Page 1
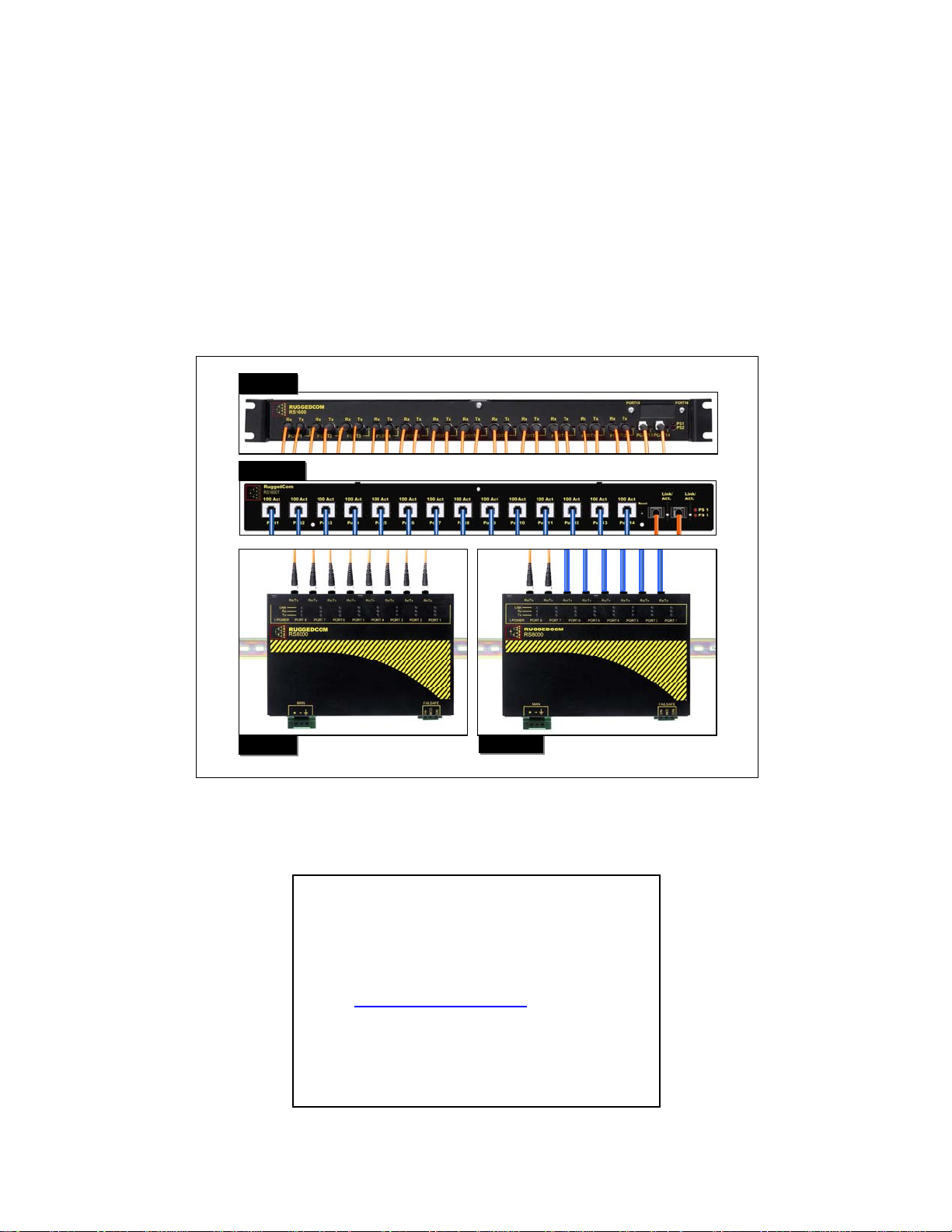
RuggedSwitch™
RS8000 / RS1600 / RS900
Product Family User Guide
RS1600
RS1600
RS1600T
RS1600T
RS8000
RS8000
RS8000T
RS8000T
RuggedCom Inc.
64 Jardin Dr. (Unit 3G)
Concord, Ontario Canada
L4K 3P3
Web:
www.ruggedcom.com
Tel: (905) 760-7799
Fax: (905) 760-9909
Toll Free: (888) 264 – 0006
Page 2

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
RUGGEDSWITCH™ USER GUIDE
FOR USE WITH RS8000, RS1600, AND RS900 PRODUCTS
RUGGEDSWITCH™ OPERATING SYSTEM V1.5
Version 1.5.1 – Aug. 3, 2004
RuggedCom
64 Jardin Drive, Unit 3G
Concord, Ontario
Canada L4K 3P3
Voice: (905) 760-7799
1-(888) 264-0006
Fax: (905) 760-9909
Support@RuggedCom.com
http://www.RuggedCom.com
Disclaimer
RuggedCom Inc. makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this
material.
RuggedCom shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or
use of this material.
Warranty
Five (5) years from date of purchase, return to factory. For warranty
details, visit www.ruggedcom.com or contact your customer service
representative
COPYRIGHT © Dec 2002 RuggedCom Inc.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
This document contains proprietary information, which is protected by
copyright. All rights are reserved.
No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced or translated
to another language without the prior written consent of RuggedCom Inc.
.
2
RuggedCom
Page 3

ABOUT THIS USER GUIDE
This guide is concerned with aiding the user in the configuration and operation of the
RuggedSwitch™ using the RuggedCom User Interface. Specifically, this guide details
aspects of:
• Accessing the User Interface
• Security (passwords)
• Configuring the switch
• Status determination
• Performance measurement
• Uploading and downloading files
• Dealing with alarms
This guide is intended solely for the purpose of familiarizing the reader with the ways
that the RuggedSwitch™ can be used to support Ethernet switching applications.
About this User Guide
Applicable Firmware Revision
This guide is applicable to RuggedSwitch™ Operating System (ROS) software
revision 1.5.x.
Who Should Use This User Guide
This guide is to be used by network technical support personnel who are familiar with
the operation of networks. Others who might find the book useful are network and
system planners, system programmers and line technicians.
How To Use This User Guide
The index of this guide has been prepared with:
• Entries to each of the “Features” sections of the manual,
• Entries to each of the “Troubleshooting” sections of the manual (located at
the end of each chapter),
• Entries to each of the Menus, organized by name.
RuggedCom
It is recommended that you use this guide along with the following applicable
documents.
RuggedSwitch™ RS8000 Family Installation Guide
RuggedSwitch™ RS1600 Family Installation Guide
RuggedSwitch™ RS900 Family Installation Guide
1
Page 4

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Rugged MediaConverter™ Installation Guide
RuggedCom Fiber Guide
White paper: Rapid Spanning Tree in Industrial Networks
Document Conventions
This publication uses the following conventions:
Note: Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials not
contained in this guide.
Quick Start Recommendations
The following description is included to aid those users experienced with switches
that may wish to attempt to configure the switch without fully reading the guide.
Commands strings have been provided with
1. Locate/mount the chassis in its final resting place.
2. Attach a PC running terminal emulation software to the RS232 port and apply
power to the chassis (default baud rate, data bits, parity - “57600 8 n”, no
hardware/software flow control). Set the terminal type to VT100. Gain access to
the UI (Type <CR>, the default password string is set to “admin”, see Chapter 1).
3. Configure the switch’s IP address (Administration, Configure IP Services, IP
Address) and Subnet Mask (Administration, Configure IP Services, Subnet).
If instead you wish the switch to load the address via DHCP, set the address type
to dynamic (Administration, Configure IP Services, IP Address Type). See
Chapter 1 for more details.
their full path from the root menu.
2
4. You may wish to change the default guest, operator and administration passwords
(Administration, Configure IP Services, Configure Passwords). See Chapter 1
for more details.
5. The ports are already set up with sensible defaults and autoselects where possible.
You may want to hard configure specific settings such as speed, duplex, flow
control and far end fault detection. Broadcast filtering is activated. See Chapter 3
for more details.
6. RSTP is enabled for the bridge by default and can be disabled if desired
(Spanning Tree, Configure Bridge RSTP Parameters, State). RSTP may also
be forced to support only legacy STP (Spanning Tree, Configure Bridge RSTP
Parameters, Version Support). Note that the switch deals with legacy STP
pathcosts by default and can be set to deal with larger path costs (Spanning Tree,
Configure Bridge RSTP Parameters, Cost Style). RSTP may also be set
enabled/disabled on a per port basis (Spanning Tree, Configure Port RSTP
Parameters, Enable). You may also want to identify controllers and IEDs by
setting the Edge parameter to True for those ports (Spanning Tree, Configure
Port RSTP Parameters, Edge). See Chapter 6 for more details.
RuggedCom
Page 5

About this User Guide
7. At this point the switch will raise links, learn addresses and forward traffic. By
default link alarms and SNMP linkUp/linkDown traps (See Chapter 1) are raised
for all ports. The Port Configuration and Status, View Port Status command
will indicate the current state of the ports in real time. The Ethernet Statistics,
View Ethernet Statistics command will provide a useful indication of traffic on
the switch. The Spanning Tree, View Port RSTP Statistics command will
provide an indication of which ports have been blocked to prevent traffic loops.
8. By default the switch has VLAN 1 configured on all ports (VLAN 1 is always
present for management purposes). IGMP is disabled for VLAN 1 by default and
can be enabled by the Virtual LANs, Configure Static VLANs, IGMP
command.
9. If remote SNMP management or traps are desired, configure the appropriate
manage station (Administration, Configure SNMP Management Stations).
10. Ports that are not in use should be disabled (Port Configuration and Status,
Configure Port Parameters Command) to improve security, increase
performance, reduce power consumption and cause the switch to run cooler.
11. Further concerns such as configuring static MAC addresses, port security, VLANs
and IGMP as well as ensuring robustness, measuring and optimizing performance
are dealt with by reading the guide fully.
For Users Migrating From Revisions ROS 1.2 and Earlier..
1. The “operator” access level has been created. The ability to configure, view and
operate product features has been aligned with the guest, operator and
administration access levels. All passwords are now stored in the configuration
file in an encrypted form.
2. The TFTP Server feature is now configurable. It may be configured to be
disabled, to only allow files to be retrieved or to provide full access.
3. The CLI shell provides a TFTP client command that can be used to upload and
download files from TFTP servers.
4. Port Mirroring has been moved from the Diagnostics menu to the Port
Configuration and Status menu.
5. The system log may now be viewed and cleared from the Diagnostics menu.
RuggedCom
3
Page 6

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Table Of Contents
About this User Guide............................................................................................................................ i
Applicable Firmware Revision.............................................................................................................. i
Who Should Use This User Guide......................................................................................................... i
How To Use This User Guide................................................................................................................ i
Document Conventions......................................................................................................................... ii
Quick Start Recommendations.............................................................................................................. ii
For Users Migrating From Revisions ROS 1.2 and Earlier.................................................................iii
Table Of Contents................................................................................................................................ iv
Chapter 1– Setting Up And Administering The Switch ........................................................................1
Introduction............................................................................................................................................1
The RuggedSwitch™ User Interface......................................................................................................1
Using the RS232 Port to Access the User Interface ..............................................................................1
The Structure of the User Interface........................................................................................................3
Making Configuration Changes.............................................................................................................4
Updates Occur In Real Time..................................................................................................................4
Alarm Indications Are Provided............................................................................................................4
The CLI Shell.........................................................................................................................................4
Administration Menu.............................................................................................................................5
Configure IP Services ............................................................................................................................5
IP Address Type.....................................................................................................................................5
IP Address..............................................................................................................................................6
Subnet ....................................................................................................................................................6
Gateway .................................................................................................................................................6
Inactivity Timeout..................................................................................................................................6
Telnet Sessions.......................................................................................................................................6
TFTP Server...........................................................................................................................................7
SNMP Get Community..........................................................................................................................7
Configuring System Identification.........................................................................................................8
Configure Passwords..............................................................................................................................8
Configure Time and Date.......................................................................................................................8
Time.......................................................................................................................................................9
Date........................................................................................................................................................9
Time Zone..............................................................................................................................................9
NTP Server Address...............................................................................................................................9
NTP Update Period................................................................................................................................9
Configure SNMP Management Stations..............................................................................................10
Community String................................................................................................................................10
Address.................................................................................................................................................10
Set Access............................................................................................................................................10
Send Traps............................................................................................................................................11
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 2 - Configuring MAC Address Management.........................................................................13
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................13
MAC Address Management Features..................................................................................................13
MAC Address Management Configuration.........................................................................................13
RuggedCom
Page 7

Table Of Contents
MAC Address Management Parameter Ranges & Default Settings....................................................13
MAC Address Tables Management Menu...........................................................................................13
Viewing MAC Addresses ....................................................................................................................14
Purge MAC Address Table..................................................................................................................15
Configure MAC Address Learning Options .......................................................................................15
Configure Static MAC Address Table.................................................................................................15
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports .......................................................................................................18
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................18
Port Features ........................................................................................................................................18
Port Applications..................................................................................................................................19
Port Security ........................................................................................................................................19
Broadcast Rate Limiting......................................................................................................................20
Controller Protection Through Loss-of-Link Management.................................................................21
Using Port Mirroring............................................................................................................................22
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................22
Configuring Port Mirroring..................................................................................................................22
Port Configuration And Status.............................................................................................................23
Port Parameter Ranges & Default Settings..........................................................................................23
Port Configuration Menu.....................................................................................................................24
Port Rate Limiting Menu.....................................................................................................................25
Port Security Menu ..............................................................................................................................26
Port Mirroring Menu............................................................................................................................28
Viewing Port Status .............................................................................................................................29
Resetting Ports .....................................................................................................................................29
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................30
Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs.........................................................................................................31
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................31
VLAN Features....................................................................................................................................31
VLAN Concepts And Issues................................................................................................................32
VLANs and Tags .................................................................................................................................32
Tagged vs. Untagged Frames...............................................................................................................32
Native VLAN.......................................................................................................................................32
Management VLAN.............................................................................................................................33
Edge And Trunk Port Types ................................................................................................................34
Forbidden Port Lists.............................................................................................................................34
VLAN Based Services ........................................................................................................................34
VLAN Applications.............................................................................................................................34
Traffic Domain Isolation......................................................................................................................34
Administrative Convenience................................................................................................................35
Reduced Hardware...............................................................................................................................35
Service Differentiation.........................................................................................................................36
VLAN Configuration...........................................................................................................................36
VLAN Parameter Ranges & Default Settings......................................................................................36
Virtual LANs Menu.............................................................................................................................37
Static VLANs Menu.............................................................................................................................37
Port VLAN Parameters Menu..............................................................................................................39
VLAN Summary Menu .......................................................................................................................42
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................43
RuggedCom
5
Page 8

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Chapter 5 – Configuring Class of Service ...........................................................................................44
Introduction to CoS..............................................................................................................................44
CoS Features........................................................................................................................................44
CoS Concepts And Issues....................................................................................................................44
CoS Operation......................................................................................................................................44
CoS Configuration ...............................................................................................................................46
CoS Parameter Ranges & Default Settings..........................................................................................46
Classes Of Service Menu.....................................................................................................................46
Global CoS Parameters Menu..............................................................................................................47
Port CoS Parameters Menu..................................................................................................................47
Priority to CoS Mapping Menu............................................................................................................48
DSCP to CoS Mapping Menu..............................................................................................................48
CoS Access Priorities Menu ................................................................................................................49
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree ...................................................................................50
Introduction .........................................................................................................................................50
RSTP Features......................................................................................................................................50
RSTP Concepts And Issues .................................................................................................................51
RSTP Operation...................................................................................................................................51
RSTP Applications...............................................................................................................................58
RSTP Configuration.............................................................................................................................61
Bridge and Port Parameter Ranges & Default Settings .......................................................................61
Spanning Tree Menu............................................................................................................................62
Bridge RSTP Parameters Menu...........................................................................................................62
Port RSTP Parameters Menu ...............................................................................................................64
RSTP Statistics ....................................................................................................................................66
Bridge RSTP Statistics Menu ..............................................................................................................66
Port RSTP Statistics Menu...................................................................................................................68
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................71
Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering........................................................................................75
Introduction to Multicast Filtering.......................................................................................................75
IGMP Features.....................................................................................................................................75
IGMP Concepts And Issues.................................................................................................................77
Router IGMP Operation.......................................................................................................................77
Switch IGMP Active and Passive Operation.......................................................................................78
Combined Router And Switch IGMP Operation.................................................................................79
Multicast Filtering Configuration ........................................................................................................82
Multicast Filtering Parameter Ranges & Default Settings...................................................................82
Multicast Filtering Menu .....................................................................................................................82
IGMP Parameters Menu......................................................................................................................82
Multicast Filtering Statistics ................................................................................................................83
IP Multicast Groups Menu...................................................................................................................83
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................86
Chapter 8 – Diagnostics.......................................................................................................................89
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................89
Using The Alarm System.....................................................................................................................89
Alarm Concepts And Issues.................................................................................................................89
Viewing And Clearing Alarms ............................................................................................................91
Viewing Alarms...................................................................................................................................91
RuggedCom
Page 9

Table Of Contents
Clearing Alarms...................................................................................................................................92
Viewing CPU Diagnostics...................................................................................................................93
Viewing and Clearing the System Log................................................................................................95
Viewing Product Identification............................................................................................................95
Load Factory Default Configuration....................................................................................................96
Resetting The Unit...............................................................................................................................96
Chapter 9 – Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics..............................................................................97
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................97
View Ethernet Statistics.......................................................................................................................98
View Ethernet Port Statistics ...............................................................................................................98
Remote Monitoring (RMON) ............................................................................................................100
RMON Historical Statistics Concepts And Issues.............................................................................101
Configure RMON History Control Table Menu................................................................................102
RMON History Samples Table Menu................................................................................................103
RMON Alarms And Events Concepts And Issues.............................................................................104
The Alarm Process.............................................................................................................................104
Alarm Generation And Hysteresis.....................................................................................................105
Delta vs. Absolute Values..................................................................................................................105
Configure RMON Alarms..................................................................................................................106
Configure RMON Events...................................................................................................................108
RMON Event Logs ............................................................................................................................109
Troubleshooting.................................................................................................................................111
Chapter 10 - Using The CLI Shell.....................................................................................................112
Introduction........................................................................................................................................112
Entering And Leaving The Shell .......................................................................................................112
Summary Of Commands....................................................................................................................113
Viewing Files.....................................................................................................................................114
Dir command......................................................................................................................................114
Viewing And Clearing Log Files ......................................................................................................114
Running Loopback Tests ...................................................................................................................115
Pinging A Remote Device..................................................................................................................116
Tracing Events ...................................................................................................................................117
Enabling Tracing................................................................................................................................117
Starting The Trace..............................................................................................................................118
Viewing DHCP Learned Information Using Ipconfig.......................................................................119
Executing Commands Remotely Through RSH................................................................................120
Resetting The Switch.........................................................................................................................120
Chapter 11 – Upgrading Firmware And Managing Configurations..................................................121
Introduction........................................................................................................................................121
Upgrading Firmware..........................................................................................................................121
Upgrading Firmware With Xmodem.................................................................................................122
Upgrading Firmware Using A TFTP Client On Your Workstation...................................................122
Upgrading Firmware Using The TFTP Client On Your RuggedSwitch™ ........................................124
Capturing Configurations...................................................................................................................125
Capturing Configurations With XModem.........................................................................................125
Capturing Configurations With TFTP...............................................................................................125
Using SQL Commands ......................................................................................................................127
Getting Started ...................................................................................................................................127
RuggedCom
7
Page 10

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Finding The Correct Table.................................................................................................................128
Retrieving Information.......................................................................................................................128
Changing Values In A Table..............................................................................................................129
Defaulting A Table.............................................................................................................................130
Using RSH And SQL.........................................................................................................................130
Appendix A - Menu Tree...................................................................................................................131
Appendix B - SNMP MIB Support....................................................................................................132
Appendix C – SNMP Trap Summary................................................................................................132
Appendix D – RMON Acceptable MIB Parameters..........................................................................133
Index...................................................................................................................................................137
RuggedCom
Page 11

Table Of Figures
TABLE OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Main Menu With Screen Elements Identified........................................................................3
Figure 2: Administration Menu .............................................................................................................5
Figure 3: IP Services Configuration Menu............................................................................................5
Figure 4: Time and Date Menu..............................................................................................................8
Figure 5: SNMP Management Stations Menu.....................................................................................10
Figure 6: Using A Router As A Gateway............................................................................................12
Figure 7: MAC Address Tables Menu.................................................................................................13
Figure 8: MAC Addresses Menu.........................................................................................................14
Figure 9: MAC Addresses Learning Options Menu............................................................................15
Figure 10: Static MAC Address Table Menu ......................................................................................16
Figure 11: Controller Protection Through FEFI..................................................................................21
Figure 12: Port Configuration And Status Menu.................................................................................23
Figure 13: Port Parameters Menu........................................................................................................24
Figure 14: Port Rate Limiting Menu....................................................................................................26
Figure 15: Port Security Menu.............................................................................................................26
Figure 16: Port Mirroring Menu ..........................................................................................................28
Figure 17: Port Status Menu ................................................................................................................29
Figure 18: Multiple and Overlapping VLANs.....................................................................................35
Figure 19: Inter-VLAN Communications............................................................................................36
Figure 20: Virtual LANs Menu............................................................................................................37
Figure 21: Static VLANs Menu...........................................................................................................37
Figure 22: Port VLAN Parameters Menu............................................................................................39
Figure 23: VLAN Summary Menu......................................................................................................42
Figure 24: Determining The CoS Of A Received Frame ....................................................................45
Figure 25: Use of CoS When Forwarding Frames ..............................................................................46
Figure 26: Classes Of Service Menu....................................................................................................46
RuggedCom
9
Page 12

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Figure 27: Global CoS Parameters Menu............................................................................................47
Figure 28: Port CoS Parameters Menu ................................................................................................47
Figure 29: Priority to CoS Mapping Menu..........................................................................................48
Figure 30: TOS DSCP to CoS Mapping..............................................................................................48
Figure 31: CoS Access Priorities Menu...............................................................................................49
Figure 32: Bridge and Port States........................................................................................................52
Figure 33: Bridge and Port Roles.........................................................................................................54
Figure 34: Example Of A Structured Wiring Configuration...............................................................58
Figure 35: Example Of A Ring Backbone Configuration....................................................................59
Figure 36: Port Redundancy ................................................................................................................60
Figure 37: Spanning Tree Menu ..........................................................................................................62
Figure 38: Bridge RSTP Parameters Menu..........................................................................................62
Figure 39: Port RSTP Parameters Menu..............................................................................................64
Figure 40: Bridge RSTP Status Menu .................................................................................................66
Figure 41: Port RSTP Parameters Menu..............................................................................................68
Figure 42: IGMP Operation Example 1...............................................................................................77
Figure 43: IGMP Operation Example 2...............................................................................................79
Figure 44: Multicast Filtering Menu....................................................................................................82
Figure 45: IGMP Parameters Menu.....................................................................................................82
Figure 46: IP Multicast Groups Menu .................................................................................................83
Figure 47: Diagnostics Menu Showing Alarm Commands.................................................................89
Figure 48: Alarms Menu......................................................................................................................91
Figure 49: CPU Diagnostics Menu......................................................................................................93
Figure 50: Viewing the System Log....................................................................................................95
Figure 51: Ethernet Statistics Menu.....................................................................................................97
Figure 52: Ethernet Statistics Menu.....................................................................................................98
Figure 53: Port Statistics Menu............................................................................................................98
RuggedCom
Page 13

Table Of Figures
Figure 54: The History Process..........................................................................................................101
Figure 55: History Control Table.......................................................................................................102
Figure 56: RMON History Samples Table ........................................................................................103
Figure 57: The Alarm Process ...........................................................................................................104
Figure 58: Applying Hysteresis to Alarm Generation.......................................................................105
Figure 59: RMON Alarm Configuration Table screens.....................................................................106
Figure 60: RMON Events Configuration Table screens....................................................................108
Figure 61: RMON Events Configuration Table screens....................................................................109
Figure 62: Running a Loopback Test ................................................................................................115
Figure 63: Displaying Trace settings ................................................................................................117
Figure 64: Changing Trace settings...................................................................................................118
Figure 65: Starting A Trace ...............................................................................................................118
Figure 66 Example of an Upgrade using XModem...........................................................................122
Figure 67 Example of an Upgrade using a TFTP client on your workstation...................................124
Figure 68 Example of an Upgrade using the TFTP client on the RuggedSwitch™...........................125
Figure 69 The sql command and SQL help .......................................................................................127
Figure 70 The sql command and SQL help .......................................................................................128
Figure 71 Selecting a table.................................................................................................................128
Figure 72 Select a parameter with a table..........................................................................................129
Figure 73 Selecting rows in a table based upon parameter values.....................................................129
Figure 74 Selecting rows in a table based upon multiple parameter values......................................129
Figure 75 Changing Values In A Table.............................................................................................129
Figure 76 Defaulting A Table............................................................................................................130
Figure 77 Bulk Inspections Using RSH and SQL .............................................................................130
RuggedCom
11
Page 14

Page 15

Chapter 1– Setting Up And Administering The Switch
Chapter 1– Setting Up And Administering The Switch
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with the RuggedCom user interface as well as
describes the following procedures:
• Configuring the IP Address and Subnet Mask
• Configuring the Gateway Address
• Configuring for DHCP Operation
• Configuring the Management Connection Inactivity Timeout
• Configuring the number of Telnet Sessions
• Configuring TFTP Server Permissions
• Configuring the SNMP Get Community Name
• Configuring the System Identification
• Configuring Passwords
• Configuring the time and date
• Configuring SNTP to keep the time and date correct
• Configuring SNMP Management Stations
The RuggedSwitch™ User Interface
Using the RS232 Port to Access the User Interface
Attach a terminal (or PC running terminal emulation software) to the RS232 port
on the rear of the chassis. The terminal should be configured for 8 bits, no parity
operation at 57.6 Kbps. Hardware and software flow control must be disabled.
Select a terminal type of VT100.
Once the terminal is connected, pressing <CR> will prompt for the password to
be entered. The switch is shipped with a default administrator password of
“admin”. Once successfully logged in, the user will be presented with the main
menu.
RuggedCom
RuggedCom
Page 16
RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
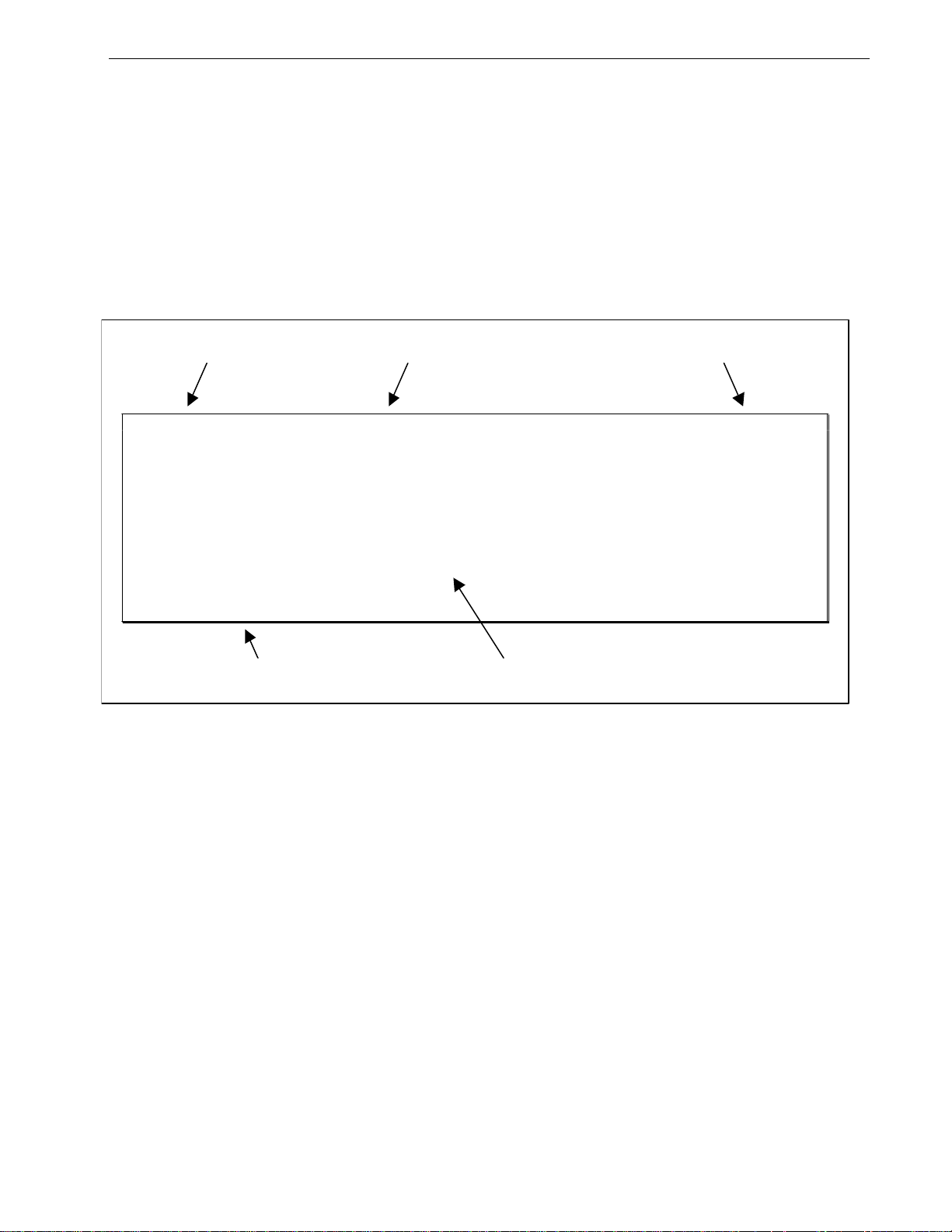
The Structure of the User Interface
The user interface is organized as a series of menus with an escape to a command
line interface (CLI) shell. Each menu screen presents the switch name (as proved
by the System Identification parameter), Menu Title, Access Level, Alarms
indicator, Sub-Menus and Command Bar.
Sub-menus are entered by selecting the desired menu with the arrow keys and
pressing the enter key. Pressing the escape key ascends to the parent menu.
System I dentification Menu Name Access Level/Alarms Indicator
My Switch Main Menu Admin Access
Administration
Port Configuration and Status
Ethernet Statistics
Spanning Tree
Virtual LANs
Classes of Service
MAC Address Tables
Multicast Filtering
Diagnostics
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell X-Logout
Comma nd Ba r Sub-Menus
Figure 1: Main Menu With Screen Elements Identified
The command bar offers a list of commands that apply to the currently displayed
menu. These commands include:
• <CTRL> Z to display help on the current command or data item
• <CTRL> S to switch to the CLI shell
• <CTRL> U/D to jump to next/previous page of a status display
The main menu also provides a <CTRL> X command, which will terminate the
session.
RuggedCom
Page 17

Making Configuration Changes
When changing a data item the user selects the data item by the cursor keys and
then pressing the enter key. The cursor will change position to allow editing of
the data item.
Typing a new value after pressing enter always erases the old parameter value. The
left and right cursor keys may be used to position the edit point without erasing
the old parameter value. The up and down cursor keys may be used to cycle
through the next higher and lower values for the parameter.
After the parameter has been edited, press enter again to change other parameters.
When all desired parameters have been modified, press <CTRL> A to apply
changes. The switch will automatically prompt you to save changes when you
leave a menu in which changes have been made.
Some menus will require you to press <CTRL> I to insert a new record of
information and <CTRL> L to delete a record.
Table Of Contents
Updates Occur In Real Time
All configuration and display menus present the values at the current instant,
automatically updating if changed from other user interface sessions or SNMP.
All statistics menus will display changes to statistics as they occur.
Alarm Indications Are Provided
Alarms are events for which the user is notified through the Diagnostics menu
View Alarms command. All configuration and display menus present an
indication of the number of alarms (in the upper right hand corner of the screen)
as they occur, automatically updating as alarms are posted and cleared.
The CLI Shell
The user interface provides a shell for operations that are more easily performed at
the command line. You may switch back and forth from the menu system and
shell by pressing <CTRL> S. For more information on the capabilities of the
shell consult Chapter 10 - Using The CLI Shell.
RuggedCom
3
Page 18

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Administration Menu
The Administration command provides the menu shown in the following Figure.
My Switch Administration Admin Access
Configure IP Services
Configure System Identification
Configure Passwords
Configure Time and Date
Configure SNMP Management Stations
Figure 2: Administration Menu
Configure IP Services
The Configure IP Services command provides the ability to change the IP
Address/mask, Gateway address, Inactivity Timeout, Telnet Sessions Allowed,
TFTP Server and SNMP Get Community parameters.
Note:
the settings as shipped from the factory.
My Switch IP Services Configuration Admin Access
IP Address Type Static
IP Address 192.168.0.1
Subnet 255.255.255.0
Gateway
Inactivity Timeout 5 min
Telnet Sessions Allowed 8
TFTP Server Get Only
SNMP Get Community public
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 3: IP Services Configuration Menu
IP Address Type
This parameter specifies if the IP configuration is static (i.e. configured through
this menu), or dynamically assigned. If dynamic IP configuration is chosen, the IP
Address, Subnet and Gateway fields will become unavailable for editing and will
not be displayed. These values will be loaded via Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) and may be viewed using the “ipconfig” shell command.
These parameters are not changed during a factory reload. The following figure shows
IP Address
This parameter specifies the IP address of the switch.
RuggedCom
Page 19

Table Of Contents
Note:
in place at the time of an address change will be lost.
Changes to the IP Address take effect immediately upon being saved. Telnet connections
Subnet
This parameter specifies the subnet mask of the switch.
Gateway
This parameter specifies the gateway IP address. This is the address to use when
forwarding packets to a network other than the one the switch belongs to. It is
only required if you intend to manage the switch from a management station that
is separated from the switch by a router.
Inactivity Timeout
This parameter specifies the amount of time after keystrokes have been pressed
before a management connection will be automatically broken. A value of zero
disables timeouts altogether.
Telnet Sessions
This parameter limits the number of Telnet sessions. A value of zero prevents any
Telnet access.
Note:
will not be able to connect via Telnet until your current connection closes.
If you disable Inactivity Timeouts
TFTP Server
This parameter controls how a TFTP client can access the switches built-in TFTP
server. A setting of “Disabled” prevents all access, “Get Only” allows retrieval of
files and “Enabled” allows storing and retrieval of files.
SNMP Get Community
This string determines the community string that may be used by any management
station for SNMP read-only access of settings. Delete this string if you wish to
prevent read-only access.
and
reduce the number of Telnet sessions to one, you
RuggedCom
5
Page 20

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Configuring System Identification
The system identification is displayed in the sign-on screen and in the upper left
hand corner of all RuggedSwitch™ menu screens. Setting the system identification
can make it easier to identify the switches within your network.
Setting the location and contact fields can provide information about where the
switch is located and who to contact in order to resolve problems.
Configure Passwords
The guest, operator and admin passwords provide differing levels of access to the
switch. Guest users can view most settings but may not change settings or run
commands. Operators cannot change settings but can reset alarms, statistics and
logs. Admin users can change settings and run commands.
Configure Time and Date
The Configure Time and Date command provides the ability to change the switch
time, date and time zone. The switch can also be configured to periodically
contact an NTP server to correct for drift in the onboard clock.
My Switch Time and Date Admin Access
Time 14:05:41
Date Jan 7, 2003
Time Zone UTC-5:00 (New York, Toronto)
NTP Server Address 0.0.0.0
NTP Update Period 60 min
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 4: Time and Date Menu
Note:
not have a non-volatile real time clock and relies upon NTP to obtain its time and date after
rebooting. The hardware revision of your RSMCPU is provided in the
Product Identification
Time
The first revision of the RuggedSwitch™ Management CPU (RSMCPU Rev A) does
Diagnostics, View
menu.
Date
The time parameter allows configuration of the local time in local 24-hour format.
The date parameter configures the date.
RuggedCom
Page 21

Time Zone
The time zone setting allows for the conversion of UTC (Universal Coordinated
Time) to local time.
NTP Server Address
This parameter specifies the IP address of the NTP (Network Time Protocol)
server used to set the on-board real time clock. Programming an address of
“0.0.0.0” disables the use of NTP. The current time setting will be overwritten at
every NTP sync time interval, as specified by the NTP update period parameter.
Table Of Contents
Note:
mechanism for obtaining the time after a start up.
If your RuggedSwitch™ is not equipped with a real time clock, NTP is the only
NTP Update Period
This parameter determines how frequently the time is updated from the NTP
server. If the update attempt fails the switch will make two more attempts (at oneminute intervals) after which an alarm is generated. The programmed update rate
will then be resumed.
RuggedCom
7
Page 22
RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
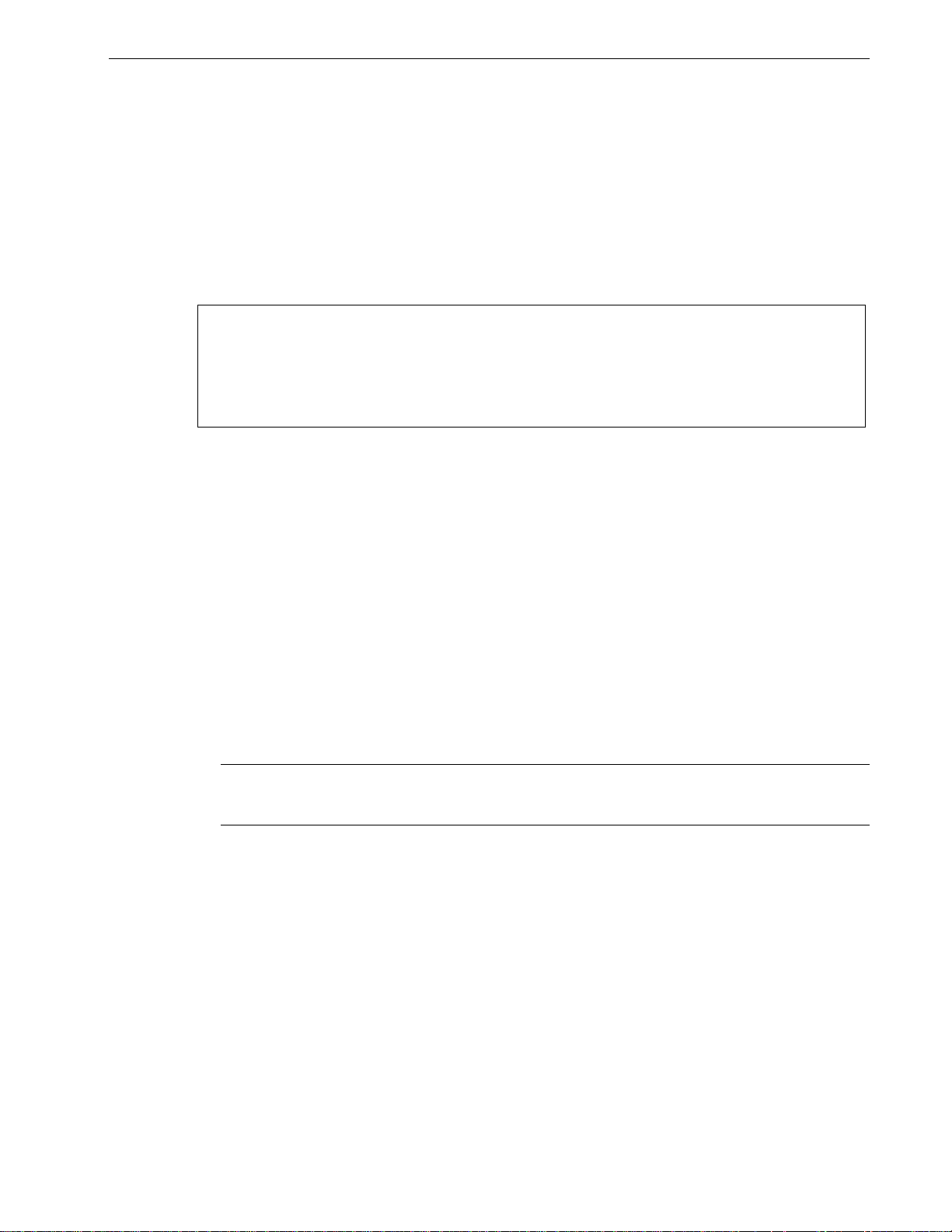
Configure SNMP Management Stations
This command identifies management stations that may configure the switch
through SNMP and receive Traps from the switch.
At shipping time and after factory reloads the switch is configured not to allow
remote management or raise Traps. Identify a management station to the switch
by executing the Configure SNMP Management Stations command and
pressing CTRL-I to create a management record, as shown below.
My Switch SNMP Management Stations Admin Access
Community String public
Address
Set Access Disabled
Send Traps Enabled
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell A-Apply
Figure 5: SNMP Management Stations Menu
You may create up to eight management stations, each of which may have
individual settings for community strings, set access permission and sending of
traps. Note that all management stations created this way inherently allow get
access and disable set access.
Community String
The community string this management station is authenticated by.
Address
The management station IP address.
Note:
If this address does not lie in the same network as the switches IP address then the
gateway address must be configured.
Set Access
If enabled, this management station may change configuration parameters.
Send Traps
The management station will be sent SNMP traps if this setting is enabled. The
traps issued are summarized in Appendix C – SNMP Trap Summary.
RuggedCom
Page 23
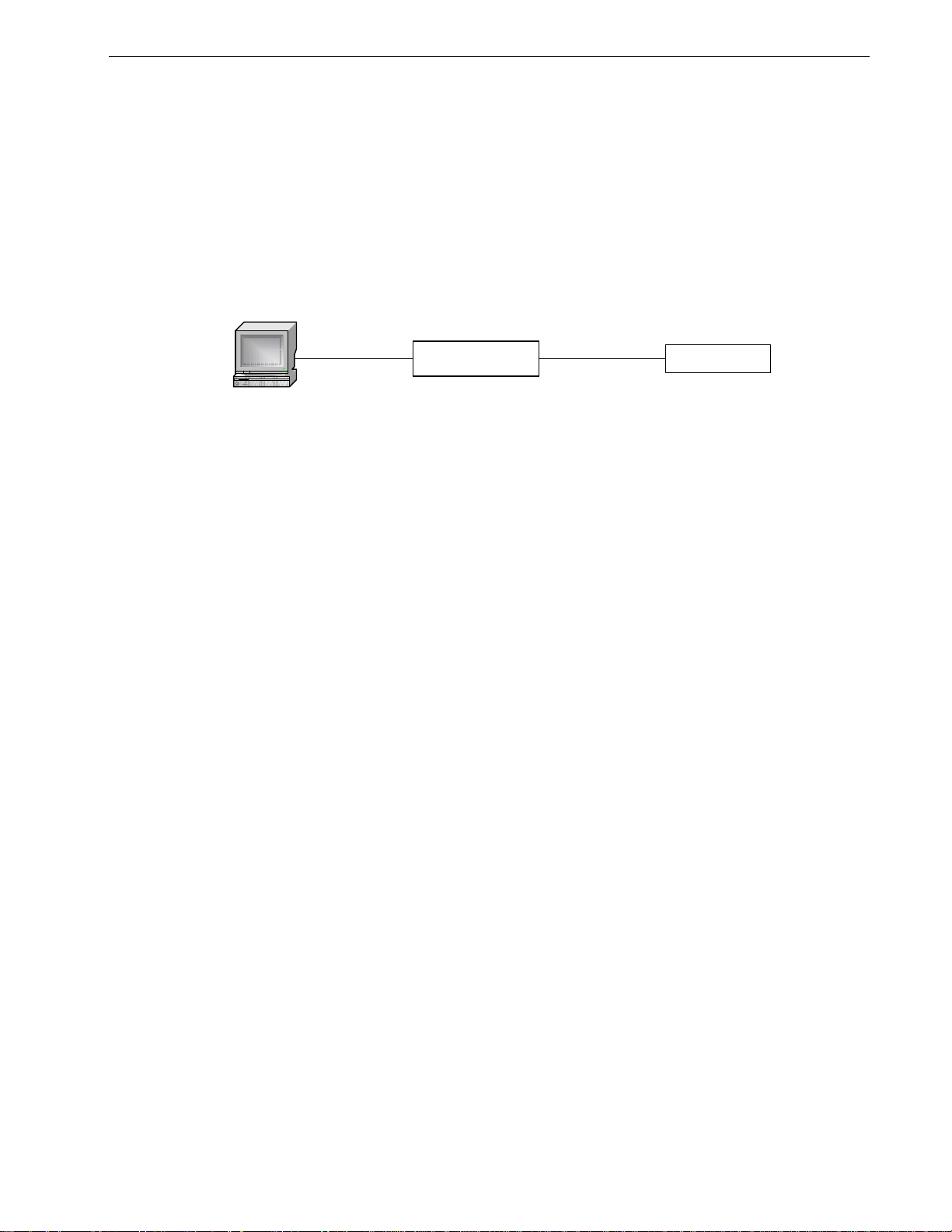
Troubleshooting
Problem One
• I have configured the IP address and a gateway. I am pinging the
Is the switch being pinged through a router? If so, the switch gateway address
must be configured. The following figure illustrates the problem.
Table Of Contents
switch but it is not responding. I am sure the switch is receiving
the ping because it’s port LEDs are flashing and the statistics
menu shows the pings. What is going on?
192.168.0.1
Workstation
192.168.0.2
Figure 6: Using A Router As A Gateway
Router RuggedSwitch
10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
TM
The router is configured with the appropriate IP subnets and will forward the ping
from the workstation to the switch. When the switch responds, however, it will
not know which its interfaces to use in order to reach the workstation and will
drop the response. Programming a gateway of 10.0.0.1 will cause the switch to
forward un-resolvable frames to the router.
This problem will also occur if the gateway address is not configured and the
switch tries to raise an SNMP trap to a host that is not on the local subnet
RuggedCom
9
Page 24

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Chapter 2 - Configuring MAC Address Management
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• Viewing learned MAC addresses
• Purging MAC Address Entries
• Configuring the switch MAC Address Aging time
• Configuring static MAC addresses
MAC Address Management Features
MAC Address management provides you with the following features:
• The ability to configure static MAC addresses.
• The ability to set the switch MAC address aging time
MAC Address Management Configuration
MAC Address Management Parameter Ranges & Default Settings
Configuration Item Default Value Supported Values
Aging Time 300 seconds 15 to 800 seconds
MAC Address Tables Management Menu
The MAC Address Tables menu is accessible from the main menu MAC Address
Tables command.
My Switch MAC Address Tables Admin Access
View MAC Addresses
Purge MAC Address Table
Configure MAC Address Learning Options
Configure Static MAC Address Table
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 7: MAC Address Tables Menu
RuggedCom
Page 25

Viewing MAC Addresses
The View MAC Addresses command presents a real time display of learned and
static MAC addresses.
My Switch MAC Addresses Admin Access
MAC Address VID Port Type CoS
00-00-85-05-9A-C4 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-01-E6-64-2B-B6 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-03-47-A0-56-F3 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-03-47-A0-57-37 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-03-47-B0-59-F3 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-06-5B-61-AC-30 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-06-5B-7A-40-BA 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-06-5B-95-B2-A4 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-06-5B-A2-51-41 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-06-5B-AF-1A-AA 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-06-5B-AF-1A-AD 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-0A-DC-00-20-00 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-0A-DC-01-01-0E 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-0A-DC-01-01-1E 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-50-BA-D4-48-16 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-50-BA-F4-E8-EB 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-C0-4F-6C-D9-1B 1 6 Dynamic Normal
00-E0-18-BB-B4-CA 1 6 Dynamic Normal
More below ...
Figure 8: MAC Addresses Menu
Chapter 2 - Configuring MAC Management
The display will change as MAC addresses are learned and aged out.
MAC Address
The learned MAC address.
VID
The VLAN the MAC address was learned upon.
Port
The port the MAC address was learned upon.
Type
Either “Static” or “Dynamic”, this parameter describes how the switch has learned
the MAC address. Dynamic addresses are learned from received frames. Static
addresses are learned from configured entries in the Static MAC Address Table.
CoS
The Class of Service associated with this MAC Address. CoS and its use is more
fully described in Chapter 5 – Configuring Class of Service.
RuggedCom
11
Page 26

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Purge MAC Address Table
This command removes all dynamic entries from the MAC address table. The
only negative impact of this operation is that it causes flooding while addresses are
relearned.
Configure MAC Address Learning Options
This menu allows you to configure MAC management related parameters.
My Switch MAC Address Learning Options Admin Access
Aging Time 300 s
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 9: MAC Addresses Learning Options Menu
Aging Time
This parameter configures the time a learned MAC address is held before being
aged out.
Configure Static MAC Address Table
This menu allows you to enter static MAC addresses or MAC addresses whose
CoS priority is automatically set to High.
My Switch Static MAC Address Table Admin Access
MAC Address VID Port CoS
00-01-E6-64-2B-B6 1 1 Normal
00-06-5B-AF-1A-AD 1 Learn High
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell D-PgDn U-PgUp I-Insert L-Delete
Figure 10: Static MAC Address Table Menu
Static MAC addresses are often configured when the user wishes to enforce port
security. The relevant MAC address (and the port it is to be restricted to) is
configured in the Static MAC addresses Table. The port is made secure by
configuration in the Port Configuration and Status menu, Configure Port
Security command.
Static MAC addresses are also configured when a device can receive but cannot
transmit frames. Static addresses are automatically displayed in the MAC
Addresses display.
Prioritized MAC addresses are configured when traffic to or from a specific device
on a LAN segment is to be assigned a higher CoS priority than other devices on
RuggedCom
Page 27

that LAN segment. Prioritized addresses function much as regular dynamic
addresses, appearing in the MAC Addresses display only while they are learned.
MAC Address
This parameter specifies the unicast address that is to be statically configured or
prioritized.
VID
This parameter configures the VLAN upon which the MAC address operates.
Port
If a static MAC address is being constructed, enter the port number upon which
the device with this address is located. If a prioritized address is being constructed
set this parameter to “Learn”.
CoS (Class of Service)
Set this parameter to normal if you want the prioritized address to have a normal
CoS priority or to high if you want the prioritized address to have a high CoS
priority
Chapter 2 - Configuring MAC Management
RuggedCom
13
Page 28

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• Configuring port physical parameters
• Configuring link alarms/traps for the port
• Configuring rate limiting
• Configuring port security
• Using Port Mirroring
• Viewing the status of ports
• Resetting all or one port
• Using the Loss-of-Link Management feature
Port Features
10BaseT/100Base Interfaces
• Uses RJ45 Connector
10BaseFL Interfaces
• Multi-mode fiber (820nm) optical ports on 62.5µm cable, 2km distances
• Single-mode fiber (1310nm) optical ports on 9µm cable, 15km distances
• Uses ST Connector
• Support Far End Fault Indication (FEFI) through withholding of link
pulses
100BaseFX Interfaces
• Multi-mode fiber (1300nm) optical ports on 62.5µm cable, 2km distances
• Single-mode fiber (1310nm) optical ports on 9µm cable, 15km distances
• Multi-mode Uses MTRJ Connector, Single-mode Uses LC Connector
• Support Far End Fault Indication Through FEFI signal
All Interfaces
• Port security
• Broadcast Rate Filtering
• Link based Alarms and Traps
RuggedCom
Page 29

• Port Latency: 10 Mbps - 16µs + frame time, 100 Mbps - 5µs + frame time
Port Applications
Port Security
Port Security provides the ability to filter or accept traffic from specific MAC
addresses.
Port Security works by inspecting the source MAC addresses of received frames
and validating them against the contents in the Static MAC Address Table (See
Chapter 2 - Configuring MAC Address Management). Unauthorized frames will be
filtered and, optionally, the port that receives the frame shutdown permanently or
for a period of time. An alarm will be raised indicating the unauthorized MAC
address (See Chapter 8 – Diagnostics).
Unicast frames to unknown destination addresses will not be flooded through
secure ports.
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports
The switch can also be programmed to learn and allow the first source MAC
address encountered on the port. This feature provides a convenient means for
network administrators to “capture” the appropriate secure addresses when
turning up a port. The MAC address will be permanently added to the Static MAC
Address Table.
Note:
specific devices. Do not apply port security on core switch connections or where traffic types such
as RSTP or IGMP are active.
Port security is applied at the edge of the network in order to restrict admission to
Broadcast Rate Limiting
Broadcast rate filtering provides a means to limit the rate of broadcast frames
accepted by each port.
Broadcast rate filtering limits the severity of broadcast storms.
RuggedCom
15
Page 30
RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
p
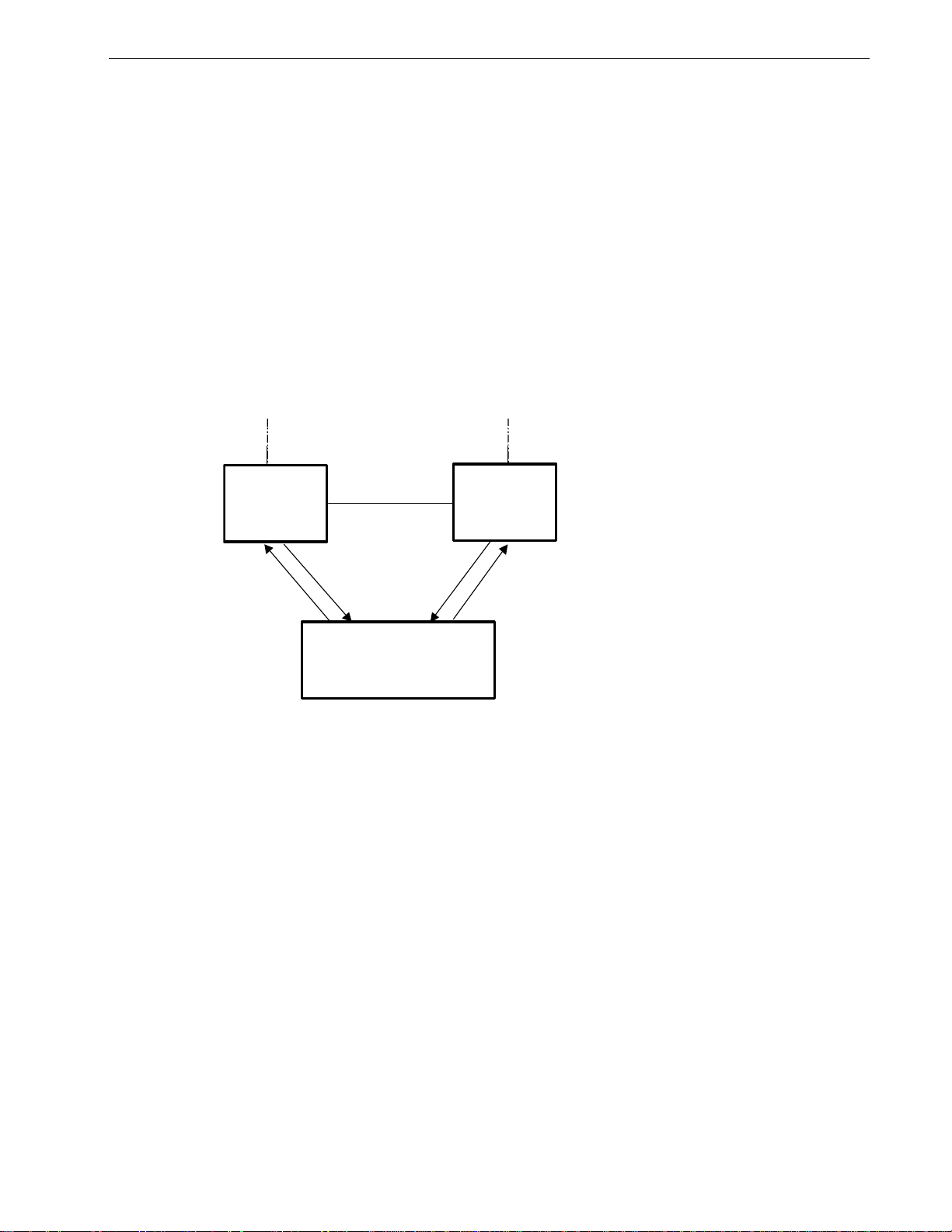
Controller Protection Through Loss-of-Link Management
Modern industrial controllers often feature backup Ethernet ports used in the
event of a link failure. When these interfaces are supported by media (such as
fiber) that employ separate transmit and receive paths, the interface can be
vulnerable to failures that occur in only one of the two paths.
Refer to the following figure. While the link between switch A and the controller
functions normally, the controller holds the backup link down. Switch B learns
that it must forward frames towards switch A in order to reach the controller.
Unfortunately, if the transmission path from the controller to switch A fails,
switch A will still generate link signals to the controller. The controller will still
detect link to switch A and will not failover to the backup port.
Swit ch A
To remainder of network..
Main Backu
Controller
Swit ch B
Figure 11: Controller Protection Through FEFI
When FEFI is enabled the switch bases generation of link signal upon its reception
of link signal. If switch A fails to receive a link signal from the controller it will
stop generating a link signal. The controller will detect the link failure and switch
to the backup port.
Part of the Controller Protection Through FEFI feature is the flushing of the
MAC address table for the controller port. Frames destined for the controller will
be flooded to switch B where they will be forwarded to the controller (after the
controller transmits its first frame).
The FEFI feature on 10BaseFL ports causes the transmitter to be disabled, which
suspends the sending of link pulses. The FEFI feature on 100BaseFX ports causes
a FEFI signal to be sent instead of a link carrier signal.
RuggedCom
Page 31

Using Port Mirroring
Introduction
Port mirroring is a management tool in which all traffic on a designated port is
copied (or mirrored) to a target port. If a protocol analyzer is attached to the
target port, the traffic stream of valid frames on any source port is made available
for analysis.
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports
Note:
errors, oversize and undersize packets, fragments, jabbers, collisions, late collisions and dropped
events).
Invalid frames received on the source port will not be mirrored. These include CRC
Configuring Port Mirroring
Select a target port that has a higher speed than the source port. Mirroring a 100
Mbps port onto a 10 Mbps port may result in an improperly mirrored stream.
Frames will be dropped if the full duplex rate of frames on the source port exceeds
the transmission speed of the target port. Since both transmitted and received
frames on the source port are mirrored to the target port, frames will be discarded
if the sum traffic exceeds the target port’s transmission rate. This problem reaches
its extreme in the case where traffic on a 100 Mbps full duplex port is mirrored
onto a 10 Mbps half duplex port.
A limitation of port mirroring occurs with multicast traffic. Multicast traffic will
be mirrored onto the target port only if the target port is a member of the same
VLANs as the source port.
Limitations of port mirroring occur with VLAN traffic. If the port selected as the
source port receives an untagged frame that will be forwarded to a tagged port, the
target port will incorrectly show the frame as having been received tagged.
If the port selected as the port mirroring target is configured as a tagged edge
VLAN port, all untagged frames received by and copied from the source port will
be sent tagged with the native VLAN for the source port. If the port selected as
the target is configured as an untagged edge VLAN port, all tags in frames copied
from the source port will be removed before transmission on the target port.
A further limitation of port mirroring is that traffic originated by the switch, such
as ping requests, may not be mirrored.
Port Configuration And Status
RuggedCom
17
Page 32

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
The main menu Port Configuration and Status command presents this menu.
Commands are provided to reset, configure and obtain the status of ports.
My Switch Port Configuration and Status Admin Access
Configure Port Parameters
Configure Port Rate Limiting
Configure Port Security
Configure Port Mirroring
View Port Status
Reset Port(s)
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 12: Port Configuration And Status Menu
Port Parameter Ranges & Default Settings
The following set of tables lists default per-port configuration parameters
Configuration Item Default Value Supported Values
Status Enabled Disabled, Enabled
Media Type (10/100BaseT) Auto Select Auto Select, 10TX Half, 10TX Full, 100TX
Half, 100TX Full
Media Type (10BaseFL) 10BaseFL Full 10BaseFL Half, 10BaseFL Full
Media Type (100BaseFX) 100BaseFX Full 100FX Half, 100FX Full
Flow Control Enabled Disabled, Enabled
FEFI Disabled Disabled, Enabled
Broadcast Rate 2000 /sec 100 to 2000 /sec, Disabled
Port Security Disabled Disabled, Enabled, Learn Single
Link Alarms Enabled Disabled, Enabled
RuggedCom
Page 33

Port Configuration Menu
The Configure Port Parameters Command will provide a summary of the
settings of all ports. Selecting a particular port and pressing enter will allow you to
configure that port.
My Switch Port Parameters Admin Access
Port 16
Name My Port Name
Status Enabled
Media Type Auto Select
Flow Control Enabled
FEFI Disabled
Link Alarms Enabled
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 13: Port Parameters Menu
Name
A mnemonic name used to identify the device connected on the port.
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports
Status
Media Type
Disabling a port will prevent all frames from being sent and received on that port.
Link integrity pulses are not sent while the port is disabled and the link/activity
LED will never be lit. You may want to disable a port for troubleshooting, to
reduce power consumption or to secure it from unauthorized connections.
Selects the speed and duplex of the port. Choosing “Auto Select” results in speed
and duplex being negotiated upon link detection; both end devices must be
autonegotiation compliant (802.3u) for the best possible results. As fiber optic
media do not support “Auto Select”, these media must be explicitly configured to
either half or full duplex.
Note:
If one end of the link is fixed to a specific speed and duplex type and the peer
autonegotiates, there is a strong possibility that the link will either fail to raise, or raise with the
wrong settings on the autonegotiating side.
Most often the autonegotiating peer will fall back to half-duplex operation, even when the fixed
side is full duplex. Full duplex operation requires that both ends are configured as such or else
severe frame loss will occur during heavy network traffic. At lower traffic volumes the link may
display few if any errors. As the traffic volume rises the fixed negotiation side will begin to
experience dropped packets while the autonegotiating side will experience excessive collisions.
Ultimately, as traffic load approaches 100% the link will become entirely unusable.
These problems can be avoided by always configuring ports to the appropriate fixed values.
RuggedCom
19
Page 34

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Flow Control
Flow Control is useful for preventing frame loss during times of severe network
traffic. Examples of this include multiple source ports concentrating to a single
destination port or a higher speed port bursting to a lower speed port.
When the port is half-duplex it is accomplished using “backpressure” where the
switch simulates collisions causing the sending device to retry transmissions
according to the Ethernet backoff algorithm. When the port is full duplex it is
accomplished using PAUSE frames which causes the sending device to stop
transmitting for a period of time.
FEFI
Enabling Far End Fault Indication (FEFI) inhibits transmitting link integrity
pulses when the receive link has failed. This allows the device at far end to detect
link failure under all circumstances.
Note:
This feature must not be enabled at both end of a link.
Link Alarms
Enabling link alarms will cause alarms and SNMP linkUp and linkDown traps to
be sent for the port.
Port Rate Limiting Menu
The Configure Port Rate Limiting Command will provide a summary of
broadcast rate limiting settings for the ports.
My Switch Port Rate Limiting Admin Access
Port Broadcasts
1 2000
2 2000
3 2000
4 2000
5 2000
6 2000
7 2000
8 2000
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 14: Port Rate Limiting Menu
Broadcasts
The switch will limit the number of accepted broadcast frames on this port to this
value each second, discarding the excess. Broadcast storm filtering may be
disabled for the port.
Port Security Menu
RuggedCom
Page 35

Security
Autolearn
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports
The Configure Port Security Command configures the ability to filter or accept
traffic from specific MAC addresses.
My Switch Port Security Admin Access
Port Security Autolearn Shutdown Time Status
1 On 2 Until reset Autolearning over, 2 addresses
2 On 1 Don't shutdown Autolearning, 0 addresses
3 On 1 10 s Autolearning over, 1 addresses
4 On 1 Until reset Port is Shutdown, 1 address
5 On Off Don't shutdown 4 addresses
6 Off Off Don't shutdown Port is Disabled
7 Off Off Don't shutdown Unsecure, 3 addresses
8 Off Off Don't shutdown Unsecure, 0 addresses
Figure 15: Port Security Menu
The port security mode, either on or off.
This may be either “off” or set to the number of addresses the switch is allowed to
self-learn.
A setting of “off” will cause the switch to match the source MAC addresses of
incoming frames against addresses already entered in the Static MAC Address
table. Frames with unmatched addresses are discarded and the shutdown action
(described below) is performed.
Any other setting will specify the number of received MAC address to self-learn.
As the switch encounters new MAC addresses in will permanently save them in the
Static MAC Address table until the autolearn limit is reached.
Note:
addresses for the port in the S at c MAC Address table
Autolearning takes place
only while there are less than “autolearn”
t i .
The “Status” parameter
will indicate whether autolearning is actually taking place. If you wish to re-autolearn, delete all
entries in the Static MAC Address table for this port.
Note:
Autolearning changes the switch configuration by adding an entry to the Static MAC
Address table. It is recommended that the operator start autolearning and then verify that the
system has learned the correct address before proceeding.
Note:
Autolearning will stop if more than “autolearn” addresses are manually entered into the
Static MAC Address table.
RuggedCom
21
Page 36

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Shutdown Time
This is the length of time to shut the port down when an unauthorized frame is
received in port security mode.
If this option is set to “Don’t Shutdown”, the frame will simply be filtered.
If this option is set to “Until Reset”, the port will be shutdown until a port reset
command is issued or the switch is reset.
This option can also take the number of seconds (1 to 86384) to hold the port
down.
Note:
The port is also reset whenever a parameter in the Port Configuration and Status menu
is changed.
Status
This parameter’s message describes the port security status including disabled
ports and ports that have been shut down because of security violations. If
autolearning is configured, this parameter displays whether it is taking place. The
number of entries in the Static MAC Address table for this port is also provided.
Port Mirroring Menu
The Configure Port Mirroring command enables port mirroring.
My Switch Port Mirroring Admin Access
Port Mirroring Disabled
Source Port 1
Target Port 1
-
Figure 16: Port Mirroring Menu
-
Port Mirroring
Enable or disable port mirroring with this command.
Note:
Source Port
Select the source port with this command.
Target Port
Select the target port with this command.
Port mirroring will be disabled upon the next reset of the switch.
RuggedCom
Page 37

Viewing Port Status
The View Port Status command shows the port status.
My Switch Port Status Admin Access
Port Name Link Speed Duplex
1 Maint. RTU Up 10 Half
2 IED Bay 6 Up 100 Full
3 IED Bay 8 Up 100 Full
4 IED Bay 9 Up 100 Full
5 IED Bay 12 Up 100 Full
6 Local Access Down 10 Half
7 U/L to Subs 22 Up 100 Full
8 U/L to Subs 24 Up 100 Full
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 17: Port Status Menu
Resetting Ports
Performs a reset of one or all Ethernet ports. This action is useful for forcing renegotiation of speed and duplex or in situations where the link partner has latched
into an inappropriate state.
Chapter 3 – Configuring the Ports
RuggedCom
23
Page 38

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Troubleshooting
Problem One
• One of my links seems to be fine at low traffic levels, but starts to
fail as traffic rates increase.
• One of my links pings OK but has problems with
FTP/SQL/HTTP/…
A possible cause of intermittent operation is that of an autonegotiation mismatch.
If one end of the link is fixed to full duplex and the peer autonegotiates, the
autonegotiating end falls back to half-duplex operation. At lower traffic volumes
the link may display few if any errors. As the traffic volume rises the fixed
negotiation side will begin to experience dropped packets while the
autonegotiating side will experience collisions. Ultimately, as traffic loads
approach 100% the link will become entirely unusable.
Note:
The command “ping 192.168.0.1 500 2” can be used to issue 500 pings each separated by 2
milliseconds to the next switch. If the link used is of high quality then no pings should be lost
and the average round trip time should be small.
Problem Two
Is it possible that the peer also has FEFI enabled? If both sides of the link have
FEFI enabled then both sides will withhold link signal generation from each other.
Problem Three
The broadcast rate applies only to admission of frames. An eight-port switch with
broadcast rate filtering set to 100 frames/sec could conceivably forward 700
broadcast frames/sec out a port.
The ping command with flood options is a useful tool for testing commissioned links.
• I am trying to use the FEFI protection feature but my links won’t
even come up.
• I programmed the broadcast rate to 100 frames/sec on all my
ports. Why can I see more than 100 frames/sec coming out my
ports?
RuggedCom
Page 39

Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• VLAN Terminology and Issues
• VLANs and their relationship to protocols such as IGMP
• Planning VLAN networks
• Configuring VLANs
• Viewing VLAN status and statistics
• Troubleshooting VLANs
Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs
VLAN Features
RuggedCom VLANs provide you with the following features:
• Per Port :
• Per VLAN :
• Per switch :
• Native VLAN is configurable.
• Modes of operation tailored to edge devices (such as a PC or IED) and to
network switch interconnections.
• A default port setting that ensures configuration-free connectivity in certain
scenarios.
• The ability to force either tagged or untagged operation on the native VLAN
• VLAN Name,
• IGMP
• Ability to exclude ports from the VLAN.
• Assignment of up to 64 VLANs (in the range of 1 to 1000).
RuggedCom
25
Page 40

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
VLAN Concepts And Issues
VLANs and Tags
A virtual LAN or VLAN is a group of devices on one or more LAN segments that
communicate as if they were attached to the same physical LAN segment. VLANs
are extremely flexible because they are based on logical instead of physical
connections.
When VLANs are introduced, all traffic in the network must belong to one or
another VLAN. Traffic on one VLAN cannot pass to another, except through an
intranetwork router or layer 3 switch.
A VLAN tag is the identification information that is present in frames in order to
support VLAN operation.
Tagged vs. Untagged Frames
Tagged frames are frames with 802.1q (VLAN) tags that specify a valid VLAN
identifier (VID). Untagged frames are frames without tags or frames that carry
802.1p (Prioritization) tags having prioritization information.
When a switch receives a tagged frame it extracts the VID. If the VID is not
allowed on the port the frame was received upon, the frame will be discarded. If
the VID is acceptable the frame will be forwarded to other ports in the same
VLAN.
Native VLAN
Each port is assigned a native VLAN number, the Port VLAN ID (PVID). When
an untagged frame is received, it is tagged with the native VLAN.
By default, when the switch transmits a frame on the native VLAN it removes the
tag before doing so. The switch can be configured to transmit frames on the
native VLAN tagged.
Management VLAN
Management traffic, like all traffic on the network, must belong to a specific
VLAN. RuggedCom switch management is always part of VLAN 1. This VLAN
is the native VLAN by default.
RuggedCom
Page 41

Edge And Trunk Port Types
Each port can be configured to take on a type of Edge or Trunk.
An Edge port attaches to a single end device (such as a PC or IED) and carries
traffic on a single pre-configured VLAN.
Trunk ports are part of the network and carry traffic for all VLANs between
switches. Trunk ports must be manually programmed with the VLANs to be
supported.
Forbidden Port Lists
Each VLAN can be configured to exclude ports from membership in the VLAN.
VLAN Based Services
IGMP Snooping
Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) provides the ability for IP
hosts and workstations to report their multicast group memberships to routers.
The switch can “snoop” or monitor these messages in order to restrict multicast
traffic streams to only the necessary parts of the network. IGMP snooping is
activated on a per-VLAN basis. See “Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering”
for information on configuring IGMP snooping.
VLAN Applications
Traffic Domain Isolation
VLANs are most often used for their ability to restrict traffic flows between
groups of devices.
Unnecessary broadcast traffic can be restricted to the VLAN that requires it.
Broadcast storms in one VLAN need not affect users in other VLANs.
Hosts on one VLAN can be prevented from accidentally or deliberately assuming
the IP address of a host on another VLAN.
RuggedCom
The use of creative bridge filtering and multiple VLANs can carve seemingly
unified IP subnets into multiple regions policed by different security/access
policies.
Multi-VLAN hosts can assign different traffic types to different VLANs.
27
Page 42

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Switch 1
VLAN 2
Switch 2
VLAN 5
Figure 18: Multiple and Overlapping VLANs
Administrative Convenience
VLANs enable equipment moves to be handled by software reconfiguration
instead the alternative, cable management. When a host’s physical location is
changed, its connection point is often changed as well. With VLANs, the host’s
VLAN membership and priority are simply copied to the new port.
VLAN 3
Switch 3
VLAN 4
Reduced Hardware
Without VLANs, traffic domain isolation requires using separate bridges for
separate networks. VLANs eliminate the need for separate bridges.
The number of networks hosts may often be reduced. Often a server is assigned
to provide services for independent networks. These hosts may be replaced by a
single multihomed host supporting each network on a its own VLAN. This host
can perform routing between VLANs.
RuggedCom
Page 43

IP Addresses
VLAN 2 – 199.85.245.0 - 199.85.245.127
VLAN 3 – 199.85.245.128 - 199.85.245.191
VLAN 4 – 199.85.245.192 - 199.85.245.255
:
Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs
VLAN 2
199.85.245.1/25
VLAN 3
Server, Router or
Layer 3 Switch
Switch
Figure 19: Inter-VLAN Communications
Service Differentiation
Programming of priority field in the VLAN tag can be used to provide classes of
service in the network. See Chapter 5 for information on configuring CoS.
VLAN Configuration
VLAN Parameter Ranges & Default Settings
199.85.245.128/26
VLAN 4
199.85.245.192/26
The following set of tables lists default VLAN configuration parameters for the
unit. For each parameter the parameter name, recommended setting and possible
range are included.
Configuration Items (All Ports) Default Value Supported Values
Configured VLANs 1 (Management VLAN) 1-1000
Port VLAN Type Edge Port Edge Port, Trunk Port
Port native VLAN (PVID) 1 1-1000
Port native VLAN format Untagged Untagged, Tagged
RuggedCom
29
Page 44

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Virtual LANs Menu
The Virtual LANs menu is accessible from the main menu Virtual LANs
command. The VLAN menu will lead you to all the other available menus for
configuring and obtaining the status of VLANs.
My Switch Virtual LANs Admin Access
Configure Static VLANs
Configure Port VLAN Parameters
View VLAN Summary
-
-
Figure 20: Virtual LANs Menu
Static VLANs Menu
The Static VLANs menu is accessible from the Virtual LANs menu Configure
Static VLANs command. This menu presents currently configured VLANs. Edit
an existing VLAN configuration by selecting it using the up and down arrow keys
and pressing enter. Delete a VLAN by selecting an entry and pressing <CTRL
D>. Configure a new VLAN by entering <CTRL I>.
My Switch Static VLANs Admin Access
VID VLAN Name Forbidden Ports IGMP
1 None On
2 SCADA IEDs None Off
3 METERING IEDs None Off
4 PROTECTION IEDs 3,6 On
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell D-PgDn U-PgUp I-Insert L-Delete
Figure 21: Static VLANs Menu
VID
Valid VLAN numbers lie in the range of 1 to 1000.
Note:
VLAN Name
Entering a meaningful name will associate this VLAN with its users.
Forbidden Ports
This parameter is used to forbid certain ports’ membership in the VLAN. Trunk
ports listed here will not be members of the VLAN.
The switch reserves the first VLAN (VLAN 1) for management purposes.
RuggedCom
Page 45

IGMP
Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs
This parameter enables or disables IGMP Snooping on the VLAN in question.
Note:
If IGMP Snooping is not enabled for the VLAN, both IGMP messages and multicast
streams from routers will be forwarded directly to all members of the VLAN. If any one
member of the VLAN joins a multicast group then
receive the multicast traffic
Configuring Multicast Filtering.
Port VLAN Parameters Menu
The Port VLAN Parameters menu is accessible from the Virtual LANs menu.
My Switch Port VLAN Parameters Admin Access
Port Type PVID PVID Format
1 Edge 1 Untagged
2 Edge 1 Untagged
3 Edge 4 Untagged
4 Edge 4 Tagged
5 Trunk 1 Untagged
6 Edge 1 Untagged
7 Edge 1 Untagged
8 Edge 1 Untagged
Figure 22: Port VLAN Parameters Menu
Type
all members of the VLAN will
. For more information on IGMP see Chapter 7 –
Port
Type
Edge
Trunk
This parameter specifies how the port treats VLANs. There are two types of
VLAN port; edge and trunk. The following table presents a brief description of
how the port type (and other) parameters serve to address specific applications.
# VLANs
Supported
1 (Native)
Configured
All
Configured
except those
in Forbidden
PVID
Format
Untagged
Tagged
Tagged or
Untagged
Usage
VLAN Unaware networks – All frames are sent and
received without the need for VLAN tags.
VLAN Aware networks – VLAN Traffic domains are
enforced on a single VLAN
Manually Configured Switch-Switch Connections –
VLANs must be manually created and administered.
Multiple-VLAN devices – Implement connections to
devices that support multiple VLANs at the same time.
list
The factory default sets the port type to “edge“.
RuggedCom
31
Page 46

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Edge Type
An edge port is always a member of only one VLAN, the native VLAN (often
called the port VLAN or PVID).
Use an edge port with PVID Format set to “tagged” when you need to service
VLAN aware equipments and with PVID Format set to “untagged” when you
need to service non-VLAN aware equipments.
Untagged frames received on edge ports will be forwarded to the network using
the port's configured native VLAN.
Tagged frames received on edge ports will be forwarded to the network only if the
tag is the same as the configured native VLAN (otherwise the frame will be
discarded).
Frames transmitted out the port will be tagged with the native VLAN or sent
untagged depending upon the PVID format parameter (see “PVID Format”
below).
Trunk Type
Trunk ports are automatically members of all VLANs and implement switch-toswitch connections.
The switch can “pass through” traffic, forwarding frames received on one trunk
port out another trunk port. The trunk ports must be members of all the VLANs
the “pass through” traffic is part of, even if none of those VLANs are used on
edge ports.
Untagged frames received on trunk ports will be forwarded using the port's native
VLAN.
Frames transmitted out the port on the native VLAN will be tagged or untagged
depending upon the PVID format (see below). Frames on other VLANs are
always sent tagged.
Note:
group of VLANs, for example when: the trunk connects to a device (such as a layer 3 router)
that supports a subset of the available VLANs.
Traffic may be manually restricted on trunk ports through the “Forbidden Ports” parameter
(See “Static VLANs Menu” above).
Sometimes it may be desirable to manually restrict the traffic on the trunk to a certain
RuggedCom
Page 47

PVID (Native VLAN)
The Port VLAN Identifier (PVID) or native VLAN specifies the VLAN id
associated with untagged (and 802.1p priority tagged) frames received on this port.
Chapter 4 – Configuring VLANs
Note:
If the VLAN configured as the PVID does not exist in the “Configure VLANs”
menu, the switch will automatically create and use it. IGMP will automatically be disabled for
that VLAN. If it is desirable for IGMP to be used on that VLAN, it can be created in the
“Configure VLANs” menu and IGMP enabled.
PVID Format
This parameter specifies whether frames transmitted on the native VLAN are to be
sent tagged or untagged.
VLAN Summary Menu
The VLAN Summary menu is accessible from the Virtual LANs menu. This menu
presents configured VLANs and the ports they are available upon. Ports that are
untagged or tagged members of the VLAN are shown under the appropriate
“Untagged Ports” or “Tagged Ports” column. The management VLAN (VLAN 1)
is always shown.
My Switch VLAN Summary Admin Access
VID Untagged Ports Tagged Ports
1 1-12, 15-16 13-14
2 None 1-2, 5, 7
3 3, 8-12 None
4 4, 15-16 None
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell D-PgDn U-PgUp
Figure 23: VLAN Summary Menu
RuggedCom
33
Page 48

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Troubleshooting
Problem One
• I don’t need VLANs at all. How do I turn them off?
Simply leave all ports set to type “Edge” and leave the native VLAN set to 1. This
is the default configuration for the switch.
Problem Two
• I have added two VLANs 2 and 3. I made a number of ports
members of these VLANS. Now I need some of the devices in one
VLAN send messages to some devices in the other VLAN.
If the devices need to communicate at the physical address layer, they must be
members of the same VLAN. If they can communicate in a layer 3 fashion (i.e.
using a protocol such as IP or IPX) you can use a router. The router will treat
each VLAN as a separate interface, which will have its own associated IP address
space.
RuggedCom
Page 49

Chapter 5 – Configuring Class of Service
Chapter 5 – Configuring Class of Service
Introduction to CoS
This chapter familiarizes the user with using the Class of Service feature.
CoS Features
RuggedSwitch™ CoS provide you with the following features:
• Ability to prioritize traffic statically by port.
• Ability to prioritize traffic by the priority field in 802.1p and 802.1q tags.
• Ability to prioritize traffic based on its source or destination MAC address.
• Ability to prioritize traffic by the TOS field in the IP header.
• Ability to set the 802.1Q access priority from an established CoS.
CoS Concepts And Issues
CoS Operation
CoS provides the ability to expedite the transmission of certain frames and port
traffic over others. The CoS of a frame can take on one of two values, either
normal or high. The default policies of the switch enforce a normal CoS for all
traffic.
Note that CoS is only used internally by the switch, but may be conveyed
externally by mapping the CoS to the priority field in the 802.1Q tags of outgoing
frames.
The CoS feature has two main phases, inspection and forwarding.
Inspection Phase
In the inspection phase the CoS priority of a received frame is determined from:
RuggedCom
• The priority field in 802.1P and 802.1Q tags
• The Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) component of the Type Of
Service (TOS) field, if the frame is IP.
• The default CoS for the port.
• A specific CoS based upon the source and destination MAC address (as set
in the Configure Static MAC Address Table menu).
35
Page 50

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Note that a frame’s CoS will be high if any of the above factors set it high. The
frame’s CoS will be low only if all of the above factors set it low.
Received frames are first examined to determine if they are IP frames. If the
frame is IP and the TOS DSCP to CoS feature is selected, the CoS is determined
from the DSCP field itself. The frame is then examined for 802.1P and 802.1Q
tags and the priority field is mapped to a CoS. If a tag is not present the default
CoS for the port is used. The source and destination MAC addresses are then
used to determine if a high CoS has been selected.
Received
Frame
Use TOS
DSCP ?
Y
Map TOS to CoS
Figure 24: Determining The CoS Of A Received Frame
After inspection, the frame is the forwarded to the egress port for transmission.
Forwarding Phase
The inspection phase results in the CoS of individual frames being determined.
When these frames are forward to the egress port they are collected into either a
normal or high priority queue.
CoS weighting selects the degree of preferential treatment that is attached high
CoS frames. The ratio of the number of high CoS to low CoS frames transmitted
can be programmed. If desired, the user can program that low CoS frames are
transmitted only after all high CoS frames have been serviced.
Frame
tagged ?
Y
Priority >
Threshold ?
Use default CoS
Y
Use Normal CoS
For Port
Use High CoS
Mac CoS
High ?
Y
Use High CoS
Leave CoS As Is
To CoS Queues
of other Ports
Srip Tag
Transmitted
Normal CoS Queue
High CoS Queue
CoS
Weighting
Selector
Port
tagged ?
Frame
tagged ?
High Cos?
Leave Tag As Is
Use High Tag
Use Normal Tag
Frame
Figure 25: Use of CoS When Forwarding Frames
If the port is configured to transmit VLAN tags and the frame was received
without a tag, the priority field value is selected from the CoS value.
RuggedCom
Page 51

CoS Configuration
CoS Parameter Ranges & Default Settings
The following set of tables lists default CoS configuration parameters for the unit.
Chapter 5 – Configuring Class of Service
Configuration Item Default
Supported Values
Value
CoS Weighting 2:1 1:1, 2:1, 4:1, 6:1, 8:1, 10:1, 12:1, 1:0
Default CoS (Per Port) Normal Normal, High
Inspect TOS (Per Port) No No, Yes
Priority to CoS Mapping (Per Access Priority) Normal Normal, High
DSCP to CoS Mapping (Per DSCP) Normal Normal, High
Normal Access Priority (Per Port) 0 0-7
High Access Priority (Per Port) 4 0-7
Classes Of Service Menu
The Classes Of Service menu is accessible from the main menu Classes Of
Service command.
My Switch Classes Of Service Admin Access
Configure Global CoS Parameters
Configure Port CoS Parameters
Configure Priority to CoS Mapping
Configure DSCP to CoS Mapping
Configure CoS Access Priorities
Figure 26: Classes Of Service Menu
Global CoS Parameters Menu
The Global CoS Parameters menu is accessible from the Classes Of Service menu.
My Switch Global CoS Parameters Admin Access
CoS Weighting 2:1
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 27: Global CoS Parameters Menu
CoS Weighting
During traffic bursts, frames queued in the switch pending transmission on a port
may have both high and normal priorities. This parameter specifies the weighting
algorithm for transmitting high priority CoS and normal priority CoS frames.
Some examples include:
1:1 - 1 high priority frame is transmitted for every normal priority frame
RuggedCom
37
Page 52

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
6:1 - 6 high priority frames are transmitted for every normal priority frame
1:0 - transmit normal priority frames only after all high priority frames are sent
Port CoS Parameters Menu
The Port CoS Parameters menu is accessible from the Classes Of Service menu.
My Switch Port CoS Parameters Admin Access
Port Default CoS Inspect TOS
1 Normal No
2 Normal No
3 Normal No
4 Normal No
5 Normal No
6 Normal No
7 Normal No
8 Normal No
Figure 28: Port CoS Parameters Menu
Default CoS
The default CoS to assign frames received upon the port. Other criteria such as
TOS DSCP and MAC CoS also play a part in determining the final frame CoS.
Inspect TOS
Whether to prioritize frames on this port based upon TOS DSCP.
Priority to CoS Mapping Menu
The Priority to CoS Mapping menu is accessible from the Classes Of Service
menu.
My Switch Priority to CoS Mapping Admin Access
Priority CoS
0 Normal
1 Normal
2 Normal
3 Normal
4 High
5 High
6 High
7 High
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 29: Priority to CoS Mapping Menu
CoS
This menu maps the priority field in an 801.1P or 802.1Q tag to a CoS.
RuggedCom
Page 53

DSCP to CoS Mapping Menu
The DSCP to CoS Mapping menu is accessible from the Classes Of Service menu.
My Switch DSCP to CoS Mapping Admin Access
DSCP CoS
0 Normal
1 Normal
2 Normal
3 Normal
4 Normal
5 Normal
6 Normal
7 Normal
8 Normal
9 Normal
More below ...
Figure 30: TOS DSCP to CoS Mapping
CoS
This menu maps the TOS DSCP from a IP frame to a CoS.
Chapter 5 – Configuring Class of Service
CoS Access Priorities Menu
The CoS Access Priorities menu is accessible from the Classes Of Service menu.
My Switch CoS Access Priorities Admin Access
Port Normal Access Priority High Access Priority
1 0 4
2 0 4
3 0 4
4 0 4
5 0 4
6 0 4
7 0 4
8 0 4
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 31: CoS Access Priorities Menu
Normal Access Priority
When frames that were originally received untagged are transmitted from a tagged
port the switch will insert an 802.1Q VLAN tag priority field based upon the
frame’s CoS. The port will insert this parameters value when the frame is
configured for normal priority CoS.
High Access Priority
The port will insert this parameters value when the frame is configured for high
priority CoS.
RuggedCom
39
Page 54

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• RSTP Issues
• Planning RSTP networks
• Configuring RSTP
• Viewing the status and statistics of RSTP
• Troubleshooting RSTP
RSTP Features
RuggedSwitch™ RSTP provides you with the following features:
• Industry standard support of Rapid Spanning Tree (802.1w), which features
a compatibility mode with legacy STP (802.1d).
• Superior performance. RuggedCom RSTP will recognize a link failure and
put an alternate port into forwarding within milliseconds.
• Special support for ring architectures. RuggedCom RSTP features
enhancements, which allow rapid recovery in rings.
• RSTP may be enabled on a per-port basis.
• Ports may be configured as edge ports, which allow rapid transitioning to
the forwarding state for non-STP hosts.
• Path costs may be hard configured or determined by port speed
negotiation, in either the STP or RSTP style.
1
• Full bridge
and port status provide a rich set of tools for performance
monitoring and debugging.
• SNMP manageable including newRoot and topologyChange traps.
1
Historically, a device implementing STP on its ports has been referred to as a bridge. RuggedCom uses the term
bridge and switch synonymously.
RuggedCom
Page 55

RSTP Concepts And Issues
The 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol was developed to allow the construction of
robust networks that incorporate redundancy while pruning the active topology of
the network to prevent loops. While STP is effective, it requires that frame
transfer must halt after a link outage until all bridges in the network are sure to be
aware of the new topology. Using the 802.1d recommended values, this period
lasts 30 seconds.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1w) is a further evolution of the 802.1d
Spanning Tree Protocol. It replaces the settling period with an active handshake
between bridges that guarantees topology information to be rapidly propagated
through the network. RSTP also offers a number of other significant innovations,
including:
• Topology changes in STP must be passed to the root bridge before they
can be propagated to the network. Topology changes in RSTP can be
originated from and acted upon by any designated bridges, leading to more
rapid propagation of address information.
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
• STP recognizes one state, blocking, for ports that should not forward.
RSTP explicitly recognizes two blocking roles, alternate and backup port
roles, including them in computations of when to learn and forward.
• STP relays configuration messages received on the root port out its
designated ports. If an STP bridge fails to receive a message from its
neighbor it cannot be sure where along the path to the root a failure
occurred. RSTP bridges generate their own configuration messages, even if
they fail to receive one from the root bridge. This leads to quicker failure
detection.
• RSTP offers edge port recognition, allowing ports at the edge of the
network to forward frames immediately after activation while at the same
time protecting them against loops.
• An improvement to age configuration messages more quickly to prevent
them from “going around in circles” in the event of a loop.
RSTP Operation
RSTP States And Roles
RSTP Bridges have roles to play, being either root or designated. One bridge, the
root bridge, is the practical center of the network. All other bridges in the
network are designated bridges.
State
RuggedCom
RSTP also assigns each port of the bridge a state and a role. The RSTP state
describes what is happening at the port in relation to address learning and frame
forwarding. The RSTP role basically describes whether the port is facing the
center or edges of the network and whether it can currently be used or not.
41
Page 56

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
There are three RSTP states: Discarding, Learning and Forwarding.
The discarding state is entered when the port is first taken into service. The port
does not learn addresses in this state and does not participate in frame transfer.
The port looks for STP traffic in order to determine its role in the network. When
it is determined that the port will play an active part in the network, the state will
change to Learning.
The learning state is entered when the port is preparing to play an active member
of the network. The port learns addresses in this state but does not participate in
frame transfer. In a network of RSTP bridges the time spent in this state is usually
quite short. RSTP bridges operating in STP compatibility mode will spend 6 to 40
seconds in this state.
Forwarding
Forwarding Timer Expires
Or Active RSTP Handshake has
Occurred
Learning
BPDUS indica te
port should not
be active
Forwarding Timer Expires
Or Active RSTP Handshake
Discarding
RSTP Disabled in any state
Link rises or falls
Disabled Link Down
RSTP Enabled
Figure 32: Bridge and Port States
After “learning” the bridge will place the port in the forwarding state. The port
both learns addresses and participates in frame transfer while in this state.
Note:
purely for purposes of management these states may be considered sub-classes of the RSTP
Discarding state. The Disabled state refers to links upon which RSTP has been disabled. The
link down state refers to links upon which RSTP is enabled but are currently down.
RuggedSwitch™ introduces two more states, Disabled and Link Down. Introduced
RuggedCom
Page 57

Role
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
There are four RSTP port roles: Root, Designated, Alternate and Backup.
If the bridge is designated (i.e. it is not the root bridge) it must have a single root
port. The root port is the “best” (i.e. quickest) way to send traffic to the root
bridge.
A port is designated if it is the best port to service the LAN segment it is
connected to. All bridges on the same LAN segment listen to each others
messages and agree on who is the designated bridge. The ports of other bridges
on the segment must become either root, alternate or backup ports
A
RP
1
Designated
Bridge
D
Figure 33: Bridge and Port Roles
2
DP
AP
Root
Bridge
3
12
DP DP
RP = Root Port
DP = Designated Port
AP = Alternate Port
BP = Backup Port
RP
1
Designated
Bridge
32
DPBP
A port is an alternate when it receives a better message from another bridge on the
LAN segment it is connected to. The message the alternate port receives is better
than the port itself would generate, but not good enough to convince it to become
the root port. The port becomes an alternate to the current root port and will
become the new root port should the current root port fail. The alternate port
does not participate in the network.
Edge Ports
RuggedCom
A port is a backup when it receives a better message from the LAN segment it is
connected to, originated from another port on the same bridge. The port is a
backup for another port on the bridge and will become active if that port fails. The
backup port does not participate in the network.
The edge port concept is that ports directly connected to end stations cannot
create bridging loops in the network and can thus directly transition to forwarding,
skipping the lengthy listening and learning stages.
Edge ports that receive configuration messages immediately lose their edge port
status and become normal spanning tree ports. A loop created on an improperly
connected edge port is thus quickly repaired.
43
Page 58

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Because an edge port services only end stations, topology change messages are not
generated when its link toggles.
Point To Point and Multipoint Links
RSTP uses a peer-peer protocol called Proposing-Agreeing to ensure transitioning
in the event of a link failure. This protocol is point to point and breaks down in
multipoint situations, i.e. when more than two bridges operate on a shared media
link.
If RSTP detects this circumstance (based upon the port’s half duplex state after
link up) it will switch off Proposing-Agreeing. The port must transition through
the learning and forwarding states spending the forward delay in each.
There are circumstances where RSTP will make an incorrect decision about the
point-to-point state of the link simply by examining the half duplex status, namely:
• The port attaches only to a single partner, but through a half duplex link.
• The port attaches to a shared media hub through a full duplex link. The
shared media link attaches to more than one RSTP enabled bridge.
In such cases the user may configure the bridge to override the half duplex
determination mechanism and force the link to be treated in the proper fashion.
Path And Port Costs
The STP path cost is the main mechanism by which root and designated ports are
chosen.2 The path cost for a designated bridge is the sum of the individual port
costs on the links between the root bridge and that designated bridge. The port
with the lowest path cost is the best route to the root bridge and is chosen as the
root port.
How Port Costs Are Generated
Port costs can be generated either as a result of link autonegotiation or manual
configuration.
When the link autonegotiation method is used the port cost is derived from the
speed of the link. This method is useful when a well-connected network has been
established. It can be used when the designer is not too concerned with the
resultant topology as long as connectivity is assured.
Manual configuration is useful when the exact topology of the network must be
predictable under all circumstances. The path cost can be used to establish the
topology of the network exactly as the designer intends.
2
In actuality the primary determinant for root port selection is the root bridge ID. Bridge ID is important mainly
at the network startup when the bridge with the lowest id is elected as the root bridge. After startup (when all
bridges agree on the root bridge’s id) the path cost is used to select root ports. If the path costs of candidates for
the root port are the same, the ID of the peer bridge is used to select the port. Finally, if candidate root ports have
the same path cost and peer bridge ID, the port ID of the peer bridge is used to select the root port. In all cases
the lower ID, path cost or port ID is selected as the best.
RuggedCom
Page 59

Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1d vs. IEEE 802.1w Costs
The IEEE 802.1d specification limits port costs to values of 1 to 65536. It
recommends that a path cost corresponding to the 1x10
Designed at a time when 9600 bps links were state of the art, this method breaks
down in modern use, as the method cannot represent a link speed higher than a
gigabit per second.
In order to remedy this problem in future applications the IEEE 802.1w
specification limits port costs to values of 1 to 200000, with a path cost
corresponding to the 2x1012 / link speed.
RuggedCom bridges support interoperability with legacy STP bridges by selecting
the style to use. In practice it makes no difference which style is used as long as it
is applied consistently across the network, or if costs are manually assigned.
Bridge Diameter
The bridge diameter is maximum number of bridges between any two points of
attachment of end stations.
The bridge diameter reflects the realization that topology information requires
time to propagate hop by hop through a network. Configuration messages that
take too long to propagate end to end through the network will result in an
unstable network.
9
/ link speed be used.
There is a relationship between the bridge diameter and the maximum age
parameter3. To achieve extended ring sizes, RuggedCom RSTP uses an age
increment of ¼ of a second. The value of the maximum bridge diameter is thus
four times the configured maximum age parameter.
Note:
Raise the value of the maximum age parameter if implementing very large bridged
networks or rings.
3
The RSTP algorithm is as follows. STP configuration messages contain “age” information. Messages transmitted
by the root bridge have an age of 0. As each subsequent designated bridge transmits the configuration message it
must increase the age by at least 1 second. When the age exceeds the value of the maximum age parameter the
next bridge to receive the message immediately discards it.
RuggedCom
45
Page 60

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
RSTP Applications
RSTP in Structured Wiring Configurations
RSTP allows you to construct structured wiring systems in which connectivity is
maintained in the event of link failures. For example a single link failure of any of
links A through Z would leave all ports of bridges 555 through 888 connected to
the network.
Figure 34: Example Of A Structured Wiring Configuration
Design Considerations for RSTP in Structured Wiring Configurations
1. Select the design parameters for the network.
What are the requirements for robustness and network failover/recovery times? Are
there special requirements for diverse routings to central host computer? Are there
any special port redundancy requirements?
2. Identify required legacy support.
Are STP bridges used in the network? These bridges do not support rapid
transitioning to forwarding. If these bridges are present can they be re-deployed
closer to the network edge?
3. Identify edge ports and ports with half duplex/shared media restrictions.
Ports that connect to host computers, IEDs and controllers may be set to edge ports in
order to guarantee rapid transitioning to forwarding as well as reduce the number of
topology change notifications in the network. Ports with half duplex/shared media
restrictions require special attention in order to guarantee that they do not cause
extended failover/recovery times.
RuggedCom
Page 61
4. Choose the root bridge and backup root bridge carefully.
The root bridge should be selected to be at the concentration point of network traffic.
Locate the backup root bridge adjacent to the root bridge. One strategy that may be
used is to tune the bridge priority to establish the root bridge and then tune each
bridge’s priority to correspond to its distance from the root bridge.
5. Identify desired steady state topology.
Identify the desired steady state topology taking into account link speeds, offered
traffic and QOS. Examine of the effects of breaking selected links taking into
account network loading and the quality of alternate links.
6. Decide upon port cost calculation strategy.
Select whether fixed or autonegotiated costs should be used? Select whether the STP
or RSTP cost style should be used.
7. Calculate and configure priorities and costs.
8. Implement the network and test under load.
RSTP in Ring Backbone Configurations
RSTP may be used in ring backbone configurations where rapid recovery is
required when a link fails. In normal operation RSTP will block traffic on one of
the links, here on link H (as indicated by the double bars). In the event of a failure
on link D, bridge 444 will unblock link H. Bridge 333 will communicate with the
network through link F.
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
Figure 35: Example Of A Ring Backbone Configuration
Design Considerations For RSTP in Ring Backbone Configurations
1. Select the design parameters for the network.
RuggedCom
What are the requirements for robustness and network failover/recovery times?
Typically, ring backbones are chosen to provide cost effective but robust network
designs.
47
Page 62

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
2. Identify required legacy support and ports with half duplex/shared media
restrictions.
These bridges should not be used if network failover/recovery times are to be
minimized.
3. Identify edge ports
Ports that connect to host computers, IEDs and controllers may be set to edge ports in
order to guarantee rapid transitioning to forwarding as well as reduce the number of
topology change notifications in the network.
4. Choose the root bridge.
The root bridge can be selected to equalize either the number of bridges, number of
stations or amount of traffic on either of its legs. It is important to realize that the ring
will always be broken in one spot and that traffic always flows through the root
5. Assign bridge priorities to the ring.
The strategy that should be used is to assign each bridge’s priority to correspond to its
distance from the root bridge. If the root bridge is assigned the lowest priority of 0,
the bridges on either side should use a priority of 4096 and the next bridges 8192 and
so on. As there are 16 levels of bridge priority available, this method provides for up
to 31 bridges in the ring.
6. Implement the network and test under load.
RSTP Port Redundancy
In cases where port redundancy is essential, RSTP allows more than one bridge
port to service a LAN. For example if port 3 is designated to carry the network
traffic of LAN A, port 4 will block. Should an interface failure occur on port 3,
port 4 would assume control of the LAN.
Figure 36: Port Redundancy
RuggedCom
Page 63

Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
RSTP Configuration
Bridge and Port Parameter Ranges & Default Settings
The following set of tables lists default STP configuration parameters for the unit.
For each parameter the parameter name, recommended setting and possible range
are included.
Bridge Parameters
Configuration Item Default Value Supported Values
State Enabled Disabled, Enabled
Version Support STP and RSTP STP, STP and RSTP
Hello Time 2 seconds 1 to 10 seconds
Max Age Time 20 seconds 6 to 40 seconds
Transmit Count 10 3 to 10
Forward Delay 15 seconds 4 to 30
Cost Style Costs follow STP (16 bit) style Costs follow STP (16 bit) style, Costs follow
RSTP (32 bit) style
Port Parameters
These configurable items apply to all ports.
Configuration Item Default Value Supported Values
Enabled Port Enabled Disabled, Enabled
Priority 128 0, 16, 32, 48, 64, 80, 96, 112, 128, 144, 160,
176, 194, 208, 224, 240
STP Cost Auto Auto, 0 to 65535
RSTP Cost Auto Auto, 0 to 2147483647
Edge Port False False, True
Point to Point Auto Auto, False, True
RuggedCom
49
Page 64

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Spanning Tree Menu
The Spanning Tree menu is accessible from the main menu Spanning Tree
command. The Spanning Tree menu will lead you to all the other available menus
for configuring and obtaining the status of RSTP ports.
My Switch Spanning Tree Admin Access
Configure Bridge RSTP Parameters
Configure Port RSTP Parameters
View Bridge RSTP Statistics
View Port RSTP Statistics
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 37: Spanning Tree Menu
Bridge RSTP Parameters Menu
The Bridge RSTP Parameters menu configures parameters that apply to all ports.
My Switch Bridge RSTP Parameters Admin Access
State Enabled
Version Support STP and RSTP
Bridge Priority 32768
Hello Time 2 s
Max Age Time 20 s
Transmit Count 10
Forward Delay 15 s
Cost Style Costs follow STP (16 bit) style
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 38: Bridge RSTP Parameters Menu
State
Enables STP or RSTP for the bridge (i.e. on all ports). Note that STP/RSTP can
be disabled on a per port basis in the Port RSTP Parameters menu.
Version Support
Selects the versions of STP to support, either STP or STP and Rapid STP.
Bridge Priority
The Bridge Priority provides a way to control the topology of the STP connected
network. The bridge with the lowest priority will become root. The desired Root
and Designated bridges can be configured for a particular topology. In the event
of a failure of the root bridge, the bridge with the next lowest priority will then
become root. Designated bridges that (for redundancy purposes) service a
common LAN also use priority to determine which bridge is active. In this way
careful selection of Bridge Priorities can establish the path of traffic flows in
normal and abnormal conditions.
RuggedCom
Page 65

Hello Time
This is the time between configuration messages issued by the root bridge.
Shorter hello times may result in faster detection of topology changes at the
expense of moderate increases in STP traffic.
Max Age Time
The time a configuration message remains valid after being issued by the root
bridge. Configure this parameter with care when many tiers of bridges exist, or
slow speed links (such as those used in WANs) are part of the network
Transmit Count
The maximum number of configuration messages on each port that may be sent in
a special event (such as recovering from a failure or bringing up a new link). After
the maximum number of messages is reached, STP will be limited to 1 message per
second. Larger values allow the network to recover from failed links more quickly.
If RSTP is being used in a ring architecture the transmit count should be larger
than the number of switches in the ring. Specifying a large value for the transmit
count renders RSTP recovery more robust in the presence of multiple link failures
that occur in a short window of time.
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
Forward Delay
The amount of time the bridge spends learning MAC addresses on a rising port
before beginning to forward traffic. Lower values allow the port to reach the
forwarding state more quickly, but at the expense of flooding unlearned addresses
to all ports.
Cost Style
This parameter selects the style of link costs to employ. STP uses 16-bit path
costs based upon 1x10E9/link speed (19 for 100 Mbps and 100 for 10 Mbps)
whereas RSTP uses 32 bit costs based upon 2x10E13/link speed (200,000 for 100
Mbps and 2,000,000 for 10 Mbps). Note that RSTP link costs are used only when
the bridge version support is set to allow RSTP and the port does not migrate to
STP.
RuggedCom
51
Page 66

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Port RSTP Parameters Menu
The Port RSTP Parameters menu configures parameters that apply to individual
ports.
My Switch Port RSTP Parameters Admin Access
Port Enabled Priority STP Cost RSTP Cost Edge Port Point to Point
1 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
2 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
3 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
4 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
5 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
6 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
7 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
8 Enabled 128 Auto Auto False Auto
Figure 39: Port RSTP Parameters Menu
Enabled
Enabling STP activates the STP or RSTP protocol for this port as per the
configuration of the Version support parameter (Bridge RSTP Parameters menu).
STP should be disabled for the port ONLY if the port does not attach to an STP
enabled bridge in any way. Failure to meet this requirement WILL result in an
undetectable traffic loop in the network. A more desirable alternative is disabling
the port is to leave STP enabled but to configure the port as an edge port. A good
candidate for disabling STP would be a port that is absolutely assured to services a
single host computer.
Priority
STP Cost
RSTP Cost
Edge Port
Selects the STP port priority part of the port ID. The port ID is composed of the
priority and port number. Ports of the same cost that attach to a common LAN
will select the port to be used based upon the port ID.
Selects to cost to use in cost calculations, when the Cost Style parameter is set to
STP on the Bridge RSTP Parameters menu. Setting the cost manually provides the
ability to preferentially select specific ports to carry traffic over others. Leave this
field set to "auto" to use the standard STP port costs as negotiated (100 for 10
Mbps links and 19 for 100 Mbps links).
Selects to cost to use in cost calculations, when the Cost Style parameter is set to
RSTP on the Bridge RSTP Parameters menu. Leave this field set to "auto" to use
the standard RSTP port costs as negotiated (2,000,000 for 10 Mbps links and
200,000 for 100 Mbps links).
Edge ports are ports that do not participate in the Spanning Tree, but still are sent
configuration messages. Edge ports transition directly to frame forwarding
RuggedCom
Page 67

without any listening and learning delays. The MAC tables of Edge ports do not
need to be flushed when topology changes occur in the STP network.
Unlike an STP disabled port, accidentally connecting an edge port to another port
in the spanning tree will result in a detectable loop. The "edgeness" of the port
will be switched off and the standard RSTP rules will apply (until the next link
outage).
Point To Point
RSTP uses a peer-to-peer protocol that provides for rapid transitioning on pointto-point links. This protocol is automatically turned off in situations where
multiple STP bridges communicate over a shared (non point to point) LAN.
The bridge will automatically take point to point to be true when the link is found
to be operating full duplex. The point-to-point parameter allows this behaviour or
overrides it, forcing point to point to be true or false. Force the parameter true
when the port operates a point-to-point link but cannot run the link full duplex.
Force the parameter false when the port operates the link full duplex, but is still
not point to point (e.g. a full duplex link to an unmanaged bridge that concentrates
two other STP bridges).
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
RuggedCom
53
Page 68

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
RSTP Statistics
Bridge RSTP Statistics Menu
The Bridge RSTP Statistics menu is accessible from the Spanning Tree menu.
My Switch Bridge RSTP Statistics Admin Access
Bridge Status Not Designated For Any LAN
Bridge ID 32768 / 00-0A-DC-00-50-00
Designated Root ID 32768 / 00-0A-DC-00-10-00
Designated Root Port 8
Root Path Cost 57
Configured Hello Time 2.0 s
Learned Hello Time 2.0 s
Configured Forward Delay 15.0 s
Learned Forward Delay 15.0 s
Configured Max Age 20.0 s
Learned Max Age 20.0 s
Total Topology Changes 12
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 40: Bridge RSTP Status Menu
Bridge Status
The status of the bridge. The status may be root, designated or not designated for
any LAN (the only active port is the root port).
Bridge ID
The Bridge Identifier of this bridge.
Designated Root ID
The Bridge Identifier of the root bridge.
Designated Root Port
If the bridge is designated, the port that provides connectivity towards the root
bridge of the network.
Root Path Cost
The total cost of the path to the root bridge, composed of the sum of the costs of
each link in the path. If custom costs have not been configured and the cost style
is STP, 100 Mbps ports will contribute a cost of 19 and 10 Mbps ports will
contribute a cost of 100 to this figure. If custom costs have not been configured
and the cost style is RSTP, 100 Mbps ports will contribute a cost of 200,000 and
10 Mbps ports will contribute a cost of 2,000,000 to this figure.
Configured Hello Time
The configured Hello time from the Bridge RSTP Parameters menu.
RuggedCom
Page 69

Learned Hello Time
The actual Hello time provided by the root bridge as learned in configuration
messages. This time is used in designated bridges.
Configured Forward Delay
The configured Forward Delay time from the Bridge RSTP Parameters menu.
Learned Forward Delay
The actual Forward Delay time provided by the root bridge as learned in
configuration messages. This time is used in designated bridges.
Configured Max Age
The configured Maximum Age time from the Bridge RSTP Parameters menu.
Learned Max Age
The actual Maximum Age time provided by the root bridge as learned in
configuration messages. This time is used in designated bridges.
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
Total Topology Changes
A count of topology changes in the network, as detected on this bridge through
link failures or as signaled from other bridges. Excessively high or rapidly
increasing counts signal network problems.
RuggedCom
55
Page 70

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Port RSTP Statistics Menu
The Bridge RSTP Statistics menu is accessible from the Spanning Tree menu.
My Switch Port RSTP Statistics Admin Access
Port Status Role Cost RX RSTs TX RSTs RX Configs
1 Disabled 0 0 0 0
2 Disabled 0 0 0 0
3 Disabled 0 0 0 0
4 Disabled 0 0 0 0
5 Link Down 0 0 0 0
6 Link Down 0 0 0 0
7 Link Down 0 0 0 0
8 Forwarding Root 19 0 0 37
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell>
Figure 41: Port RSTP Parameters Menu
Status
The status of the port. This may be one of the following:
Disabled
Role
STP is disabled on this port.
Link Down
STP is enabled on this port but the link is down.
Discarding
The link is not used in the STP topology but is standing by.
Learning
The port is learning MAC addresses in order to prevent flooding when it begins
forwarding traffic
Forwarding
The port is forwarding traffic.
The port’s role. This may be one of the following:
Designated
The port is designated for (i.e. carries traffic towards the root for) its LAN.
Root
The port on the bridge providing connectivity towards the root bridge.
RuggedCom
Page 71

Cost
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
Backup
The port is attached to a LAN that is serviced by another port on the bridge. It is
not used but is standing by. If a failure of the port that is currently designated for
the LAN occurs the backup port will become designated for the LAN.
Alternate
The port is attached to a bridge that provides connectivity to the root bridge. It is
not used but is standing by. If a failure of the current root port occurs this port
will become the new root. If there are multiple alternate ports the best candidate
(cost wise) will be elected root.
The cost of this port. If the Bridge RSTP Parameters Cost Style is set to STP, 100
Mbps ports will contribute a cost of 19 and 10 Mbps ports contribute a cost of
100. If the Cost Style is set to RSTP, 100 Mbps ports will contribute a cost of
200,000 and 10 Mbps ports contribute a cost of 2,000,000. Note that even if the
Cost style is set to RSTP, a port that migrates to STP will have its cost limited to a
maximum of 65535.
RX RSTs
TX RSTs
RX Configs
TX Configs
RX Tcns
TX Tcns
The count of RSTP configuration messages received on this port.
The count of RSTP configuration messages transmitted on this port.
The count of STP configuration messages received on this port.
The count of STP configuration messages transmitted on this port.
The count of configuration change notification messages received on this port.
Excessively high or rapidly increasing counts signal network problems.
The count of configuration messages transmitted on this port.
Designated Root ID
Provided on the root ports of designated bridges, the Bridge Identifier of the
bridge this port is connected to.
RuggedCom
57
Page 72

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Troubleshooting
Problem One
• When I connect up a new port the network locks up solid. The
port status LEDs are flashing madly.
• Occasionally, the network seems to experience a lot of flooding.
All the ports seem to experience significant traffic. The problem
lasts a few seconds and then goes away.
• One of my switches displays a strange behaviour where the root
port hops back and forth between two switch ports and never
settles down.
Is it possible that one of the switches in the network or one of the ports on a
switch in the network have STP disabled and accidentally connects to another
switch? If this has occurred then a traffic loop has been formed.
If the problem appears to be transient in nature, it is possible that ports that are
part of the spanning tree have been configured as edge ports. After the link layers
have risen on edge ports, STP will directly transition them (perhaps improperly) to
the forwarding state. If an RSTP configuration message is then received the port
will be returned to blocking. A traffic loop may be formed for the length of time
the port was in forwarding.
If one of the switches appears to flap the root from one port to another the
problem may be one of traffic prioritization (See problem five).
Another possible cause of intermittent operation is that of an autonegotiation
mismatch. If one end of the link is fixed to full duplex and the peer
autonegotiates, the autonegotiating end will fallback to half-duplex operation. At
lower traffic the volumes the link may display few if any errors. As the traffic
volume rises the fixed negotiation side will begin to experience dropped packets
while the autonegotiating side will experience collisions. Ultimately, as traffic
loads approach 100% the link will become entirely unusable. At this point RSTP
will not be able to transmit configuration messages over the link and the spanning
tree topology will breakdown. If an alternate trunk exists RSTP will activate it in
the place of the congested port. Since activation of the alternate port often
relieves the congested port of its traffic, the congested port will once again
become reliable. RSTP will promptly enter it back into service, beginning the
cycle once again. The root port will flap back and forth between two ports on the
switch.
Problem Two
• My PC/IED/Device is on your switch. After I reset the switch, it
takes a long time before it comes up.
Is it possible that the RSTP edge setting for this port is set to false? If edge is set
false the bridge will make the port go through two forward delay times before the
port can send or receive frames. If edge is set true the bridge will transition the
port directly to forwarding upon link up.
RuggedCom
Page 73

Another possible explanation is that some links in the network run half duplex.
RSTP uses a peer-peer protocol called Proposing-Agreeing to ensure transitioning
in the event of a link failure. This protocol requires full duplex operation. When
RSTP detects a non-half duplex port it cannot use the Proposing-Agreeing
protocol and must make the port transition the slow (i.e. STP) way. If possible
configure the port for full duplex operation otherwise configure the port’s Point to
Point setting to true. Either will allow the Proposing-Agreeing protocol to be
used.
Problem Three
Is it possible that ports participating in the topology have been configured to STP
mode or that the port’s Point to Point parameter is set false? STP and multipoint
ports converge slowly after failures occur.
Is it possible that the port has migrated to STP? If the port is connected to the
LAN segment by shared media and STP bridges are connected to that media then
convergence after link failure will be slow.
Chapter 6 – Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
• When I test your switch by deliberately breaking a link, it takes a
long time before I can poll devices past the switch. I thought
RSTP was supposed to be fast. What is happening?
Delays on the order of tens or hundreds of milliseconds can result in
circumstances where the link broken is the sole link to the root bridge and the
secondary root bridge is poorly chosen. The worst of all possible designs occurs
when the secondary root bridge is located at the farthest edge of the network from
the root. In this case a configuration message will have to propagate out to the
edge and then back in order to reestablish the topology.
Problem Four
A properly operating unmanaged bridge is transparent to configuration messages.
The managed bridges will exchange configuration messages through the
unmanaged bridge part of the ring as if it is non-existent. When a link in the
unmanaged part of the ring fails however, the managed bridges will only be able to
detect the failure through timing out of hello messages. Full connectivity will
require three hello times plus two forwarding times to be restored.
Problem Five
• My network is composed of ring of bridges of which two
(connected to each other) are managed and the rest of
unmanaged. Why does the RSTP protocol work quickly when I
break a link between the managed bridges but not in the
unmanaged bridge part of the ring?
RuggedCom
• The switch is up and running and working fine. Then I start a
certain application and the network becomes unstable. After I
stop the application the network goes back to running normally.
RSTP sends its configuration messages using the highest possible priority level. If
QOS is configured to allow traffic flows at the high priority level and these traffic
59
Page 74

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
flows burst continuously to 100% of the line bandwidth, STP can be disrupted.
Restrict the traffic flows to below 100%.
Problem Six
• After I bring up a new port the root moves on to that port, and I
don’t want it to.
• The port that I want to become root won’t do so.
Is it possible that the port cost is incorrectly programmed or that autonegotiation
derives an undesired value? Inspect the port and path costs with each port active
as root.
Problem Seven
• My IED/Controller doesn’t work with your switch.
Certain low CPU bandwidth controllers have been found to behave less than
perfectly when they receive unexpected traffic. Try disabling STP for the port.
If the controller fails around the time of a link outage then there is the remote
possibility that frame misordering or duplication may be the cause of the problem.
Try setting the root port of the failing controllers bridge to STP.
Problem Eight
Inspect network statistics to determine if the root bridge is receiving TCNs around
the time of frame loss. It may be possible that you have problems with
intermittent links in your network.
Problem Nine
Examine the RSTP port statistics to determine the port from which the TCNs are
arriving. Sign-on to the switch at the other end of the link attached to that port.
Repeat this step until the switch generating the TCNs is found (i.e. the switch that
is itself not receiving a large number of TCNs). Determine the problem at that
switch.
• My network runs fine with your switch but I occasionally lose
polls to my devices.
• I’m getting lots of TCNs at the root, where are they coming from?
RuggedCom
Page 75

Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering
Chapter 7 – Configuring MULTICAST FILTERING
Introduction to Multicast Filtering
RuggedSwitch™ accomplishes multicast Filtering through the use of the Internet
Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping.
IGMP is used by IP hosts to report their host group memberships to multicast
routers. As hosts join and leave specific multicast groups, streams of traffic are
directed to or withheld from that host.
The IGMP protocol operates between multicast routers and IP hosts. When an
unmanaged switch is placed between multicast routers and their hosts, the
multicast streams will be distributed to all ports. This may introduce significant
traffic onto ports that do not require it and receive no benefit from it.
RuggedCom switches with IGMP Snooping enabled will act upon IGMP messages
sent from the router and the host, restricting traffic streams to the appropriate
LAN segments.
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• IGMP Terminology and Issues
• Configuring IGMP Snooping
• Viewing IGMP Snooping status and statistics
• Troubleshooting IGMP Snooping
IGMP Features
RuggedCom IGMP provides you with the following features:
• Industry standard support of IGMP (RFC 1112, RFC 2236) versions 1 and
Note: RuggedSwitch™ IGMP Snooping supports
version 2 and hosts using either IGMP version 1 and 2.
• IGMP may be enabled on a per VLAN basis.
2 in active and passive roles.
multicast routers using IGMP
RuggedCom
• Multicast Routers may be statically configured or dynamically recognized.
• “Routerless” operation.
• Support of up to 256 multicast groups.
61
Page 76

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
IGMP Concepts And Issues
Router IGMP Operation
The following figure provides a simple example of IGMP use. One “producer” IP
host (P1) is generating two IP multicast streams, M1 and M2. There are four
potential “consumers” of these streams, C1 through C4.
The multicast router discovers which host wishes to subscribe to which stream by
sending general membership queries to each of the segments.
Membership Query
M2 Membership Re port
C1 C2 C3 C4
P1
Multicast
Router
M1 M2
Membership Query
M1 Membership Re port
Figure 42: IGMP Operation Example 1
In this example the general membership query sent to the C1-C2 segment is
answered by membership report indicating the desire to subscribe to stream M2.
The router will forward the M2 stream onto the C1-C2 segment. In a similar
fashion the router discovers that it must forward M1 onto segment C3-C4.
Note:
Membership reports are also referred to as “joins”.
A consumer may join any number of multicast groups, issuing a membership
report for each group. Hosts on the segment note membership reports from other
hosts and will suppress their own reports accordingly. In this way the IGMP
protocol guarantees the segment will issue only one join for each group.
The router periodically queries each of its segments, in order to determine if at
least one consumer still subscribes to a given stream. If no responses occur within
a given timeout period (usually about two query intervals) the router will prune the
multicast stream from the given segment.
A more usual method of pruning occurs when consumers wishing to unsubscribe
issue an IGMP “leave group” message. The router will immediately issue a groupspecific membership query to determine if there are any remaining subscribers of
that group on the segment. After the last consumer of a group has un-subscribed,
the router will prune the multicast stream from the given segment.
RuggedCom
Page 77

Switch IGMP Active and Passive Operation
The IGMP Snooping protocol provides a means for switches to snoop (i.e. watch)
the operation of routers, respond with joins/leaves on the behalf of consumer
ports and to prune multicast streams accordingly.
There are two modes of IGMP the switch can be configured to assume, active and
passive.
Active Mode
When such a switch is used without a multicast router, it is able to function as if
it is a multicast router. The switch acts as a multicast router, sending
general/specific queries, processing leaves/joins and actively pruning the network.
When such a switch is used in a network with a multicast router, it is able to
assist the multicast router. The switch relies upon the router to issue general
queries, which it relays to consumers. The switch assists the router by issuing its
own specific queries, responding to the router with leaves/joins and actively
pruning the network.
Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering
Passive Mode
Some routers have problems with switches running IGMP and will mistakenly
recognize them as routers. To enable operation with such broken and older
routers, the RuggedSwitch™ can be configured to run Passive IGMP. This mode
prevents the switch from sending the queries that can confuse the router, but at
the cost of slower pruning.
Note:
can issue specific queries to determine when the last member has left a multicast group. This
leads to rapid pruning. Passive mode switches are not allowed to send queries of any kind.
They must age out information gathered by router queries, which leads to much slower pruning.
Note:
not be able to forward multicast streams at all!
Active mode IGMP is much to be preferred to passive mode. In active mode the switch
A switch running in passive mode requires the presence of a multicast router or it will
RuggedCom
63
Page 78

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Combined Router And Switch IGMP Operation
This section describes the additional challenges of multiple routers, VLAN
support and switching.
Producer P1 resides upon VLAN 2 while P2 resides upon VLAN 3. Consumer C1
resides upon both VLANs whereas C2 and C3 reside upon VLANs 3 and 2,
respectively. Router 2 resides upon VLAN 2, presumably to forward multicast
traffic to a remote network or act as a source of multicast traffic itself.
Starting Up
P1
VLAN 2
P2
Multicast
Router 1
VLAN 3
VLAN 2
VLAN 2
Switch
VLAN 2,3 VLAN 3 VLAN 2
C1 C2 C3
Multicast
Router 2
Figure 43: IGMP Operation Example 2
Multicast routers use IGMP to elect a master router known as the querier. All
other routers become of non-queriers, participating only forward multicast traffic.
If both switches and routers are present, a router always becomes the querier.
Routers and switches can always distinguish each other from the source IP address
in the IGMP query. A router uses its own source address while the switch always
uses an address of 0.0.0.0 for queries, joins and leaves.
At startup a switch in active IGMP mode will begin generating general
membership queries for each VLAN on each port every switch query interval. If
the switch detects a querier router on a particular VLAN it will stop generating its
own queries and relay those from the querier.
A switch starting up in passive mode will simply wait for queries from a router.
In this example we will assume that the two routers agree that router 1 is the
querier for VLAN 2 and router 2 is simply a non-querier. In this case, the switch
will periodically receive queries from router 1 and, thus, maintain the information
which port links the multicast router. However, the switch port that links to router
2 must be manually configured as “router port”, otherwise, the switch will not
send neither multicast streams or joins/leaves to router 2.
RuggedCom
Page 79

Note that VLAN 3 does not have an external multicast router. The switch will
operating in its “routerless” mode and issue general membership queries as if it is
the router.
Processing Joins
If host C1 desires to subscribe to the multicast streams for both P1 and P2, it will
generate two joins. The join from C1 on VLAN 2 will cause the switch to
immediately initiate its own join to multicast router 1 (and to issue its own join as
a response to queries).
The join from C1 for VLAN 3 will cause the switch to immediately begin
forwarding multicast traffic from P2 to C2.
Processing Leaves
When host C1 decides to leave a multicast group it will issue a leave request to the
switch. If the switch is in active mode it will specific poll the port to determine if
C1 is the last member of the group on that port. If C1 is the last (or only)
member, the switch will issue a leave to the router and the group will immediately
be pruned from the port.
Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering
If the switch is configured to run in passive mode, it will age out the membership
of C1 in the group before pruning.
Should host C1 leave the multicast group without issuing a leave group message
and then fail to respond to a general membership query, the switch will stop
forwarding traffic after two queries.
Multicast Sources
When a multicast source starts multicasting, the traffic stream will be immediately
blocked on segments from which joins have not been received.
Should a multicast source stop issuing multicast traffic, the switch will age out
knowledge of the multicast source after about two query intervals.
IGMP And RSTP
An RSTP change of topology can render the routes selected to carry multicast
traffic as incorrect. This results in lost multicast traffic.
If RSTP detects change in the network topology, IGMP will take some actions to
avoid loss of multicast connectivity:
RuggedCom
• The switch will immediately issue IGMP queries (if in IGMP active mode)
to obtain potential new group membership information.
• The switch will immediately begin to flood all multicast traffic through all
the ports that are not configured as RSTP Edge Ports for about 2 switch
query intervals.
65
Page 80

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Multicast Filtering Configuration
Multicast Filtering Parameter Ranges & Default Settings
The following set of tables lists default IGMP configuration parameters for the
switch.
Configuration Item Default Value Supported Values
IGMP Mode Active Active, Passive
IGMP Query Interval 60 Seconds 10 to 3600 seconds
Router Ports None A list of ports
IGMP Operational Status (per VLAN) Off Off, On
Multicast Filtering Menu
The Multicast Filtering menu is available from the main menu Multicast Filtering
command.
My Switch Multicast Filtering Admin Access
Configure IGMP Parameters
View IP Multicast Groups
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 44: Multicast Filtering Menu
IGMP Parameters Menu
IGMP parameters are configured from this menu. Note that the activation of
IGMP on a per-VLAN basis is configured using the Virtual LANs menu
Configure VLANs command.
My Switch IGMP Parameters Admin Access
Mode Active
Query Interval 60 s
Router Ports None
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 45: IGMP Parameters Menu
Mode
This parameter sets the IGMP mode to active or passive.
In active mode the switch generates IGMP queries, if and when queries from a
multicast router are not detected. In passive mode the switch passively snoops
IGMP traffic and never sends IGMP queries.
RuggedCom
Page 81

Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering
Note:
of traffic. Use passive mode only with routers that have problems identifying IGMP enabled
switches. A switch running in passive mode requires the presence of a multicast router or it will
not be able to forward multicast streams at all!
Query Interval
In active mode, this is the time interval between IGMP queries sent by the switch.
The query interval also forms the basis for the Group Membership Interval, a
timer that is two query intervals plus 10 seconds in duration. The Group
Membership Interval is used in active and passive mode.
Router Ports
This parameter specifies ports that connect to multicast routers.
Note:
The switch sends IGMP join messages only to router ports (either statically configured or
dynamically discovered).
Active mode IGMP is much to be preferred to passive mode, resulting in rapid pruning
It is important that you configure all router ports or the switch will not know of them.
Multicast Filtering Statistics
IP Multicast Groups Menu
The IP Multicast Groups menu is accessible from the Multicast Filtering menu
View IP Multicast Groups command.
My Switch IP Multicast Groups Admin Access
VID IP Address Source Port Joined Ports Router Ports MAC Address
2 224.100.100.129 None 6 6 01-00-5E-64-64-81
2 225.101.100.129 3 8 6 01-00-5E-65-64-81
3 224.200.100.146 2 7 None 01-00-5E-C8-64-92
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell D-PgDn U-PgUp
Figure 46: IP Multicast Groups Menu
VID
The VLAN for which the following IGMP information pertains.
IP Address
RuggedCom
This is the multicast group IP address as used by the producer.
67
Page 82

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Source Port
This is the port receiving the multicast stream as described by this entry. Source
port information will be aged out after about two query intervals.
Note:
display information about the first source it detects. If a detected multicast traffic source
“moves” to a different port (or another source of the same group becomes active) the switch will
re-detect it after multicast source port information is aged out (about two query intervals later).
Joined Ports
These are the ports that have subscribed (with joins) to the source port’s traffic.
Joined ports will be aged out, if no IGMP join messages are received by those
ports for a certain amount of time (about 2 query intervals).
Router Ports
These are ports that connect to multicast routers. These ports must receive the
multicast streams in order to have the potential of distributing them to more
distant hosts. Dynamically discovered router ports will be aged out if no
appropriate multicast router traffic is received on those ports (after about 2 query
intervals).
MAC Address
The MAC address corresponds to the multicast group address. The addresses are
related in the following fashion:
The switch can detect only one multicast traffic source at any one time. The switch will
Multicast address W.X.Y.Z <-> MAC address 01-00-5E-XX-YY-ZZ
where XX, YY and ZZ are simply X, Y and Z coded in hexadecimal
Astute readers will have noted that addresses such as 224.1.1.1 and 225.1.1.1 will
both map onto the same MAC address (01-00-5E-01-01-01). This is indeed a
problem for which the IEEE Network Working Group currently has no solution.
Users are advised to be aware of and avoid this problem.
RuggedCom
Page 83

Troubleshooting
Problem One
• When I start a multicast traffic feed it is always distributed to all
Is IGMP enabled for the VLAN? Multicasts will be distributed to all members of
the VLAN unless IGMP is enabled.
Problem Two
• Computers on my switch receive the multicast traffic just fine, but
Is the port used to connect the router included in the Router Ports parameter of
the VLANs menu?
To determine whether the multicast stream is being delivered to the router, run the
Ethernet Statistics menu View Ethernet Statistics command. Verify that the
traffic count transmitted to the router is same as the traffic count received from
the multicasting source.
Chapter 7 – Configuring Multicast Filtering
members of the VLAN.
I can’t get the stream through a connected router.
Problem Three
Video serving is a resource-intensive application. Because it uses isochronous
workload, data must be fed at a prescribed rate or end users will see glitches in the
video. Networks that carry data from the server to the client must be engineered
to handle this heavy, isochronous workload.
Video streams can consume large amounts of bandwidth. Features and capacity of
both server and network (including routers, bridges, switches, and interfaces)
impact the streams.
You should not exceed 60% of the maximum interface bandwidth. For example, if
using a 10 Mbps Ethernet, you should run a single multicasting source at no more
than 6 Mbps, or two sources at 3 Mbps.
Router ports will carry the traffic of all multicast groups, so it is especially
important to consider these ports in your design
Note that multicasting will definitely introduce latency in all traffic on the
network. Plan your network carefully in order to account for capacity and latency
concerns.
• The video stream at one of my end stations is of pretty poor
quality.
RuggedCom
69
Page 84

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Problem Four
• Multicast streams of some groups are not forwarded properly.
Some segments without subscribers receive the traffic while some
segments with subscribers don’t.
Ensure there are you do have a situation where differing multicast groups have
multicast IP addresses that map to the same multicast MAC Address. The switch
forwarding operation is MAC Address based and will not work properly for several
groups mapping to the same MAC Address.
Problem Five
• Computers on my switch issue join requests but don’t receive
multicast streams from a router.
Is your multicast router running IGMP version 2? It must run IGMP version 2 in
order for IGMP Snooping to operate properly.
Problem Six
• I connect or disconnect some switch ports and multicast goes
everywhere. Is IGMP broken?
No, it’s a proper switch behaviour. When the switch detects a change in the
network topology through RSTP it acts to avoid loss of multicast traffic. It
immediately starts issuing its own IGMP queries to quickly obtain group
membership information. It also starts forwarding all multicast traffic to all ports
that are not Edge Ports (because they may potentially link to routers). This may
result in some undesired flooding of multicast traffic, however, it guarantees that
all devices interested in the traffic will keep receiving it with no break. The
flooding will stop when the “false” router ports are aged out (about 2 switch query
intervals). Note that the same behaviour will be observed when the switch resets
or when IGMP Snooping is being enabled for the VLAN (in the latter case
flooding will only be observed within the VLAN being configured).
RuggedCom
Page 85

Chapter 8 – Diagnostics
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• Using The Alarm System to view and clear Alarms
• Viewing and clearing the System Log
• Viewing CPU Diagnostics
• Loading the Factory Default Configuration
• Viewing the Product Identification
• Resetting the switch
Chapter 8 – Diagnostics
Using The Alarm System
Alarm Concepts And Issues
Alarms are the occurrence of events of interest that are logged by the switch. If
alarms have occurred the switch will indicate the number of alarms in the top right
corner of all menu screens.
My Switch Diagnostics 5 ALARMS!
View Alarms
Clear Alarms
View System Log
Clear System Log
View CPU Diagnostics
View Product Identification
Load Factory Default Configuration
Reset Unit
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 47: Diagnostics Menu Showing Alarm Commands
Types Of Alarms
There are two broad types of alarms, active and passive alarms.
RuggedCom
Active Alarms
Active alarms are ongoing. They signify states of operation that are not in
accordance with normal operation. Examples of active alarms include links that
should be active but are not or error rates that are continuously exceeding a certain
threshold.
71
Page 86

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Active alarms are removed (cleared) either by solving the original cause of the
alarm or by disabling the alarm itself.
Passive Alarms
Passive alarms are historic in nature. They signify events that represented
abnormal conditions in the past, and do not affect the current operational status.
Examples of passive alarms include authentication failures or error rates that
temporarily exceeded a certain threshold.
Passive alarms are cleared through the diagnostics menu Clear Alarms command.
RMON generated alarms are passive.
Note:
Alarms are volatile in nature. All alarms (active and passive) are cleared at startup.
Format of Alarms
Every alarm includes the following information:
• The time of the alarm occurrence
• The alarm level
• The alarm description
Alarm Time
The alarm time provides the month, hour and minute at which the alarm occurred.
Note:
configured in order to obtain the time of day used in alarms. SNTP will typically obtain the
correct real time via the network within seconds after startup. Alarms occurring before SNTP
obtains the time will be displayed relative to midnight of January 1rst.
If the hardware is not equipped with a real time clock the SNTP feature must be
Alarm Level
The alarm level provides an indication of the severity of the alarm. The possible
levels correspond to those described in the UNIX SysLog facility.
Severity Level SysLog Keyword Alarm Keyword Description
0 emergencies
1 alerts
2 critical
3 errors
4 warnings
5 notifications
6 informational
7 debugging
EMRG
ALRT
CRIT
ERRO
WARN
NOTE
INFO
DEBG
Normal but significant conditions
System unusable
Immediate action required
Critical condition
Error conditions
Warning conditions
Informational messages
Debugging messages
Alarm Description
RuggedCom
Page 87

Each alarm has an associated description string. The string will include a port
number if it is relevant. The description may also provide an indication of the
recent rate at which this alarm is occurring (if the alarm has occurred previously).
Alarms And The Critical Failure Relay
All active alarms will immediately de-energize the critical fail relay (thus signifying
a problem). The relay will be re-energized when the last outstanding active alarm
is cleared.
Viewing And Clearing Alarms
Viewing Alarms
The Alarms Menu is available from the Diagnostics menu View Alarms command.
Alarms are displayed in the order in which they occurred, even if the real time
clock was incorrect at the time of the alarm.
Chapter 8 – Diagnostics
My Switch Alarms 6 ALARMS!
Level Time Description
WARN Jan 5 17:55 Port 8 down is occurring (2 times in 192 sec)
WARN Jan 5 18:30 Port 13 down has occurred (9 times in 19 hr)
WARN Jan 5 19:10 Port 5 is down
WARN Jan 6 13:44 Port 7 down has occurred (2 times in 23 hr)
WARN Jan 6 17:40 Port 12 was down
WARN Jan 6 23:02 Port 6 is down
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell D-PgDn U-PgUp
Figure 48: Alarms Menu
Clearing Alarms
The Diagnostics menu Clear Alarms command will clear all alarms.
RuggedCom
73
Page 88

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Viewing CPU Diagnostics
The CPU Diagnostics Menu is available from the Diagnostics menu View CPU
Diagnostics command. The parameters presented in this menu are read-only.
My Switch CPU Diagnostics Admin Access
Running Time 265 days, 22:38:05
Total Powered Time 488 days, 12:15:07
CPU Usage 0.6 %
RAM Total 16777216
RAM Available 9347069
Temperature 31 C
Figure 49: CPU Diagnostics Menu
Running Time
This parameter presents the time since reboot in days and hours.
Total Powered Time
This parameter presents the cumulative powered up time of the product
Note:
revision 2 or greater. The hardware revision is provided in the
Product Identification
CPU Usage
This parameter presents the CPU usage.
RAM Total
This parameter presents the total amount of memory available to the switch’s
processor.
RAM Available
This parameter presents the amount of memory available to be consumed by the
switch’s processor.
Temperature
This parameter will appear only if the RuggedSwitch™ Management CPU is hardware
Diagnostics, View
menu.
This parameter presents the current internal temperature of the switch.
Note:
revision 2 or greater. The hardware revision is provided in the
Product Identification
This parameter will appear only if the RuggedSwitch™ Management CPU is hardware
Diagnostics, View
menu.
RuggedCom
Page 89

Viewing and Clearing the System Log
The View System Log command displays entries made in the system log. The
system log records various events including reboots, user sign-ons, alarms and
configuration saves.
My Switch syslog.txt Admin Access
Nov 11 14:25:40.363 INFO System log cleared
Nov 12 16:50:53.058 INFO Guest logged in
Nov 12 21:52:11.406 INFO Flashing config.csv started
Nov 12 21:52:11.968 INFO Flashing config.csv done
Nov 12 21:52:12.051 INFO Flashing config.bak started
Nov 12 21:52:12.913 INFO Flashing config.bak done
Nov 12 21:52:14.600 INFO Admin logged in
Nov 12 21:52:14.704 INFO Port 5 is up
Nov 12 21:52:15.284 INFO Port 2 is up
Nov 12 21:52:20.334 INFO Last Running time Nov 13 16:35:59.000
Nov 12 21:52:20.335 INFO System started - RuggedSwitch_Boot_v1.2.0 Nov 12
Nov 12 21:52:23.494 INFO Starting ROS v1.4.0 HwID:RSMCPU (40-00-0008 Rev B1)
Nov 12 21:52:24.920 INFO Running RS8000T-HI-MM-MS MAC Addr:00-0A-DC-40-AB-08 Ser
ial#:6734219
Nov 12 21:56:06.520 INFO Port 5 is up
Nov 12 21:56:07.100 INFO Port 3 is up
Press space to continue ...
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Chapter 8 – Diagnostics
Figure 50: Viewing the System Log
The system log will continue to accumulate information until becomes full. There
is enough room in the file to accumulate logs for months or years under normal
operation.
The Clear System Log command will clear the log. Clearing the log is
recommended after a firmware upgrade.
Viewing Product Identification
The View Product Identification command presents the following information:
• The product base MAC Address (i.e. the MAC address of port 1).
• The product Order Code.
• The product Serial Number.
• The version of the Boot code that has been loaded onto the product.
• The version of the Main Application code that has been loaded onto the
product.
RuggedCom
• The hardware revision of the RuggedSwitch™ Management CPU.
75
Page 90

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Load Factory Default Configuration
The Load Factory Default Configuration command will re-load all configuration
parameters to factory default values. Configuration parameters that affect the
connection to the switch (as provided by the Configure IP Services menu) will not
be modified. A prompt will be displayed requesting confirmation of this action.
Resetting The Unit
The Reset Device command will close all open Telnet connections and warm
start the unit.
RuggedCom
Page 91

Chapter 9 - Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics
Chapter 9 – Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics
Introduction
This chapter familiarizes the user with:
• Viewing Ethernet Statistics
• Viewing and Clearing Ethernet Port Statistics
• Configuring RMON History Control
• Viewing RMON History Samples
• Configuring RMON Alarms
• Configuring RMON Events
• Viewing RMON Event Logs
The Ethernet Statistics menu is accessible from the main menu Ethernet
Statistics command.
My Switch Ethernet Statistics Admin Access
View Ethernet Statistics
View Ethernet Port Statistics
Clear Ethernet Port Statistics
Configure RMON History Controls
Configure RMON Alarms
Configure RMON Events
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell
Figure 51: Ethernet Statistics Menu
RuggedCom
77
Page 92

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
View Ethernet Statistics
Ethernet statistics provides a continuously updated (once per second) view of the
traffic on all ports.
My Switch Ethernet Statistics Admin Access
Port State InOctets OutOctets InPkts OutPkts ErrorPkts
1 Up 53412 319576 47 519 0
2 Up 17600 15482 275 247 0
3 Down 0 0 0 0 0
4 Down 0 0 0 0 0
5 Down 0 0 0 0 0
6 Down 0 0 0 0 0
7 Down 0 0 0 0 0
8 Up 55068 70012 766 322 0
Figure 52: Ethernet Statistics Menu
This traffic view is useful when the origin and destination of a traffic flow needs
to be determined. The ErrorPkts field provides a sum total of all the individual
sources of port errors as described in the Ethernet Port statistics menu.
View Ethernet Port Statistics
Ethernet port statistics provide a continuously updated (once per second) detailed
view of the traffic on a single port.
My Switch Ethernet Port Statistics Admin Access
Select Port: 3 Link Status:
Link Up
Speed 100
Duplex Full
Statistics:
InOctets 8436846 Collisions 0
OutOctets 38272361 LateCollisions 0
InPkts 40811 Pkt64Octets 137413
OutPkts 190282 Pkt65to127Octets 53701
TotalInOctets 8442416 Pkt128to255Octets 13792
TotalInPkts 40860 Pkt256to511Octets 5737
InBroadcasts 439 Pkt512to1023Octets 1540
InMulticasts 3391 Pkt1024to1536Octets 18959
CRCAlignErrors 0 DropEvents 0
OversizePkts 0 OutBroadcasts 25259
Fragments 0 OutMulticasts 119281
Jabbers 0 UndersizePkts 0
This traffic view is useful when the exact source of error or traffic mix needs to be
determined. The statistics are as described in the following tables.
-
-
Figure 53: Port Statistics Menu
Cumulative Statistics of Packet/Byte Counts
InOctets This counter is incremented once for every data octet of good packets (Unicast
+ Multicast + Broadcast) received.
OutOctets This counter is incremented for every data octet of a transmitted good packet.
RuggedCom
Page 93

Chapter 9 - Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics
InPkts This counter is incremented once for every good packet (Unicast + Multicast +
Broadcast) received.
OutPkts This counter is incremented once for every transmitted good packet.
TotalInOctets This counter is incremented once for every data octet of all received packets,
including packets that (for whatever reason) will be dropped. This counter
should reflect all the data octets received on the line.
TotalInPkts This counter is incremented once for every received packet. This includes (for
whatever reason) rejected and dropped packets. This counter should reflect all
packets received on the line.
InBroadcasts This counter is incremented once for every good Broadcast packet received.
InMulticasts This counter is incremented once for every good Multicast packet received.
This counter does not include Broadcast packets.
OutBroadcasts The number of Multicast frames sent not including Broadcast packets.
OutMulticasts The number of Broadcast frames sent.
DropEvents This counter is incremented once for every received packet that must be
dropped due to insufficient switch resources.
Cumulative Error Statistics
CRCAlignErrors This counter is incremented for every received packet with an invalid CRC.
OversizePkts This counter is incremented once for every received packet that is greater than
1536 bytes (that have an valid CRC).
Fragments This counter is incremented once for every received packet that is less than 64
bytes in length.
Jabbers This counter is incremented once for every received packet that is greater than
1536 bytes (that have an invalid CRC).
Collisions This counter is incremented once for every detected collision event.
LateCollisions This counter is incremented once for every detected late collision event.
UndersizePkts This counter is incremented once for every received packet that is smaller than
64 and has valid CRC.
Packet Count By Size of Packet
Pkt64Octets This counter is incremented once for every received and transmitted packet
with size of 64 bytes. This counter does not include rejected received packets.
Pkt65to127Octets This counter is incremented once for every received and transmitted packet
with size of 65 to 127 bytes. Rejected received packets are not counted.
Pkt128to255Octets This counter is incremented once for every received and transmitted packet
with size of 128 to 255 bytes. Rejected received packets are not counted.
Pkt256to511Octets This counter is incremented once for every received and transmitted packet
with size of 256 to 511 bytes. Rejected received packets are not counted.
Pkt512to1023Octets This counter is incremented once for every received and transmitted packet
with size of 512 to 1023 bytes. Rejected received packets are not counted.
Pkt1024to1536Octets This counter is incremented once for every received and transmitted packet
with size of 1024 to 1536 bytes. Rejected received packets are not counted.
Remote Monitoring (RMON)
The RuggedSwitch™ Remote Monitor (RMON) package provides the following
capabilities:
RuggedCom
79
Page 94

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
• The ability to collect historical statistics in order to review performance and
operation of Ethernet ports.
• The ability to record a log entry and/or generate an SNMP trap when the
rate of occurrence of a specified event is exceeded.
These capabilities are provided through the following menus:
• RMON History Control Table – This menu controls the periodic statistical
sampling of data and corresponds to the RFC 2819 (RMON-MIB) History
Group.
• RMON History Samples Table – Reached through the History control
menu, this menu provides the ability to view collected history samples of
statistics on the Ethernet interface. These samples corresponds to the RFC
2819 (RMON-MIB) Ethernet History Group.
• RMON Alarms Table – Monitors a specific management information base
(MIB) object for a specified interval, generates an alarm at a specified value
(rising threshold or falling threshold). Alarms are logged in the switch
alarm menu and can be used to triggers RMON events.
• RMON Events Table – Determines the action to take when an event is
triggered by an alarm. The action can be to generate a log entry and/or an
SNMP trap.
• RMON Events Logs Table - Reached through the RMON Events Table
menu, this menu provides the ability to view collected logs.
RuggedCom
Page 95

Chapter 9 - Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics
RMON Historical Statistics Concepts And Issues
Historical statistics allow users to program the switch to take “snapshots” of the
RMON-MIB history statistics of a port at regular intervals. Each user creates a
record that describes:
• The port to capture the statistics for
• The interval between each sample taken
• The total number of samples (called RMON buckets) to keep
• Information about the user that created the record, i.e. the “owner”
Each bucket contains the time at which the sample was taken and the following
statistics for each port: DropEvents, Octets, Pkts, BroadcastPkts, MulticastPkts,
CRCAlignErrors, UndersizePkts, OversizePkts, Fragments, Jabbers, Collisions and
Utilization. The utilization statistic reflects the percentage of line bandwidth used
including the 64-bit preamble and 96-bit interframe gap of each received packet.
RMON History Control Record
Bucket
System Statistics
Interval
Capture
Bucket
Bucket
Bucket
Figure 54: The History Process
The number of RMON buckets allotted for the record determines how many
samples are stored and thus how far back in time statistics will reach. When all of
the allotted buckets have been filled, the oldest bucket is recycled.
The record’s owner field is a string that describes the creator of the record (and
any relevant contact information). The intent being to provide a means for users
to contact each other in order to share the use of specific records and to
coordinate the deletion of records.
Many records can be constructed, each detailing specific ports and capture
intervals. If enough records are constructed the switch may not be able to allocate
enough buckets and will reduce the depth of the last entered record.
Note that records entered through SNMP are also viewable from the menu system.
RuggedCom
81
Page 96

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Configure RMON History Control Table Menu
The History Control Table stores configuration records that define a users sample
collection. Collected samples can be viewed by using the arrow keys to select a
particular record and pressing <CTRL> V.
My Switch RMON History Control Table Admin Access
Index Port Requested Buckets Granted Buckets Interval Owner
1 5 70 70 4 Monitor
33 3 30 30 3000 Monitor
1200 5 20 20 2 Monitor
<CTRL> Z-Help S-Shell I-Insert L-Delete V-View
Figure 55: History Control Table
Index
The RMON History Control record index. When creating a new record, enter an
unused number in this field.
Port
The port to monitor.
BucketsReq
The number of buckets (1 to 4000) requested. The default value is 50.
BucketsGranted
The number of buckets granted for this record. This field is not editable.
Interval
The number of seconds (1 to 3600) between samples. The default value is 1800.
Owner
A field describing the person who configured this record and any applicable
contact information. The RMON specification recommends that the string always
start with the word “monitor”.
RuggedCom
Page 97

RMON History Samples Table Menu
History samples for a particular record in the RMON History Control Table are
displayed by selecting a particular record there and pressing <CTRL> V. The
index of the record will be included in the resulting menu title of the sample
screen.
The table will present a series of samples. The Sample number starts with one and
increases by one with each new log entry. The oldest samples are deleted in favour
of new samples when the allotted buckets are used.
The StartTime provides the system time when the measurement interval started.
The remaining fields provide the counts for each statistic as measured in the
sample period.
Statistics collection begins whenever the History Control record is created and
when the switch is initialized. As new samples are added, the window is
automatically updated.
Chapter 9 - Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics
My Switch RMON History 1 Samples Table Admin Access
Sample StartTime DropEvents InOctets InPkts InBroadcasts
13 0 days, 00:00:50 0 623 5 2
14 0 days, 00:00:54 0 446 5 1
15 0 days, 00:00:58 0 383 5 2
16 0 days, 00:01:02 0 288 4 2
17 0 days, 00:01:06 0 384 6 1
18 0 days, 00:01:10 0 1217 10 8
19 0 days, 00:01:14 0 192 3 1
20 0 days, 00:01:18 0 193 3 0
21 0 days, 00:01:22 0 192 3 1
22 0 days, 00:01:26 0 256 4 2
23 0 days, 00:01:30 0 367 4 2
24 0 days, 00:01:34 0 128 2 0
25 0 days, 00:01:38 0 192 3 1
26 0 days, 00:01:42 0 192 3 1
27 0 days, 00:01:46 0 629 5 1
28 0 days, 00:01:50 0 502 4 1
29 0 days, 00:01:54 0 256 4 2
30 0 days, 00:01:58 0 192 3 1
More right and below ...
Figure 56: RMON History Samples Table
RuggedCom
83
Page 98

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
RMON Alarms And Events Concepts And Issues
The Alarm Process
The RMON Alarms Table allows the user to create records that configure the
switch to examine the state of a specific statistic variable.
The record contains an upper and a lower threshold for legal values of the statistic
in a given interval. This provides the ability to detect events occurring more
quickly than a specified maximum rate or less quickly than a specified minimum
rate.
When a statistic value’s rate of change exceeds its limits an internal alarm of INFO
level is always generated. Internal alarms can be viewed using the Diagnostics
menu, View Alarms command.
Additionally, the record’s owner can decide whether a statistic threshold crossing
should result in further activity. The RMON Alarm record points to a particular
RMON Event Record, which can generate an SNMP trap, an entry in the switch’s
event log or both. The RMON Event Record can “steer” alarms towards different
communities of trap receivers.
The alarm record can point to a different event record for each of the thresholds,
so combinations such as “trap on rising threshold” or “trap on rising threshold,
log and trap on falling threshold” are possible.
RMON Alarm Record RMON Event Record
Rising Trap
System
Statistics
Threshold
Crossing
Logic
Internal Alarm
First
Alarm
Logic
Rising Alarm
Falling Alarm
Event
Generation
Logic
Rising Log
Falling Trap
Falling Log
Figure 57: The Alarm Process
The owner of the alarm has the choice what happens if the very first statistic
measurement (after switch reset or after the record is created) immediately exceeds
the configured thresholds. The owner can decide whether or not to generate an
alarm.
RuggedCom
Page 99

Alarm Generation And Hysteresis
The ability to configure upper and lower thresholds on the value of a measured
statistic provide for the ability to add hysteresis to the alarm generation process.
If the value of the measured statistic over time is compared to a single threshold,
alarms will be generated each time the statistic crosses the threshold. If the
statistic’s value fluctuates around the threshold, an alarm can generated every
measurement period. Programming different upper and lower thresholds eliminate
spurious alarms. The statistic value must “travel” between the thresholds before
alarms can be generated.
The following figure illustrates the very different patterns of alarm generation
resulting from a statistic sample and the same sample with hysteresis applied.
Statistic Value
Chapter 9 - Using Ethernet And RMON Statistics
Rising Rising
Falling
Falling Rising
Figure 58: Applying Hysteresis to Alarm Generation
Delta vs. Absolute Values
There are two methods to evaluate a statistic in order to determine when to
generate an event; these are the delta and absolute methods.
For most statistics (such as line errors) it is appropriate to alarm when a rate is
exceeded. The alarm record defaults to the “delta” measurement method, which
examines changes in a statistic at the end of each measurement period.
Upper = Lower
Threshold
Falling
Rising
Upper Threshold
Lower Threshold
Time
RisingFalling
Alarms
RuggedCom
It may be desirable to alarm when the total, or absolute, number of events crosses a
threshold. In this case, set the measurement period type to “absolute”.
85
Page 100

RuggedSwitch™ User Guide
Configure RMON Alarms
The Alarms Table stores configuration records that define statistics, their polling
periods and threshold parameters.
My Switch RMON Alarms Admin Access
Index Variable Rising Thr Falling Thr
1 ifInOctets.5 10000 100000
2 ifOutOctets.5 10000 100000
More right ...
Index
Variable
-
Figure 59: RMON Alarm Configuration Table screens
-
-
The index of the RMON Alarms entry.
The MIB object identifier of the particular variable to be sampled. Only variables
that resolve to an ASN.1 primitive type of INTEGER (INTEGER, Integer32,
Counter32, Counter64, Gauge, or TimeTicks) may be sampled. The “rmon” shell
command will list the names of the objects that are eligible for monitoring with
RMON Alarms. A detailed description of the objects is also included in Appendix
D – RMON Acceptable MIB Parameters.
-
If the statistic is port based, a decimal point and the port number must be
appended to the identifier.
Rising Threshold
A rising threshold for the sampled statistic, the value the statistic must rise above
before a rising alarm will be generated.
Falling Threshold
A falling threshold for the sampled statistic, the value the statistic must decrease to
before a falling alarm will be generated.
Value
The value of the statistic during the last sampling period. This is the value that is
compared with the rising and falling thresholds.
Type
The method of sampling the selected variable and calculating the value to be
compared against the thresholds.
Interval
The time interval in seconds over which the data is sampled and compared with
the rising and falling thresholds.
RuggedCom
 Loading...
Loading...