Rockwell Automation 1756 ControlLogix, 1756 GuardLogix, 1769 CompactLogix, 1769 Compact GuardLogix, 1789 SoftLogix Programming Manual
...Page 1

Programming Manual
Logix 5000 Controllers Major, Minor, and I/O Faults
1756 ControlLogix, 1756 GuardLogix, 1769 CompactLogix,
1769 Compact GuardLogix, 1789 SoftLogix, 5069
CompactLogix, 5069 Compact GuardLogix, Studio 5000
Logix Emulate
Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P
Original Instructions
Page 2
Logix 5000 Controllers Major, Minor, and I/O Faults
personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard, and recognize the consequence.
IMPORTANT
Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
temperatures.
for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Important User Information
Read this document and the documents listed in the additional resources section about installation, configuration, and
operation of this equipment before you install, configure, operate, or maintain this product. Users are required to familiarize
themselves with installation and wiring instructions in addition to requirements of all applicable codes, laws, and standards.
Activities including installation, adjustments, putting into service, use, assembly, disassembly, and maintenance are required to
be carried out by suitably trained personnel in accordance with applicable code of practice.
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may be
impaired.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use
or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or liability for
actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or software
described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc., is
prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment, which may lead to
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
Labels may also be on or inside the equipment to provide specific precautions.
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that dangerous voltage may be present.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that surfaces may reach dangerous
ARC FLASH HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a motor control center, to alert people to potential Arc Flash. Arc Flash
will cause severe injury or death. Wear proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Follow ALL Regulatory requirements for safe work practices and
2 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 3

Summary of changes
Topic Name
Reason
This manual includes new and updated information. Use these reference
tables to locate changed information.
Grammatical and editorial style changes are not included in this summary.
Global changes
The Legal noticeshave been updated.
New or enhanced features
This table contains a list of topics changed in this version, the reason for the
change, and a link to the topic that contains the changed information.
Minor Fault Codes on page 33 Updated the Minor Fault Code list to include minor fault type 16,
code 1.
Major fault codes on page 25 Updated the Major Fault Code list to include major fault type 4,
code 95.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 3
Page 4

Page 5

Summary of changes
Major Faults
Minor Faults
I/O Fault Codes
Index
Table of Contents
Preface
Additional resources ................................................................................... 7
Legal Notices ............................................................................................... 7
Chapter 1
Major Fault State ......................................................................................... 9
Recover from a major fault ................................................................... 9
Important points regarding Add-On Instructions ............................ 10
Fault handling during prescan and postscan .................................... 11
Placement of fault routines ................................................................. 12
Choose where to place the fault routine ............................................. 12
Create a fault routine for a program ......................................................... 13
Change a fault routine assignment of a program ............................. 14
Create a routine for the controller fault handler ..................................... 15
Create a routine for the power-up handler .............................................. 17
Programmatically clearing a major fault .................................................. 19
Create a data type to store fault information ................................... 20
Write a routine to clear the fault ......................................................... 21
Clear a major fault during prescan .......................................................... 22
Test a fault routine .....................................................................................23
Create a user-defined major fault ............................................................ 24
Major fault codes ....................................................................................... 25
Chapter 2
Identify minor faults ................................................................................. 31
Minor fault examples ...........................................................................32
Minor fault codes ........................................................................................ 33
Chapter 3
Indications of I/O faults ............................................................................ 37
I/O Fault Codes ......................................................................................... 38
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 5
Page 6

Page 7

Resource
Description
Manual, publication 1756-RM003
available instruction for a Logix5000 controller.
and other certification details.
Legal Notices
Preface
This manual shows how to monitor and handle major and minor controller
faults. The manual also provides lists of major, minor, and I/O fault codes to
use to troubleshoot the system.
This manual is one of a set of related manuals that show common procedures
for programming and operating Logix 5000 controllers.
Additional resources
For a complete list of common procedures manuals, refer to the
Logix 5000
Controllers Common Procedures Programming Manual, publication 1756PM001.
The term Logix 5000 controller refers to any controller based on the Logix
5000 operating system.
These documents contain additional information concerning related
products from Rockwell Automation.
Logix5000 Controllers General Instructions Reference
Product Certifications website, http://www.ab.com Provides declarations of conformity, certificates,
Provides programmers with details about each
View or download publications at
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/
. To order paper copies of
technical documentation, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or
Rockwell Automation sales representative.
Rockwell Automation publishes legal notices, such as privacy policies, license
agreements, trademark disclosures, and other terms and conditions on the
Legal Notices
page of the Rockwell Automation website.
End User License Agreement (EULA)
You can view the Rockwell Automation End-User License Agreement ("EULA")
by opening the License.rtf file located in your product's install folder on your
hard drive.
Open Source Licenses
The software included in this product contains copyrighted software that is
licensed under one or more open source licenses. Copies of those licenses are
included with the software. Corresponding Source code for open source
packages included in this product are located at their respective web site(s).
Alternately, obtain complete Corresponding Source code by contacting
Rockwell Automation via the Contact form on the Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 7
Page 8

Preface
website: http://www.rockwellautomation.com/global/about-
us/contact/contact.page
Please include "Open Source" as part of the request text.
A full list of all open source software used in this product and their
corresponding licenses can be found in the OPENSOURCE folder. The default
installed location of these licenses is
Files\Rockwell\Help\FactoryTalk Services Platform\Release
Notes\OPENSOURCE\index.htm
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common
.
8 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 9
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
Example:
Major Fault State
Chapter 1
Major Faults
This chapter explains major fault codes and how to work with them in the
Logix Designer application.
If a fault condition occurs that prevents an instruction from running, the
instruction aborts and the controller reports a major fault. A major fault halts
logic execution and the controller switches to faulted mode (the OK LED
flashes red).
Depending on the application, you may not want all major faults to shut down
the system. If you do not want all major faults to shut down the system, create
a fault routine to clear the fault and let the application continue to run.
The process of resuming execution after the fault clears is known as fault
recovery.
Do not use fault routines to continually clear all faults on the controller. Program the
fault routine to be selective in the types and number of faults cleared. It is also a
good idea to log the fault occurrence to analyze it later.
When an instruction generates an error due to a fault (for example, a COP with an
indirect addressing programming error), the fault routine skips the instruction and
does not run. This occurs with all instructions.
In a system that uses recipe numbers as indirect addresses, an incorrectly typed number
could produce a major fault.
To keep the entire system from shutting down in the event of this fault, program a fault
routine to clear type 4, code 20, major faults.
See also
Create a routine for the controller fault handler on page 15
Recover from a major fault
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 9
Clear a major fault during prescan on page 22
These examples show fault routines with logic that take specific action after a
major fault. If the fault clears, the faulted instruction does not run and
execution resumes with the next instruction.
Page 10

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Important points regarding
Example 1
In this example, a JSR instruction passes an input parameter containing an
indirect address that is out of bounds. If the fault clears, the JSR instruction
aborts (the subroutine does not run) and execution resumes with the EQU
instruction.
Example 2
In this example, the logic inside an Add-On Instruction generates a fault.
While the logic of an Add-On Instruction may look like a subroutine, it is not–
the Add-On Instruction is an instruction. When a fault occurs inside an AddOn Instruction, the remainder of the Add-On Instruction aborts. If the fault
clears, execution resumes with the MOV instruction.
Add-On Instructions
10 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Keep these considerations in mind when using Add-On Instructions and
major faults.
• The Add-On Instruction stops running at the instruction that caused
the fault. This means that the remainder of the scan mode routine does
not run.
Page 11

Fault handling during
Chapter 1 Major Faults
• If the fault clears, execution resumes at the instruction following the
top-level Add-On Instruction invocation. For example, assume the
Add-On Instruction myAoi in Example 2 invokes a nested Add-On
Instruction myNested, which invokes another nested Add-On
Instruction inner. Furthermore, assume that an instruction inside of
inner causes a fault. If the fault clears, execution resumes with the
MOV instruction (the remainder of inner does not execute; the
remainder of myNested does not execute; and the remainder of myAoi
does not execute.)
• During prescan:
• The Logic routine runs (in prescan mode).
• The Prescan routine runs (in normal scan mode).
• During postscan:
• The Logic routine runs (in postscan mode).
• The Postscan routine runs (in normal scan mode).
If a fault occurs while processing the Logic routine, the Add-On Instruction
aborts (the remainder of the Logic routine does not run and the pre-scan and
post-scan routines do not run). If the fault clears, execution resumes at the
instruction following the top-level Add-On Instruction invocation.
prescan and postscan
See also
Create a fault routine for a program on page 13
The behavior of each instruction varies depending on the mode in which it
runs–true, false, prescan, or postscan. For details about what a specific
instruction does in each mode, see the
Instructions Reference Manual, publication number 1756-RM003.
• Prescan provides a system-defined initialization of the user program
when the controller switches from program mode to run mode.
• Postscan provides a system-defined re-initialization of the logic
invoked from an SFC action, when the action shuts down (if SFCs are
configured for Automatic Reset).
If an array index is out of range during prescan, the controller could generate
a major fault. There are a number of ways this could happen: the controller
loses power, encounters a major fault, or the project is saved while online.
Because the user program, during prescan and postscan, cannot assign values
to tags, the only way to correct these issues is to manually initialize the index
variables using the Logix Designer application or to write a fault handler to
ignore the array faults during prescan. To reduce the need for manual
intervention, the Logix Designer application includes an internal fault
Logix 5000 Controllers General
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 11
Page 12

Chapter 1 Major Faults
values when an action is shut down.
To clear the fault when
See this section
Condition
Fault Type
Placement of fault routines
Choose where to place the
handler. This handler is only used during prescan and only clears array faults
(type 4, fault codes of 20 of 83).
Tip: Array faults are not ignored during postscan because the user program controls index tag
Use a fault routine to program logic to take specific action after a fault, such
as clearing the fault and continuing to run. Configure fault routines to a
program, controller, or to the Power-Up Handler.
ProgramFaultRoutine
ControllerFaultRoutine
Power-UpFaultHandlerRoutine
See also
Create a fault routine for a program on page 13
Create a routine for the controller fault handler on page 15
Create a routine for the power-up handler on page 17
fault routine
12 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Where to place the fault routine depends on the type of fault. Use this table to
determine where in the project to configure the fault routine.
The execution of an instruction faults 4 Creating a Fault Routine for a Program
Page 13
To clear the fault when
See this section
Condition
Fault Type
A motion axis faults
11
mode
Handler
Create a fault routine for a
Communication with an I/O module fails 3 Creating a Routine for the Controller
Watchdog timer for a task expires 6
Chapter 1 Major Faults
Fault Handler
program
The controller powers up in Run or Remote Run
1 Creating a Routine for the Power-Up
See also
Create a fault routine for a program on page 13
Create a routine for the controller fault handler on page 15
Create a routine for the power-up handler on page 17
Configure any routine as the fault routine for a program. The routine
executes when a program fault occurs before the controller transitions to
fault mode.
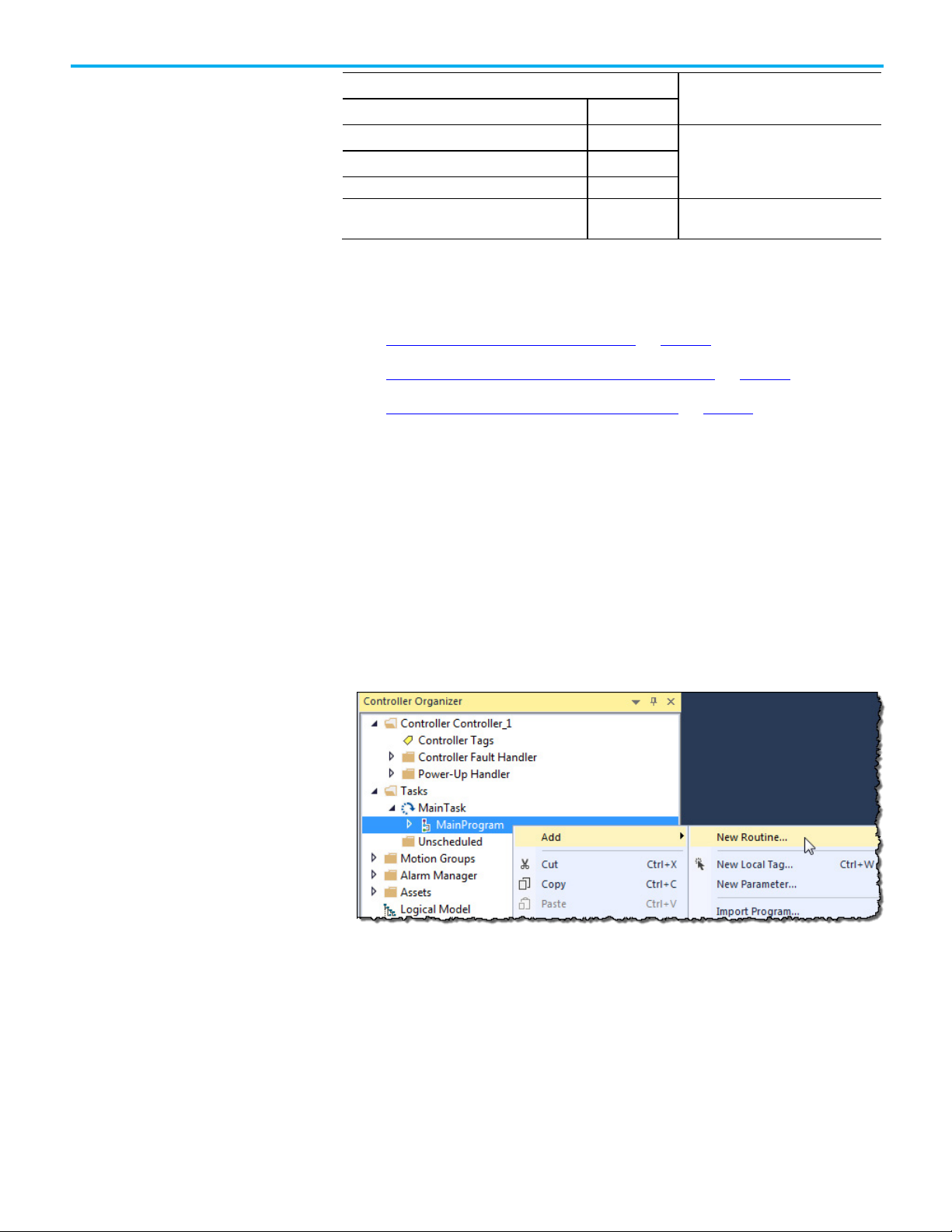
To create a fault routine for a program:
1. Open the project in the Logix Designer application.
2. In the Controller Organizer, right-click MainProgram and select
Add>New Routine.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 13
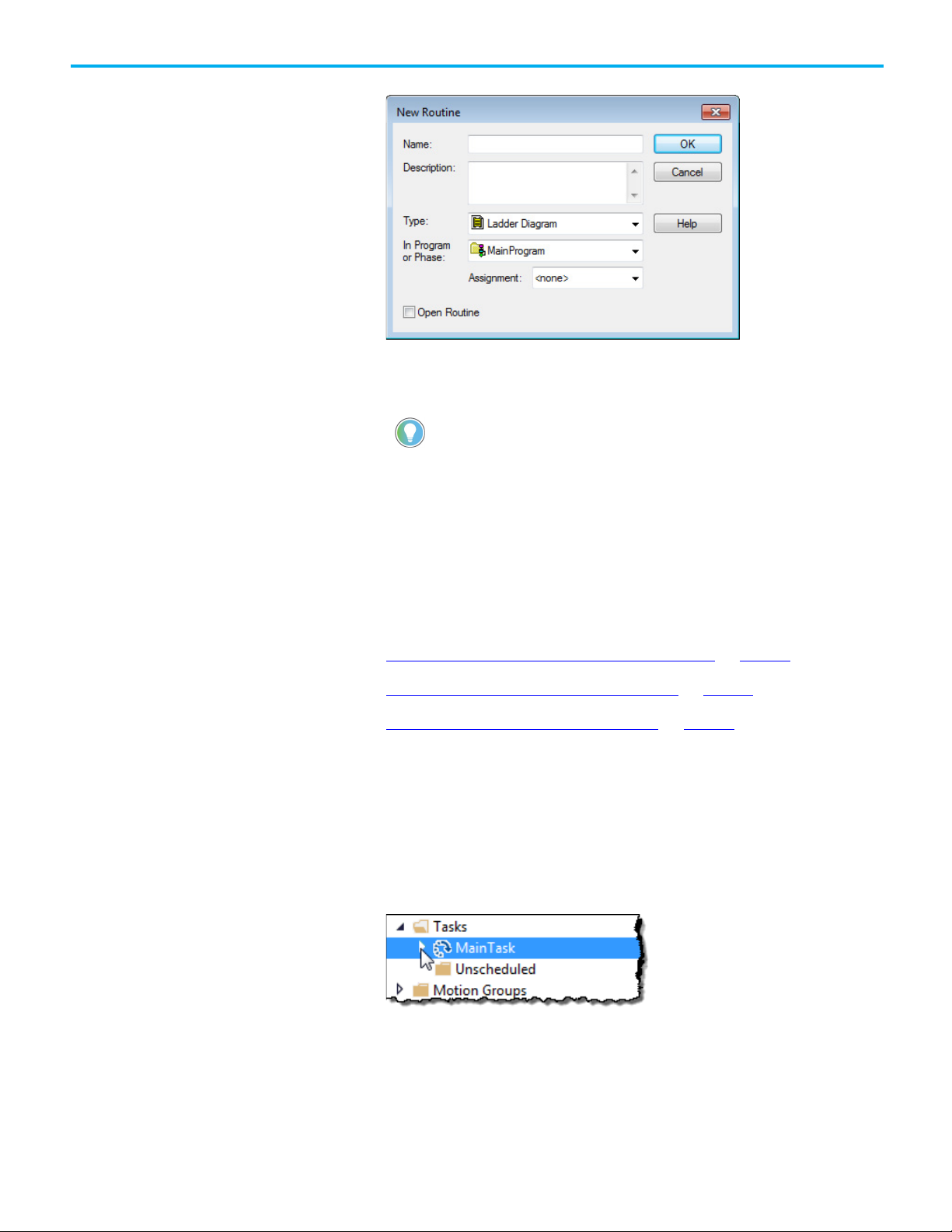
3. On the New Routine dialog box, in Name, type the name of the
routine.
Page 14
Chapter 1 Major Faults
Change a fault routine
4. (optional) In Description, type a description of the routine.
5. In Type, use the default setting, Ladder Diagram.
6. In In Program or Phase, use the default setting, MainProgram.
Tip: If creating a fault routine for the Power-Up Handler or Controller Fault Handler, specify
the program name of either program in In Program or Phase.
7. In Assignment, select Fault.
8. (optional) Select Open Routine to immediately open the ladder logic
program.
9. Select OK.
assignment of a program
See also
Create a routine for the controller fault handler on page 15
Create a routine for the power-up handler on page 17
Choose where to place the fault routine on page 12
Complete these steps to change the routine assigned as the fault routine.
To change a fault routine assignment of a program:
1. In the Controller Organizer, expand the MainTask.
14 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 15
IMPORTANT
This occurs with all instructions.
Chapter 1 Major Faults
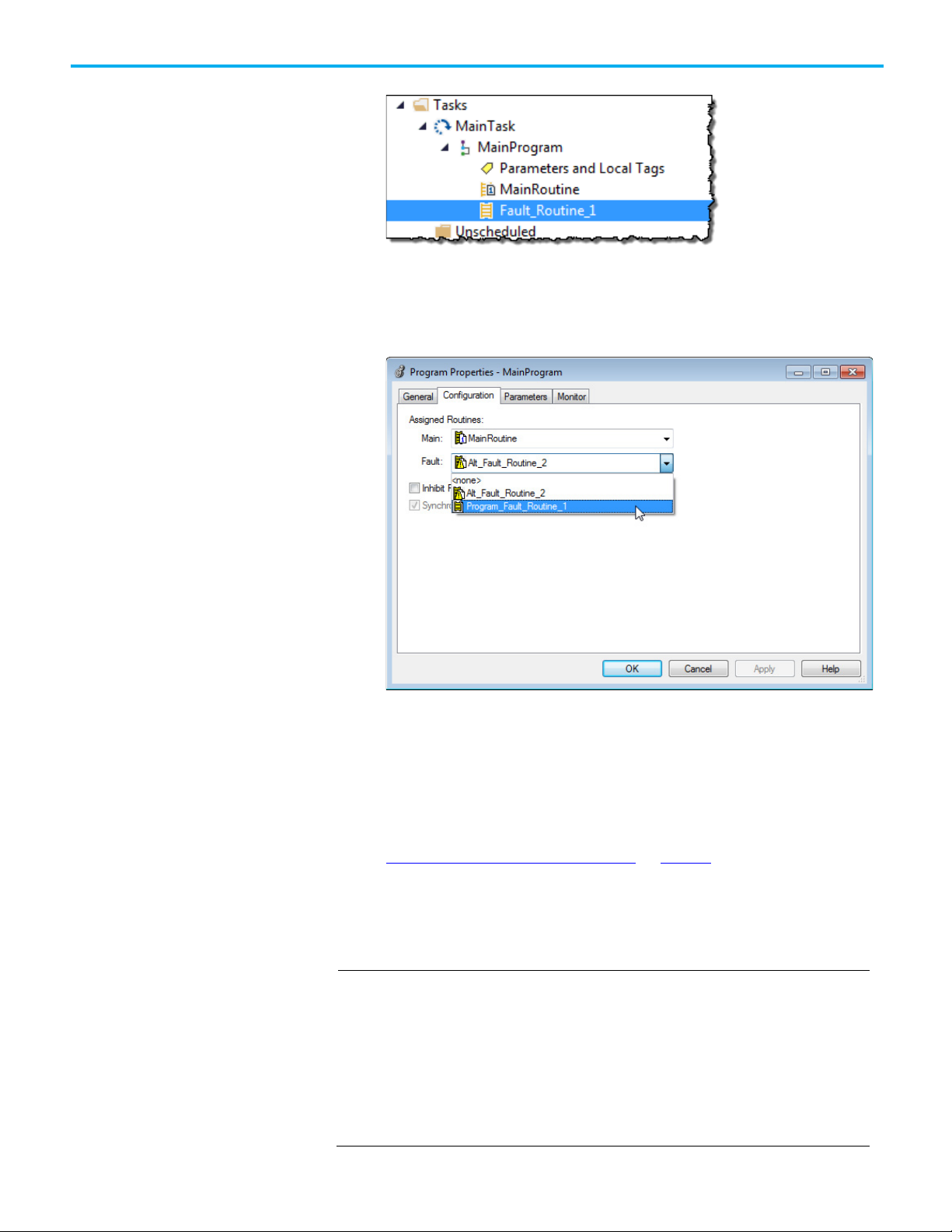
If there is already a fault routine, it appears in the MainProgram.
2. Right-click MainProgram and select Properties.
3. On the Program Properties - MainProgram dialog box, select the
Configuration tab.
4. In Fault, choose the routine to be the program’s fault routine.
Create a routine for the controller fault handler
5. Select OK.
The program specified in step 4 is now indicated as the fault routine in
the MainProgram.
See also
Create a fault routine for a program on page 13
Use these steps to create a fault routine to operate as the controller fault
handler. Program tags are automatically created during this process.
When programming the fault handler, remember that any instruction that is skipped
as part of the fault-handling program does not run when the main tasks and
associated programs run.
For example, if the fault handler skips a JSR instruction that is causing a major fault,
then that JSR instruction, including all of the programming within the subroutine,
does not run.
When an instruction generates an error due to a fault (for example, a COP with an
indirect addressing programming error), the instruction is skipped and does not run.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 15
Page 16
Chapter 1 Major Faults
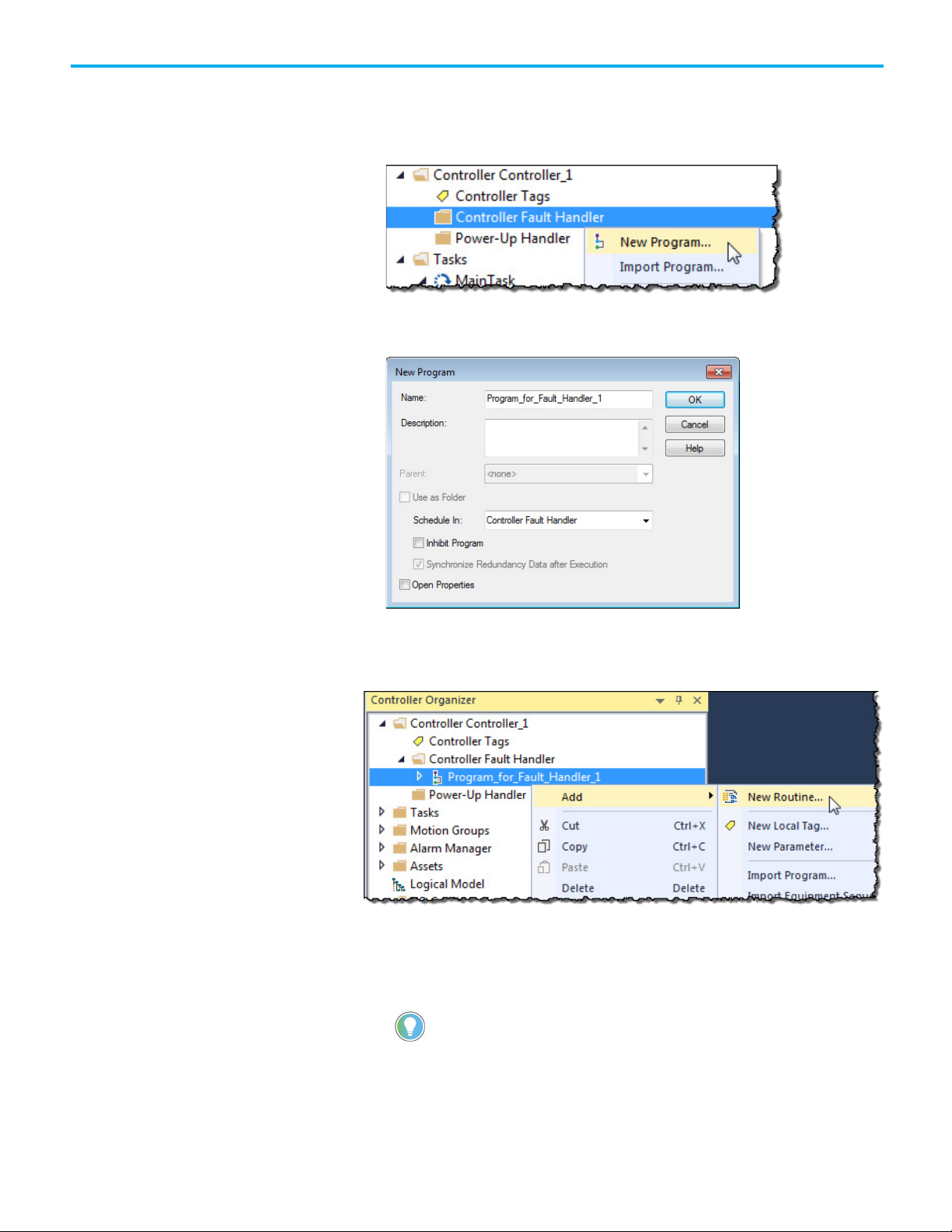
To create a routine for the controller fault handler:
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click Controller Fault Handler and
select New Program.
2. On the New Program dialog box, in Name, type a program name.
Verify that Schedule in is set to Controller Fault Handler.
3. Select OK.
4. In the Controller Organizer, right-click the program created in step 2
and select Add>New Routine.
5. On the New Routine dialog box, in Name, type a name for the routine.
6. In Type, choose the type of routine to create. The default is Ladder
Diagram.
7. In Assignment, use the default setting, Main.
Tip: Even though Fault is an option in the Assignment, assigning the routine as a fault
routine within the Controller Fault Handler is not necessary.
8. Select OK.
16 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 17

To
Do this
the controller enters the faulted state.
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
Create a routine for the
power-up handler
Chapter 1 Major Faults
The fault routine is created in the Controller Fault Handler program.
9. Double-click the fault routine to edit it.
See also
Recover from a major fault on page 9
Fault handling during prescan and postscan on page 11
The Power-Up Handler is an optional task that executes when the controller
powers up in Run or Remote Run modes.
Prevent the controller from returning to Run or
Remote mode
Direct the controller to take specific actions,
then resume normal operation when power
restored
Do not use fault routines to continually clear all faults on the controller. Program the
fault routine to be selective in the types and number of faults cleared.
When an instruction generates an error due to a fault (for example, a COP with an
indirect addressing programming error), the routine skips the instruction and the
instruction does not run. This occurs with all instructions.
Leave the routine for the Power-Up Handler empty. When
power restored, a major fault (type 1, code 1) occurs and
In the Power-Up Handler fault routine, complete these
steps.
1. Clear the major fault (type 1, code 1).
2. Run the appropriate logic for the specific actions
required.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 17
Page 18

Chapter 1 Major Faults
To create a routine for the power-up handler:
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click Power-Up Handler and select
New Program.
2. On the New Program dialog box, in Name, type a program name.
3. Select OK. The program is added to the Power-Up Handler.
4. Right-click the program you created in step 2 and click
Add>New Routine.
18 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 19

within the Power-Up Handler is not necessary.
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
instruction does not run. This occurs with all instructions.
Programmatically clearing
Chapter 1 Major Faults
5. On the New Routine dialog box, in Name, type the name of the
routine.
6. In Assignment, keep the default setting, Main.
Tip: Even though Fault is an option in Assignment, assigning the routine as a fault routine
7. Click OK. The fault routine is added to the Power-Up Handler.
a major fault
8. Double-click new routine to edit.
See also
Major fault codes on page 25
To programmatically clear a major fault that occurs during the execution of
the project:
• Create a data type to store fault information
• Write a fault routine to clear the fault
Do not use fault routines to continually clear all faults on the controller. Program the
fault routine to be selective in the types and number of faults cleared.
When an instruction generates an error due to a fault (for example, a COP with an
indirect addressing programming error), the routine skips the instruction and the
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 19
Page 20

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Attribute
Data Type
Instruction
Description
Create a data type to store
fault information
See also
Create a data type to store fault information on page 20
Write a routine to clear the fault on page 21
Logix 5000 controllers store system information in objects. Unlike PLC-5 or
SLC 500 controllers, there is no status file.
• To access system information, use a Get System Value (GSV) or Set
System Value (SSV) instruction.
• To get status information about a program, access the Program object.
• To get fault information for the program, access the MajorFaultRecord
attribute of the Program object.
MajorFaultRecord DINT[11] GSV
SSV
Records major faults for this program.
Specifies the program name to determine which
Program object to use, or specifies THIS to
access the Program object for the program that
contains the GSV or SSV instruction.
To simplify access to the MajorFaultRecord attribute, complete these steps to
create a user-defined data type.
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click User-Defined and select New
Data Type.
2. On the New Data Type window, enter the data type information as
shown in the table.
20 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 21

Data Type: FAULTRECORD
Name
Description
of the Program object.
Members
Type
INT
Decimal
Fault type (program, I/O, and so forth)
Code
INT
Decimal
Unique code for the fault
Info
DINT[8]
Hex
Fault specific information
Write a routine to clear the
Name Data Type Style Description
Time_Low DINT Decimal Lower 32 bits of the fault timestamp
Time_High DINT Decimal Upper 32 bits of the fault timestamp
3. Select OK.
See also
Major fault codes on page 25
Chapter 1 Major Faults
FAULTRECORD
Stores the MajorFaultRecord attribute or MinorFaultRecord attribute
value
value
fault
Minor fault codes on page 33
A fault routine normally contains logic to identify the program fault. Some
fault routines also contain logic to clear the fault. If a fault clears, the routine
continues executing at the instruction immediately after the instruction that
caused the program fault, and the controller does not enter fault mode. If a
fault routine does not clear the fault, the controller invokes the Controller
Fault Handler program.
Use this example to write a fault routine to clear a major fault.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 21
Page 22

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Item
Reason
Description
structure, enter the first member of the tag.
type of fault that you want to clear.
clear.
clears and the controller resumes execution.
If controller is revision
Then
(out of range) produces a major fault.
12.x
See the release notes for the firmware of your controller.
array subscript that is beyond the range of the array (out of range).
IMPORTANT
Clear a major fault during
Gets the fault type and
code
Checks for a specific
fault.
Sets the fault code
and fault type to zero
Clears the fault The SSV instruction writes:
The GSV instruction:
• Accesses the MajorFaultRecord attribute of this program. This attribute stores information about the fault.
Stores the fault information in the major_fault_record (of type FAULTRECORD) tag. When the tag is based on a
•
The first EQU instruction checks for a specific type of fault, such as program, I/O. In Source B, enter the value for the
The second EQU instruction checks for a specific fault code. In Source B, enter the value for the code that you want to
The first CLR instruction sets the value of the fault type in the major_fault_record tag to zero.
Add the second CLR instruction sets the value of the fault code in major_fault_record tag to zero.
• The new values to the MajorFaultRecord attribute of this program.
• The values contained in the major_fault_record tag. Because the Type and Code member are set to zero, the fault
See also
Create a data type to store fault information on page 20
prescan
If the controller faults immediately after it switches to Run mode, examine
the prescan operation for the fault. Depending on the revision of the
controller, an array subscript that is beyond the range of the array (out of
range) during prescan might cause a fault.
11.x or earlier During prescan, an array subscript that is beyond the range of the array
13.0 or later During prescan, the controller automatically clears any faults due to an
This example shows a fault routine that clears a major fault that occurs during
prescan.
It is good programming practice to check for a specific fault before clearing that
fault.
22 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 23

Item
Reason
Description
• When the controller begins to run the logic, the CPU_scanning bit is always on.
caused the fault.
is too large, or a POS or LEN value of a CONTROL structure is invalid.
set to zero, the fault clears and the logix starts running again.
Test a fault routine
Chapter 1 Major Faults
Identifies when the
controller is in
prescan.
Gets the fault type and
code
Checks for a specific
fault
Clears the fault The SSV instruction does the following:
The program's fault routine uses the status of this bit to determine if the fault occurred during
prescan or normal scan of the logic.
• During prescan, this bit is off. During prescan, the controller resets all bits referenced by OTE
instructions.
The GSV instruction does the following:
• Accesses the program's MajorFaultRecord attribute. This attribute stores information about the
fault.
• Stores the fault information in the major_fault_record (of type FAULTRECORD) tag. When entering a
tag that is based on a structure, enter the first member of the tag.
The first EQU instruction checks for a fault of Type 4, which means that an instruction in this program
The second EQU instruction checks for a fault of Code 20, which means that either an array subscript
The first CLR instruction sets the value of the fault type in the major_fault_record tag to zero.
The second CLR instruction sets the value of the fault type in the major_fault_record tag to zero.
• Writes the new values to the program's MajorFaultRecord attribute.
• Writes the values contained in the major_fault_record tag. Because the Type and Code member are
See also
Use a JSR instruction to test a program's fault routine without creating an
error (simulate a fault).
To test a fault routine:
1. Create a BOOL tag to initiate the fault.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 23
Fault handling during prescan and postscan on page 11
Page 24

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Example:
2. In the main routine or a subroutine of the program, enter this rung,
where:
• test_fault_routine is the tag to initiate the fault.
• Fault_Routine is the fault routine of the program.
When test_fault_routine is on, a major fault occurs and the controller
executes Fault_Routine.
See also
Create a user-defined major fault on page 24
Create a user-defined major fault
To suspend (shut down) the controller based on conditions in the application,
create a user-defined major fault. With a user-defined major fault:
• The fault type = 4.
• Define a value for the fault code. Choose a value between 990 and 999.
Logix Designer reserves these codes for user-defined faults.
• The controller handles the fault the same as other major faults:
• The controller changes to the Program mode and stops executing
the logic.
• Sets the outputs to their configured state or value for faulted mode.
When Tag_1.0 = 1, produce a major fault and generate a fault code of 999.
To create a user-defined major fault:
1. Create a fault routine for the program if one does not exist.
2. Configure the program to use the fault routine if it is not already
assigned.
3. In the main routine of the program, enter this rung, where:
• Tag_1.0 is the tag used to initiate the fault
• Fault_Routine_1 is the fault routine of the program
• 999 is the value of the fault code
24 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 25

Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
1 1 The controller powered on in Run mode.
Execute the power up handler.
Major fault codes
4. When the major fault occurs, the controller enters faulted mode.
Outputs go to the faulted state. The Major Faults tab in the Controller
Properties dialog box displays code 999.
See also
Create a fault routine for a program on page 13
Change a fault routine assignment of a program on page 14
Major fault codes on page 25
The type and code correspond to the type and code displayed in these
locations.
• Controller Properties dialog box, Major Faults tab
• Program object, MajorFaultRecord attribute
Chapter 1 Major Faults
The major fault list includes:
1 16 I/O communication configuration fault detected.
(CompactLogix 1768-L4x controllers only.)
1 40 If the controller uses a battery, then the battery
does not contain enough charge to save the user
program on power down.
If the controller uses an ESM (Energy Storage
Module), then the ESM does not contain enough
charge to save the user program on power down.
1 60 For a controller with no memory card installed,
the controller:
• Detected a non-recoverable fault.
• Cleared the project from memory.
Reconfigure the number of communication modules on the 1768 bus
side of the controller:
• 1768-L43 has a maximum of two modules.
• 1768-L45 has a maximum of four modules.
• Up to four Sercos modules
•
Up to two NetLinx communication modules
To recover from the fault:
• For controllers that use a battery, replace the battery.
• For controllers that use an ESM (Energy Storage Module):
• Allow the ESM to fully charge before powering down the
controller.
• Replace the ESM if the ESM is removable, or replace the
controller if the ESM is not removable.
•
If the problem persists, contact Rockwell Automation support.
To recover from the fault:
1. Clear the fault.
2. Download the project.
3. Change to Remote Run or Run mode.
If the fault persists:
Before cycling power to the controller, record the state of the OK and RS232
status indicators.
Contact Rockwell Automation support.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 25
Page 26

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
• Cleared the project from memory.
mode.
21
program conversion process.
.LEN is invalid.
array size or go beyond dimensions defined.
instruction.
error.
accumulated value.
accumulated.
4
42
JMP to a label that did not exist or was deleted.
Correct the JMP target or add the missing label.
subroutine.
4
90
Using a safety instruction outside a safety task.
Place the safety instruction inside the safety task.
4
94
Nesting limits exceeded.
Restructure the project to reduce the subroutine nesting levels.
error.
1 61 For a controller with a memory card installed, the
controller:
• Detected a non-recoverable fault.
• Wrote diagnostic information to the memory
card.
1 62 For a controller with a Secure Digital (SD) card
installed, the controller:
• Detected a nonrecoverable fault.
• Wrote diagnostic information to the memory
card.
To recover from the fault:
1. Clear the fault.
2. Download the project.
3. Change to Remote Run/Run mode.
If the fault persists, contact Rockwell Automation support.
To recover from the fault:
1. Clear the fault.
2. Download the project.
3. Change to Remote Run or Run mode.
If the fault persists, contact Rockwell Automation support.
When in this state, the controller will not open
any connections or allow a transition to Run
3 16 A required I/O module connection failed. To recover from the fault, check:
• The I/O module is in the chassis.
• The electronic keying requirements.
• The Controller Properties Major Faults tab and the Module
Properties Connection tab for more information about the fault.
3 20
3 23 At least one required connection was not
Possible problem with the chassis. Not recoverable - replace the chassis.
Wait for the controller I/O light to turn green before changing to Run
established before going into Run mode.
mode.
4 16 Unknown instruction encountered. Remove the unknown instruction. This probably happened due to a
4 20 Array subscript too big, control structure .POS or
Adjust the value to be within the defined range. Don’t exceed the
4 21 Control structure .LEN or .POS < 0. Adjust the value so that it is > 0.
4 31 The parameters of the JSR instruction do not
match those of the associated SBR or RET
4 34 A timer instruction has a negative preset or
4 82 A sequential function chart (SFC) called a
Pass the appropriate number of parameters. If too many
parameters are passed, the extra ones are ignored without any
Fix the program to not load a negative value into timer preset or
Remove the jump back to the calling SFC.
subroutine and the subroutine tried to jump back
to the calling SFC. Occurs when the SFC uses
either a JSR or FOR instruction to call the
4 83 The data tested was not inside the required
limits. This occurs with array subscripts used
Adjust the value to be within the valid range. Do not exceed the
array size or go beyond the dimensions defined.
with Boolean arrays and bit level addressing.
4 84 Stack overflow. Reduce the subroutine nesting levels or the number of parameters
passed.
4 89 In an SFR instruction, the target routine does not
Correct the SFR target or add the missing step.
contain the target step.
4 91 Equipment Phase instruction is being called from
Only use the instruction in an Equipment Phase program.
outside an Equipment Phase program.
4 95 The built-in instruction contains an internal
26 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Contact Rockwell Automation support.
Page 27

Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
much with a single controller).
unlocked.
revision of the controller.
checksum.
7
44
Failed to restore processor memory.
Contact Rockwell Automation support.
limit.
limit, and then execute Motion Axis Fault Reset.
limit.
limit, and then execute Motion Axis Fault Reset.
Chapter 1 Major Faults
4 990 -
999
6 1 Task watchdog expired.
User-defined major fault.
User task has not completed in specified period
of time. A program error caused an infinite loop,
Increase the task watchdog, shorten the execution time, make the
priority of this task higher, simplify higher priority tasks, or move
some code to another controller.
or the program is too complex to execute as
quickly as specified, or a higher priority task is
keeping this task from finishing (trying to do too
7 40 Store to nonvolatile memory failed. To recover from the fault:
• Try again to store the project to nonvolatile memory.
• If the project fails to store to nonvolatile memory, replace the
memory board.
If you are using a 1756-L7x controller, verify that the SD card is
•
7 41 Load from nonvolatile memory failed due to
controller type mismatch.
Change to a controller of the correct type or download the project
and store it on the memory card.
7 42 Load from nonvolatile memory failed because
the firmware revision of the project in
Update the controller firmware to the same revision level as the
project that is in nonvolatile memory.
nonvolatile memory does not match the firmware
7 43 Load from nonvolatile memory failed due to bad
Contact Rockwell Automation support.
7 50 The log file certificate can not be verified. When
the controller starts up it attempts to verify the
log file key/certificate combination. Depending
on the verification, the controller takes one of
the following actions:
• If the controller verifies the existing log file
certificate, the controller continues with
existing log directory.
• If the existing certificate cannot be verified,
the controller logs a major fault and attempts
to create a new certificate.
• If the controller successfully creates a new
certificate, it creates a backup log
subdirectory, moves the existing files to that
directory, and continues logging and signing
with the new verification key and log file
certificate.
• If the controller cannot create a new
certificate, the controller writes log entries
to the existing log directory, but does not
update signature files in that directory.
8 1 Attempted to place controller in Run mode with
keyswitch during download.
11 1 Actual position has exceeded positive overtravel
Clear the fault and power cycle the controller. If the problem
persists, contact Rockwell Automation support.
Wait for the download to complete and clear the fault.
Move axis in negative direction until position is within overtravel
11 2 Actual position has exceeded negative overtravel
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 27
Move axis in positive direction until position is within overtravel
Page 28

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
tolerance.
Fault Reset.
Reset.
signals are not in quadrature.
11 6 Drive Fault input was activated.
Clear Drive Fault, and then execute Motion Axis Fault Reset.
module.
fault.
module.
11
10
Motor fault has occurred.
See the DriveFaults axis tag for more information.
11
11
Motor thermal fault has occurred.
See the DriveFaults axis tag for more information.
11
12
Motor thermal fault has occurred.
See the DriveFaults axis tag for more information.
11
14
Drive enable input fault has occurred.
Re-enable the drive enable input and clear the fault.
11
15
Drive phase loss fault has occurred.
Restore full power connection to the drive and clear the fault.
clear the major fault.
system.
modes to Run.
11 3 Actual position has exceeded position error
Move the position within tolerance and then execute Motion Axis
11 4 Encoder channel A, B, or Z connection is broken. Reconnect the encoder channel, and then execute Motion Axis Fault
11 5 Encoder noise event detected or the encoder
Fix encoder cabling, and then execute Motion Axis Fault Reset.
11 7 Synchronous connection incurred a failure. First execute Motion Axis Fault Reset. If that does not work, pull
servo module out and plug back in. If all else fails, replace servo
11 8 Servo module has detected a serious hardware
Replace the module.
11 9 Asynchronous Connection has incurred a failure. First execute Motion Axis Fault Reset. If that does not work, pull
servo module out and plug back in. If all else fails, replace servo
11 13 SERCOS ring fault has occurred.
Verify the integrity of the SERCOS fiber-optic ring network and the
devices on it.
11 16 Drive guard fault has occurred. See the GuardFaults axis tag for more information.
11 32 The motion task has experienced an overlap. The group’s coarse rate is too high to maintain correct operation.
Clear the group fault tag, raise the group’s update rate, and then
12 32 Power to a disqualified secondary controller has
been cycled and no partner chassis or controller
was found upon power up.
To recover from the fault, verify that:
• A partner chassis is connected.
• Power is applied to both redundant chassis.
• Partnered controllers have the same:
• catalog number.
• slot number.
• firmware revision.
12 33 An unpartnered controller has been identified in
the new primary chassis after a switchover.
To recover from the fault, either:
• Remove the unpartnered controller and troubleshoot the cause of
the switchover.
• Add a partner controller to the secondary chassis.
Troubleshoot the cause of the switchover, and synchronize the
•
12 34 Just after a switchover occurs, the keyswitch
positions of the primary and secondary
controllers are mismatched.
The old primary controller is in Program mode
and the new primary controller is in Run mode.
To recover from the fault, either:
• Change the keyswitches from Run to Program to Run mode twice
to clear the fault.
Use the Logix Designer application to go online with the
•
controllers. Then, clear the faults and change both the controllers’
28 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 29

Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
program again to allow the safety task to run.
14 8 Coordinated System Time Master (CST) not found.
Clear the fault. Configure a device to be the CST master.
replace the safety partner.
temperature and apply the required clearance around the chassis.
specific initialization fault has occurred.
specific axis fault has occurred.
Motion Fault bits for details about the fault that occurred.
Chapter 1 Major Faults
14 1 Safety Task watchdog expired.
User task has not completed in a specified
period of time. A program error caused an
infinite loop, the program is too complex to
execute as quickly as specified, a higher priority
task is keeping this task from finishing, or the
Clear the fault.
If a safety task signature exists, safety memory is re-initialized and
the safety task begins executing.
If a safety task signature does not exist, you must re-download the
program to allow the safety task to run.
Reinsert the safety partner, if it was removed.
safety partner has been removed.
14 2 An error exists in a routine of the safety task. Correct the error in the routine in the user-program logic.
14 3 Safety Partner is missing. Install a compatible safety partner.
14 4 Safety Partner is unavailable. Install a compatible safety partner.
14 5 Safety Partner hardware is incompatible. Install a compatible safety partner.
14 6 Safety Partner firmware is incompatible. Install a compatible safety partner.
14 7 Safety task is inoperable.
This fault occurs when the safety logic is invalid,
for example a mismatch in logic exists between
the primary controller and safety partner, a
watchdog timeout occurred, or memory is
Clear the fault.
If a safety task signature exists, safety memory is re-initialized
using the safety task signature and the safety task begins
executing.
If a safety task signature does not exist, you must download the
corrupt.
14 9 Safety partner nonrecoverable controller fault. Clear the fault and download the program. If the fault persists,
17 34 Controller internal temperature has exceeded
operating limit.
17 37 Controller has recovered from an internal
temperature fault.
Measures should be taken to reduce the ambient temperature of the
module. Follow the recommended limits for the ambient (inlet)
Generated when the controller recovers from automatic shutdown.
Shutdown occurs when the modules's temperature exceeds the
temperature threshold of the preservation fault. When the
temperature decreases to a suitable level, this re-enables the
controller voltages and generates the Type 17, Code 37 fault.
18 1 The CIP Motion drive has not initialized correctly. To determine corrective action, see Initialization Faults Attributes
for details about the type of fault that occurred.
18 2 The CIP Motion drive has not initialized correctly.
This fault is indicated when a manufacturer-
18 3 The Physical Axis Fault bit is set, indicating a
fault on the physical axis.
To determine the corrective action, see CIP Initialization Fault - Mfg
attributes for details about the fault that occurred.
To determine corrective action, see CIP Axis Fault attributes for
details about the fault that occurred.
18 4 The Physical Axis Fault bit is set, indicating fault
on the physical axis.
To determine corrective action, see CIP Initialization Fault - Mfg
attributes attributes for details about the fault that occurred.
This fault is indicated when a manufacturer-
18 5 A motion fault occurred. To determine corrective action, see the Motion Fault attribute and
18 6 A CIP Motion Drive fault has occurred.
Reconfigure the faulted motion module to correct the fault.
Usually the fault affects all the axis associated
with the module and all of the associated axes
are shutdown.
18 7 A motion group fault has occurred.
Reconfigure the entire motion subsystem to correct the fault.
Usually the fault affects all of the axes
associated with a motion group.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 29
Page 30

Chapter 1 Major Faults
Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
Motion Drive was unsuccessful.
cannot be recovered.
specific APR fault has occurred.
Guard Safety functionality is used.
the transition to run or test mode.
the controller.
18 8 A fault has occurred during the configuration of a
CIP Motion Drive.
Typically, this fault occurs after an attempt to
update an axis configuration attribute of a CIP
18 9 An Absolute Position Recovery (APR) fault has
occurred and the absolute position of the axis
18 10 An Absolute Position Recovery (APR) fault has
occurred and the absolute position of the axis
cannot be recovered.
This fault is indicated when a manufacturer-
18 128 A fault specific to the Guard Motion safety
function has occurred.
This fault is applicable only when a drive with
20 1 A required license is missing or expired during
See also
Minor fault codes on page 9
To determine the corrective action, see the Configuration Fault in
the Attribute Error Code and Attribute Error ID attributes associated
with the motion or 1756-ENxT module.
To determine the corrective action, see the APR Fault to determine
the cause of the fault.
To determine the corrective action, see the APR Fault - Mfg
attributes to determine the cause of the fault.attributes
To determine the corrective action, see the Guard Motion attributes
and Guard Status bits to determine the cause of the fault.
Insert a CmCard containing all licenses required by the project in
I/O fault codes on page 38
30 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 31

To check for a
Do this
power supply (UPS) fault
Name
Data Type
Style
Type
INT
Decimal
Code
INT
Decimal
Info
DINT[8]
Hex
S:MINOR remains set until the end of the scan.
Identify minor faults
Minor Faults
This chapter explains minor fault codes and how to work with them in the
Logix Designer application.
Use this table to understand how to use ladder logic to monitor information
about common minor faults.
Task overlap 1. Enter a GSV instruction that gets the FaultLog object, MinorFaultBits attribute.
2. Monitor bit 6.
Load from nonvolatile
memory
1. Enter a GSV instruction that gets the FaultLog object, MinorFaultBits attribute.
2. Monitor bit 7.
Chapter 2
Serial port fault 1. Enter a GSV instruction that gets the FaultLog object, MinorFaultBits attribute.
2. Monitor bit 9.
Low battery, energy storage
status or uninterruptable
Instruction-related fault 1. Create a user-defined data type that stores the fault information. Name the data type FaultRecord
1. Enter a GSV instruction that gets the FaultLog object, MinorFaultBits attribute.
2. Monitor bit 10.
and assign the following members.
TimeLow DINT Decimal
TimeHigh DINT Decimal
1. Create a tag that stores the values of the MinorFaultRecord attribute.
2. From the Data Type menu in step 1 of this instruction, choose the data type.
3. Monitor S:MINOR.
4. Use a GSV instruction to get the values of the MinorFaultRecord attribute if S:MINOR is on.
5. Reset S:MINOR if you want to detect a minor fault that is cause by another instruction.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 31
See also
Minor fault codes on page 33
Page 32

Chapter 2 Minor Faults
Example:
or is missing.
Example:
• If S:MINOR is set, the GSV instruction gets information about the fault and resets S:MINOR.
Minor fault examples
Use these examples to check for minor faults.
Checks for a low battery warning
Checks for a minor fault.
Minor_fault_check times for 1 minute (60000 ms) and then automatically restarts itself.
Every minute, minor_fault_check.DN turns on for one scan. When this occurs, the GSV instruction gets the value of
the FaultLog object, MinorFaultBits attribute, and stores it in the minor_fault_bits tag. Because the GSV instruction
only runs once every minute, the scan time of most scans is reduced.
If minor_fault_bits.10 is on, depending on the controller, the battery is low or the ESM or UPS needs to be replaced
Checks for a minor fault that is caused by a specific instruction
Check for a minor fault that is caused by an instruction.
• Multiply value_a by 1000000 and check for a minor fault, such as a math overflow.
• To make sure that a previous instruction did not produce the fault, the rung first clears S:MINOR.
• The rung then executes the multiply instruction.
• If the instruction produces a minor fault, the controller sets S:MINOR.
32 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 33

Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
has failed.
Module RPI Overlap faults.
Minor fault codes
See also
Create a data type to store fault information on page 20
Chapter 2 Minor Faults
Minor faults get recorded in these locations.
• Controller Properties dialog box, Minor Faults tab
• Program object, MinorFaultRecord attribute
The minor fault list includes:
1 15 • A 1769 power supply is connected directly to the
controller’s 1768 CompactBus, with an invalid
configuration.
The 1768 power supply powering the controller
•
3 1 Bus off condition. The connections between the
controller and the I/O modules are broken.
3 94 The current RPI update of an I/O module overlaps
with its previous RPI update.
• Remove the power supply from the 1768 CompactBus and
cycle power to the system.
• Replace the power supply.
Complete these steps to identify the source of the BUS OFF
fault:
The number of local expansion modules in the project matches the
number of modules that are physically installed in the system.
All mounting bases are locked and I/O modules are securely installed on
mounting bases.
All 1734 POINT I/O modules are configured to use the Autobaud rate.
If these steps do not remedy the fault condition, contact
Rockwell Automation support.
Set the RPI rate of the I/O modules to a higher numerical value.
Rockwell Automation recommends that the CompactLogix 5370
L2 and CompactLogix 5370 L3 control systems do not run with
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Minor Faults
Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
Knowledgebase Answer ID 1028837.
adjusting values.
was not found.
4
35
PID delta time 0.
Adjust the PID delta time so that it is > 0.
4
36
PID setpoint out of range.
Adjust the setpoint so that it is in range.
string contains.
or equal to the DATA size of the Source.
• Delete the AHL instruction.
to execute again.
bit 7.
persists.
3 100 The potential exists for data integrity loss with the
module because either or both of the input/output
size > 16 bytes and the module does not support
start and end integrity.
Recover methods:
• Decrease input/output sizes to <= 16 bytes which avoids data
integrity loss concern.
• Contact the module provider to inquire about a version that
supports the start and end integrity function.
For more information, see Rockwell Automation
•
4 4 An arithmetic overflow occurred in an instruction. Fix program by examining arithmetic operations (order) or
4 5 In a GSV/SSV instruction, the specified instance
4 6 In a GSV/SSV instruction, either:
Check the instance name.
Check the Class name and Attribute name.
• Specified Class name is not supported
• Specified Attribute name is not valid
4 7 The GSV/SSV destination tag was too small to hold
Fix the destination or source so it has enough space.
all of the data.
4 30 Bad parameters passed through to the ASCII port. Verify the ASCII configuration settings.
4 51 The LEN value of the string tag is greater than the
DATA size of the string tag.
• Check that no instruction is writing to the LEN member of the
string tag.
In the LEN value, enter the number of characters that the
•
4 52 The output string is larger than the destination. Create a new string data type that is large enough for the
output string. Use the new string data type as the data type for
the destination.
4 53 The output number is beyond the limits of the
destination data type.
Either:
• Reduce the size of the ASCII value.
•
Use a larger data type for the destination.
4 56 The Start or Quantity value is invalid. • Check that the Start value is between 1 and the DATA size of
the Source.
Check that the Start value plus the Quantity value is less than
•
4 57 The AHL instruction failed to execute because the
serial port is set to no handshaking.
6 2 Periodic task overlap.
Periodic task has not completed before it is time
6 3 Event task overlap.
Event task has not completed before it is time to
execute again.
7 49 When the controller loads a project from
Either:
• Change the Control Line setting of the serial port.
Make changes such as simplifying programs, lengthening the
period, or raising the relative priority.
Make changes such as simplifying programs, lengthening the
period, raising the relative priority, or slowing the triggering
event.
Clear the fault.
nonvolatile memory, it logs this minor fault and
sets the FaultLog object, MinorFaultBits attribute,
34 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
9 0 Unknown error while servicing serial port Contact Rockwell Automation Technical Support if the problem
9 1 The CTS line is not correct for current
configuration.
Disconnect and reconnect the serial port cable to the controller.
Verify cabling is correct.
Page 35

Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
• A station number greater than 254 was encountered.
unspecified.
Port Protocol tab, under Controller Properties.
10
10
Battery not detected or needs to be replaced.
Install new battery.
replaced.
attribute or controller program at power down.
controller program at power down.
recovered.
type and fault code.
Chapter 2 Minor Faults
9 2 Poll list error.
A fault was detected with the DF1 master’s poll list,
such as specifying more stations than the size of
the file, specifying more than 255 stations, trying
to index past the end of the list, or polling the
broadcast address (STN #255).
9 3 The RS-232 DF1 Master Active Station Tag is
9 5 DF1 slave poll timeout.
Check for the following errors:
• Total number of stations is greater than the space in the poll
list tag.
• Total number of stations is greater than 255.
• Current station pointer is greater than the end of the poll list
tag.
Specify a tag to be used for the Active Station Tag on the Serial
Determine and correct delay for polling.
The poll watchdog timed out for slave. The master
has not polled this controller in the specified
amount of time.
9 9 The modem contact is lost.
Correct modem connection to the controller.
The DCD or DSR control lines are not being
received in the proper sequence and/or state.
9 10 Data has been dropped or lost from the serial port. Slow down the rate at which the initiator is sending data.
10 11 Safety partner battery not detected or needs to be
10 12 The Energy Storage Module (ESM) is not installed.
Install new battery.
Install an ESM in the controller.
If the controller is powered-down, the
WallClockTime attribute and program are not
maintained.
10 13 The installed ESM is not compatible with the
controller.
10 14 The ESM needs to be replaced due to a hardware
Replace the installed ESM with one that is compatible with the
controller.
Replace the ESM.
fault.
It is not capable of maintaining the WallClockTime
10 15 The ESM cannot store enough energy in the ESM to
maintain the WallClockTime attribute or the
10 16 The uninterruptable power supply (UPS) is missing
or not ready.
Replace the ESM.
Either:
• Install the UPS.
• Check the UPS to make sure it is adequately charged to
provide backup power in the event of power loss.
10 17 The UPS battery has failed and needs to be
Replace the battery in the UPS.
replaced.
13 21 Wall Clock Time out of range. Make sure the Wall Clock Time is set to the correct date/time.
14 12 The Safety project is configured as SIL2/PLd and a
Safety Partner is present.
16 1 This fault occurs when the buffer that stores
unwritten controller log messages runs out of
room and overwrites log messages.
Make sure there is no Safety Partner installed to the right of the
primary controller.
To remove the state that causes this fault, insert an SD Card
into the controller and wait for the controller log to write out the
messages from the controller log buffer.
Log messages that have already been overwritten cannot be
17 1...n An internal controller diagnostic has failed. Contact Rockwell Automation Technical Support with the fault
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Minor Faults
Type
Code
Cause
Recovery Method
Technical Support for further assistance.
controller is in run or test mode.
in the controller.
17 35 Controller internal temperature is approaching
operating limit.
Measures should be taken to reduce the ambient temperature
of the module. Follow the recommended limits for the ambient
(inlet) temperature and apply the required clearance around the
chassis.
17 36 A fan is not present, or is not maintaining desired
Replace the fan.
speed.
19 4 Ethernet Port Fault EtherNet/IP data storm detected.
Investigate network traffic on the Ethernet port and clear the
fault. If problems persists, contact Rockwell Automation
20 1 A required license is missing or expired while the
Insert a CmCard containing all licenses required by the project
See also
Major fault codes on page 25
I/O fault codes on page 38
36 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 37

Indications of I/O faults
Chapter 3
I/O Fault Codes
This chapter explains I/O fault codes and how to work with them in the Logix
Designer application.
The indication of I/O faults displays in various ways depending on the
controller.
• The I/O indicator of the controller (shown in examples below) flashes
green or red.
• The controller status display indicates I/O fault messages.
• The I/O status indicator and messages show in the controller status
area of the Logix Designer application. The indicator flashes green or
red and the corresponding status message indicates an error.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 37
Page 38

Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
I/O Fault Codes
• A yellow warning symbol appears on the module in the
I/O Configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
• A module fault code and description appear in the Connection tab of
the Module Properties dialog box.
Depending where the fault code displays, the code format contains either the
full Hexadecimal number (for example, 16#000A) or the last characters of the
code (for example, #000A).
This table lists common I/O fault codes and a corresponding description and
recovery method when applicable. Each code is listed by the full Hexadecimal
number.
Faults 16#0000 - 16#00ff
16#0001 Connection Error. A connection to a module failed.
38 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 39

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
module’s rotary switch settings.
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
16#0007
Connection Request Error: Bad Class.
A service request is unconnected, but should be connected.
not supported by the module.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#0002 Resource unavailable.
Either:
• there are not enough connections available either for the controller or
for the communication module being used to connect through.
Check the connection use of the controller or communication module. If
all of the connections are used, try to free some of the used
connections or add another module to route the errant connection
through.
• the I/O memory limits of the controller are exceeded.
Check the I/O memory available and make program or tag changes if
needed.
• the I/O module targeted does not have enough connections available.
Check the number of controllers making a connection to this I/O module
and verify that the number of connections is within the limits of the I/O
module.
16#0005 Connection Request Error: Bad Class The controller is attempting to make a connection to the module and has
received an error.
Either:
• the configured address for the connection to the module is incorrect.
• the module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic
keying test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module
options were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact
Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
If you are using a 1756-DHRIO module, verify that the Channel type
selected in the software (DH+ or remote I/O network) matches the
16#0006 Connection Request Error: Bad Class.
16#0008 Service Request Error: Unsupported Service The controller is attempting to request a service from the module that is
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 39
Either:
• the response buffer is too small to handle the response data.
• the module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic
keying test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module
options were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact
Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
Page 40

Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
applicable.
Refer to the Module Info tab to determine the exact cause.
16#000D
Object already exists.
An I/O map instance is created where the instance is already in use.
be changed.
to perform requested service.
Verify that the correct module is being targeted.
16#0014
Undefined or unsupported attribute.
A MSG instruction is configured to change an attribute that does not exist.
Verify that the correct module is being targeted.
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
16#0009 Module Configuration Invalid: parameter error.
Tip: Additional Fault Information for this fault
will be displayed as a hex code on the
Connection Tab.
The configuration for the module is invalid. The module configuration may
have been changed in the Data Monitor or programmatically.
If available for the module, access the Connections tab of the Module
Properties dialog box for the additional fault code. The additional fault
code indicates the configuration parameter that is causing the fault. You
may have to correct multiple parameters before this fault is cleared and
connection is properly established.
16#000A
An attribute in the Get_Attributes_List or
Set_Attributes_List has a non-zero status.
Either:
• a connection is being created where the connection type is invalid.
• an object attribute or tag value is invalid.
If an object attribute or tag is invalid, export the Logix Designer file, then
re-import it. Reschedule the ControlNet network after re-importing if
16#000C Service Request Error: Invalid mode/state
for service request.
The controller is attempting to request a service from the module and has
received an error. First, verify that the module is not faulted.
For an I/O module, this may indicate that the module has one of these
conditions:
• Limited communication, but has a Major Fault
• A firmware update needs to be completed or is currently being
completed.
16#000E Attribute value cannot be set. A MSG instruction is configured to change an attribute value that cannot
16#000F Access permission denied for requested
service.
16#0010 Mode or state of module does not allow object
A MSG instruction has been configured to delete a map object that cannot
be deleted.
The state of the device prevents a service request from being handled.
16#0011 Reply data too large. The reply to a message has a data size that is too large for the
destination.
Change the destination to a tag that can handle the data size and type
being returned.
16#0013 Module Configuration Rejected: Data size too
small.
16#0015 Module Configuration Rejected: Data size too
large.
The configuration for the module is invalid - not enough configuration
data was sent.
The configuration for the module is invalid - too much configuration data
was sent.
Faults 16#0100 - 16#01ff
16#0100 Connection Request Error: Module in Use. • The connection being accessed is already in use.
40 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Either:
• The controller is attempting to make a specific connection to a module
and the module cannot support more than one of these connections.
• The target of a connection recognizes that the owner is attempting to
remake a connection that is already running.
Page 41

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
Configure both the Owner and the Listen-Only connection as Multicast.
16#0107
Connection Request Error: Unknown type.
A connection being accessed was not found.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#0103 Service Request Error: CIP transport class
not supported.
16#0106 Connection Request Error: Module owned
and configured by another controller.
Module may accept only one connection if
Unicast is used.
Either:
• The controller is requesting services not supported by the module.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
An ownership conflict occurred for the connection.
One of these conditions exists:
• The Connection Request to this module has been rejected due to an
Ownership conflict with another Owner (for example, another Controller).
This may occur with modules such as output modules that only allow a
single Owner to configure and control its outputs.
This fault may also occur if the module is configured as Listen Only and
supports only one connection.
• If the Owner is connected to the module using a Unicast connection over
EtherNet/IP, other connections to the module fail since the Owner
controls the one connection.
If the Owner is connected to the module using a Multicast connection
over EtherNet/IP, Unicast connections to the module fail since the Owner
controls the one connection.
16#0108 Connection Request Error: Connection type
(Multicast/Unicast) not supported.
The controller is requesting a connection type not supported by the module.
One of these conditions exists:
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
• The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Keying options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
• You may have configured a consumed tag to use a Unicast connection,
but the producing controller does not support Unicast connections.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 41
Page 42

Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
correct.
first.
values.
16#0109 Connection Request Error: Invalid
connection size.
Tip: Additional Error Information for this
fault will be displayed as the tag name
associated with the connection instance
number that has the fault.
16#0110 Connection Request Error: Module not
configured.
The connection size is inconsistent with that expected.
Either:
• the controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and
cannot - the size of the connection is invalid.
• the controller may be attempting to connect to a tag in a producing
controller whose size does not match the tag in this controller.
• the module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
• the fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Keying options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
If the module is a 1756 ControlNet module, verify that the chassis size is
correct.
For remote I/O adapters, verify that the rack size and/or rack density is
The controller is attempting to set up a Listen Only connection with the
module and cannot - the module has not been configured and connected to
by an Owner (for example, another Controller).
This controller is not an Owner of this module because it is attempting to
establish a Listen Only connection, which requires no module configuration.
It cannot connect until an Owner configures and connects to the module
16#0111 Requested Packet Interval (RPI) out of
range.
Either:
• the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) specified is invalid for this module or
for a module in the path to this module. See the Advanced tab to enable
the RPI from the producer.
• the module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
• for Listen Only connections: the RPI set by the owner of this module is
slower than the one requested. Either increase the requested RPI or
decrease the RPI the owner controller is using.
See the Connection tab in the Module Properties dialog box for valid RPI
42 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 43

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
connections.
the module created in the software and the actual module hardware.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#0113 Connection Request Error: Module
connection limit exceeded.
16#0114 Electronic Keying Mismatch: Electronic
keying product code and/or vendor ID
mismatch.
16#0115 Electronic Keying Mismatch: Electronic
Keying product type mismatch.
16#0116 Electronic Keying Mismatch: Major and/or
Minor revision invalid or incorrect.
The number of connections is greater than what is available on the module.
The number of connections must be reduced or the hardware must be
upgraded.
To reduce the number of connections:
• Change the Flex I/O communication adapter Comm Format from Input or
Output configuration to Rack Optimization. When the Comm Format
changes, the adapter must be removed and recreated in the I/O
configuration tree.
If the configuration uses messaging over ControlNet, sequence the
•
messages to reduce the number that are executing at the same time, or
reduce the number of messages. Messages (MSG instructions) also use
The Product Code of the actual module hardware does not match the
Product Code of the module created in the software.
Electronic Keying failed for this module. You may have a mismatch between
The Product Type of the actual module hardware does not match the
Product Type of the module created in the software.
Electronic Keying failed for this module. You may have a mismatch between
the module created in the software and the actual module hardware.
The Major and/or Minor revisions of the module do not match the Major
and/or Minor revisions of the module created in the software.
Verify that you have specified the correct Major and Minor Revision if you
have chosen Compatible Module or Exact Match keying.
Electronic Keying failed for this module. You may have a mismatch between
the module created in the software and the actual module hardware.
16#0117 Connection Request Error: Invalid
Connection Point.
Tip: Additional Error Information for this
fault appears as the tag name associated
with the controller to controller (C2C) that
has the fault.
The connection is to an invalid port or port that is already in use.
One of these conditions exists:
• Another controller owns this module and has connected with a
Communications Format different than the one chosen by this controller.
Verify that the Communications Format chosen is identical to that
chosen by the first owner controller of the module.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
• The controller may be attempting to connect to a nonexistent tag in a
producing controller.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 43
Page 44

Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
not open.
Verify that this number has not been exceeded.
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
use.
16#0118 Module Configuration Rejected: Format
error.
16#0119 Connection Request Error: Module not
owned.
16#011A Connection Request Error: Out of
Connection Resources
An invalid configuration format is used.
One of these conditions exists:
• The configuration class specified does not match the class supported by
the module.
• The connection instance is not recognized by the module.
• The path specified for the connection is inconsistent.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the
module specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing
the connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected
to does not have the same features or settings as the module specified
in the I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or
service being attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
The controlling connection is not open.
Where a Listen Only connection is requested, the controlling connection is
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and
cannot - resources required are unavailable.
If the module is a 1756 ControlNet module, up to five controllers can make
Rack Optimization connections to the module. Verify that this number has
not been exceeded.
If the module is a 1794-ACN15, 1794-ACNR15, or 1797-ACNR15 adapter, only
one controller can make a Rack Optimization connection to the module.
16#0203 Connection timed out. The owner or originator recognizes that the target device is on the network or
16#0204 Connection Request Error: Connection
request timed out.
44 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Faults 16#0200 - 16#02ff
backplane, however, I/O data and messages are not being responded to. In
other words, the target can be reached, but its response is not as expected.
For example, this fault may be indicated where multicast Ethernet packets are
not returned.
When this fault occurs, the controller usually attempts to continuously remove
and remake the connection.
If you are using FLEX I/O modules, verify that you are using the correct
terminal device.
The controller is attempting to make a connection, however, the target module
is not responding.
The device also appears to be missing from the backplane or network.
To recover, take these actions:
• Verify that the module has not been removed and is still functioning and
receiving power.
• Verify that the correct slot number has been specified.
• Verify that the module is properly connected to the network.
If you are using FLEX I/O modules, verify that the correct terminal block is in
Page 45

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#0205 Connection Request Error: Invalid
parameter.
16#0206 Connection Request Error: Requested
size too large.
Either:
• The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - a parameter is in error.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the
connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to
does not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the
I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
Either:
• The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - the request size is too large.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the
connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to
does not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the
I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 45
Page 46
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
Distribute the load on another bridge module.
ControlNet software to schedule or reschedule the ControlNet network.
cleared when the CCM is located.
Verify that all modules in the I/O Configuration tree are the correct modules.
Faults 16#0301 - 16#03ff
16#0301 Connection Request Error: Out of buffer
memory.
16#0302 Connection Request Error: Out of
communication bandwidth.
One of these conditions may exist:
• The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - a module in the path is out of memory.
• The controller may be attempting to connect to a tag in a producing controller
that is not marked as being produced.
• The controller may be attempting to connect to a tag in a producing controller.
That tag may not be configured to allow enough consumers.
• Reduce the size or number of connections through this module.
• One of the network modules between the module and the controller may be out
of memory. Check network configuration of the system.
• The module may be out of memory. Check system configuration and
capabilities of module.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the connection
or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying test.
This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options were used
in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to does
not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the I/O
configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - a module in the path has exceeded its communication
bandwidth capacity.
Increase the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) and reconfigure your network with
RSNetWorx.
16#0303 Connection Request Error: No bridge
available.
16#0304 Not configured to send scheduled data. The ControlNet module is not scheduled to send data. Use RSNetWorx for
16#0305 Connection Request Error: ControlNet
configuration in controller does not
match configuration in bridge.
16#0306 No ControlNet Configuration Master
(CCM) available.
16#0311 Connection Request Error: Invalid port. The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
46 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - a module in the path has exceeded its communication
bandwidth capacity.
Distribute the load on another bridge module.
The ControlNet configuration in the controller does not match the configuration
in the bridge module. This may occur because a ControlNet module was changed
after the network was scheduled, or because a new control program has been
loaded into the controller.
Use RSNetWorx for ControlNet software to reschedule the connections.
The ControlNet Configuration Master (CCM) cannot be found. The 1756-CNB and
PLC-5C modules are the only modules capable of being a CCM and the CCM must
be node number 1.
Verify that a 1756-CNB or PLC-5C module is at node number 1 and is functioning
properly.
This fault may temporarily occur when the system is powered up and will be
received an error.
Page 47

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
to this module.
number selected.
number of consumers on the tag.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#0312 Connection Request Error: Invalid link
address.
16#0315 Connection Request Error: Invalid
segment type.
16#0317 Connection Request Error: Connection
not scheduled.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - an invalid link address has been specified. A link address can
be a slot number, a network address, or the remote I/O chassis number and
starting group.
Verify that the chosen slot number for this module is not greater than the size of
the rack.
Verify that the ControlNet node number is not greater than the maximum node
number configured for the network in RSNetWorx for ControlNet software.
The segment type or route is invalid.
Either:
• the controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - the connection request is invalid
• the module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the connection
or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying test.
This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options were used
in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to does
not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the I/O
configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
The controller is attempting to set up a ControlNet connection with the module
and has received an error.
Use RSNetWorx for ControlNet software to schedule or reschedule the connection
16#0318 Connection Request Error: Invalid link
address - cannot route to self.
16#0319 Connection Request Error: No secondary
resources available in redundant
chassis.
16#031a Connection Request Error: Rack
Connection Refused.
16#031e Connection Request Error: Cannot
consume tag.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - the link address is invalid.
Verify that the associated ControlNet module has the correct slot and/or node
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error - the redundant module does not have the necessary resources
to support the connection.
Reduce the size or number of connections through this module or add another
controller or ControlNet module to the system.
The controller is attempting to set up a Direct connection with the module and
has received an error. A Rack Optimized connection has already been established
to this module through the 1756-CNB/R in the same chassis.
• Connect to this module via the 1756-CNB/R in the same chassis.
• Connect to this module via a different 1756-CNB/R in order to use a Direct
connection.
• Change the first connection from Rack Optimized to Direct, and then
reestablish the second direct connection.
• Connect to this module from a controller in the same chassis as the module (do
not connect via 1756-CNB/R.
• The controller is attempting to connect to a tag in a producing controller and
has received an error.
The controller is attempting to connect to a tag in a producing controller and
•
that tag has already been used by too many consumers. Increase the maximum
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 47
Page 48
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
consume tag.
symbol instance.
• the connection requested is not a listener or a controlling connection type.
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
controlling application for information on how to do this.
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
Rockwellautomation.com.
Rockwellautomation.com.
returned an error from the module. Check for duplicate Drive Nodes.
module.
16#031f Connection Request Error: Cannot
16#0322 Connection Request Error: Connection
point mismatch
No SC (servicing controller) connection object was found that corresponds to a
A connection point mismatch has occurred.
Either:
• a new connection requested does not match the existing connection. Check
the controllers that are using the connection and verify that all the
configurations are identical.
Faults 16#0800 - 16#08ff
16#0800 Network link in path to module is offline. No interpretation available.
16#0801 Incompatible multi-cast RPI. No interpretation available.
16#0810 No target application data available. The controlling application has not initialized the data to be produced by
the target device. This may be caused when "Send Data" connections are
configured in a target device and the controlling application for that target
device has not initialized the data to be produced.
For the target device associated with the "Send Data" connection reporting
this connection error, start the controlling application and perform at least
one write of data. Refer to the documentation for the target device and its
16#0814 Connection Request Error: Data Type
Mismatch.
Faults 16#fd00 - 16#08ff
16#fd03 Connection Request Error: Required Connection
missing
16#fd04 Connection Request Error: No CST Master
Detected
16#fd05 Connection Request Error: No Axis or Group
Assigned.
Invalid connection status information was found.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and
has received an error - this module requires a particular set of
connections and connection types, and one of those connection types is
missing.
• Contact Rockwell Automation technical support at
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and
has received an error - this module requires a CST master in the chassis.
• Configure a module (typically a controller) in this chassis to be the CST
master.
• Contact Rockwell Automation technical support at
Rockwellautomation.com.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and
has received an error - this module requires an axis or group table
assigned.
• Assign a Group or Axis.
• Contact Rockwell Automation technical support at
16#fd06 Transition Fault The controller command to transition the SERCOS ring to a new phase
16#fd07 Incorrect SERCOS Data Rate An attempt to configure the SERCOS ring failed. The baud rate for all
48 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
devices must be the same and supported by the drives and the SERCOS
Page 49

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
• Error in drive data returned to SERCOS module
returned an error.
selection in the Expansion I/O list.
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
pointer.
received an error.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#fd08 SERCOS Comm Fault Mainly two sets of faults may cause a Comm. Fault - Physical and
interface faults.
A possible source of physical faults is:
• Broken ring
• Loose connector
• Fiber optics not clean
• Electrical noise due to improper drive grounding
• Too many nodes on the ring
Interface errors are encountered when you are configuring third party
drives.
A possible source of interface errors is:
• No SERCOS MST (Protocol Error)
• Missed AT (drive did not send data when expected)
• SERCOS timing error in phase 3
16#fd09 Node Initialization Fault An attempt by the controller to configure the node for cyclic operation
16#fd0a Axis Attribute Error A bad response was received from a motion module.
16#fd0c Error Different Grandmaster Fault The end device has a different grandmaster than the controller.
16#fd1f Bad Safety Protocol Format An error occurred adding the safety network segment to a route.
16#fd20 No Safety Task No safety task appears to be running.
16#fd22 Chassis Size Mismatch Verify the number of physical expansion I/O modules configured for the
controller and then update the number of modules selected from the
Expansion I/O list on the General page in the Controller Properties dialog.
16#fd23 Chassis Size Exceeded To verify the number of physical expansion I/O the controller supports,
open the Controller Properties dialog and expand the Expansion I/O list on
the General page.
Configure the number of physical expansion I/O modules to match the
16#fe01
16#fe02 Requested Packet Interval (RPI) out of range. The Requested Packet Interval (RPI) specified is invalid for this module.
16#fe03
16#fe04 Connection Request Error: Invalid input data
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 49
Faults 16#fe00 - 16feff
An invalid configuration format was encountered.
•
The input connection point has not been set.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
See the Connection tab for valid RPI values.
Page 50

Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
pointer.
received an error.
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
16#fe05 Connection Request Error: Invalid input data
size.
16#fe06
16#fe07
16#fe08 Connection Request Error: Invalid output data
16#fe09 Connection Request Error: Invalid output data
size.
Either:
• The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the
connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to
does not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the
I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
The input force point has not been set.
The output connection point has not been set.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
Either:
• The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the
connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to
does not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the
I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
16#fe0a
16#fe0b Invalid symbol string. Either:
50 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
The output force pointer has not been set.
• The tag to be consumed on this module is invalid. Verify that the tag is
marked as being produced.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the
connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to
does not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the
I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
Page 51

Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
16#fe0e
Automatic Firmware Update in progress.
The module is currently being updated.
file incompatible with the module.
file not found.
file invalid.
16#fe12
Automatic Firmware Update Failed.
An error has occurred while updating the module.
Active Connections.
identity.
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
Verify that the path to this module is a valid length.
being in an invalid state.
Verify that the path to this module is a valid length.
Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
16#fe0c Invalid PLC-5 instance number. The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the PLC-5 and has
received an error.
Verify that the instance number specified has been properly specified in the
PLC-5.
16#fe0d Tag does not exist in peer controller. The symbol instance number was found to not be set.
16#fe0f Automatic Firmware Update Failed: Firmware
16#fe10 Automatic Firmware Update Failed: Firmware
16#fe11 Automatic Firmware Update Failed: Firmware
16#fe13 Automatic Firmware Update Failed: Detected
16#fe14 Automatic Firmware Update pending:
Searching NVS file for appropriate module
16#fe22
16#fe23
Faults 16#ff00 - 16#ffff
16#ff00 Connection Request Error: No connection
instance.
16#ff01 Connection Request Error: Path to module
too long.
Firmware supervisor has attempted to update an unsupported module.
The firmware file to update the module cannot be found.
The firmware file is corrupted.
An active connection could not be made to the target module.
The firmware file is currently being read.
The target-to-originator netparams connection type is invalid.
The target-to-originator netparams connection does not specify whether
unicast is allowed.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error.
Verify that the physical module is the same module type (or is a compatible
module) as created in the software.
If the module is a 1756-DHRIO module in a remote chassis (connected via a
ControlNet network), verify that the network has been scheduled with
RSNetWorx software.
Even after the network has been scheduled with RSNetWorx for ControlNet
software, if you are online and if the 1756-DHRIO module is configured for DH+
network only, a #ff00 Module Fault (no connection instance) may occur. The
module is properly communicating even though Faulted is displayed as its
Status on the Module Properties dialog box. Disregard the error message and
fault status and continue.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error.
16#ff04
16#ff08 Connection Request Error: Invalid path to
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 51
module.
The remote controller’s map instance attempted to access a connection while
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error.
Page 52

Chapter 3 I/O Fault Codes
Code
String
Explanation and Possible Causes/Solutions
16#ff0b Module Configuration Invalid: bad format. Either:
16#ff0e Connection Request Error: No connections
accepted to bridge.
See also
• The configuration for the module is invalid.
• The module in use (that is, the physical module) is different than the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree and is therefore causing the
connection or service to fail.
The fault may occur even when the module passed the electronic keying
test. This may result when Disable Keying or Compatible Module options
were used in the module configuration instead of the Exact Match option.
Despite passing the electronic keying test, the module being connected to
does not have the same features or settings as the module specified in the
I/O configuration tree and does not support the connection or service being
attempted.
Check the module in use and verify that it exactly matches the module
specified in the I/O configuration tree of the Logix Designer application.
The controller is attempting to set up a connection with the module and has
received an error.
Major fault codes on page 25
Minor fault codes on page 33
52 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 53

Index
Index
monitor minor 31
routine, create 13
shown in Module Properties 37
test a fault routine 22
Fault Handler
create routine 15
fault handling during prescan and postscan
1
11
1756-L2x
I/O fault indicator 37
1756-L6x
I/O fault indicator 37
C
CIP Motion
major fault codes 23
clear
major fault 9, 18
codes
I/O faults 37, 38
major fault 23
minor fault 33
controller
shut down 23
status in RSLogix 5000 37
suspend 23
create
data type
store fault information 19
fault routine 13
routine for Fault Handler 15
routine for Power-Up Handler 16
E
I
I/O 38
configuration warning 37
I/O faults
indication of 37
indicator
I/O fault 37
indirect address 21
instruction causing minor fault 31
M
major fault
codes 23
create user-defined 23
develop fault routine 9
how to cleare 18
major faults
CIP Motion 23
minor fault
codes 33
logic 31
Module Properties
fault in 37
motion
major faults 23
ESM fault 31, 33
F
fault
clear 9
codes, I/O 38
codes, major 23
codes, minor 33
create user-defined 23
develop routine to clear fault 9
during prescan 21
I/O 38
indirect address 21
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020 53
Power-Up Handler
prescan
program
recovering from a major fault 9
P
create a routine 16
clear a major fault 21
create fault routine 13
R
important points regarding Add-On
Instructions 9
Page 54

Index
routine 13
create fault 13
Fault Handler 15
Power-Up Handler, create 16
S
shut down the controller 23
status
controller in RSLogix 5000 37
store faults
create data type 19
suspend
controller 23
T
test a fault routine 22
U
UPS fault 31, 33
warning
ESM fault 31, 33
UPS fault 31, 33
W
54 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Page 55

Technical Support Center
Knowledgebase
Local Technical Support Phone Numbers
Literature Library
Product Compatibility and Download Center
Rockwell Automation support
Use these resources to access support information.
(PCDC)
Find help with how-to videos, FAQs, chat, user forums, and product notification
updates.
Access Knowledgebase articles. rok.auto/knowledgebase
Locate the telephone number for your country. rok.auto/phonesupport
Find installation instructions, manuals, brochures, and technical data publications. rok.auto/literature
Get help determining how products interact, check features and capabilities, and
find associated firmware.
rok.auto/support
rok.auto/pcdc
Documentation feedback
Your comments help us serve your documentation needs better. If you have any suggestions on how to improve our content, complete the form at
rok.auto/docfeedback
.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
At the end of life, this equipment should be collected separately from any unsorted municipal waste.
Rockwell Automation maintains current product environmental information on its website at rok.auto/pec.
Allen-Bradley, expanding human possibility, Logix, Rockwell Automation, and Rockwell Software are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
EtherNet/IP is a trademark of ODVA, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
Rockwell Otomayson Ticaret A.Ş. Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752, İçerenkÖy, İstanbul, Tel: +90 (216) 5698400 EEE YÖnetmeliğine Uygundur
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM014M-EN-P - September 2020
Supersedes Publication 1756-PM014L-EN-P - November 2018 Copyright © 2020 Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...