Page 1
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
MANUEL D’UTILISATION
MANUAL DEL OPERADOR
10 in. TABLE SAW
SCIE À TABLE de 254 mm (10 po)
SIERRA DE MESA de 254 mm (10 pulg.)
RTS11/RTS11T
The saw has been engineered and manufactured to our high standard for dependability, ease of operation, and operator
safety. When properly cared for, it will give you years of rugged, trouble-free performance.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury, the user must read and understand the operator’s manual before using
this product.
SAVE THIS MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
Cette scie a été conçue et fabriquée conformément aux strictes
normes de fiabilité, simplicité d’emploi et sécurité d’utilisation.
Correctement entretenu, cet outil vous donnera des années de
fonctionnement robuste et sans problème.
AVERTISSEMENT : Pour réduire les risques de
blessures, l’utilisateur doit lire et veiller à bien comprendre le
manuel d’utilisation avant d’employer ce produit.
CONSERVER CE MANUEL POUR
FUTURE RÉFÉRENCE
Su sierra ha sido diseñado y fabricado de conformidad con
nuestras estrictas normas para brindar fiabilidad, facilidad de uso
y seguridad para el operador. Con el debido cuidado, le brindará
muchos años de sólido funcionamiento y sin problemas.
ADVERTENCIA: Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones,
el usuario debe leer y comprender el manual del operador antes
de usar este producto.
GUARDE ESTE MANUAL PARA
FUTURAS CONSULTAS
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE DES MATIÈRES / ÌNDICE DE CONTENIDO
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................................................2
Introduction / Introducción
General Safety Rules ..................................................................................................................................................... 3-4
Règles de sécurité générales / Reglas de seguridad generales
Specific Safety Rules .....................................................................................................................................................4-5
Règles de sécurité particulières / Reglas de seguridad específicas
Symbols ............................................................................................................................................................................ 6
Symboles / Símbolos
Electrical ........................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Caractéristiques électriques / Aspectos eléctricos
Glossary of Terms ............................................................................................................................................................. 8
Glossaire / Glosario de términos
Features .......................................................................................................................................................................9-11
Caractéristiques / Características
Tools Needed .................................................................................................................................................................. 12
Outils nécessaires / Herramientas necesarias
Loose Parts .................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Pièces détachées / Piezas sueltas
Assembly ...................................................................................................................................................................14-21
Assemblage / Armado
Operation ...................................................................................................................................................................22-38
Utilisation / Funcionamiento
Adjustments ...............................................................................................................................................................38-41
Réglages / Ajustes
Maintenance ..............................................................................................................................................................41-42
Entretien / Mantenimiento
Accessories ....................................................................................................................................................................42
Accessoires / Accesorios
Troubleshooting .............................................................................................................................................................. 43
Dépannage / Solución de problemas
Parts Ordering and Service ...............................................................................................................................Back page
Commande de pièces et réparation / Pedidos de piezas y servicio
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION / INTRODUCCIÓN
This product has many features for making its use more pleasant and enjoyable. Safety, performance, and dependability
have been given top priority in the design of this product making it easy to maintain and operate.
* * *
Ce produit offre de nombreuses fonctions destinées à rendre son utilisation plus plaisante et satisfaisante. Lors de la
conception de ce produit, l’accent a été mis sur la sécurité, les performances et la fiabilité, afin d’en faire un outil facile à
utiliser et à entretenir.
* * *
Este producto ofrece numerosas características para hacer más agradable y placentero su uso. En el diseño de este producto
se ha conferido prioridad a la seguridad, el desempeño y la fiabilidad, por lo cual se facilita su manejo y mantenimiento.
2
Page 3

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
WARNING:
Read and understand all instructions. Failure to follow
all instructions listed below, may result in electric shock,
fire and/or serious personal injury.
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS
KNOW YOUR POWER TOOL. Read the operator’s
manual carefully. Learn the saw’s applications and
limitations as well as the specific potential hazards related
to this tool.
GUARD AGAINST ELECTRICAL SHOCK BY
PREVENTING BODY CONTACT WITH GROUNDED
SURFACES. For example, pipes, radiators, ranges,
refrigerator enclosures.
KEEP GUARDS IN PLACE and in good working order.
REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES. Form
habit of checking to see that keys and adjusting wrenches
are removed from tool before turning it on.
KEEP WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents. DO NOT leave tools or pieces
of wood on the saw while it is in operation.
DO NOT USE IN DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTS. Do
not use power tools in damp or wet locations or expose
to rain. Keep the work area well lit.
KEEP CHILDREN AND VISITORS AWAY. All visitors
should wear safety glasses and be kept a safe distance
from work area. Do not let visitors contact tool or
extension cord while operating.
MAKE WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF with padlocks and
master switches, or by removing starter keys.
DON’T FORCE TOOL. It will do the job better and safer
at the feed rate for which it was designed.
USE RIGHT TOOL. Don’t force the tool or attachment to
do a job it was not designed for. Don’t use it for a purpose
not intended.
USE THE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure
your extension cord is in good condition. Use only a
cord heavy enough to carry the current your product
will draw. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line
voltage resulting in loss of power and overheating. A wire
gauge size (A.W.G.) of at least 14 is recommended for an
extension cord 25 feet or less in length. If in doubt, use
the next heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number,
the heavier the cord.
DRESS PROPERLY. Do not wear loose clothing, gloves,
neckties, or jewelry. They can get caught and draw you
into moving parts. Also wear protective hair covering to
contain long hair.
ALWAYS WEAR EYE PROTECTION WITH SIDE
SHIELDS MARKED TO COMPLY WITH ANSI Z87.1.
Failure to do so could result in objects being thrown into
your eyes, resulting in possible serious injury.
SECURE WORK. Use clamps or a vise to hold work when
practical. It’s safer than using your hand and frees both
hands to operate tool.
DON’T OVERREACH. Keep proper footing and balance
at all times.
MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep tools sharp
and clean for better and safer performance. Follow
instructions for lubricating and changing accessories.
DISCONNECT TOOLS. When not in use, before
servicing, or when changing attachments, blades, bits,
cutters, etc., all tools should be disconnected.
AVOID ACCIDENTAL STARTING. Be sure switch is off
when plugging in any tool.
USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Consult the
operator’s manual for recommended accessories. The
use of improper accessories may risk injury.
NEVER STAND ON TOOL. Serious injury could occur if
the tool is tipped or if the cutting tool is unintentionally
contacted.
CHECK DAMAGED PARTS. Before further use of the
tool, a guard or other part that is damaged should be
carefully checked to determine that it will operate properly
and perform its intended function. Check for alignment
of moving parts, binding of moving parts, breakage of
parts, mounting and any other conditions that may affect
its operation. A guard or other part that is damaged must
be properly repaired or replaced by an authorized service
center to avoid risk of personal injury.
USE THE RIGHT DIRECTION OF FEED. Feed work into
a blade or cutter against the direction of rotation of blade
or cutter only.
NEVER LEAVE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED. TURN
THE POWER OFF. Don’t leave tool until it comes to a
complete stop.
PROTECT YOUR LUNGS. Wear a face or dust mask if
the cutting operation is dusty.
PROTECT YOUR HEARING. Wear hearing protection
during extended periods of operation.
DO NOT ABUSE CORD. Never yank cord to disconnect
from receptacle. Keep cord away from heat, oil, and sharp
edges.
WHEN OPERATING A POWER TOOL OUTSIDE, USE
AN OUTDOOR EXTENSION CORD MARKED “W-A”
OR “W”. These cords are rated for outdoor use and
reduce the risk of electric shock.
ALWAYS KEEP THE BLADE GUARD AND RIVING
KNIFE (SPLITTER) IN PLACE and in working order.
KEEP BLADES CLEAN, SHARP, AND WITH SUFFICIENT
SET. Sharp blades minimize stalling and kickback.
3 - English
Page 4

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
KEEP HANDS AWAY FROM CUTTING AREA. Keep
hands away from blades. Do not reach underneath work
or around or over the blade while blade is rotating. Do not
attempt to remove cut material when blade is moving.
BLADE COASTS AFTER BEING TURNED OFF.
NEVER USE IN AN EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERE. Normal
sparking of the motor could ignite fumes.
INSPECT TOOL CORDS PERIODICALLY. If damaged,
have repaired by a qualified service technician at an
authorized service facility. The conductor with insulation
having an outer surface that is green with or without
yellow stripes is the equipment-grounding conductor.
If repair or replacement of the electric cord or plug is
necessary, do not connect the equipment-grounding
conductor to a live terminal. Repair or replace a damaged
or worn cord immediately. Stay constantly aware of cord
location and keep it well away from the rotating blade.
INSPECT EXTENSION CORDS PERIODICALLY and
replace if damaged.
GROUND ALL TOOLS. If tool is equipped with three-
prong plug, it should be plugged into a three-hole
electrical receptacle.
CHECK WITH A QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN or service
personnel if the grounding instructions are not completely
understood or if in doubt as to whether the tool is properly
grounded.
USE ONLY CORRECT ELECTRICAL DEVICES: 3-wire
extension cords that have 3-prong grounding plugs and
3-pole receptacles that accept the tool’s plug.
DO NOT MODIFY the plug provided. If it will not fit the
outlet, have the proper outlet installed by a qualified
electrician.
KEEP TOOL DRY, CLEAN, AND FREE FROM OIL AND
GREASE. Always use a clean cloth when cleaning. Never
use brake fluids, gasoline, petroleum-based products, or
any solvents to clean tool.
STAY ALERT AND EXERCISE CONTROL. Watch what
you are doing and use common sense. Do not operate
tool when you are tired. Do not rush.
DO NOT USE TOOL IF SWITCH DOES NOT TURN IT
ON AND OFF. Have defective switches replaced by an
authorized service center.
USE ONLY CORRECT BLADES. Do not use blades with
incorrect size holes. Never use blade washers or blade
bolts that are defective or incorrect. The maximum blade
capacity of the saw is 10 in. (254 mm).
BEFORE MAKING A CUT, BE SURE ALL ADJUSTMENTS
ARE SECURE.
BE SURE BLADE PATH IS FREE OF NAILS. Inspect for
and remove all nails from lumber before cutting.
NEVER TOUCH BLADE or other moving parts during
use.
NEVER START A TOOL WHEN ANY ROTATING
COMPONENT IS IN CONTACT WITH THE WORKPIECE.
DO NOT OPERATE A TOOL WHILE UNDER THE
INFLUENCE OF DRUGS, ALCOHOL, OR ANY
MEDICATION.
WHEN SERVICING use only identical replacement parts.
Use of any other parts may create a hazard or cause
product damage.
USE ONLY RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES listed
in this manual or addendums. Use of accessories that
are not listed may cause the risk of personal injury.
Instructions for safe use of accessories are included with
the accessory.
DOUBLE CHECK ALL SETUPS. Make sure blade is tight
and not making contact with saw or workpiece before
connecting to power supply.
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
FIRMLY BOLT THE SAW TO A WORK BENCH OR LEG
STAND at approximately hip height.
DO NOT OPERATE THE SAW WITHOUT THE STAND
ON THE FLOOR.
GUARD AGAINST KICKBACK. Kickback occurs when
the blade stalls rapidly and workpiece is driven back
towards the operator. It can pull your hand into the blade
resulting in serious personal injury. Stay out of blade path
and turn switch off immediately if blade binds or stalls.
USE RIP FENCE. Always use a fence or straight edge
guide when ripping.
SUPPORT LARGE PANELS. To minimize risk of blade
pinching and kickback, always support large panels.
4 - English
REMOVE ALL FENCES AND AUXILIARY TABLES
before transporting saw. Failure to do so can result in an
accident causing possible serious personal injury.
ALWAYS USE BLADE GUARD, RIVING KNIFE, AND
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS on all “through-sawing”
operations. Through-sawing operations are those in
which the blade cuts completely through the workpiece
as in ripping or cross cutting. Keep the blade guard down,
the anti-kickback pawls down, and the riving knife in
place.
ALWAYS SECURE WORK firmly against rip fence, miter
fence, or miter gauge.
ALWAYS USE A PUSH STICK FOR RIPPING NARROW
STOCK. A push stick is a device used to push a
Page 5

SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
workpiece through the blade instead of using your hands.
Size and shape can vary but the push stick must always
be narrower than the workpiece to prevent the push stick
from contacting the saw blade. When ripping narrow
stock, always use a push stick, or the jig mentioned in the
How to Make A Jig (For Rip Cutting Narrow Workpiece)
section of this manual, so your hand does not come close
to the saw blade. Use a featherboard and push blocks
for non-through cuts.
WHEN MAKING NON-THROUGH RIP CUTS, always
use a push stick, push block, and/or featherboard so your
hands do not come within 3 inches of the saw blade.
WHEN RIPPING NARROW STOCK, always use a push
stick, push block, jig ( designed for narrow ripping), or
featherboard.
NEVER perform any operation “freehand” which means
using only your hands to support or guide the workpiece.
Always use either the rip fence or miter gauge to position
and guide the work.
NEVER stand or have any part of your body in line with
the path of the saw blade.
NEVER reach behind, over, or within three inches of the
blade or cutter with either hand for any reason.
ALWAYS REMOVE THE RIP FENCE from the saw when
cross cutting.
DO NOT USE THE MITER GAUGE AND RIP FENCE
during the same operation.
NEVER use rip fence as cutoff gauge when cross cutting.
NEVER attempt to free a stalled saw blade without first
turning the saw OFF and disconnecting the saw from the
power source.
PROVIDE ADEQUATE SUPPORT to the rear and sides
of the saw table for wide or long workpieces.
AVOID KICKBACKS (work thrown back toward you) by:
a) Keeping blade sharp.
b) Keeping rip fence parallel to the saw blade.
c) Keeping riving knife, anti-kickback pawls, and blade
guard in place and operating.
d) Not releasing the work before it is pushed all the way
past the saw blade using a push stick.
e) Not ripping work that is twisted or warped or does
not have a straight edge to guide along the fence.
IF THE POWER SUPPLY CORD IS DAMAGED, it must
be replaced only by the manufacturer or by an authorized
service center to avoid risk.
AVOID AWKWARD OPERATIONS AND HAND
POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause your hand
to move into the cutting tool.
USE ONLY RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES listed
in this manual or addendums. Use of accessories that
are not listed may cause the risk of personal injury.
Instructions for safe use of accessories are included with
the accessory.
MAKE SURE THE WORK AREA HAS AMPLE LIGHTING
to see the work and that no obstructions will interfere with
safe operation BEFORE performing any work using the
table saw.
ALWAYS TURN OFF SAW before disconnecting it, to
avoid accidental starting when reconnecting to power
supply.
ONLY USE BLADES within the thickness range stamped
on the riving knife.
THIS TOOL should have the following markings:
a) Wear eye protection.
b) Use saw blade guard and riving knife for every
operation for which it can be used, including all
through sawing.
c) Keep hands out of the line of saw blade.
d) Use a push stick when required.
e) Pay particular attention to instructions on reducing
risk of kickback.
f) Do not perform any operation freehand.
g) Never reach around or over the saw blade.
h) Never operate saw on floor or below waist height.
NEVER CUT MORE THAN ONE PIECE OF MATERIAL
AT A TIME.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS. Refer to them frequently
and use to instruct other users. If you loan someone this
tool, loan them these instructions also.
5 - English
Page 6
SYMBOLS
The following signal words and meanings are intended to explain the levels of risk associated with this product.
SYMBOL SIGNAL MEANING
DANGER:
WARNING:
CAUTION:
NOTICE:
Some of the following symbols may be used on this tool. Please study them and learn their meaning. Proper interpretation
of these symbols will allow you to operate the tool better and safer.
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a hazardous situation, that, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury.
(Without Safety Alert Symbol) Indicates information considered important, but
not related to a potential injury (e.g. messages relating to property damage).
SYMBOL NAME DESIGNATION/EXPLANATION
Safety Alert Indicates a potential personal injury hazard.
Read Operator’s Manual
To reduce the risk of injury, user must read and understand
operator’s manual before using this product.
Eye Protection
No Hands Symbol
Wet Conditions Alert Do not expose to rain or use in damp locations.
V Volts Voltage
A Amperes Current
Hz Hertz Frequency (cycles per second)
min Minutes Time
Alternating Current Type of current
n
o
.../min Per Minute Revolutions, strokes, surface speed, orbits, etc., per minute
No Load Speed Rotational speed, at no load
Always wear eye protection with side shields marked to comply
with ANSI Z87.1.
Failure to keep your hands away from the blade will result in
serious personal injury.
6 - English
Page 7
ELECTRICAL
EXTENSION CORDS
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3-prong grounding
plugs and 3-pole receptacles that accept the tool’s plug.
When using a power tool at a considerable distance from
the power source, use an extension cord heavy enough
to carry the current that the tool will draw. An undersized
extension cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in
a loss of power and causing the motor to overheat. Use the
chart provided below to determine the minimum wire size
required in an extension cord. Only round jacketed cords
listed by Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL) should be used.
**Ampere rating (on tool faceplate)
0-2.0 2.1-3.4 3.5-5.0 5.1-7.0 7.1-12.0 12.1-16.0
Cord Length Wire Size (A.W.G.)
25’ 16 16 16 16 14 14
50’ 16 16 16 14 14 12
100’ 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Used on 12 gauge - 20 amp circuit.
NOTE: AWG = American Wire Gauge
When working with the tool outdoors, use an extension cord
that is designed for outside use. This is indicated by the
letters “W-A” or “W” on the cord’s jacket.
Before using an extension cord, inspect it for loose or
exposed wires and cut or worn insulation.
WARNING:
Keep the extension cord clear of the working area.
Position the cord so that it will not get caught on lumber,
tools or other obstructions while you are working with a
power tool. Failure to do so can result in serious personal
injury.
WARNING:
Check extension cords before each use. If damaged
replace immediately. Never use product with a damaged
cord since touching the damaged area could cause
electrical shock resulting in serious injury.
SPEED AND WIRING
The no-load speed of this tool is approximately 4,700 rpm.
This speed is not constant and decreases under a load or
with lower voltage. For voltage, the wiring in a shop is as
important as the motor’s horsepower rating. A line intended
only for lights cannot properly carry a power tool motor. Wire
that is heavy enough for a short distance will be too light for
a greater distance. A line that can support one power tool
may not be able to support two or three tools.
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
This product must be grounded. In the event of a malfunction
or breakdown, grounding provides a path of least resistance
for electric current to reduce the risk of electric shock. This
tool is equipped with an electric cord having an equipmentgrounding conductor and a grounding plug. The plug must be
plugged into a matching outlet that is properly installed and
grounded in accordance with all local codes and ordinances.
Do not modify the plug provided. If it will not fit the outlet,
have the proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician.
WARNING:
Improper installation of the grounding plug can result in a
risk of electric shock. When repair or replacement of the
cord is required, do not connect the grounding wire to
either flat blade terminal. The wire with insulation having
an outer surface that is green with or without yellow
stripes is the grounding wire.
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if the
grounding instructions are not completely understood, or if
in doubt as to whether the tool is properly grounded.
Repair or replace a damaged or worn cord immediately.
This product is for use on a nominal 120 volt circuit and has
a grounding plug similar to the plug illustrated in figure 1.
Only connect the product to an outlet having the same
configuration as the plug. Do not use an adapter with this
product.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
This product is powered by a precision built electric motor.
It should be connected to a power supply that is 120 V, AC
only (normal household current), 60 Hz. Do not operate
this product on direct current (DC). A substantial voltage
drop will cause a loss of power and the motor will overheat.
If the saw does not operate when plugged into an outlet,
double check the power supply.
7 - English
GROUNDING
PIN
120 V GROUNDED
OUTLET
Fig. 1
Page 8

GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Anti-Kickback Pawls (radial arm and table saws)
A device which, when properly installed and maintained,
is designed to stop the workpiece from being kicked back
toward the front of the saw during a ripping operation.
Arbor
The shaft on which a blade or cutting tool is mounted.
Bevel Cut
A cutting operation made with the blade at any angle other
than 90° to the table surface.
Chamfer
A cut removing a wedge from a block so the end (or part of
the end) is angled rather than at 90°.
Compound Cut
A cross cut made with both a miter and a bevel angle.
Cross Cut
A cutting or shaping operation made across the grain or the
width of the workpiece.
Cutter Head (planers and jointer planers)
A rotating cutterhead with adjustable blades or knives. The
blades or knives remove material from the workpiece.
Dado Cut (table saws and compound sliding miter saws)
A non-through cut which produces a square, three-sided
notch or trough in the workpiece.
Featherboard (table saws)
A device used to help control the workpiece by guiding
it securely against the table or fence during any ripping
operation.
FPM or SPM
Feet per minute (or strokes per minute), used in reference
to blade movement.
Freehand
Performing a cut without the workpiece being guided by a
fence, miter fence, or other aids.
Gum
A sticky, sap-based residue from wood products.
Heel
Alignment of the blade to the miter gauge groove.
Kerf
The material removed by the blade in a through cut or the
slot produced by the blade in a non-through or partial cut.
Kickback
A hazard that can occur when the blade binds or stalls,
throwing the workpiece in the direction of the spinning blade.
Miter Cut
A cutting operation made with the workpiece at any angle
to the blade other than 90°.
Non-Through Cuts (table saws and compound sliding
miter saws)
Any cutting operation where the blade does not extend
completely through the thickness of the workpiece. This is
a cut where the blade will not cut the workpiece into two
pieces.
8 - English
Pilot Hole (drill presses and scroll saws)
A small hole drilled in a workpiece that serves as a guide
for drilling large holes accurately or for insertion of a scroll
saw blade.
Push Blocks (jointer planers)
Device used to feed the workpiece over the jointer planer
cutterhead during any operation. This aid helps keep the
operator’s hands well away from the cutterhead.
Push Blocks and Push Sticks (table saws)
Devices used to feed the workpiece through the saw blade
during cutting operations. When making a narrow rip cut
without a jig or similar cutting aid, always use a push stick
(not a push block). A push block can be used for narrow
ripping operations, if a jig or similar cutting aid is used.
These aids help keep the operator’s hands well away from
the blade.
Rabbet
A non-through cut positioned on the end or edge of the
workpiece which produces a square, two-sided notch or
trough in the workpiece.
Resaw (table saws and band saws)
A cutting operation to reduce the thickness of the workpiece
to make thinner pieces.
Resin
A sticky, sap-based substance that has hardened.
Revolutions Per Minute (RPM)
The number of turns completed by a spinning object in one
minute.
Ripping or Rip Cut (table saws)
A cutting operation along the length of the workpiece and
typically in the direction of the grain.
Riving Knife/Spreader/Splitter (table saws)
A metal piece, slightly thinner than the blade, which helps
keep the kerf open and also helps to prevent kickback.
Saw Blade Path
The area over, under, behind, or in front of the blade. As it
applies to the workpiece, that area which will be or has been
cut by the blade.
Snipe (planers)
Depression made at either end of a workpiece by cutter
blades when the workpiece is not properly supported.
Taper Cut
A cut where the material being cut has a different width at
the beginning of the cut from the end.
Through Sawing
Any cutting operation where the blade extends completely
through the thickness of the workpiece. This type of cut will
separate a single workpiece into two pieces.
Workpiece or Material
The item on which the operation is being done.
Worktable
Surface where the workpiece rests while performing a
cutting, drilling, planing, or sanding operation.
Page 9
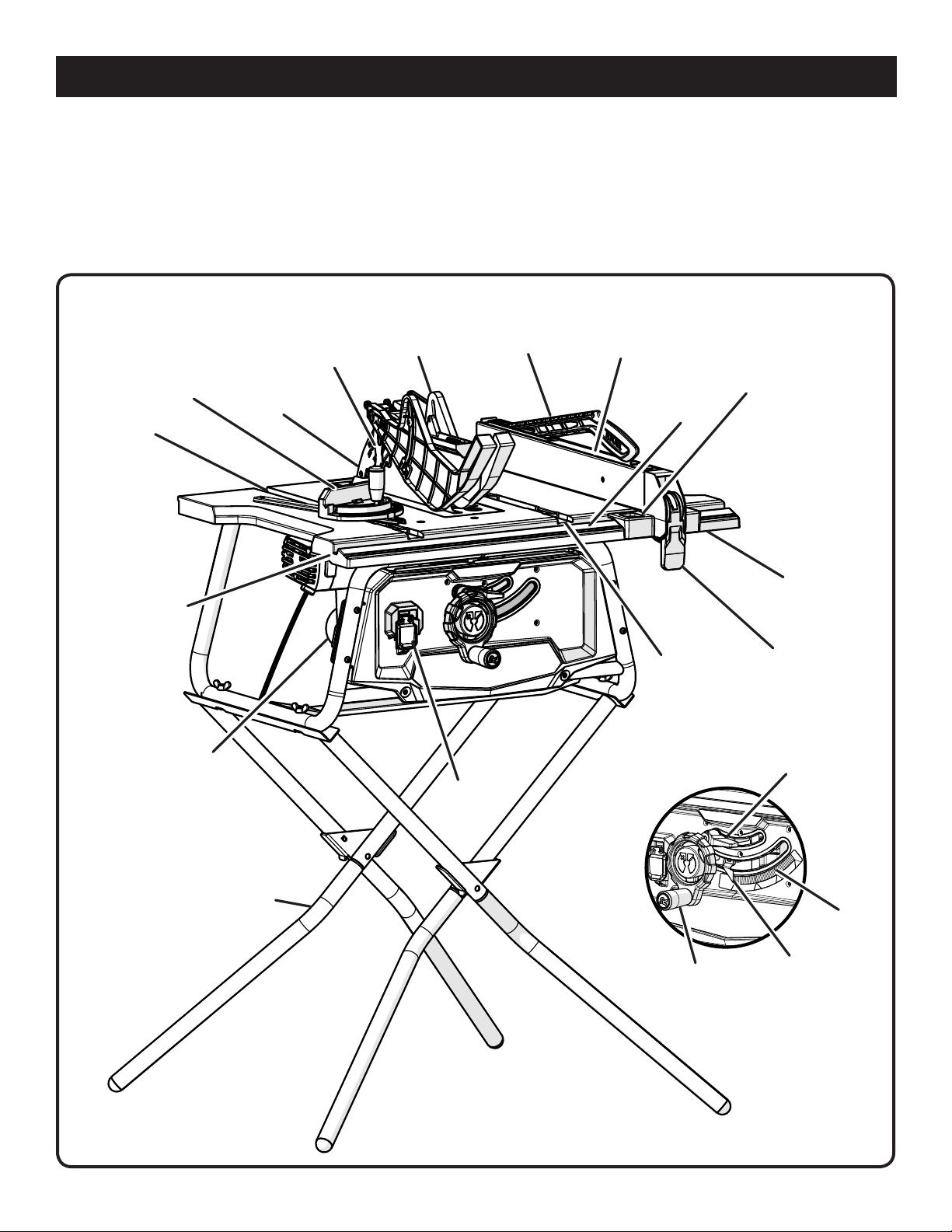
FEATURES
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
Blade Arbor ..............................................................5/8 in.
Blade Diameter .......................................................... 10 in.
Blade Tilt .................................................................0˚ - 45˚
Dado Capacity ..........................................................1/2 in.
Rating ...............................................120 V, AC only, 60 Hz
Input .....................................................................15 Amps
No Load Speed ....................................4,700 r/min. (RPM)
Cutting Depth at 0˚ ...................................................... 3 in.
Cutting Depth at 45˚ ..............................................2-1/2 in.
MITER
GAUGE
MITER GAUGE
GROOVE
FRONT
RAIL
ANTI-KICKBACK
PAWLS
DUST
CHUTE
RIVING
KNIFE
BLADE
GUARD
SWITCH
PUSH STICK
STORAGE
RIP
FENCE
RIP SCALE
INDICATOR
RIP
SCALE
MITER GAUGE
GROOVE
BLADE
WRENCH
STORAGE
LOCKING
LEVER
BEVEL
LOCKING LEVER
LEG
STAND
9 - English
HEIGHT/BEVEL
ADJUSTING
HANDWHEEL
BEVEL
SCALE
BEVEL
INDICATOR
Fig. 2
Page 10
FEATURES
KNOW YOUR TABLE SAW
See Figure 2.
The safe use of this product requires an understanding of
the information on the tool and in this operator’s manual as
well as a knowledge of the project you are attempting. Before
use of this product, familiarize yourself with all operating
features and safety rules.
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS - Kickback is a hazard in which
the workpiece is thrown back toward the operator. The teeth
on the removable anti-kickback pawls point away from the
workpiece. If the workpiece should be pulled back toward
the operator, the teeth dig into the wood to help prevent or
reduce the possibility of kickback. The anti-kickback pawls
may be bypassed.
BEVEL SCALE - The easy-to-read scale on the front of the
cabinet shows the exact blade angle.
BLADE - For maximum performance, it is recommended
that you use the 10 in. carbide tipped combination blade
provided with the saw. The blade is raised and lowered
with the height/bevel adjusting handwheel. Bevel angles
are locked with the bevel locking lever. Additional blade
styles of the same high quality are available for specific
operations such as ripping. Your local dealer can provide
you with complete information.
Blade kerf width must be within the limits stamped on the
riving knife.
DUST CHUTE - The built-in dust chute makes it easy to
dispose of sawdust. A vacuum hose may be attached to
the dust chute.
HEIGHT/BEVEL ADJUSTING HANDWHEEL - Located on
the front of the cabinet, use this handwheel to lower and raise
the blade for height adjustments or blade replacement. This
handwheel also makes the adjustment for bevel angles easy.
MITER GAUGE - The miter gauge aligns the wood for a
cross cut. The easy-to-read indicator shows the exact angle
for a miter cut.
MITER GAUGE GROOVES - The miter gauge rides in the
grooves on the saw table.
PUSH STICK AND WRENCH STORAGE - Convenient
storage for the push stick and wrenches is located
underneath the saw table.
RIP FENCE - A sturdy metal fence guides the workpiece
and is secured with the locking handle. Push stick storage
is located on the rip fence.
RIP SCALE - Located on the front rail, the easy-to-read rip
scale provides precise measurements for rip cuts.
RIVING KNIFE - A removable metal piece of the blade
guard assembly, slightly thinner than the saw blade, which
helps keep the kerf open and prevent kickback. When in the
through sawing, or “up” position, it is higher than the saw
blade. When in the non-through sawing, or “down” position,
it is below the saw blade teeth.
WARNING:
Do not use blades rated less than the speed of this tool.
Failure to heed this warning could result in personal
injury.
BLADE GUARD - Always keep the removable blade guard
down over the saw blade for through-sawing cuts.
BEVEL LOCKING LEVER - This lever, placed just under
the saw table surface on the front of the cabinet, locks the
angle setting of the blade.
SWITCH ASSEMBLY - This saw has an easy access switch
assembly located below the front rail.
10 - English
Page 11
FEATURES
OPERATING COMPONENTS
The upper portion of the blade projects up through the table
and is surrounded by an insert called the throat plate. The
height of the blade is set with a handwheel on the front of the
cabinet. Detailed instructions are provided in the Operation
section of this manual for the basic cuts: cross cuts, miter
cuts, bevel cuts, and compound cuts.
The rip fence is used to position work for lengthwise cuts.
A scale on the front rail shows the distance between the rip
fence and the blade.
It is very important to use the blade guard assembly for
all through-sawing operations. The blade guard assembly
includes: riving knife and blade guard with anti-kickback
pawls.
SWITCH ASSEMBLY
See Figure 3.
This saw is equipped with an on/off switch that has a built-in
locking feature. This feature is intended to prevent unauthorized and possible hazardous use by children and others.
WARNING:
ALWAYS make sure your workpiece is not in contact with
the blade before operating the switch to start the tool.
Failure to heed this warning may cause the workpiece to
be kicked back toward the operator and result in serious
personal injury.
WARNING:
To reduce the risk of accidental starting, ALWAYS make
sure the switch is in the OFF ( O ) position before plugging
tool into the power source.
SWITCH
OFF
SWITCH
ON
TO TURN THE SAW ON:
Lift the switch to turn ON ( l ).
TO TURN THE SAW OFF:
Press the switch down to turn OFF ( O ).
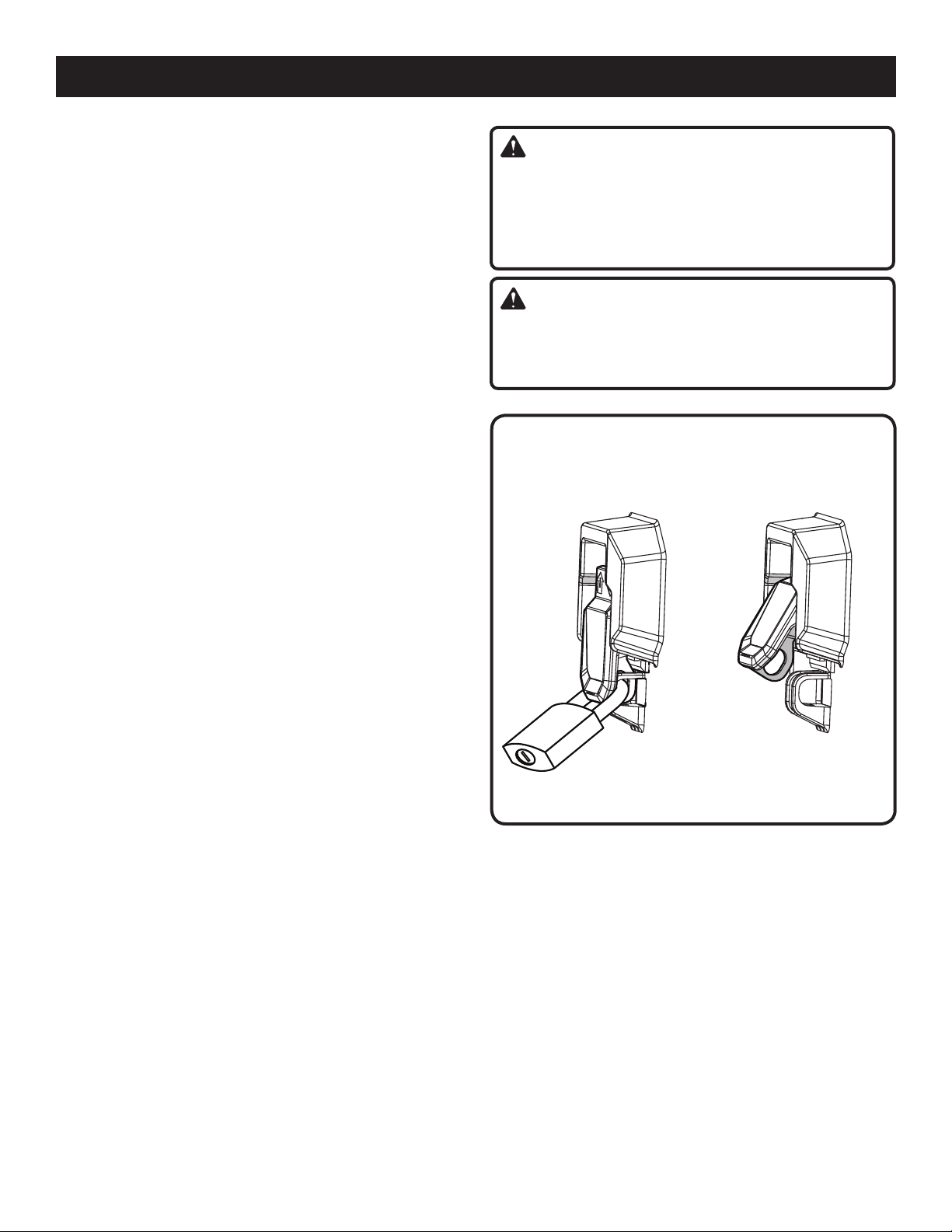
TO LOCK THE SAW:
With the saw turned OFF, install a padlock (not included)
through the hole in the switch.
Fig. 3
11 - English
Page 12
TOOLS NEEDED
The following tools (not included or drawn to scale) are needed for assembly and making adjustments:
PHILLIPS
SCREWDRIVER
FRAMING SQUARE
13mm WRENCH
FLATHEAD
SCREWDRIVER
COMBINATION
SQUARE
C-CLAMPS
SOCKET WRENCH
AND SOCKETS (8 mm
and 13 mm)
Fig. 4
12 - English
Page 13
LOOSE PARTS
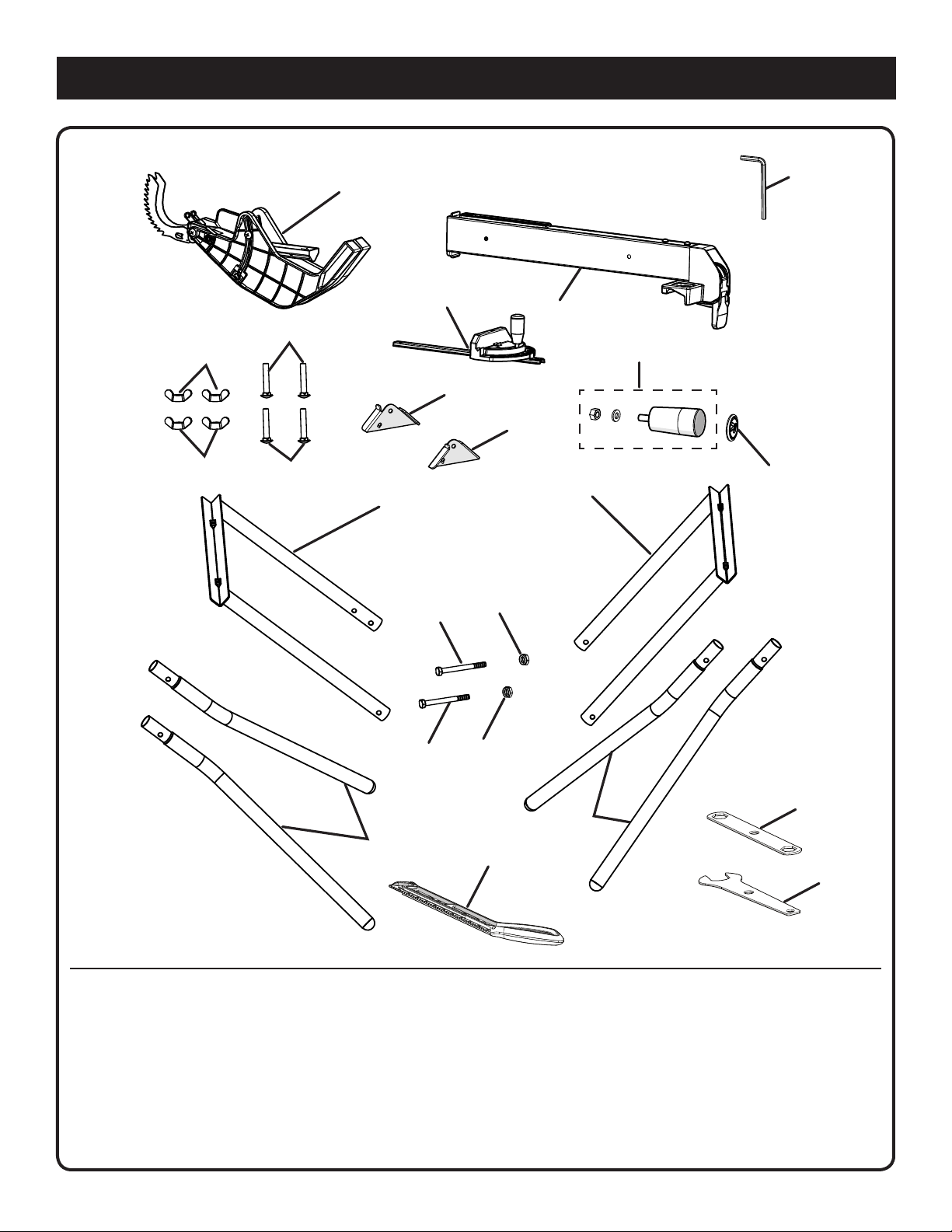
The following items are included with your table saw:
A
M
L
F
B
E
C
G
H
L
M
J
N
N
K
O
O
P
I
K
D
Q
R
A. Blade Guard with anti-kickback pawls .................... 1
B. Miter Gauge ............................................................. 1
C. Handle Assembly ..................................................... 1
D. Handle End Cap ....................................................... 1
E. Rip Fence ................................................................. 1
F. Hex Key (5 mm) ....................................................... 1
G. Stand hinge (F) ......................................................... 1
H. Stand hinge (R) ........................................................ 1
I. Support bracket (outside) ........................................ 1
13 - English
Fig. 5
J. Support bracket (inside)........................................... 1
K. Stand legs ................................................................ 4
L. Wing Nuts ................................................................ 4
M. Carriage Bolts .......................................................... 4
N. Leg Stand Bolts ....................................................... 2
O. Hex Nuts .................................................................. 2
P. Push Stick ................................................................ 1
Q. Closed End Wrench ................................................. 1
R. Open End Wrench .................................................... 1
Page 14
ASSEMBLY
UNPACKING
This product requires assembly.
Carefully lift saw from the carton and place it on a level
work surface.
NOTE: This tool is heavy. To avoid back injury, keep your
knees bent and lift with your legs, not your back, and get
help when needed.
WARNING:
Do not use this product if any parts on the Loose Parts List
are already assembled to your product when you unpack
it. Parts on this list are not assembled to the product by
the manufacturer and require customer installation. Use
of a product that may have been improperly assembled
could result in serious personal injury.
Inspect the tool carefully to make sure no breakage or
damage occurred during shipping.
Do not discard the packing material until you have
carefully inspected the tool, identified all loose parts, and
satisfactorily operated the tool.
The saw is factory set for accurate cutting. After
assembling it, check for accuracy. If shipping has
influenced the settings, refer to specific procedures
explained in this manual.
If any parts are damaged or missing, please call
1-800-525-2579 for assistance.
WARNING:
If any parts are damaged or missing, do not operate this
tool until the parts are replaced. Use of this with damaged
or missing parts could result in serious personal injury.
WARNING:
Do not connect to power supply until assembly is
complete. Failure to comply could result in accidental
starting and possible serious personal injury.
WARNING:
Never stand directly in line with the blade or allow hands
to come closer than 3 in. to the blade. Do not reach over
or across the blade. Failure to heed this warning can
result in serious personal injury.
WARNING:
To avoid serious personal injury, always make sure the
table saw is securely mounted to a workbench or an
approved leg stand. NEVER operate the saw on the floor.
MOUNTING HOLES
The table saw must be mounted to a firm supporting surface
such as a workbench or leg stand. Four bolt holes have been
provided in the saw’s frame for this purpose.
To mount the saw to a work bench, insert bolts that are
of sufficient length to accommodate the saw base, lock
washers, hex nuts, and the thickness of the workbench or
other mounting surface. Tighten all bolts or screws securely.
Carefully check the workbench after mounting to make sure
that no movement can occur during use. If any tipping,
sliding, or walking is noted, secure the workbench to the
floor before operating.
To mount the saw to the leg stand, refer to specific
procedures explained later in this section.
WARNING:
Do not attempt to modify this tool or create accessories
not recommended for use with this tool. Any such
alteration or modification is misuse and could result in a
hazardous condition leading to possible serious personal
injury.
14 - English
Page 15
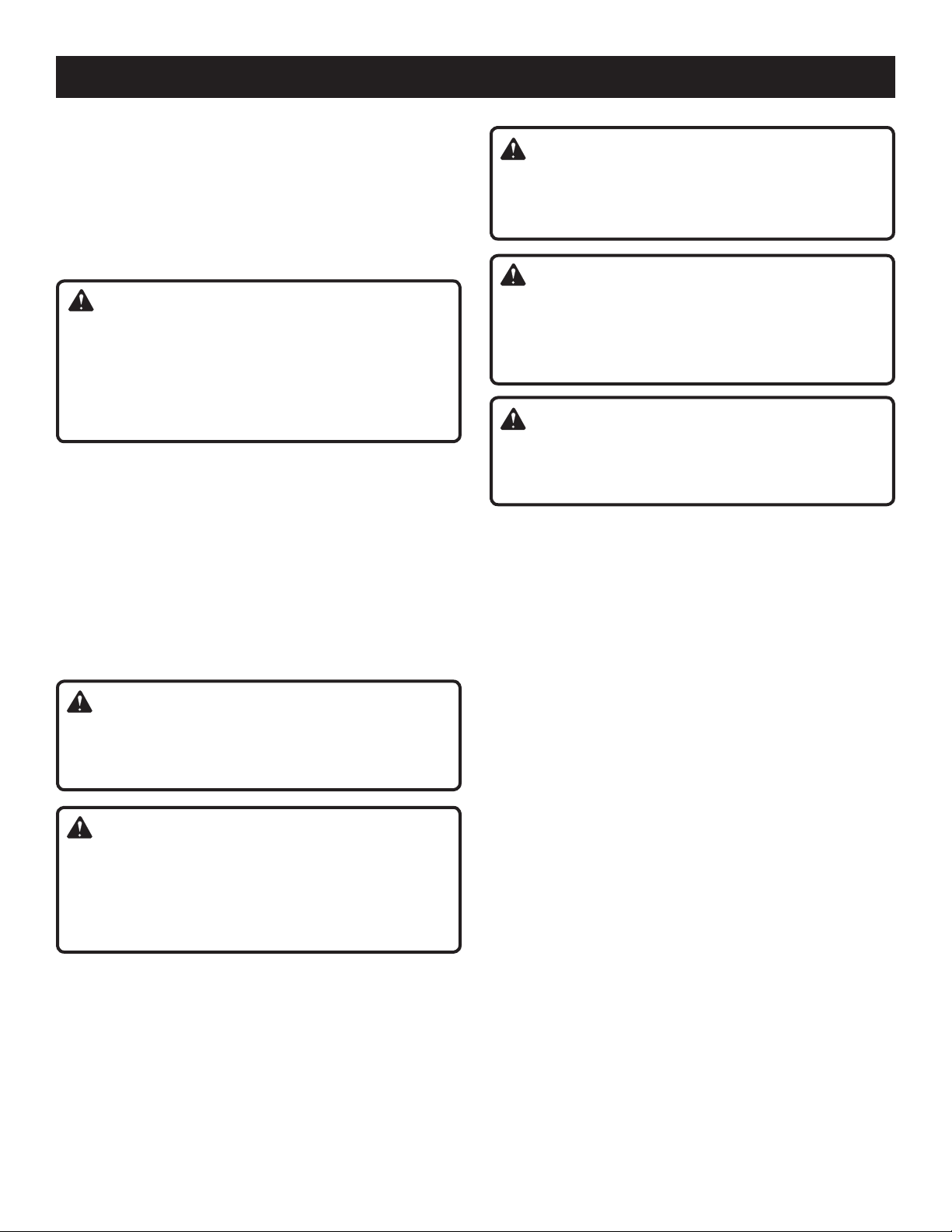
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLING THE STAND
See Figures 6 - 8.
NOTE: Do not use this leg stand with other equipment or
for other purposes.
Lay outside support bracket, on a flat surface. Place inside
support bracket on top of outside support bracket with
the top rails facing each other.
Insert stand legs into the support brackets. Angled ends
of stand legs should face away from each other so they
resemble a “V”.
Place hinge R between leg assembly on right side. Repeat
with hinge F on left side.
Carefully align holes in legs and hinge. Install hardware
through holes.Tighten hardware securely.
INSIDE
SUPPORT
BRACKET
STAND LEG
MOUNTING THE TABLE SAW TO THE LEG
STAND
See Figure 9.
WARNING:
Do not lift the saw without help. The saw weighs
approximately 55 lbs. Hold it close to your body. Keep
your knees bent and lift with your legs, not your back.
Ignoring these precautions can result in back injury.
Place the stand on level ground and open to its fully
extended position.
Position the table saw onto the stand so that the holes in
the saw’s frame are aligned with the holes in the stand’s
brackets.
NOTE: Make sure the table saw’s frame is flush against
the stand and that all the stand legs are touching the
ground.
Install leg stand bolts through the holes in the brackets
and frame. Secure with wing nuts and tighten securely.
Be sure the table saw is on level ground and the stand is
sturdy before use.
OUTSIDE
SUPPORT
BRACKET
INSIDE
SUPPORT
BRACKET
OUTSIDE
SUPPORT
BRACKET
STAND
HINGE (F)
HOLES
STAND
HINGE (R)
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
INSIDE LEG
ASSEMBLY
HEX
NUT
STAND
BOLT
OUTSIDE LEG
ASSEMBLY
Fig. 8
WING
NUT
15 - English
LEG
STAND
BOLTS
Fig. 9
Page 16
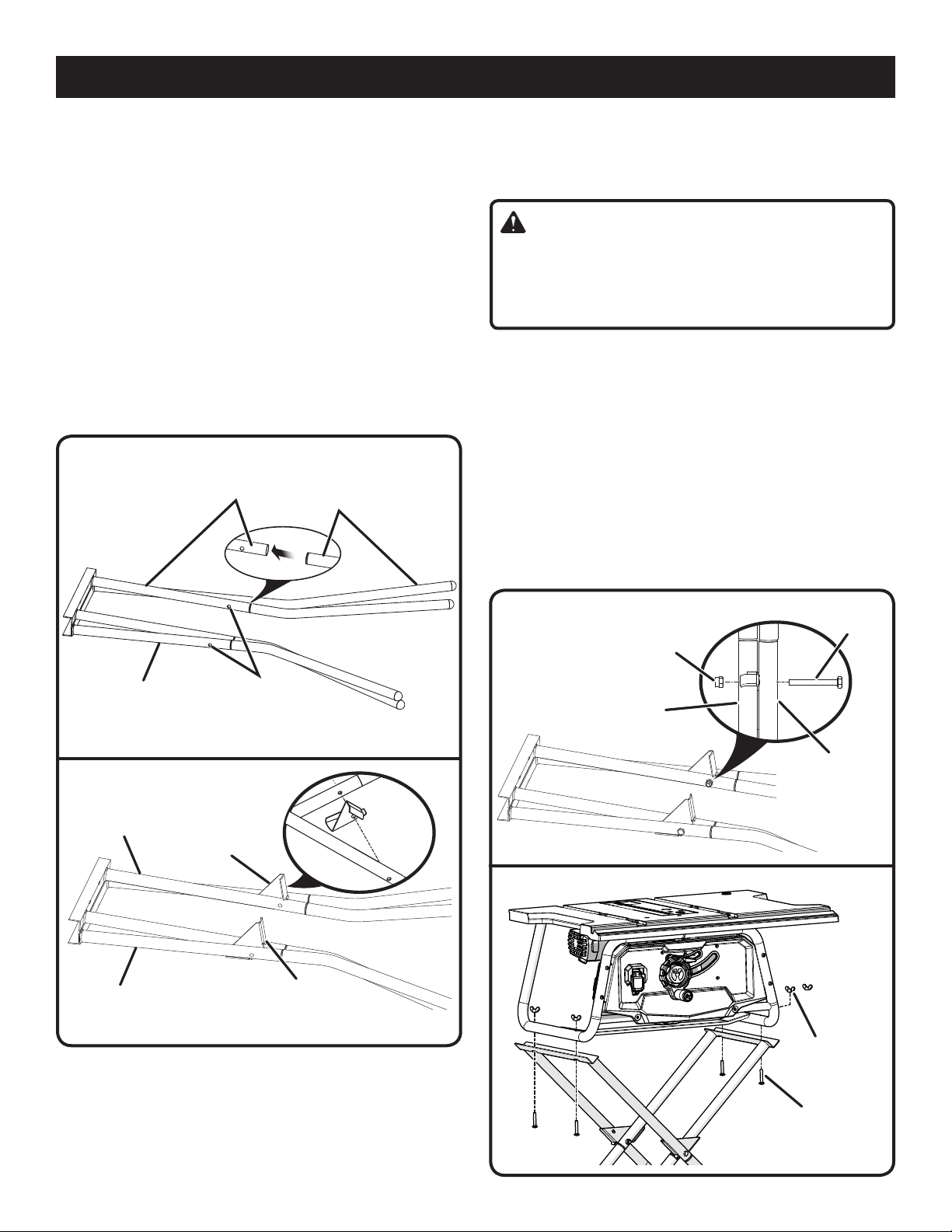
ASSEMBLY
INSTALLING THE HANDLE
See Figure 10.
Remove the hex nut from the bolt in the handle but do
not remove the bolt.
Slide a washer onto the bolt.
Place the nylon hex nut into the recessed hole on the
back of the height/bevel adjusting handwheel and hold
in place.
Insert the handle and screw into the hole on the height/
bevel adjusting handwheel.
Using a flathead screwdriver, turn the screw clockwise
and tighten in place.
Cover the end of the handle with the cap.
REMOVING/REINSTALLING THE THROAT
PLATE
See Figure 11.
Lower the blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting
handwheel counterclockwise.
To remove the throat plate, locate the latch that holds the
plate in place. Place your thumb and index finger into the
holes and pull together until the latch releases. Lift and
pull the throat plate out toward the front of the saw.
To reinstall the throat plate, first slip the tab into the slot
at the back of the saw. Place your fingers into the holes
and pull together. Push down to secure in place.
NUT
WASHER
BOLT
HEIGHT/BEVEL
ADJUSTING
HANDWHEEL
HANDLE
HANDLE
END CAP
Fig. 10
THROAT
PLATE
16 - English
RIVING
KNIFE
Fig. 11
Page 17
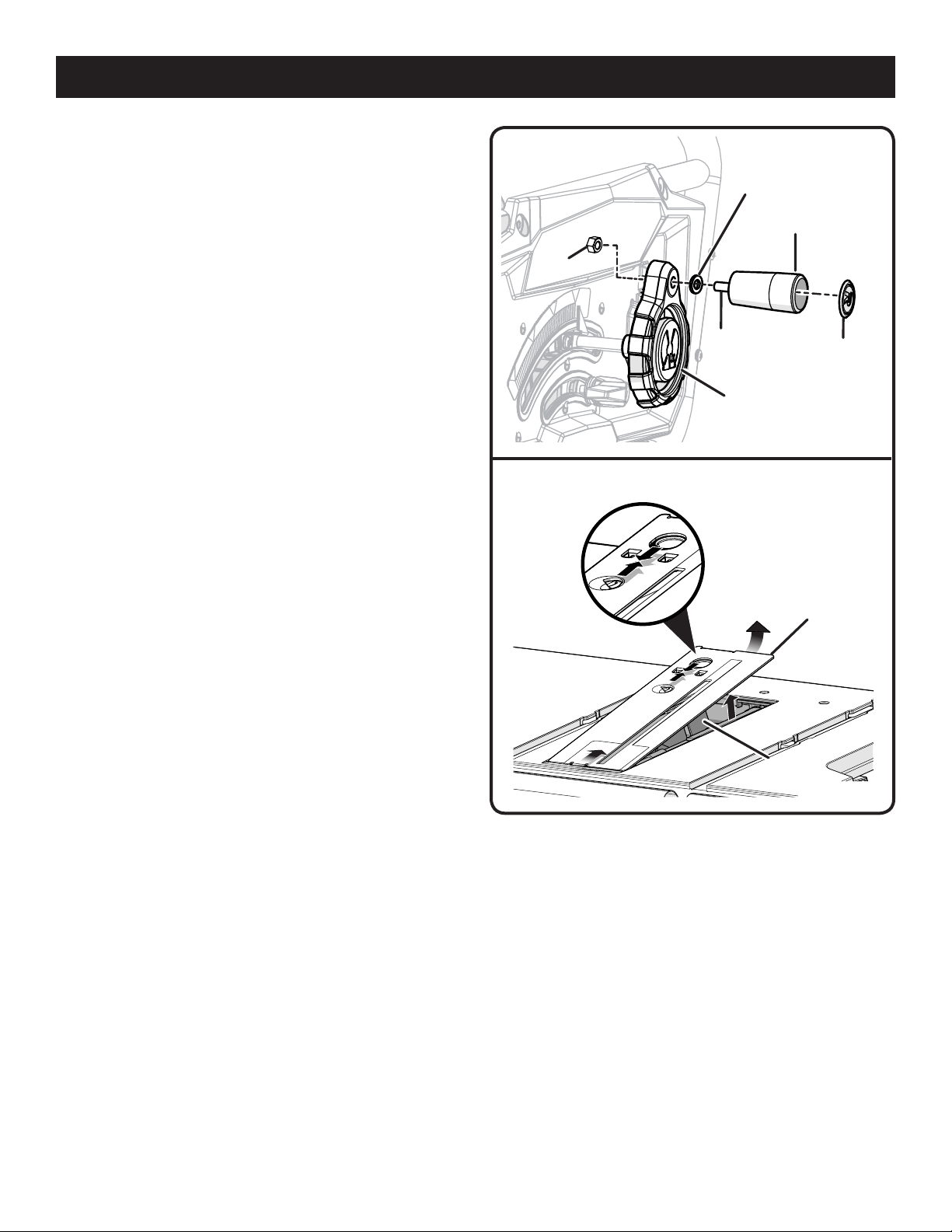
ASSEMBLY
CHANGING RIVING KNIFE POSITIONS
See Figure 12.
This saw is shipped with a riving knife that should be placed
in the “down” position for non-through cutting and must be
placed in the “up” position for all other cutting operations.
Unplug the saw.
To place in the “up” position for all through cutting:
Remove the throat plate.
Raise the saw blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting
handwheel clockwise.
Unlock the release lever by pulling it up.
Grasp the riving knife and pull it towards the right side of
the saw to release the riving knife from the spring-loaded
riving clamp.
Pull the riving knife up until the internal pins are engaged
and the riving knife is above the saw blade.
Lock the release lever by pushing the lever down.
Reinstall the throat plate.
To place in riving knife “down” position for all nonthrough cutting:
Remove the throat plate.
Raise the saw blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting
handwheel clockwise.
Unlock the release lever by pulling it up.
Grasp the riving knife and pull it towards the right side of
the saw to release the riving knife from the spring-loaded
riving clamp.
Push the riving knife down until it is below the saw blade.
Pull the riving knife up until the internal pins are engaged
and the riving knife is above the saw blade.
Lock the release lever by pushing the lever down.
Reinstall the throat plate.
RELEASE
LEVER
(UNLOCKED)
IN “UP” POSITION FOR THROUGH CUTTING
RELEASE
LEVER
(LOCKED)
IN “DOWN” POSITION FOR NON-THROUGH CUTTING
17 - English
Fig. 12
Page 18
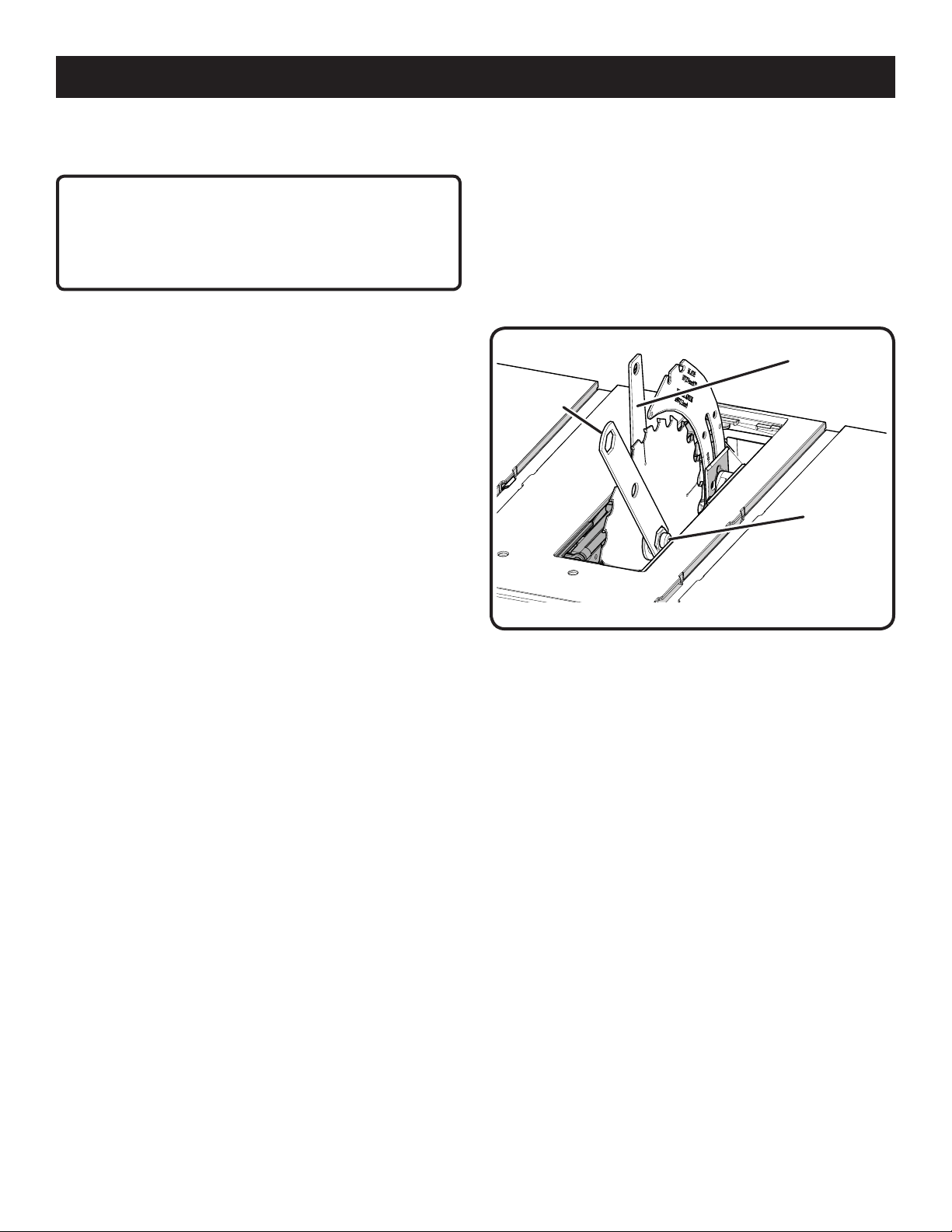
ASSEMBLY
CHECKING SAW BLADE INSTALLATION
See Figure 13.
NOTICE:
To work properly, the saw blade teeth must point down
toward the front of the saw. Failure to heed this warning
could cause damage to the saw blade, the saw, or the
workpiece.
Unplug the saw.
Lower the saw blade and remove the throat plate.
Make sure the bevel locking lever is securely pushed to
the left. (See figure 26.) Raise the saw blade to its full
height by turning the height/bevel adjusting handwheel
clockwise.
Place riving knife in the “up” position.
To loosen the blade:
Remove the blade wrench from the blade wrench storage
area.
Using blade wrenches, place the flat open end of a blade
wrench on the flats on the arbor shaft.
Insert the closed end of the blade wrench over the blade
nut. Holding both wrenches firmly, pull the wrench (right
side) forward to the front of the machine.
To tighten the blade:
Using the blade wrench, place the flat open end into the
flats on the arbor shaft.
Insert the closed end of the blade wrench over the blade
nut. Holding both wrenches firmly, push the wrench (right
side) to the back of the machine. Make sure the blade
nut is securely tightened. Do not overtighten.
Reinstall the throat plate.
Check all clearances for free blade rotation.
BLADE
WRENCH
BLADE
WRENCH
BLADE
NUT
Fig. 13
18 - English
Page 19
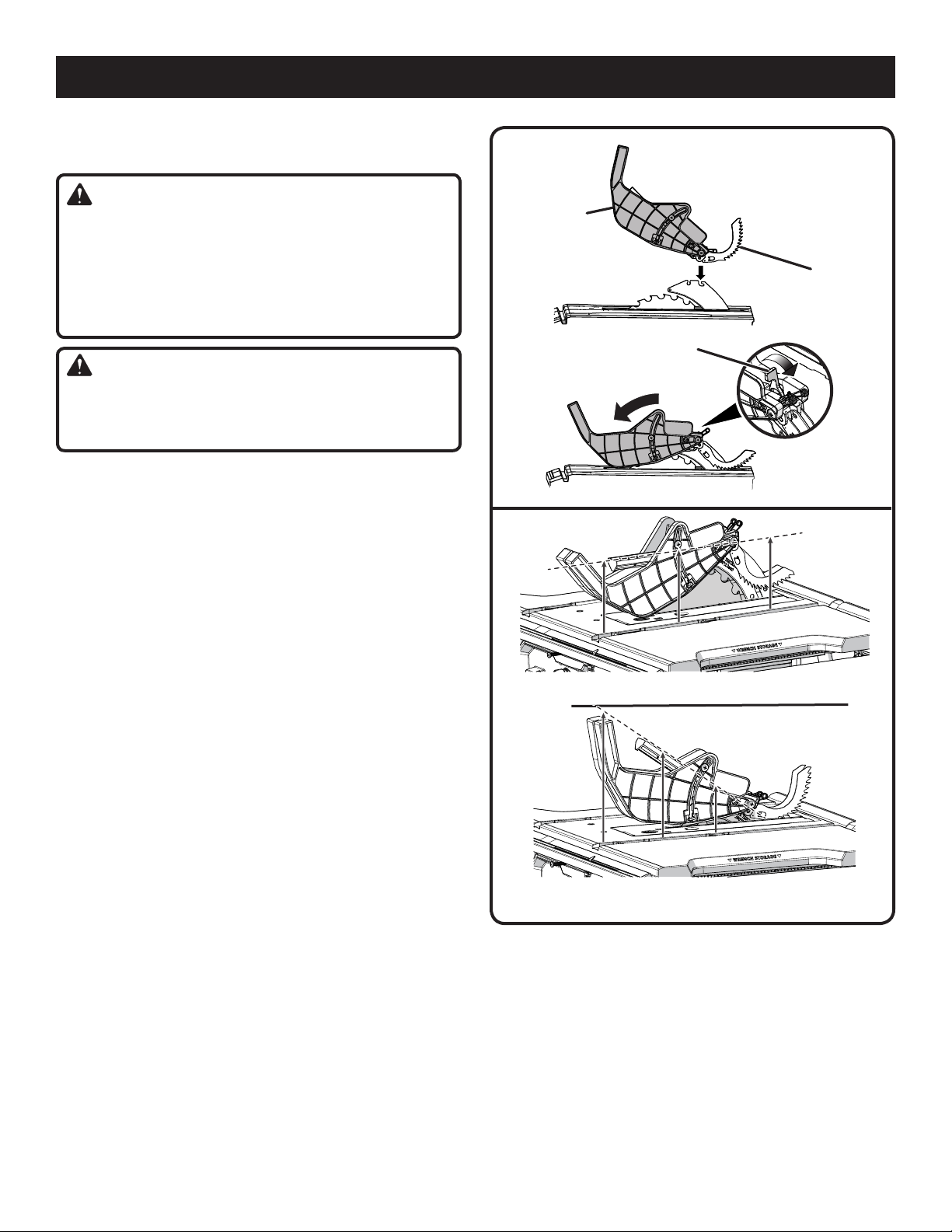
ASSEMBLY
INSTALLING THE BLADE GUARD
See Figures 14 - 15.
WARNING:
Always install the blade guard onto the riving knife in
the “up” position to provide proper blade coverage.
Installing the guarding components onto the riving knife
in any other position will prevent them from working
as designed, which could increase the risk of serious
personal injury.
WARNING:
Replace the blade guard if the anti-kickback pawls are
dull or damaged. Dull or damaged pawls may not stop
a kickback increasing the risk of serious personal injury.
Anti-kickback pawls are part of the blade guard for this saw.
They should only be used for through cuts. When not needed,
they may be positioned to be out of the way.
Unplug the saw.
Raise the saw blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting
handwheel clockwise.
Place riving knife in “up” position.
Reinstall the throat plate.
To install blade guard:
Lift the guard lever up to unlock.
With the front of the blade guard raised, lower the back
of the guard into the riving knife in the position shown.
Push the front of the guard down until it is parallel to the
table (see figure 15). If the blade guard is not parallel to
the table, the riving knife is not in the “up” position.
Lock the guard in place by pushing the guard lever down.
The blade guard side barriers may be lifted and folded
back, then positioned out of the way without being
removed for easier measurement.
NOTE: Blade alignment can be adjusted for different blade
widths. Refer to: To Check and Align the Riving Knife and
Saw Blade. Check the blade guard assembly for clearances
and free movement.
BLADE
GUARD
GUARD
LEVER
CORRECT
INCORRECT
ANTI-
KICKBACK
PAWLS
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
19 - English
Page 20
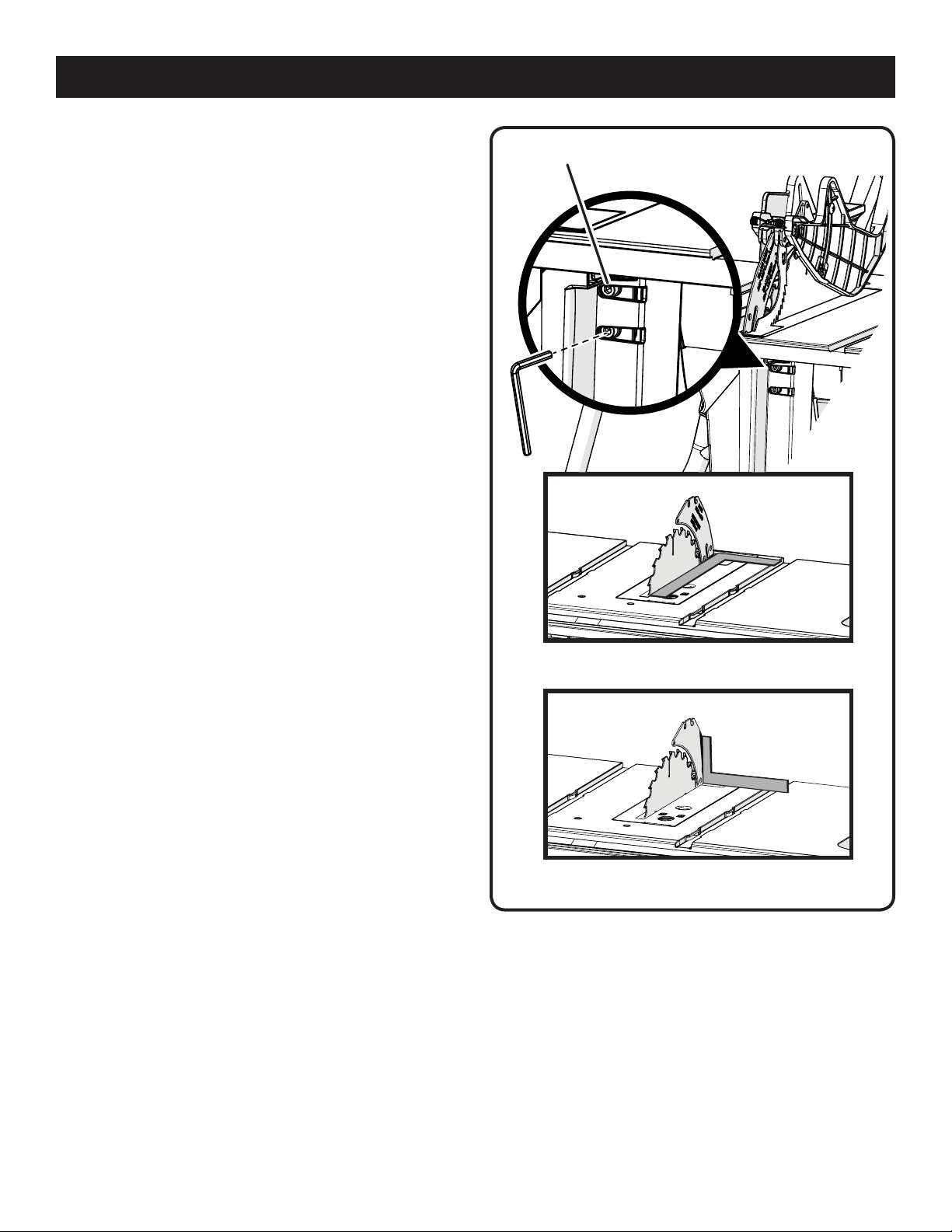
ASSEMBLY
TO CHECK AND ALIGN THE RIVING KNIFE
AND SAW BLADE
See Figure 16.
To check alignment of the riving knife:
Unplug the saw.
Raise the saw blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting
handwheel clockwise.
Remove the blade guard. Place a framing square or
straight edge against both the saw blade and the riving
knife.
NOTE: Place framing square between carbide teeth and
measure from blade. This step will insure framing square
is square against blade from the front to back of blade.
The saw blade and riving knife are aligned when the
framing square contacts both the blade and riving knife
evenly with no gaps.
If the riving knife is out of alignment with the saw blade,
adjustment is needed. The riving knife must be in alignment
front to back (horizontally) and top to bottom (vertically).
To adjust (horizontally and vertically):
Remove the blade guard.
From the back of the saw, loosen the screws holding the
mounting bracket.
Reposition the riving knife left or right as needed to align
the riving knife with the saw blade.
Once properly aligned, securely retighten all screws.
Check again for squareness and continue to adjust if
needed.
SCREWS
HORIZONTAL
ADJUSTMENT
20 - English
VERTICAL
ADJUSTMENT
Fig. 16
Page 21
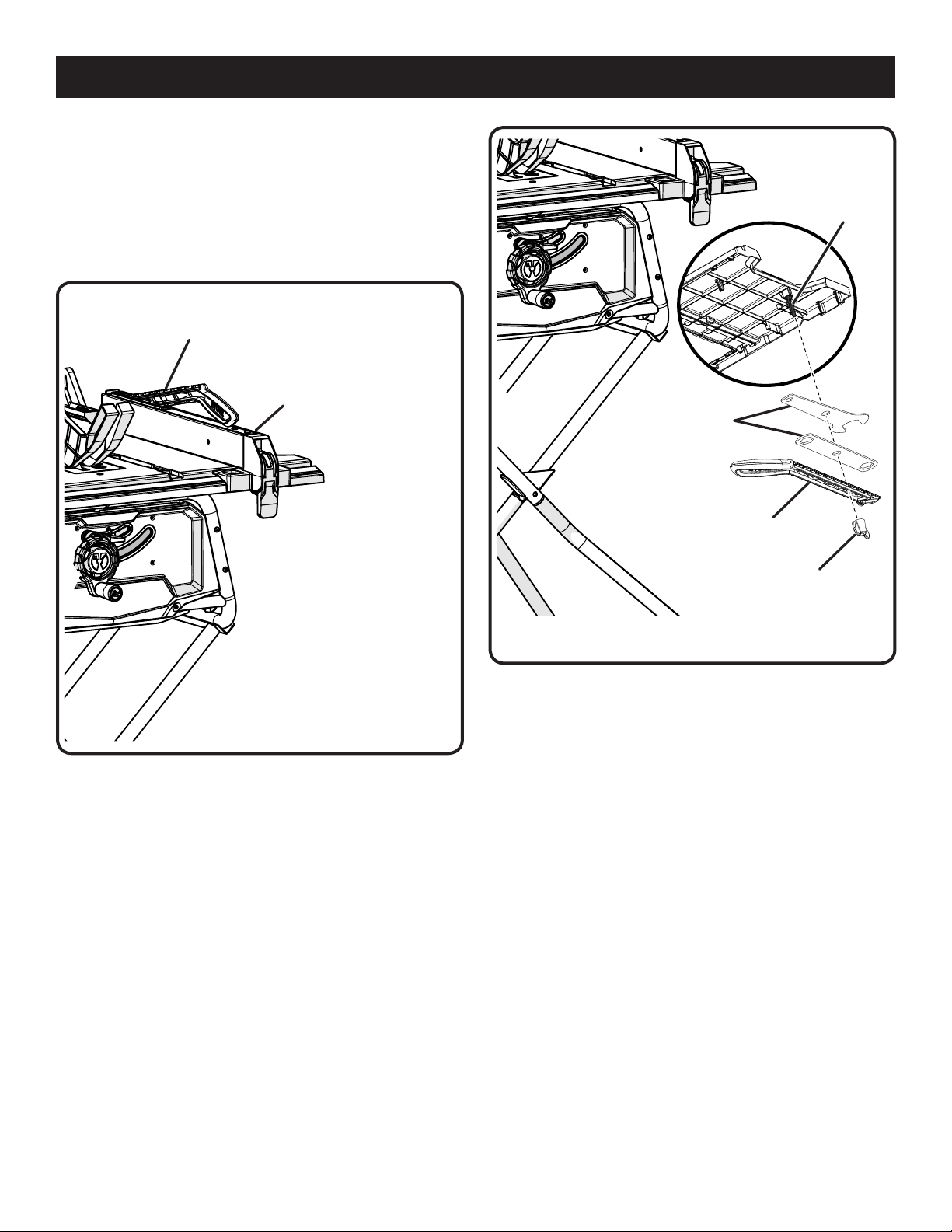
ASSEMBLY
STORING TABLE SAW ACCESSORIES
See Figures 17 and 18.
When not in use, wrenches and the push stick may be stored
on the underside of the saw table, secured by a wing nut.
Additional storage for the push stick is located on top of the
rip fence. To use the storage area, insert the tip of the push
stick into the slot until it clicks into place.
PUSH STICK
STORAGE
RIP
FENCE
BLADE
WRENCH
STORAGE
BLADE
WRENCHES
PUSH
STICK
Fig. 17
WING
NUT
Fig. 18
21 - English
Page 22
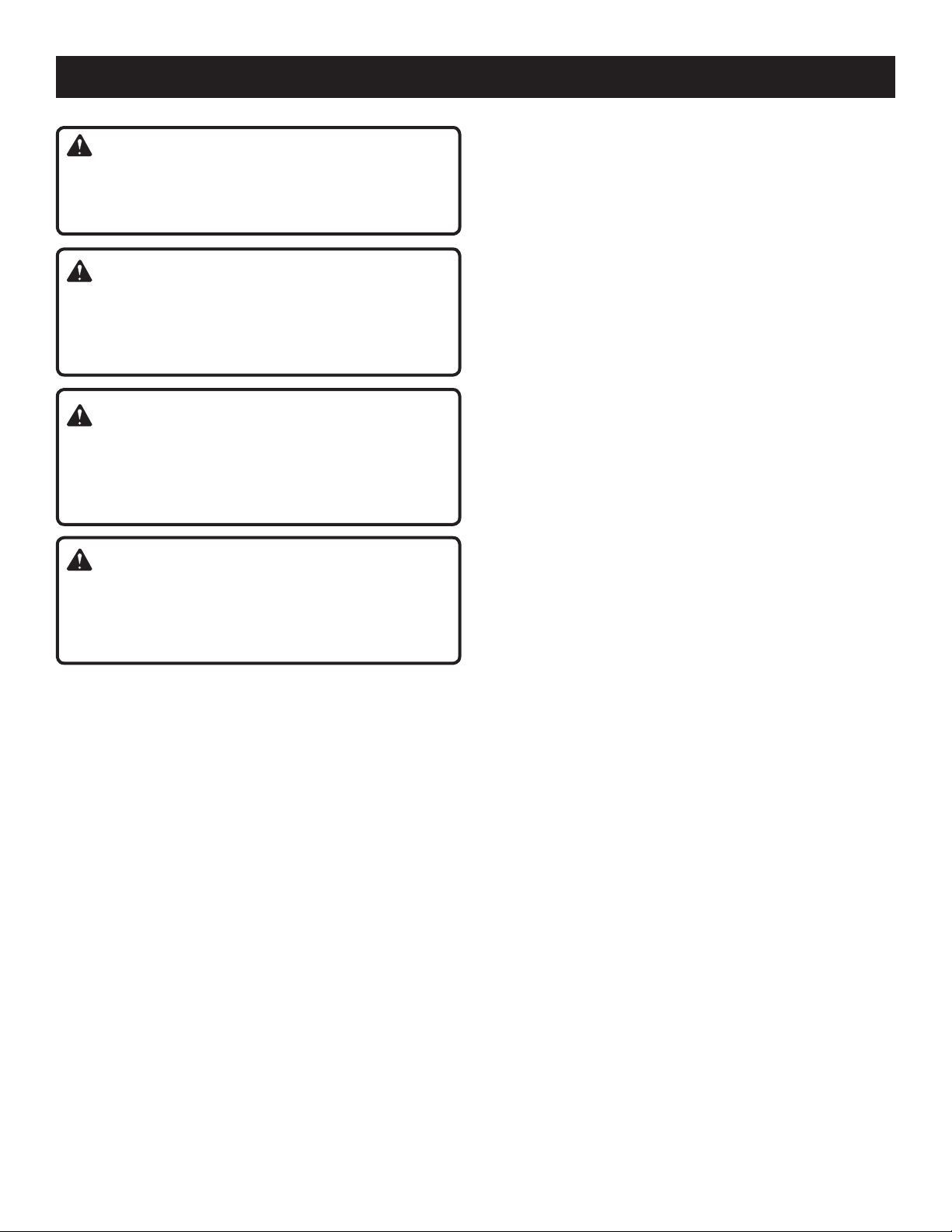
OPERATION
WARNING:
Do not allow familiarity with tools to make you careless.
Remember that a careless fraction of a second is
sufficient to inflict severe injury.
WARNING:
Always wear eye protection with side shields marked to
comply with ANSI Z87.1. Failure to do so could result in
objects being thrown into your eyes, resulting in possible
serious injury.
WARNING:
Do not use any attachments or accessories not
recommended by the manufacturer of this tool. The use
of attachments or accessories not recommended can
result in serious personal injury.
WARNING:
Although many of the illustrations in this manual are
shown with the blade guard removed for clarity, do
not operate the saw without the blade guard unless
specifically instructed to do so.
APPLICATIONS
You may use this tool for the purposes listed below:
Straight line cutting operations such as cross cutting,
ripping, mitering, beveling, and compound cutting
Dado with optional accessories
Cabinet making and woodworking
NOTE: This table saw is designed to cut wood and wood
composition products only.
BASIC OPERATION OF THE TABLE SAW
The 3-prong plug must be plugged into a matching outlet
that is properly installed and grounded according to all
local codes and ordinances. Improper connection of the
equipment can result in electric shock. Do not modify the
plug if it will not fit the outlet. Have the correct outlet installed
by a qualified electrician. Refer to the Electrical section in
this manual.
CAUSES OF KICKBACK
Kickback can occur when the blade stalls or binds, kicking
the workpiece back toward you with great force and speed. If
your hands are near the saw blade, they may be jerked loose
from the workpiece and may contact the blade. Obviously,
kickback can cause serious injury, and it is well worth using
precautions to avoid the risks.
22 - English
Kickback can be caused by any action that pinches the
blade in the wood such as:
Making a cut with incorrect blade depth
Sawing into knots or nails in the workpiece
Twisting the wood while making a cut
Failing to support work
Forcing a cut
Cutting warped or wet lumber
Using the wrong blade for the type of cut
Not following correct operating procedures
Misusing the saw
Failing to use the anti-kickback pawls
Cutting with a dull, gummed-up, or improperly set blade
AVOIDING KICKBACK
Always use the correct blade depth setting. The top of
the blade teeth should clear the workpiece by 1/8 in. to
1/4 in.
Inspect the work for knots or nails before beginning a
cut. Knock out any loose knots with a hammer. Never
saw into a loose knot or nail.
Always use the rip fence when rip cutting. Use the miter
gauge when cross cutting. This helps prevent twisting
the wood in the cut.
Always use clean, sharp, and properly-set blades. Never
make cuts with dull blades.
To avoid pinching the blade, support the work properly
before beginning a cut.
When making a cut, use steady, even pressure. Never
force cuts.
Do not cut wet or warped lumber.
Use extra caution when cutting some prefinished or
composition wood products as the anti-kickback pawls
may not always be effective.
Always guide your workpiece with both hands or with
push sticks and/or push blocks. Keep your body in a
balanced position to be ready to resist kickback should
it occur. Never stand directly in line with the blade.
Use of a featherboard will help hold the workpiece securely
against the saw table or fence.
Clean the saw, blade guard, under the throat plate, and
any areas where saw dust or scrap workpieces may gather.
Use the right type of blade for the cut being made.
Always use the riving knife for every operation where it
is allowed. The use of this device will greatly reduce the
risk of kickback.
Page 23
OPERATION
3/4 in.
3 1/2 in.
21 in.
CUTTING AIDS
See Figure 19.
Push sticks are devices that may be used for pushing a
workpiece through the blade in any rip cut. When making
non-through cuts or ripping narrow stock, always use a
push stick, push block, and/or featherboard so your hands
do not come within 3 inches of the saw blade. They can be
made in various sizes and shapes from scrap wood and
used in a specific project. The stick must be narrower than
the workpiece, with a 90˚ notch in one end and shaping for
a grip on the other end.
A push block has a handle fastened by recessed screws
from the underside. Use push blocks for narrow cuts and
all non-through cuts.
PUSH STICKS
PUSH BLOCKS
CAUTION:
Be sure the screws in a push block are recessed to avoid
damaging the saw or workpiece.
AUXILIARY FENCE
An auxiliary fence is a device used to close the gap between
the rip fence and the saw table. Always make and use and
auxiliary fence when ripping material 1/8 in. or thinner.
HOW TO MAKE AND ATTACH AN AUXILIARY
FENCE (FOR RIP CUTTING THIN
WORKPIECE)
See Figure 20.
Rip fence holes are used to secure an auxiliary fence which
requires a piece of wood 3/4 in. thick, 3-1/2 in. wide, and
21 in. long to make.
To attach the auxiliary fence to the rip fence:
Place the wood against the rip fence and resting firmly
on the saw table.
From the back side of the rip fence, secure the wood to
the fence using 1-3/4 in. wood screws.
Fig. 19
Fig. 20
STOP
JIG
HANDLE
HOW TO MAKE A JIG (FOR RIP CUTTING
NARROW WORKPIECE)
See Figure 21.
If ripping a narrow workpiece places the hands too close to
the blade, it will be necessary to make and use a jig.
To make a jig:
Attach a handle to a long, straight piece of wood and
secure from the underside using recessed screws.
Cut an L-shaped stop in the side of the jig.
To use a jig:
Position the workpiece flat on the table with the edge
flush against the jig and against the stop.
Holding the jig handle and using a push block and/or push
stick, make the rip cut as described on page 31 later in
this section.
23 - English
JIG
Fig. 21
Page 24
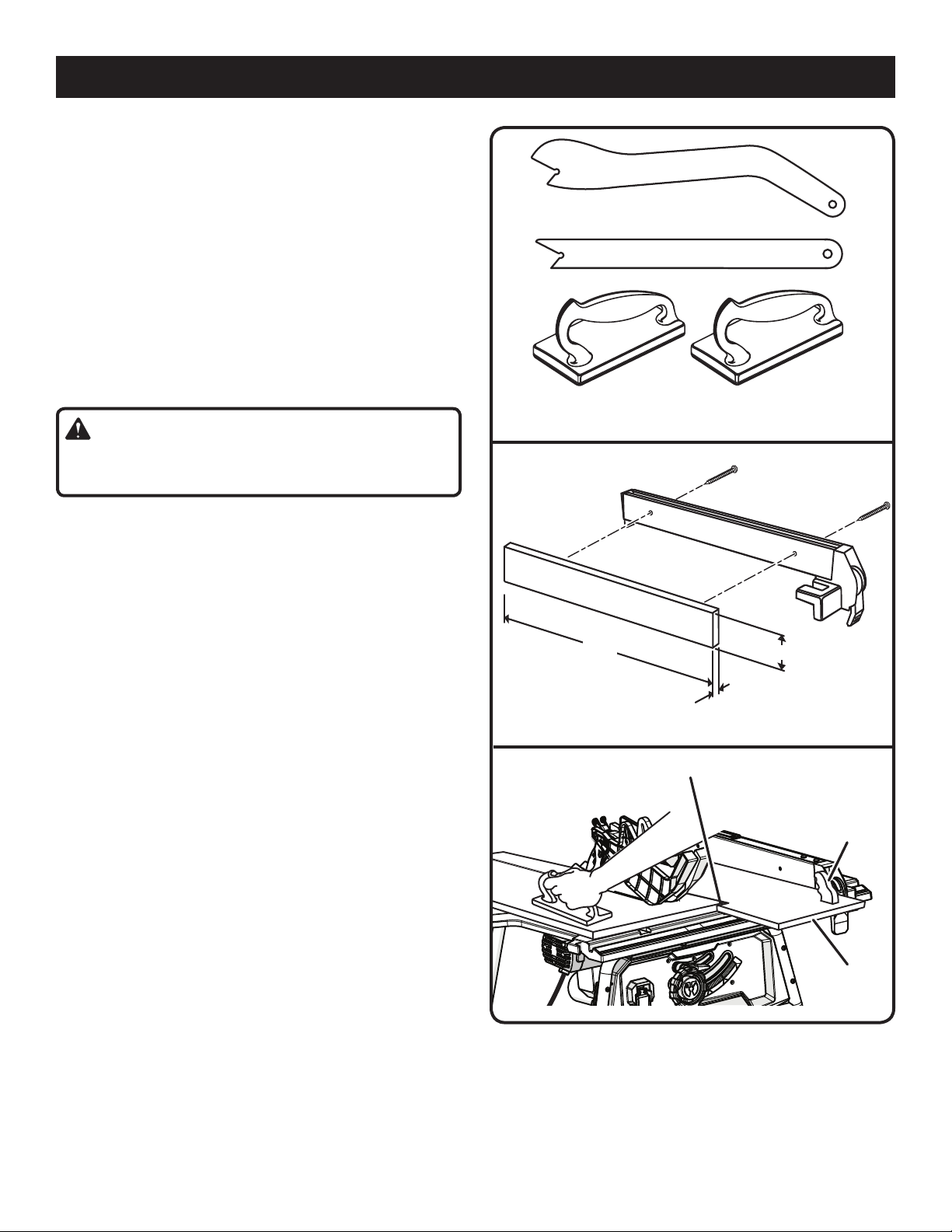
OPERATION
2 1/2 in.
12 in.
3/4 in.
4 in.
1/4 in.
1/8 in.
70°
FEATHERBOARD
A featherboard is a device used to help control the
workpiece by holding it securely against the table or fence.
Featherboards are especially useful when ripping small
workpieces and for completing non-through cuts. The end
is angled with a number of short kerfs to give a friction hold
on the workpiece and locked in place on the table with a
C-clamp. Test to ensure it can resist kickback.
WARNING:
Place the featherboard against the uncut portion of the
workpiece to avoid kickback that could cause serious
personal injury.
HOW TO MAKE A FEATHERBOARD
See Figure 22.
The featherboard is an excellent project for the saw. Select
a solid piece of lumber approximately 3/4 in. thick, 2-1/2 in.
wide and 12 in. long. Mark the center of the width on one
end of the stock. Miter the width to 70° (see page 32 for
information on miter cuts). Mark the board from the widest
point at four inches.
Prepare the saw for ripping as discussed on page 31. Set the
rip fence to allow approximately a 1/4 in. “finger” to be cut in
the stock. Feed the stock only to the mark previously made at
4 in. Turn the saw OFF and allow the blade to completely stop
rotating before removing the stock. Reset the rip fence and
cut spaced rips into the workpiece to allow approximately
1/4 in. fingers and 1/8 in. spaces between the fingers.
Place the workpiece against the fence and over the saw
blade area. Adjust the featherboard to apply resistance to
the workpiece just forward of the blade. Attach C-clamps to
further secure the featherboard to the edge of the saw table.
WARNING:
Do not locate the featherboard to the rear of the
workpiece. If positioned improperly, kickback can result
from the featherboard pinching the workpiece and
binding the blade in the saw kerf. Failure to heed this
warning can result in serious personal injury.
PUSH
BLOCK
PUSH
STICK
BEVEL
LOCKING
LEVER
FEATHERBOARD
Fig. 23
HOW TO MOUNT A FEATHERBOARD
See Figure 23.
Completely lower the saw blade. Position the rip fence to
the desired adjustment for the cut to be performed and lock.
Fig. 22
24 - English
Page 25
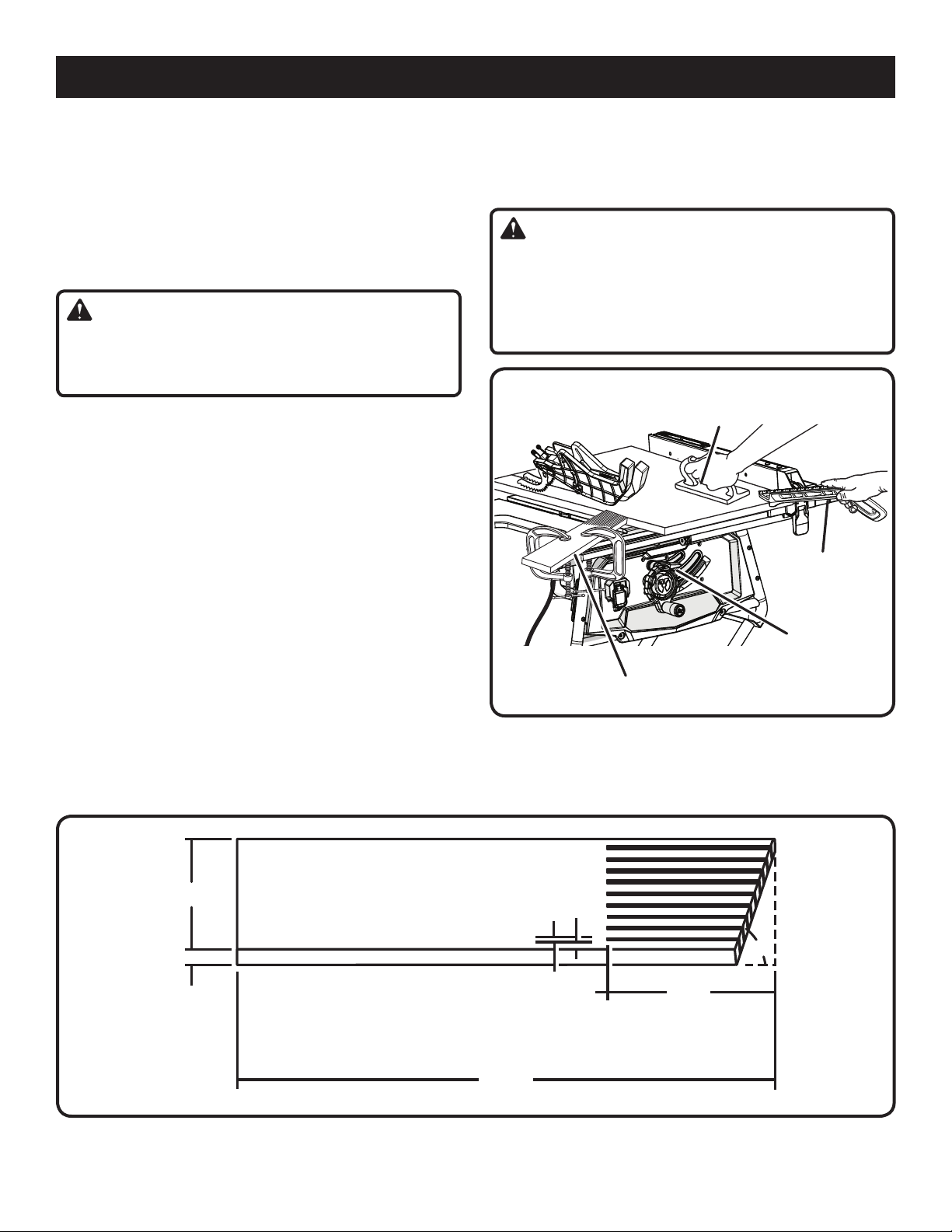
OPERATION
TYPES OF CUTS
See Figure 24.
There are six basic cuts: 1) the cross cut, 2) the rip cut, 3)
the miter cut, 4) the bevel cross cut, 5) the bevel rip cut,
and 6) the compound (bevel) miter cut. All other cuts are
combinations of these basic six. Operating procedures for
making each kind of cut are given later in this section.
WARNING:
Always make sure the blade guard is in place and working
properly when making these cuts to avoid possible injury.
1
CROSS CUT
2
Cross cuts are straight 90° cuts made across the grain of
the workpiece. The wood is fed into the cut at a 90° angle
to the blade, and the blade is vertical.
Rip cuts are made with the grain of the wood. To avoid
kickback while making a rip cut, make sure one side of the
wood rides firmly against the rip fence.
Miter cuts are made with the wood at any angle to the
blade other than 90°. The blade is vertical. Miter cuts tend
to “creep” during cutting. This can be controlled by holding
the workpiece securely against the miter gauge.
WARNING:
Always use a push stick with small pieces of wood, and
also to finish the cut when ripping a long narrow piece
of wood, to prevent your hands from getting close to the
blade.
Bevel cuts are made with an angled blade. Bevel cross cuts
are across the wood grain, and bevel rip cuts are with the
grain.
Compound (or bevel) miter cuts are made with an angled
blade on wood that is angled to the blade. Be thoroughly
familiar with making cross cuts, rip cuts, bevel cuts, and
miter cuts before trying a compound miter cut.
RIP CUT
3
MITER CUT
4
BEVEL CROSS CUT
5
BEVEL RIP CUT
CUTTING TIPS
Dado and rabbet cuts are non-through cuts which can be
either rip cuts or cross cuts. Carefully read and understand
all sections of this operator’s manual before attempting any
operation.
WARNING:
Do not use blades rated less than the speed of this tool.
Failure to heed this warning could result in personal injury.
The kerf (the cut made by the blade in the wood) will be
wider than the blade to avoid overheating or binding.
Make allowance for the kerf when measuring wood.
25 - English
6
COMPOUND (BEVEL) MITER CUT
Fig. 24
Make sure the kerf is made on the waste side of the
measuring line.
Cut the wood with the finish side up.
Knock out any loose knots with a hammer before making
the cut.
Always provide proper support for the wood as it comes
out of the saw.
Page 26
OPERATION
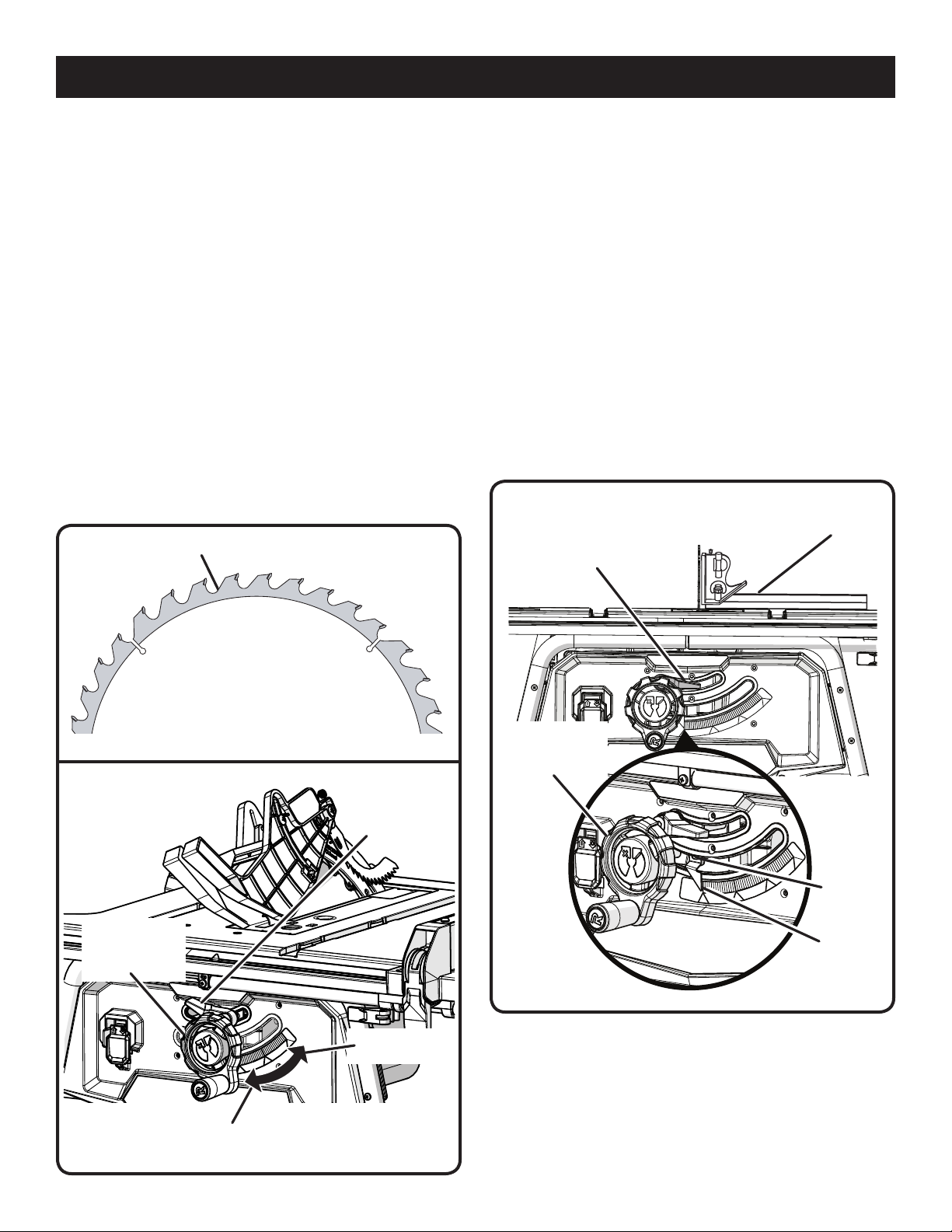
TO CHANGE BLADE DEPTH
See Figure 25.
The blade depth should be set so that the outer points of
the blade are higher than the workpiece by approximately
1/8 in. to 1/4 in. but the lowest points (gullets) are below
the top surface.
Turn the bevel lock lever to the right.
Raise the blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting
handwheel clockwise or lower it by turning the handwheel
counterclockwise.
TO CHANGE BLADE ANGLE (BEVEL)
See Figure 26.
This table saw has a rack and pinion bevel control that allows
you to make angled cuts from 90° to 45°.
NOTE: A 90° cut has a 0° bevel and a 45° cut has a 45° bevel.
Unplug the saw.
Loosen bevel control by turning bevel lock lever all the
way to the left. If it needs to be further loosened, pull
GULLET
spring-loaded bevel lock lever out and rotate it back to
the right. Release bevel locking lever and allow it to seat
(lock) in its original position. Turn it to the left again until
loose.
Move the height adjusting handwheel to the right to bevel
to 45° bevel angle.
Tighten bevel control by turning bevel lock lever to the
right. If it needs to be tightened more, pull the springloaded bevel lock lever out and rotate it to the left. Then
release bevel lock lever and allow it to return to its original
position. Rotate to the right again. Repeat this process
until bevel lock lever is securely tightened.
TO ADJUST THE BEVEL INDICATOR
See Figure 27.
If the bevel indicator is not at zero when the saw blade is at
90°, adjust the indicator by loosening the screw and setting
it at 0° on the bevel scale. Retighten the screw.
COMBINATION
BEVEL
LOCKING
LEVER
SQUARE
HEIGHT/BEVEL
ADJUSTING
HANDWHEEL
TO DECREASE
ANGLE
Fig. 25
BEVEL
LOCKING
LEVER
TO INCREASE
ANGLE
Fig. 26
HEIGHT/BEVEL
ADJUSTING
HANDWHEEL
SCREW
BEVEL
INDICATOR
Fig. 27
26 - English
Page 27
OPERATION
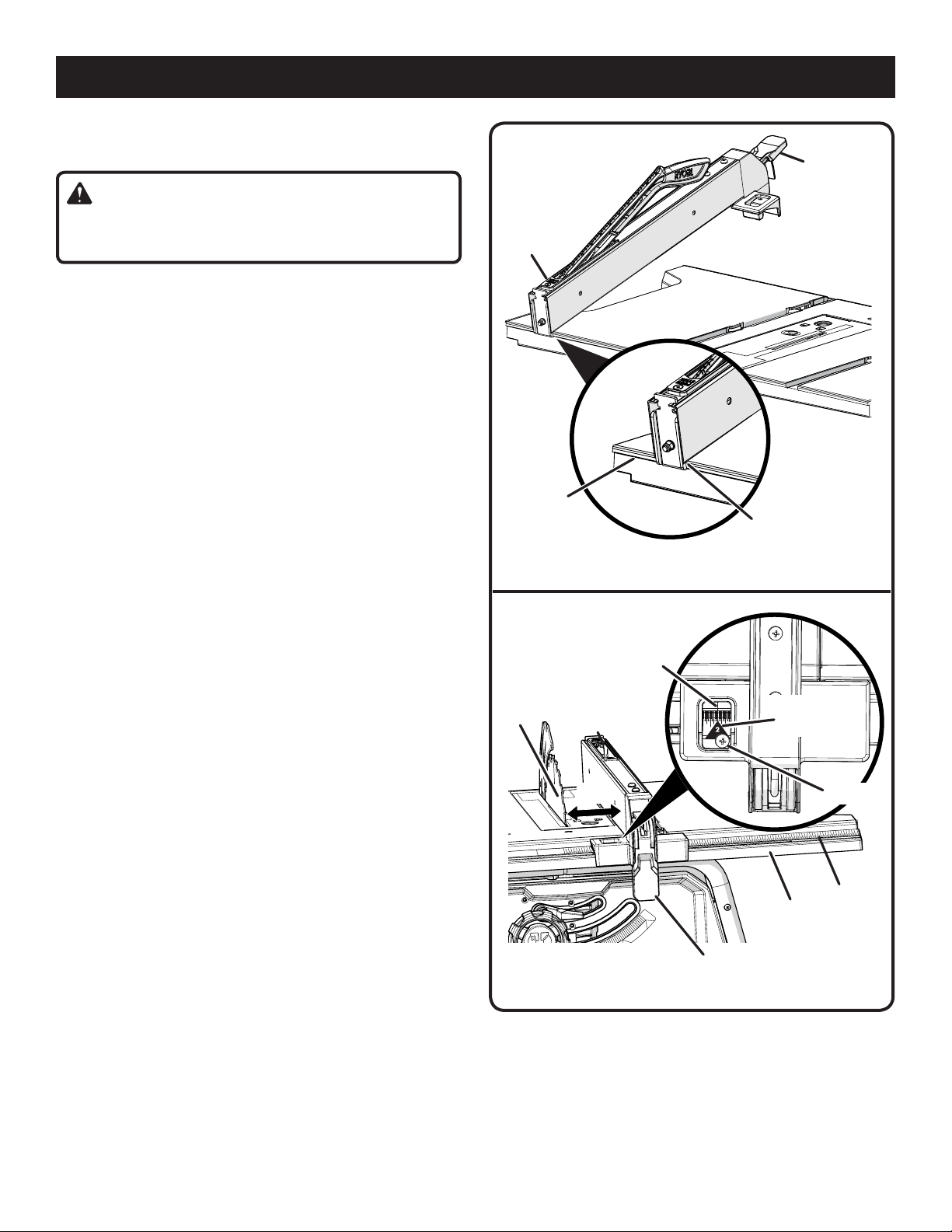
TO USE THE RIP FENCE
See Figure 28.
WARNING:
To reduce the risk of injury, always make sure the rip fence
is parallel to the blade before beginning any operation.
Loosen the rip fence by lifting the locking lever.
Place the rear lip on the rear of the saw table and pull
slightly toward the front of the unit.
Lower the front end of the rip fence onto the guide
surfaces on top of the front rail.
Check for smooth gliding action.
Position the rip fence the desired distance from the blade.
With the rip fence flat on the saw table, push the fence
towards the front rail to align the fence to the saw table.
Push the locking lever down to align and secure the
fence. When securely locked, the locking lever should
point downward.
Ensure the locking lever secures the rip fence in place. If
adjustments are needed, see To Check The Tightness Of
The Rip Fence Locking Lever in the Adjustment section
of this manual.
LOCKING
LEVER
RIP
FENCE
FRONT
RAIL
REAR
LIP
Fig. 28
TO SET THE RIP FENCE SCALE INDICATOR
TO THE BLADE
See Figure 29.
Use the indicator on the rip fence to position the fence along
the scale on the front rail.
NOTE: The blade guard must be removed to perform this
adjustment. Reinstall the blade guard when the adjustment
is complete.
Begin with the blade at a zero angle (straight up).
Unplug the saw.
Loosen the rip fence by lifting the locking lever.
Using a framing square, set the rip fence 2 in. from the
blade tip edge.
Loosen the screw on the scale indicator and align with
the 2 in. mark as shown.
Tighten the screw and check the dimension and the rip
fence.
BLADE
SCALE
INDICATOR
RIP
FENCE
2 in.
LOCKING
LEVER
2 in.
MARK
SCREW
SCALE
FRONT
RAIL
Fig. 29
27 - English
Page 28
OPERATION
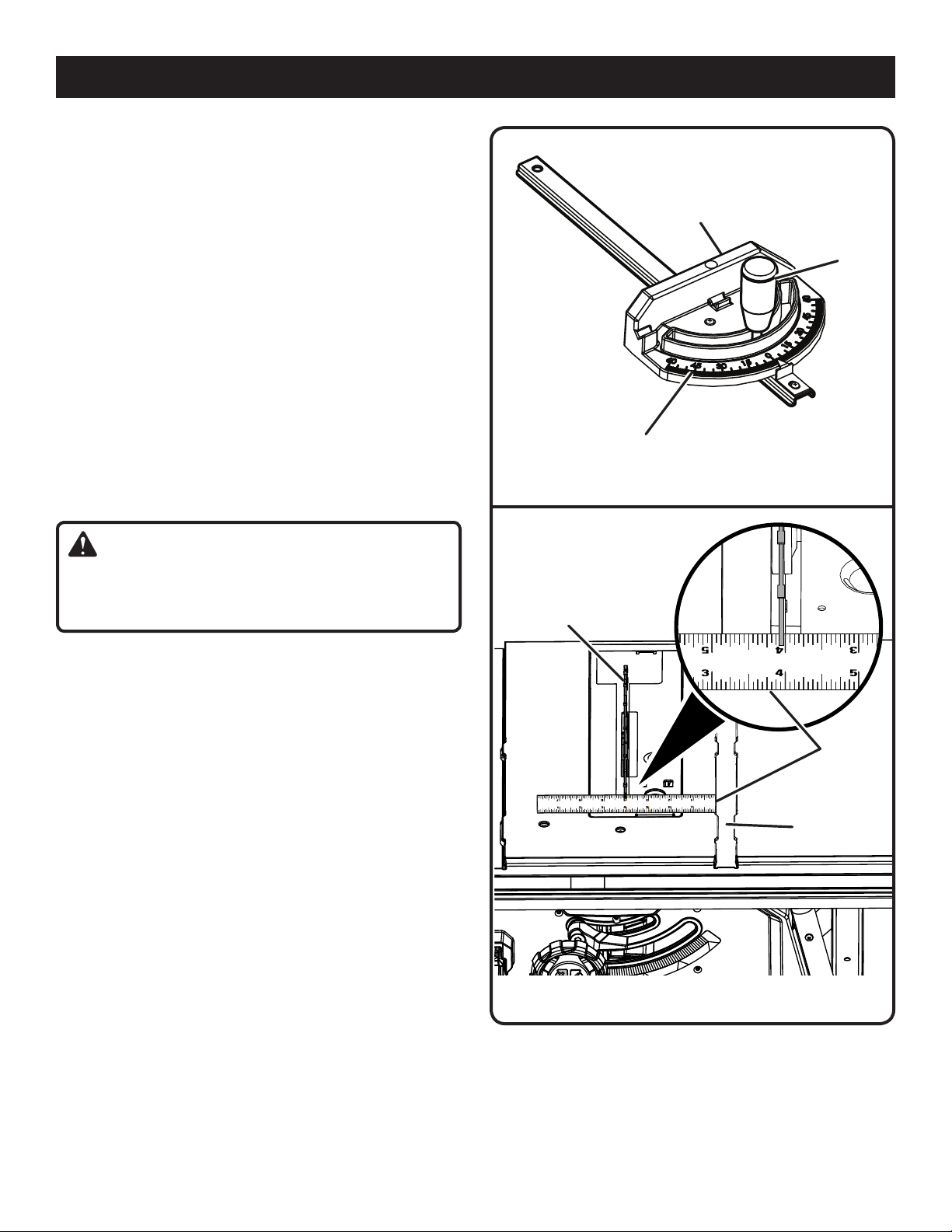
TO USE THE MITER GAUGE
See Figure 30.
The miter gauge provides greater accuracy in angled cuts.
For very close tolerances, test cuts are recommended.
There are two miter gauge grooves, one on either side of
the blade. When making a 90° cross cut, you can use either
miter gauge groove. When making a beveled cross cut (the
blade tilted in relation to the table) the miter gauge should be
located in the groove on the right so that the blade is tilted
away from the miter gauge and your hands.
The miter gauge can be turned 60° to the right or left.
Loosen the lock knob.
With the miter gauge in the miter gauge groove, rotate
the gauge until the desired angle is reached on the scale.
Retighten the lock knob.
ADJUSTING THE BLADE PARALLEL TO THE
MITER GAUGE GROOVE (REMOVING HEEL)
See Figures 31 - 33.
MITER
GAUGE BODY
LOCK
KNOB
MITER
GAUGE
Fig. 30
WARNING:
The blade must be made parallel to the miter gauge
groove so the wood does not bind resulting in kickback.
Failure to do so could result in serious personal injury.
Do not loosen any bolts for this adjustment until you have
checked with a ruler and made test cuts to be sure adjustments are necessary. Once the bolts are loosened, these
items must be reset.
Unplug the saw.
Remove the blade guard and riving knife. Raise the blade
by turning the height/bevel adjusting handwheel.
Mark beside one of the blade teeth at the front of the
blade. Using a ruler, measure the distance from the inside
face of the blade tooth to the left edge of the right miter
gauge groove.
NOTE: For greater accuracy, place the marked blade
tooth on top of the ruler.
Turn the blade so the marked tooth is at the back.
Move the ruler to the rear and again measure the distance
from the inside face of the blade tooth to the left edge
of the right miter gauge groove. If the distances are the
same, the blade and the miter gauge groove are parallel.
Replace blade guard and riving knife.
BLADE
TOOTH
RULER
MITER GAUGE
GROOVE
Fig. 31
28 - English
Page 29
OPERATION
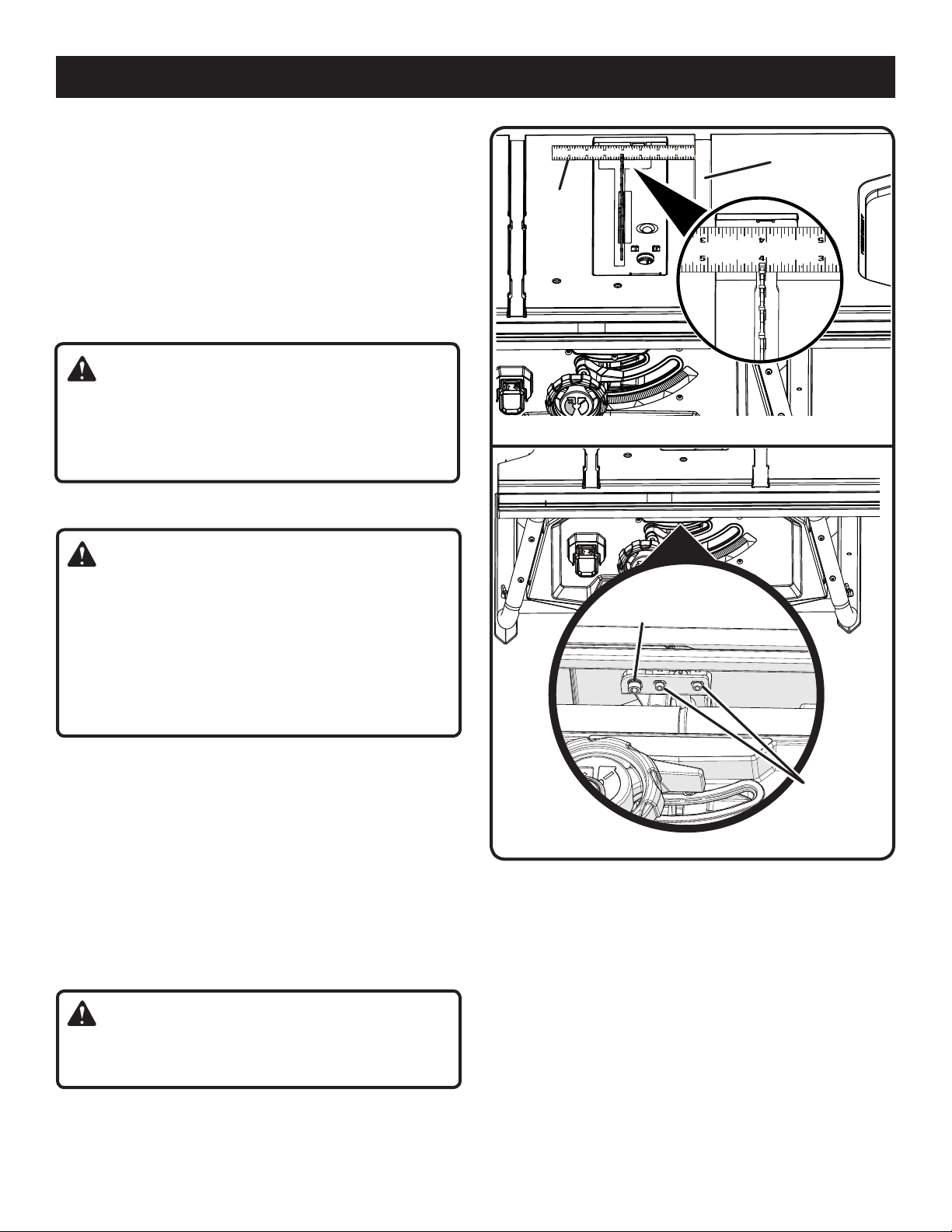
If the distances are different:
Remove the blade guard and riving knife. Raise the blade
by turning the height/bevel adjusting handwheel.
Loosen the locking bolts by turning towards the left.
NOTE: The bolts are located above the height/bevel
adjusting handwheel and under the saw table in the front
of the saw.
Turn adjusting bolt left or right until the blade is square.
Tighten the locking bolts. Check again for squareness
and continue to adjust if needed.
WARNING:
To reduce the risk of injury from kickback, align the rip
fence to the blade following any blade adjustments.
Always make sure the rip fence is parallel to the blade
before beginning any operation.
MAKING CUTS
WARNING:
Before making any cuts, make sure that the table saw
stand is on a firm level surface where there is plenty of
room to handle and properly support the table saw and
the workpiece. If a suitable location can not be found,
then the saw should not be used. Operating the saw in a
location that does not provide adequate space and stable
footing for the table saw stand could create a tipping
hazard which could result in serious personal injury.
MITER GAUGE
GROOVE
RULER
Fig. 32
ADJUSTING
BOLT
This table saw can perform a variety of cuts that are not all
mentioned in this manual. DO NOT attempt to make any cuts
not covered here unless you are thoroughly familiar with the
proper procedures and necessary accessories. Your local
library has many books on table saw usage and specialized
woodworking procedures for your reference.
The blade provided with the saw is a high-quality combination
blade suitable for ripping and cross cut operations. Carefully
check all setups and rotate the blade one full revolution to
assure proper clearance before connecting saw to power
source. Stand slightly to the side of the blade path to reduce
the chance of injury should kickback occur.
WARNING:
Do not use blades rated less than the speed of this tool.
Failure to heed this warning could result in personal injury.
29 - English
LOCKING
BOLTS (2)
Fig. 33
Use the miter gauge when making cross, miter, bevel, and
compound miter cuts. To secure the angle, lock the miter
gauge in place by twisting the lock knob clockwise. Always
tighten the lock knob securely in place before use.
NOTE: It is recommended that you place the piece to be
saved on the left side of the blade and that you make a test
cut on scrap wood first.
Page 30
OPERATION
TO MAKE A CROSS CUT
See Figures 34 - 35.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid serious possible injury.
WARNING:
Using the rip fence as a cutoff gauge when cross cutting
will result in kickback which can cause serious personal
injury.
Remove the rip fence.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Set the miter gauge to 0° and tighten the lock knob.
Make sure the wood is clear of the blade before turning
on the saw.
To turn the saw ON, lift the switch button.
To turn saw OFF, press the switch button down.
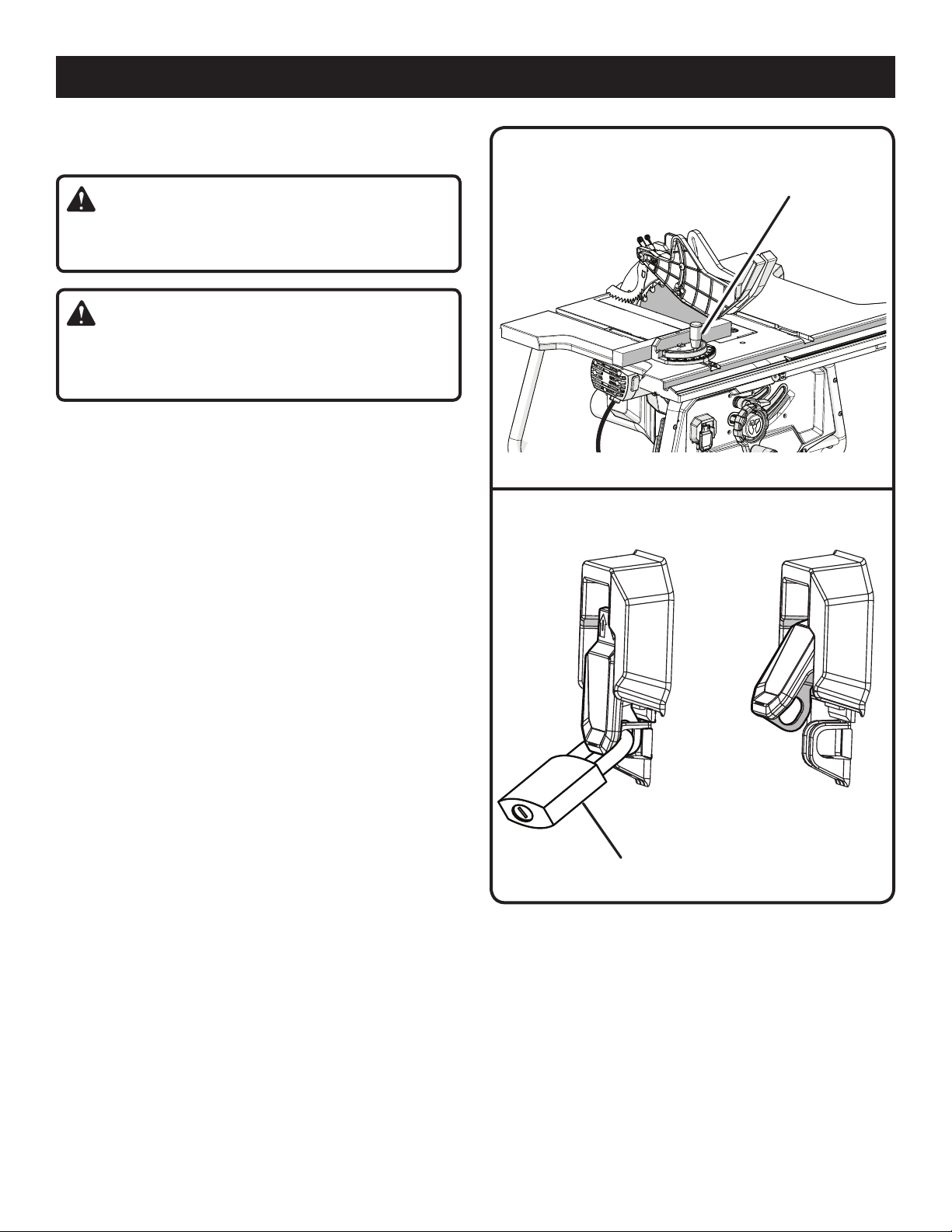
NOTE: To prevent unauthorized use, install a padlock
(not included) through the hole in the switch as shown in
figure 35.
Let the blade build up to full speed before moving the
workpiece into the blade.
Hold the workpiece firmly with both hands on the miter
gauge and feed the workpiece into the blade.
NOTE: The hand closest to the blade should be placed
on the miter gauge lock knob and the hand farthest from
the blade should be placed on the workpiece.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
SWITCH
OFF
CROSS CUT
PLACE RIGHT HAND ON
MITER GAUGE HERE
Fig. 34
SWITCH
ON
30 - English
PADLOCK
Fig. 35
Page 31

OPERATION
MAKING A RIP CUT
See Figure 36.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid serious possible injury.
WARNING:
Taper cuts must only be made with a special jig, which is
commercially available. Do not attempt a free hand taper
cut on this saw. Failure to follow these instructions could
result in serious personal injury.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Position the rip fence the desired distance from the blade
for the cut and securely lock the handle.
When ripping a long workpiece, place a support the same
height as the table surface behind the saw, and on the
sides as needed, for the cut work.
Install feather board in the appropriate position for the
cut being made.
Make sure the wood is clear of the blade before turning
on the saw.
Turn the saw on.
Position the workpiece flat on the table with the edge
flush against the rip fence. Let the blade build up to full
speed before feeding the workpiece into the blade.
RIP CUT
RIP
BLADE
Once the blade has made contact with the workpiece, use
the hand closest to the rip fence to guide it. Make sure
the edge of the workpiece remains in solid contact with
both the rip fence and the surface of the table. If ripping
a narrow piece, use a push stick, push blocks and/or a
narrow ripping jig to move the piece through the cut and
past the blade.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
FENCE
PUSH
STICK
Fig. 36
31 - English
Page 32

OPERATION
MAKING A MITER CUT
See Figure 37.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid possible serious injury.
Remove the rip fence.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Set the miter gauge to the desired angle and tighten the
lock knob.
Make sure the wood is clear of the blade before turning
on the saw.
Turn the saw on.
Let the blade build up to full speed before moving the
workpiece into the blade.
Hold the workpiece firmly with both hands on the miter
gauge and feed the workpiece into the blade.
NOTE: The hand closest to the blade should be placed
on the miter gauge lock knob and the hand farthest from
the blade should be placed on the workpiece.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
MAKING A BEVEL CROSS CUT
See Figures 38 - 39.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid possible serious injury.
MITER CUT
BLADE
STRAIGHT
MITER GAUGE
ANGLED
VIEWED FROM THE FRONT, BELOW THE TABLE SAW
BEVEL
LOCKING
LEVER
TO
TIGHTEN
Fig. 37
WARNING:
The miter gauge must be on the right side of the blade
to avoid trapping the wood and causing kickback.
Placement of the miter gauge to the left of the blade will
result in kickback and the risk of serious personal injury.
Remove the rip fence.
Unlock the bevel locking lever.
Adjust the bevel angle to the desired setting.
Lock the bevel locking lever.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Set the miter gauge to 0° and tighten the lock knob.
Make sure the wood is clear of the blade before turning
on the saw.
Turn the saw on.
Let the blade build up to full speed before moving the
workpiece into the blade.
32 - English
TO
LOOSEN
HEIGHT/BEVEL
ADJUSTING
HANDWHEEL
Fig. 38
Page 33

OPERATION
Hold the workpiece firmly with both hands on the miter
gauge and feed the workpiece into the blade.
NOTE: The hand closest to the blade should be placed
on the miter gauge lock knob and the hand farthest from
the blade should be placed on the workpiece.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
MAKING A BEVEL RIP CUT
See Figure 40.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid serious personal injury.
WARNING:
The rip fence must be on the right side of the blade
to avoid trapping the wood and causing kickback.
Placement of the rip fence to the left of the blade will
result in kickback and the risk of serious personal injury.
BLADE
ANGLED
BLADE
ANGLED
BEVEL CROSS CUT
MITER GAUGE
STRAIGHT
Fig. 39
BEVEL RIP CUT
RIP FENCE
Remove the miter gauge.
Install feather board in the appropriate position for the
cut being made.
Unlock the bevel locking lever.
Adjust the bevel angle to the desired setting.
Lock the bevel locking lever.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Position the rip fence the desired distance from the blade
for the cut and securely lock the handle.
Make sure the wood is clear of the blade before turning
on the saw.
When ripping a long workpiece, place a support the same
height as the table surface behind the saw, and on the
sides as needed, for the cut work.
Turn the saw on.
Position the workpiece flat on the table with the edge
flush against the rip fence. Let the blade build up to full
speed before feeding the workpiece into the blade.
Once the blade has made contact with the workpiece, use
the hand closest to the rip fence to guide it. Make sure
SCALE
Fig. 40
the edge of the workpiece remains in solid contact with
both the rip fence and the surface of the table. If ripping
a narrow piece, use a push stick and/or push blocks to
move the piece through the cut and past the blade.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
33 - English
Page 34

OPERATION
MAKING A COMPOUND (BEVEL) MITER CUT
See Figure 41.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid possible serious injury.
WARNING:
The miter gauge must be on the right side of the blade
to avoid trapping the wood and causing kickback.
Placement of the miter gauge to the left of the blade will
result in kickback and the risk of serious personal injury.
Remove the rip fence.
Unlock the bevel locking lever.
Adjust the bevel angle to the desired setting.
Lock the bevel locking lever.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Set the miter gauge to the desired angle and tighten the
lock knob.
Make sure the wood is clear of the blade before turning
on the saw.
Turn the saw on.
Let the blade build up to full speed before moving the
workpiece into the blade.
Hold the workpiece firmly with both hands on the miter
gauge and feed the workpiece into the blade.
NOTE: The hand closest to the blade should be placed
on the miter gauge lock knob and the hand farthest from
the blade should be placed on the workpiece.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
COMPOUND (BEVEL) MITER CUT
PLACE LEFT HAND ON
MITER GAUGE HERE
Fig. 41
34 - English
Page 35

OPERATION
MAKING A LARGE PANEL CUT
See Figure 42.
Make sure the saw is properly secured to a work surface to
avoid tipping from the weight of a large panel.
WARNING:
Make sure the blade guard assembly is installed and
working properly to avoid possible serious injury.
WARNING:
Never make freehand cuts (cuts without the miter gauge
or rip fence). Unguided workpieces can result in serious
injury.
Install feather board in the appropriate position for the
cut being made.
Place a support the same height as the top of the saw
table behind the saw, and on the sides as needed, for
the cut work. Add supports to the sides as needed.
Depending on the shape of the panel, use the rip fence
or miter gauge. If the panel is too large to use either the
rip fence or the miter gauge, it is too large for this saw.
Make sure the wood does not touch the blade before you
turn on the saw.
Turn the saw on.
Position the workpiece flat on the table with the edge
flush against the rip fence. Let the blade build up to full
speed before feeding the workpiece into the blade.
Use a push stick to move the piece through the cut and
past the blade.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
SUPPORT
LARGE PANEL CUT
RIP FENCE
HEIGHT/BEVEL
ADJUSTING
HANDWHEEL
Fig. 42
35 - English
Page 36

OPERATION
MAKING A NON-THROUGH CUT
See Figure 43.
Non-through cuts (made with a standard 10 in. blade) can be
made with the grain (ripping) or across the grain (cross cut).
The use of a non-through cut is essential to cutting grooves,
rabbets, and dadoes. This is the only type cut that is made
without the blade guard assembly installed. Make sure the
blade guard assembly is reinstalled upon completion of this
type of cut. Read the appropriate section which describes
the type of cut in addition to this section on non-through or
dado cuts. For example, if your non-through cut is a straight
cross cut, read and understand the section on straight cross
cuts before proceeding.
WARNING:
When making a non-through cut, the blade is covered
by the workpiece during most of the cut. Be alert to
the exposed blade at the start and finish of every cut to
reduce the risk of personal injury.
WARNING:
Never feed wood with your hands when making any
non-through cut such as rabbets or dadoes. To avoid
personal injury, always use push blocks, push sticks,
and featherboards.
Lock the bevel locking lever.
Set the blade to the correct depth for the workpiece.
Depending on the shape and size of the wood, use either
the rip fence or miter gauge.
Plug the saw into the power source and turn the saw on.
Let the blade build up to full speed before moving the
workpiece into the blade.
Always use push blocks, push sticks, and/or feather-
boards appropriately when making non-through cuts to
reduce the risk of serious injury.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
Once all non-through cuts are completed:
Unplug the saw.
Reinstall the riving knife in the “up” position then install
the blade guard.
NON-THROUGH CUT
BLADE GUARD
REMOVED
Unplug the saw.
Remove the blade guard.
Place riving knife in “down” position.
Unlock the bevel locking lever.
Adjust the bevel angle to 0°.
PUSH
STICK
Fig. 43
36 - English
Page 37

OPERATION
MAKING A DADO CUT
See Figure 44.
An optional dado throat plate is required for this procedure
(see the Accessories section of this manual and check with
the retailer where the table saw was purchased). All blades
and dado sets must not be rated less than the speed of this
tool. This saw is designed for use with a 6 in. stack dado
(up to width of 1/2 in.). Do not use an adjustable dado or
molding cutters on this saw.
WARNING:
When making a non-through cut, the blade is covered
by the workpiece during most of the cut. Be alert to
the exposed blade at the start and finish of every cut to
reduce the risk of personal injury.
WARNING:
Always put all blade washers in proper location when
reinstalling standard blade. Failure to do so can result in
possible injury and damage to the tool.
WARNING:
Always use push blocks, push sticks, and/or featherboards
when making dado cuts to avoid the risk of serious injury.
Unplug the saw.
Remove the blade guard, throat plate, and riving knife.
Remove the blade nut, blade washer, and saw blade.
NOTE: Always store the blade washer and throat plate
in a secure location.
Mount the dado blade, according to manufacturer instruc-
tions, using the blade and chippers appropriate for the
desired width of cut.
Reinstall the blade nut.
NOTE: The blade washer may be used provided the arbor
shaft extends slightly beyond the arbor nut.
Make sure the blade nut is fully engaged and the arbor
extends past a securely tightened blade nut.
Place release lever in locked position.
Install the dado throat plate and rotate the blade by hand
to make sure it turns freely then lower the blade.
Depending on the shape and size of the wood, use either
the rip fence or miter gauge.
Install feather board in the appropriate position for the
cut being made.
Turn the saw on.
NOTE: Make sure the wood does not touch the blade
before you turn on the saw. Let the blade build up to full
speed before feeding the workpiece into the blade.
Position the workpiece flat on the table with the edge
flush against the rip fence or miter gauge and hold firmly
against the saw table.
Use a push block or push stick to move the wood through
the cut past the blade. Never push a small piece of wood
into the blade with your hand, always use a push stick.
The use of push blocks, push sticks, and featherboards
are necessary when making non-through cuts.
When the cut is made, turn the saw off. Wait for the
blade to come to a complete stop before removing the
workpiece.
Once all dado cuts are completed:
Unplug the saw.
Remove the dado throat plate and reinstall standard throat
plate.
Remove the dado blade and reinstall the standard cutting
blade.
Reinstall the riving knife in the “up” position, then install
the blade guard.
DADO CUT
BLADE GUARD
REMOVED
Fig. 44
37 - English
Page 38

OPERATION
DUST CHUTE
See Figure 45.
This saw features a dust chute for convenience in discharging
sawdust. A standard shop vac can be attached to the chute,
located under the back side of the saw cabinet.
During periods of extended use, the dust chute should be
emptied and cleaned to prevent buildup of sawdust and
to make sure there are no obstructions that could hinder
maximum performance.
To clean the dust chute:
Unplug the saw.
Loosen the screw at the bottom of the dust chute.
Remove the cover.
Shake out any sawdust and wipe with a clean dry cloth,
as needed.
Replace the cover and securely tighten the screw.
SCREW
DUST
CHUTE
Fig. 45
ADJUSTMENTS
WARNING:
Before performing any adjustment, make sure the tool
is unplugged from the power supply and the switch is in
the OFF ( O ) position. Failure to heed this warning could
result in serious personal injury.
To avoid unnecessary set-ups and adjustments, a good
practice is to check your setups carefully with a framing
square and make practice cuts in scrap wood before making
finish cuts in good workpieces. Do not start any adjustments
until you have checked with a square and made test cuts to
be sure adjustments are needed.
REPLACING THE BLADE
See Figures 46 - 48.
Blade kerf width must be within the limits stamped on the
riving knife.
Unplug the saw.
Remove the blade guard and anti-kickback pawls.
Lower the saw blade and remove the throat plate.
Make sure the bevel locking lever is locked.
Raise the saw blade to full height.
Insert the open end of the blade wrench onto the flats on
the arbor shaft.
Insert the closed end of the blade wrench over the blade
nut. Holding both wrenches firmly, pull the outside wrench
(right side) forward while pushing the inside (left side) to
the back of the saw. Remove the blade nut and blade
washer.
Unlock the release locking lever and remove the blade.
NOTE: Arbor shaft has right hand threads.
BLADE
WRENCH
BLADE
WRENCH
Fig. 46
38 - English
Page 39

ADJUSTMENTS
To install a standard blade:
Place the new blade on the arbor shaft (the teeth must
point down toward the front of the saw to work properly).
Place the blade washer and the blade nut over the arbor
shaft. Be sure the flat side of the blade washer faces
the blade and that all items are snug against the arbor
housing. Make sure the blade nut is securely tightened.
Do not overtighten.
Lock the release lever.
Rotate the blade by hand to make sure it turns freely.
Lower the saw blade and reinstall the throat plate.
Check all clearances for free blade rotation.
NOTE: To replace the blade with an accessory blade, follow
the instructions provided with the accessory.
BLADE
BLADE
WASHER
TO SET THE BLADE AT 0° AND 45°
See Figures 49 - 50.
The angle settings of the saw have been set at the factory
and, unless damaged in shipping, should not require setting
during assembly. After extensive use, they may need to be
checked.
Unplug the saw.
Raise the blade.
Remove the blade guard assembly.
If the blade is not perfectly vertical (0°):
Unlock the bevel locking lever.
Loosen the 0° adjustment screw.
Place a combination square beside the blade on the
right. The edge of the square and the saw blade should
be parallel.
NOTE: Make sure that the square contacts the flat part
of the saw blade, not the blade teeth.
Lock the bevel locking lever.
Tighten the adjustment screw. Check again for squareness
and continue to adjust if needed.
THROAT
PLATE
BLADE
NUT
ARBOR
SHAFT
RIVING
KNIFE
BLADE
Fig. 47
0° ADJUSTMENT
SCREW
HANDLE
BLADE
COMBINATION
SQUARE
BEVEL
LOCKING
LEVER
BEVEL
INDICATOR
Fig. 49
Fig. 48
39 - English
Page 40

ADJUSTMENTS
If the blade is not an exact 45°:
Unlock the bevel locking lever.
Loosen the 45° adjustment screw.
Place a combination square beside the blade on the
right. The edge of the square and the saw blade should
be parallel.
NOTE: Make sure that the square contacts the flat part
of the saw blade, not the blade teeth.
Lock the bevel locking lever.
Tighten the adjustment screw. Check again for squareness
and continue to adjust if needed.
If needed, adjust the bevel indicator to 45°.
Make a test cut.
The adjustment screws must be below the saw table surface
so the workpiece doesn’t catch on uneven edges. If unable
to make this adjustment, take the product to an authorized
service center.
BLADE
45° ADJUSTMENT
SCREW
45°
COMBINATION
SQUARE
TO CHECK THE ALIGNMENT OF THE RIP
FENCE TO THE BLADE
See Figure 51.
The rip fence must be parallel to the saw blade and the miter
gauge grooves.
WARNING:
A misaligned rip fence can cause kickbacks and jams.
To reduce the risk of injury, always maintain proper rip
fence alignment.
Unplug the saw.
Remove the blade guard, riving knife, and anti-kickback
pawls. Raise the blade by turning the height/bevel adjusting handwheel.
Verify the blade is parallel to the miter gauge groove as
described in the Adjusting the Blade Parallel to the Miter
Gauge Groove (Removing Heel) section in Operation.
Move the rip fence near the saw blade (about three inches
away) and lock the rip fence in place with the locking
lever.
Mark beside one of the blade teeth at the front of the
blade. Using a ruler, measure the distance from the inside
face of the blade tooth to the to the inside face of the rip
fence.
NOTE: For greater accuracy, place the marked blade
tooth on top of the ruler.
HANDLE
BEVEL
LOCKING
LEVER
INDICATOR
BEVEL
Fig. 50
40 - English
BLADE
TOOTH
RIP
FENCE
RULER
SCREWS
LOCKING
LEVER
Fig. 51
Page 41

ADJUSTMENTS
Turn the blade so the marked tooth is at the back.
Move the ruler to the rear and again measure the distance
from the inside face of the blade tooth to the inside face
of the rip fence. If the distances are the same, the blade
and the rip fence are parallel.
If the distances are different:
Unlock the rip fence.
Loosen the two screws located on top of the rip fence.
Adjust the rip fence.
Alternately retighten the screws. Recheck alignment.
Repeat steps as needed until rip fence is correctly aligned.
Replace blade guard, riving knife, and anti-kickback pawls.
TO CHECK THE TIGHTNESS OF THE RIP
FENCE LOCKING LEVER
See Figure 52.
The locking lever on the rip fence should hold the rip fence
securely against the front and back rails. The lever should
not be difficult to push down and lock. To assure proper
fence lock adjustment:
Lock the rip fence in place.
Try moving the fence from side-to-side. If the fence moves,
tighten the lock nut 1/4 turn.
With the rip fence in the locked position, recheck rip fence
parallelism with the blade and adjust if necessary.
LOCK NUT
Fig. 52
MAINTENANCE
WARNING:
When servicing, use only identical replacement parts.
Use of any other parts may create a hazard or cause
product damage.
WARNING:
Always wear eye protection with side shields marked
to comply with ANSI Z87.1 during product operation. If
operation is dusty, also wear a dust mask.
WARNING:
Before performing any maintenance, make sure the tool
is unplugged from the power supply and the switch is in
the OFF ( O ) position. Failure to heed this warning could
result in serious personal injury.
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
Avoid using solvents when cleaning plastic parts. Most
plastics are susceptible to damage from various types of
commercial solvents and may be damaged by their use. Use
clean cloths to remove dirt, dust, oil, grease, etc.
WARNING:
Do not at any time let brake fluids, gasoline, petroleumbased products, penetrating oils, etc., come in contact
with plastic parts. Chemicals can damage, weaken, or
destroy plastic which may result in serious personal injury.
Periodically check all clamps, nuts, bolts, and screws for
tightness and condition. Make sure the throat plate is in
good condition and in position.
Check the blade guard assembly.
To maintain the table surfaces, fence, and rails, periodi-
cally apply paste wax to them and buff to provide smooth
functioning.
Protect the blade by cleaning out sawdust from underneath
the table and in the blade teeth. Use a resin solvent on
the blade teeth.
Clean plastic parts only with a soft damp cloth. DO
NOT use any aerosol or petroleum solvents.
LUBRICATION
All of the bearings in this tool are lubricated with a sufficient
amount of high grade lubricant for the life of the unit under
normal operating conditions. Therefore, no further lubrication
is required.
41 - English
Page 42

MAINTENANCE
CLEANING THE RIVING KNIFE LOCK LEVER
PLATES
See Figure 53.
The locking lever on the riving knife may become difficult to
lock securely after extended use due to sawdust or debris
falling into the plates.
Unplug the saw.
Unlock the lever to remove the riving knife.
Wipe the area with a clean dry cloth or use compressed
air to blow away debris.
Reinstall the riving knife and turn the lever to lock the
riving knife in place.
WARNING:
Do not use the saw if the lock lever does not fully close.
Failure to do so may cause serious personal injury.
RIVING
KNIFE
LOCK
LEVER
PLATES
Fig. 53
ACCESSORIES
Look for these accessories where you purchased this product or call 1-800-525-2579:
Dado Throat Plate........................................................................................................................................089240015199
WARNING:
Current attachments and accessories available for use with this product are listed above. Do not use any attachments
or accessories not recommended by the manufacturer of this product. The use of attachments or accessories not
recommended can result in serious personal injury.
42 - English
Page 43

TROUBLESHOOTING
PROBLEM CAUSE SOLUTION
Excess vibration. Blade is out of balance.
Blade is damaged.
Saw is not mounted securely.
Work surface is uneven.
Blade is warped.
Rip fence does not move smoothly. Rip fence not mounted correctly.
Rails are dirty or sticky.
Clamp screw is out of adjustment.
Rip fence does not lock at rear. Clamp screw is out of adjustment. Adjust clamp screw clockwise.
Cutting binds or burns work. Blade is dull.
Blade is heeling.
Work is fed too fast.
Rip fence is misaligned.
Wood is warped.
Riving knife is out of alignment.
Wood edges away from rip fence
when ripping.
Blade not properly sharpened or set. Resharpen or set blade.
Replace blade.
Replace blade.
Tighten all hardware.
Reposition on flat surface. Adjust legs of
optional stand.
Check saw blade installation. Replace
blade if necessary.
Remount the rip fence.
Clean and wax rails.
Adjust clamp screw counterclockwise.
Replace or sharpen blade.
See Adjusting the Blade Parallel to the
Miter Gauge Groove (Removing Heel).
Slow the feed rate.
Align the rip fence.
Replace the wood. Always cut with convex
side to table surface.
See To Check and Align the Riving Knife
and Saw Blade in the Assembly section.
Saw does not make accurate 90˚ or
45˚ cuts.
Height/bevel adjusting hand-wheel
is hard to turn.
Saw does not start. Motor cord or wall cord is not plugged in.
Blade makes poor cuts. Blade is dull or dirty.
Blade does not lower when turning
height/bevel adjusting handwheel.
Motor labors in rip cut. Blade not proper for rip cut. Change blade; rip blade typically has
Positive stops inside cabinet need
adjusting (Bevel Cuts).
Miter gauge is misaligned (Miter Cuts).
Gears or screw post inside cabinet are
clogged with saw dust.
Circuit fuse is blown.
Circuit breaker is tripped.
Cord or switch is damaged.
Blade is wrong type for cut being made.
Blade is mounted backwards.
Locking lever is not at full left position. Move locking lever to left.
Adjust positive stops.
Adjust the miter gauge.
Clean the gears or screw post.
Plug in motor cord or wall cord.
Replace circuit fuse.
Reset circuit breaker.
Have the cord or switch replaced at your
nearest authorized service center.
Clean, sharpen, or replace blade.
Replace with correct type.
Remount blade.
fewer teeth.
43 - English
Page 44

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
AVERTISSEMENT :
Lire attentivement toutes les instructions. Le non-
respect des instructions ci-dessous peut entraîner un choc
électrique, un incendie et des blessures graves.
LIRE TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS
VEILLER À BIEN CONNAÎTRE L’OUTIL. Lire attentivement
le manuel d’utilisation. Apprendre les applications et les
limites de la scie, ainsi que les risques spécifiques relatifs à
son utilisation.
SE PROTÉGER DES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES EN ÉVITANT
TOUT CONTACT DU CORPS AVEC DES SURFACES MISES
À LA TERRE. Par exemple : tuyaux, radiateurs, cuisinières,
réfrigérateurs.
MAINTENIR TOUS LES DISPOSITIFS DE PROTECTION
EN PLACE et en bon état de fonctionnement.
RETIRER LES CLÉS ET OUTILS DE RÉGLAGE. Prendre
l’habitude de vérifier que tous les outils et clés de réglage
ont été retirés de l’outil avant de le mettre en marche.
GARDER LE LIEU DE TRAVAIL PROPRE. Les établis
encombrés et les endroits sombres sont propices aux
accidents. NE PAS laisser d’outils ou de pièces de bois sur
la scie en fonctionnement.
NE PAS UTILISER DANS DES ENVIRONNEMENTS
DANGEREUX. Ne pas utiliser les outils électriques dans
des endroits mouillés ou humides, ne pas les exposer à la
pluie. Garder le lieu de travail bien éclairé.
GARDER LES ENFANTS ET VISITEURS À L’ÉCART. Tous
les visiteurs doivent porter des lunettes de sécurité et se
tenir à bonne distance de la zone de travail. Ne pas laisser
les visiteurs toucher l’outil ou son cordon d’alimentation
pendant le fonctionnement.
ASSURER LA SÉCURITÉ DES ENFANTS en installant des
cadenas et des disjoncteurs ou en retirant les clés de contact.
NE PAS FORCER L’OUTIL. Il exécutera le travail mieux et
de façon moins dangereuse s’il fonctionne dans les limites
prévues.
UTILISER L’OUTIL APPROPRIÉ. Ne pas utiliser l’outil ou un
accessoire pour effectuer un travail pour lequel il n’est pas
conçu. Ne ne pas utiliser l’outil pour une application non prévue.
UTILISER UN CORDON PROLONGATEUR ADÉQUAT.
S’assurer que le cordon prolongateur est en bon état.
Utiliser exclusivement un cordon d’une capacité suffisante
pour supporter le courant de fonctionnement de l’outil. Un
cordon de capacité insuffisante causerait une baisse de la
tension de ligne, entraînant une perte de puissance et une
surchauffe. Un calibre de fil (A.W.G) d’au minimum 14 est
recommandé pour un cordon prolongateur de 7,5 m (25 pi)
ou moins. En cas de doute, utiliser un cordon du calibre
immédiatement supérieur. Moins le numéro de calibre est
élevé, plus la capacité du fil est grande.
PORTER UNE TENUE APPROPRIÉE. Ne pas porter de
vêtements amples, gants, cravate ou bijoux. Ces articles
pourraient être happés et tirer la main ou une partie du corps
dans les pièces en mouvement. Les cheveux longs doivent
être ramassés sous un couvre-chef.
TOUJOURS PORTER UNE PROTECTION OCULAIRE
MUNIE D’ÉCRANS LATÉRAUX CERTIFIÉE CONFORME
À LA NORME ANSI Z87.1. Si cette précaution n’est pas
prise, des objets peuvent être projetés dans les yeux et
causer des lésions graves.
ASSUJETTIR LES PIÈCES. Dans la mesure du possible,
utiliser des serre-joints ou un étau pour maintenir la pièce.
Cette pratique réduit les risques et laisse les deux mains libres.
NE PAS TRAVAILLER HORS DE PORTÉE. Toujours se tenir
bien campé et en équilibre.
ENTRETENIR SOIGNEUSEMENT LES OUTILS. Garder
les outils bien affûtés et propres pour accroître la sécurité
et les performances. Suivre les instructions de lubrification
et de changement d’accessoires.
DÉBRANCHER TOUS LES OUTILS. Tous les outils doivent
être débranchés lorsqu’ils ne sont pas en usage et avant
toute opération d’entretien ou de changement d’accessoire,
lame, foret, fers, etc.
ÉVITER LES DÉMARRAGES ACCIDENTELS. S’assurer que
le commutateur est en position d’arrêt avant de brancher
un outil.
UTILISER LES ACCESSOIRES RECOMMANDÉS. Voir
les accessoires recommandés dans le manuel d’utilisation.
L’utilisation d’accessoires inadéquats peut causer des
blessures.
NE JAMAIS MONTER SUR L’OUTIL. Un basculement de
l’outil ou le contact accidentel avec l’accessoire de coupe
peut causer des blessures graves.
VÉRIFIER L’ÉTAT DES PIÈCES. Avant d’utiliser l’outil de
nouveau examiner soigneusement les pièces et dispositifs de
protection qui semblent endommagés afin de déterminer s’ils
fonctionnent correctement et s’ils remplissent les fonctions
prévues. Vérifier l’alignement des pièces mobiles, s’assurer
qu’aucune pièce n’est bloquée ou cassée, vérifier la fixation
de chaque pièce et s’assurer qu’aucun autre problème ne
risque d’affecter le bon fonctionnement de l’outil. Pour
éviter les risques de blessures, toute protection ou pièce
endommagée doit être correctement réparée ou remplacée
dans un centre de réparations agréé.
ENGAGER LES PIÈCES DANS LE SENS CORRECT. Le
matériau à couper ne doit être engagé que contre le sens
de rotation de la lame.
NE JAMAIS LAISSER L’OUTIL EN FONCTIONNEMENT
SANS SURVEILLANCE. COUPER L’ALIMENTATION
ÉLECTRIQUE. Ne pas s’éloigner de l’outil avant qu’il soit
parvenu à un arrêt complet.
PORTER UNE PROTECTION RESPIRATOIRE. Porter
un masque facial ou respiratoire si le travail produit de la
poussière.
PORTER UNE PROTECTION AUDITIVE. Porter une
protection auditive durant les périodes d’utilisation prolongée.
NE PAS MALTRAITER LE CORDON D’ALIMENTATION.
Ne jamais tirer sur le cordon pour le débrancher de la prise
secteur. Garder le cordon à l’écart de la chaleur, de l’huile
et des objets tranchants.
POUR LES TRAVAUX À L’EXTÉRIEUR, UTILISER UN
CORDON SPÉCIALEMENT CONÇU À CET EFFET,
MARQUÉ « W-A » OU « W ». Ces cordons réduisent les
risques de choc électrique.
TOUJOURS GARDER LA GARDE DE LAME ET
L’ÉCARTEUR EN PLACE et en bon état de fonctionnement.
3 − Français
Page 45

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
GARDER LES LAMES PROPRES, BIEN AFFÛTÉES ET
SUFFISAMMENT AVOYÉES. Des lames affûtées réduisent
les risques de blocage et de rebond.
GARDER LES MAINS À L’ÉCART DE LA ZONE DE
COUPE. Garder les mains à l’écart des lames. Ne pas mettre
les mains sous le travail, ou autour ou au dessus de la lame
lorsqu’elle est en rotation. Ne pas essayer de retirer une
pièce coupée pendant que la lame est en rotation.
LES LAMES CONTINUENT DE TOURNER EN ROUE LIBRE
UNE FOIS QUE LA SCIE EST ÉTEINTE.
NE JAMAIS UTILISER CET OUTIL DANS UNE
ATMOSPHÈRE EXPLOSIVE. Les étincelles normalement
produite par le moteur pourraient enflammer les vapeurs.
INSPECTER RÉGULIÈREMENT LES CORDONS DE
L’OUTIL. Faire remplacer tout commutateur défectueux par
un technicien qualifié ou un centre de réparations agréé. Le fil
à gaine verte, avec ou sans traceur jaune est le fil de terre. Si
le cordon doit être réparé ou remplacé, ne pas connecter le
fil de terre de l’outil sur une borne sous tension. Tout cordon
endommagé doit être réparé ou remplacé immédiatement.
Toujours rester conscient de l’emplacement du cordon et
veiller à le tenir à l’écart de la lame en rotation.
INSPECTER RÉGULIÈREMENT LES CORDONS
PROLONGATEURS et les remplacer s’ils sont endommagés.
METTRE TOUS LES OUTILS À LA TERRE. Si un outil est
équipé d’une fiche à trois broches, il doit être branché sur
une prise secteur à trois trous.
CONSULTER UN ÉLECTRICIEN QUALIFIÉ ou le personnel
de service si les instructions de mise à la terre ne sont pas
bien comprises, ou en cas de doute au sujet de la mise à la
terre.
N’UTILISER QUE DES ACCESSOIRES ÉLECTRIQUES
APPROPRIÉS : Utiliser exclusivement des cordons
prolongateurs à 3 fils doté d’une fiche à prise de terre
branchés sur une prise triphasée compatible avec la fiche
de l’outil.
NE PAS MODIFIER la fiche fournie. Si elle ne peut pas
être insérée dans la prise secteur, faire installer une prise
adéquate par un électricien qualifié.
GARDER L’OUTIL SEC, PROPRE ET EXEMPT D’HUILE
OU DE GRAISSE. Toujours utiliser un chiffon propre pour le
nettoyage. Ne jamais utiliser de liquide de freins, d’essence
ou de produits à base de pétrole pour nettoyer l’outil.
RESTER VIGILANT ET GARDER LE CONTRÔLE. Se
montrer attentif et faire preuve de bon sens. Ne pas utiliser
l’outil en état de fatigue. Ne pas se presser.
NE PAS UTILISER L’OUTIL SI LE COMMUTATEUR NE
PERMET PAS DE LE METTRE EN MARCHE OU DE
L’ARRÊTER.Faire remplacer les commutateurs défectueux
dans un centre de réparations agréé.
N’UTILISER QUE LES LAMES APPROPRIÉES. Ne pas
utiliser de lames dont le trou n’est pas de la taille correcte.
Ne jamais utiliser de rondelles ou boulons de lame défectueux
ou de type incorrect. La taille maximum de lame pouvant
être utilisée sur cette scie est de 254 mm (10 po).
S’ASSURER QUE TOUS LES DISPOSITIFS DE
PROTECTION FONCTIONNENT CORRECTEMENT AVANT
D’EFFECTUER UNE COUPE.
S’ASSURER QU’AUCUN CLOU NE SE TROUVE SUR LA
TRAJECTOIRE DE LA LAME. Inspecter la pièce et retirer
les clous éventuels avant de la couper.
NE JAMAIS TOUCHER LA LAME ou les pièces en
mouvement pendant le fonctionnement.
NE JAMAIS METTRE UN OUTIL EN MARCHE
LORSQU’UNE PIÈCE EN ROTATION QUELCONQUE EST
EN CONTACT AVEC LA PIÈCE À COUPER.
NE PAS UTILISER CET OUTIL SOUS L’INFLUENCE DE
L’ALCOOL, DE DROGUES OU DE MÉDICAMENTS.
Utiliser exclusivement des pièces identiques à celles d’origine
POUR LES RÉPARATIONS. L’usage de toute autre pièce
pourrait créer une situation dangereuse ou endommager
l’outil.
UTILISER EXCLUSIVEMENT LES ACCESSOIRES
RECOMMANDÉS dans ce manuel ou ses addendas.
L’emploi de tout accessoire non recommandé peut
présenter un risque de blessure. Les instructions de
sécurité d’utilisation sont fournies avec les accessoires.
VÉRIFIER DEUX FOIS TOUS LES RÉGLAGES. S’assurer
que la lame est bien serrée et ne touche ni la scie, ni la
pièce à couper avant de brancher la scie sur le secteur.
RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ PARTICULIÈRES
ASSUJETTIR OU BOULONNER SOLIDEMENT LA SCIE
SUR UN ÉTABLI OU UN STAND, approximativement à la
hauteur des hanches.
NE PAS FAIRE FONCTIONNER LA SCIE SANS AVOIR
DÉPOSÉ LE SUPPORT SUR LE SOL.
SE PROTÉGER DES REBONDS. Le rebond se produit
lorsqu’un blocage soudain de la lame dans le bois cause la
projection de la pièce en train d’être coupée en direction de
l’opérateur. Ceci peut tirer la main contre la lame et causer
des blessures graves Rester à l’écart de la ligne de coupe et
arrêter immédiatement la scie si la lame est bloquée, stoppe
ou se coince.
4 − Français
UTILISER LE GUIDE LONGITUDINAL. Toujours utiliser un
guide ou une règle pour le sciage en long.
SOUTENIR LES PANNEAUX DE GRANDE TAILLE. Pour
minimaliser le risque de pincement de la lame et de rebond,
toujours soutenir les panneaux de grande taille.
RETIRER TOUS LES GUIDES ET TOUTES LES TABLES
AUXILIAIRES avant de transporter la scie. Le non-respect
de cette précaution peut entraîner un accident et des
blessures graves.
Page 46

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ PARTICULIÈRES
TOUJOURS UTILISER LA GARDE DE LAME, COUTEAU
DIVISEUR ET LES GRIFFES ANTIREBOND lors des coupes
« traversantes ». Une coupe est appelée « traversante »
lorsque la lame coupe une pièce de bois de part en part,
dans le sens de la longueur ou de la largeur. Garder la garde
de lame ainsi que les griffes antirebond abaissées et couteau
diviseur en place.
TOUJOURS ASSUJETTIR la pièce à couper fermement
contre le guide longitudinal ou le guide d’onglets.
TOUJOURS UTILISER UN BÂTON POUSSOIR LORS
DE LA REFENTE DES PLANCHES ÉTROITES. Un bâton
poussoir est un instrument permettant de pousser une pièce
contre la lame au lieu de le faire avec les mains. Bien que
la taille et la forme puissent varier, le bâton poussoir doit
toujours être plus étroit que la pièce à couper afin qu’il ne
risque pas de toucher la lame. Lors de la refente de matériau
étroit, toujours utiliser le poussoir ou le gabarit mentionné
au chapitre « Comment faire un gabarit » (pour la refente
de pièce à travailler étroite) dans ce manuel afin de garder
la main éloignée de la lame de la scie. Pour les coupes non
traversantes, utiliser un bloc poussoir et des cales-guides.
LORS DU COUPES LONGITUDINAL NON TRAVERSANTE,
toujours utiliser un bâton poussoir, bloc poussoir et/ou
cale-guide afin de ne pas riquer que les mains à moins de
76,2 mm (3 po) de la lame.
LORS DE LA REFENTE DES PLANCHES ÉTROITES,
toujours utiliser un bâton poussoir, bloc poussoir, gabarit
(conçu pour la refente étroite), et/ou cale-guide.
NE JAMAIS effectuer quelque opération que ce soit à
« main levée », c’est-à-dire en utilisant seulement les mains
pour soutenir ou guider une pièce. Toujours utiliser le guide
longitudinal ou le guide à onglet pour positionner et guider
la pièce.
NE JAMAIS se tenir ou laisser une partie du corps se trouver
dans la trajectoire de la lame.
NE JAMAIS placer la main ou les doigts derrière,
au-dessous ou à moins de 76 mm (3 po) de la lame ou de
sa trajectoire.
ENLEVEZ TOUJOURS LE GUIDE LONGITUDINAL quand
vous coupez à transversale.
NE PAS UTILISER LE GUIDE D’ONGLET ET LE GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL en même temps.
NE JAMAIS utiliser le guide longitudinal comme guide lors
des coupes transversales.
NE JAMAIS essayer de débloquer une lame coincées avant
d’avoir ÉTEINT et débranché la scie.
FOURNIR UN SUPPORT ADÉQUAT à l’arrière et sur les
côtés de la table de scie, pour les pièces très larges ou
longues.
ÉVITER LES REBONDS (pièces projetées en direction de
l’opérateur) en :
a) Gardant la lame affûtée.
b) Gardant le guide longitudinal parallèle à la lame.
c) Gardant les griffes antirebond, le couteau diviseur et la
garde de lame en place en en état de fonctionnement.
d) Ne retirant pas la pièce avant qu’elle ait été poussée
au-delà de la lame au moyen d’un bâton poussoir.
e) Ne sciant pas en long une pièce voilée, déformée ou
dont le chant ne repose pas à plat contre le guide,
dans le sens de la longueur (refente).
SI LE CORDON D’ALIMENTATION EST ENDOMMAGÉ,
il doit être remplacé uniquement pas le fabricant ou par un
centre de réparation agréé pour éviter tout risque.
ÉVITER LES OPÉRATIONS ET POSITIONS INCOMMO DES
pouvant causer un glissement soudain des mains vers la
lame.
UTILISER EXCLUSIVEMENT LES ACCESSOIRES
RECOMMANDÉS dans ce manuel ou ses addendas.
L’emploi de tout accessoire non recommandé peut
présenter un risque de blessure. Les instructions de sécurité
d’utilisation sont fournies avec les accessoires.
S’ASSURER QUE LA ZONE DE TRAVAIL EST
SUFFISAMMENT ÉCLAIRÉE pour voir ce que l’on fait et
qu’aucun obstacle ne peut nuire à la sécurité d’utilisation
AVANT d’effectuer quelque coupe que ce soit.
TOUJOURS ÉTEINDRE LA SCIE avant de la débrancher
pour éviter un démarrage accidentel lors du branchement
pour l’utilisation suivante.
UTILISER SEULEMENT LES LAMES dans la gamme
d’épaisseur a timbré sur le couteau diviseur.
Les avertissements ci-dessous doivent être apposés sur
CET OUTIL :
a) Porter une protection oculaire.
b) Utiliser la garde de lame et le couteau diviseur pour
toutes les opérations le permettant, y compris toutes
les coupes traversantes.
c) Garder les mains hors du passage de la lame.
d) Utiliser un bâton poussoir lorsque nécessaire.
e) Prêter une attention particulière aux instructions
relatives à la réduction des risques de rebond.
f) Ne jamais travailler à main levée.
g) Ne jamais passer la main derrière ou au-dessus et la
lame.
h) Ne jamais utiliser a scie sur le plancher ou au dessous
de la hauteur de taille.
NE JAMAIS COUPER PLUS QU’UN MORCEAU DE
MATÉRIEL À LA FOIS.
CONSERVER CES INSTRUCTIONS. Les consulter
fréquemment et les utiliser pour instruire les autres utilisateurs.
Si cet outil est prêté, il doit être accompagné de ces
instructions.
5 − Français
Page 47

SYMBOLES
Les termes de mise en garde suivants et leur signification ont pour but d’expliquer le degré de risques associé à
l’utilisation de ce produit.
SYMBOLE SIGNAL SIGNIFICATION
DANGER :
AVERTISSEMENT :
ATTENTION :
AVIS :
Certains des symboles ci-dessous peuvent être utilisés sur l’outil. Veiller à les étudier et à apprendre leur signification.
Une interprétation correcte de ces symboles permettra d’utiliser l’outil plus efficacement et de réduire les risques.
Indique une situation dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, aura pour
conséquences des blessures graves ou mortelles.
Indique une situation dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait
entraîner des blessures graves ou mortelles.
Indique une situation dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourraît
entraîner des blessures légères ou de gravité modérée.
(Sans symbole d’alerte de sécurité) Indique les informations jugées
importantes sans toutefois représenter un risque de blessure (ex. :
messages concernant les dommages matériels).
SYMBOLE NOM DÉSIGNATION / EXPLICATION
Symbole d’alerte de sécurité Indique un risque de blessure potentiel.
Pour réduire les risques de blessures, l’utilisateur doit lire et
Lire le manuel d’utilisation
veiller à bien comprendre le manuel d’utilisation avant d’utiliser
ce produit.
Protection oculaire
Symbole Mains à l’écart
Avertissement concernant
l’humidité
V Volts Tension
A Ampères Intensité
Hz Hertz Fréquence (cycles par seconde)
min Minutes Temps
Courant alternatif Type de courant
n
o
.../min Par minute Tours, coups, vitesse périphérique, orbites, etc., par minute
Vitesse à vide Vitesse de rotation à vide
Toujours porter une protection oculaire avec écrans latéraux
certifiée conforme à la norme ANSI Z87.1.
Le non-respect de cette mise en garde peut entraîner des
blessures graves.
Ne pas exposer à la pluie ou l’humidité.
6 − Français
Page 48

CARACTÉRISTIQUES ÉLECTRIQUES
CORDONS PROLONGATEURS
Utiliser exclusivement des cordons prolongateurs à trois fils doté
d’une fiche à prise de terre brabchés sur une prise triphasée
compatible avec la fiche de l’outil. Lors de l’utilisation d’un outil
électrique à grande distance d’une prise secteur, veiller à utiliser
un cordon prolongateur d’une capacité suffisante pour supporter
l’appel de courant de l’outil. Un cordon de capacité insuffisante
causerait une baisse de la tension de ligne, entraînant une
perte de puissance et une surchauffe. Se reporter au tableau
ci-dessous pour déterminer le calibre minimum de fil requis pour
un cordon donné. Utiliser exclusivement des cordons à gaine
ronde homologués par Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL).
**Intensité nominale (sur la plaquette signalétique de l’outil)
0-2,0 2,1-3,4 3,5-5,0 5,1-7,0 7,1-12,0 12,1-16,0
Longueur Calibre de fil
du cordon (A.W.G.)
25’ 16 16 16 16 14 14
50’ 16 16 16 14 14 12
100’ 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Utilisé sur circuit de calibre 12 – 20 A.
NOTE : AWG = American Wire Gauge
Pour les travaux à l’extérieur, utiliser un cordon prolongateur
spécialement conçu à cet effet. La gaine des cordons de ce
type porte l’inscription « W-A » ou « W ».
Avant d’utiliser un cordon prolongateur, vérifier que ses fils
ne sont ni détachés ni exposés et que son isolation n’est ni
coupée, ni usée.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Maintenir le cordon prolongateur à l’écart de la zone de
travail. Lors du travail avec un cordon électrique, placer le
cordon de manière à ce qu’il ne risque pas de se prendre
dans les pièces de bois, outils et autres obstacles. Ne pas
prendre cette précaution peut entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Vérifier l’état des cordons prolongateurs avant chaque
utilisation. Remplacer immédiatement tout cordon
endommagé. Ne jamais utilise un outil dont le cordon
d’alimentation est endommagé car tout contact avec la
partie endommagée pourrait causer un choc électrique et
des blessures graves.
VITESSE ET CÂBLAGE
La vitesse à vide de cet produit est d’environ 4 700 r/min (RPM).
La vitesse n’est pas constante et elle diminue sous une charge
ou en présence d’une baisse de tension. Le câblage de l’atelier
est aussi important que la puissance nominale du moteur. Une
ligne conçue seulement pour l’éclairage ne peut pas alimenter
correctement le moteur d’un outil électrique. Un fil électrique
d’une capacité suffisante pour une courte distance ne le sera
pas nécessairement pour une distance plus longue. Une ligne
dont la capacité est suffisante pour un outil électrique ne l’est
pas nécessairement pour deux ou trois.
INSTRUCTIONS DE MISE À LA TERRE
Ce produit doit être fondé. En cas de problème de fonctionnement
ou de panne, la mise à la terre fournit un chemin de résistance
au courant électrique, pour réduire le risque de choc électrique.
Cet produit est équipé d’un cordon électrique avec conducteur
et fiche de mise à la terre. Le cordon doit être branché sur une
prise correctement installée et mise à la terre conformément à
tous les codes et réglementations locaux en vigueur.
Ne pas modifier la fiche fournie. Si elle ne peut pas être insérée
dans la prise secteur, faire installer une prise adéquate par un
électricien qualifié.
AVERTISSEMENT :
L’usage d’un cordon prolongateur incorrect peut présenter
des risques de choc électrique. Si le cordon doit être réparé
ou remplacé, ne pas connecter le fil de terre de l’outil sur
une borne sous tension.Le fil à gaine verte, avec ou sans
traceur jaune est le fil de terre.
Consulter un électricien qualifié ou le personnel de service si
les instructions de mise à la terre ne sont pas bien comprises,
ou en cas de doute au sujet de la mise à la terre.
Tout cordon endommagé doit être réparé ou remplacé
immédiatement.
Ce produit est pour l’usage sur un nominal 120 circuit de volt
et a un fonder bouche similaire au bouchon illustré dans la
figure 1. Seulement connecter le produit à une sortie ayant
la même configuration comme le bouchon. Ne pas utiliser un
adaptateur avec ce produit.
CONNEXION ÉLECTRIQUE
Cet outil est équipé d’un moteur électrique de précision. Elle
doit être branchée uniquement sur une alimentation 120 V,
c.a. (courant résidentiel standard), 60 Hz. Ne pas utiliser cet
produit sur une source de courant continu (c.c.). Une chute
de tension importante causerait une perte de puissance et
une surchauffe du moteur. Si l’outil ne fonctionne pas une fois
branché, vérifier l’alimentation électrique.
7 − Français
BROCHE DE
TERRE
PRISE SECTEUR 120 V
MISE À LA TERRE
Fig. 1
Page 49

GLOSSAIRE
Griffes antirebond (scies à table et radiales)
Dispositifs qui, s’ils sont correctement installés et entretenus,
sont conçus pour empêcher que la pièce coupée soit propulsée
en direction de l’opérateur durant la refente.
Axe
Pièce sur laquelle une lame ou un outil de coupe est monté.
Coupe en biseau
Coupe effectuée avec la lame sur toute position autre que
perpendiculaire (90°) à la table.
Chanfrein
Coupe en biseau effectuée sur l’extrémité (ou une partie de
l’extrémité) d’une pièce, de manière à ce qu’il présente un
angle autre que 90°.
Coupe composée
Coupe transversale présentant un angle d’onglet et un angle
de biseau.
Coupe transversale
Coupe ou profilage effectué en travers du grain de la pièce.
Tête de coupe (raboteuses et raboteuses/dégauchisseuses)
Pièce rotative munie de lames réglables. La tête de coupe
enlève du matériau de la pièce.
Rainage (scies à table et scies à onglets composés)
Entaille qui produit une rainure ou gorge de forme rectangulaire
dans la pièce de bois.
Cale-guide (scies à table)
Dispositif utilisé pour faciliter le contrôle de la pièce à couper
en la guidant contre la table ou le guide lors des coupes
longitudinales.
pi/min ou coups/min
Nombre de pieds par minute (ou coups par minute). Terme
utilisé en référence au mouvement de la lame.
Main levée
Exécution d’une coupe sans que la pièce soit soutenue par un
gide longitudinal, un guide d’onglet ou autre dispositif.
Gomme
Résidu collant formé par la sève du bois.
Talon
Alignement de la lame par rainures du guide d’onglet.
Trait de scie
Quantité de matériau éliminé par la lame lors de coupes
traversantes ou l’entaille produite lors de coupes non
traversantes ou partielles.
Rebond
Réaction dangereuse se produisant lorsque la lame est pincée
ou bloquée et projetant la pièce en train d’être coupée dans le
sens de la rotation de la lame.
Coupe d’onglet
Coupe effectuée avec la lame sur toute position autre que
perpendiculaire (90°) à la table.
Coupes non traversantes (scies à table et scies à onglets
composés)
Toute coupe avec laquelle la lame ne traverse pas complètement
la pièce. Il s’agit de faire une coupe sans que la lame coupe la
pièce à travailler en deux.
8 − Français
Trou pilote (perceuses à colonne et scie à découper)
Petit trou pratiqué dans une pièce servant de guide pour assurer
la précision d’un trou de plus grand diamètre ou pour l’insertion
d’une lame de scie à découper.
Blocs poussoirs (pour dégauchisseuses/raboteuses)
Dispositifs utilisés pour pousser le matériau contre la tête de
coupe lors de toute opération. Ce dispositif aide à tenir la main
de l’opérateur bien à l’écart de la lame.
Blocs poussoirs et bâtons poussoirs (pour scies à table)
Dispositifs utilisés pour pousser le matériau contre la lame
lors de la coupe. Toujours utiliser un poussoir (et non un bloc)
pour effectuer une refente étroite sans l’aide d’un gabarit ou
d’un autre accessoire semblable. Il est possible d’utiliser un
bloc pour effectuer une refente étroite si un gabarit ou un autre
accessoire semblable est utilisé. Ce dispositif aide à tenir la
main de l’opérateur bien à l’écart de la lame.
Feuillure
Entaille située au bout ou sur le bord de la pièce de bois qui y
produit une rainure ou une gorge de forme rectangulaire.
Refente (scies à table et scies à ruban)
Opération de coupe destinée à réduire l’épaisseur d’une pièce
pour en produire plusieurs, plus minces.
Résine
Résidu collant formé par la sève du bois durcie.
Tours minute (RPM)
Nombre de rotations effectuées par un objet en une minute.
Coupe longitudinale ou refente (scies à table)
Opération de coupe dans le sens de la longueur de la pièce et
normalement dans le sens du grain du bois.
Couteau diviseur/écarteur (scies à table)
Pièce de métal légèrement plus mince que la lame, gardant le
trait de scie ouvert pour empêcher le rebond.
Trajectoire de la lame de scie
Zone au-dessus, au-dessous, en avant ou en arrière de la lame.
En ce qui concerne la pièce, la partie qui sera ou a été coupée
par la lame.
Sifflet (raboteuses)
Enfoncement à l’extrémité d’une pièce causé par les lames de la
tête de coupe lorsque la pièce n’est pas correctement soutenue.
Effiler la Coupe
Une coupe où le matériel est coupe a une ancho différente au
début de la coupe de la la fin.
Coupe traversante
Toute opération de coupe avec laquelle la lame traverse toute
l’épaisseur de la pièce. Cette sorte de coupe séparera une pièce
à travailler en deux morceaux.
Pièce ou matériau
L’article sur lequel le travail est effectué.
Table
Surface sur laquelle la pièce repose lors des opérations de
coupe, de perçage, de rabotage ou de ponçage.
Page 50

FEATURES
FICHE TECHNIQUE
Axe de lame ................................................16 mm (5/8 po)
Diamètre de la lame...................................254 mm (10 po)
Inclinaison de la lame .............................................. 0˚ - 45˚
Capacité de rainure .................................12,7 mm (1/2 po)
Tension ................................. 120 V, c.a. seulement, 60 Hz
GARDE DE
LAME
INDICATEUR
D’ONGLET
RAINURES DU
GUIDE D’ONGLET
COUTEAU
FENDEUR
GRIFFES
ANTIREBOND
Alimentation.................................................................15 A
Vitesse à vide ........................................4 700 r/min (RPM)
Profondeur de coupe à 0° : ...........................76 mm (3 po)
Profondeur de coupe à 45° : .................. 64 mm (2-1/2 po)
RANGEMENT
POUR
POUSSOIR
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
ÉCHELLE DE
REFENTE
CURSEUR DE
REFENTE
RAIL
AVANT
CHUTE À
COPEAUX
STAND
COMMUTATEUR
RAINURES DU
GUIDE D’ONGLET
VERROUILLAGE DE
VOLANT DE
RÉGLAGE DE
HAUTEUR / BISEAU
RANGEMENT
DE CLÉ DE
LAME
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
LEVIER DE
BISEAU
ÉCHELLE DE
BISEAU
INDICATEUR
DE BISEAU
9 − Français
Fig. 2
Page 51

CARACTÉRISTIQUES
POUR SE FAMILIARISER AVEC LA SCIE À
TABLE
Voir la figure 2.
L’utilisation sûre de ce produit exige une compréhension
des renseignements figurant sur l’outil et contenus dans le
manuel d’utilisation, ainsi qu’une bonne connaissance du
projet entrepris. Avant d’utiliser ce produit, se familiariser
avec toutes ses fonctions et règles de sécurité.
GRIFFES ANTIREBOND – Le rebond pose un danger : la
pièce de bois est projetée vers l’utilisateur. Les dents des
griffes antirebond sont orientée à l’écart de la pièce. Si la
pièce est tirée en direction de l’opérateur, les griffes mordent
dans le bois pour empêcher ou réduire le rebond. Les griffes
antiretour peuvent être contournées.
ÉCHELLE DE BISEAU – Le échelle facile à lire du devant
du bâti indique l’angle exact de la lame.
LAME – Pour une performance maximum, il est recommandé
d’utiliser la lame combinée à carbure de 10 po (254 mm)
fournie avec la scie. La lame est élevée et abaissée au moyen
du volant de réglage de hauteur / biseau. Les angles de
biseau sont verrouillés au moyen du levier de verrouillage de
biseau. Des lames supplémentaires de même haute qualité
sont disponibles pour des tâches spécifiques telles que le
sciage en long. Vous pouvez trouver toute l’information chez
votre concessionnaire local.
La trait de scie lame doit être dans les limites affranchies
sur le couteau diviseur.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser de lames dont la vitesse de rotation
nominale est inférieure à celle de l’outil. Le non-respect
de cet avertissement pourrait entraîner des blessures
graves.
GARDE DE LAME - Toujours laisser la détachable garde de
lame abaissée sur la lame pour des coupes traversantes.
LEVIER DE VERROUILLAGE DE BISEAU – Ce levier, placé
juste au-dessous de la surface de la table de travail à l’avant
du bâti, verrouille le réglage d’angle de la lame.
CHUTE À COPEAUX - La chute à copeaux intégrée facilite
l’élimination de la sciure. Un tuyau d’aspirateur peut être fixé
à la chute à copeaux.
VOLANT DE RÉGLAGE DE HAUTEUR / BISEAU – Situé
sur le devant du bâti, ce volant permet d’abaisser et relever
la lame pour effectuer les réglages ou les remplacements.
Il permet également de régler facilement l’angle de biseau.
GUIDE D’ONGLET – Le guide d’onglet aligne le bois pour
les coupes transversales. Le rapporteur facile à lire indique
l’angle exact pour la coupe de l’onglet.
RAINURES DE GUIDE D’ONGLET – Le guide d’onglet se
déplace dans les rainures de la table de scie.
RANGEMENT POUR POUSSOIR ET CLÉ - Un rangement
pratique pour le poussoir et les clés se situe sous le banc
de scie.
GUIDE LONGITUDINAL - Un robuste guide métallique,
verrouillé par une poignée, guide la pièce à couper. Le
rangement pour le poussoir est situé sur le guide longitudinal.
ÉCHELLE DE REFENTE - Sur le rail avant, l’échelle de
refente facile à lire donne des mesures précises pour les
coupes longitudinales.
COUTEAU DIVISEUR - Pièce de détachable métal de
l’ensemble de garde de lame, légèrement plus mince que la
lame, gardant le trait de scie ouvert pour empêcher le rebond.
Quand dans le hors du passage tête de coupe, ou « en haut
» la position, le c’est plus haut que la lame de scie. Quand
dans le coupes non traversante, ou « en bas » la position,
le c’est au dessous des dents de lame de scie.
ENSEMBLE DE COMMUTATEUR - La scie à table est dotée
d’un ensemble de commutateur facile d’accès, se trouvant
au-dessous du rail avant.
10 − Français
Page 52

CARACTÉRISTIQUES
DESCRIPTION DES COMPOSANTS
La partie supérieure de la lame traverse la table et elle est
entourée par un insert appelé plaque à gorge. La hauteur
de la lame est ajustée par un volant de réglage situé à
l’avant du bâti. Des instructions détaillées pour les coupes
élémentaires se trouvent dans la section Utilisation de ce
manuel : coupes transversales, coupes d’onglet, coupes
en biseau et coupes composées.
Le guide longituninal permet de positionner les pièces à
couper dans le sens de la longueur. Une échelle graduée
à l’avant de la table de la scie indique la distance entre le
guide longitudinal et la lame.
Il est impératif d’utiliser la garde de lame pour toutes
les coupes traversantes. L’ensemble de protège-lame
comprend : un couteau fendeur et un protège-lame avec
des griffes antiretour.
ENSEMBLE DE COMMUTATEUR
Voir la figure 3.
Ce produit est équipé d’un commutateur avec dispositif de
verrouillage intégré. Ce dispositif est conçu pour empêcher
l’utilisation non autorisée et potentiellement dangereuse par
des enfants ou personnes non compétentes.
AVERTISSEMENT :
TOUJOURS s’assurer que la pièce n’est pas en contact
avec la lame avant de mettre le commutateur de l’outil en
position de marche. Ne pas prendre cette précaution peut
causer le rebond de la pièce en direction de l’opérateur
et d’entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter un démarrage accidentel, TOUJOURS
s’assurer que le commutateur est en position d’ARRÊT
( O ) avant de brancher l’outil.
COMMUTATEUR EN
POSITION D’ARRÊT
COMMUTATEUR EN
POSITION DE MARCHE
POUR METTRE LA SCIE EN MARCHE :
Relever pour mettre la scie en MARCHE ( I ).
POUR ARRÊTER LA SCIE :
Abaisser le commutateur en position d’ARRÊT ( O ).
POUR VERROUILLER LA SCIE :
Avec la scie ÉTEINDRE, installer un cadenas (non inclus)
dans le trou de la commutateur.
Fig. 3
11 − Français
Page 53

OUTILS NÉCESSAIRES
Les outils suivants (non inclus ou dessiné pour escalader) sont nécessaires pour effectuer l’assemblage et les réglages :
TOURNEVIS
PHILLIPS
ÉQUERRE DE CHARPENTIER
CLÉ (13mm)
TOURNEVIS PLAT
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
SERRE-JOINTS
CLÉ À DOUILLES
ET DOUILLES
(8 mm et 13 mm)
Fig. 4
12 − Français
Page 54

PIÈCES DÉTACHÉES
Les articles suivant sont inclus avec la scie à table :
A
B
E
M
L
G
H
L
M
J
N
O
I
C
F
D
N
K
A. Garde de lame avec griffes antiretour...................... 1
B. Guide d’onglet ......................................................... 1
C. Ensemble de poignée .............................................. 1
D. Capuchon du bout de la poignée ............................ 1
E. Guide longitudinal .................................................... 1
F. Clé hex. (5 mm) ........................................................ 1
G. Entretoise du support à patte (F) ............................. 1
H. Entretoise du support à patte (R) ............................. 1
I. Ferrure de support (extérieur) .................................. 1
13 − Français
O
Q
K
P
R
Fig. 5
J. Ferrure de support (intérieur) ................................... 1
K. Pattes du support .................................................... 4
L. Écrou à oreilles ........................................................ 4
M. Boulons de carrossier .............................................. 4
N. Boulons du support à pattes ................................... 2
O. Écrous hexagonal .................................................... 2
P. Bâton poussoir......................................................... 1
Q. Fermeture de clé de lame ........................................ 2
R. Ouvrir clé plate ......................................................... 2
Page 55

ASSEMBLAGE
DÉBALLAGE
Ce produit doit être assemblé.
Sortir la scie du carton avec précaution et la poser une
un plan de travail stable.
NOTE : Cet outil est lourd. Pour éviter des problèmes
lombaires, garder les genous pliés, soulever avec les
jambes, pas avec le dos et demander de l’aide lorsque
nécessaire.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser le produit si, en le déballant, vous
constatez que des éléments figurant dans la liste des
pièces détachées sont déjà assemblés. Certaines pièces
figurant sur cette liste n’ont pas été assemblées par le
fabricant et exigent une installation. Le fait d’utiliser un
produit qui a été assemblé de façon inadéquate peut
entraîner des blessures.
Examiner soigneusement l’outil pour s’assurer que rien
n’a été brisé ou endommagé en cours de transport.
Ne pas jeter les matériaux d’emballage avant d’avoir
soigneusement examiné l’outil, s’être assuré qu’aucune
pièce ne manque et avoir procédé à un essai satisfaisant.
La scie est réglée en usine pour effectuer une coupe
précise. Après l’avoir assemblée, vérifier sa précision. Si
les réglages ont été modifiés en cours d’expédition, voir
les procédures spécifiques présentées dans ce manuel.
Si des pièces sont manquantes ou endommagées, appeler
le 1-800-525-2579.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Si des pièces manquent ou sont endommagées, ne pas
utiliser cet outil avant qu’elles aient été remplacées. Le
fait d’utiliser ce produit même s’il contient des pièces
endommagées ou s’il lui manque des pièces peut
entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas brancher sur le secteur avant d’avoir terminé
l’assemblage. Le non-respect de cet avertissement peut
causer un démarrage accidentel, entraînant des blessures
graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne jamais se tenir en ligne avec la lame ou laisser les
mains approcher la lame à moins de 76,2 mm (3 po).
Ne pas essayer de passer la main au-dessus ou au-delà
de la lame. Le non-respect de cette mise en garde peut
entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter des blessures graves, toujours s’assurer que
la scie à table est solidement fixée sur un établi ou un
stand approuvé. NE JAMAIS utiliser la scie posée sur
le sol.
TROUS DE MONTAGE
La scie à table doit être montée solidement sur un plan de
travail ferme, tel qu’un établi ou un stand. Pour ce faire, la
cadre de la scie comporte quatre trous.
Pour le montage sur un établi, les boulons doivent être assez
longs pour traverser la base de la scie, les rondelles frein,
les écrous et l’établi elles frein, les écrous et l’établi ou autre
surface de fixation. Serrer les boulons ou vis fermement.
Une fois le montage terminé, vérifier soigneusement l’établi
pour s’assurer qu’aucun mouvement ne peut se produire en
cours d’utilisation. Si l’établi bascule, glisse ou se déplace,
l’assujettir sur le sol avant d’utiliser la scie.
Pour le montage sur le stand, lire le specific procédures
spécifiques expliquées plus loin dans cette section.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas essayer de modifier cet outil ou de créer des
accessoires non recommandés pour l’outil. De telles
altérations ou modifications sont considérées comme
un usage abusif et peuvent créer des conditions
dangereuses, risquant d’entraîner des blessures graves.
14 − Français
Page 56

ASSEMBLAGE
ASSEMBLAGE DE STAND
Voir les figures 6 à 8.
NOTE : Ne pas se stand à un usage autre que celui pour
lequel il est conçu.
Déployer la ferrure de support vers l’extérieur et sur une
surface plane. Placer la ferrure de support intérieur sur le
dessus de la ferrure de support extérieure en positionnant
les rails face à face.
Insérer les pattes du support dans les ferrures de support.
Les extrémités inclinées des pattes de support doivent
être à l’opposé l’une de l’autre de manière à former un
« V ».
Installer l’entretoise « R » entre l’assemblage de patte du
côté droit. Répéter pour l’entretoise « F » pour le côté
gauche.
Aligner soigneusement les trous des pattes avec
l’entretoise. Installer la quincaillerie dans les trous. Serrer
fermement la quincaillerie.
FERRURE DE
SUPPORT
(INTÉRIEUR)
PATTE DU
SUPPORT
MONTAGE DU SUPPORT SUR LA BASE DE
LA SCIE
Voir la figure 9.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne soulevez pas la scie sans l’aide d’une autre personne.
La scie pèse environ 55 lb. Tenez-la près de votre corps,
pliez les genoux et soulevez-la avec les jambes, et non
pas avec le dos. Si ces précautions ne sont pas prises,
vous pourrez vous faire mal au dos.
Placer la base sur une surface plate et l’ouvrir
complètement.
Placer la scie à table sur le support de manière à ce que
les trous dans le cadre de la scie soient alignés avec les
trous dans les brides du support.
NOTE : S’assurer que le cadre de la scie à table est à
plat contre le support et que toutes les pattes du support
touchent au sol.
BOULON DU
SUPPORT À
ÉCROU
HEXAGONAL
PATTES
FERRURE DE
SUPPORT
(EXTERIOR)
FERRURE DE
SUPPORT
(INTÉRIEUR)
FERRURE DE
SUPPORT
(EXTERIOR)
TROU
ENTRETOISE
DU SUPPORT À
PATTE (F)
DU SUPPORT À
ENTRETOISE
PATTE (R)
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
ENSEMBLES
PATTES
(INTÉRIEUR)
ENSEMBLES
PATTES
(EXTERIOR)
ÉCROU À
OREILLES
BOULON DU
SUPPORT À
PATTE
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
15 − Français
Page 57

ASSEMBLAGE
Installer les boulons des pattes du support dans les trous
des brides et du cadre. Sécuriser avec les vis papillons
et serrer fermement.
S’assurer que la scie placée sur une surface à niveau et
que le support est stable avant d’utiliser l’outil.
INSTALLATION DE LA POIGNÉE
Voir la figure 10.
Retirer l’écrou hexagonal du boulon de la poignée, mais
ne pas retirer le boulon.
Glisser une rondelle sur le boulon.
Insérer l’écrou en nylon dans le trou en retrait du volant
de réglage de hauteur / biseau et le maintenir en place.
Insérer la poignée y vis dans le trou du volant de réglage
de hauteur / biseau.
Serrer la vis en la tournant vers la droite avec un tournevis
plat.
Recouvrir le bout de la poignée en poussant le capuchon
en place.
RETRAIT/REMPLACEMENT DE LA PLAQUE
À GORGE
Voir la figure 11.
Abaisser la lame en tournant le volant de réglage de hauteur/
biseau vers la gauche.
Pour retirer la plaque à gorge, situer le loquet qui retient la
plaque en place. Placer le pouce et l’index dans les trous et
tirer jusqu’à ce que le loquet se libère. Soulever et tirer sur
la plaque à gorge vers le devant de la scie.
Pour réinstaller la plaque à gorge, la première glisser la
languette dans la fente de l’arrière de la scie. Placer les
doigts dans les trous et tirer. Pousser vers le bas pour fixer.
ECROU
RONDELLE
BOULON
CAPUCHON
POIGNÉE
VOLANT DE
RÉGLAGE DE
HAUTEUR / BISEAU
Fig. 10
PLAQUE À
GORGE
COUTEAU
DIVISEUR
Fig. 11
16 − Français
Page 58

ASSEMBLAGE
POUR CHANGER ENTRE UNE COUTEAU
DIVISEUR
Voir la figure 12.
Cette scie est expédiée avec le couteau diviseur a placé dans
la coupe de non traversante ou « en bas » la position et doit
être en.« en haut » la position pour toutes autres opérations
de coupe.
Débrancher la scie.
Placer en la position « en haut » pour tout par les coupes
traversante :
Retrait de la plaque à gorge.
Élever la lame de scie en tournant le volant de réglage de
hauteur / biseau vers la droite.
Ouvrir le levier de dégagement en le tirant en haut.
S’emparer de le couteau diviseur et le tirer vers le côté droit
de la scie pour relâcher le couteau diviseur du serre-joint de
couteau diviseur.
Le tire le couteau diviseur en haut jusqu’à ce que es goupilles
internes sont engagées et l’écarteur c’est ci-dessus de la
lame de scie.
Verrouiller le levier de dégagement en appuyant le levier.
Réinstallez de la plaque à gorge.
Placer en la position « en bas » pour tout par les coupes
non traversante :
Retirer de la plaque à gorge.
Élever la lame de scie en tournant le volant de réglage de
hauteur / biseau vers la droite.
Ouvrir le levier de dégagement en le tirant en haut.
S’emparer de le couteau diviseur et le tirer vers le côté droit
de la scie pour relâcher le couteau diviseur du serre-joint de
couteau diviseur.
Appuyer le couteau diviseur jusqu’à ce que c’est au
dessous de la lame de scie
Le tire le couteau diviseur en haut jusqu’à ce que es goupilles
internes sont engagées et le couteau diviseur c’est ci-dessus
de la lame de scie.
Verrouiller le levier de dégagement en appuyant le levier.
Réinstallez de la plaque à gorge.
LEVIER DE
DÉGAGEMENT
(DÉVERROUILLÉE)
EN « HAUT » POSITION POUR TOUT PAR TRAVERSANTE
LEVIER DE
DÉGAGEMENT
(VERROUILLÉE)
EN « BAS » POSITION POUR TOUTE
COUPE DE NON TRAVERSANTE
Fig. 12
17 − Français
Page 59

ASSEMBLAGE
VÉRIFICATION DE L’INSTALLATION DE LA
LAME
Voir la figure 13.
AVIS :
Pour que la lame fonctionne correctement, ses dents
doivent être orientées vers le bas et l’avant de la scie.
Le non respect de cet avertissement pourrait causer un
dommage à la lame, la scie, ou la pièce à travailler.
Débrancher la scie.
Abaisser la lame et retirer la plaque à gorge.
S’assurer que le levier de verrouillage de biseau est
poussé à fond vers la gauche, voir la figure 26. Relever
la lame au maximum en tournant le volant de réglage de
hauteur/biseau vers la droite.
Placer le couteau diviseur en la posición « en haut ».
Pour desserrer la lame :
Retirer la clé de lame de la zone de rangement de clé de
lame.
Engager la plus des clés plates sur les méplats de l’axe
d’entraînement.
Engager l’extrémité fermée de la plus clé sur écrou de
lame. Saisir les deux clés fermement et tirer la plus grande
(côté droit) vers l’avant de la machine.
Pour serrer la lame :
Engager la plus des clés sur les méplats de l’axe
d’entraînement.
Engager l’extrémité fermé de la plus clé sur écrou de
lame. Saisir les deux clés (côté droit) fermement et tirer
la plus vers l’arrière de la machine. S’assurer que l’écrou
de lame est fermement serré. Ne pas trop serrer.
Remettre la plaque à gorge en place.
Vérifier que la lame tourne librement, sans toucher quoi
que ce soit.
CLÉ
À LAME
CLÉ
À LAME
ÉCROU
DE LAME
Fig. 13
18 − Français
Page 60

ASSEMBLAGE
INSTALLATION DE PROTÈGE-LAME
Voir les figures 14 et 15.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours installer le protège-lame et les griffes antirebond
sur le couteau diviseur vers le haut afin de protéger
adéquatement la lame. L’installation de composants
protecteurs sur le couteau diviseur dans toute autre
position nuira au bon fonctionnement du couteau diviseur
et augmentera le risque de blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Remplacer le protège-lame si les griffes antiretour sont
émoussées ou endommagées. Les griffes émoussées
ou endommagées pourraient ne pas arrêter un retour,
augmentant ainsi le risque de blessure grave.
PROTÈGE-
LAME
GRIFFES
ANTIREBOND
LEVIER DU
GARDE
Les griffes antiretour font partie du protège-lame de cette
scie. Elles devraient seulement être utilisées pour les coupes
complètes. Lorsqu’on n’en a pas besoin, elles peuvent être
placées hors du chemin.
Débrancher la scie.
Élever la lame de scie en tournant le volant de réglage
de hauteur / biseau vers la droite.
Placer le couteau diviseur en la posición « en haut ».
Réinstaller la plaque à gorge.
Installation de protège-lame :
Soulever le levier du garde en haut pour déverrouiller.
Avec le devant du protège-lame a élevé, abaisser le dos
du garde dans le trou de milieu le couteau diviseur comme
illustré. Appuyer le devant du garde jusqu’à ce que c’est
parallèle à la table (voir la figure 15). Si le protège-lame
n’est pas parallèle la table, le couteau diviseur n’est pas dans
« en haut » la position.
Verrouiller le garde à sa place en appuyant le levier du
garde.
Les barrières latérales du protège-lame peuvent être
soulevées et repliées, et ensuite placées hors du chemin
sans être retirées pour faciliter la mesure.
NOTE : L’alignement peut être réglé en fonction de différentes
largeurs de lame. Voir : Vérification et alignement du
couteau diviseur et la lame. Vérifier que la garde de lame
fonctionne librement, sans heurter d’autres pièces.
CORRECT
INCORRECT
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
19 − Français
Page 61

ASSEMBLAGE
VÉRIFICATION ET ALIGNEMENT DU COUTEAU
DIVISEUR ET LA LAME
Voir la figure 16.
Vérification de l’alignement du couteau diviseur :
Débrancher la scie.
Élever la lame de scie en tournant le volant de réglage
de hauteur / biseau vers la droite.
Relever les griffes antirebond et ensemble de protège-
lame. Placer une équerre de charpentier à côté de la lame
et ensemble de protège-lame.
NOTE : Placez l’équerre de charpentier entre les dents
àpointes carbure et mesurez à partir de la lame. Cette
étapepermet de s’assurer que l’équerre de charpentier
est bienappliquée contre la lame de l’avant à l’arrière
La lame de la scie et le couteau diviseur sont alignés
lorsque l’équerre de charpentier contacte la lame et le
couteau diviseur uniformément, sans laisser d’espace.
Si le couteau diviseur n’est pas alignée sur la lame, un
réglage est nécessaire. Le couteau diviseur doit être dans
l’alignement de l’avant vers l’arrière (horizontalement) et le
dessus pour inférieure (verticalement).
Réglage (horizontale et verticale) :
Relever les griffes antirebond et ensemble de protège-
lame.
Vue de arrière le scie, desserrer le vis le support de
montage.
Repositionner le couteau diviseur à ce que la lame soit
parfaitement alignée sur le couteau diviseur.
Une fois la garde correctement alignée, reserrer
fermement l’écrou papillon.
Vérifier de nouveau l’alignement et continuer à ajuster
effectuer les réglages éventuels.
VIS
PRÉCISION HORIZONTALE
20 − Français
PRÉCISION VERTICALE
Fig. 16
Page 62

ASSEMBLAGE
RANGER LES ACCESSOIRES DU BANC DE
SCIE
Voir les figures 17 et 18.
Lorsqu’on ne les utilise pas, les clés et le poussoir peuvent
être rangés en dessous du banc de scie, fixés avec un écrou
à oreilles.
Il y a du rangement supplémentaire pour le poussoir sur le
dessus du guide longitudinal. Pour utiliser le rangement,
insérer le poussoir dans la fente jusqu’à ce qu’il y ait un
déclic.
RANGEMENT POUR
BÂTON POUSSOIR
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
RANGEMENT
DE CLÉ DE
LAME
CLÉS POUR
LAME
BÂTON
POUSSOIR
Fig. 17
ÉCROU À
OREILLES
Fig. 18
21 − Français
Page 63

UTILISATION
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas laisser la familiarité avec les outils faire oublier
la prudence. Ne pas oublier qu’une fraction de seconde
d’inattention peut entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours porter une protection oculaire certifiée conforme
à la norme ANSI Z87.1. Si cette précaution n’est pas prise,
des objets peuvent être projetés dans les yeux et causer
des lésions graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser d’outils ou accessoires non recommandés
par le fabricant pour cet outil. L’utilisation de pièces et
accessoires non recommandés peut entraîner des blessures
graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Bien que beaucoup des illustrations de ce manuel montrent
la scie sans la garde de lame pour plus de clarté, la scie
ne doit être utilisée sans la garde que si les instructions
l’indiquent expressément.
APPLICATIONS
Cet outil peut être utilisé pour les applications ci-dessous :
Coupes en ligne droite telles que les coupes
transversales, longitudinales, d’onglets, en biseau et
composées
La scie peut être utilisée pour le rainage, avec des
accessoires en option
Ébénisterie et menuiserie
NOTE : Cette scie à table est conçue pour couper du bois et
de l’aggloméré uniquement.
UTILISATION ÉLÉMENTAIRE DE LA SCIE À
TABLE
La fiche à 3 broches doit être branchée sur une prise appropriée,
correctement installée et mise à la terre conformément à tous les
codes et réglementations locaux en vigueur. Un branchement
incorrect de l’équipement peut entraîner un choc électrique. Ne
pas modifier la fiche si elle ne s’insère pas dans la prise. Faire
installer une prise appropriée par un électricien qualifié. Voir la
section Caractéristiques Électricité de ce manuel.
CAUSES DE REBONDS
Un rebond peut se produire lorsque la lame se bloque ou se
coince et propulse violemment la pièce à couper en direction
de l’opérateur. Si les mains se trouvent près de lame, elles
pourraient être éjectées de la pièce et entrer en contact
avec la lame. Il est évident que le rebond peut causer des
blessures graves et il est vivement recommandé de prendre des
22 − Français
précautions afin d’éviter ce risque. Il est évident que le rebond
peut causer des blessures graves et il est vivement recommandé
de prendre des précautions afin d’éviter ce risque.
Le rebond peut être causé par toute action causant le pincement
de la lame dans le bois. Par exemple :
Réglage de profondeur de coupe incorrect
Sciage de noeuds ou de clous dans le bois
Déviation du bois en cours de coupe
Pièce à couper non soutenue
Coupe forcée
Coupe de planches humides ou voilées
Utilisation d’une lame inadéquate pour le type de coupe
Ne pas suivre les procédures de travail correctes
Utilisation incorrecte de la scie
Non utilisation des griffes antirebond
Coupe avec une lame émoussée, encrassée ou mal réglée
POUR ÉVITER LE REBOND
Toujours utiliser le réglage de profondeur de coupe
correct. La pointe des dents de la lame doit dépasser la
pièce de 3,2 à 6,4 mm (1/8 po à 1/4 po).
S’assurer de l’absence de noeuds ou de clous dans le
bois avant de commencer une coupe. Retirer les noeuds
décollés à l’aide d’un marteau. Ne jamais scier de noeuds
décollés ou de clous.
Toujours utiliser le guide longitudinal pour les coupes en
long. Toujours utiliser le guide d’onglet pour les coupes
transversales. Ceci évite la déviation du bois pendant la
coupe.
Toujours utiliser des lames propres, bien affûtées et
correctement réglées. Ne jamais couper avec une lame
émoussée.
Afin d’éviter le pincement de la lame, soutenir la pièce
avant de commencer la coupe.
Appliquer une pression constante et régulière sur la pièce.
Ne jamais forcer la coupe.
Ne pas couper des planches humides ou voilées.
Utiliser la attention extra en coupant quelque prefinished
ou les produits de bois de composition comme les griffes
antirebond toujours ne peuvent pas être efficaces.
Toujours diriger votre la pièce avec les deux mains ou
avec des bâtons poussoirs et/ou blocs poussoirs. Se tenir
bien campé afin de pouvoir la maîtriser en cas de rebond.
Ne jamais se tenir en ligne avec la lame.
L’usage d’un cale-guide aidera la prise la pièce assurément
contre la table de scie ou le guide.
Nettoyer la scie, le protège-lame, sous la plaque à gorge,
et n’importe quels sciure où n’importe quelle poussière de
scie ou les pièces de fragment peuvent rassembler.
Utiliser des lames dont le type correspond au type de coupe.
Toujours utiliser couteau diviseur pour chaque opération où
il est permis. L’usage de cet appareil réduira fort le risque
de rebond.
Page 64

3/4 po
3 1/2 po
21 po
UTILISATION
CONSEILS DE COUPE
Voir la figure 19.
Les bâtons poussoir permettent de pousser une pièce contre
la lame en toute sécurité dans coupe longitudinal. En faiant les
coupes de non traversante ou refente des planches étroites
toujours utiliser un bâton poussoir, bloc poussoir et/ou caleguide afin de ne pas riquer que les mains à moins de 76,2 mm
(3 po) de la lame. Leur forme et taille peuvent varier en fonction
du travail à exécuter et il peuvent être fabriqués avec une chute
de bois. Le bâton doit être plus étroit que la pièce et présenter
une découpe à 90˚ à une extrémité et découpe permettant de
le saisir fermement à l’autre.
Un bloc poussoir est muni d’une poignée fixée par des vis
noyées, insérées par le dessous. Il doit être utiliser pour les
coupes non traversantes.
ATTENTION :
S’assurer que la vis du bloc poussoir est noyée afin qu’elle
ne risque pas d’endommager la scie ou la pièce.
GUIDE AUXILIAIRE
Une guide auxiliaire est un appareil qui est utilisé fermer l’écart
entre la guide longitudinal et la table de scie. Toujours la marque
et utilise et la guide auxiliaire en déchirant du matériel 1/8 po
ou plus mince.
BÂTONS POUSSOIRS
BLOCS POUSSOIRS
Fig. 19
COMMENT FABRIQUER ET CONNEXION
UNE GUIDE AUXILIAIRE (POUR LA COUPE
LONGITUDINAL PIÈCE DE FABRICATION
DILUER)
Voir la figure 20.
Les trous du guide longitudinal sont utilisés pour fixer le guide
auxiliaire qui exige un morceau de bois de 19,05 mm (3/4 po)
de profondeur, 88,9 mm (3-1/2 po) de hauteur et 533,4 mm
(21 po) de long pour être fabriqué.
Pour fixer le guide auxiliaire à la guide longitudinal :
Placer le bois contre le guide d’onglet et reposer sur la table
de scie.
Du côté arrière de la guide longitudinal, bloquer le bois sur
le guide longitudinal avec des vis de bois de 1-3/4 po.
COMMENT FAIRE UNE SAUTEUSE (POUR LA
COUPE LONGITUDINAL LA REFENTE DES
PLANCHES PIÈCE)
Voir la figure 21.
Si refente des planches étroites place les mains ferment aussi
à la lame, le ce sera nécessaire de faire et utiliser une sauteuse.
Pour effectuer une sauteuse:
Attacher une poignée à un morceau long et droit de bois et
obtient du dessous utilisant des vis noyées.
Couper un arrêt en forme de L dans le côté de la sauteuse
23 − Français
Fig. 20
BUTEÉ
POIGNÉE EN
SAUTEUSE
SAUTEUSE
Fig. 21
Pour utiliser sauteuse:
Disposer la pièce plate sur la table avec l’éclat de bord
contre la sauteuse et contre buteé.
L’avoir la poignée de sauteuse et l’utilisation d’un bâton
poussoir et/ou de bloc poussoir , faire la coupe longitudinal
comme décrit à la page 31 ultérieur dans cette section.
Page 65

2 1/2 po
12 po
3/4 po
4 po
1/4 po
1/8 po
70°
UTILISATION
CALE-GUIDE
Une cale-guide est un dispositif qui permet de contrôler la
pièce en la guidant fermement contre la table ou le guide. Les
cales-guides sont surtout utiles lors de coupes en long de
petites pièces et de coupes non traversantes. L’extrémité est
oblique, avec plusieurs courtes entailles permettant de maintenir
la pièce par friction. Assujettir la cale guide sur la table avec un
serre-joint. Vérifier qu’elle peut résister au rebond en limitant le
mouvement vers l’avant de la pièce.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Placer la cale-guide contre la partie non coupée de la pièce
afin d’éviter un rebond qui pourrait entraîner des blessures
graves.
COMMENT FABRIQUER UNE CALE-GUIDE
Voir la figure 22.
La cale-guide est un excellent projet pour la scie. Sélectionner
une planche de bois solide d’environ 19 mm (3/4 po) d’épaisseur
environ, 63,5 mm (2-1/2 po) de large et 304,8 mm (12 po) de
long. Marquer le centre de la largeur sur l’une des extrémités
de la planche. Couper une des extrémités à 70° « pour des
informations sur les coupes d’onglets, voir la page 32 ». Marquer
la planche à 101,6 mm (4 po) de cette point le plus large.
Préparer la scie pour une coupe longitudunale comme expliqué
à la page 31. Régler le guide longitudinal afin de pouvoir couper
un « doigt » d’environ 6 mm (1/4 po) dans la planche. Avancer
la planche seulement jusqu’au repère de 101,6 mm (4 po).
ARRÊTER la scie et attendre que la lame soit complètement
immobilisée avant de retirer la planche. Ajuster le guide et
effectuer des coupes longitudinales dans la pièce pour obtenir
des entailles d’environ 6 mm (1/4 po), séparées de 3 mm
(1/8 po).
COMMENT INSTALLER UNE CALE-GUIDE
Voir la figure 23.
Abaisser complètement la lame. Placer le guide longitudinal à la
distance voulue de la lame pour la coupe et le verrouiller. Placer
la pièce à couper contre le guide à proximité de la lame. Ajuster
la cale-guide de manière à appliquer une résistance juste en
avant de la lame. Utiliser un serre-joints pour mieux maintenir
la cale-guide contre le bord de la table de la scie.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas placer la cale-guide à l’arrière de la pièce. Lorsque
l’entaille n’est pas correctement postionnée, le rebond
peuvent être causé par le pincement de la pièce par la
cale-guide et le blocage de la lame dans le trait de scie.
Le non-respect de cette mise en garde peut entraîner des
blessures graves.
BLOC-
POUSSOIR
BÂTON
POUSSOIR
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE LA COUPE EN
CALE-GUIDE
BISEAU
Fig. 23
Fig. 22
24 − Français
Page 66

UTILISATION
TYPES DE COUPE
Voir la figure 24.
Il y a six principaux types de coupe : 1) coupe transversale,
2) coupe longitudinale, 3) coupe d’onglet, 4) coupe transversale
en biseau, 5) coupe en long en biseau et 6) coupe d’onglet
composé (en biseau). Toutes les autres coupes sont des
combinaisons de ces six types de coupe. Les méthodes de
travail pour chaque type de coupe sont expliquées plus loin
dans cette section.
1
COUPE TRANSVERSALE
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours s’assurer que la garde de lame et les griffes
antirebond sont en place et fonctionnent correctement
pendant les coupes afin d’éviter le risque de blessures.
Les coupes transversales sont des coupes droites à 90º
effectuées en travers du grain de la pièce de bois. La pièce est
engagée à 90° par rapport à la lame et celle-ci est verticale.
Les coupes longitudinales sont effectuées dans le sens du grain
du bois. Afin d’éviter tout rebond pendant une coupe en long,
s’assurer qu’un des côtés de la pièce de bois est fermement
appuyée contre le guide.
Les coupes d’onglet sont celles effectuées avec la planche sur
toute position autre que 90°. La lame est verticale. Les planches
ont tendance à glisser pendant la coupe d’onglets. Cela peut
être contrôlé en maintenant la pièce fermement contre le guide
d’onglet.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours utiliser un bâton poussoir lors de la coupe
longitudinale de pièces longues et étroites afin d’éviter que
les mains n’approchent trop de la lame.
Les coupes en biseau sont effectuées avec la lame en biais. Les
coupes transversales en biseau sont effectuées contre le grain
du bois et les coupes en long en biseau dans le sens du grain.
Les coupes d’onglet composé (ou en biseau) sont effectuées
avec une lame en biais, la pièce étant placée en oblique
par rapport à la lame. Bien se familiariser avec les coupes
transversales, longitudinales, en biseau et d’onglets avant
d’essayer d’exécuter une coupe d’onglet composée.
2
COUPE LONGITUDINALE
3
COUPE D’ONGLET
4
COUPE TRANSVERSALE EN BISEAU
5
COUPE LONGITUDINALE EN BISEAU
6
CONSEILS DE COUPE
Les rainages et feuillures sont des coupes non traversantes
qui peuvent être soit longitudinales, soit transversales. Lire
attentivement et veiller à bien comprendre toutes les sections
de ce manuel d’utilisation avant d’entreprendre une coupe
quelconque.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser de lames dont la vitesse de rotation nominale
est inférieure à celle de l’outil. Le non-respect de cet
avertissement pourrait entraîner des blessures graves.
25 − Français
COUPE D’ONGLET COMPOSÉ (EN BISEAU)
Fig. 24
Le trait de scie (entaille pratiquée par la lame dans le bois)
sera plus large que la lame afin d’éviter une surchauffe ou un
blocage. Lors des mesures, ne pas oublier de tenir compte
du trait de scie.
S’assurer que le trait de scie est effectué sur le côté chute
de la ligne de mesure.
Page 67

UTILISATION
Couper le bois côté fini vers le haut.
Retirer les noeuds décollés à l’aide d’un marteau avant
d’effectuer la coupe.
Toujours utiliser un support adéquat sous une planche à la
sortie de la scie.
RÉGLAGE DE LA PROFONDEUR DE LAME
Voir le figure 25.
La profondeur de coupe doit être réglée pour que les pointes
extérieurs des dents de la lame dépassent la pièce de bois
d’environ 3 à 6 mm (1/8 à 1/4 po) mais que les points les plus bas
(creux) soient au-dessous de la surface supérieure de la pièce.
Pousser le levier de verrouillage de biseau vers la droite.
Relever la lame en tournant le volant de réglage de hauteur
/ biseau vers la droite ou l’abaisser en tournant le volant de
réglage vers la gauche.
CREUX
RÉGLAGE DE L’ANGLE DE LAME (BESEAU)
Voir le figure 26.
La scie à table est équipée d’une commande à crémaillère
permettant d’effectuer des coupes en biseau de 90 à 45°.
NOTE : Pour une coupe à 90°, le réglage de biseau est de 0°
et pour une coupe à 45°, le réglage est de 45°.
Débrancher la scie.
Desserrer la commande de biseau en tournant le lever de
verrouillage à fond vers la gauche. S’il est nécessaire de le
desserrer davantage, tourner le levier chargé par ressort vers
l’extérieur, puis le tourner vers la droite. Relâcher le levier
et permet la manette de réglage de lame placer (la serrure)
dans sa position originale. Le tourner de nouveau jusqu’à
ce qu’il soit desserré.
Placez le volant de réglage de hauteur vers la droite ajuster
le guide de biseau sur l’angle de 45°.
Resserrer la commande de biseau en tournant le levier
de verrouillage vers la droite. S’il est nécessaire de le
serrer davantage, tourner le levier chargé par ressort vers
l’extérieur, puis le tourner vers la gauche. Relâcher le levier
et le laisser retourner à sa position originale. Tourner de
nouveau vers la droite. Répéter cette procédure jusqu’à ce
que le levier soit fermement serré.
VOLANT DE
RÉGLAGE DE
HAUTEUR /
BISEAU
POUR RÉDUIRE
L’ANGLE
Fig. 25
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
POUR
AUGMENTER
L’ANGLE
Fig. 26
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
VOLANT DE
RÉGLAGE DE
HAUTEUR /
BISEAU
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
VIS
INDICATEUR
DE BISEAU
Fig. 27
26 − Français
Page 68

UTILISATION
RÉGLAGE DE L’INDICATEUR DE BISEAU
Voir la figure 27.
Si l’indicateur de biseau n’est pas sur zéro lorsque la lame de
la scie est à 90°, le régler en desserrant la vis et en le plaçant
sur la graduation 0° de l’échelle de biseau. Resserrer la vis.
LEVIER DE
BLOCAGE
UTILISATION DU GUIDE LONGITUDINAL
See Figure 28.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour réduire le risque de blessures, toujours vérifier que
le guide longitudinal est parallèle à la lame avant de
commencer une coupe.
Desserrer le guide longitudinal en relevant le levier de
verrouillage.
Placer le rebord arrière du guide sur l’arrière de la scie à
table et le tirer légèrement vers l’avant.
Abaisser l’extrémité avant sur les surfaces de guide du rail
avant.
Vérifier la facilité du glissement.
Placer le guide longitudinal à la distance voulue de la lame.
Avec la guide longitudinal plate sur la table de scie, pousser
la guide vers la rail avant pour aligner la guide à la rainure
du guide d’onglet.
Abaisser le levier de verrouillage pour aligner et bloquer le
guide. Si bien verrouillé, le levier de verrouillage devrait être
orienté vers le bas.
S’assurer que le levier de verrouillage tient bien le guide
de refente en place. Si des réglages sont nécessaires, voir
Vérification de l’étanchéité du levier de verrouillage du guide
longitudinal à la section Réglages de ce manuel.
LAME
RAIL
AVANT
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
LÈVRE
ARRIÈRE
Fig. 28
INDICATEUR
D’ÉCHELLE
MESURE
2 po
POUR RÉGLER L’ÉCHELLE GRADUÉE SUR LA
LAME
Voir la figure 29.
Utiliser l’indicateur sur le guide longitudinal pour positionner le
guide par rapport à l’échelle sur le rail devant.
NOTE : Le les griffes antirebond et ensemble de protège-lame
doit être retirée pour effectuer ce réglage. Une fois le réglage
effectué, réinstaller le protège-lame.
Commencer avec la lame réglée sur zéro degré (à la verticale).
Débrancher la scie.
Desserrer le guide longitudinal en relevant le levier de
verrouillage.
À l’aide d’une équerre de charpentier, régler le guide
longitudinal à 2 po (51 mm) de la pointe des dents de la
lame.
Desserrer la vis de l’indicateur et placer ce dernier sur la
graduation 51 mm (2 po), comme illustré.
Resserrer la vis, puis vérifier la dimension et la position du
guide longitudinal.
27 − Français
2 po
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
VIS
ÉCHELLE
RAIL
AVANT
Fig. 29
Page 69

UTILISATION
UTILISATION DU GUIDE D’ONGLET
Voir la figure 30.
Le guide d’onglet permet d’effectuer des coupes en biais de
grande précision. Il est recommandé d’effectuer des coupes
d’essai lorsque les tolérances sont réduites.
Il y a deux rainures de guide d’onglet, une de chaque côté de
la lame. Elle peuvent toutes deux être utilisées pour les coupes
transversales à 90°. Lors des coupes transversales en biseau
(lame inclinée par rapport à la table), le guide d’onglet doit être
placé dans la rainure de droite, de manière à ce que la lame
soit inclinée dans la direction opposée au guide et à la main
de l’opérateur.
Le guide d’onglet peut être tourné de 60° à droite ou à gauche.
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage.
Le guide d’onglet étant inséré dans la gorge de la table, le
tourner sur l’angle désiré.
Resserrer le bouton de verrouillage.
RÉGLAGE DE LA LAME PARALLÈLEMENT À LA
RAINURE DU GUIDE D’ONGLET (SUPPRESSION
DU TALON)
Voir les figures 31 a 33.
CORPS DE GUIDE
D’ONGLET
GUIDE
D’ONGLET
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
Fig. 30
AVERTISSEMENT :
La lame doit être parallèle à la rainure du guide d’onglet
afin que le bois ne pince pas la lame, entraînant ainsi un
rebond. Ne pas prendre cette précaution peut entraîner des
blessures graves.
Ne desserrer aucune bouton pour effectuer ce réglage
avant d’avoir vérifié le parallélisme avec une règle et excuté
des coupes d’essai, pour déterminer si des réglages sont
nécessaires. Une fois les bouton desserrées, les réglages
doivent être refaits.
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer la garde de lame, le couteau diviseur et griffes
antirebond. Relever la lame au maximum en tournant le
volant de réglage de hauteur / biseau.
Tracer un repère à côté de l’une des dents de l’avant de la
lame. À l’aide d’une règle, mesurer la distance entre la face
intérieure de la dent de lame et le rebord gauche de la rainure
droite du guide d’onglet.
NOTE : Pour une précision accrue, positionner la dent
marquée de la lame sur le dessus de la règle.
Tourner la lame pour que la dent marquée se trouve à l’arrière.
Déplacer la règle vers l’arrière et mesurer de nouveau la
distance entre la face intérieure d’une dent de lame et le
rebord gauche de la rainure droite du guide d’onglet. Si les
distances sont identiques, la lame et la rainure du guide à
onglet sont parallèles.
Replacer la garde de lame, le couteau diviseur et griffes
antirebond.
DENT DE
LAME
RÈGLE
RAINURE
DU GUIDE
D’ONGLET
Fig. 31
28 − Français
Page 70

UTILISATION
Si les distances mesurées sont différentes :
Retirer la garde de lame et couteau diviseur. Relever la lame
au maximum en tournant le volant de réglage de hauteur /
biseau.
Desserrer les boulons de verrouillage en tournant vers la
gauche.
NOTE : Les boulons sont situés au-dessus du volant à main
d’ajustement de la hauteur/du biseau et au-dessous de la
scie à table sur le devant de la scie.
Tourner le boulon d’ajustement vers la gauche ou la droite
jusqu’à ce que la lame soit correctement alignée.
Serrer les boulons de verrouillage. Vérifier de nouveau
l’alignement et effectuer les réglages éventuels.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour réduire le risque des blessures causées par un rebond,
alignez le guide à onglet et la lame après chaque ajustement
de la lame. Assurez-vous toujours que le guide à onglet soit
parallèle à la lame avant de commencer l’utilisation.
EXÉCUTION DE COUPES
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avant d’effectuer des coupes, s’assurer que le support
de la scie à table est sur une surface ferme et de niveau
avec suffisamment d’espace pour manipuler et soutenir
correctement la scie à table et la pièce de travail. S’il est
impossible de trouver un emplacement convenable, ne pas
utiliser la scie. Opérer la scie dans un emplacement qui ne
possède pas suffisamment d’espace ainsi qu’une bonne
stabilité pour le support de la scie à table peut produire
un risque de basculement et causer des blessures graves.
RAINURE
DU GUIDE
D’ONGLET
RÈGLE
Fig. 32
BOUTON DE
RÉGLAGE
La scie à table peut exécuter un assortiment de coupes qui ne
sont pas tout mentionné dans ce manuel. NE PAS tente de faire
n’importe quelles coupures n’ont pas couvert ici à moins que
vous êtes à fond familier avec les procédures correctes et les
accessoires nécessaires. Votre bibliothèque locale a beaucoup
de livres sur la scie à table l’usage et les procédures de travail
du bois spécialisé pour votre référence.
La lame fournie avec la scie est une lame mixte de haute
qualité qui peut être utilisée pour les coupes longitudinales et
transversales. Vérifier attentivement tous les réglages et faire
tourner la lame d’un tour complet pour assurer qu’elle tourne
librement avant de brancher la scie. Se tenir légèrement sur le
trajectoire de la lame pour réduire les possibilités de blessure
en cas de rebond.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser de lames dont la vitesse de rotation nominale
est inférieure à celle de l’outil. Le non respect de cet
avertissement pourrait entraîner des blessures graves.
29 − Français
BOULONS DE
VERROUILLAGE (2)
Fig. 33
Utiliser le guide d’onglet lors de coupes transversales, à onglet,
en biseau et à onglet composé. Pour verrouiller l’angle, tourner
le bouton de verrouillage du guide d’onglet vers la droite.
Toujours serrer fermement le bouton de verrouillage avant
d’utiliser la scie.
NOTE : Il est recommandé de placer la pièce à conserver sur
la gauche de la lame et de d’abord faire un essai sur une chute
de bois.
Page 71

UTILISATION
POUR EFFECTUER UNE COUPE
TRANSVERSALE
Voir les figures 34 et 35.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter des risques de blessures graves, s’assurer que
la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne correctement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Lors d’une coupe transversale, l’utilisation du guide
longitudinal causerait un rebond pouvant causer des
blessures graves.
Retirer le guide longitudinal.
Régler la lame sur la profondeur de coupe correcte pour
la pièce.
Régler le guide d’onglet sur 0° et serrer le bouton de
verrouillage.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que le bois
ne touche pas la lame.
Pour mettre la scie en MARCHE, relever le commutateur.
Pour ÉTEINDRE la scie, abaisser le commutateur.
NOTE : Pour éviter une utilisation non autorisée, installer un
cadenas (non inclus) dans le trou de la commutateur, comme
illustré à la figure 33.
Laisser la lame parvenir à sa vitesse maximale avant d’engager
la pièce.
Maintenir la pièce fermement avec les deux mains sur le
guide d’onglet et engager la pièce sur la lame.
NOTE : La main la plus proche de la lame doit être placée
sur le bouton de verrouillage du guide d’onglet et la main la
plus éloignée, sur la pièce à couper.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que la
lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
COUPE TRANSVERSALE
COMMUTATEUR EN
POSITION D’ARRÊT
PLACER LA MAIN DROITE
SUR LE GUIDE ICI
Fig. 34
COMMUTATEUR
EN POSITION
DE MARCHE
30 − Français
CADENA
Fig. 35
Page 72

UTILISATION
COUPE LONGITUDINALE
Voir la figure 36.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Afin d’éviter le risque de blessures graves, s’assurer que
la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne correctement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Les coupe de effiler doivent être seulement faites avec une
sauteuse spéciale, qui est disponible dans le commerce. Ne
pas tenter la coupe de effiler de à main levée sur cette scie.
Le non respect des instructions de sécurité peut entraîner
des blessures graves.
Régler la lame sur la profondeur de coupe correcte pour
la pièce.
Placer le guide longitudinal à la distance voulue de la lame
pour la coupe et verrouiller fermement la poignée.
Lors de la refente d’une pièce de travail longue, placer un
élément de soutien de la même hauteur que la surface de la
table derrière la scie et sur les côtés au besoin, pour soutenir
les pièces coupées.
Installer la cale-guide en la position appropriée pour le
type de coupe.
Avant d’allumer la scie, s’assurer que le bois ne touche
pas la lame.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
COUPE LONGITUDINALE
GUIDE
LAME
LONGITUDINAL
ÉCHELLE
Fig. 36
Placer la pièce à couper à plat sur la table, son bord solidement
appuyé contre le guide longitudinal. Laisser la lame parvenir
à sa vitesse maximum avant d’engager la pièce.
Une fois la pièce en contact avec la lame, utiliser la main
la plus proche du guide longitudinal pour guider la pièce.
S’assurer que le bord de la pièce est fermement en contact
avec le guide longitudinal et la surface de la table. Lors de
la refente d’une pièce de travail étroite, utiliser un bâton
poussoir, un bloc poussoir et/ou un gabarit pour la refente
d’une pièce étroite pour déplacer la pièce dans la zone de
coupe et au-delà de la lame.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que la
lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
31 − Français
Page 73

UTILISATION
COUPE D’ONGLET
Voir la figure 37.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Afin d’éviter le risque de blessures graves, s’assurer que
la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne correctement.
Retirer le guide longitudinal.
Régler la lame sur la profondeur de coupe correcte pour
la pièce.
Régler le guide d’onglet sur l’angle voulu et serrer le
bouton de verrouillage.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que le bois
ne touche pas la lame.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
Laisser la lame parvenir à sa vitesse maximale avant
d’engager la pièce.
Maintenir la pièce fermement avec les deux mains sur le
guide d’onglet et engager la pièce sur la lame.
NOTE: La main la plus proche de la lame doit être placée
sur le bouton de verrouillage du guide d’onglet et la main
la plus éloignée, sur la pièce à couper.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que
la lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
COUPE TRANSVERSALE EN BISEAU
Voir les figures 38 et 39.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Afin d’éviter le risque de blessures graves, s’assurer que
la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne correctement.
COUPE D’ONGLET
LAME
DROITE
GUIDE
D’ONGLET
RÉGLÉ SUR
UN ANGLE
VUE DE FACE, AU-DESSOUS DE LA SCIE À TABLE
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
POUR
SERRAGE
Fig. 37
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter de coincer le bois et causer un rebond, le guide
d’onglet doit toujours se trouver sur la droit de la lame.
Le placement du guide d’onglet sur la gauche de la lame
causerait un rebond susceptible d’entraîner des blessures
graves.
Retirer le guide longitudinal.
Désengager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Ajuster le guide de biseau sur l’angle désiré.
Engager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Régler la lame sur la profondeur de coupe correcte pour
la pièce.
Régler le guide d’onglet sur 0° et serrer le bouton de
verrouillage.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que le bois
ne touche pas la lame.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
32 − Français
POUR
DESSERRER
VOLANT DE
RÉGLAGE DE
HAUTEUR / BISEAU
Fig. 38
Page 74

UTILISATION
Laisser la lame parvenir à sa vitesse maximale avant
d’engager la pièce.
Maintenir la pièce fermement avec les deux mains sur le
guide d’onglet et engager la pièce sur la lame.
NOTE: La main la plus proche de la lame doit être placée
sur le bouton de verrouillage du guide d’onglet et la main
la plus éloignée, sur la pièce à couper.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que
la lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
COUPE LONGITUDINALE EN BISEAU
Voir la figure 40.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Afin d’éviter le risque de blessures graves, s’assurer que
la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne correctement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter de coincer le bois et causer un rebond, le guide
longitudinal doit toujours se trouver sur la droit de la lame.
Le placement du guide longitudinal sur la gauche de la lame
causerait un rebond susceptible d’entraîner des blessures
graves.
COUPE TRANSVERSALE EN BISEAU
LAME
INCLINÉE
COUPE LONGITUDINALE EN BISEAU
LAME INCLINÉE
GUIDE
D’ONGLET
DROIT
Fig. 39
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
Retirer la guide d’onglet.
Installer la cale-guide en la position appropriée pour le
type de coupe.
Désengager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Ajuster le guide de biseau sur l’angle désiré.
Engager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Régler la lame sur la profondeur de coupe correcte pour
la pièce.
Placer le guide longitudinal à la distance voulue, à la
gauche de la lame et verrouiller la poignée.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que le bois
ne touche pas la lame.
Lors de la refente d’une pièce de travail longue, placer un
élément de soutien de la même hauteur que la surface de la
table derrière la scie et sur les côtés au besoin, pour soutenir
les pièces coupées.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
Coloque la pieza de trabajo plana sobre la mesa con la
orilla pegada contra la guía de corte al hilo. Permita que la
hoja alcance la velocidad plena antes de avanzar la pieza
de trabajo hacia la hoja.
ÉCHELLE
Fig. 40
Une fois la pièce en contact avec la lame, utiliser la main
la plus proche du guide longitudinal pour guider la pièce.
S’assurer que le bord de la pièce est fermement en contact
avec le guide longitudinal et la surface de la table. Lors de
la coupe longitudinale d’une pièce étroite, la pousser bâton
et/our block poussoir jusqu’au delà de la lame.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que la
lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
33 − Français
Page 75

UTILISATION
COUPE D’ONGLET COMPOSÉ (EN BISEAU)
Voir la figure 41.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Afin d’éviter le risque de blessures graves, s’assurer que
la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne correctement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter de coincer le bois et causer un rebond, le guide
d’onglet doit toujours se trouver sur la droit de la lame.
Le placement du guide d’onglet sur la gauche de la lame
causerait un rebond susceptible d’entraîner des blessures
graves.
Retirer le guide longitudinal.
Désengager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Ajuster le guide de biseau sur l’angle désiré.
Engager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Régler la lame sur la profondeur de coupe correcte.
Régler le guide d’onglet sur l’angle voulu et serrer le
bouton de verrouillage.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que le bois
ne touche pas la lame.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
Laisser la lame parvenir à sa vitesse maximale avant
d’engager la pièce.
Maintenir la pièce fermement avec les deux mains sur le
guide d’onglet et engager la pièce sur la lame.
NOTE : La main la plus proche de la lame doit être placée
sur le bouton de verrouillage du guide d’onglet et la main
la plus éloignée, sur la pièce à couper.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que
la lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
COUPE D’ONGLET COMPOSÉ (EN BISEAU)
PLACER LA MAIN GAUCHE
SUR LE GUIDE ICI
Fig. 41
34 − Français
Page 76

UTILISATION
COUPE D’UNE PIÈCE DE GRANDE TAILLE
Voir la figure 42.
S’assurer que la scie est solidement assujettie sur le plan de
travail, afin que le poids d’une grande planche ne risque pas
de la faire basculer.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Afin d’éviter le risque de blessures graves, s’assurer
que la garde de lame est installée et fonctionne
correctement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne jamais effectuer de coupes à main levée (coupes sans
le guide d’onglet ou le guide longitudinal). Main levée les
pièces peuvent entraîner des blessures graves.
Installer la cale-guide en la position appropriée pour le type
de coupe.
Placer un support à la même hauteur que la table derrière
la scie, et sur les côtés au besoin, pour soutenir les pièces
coupées. Ajouter des supports sur les côtés selon le besoin.
Selon la forme de la planche, utiliser le guide longitudinal ou
le guide d’onglet. Si la planche est trop grande pour permettre
d’utiliser le guide longitudinal ou le guide d’onglet, elle est
trop grande pour cette scie.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que le bois ne
touche pas la lame.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
Placer la pièce à couper à plat sur la table, son bord solidement
appuyé contre le guide longitudinal. Laisser la lame parvenir
à sa vitesse maximum avant d’engager la pièce.
La pousser avec un bâton jusqu’au delà de la lame.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que la
lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
COUPE D’UNE PLANCHE DE GRANDE TAILLE
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
SUPPORTS
VOLANT DE
RÉGLAGE DE
HAUTEUR /
BISEAU
Fig. 42
35 − Français
Page 77

UTILISATION
COUPE NON TRAVERSANTE
Voir la figure 43.
Les coupes non traversantes (a fait avec une norme lame de
10 po) peuvent être effectuées avec le grain (longitudinale) ou
contre le grain (transversale). L’utilisation d’une coupe non
transversante est essentielle pour couper les rainures et les
feuillures. Seul ce type de coupe est effectué sans le garde
lame. S’assurer que la garde de lame est réinstallée après avoir
exécuté de telles coupes. Outre la présente section sur les
coupes non traversantes ou de rainage, lire la section appropriée
sur le type de coupe. Par exemple, si la coupe non traversante
est transversale, lire et comprendre la section sur les coupes
transversales avant de procéder.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Lors d’une coupe non traversante, la lame est couverte par
la pièce pendant la plus grande partie de la coupe. Se méfier
de la lame exposée au début et à la fin de chaque coupe
pour éviter le risque de blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avec les coupes non traversantes telles que les feuillures
ou les rainages, ne jamais engager le bois avec les mains.
Pour éviter des blessures, toujours utiliser un bloc / bâton
poussoir et des cales guide.
Régler la profondeur de lame correcte pour la pièce.
Selon la forme et de la taille du bois, utiliser le guide
longitudinal ou le guide d’onglet.
Brancher la scie et tourner le scie.
Laisser la lame parvenir à sa vitesse maximale avant
d’engager la pièce.
Toujours utiliser un bloc poussoir, un bâton poussoir
et/ou une cale-guide appropriée lors des coupes non
traversantes, pour réduire des blessures graves.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que
la lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
Une fois toutes les coupes non traversantes terminées :
Débrancher la scie.
Abaisser tle couteau diviseur en la posición « en haut » alors
installer la lame et réinstaller la garde de lame.
COUPE NON TRAVERSANTE
GARDE DE
LAME RETIRÉE
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer la garde de lame
Placer le couteau diviseur en la posicion « en bas ».
Désengager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Ajuster le guide de biseau sur l’angle 0°.
Engager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
BÂTON
POUSSOIR
Fig. 43
36 − Français
Page 78

UTILISATION
EXÉCUTION D’UN RAINAGE
Voir la figure 44.
Une plaque à gorge spéciale en option est requise pour cette
procédure (voir la section Accessoires de ce manuel et consulter
le magasin le plus proche). Toutes les lames standard, à rainer
et moulurer doivent présenter une vitesse de rotation nominale
est inférieure à celle de l’outil. La scie est conçue pour être
utilisée avec des lames à rainure double de 152,4 mm (6 po)
(avec une épaisseur jusqu’à 13 mm [1/2 po]). Ne pas utiliser
une lame réglable ou les coupeurs de moulure sur cette scie.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Lors d’une coupe non traversante, la lame est couverte par
la pièce pendant la plus grande partie de la coupe. Se méfier
de la lame exposée au début et à la fin de chaque coupe
pour éviter le risque de blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours mettre l’ensemble des rondelles de lame au point
approprié au moment de réinstaller une lame standard. Ne
pas respecter cette directive peut causer des blessures et
endommager l’outil.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours utiliser un bloc poussoir, un bâton poussoir et/ou
une cale-guide lors du rainage, pour éviter des blessures
graves.
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer la garde de lame, plaque à gorge, et couteau diviseur.
Retirer écrou de lame, rondelle de lame et lame de scie.
NOTE : Toujours emmagasiner la rondelle de lame et la
plaque à gorge dans un emplacement assuré.
Monter la lame, selon les instructions de fabricant, à rainer
à l’aide de la lame et des cales appropriées pour obtenir la
largeur de coupe désirée.
Réinstaller le écrou de lame.
NOTE : La rondelle de lame ne peut être utilisée que si l’axe
dépasse légèrement de l’écrou.
S’assurer que écrou de lame est pleinement engagé et l’axe
dépasse d’au moins un filetage complet de écrou de lame
fermement serré.
Placer le levier de degagement en la posición verrouillée
GARDE DE
RAINAGE
LAME RETIRÉE
Fig. 44
Installer la plaque à gorge de rainage et faire tourner la
lame à la main pour s’assurer qu’elle fonctionne librement
et l’abaisser.
Selon la forme et de la taille du bois, utiliser le guide
longitudinal ou le guide d’onglet.
Si faire une coupe longitudinal, installer la cale-guide en la
position appropriée pour le type de coupe.
Mettre le commutateur en position de marche.
NOTE : Avant de mettre la scie en marche, s’assurer que
le bois ne touche pas la lame. Laisser la lame parvenir à sa
vitesse maximum avant d’engager la pièce.
Placer la pièce à couper à plat sur la table, son bord solidement
appuyé contre le guide longitudinal ou le guide d’onglet et
tenir fermement contre la table de scie.
Utiliser un bloc ou un bâton poussoir pour pousser le bois
au-delà de la lame. Ne jamais pousser une petite pièce de
bois contre la lame avec les mains, toujours utiliser un bâton
poussoir. Avec les coupes non traversantes, l’utilisation des
blocs poussoir, bâtons poussoir et cales-guide est nécessaire.
Une fois la coupe effectuée, arrêter la scie. Attendre que la
lame s’arrête complètement avant de retirer la pièce.
Une fois toutes le coupe rainage terminées :
Débrancher la scie.
Enlever la plaque à gorge pour rainures et réinstaller la plaque
à gorge standard.
Enlever la lame pour rainures et réinstaller la lame de coupe
standard.
Réinstaller l’écarteur dans la posiiton vers le haut et réinstaller
la garde de lame.
37 − Français
Page 79

UTILISATION
CHUTE À COPEAUX
Voir la figure 45.
Cette scie comprend une chute à copeaux utile pour débarrasser
la sciure. Un aspirateur d’atelier ordinaire peut être fixé à la
chute, située sous le dessous du boîtier de la scie.
Pendant une période d’utilisation prolongée, la chute à copeaux
devrait être vidée et nettoyée pour éviter une accumulation
de sciure et pour s’assurer qu’il n’y a pas une obstruction qui
pourrait gêner à la performance optimale.
Pour nettoyer la chute à copeaux :
Débrancher la scie.
Desserrer la vis au bas de la chute à copeaux.
Retirer le couvercle.
Brasser pour retirer toute sciure et nettoyer avec un chiffon
propre et sec, au besoin.
Remettre le couvercle en place et bien serrer la vis.
RÉGLAGES
VIS
CHUTE À
COPEAUX
Fig. 45
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avant d’effectuer tout réglage, s’assurer que l’outil est
débranché et que son commutateur est en position
d’ARRÊT (OFF). Le non-respect de cet avertissement
pourrait entraîner des blessures graves.
Pour éviter des ajustements inutiles, il est bon de vérifier les
réglages soigneusement au moyen d’une équerre de charpentier
et de pratiquer des coupes d’essais sur des chutes, avant de
travailler sur une bonne pièce. Ne procéder à aucun réglage
avant d’avoir effectué des vérifications avec une équerre et
exécuté des coupes d’essai, pour s’assurer que des réglages
sont nécessaires.
REMPLACEMENT DE LA LAME
Voir les figures 46 à 48.
La trait de scie lame doit être dans les limites affranchies sur
le couteau diviseur.
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer la garde de lame et griffes antirebond.
Abaisser la lame et retirer la plaque de gorge.
S’assurer que le levier de verrouillage de biseau est verrouillée.
Relever la lame au maximum en tournant.
Insérer la clé de lame le bout ouvert méplats de axe de lame.
Engager l’extrémité fermé de la plus clé de lame sur l’écrou.
L’avoir les deux clés fermement, tirer l’hors de la clé (le côté
droite) en avant pendant que pousser l’intérieur (le côté de
gauche) au arrière de la scie. Retire la écrou de lame et
rondelle de lame.
Déverrouiller segurar la palanca de afloje et retirer la lame.
NOTE : L’axe de lame est enfile de droite.
CLÉ DE
LAME
CLÉ DE
LAME
Fig. 46
38 − Français
Page 80

RÉGLAGES
Installation d’une lame standard :
Placer la lame sur l’axe (pour qu’elle fonctionne correctement,
ses dents doivent être orientées vers le bas et l’avant de la
scie).
Installer la rondelle de la lame et écrou de lame sur axe de
lame. S’assurer que le côté plat de la rondelle est placé
contre la lame et que toutes les pièces sont bien serrées
contre le support de l’axe. S’assurer que écrou de lame soit
fermement serré. Ne pas trop serrer.
Verrouiller le levier de dégagement.
Faire tourner la lame à la main pour s’assurer qu’elle
fonctionne librement.
Abaisser la lame et remettre la plaque à gorge en place.
Vérifier que la lame tourne librement, sans toucher quoi que
ce soit.
NOTE : Pour l’installation d’une lame spéciale, suivre les
instructions fournies avec cette lame.
LAME
RONDELLE
DE LAME
RÉGLAGE DE LA LAME À 0° ET 45°
Voir les figures 49 et 50.
La scie a été réglée en usine et, à moins qu’elle ait été
endommagée en cours de transport, aucun réglage ne devrait
être nécessaire. Arpès un usage prolongé, il peut être nécessaire
de vérifier les réglages.
Débrancher la scie.
Relever la lame.
Retirer le ensemble la garde de lame.
Si la lame n’est pas parfaitement verticale (0°) :
Désengager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Desserrer le vis de réglage de 0°.
Placer une équerre combinée à côté de la lame, sur la en
droit. Le bord de la équerre et la lame de scie doivent être
parallèles.
NOTE : Assurez-vous que les contacts carrés la partie
équerre de la lame de scie, pas les dents de scie.
Engager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Serrer vis de réglage. Vérifier de nouveau l’alignement et
continuer à ajuster effectuer les réglages éventuels.
LAME
VIS DE
RÉGLAGE À 0°
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
PLAQUE À
GORGE
ÉCROU DE
LAME
AXE DE
LAME
COUTEAU
DIVISEUR
Fig. 47
LAME
POIGNÉE
INDICATEUR
DE BISEAU
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
Fig. 49
Fig. 48
39 − Français
Page 81

RÉGLAGES
Si la lame n’est pas parfaitement à 45° :
Désengager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Desserrer le vis de réglage de 45°.
Placer une équerre combinée à côté de la lame, sur la en
droit. Le bord de la équerre et la lame de scie doivent être
parallèles.
NOTE : Assurez-vous que les contacts carrés la partie
équerre de la lame de scie, pas les dents de scie.
Engager le levier de verrouillage de biseau.
Serrer vis de réglage. Vérifier de nouveau l’alignement et
continuer à ajuster effectuer les réglages éventuels.
Placer l’indicateur d’onglet sur 45°.
Effectuer une coupe d’essai.
La vis de réglage doit être en dessous de la table de la scie
surface de sorte que la pièce ne capture pas sur les bords
irréguliers. S’il est impossible de procéder à cet réglage, prendre
le produit à un centre de service autorisé.
LAME
VIS DE
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
RÉGLAGE À 45°
45°
VÉRIFICATION DE L’ALIGNEMENT DU GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL SUR LA LAME
Voir la figure 51.
Le guide longitudinal doit être installé en parallèle avec la lame
et les rainures du guide d’onglet.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Un guide longitudinal incorrectement aligné peut causer
des rebonds et des blocages. Pour réduire les risques
de blessures,maintenir l’alignement correct du guide
longitudinal.
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer la garde de lame, le couteau diviseur et griffes anti-
rebond. Relever la lame au maximum en tournant le volant
de réglage de hauteur / biseau.
Vérifier que la lame est parallèle avec la rainure du guide
d’onglet, conformément à ce qui est décrit à la section Réglage de la lame parallèlement à la rainure du
guide d’onglet (suppression du talon) dans la section
Utilisation.
Amener le guide longitudinal près de la lame de la scie (à
environ 76,20 mm [3 po] de la lame), puis verrouiller le guide
à l’aide du levier de verrouillage.
Faites une marque derrière une dent sur le devant de la
lame. À l’aide d’une règle, mesurer la distance entre la face
intérieure de la dent de lame et la face intérieure du guide
longitudinal.
POIGNÉE
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
Fig. 50
40 − Français
DENT DE
LAME
GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
RÈGLE
VIS
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
Fig. 51
Page 82

RÉGLAGES
NOTE : Pour une précision accrue, positionner la dent mar-
quée de la lame sur le dessus de la règle.
Tournez la lame pour que la dent marquée se retrouve en
arrière.
Déplacer la règle vers l’arrière et mesurer de nouveau la
distance entre la face intérieure de la dent de lame et la
face intérieure du guide longitudinal. Si les distances sont
identiques, la lame et le guide longitudinal sont parallèles.
Si les distances mesurées sont différentes :
Déverrouillez le guide longitudinal
Déserrer les deux vis situées sur le guide de coupe.
Régler le guide longitudinal.
Serrer les vis alternance. Vérifier de nouveau l’alignement.
Répéter la procédure selon le besoin jusqu’à ce que le guide
longitudinal soit correctement aligné.
Replacer la garde de lame et le couteau diviseur et griffes
antirebond.
VÉRIFICATION DE L’ÉTANCHÉITÉ DU
LEVIER DE VERROUILLAGE DU GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
Voir le figure 52.
Le levier de verrouillage du guide longitudinal doit maintenir ce
dernier fermement appuyé contre les rails avant et arrière. Le
levier doit pouvoir être abaissé et verrouillé sans effort. Pour
assurer un réglage correct du verrouillage de guide :
Verrouiller le guide longitudinal à sa place.
Essayer déplaçant le guide longitudinal du côté-à-le côté.
si la le guide se déplace, resserre l’écrou de verrouillage 1/4
virage.
Une fois le guide longitudinal en position verrouillée, vérifier
de nouveau son parallélisme avec la lame et le régler selon
le besoin.
ÉCROU DE
BLOCAGE
Fig. 52
ENTRETIEN
AVERTISSEMENT :
Utiliser exclusivement des pièces d’origine pour les
réparations. L’usage de toute autre pièce pourrait créer une
situation dangereuse ou endommager l’outil.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours porter une protection oculaire certifiée conforme
à la norme ANSI Z87.1 lors de l’utilisation de produit. Si
une opération dégage de la poussière, porter également un
masque anti-poussière.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avant d’effectuer tout entretien, assurez-vous que la outil est
débranchée et que le commutateur est en position ARRÊT
( O ). Le non-respect de cette règle peut occasionner de
graves blessures.
ENTRETIEN GÉNÉRAL
Éviter d’utiliser des solvants pour le nettoyage des pièces en
plastique. La plupart des matières plastiques peuvent être
endommagées par divers types de solvants du commerce.
Utiliser un chiffon propre pour éliminer la saleté, la poussière,
l’huile, la graisse, etc.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne jamais laisser de liquides tels que le fluide de freins,
l’essence, les produits à base de pétrole, les huiles
pénétrantes, etc., entrer en contact avec les pièces en
plastique. Les produits chimiques peuvent endommager,
affaiblir ou détruire le plastique, ce qui peut entraîner des
blessures graves.
Vérifier régulièrement le serrage et l’état de tous les colliers,
écrous boulons et vis. S’assurer que la plaque à gorge est
en bon état et bien en place.
Vérifier la garde de lame.
Appliquer périodiquement de la cire en pâte sur la table, le
guide et les rails pour assurer un fonctionnement en douceur.
Éliminer la sciure se trouvant au-dessous de la table et entre
les dents de la lame pour protéger cette dernière. Utiliser un
solvant à résine pour le nettoyage des dents de la lame.
Nettoyer les pièces en plastique uniquement avec un
chiffon doux humide. NE PAS utiliser de produits en aérosol
ni de solvants pétroliers.
41 − Français
Page 83

ENTRETIEN
LUBRIFICATION
Tous les roulements de cet outil sont enduits d’une quantité
suffisante de lubrifiant de haute qualité pour la durée de vie de
l’outil, dans des conditions d’utilisation normales. Aucune autre
lubrification n’est donc nécessaire.
NETTOYER LES PLAQUES DU LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE DU COUTEAU FENDEUR
Voir le figure 53.
Le loquet de verrouillage du couteau fendeur peut devenir
difficile à bien verrouiller après une utilisation prolongée à
cause de la sciure ou des débris se logeant dans les plaques.
Débrancher la scie.
Déverrouiller le levier pour retirer le couteau fendeur.
Nettoyer l’endroit avec un chiffon propre et sec, ou utiliser
de l’air comprimé pour souffler les débris.
Réinstaller le couteau fendeur et tourner le levier pour le
verrouiller en place.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser la scie si le levier de verrouillage ne
se ferme pas complètement. Ne pas prendre cette
précaution peut causer des blessures graves.
COUTEAU
DIVISEUR
LEVIER DE
BLOCAGE
PLAQUES
Fig. 53
ACCESSOIRES
Rechercher ces accessoires où vous avez acheté ce produit ou en appelant au 1-800-525-2579 :
Plaque à gorge pour lame .....................................................................................................................................089240015199
AVERTISSEMENT :
Les outils et accessoires disponibles actuellement pour cet outil sont listés ci-dessus. Ne pas utiliser d’outils ou accessoires
non recommandés pour cet outil. L’utilisation de pièces et accessoires non recommandés peut entraîner des blessures graves.
42 − Français
Page 84

DÉPANNAGE
PROBLÈME CAUSE SOLUTION
Vibrations excessives. Lame déséquilibrée.
Lame endommagée.
La scie n’est pas solidement assujettie.
Surface de travail irrégulière.
Lame voilée.
Le guide longitudinal ne se déplace
pas en douceur.
Le guide longitudinal ne se verrouille
pas à l’arrière.
La lame se bloque ou brûle le bois. Lame émoussée.
Le chant de la pièce n’est pas
appuyé contre le guide longitudinal
lors de la refente.
Les coupes à 90 ou 45˚ sont
imprécises.
Le volant de réglage de hauteur /
biseau est difficile à tourner.
La scie ne démarre pas. Cordon du moteur ou prolongateur pas
Guide longitudinal pas correctement
installé.
Rails encrassés ou collants.
Vis de serrage déréglée.
Vis de serrage déréglée. Tourner la vis de serrage vers la droite.
Lame désalignée.
Pièce à couper avancée trop rapidement.
Guide longitudinal mal aligné.
Planche voilée.
Couteau diviseur mal aligné.
Lame incorrectement affûtée ou installée. Affûter ou ajuster la lame.
Les butées de l’intérieur du bâti doivent
être réglées (coupes en biseau).
Guide d’onglet pas correctement aligné
(coupe d’onglets).
Les engrenages ou la vis sans fin de
l’intérieur de l’armoire sont bloqués par
de la sciure.
branché.
Fusible de circuit grillé.
Disjoncteur déclenché.
Cordon ou commutateur endommagé.
Remplacer la lame.
Remplacer la lame.
Serrer tous les écrous, vis et boulons.
Repositionner sur une surface plane. Régler les
pieds du stand en option.
Vérifier le montage de la lame. Remplacer la lame
si nécessaire.
Réinstaller le guide longitudinal.
Nettoyer et cirer les rails.
Tourner la vis de serrage vers la gauche.
Remplacer ou affûter la lame.
Voir « Réglage de la lame parallèlement
à la rainure du guide d’onglet
(suppression du talon) ».
Ralentir l’avance.
Aligner le guide longitudinal.
Changer de pièce à couper. Toujours couper avec
le côté convexe face à la table.
Voir « Vérification et alignement du couteau
diviseur et la lame » à la section Assemblage.
Régler les butées fixes.
Régler le guide d’onglet.
Nettoyer les engrenages ou la vis sans fin.
Brancher le cordon du moteur ou le prolongateur.
Remplacer le fusible.
Réarmer le disjoncteur.
Faire remplacer le cordon ou le commutateur
dans un centre de réparations agréé.
La lame ne coupe pas correctement. Lame émoussée ou encrassée.
Lame de type incorrect pour la coupe.
Lame montée à l’envers.
La lame ne s’abaisse pas lorsque
le volant de réglage de hauteur /
biseau est tourné.
Le moteur force lors d’une coupe
longitudinale.
Le levier de verrouillage n’est pas poussé
à fond vers en bas.
Lame incorrecte pour la coupe
longitudinale.
43 − Français
Nettoyer, affûter ou remplacer la lame.
Utiliser une lame de type approprié.
Réinstaller la lame.
Pousser le levier à fond vers en bas.
Remplacer la lame par une lame pour coupe
longitudinale, qui en général comporte moins
de dents.
Page 85

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD GENERALES
ADVERTENCIA:
Lea y asegúrese de entender todas las instrucciones. El
incumplimiento de las instrucciones siguientes puede ser causa
de descargas eléctricas, incendios y lesiones graves.
LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES
FAMILIARÍCESE CON SU HERRAMIENTA ELÉCTRICA.
Lea cuidadosamente el manual del operador. Aprenda los
usos y limitaciones de la sierra, así como los posibles peligros
específicos de esta herramienta.
PROTÉJASE DE DESCARGAS ELÉCTRICAS EVITANDO
TOCAR CON EL CUERPO SUPERFICIES CONECTADAS A
TIERRA. Por ejemplo, tubos, radiadores, estufas y cajas de
refrigeradores.
MANTENGA LAS PROTECCIONES COLOCADAS y en buenas
condiciones de trabajo.
RETIRE TODA LLAVE Y HERRAMIENTA DE AJUSTE. Hágase
el hábito de comprobar que se haya retirado de la herramienta
eléctrica toda llave y herramienta de ajuste antes de encenderla.
MANTENGA LIMPIA LA ZONA DE TRABAJO. Una mesa o
zona de trabajo mal despejada es causa común de accidentes.
NO deje herramientas o piezas de madera en la sierra mientras
esté funcionando.
NO UTILICE LA HERRAMIENTA EN ENTORNOS
PELIGROSOS. No utilice herramientas eléctricas en lugares
húmedos o mojados ni las exponga a la lluvia. Mantenga bien
iluminada el área de trabajo.
MANTENGA ALEJADOS A LOS NIÑOS Y DEMÁS
CIRCUNSTANTES. Todos los presentes deben usar anteojos
de seguridad y permanecer a una distancia segura del área
de trabajo. No permita que ninguno de los presentes toque la
herramienta ni la extensión eléctrica mientras la unidad esté
funcionando.
HAGA SU TALLER A PRUEBA DE NIÑOS, con candados,
interruptores maestros y retirando las llaves de arranque.
NO FUERCE LA HERRAMIENTA. Funcionará mejor y con
mayor seguridad si se usa a la velocidad de avance para la
que fue diseñada.
USE LA HERRAMIENTA APROPIADA EN CADA CASO. No
fuerce la herramienta ni ningún accesorio a efectuar tareas
para las que no fueron hechos. No la use para propósitos no
indicados en las instrucciones.
USE UN CABLE DE EXTENSIÓN ADECUADO. Asegúrese
de que la extensión eléctrica esté en buen estado. Si se utiliza
un cable de extensión, debe ser del calibre suficiente para
soportar la corriente que consume el producto. Un cordón de
grosor insuficiente causará una caída del voltaje de línea, lo que
produce recalentamiento y pérdida de potencia. Se recomienda
un calibre mínimo de 14 (A.W.G.) para cables de extensión de
7,6 metros (25 pies) de largo o menos. Si tiene alguna duda,
utilice un cable del calibre más grueso siguiente. Cuanto menor
es el número de calibre, tanto mayor es el grosor del cordón.
USE ROPA ADECUADA. No use ropa holgada, guantes flojos,
corbata ni alhajas. Podrían engancharse y tirar de usted hacia
partes en movimiento. Si tiene el pelo largo, cúbraselo para que
quede recogido.
SIEMPRE UTILICE PROTECCIÓN OCULAR QUE CUBRA
LOS LATERALES CON LA ETIQUETA QUE INDIQUE EL
CUMPLIMIENTO DE LA NORMA ANSI Z87.1. La inobservancia
de esta advertencia podría provocar que se le metan objetos
en los ojos, lo que puede provocar lesiones graves.
AFIANCE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO. Cuando convenga, sujete
la pieza de trabajo con prensas de mano o de banco. Es más
seguro que detenerla manualmente y así ambas manos quedan
libres para manejar la herramienta.
NO SE ESTIRE PARA ALCANZAR OBJETOS. Mantenga una
postura firme y buen equilibrio en todo momento.
DÉ UN MANTENIMIENTO CUIDADOSO A LAS
HERRAMIENTAS. Manténgalas afiladas y limpias para que
funcionen mejor y sin riesgos. Siga las instrucciones referentes
al cambio y lubricación de accesorios.
DESCONECTE LAS HERRAMIENTAS. Todas las herramientas
deben desconectarse cuando ya no vayan a usarse o cuando
deban cambiarse aditamentos, hojas de corte, brocas, fresas,
etc.
EVITE UN ARRANQUE ACCIDENTAL DE LA UNIDAD. Antes
de conectar la herramienta a la corriente, compruebe que el
interruptor esté en posición de apagado.
USE LOS ACCESORIOS RECOMENDADOS. Consulte
este manual del operador, donde aparecen los accesorios
recomendados. El empleo de accesorios inadecuados puede
plantear el riesgo de lesiones.
NO SE PARE NUNCA EN LA HERRAMIENTA. Pueden
producirse lesiones graves si la herramienta eléctrica se vuelca
o si se toca accidentalmente la herramienta de corte.
INSPECCIONE LAS PIEZAS DAÑADAS. Antes de seguir
utilizando la herramienta, es necesario inspeccionar
cuidadosamente toda protección o pieza dañada, para verificar
si funcionará correctamente y cumplirá la función a la que
está destinada. Compruebe que las partes móviles estén bien
alineadas y que no estén trabadas, que no haya piezas rotas,
el montaje de las partes y cualquier otra condición que pudiera
afectar su funcionamiento. Toda protección o pieza que esté
dañada debe repararse apropiadamente o reemplazarse en un
centro de servicio autorizado.
AVANCE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO EN LA DIRECCIÓN
CORRECTA. Empuje la pieza de trabajo hacia la hoja o
herramienta de corte solamente contra el sentido de rotación
de ésta.
NUNCA DEJE DESATENDIDA LA HERRAMIENTA
FUNCIONANDO. APAGUE LA CORRIENTE. No se aleje de
la herramienta hasta ver que se detenga totalmente.
PROTÉJASE LOS PULMONES. Use una careta o mascarilla
contra el polvo si la operación de corte genera mucho polvo.
PROTÉJASE EL OÍDO. Durante períodos largos de uso de la
unidad póngase protección para los oídos.
NO MALTRATE EL CABLE ELÉCTRICO. Nunca tire del cable
para desconectarlo de la toma de corriente. Mantenga el cable
eléctrico alejado del calor, del aceite y de bordes afilados.
AL UTILIZAR UNA HERRAMIENTA ELÉCTRICA EN EL
EXTERIOR, UTILICE UN CORDÓN ELÉCTRICO DE
EXTENSIÓN QUE LLEVE LAS MARCAS “W-A” O “W”. Estos
cordones eléctricos están aprobados para el uso en exteriores
y reducen el riesgo de descargas eléctricas.
3 − Español
Page 86

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD GENERALES
SIEMPRE MANTENGA EL PROTECTOR DE LA HOJA Y EL
SEPARADOR (PLACA ABRIDORA) EN SU LUGAR y en buenas
condiciones de funcionamiento.
MANTENGA LAS HOJAS DE CORTE LIMPIAS Y AFILADAS.
Las hojas de corte afiladas reducen al mínimo los paros y los
contragolpes.
MANTENGA LAS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL ÁREA DE CORTE.
Mantenga las manos alejadas de la hoja de corte. No meta las
manos por abajo de la pieza de trabajo ni alrededor o por encima
de la hoja de corte mientras ésta está girando. No intente retirar
ningún material cortado mientras la hoja de corte esté girando.
LA HOJA DE CORTE CONTINÚA GIRANDO POR INERCIA
DESPUÉS DE APAGAR LA UNIDAD.
NUNCA UTILICE LA UNIDAD EN UNA ATMÓSFERA
EXPLOSIVA. El chispeo normal del motor podría encender los
gases presentes.
REVISE PERIÓDICAMENTE LOS CABLES DE LA
HERRAMIENTA. Si están dañados, llévelos a un centro de
servicio autorizado para que los revise un técnico de servicio
calificado. El conductor con aislamiento que tiene una superficie
exterior verde con o sin tiras amarillas es el conductor de
conexión a tierra del equipo. Si el cable o la clavija necesitan
reparación o reemplazo, no conecte el conductor de conexión a
tierra a una terminal portadora de corriente. Repare o reemplace
de inmediato todo cable dañado o gastado. Tenga presente
siempre la ubicación del cable y manténgalo bien alejado de
la hoja giratoria.
REVISE PERIÓDICAMENTE LOS CABLES DE EXTENSIÓN
y reemplácelos si están dañados.
CONECTE A TIERRA TODA HERRAMIENTA ELÉCTRICA. Si
la herramienta está provista de una clavija de tres puntas, debe
conectarse en un enchufe eléctrico de tres polos.
CONSULTE A UN ELECTRICISTA CALIFICADO o técnico de
servicio si no ha comprendido completamente las instrucciones
de conexión a tierra o si no está seguro de que la herramienta
está bien conectada a tierra.
USE SOLAMENTE LOS DISPOSITIVOS ELÉCTRICOS
CORRECTOS: cables de extensión de 3 conductores, con
clavijas de tres puntas y contactos de tres polos que acepten
la clavija del cable de la herramienta.
NO MODIFIQUE la clavija suministrada. Si no entra en la toma
de corriente, llame a un electricista calificado para que instale
una toma de corriente adecuada.
MANTENGA LA HERRAMIENTA SECA, LIMPIA Y LIBRE DE
ACEITE Y GRASA. Siempre utilice un paño limpio para limpiar
la unidad. No use nunca líquido para frenos, gasolina, productos
a base de petróleo ni solventes para limpiar la herramienta.
PERMANEZCA ALERTA Y EN CONTROL. Preste atención
a lo que esté haciendo y aplique el sentido común. No utilice
la herramienta cuando esté cansado. No haga las cosas con
prisa.
NO USE LA HERRAMIENTA SI EL INTERRUPTOR NO
ENCIENDE O NO APAGA. Todo interruptor defectuoso debe
llevarse a reparar a un centro de servicio autorizado.
USE SÓLO LAS HOJAS DE CORTE CORRECTAS. No use
hojas con orificios de tamaño incorrecto. Nunca utilice arandelas
ni pernos de hoja de corte que estén dañados o no sean los
adecuados. La sierra admite hojas de un diámetro máximo de
254 mm (10 pulg).
ANTES DE EFECTUAR UN CORTE VERIFIQUE QUE TODOS
LOS COMPONENTES PRESENTEN EL AJUSTE CORRECTO.
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE NO HAYA CLAVOS EN LA
TRAYECTORIA DE LA HOJA. Inspeccione la madera en busca
de clavos y elimínelos todos antes de empezar a cortar.
NUNCA TOQUE LA HOJA ni ninguna otra pieza en movimiento
durante el funcionamiento de la unidad.
NUNCA ARRANQUE LA HERRAMIENTA CUANDO UN
COMPONENTE GIRATORIO ESTÉ EN CONTACTO CON LA
PIEZA DE TRABAJO.
NO UTILICE NINGUNA HERRAMIENTA SI SE ENCUENTRA
BAJO LOS EFECTOS DE DROGAS, ALCOHOL O
MEDICAMENTOS.
AL DAR MANTENIMIENTO a la unidad, utilice solamente
piezas de repuesto idénticas. El empleo de piezas diferentes
puede causar un peligro o dañar el producto.
UTILICE SOLAMENTE LOS ACCESORIOS señalados en este
manual o en los apéndices. El uso de accesorios no mencionados
en este manual plantea el riesgo de que ocurran lesiones
corporales. Cada accesorio se acompaña de instrucciones
para su uso sin riesgos.
REVISE DOS VECES TODA LA CONFIGURACIÓN DE LA
HERRAMIENTA. Asegúrese de que la hoja esté apretada y de
que no toque la sierra ni la pieza de trabajo antes de conectar
la unidad al suministro de corriente.
REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD ESPECÍFICAS
ATORNILLE FIRMEMENTE LA SIERRA A UN BANCO DE
TRABAJO O PEDESTAL DE PATAS aproximadamente a la
altura de la cadera.
NO HAGA FUNCIONAR LA SIERRA SIN QUE LA BASE
ESTÉ SOBRE EL PISO.
PROTÉJASE DE UN CONTRAGOLPE. El contragolpe
sucede cuando la hoja se detiene rápidamente y la pieza de
trabajo sale proyectada hacia el operador. Puede tirar de la
mano hacia la hoja y producir lesiones corporales graves.
Manténgase fuera de la trayectoria de la hoja y apague de
inmediato el interruptor si la hoja se traba o se detiene.
4 − Español
USE LA GUÍA DE CORTE AL HILO. Siempre utilice una guía
o una regla (tira recta) al efectuar cortes al hilo.
APOYE LOS PANELES GRANDES. Para reducir al mínimo
el riesgo de que la hoja de corte se trabe y se produzca un
contragolpe, apoye debidamente los paneles grandes.
RETIRE TODAS LAS GUÍAS Y MESAS AUXILIARES antes
de transportar la sierra. De lo contrario, puede producirse un
accidente que origine lesiones corporales graves.
SIEMPRE USE EL PROTECTOR DE LA HOJA DE CORTE,
EL CUCHILLA SEPARADOR Y LOS TRINQUETES
ANTICONTRAGOLPE en todas las operaciones de
Page 87

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD ESPECÍFICAS
“aserrado con traspaso”. Las operaciones de aserrado con
traspaso son aquéllas en que la hoja corta traspasando
completamente la pieza de trabajo, como en el corte al hilo
o el transversal. Mantenga abajo el protector de la hoja y
los trinquetes anticontragolpe, y el cuchilla separador en su
lugar.
SIEMPRE ASEGURE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO firmemente
contra la guía de corte al hilo o la guía de corte a inglete.
SIEMPRE UTILICE UN PALO DE EMPUJAR AL ASERRAR
AL HILO PIEZAS ANGOSTAS. Un palo empujador es un
implemento que sirve para empujar la pieza de trabajo por
la hoja de corte en lugar hacerlo con las manos. El tamaño
y la forma pueden variar, pero el palo de empujar siempre
debe ser más angosto que la pieza de trabajo, para evitar
que toque la hoja de la sierra. Al aserrar al hilo material
estrecho, use siempre un palo de empujar, o la sierra vaivén
mencionado en la sección Cómo hacer un serrado (para
piezas de trabajo de cortes transversales estrechos) de este
manual, de manera que la mano no se acerque a la hoja de
la sierra. Para cortes parciales sin traspaso utilice un peine y
bloques empujadores.
AL HACER CORTES AL HILO NO PASANTE, siempre utilice
un palos empujadora, bloque empujador y/o peine de sujeción
tan sus manos no vienen dentro de 3 pulg. de la hoja de sierra.
AL CORTE LONGITUDINAL ESTRECHE ACCIONES, siempre
utilice un palos empujadora, bloque empujador, serrado
(diseñado para cortes transversales estrechos), y/o peine de
sujeción.
NUNCA realice ninguna operación “a pulso”, o sea nunca
use solamente las manos para dar apoyo o guiar la pieza de
trabajo. Siempre use la guía de corte al hilo o la guía de corte
a inglete y oriente la pieza de trabajo.
NUNCA se pare ni tenga ninguna parte del cuerpo en línea
con la trayectoria de la hoja de la sierra.
NUNCA se estire por detrás o por encima de la hoja o
herramienta de corte, ni a menos de 76 mm (3 pulg) de ésta
con ninguna mano, por ninguna razón.
SIEMPRE RETIRE LA GUÍA DE CORTE AL HILO de la
sierra al realizar cortes transversales.
NO UTILICE LA GUÍA DE CORTE A INGLETE Y LA DE
CORTE AL HILO en la misma operación de corte.
NUNCA utilice la guía de corte al hilo como guía tope al
efectuar cortes transversales.
NUNCA intente liberar la hoja de la sierra cuando esté
trabada, sin antes APAGAR y desconectar la sierra de la
toma de corriente.
APOYE ADECUADAMENTE la parte posterior y los lados
de la mesa de la sierra al cortar piezas de trabajo anchas o
largas.
EVITE CONTRAGOLPES (que la pieza de trabajo salga
lanzada hacia usted) haciendo lo siguiente:
a) Mantenga limpia la hoja.
b) Mantenga la guía de corte al hilo paralela a la hoja de la
sierra.
c) Mantenga el cuchilla separadora, los trinquetes anti-
contragolpe y el protector de la hoja en su lugar y en buenas
condiciones de funcionamiento.
d) No suelte la pieza de trabajo hasta haberla hecho pasar por
completo por la sierra, con un empujador.
e) No corte al hilo piezas de trabajo torcidas o combas o que
no tengan un canto recto que permita dirigirlas por la guía
de corte al hilo.
SI ESTÁ DAÑADO EL CORDÓN DE CORRIENTE, debe ser
reemplazado únicamente por el fabricante o en un centro de
servicio autorizado para evitar riesgos.
EVITE OPERACIONES Y POSICIONES EXTRAÑAS DE LAS
MANOS en las cuales un deslizamiento rápido puede hacer
que la mano toque la herramienta de corte.
USE SOLAMENTE LOS ACCESORIOS señalados en
este manual o en los apéndices. El uso de accesorios no
mencionados en este manual plantea el riesgo de que
ocurran lesiones corporales. Cada accesorio se acompaña
de instrucciones para su uso sin riesgos.
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE TODA EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO ESTÉ
BIEN ILUMINADA para ver la pieza de trabajo y que ninguna
obstrucción impida una operación segura ANTES de efectuar
cualquier trabajo con la sierra.
SIEMPRE APAGUE LA SIERRA antes de desconectarla,
para evitar un arranque accidental de la misma al volver a
conectarla al suministro de corriente.
UTILICE SOLAMENTE LAS HOJAS dentro de la gama del
espesor estampó en el cuchilla separadora.
ESTA HERRAMIENTA tendrá los siguientes avisos:
a) Póngase protección ocular.
b) Utilice la protección de la hoja y la cuchilla separadora en
toda operación en la que pueda usarse, como el aserrado
con traspaso.
c) Mantenga las manos alejadas de la línea de la hoja de corte.
d) Cuando se requiera, utilice un palo de empujar.
e) Preste especial atención a las instrucciones sobre cómo
reducir el riesgo de un contragolpe.
f) No efectúe a pulso ninguna operación.
g) Nunca trate de alcanzar nada cerca o por encima de la hoja
de corte.
h) Nunca utilice la sierra en el piso ni debajo de altura de
cintura.
NUNCA CORTE MÁS DE UN PEDAZO DE MATERIAL A LA
VEZ.
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES. Consúltelas con
frecuencia y empléelas para instruir a otros usuarios. Si
presta a alguien esta herramienta, facilítele también las
instrucciones.
5 − Español
Page 88

SÍMBOLOS
Las siguientes palabras de señalización y sus significados tienen el objeto de explicar los niveles de riesgo relacionados con este
producto.
SÍMBOLO SEÑAL SIGNIFICADO
PELIGRO:
ADVERTENCIA:
PRECAUCIÓN:
AVISO:
Es posible que se empleen en esta herramienta algunos de los siguientes símbolos. Le suplicamos estudiarlos y aprender su
significado. Una correcta interpretación de estos símbolos le permitirá utilizar mejor y de manera más segura la herramienta.
Indica una situación peligrosa, la cual, si no se evita, causará la muerte o lesiones serias.
Indica una situación peligrosa, la cual, si no se evita, podría causar la muerte o lesiones serias.
Indica una situación peligrosa, la cual, si no se evita, podría causar lesiones menores o leves.
(Sin el símbolo de alerta de seguridad) Indica la información que se considera importante,
pero no relacionada con lesiones potenciales (por ej. en relación a daños a la propiedad).
SÍMBOLO NOMBRE DENOMINACIÓN/EXPLICACIÓN
Alerta de seguridad Indica un peligro posible de lesiones personales.
Lea el manual del operador
Protección ocular
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, el usuario debe leer y comprender el
manual del operador antes de usar este producto.
Siempre póngase protección ocular con protección lateral con la
marca de cumplimiento de la norma ANSI Z87.1.
Símbolo de no acercar las manos
Alerta de condiciones
húmedas
V Volts Voltaje
A Amperes Corriente
Hz Hertz Frecuencia (ciclos por segundo)
min Minutos Tiempo
Corriente alterna Tipo de corriente
n
o
.../min Por minuto Revoluciones, carreras, velocidad superficial, órbitas, etc., por minuto
Velocidad en vacío Velocidad de rotación, en vacío
Si no mantiene las manos alejadas de la hoja de corte, se causará serias
lesiones corporales.
No exponga la unidad a la lluvia ni la use en lugares húmedos.
6 − Español
Page 89

ASPECTOS ELÉCTRICOS
CORDONES DE EXTENSIÓN
Sólo utilice cordones de extensión de 3 conductores con clavijas de
tres patillas y receptáculos de tres polos que acepten la clavija del
cordón de la herramienta. Al utilizar una herramienta eléctrica a una
distancia considerable del suministro de corriente, asegúrese de
utilizar un cordón de extensión del grueso suficiente para soportar
el consumo de corriente de la herramienta. Un cordón de extensión
de un grueso insuficiente causa una caída en el voltaje de línea,
además de producir una pérdida de potencia y un recalentamiento
del motor. Básese en la tabla suministrada abajo para determinar
el calibre mínimo requerido de los conductores del cordón de
extensión. Solamente deben utilizarse cordones con forro redondo
registrados en Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL).
**Amperaje (aparece en la placa frontal)
0-2,0 2,1-3,4 3,5-5,0 5,1-7,0 7,1-12,0 12,1-16,0
Longitud del cordón Calibre conductores (A.W.G.)
25’ 16 16 16 16 14 14
50’ 16 16 16 14 14 12
100’ 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Se usa en los circuitos de calibre 12, 20 amp.
NOTA: AWG = Calibre conductores norma americana
Al trabajar a la intemperie con el producto, utilice un cordón de
extensión fabricado para uso en el exterior. Tal característica está
indicada con las letras “W-A” o “W” en el forro del cordón.
Antes de utilizar un cordón de extensión, inspecciónelo para ver
si tiene conductores flojos o expuestos y aislamiento cortado o
gastado.
durante el corte o con un voltaje bajo. En cuanto al voltaje, el
cableado de un taller es tan importante como la potencia nominal
del motor. Una línea destinada sólo para luces no puede alimentar el
motor de una herramienta eléctrica. El cable con el calibre suficiente
para una distancia corta será demsiado delgado para una mayor
distancia. Una línea que alimenta una herramienta eléctrica quizá
no sea suficiente para alimentar dos o tres herramientas.
INSTRUCCIONES DE CONEXIÓN A TIERRA
Este producto debe conectarse a tierra. En caso de un mal
funcionamiento o desperfecto, la conexión a tierra brinda a la
corriente eléctrica una trayectoria de mínima resistencia para
disminuir el riesgo de una descarga eléctrica. Esta herramienta está
equipada de un cordón eléctrico con un conductor y una clavija
de conexión a tierra para equipo. La clavija debe conectarse en
una toma de corriente igual que esté instalada y conectada a tierra
correctamente, de conformidad con los códigos y reglamentos de
la localidad.
No modifique la clavija suministrada. Si no entra en la toma de
corriente, llame a un electricista calificado para que instale una
toma de corriente adecuada.
ADVERTENCIA:
Si se conecta de forma incorrecta el conductor de conexión
a tierra del equipo puede presentarse un riesgo de descarga
eléctrica. Si es necesaria la reparación o reemplazo del cordón
eléctrico o de la clavija, no conecte el conductor de conexión a
tierra a una terminal portadora de corriente. El conductor con
aislamiento que tiene una superficie exterior verde con o sin
tiras amarillas es el conductor de conexión a tierra del equipo.
ADVERTENCIA:
Mantenga el cordón de extensión fuera del área de trabajo. Al
trabajar con una herramienta eléctrica, coloque el cordón de tal
manera que no pueda enredarse en la madera, herramientas ni
en otras obstrucciones. La inobservancia de esta advertencia
puede causar lesiones serias.
ADVERTENCIA:
Inspeccione los cordones de extensión cada vez antes de
usarlos. Si están dañados reemplácelos de inmediato. Nunca
utilice la herramienta con un cordón dañado, ya que si toca la
parte dañada puede producirse una descarga eléctrica, y las
consecuentes lesiones serias.
CONEXIÓN ELÉCTRICA
Esta herramienta está impulsada por un motor eléctrico fabricado
con precisión. Debe conectarse únicamente a una línea de voltaje
de 120 V, de corriente alterna solamente (corriente normal
para uso doméstico), 60 Hz. No utilice esta herramienta con
corriente continua (c.c.). Una caída considerable de voltaje causa
la pérdida de potencia y el recalentamiento del motor. Si la sierra
no funciona al conectarla en una toma de corriente, vuelva a revisar
el suministro de corriente.
VELOCIDAD Y CABLEADO
La velocidad en vacío de esta
aproximadamente. Esta velocidad no es constante y disminuye
producto
es de 4 700 r/min
Consulte a un electricista calificado o técnico de servicio si no ha
comprendido completamente las instrucciones de conexión a tierra
o si no está seguro si la herramienta está bien conectada a tierra.
Repare o reemplace de inmediato todo cordón dañado o gastado.
Este producto se debe usar con un circuito de 120 V nominales
y tiene una clavija de conexión a tierra similar a la clavija que se
muestra en la figura 1. Conecte el producto únicamente a una toma
de corriente que tenga la misma configuración que la clavija. No
use un adaptador con este producto.
PUNTA DE CONEXIÓN
A TIERRA
TOMA DE CORRIENTE
CON TIERRA, DE 120 V
Fig. 1
7 − Español
Page 90

GLOSARIO DE TÉRMINOS
Trinquetes anticontragolpe (sierras radiales y de mesa)
Es un dispositivo, el cual, cuando se instala y da mantenimiento
correctamente, sirve para detener la pieza de trabajo para no ser
lanzada hacia atrás, hacia la parte frontal la sierra durante una
operación de corte al hilo.
Árbol
Es el eje donde se monta una hoja o herramienta de corte.
Corte en bisel
Es una operación de corte efectuada con la hoja a un ángulo
diferente de 90° con respecto a la superficie de la mesa.
Chaflán
Es un corte efectuado para eliminar una cuña de un bloque de
manera que el extremo (o una parte del mismo) quede a un ángulo
diferente de 90°.
Corte combinado
Es un corte transversal efectuado a inglete y a bisel.
Corte transversal
Es una operación de corte o fresado efectuada a través de la fibra
o ancho de la pieza de trabajo.
Cabeza de corte (cepillos normales y de juntas)
Es una cabeza de corte giratoria con hojas o cuchillas ajustables.
Las hojas o cuchillas eliminan material de la pieza de trabajo.
Corte de ranura (sierras de mesa y sierras ingleteadoras
deslizantes combinadas)
Un corte no pasante que produce una muesca cuadrada, de tres
lados o en V en la pieza de trabajo.
Peine de sujeción (sierras de mesa)
Es un dispositivo empleado como ayuda para controlar la pieza de
trabajo guiándola con seguridad contra la mesa o la guía durante
las operaciones de corte al hilo.
PPM o CPM
Pies por minuto (o carreras por minuto), se emplea refiriéndose al
movimiento de la hoja.
A pulso
Es efectuar un corte sin guiar la pieza de trabajo con ninguna guía,
guía de ingletes ni ningún otro medio.
Goma
Es el residuo pegajoso de savia presente en la madera.
Talón
Es la alineación de la hoja con respecto a la ranura de la guía de
inglete.
Corte
Es la cantidad de material eliminado por la hoja en un corte
completo con traspaso, o en una ranura producida por la hoja en
un corte sin traspaso o parcial.
Contragolpe
Es un peligro que puede ocurrir cuando la hoja se atora o se
atasca, y lanza la pieza de trabajo hacia atrás, en la dirección de
la hoja giratoria.
Corte a inglete
Es una operación de corte efectuada con la pieza de trabajo a un
ángulo diferente de 90° con respecto a la hoja.
Cortes sin traspaso (sierras de mesa y sierras ingleteadoras
deslizantes combinadas)
Es cualquier operación de corte en la cual la hoja de corte no
traspasa completamente el espesor de la pieza de trabajo. Este
es un corte en el cual la hoja no corta la pieza de trabajo en dos
pedazos.
Agujero guía (taladradoras de columna y sierras caladoras)
Es un agujero pequeño taladrado en una pieza de trabajo, el cual
sirve como guía para taladrar con precisión agujeros más grandes
o para la colocación de la hoja de la sierra caladora.
Bloques empujadores (para cepillos de juntas)
Son dispositivos empleados para avanzar la pieza de trabajo por
el cepillo de juntas durante cualquier operación. Este medio ayuda
al operador a mantener las manos alejadas de la cabeza de corte.
Bloques y palos empujadores (para sierras de mesa)
Son dispositivos empleados para avanzar la pieza de trabajo
a través de la sierra durante operaciones de corte. Para las
operaciones de cortes al hilo angostos debe emplearse un palo
empujador (no un bloque empujador). Estos medios ayudan al
operador a mantener las manos alejadas de la hoja de corte.
Rebaje
Un corte no pasante ubicado en el extremo o borde de la pieza
de trabajo que produce una muesca cuadrada, de dos lados o en
V en la pieza de trabajo.
Reaserrado (sierras de mesa y sierras de banda)
Es una operación de corte efectuada para reducir el espesor de la
pieza de trabajo para hacer piezas más delgadas.
Resina
Es la sustancia pegajosa a base de savia que se endurece.
Revoluciones por minuto (RPM)
Es el número de vueltas realizadas por un objeto en movimiento
de giro en un minuto.
Corte longitudinal o al hilo (sierras de mesa)
Es una operación de corte paralela al largo de la pieza de trabajo
y generalmente en la dirección del grano.
Cuchilla separadora/Abridor/Separador (sierras de mesa)
Es una pieza metálica, levemente más delgada que la hoja, la cual
se emplea para mantener abierto el corte y también ayuda a evitar
un contragolpe.
Trayectoria de la hoja de la sierra
Es el área encima, abajo, detrás o delante de la hoja. En relación
con la pieza de trabajo, es el área que será o ha sido cortada por
la hoja.
Redondeo de aristas (cepillos)
Es una depresión hecha en cualquiera de los dos extremos de una
pieza de trabajo por las cuchillas de corte cuando no se proporciona
un apoyo adecuado a la pieza de trabajo.
Cónico Corte
Un corte donde el material para ser corte tiene una anchura
diferente al principio del corte del el fin.
Aserrado con traspaso
Es cualquier operación de corte en la cual la hoja de corte traspasa
completamente el espesor de la pieza de trabajo. Este tipo de corte
separa la pieza de trabajo simple en dos pedazos.
Pieza de trabajo o material
Es la pieza a la que se efectúa la operación.
Mesa
Es la superficie sobre la cual descansa la pieza de trabajo mientras
se le efectúa una operación de corte, taladrado, cepillado o lijado.
8 − Español
Page 91

CARACTERÍSTICAS
ESPECIFICACIONES DEL PRODUCTO
Árbol de la hoja de corte ........................16 mm (5/8 pulg.)
Diámetro de la hoja ...............................254 mm (10 pulg.)
Inclinación de la hoja ...............................................0˚ - 45˚
Capacidad de ranurado ......................12,7 mm (1/2 pulg.)
Especificaciones eléctricas ..... 120 V, sólo corr. alt., 60 Hz
Corriente de entrada ...................................................15 A
Velocidad en vacío ................................4 700 r/min (RPM)
Profundidad de corte a 0˚: .........................76 mm (3 pulg.)
Profundidad de corte a 45˚: ................ 64 mm (2-1/2 pulg.)
RANURA DE
LA GUÍA DE
INGLETES
RIEL
DELANTERO
TRINQUETES
ANTICONTRAGOLPE
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
VERTEDERO
DE ASERRÍN
CUCHILLA
SEPARADORA
PROTECCIÓN
DE LA HOJA
INTERRUPTOR
COMPARTIMENTO
DE ALMACENAMIENTO
PARA PALO EMPUJADOR
GUÍA
DE CORTE AL
HILO
ESCALA DE
CORTE AL
HILO
RANURA DE
LA GUÍA DE
INGLETES
INDICADOR
ESCALA DE
CORTE AL HILO
LUGAR DE
GUARDAR
LA LLAVE
DE LA HOJA
PALANCA DE
FIJACIÓN
PALANCA DE
FIJACIÓN DE
BISEL
PEDESTAL
9 − Español
VOLANTE DE
AJUSTE DE ALTURA
Y BISEL
ESCALA DE
BISELES
INDICADOR DE
BISEL
Fig. 2
Page 92

CARACTERÍSTICAS
FAMILIARÍCESE CON LA SIERRA DE MESA
Vea la figura 2.
El uso seguro que este producto requiere la comprensión de
la información impresa en la herramienta y en el manual del
operador así como ciertos conocimientos sobre el proyecto
a realizar. Antes de usar este producto, familiarícese con
todas las características de funcionamiento y normas de
seguridad.
TRINQUETES ANTICONTRAGOLPE - El contragolpe es
un peligro en el cual la pieza de trabajo resulta lanzada
hacia atrás, en dirección del operador. Los trinquetes
anticontragolpe apuntan hacia la dirección opuesta de la
pieza de trabajo. En caso de que ésta resulte empujada
hacia el operador, entonces los dientes muerden la madera
para impedir o reducir la posibilidad de un contragolpe. Los
trinquetes anticontragolpe pueden eludirse.
ESCALA DE BISELES - Esta escala de fácil lectura, situada
en la parte frontal de la armazón de la sierra, muestra el
ángulo exacto de la hoja de corte.
HOJA - Para un óptimo desempeño, se recomienda el uso
de la hoja de corte de 254 mm (10 pulg.) con puntas de
carburo suministrada con la sierra. La hoja se sube y baja
con el volante de ajuste de altura. Los ángulos de bisel se
fijan con la palanca de fijación de bisel. Hay disponibles
estilos adicionales de hojas de corte de la misma alta
calidad para operaciones específicas tales como el corte
al hilo. El distribuidor de la localidad puede proporcionarle
la información completa.
La anchura del corte debe estar dentro de los límites
estampados en el cuchilla separadora.
ADVERTENCIA:
No utilice hojas con una velocidad nominal inferior a la de
esta herramienta. La falta de atención a esta advertencia
puede causar lesiones corporales.
VERTEDERO DE ASERRÍN - El vertedero de aserrín
incorporado permite desechar el aserrín de manera sencilla.
Puede conectar una manguera de aspiradora al vertedero
de aserrín.
VOLANTE DE AJUSTE DE ALTURA Y BISEL - Este volante,
situado en la parte delantera de la armazón de la unidad,
sirve para subir y bajar la hoja con el fin de efectuar ajustes
a la altura de la misma, o reemplazarla. Este volante también
facilita el ajuste del ángulo de biselado.
GUÍA DE INGLETES - La guía de ingletes sirve para alinear
la madera para cortes transversales. Este indicador de fácil
lectura muestra el ángulo exacto para cortes a inglete.
RANURAS DE LA GUÍA DE INGLETES - La guía de ingletes
se desplaza por las ranuras de la mesa de la sierra.
COMPARTIMENTO DE ALMACENAMIENTO PARA PALO
EMPUJADOR Y LLAVES - Lugar de almacenamiento
práctico para el palo empujador y las llaves ubicado debajo
de la sierra.
GUÍA DE CORTE AL HILO - Es una resistente guía metálica
que sirve de apoyo a la pieza de trabajo y se fija con la manija
de bloqueo. El compartimento de almacenamiento para el
palo empujador se encuentra sobre la guía de corte al hilo.
ESCALA DE CORTE AL HILO- Esta escala de corte al hilo
de fácil lectura se encuentra en el riel delantero, y permite
obtener mediciones exactas en los cortes al hilo.
CUCHILLA SEPARADORA - Es una separable pieza
metálica, levemente más delgada que la hoja de la sierra,
la cual se emplea para mantener abierto el corte y evitar así
un contragolpe. Cuándo en el por lanzamiento, o “arriba”
posición, es más alto que la hoja de sierra. Cuándo en el
corte no pasante que aserrado, o “hacia abajo” posición,
está debajo de los dientes de hoja de sierra.
CONJUNTO DEL INTERRUPTOR - Esta sierra de mesa
dispone de un conjunto del interruptor de corriente de fácil
acceso ubicado bajo el riel delantero.
PROTECIÓN DE LA HOJA - Siempre mantenga la separable
protección de la hoja sobre ésta al efectuar cortes con
traspaso del espesor de la pieza.
PALANCA DE FIJACIÓN DE BISEL - Esta palanca, situada
justo bajo la superficie de la mesa de la sierra al frente de
la armazón de la sierra, sirve para fijar el ángulo de la hoja.
10 − Español
Page 93

CARACTERÍSTICAS
COMPONENTES DEL FUNCIONAMIENTO
La porción superior de la hoja sobresale de la mesa, y está
rodeada por un inserto llamado placa de la garganta. La altura
de la hoja se fija por medio de un volante ubicado en la parte
frontal de la armazón. Se incluyen instrucciones detalladas
para los cortes básicos en la sección Funcionamiento de
este manual: cortes rectos transversales, cortes en inglete,
cortes en bisel y cortes compuestos.
La guía de corte al hilo se emplea para acomodar la pieza
de trabajo con el fin de efectuar cortes longitudinales. Una
escala situada en el riel delantero muestra la distancia
existente entre la guía de corte al hilo y la hoja.
Es muy importante utilizar el conjunto de protección de
la hoja en todas las operaciones de corte con traspaso.
El conjunto de protección de la hoja incluye: la cuchilla
separadora y la protección de la hoja con trinquetes
anticontragolpe.
CONJUNTO DEL INTERRUPTOR
Vea la figura 3.
Esta sierra está equipada con un conjunto del interruptor
dotado de cerradura de llave integrada. Esta característica
tiene la finalidad de evitar el uso no autorizado y posiblemente
peligroso por niños y otras personas.
PARA ENCENDER LA SIERRA:
Para encenderla, levante de mismo a la posición de
ENCENDIDO ( I ).
PARA APAGAR LA SIERRA:
Para apagarla, baje de interruptor a la posición de
APAGADO ( O ).
PARA ASEGURAR LA SIERRA:
Avec la scie ÉTEINDRE, installer un cadenas (non
inclus) dans le trou de la commutateur.
ADVERTENCIA:
SIEMPRE asegúrese de que la pieza de trabajo no toque
la hoja, antes de accionar el interruptor para encender
la herramienta. La falta de atención a esta advertencia
puede causar el lanzamiento violento de la pieza de
trabajo hacia el operador, con posibilidad de lesiones
graves.
ADVERTENCIA:
Para reducir el riesgo de un arranque accidental,
SIEMPRE asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en
la posición de APAGADO ( O ) antes de conectar la
herramienta en la toma de corriente.
INTERRUPTOR EN POSICIÓN
DE ENCENDIDO
INTERRUPTOR EN POSICIÓN
DE APAGADO
Fig. 3
11 − Español
Page 94

HERRAMIENTAS NECESARIAS
Para armar la unidad y efectuar ajustes se necesitan las siguientes herramientas (no incluido o dibujado para
escalar):
DESTORNILLADOR DE
CABEZA PHILLIPS
ESCUADRA DE CARPINTERO
LLAVE 13 mm
DESTORNILLADOR
DE PUNTA PLANA
ESCUADRA DE
COMBINACIÓN
LLAVE DE CASQUILLO
y CUBOS CUADRADOS
(8 mm y 13 mm)
PRENSAS EN C
Fig. 4
12 − Español
Page 95

PIEZAS SUELTAS
Con la sierra de mesa vienen incluidos los siguientes artículos:
A
B
M
L
G
H
F
E
C
L
M
J
N
N
K
O
O
P
I
K
D
Q
R
A. Protección de la hoja con
trinquetes anticontragolpe ....................................... 1
B. Guía de ingletes ....................................................... 1
C. Conjunto del mango ................................................ 1
D. Tapa del extremo del mango ................................... 1
E. Guía de corte al hilo ................................................. 1
F. Llave hexagonal (5 mm) ........................................... 1
G. Riostra del pedestal de pata “F” .............................. 1
H. Riostra del pedestal de pata “R” ............................. 1
I. Placa de soporte (exterior) ....................................... 1
13 − Español
Fig. 5
J. Placa de soporte (interior) ........................................ 1
K. Patas de pedestal .................................................... 4
L. Tuercas de mariposa................................................ 4
M. Pernos de carruaje ................................................... 4
N. Pernos del pedestal de patas .................................. 2
O. Tuercas hexagonal ................................................... 2
P. Palo empujadora ...................................................... 1
Q. Cierre el llave ........................................................... 1
R. Abra el llave ............................................................. 1
Page 96

ARMADO
DESEMPAQUETADO
Este producto requiere armarse.
Levante cuidadosamente de la caja la sierra y colóquela sobre
una superficie de trabajo nivelada.
NOTA: Esta herramienta es pesada. Para evitar lesionarse la
espalda, mantenga dobladas las rodillas, levante con las piernas,
no con la espalda, y obtenga ayuda cada vez que la necesite.
ADVERTENCIA:
No utilice este producto si alguna pieza incluida en la lista
de piezas sueltas ya está ensamblada al producto cuando lo
desempaqueta. El fabricante no ensambla las piezas de esta
lista en el producto. Éstas deben ser instaladas por el usuario.
El uso de un producto que puede haber sido ensamblado de
forma inadecuada podría causar lesiones personales graves.
Inspeccione cuidadosamente la herramienta para verificar que
no haya sufrido ninguna rotura o daño durante el transporte.
No deseche el material de empaquetado antes de terminar de
inspeccionar cuidadosamente la herramienta, identificar todas
las piezas sueltas y utilizar satisfactoriamente la herramienta.
La sierra viene ajustada desde la fábrica para realizar cortes
exactos. Después de armarla verifique la exactitud de la misma.
Si en el envío resultaron afectados los ajustes, consulte los
procedimientos específicos explicados en este manual.
Si hay piezas dañadas o faltantes, sírvase llamar al
1-800-525-2579, donde le brindaremos asistencia.
ADVERTENCIA:
Si hay piezas dañadas o faltantes, no utilice esta herramienta
sin haber reemplazado todas las piezas. Usar este producto
con partes dañadas o faltantes puede causar lesiones serias
al operador.
ADVERTENCIA:
No intente modificar esta herramienta ni hacer accesorios no
recomendados para ella. Cualquier alteración o modificación
constituye un uso indebido, y puede crear una situación
peligrosa que culmine en lesiones corporales graves.
ADVERTENCIA:
No conecte la unidad a la toma de corriente antes de terminar
de armarla. De lo contrario, la unidad puede ponerse en marcha
accidentalmente, con el consiguiente riesgo de lesiones graves.
ADVERTENCIA:
Nunca se pare directamente en la misma línea de la hoja ni
acerque las manos a menos de 76,2 mm (3 pulg) de ella. No
trate de alcanzar nada extendiendo el brazo por encima o
alrededor de la hoja. La falta de atención a esta advertencia
puede redundar en lesiones graves.
ADVERTENCIA:
Para evitar lesiones graves, siempre asegúrese de que la sierra
de mesa esté firmemente montada en un banco de trabajo o
en un pedestal de patas aprobado. NUNCA utilice la sierra
colocada en el piso.
AGUJEROS DE MONTAJE
La sierra de mesa debe montarse en una superficie de soporte
firme, como un banco de trabajo o un pedestal de patas. Hay
cuatro agujeros para perno en la armazón de la sierra para este fin.
Si se atornilla a un banco de trabajo, los pernos deben ser de la
suficiente longitud para dar acomodo a la base de la sierra, las
arandelas de seguridad, las tuercas hexagonales y el espesor
del banco de trabajo o otra superficie de montaje. Apriete
firmemente los pernos o los tornillos. Después del montaje revise
cuidadosamente el banco de trabajo para asegurarse de que no
haya ocurrido ningún desplazamiento. Si el banco de trabajo se
inclina, desliza o camina, asegúrelo al piso antes de utilizar la
unidad.
Para instalar la sierra en el pedestal, consulte el procedimientos
específicos, más abajo en este manual.
14 − Español
Page 97

ARMADO
ARMADO DEL PEDESTAL
Vea las figuras 6 a 8.
NOTA: No use este pedestal de patas con otros equipos ni para
otros propósitos.
Apoye la placa de soporte exterior en una superficie plana.
Coloque la placa de soporte interior sobre la placa de soporte
exterior con los rieles superiores de frente.
Inserte las patas del pedestal en las placas de soporte. Los bordes
en ángulo de las patas del pedestal deben estar enfrentadas
de tal manera que formen una “V”.
Coloque la riostra R entre el conjunto de la pata del lado derecho.
Haga lo mismo con la riostra F del lado izquierdo.
Alinee con cuidado los orificios de las patas y la riostra. Instale
la tornillería a través de los orificios tal. Apriete toda la ferretería.
PLACA DE
SOPORTE
(INTERIOR)
PATA DE
PEDESTAL
MONTAJE DEL PEDESTAL CON PATAS EN LA
BASE DE LA SIERRA DE MESA
Vea la figura 9.
ADVERTENCIA:
No levante la sierra sin tener ayuda. De la sierra pesa
aproximadamente 55 libras. Manténgala cerca de su cuerpo.
Mantenga sus rodillas dobladas y levante con sus piernas, no
con su espalda. El incumplimiento de estas advertencias puede
resultar en una lesión a la espalda.
Coloque el pedestal en un suelo nivelado y ábralo hasta la
posición completamente extendida.
Coloque la sierra de mesa sobre el pedestal de modo que los
orificios del marco de la sierra queden alineados con los orificios
de los soportes del pedestal.
NOTA: Asegúrese de que el marco de la sierra de mesa quede
alineado sobre el pedestal y de que todas las patas del pedestal toquen el suelo.
PERNO DEL
PEDESTAL
TUERCA
HEXAGONAL
DE PATAS
PLACA DE
SOPORTE
(EXTERIOR)
PLACA DE
SOPORTE
(INTERIOR)
PLACA DE
SOPORTE
(EXTERIOR)
ORIFICIOS)
RIOSTRA DEL
PEDESTAL DE
PATA (F)
RIOSTRA DEL
PEDESTAL DE
PATA (R)
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
CONJUNTOS DE
PATAS (INTERIOR)
CONJUNTOS
DE PATAS
(INTERIOR)
Fig. 8
TUERCA DE
MARIPOSA
PERNO DEL
PEDESTAL DE PATAS
15 − Español
Fig. 9
Page 98

ARMADO
Instale los pernos del pedestal con patas en los orificios de
los soportes y el marco. Asegúrelos con tuercas maripo-sa y
ajústelos con firmeza.
Asegúrese de que la sierra de losas está en terreno nivelado y
de que el pedestal esté firme antes de usarlo.
PARA INSTALAR MANGO
Vea la figura 10.
Quite la tuerca hexagonal del perno del mango, pero sin quitar
el perno.
Coloque una arandela en el perno.
Coloque la tuerca de nylon en el agujero en hueco de la parte
trasera del volante de ajuste de altura y manténgala en su
lugar.
Introduzca el mango y el tornillo en el agujero del volante de
ajuste de altura.
Con un destornillador de punta plana gire a la derecha el
tornillo y apriételo.
Cubra el extremo del mango empujando la tapa en su lugar.
PARA QUITAR Y PONER LA PLACA DE LA
GARGANTA
Vea la figura 11.
Gire a la izquierda el volante de ajuste de altura y bisel para
bajar la hoja de la sierra.
Para quitar la placa de la garganta, localice el pestillo que
sostiene la placa. Coloque el pulgar y el dedo índice en los
orificios y empuje hacia dentro hasta liberar el pestillo. Eleve
y tire de la placa de la garganta hacia la parte delantera de la
sierra.
Para volver a instalar la placa de la garganta, deslice primero la
orejeta hacia adentro de la ranura situada en la parte posterior
de la sierra. Coloque los dedos en los orificios y empuje hacia
dentro. Empuje hacia abajo para asegurar la placa en su lugar.
TUERCA
ARANDELA
MANGO
PERNO
VOLANTE DE
AJUSTE DE
ALTURA Y BISEL
PLACA DE LA
GARGANTA
CUCHILLA
SEPARADORA
TAPA
Fig. 10
Fig. 11
16 − Español
Page 99

ARMADO
PARA CAMBIAR POSICIÓN UN CUCHILLA
SEPARADORA
Vea la figura 12.
La sierra es enviado con el cuchilla separadora colocó en el corte
no pasante o “abajo” la posición (cuchilla separadora la posición)
y debe estar ser colocado en el lanzamiento o “arriba” la posición
para todas las otras operaciones cortes.
Desconecte la sierra.
Para colocar en la posición de “arriba” para todo por cortes
pasante:
Desmontaje de la placa de la garganta.
Eleve la hoja de la sierra, para ello, gire a la derecho el volante
de ajuste de altura y bisel.
Desbloquear la palanca de afloje tirandolo arriba.
Alcanae el cuchilla separador y tire hacia lado derecho del
sierra para soltar de la el separador de la munis de ressorts de
la abrazadera cuchilla separadora.
Tire el cuchilla separador hasta que los pasadores interno son
enganchada et el separador esté arriba del hoja de la sierra.
Asegurar la palanca de afloje empujando la palanca hacia abajo.
Réinstaller de la placa de la garganta.
Para colocar en la posición de “abajo” para todo por cortes
cortes no pasante:
Desmontaje de la placa de la garganta.
Eleve la hoja de la sierra, para ello, gire a la izquierdo el volante
de ajuste de altura y bisel.
Desbloquear la palanca de afloje tirandolo arriba.
Alcanae el cuchilla separador y tire hacia lado derecho del
sierra para soltar de la el separador de la munis de ressorts de
la abrazadera cuchilla separadora.
Apriete el cuchillo separadora hasta los pasadores interno son
enganchada et el cuchilla separador esté debajo del hoja de la
sierra.
Tire el cuchilla separador hasta que los pasadores interno son
enganchada et el separador esté arriba del hoja de la sierra.
Asegurar la palanca de afloje empujando la palanca hacia abajo.
Réinstaller de la placa de la garganta.
PALANCA DE
AFLOJE
(DESBLOQUEO)
EN POSICIÓN CUCHILLA SEPARADOR
PARA TODO POR PASANTE
PALANCA DE
AFLOJE
(ASEGURADA)
EN POSICIÓN CUCHILLA SEPARADORA PARA TODO
CORTAR DE NO PASANTE
17 − Español
Fig. 12
Page 100

ARMADO
PARA REVISAR LA INSTALACIÓN DE LA HOJA
DE LA SIERRA
Vea la figura 13.
AVISO:
Para funcionar correctamente, los dientes de la hoja deben
apuntar hacia la parte frontal de la sierra, hacia abajo. La
inobservancia de esta advertencia podría causar daños a la
hoja de la sierra, la sierra o la pieza de trabajo.
Desconecte la sierra.
Baje la hoja de la sierra y quite la placa de la garganta.
Asegúrese de que la palanca de fijación de bisel esté fijamente
a la izquierda (vea la figura 26.) Suba la hoja a su máxima altura;
para ello, gire a la derecha el volante de ajuste de altura y bisel.
Colocar cuchilla separador en la posición “arriba”.
Para aflojar la hoja:
Quite la llave de la hoja de la área de guardar la llave de la hoja.
Coloque el extremo abierto plano de la llave de la hoja en las
partes planas del árbol.
Coloque el extremo cerrado de la llave de la hoja en la tuerca
de la hoja. Sujetando firmemente ambas llaves, tire de la llave
(lado derecho) hacia la parte delantera de la máquina.
Para apretar la hoja:
Coloque el extremo abierto plano de la llave pequeña de la hoja
en las partes planas del árbol.
Coloque el extremo cerrado de la llave de la hoja en la tuerca
de la hoja. Sujetando firmemente ambas llaves (lado derecho),
empuje la llave hacia la parte posterior de la máquina. Asegúrese
de que la tuerca de la hoja esté firmemente apretada. No efectúe
un apriete excesivo.
Vuelva a instalar la placa de la garganta.
Verifique la existencia de los espacios necesarios para permitir
el giro libre de la hoja.
LLAVE DE
HOJA
LLAVE DE
HOJA
TUERCA
DE LA
HOJA
Fig. 13
18 − Español
 Loading...
Loading...