Page 1

User Manual
Original Instructions
440G-EZ Interlocking Safety Switch
Catalog Numbers 440G-EZS21STL05J, 440G-EZS21STL05H
Page 2

Important User Information
Read this document and the documents listed in the additional resources section about installation, configuration, and
operation of this equipment before you install, configure, operate, or maintain this product. Users are required to
familiarize themselves with installation and wiring instructions in addition to requirements of all applicable codes, laws,
and standards.
Activities including installation, adjustments, putting into service, use, assembly, disassembly, and maintenance are
required to be carried out by suitably trained personnel in accordance with applicable code of practice.
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may
be impaired.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from
the use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or
liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or
software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation,
Inc., is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous
environment, which may lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property
damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard, and recognize the consequence.
IMPORTANT Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Labels may also be on or inside the equipment to provide specific precautions.
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that dangerous
voltage may be present.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that surfaces may
reach dangerous temperatures.
ARC FLASH HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a motor control center, to alert people to
potential Arc Flash. Arc Flash will cause severe injury or death. Wear proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Follow ALL
Regulatory requirements for safe work practices and for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface
Who Should Use This Publication?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Terminology. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Summary of Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Additional Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Chapter 1
Safety Information Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Intended Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Requirements for Qualified Personnel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Project Planning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Mechanical Mounting, Electrical Installation,
and Commissioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Operation and Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Chapter 2
Product Overview Structure and Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Product Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Product Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Locking Principle. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Protective Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Status Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 3
Project Planning Manufacturer of the Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Operating Entity of the Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Mounting Location. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Distance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Mounting Methods. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Electrical Control Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
OSSDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Course of the OSSD Test Over Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Locking Solenoid Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Application Diagnostic Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Thorough-check Concept. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Regular Thorough Check Minimum Requirements . . . . . . . . . . 18
Chapter 4
Installation Mount Multiple Safety Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Mount the Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Mount the Actuator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 5
Wiring Notes on c-UL-us . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Device Connection (M12, 5-pin). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Device Connection (M12, 8-pin). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Connect Safety Switches with T-connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Chapter 6
Commissioning Switch On. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Thorough-check Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Chapter 7
Maintenance and
Troubleshooting
Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Clean the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Regular Thorough Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Appendix A
Specifications Technical Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Approximate Dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Appendix B
Ordering Information Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Appendix C
Replacement Parts/Accessories Replacement Parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Appendix D
Declaration of Conformity (DoC) EU DoC (excerpt) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Complete EU DoC for Download. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
4 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 5
Preface
This user manual contains the information that is needed during the lifecycle of
the 440G-EZ electromagnetic safety switch.
This user manual must be made available to all people who work with the safety
switch. The structure of this user manual is based on the lifecycle phases of the
safety switch: project planning, mounting, electrical installation, commissioning,
operation, and maintenance.
Who Should Use This Publication?
Terminology
These operating instructions are intended for use by the following:
• Project developers (planners, developers, designers)
•Installers
•Electricians
• Safety experts (such as CE authorized representatives, compliance officers,
and people who test and approve the application)
•Operators
•Maintenance personnel
The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout this manual. For
definitions of terms not listed here, refer to the Allen-Bradley Industrial
Automation Glossary, publication AG-7.1
Term Definition
Dangerous state A status of the machine or facility, where people can be injured. Protective devices help prevent this
risk if the machine is operated within its intended use.
The figures in this document always show the dangerous state of the machine as movement of a
machine part. In practice, there are different dangerous states, such as:
• Machine movements
•Electrical parts
• Visible and invisible beam
• A combination of multiple hazards
.
Summary of Changes
This publication contains updated information in Tab le 3 o n pa ge 31 .
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 5
Page 6

Preface
Additional Resources
These documents contain additional information concerning related products
from Rockwell Automation.
Resource Description
440G-EZ Interlocking Safety Switch Installation
Instructions, publication 440G-IN019
Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding Guidelines,
publication 1770-4.1
Product Certifications website: rok.auto/certifications Provides declarations of conformity, certificates, and
You can view or download publications at rok.auto/literature
Provides installation information for 440G-EZ switches.
Provides general guidelines for installing a
Rockwell Automation® industrial system.
other certification details.
.
6 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 7

Safety Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
Intended Use
This chapter contains general safety information about the safety switch.
Further information about specific product use situations can be found in the
relevant chapters.
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
• Read this publication carefully and make sure that you understand the content
fully before working with the device.
• Follow all safety notes in this publication.
The 440G electromagnetic safety switch is a transponder safety switch with a
locking function, which is controlled without contact by actuators and is suitable
for the following applications:
• Monitoring of movable physical guards
• Locking device for process protection
The safety switch must only be used within the limits of the prescribed and
specified technical data and operating conditions.
Incorrect use, improper modification of, or tampering with the safety switch
invalidates any warranty from Rockwell Automation; in addition, any
responsibility and liability of Rockwell Automation for damage and secondary
damage that this action causes is excluded.
The safety switch is not suitable for the ambient conditions such as, but not
limited, to the following:
• Applications in which the dangerous state cannot be ended immediately
(stopping time)
• Radioactivity (exception: natural radioactivity)
•Vacuum or high pressure
• High UV load
• In the vicinity of low-frequency RFID devices
• In the vicinity of magnetic fields
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 7
Page 8

Chapter 1 Safety Information
ATT EN TI ON : Improper use of the safety switch
If a voltage drop occurs, the locking device unlocks regardless of whether the
dangerous state of the machine has ended.
This safety switch has a simple electromagnetic locking device. There is no locking
device monitoring.
• Do not use the safety switch as a safety locking device according to EN 14119.
• Do not use the safety switch in applications in which the dangerous state
cannot be ended immediately (stopping/run-down time).
IMPORTANT Passing metal chips may impair the function of the safety switch.
Requirements for Qualified Personnel
Only qualified safety personnel can configure, mount, connect, commission, and
service the safety switch.
Project Planning
For project planning, a person is considered competent when they have expertise
and experience in the selection and use of protective devices on machines and is
familiar with the relevant technical rules and national work safety regulations.
Mechanical Mounting, Electrical Installation, and Commissioning
For the task, a person is considered qualified when they have the expertise and
experience in the relevant field and is sufficiently familiar with the application of
the protective device on the machine to be able to assess whether it is in an
operationally safe state.
Operation and Maintenance
For operation and maintenance, a person is considered competent when they
have the expertise and experience in the relevant field and is sufficiently familiar
with the application of the protective device on the machine and the machine
operator has instructed them in its operation.
8 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 9
Product Overview
123
4
65
Chapter 2
Structure and Function
Product Features
The safety switch is an interlocking device with a locking device consisting of a
non-contact sensor with locking solenoid and a coded actuator. The actuator has
a low coding level.
If the protective device is closed, the actuator is led to the sensor. When the
actuation field is reached, the actuator code is read out and evaluated by RFID. If
the code is valid, the safe output signal switching device (OSSD) switches.
If the locking solenoid is supplied with power, the locking device is active.
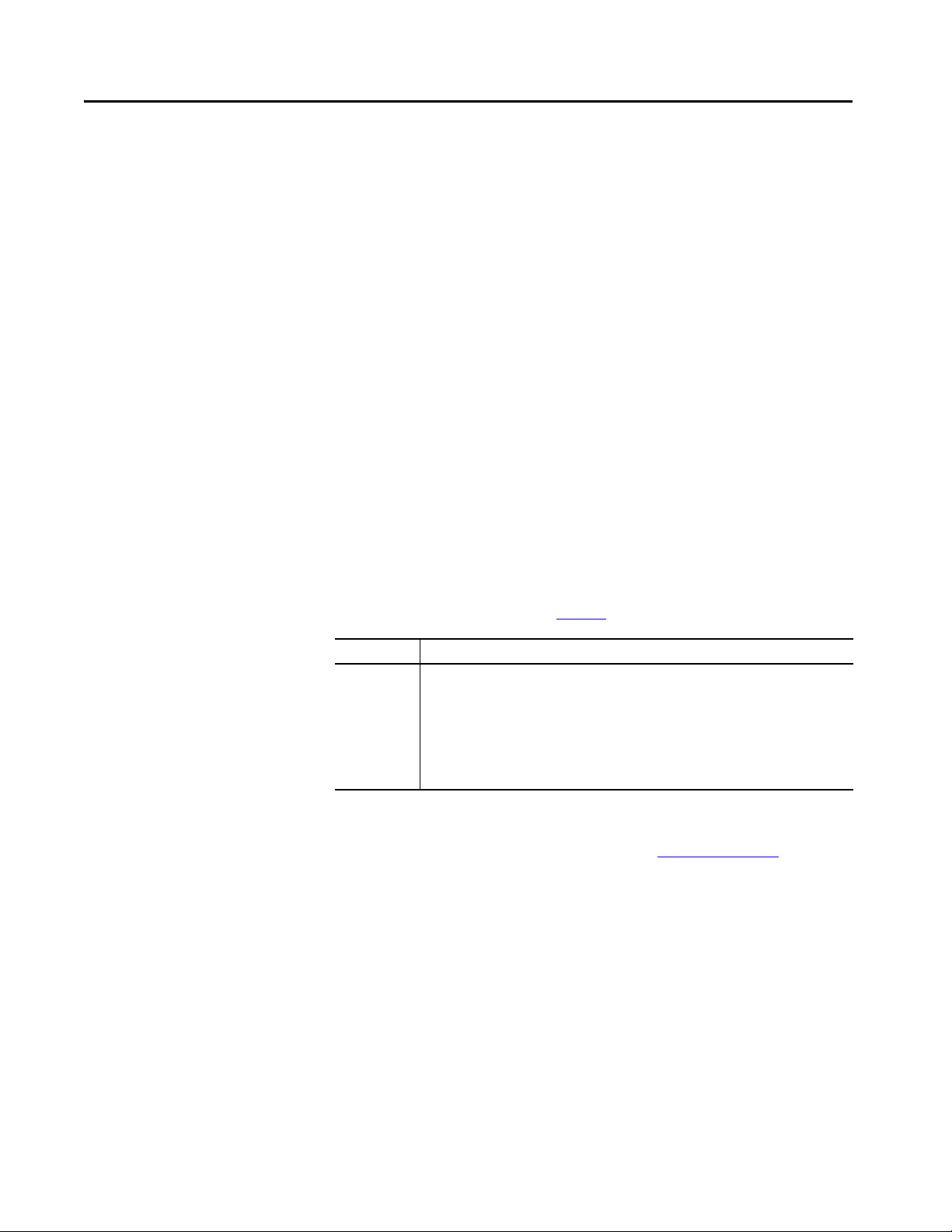
Figure 1 - Sensor Overview
Item Description
1 Locking solenoid
2 Sensor surface
3Cover plate
4Plug connector IN
5 LOCK light-emitting diode (LED)
6OSSD LED
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 9
Page 10
Chapter 2 Product Overview
123
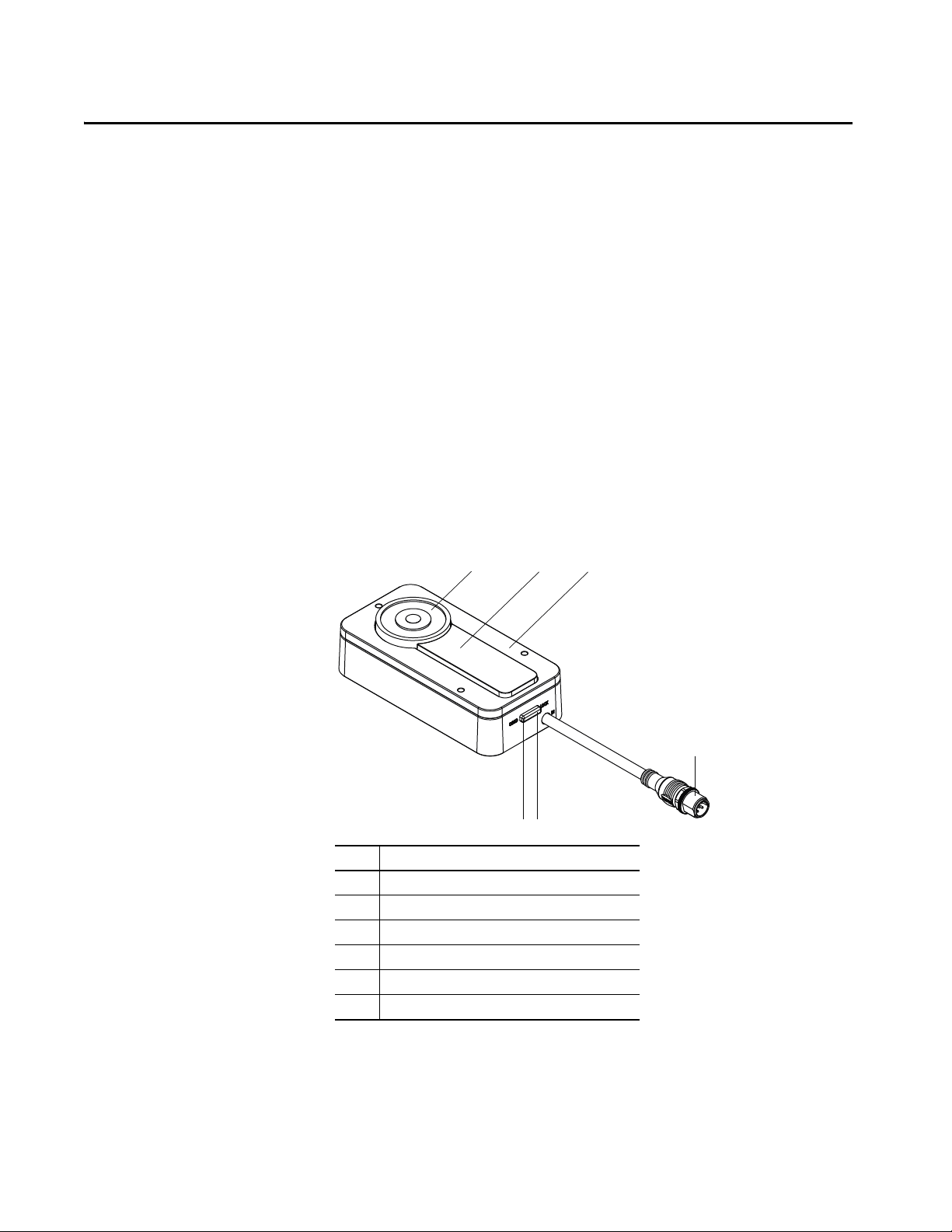
Figure 2 - Actuator Overview
Item Description
1 Anchor plate
2Protective cap
3Actuator surface
Product Models
The safety switch is available in different models. The following is an overview of
unique features of the models:
• One cable with M12 plug connector (5-pin)
• One cable with M12 plug connector (8-pin)
Locking Principle
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If a voltage drop occurs, the locking device unlocks regardless of whether the
dangerous state of the machine has ended.
• Do not use the safety switch in applications where the dangerous state cannot
be ended immediately (stopping/run-down time).
Power to Lock Principle
• Lock locking device: voltage at locking device input
• Unlock locking function: no voltage at locking device input
If voltage is interrupted, the locking device is unlocked and the protective device
can be opened immediately.
The locking device is not monitored, which means that the safety switch does not
check whether the anchor plate is applied to the solenoid.
10 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 11

Product Overview Chapter 2
21
Protective Functions
The safety switch has the following internal protective functions:
• Short-circuit protection at all outputs
• Cross-circuit monitoring at OSSDs
• Overload protection on OSSDs
• Supply voltage reverse polarity protection
Status Indicators
The safety switch displays important status information with the status
indicators.
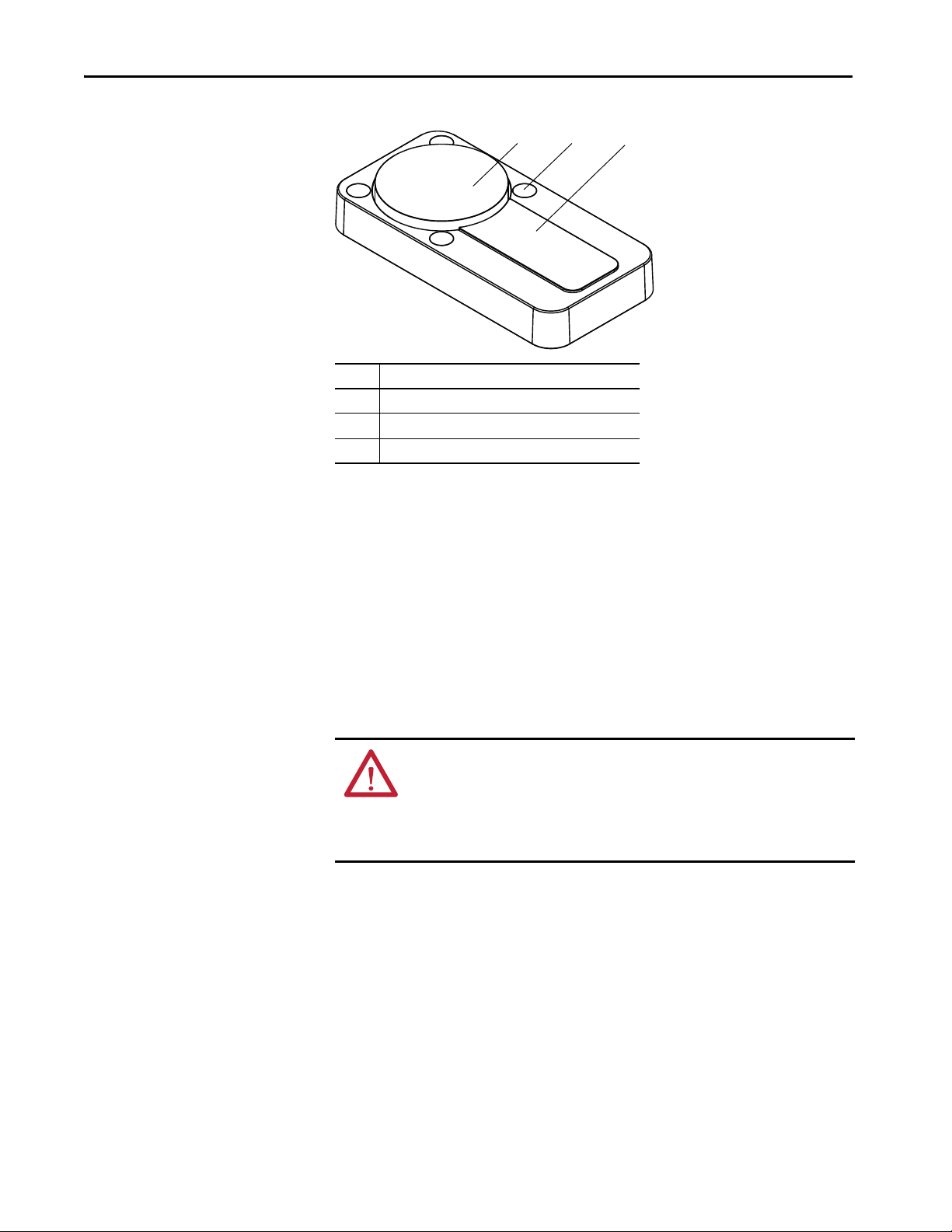
Figure 3 - Status Indicators
Item Name Color Description
1 OSSD Green/Red Green when the OSSD pair is in the ON state.
Red when the OSSD pair is in the OFF state.
2 LOCK Yellow Turns ON when the magnet is supplied with voltage.
(1) When a load is applied to the application diagnostic output that is too high, the red OSSD status indicator remains continuously ON.
The actual switching behavior of the safety switch is not affected.
(1)
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 11
Page 12

Chapter 2 Product Overview
Notes:
12 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 13
Project Planning
Chapter 3
Manufacturer of the Machine
Operating Entity of the Machine
ATT EN TI ON : Failure to comply with obligations of manufacturer.
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
• Conduct a risk assessment before using the safety switch.
• Do not tamper with, open, or modify the components of the safety switch.
• Do not repair defective devices – they must be replaced instead.
• Make sure that switch-on commands, which bring about a dangerous state of
the machine, are not enabled until the protective device is closed.
• Make sure that a stop command is triggered when the protective device is
opened during the dangerous machine state.
• The safety switches must not be defeated (that is, contacts jumpered), rotated
away, removed, or rendered ineffective in any other way. If necessary, put
measures in place to reduce possibilities for defeat.
ATT EN TI ON : Failure to comply with obligations of the operating entity.
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
• Modifications to the machine and modifications to the mechanical mounting of
the safety switch necessitate a new risk assessment. The results of this risk
assessment may require the operating entity of the machine to fulfill the
obligations of the manufacturer.
• Apart from during the procedures described in this document, the components
of the safety switch must not be opened or modified.
• Do not perform repair work on the components. Improper repair of the safety
switch can lead to a loss of the protective function.
• Verify that there is no bypassing by replacement actuators. Restrict access to
actuators.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 13
Page 14
Chapter 3 Project Planning
Assembly
ATT EN TI ON : Bypassing the protective device.
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
Avoid incentives to manipulate the safety switch by taking at least one of the
following measures:
• Cover the sensor and the actuator with additional equipment or protect them
against access.
• If possible use permanent mounting methods for actuators (for example, glue,
safety screws, or rivets).
Mounting Location
• Select the mounting location so that the sensor and actuator are accessible
for maintenance work and are protected against damage.
• Select a mounting location for the sensor that is as far away from the door
hinge as possible.
• If necessary, fit an additional stop for the moving protective device.
Distance
When several safety switches are mounted to the machine, they must be mounted
at a minimum distance to one another see Mount Multiple Safety Switches on
page 19
Alignment
The safety switch can be mounted in any alignment. When mounted
horizontally, the anchor plate with rotating bearings increases the manipulation
protection. When mounted horizontally, if the movable physical guard triggers
the actuator, the magnet holds the actuator. As the anchor plate has rotating
bearings, the gravitational force rotates the actuator surface away from the sensor
surface and the OSSDs go into the OFF state.
Mounting Methods
The sensor can be mounted in the following ways:
• Surface mount: The sensor is mounted on the fixed part of the protective
device (for example, door frame).
•Flush mount
device (for example, door frame). There must be a suitable recess in the
mounting surface. The thickness of the mounting surface must be
1.5…3 mm (0.06…0.12 in.).
(1)
: The sensor is mounted in the fixed part of the protective
(1) For the recess dimensions for flush mounting, see Figure 12 on page 34
14 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 15

Project Planning Chapter 3
Electrical Control Integration
Switch-on commands that put the machine in a dangerous state can only be
activated when the protective device is closed. When the machine goes into a
dangerous state, a stop command must be triggered if the protective device is
opened. Depending on the safety concept, a safety relay or a safety controller
analyzes the signal.
The control that is connected and all devices responsible for safety must comply
with the required Performance Level and the required category (for example,
according to ISO 13849-1).
OSSDs
Safety switches with local inputs and outputs can be directly integrated into the
machine controller.
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
• Make sure that the following control and electrical requirements are met so the
protective function can be fulfilled.
• The output signals from an OSSD pair must not be connected to each
other.
• In the machine controller, both signals from an OSSD pair must be
processed separately.
Figure 4 - Dual-channel and isolated connection of OSSD 1 and OSSD 2
• The machine must switch to the safe state at any time if at least one OSSD
in an OSSD pair switches to the OFF state.
• Prevent the formation of a potential difference between the load and the
protective device. If you connect loads to the OSSDs (safety outputs) that
then also switch if controlled with negative voltage (for example,
electromechanical contactor without reverse polarity protection diode),
you must connect the 0V connections of these loads and the connections
of the corresponding protective device individually and directly to the
same 0V terminal strip. If there is a fault, this way verifies that there can be
no potential difference between the 0V connections of the loads and the
connections of the corresponding protective device.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 15
Page 16

Chapter 3 Project Planning
Figure 5 - No Potential Difference Between Load and Protective Device
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
Downstream contactors must be positively guided and monitored depending on
applicable national regulations or required reliability of the safety function.
• Make sure that downstream contactors are monitored (external device
monitoring, EDM).
Requirements for the Electrical Control of the Machine
• Use the control without test pulses. The safety switch is self-testing.
• The safety switch tests the OSSDs at regular intervals. To conduct this
test, it switches each OSSD briefly (for max. 1 ms) to the OFF state and
checks whether this channel is voltage-free during this time.
Make sure that the control of the machine does not react to these test
pulses and the machine does not switch off.
• The inputs of a connected evaluation unit must be positive-switching
(PNP), as the two outputs of the safety switch send a level of the supply
voltage in the switched on state.
The OSSDs are short-circuit protected to 24V DC and 0V. When the actuator is
in the response range of the sensor, the OSSDs signal the ON state with the
HIGH signal level (nonisolated). If the actuator is removed from the response
range of the sensor or there is a device fault, the OSSDs signal the OFF state with
the LOW signal level.
The safety switch complies with the regulations for electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) for the industrial sector (Radio Safety Class A). Radio
interference cannot be ruled out when used in residential areas.
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
• Make sure that the following control and electrical requirements are met so the
safety switch can fulfill its protective function.
16 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 17

Project Planning Chapter 3
OSSD 1
V
t
OSSD 2
V
t
300 μs
300 μs
(1)
• The external voltage supply of the safety switch must be able to withstand
brief power failures of 20 ms as specified in IEC 60204-1.
• The power supply unit must provide safe isolation according to IEC
61140 (SELV/PELV). We have suitable power supplies available as
accessories, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or
Rockwell Automation sales office.
Course of the OSSD Test Over Time
Figure 6 - Course of the OSSD test over time
(1) Usually every 40 ms. The interval is dynamic and can be smaller than 40 ms.
Locking Solenoid Control
The locking solenoid is activated through the upstream control. There is no
internal activation or deactivation of the locking solenoid through the safety
switch. The locking device and locking force are not monitored. When the
machine starts, the following sequence must be followed:
1. Check whether safety switch OSSDs are in the ON state.
2. Supply the locking solenoid with power.
3. Start the machine.
Application Diagnostic Output
The application diagnostic output signal changes as soon as the actuator is moved
into or out of the response range of the safety switch. That is, when the movable
protective device is opened or closed. This output is not a safety output.
Table 1 - Switching Behavior of the Application Diagnostic Output
Actuator Application Diagnostic Output
Actuator not in the response area, or safety switch in an error state OFF
Actuator in the response area ON
For more information, see Specifications on page 31
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 17
.
Page 18

Chapter 3 Project Planning
Thorough-check Concept
Appropriately qualified safety personnel must test the safety switch during
commissioning, after modifications, and at regular intervals; see Thorough-
check Requirements on page 27.
Regular thorough checks serve to investigate the effectiveness of the safety switch
and discover anomalies that result from modifications or external influences
(such as damage or manipulation).
The manufacturer and operating entity must define the type and frequency of the
thorough checks on the machine based on the application conditions and the risk
assessment. The process of defining the thorough checks must be documented in
a traceable manner.
Regular Thorough Check Minimum Requirements
The following thorough checks must be conducted at least once a year:
• Thorough check of the protective function of the safety switch
• Thorough check of the switch housing for damage
• Thorough check of the switch cables for damage
• Thorough check of the safety switch for signs of misuse or manipulation
• Thorough check of the locking solenoid for correct function
18 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 19

Installation
Chapter 4
Mount Multiple Safety Switches
Mounting
IMPORTANT When several safety switches are mounted, the minimum distance between
the individual systems must be followed to avoid mutual interference.
Figure 7 - Spacing Requirement
260
(10.24)
260 (10.24)
The sensor can be mounted in the following ways:
• Surface mount — The sensor is mounted on the fixed part of the
protective device (for example, door frame).
• Flush mount — The sensor is mounted in the fixed part of the protective
device (for example, door frame). There must be a suitable recess in the
mounting surface. The thickness of the mounting surface must be between
1.5…3 mm (0.06…0.12 in.)
For recess dimensions for flush mounting, see Figure 12 on page 34
IMPORTANT Install the safety switch horizontally to help increase protection against
manipulation.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 19
Page 20

Chapter 4 Installation
Tightening torque: 1 N•m
Mount the Sensor
1. Unscrew the fixing screw (hexagon socket, 2 mm [0.08 in.]) and remove
the cover plate.
2. Mount the sensor on the fixed part of the protective device with 4 x M4
screws and secure it with four nuts.
• For surface mount: mount the sensor on the fixed part of the protective
device. The screws can be set in the front or the back.
20 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 21

Installation Chapter 4
Tightening torque: 1 N•m
• For flush mount: mount the sensor in the fixed part of the protective
device.
3. Set cover plate on the sensor.
4. Tighten the fixing screws to 1 N•m.
Mount the Actuator
1. Align the actuator to the mounted sensor.
2. Mount the actuator on the moving part of the protective device (for
example, door) with 4 x M4 screws. Tightening torque: 1 N•m. Use
disposable screws if possible.
• Maximum angle between sensor and actuator when protective device is
closed is 3°
≤3°
3. Cover drill holes of the actuator with protective caps.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 21
Page 22

Chapter 4 Installation
Notes:
22 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 23

Wiring
Chapter 5
Notes on c-UL-us
Device Connection (M12, 5-pin)
For use according to the requirements of UL 508, the following conditions must
also be met:
• Voltage supply Uv sensor secured with 2 A fuse
• Voltage supply Uv magnet secured with 2 A fuse
Figure 8 - Device Connection Pin Assignment (Male Connector, M12, 5-pin, A-coded)
12
5
43
Pin Wire Color
1 Brown +24V DC Safety switch voltage supply
2 White OSSD 1 OSSD 1 output
3 Blue 0V 0V DC voltage supply
4 Black OSSD 2 OSSD 2 output
5 Gray Magnet Magnet activation 24V DC
(1) Applies to the extensi on cables recommended as accessories.
(1)
Designation Description
IMPORTANT Pay attention to tightness of the plug connector.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 23
Page 24

Chapter 5 Wirin g
8
2
3
4
1
6
75
Device Connection (M12, 8-pin)
Figure 9 - Device Connection Pin Assignment (Male Connector, M12, 8-pin, A-coded)
Pin Wire Color
1 White Aux Application diagnostic output (not safe)
2 Brown +24V DC Safety switch voltage supply
3 Green Magnet Magnet activation 24V DC
4 Yellow In 2 OSSD 2 input
5 Gray OSSD 1 OSSD 1 output
6 Pink OSSD 2 OSSD 2 output
7 Blue 0V 0V DC voltage supply
8 Red In 1 OSSD 1 input
(1) Applies to the extensi on cables recommended as accessories.
(2) When used as an individual safety switch or as the first safety switch in a cascade apply 24V DC.
(1)
Designation Description
(2)
(2)
IMPORTANT Pay attention to tightness of the plug connector.
24 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 25

Wiri ng Chapter 5
Safety A
Safety B
Lock
0V
24V
54 4 4
111
333
2
2
1
7
6
3
8
4
5
2
1
4
5
3
Connect Safety Switches with T-connectors
The following connection system components facilitate connection.
Item Connection Cat. No.
Safety-wired Splitter/T-Port
1
898D-438Y-D8
Safety-wired Shorting Plug 898D-418U-DM
PWR
2
8-pin Device Patchcords Cat. No.
Pin 1
Pin 2
Pin 3
Pin 4
Pin 5
OSSD 1+
NA
OSSD 2+
NA
(1)
1 m (3.3 ft) 889D-F8ABDM-1
3
2 m (6.6 ft) 889D-F8ABDM-2
5 m (16.4 ft) 889D-F8ABDM-5
10 m (32.8 ft)
5-pin Patchcords Cat. No.
889D-F8ABDM-10
(1)
1 m (3.3 ft) 889D-F5ACDM-1
4
2 m (6.6 ft)
889D-F5ACDM-2
5 m (16.4 ft) 889D-F5ACDM-5
10 m (32.8 ft) 889D-F5ACDM-10
2 m (6.6 ft) 889D-F5AC-2
5
5 m (16.4 ft) 889D-F5AC-5
10 m (32.8 ft)
5-pin Cordsets
(1)
Cat. No.
889D-F5AC-10
(1) Add the letter S to above catalog numbers for stainless steel connectors (example: 889DS-F5AC-1).
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 25
Page 26

Chapter 5 Wirin g
Notes:
26 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 27

Commissioning
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
• Before commissioning the machine, have qualified safety personnel check and
release it.
• Make sure that the time for the safety requirement (closing the protective
device again) is longer than the response time.
Chapter 6
Switch On
Thorough-check Requirements
The device initializes after it is switched on. OSSDs are switched off in the
meantime. The OSSD light-emitting diode lights up after initialization.
The protective device and its application must be thoroughly checked in the
following situations:
• Before commissioning
• After changes to the configuration or the safety function
• After changes to the mounting, the alignment, or the electrical connection
• After exceptional events, such as after a manipulation has been detected,
after modification of the machine, or after replacing components
The thorough check verifies the following:
• All relevant regulations are complied with and the protective device is
active for all operating modes of the machine.
• The documentation corresponds to the state of the machine, including the
protective device.
Qualified safety personnel or specially qualified and authorized personnel must
conduct the thorough checks and must be document results in a traceable
manner.
IMPORTANT • Check whether the protective device of the machine is effective in all
operating modes in which the machine can be set.
• Verify that operating personnel have been instructed in the function of the
protective device before starting work on the machine. The machine
operator has overall responsibility for the instruction, which qualified
personnel must conduct.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 27
Page 28

Chapter 6 Commissioning
Notes:
28 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 29

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Chapter 7
Maintenance
Clean the Switch
IMPORTANT • Do not use aggressive cleaning agents (such as isopropanol or spirit).
• Do not use any substances that hinder the wetting properties of lacquers.
• We recommend anti-static cleaning agents.
Regular Thorough Check
The safety switch must be checked regularly. The type and frequency of thorough
checks is defined by the manufacturer and the operating entity of the machine,
see Thorough-check Concept on page 18
The regular thorough checks serve to investigate the effectiveness of the safety
switch and detect any ineffectiveness due to modifications or external influences
(for example, damage or manipulation).
IMPORTANT Conduct the thorough checks according to the instructions from the
manufacturer and the machine user.
.
Troubleshooting
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
• Immediately shut down the machine if the behavior of the machine cannot be
clearly identified.
• If a machine fault cannot be determined or safely rectified, immediately shut
down the machine.
• Secure the machine so that it cannot switch on unintentionally.
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to unexpected starting of the machine.
When any work is taking place, use the protective device to secure the machine or
to verify that the machine is not switched on unintentionally.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 29
Page 30

Chapter 7 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
ATT EN TI ON : Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device.
If non-compliant, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine may not be
stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
• Do not repair device components.
• Do not modify or manipulate device components.
• Apart from during the procedures described in this document, the device
components must not be opened.
IMPORTANT If you cannot remedy the fault with the help of the information that is provided
in this chapter, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or
Rockwell Automation sales office.
Perform one of the following steps when an error occurs:
• Check voltage supply.
• Check cables.
• Check alignment of safety switch and actuator.
• Check ambient conditions (for example, interfering RFID frequencies or
magnetic fields, distances to other safety switches).
IMPORTANT If a safety switch has a fault in a cascade with an end connector, the OSSDs of
all safety switches between the safe evaluation unit and the safety switch
concerned switch into the OFF state.
30 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 31

Specifications
Appendix A
Technical Data
Table 2 - Features
Attribute Value
Safe switch on distance S
Typical switch on distance S
Safe switch off distance S
Max. actuation frequency 0.5 Hz
Locking force 500 N (112.4 lbf)
Magnetic retaining force when not supplied with power 25 N (5.6 lbf )
Alignment tolerance for locking device
Vertical 5 mm (0.2 in.)
Horizontal 5 mm (0.2 in.)
Aperture angle 3°
ao
o
ar
4 mm (0.16 in.)
15 mm (0.59 in.)
45 mm (1.77 in.)
Table 3 - Safety
Attribute Value
Standards IEC 60947-5-3, IEC 60947-5-1, IEC 61508, EN ISO 13849-1,
Safety Classification (Guard door sensing) PLe Category 4 per ISO 13949-1, SIL 3 per IEC 61508 and
Certifications CE Marked for all applicable EU directives,
Performance level PL e (ISO 13849-1)
Category 4 (ISO 13849)
Safety integrity level SIL 3 (EN 61508)
SIL claim limit SILCL 3 (EN 62061)
PFHd (mean probability of a dangerous failure per hour) 1.5 x 10
T
(mission time) 20 years (ISO 13849-1)
M
Type Type 4 (ISO 14119)
Coding level Low coding level (ISO 14119)
Safe state when a fault occurs At least one OSSD is in the OFF state
(1) In a cascade, the performance level for the cascade as a whole depends on the number and type of devices in the cascade. PL e i s
only possible in cascades with a maximum of 6 devices.
IEC 62061, ISO 14119, UL 508
IEC 62061
c-UL-us (UL 508), TÜV, C-tick
(1)
-8
at 40 °C (104 °F) and 1000 m (3280.8 ft) above
sea level
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 31
Page 32

Appendix A Specifications
Table 4 - System Connection of Variant with 1 x M12 Plug Connector, 5-pin
Attribute Value
Voltage supply
Local inputs and outputs
Male connector, M12, 5-pin, A-coded (common plug
connector for voltage supply and outputs)
Length of connecting cable 150 mm (5.91 in.)
Table 5 - System Connection of Variant with 1 x M12 Plug Connector, 8-pin
Attribute Value
Voltage supply
Local inputs and outputs
Male connector, M12, 8-pin, A-coded (common plug
connector for voltage supply as well as inputs and
outputs)
Length of connecting cable 150 mm (5.91 in.)
Table 6 - Electrical
Attribute Value
OSSD pairs 1
Rated impulse withstand voltage U
imp
Pollution degree 3 (external, according to EN 60947-1)
Power-up delay (after supply voltage applied)
(1)
Supply voltage when an individual safety switch is connected
Supply voltage V
Supply voltage V
sensor 24 V DC (19.2…28.8V) Class 2 supply
v
magnet 24 V DC (19.2…28.8V) Class 2 supply
v
Supply voltage when an cascade is connected
Supply voltage V
Supply voltage V
sensor 24 V DC (22.8…28.8V) Class 2 supply
v
magnet 24 V DC (21.6…28.8V) Class 2 supply
v
Muting time when supply voltage is interrupted 4 ms
Rated insulation voltage Ui 32V DC
Cable capacitance 400 nF (for Out A and Out B)
Device fuse 0.6…1 A
Current consumption at 24 V
Locking device deactivated 50 mA
Locking device active 350 mA
Protection class III (EN 61140/IEC 61140)
Response time
Release time
Risk time
(1) Once the supply voltage has been switched on, the OSSDs are in the OFF state during the time delay before availability. The time
specified applies to one sensor; in a cascade, 0.1 s must be added per sensor.
(2) Response time for moving the OSSDs into the OFF state when the actuator is removed from the response area or when the OSSD
input signals go into the OFF state.
(3) Response time for moving the OSSDs into the ON state when the ac tuator is detected by the sensor and the OSSD input signals are in
the ON state.
(4) The risk time is the time n eeded to detect internal and externa l faults. External errors affect t he OSSDs (short-circuit to an OSSD and
cross-circuit between the two OSSDs). At least one of the two OSSDs is safely switched off during the risk time.
(5) In a cascade, the value is multiplied by the number of safety switches in the cascade.
(2)
(3)
(4)
1500V
2.5 s
≤50 ms
≤100 ms
≤100 ms
(5)
(5)
(5)
32 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 33

Specifications Appendix A
Table 7 - Mechanical Data
Attribute Value
Dimensions (W x H x D)
Safety switch 120 x 60 x 38.5 mm (4.72 x 2.36 x 1.52 in.)
Actuator 120 x 60 x 20.5 mm (4.72 x 2.36 x 0.81 in.)
Material
Sensor housing Anodized aluminum
Actuator housing Fiber-glass-reinforced PVC
Anchor plate Nickel-plated steel
Wei ght
Safety switch 510 g (18 oz)
Actuator 210 g (7.41 oz)
Table 8 - Inputs
Attribute Value
Rated voltage 24 V DC
ON state ≤5 mA
OFF state 0 mA
ON state 19.2…28.8V DC
OFF state 0…2V DC
Table 9 - Outputs
Attribute Value
2 OSSDs (Out 1 and Out 2) 2 x PNP, max. 100 mA, short-circuit protected and
1 Application diagnostic output (Aux) 25 mA max
Switching voltage (all outputs)
ON state 19.2…28.8V DC
OFF state 0…2V DC
Switching current (OSSDs)
ON state ≤100 mA
OFF state ≤500 μA
Test pulse duration (OSSDs) 300 μs
(1) A higher load affects the behavior of the status indicators, see Status Indicators on page 11.
overload-proof
(1)
, short-circuit protected (resistive load)
Table 10 - Enviroment
Attribute Value
Enclosure rating IP 67 (IEC 60529)
Ambient operating temperature -20…+55 °C (-4…+131 °F)
Storage temperature -25…+70 °C (-13…+158 °F)
Relative humidity 50% at 70 °C (158 °F) (IEC 60947-5-2)
Vibration resistance 1 mm/10…55 Hz (IEC 60068-2-6)
Shock resistance 30 g, 11 ms (IEC 60068-2-27)
EMC In accordance with IEC 61326-3-1, IEC 60947-5-2, IEC
Minimum distance between two safety switches Depending on alignment, see Mount Multiple Safety
60947-5-3, and EN 300330 V2.1.1
Switches on page 19.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 33
Page 34

Appendix A Specifications
(1)
Approximate Dimensions
Figure 10 - 440G-EZ Sensor with 1 x M12 Male Connector [mm (in.)]
122 (4.8)
42
(1.65)
14.5
(0.57)
6.5
(0.26)
4.5
(0.18)
44
(1.73)
(0.94)
10
(0.39)
12.5
(0.49)
5.7
(0.22)
L
(1) L = 150±2 mm (5.91±0.79 in.)
120 (4.73)
Figure 11 - 440G-EZ Sensor Actuator [mm (in.)]
17.8
(0.70)
3.7
(0.15)
4.5 (0.18)
8 (0.31)
6
(0.24)
16.8
(0.66)
20.5
(0.81)
5.5
(0.22)
44
(1.73)
34
(1.34)
60
(2.36)
24
120 (4.72)
44 (1.73)
10 (0.39)
8
(0.31)
44
(1.73)
Figure 12 - Flush Mounting [mm (in.)]
44 (1.73)
14.4 (0.57)
15.2
(0.60)
28
(1.10)
16.3 (0.64)
Ø42
(1.65)
83.5 (3.29)
(2.36)
22
(0.87)
32 (1.26)
Ø5 (0.20) x 4
60
22
(0.87)
14.4
(0.57)
44
(1.73)
34 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 35

Ordering Information
Appendix B
Package Contents
Ordering Information
•Safety switch
•Actuator
• Four protective caps
•Safety note
• Mounting instructions
Table 11 - 440G-EZ Product Selection
Sensor Connection Type Cat. No.
Electromagnetic switch
Cable with 5-pin M12 connector
Electromagnetic Switch
Cable with 8-pin M12 connector
440G-EZS21STL05J
440G-EZS21STL05H
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 35
Page 36

Appendix B Ordering Information
Notes:
36 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 37

Replacement Parts/Accessories
Appendix C
Replacement Parts
Accessories
Description Cat. No.
Actuator
Table 12 - DC Micro (M12) Cables
Description Cat. No.
8-pin cordset — female, straight
8-pin patchcord — female, straight 889D-F8ABDM-x
5-pin cordset — female, straight 889D-F5AC-x
5-pin patchcord — female, straight 889D-F5ACDM-x
(1) Replace the x with a 2 (2 m), 5 (5 m), or 10 (10 m) for standard cable lengths.
(2) Replace the x with a 1 (1 m), 2 (2 m), 3 (3 m), 5 (5 m), or 10 (10 m) for standard cable lengths
440G-EMAS
889D-F8AB-x
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 37
Page 38

Appendix C Replacement Parts/Accessories
Notes:
38 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 39

Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
Appendix D
EU DoC (excerpt)
Complete EU DoC for Download
The undersigned, who represents the manufacturer below, hereby declares that
the product complies with the regulations of the EU directive(s) below
(including all relevant changes), and that it is based on the relevant standards
and/or technical specifications.
You can find the EU declaration of conformity for the protective device at
rok.auto/certifications
.
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 39
Page 40

Appendix D Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
Notes:
40 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 41

A
accessories 37
actuator
21
mount
overview
10
alignment
application
approximate dimension 34
assembly
14
diagnostic output
14
17
C
clean
29
switch
commission
concept
conformity
connect
content
control
c-UL-us
27
thorough-check
declaration of
safety switch
T-connector
35
package
locking solenoid
23
note
18
39
25
17
D
dangerous state 5
declaration of conformity
device connection
M12, 5-pin
M12, 8-pin
diagnostic output
application
dimension
approximate
distance
39
DoC
23
24
17
34
14
E
electrical
installation
electrical control
integration
requirement
8
15
16
F
features
9
product
flush mount
19
39
9
function
protective
11
I
indicator
11
status
information
7
safety
installation
integration
intended use
introduction
19
electrical
commission
electrical control
7
safety information
8
15
7
L
location
14
mounting
locking principle
locking solenoid
control
10
17
M
M12, 5-pin
device connection
M12, 8-pin
device connection
machine
manufacturer
operating entity 13
maintenance
manufacturer
machine
mechanical mounting
method
mounting
minimum requirement
thorough-check
model
10
mount
actuator
flush
19
multiple safety switches 19
sensor
20
surface
mounting 19
multiple safety switches
19
location
mechanical
method
14
19
mount
23
24
13
8, 29
13
8
14
18
21
14
8
Index
Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020 41
Page 42

Index
O
operating entity
13
machine
operation
ordering information
OSSD
overview
8
15
test
course over time
actuator
product
9
sensor
9
10
P
package content 35
personnel
8
qualified
planning
8, 13
project
Power to Lock
10
principle
principle
Power to Lock
product
features
model 10
overview
project planning
protective function
10
9
9
8, 13
11
35
17
S
safety
information
safety switch
connect
sensor
mount
overview
specifications
status indicator
structure
surface mount
switch
clean
switch on 27
7
T-connector
20
9
31
11
9
19
29
25
T
terminology 5
thorough-check
minimum requirement
regular
29
requirement 27
thorough-check concept
troubleshooting
29
W
wiring 23
18
18
Q
qualified personnel
requirement
8
R
regular thorough check 29
replacement part
requirement
electrical control
minimum
qualified personnel
thorough-check
37
16
thorough-check
8
27
18
42 Rockwell Automation Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Page 43

Page 44

Rockwell Automation Support
Rockwell Otomasyon Ticaret A.Ş., Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752 İçerenköy, İstanbul, Tel: +90 (216) 5698400
Use the following resources to access support information.
Technical Support Center Knowledgebase Articles, How-to Videos, FAQs, Chat,
Local Technical Support Phone
Numbers
Direct Dial Codes Find the Direct Dial Code for your product. Use the
Literature Library Installation Instructions, Manuals, Brochures, and
Product Compatibility and
Download Center (PCDC)
User Forums, and Product Notification Updates.
Locate the phone number for your country. http://www.rockwellautomation.com/global/support/get-support-now.page
code to route your cal l directly to a technic al suppor t
engineer.
Technical Data.
Get help determining how products interact, check
features and capabilities, and find associated
firmware.
https://rockwellautomation.custhelp.com/
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/global/support/direct-dial.page
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/global/literature-library/overview.page
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/global/support/pcdc.page
Documentation Feedback
Your comments will help us serve your documentation needs better. If you have any suggestions on how to improve this
document, complete the How Are We Doing? form at http://literature.rockwellautomation.com/idc/groups/literature/
documents/du/ra-du002_-en-e.pdf.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
At the end of life, this equipment should be collected separately from any unsorted municipal waste.
Rockwell Automation maintains current product environmental information on its webs ite at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/rockwellautomation/about-us/sustainability-ethics/product-environmental-compliance.page.
Allen-Bradley, Rockwell Automation, and Rockwell Softwa re are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respec tive companies.
Publication 440G-UM003B-EN-P - June 2020
Supersedes Publication 440G-UM003A-EN-P – February 2020 Copyright © 2020 Rockwell Auto mation, Inc. All rights reserved. Pr inted in the U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...