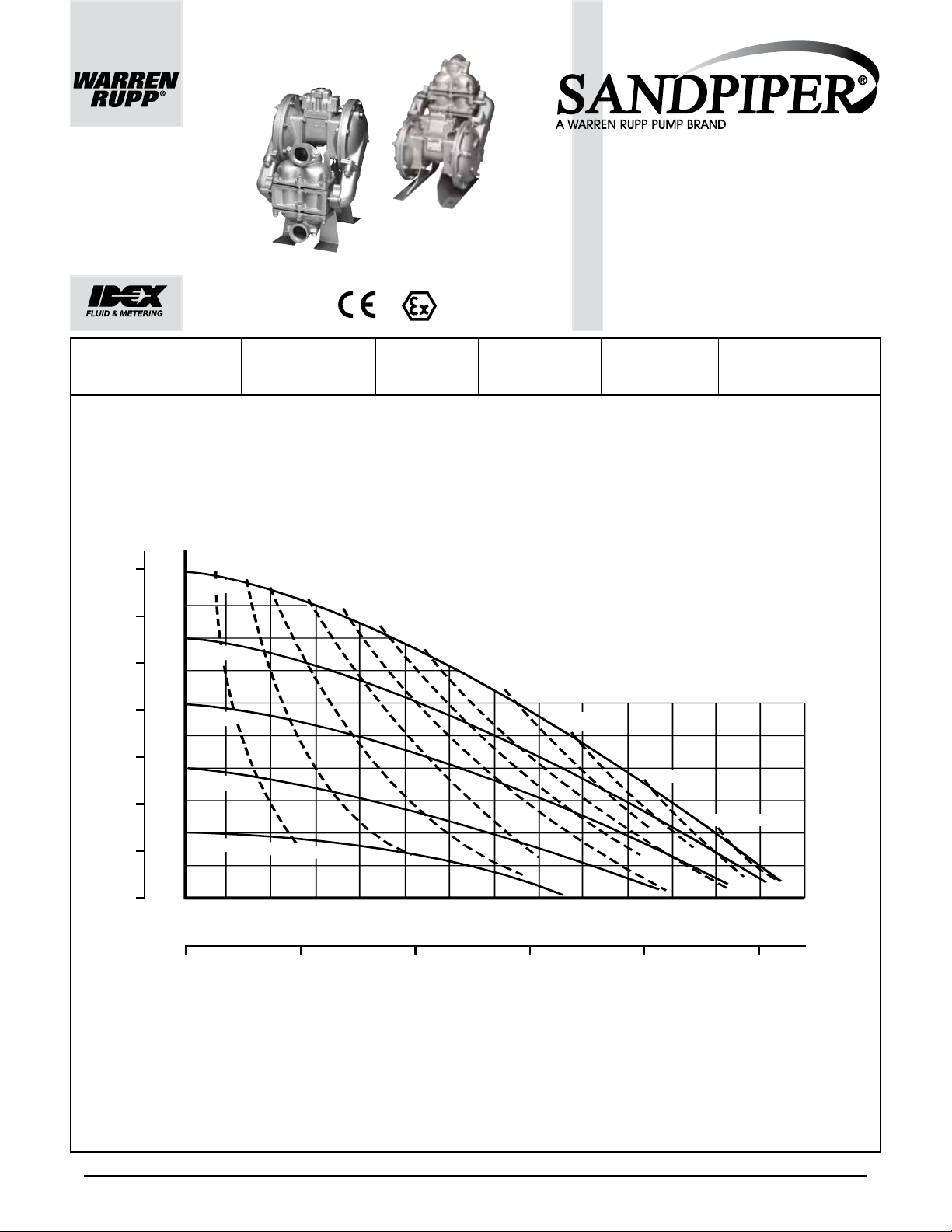
ENGINEERING, PERFORMANCE
& CONSTRUCTION DATA
INTAKE/DISCHARGE PIPE SIZE
2 " (50mm) NPT (F)
PSI
BAR
100
90
80
70
60
10(17)
100 PSI
80 PSI
60 PSI
7
6
5
4
50
HEAD
3
40
40 PSI
30
2
20
1
20 PSI Air Inlet Pressure
10
CAPACITY AIR VALVE SOLIDS-HANDLING HEADS UP TO
0 to 135 gallons per minute
(0 to 511 liters per minute)
AIR CONSUMPTION
SCFM (M
20(34)
30(51)
40(68)
3
/hr)
50(85)
3
No-lube, no-stall
design
Up to
/8 in. (9mm)
125 psi or 289 ft. of water
2
(8.8 Kg/cm
or 88 meters)
MODEL HDB2 Performance Curve
Performance based on the following: elastomer fitted pump, flooded suction,
water at ambient conditions. The use of other materials and varying hydraulic
60(101.9)
70(118.9)
conditions may result in deviations in excess of 5%.
80(135.9)
90(152.9)
95(161.4)
100(169.9)
DISPLACEMENT/STROKE
.43 Gallon / 1.63 liter
0
0
0 20
40 60
80
100
120
U.S. Gallons per minute
0 200 300 400 500
100
Liters per minute
CAPACITY
SANDPIPER® pumps are designed to be powered only by compressed air.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 1
140
Page 4
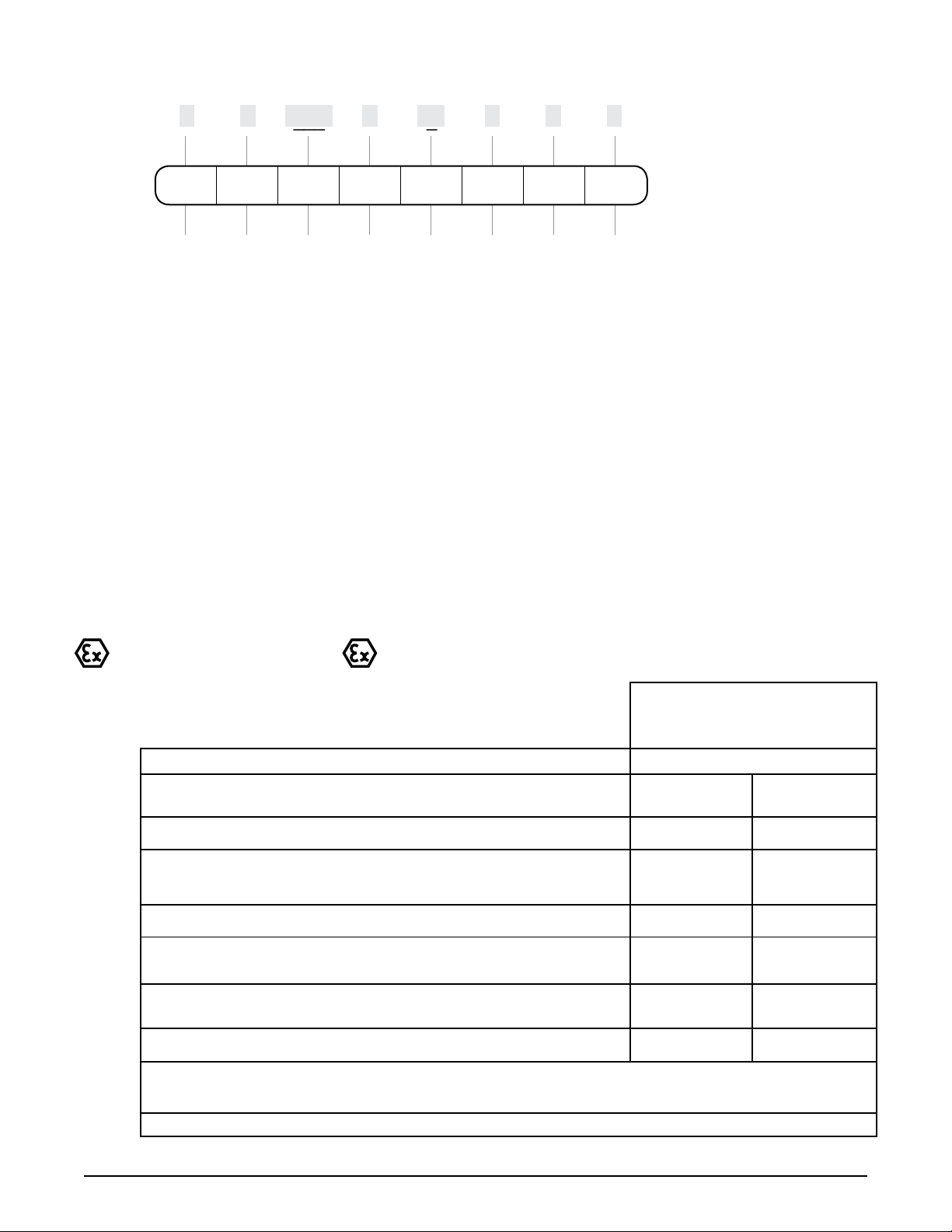
Explanation of Pump Nomenclature, HDB2
II 2GD T5
II 2GD T5
Your Model #:
__ __ _____ __ ___ __ __ __
(ll in from pump
nameplate)
Pump Pump Pump
Series Design Size Porting
Model #:
XX X XXXX, X XX X XX X
Pump Series
S SANDPIPER
®
Pump Design
B Soilid Ball
Pump Size
2 2"
Discharge Porting Position
D Bottom
S Side
ET Dual Top
ES Dual Side
Diaphragm Check Valve Materials
B Nitrile
C FKM with PTFE
F FDA Accepted White Nitrile
GN Neoprene Backup with PTFE Overlay
and PTFE Check Balls
GR Hytrel Backup w/
PTFE Overlay/PTFE Balls
GZ PTFE/Nitrile Bonded
One-Piece/PTFE Balls
H EPDM with PTFE
N Neoprene
R Hytrel
S Santoprene
U Santoprene with PTFE
V FKM
Discharge Diaphragm/ Design
Options
Valve
Level
Your Serial #: (ll in from pump nameplate) _____________________________________
Construction
Design Level
3
Construction
A Aluminum Wetted, Aluminum Air
SI Stainless Steel Wetted, Cast Iron Air
SS Stainless Steel Wetted, Aluminum Air
HC Alloy-C Wetted, Aluminum Air
HI Alloy-C Wetted, Cast Iron Air
Options
P1 Intrinsically Safe ATEX Compliant
Pulse Output
II 1 G c T5
II 3/1 G c T5
II 1 D c T100oC
I M1 c
I M2 c
Models equipped with
Cast Iron, Stainless
Steel, or Alloy C wetted
parts, and Cast Iron midsection parts. See page
19 for ATEX Explanation
of EC-Type Certicate.
II 2 G c T5
II 3/2 G c T5
II 2 D c T100oC
All models, including
pumps equipped with
Aluminum wetted and
midsection parts.
See page 19 for ATEX
Explanation of Type
Examination Certicate.
Materials
Nitrile General purpose, oil-resistant. Shows good solvent, oil, water and hydraulic uid resistance. Should
not be used with highly polar solvents
like acetone and MEK, ozone, chlorinated hydrocarbons and nitro hydrocarbons.
EPDM Shows very good water and chemical resistance. Has poor resistance to oil and solvents, but is fair in
ketones and alcohols.
NEOPRENE All purpose. Resistant to vegetable oils. Generally not affected by moderate chemicals, fats,
greases and many oils and solvents. Generally
attacked by strong oxidizing acids, ketones, esters, nitro hydrocarbons and chlorinated aromatic hydrocar
bons.
®
Good on acids, bases, amines and glycols at room temperature.
HYTREL
PTFE Chemically inert, virtually impervious. Very few chemicals are known to react chemically with
PTFE: molten alkali metals, turbulent liquid or gaseous uorine and a few uoro-chemicals such as
chlorine triuoride or oxygen diuoride which readily liberate free uorine at elevated temperatures.
FKM (Fluorocarbon) shows good resistance to a wide range of oils and solvents; especially all aliphatic,
aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons, acids, animal
and vegetable oils. Hot water or hot aqueous solutions (over 70°F) will attack FKM.
®
Santoprene
lent abrasion resistance.
CF-8M Stainless Steel equal to or exceeding ASTM specication A743 for corrosion resistant iron chro-
‡
mium, iron chromium nickel, and nickel based alloy castings for general applications. Commonly referred
to as 316 Stainless Steel in the pump industry.
Injection molded thermoplastic elastomer with no fabric layer. Long mechanical ex life. Excel-
Maximum and Minimum Temperatures are the limits for which
these materials can be operated. Temperatures coupled with
pressure affect the longevity of diaphragm pump components.
Maximum life should not be expected at the extreme limits of
the temperature ranges.
Maximum Minimum
-
Operating Temperatures
190°F -10°F
88°C -23°C
280°F -40°F
138°C -40°C
200°F -10°F
93°C -23°C
220°F -20°F
104°C -29°C
220°F -35°F
104°C -37°C
350°F -40°F
177°C -40°C
275°F -40°F
135°C -40°C
ALLOY C CW-12MW equal to or exceeding ASTM A494 specication for nickel and nickel alloy castings.
For specic applications, always consult “Chemical Resistance Chart" Technical Bulletin
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 2
Page 5
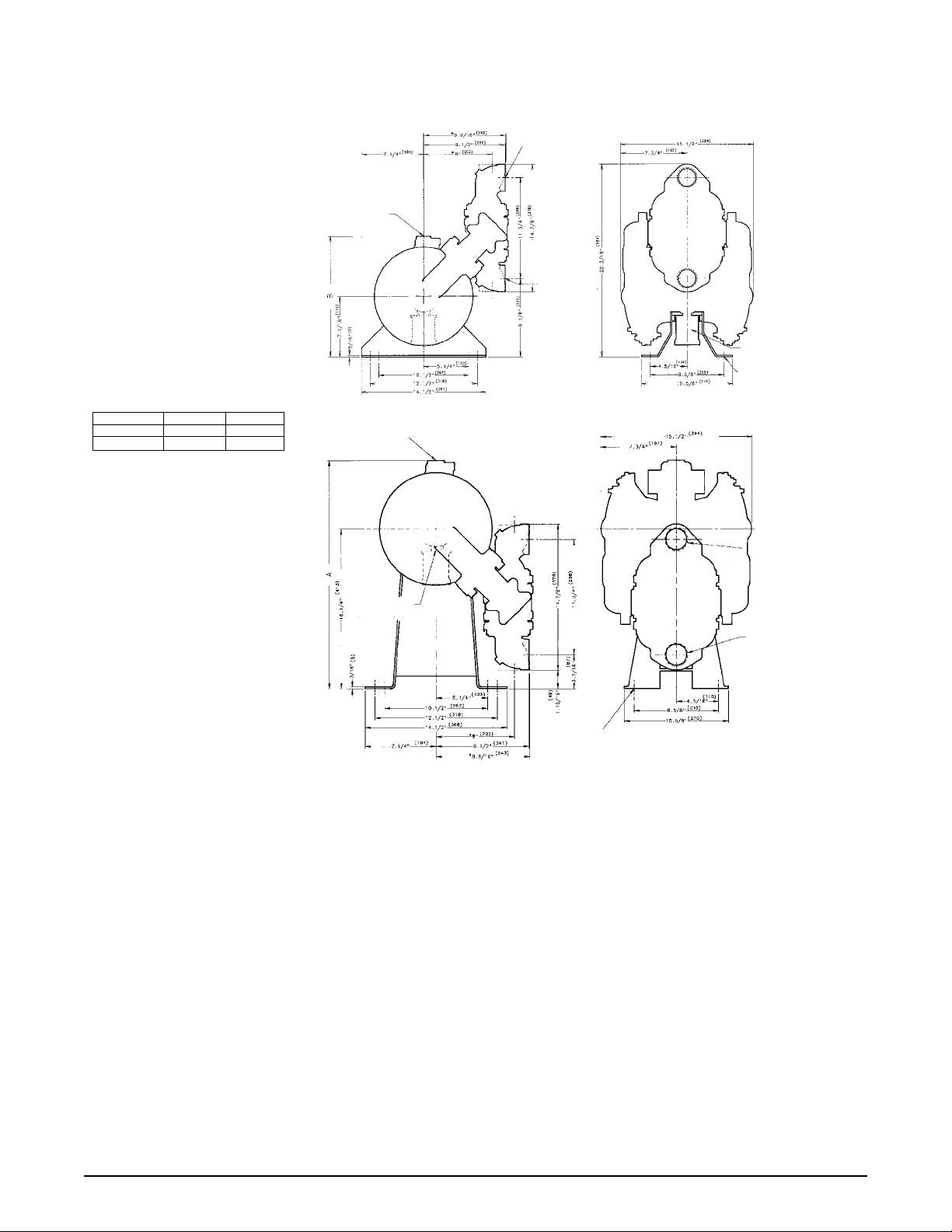
Dimensions:
HDB2
Dimensions are ± 1/8"
Figures in parenthesis = millimeters
TOP
DISCHARGE
PORTING
* Indicates dimensions with suction
and discharge ports rotated 180°
to a vertical position.
Dimension A B
Standard Pump 23 ¼" (590) 14 1/16" (357)
Pulse Output Kit 23
13
/16" (605) 14 5/8" (371)
BOTTOM
DISCHARGE
PORTING
* Indicates dimensions with suction
and discharge ports rotated 180°
to a vertical position.
DISCHARGE PORT
2” NPT(F)
AIR INLET
3/4” NPT(F)
SUCTION PORT
2” NPT(F)
* INDICATES DIMENSIONS WITH SUCTION AND DISCHARGE
PORTS ROTADED 180° TO A VERTICAL POSITION.
AIR INLET
3/4” NPT(F)
AIR EXHAUST
3/4” NPT(F)
AIR EXHAUST
3/4” NPT(F)
(11)
7/16” DIA.
MOUNTING HOLES
TYP. (8) PLACES
DISCHARGE PORT
2” NPT(F)
SUCTION PORT
2” NPT(F)
(11)
7/16” DIA.
MOUNTING HOLES
TYP. (8) PLACES
* INDICATES DIMENSIONS WITH SUCTION AND DISCHARGE
PORTS ROTADED 180° TO A VERTICAL POSITION.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 3
Page 6

SERVICE & OPERATING MANUAL
II 2GD T5
Original Instructions
See pages 18 & 19
for ATEX ratings
Model HDB2 Type 3
PLEASE NOTE!
The photos shown in this manual are for general instruction only. YOUR SPECIFIC
MODEL MAY NOT BE SHOWN. Always refer to the parts list and exploded view
drawing for your specific model when installing, disasembling or servicing
your pump.
PRINCIPLE OF PUMP OPERATION
This ball check valve pump is powered by compressed air and is a 1:1 pressure ratio
design. The pump is alternately pressurize through the inner side of one diaphragm
chamber, while simultaneously exhausting the other inner chamber. Air pressure
causes the diaphragms, (which are connected by a common rod,) to move endwise.
Air pressure is applied over the entire surface of the diaphragm, while liquid is discharged from the opposite side. The diaphragm operates under a balanced condition
during the discharge stroke, and the unit can be operated at discharge heads over
200 feet (61 meters) of water head.
The diaphragms are connected by a common rod, secured by plates to the center
of the diaphragms. One diaphragm performs the discharge stroke, while the other is
pulled to perform the suction stroke in the opposite chamber.
For maximum diaphragm life, keep the pump as close to the liquid being pumped
as possible. Positive suction head in excess of 10 feet of liquid (3.048 meters) may
require a back pressure regulating device. This will maximize diaphragm life.
Alternate pressuring and exhausting of the diaphragm chamber is performed by
means of an externally mounted, pilot operated, four-way spool type air distribution
valve. When the spool shifts to one end of the valve body, inlet air pressure is applied
to one diaphragm chamber and the other diaphragm chamber exhausts air. When the
spool shifts to the opposite end of the valve body, the porting of chambers is reversed.
The air distribution valve spool is moved by an internal pilot valve which alternately
pressurizes one side of the air distribution valve spool, while exhausting the other
side. The pilot valve is shifted at each end of the diaphragm stroke by the diaphragm
plate coming in contact with the end of the pilot spool. This pushes the pilot valve into
position for shifting of the air distribution valve.
The chambers are manifolded together with a suction and discharge check valve
for each chamber which maintains ow in one direction through the pump.
INSTALLATION & START-UP
Locate the pump as close to the product being pumped as possible. Keep suction
line length and number of ttings to a minimum. Do not reduce line size.
For installations of rigid piping, short exible sections of hose should be installed
between pump and piping. This reduces vibration and strain to the piping system.
A Warren Rupp Tranquilizer
pulsation in ow.
This pump was tested at the factory prior to shipment and is ready for operation.
It is self-priming from a dry start for suction lifts of 20 feet (6.096 meters) or less. For
suction lifts exceeding 20 feet of liquid, ll the chambers with liquid prior to priming.
®
surge suppressor is recommended to further reduce
AIR SUPPLY
Air supply pressures cannot exceed 125 psi (8.61 bar). Connect the pump air inlet
to an air supply of sufcient capacity and pressure required for desired performance.
When the air line is solid piping, use a short length of exible hose [not less than
3/4" (19mm) in diameter] between pump and piping to eliminate strain to pipes.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 4
Page 7
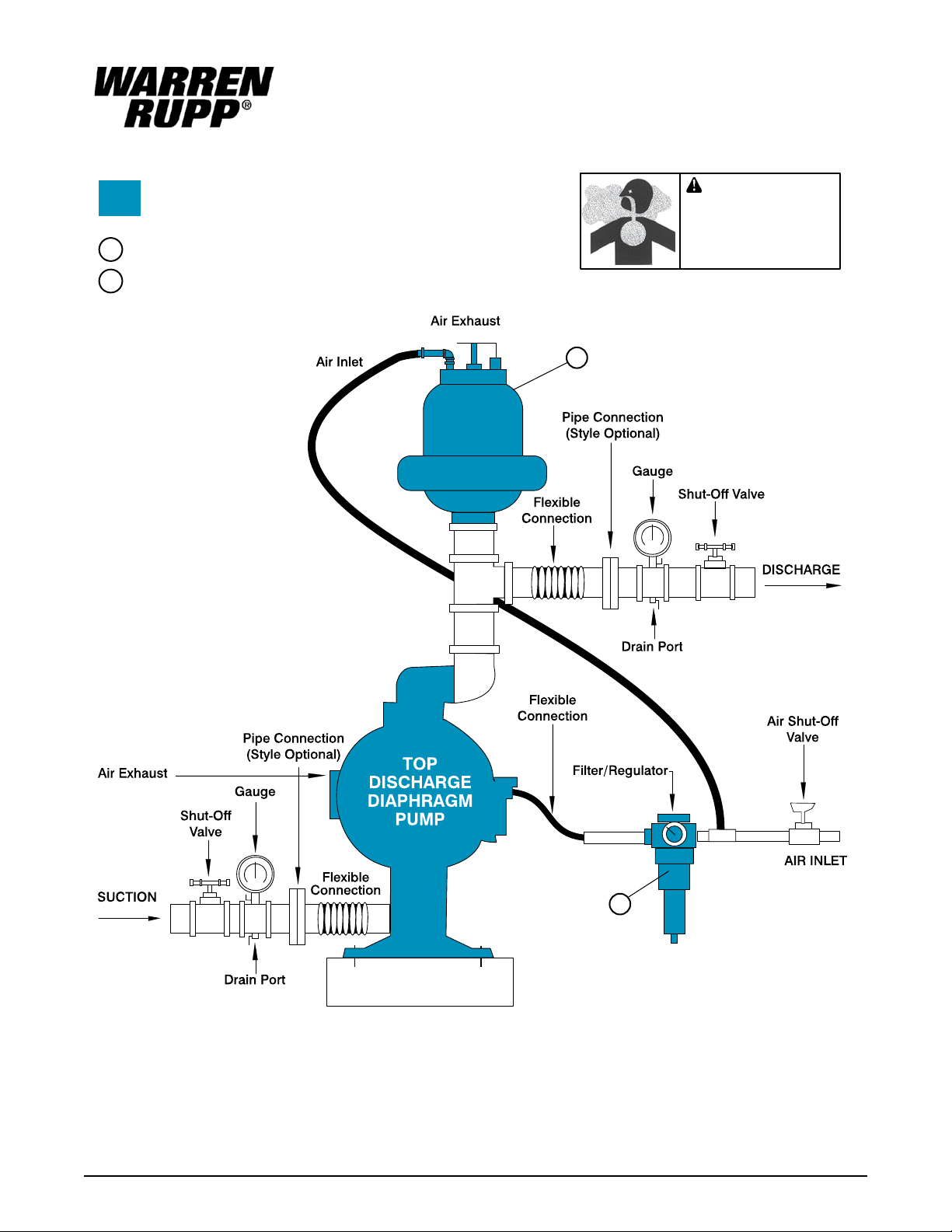
INSTALLATION GUIDE
Top Discharge Ball or Flap Valve Unit
Available from
Warren Rupp
1
Tranquilizer
Filter/Regulator�
2
®
/Surge Supressor
CAUTION
The air exhaust should be
piped to an area for safe
disposition of the product
being pumped, in the event
of a diaphragm failure.
1
Surge
Suppressor
2
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 5
Page 8

AIR INLET & PRIMING
For start-up, open an air valve approximately 1/2" to 3/4" turn. After the unit primes,
an air valve can be opened to increase ow as desired. If opening the valve increases
cycling rate, but does not increase ow rate, cavitation has occurred, and the valve
should be closed slightly.
For the most efcient use of compressed air and the longest diaphragm life, throttle
the air inlet to the lowest cycling rate that does not reduce ow.
AIR EXHAUST
If a diaphragm fails, the pumped liquid or fumes can enter the air end of the pump,
and be exhausted into the atmosphere. When pumping hazardous or toxic materials,
pipe the exhaust to an appropriate area for safe disposition.
This pump can be submerged if materials of construction are compatible with the
liquid. The air exhaust must be piped above the liquid level. Piping used for the air
exhaust must not be smaller than 1" (2.54 cm). Reducing the pipe size will restrict
air ow and reduce pump performance .When the product source is at a higher level
than the pump (ooded suction), pipe the exhaust higher than the product source to
prevent siphoning spills.
Freezing or icing-up of the air exhaust can occur under certain temperature and
humidity conditions. Use of an air dryer unit should eliminate most icing problems.
BETWEEN USES
When used for materials that tend to settle out or transform to solid form, the pump
should be completely ushed after each use, to prevent damage. Product remaining
in the pump between uses could dry out or settle out. This could cause problems
with valves and diaphragms at re-start. In freezing temperatures, the pump must be
drained between uses in all cases.
CHECK VALVE SERVICING
For best priming and most efcient pumping performance, it is important to maintain
check valves and valve seats in good condition for proper sealing. Need for inspection
or service of ball valves is usually indicated by poor priming, unstable cycling, reduced
performance, or pump cycles but will not pump.
Inspection and service of check valves requires the removal of ve hex nuts and
one capscrew for each set of check valves (i.e., suction & discharge), providing
access to the two ball valves and their valve seats. New ball valves are 3
in diameter and will require replacement when worn to approximately 3
diameter.
5
/8" (9.21 cm)
3
/8" (8.57 cm)
DIAPHRAGM SERVICING
Need for inspection or service of diaphragm is usually indicated when unit pumps
from one chamber only and air is discharged out pump discharge port or when liquid
being pumped is discharged through air exhaust port.
To service diaphragms remove two capscrews which secure the chamber to the
manifold assembly, and twelve hex nuts that secure the chamber to the main pump
assembly. To remove diaphragms, loosen diaphragm assembly by turning it out of
the diaphragm rod using a 1
outer chamber will permit removal of second diaphragm assembly and diaphragm rod
as a unit.
To remove the diaphragm from the diaphragm assembly, hold the diaphragm rod
in a clamping device, making sure to protect the rod surface of shaft so as not to
scratch or damage it in any way. With a wrench turn the diaphragm assembly out of the
diaphragm rod. To disassemble the components, turn a 5/16-18 UNC capscrew by
hand into the tapped hole in the inner diaphragm plate. This will keep the plate from
turning while the capscrew is removed. To remove the capscrew, place the assembly
in a vise so the two protruding ends of screws are loose in the vise jaws (approximately
7/8" apart). Turn the center screw loose from the back plate and the assembly will
come apart.
1
/8" (2.857 cm) socket or wrench. Removal of opposite
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 6
Page 9

REASSEMBLY
All procedures for reassembling the pump are the reverse of the disassembly
instructions with further instructions as shown:
The diaphragm assemblies are to be installed with the natural bulge outward or
toward the head of the center screw. Make sure both plates are installed with outer radii
against the diaphragm. After all components are in position in a vise and hand tight,
set a torque wrench for 40 ft. pounds (54.23 Newton meters) using a 1
socket. After each diaphragm sub assembly has been completed, thread one assembly
into the diaphragm rod. Make sure the 5/16-18 UNC capscrew has been removed
from the inner plate and the diaphragm rod bumper is in place on the diaphragm rod.
Install this sub assembly into the pump and secure by installing the outer chamber
in place and tightening the capscrews. This will hold the assembly in place while the
opposite side is installed. Install the second diaphragm assembly into the diaphragm
rod checking to see that the diaphragm rod bumper is in place. Tighten to 30 ft. lbs.
(40.67 Newton meters) torque before installing the outer chamber in place. If the holes
in the diaphragm ange do not align with the holes in the inner chamber ange, turn
the diaphragm assembly in the direction of tightening to align the holes so that the
capscrews can be inserted. This nal torquing of the last diaphragm assembly will lock
the two diaphragm assemblies together. Secure the last outer chamber by tightening
down the securing nuts gradually and evenly. This tightening procedure should be
done on both sides.
When reinstalling check valves, take care that the seat gaskets are aligned properly
before securing porting ange in place.
1
/8" (2.857 cm)
A Note about Air Valve Lubrication
The SANDPIPER pump’s pilot valve and main air valve assemblies are designed
to operate WITHOUT lubrication. This is the preferred mode of operation. There
may be instances of personal preference, or poor quality air supplies when lubrication of the compressed air supply is required. The pump air system will operate with
properly lubricated compressed air supplies. Proper lubrication of the compressed air
supply would entail the use of an air line lubricator (available from Warren Rupp) set
to deliver one drop of 10 wt., non-detergent oil for every 20 SCFM of air the pump
consumed at its point of operation. Consult the pump’s published Performance Curve to
determine this.
It is important to remember to inspect the sleeve and spool set routinely. It should
move back and forth freely. This is most important when the air supply is lubricated.
If a lubricator is used, oil accumulation will, over time, collect any debris from the
compressed air. This can prevent the pump from operating properly.
Water in the compressed air supply can create problems such as icing or freezing of the exhaust air causing the pump to cycle erratically, or stop operating. This
can be addressed by using a point of use air dryer to supplement a plant’s air drying
equipment. This device will remove excess water from the compressed air supply and
alleviate the icing or freezing problem.
ESADS+Plus®: Externally Serviceable Air Distribution
System
Please refer to the exploded view drawing and parts list in the Service Manual
supplied with your pump. If you need replacement or additional copies, contact your
local Warren Rupp Distributor, or the Warren Rupp factory Literature Department at
the number shown below. To receive the correct manual, you must specify the MODEL
and TYPE information found on the name plate of the pump.
The main air valve sleeve and spool set is located in the valve body mounted on
the pump with four hex head capscrews. The valve body assembly is removed from
the pump by removing these four hex head capscrews.
With the valve body assembly off the pump, access to the sleeve and spool set is
made by removing four hex head capscrews (each end) on the end caps of the valve
body assembly. With the end caps removed, slide the spool back and forth in the
sleeve. The spool is closely sized to the sleeve and must move freely to allow for proper
pump operation. An accumulation of oil, dirt or other contaminants from the pump’s
air supply, or from a failed diaphragm, may prevent the spool from moving freely.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 7
Page 10

This can cause the spool to stick in a position that prevents the pump from operating.
If this is the case, the sleeve and spool set should be removed from the valve body
for cleaning and further inspection.
Remove the spool from the sleeve. Using an arbor press or bench vise (with an
improvised mandrel), press the sleeve from the valve body. Take care not to damage
the sleeve. At this point, inspect the o-rings on the sleeve for nicks, tears or abrasions.
Damage of this sort could happen during assembly or servicing. A sheared or cut
o-ring can allow the pump’s compressed air supply to leak or bypass within the air
valve assembly, causing the pump to leak compressed air from the pump air exhaust
or not cycle properly. This is most noticeable at pump dead head or high discharge
pressure conditions. Replace any of these o-rings as required or set up a routine,
preventive maintenance schedule to do so on a regular basis. This practice should
include cleaning the spool and sleeve components with a safety solvent or equivalent,
inspecting for signs of wear or damage, and replacing worn components.
To re-install the sleeve and spool set, lightly lubricate the o-rings on the sleeve
with an o-ring assembly lubricant or lightweight oil (such as 10 wt. air line lubricant).
Press the set into the valve body easily, without shearing the o-rings. Re-install one
end cap, gasket and bumper on the valve body. Using the arbor press or bench vise
that was used in disassembly, press the sleeve back into the valve body. You may
have to clean the surfaces of the valve body where the end caps mount. Material
may remain from the old gasket. Old material not cleaned from this area may cause
air leakage after reassembly. Take care that the bumper stays in place allowing the
sleeve to press in all the way. Re-install the spool, the opposite end cap, gasket and
bumper on the valve body. After inspecting and cleaning the gasket surfaces on the
valve body and intermediate, re-install the valve body on the pump using new gaskets.
Tighten the four hex head capscrews evenly and in an alternating cross pattern.
PILOT VALVE
The pilot valve assembly is accessed by removing the main air distribution valve
body from the pump and lifting the pilot valve body out of the intermediate housing.
Most problems with the pilot valve can be corrected by replacing the o-rings.
Always grease the spool prior to inserting it into the sleeve. If the sleeve is removed
from the body, reinsertion must be at the chamfered side. Grease the o-rings to slide
the sleeve into the valve body. Securely insert the retaining ring around the sleeve.
When reinserting the pilot valve, push both plungers (located inside the intermediate
bracket) out of the path of the pilot valve spool ends to avoid damage.
PILOT VALVE ACTUATOR
Bushings for the pilot valve actuators are threaded into the intermediate bracket
from the outside. The plunger may be removed for inspection or replacement. First
remove the air distribution valve body and the pilot valve body from the pump. The
plungers can be located by looking into the intermediate. It may be necessary to
use a ne piece of wire to pull them out. The bushing can be turned out through the
inner chamber by removing the outer chamber assembly. Replace the bushings if
pins have bent.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 8
Page 11

TROUBLESHOOTING
PROBLEM: Pump cycles but will not pump. (Note: higher suction lifts require faster cycling speed for priming.)
POSSIBLE CAUSES:
A. Air leak in suction line.
B. Excessive suction lift.
C. Check valve not closing.
D. Leakage at joint of suction manifold or elbow ange.
E. Suction line plugged.
F. Diaphragm ruptured.
PROBLEM: Pump will not cycle. (Note: Always disconnect air supply to relieve air pressure before disassembling
any portion of pump.)
POSSIBLE CAUSES:
A. Discharge hose or line plugged, or discharge head requirement greater than air supply pressure.
(Disconnect discharge line to check.)
B. Spool in air distribution valve not shifting. (Remove end cap and check spool — must slide freely.)
C. Diaphragm ruptured. (Air will escape out discharge line in this case.)
D. Blockage in diaphragm chamber preventing movement. (Shut off air supply and reopen after pressure is relieved.)
E. Plugged or dirty exhaust mufer.
PROBLEM: Uneven discharge ow. (Indicates one chamber not operating properly.)
POSSIBLE CAUSES:
A. Check valve not sealing properly in one chamber.
B. Diaphragm failure in one chamber.
C. Air leak at suction manifold joint or elbow ange one side.
D. Plugged or dirty mufer.
For additional information, see the Warren Rupp Troubleshooting Guide.
WARRANTY:
This unit is guaranteed for a period of ve years against defective material and workmanship.
RECOMMENDED WARREN RUPP ACCESSORIES
TO MAXIMIZE PUMP PERFORMANCE:
• Tranquilizer® Surge Suppressor: For nearly pulse-free ow.
• Warren Rupp Filter/Regulator: For modular installation and service
convenience.
• Warren Rupp Speed Control: For manual or programmable process
control. Manual adjustment or 4-20mA reception.
For more detailed information on these accessories,
contact your local Warren Rupp Factory-Authorized Distributor,
or Warren Rupp corporate headquarters.
Available Service Kits
Part No. Description
476-247-000 Air End Kit
Seals, O-Rings, Gaskets, Sleeve and Spool Set, Plungers,
Bushings, Pilot Valve Assembly
476-245-354 Santoprene Diaphragms, Check Balls, Gaskets, Seals, Nitrile O-Rings
476-245-360 Nitrile Diaphragms, Weighted Check Balls, O-Rings, Gaskets,
Seals, Wear Pads
476-245-364 EPDM Diaphragms and Weighted Check Balls, Gaskets, Seals,
Wear Pads, Nitrile O-Rings
476-245-365 Neoprene Diaphragms and Weighted Check Balls, Gaskets, Seals,
Wear Pads, Nitrile O-Rings,
476-245-633 FKM Diaphragms, PTFE Check Balls, Gaskets and O-Rings,
Seals, Wear Pads
476-043-635 PTFE Overlay Diaphragms, Check Balls, Gaskets and O-Rings,
Seals, Neoprene Backup Diaphragm
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 9
Page 12

IMPORTANT SAFETY
INFORMATION
IMPORTANT
Read these safety warnings
Read these safety warnings
and instructions in this
and instructions in this
manual completely, before
manual completely, before
installation and start-up
of the pump. It is the responsibility of the
of the pump. It is the responsibility of the
purchaser to retain this manual for reference.
purchaser to retain this manual for reference.
Failure to comply with the recommendations
Failure to comply with the recommendations
stated in this manual will damage the pump,
stated in this manual will damage the pump,
and void factory warranty.
and void factory warranty.
prevent leakage. Follow recommended torques
stated in this manual.
gas will void the warranty.
pressurized and must be bled of its pressure.
installation and start-up
CAUTION
Before pump operation,
inspect all gasketed
fasteners for looseness
caused by gasket creep. Retorque loose fasteners to
CAUTION
Pump not designed,
tested or certied to be
powered by compressed
natural gas. Powering
the pump with natural
WARNING
Before maintenance or
repair, shut off the compressed air line, bleed the
pressure, and disconnect
the air line from the pump.
The discharge line may be
WARNING
Take action to prevent static
sparking. Fire or explosion
can result, especially when
handling ammable liquids.
containers or other miscellaneous equipment
must be grounded. (See page 11)
The pump, piping, valves,
WARNING
This pump is pressurized
internally with air pressure
during operation. Always
make certain that all bolting
is in good condition and
bolting is reinstalled during assembly.
that all of the correct
WARNING
When used for toxic or
aggressive uids, the pump
should always be ushed
clean prior to disassembly.
WARNING
Before doing any maintenance on the pump,
be certain all pressure is
completely vented from the
pump, suction, discharge,
openings and connections. Be certain the air
supply is locked out or made non-operational,
so that it cannot be started while work is being
done on the pump. Be certain that approved
eye protection and protective clothing are worn
all times in the vicinity of the pump. Failure to
follow these recommendations may result in
serious injury or death.
piping, and all other
WARNING
Airborne particles and
loud noise hazards.
Wear ear and eye
protection.
WARNING
In the event of diaphragm
rupture, pumped material
may enter the air end of the
pump, and be discharged
into the atmosphere. If
pumping a product which is hazardous or toxic,
the air exhaust must be piped to an appropriate
area for safe disposition.
kg
WARNING
Use safe practices
when lifting
RECYCLING
Many components of SANDPIPER® AODD pumps are made
of recyclable materials (see chart on page 11 for material
specications). We encourage pump users to recycle worn out parts
and pumps whenever possible, after any hazardous pumped uids
are thoroughly ushed.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 10
Page 13

Grounding The Pump
One eyelet is fastened to the pump hardware.
One eyelet is installed to a true earth ground.
WARNING
Take action to prevent static sparking. Fire or explosion can result,
especially when handling ammable
liquids. The pump, piping, valves,
containers or other miscellaneous
equipment must be grounded.
This 8 foot long (244 centimeters) Ground
Strap, partnumber 920-025-000 can be
ordered as a service item.
To reduce the risk of static electrical sparking, this pump must be grounded.
Check the local electrical code for detailed grounding instruction and the
type of equipment required, or in the absence of local codes, an industry
or nationally recognized code having juristiction over specic installations.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 11
Page 14

MATERIAL CODES
THE LAST 3 DIGITS OF PART NUMBER
000 Assembly, sub-assembly;
and some purchased items
010 Cast Iron
012 Powered Metal
015 Ductile Iron
020 Ferritic Malleable Iron
025 Music Wire
080 Carbon Steel, AISI B-1112
100 Alloy 20
110 Alloy Type 316 Stainless Steel
111 Alloy Type 316 Stainless Steel
(Electro Polished)
112 Alloy C
113 Alloy Type 316 Stainless Steel
(Hand Polished)
114 303 Stainless Steel
115 302/304 Stainless Steel
117 440-C Stainless Steel (Martensitic)
120 416 Stainless Steel
(Wrought Martensitic)
123 410 Stainless Steel
(Wrought Martensitic)
148 Hardcoat Anodized Aluminum
149 2024-T4 Aluminum
150 6061-T6 Aluminum
151 6063-T6 Aluminum
152 2024-T4 Aluminum (2023-T351)
154 Almag 35 Aluminum
155 356-T6 Aluminum
156 356-T6 Aluminum
157 Die Cast Aluminum Alloy #380
158 Aluminum Alloy SR-319
159 Anodized Aluminum
162 Brass, Yellow, Screw Machine Stock
165 Cast Bronze, 85-5-5-5
166 Bronze, SAE 660
170 Bronze, Bearing Type, Oil Impregnated
175 Die Cast Zinc
180 Copper Alloy
305 Carbon Steel, Black Epoxy Coated
306 Carbon Steel, Black PTFE Coated
307 Aluminum, Black Epoxy Coated
308 Stainless Steel, Black PTFE Coated
309 Aluminum, Black PTFE Coated
310 PVDF Coated
313 Aluminum, White Epoxy Coated
330 Zinc Plated Steel
331 Chrome Plated Steel
332 Aluminum, Electroless Nickel Plated
333 Carbon Steel, Electroless
Nickel Plated
335 Galvanized Steel
336 Zinc Plated Yellow Brass
337 Silver Plated Steel
340 Nickel Plated
342 Filled Nylon
351 Food Grade Santoprene; Color: NATURAL
353 Geolast; Color: BLACK
354 Injection Molded #203-40
Santoprene- Duro 40D +/-5; Color: RED
355 Thermal Plastic
356 Hytrel; Color: BLUE
357 Injection Molded Polyurethane;
Color: GREEN
358 Urethane Rubber; Color: NATURAL
(Some Applications)
(Compression Mold)
359 Urethane Rubber; Color: NATURAL
360 Nitrile Rubber; Color Coded: RED
361 Nitrile
363 FKM (Fluorocarbon).
Color Coded: YELLOW
364 E.P.D.M. Rubber. Color Coded: BLUE
365 Neoprene Rubber;
Color Coded: GREEN
366 Food Grade Nitrile; Color: WHITE
368 Food Grade EPDM; Color: GRAY
370 Butyl Rubber
Color Coded: BROWN
371 Philthane (Tuftane)
374 Carboxylated Nitrile
375 Fluorinated Nitrile
378 High Density Polypropylene
379 Conductive Nitrile;
Color Coded: RED & SILVER
384 Conductive Neoprene;
Color Coded: GREEN & SILVER
405 Cellulose Fibre
408 Cork and Neoprene
425 Compressed Fibre
426 Blue Gard
440 Vegetable Fibre
465 Fibre
500 Delrin 500
501 Delrin 570
502 Conductive Acetal, ESD-800;
Color: BLACK
503 Conductive Acetal, Glass-Filled
Color: BLACK; Color Coded: YELLOW
505 Acrylic Resin Plastic
506 Delrin 150
520 Injection Molded PVDF; Color: NATURAL
521 Injection Molded Conductive PVDF;
Color: BLACK; Color Coded: LIGHT
GREEN
540 Nylon
541 Nylon
542 Nylon
544 Nylon Injection Molded
550 Polyethylene
551 Glass Filled Polypropylene; Color: BLACK
552 Unlled Polypropylene; Color: NATURAL
555 Polyvinyl Chloride
556 Black Vinyl
557 Conductive Polypropylene;
Color: BLACK; Color Coded: SILVER
558 Conductive HDPE; Color: BLACK
Color Coded: SILVER
559 Conductive Polypropylene; Color: BLACK
Color Coded: SILVER
570 Rulon II
580 Ryton
590 Valox
591 Nylatron G-S
592 Nylatron NSB
600 PTFE (virgin material)
Tetrauorocarbon (TFE)
601 PTFE (Bronze and moly lled)
602 Filled PTFE
603 Blue Gylon
604 PTFE
606 PTFE
607 Envelon
608 Conductive PTFE; Color: BLACK
610 PTFE Encapsulated Silicon
611 PTFE Encapsulated FKM
632 Neoprene/Hytrel
633 FKM/PTFE
634 EPDM/PTFE
635 Neoprene/PTFE
637 PTFE , FKM/PTFE
638 PTFE , Hytrel/PTFE
639 Nitrile/TFE
643 Santoprene®/EPDM
644 Santoprene®/PTFE
656 Santoprene Diaphragm and
Check Balls/EPDM Seats
661 EPDM/Santoprene
666 FDA Nitrile Diaphragm,
PTFE Overlay, Balls, and Seals
668 PTFE, FDA Santoprene/PTFE
Delrin is a registered
tradename of E.I. DuPont.
Gylon is a registered tradename
of Garlock, Inc.
Nylatron is a registered tradename
of Polymer Corp.
Santoprene is a registered tradename
of Exxon Mobil Corp.
Rulon II is a registered tradename
of Dixion Industries Corp.
Ryton is a registered tradename
of Phillips Chemical Co.
Valox is a registered tradename
of General Electric Co.
PortaPump, Tranquilizer and SludgeMaster are
registered tradenames of Warren Rupp, Inc.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 12
Page 15

Composite Repair Parts List
ITEM TOTAL
NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION RQD.
1 114.002.010. Bracket Assembly, Intermediate 1
1 114.002.156. Bracket Assembly, Intermediate 1
2 070.006.170. Bearing, Sleeve 2
3 720.004.360. Seal, U-Cup 2
4 135.016.162. Bushing Assembly, Threaded 2
5 560.001.360. O-Ring 2
6 620.011.114. Plunger, Actuator 2
7 095.073.001. Pilot Valve Body Assy.
7-A 095.070.558. Pilot Valve Body 1
7-B 755.025.000. Sleeve (w/O-Ring) 1
7-C 560.033.360. O-Ring (Sleeve) 4
7-D 775.026.000. Spool (w/O-Ring) 1
7-E 560.023.360. O-Ring (Spool) 2
7-F 675.037.080. Retaining Ring 1
8 360.041.379. Gasket, Valve Body 1
9 530.036.000. Mufer, Exhaust 1
10 031.012.000. Sleeve & Spool Set 1
11 095.043.010. Body, Valve 1
095.043.156. Body, Valve 1
12 132.014.358. Bumper, Valve Spool 2
13 165.011.010. Cap, End 2
165.011.157. Cap, End 2
14 360.010.425. Gasket, End Cap 2
15 560.020.360. O-Ring 6
16 170.032.330. Capscrew, Hex Head 8
17 170.045.330. Capscrew, Hex Head 4
18 360.048.425. Gasket, Valve Body 1
19 132.002.360. Bumper, Diaphragm 2
20 560.022.360. O-Ring 2
21 685.007.120. Rod, Diaphragm 1
22 612.047.330. Plate, Diaphragm — Inner 2
25 170.060.330. Capscrew, Hex Head 16
26 170.024.330. Capscrew, Hex Head 4
27 170.058.330. Capscrew, Hex Head 4
28 170.030.330. Capscrew, Hex Head 8
29 807.038.330. Stud 4
30 807.039.330. Stud 12
31 900.005.330. Washer, Lock 4
32 900.003.330. Washer, Lock 20
33 900.006.330. Washer, Lock 12
34 545.007.330. Nut, Hex 12
35 545.008.330. Nut, Hex 12
36 545.005.330. Nut, Hex 4
37 196.001.010. Chamber, Inner 2
196.001.157. Chamber, Inner 2
38 115.053.080. Bracket, Foot Mounting 2
1
1
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 13
Page 16

ITEM TOTAL
NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION RQD.
39 560.047.360. O-Ring 2
560.060.611. O-Ring 2
40 685.032.080. Rod, Connector 1
41 722.035.110. Seat Assembly, Ball Check Valve 2
(for use with PTFE
balls only)
722.035.112. Seat Assembly, Ball Check Valve 2
(for use with PTFE balls only)
722.097.110. Seat Assembly
722.097.112. Seat Assembly
42 286.007.360. Diaphragm 2
286.007.364. Diaphragm 2
286.007.365. Diaphragm 2
286.007.363. Diaphragm 2
286.007.366. Diaphragm 2
286.007.356. Diaphragm 2
286.007.354. Diaphragm 2
43 196.035.010. Chamber, Diaphragm — Outer 2
196.035.110. Chamber, Diaphragm — Outer 2
196.035.112. Chamber, Diaphragm — Outer 2
196.035.156. Chamber, Diaphragm — Outer 2
44 612.039.010. Plate Assembly, Diaphragm 2
612.097.110. Plate Assembly, Diaphragm 2
612.097.112. Plate Assembly, Diaphragm 2
612.039.157. Plate Assembly, Diaphragm 2
45 312.033.010. Elbow, Manifold 2
312.033.110. Elbow, Manifold 2
312.033.112. Elbow, Manifold 2
312.033.156. Elbow, Manifold 2
46 334.025.010. Flange, Threaded 2
334.025.110. Flange, Threaded 2
334.025.112. Flange, Threaded 2
334.025.156. Flange, Threaded 2
47 334.026.010. Flange, Porting — Suction 1
334.026.110. Flange, Porting — Suction 1
334.026.112. Flange, Porting — Suction 1
334.026.156. Flange, Porting — Suction 1
48 334.027.010. Flange, Porting — Discharge 1
334.027.110. Flange, Porting — Discharge 1
334.027.112. Flange, Porting — Discharge 1
334.027.156. Flange, Porting — Discharge 1
49 518.027.010. Manifold 1
518.027.110. Manifold 1
518.027.112. Manifold 1
518.027.156. Manifold 1
ITEM TOTAL
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 14
Page 17

NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION RQD.
50 360.049.425. Gasket, Flange 2
360.049.603. Gasket, Flange 2
51 360.050.379. Gasket, Manifold 4
360.050.384. Gasket, Manifold 4
360.050.608. Gasket, Manifold 4
52 618.003.110. Pipe Plug 4
618.003.112. Plug, Pipe 4
618.003.330. Plug, Pipe (Cast Iron and Aluminum wetted end) 4
53 675.013.360. Ring, Sealing 2
675.013.365. Ring, Sealing 2
675.013.363. Ring, Sealing 2
675.013.364. Ring, Sealing 2
675.013.600. Ring, Sealing 2
54 050.017.360W. Ball, Check Valve 4
050.017.364W. Ball, Check Valve 4
050.017.354. Ball, Check Valve 4
050.017.365W. Ball, Check Valve 4
050.018.600. Ball, Check Valve 4
55 115.057.080. Bracket, Foot Mtg. 2
56 900.004.330. Washer, Lock 2
57 545.004.330. Nut, Hex 2
58 286.020.604. Diaphragm 2
59 901.025.115. Washer 2
62 618.003.330. Pipe Plug (air end) 2
63 570.009.360. Pad, Wear (Not used on PTFE units) 2
570.009.363. Pad, Wear 2
570.009.364. Pad, Wear 2
570.009.365. Pad, Wear 2
NOT SHOWN:
031.019.010. (Cast Iron Center) (1)
031.019.156. (Aluminum Center) (1)
Includes items 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16
Available in kit form. Order P/N 031.055.000., which also includes items 6, 8, 18, 61.
**BOTTOM PORTING is recommended for pumping material containing solids which could settle out in the pumping chambers.
**TOP PORTING is recommended if there is a possibility of entrapped air vapors inhibiting the pumping action.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 15
Page 18

Composite Repair Drawing
A = These Items Available in Kit Form Only.
Order Angle Valve Kit P/N 475-102-000.
For Types DGN, TGN
©2010 Warren Rupp, Inc. All rights reserved.
®SANDPIPER is a registered tradename of Warren Rupp, Inc.
Printed in U.S.A.
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 16
Ribs on Virgin PTFE Diaphragm are
to be toward the pumping material.
Page 19

Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer:
®
Warren Rupp, Inc.
Mansfield, Ohio, 44902 USA
certifies that Air-Operated Double Diaphragm Pump Series: HDB, HDF,
M Non-Metallic, S Non-Metallic, M Metallic, S Metallic, T Series, G Series, RS Series
U Series, EH and SH High Pressure, W Series, SMA and SPA Submersibles,
and Tranquilizer Surge Suppressors comply with the European Community
Directive 2006/42/EC on Machinery, according to Annex VIII. This product
has used Harmonized Standard EN809:1998+A1:2009, Pumps and Pump Units
for Liquids - Common Safety Requirements, to verify conformance.
Signature of authorized person
, 800 N. Main Street
October 20, 2005
Date of issue
David Roseberry
Printed name of authorized person
Revision Level: F
hdb2smdl3sm-rev0614 Model HDB2 Page 17
Engineering Manager
Title
April 19, 2012
Date of revision
Page 20

EC Declaration of Conformity
In accordance with ATEX Directive 94/9/EC,
Equipment intended for use in potentially explosive environments.
Manufacturer:
Warren Rupp, Inc.
A Unit of IDEX Corportion
800 North Main Street
P.O. Box 1568
Mansfield, OH 44902 USA
EN 60079-25: 2011
For pumps equipped with Pulse Output ATEX Option
Quality B.V. (0344)
AODD Pumps and Surge Suppressors
For Type Examination Designations, see page 2 (back)
AODD (Air-Operated Double Diaphragm) Pumps
EC Type Examination Certificate No. Pumps: KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
DEKRA Certification B.V. (0344)
Meander 1051
6825 MJ Arnhem
The Netherlands
®
Applicable Standard:
EN13463-1: 2009
EN13463-5: 2011
DATE/APPROVAL/TITLE:
14 MAY 2014
David Roseberry, Engineering Manager
Page 21

EC Declaration of Conformity
ATEX Summary of Markings
Type Marking Listed In
Pump types, S1F, S15, S20,
and S30 provided with the
pulse output option
Pump types, S1F, S15, S20,
and S30 provided with the
integral solenoid option
Pump types, HDB1½, HDB40,
HDB2, HDB50, HDB3, HDF1,
HDF25, HDF2, HDF3M, PB¼,
S05, S1F, S15, S20, S30, SB1,
SB25, ST1½, ST40, G15, G20,
and G30, without the above
listed options, no aluminum
parts
Pump types, DMF2, DMF3,
HDB1½, HDB40, HDB2,
HDB50, HDB3, HDF1, HDF25,
HDF2, HDF3M, PB¼, S05, S1F,
S15, S20, S30, SB1, SB25,
SE½, ST1, ST25, ST1½, ST40,
U1F, G05, G1F, G15, G20, and
G30
Surge Suppressors all types II 2 G T5
EC Type Certificate No. Pumps: KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
Type Certificate No. Pumps: KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
Type Certificate No. Suppressors: KEMA 09ATEX0073
II 2 G Ex ia c IIC T5
II 3/2 G Ex ia c IIC T5
II 2 D
Ex c iaD 20 IP67 T100oC
II 2 G EEx m c II T5
II 3/2 G EEx m c II T5
II 2 D c IP65 T100
II 1 G c T5
II 3/1 G c T5
II 1 D c T100
I M1 c
I M2 c
II 2 G c T5
II 3/2 G c T5
II 2 D c T100
II 3/2 G T5
II 2 D T100
Non-Conductive
Fluids
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
CE 0344
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
o
C
o
C
o
C
o
C
CE 0344
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
CE 0344
KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
CE
KEMA 09ATEX0073
CE
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0071 X
KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
KEMA 09ATEX0072 X
KEMA 09ATEX0073
KEMA 09ATEX0073
KEMA 09ATEX0073
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Pumps marked with equipment Category II 3/1 G (internal 3 G /
eternal 1 G), 1D, M1 and M2 when used for non-conductive fluids.
The pumps are Category II 2 G when used for conductive fluids.
Pumps and surge suppressors marked with equipment Category II 3/2
(internal 3 G / external 2 G), 2D when used for non-conductive fluids.
The pumps are Category II 2 G when used for conductive fluids.
 Loading...
Loading...