
BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
I2C BUS compatible serial EEPROM
BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W /
BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W /
BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
The BR24C01A-W, BR24C02-W, and BR24C04-W series are 2-wire (I2C BUS type) serial EEPROMs which are
electrically programmable.
∗ I2C BUS is a registered trademark of Philips.
!!!!
Applications
VCRs, TVs, printers, car stereos, cordless telephones, short wave radios, programmable DIP switches
!!!!
Features
1) 128×8bits (1k) serial EEPROM.
6) Page write function.
(BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W)
256×8bits (2k) serial EEPROM.
(BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W)
512×8bits (4k) serial EEPROM.
7) DATA security
(BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W)
2) Two wire serial interface.
3) Operating voltage range : 2.7V∼5.5V
4) Low current consumption
8) Noise filters at SCL and SDA pins.
9) Address can be incremented automatically during
Active (at 5V) : 1.5mA (Typ.)
Standby (at 5V) : 0.1µA (Typ.)
5) Auto erase and auto complete functions can be used
during write operations.
10) Compact packages.
11) Rewriting possible up to 100,000 times
12) Data can be stored for ten years without corruption.
!!!!Absolute maximum ratings (Ta = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit
V
Applied voltage −0.3
Power dissipation
Storage temperature −65
Operating temperature °C
Input voltage
∗1 Reduced by 3.0mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
∗2 Reduced by 4.5mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
∗3 Reduced by 8.0mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
CC
Pd
Tstg
Topr
−
300(SSOP−B8)
450(SOP8, SOP−J8)
800(DIP8)
~+6.5 V
~+125 °C
~+85
−40
−0.3~VCC+0.3
∗1
∗2
∗3
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W : 8 bytes
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W : 8 bytes
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W : 16 bytes
Write protect feature
Inhibit to WRITE at low V
CC
read operations.
mW
V
BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
!!!!Recommended operating conditions (Ta = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit
Power supply voltage
Input voltage V
CC
V
IN
2.7~5.5 (WRITE)
2.7
~
5.5 (READ)
0~V
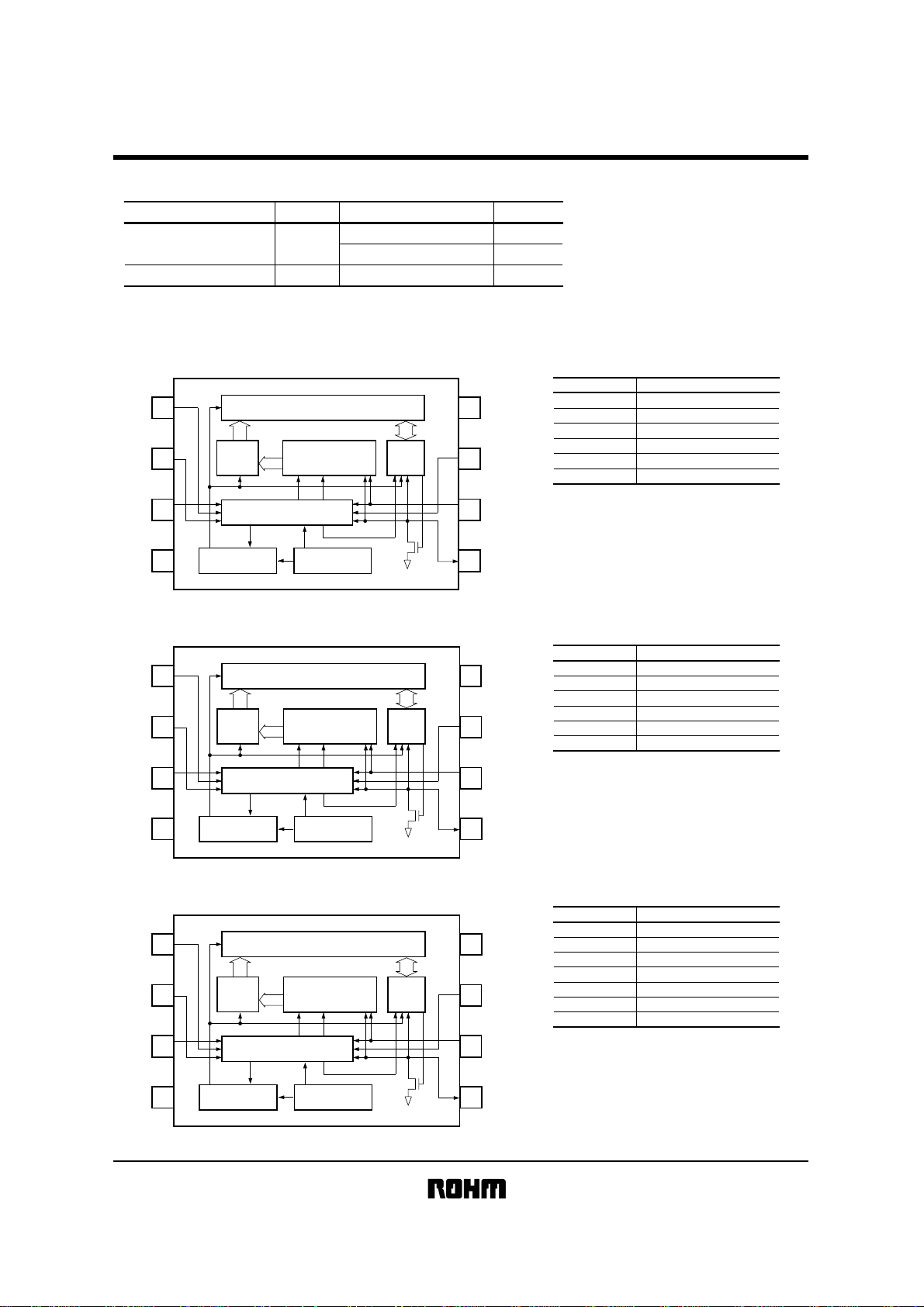
!!!!Block diagram
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W
7bits
7bits
START STOP
CONTROL LOGIC
1kbits EEPROM ARRAY
SLAVE WORD
·
ADDRESS REGISTER
VCC LEVEL DETECT
ACK
8bits
DATA
REGISTER
GND
A0
A1
A2
1
2
3
4
ADDRESS
DECODER
HIGH VOLTAGE GEN.
V
V
CC
V
!!!!Pin descriptions
Pin name Function
CC
V
8
7
WP
SCL
6
SDA
5
A0, A1, A2 Slave address setting pin
SCL Serial data clock
SDA Serial data input / output
WP Write protect pin
CC
V
Power supply
GND Ground
∗ An open drain output requires a pull-up resistor.
∗
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
8bits
8bits
START STOP
CONTROL LOGIC
2kbits EEPROM ARRAY
ADDRESS REGISTER
GND
A0
A1
A2
1
2
3
4
ADDRESS
DECODER
HIGH VOLTAGE GEN.
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
9bits
9bits
START STOP
CONTROL LOGIC
4kbits EEPROM ARRAY
ADDRESS REGISTER
A0
A1
A2
1
2
ADDRESS
DECODER
3
SLAVE WORD
·
VCC LEVEL DETECT
SLAVE WORD
·
ACK
ACK
8bits
DATA
REGISTER
8bits
DATA
REGISTER
Pin name Function
CC
V
8
A0, A1, A2
SCL
SDA
Slave address setting pin
Serial data clock
Serial data input / output
∗
WP Write protect pin
7
WP
CC
V
Power supply
GND Ground
∗ An open drain output requires a pull-up resistor.
SCL
6
SDA
5
Pin name
Function
A0 N.C.
CC
V
8
7
WP
A1, A2 Slave address setting pin
SCL
SDA
Serial data clock
Serial data input / output
WP Write protect pin
V
CC
Power supply
∗
GND Ground
SCL
6
∗ An open drain output requires a pull-up resistor.
GND
4
HIGH VOLTAGE GEN.
VCC LEVEL DETECT
SDA
5
BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
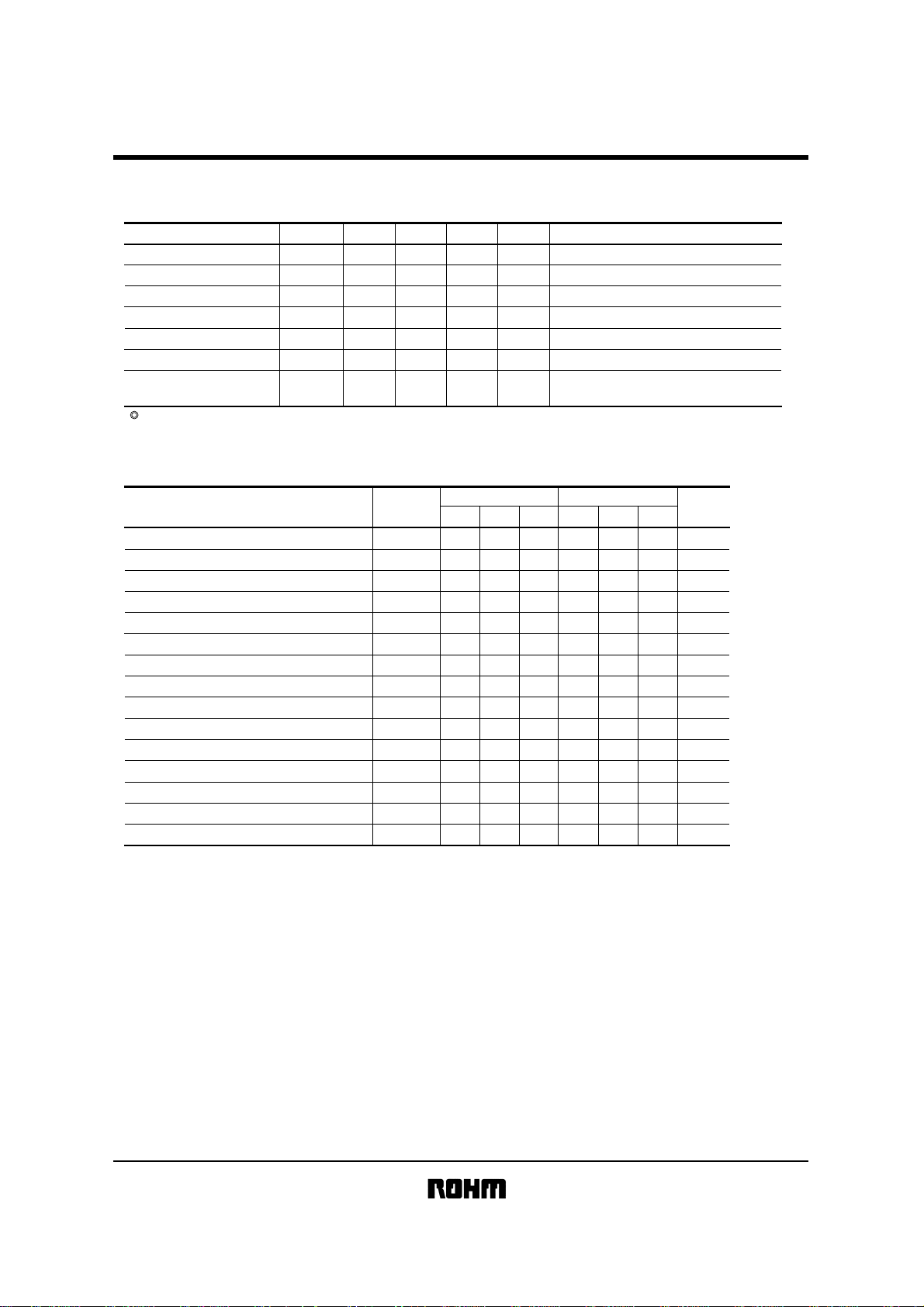
!!!!Electrical characteristics
DC characteristics (unless otherwise noted, Ta = −40 to + 85 °C, V
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Conditions
0.7V
Input high level voltage
Input low level voltage
Output low level coltage
Input leakage current I
Output leakage current I
operatingcurrent dissipation I
Standby current I
Not designed for radiation resistance.
IH
V
V
IL
V
OL
LI
LO
CC
SB
CC
−−
−−
−−
−1
−
−1 −
−
−
−
−
0.3V
= 2.7 to 5.5V)
CC
V
CC
V
0.4 V
1 µA
1 µA
2.0 mA
2.0 µA
OL
=3.0mA(SDA)
I
VIN=0V~V
V
V
V
CC
OUT
=0V~V
CC
CC
=5.5V, f
SCL
=400kHz
CC
=5.5V, SDA·SCL=V
A0, A1, A2=GND, WP=GND
Operating timing characteristics (unless otherwise noted, Ta = −40 to + 85 °C, VCC = 2.7 to 5.5V)
Parameter Symbol
SCL frequency
Data clock HIGH time
Data clock LOW time t
SDA / SCL rise time t
SDA / SCL fall time t
Start condition hold time t
Start condition setup time t
Input data hold time t
Input data setup time t
HD
SU
HD
SU
Output data delay time t
Output data hold time t
Stop condition setup time t
SU
Bus open time before start of transfer t
Noise erase valid time (SCL / SDA pins) t
f
SCL
t
HIGH
LOW
R
F
: STA
: STA
: DAT ns
: DAT ns
PD
DH
: STO
BUF
WR
t
I
Vcc=5V±10% Vcc=3V±10%
Min.
−
0.6
1.2
−
−
0.6
0.6
0
100
0.1
0.1
0.6
1.2
−
−
Typ.
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
Max.
400
−
−
0.3
0.3
−
−
−
−
0.9
−
−
−
10
0.05
Min.
−
4.0
4.7
−
−
4.0
4.7
0
250
0.2
0.2
4.7
4.7
−
−
Typ.
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
Max.
100
−
−
1.0
0.3
−
−
−
−
3.5
−
−
−
10 msInternal write cycle time
0.1
−
−
CC
Unit
kHz
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
!!!!Timing charts
SCL
SDA
(input)
SDA
(output)
SCL
SDA
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
t
HIGH
t
DH
tSU : STOtHD : STA tSU : STA
tHD :
t
BUF
STA
t
t
R
tSU : DAT tHD : DAT
START BIT STOP BIT
F
t
LOW
t
PD
· Data is read on the rising edge of SCL.
· Data is output in synchronization with the falling edge of SCL.
Fig.1 Synchronized data input / output timing
SCL
ACKD0
Fig.2 Write cycle timing
WR
t
Start conditionStop condition
!!!!
Circuit operation
SDA
Write data
(n address)
(1) Start condition (recognition of start bit)
Before executing any command, when SCL is HIGH, a start condition (start bit) is required to cause SDA to fall from
HIGH to LOW. This IC is designed to constantly detect whether there is a start condition (start bit) for the SDA and
SCL line, and no commands will be executed unless this condition is satisfied.
(See Fig.1 for the synchronized data input / output timing.)
(2) Stop condition (recognition of stop bit)
To stop any command, a stop condition (stop bit) is required. A stop condition is achieved when SDA goes from
LOW to HIGH while SCL is HIGH. This enables commands to be completed.
(See Fig.1 for the synchronized data input / output timing.)
(3) Precautions concerning write commands
In the WRITE mode, the transferred data is not written to the memory unless the stop bit is executed.

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
(4) Device addressing
– BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W, BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
1) Make sure the slave address is output from the master immediately after the start condition.
2) The upper four bits of the slave address are used to determine the device type. The device code for this IC is
fixed at “1010”.
3) The next three bits of the slave address (A2, A1, A0 … device address) are used to select the device. This IC
can address up to eight devices on the same bus.
4) The lowermost bit of the slave address (R / W … READ / WRITE) is used to set the write or read mode as follows.
R / W set to 0 … Write
(Random read word address setting is also 0)
R / W set to 1 … Read
A2 A1 A01010 R / W
– BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
1) Make sure the slave address is output from the master in continuation with the start condition.
2) The upper four bits of the slave address are used to determine the device type. The device code for this IC is
fixed at “1010”.
3) The next two bits of the slave address (A2, A1, … device address) are used to select the device. This IC can
address up to four devices on the same bus.
4) The next bit of the slave address (PS … Page Select) is used to select the page. As shown below, it can write to
or read from any of the 256 words in the two pages in memory.
PS set to 0 … Page 1 (000 to 0FF)
PS set to 1 … Page 2 (100 to 1FF)
5) The lowermost bit of the slave address (R / W … READ / WRITE) is used to set the write or read mode as follows.
R / W set to 0 … Write
(Random read word address setting is also 0)
R / W set to 1 … Read
A2 A1 PS1010 R / W
(5) Write protect (WP)
When WP pin set to V
enable to write to all address. Either control this pin or connect to GND (or V
(High level), write protect is set by all address. When WP pin set to GND (Low level),
CC
). It is inhibited from being left
CC
unconnected.
(6) ACK signal
The acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is determined by software and is used to indicate whether or not a data transfer
is proceeding normally. The transmitting device, whether the master or slave, opens the bus after an 8-bit data
output (µ-COM when a write or read command of the slave address input ; this IC when reading data).
For the receiving device during the ninth clock cycle, SDA is set to LOW and an acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is
sent to indicate that it received the 8-bit data (this IC when a write command or a read command of the slave address
input, µ-COM when a read command data output).
The ICs output a LOW acknowledge signal (ACK signal) after recognizing the start condition and slave address (8
bits).
When data is being write to the ICs, a LOW acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is output after the receipt of each eight
bits of data (word address and write data).

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
When data is being read from the IC, eight bits of data (read data) are output and the IC waits for a returned LOW
acknowledge signal (ACK signal). When an acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is detected and a stop condition is not
sent from the master (µ-COM) side, the IC continues to output data. If an acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is not
detected, the IC interrupts the data transfer and ceases reading operations after recognizing the stop condition (stop
bit). The IC then enters the waiting or standby state.
(See Fig.3 for acknowledge signal (ACK signal) response.)
Start condition (start bit)
SCL
(from µ-COM)
SDA
(µ-COM output data)
SDA
(IC output data)
1
8
9
Acknowledge signal (ACK signal)
Fig.3 Acknowledge (ACK signal) response
(during write and read slave address input)
(7) Byte write cycle
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
W
R
I
T
E
WORD
ADDRESS
DATA
S
T
O
P
SDA
LINE
WP
1 0 1 0 A2 A1 A0 D7 D0
R
/
W
WA
∗
6
A
C
K
Fig.4
WA
0
A
C
K
A
C
K

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
S
T
A
SDA
LINE
R
T
ADDRESS
1 0 1 0 A2 A1 A0 D7 D0
WP
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
SLAVE
W
R
I
T
E
WA
A
R
C
/
K
W
7
WORD
ADDRESS
WA
0
A
C
K
DATA
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
Fig.5
W
R
I
T
E
WORD
ADDRESS
DATA
S
T
O
P
SDA
LINE
1 0 1 0 A2 A1 PS D7 D0
WA
7
A
R
C
/
K
W
WA
0
A
C
K
WP
Fig.6
• Data is written to the address designated by the word address (n address).
• After eight bits of data are input, the data is written to the memory cell by issuing the stop bit.
(8) Page write cycle
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
10 01A2A1A0
W
R
I
T
E
A
R
C
/
K
W
ADDRESS(n)
WA
∗
6
WORD
WA
0
A
C
K
D7
DATA(n)
D0
A
C
K
A
C
K
DATA(n+7)
D0
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
WP
Fig.7

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
• A 8-byte write is possible using this command.
• Th page write command arbitrarily sets the upper four bits (WA6 to WA3) of the word address. The lower three bits
(WA2 and WA0) can write up to eight bytes of data with the address being incremented internally.
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
SDA
LINE
WP
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
10 01A2A1A0
W
R
I
T
E
A
R
C
/
K
W
ADDRESS(n)
WA
7
WORD
WA
0
Fig.8
A
C
K
D7
DATA(n)
DATA(n+7)
D0 D0
A
C
K
A
C
K
• A 8-byte write is possible using this command.
• Th page write command arbitrarily sets the upper five bits (WA7 to WA3) of the word address. The lower three bits
(WA2 and WA0) can write up to eight bytes of data with the address being incremented internally.
S
T
O
P
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
SDA
LINE
WP
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
10 01A2A1PS
W
R
I
T
E
A
R
C
/
K
W
ADDRESS(n)
WA
7
WORD
WA
0
Fig.9
A
C
K
D7
DATA(n)
DATA(n+15)
D0 D0
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
• A 16-byte write is possible using this command.
• Th page write command arbitrarily sets the upper four bits (WA7 to WA4) of the word address. The lower four bits
(WA3 and WA0) can write up to sixteen bytes of data with the address being incremented internally.

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
(9) Current read cycle
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W
S
T
A
R
T
SDA
LINE
11
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
S
T
A
R
T
SDA
LINE
11
R
SLAVE
ADDRESS
0 0 A2 A1 A0 D7 D0
SLAVE
ADDRESS
0 0 A2 A1 A0 D7 D0
E
A
D
R
/
W
Fig.10
R
E
A
D
R
/
W
A
C
K
A
C
K
DATA
DATA
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
Fig.11
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
11
0 0 A2 A1 PS D7 D0
R
E
A
D
R
/
W
Fig.12
S
DATA
A
C
K
T
O
P
A
C
K
• In case the previous operation is random or current read (which includes sequential read respectively), the internal
address counter is increased by one from the last accessed address (n). Thus current read outputs the data of the
next word address (n+1).
If the last command is byte or page write, the internal address counter stays at the last address (n). Thus current
read outputs the data of the word address (n).
If the master does not transfer the acknowledge but does generate a stop condition, the current address read
operation only provides s single byte of data.
At this point, this IC discontinues transmission.
• When an ACK signal LOW is detected after D0 and a stop condition is not sent from the master (µ-COM), the next
word address data can be read. [All words all read enabled]
(See Fig.16 to 18 for the sequential read cycles.)
• This command is ended by inputting HIGH to the ACK signal after D0 and raising the SDA signal (stop condition) by
setting SCL to HIGH.

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
(10) Random read cycle
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W
W
R
I
T
E
R
A
/
C
W
K
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2A1A0
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
W
R
I
T
E
R
A
/
C
W
K
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2 A1A0
ADDRESS(n)
WA
∗
6
ADDRESS(n)
WA
7
WORD
WORD
WA
0
Fig.13
WA
0
Fig.14
S
T
A
R
T
A
C
K
S
T
A
R
T
A
C
K
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2 A1A0 D7 D0
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2A1A0 D7 D0
R
E
A
D
R
A
/
C
W
K
R
E
A
D
R
A
/
C
W
K
DATA(n)
DATA(n)
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
W
R
I
T
E
R
A
/
C
W
K
ADDRESS(n)
WA
7
WORD
WA
S
T
A
R
T
0
A
C
K
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2A1PS D7 D0
R
E
A
D
R
A
/
C
W
K
DATA(n)
Fig.15
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2 A1PS
• This command can read the designated word address data.
• When an ACK signal LOW is detected after D0 and a stop condition is not sent from the master (µ-COM), the next
word address data can be read. [All words all read enabled]
(See Fig.16 to 18 for the sequential read cycles.)
• This command is ended by inputting a HIGH signal to the ACK signal after D0 and raising the SDA signal (stop
condition) by raising SCL to HIGH.
S
T
O
P
A
C
K

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
(11) Sequential read cycle (For a current read)
BR24C01A-W / AF-W / AFJ-W / AFV-W
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2 A1A0 D7 D7D0 D0
R
E
A
D
A
R
C
/
K
W
BR24C02-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2 A1A0 D7 D7D0 D0
R
E
A
D
A
R
C
/
K
W
DATA(n)
DATA(n)
Fig.16
Fig.17
S
T
DATA(n+x)
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
DATA(n+x)
O
P
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
BR24C04-W / F-W / FJ-W / FV-W
SDA
LINE
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
110 0 A2 A1PS D7 D7D0 D0
R
E
A
D
R
/
W
DATA(n)
A
C
K
Fig.18
A
C
K
A
C
K
DATA(n+x)
• When an ACK signal LOW is detected after D0 and a stop condition is not sent from the master (µ-COM), the next
word address data can be read. [All words can be read]
• This command is ended by inputting a HIGH signal to the ACK signal after D0 and raising the SDA signal (stop
condition) using the SCL signal HIGH.
• Sequential reading can also be done with a random read.
S
T
O
P
A
C
K

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
!!!!Operation notes
(1) During power rise
During power rise, the V
may rise passing though the low voltage domain in which the IC internal circuit does not
CC
work. For this reason, there is a risk of misoperation when the power rises without full IC internal reset.
To prevent this, pay attention to the following points during a power rise.
1) Set SCL = SDA = “HIGH”
2) Raise the power so as to active the Power On Reset (P. O. R) circuit.
Follow the steps below as to operate the P. O. R. circuit properly.
1) Set the power rise time (tR) to within 10ms.
2) Set the OFF domain for once power has been cut to 100mS minimum.
V
CC
t
t
OFF
R
(2) SDA terminal pull-up resistance
The SDA terminal is an open drain output. Consequently, it requires an external pull-up resistance. The
appropriate pull-up resistance value is selected from the IC V
measuring data, as well as V
and ILI and other personal icons that control the IC in question.
IL
features., which have been appended as
OL-IOL
Recommended values 2.0k to 10kW
0.45
0.4
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE : VOL (V)
0.05
0
01
VCC=3.0V VCC=5.0V VCC=3.0V
Ta=85°C Ta=−40°C
2
345
OUTPUT CURRENT : IOL (mA)
VCC=3.0V VCC=5.0V VCC=5.0V
Ta=25°C
Fig.19 VOL−I
OL
features (Note : Typ.)
Note : All memory array data are set to “FF” status at time of shipping.

BR24C01A-W / BR24C01AF-W / BR24C01AFJ-W / BR24C01AFV-W / BR24C02-W / BR24C02F-W /
Memory ICs
BR24C02FJ-W / BR24C02FV-W / BR24C04-W / BR24C04F-W / BR24C04FJ-W / BR24C04FV-W
!!!!External dimensions (Units : mm)
BR24C01A-W
BR24C02-W
BR24C04-W
BR24C01AFJ-W
BR24C02FJ-W
BR24C04FJ-W
9.3 ± 0.3
85
14
0.51Min.
2.54
3.2 ± 0.2 3.4 ± 0.3
4.9 ± 0.2
85
6.0 ± 0.3
3.9 ± 0.2
1.375 ± 0.1
0.175
1.27
0.5 ± 0.1
76
4123
0.42 ± 0.1
0.1
DIP8
0.45Min.
6.5 ± 0.3
7.62
0 ~ 15
0.2 ± 0.1
BR24C01AF-W
BR24C02F-W
BR24C04F-W
5.0 ± 0.2
85
4.4 ± 0.2
6.2 ± 0.3
0.3 ± 0.1
1.5 ± 0.1
0.11
1.27
41
0.4 ± 0.1
0.3Min.
0.15 ± 0.1
0.15
SOP8
BR24C01AFV-W
BR24C02FV-W
BR24C04FV-W
6.4 ± 0.3
(0.52)
4.4 ± 0.2
3.0 ± 0.2
1
0.65
548
0.22 ± 0.1
0.15 ± 0.1
1.15 ± 0.1
0.1
0.3Min.
0.1
SOP-J8
SSOP-B8
 Loading...
Loading...