Page 1
page 1/36
#
Direction des Recherches et des Développements Etablissement de VELIZY
VELIZY R&D Center
NOTE D'ETUDE / TECHNICAL DOCUMENT
REFERENCE
URD1 – OTL 5665.1– 002 /
70 884
Code
C
TITRE / TITLE :
Edition
N°
Nom
03
Name
Signature
Date
Rédacteur(s)
Author(s)
J.DUMONT T. Fu M. Boutboul E. Sillère
27/06/08
TA1
HiloNC Application note
Chef de projet
Project design
manager
NOM DE L’ETUDE
Approbations /Approvals
Responsable
d’entité /
Product design
manager
ETUDE / PROJECT
HiloNC Module
Chef Unité
R&D unit
manager
Assurance
Qualité /
R&D quality
assurance
RESUME / SUMMARY
This document is HiloNC module application note.
Mots clés / Keywords : Cellular, module, GSM, GPRS, application, M2M
DIFFUSION INTERNE / INTERNAL DISTRIBUTION
√
REDACTEUR(S) / AUTHOR (S) + F.FREULON, F.GOUERE .
Distribution externe pour les prestataires de services : renseigner dans la rubrique ci-dessous sous la forme
« SOCIETE (P. Nom) »
DIFFUSION EXTERNE sous convention de confidentialité :
EXTERNAL DISTRIBUTION with confidentiality agreement :
………….
Enregistrement relatif à la qualité (ERQ) / Quality record
A déposer en enveloppe soleau / Put in a soleau envelope
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 2
page 2/36
Direction des Recherches et des Développements Etablissement de VELIZY
VELIZY R&D Center
NOTE D'ETUDE / TECHNICAL DOCUMENT
FICHE RECAPITULATIVE / SUMMARY SHEET
Ed
1
2
3 10/11/2008 URD1– OTL 5665.1–
Date
Date
27/06/2008
07/10/2008
Référence
Reference
URD1– OTL 5665.1–
002 / 70 884
URD1– OTL 5665.1–
002 / 70 884
002 / 70 884
Rédacteur(s)
Author(s)
Steven Long
Bingming Chen
AMMARI. M. DUMONT J. §3.6 and §3.10;
AMMARI M. Dumont J. §3.1, §3.9, §3.12 Clarification on Vbackup
Relecteur(s)
Reviser(s)
Tiejun Fu / M.
Boutboul
Pages modifiées
/ Changed pages
Création du document /
P25
Observations
Comments
Document creation
UART Update
connection. Reset
duration 10ms. Sim card
connection figure 3.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 3

page 3/36
HiloNC Application Note
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 4

page 4/36
Direction des Recherches et des Développements Etablissement de VELIZY
VELIZY R&D Center
SOMMAIRE / CONTENTS
Direction des Recherches et des Développements Etablissement de VELIZY...........................................................1
NOTE D'ETUDE / TECHNICAL DOCUMENT ..........................................................................................................1
Direction des Recherches et des Développements Etablissement de VELIZY...........................................................2
NOTE D'ETUDE / TECHNICAL DOCUMENT ..........................................................................................................2
FICHE RECAPITULATIVE / SUMMARY SHEET....................................................................................................2
SOMMAIRE / CONTENTS..........................................................................................................................................4
FIGURES LIST ............................................................................................................................................................6
1. OVERVIEW...........................................................................................................................................................7
1.1 OBJECT OF THE DOCUMENT..................................................................................................................7
1.1 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS.......................................................................................................................7
1.2 MODIFICATION OF THIS DOCUMENT....................................................................................................7
1.3 CONVENTIONS............................................................................................................................................7
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM................................................................................................................................................8
3. FUNCTIONAL INTEGRATION............................................................................................................................9
3.1 HOW TO CONNECT TO A SIM CARD....................................................................................................10
3.2 HOW TO CONNECT THE AUDIOS?.......................................................................................................11
3.2.1 Connecting microphone and speaker................................................................................................11
3.2.2 Recommended characteristics for the microphone and speaker....................................................12
3.3 PWM............................................................................................................................................................13
3.3.1 PWM outputs...........................................................................................................................................13
3.3.2 PWM for Buzzer connection..................................................................................................................14
3.4 POWER SUPPLY.......................................................................................................................................14
3.5 EXAMPLE OF POWER SUPPLY .............................................................................................................15
3.5.1 Example 1............................................................................................................................................15
3.5.2 Example 2............................................................................................................................................15
3.5.3 Example 3............................................................................................................................................16
3.6 V24...............................................................................................................................................................16
3.6.1 Complete V24 – connection HiloNC - host........................................................................................16
3.6.2 Complete V24 interface with PC........................................................................................................17
3.6.3 Partial V24 (RX-TX-RTS-CTS) – connection HiloNC - host............................................................18
3.6.4 Partial V24 (RX-TX) – connection HiloNC - host..............................................................................19
3.6.5 Design impact on DTR usage ............................................................................................................19
3.7 SPI ...............................................................................................................................................................19
3.8 GPIO............................................................................................................................................................20
3.9 BACKUP BATTERY...................................................................................................................................20
3.9.1 Backup battery function feature.........................................................................................................20
3.9.2 Current consumption on the backup battery.....................................................................................20
3.9.3 Charge by internal HiloNC charging function....................................................................................20
3.9.4 Backup Battery technology recommended .......................................................................................21
3.10 HARDWARE POWER MANAGEMENT AND MULTIPLEXING INTERFACES....................................22
3.11 STARTING THE MODULE........................................................................................................................22
3.12 MODULE RESET........................................................................................................................................22
3.13 MODULE SWITCH OFF............................................................................................................................22
3.14 SLEEP MODE MANAGEMENT................................................................................................................23
4. MANDATORY POINTS FOR THE FINAL TESTS AND TUNING.....................................................................24
5. ESD & EMC RECOMMENDATIONS.................................................................................................................24
5.1 HILONC ALONE.........................................................................................................................................24
5.2 CUSTOMER’S PRODUCT WITH HILONC..............................................................................................24
5.2.1 Analysis ................................................................................................................................................24
5.2.2 Recommendations to avoid ESD issues...........................................................................................24
6. RADIO INTEGRATION.......................................................................................................................................25
6.1 ANTENNA ...................................................................................................................................................25
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 5

page 5/36
6.2 GROUND LINK AREA................................................................................................................................25
6.3 LAYOUT......................................................................................................................................................25
6.4 MECHANICAL SURROUNDING...............................................................................................................26
6.5 OTHER RECOMMENDATIONS – TESTS FOR PRODUCTION/DESIGN...........................................26
7. AUDIO INTEGRATION......................................................................................................................................26
7.1 MECHANICAL INTEGRATION AND ACOUSTICS.................................................................................26
7.2 ELECTRONICS AND LAYOUT.................................................................................................................27
8. RECOMMENDATIONS ON LAYOUT OF CUSTOMER’S BOARD...................................................................28
8.1 GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS ON LAYOUT....................................................................................28
8.1.1 Ground .................................................................................................................................................28
8.1.2 Power supplies.....................................................................................................................................28
8.1.3 Clocks...................................................................................................................................................28
8.1.4 Data bus and other signals.................................................................................................................28
8.1.5 Radio....................................................................................................................................................28
8.1.6 Audio (see also § 10.2).......................................................................................................................28
8.2 EXAMPLE OF LAYOUT FOR CUSTOMER’S BOARD...........................................................................29
9. RECOMMANDATIONS FOR CUSTOMER INDUSTRIALIZATION..................................................................29
9.1 MOISTURE LEVEL.....................................................................................................................................30
9.2 PACKAGE...................................................................................................................................................30
9.3 SOLDER MASK..........................................................................................................................................32
9.4 SOLDER PASTE........................................................................................................................................32
9.5 PROFILE FOR REFLOW SOLDERING...................................................................................................32
9.6 SMT MACHINE...........................................................................................................................................34
9.7 UNDERFILL.................................................................................................................................................34
9.8 SECOND REFLOW SOLDERING............................................................................................................35
9.9 HAND SOLDERING...................................................................................................................................35
9.10 REWORK....................................................................................................................................................35
10. LABEL.............................................................................................................................................................35
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 6

page 6/36
FIGURES LIST
Figure 1: Block diagram of HiloNC module......................................................................................................................8
Figure 2: SIM Card signals.............................................................................................................................................10
Figure 3: Protections: EMC and ESD components close to the SIM................................................................................10
Figure 4: Audio connection.............................................................................................................................................11
Figure 5 : Filter and ESD protection of microphone........................................................................................................12
Figure 6: Filter and ESD protection of 32 ohms speaker.................................................................................................12
Figure 7: Buzzer connection...........................................................................................................................................14
Figure 8: GSM/GPRS Burst............................................................................................................................................14
Figure 9: Example of power supply based on a DC/DC step down converter...................................................................15
Figure 10: Example of power supply based on regulator..................................................................................................15
Figure 11: Example with Linear LT1913........................................................................................................................16
Figure 12: Complete V24 connection between HiloNC and host......................................................................................17
Figure 13: connection to a data cable..............................................................................................................................18
Figure 14: Partial V24 connection (4 wires) between HiloNC and host...........................................................................18
Figure 15: Partial V24 connection (2 wires) between HiloNC and host...........................................................................19
Figure 16: Backup battery internally charged..................................................................................................................21
Figure 17: Charging curve of backup battery...................................................................................................................21
Figure 18: Hardware interface between HiloNC and host................................................................................................22
Figure 19: Antenna connection.......................................................................................................................................25
Figure 20: Forbidden area for via....................................................................................................................................26
Figure 21: Layout of audio differential signals on a layer n.............................................................................................29
Figure 22: Adjacent layers of audio differential signals...................................................................................................29
Figure 23: layer allocation for a 6 layers circuit..............................................................................................................29
Figure 24 : Solder mask design.......................................................................................................................................32
Figure 25 : Typical thermal profile.................................................................................................................................33
Figure 26 : CMS fiducials positions................................................................................................................................34
Figure 27 : Underfill holes..............................................................................................................................................35
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 7

page 7/36
1. OVERVIEW
1.1 OBJECT OF THE DOCUMENT
The aim of this document is to describe some examples of hardware solutions for developing some products
around the Sagem Communications HiloNC GPRS Module. Most part of these solutions is not mandatory. Use
them as suggestions of what should be done to have a working product and what should be avoided thanks to
our experiences.
This document suggests how to integrate the HiloNC GPRS module in machine devices such as automotive,
AMM (Automatic Metering Management), tracking system: connection with external devices, layout advises,
external components (decoupling capacitors…).
1.1 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
URD1 OTL 5665.1 001 70883 - HiloNC technical specification
URD1 OTL 5635.1 008 70248 - AT Command Set for SAGEM Hilo Modules
1.2 MODIFICATION OF THIS DOCUMENT
The information presented in this document is supposed to be accurate and reliable. Sagem Communications
assumes no responsibility for its use, nor any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may
result from its use.
This document is subject to change without notice.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
1.3 CONVENTIONS
SIGNAL NAME : All signal name available on the pads of the HiloNC module is written in italic.
Specific attention must be granted to the information given here.
F
1.4 DECLARATION
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received; including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 8
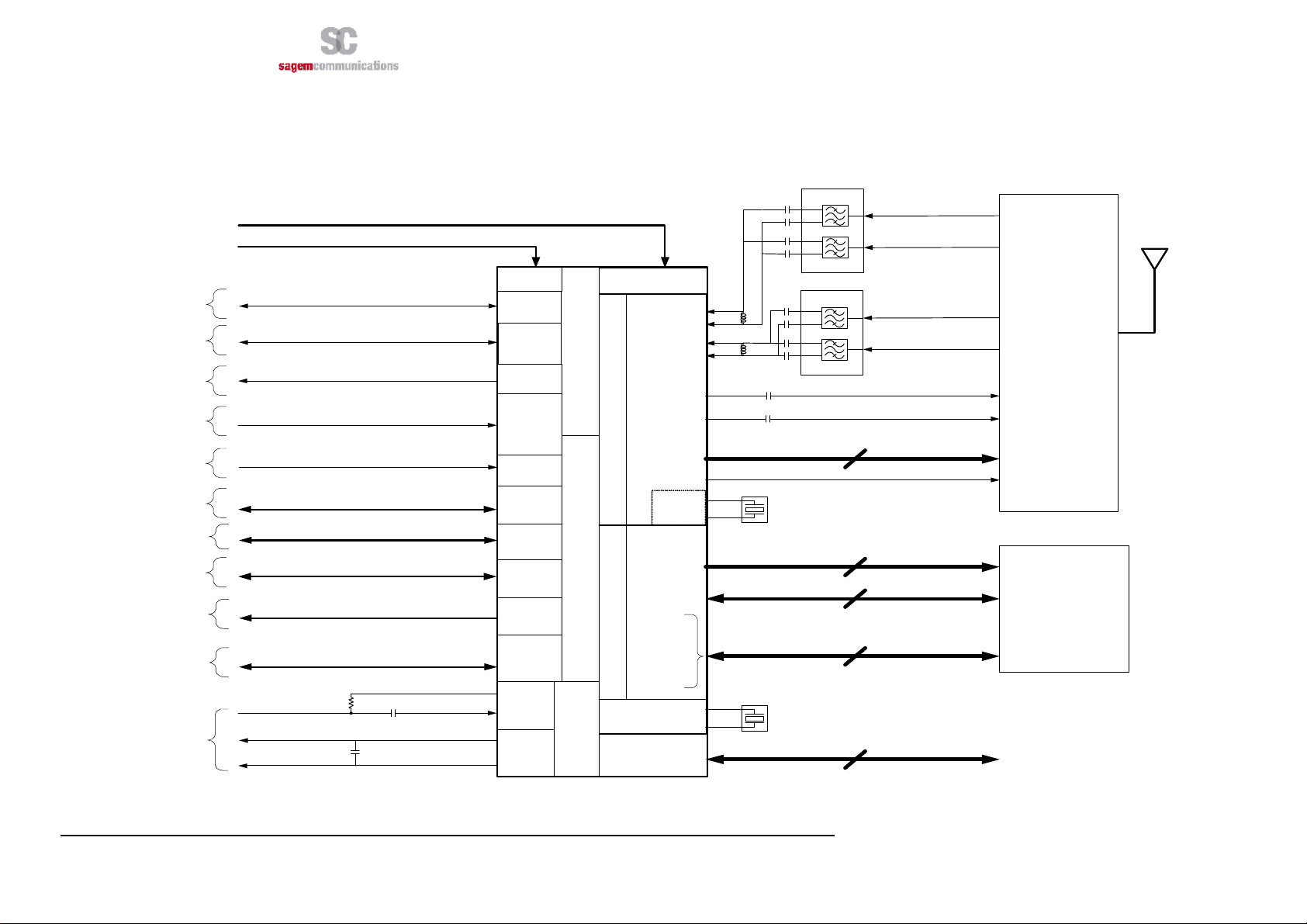
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
3 +2
Pads
3
Pads
1Pad
1Pad
1Pad
1Pad
1Pad
5 Pads
5
Pads
4Pads
3Pads
8Pads
3 Pads
SPI_CLK /SPI_IRQ/SPI_OUT/SPI_IN/
SIM_DATA/SIM_CLK/SIM_RST/VSIM
RXD/RTS/CTS/TXD/DCD/DTR/DSR/RI
RESET
VBACKUP
VGPIO
POK_IN
AUX_ADC0
SPI_SEL
GPIO[1:5]
PWM[0:2]
page 8/36
Dual Saw Filter (850/900)
Band 1
(850MHz)
(900MHz)
Band 2
Dual Saw Filter (1800/1900)
Band1
(1800MHz)
(1900MHz)
Band2
26MHz
32.768KHz
850/900/1800/1900
External Memory
9 Pads
INTMIC_BIAS
INTMIC_P
HSET_OUT_P
HSET_OUT_N
VBATT
V
G
PIO
In Out
PowerSupplySystem
RESET
VBACK
UP
CONTROL
POWER
ADC SPI
PERIPHERALS
GPIO SIM PWM
UART
Subsystem
GROUND
RFSubsystem
FE_CTRL
Ramp_DAC
ADDR
[22:1]
DATA [15:0]
NCS_RAM
NCS_Flash
NUB
EMC Subsystem
NLB
NOE
NWE
RFIL
RFIH
RFOL
RFOH
DCXO
Audio
RTC
TMS/RTCK/TCK/NTRST /TDI/TDO/ TEST / TEST1 / TEST2
JTAG
Figure 1: Block diagram of HiloNC module
PA+Switch
Antenna
pad
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 9

page 9/36
3. FUNCTIONAL INTEGRATION
The improvement of Silicon technologies heads toward functionality improvement, less power consumption.
The HiloNC module meets all these requirement and use last high end technology.
All digital I/Os among the 51 pads are in 2.8V domain which is suitable for most systems except :
F
- VSIM (the SIM I/Os at 1.8V or 2.9V)
- VBAT (from 3.2V to 4.5V).
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 10
page 10/36
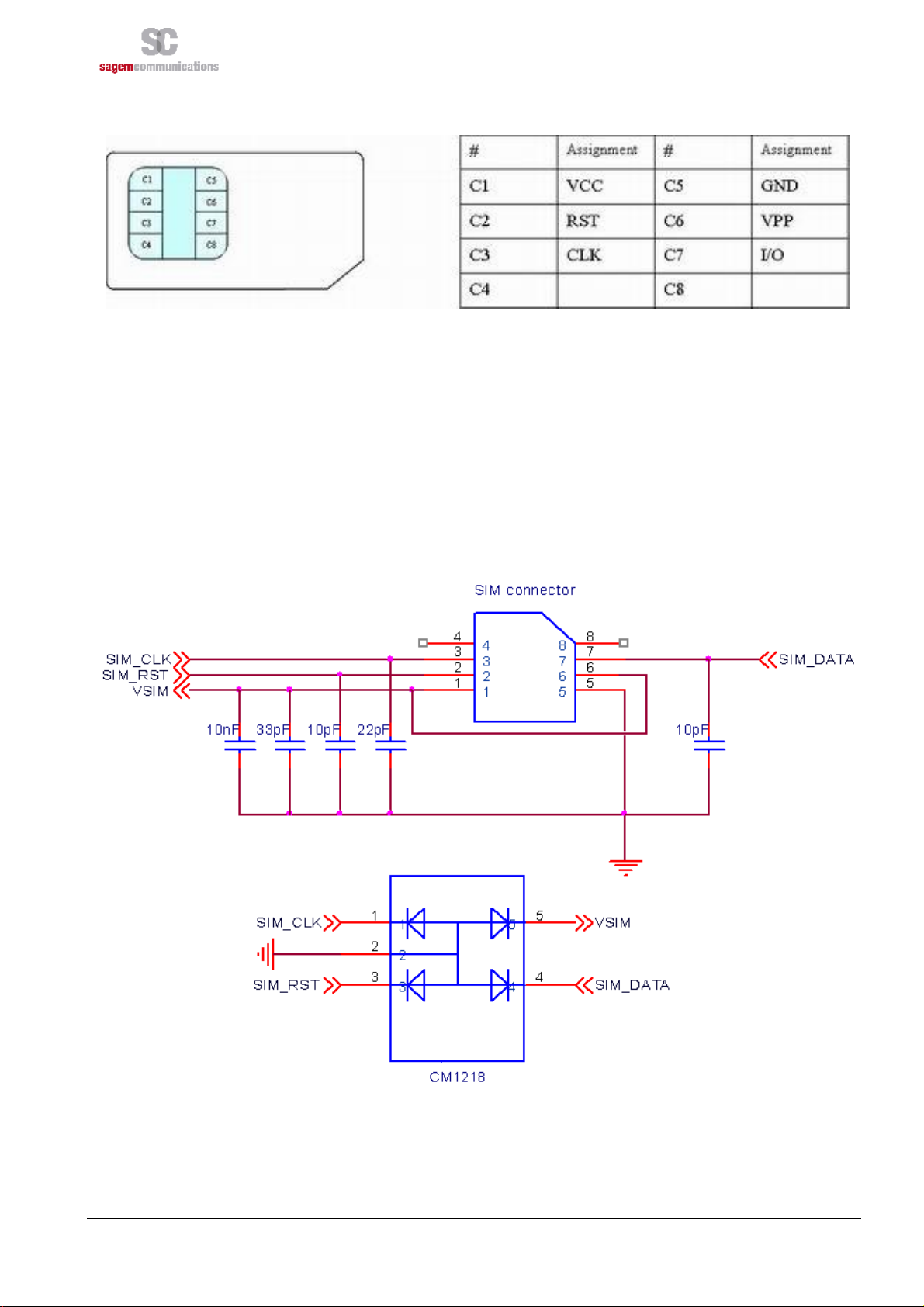
3.1 HOW TO CONNECT TO A SIM CARD
Figure 2: SIM Card signals
HiloNC module provides the SIM signals on the 51 pads. A SIM card holder with 6 pads needs to be adopted to
use the SIM function.
Decoupling capacitors have to be added on SIM_CLK, SIM_RST, VSIM and SIM_DATA signals as close
F
as possible to the SIM card connector to avoid EMC issues.
Use ESD protection components to protect SIM card and module I/Os against Electro Static Discharges.
F
The following schematic show how to protect the SIM access for 6 pads connector.
Figure 3: Protections: EMC and ESD components close to the SIM
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 11
page 11/36
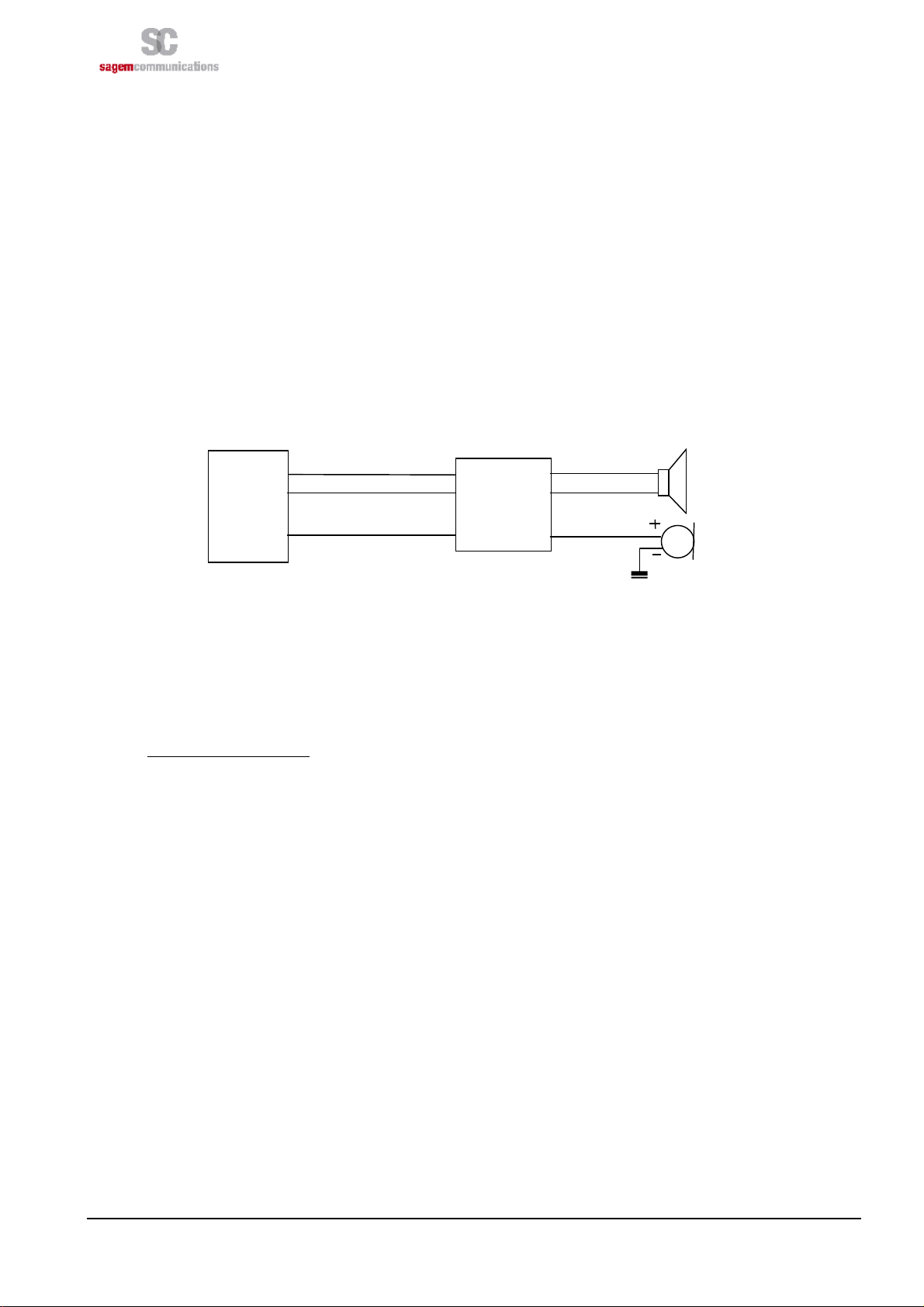
3.2 HOW TO CONNECT THE AUDIOS?
The HiloNC module features one input audio path and one output audio path. The input path is single-end while
the output path is differential. In this following chapter examples of design will be given including protections
against EMC and ESD and some notes about the routing rules to follow to avoid the TDMA noise usually
present in this sensitive area of design.
Please note that acoustic competences are mandatory to get accurate audio performance on customer’s
F
product.
3.2.1 Connecting microphone and speaker
The HiloNC module can manage an external microphone (INTMIC_P) in single-end mode and an external
speaker (HSET_OUT_P / HSET_OUT_N) in differential mode. Thus, one speaker and one microphone can be
connected to the module. The bias supply to microphone is implemented in the module.
The speaker connected to the module should be 32 ohms.
F
HiloNC
If the design is ESD or EMC sensitive we strongly recommend to read the notes below.
The weakness can either come from the PCB routing and placement or from the chosen components (or both).
3.2.1.1 Notes for microphone
Pay attention to the microphone device, it must not be sensitive to RF disturbances.
F
Some microphones include two spatial microphones inside the same shell and allow to make an electrical
F
difference between the environment noise (received by one of the two mic.) and the active signal
(received by the other mic. + noise) resulting in a very high SNR.
HSET_OUT_P
HSET_OUT_N
INTMIC_P
Filter and
ESD
protection
Figure 4: Audio connection
32ohms speaker
MIC
If you need to have deported microphone out of the board with long wires, you should pay attention to the
F
EMC and ESD effect. It is also the case when your design is ESD sensitive. In those cases, add the
following protections to improve your design.
F
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
To ensure proper operation of such sensitive signals, they have to be isolated from the others by
analogue ground on customer’s board layout. (Refer to Layout design chapter)
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 12

page 12/36
HiloNC
INTMIC_P
Ferrite Bead
MIC
18pF
ESD protection
Figure 5 : Filter and ESD protection of microphone
3.2.1.2 Notes for speaker
As explained for the microphone, if the speaker is deported out of the board or is sensitive to ESD, use the
schematic here after to improve the audio.
ESD protection
speaker
ESD protection
HiloNC
HSET_OUT_P
HSET_OUT_N
18pF
Ferrite Bead
Ferrite Bead
18pF
Figure 6: Filter and ESD protection of 32 ohms speaker
HSET_OUT_P, HSET_OUT_N tracks must be larger than other tracks: 0.1 mm.
F
As described in the layout chapter, differential signals have to be routed in parallel (HSET_OUT_P and
F
HSET_OUT_N signals)
The impedance of audio chain (filter + speaker) must be lower than 32 Ohm.
F
3.2.2 Recommended characteristics for the microphone and speaker
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 13

page 13/36
3.2.2.1 Recommended characteristics for the microphone
Item to be inspected Acceptance criterion
Sensitivity - 40 dB SPL +/-3 dB (0 dB = 1 V/Pa @ 1kHz)
Frequency response Limits (relatives values)
Freq. (Hz) Lower limit Upper limit
100 -1 1
200 -1 1
300 -1 1
1000 0 0
2000 -1 1
3000 -1.5 1.5
3400 -2 2
4000 -2 2
Current consumption 1 mA (maximum)
Operating voltage DC 1 to 3 V (minimum)
S / N ratio 55 dB minimum (A-Curve at 1 kHz, 1 Pa)
Directivity Omni-directional
Maximum input sound pressure level 100 dB SPL (1 kHz)
Maximum distortion 1%
Radio frequency protection Over 800 -1200 MHz and 1700 -2000 MHz, S/N ratio 50
dB minimum (signal 1 kHz, 1 Pa)
3.2.2.2 Recommended characteristics for the speaker
Item to be inspected Acceptance criterion
Input power: rated / max 0.1W (Rate)
Audio chain impedance 32 ohm +/- 10% at 1V 1KHz
Frequency Range 300 Hz ~ 4.0 KHz
Sensitivity (S.P.L) >105 dB at 1KHz with IEC318 coupler,
Distortion 5% max at 1K Hz, nominal input power
3.3 PWM
3.3.1 PWM outputs
The HiloNC module can manage two PWM outputs.
They can be configured with appropriate AT command (for more details refer to AT command set for Sagem
HiloNC module specification).
User application can set for each output:
- Frequency between : 25.6KHz and 1083.3KHz
- Duty range from: 0 to 100%
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 14

page 14/36
Please note available PWM frequencies are too high to be used to make LEDs blinking. If purpose is to
F
make LEDs blinking (for network states indication for example), GPIO usage is more accurate.
3.3.2 PWM for Buzzer connection
The HiloNC module can manage a dedicate PWM output to drive a buzzer. The buzzer can be used to alarm
for abnormal state.
Resistors should be added to protect the buzzer. The value of these resistors depends on the buzzer and
F
the transistor. Normally, they can be set as 1K ohm.
VBAT
HiloNC
R2
PWM2
Figure 7: Buzzer connection
3.4 POWER SUPPLY
The HiloNC module can be supplied by a battery or any DC/DC converter compliant with the module supply
range 3.2V to 4.5V 2.2 A.
The PCB tracks must be well dimensioned to support 2.2 A maximum current. The voltage ripple caused
F
by resistance of power supply path (Battery internal resistance, tracks and contact resistance) could
result in the low voltage to the module.
The HiloNC module does not manage the battery charging.
F
3.4.1.1 Burst conditions
R1
- Communication mode (worst case: 2 continuous GSM time-slot pulse):
A
1.8
A 47µF capacitor is highly recommended for VBAT and close to the module.
F
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
GPRS Class10
0
577us
1.15ms
Figure 8: GSM/GPRS Burst
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
4.615ms
Page 15

page 15/36
3.5 EXAMPLE OF POWER SUPPLY
3.5.1 Example 1
It the following application note from Linear Technology LTC3440, this schematic is an example of a DC/DC
power supply able to power 3.6V under 2.1A. This can be use with a AC/DC 5V unit or an USB or PCMCIA bus
as input power source.
Figure 9: Example of power supply based on a DC/DC step down converter
3.5.2 Example 2
If the whole power consumption is not an issue, this example of a voltage regulator used with an AC/DC 5V
converter, can be used as a DC power supply.
The voltage output is given by:
VOUT = 1.235V × [1 + (R1 / R2)]
To have 3.7V out R1=560K & R2=271.8K
(270K+1.8K)
Figure 10: Example of power supply based on regulator
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 16

page 16/36
3.5.3 Example 3
Simple boost converter with Linear LT1913 (see LT1316 evaluation kit document).
Figure 11: Example with Linear LT1913
3.6 V24
The HiloNC module features a V24 interface to communicate with the Host through AT commands or for easy
firmware upgrading purpose.
It is recommended to manage an external access to the V24 interface, in order to allow easy software
F
upgrade (baud rate up to 460.8kbps, validated with ATEN USB/Serial converter).
Pull-up resistors must be connected to DCD, DSR and RI signals if these signals are used.
F
3.6.1 Complete V24 – connection HiloNC - host
A V24 interface is provided on the 51 pads of the HiloNC module with the following signals: RTS/CTS,
RXD/TXD, DSR, DTR, DCD, RI.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 17

page 17/36
RTS
RTS
37
represented
RTS
RTS
OUT
IN
Note: pin 5 is GND
1 6 9 5
7
37
HiLoNC Module
39
40
33
34
35
36
38
TXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
RXD
DTE Device
RXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
TXD
2.8V signals
Note: GND is not
2.8V signals
DCE point of view DTE point of view
Figure 12: Complete V24 connection between HiloNC and host
3.6.2 Complete V24 interface with PC
It supports speeds up to 115.2 Kbps and may be used in auto bauding mode.
To use the V24 interface, some adaptation components are necessary to convert the +2.8V signals from the
HiloNC to +/- 5V signals compatible with a PC.
To create your own data cable (for software download purpose…etc…) please refer to the following schematic
as an example:
HiLoNC Module
39
40
33
34
35
36
38
2.8V signals
DCE point of view DTE point of view
TXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
RXD
RS232 Transceiver
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
IN
IN
RXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
TXD
3.1V to +/-5.5V
signals
Figure 13: connection to a data cable
2
8
6
1
9
4
3
SUBD9 Female
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 18

page 18/36
RTS
RTS
37
represented
Figure 14: Example of a connection to a data cable
3.6.3 Partial V24 (RX-TX-RTS-CTS) – connection HiloNC - host
When using only RX/TX/RTS/CTS instead of the complete V24 link, we recommend following schematic.
HiLoNC Module
39
40
33
34
35
36
38
2.8V signals
Figure 15: Partial V24 connection (4 wires) between HiloNC and host
TXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
RXD
RXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
TXD
Note: GND is not
DTE Device
2.8V signals
As we need DTR active (low electrical level), a loop DSR on DTR is sufficient because DSR is active
F
(low electrical level) once the HiloNC is switched on.
DCD and RI can stay not connected and floating.
F
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 19

page 19/36
RTS
RTS
37
represented
3.6.4 Partial V24 (RX-TX) – connection HiloNC - host
When using only RX/TX instead of the complete V24 link, we recommend following schematic.
HiLoNC Module
39
40
33
34
35
36
38
2.8V signals
DCE point of view DTE point of view
Figure 16: Partial V24 connection (2 wires) between HiloNC and host
TXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
RXD
Note: GND is not
DTE Device
RXD
CTS
DSR
DCD
RI
DTR
TXD
2.8V signals
We need DTR active (low electrical level), a loop DSR on DTR is sufficient because DSR is active (low
F
electrical level) once the HiloNC is switched on.
We need RTS active (low electrical level), a loop RTS on CTS is sufficient because CTS is active (low
F
electrical level) once the HiloNC is switched on.
DCD and RI can stay not connected and floating.
F
3.6.5 Design impact on DTR usage
The designer must consider when choosing V24 design that DTR can be used for several purposes :
- flow control of V24 interface (see chapter 3.6.2)
- enter/exit sleep mode of HiloNC module if AT+KSLEEP=0 has been configured (see chapter 3.14)
- switch between command/data modes
F
Depending of the HiloNC/Host V24 connexion, the DTR can be usable by customer or not (if always
connected to DSR) and then has impact on sleep mode management and AT command/data modes
management.
3.7 SPI
HiloNC module manages a host SPI interface. This SPI interface is dedicated for trace.
Sagem Communications strongly recommends leaving this interface externally accessible for trace (e.g.
F
access by test point pads).
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 20

page 20/36
3.8 GPIO
There are five GPIOs available on HiloNC. The GPIO1, GPIO2 and GPIO3 have internal pull-up resistors while
GPIO4 and GPIO5 are open collector.
If GPIO4 and GPIO5 are used as output, they must be pulled up to VGPIO. The typical value of the pull-
F
up resisters is 100K ohms.
3.9 BACKUP BATTERY
3.9.1 Backup battery function feature
3.9.1.1 With backup battery
A backup battery can be connected to the module in order to supply internal RTC (Real Time Clock) when the
main power supply is removed. Thus, when the main power supply is removed, the RTC is still supplied and the
module keeps the time running.
With external backup battery:
- If VBAT < 3V, internal RTC is supplied by VBACKUP.
- If VBAT > =3V, internal RTC is supplied by VBAT.
3.9.1.2 Without backup battery
Without backup battery
- If VBAT > 1.5V, internal RTC is supplied by VBAT.
- If VBAT < 1.5V, internal RTC is not supplied.
VBACKUP input of the module has to be connected to a 10µF capacitor (between VBACKUP and GND).
F
SAGEM does not recommend to connect VBACKUP signal to VBAT. However, if VBACKUP has been
F
connected to VBAT, this has no influence if VBAT is between 3.2V and 4.2V. For VBAT above 4.2V the module
can take a longer time to start at low temperature.
3.9.2 Current consumption on the backup battery
When the power supply is removed, the internal RTC will be supplied by backup battery.
F
3.9.3 Charge by internal HiloNC charging function
The charging function is available on the HiloNC without any additional external power supply (the charging
power supply is provided by the HiloNC).
To calculate the backup battery capacity, consider that Current consumption for RTC on the backup
battery is below 2,6µA depending on the temperature.
Pin Name
VBACKUP
Min Max
2.6µA
Charge of the back-up battery occurs only when main power supply VBAT is provided.
F
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 21

page 21/36
The recommended schematic is given hereafter:
VBACKUP
HiloNC
R
Figure 17: Backup battery internally charged
The resistor R depends on the charging current value provided by the battery manufacturer.
The charging curve which is done by the HiloNC is given hereafter:
Figure 18: Charging curve of backup battery
3.9.4 Backup Battery technology recommended
3.9.4.1 Manganese Silicon Lithium-Ion rechargeable Battery
Sagem Communications does not recommend using this kind of technology because of the following
drawbacks:
• The maximum discharge current is limited (Shall be compliant with the module characteristics).
• The over-discharge problem: most of the Lithium Ion rechargeable batteries are not able to recover their charge when
their voltage reaches a low-level voltage. To avoid this, it is necessary to add a safety component to disconnect the
backup .battery in case of over–discharge condition. In such a case, this implementation is too complicated (too much
components for that function).
• The charging current has to be regulated.
Sagem Communications does not recommend using this kind of backup battery technology.
F
3.9.4.2 Capacitor battery
These kinds of backup battery have not the drawbacks of the Lithium Ion rechargeable battery.
As there are only capacitors:
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 22

page 22/36
· The maximum discharge current is generally bigger,
· There is no problem of over-discharge: the capacitor is able to recover its full charge even if its voltage has
previously fallen to 0V.
· There is no need to regulate the charging current.
Moreover, this kind of battery is available in the same kind of package than the Lithium Ion cell and fully
compatible on a mechanical point of view. The only disadvantage is that the capacity of this kind of battery is
significantly smaller than Manganese Silicon Lithium Ion battery. But for this kind of use (supply internal RTC
when the main battery is removed), the capacity is generally enough.
Sagem Communications strongly recommends using this kind of backup battery technology.
F
3.10 HARDWARE POWER MANAGEMENT AND MULTIPLEXING INTERFACES
In case hardware power management and multiplexing are used, it is necessary to isolate host and HiloNC
module in order not to generate current re-injection when HiloNC is switched-off.
Typical schematic (only useful signals are represented):
VGPIO
DTR, RTS, RXD
Tri-state command Buffer
HiloNC
DCD, DSR, CTS, TXD, RI
Solution 1 Solution 2
Figure 19: Hardware interface between HiloNC and host
In general, solution1 is enough to protect HiloNC module.
Host
3.11 STARTING THE MODULE
First power up VBAT, which must be in the range 3.2V – 4.5V, and able to provide 2.2A during the TX bursts
(Refer to the module specification for more details).
To start the module, a low level pulse must be sent on POK_IN during 1 s minimum (at 25°C).
After a few seconds, the module puts in active state CTS when it is ready to receive AT commands.
3.12 MODULE RESET
To reset the module, a low level pulse must be sent on RESET pad during 10 ms.
3.13 MODULE SWITCH OFF
AT command “AT*PSCPOF” allows to switch off the module.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 23

page 23/36
3.14 SLEEP MODE MANAGEMENT
AT command “AT+KSLEEP” allows to configure the sleep mode.
When AT+KSLEEP=1 is configured :
· the HiloNC module decides by itself when it enters in sleep mode (no more task running).
· “0x00” character on serial link wakes up the HiloNC module.
When AT+KSLEEP=0 is configured :
· the HiloNC module is active when DTR signal is active (low electrical level).
· when DTR is deactivated (high electrical level), the HiloNC module enters in sleep mode after a while.
· on DTR activation (low electrical level), the HiloNC module wakes up.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 24

page 24/36
4. MANDATORY POINTS FOR THE FINAL TESTS AND TUNING
The design of the customer’s board (on which the module is soldered) must provide an access to following
signals when the final product will be completely integrated.
To upgrade the module software, Sagem Communications recommends providing a direct access to the
F
module serial link through an external connector or any mechanism allowing the upgrade of the module
without opening the whole product.
Serial link:
TXD Output
RXD Input UART receive
UART transmit
To debug the module software, Sagem Communications recommends providing a direct access to the
F
module debug port SPI (5 I/Os) through internal test points (TP) located on the customer's main board.
5. ESD & EMC RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 HILONC ALONE
The HiloNC module alone can hold 2KV on each of the 51 pads including the RF pad.
5.2 CUSTOMER’S PRODUCT WITH HILONC
If customer’s design must stand more than 2kV on electrostatic discharge, following recommendation must be
taken into account.
5.2.1 Analysis
ESD current can penetrate inside the device via the typical following components:
· SIM connector
· Microphone
· Speaker
· Battery / data connector
· All pieces with conductive paint (plastron, special keys, etc...)
In order to avoid ESD issues, efforts shall be done to decrease the level of ESD current on electronic
F
components located inside the device (customer’s board, input of the HiloNC module, etc…)
5.2.2 Recommendations to avoid ESD issues
Insure good ground connections of the HiloNC module to the customer’s board.
F
Flex (if any) shall be shielded and FPC connectors shall be correctly grounded at each extremity.
F
Put capacitor 100nF on battery (not on charger), or better put varistor or ESD diode in parallel on battery
F
and charger wires and on all wires on bottom connector.
F
devices.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Uncouple microphone and speaker by putting capacitor or varistor in parallel of each wire of these
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 25

page 25/36
6. RADIO INTEGRATION
6.1 ANTENNA
- Antenna contact
• 50Ω line matching (between module and customer’s board, and with RF test point)
Figure 20: Antenna connection
F
F
6.2 GROUND LINK AREA
Keep matching circuit on customer’s board but with direct connection in the first step – it could be
necessary to make some adjustment later, during RF qualification stage.
The selected antenna must comply with FCC RF exposure limits in GSM850 and PCS1900 band :
- GSM850 : MPE < 0.55mW/cm
- PCS1900 : ERP < 3W
2
(Distance is 20 cm)
Sagem Communications emphasizes the fact that a good ground contact is needed between the module and
the customer’s board to have the best radio performances (spurious, sensitivity…).
All HiloNC GND pads must be connected to the GND of the customer’s board.
F
6.3 LAYOUT
Warning : Isolate RF line and antenna from others bus or signals
No signals on 50 ohms area and if that is not possible, add ground shielding using different layers.
F
Do not add any ground layer under the antenna contact area.
F
Be careful on the position of the network LED (sometimes situated in front of the antenna pad ...)
F
Do not put any via and lines on all the forbidden area under the module, shown as the grey area on the
F
figure below.
Varnish must be present on all the grey area (expect solder pads) to isolate HiloNC module from the
F
customer’s board.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 26

page 26/36
Figure 21: Forbidden area for via and lines
6.4 MECHANICAL SURROUNDING
Avoid any metallic part around the antenna area
F
Keep jacks, FPCs and battery contact far from antenna area (FLEX)
F
FPC has to be a shielded one
F
6.5 OTHER RECOMMENDATIONS – TESTS FOR PRODUCTION/DESIGN
Sagem Communications guarantees the RF performances in conductive mode but strongly recommends
making RF measurements in an anechoic chamber in radiated mode (tests conditions for FTA): the radiated
performances strongly depend on radio integration (layout, antenna, matching circuit, ground area…..)
7. AUDIO INTEGRATION
Audio mandatory tests for FTA are in handset mode only so a particular care must be brought to the design of
audio (mechanical integration, gasket, electronic) in this mode.
The audio norms which describe the audio tests are 3GPP TS 26.131 & 3GPP TS 26.132.
Please note that acoustic competences are mandatory to get accurate audio performance on customer’s
F
product.
7.1 MECHANICAL INTEGRATION AND ACOUSTICS
Particular care to Handset Mode: FTA
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 27

page 27/36
To get a better audio output design (speaker part) :
The speaker must be completely sealed on front side.
F
The front aperture must be compliant with speaker supplier’s specifications
F
The back volume must be completely sealed.
F
The sealed back volume must be compliant with speaker supplier’s specifications
F
Take care of the design of the speaker gasket (elastomer).
F
Foresee a stable and large enough area for the gasket of the artificial ear.
F
To get a better audio input design (microphone part) :
Take care of the design of the microphone (elastomer).
F
All receivers must be completely sealed on front side.
F
Microphone sensitivity depends on the shape of the device eg. about –40 ±3 dBV/Pa for clamshell.
F
Promote the use of pre-amplified microphone. If needed, use a pre-amplification stage.
F
As audio input and ouput are strongly linked :
Place the microphone and the speaker as far as possible from one another.
F
7.2 ELECTRONICS AND LAYOUT
Avoid Distortion & Burst noise
Audio signals must be symmetric (same components on each path).
F
Differential signals must be routed parallel.
F
Audio layer must be surrounded by 2 ground layers.
F
The link from one component to the ground must be as short as possible.
F
If possible separate the PCB of the microphone and the one of the speaker.
F
Reduce as much as possible the number of electronics components (loss of quality, more dispersion).
F
Audio tracks must be larger than 0.5 mm.
F
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 28

page 28/36
8. RECOMMENDATIONS ON LAYOUT OF CUSTOMER’S BOARD
8.1 GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS ON LAYOUT
There are many different types of signals in the module which are disturbing each other. Particularly, Audio
signals are very sensitive to external signals as VBAT
to avoid disruptions or abnormal behaviour.
8.1.1 Ground
A ground plane as complete as possible
F
F
F
8.1.2 Power supplies
F
F
8.1.3 Clocks
Ground of components has to be connected to the ground layer through many vias not regularly
distributed.
Top and bottom layer shall have as much as possible of ground planes.
Plan for power supply signals (VBAT, VGPIO), no loop.
Suitable power supply (VBAT, VGPIO) track width, thickness.
(1).
... Therefore it is very important to respect some rules
Clock signals must be shielded between two grounds plans and bordered with ground vias.
F
8.1.4 Data bus and other signals
Data bus and commands have to be routed on the same plane, none of the lines of the bus shall be
F
parallel to other lines
Lines crossing shall be perpendicular
F
Suitable other signals track width, thickness.
F
Data bus must be protected by upper and lower ground plans
F
8.1.5 Radio
Provide a 50 Ohm microstrip line for antenna connection
F
8.1.6 Audio (see also § 10.2)
Differential signals have to be routed together, parallel (for example HSET_OUT_P/HSET_OUT_N).
F
Audio signals have to be isolated, by pair, from all the other signals (ground all around each pair).
F
Cancel any loops between VBAT and GND next to the speaker to avoid the TDMA burst noise in the
F
speaker during a communication.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 29

page 29/36
The single-end audio signal should be adopted the same rules as differential signals.
F
GND
HSET_OUT_P
HSET_OUT_N
GND
Figure 22: Layout of audio differential signals on a layer n
GND
HSET_OUT_P
GND
Layer n-1
Layer n
Layer n+1
Figure 23: Adjacent layers of audio differential signals
(1).
Warning: Magnetic field generated by VBAT tracks may disturb the speaker, causing audio burst noise. In
this case, one shall modify routing of the VBAT tracks to reduce the phenomena.
8.2 EXAMPLE OF LAYOUT FOR CUSTOMER’S BOARD
The figure Figure 24 shows an example of layer allocation for a 6 layers circuit (for reference only):
Layer 1: Components (HiloNC)
Layer 2: Bus
Layer 3: Power supply
Layer 4: Complete GND layer
Layer 5: Audio, clocks, sensitive signals
Layer 6: GND,test points
Figure 24: layer allocation for a 6 layers circuit
9. RECOMMANDATIONS FOR CUSTOMER INDUSTRIALIZATION
Please note for following chapters that except where standards are indicated, the given characteristics should
be considered as validated conditions used on Sagem Communication product.
Other conditions depending of the customer’s factory process are not validated but can be submitted to
F
Sagem Communication for proficiency.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 30

page 30/36
9.1 MOISTURE LEVEL
According to IPC/JEDEC J-STD 20, the HiloNC has the following MSL level : 3 (Targeted).
Floor Life
Standard Accelerated Equivalent
Time Conditions Time (hours) Conditions Time (hours) Conditions
3 168 hours <= 30°C/60% RH
It means that the customer’s factory must process and solder the HiloNC on the customer’s board at least 168
hours (7 days) after the HiloNC sealed package have been opened. This duration is given for factory floor
conditions of T°<30°C, HR 60%.
If this duration can not be fulfilled, the HiloNC part must be baked again.
F
192 +5/-0 30°C / 60% RH
Soak requirements Level
40 +1/-0 60°C / 60%RH
9.2 PACKAGE
The HiloNC module is delivered in Tape and Reel package which is hermetically sealed to prevent from
moisture and ESD.
The characteristics of the T&R are given in the drawing below.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 31

page 31/36
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 32

page 32/36
9.3 SOLDER MASK
Below are given soldering characteristics to report the HiloNC on the customer’s board.
Copper footprint is shown in yellow on the figure below. Solder mask footprint is shown in pink.
Please note that copper mask and solder mask do not strictly recover themselves.
F
Figure 25 : Solder mask design
9.4 SOLDER PASTE
Solder paste : M705-GRN360-K-V (Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd.)
Alloy composition : Sn96.5-Ag3.0-Cu0.5
Melting temperature : solidus 216°C / Peak 217°C / liquidus 220°C
Sagem Communication recommends a stencil thickness of 135 µm.
F
9.5 PROFILE FOR REFLOW SOLDERING
A convection type soldering oven is recommended.
Typical usable profile is shown on the next figure. The final profile has to be tuned depending on other
elements like solder paste, customer’s board, other components,…
Peak temperature : 245°C
Average ramp up rate : 3°C/second max
Average ramp down rate : TBC
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 33

page 33/36
Figure 26 : Typical thermal profile
The HiloNC module is a Lead-free product which has been validated integrated in a lead-free product, using a lead-free factory process.
No test has been performed using a leaded process. Sagem Communication does not recommend to use a factory leaded process and does not guarantee any
F
reliable result on the final product.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 34

page 34/36
9.6 SMT MACHINE
HiloNC is optimized for use with pick-and-place machines.Optical inspection for placement is possible with
SMD fiducials placed on the bottom side of the HiloNC. SMD fiducials are not symmetrical in order to help
optical inspection to define the right orientation.
Figure 27 : CMS fiducials positions
9.7 UNDERFILL
Despite its important reliability, some customer could request for some specific and extreme applications the
underfill of onboard components.
The HiloNC’s shield has be designed accordingly to allow this process, as shown in the figure below.
More details will be given in a specific application note.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 35

page 35/36
Underfill Holes
Figure 28 : Underfill holes
9.8 SECOND REFLOW SOLDERING
Even if Sagem Communications recommends a single reflow soldering, a second reflow soldering can be
conceivable (only if underfill has not been already performed). Positive tests have been performed with HiloNC
on the bottom side.
Second reflow soldering is not possible if HiloNC module has been already underfilled.
F
9.9 HAND SOLDERING
Hand soldering is possible.
An especial care must be considered to properly position the HiloNC on its copper footprint during hand
F
soldering. Begin with pads diagonally opposite to help in proper positioning.
9.10 REWORK
Rework is possible, for repair purpose for example.
An especial care must be considered in order not to overheat the HiloNC.
F
10. LABEL
The HiloNC module is labelled with its own FCC ID(VW3HILONC) on its bottom side. When the module is
installed in customer’s product, the FCC ID label on the module will not be visible. To avoid this case, an
exterior label must be stuck on the surface of customer’s product signally to indicate the FCC ID of the
enclosed module. This label can use wording such as the following: “Contains Transmitter module FCC ID:
VW3HILONC” or “Contains FCC ID: VW3HILONC”.
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
Page 36

page 36/36
Note d’étude / Technical document : URD1– OTL 5665.1– 002 / 70 884 Edition 03
Document Sagem Communications Reproduction et divulgation interdites
Sagem Communications document. Reproduction and disclosure prohibited
 Loading...
Loading...