ROHM BR93LL46F, BR93LL46FV Datasheet

1
Memory ICs
1,024-Bit Serial Electrically Erasable PROM
BR93LL46F / BR93LL46FV
•
Features
• Low power CMOS technology
• 64 × 16 bit configuration
• 1.8V to 4.0V operation
• Low power dissipation
– 0.5mA (typ.) active current
– 0.4µA (typ.) standby current
• Auto increment for efficient data dump
• Automatic erase-before-write
• Hardware and software write protection
– Defaults to write-disabled state at power up
– Software instructions for write-enable / disable
– Vcc lockout inadvertent write protection
• 8-pin SOP / 8-pin SSOP-B packages
• Device status signal during write cycle
• 100,000 ERASE / WRITE cycles
• 10 years Data Retention
•
Pin assignments
•
Pin descriptions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
DO
DISK
N.C. N.C.
CS
GND
BR93LL46F
BR93LL46FV
VCC
(SOP8 / SSOP-B8)
Pin Name Function
N.C. Not connected
Power supply
Chip select input
Serial clock input
Start bit, operating code, address, and
serial data input
Serial data output, READY / BUSY
internal status display output
Ground
Not connected
V
CC
CS
SK
DI
DO
GND
N.C.
•
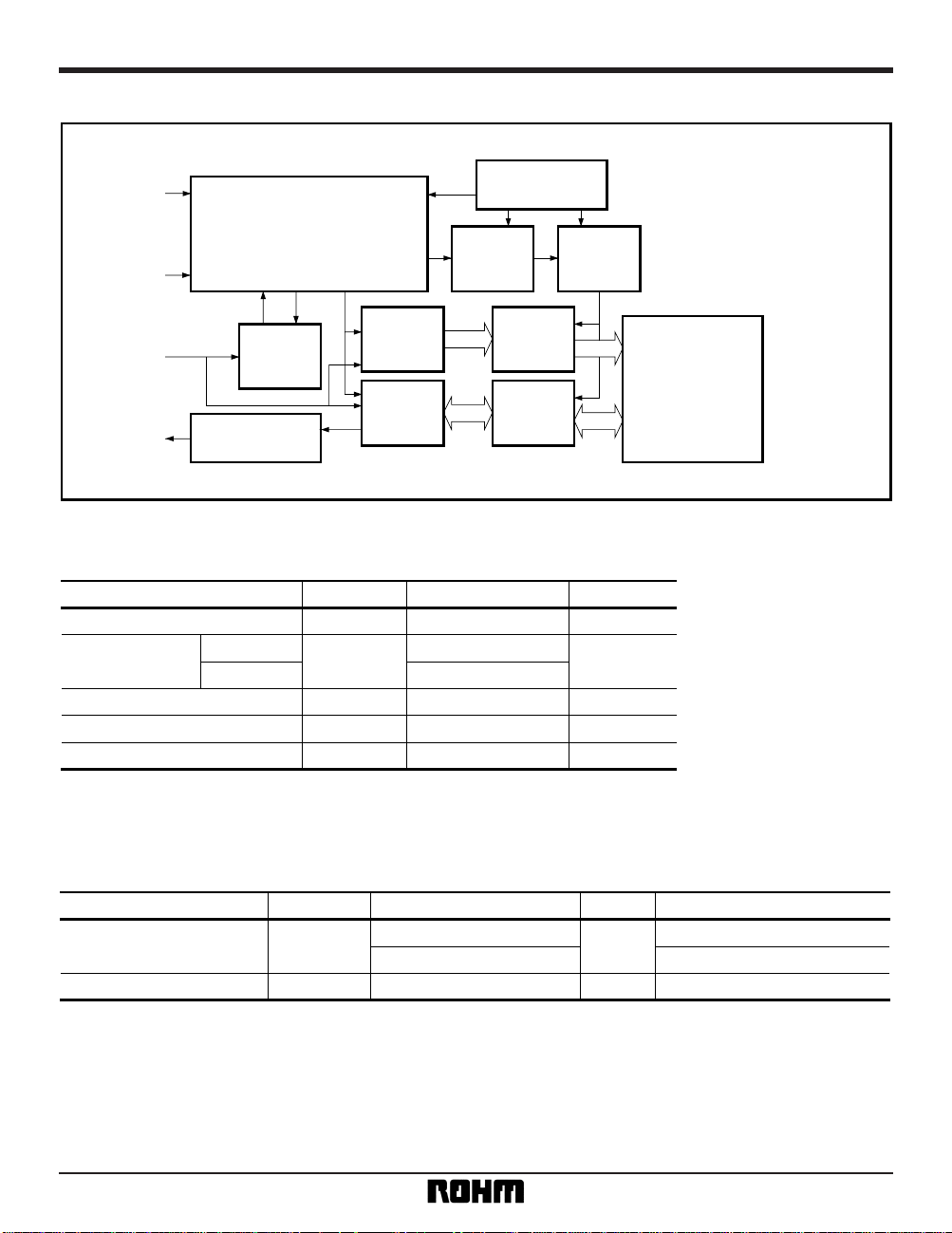
Overview
The BR93LC46F and BR93LL46FV are CMOS serial input / output-type memory circuits (EEPROMs) that can be
programmed electrically. Each is configured of 64 words × 16 bits (1,024 bits), and each word can be accessed indi-
vidually and data read from it and written to it. Operation control is performed using five types of commands. The
commands, addresses, and data are input through the DI pin under the control of the CS and SK pins. In a write
operation, the internal status signal (READY or BUSY) can be output from the DO pin.
2
Memory ICs BR93LL46F / BR93LL46FV
•
Block diagram
Command
register
Data
register
Address
buffer
Dummy bit
DO
DI
SK
CS
16bit
16bit
6bit
6bit
Address
decoder
Command decode
Control
Clock generation
Power supply
voltage detector
High voltage
generator
Write
disable
1,024-bit
EEPROM array
R / W
AMP.
•
Absolute maximum ratings
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit
V
CC – 0.3 ~ + 7.0 V
Pd
350
∗
1
300
∗
2
BR93LL46F
BR93LL46FV
mW
Tstg – 65 ~ + 125 °C
Topr – 20 ~ + 70 °C
— – 0.3 ~ V
CC + 0.3 V
∗
1 Reduced by 3.5mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
∗
2 Reduced by 3.0mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
Applied voltage
Power dissipation
Storage temperature
Operating temperature
Terminal voltage
•
Recommended operating conditions
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit Conditions
Power supply voltage
Input voltage
V
CC
1.8 ~ 4.0
2.0 ~ 4.0
Ta = 0 ~ 70°C
Ta = – 20 ~ + 70°C
V
0 ~ V
CC VV
IN —
3
Memory ICs BR93LL46F / BR93LL46FV
•
Electrical characteristics (unless otherwise noted, Ta = – 20 to + 70°C, VCC = 1.8 to 4.0V)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Conditions
V
IL – 0.3 —
0.2
V
× V
CC
VIH
0.8
—
VCC +
V
0.3× V
CC
VOL1 — — 0.3 V IOL = 1.0mA
V
OL2 — — 0.2 V IOL = 20µA
V
OH2
VCC –
——VI
OH = 100µA
0.3
I
LI – 1.0 — µAVIN = 0V ~ VCC
ILO – 1.0 — µAVOUT = 0V ~ VCC, CS = GND
I
CC1 — 0.5 1.0 mA
V
IN = VIH / VIL, DO = OPEN, fSK = 250kHz
WRITE
I
CC2 — 0.4 1.0 mA
VIN = VIH / VIL, DO = OPEN, fSK = 250kHz, READ
ISB — 0.4 1.0 µA CS = SK = DI = GND, DO = OPEN
1.0
1.0
∗
1 About the operating current dissipation
I
CC1
indicates the average current dissipation during a writing operation, and I
CC2
indicates the average current dissipation during a reading operation.
Because this is internal logic switching current, it changes based on the SK frequency.
∗
2 About the standby current
This is the current dissipation when all inputs are CMOS level and in static state.
Input low level voltage
Input high level voltage
Output low level voltage 1
Output low level voltage 2
Output high level voltage 2
Input leakage current
Output leakage current
Operating current dissipation 1
Operating current dissipation 2
Standby current
—
—
•
Operation timing characteristics (Ta = – 20 to + 70°C, VCC = 1.8 to 4.0 V)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
SK clock frequency
SK "H" time
SK "L" time
CS "L" time
CS setup time
DI setup time
CS hold time
DI hold time
Data "1" output delay time
Data "0" output delay time
Time from CS to output confirmation
Time from CS to output High impedance
Write cycle time
f
SK — — 250 kHz
t
SKH 1——µs
t
SKL 1——µs
t
CS 1——µs
t
CSS 200 — — ns
t
DIS 400 — — ns
t
CSH 0——ns
t
DIH 400 — — ns
t
PD1 ——2 µs
t
PD0 ——2 µs
t
SV —— 2 µs
t
DF — — 400 ns
t
E / W ——25ms
4
Memory ICs BR93LL46F / BR93LL46FV
•
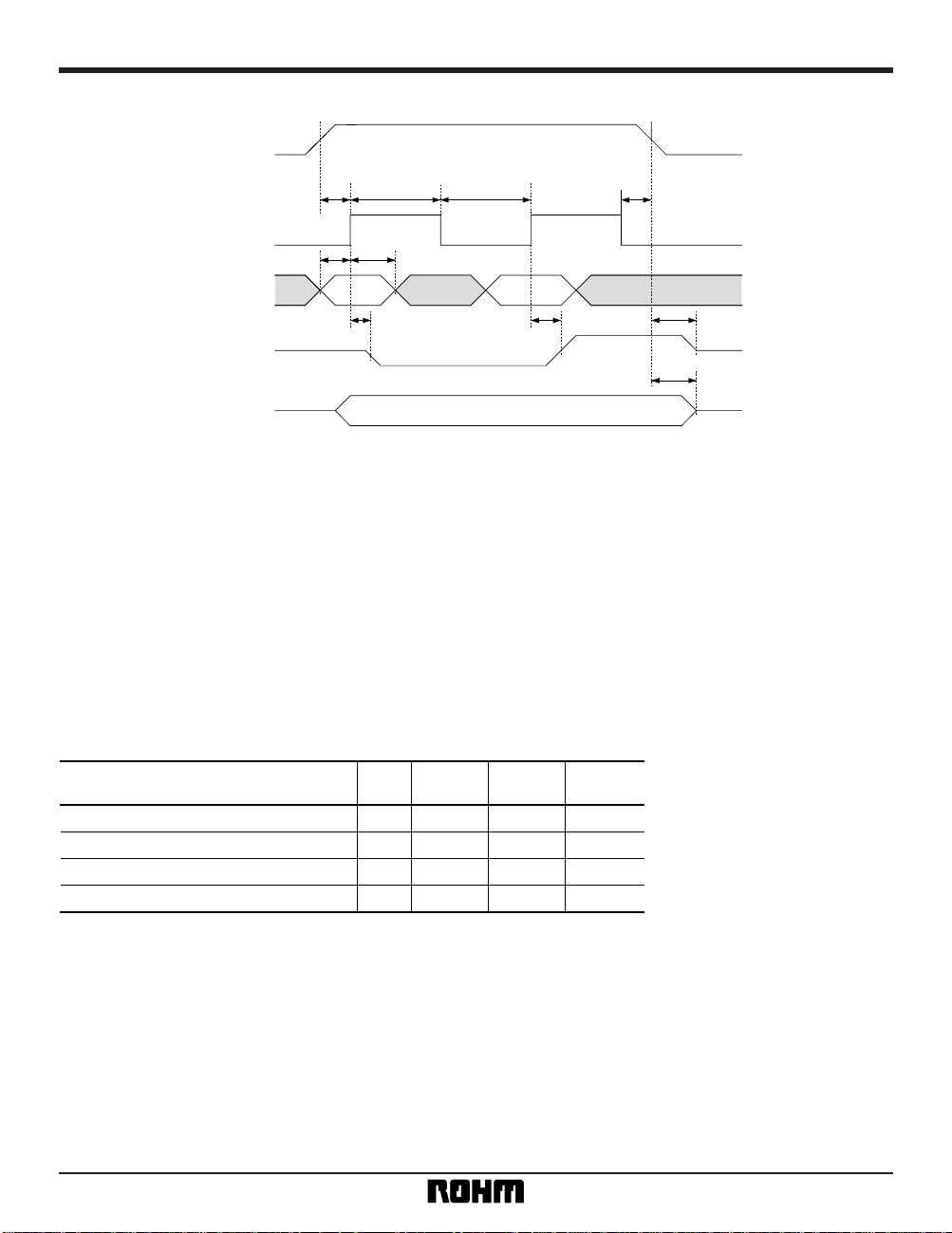
Timing chart
CS
SK
DI
STATUS VALID
DO (READ)
DO (WRITE)
tDIS
tSKH tSKL
tCSH
tDIH
tDF
tDF
tCSS
tPD0
tPD1
Fig. 1 Synchronous data timing
(1) Data is acquired from DI in synchronization with the
SK rise.
(2) During a reading operation, data is output from DO
in synchronization with the SK rise.
(3) During a writing operation, a Status Valid (READY
or BUSY) is valid from the time CS is HIGH until time
t
CS after CS falls following the input of a write command
and before the output of the next command start bit.
Also, DO must be in a HIGH-Z state when CS is LOW.
(4) After the completion of each mode, make sure that
CS is set to LOW, to reset the internal circuit, before
changing modes.
•
Circuit operation
(1) Command mode
Command
Start
bit
Operating
code
Address Data
1 10 A5 ~ A0
1 00 11XXXX
1 01 A5 ~ A0 D15 ~ D0
1 00 00XXXX
X: Either VIH or VIL
Read (READ)
Write enabled (WEN)
Write (WRITE)
Write disabled (WDS)
(
∗
1
)
W
(
∗
2
)
—
—
—
∗ About the start bit
With these ICs, commands are not recognized or acted
upon until the start bit is received. The start bit is taken
as the first “1” that is received after the CS pin rises.
(∗1) After setting of the read command and input of the
SK clock, data corresponding to the specified address
is output, with data corresponding to upper addresses
then output in sequence. (Auto increment function)
(∗2) When the write command is executed, all data in
the selected memory cell is erased automatically, and
the input data is written to the cell.
 Loading...
Loading...