Samsung K4H561638B-TLB0, K4H561638B-TLA2, K4H561638B-TLA0, K4H561638B-TCB0, K4H560838B-TLA2 Datasheet
...
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
DDR SDRAM Specification
Version 0.3
- 1 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000

256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
Revision History
Version 0 (May, 2000)
- First version for internal review of 256Mb B-die.
Version 0.1(July,2000)
- Added DC target spec values
- Deleted tDAL in AC parameter X
Version 0.2(October,2000)
- Updated DC current spec
Version 0.3(November,2000)
- Changed spec to preliminery from target
- 2 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000

256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
Contents
Revision History
General Information
1. Key Features
1.1 Features
1.2 Operating Frequencies
2. Package Pinout & Dimension
2.1 Package Pintout
2.2 Input/Output Function Description
2.3 66 Pin TSOP(II)/MS-024FC Package Physical Dimension
3. Functional Description
3.1 Simplified State Diagram
3.2 Basic Functionality
3.2.1 Power-Up Sequence
3.2.2 Mode Register Definition
3.2.2.1 Mode Register Set(MRS)
3.2.2.2 Extended Mode Register Set(EMRS)
3.2.3 Precharge
3.2.4 No Operation(NOP) & Device Deselect
3.2.5 Row Active
3.2.6 Read Bank
3.2.7 Write Bank
3.3 Essential Functionality for DDR SDRAM
3.3.1 Burst Read Operation
3.3.2 Burst Write Operation
3.3.3 Read Interrupted by a Read
3.3.4 Read Interrupted by a Write & Burst Stop
3.3.5 Read Interrupted by a Precharge
3.3.6 Write Interrupted by a Write
2
7
8
8
8
9
9
10
11
12
12
13
13
14
14
16
17
17
18
18
18
19
19
20
21
21
22
23
- 3 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000

256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
3.3.7 Write Interrupted by a Read & DM
3.3.8 Write Interrupted by a Precharge & DM
3.3.9 Burst Stop
3.3.10 DM masking
3.3.11 Read With Auto Precharge
3.3.12 Write With Auto Precharge
3.3.13 Auto Refresh & Self Refresh
3.3.14 Power Down
4. Command Truth Table
5. Functional Truth Table
6. Absolute Maximum Rating
7. DC Operating Conditions & Specifications
7.1 DC Operating Conditions
7.2 DDR SSDRAM spec Items and Test Conditions
7.3 DDR SDRAM IDD spec Table
8. AC Operating Conditions & Timming Specification
8.1 AC Operating Conditions
8.2 AC Timming Parameters & Specification
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
37
37
37
38
41
41
42
9. AC Operating Test Conditions
10. Input/Output Capacitance
11. IBIS: I/V Characteristics for Input and Output Buffers
11.1 Normal strength driver
44
44
45
45
47
11.2 Half strength driver
12. QFC function
QFC definition
QFC timming on Read Operation
QFC timming on Write operation with tDQSSmax
QFC timming on Write operation with tDQSSmin
QFC timming example for interrupted writes operation
Timing Diagram
- 4 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
49
49
49
50
50
51
52

256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
List of tables
Table 1 : Operating frequency and DLL jitter
Table 2. : Column address configurtion
Table 3 : Input/Output function description
Table 4 : Burst address ordering for burst length
Table 5 : Bank selection for precharge by bank address bits
Table 6 : Operating description when new command asserted while
read with auto precharge is issued
Table 7 : Operating description when new command asserted while
write with auto precharge is issued
Table 8 : Command truth table
Table 9-1 : Functional truth table
Table 9-2 : Functional truth table (contiued)
Table 9-3 : Functional truth table (contiued)
Table 9-4 : Functional truth table (contiued)
Table 10 : Absolute maximum raings
Table 11 : DC operating condtion
Table 12 : DDR SDRAM spec Items and Test Conditions
Table 13 : DDR SDRAM IDD spec Table
Table 14 : AC operating condition
Table 15 : AC timing parameters and specifications
Table 16 : AC operating test conditions
Table 17 : Input/Output capacitance
Table 18 : Pull down and pull up current values for normal strength driver
Table 19 : Pull down and pull up current values for half strength driver
8
9
10
15
17
28
29
32
33
34
35
36
37
37
38
40
41
43
44
44
46
48
- 5 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
List of figures
Figure 1 : 256Mb Package Pinout
Figure 2 : Package dimension
Figure 3 :State digram
Figure 4 : Power up and initialization sequence
Figure 5 : Mode register set
Figure 6 : Mode register set sequence
Figure 7 : Extend mode register set
Figure 8 : Bank activation command cycle timing
Figure 9 : Burst read operation timing
Figure 10 : Burst write operation timing
Figure 11 : Read interrupted by a read timing
Figure 12 : Read interrupted by a write and burst stop timing
Figure 13 : Read interrupted by a precharge timing
Figure 14 : Write interrupted by a write timing
Figure 15 : Write interrupted by a read and DM timing
Figure 16 : Write interrupted by a precharge and DM timing
Figure 17 : Burst stop timing
Figure 18 : DM masking timing
Figure 19 : Read with auto precharge timing
Figure 20 : Write with auto precharge timing
Figure 21 : Auto refresh timing
Figure 22 : Self refresh timing
Figure 23 : Power down entry and exit timing
Figure 24 : Output Load Circuit (SSTL_2)
Figure 25 : I / V characteristics for input/output buffers:
pull-up(above) and pull-down(below) for normal strength driver
Figure 26 : I / V characteristics for input/output buffers:
pull-up(above) and pull-down(below) for half strength driver
Figure 27 : QFC timing on read operation
Figure 28 : QFC timing on write operation with tDQSSmax
Figure 29 : QFC timing on write operation with tDQSSmin
Figure 30 : QFC timing example for interrupted writes operation
6
11
12
13
14
15
16
18
19
20
21
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
30
31
44
45
47
49
50
50
51
- 6 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
General Information
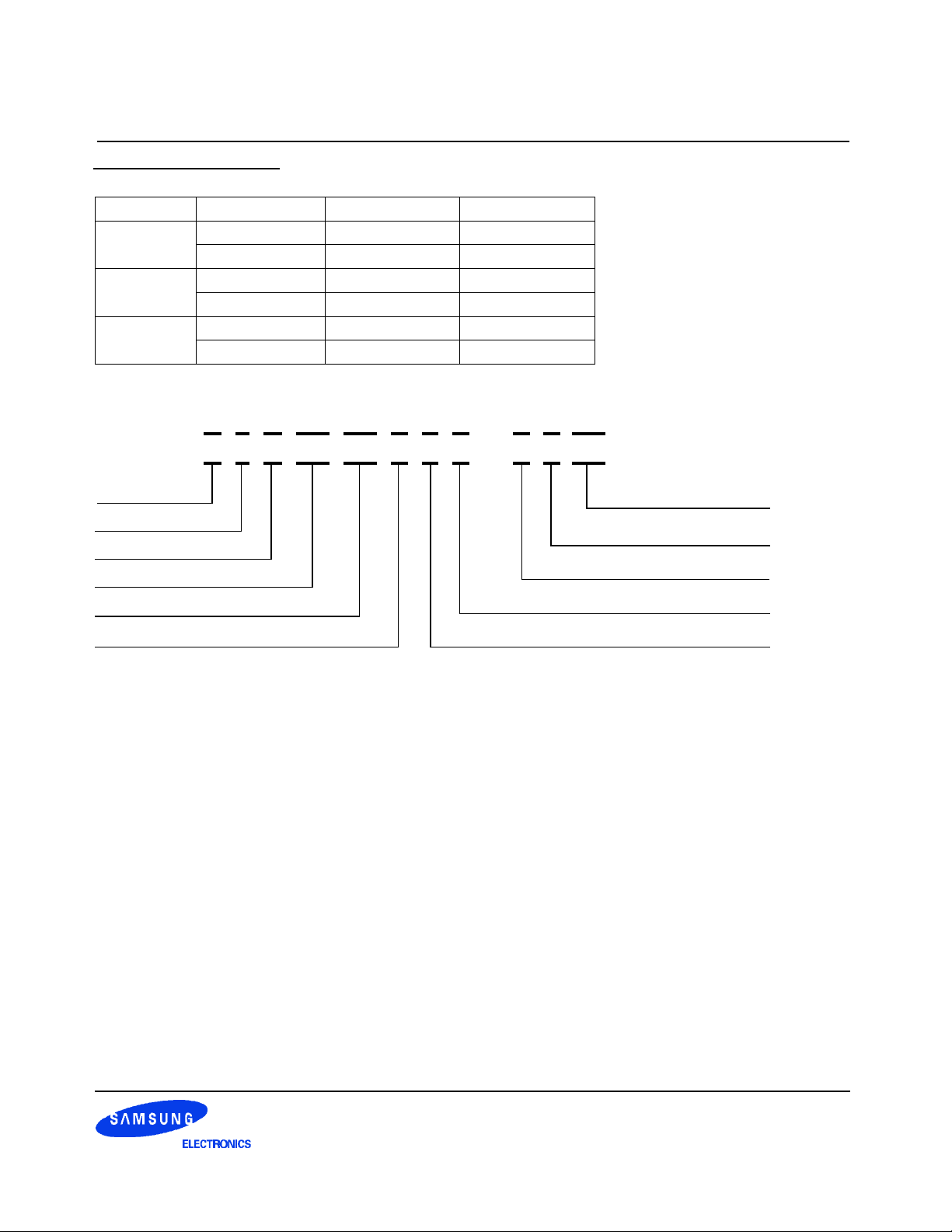
Organization 133Mhz w/ CL=2 133Mhz w/ CL=2.5 100Mhz w/ CL=2
64Mx4
32Mx8
16Mx16
K4H560438B-TCA2 K4H560438B-TCB0 K4H560438B-TCA0
K4H560438B-TLA2 K4H560438B-TLB0 K4H560438B-TLA0
K4H560838B-TCA2 K4H560838B-TCB0 K4H560838B-TCA0
K4H560838B-TLA2 K4H560838B-TLB0 K4H560838B-TLA0
K4H561638B-TCA2 K4H561638B-TCB0 K4H561638B-TCA0
K4H561638B-TLA2 K4H561638B-TLB0 K4H561638B-TLA0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
K 4 H XX XX X X X - X X
Memory
DRAM
Small Classification
Density and Refresh
Organization
Bank
1. SAMSUNG Memory : K
2. DRAM : 4
3. Small Classification
H : DDR SDRAM
4. Density & Refresh
64 : 64M 4K/64ms
28 : 128M 4K/64ms
56 : 256M 8K/64ms
51 : 512M 8K/64ms
1G : 1G 16K/32ms
5. Organization
04 : x4
08 : x8
16 : x16
32 : x32
6. Bank
3 : 4 Bank
7. Interface (VDD & VDDQ)
8: SSTL-2(2.5V, 2.5V)
XX
Speed
Temperature & Power
Package
Version
Interface (VDD & VDDQ)
8. Version
M : 1st Generation
A : 2nd Generation
B : 3rd Generation
C : 4th Generation
D : 5th Generation
E : 6th Generation
9. Package
T : TSOP2 (400mil x 875mil)
10. Temperature & Power
C : (Commercial, Normal)
L : (Commercial, Low)
11. Speed
A0 : 10ns@CL2
A2 : 7.5ns@CL2
B0 : 7.5ns@CL2.5
- 7 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
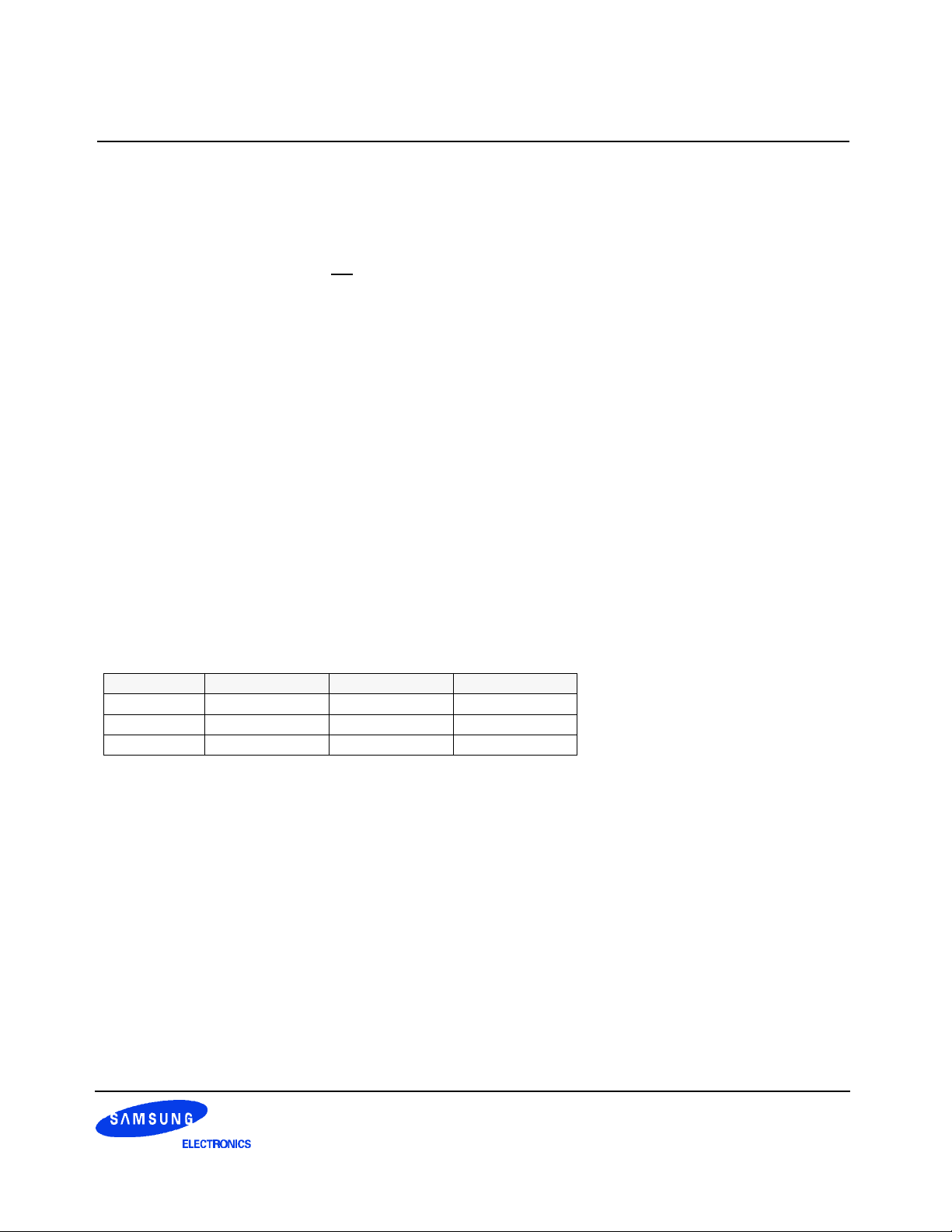
1. Key Features
1.1 Features
• Double-data-rate architecture; two data transfers per clock cycle
• Bidirectional data strobe(DQS)
• Four banks operation
• Differential clock inputs(CK and CK)
• DLL aligns DQ and DQS transition with CK transition
• MRS cycle with address key programs
-. Read latency 2, 2.5 (clock)
-. Burst length (2, 4, 8)
-. Burst type (sequential & interleave)
• All inputs except data & DM are sampled at the positive going edge of the system clock(CK)
• Data I/O transactions on both edges of data strobe
• Edge aligned data output, center aligned data input
• LDM,UDM/DM for write masking only
• Auto & Self refresh
• 7.8us refresh interval(8K/64ms refresh)
• Maximum burst refresh cycle : 8
• 66pin TSOP II package
1.2 Operating Frequencies
- A2(DDR266A) - B0(DDR266B) - A0(DDR200)
Speed @CL2 133MHz 100MHz 100MHz
Speed @CL2.5 - 133MHz -
DLL jitter ±0.75ns ±0.75ns ±0.8ns
*CL : Cas Latency
Table 1. Operating frequency and DLL jitter
- 8 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
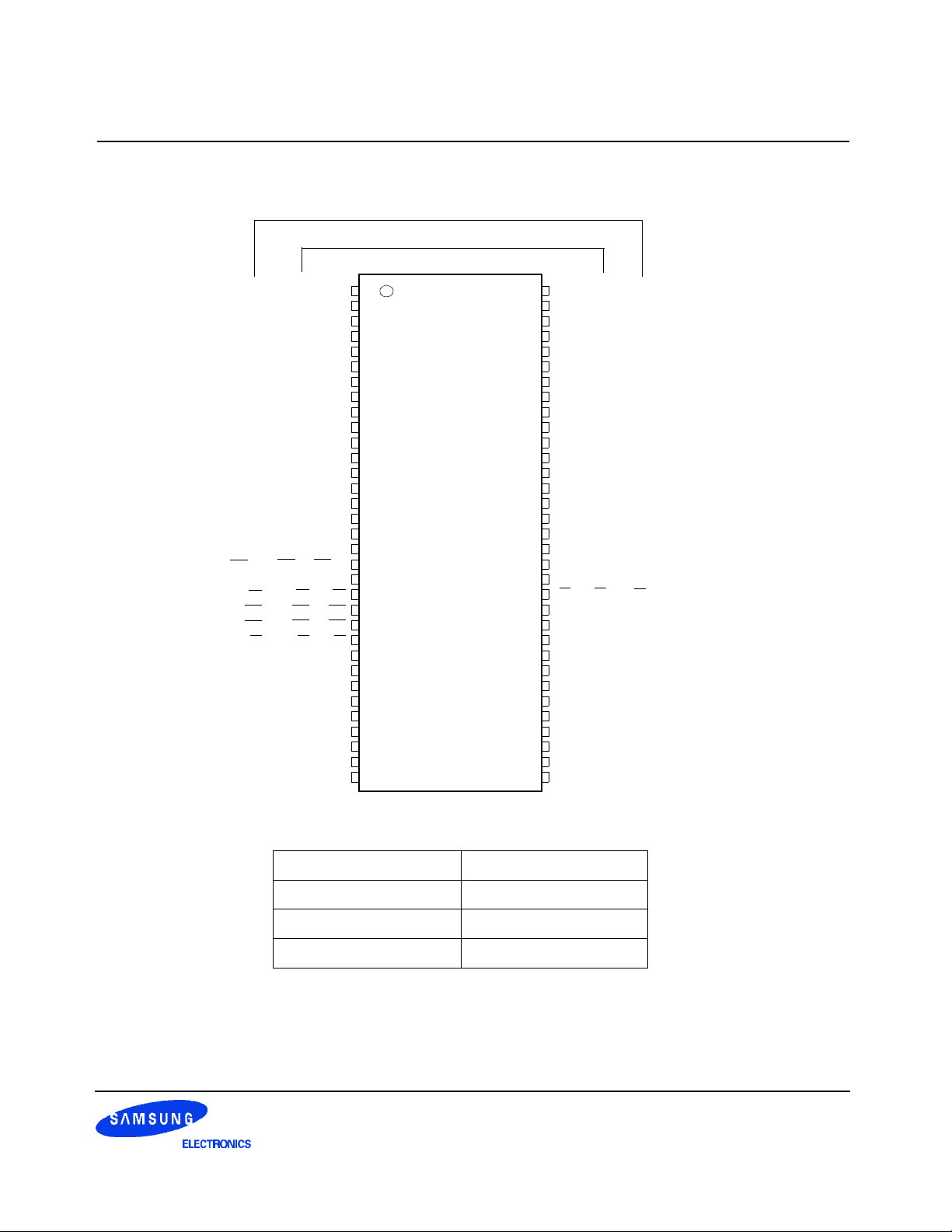
2. Package Pinout & Dimension
2.1 Package Pinout
VDD
DQ0
VDDQ
DQ1
DQ2
VSSQ
DQ3
DQ4
VDDQ
DQ5
DQ6
VSSQ
DQ7
NC
VDDQ
LDQS
NC
VDD
QFC/NC
LDM
WE
CAS
RAS
CS
NC
BA0
BA1
AP/A10
A0
A1
A2
A3
VDD
VDD
VDD
DQ0
NC
VDDQ
VDDQ
NC
NC
DQ1
DQ0
VSSQ
VSSQ
NC
NC
DQ2
NC
VDDQ
VDDQ
NC
NC
DQ3
DQ1
VSSQ 12
VSSQ
NC 13
NC
NC
NC
VDDQ
NC
NC
NC
NC
VDD
WE
CAS
RAS
BA0
BA1
VDD
NC
CS
NC
VDD
QFC/NC
NC
WE
CAS
RAS
CS
NC
BA0
BA1
AP/A10
A0
A1
A2
A3
VDD
QFC/NC
AP/A10
16Mb x 16
32Mb x 8
64Mb x 4
VSS
VSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
66 PIN TSOP(II)
11
(400mil x 875mil)
(0.65 mm PIN PITCH)
14
Bank Address
15VDDQ
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
A0
29
A1
30
A2
31
A3
32
33
BA0-BA1
Row Address
A0-A12
Auto Precharge
A10
MS-024FC
66
NC
65
VSSQ
64
NC
63
DQ3
62
VDDQ
61
NC
60
NC
59
VSSQ
58
NC
57
DQ2
56
VDDQ
55
NC
54
NC
53
VSSQ
52
DQS
51
NC
50
VREF
49
VSS
48
DM
47
CK
46
CK
45
CKE
44
NC
43
A12
42
A11
41
A9
40
A8
39
A7
38
A6
37
A5
36
A4
35
VSS
34
DQ7
VSSQ
NC
DQ6
VDDQ
NC
DQ5
VSSQ
NC
DQ4
VDDQ
NC
NC
VSSQ
DQS
NC
VREF
VSS
DM
CK
CK
CKE
NC
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
VSS
VSS
DQ15
VSSQ
DQ14
DQ13
VDDQ
DQ12
DQ11
VSSQ
DQ10
DQ9
VDDQ
DQ8
NC
VSSQ
UDQS
NC
VREF
VSS
UDM
CK
CK
CKE
NC
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
VSS
FIgure 1. 256Mb package Pinout
Organization Column Address
64Mx4 A0-A9, A11
32Mx8 A0-A9
16Mx16 A0-A8
DM is internally loaded to match DQ and DQS identically.
Table 2. Column address configuration
- 9 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
2.2 Input/Output Function Description
SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
CK, CK Input Clock : CK and CK are differential clock inputs. All address and control input signals are sam-
CKE Input Clock Enable : CKE HIGH activates, and CKE LOW deactivates internal clock signals, and
CS Input Chip Select : CS enables(registered LOW) and disables(registered HIGH) the command
RAS, CAS, WE Input Command Inputs : RAS, CAS and WE (along with CS) define the command being entered.
LDM,(U)DM Input Input Data Mask : DM is an input mask signal for write data. Input data is masked when DM is
BA0, BA1 Input Bank Addres Inputs : BA0 and BA1 define to which bank ACTIVE, READ, WRITE or PRE-
A [n : 0] Input Address Inputs : Provide the row address for ACTIVE commands, the column address and
DQ I/O Data Input/Output : Data bus
LDQS,(U)DQS I/O Data Strobe : Output with read data, input with write data. Edge-aligned with read data, cen-
QFC Output FET Control : Optional. Output during every Read and Write access. Can be used to control
NC - No Connect : No internal electrical connection is present.
VDDQ Supply DQ Power Supply : +2.5V ± 0.2V.
VSSQ Supply DQ Ground.
VDD Supply Power Supply : +2.5V ± 0.2V (device specific).
VSS Supply Ground.
VREF Input SSTL_2 reference voltage.
pled on the positive edge of CK and negative edge of CK. Output (read) data is referenced to
both edges of CK. Internal clock signals are derived from CK/CK.
device input buffers and output drivers. Deactivating the clock provides PRECHARGE
POWER-DOWN and SELF REFRESH operation (all banks idle), or ACTIVE POWER-DOWN
(row ACTIVE in any bank). CKE is synchronous for all functions except for disabling outputs,
which is achieved asynchronously. Input buffers, excluding CK, CK and CKE are disabled
during power-down and self refresh modes, providing low standby power. CKE will recognize
an LVCMOS LOW level prior to VREF being stable on power-up.
decoder. All commands are masked when CS is registered HIGH. CS provides for external
bank selection on systems with multiple banks. CS is considered part of the command code.
sampled HIGH along with that input data during a WRITE access. DM is sampled on both
edges of DQS. DM pins include dummy loading internally, to matches the DQ and DQS loading. For the x16, LDM corresponds to the data on DQ0-DQ7 ; UDM correspons to the data on
DQ8-DQ15.
CHARGE command is being applied.
AUTO PRECHARGE bit for READ/WRITE commands, to select one location out of the memory array in the respective bank. A10 is sampled during a PRECHARGE command to determine whether the PRECHARGE applies to one bank (A10 LOW) or all banks (A10 HIGH). If
only one bank is to be precharged, the bank is selected by BA0, BA1. The address inputs also
provide the op-code during a MODE REGISTER SET command. BA0 and BA1 define which
mode register is loaded during the MODE REGISTER SET command (MRS or EMRS).
tered in write data. Used to capture write data. For the x16, LDQS corresponds to the data on
DQ0-DQ7 ; UDQS corresponds to the data on DQ8-DQ15.
isolation switches on modules.
Table 3. Input/Output Function Description
- 10 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
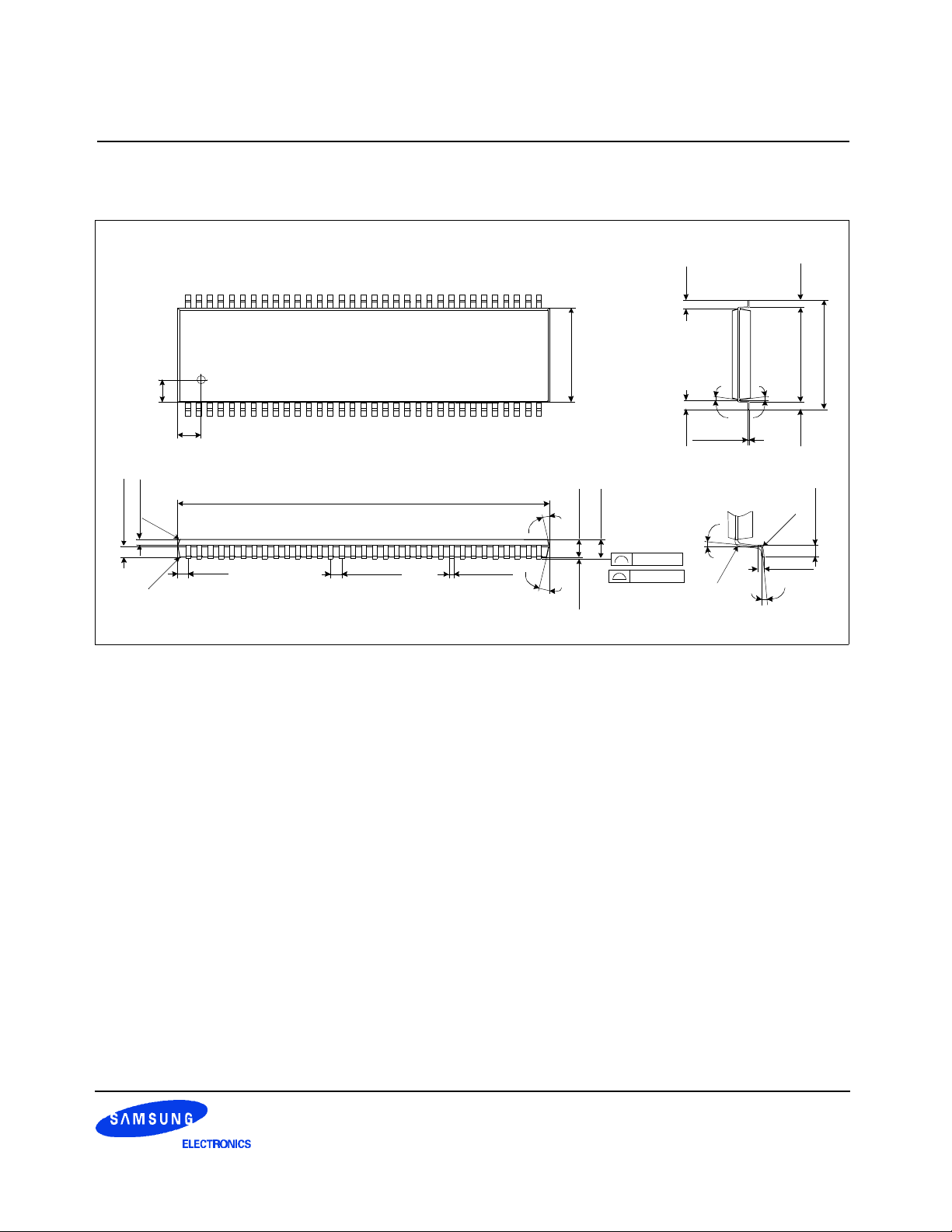
2.3 66 Pin TSOP(II)/MS-024FC Package Physical Dimension
Units : Millimeters
#66 #34
(1.50)
#1 #33
(1.50)
(
R
0
.
1
5
)
0.210±0.05
0.665±0.05
5)
1
0.
(R
NOTE
1. ( ) IS REFERENCE
2. [ ] IS ASS’Y OUT QUALITY
22.22±0.10
(10×)
0.65TYP(0.71)
0.65±0.08
0.30±0.08
(10×)
Figure 2. Package dimension
10.16±0.10
1.20MAX
1.00±0.10
0.05 MIN
0.10 MAX
[ ]
0.075 MAX
(0.80)
(0.80)
0.125
4
(
(10×)(10×)
+0.075
-0.035
)
×
0
R
(
R0
(
)
5
2
.
0.25TYP
0×~8×
11.76±0.20
(0.50) (0.50)(10.76)
5)
.2
0.45~0.75
- 11 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
3. Functional Description
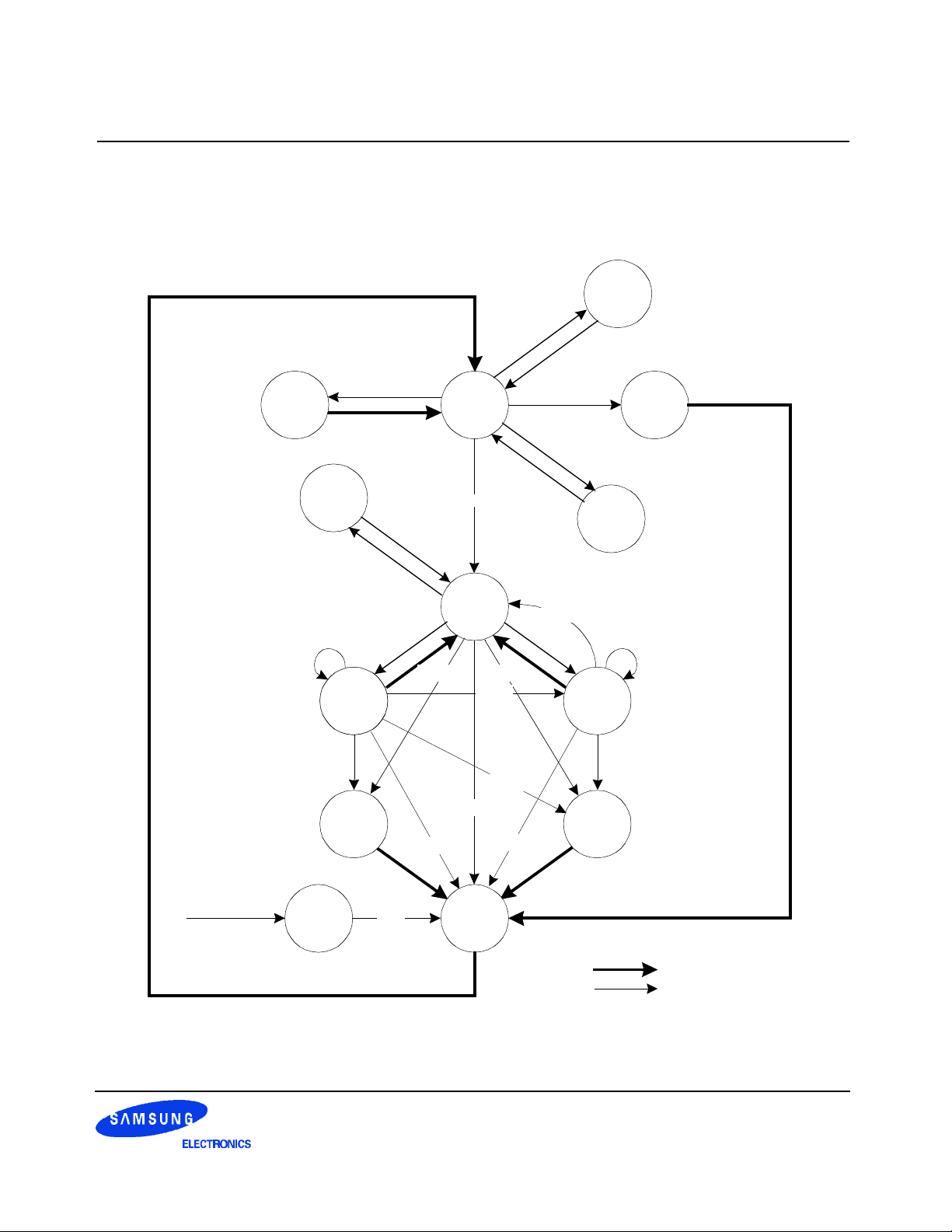
3.1 Simplified State Diagram
SELF
REFRESH
REFS
REFSX
MODE
REGISTER
SET
MRS
IDLE
REFA
CKEL
AUTO
REFRESH
POWER
APPLIED
POWER
DOWN
WRITEA
POWER
ON
CKEH
WRITEA
WRITE
WRITE
PRE
CKEH
ACT
CKEL
ROW
ACTIVE
WRITEA READA
READ
READA
PRE
PRE
CHARGE
PRE
PRE
POWER
DOWN
BURST STOP
READ
READ
READA
READAWRITEA
Figure 3. State diagram
- 12 -
Automatic Sequence
Command Sequence
WRITEA : Write with autoprecharge
READA : Read with autoprecharge
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
3.2 Basic Functionality
3.2.1 Power-Up and Initialization Sequence
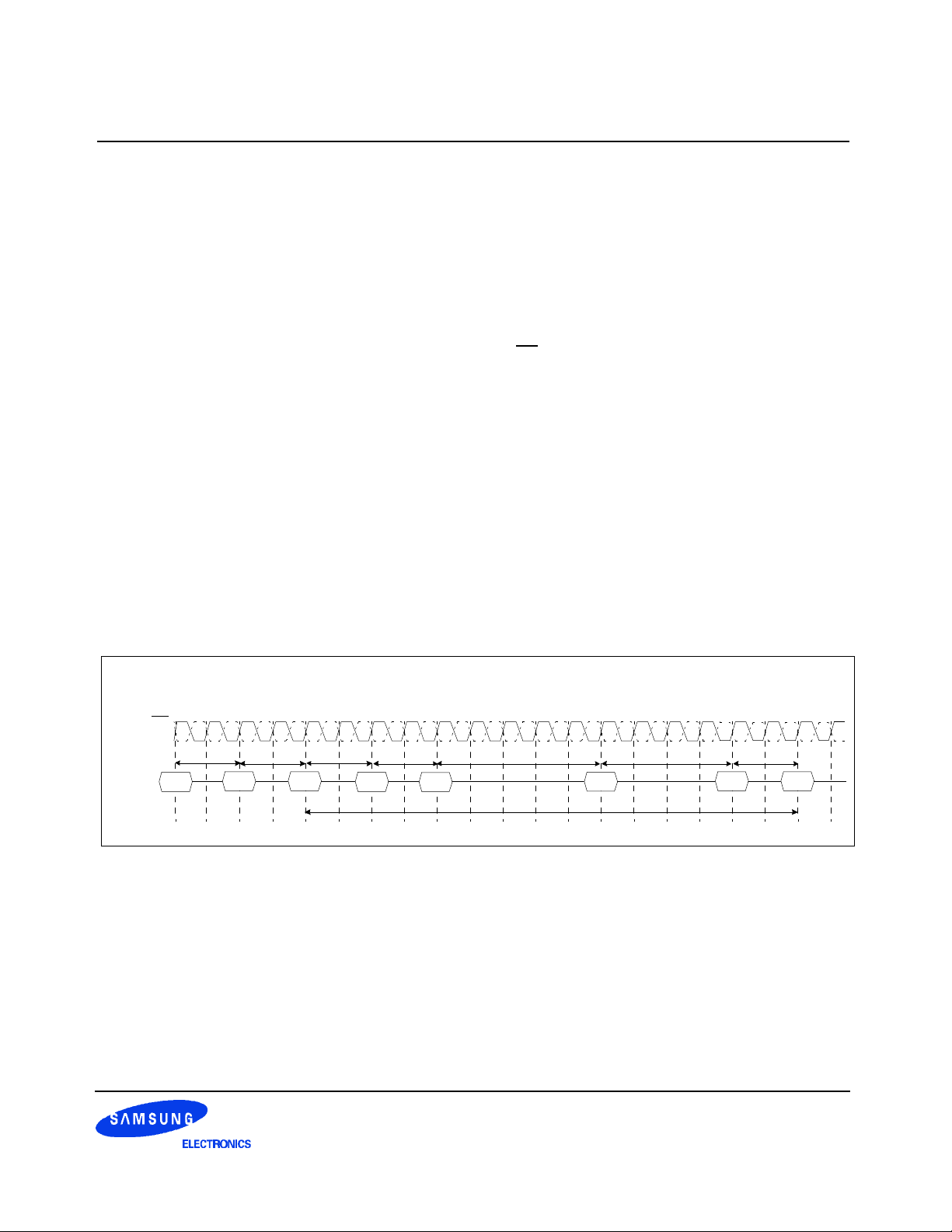
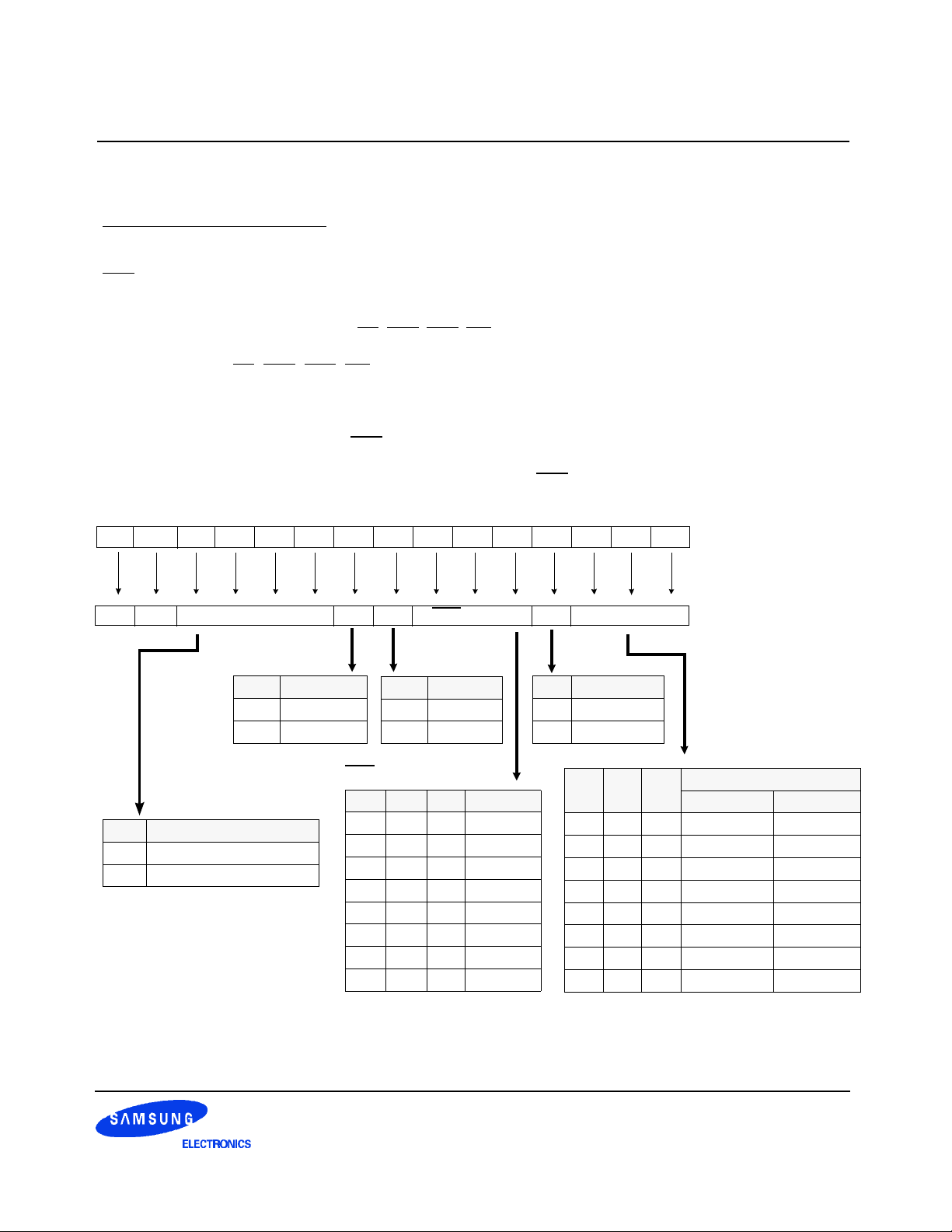
The following sequence is required for POWER UP and Initialization.
1. Apply power and attempt to maintain CKE at a low state(all other inputs may be undefined.)
- Apply VDD before or at the same time as VDDQ.
- Apply VDDQ before or at the same time as VTT & Vref.
2. Start clock and maintain stable condition for a minimum of 200us.
3. The minimum of 200us after stable power and clock(CK, CK), apply NOP & take CKE high.
4. Issue precharge commands for all banks of the device.
*1
5. Issue EMRS to enable DLL.(To issue "DLL Enable" command, provide "Low" to A0, "High" to BA0 and "Low"
to all of the rest address pins, A1~A11 and BA1)
6. Issue a mode register set command for "DLL reset". The additional 200 cycles of clock input is required to
*1
lock the DLL.
(To issue DLL reset command, provide "High" to A8 and "Low" to BA0)
*2
7. Issue precharge commands for all banks of the device.
8. Issue 2 or more auto-refresh commands.
9. Issue a mode register set command with low to A8 to initialize device operation.
*1 Every "DLL enable" command resets DLL. Therefore sequence 6 can be skipped during power up.
Instead of it, the additional 200 cycles of clock input is required to lock the DLL after enabling DLL.
*2 Sequence of 6 & 7 is regardless of the order.
Power up & Initialization Sequence
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
CK
CK
Command
precharge
ALL Banks
tRP
EMRS
2 Clock min.
MRS
DLL Reset
∼
∼
2 Clock min.
precharge
ALL Banks
tRP
1st Auto
Refresh
tRFC
∼
∼
∼
∼
min.200 Cycle
∼
∼
2nd Auto
Refresh
Figure 4. Power up and initialization sequence
- 13 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
tRFC
∼
∼
∼
∼
∼
∼
∼
∼
Mode
Register Set
2 Clock min.
Any
Command
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
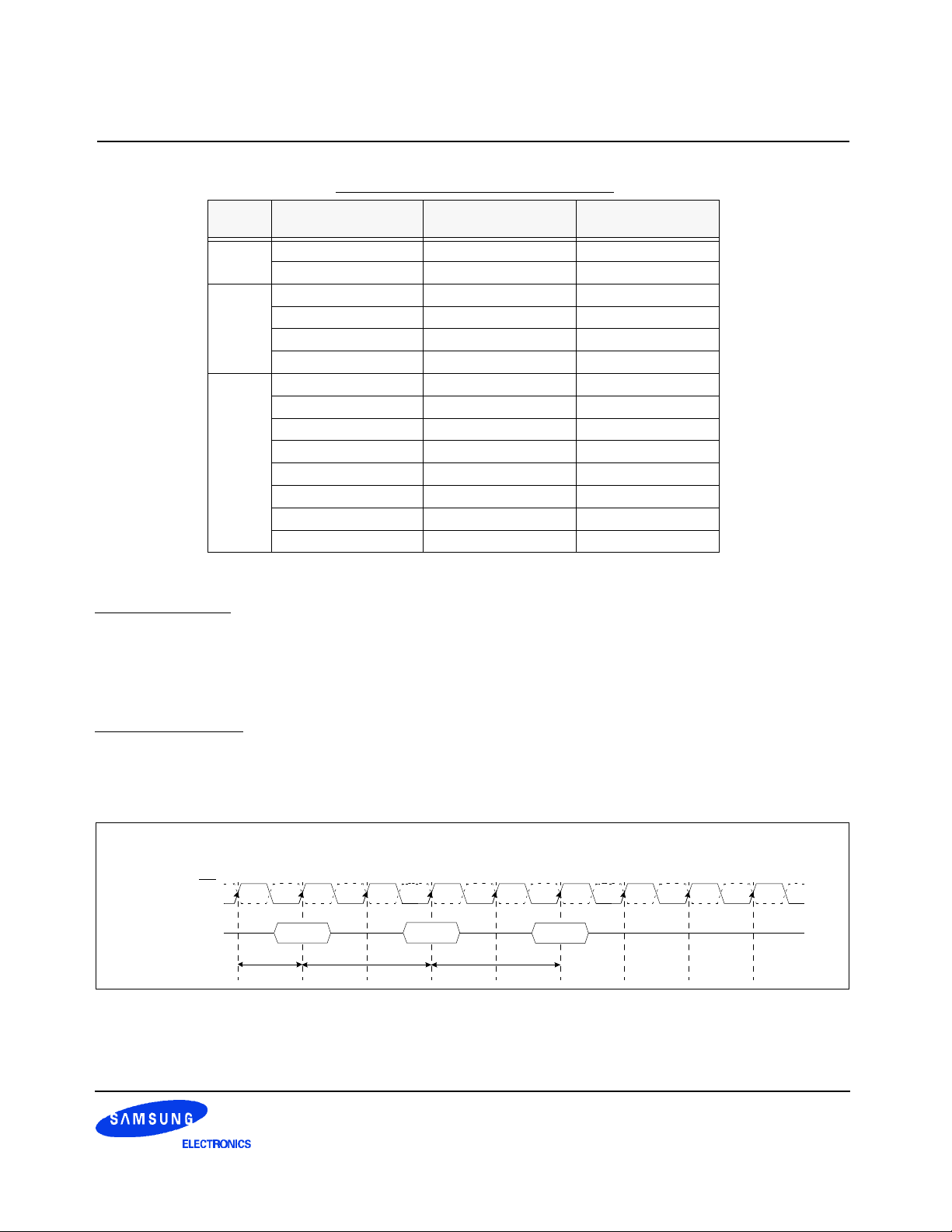
3.2.2 Mode Register Definition
3.2.2.1 Mode Register Set(MRS)
The mode register stores the data for controlling the various operating modes of DDR SDRAM. It programs
CAS latency, addressing mode, burst length, test mode, DLL reset and various vendor specific options to make
DDR SDRAM useful for variety of different applications. The default value of the mode register is not defined,
therefore the mode register must be written after EMRS setting for proper DDR SDRAM operation. The mode
register is written by asserting low on CS, RAS, CAS, WE and BA0(The DDR SDRAM should be in all bank precharge with CKE already high prior to writing into the mode register). The states of address pins A0 ~ A12 in
the same cycle as CS, RAS, CAS, WE and BA0 going low are written in the mode register. Two clock cycles
are requested to complete the write operation in the mode register. The mode register contents can be
changed using the same command and clock cycle requirements during operation as long as all banks are in
the idle state. The mode register is divided into various fields depending on functionality. The burst length uses
A0 ~ A2, addressing mode uses A3, CAS latency(read latency from column address) uses A4 ~ A6. A7 is used
for test mode. A8 is used for DLL reset. A7 must be set to low for normal MRS operation. Refer to the table for
specific codes for various burst lengths, addressing modes and CAS latencies.
BA1
BA0
RFU
0
BA0 An ~ A0
0 (Existing)MRS Cycle
1 Extended Funtions(EMRS)
* RFU(Reserved for future use)
should stay "0" during MRS
cycle.
A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
A12
A8 DLL Reset
0 No
1 Yes
TM CAS Latency BT Burst LengthRFU DLL
A7 mode
0 Normal
1 Test
CAS Latency
A6 A5 A4 Latency
0 0 0 Reserve
0 0 1 Reserve
0 1 0 2
0 1 1 (3)
1 0 0 Reserve
1 0 1 (1.5)
1 1 0 2.5
1 1 1 Reserve
Address Bus
Mode Register
A3 Burst Type
0 Sequential
1 Interleave
Burst Length
A2 A1 A0
0 0 0 Reserve Reserve
0 0 1 2 2
0 1 0 4 4
0 1 1 8 8
1 0 0 Reserve Reserve
1 0 1 Reserve Reserve
1 1 0 Reserve Reserve
1 1 1 Reserve Reserve
Sequential Interleave
Latency
Figure 5. Mode Register Set
- 14 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
Burst Address Ordering for Burst Length
Burst
Length
2
4
8
Starting
Address(A2, A1, A0)
Sequential Mode Interleave Mode
xx0 0, 1 0, 1
xx1 1, 0 1, 0
x00 0, 1, 2, 3 0, 1, 2, 3
x01 1, 2, 3, 0 1, 0, 3, 2
x10 2, 3, 0, 1 2, 3, 0, 1
x11 3, 0, 1, 2 3, 2, 1, 0
000 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
001 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0 1, 0, 3, 2, 5, 4, 7, 6
010 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1 2, 3, 0, 1, 6, 7, 4, 5
011 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2 3, 2, 1, 0, 7, 6, 5, 4
100 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 3 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 3
101 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 5, 4, 7, 6, 1, 0, 3, 2
110 6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 6, 7, 4, 5, 2, 3, 0, 1
111 7, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
Table 4. Burst address ordering for burst length
DLL Enable/Disable
The DLL must be enabled for normal operation. DLL enable is required during power-up initialization, and
upon returing to normal operation after having disabled the DLL for the purpose of debug or evaluation (upon
exiting Self Refresh Mode, the DLL is enabled automatically). Any time the DLL is enabled, 200 clock cycles
must occur before a READ command can be issued.
Output Drive Strength
The normal drive strength for all outputs is specified to be SSTL_2, Class II. Some vendors might also support
a weak driver strength option, intended for lighter load and/or point-to-point environments. I-V curves for the
normal drive strength and weak drive strength will be included in a future revision of this document.
Mode Register Set
20 1 53 4 86 7
*1
tRP
Mode
Register Set
*2
2 Clock min.
Any
Command
Command
CK
CK
tCK
Precharge
All Banks
*1 : MRS can be issued only at all bank precharge state.
*2 : Minimum tRP is required to issue MRS command.
Figure 6. Mode Register Set sequence
- 15 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
256Mb DDR SDRAM Preliminary
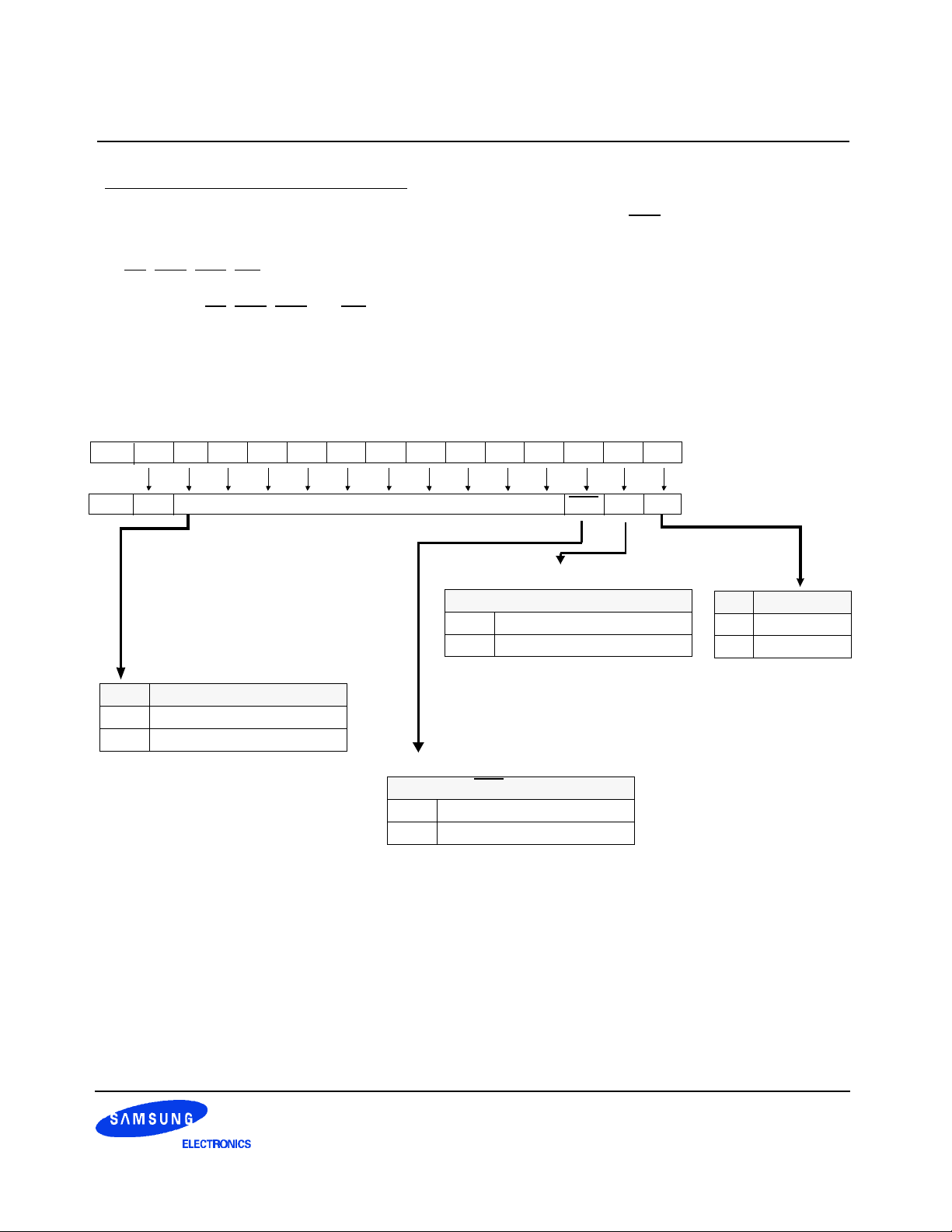
3.2.2.2 Extended Mode Register Set(EMRS)
The extended mode register stores the data for enabling or disabling DLL, QFC and selecting output driver
size. The default value of the extended mode register is not defined, therefore the extened mode register must
be written after power up for enabling or disabling DLL. The extended mode register is written by asserting low
on CS, RAS, CAS, WE and high on BA0(The DDR SDRAM should be in all bank precharge with CKE already
high prior to writing into the extended mode register). The state of address pins A0 ~ A11 and BA1 in the
same cycle as CS, RAS, CAS and WE going low are written in the extended mode register. Two clock cycles
are required to complete the write operation in the extended mode register. The mode register contents can
be changed using the same command and clock cycle requirements during operation as long as all banks are
in the idle state. A0 is used for DLL enable or disable. "High" on BA0 is used for EMRS. All the other address
pins except A0 and BA0 must be set to low for proper EMRS operation. Refer to the table for specific codes.
A12
BA1 BA0
1
RFU RFU : Must be set "0"
BA0 An ~ A0
0 (Existing)MRS Cycle
1 Extended Funtions(EMRS)
A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Output Driver Impedence Control
0 Normal
1 Weak
QFC control
0 Disable(Default)
1 Enable
QFC
D.I.C
DLL
Address Bus
Extended Mode Register
A0 DLL Enable
0 Enable
1 Disable
Figure 7. Extend Mode Register set
- 16 -
REV. 0.3 November 2. 2000
 Loading...
Loading...