Ryobi MMA-140 Owner's Operating Manual
OWNER’S OPERATING MANUAL
MMA INVERTER WELDER
MODEL MMA-140
KEEP THIS MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
Your new inverter generator has been engineered and manufactured to Ryobi’s
high standard of dependability, ease of operation and operator safety. Properly
cared for, it will give you years of rugged, trouble free performance. If you use
your inverter generator properly and only for what it is intended, you will enjoy
years of safe, reliable service.
SPE CIFICATIONS
Rated input power supply......................................................AC 230V±5% 50/60Hz
Rated input capacity......................................................................................5.3KVA
Current adjustment range........................................................................... 20-140A
Rated duty cycle...................................................................
............................. 80%
Rated voltage..........................................................................................20.8-25.6
No load voltage.................................................................................................. 63V
V
Overall efficiency................................................................................................80%
Housing protection grade......
..........................................................................IP21S
Power factor..............................................................................................0.73 cosφ
Insulation grade...................................................................................................... F
Electrode diameter.........................................................................
..........1.6-3.2mm
Noise......................................................................................................... <70dB(A)
Dimensions............................................................................... 287 x 120 x 247mm
Net weight........................................................................................................ 3.8kg
THANK YOU FOR BUYING A RYOBI
MMA INVERTER WELDER
CAUTION: Carefully read through this entire owner’s
manual, paying close attention to the general
safety rules and rules for safe operation,
before using.
1
2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
The purpose of safety rules is to attract your
a
ttention to possible dangers. The safety symbols
and the explanations with them, require your
c
areful attention and understanding. The safety
w
arnings do not by themselves eliminate any
danger. The instruction or warnings they give are
not substitutes for proper accident prevention
measures.
SAFETY ALERT SYMBOL. Indicates
danger, caution or warning. May be used
in conjunction with other symbols or
pictures.
Failure to obey a safety warning can result in
serious injury to yourself or to others. Always follow
the safety precautions to reduce the risk of fire,
electric shock and personal injury.
Do not attempt to operate this tool until you have
read thoroughly and completely understood the
safety rules, etc. contained in this manual. Failure
to comply can result in accidents involving fire,
electric shock or serious personal injury. Save this
Owners Operating Manual and review it frequently
for continual safe operation and for instructing
others who may use this tool.
EMF INFORMATION
Considerations About Welding And The Effects Of
Low Frequency Electric And Magnetic Fields.
Welding current, as it flows through welding cables,
will cause electro- magnetic fields. There has been
and still is some concern about such fields.
However, after examining more than 500 studies
spanning 17 years of research, a special blue
ribbon committee of the National Research Council
concluded that: “The body of evidence, in the
committee’s judgment, has not demonstrated that
exposure to power- frequency electric and
magnetic fields is a human-health hazard.”
However, studies are still going forth and evidence
continues to be examined. Until the final
conclusions of the research are reached, you may
wish to minimize your exposure to electromagnetic
fields when welding or cutting.
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the
following procedures:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or
taping them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from
the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far
a
way from operator as practical.
5. Connect work clamp to work piece as close
t
o the weld as possible.
ABOUT PACEMAKERS
Pacemaker wearers consult your doctor first. If
cleared by your doctor, then following the above
procedures is recommended.
WELDING HAZARDS
The symbols shown below are used throughout this
manual to call attention to and identify possible
hazards. When you see the symbol, watch out, and
follow the related instructions to avoid the hazard.
Only qualified persons should service, test,
maintain, and repair this unit.
During servicing, keep everybody, especially
children, away.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin; NOISE can
damage hearing. Arc rays from the welding
process produce intense heat and strong
ultraviolet rays that can burn eyes and skin.
Noise from some processes can damage
hearing.
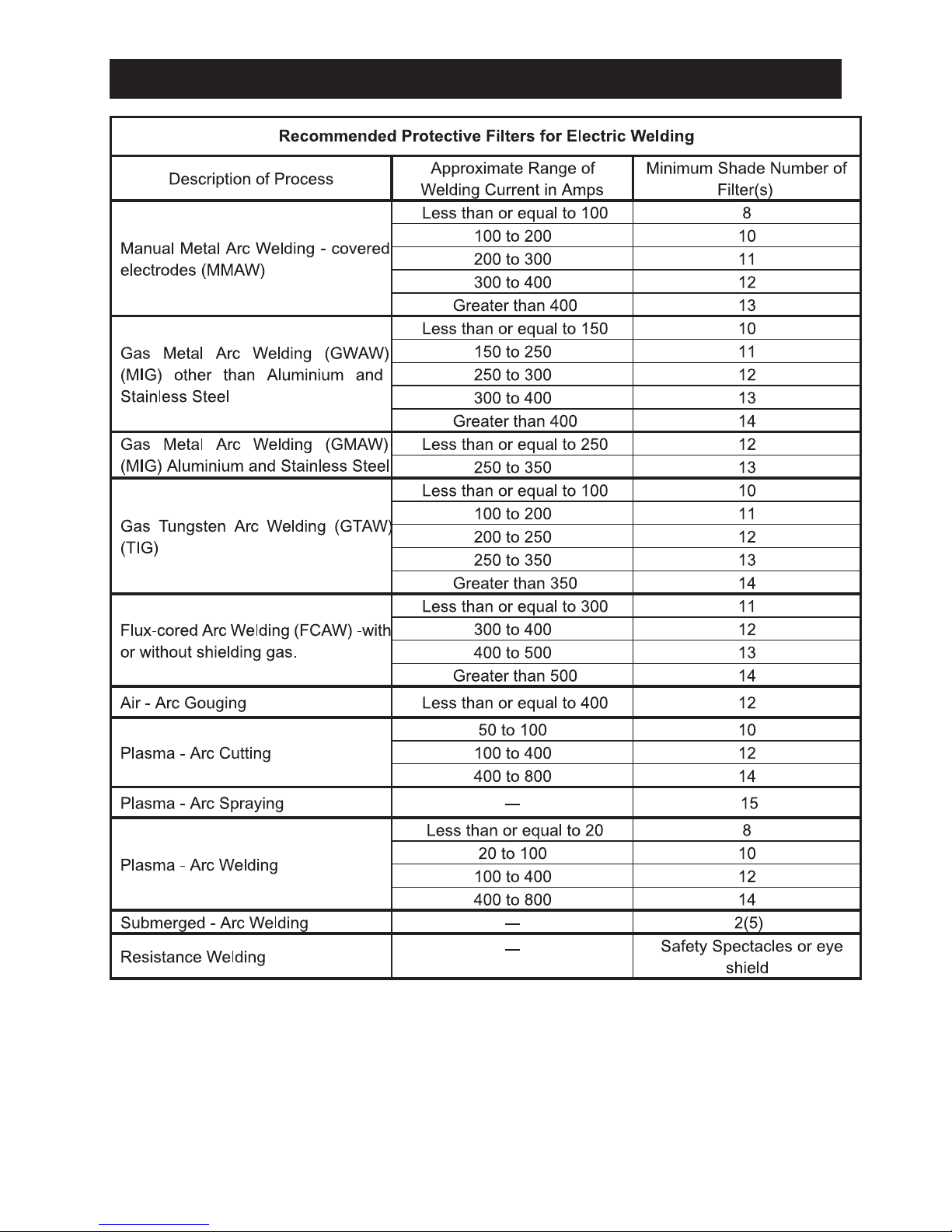
1. Wear a welding helmet fitted with a proper
shade of filter (ANSI Z49.1) to protect your
face and eyes when welding or watching.
2. Wear approved safety glasses. Side shields
recommended. Never wear contact lenses
while welding.
3. Use protective screens or barriers to protect
others from flash and glare; warn others not
to watch the arc.
4. Wear protective clothing made from durable,
flame-resistant material (wool and leather)
and foot protection.
5. Use approved ear plugs or ear muffs if noise
level is high.
ARC RAYS
Can Burn
3
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS

4
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal
shocks or severe burns. The electrode and
work circuit is electrically live whenever the
output is on. The input power circuit and
machine internal circuits are also live when
power is on. In semiautomatic or automatic
wire welding, the wire, wire reel, drive roll
housing, and all metal parts touching the
welding wire are electrically live. Incorrectly
installed or improperly grounded equipment is
a hazard.
1. Do not touch live electrical parts.
2. Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body
protection.
3. Insulate yourself from work and ground using
dry insulating mats or covers.
4. Disconnect input power or stop engine before
installing or servicing this equipment. Lock input
power disconnect switch open, or remove line
fuses so power cannot be turned on
accidentally.
5. Properly install and ground this equipment
according to its Owner’s Manual and national,
state, and local codes.
6. Turn off all equipment when not in use.
Disconnect power to equipment if it will be left
unattended or out of service.
7. Use fully insulated electrode holders. Never dip
holder in water to cool it or lay it down on the
ground or the work surface. Do not touch
holders connected to two welding machines at
the same time or touch other people with the
holder or electrode.
8. Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or
poorly spliced cables.
9. Do not wrap cables around your body.
10. Ground the workpiece to a good electrical
(earth) ground.
11. Do not touch electrode while in contact with
the work (ground) circuit.
12. Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair
or replace damaged parts at once.
13. In confined spaces or damp locations, do not
u
se a welder with AC output unless it is
equipped with a voltage reducer. Use
e
quipment with DC output.
14. Wear a safety harness to prevent falling if
w
orking above floor level.
15. Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous to your
health. Welding produces fumes and gases.
Breathing these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your health.
1. Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not
breath the fumes.
2. If inside, ventilate the area and/or use
exhaust at the arc to remove welding fumes
and gases.
3. If ventilation is poor, use an approved air-
supplied respirator.
4. Read the Material Safety Data Sheets
(MSDSs) and the manufacturer’s instruction
for metals, consumables, coatings, and
cleaners.
5. Work in a confined space only if it is well
ventilated, or while wearing an air-supplied
respirator.
Shielding gases used for welding can displace
air causing injury or death. Be sure the
breathing air is safe.
6. Do not weld in locations near degreasing,
cleaning, or spraying operations. The heat
and rays of the arc can react with vapors to
form highly toxic and irritating gases.
7. Do not weld on coated metals, such as
galvanized, lead, or cadmium plated steel,
unless the coating is removed from the weld
area, the area is well ventilated, and if
necessary, while wearing an airsupplied
respirator. The coatings and any metals
containing these elements can give off toxic
fumes if welded.
ELECTRIC SHOCK
Can Kill
FUMES & GASES
Can Be Dangerous

FLYING SPARKS AND HOT METAL can cause
injury.
Chipping and grinding cause flying metal.
As welds cool, they can throw off slag.
1. Wear approved face shield or safety goggles.
Side shields recommended.
2. Wear proper body protection to protect skin.
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high
pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode.
Since gas cylinders are normally part of the
welding process, be sure to treat them
carefully.
1. Protect compressed gas cylinders from
excessive heat, mechanical shocks, and arcs.
2. Install and secure cylinders in an upright
position by chaining them to a stationary
support or equipment cylinder rack to
prevent falling or tipping.
3. Keep cylinders away from any welding or other
electrical circuits.
4. Never allow a welding electrode to touch any
cylinder.
5. Use only correct shielding gas cylinders,
regulators, hoses, and fittings designed for the
specific application; maintain them and
associated parts in good condition.
6. Turn face away from valve outlet when opening
cylinder valve.
7. Keep protective cap in place over valve except
when cylinder is in use or connected for use.
W
ELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Sparks and spatter fly off from the welding arc.
The flying sparks and hot metal, weld spatter,
hot workpiece, and hot equipment can cause
fires and burns. Accidental contact of electrode
or welding wire to metal objects can cause
sparks, overheating, or fire.
1. Protect yourself and others from flying sparks
and hot metal.
2. Do not weld where flying sparks can strike
flammable material.
3. Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of
the welding arc. If this is not possible, tightly
cover them with approved covers.
4. Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials
from welding can easily go through small
cracks and openings to adjacent areas.
5. Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher
nearby.
6. Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor,
bulkhead, or partition can cause fire on the
hidden side.
7. Do not weld on closed containers such as
tanks or drums.
8. Connect work cable to the work as close to
the welding area as practical to prevent
welding current from traveling long, possibly
unknown paths and causing electric shock and
fire hazards.
9. Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
10. Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off
welding wire at contact tip when not in use.
11. When not welding, make certain no part of the
electrode circuit is touching the work or
ground. Accidental contact can cause
overheating and create a fire hazard.
5
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
FLYING SPARKS
Can Cause Injury
CYLINDERS Can
Explode If Damaged
WELDING Can
Cause Fire or Injury

6
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
M
oving parts, such as fans, rotors, and belts
can cut fingers and hands and catch loose
clothing.
1. Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards
closed and securely in place.
2. Stop engine before installing or connecting
unit.
3. Have only qualified people remove guards or
covers for maintenance and troubleshooting as
necessary.
4. To prevent accidental starting during servicing,
disconnect negative (-) battery cable from
battery.
5. Keep hands, hair, loose clothing, and tools
away from moving parts.
6. Reinstall panels or guards and close doors
when servicing is finished and before starting
engine.
SPARKS can cause BATTERY GASES TO EXPLODE; BATTERY ACID can burn eyes and
skin. Batteries contain acid and generate explosive gases.
1. Always wear a face shield when working on
a battery.
2. Stop engine before disconnecting or
connecting battery cables.
3. Do not allow tools to cause sparks when
working on a battery.
4. Do not use welder to charge batteries or jump
start vehicles.
5. Observe correct polarity (+ and –) on
STEAM AND PRESSURIZED HOT COOLANT
can burn face, eyes, and skin.
The coolant in the radiator can be very hot and
under pressure.
1. Do not remove radiator cap when engine is
hot. Allow engine to cool.
2. Wear gloves and put a rag over cap area when
removing cap.
3. Allow pressure to escape before completely
removing cap.
1. High-frequency (H.F.) can interfere with radio
navigation, safety services, computers, and
communications equipment.
2. Have only qualified persons familiar with
electronic equipment install, test, and service
H.F. producing units.
3. The user is responsible for having a qualified
electrician promptly correct any interference
problem resulting from the installation.
4. If notified by the FCC about interference, stop
using the equipment at once.
5. Have the installation regularly checked and
maintained.
6. Keep high-frequency source doors and panels
tightly shut, keep spark gaps at correct setting,
and use grounding and shielding to minimize
the possibility of interference.
MOVING PARTS
Can Cause Injury
SPARKS Can Cause
BATTERY GASES
TO EXPLODE
SPARKS Can Cause
BATTERY GASES
TO EXPLODE
H.F. RADIATION Can
Cause Interference

1. Electric current flowing through any conductor
causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields
(EMF). Welding current creates EMF fields
around welding cables and welding machines.
2. EMF fields may interfere with some
pacemakers, and welders having a pacemaker
should consult their physician before welding.
3. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have
other health effects which are now not known.
4. All welders should use the following
procedures in order to minimize exposure to
EMF fields from the welding circuit:
5. Route the electrode and work cables together Secure them with tape when possible.
6. Never coil the electrode lead around your
body.
7. Do not place your body between the electrode
and work cables. If the electrode cable is on
your right side, the work cable should also be
on your right side.
8. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as
close as possible to the area being welded.
9. Do not work next to welding power source.
1. Lift unit with handle on top of case.
2. Use handcart or similar device of adequate
capacity.
3. If using a fork lift vehicle, place and secure
unit on a proper skid before transporting.
1
. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on the
equipment.
2. Install equipment in accordance with the
countries National Electrical Code, all local
codes and the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
3. Ground the equipment in accordance with the
countries National Electrical Code and the
manufacturer’s recommendations.
1. Do not touch hot parts bare handed.
2. Allow cooling period before working on
welding gun or torch.
1. Do not place unit on, over, or near
combustible surfaces.
2. Do not service unit near flammables.
1. Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards or parts.
2. Use proper static-proof bags and boxes to
store, move, or ship PC boards.
7
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS
May Be Dangerous
FALLING UNIT Can
Cause Injury
FOR ELECTRICALLY
Powered Equipment
HOT PARTS Can
Cause Severe Burns
FIRE or EXPLOSION
Hazard
STATIC Can Damage
PC Boards
8
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1
. Allow cooling period; follow rated duty cycle.
2. Reduce current or reduce duty cycle before
starting to weld again.
3. Do not block or filter airflow to unit.
1
. Consult the Owner’s Manual for welding
safety precautions. Do not install, operate or
repair this equipment without reading this
manual and the safety precautions throughout.
2. Use only genuine replacement parts
OVERUSE Causes
OVERHEATING
READ THE
INSTRUCTIONS
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1. ALWAYS ensure that there is full free air
circulating around the outer casing of the
machine, and that the louvres are
unobstructed.
2. ALWAYS use a proper welding face shield or
helmet, with suitable filter lenses. Proper
gloves and working clothes should be worn at
all times.
3. ALWAYS check that the pressure regulator and
gauges are working correctly. DO NOT
lubricate the regulator.
4. ALWAYS use the correct regulator. Each
regulator is designed to be used with a specific
gas.
5. ALWAYS inspect the hose before use to
ensure it is in good condition.
6. ALWAYS keep the free length of gas hose
outside the work area.
7. ALWAYS remove all flammable materials from
the welding area.
8. NEVER remove any of the panels unless the
machine is disconnected from the supply, AND
never use the machine with any of the panels
removed.
9. NEVER attempt any electrical or mechanical
repair unless your are a qualified technician.
If you have a problem with the machine contact
your local RYOBI dealer.
10. NEVER use or store in a wet/damp
environment. DO NOT EXPOSE TO RAIN.
11. NEVER use gas from a cylinder, the content
of which is unknown. It is important to ensure
the appropriate gas is being used.
12. NEVER use a damaged cylinder.
13. NEVER lift the cylinder by the valve.
14. NEVER expose the cylinder to a heat source
or sparks.
15. NEVER continue to weld, if, at any time, you
feel even the smallest electric shock. Stop
welding IMMEDIATELY, and DO NOT attempt
to use the machine until the fault is diagnosed
and corrected.
16. NEVER use the welder with input connections
greater than 10M in length.
17. NEVER point the torch at any person or
animal.
18. NEVER touch the torch nozzle until the welder
is switched OFF and the nozzle has been
allowed to cool off.
19. NEVER connect, disconnect, or attempt to
service the torch, until the machine is switched
OFF and disconnected from the mains supply.
20. NEVER allow the cables to become wrapped
around the operator or any person in the
vicinity.
21. Safety devices such as interlocks and circuit
breakers should not be disconnected or
shunted out.
22. Before installation, inspection, or service of
equipment, shut OFF all power and remove
line fuses to prevent accidental turning ON
of power.
23. Do not open power circuit or change polarity
while welding.

9
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
24. If, in an emergency, it must be disconnected,
g
uard against shock burns, or flash from switch
arcing. Always shut OFF and disconnect all
p
ower to equipment. Power disconnect switch
m
ust be available near the welding power
source.
25. Fully insulated electrode holders should be
used. Do NOT use holders with protruding
screws or with any form of damage.
26. Fully insulated lock-type connectors should be
u
sed to join welding cable.
27. Frequently inspect cables for wear, cracks and
d
amage. IMMEDIATELY REPLACE those with
excessively worn or damaged insulation to
a
void possibly lethal shock from bared cable.
Cables with damaged areas may be taped to
give resistance equivalent to original cable.
Keep cable dry, free of oil and grease, and
protected from hot metal and sparks.
INSTALLATION
ENVIRONMENT
These units are designed for use in environments
with increased hazard of electric shock.
A. Examples of environments with increased
hazard of electric shock are:
1. In locations in which freedom of movement is
restricted, so that the operator is forced to
perform the work in a cramped (kneeling,
sitting or lying) position with physical contact
with conductive parts.
2. In locations which are fully or partially limited
by conductive elements, and in which there is
a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact
by the operator.
3. In wet or damp hot locations where humidity
or perspiration considerable reduces the skin
resistance of the human body and the
insulation properties of accessories.
B. Environments with increased hazard of electric
shock do not include places where electrically
conductive parts in the near vicinity of the
operator, which can cause increased hazard,
have been insulated.
LOCATION
This machine can operate in harsh environments.
However, it is important that simple preventative
measures are followed to assure long life and reliable operation:
• This machine must be located where there is
free circulation of clean air without restrictions
for air movement to and from the air vents. Do
not cover the machine with paper, cloth or rags
when switched on.
• Dirt and dust that can be drawn into the
machine should be kept to a minimum.
• This machine has a protection rating of IP21S.
Keep it dry and do not place it on wet ground
or in puddles. Do not use in wet or damp
locations. Store indoors.
• Locate the machine away from radio controlled
machinery. Normal operation may adversely
affect the operation of nearby radio controlled
machinery, which may result in injury or
equipment damage.
Read the section on electromagnetic compatibility
in this manual.
• Do not operate in areas with an ambient
temperature greater than 40°C.
TILTING
Place the machine directly on a secure, level
surface.
Do not place or operate this machine on a surface
with an incline greater than 15° from horizontal.
The machine may topple over if this procedure is
not followed.
VENTILATION
This cutting machine can create powerful cutting
current and has strict cooling requirements that
cannot be met with natural ventilation. Therefore
the built-in fan is very important in enabling the
machine to work stable with effective cooling. The
operator should make sure that the louvers be
uncovered and unblocked. The minimum distance
between the machine and nearby objects should
be 25cm.
 Loading...
Loading...