Page 1
lash memory programming software
User’s Manual
All information contained in these materials, including products and product specifications,
website (http://www.renesas.com).
Rev. 2.00 Apr 2021
www.renesas.com
[
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08
F
represents information on the product at the time of publication and is subject to change by
Renesas Electronics Corp. without notice. Please review the latest information published by
Renesas Electronics Corp. through various means, including the Renesas Electronics Corp.
© 2021 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Corporate Headquarters
Contact information
Trademarks
Notice
1. Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided only to illustrate the operation of semiconductor products
and application examples. You are fully responsible for the incorporation or any other use of the circuits, software, and information in the design of your
product or system. Renesas Electronics disclaims any and all liability for any losses and damages incurred by you or third parties arising from the use of
these circuits, software, or information.
2. Renesas Electronics hereby expressly disclaims any warranties against and liability for infringement or any other claims involving patents, copyrights, or
other intellectual property rights of third parties, by or arising from the use of Renesas Electronics products or technical information described in this
document, including but not limited to, the product data, drawings, charts, programs, algorithms, and application examples.
3. No license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted hereby under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of Renesas Electronics or
others.
4. You shall be responsible for determining what licenses are required from any third parties, and obtaining such licenses for the lawful import, export,
manufacture, sales, utilization, distribution or other disposal of any products incorporating Renesas Electronics products, if required.
5. You shall not alter, modify, copy, or reverse engineer any Renesas Electronics product, whether in whole or in part. Renesas Electronics disclaims any
and all liability for any losses or damages incurred by you or third parties arising from such alteration, modification, copying or reverse engineering.
6. Renesas Electronics products are classified according to the following two quality grades: “Standard” and “High Quality”. The intended applications for
each Renesas Electronics product depends on the product’s quality grade, as indicated below.
"Standard": Computers; office equipment; communications equipment; test and measurement equipment; audio and visual equipment; home
"High Quality": Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.); traffic control (traffic lights); large-scale communication equipment; key
Unless expressly designated as a high reliability product or a product for harsh environments in a Renesas Electronics data sheet or other Renesas
Electronics document, Renesas Electronics products are not intended or authorized for use in products or systems that may pose a direct threat to
human life or bodily injury (artificial life support devices or systems; surgical implantations; etc.), or may cause serious property damage (space system;
undersea repeaters; nuclear power control systems; aircraft control systems; key plant systems; military equipment; etc.). Renesas Electronics disclaims
any and all liability for any damages or losses incurred by you or any third parties arising from the use of any Renesas Electronics product that is
inconsistent with any Renesas Electronics data sheet, user’s manual or other Renesas Electronics document.
7. No semiconductor product is absolutely secure. Notwithstanding any security measures or features that may be implemented in Renesas Electronics
hardware or software products, Renesas Electronics shall have absolutely no liability arising out of any vulnerability or security breach, including but not
limited to any unauthorized access to or use of a Renesas Electronics product or a system that uses a Renesas Electronics product. RENESAS
ELECTRONICS DOES NOT WARRANT OR GUARANTEE THAT RENESAS ELECTRONICS PRODUCTS, OR ANY SYSTEMS CREATED USING
RENESAS ELECTRONICS PRODUCTS WILL BE INVULNERABLE OR FREE FROM CORRUPTION, ATTACK, VIRUSES, INTERFERENCE,
HACKING, DATA LOSS OR THEFT, OR OTHER SECURITY INTRUSION (“Vulnerability Issues”). RENESAS ELECTRONICS DISCLAIMS ANY AND
ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY ARISING FROM OR RELATED TO ANY VULNERABILITY ISSUES. FURTHERMORE, TO THE EXTENT
PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, RENESAS ELECTRONICS DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH
RESPECT TO THIS DOCUMENT AND ANY RELATED OR ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE OR HARDWARE, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
8. When using Renesas Electronics products, refer to the latest product information (data sheets, user’s manuals, application notes, “General Notes for
Handling and Using Semiconductor Devices” in the reliability handbook, etc.), and ensure that usage conditions are within the ranges specified by
Renesas Electronics with respect to maximum ratings, operating power supply voltage range, heat dissipation characteristics, installation, etc. Renesas
Electronics disclaims any and all liability for any malfunctions, failure or accident arising out of the use of Renesas Electronics products outside of such
specified ranges.
9. Although Renesas Electronics endeavors to improve the quality and reliability of Renesas Electronics products, semiconductor products have specific
characteristics, such as the occurrence of failure at a certain rate and malfunctions under certain use conditions. Unless designated as a high reliability
product or a product for harsh environments in a Renesas Electronics data sheet or other Renesas Electronics document, Renesas Electronics products
are not subject to radiation resistance design. You are responsible for implementing safety measures to guard against the possibility of bodily injury,
injury or damage caused by fire, and/or danger to the public in the event of a failure or malfunction of Renesas Electronics products, such as safety
design for hardware and software, including but not limited to redundancy, fire control and malfunction prevention, appropriate treatment for aging
degradation or any other appropriate measures. Because the evaluation of microcomputer software alone is very difficult and impractical, you are
responsible for evaluating the safety of the final products or systems manufactured by you.
10. Please contact a Renesas Electronics sales office for details as to environmental matters such as the environmental compatibility of each Renesas
Electronics product. You are responsible for carefully and sufficiently investigating applicable laws and regulations that regulate the inclusion or use of
controlled substances, including without limitation, the EU RoHS Directive, and using Renesas Electronics products in compliance with all these
applicable laws and regulations. Renesas Electronics disclaims any and all liability for damages or losses occurring as a result of your noncompliance
with applicable laws and regulations.
11. Renesas Electronics products and technologies shall not be used for or incorporated into any products or systems whose manufacture, use, or sale is
prohibited under any applicable domestic or foreign laws or regulations. You shall comply with any applicable export control laws and regulations
promulgated and administered by the governments of any countries asserting jurisdiction over the parties or transactions.
12. It is the responsibility of the buyer or distributor of Renesas Electronics products, or any other party who distributes, disposes of, or otherwise sells or
transfers the product to a third party, to notify such third party in advance of the contents and conditions set forth in this document.
13. This document shall not be reprinted, reproduced or duplicated in any form, in whole or in part, without prior written consent of Renesas Electronics.
14. Please contact a Renesas Electronics sales office if you have any questions regarding the information contained in this document or Renesas
Electronics products.
(Note1) “Renesas Electronics” as used in this document means Renesas Electronics Corporation and also includes its directly or indirectly controlled
(Note2) “Renesas Electronics product(s)” means any product developed or manufactured by or for Renesas Electronics.
subsidiaries.
electronic appliances; machine tools; personal electronic equipment; industrial robots; etc.
financial terminal systems; safety control equipment; etc.
(Rev.5.0-1 October 2020)
TOYOSU FORESIA, 3-2-24 Toyosu,
Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0061, Japan
www.renesas.com
Renesas and the Renesas logo are trademarks of Renesas
Electronics Corporation. All trademarks and registered trademarks
are the property of their respective owners.
For further information on a product, technology, the most up-to-date
version of a document, or your nearest sales office, please visit:
www.renesas.com/contact/.
© 2021 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 3

General Precautions in the Handling of Microprocessing Unit and Microcontroller
Unit Products
The following usage notes are applicable to all Microprocessing unit and Microcontroller unit products from Renesas. For detailed usage notes on the products
covered by this document, refer to the relevant sections of the document as well as any technical updates that have been issued for the products.
1. Precaution against Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
A strong electrical field, when exposed to a CMOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps
must be taken to stop the generation of static electricity as much as possible, and quickly dissipate it when it occurs. Environmental control must be
adequate. When it is dry, a humidifier should be used. This is recommended to avoid using insulators that can easily build up static electricity.
Semiconductor devices must be stored and transported in an anti-static container, static shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement
tools including work benches and floors must be grounded. The operator must also be grounded using a wrist strap. Semiconductor devices must not be
touched with bare hands. Similar precautions must be taken for printed circuit boards with mounted semiconductor devices.
2. Processing at power-on
The state of the product is undefined at the time when power is supplied. The states of internal circuits in the LSI are indeterminate and the states of
register settings and pins are undefined at the time when power is supplied. In a finished product where the reset signal is applied to the external reset
pin, the states of pins are not guaranteed from the time when power is supplied until the reset process is completed. In a similar way, the states of pins in
a product that is reset by an on-chip power-on reset function are not guaranteed from the time when power is supplied until the power reaches the level
at which resetting is specified.
3. Input of signal during power-off state
Do not input signals or an I/O pull-up power supply while the device is powered off. The current injection that results from input of such a signal or I/O
pull-up power supply may cause malfunction and the abnormal current that passes in the device at this time may cause degradation of internal elements.
Follow the guideline for input signal during power-off state as described in your product documentation.
4. Handling of unused pins
Handle unused pins in accordance with the directions given under handling of unused pins in the manual. The input pins of CMOS products are
generally in the high-impedance state. In operation with an unused pin in the open-circuit state, extra electromagnetic noise is induced in the vicinity of
the LSI, an associated shoot-through current flows internally, and malfunctions occur due to the false recognition of the pin state as an input signal
become possible.
5. Clock signals
After applying a reset, only release the reset line after the operating clock signal becomes stable. When switching the clock signal during program
execution, wait until the target clock signal is stabilized. When the clock signal is generated with an external resonator or from an external oscillator
during a reset, ensure that the reset line is only released after full stabilization of the clock signal. Additionally, when switching to a clock signal produced
with an external resonator or by an external oscillator while program execution is in progress, wait until the target clock signal is stable.
6. Voltage application waveform at input pin
Waveform distortion due to input noise or a reflected wave may cause malfunction. If the input of the CMOS device stays in the area between V
and V
(Min.) due to noise, for example, the device may malfunction. Take care to prevent chattering noise from entering the device when the input level
IH
is fixed, and also in the transition period when the input level passes through the area between V
7. Prohibition of access to reserved addresses
Access to reserved addresses is prohibited. The reserved addresses are provided for possible future expansion of functions. Do not access these
addresses as the correct operation of the LSI is not guaranteed.
8. Differences between products
Before changing from one product to another, for example to a product with a different part number, confirm that the change will not lead to problems.
The characteristics of a microprocessing unit or microcontroller unit products in the same group but having a different part number might differ in terms of
internal memory capacity, layout pattern, and other factors, which can affect the ranges of electrical characteristics, such as characteristic values,
operating margins, immunity to noise, and amount of radiated noise. When changing to a product with a different part number, implement a system-
evaluation test for the given product.
(Max.) and VIH (Min.).
IL
(Max.)
IL
Page 4

Use this software after sufficiently confirming the manual of the microcontroller in use.
How to Use This Manual
1. Purposes and Target Readers
The purpose of this manual is to give users an understanding of the basic specifications and correct use of the
Renesas Flash Programmer. This manual is intended for users who are using the flash programmer in
designing and developing a system that employs a Renesas Electronics microcontroller equipped with on-chip
flash memory.
It is assumed that the readers of this manual have a basic knowledge of microcontrollers, Windows, and
Linux, and some knowledge of electrical and logic circuits.
2. Conventions
• Note: Footnote for item marked with “Note” in the text.
• Caution: Information requiring particular attention
• Remark: Supplementary information
• Numeral representations: Binary ... xxxx or xxxxB
Decimal ... xxxx
Hexadecimal ... 0xXXXX or xxxxH
• “ ”: Any character or item on the screen that can be selected or input
• : Name of a button
• [ ]: Name of a command, dialog box, tabbed page, option, or area on the screen
Page 5
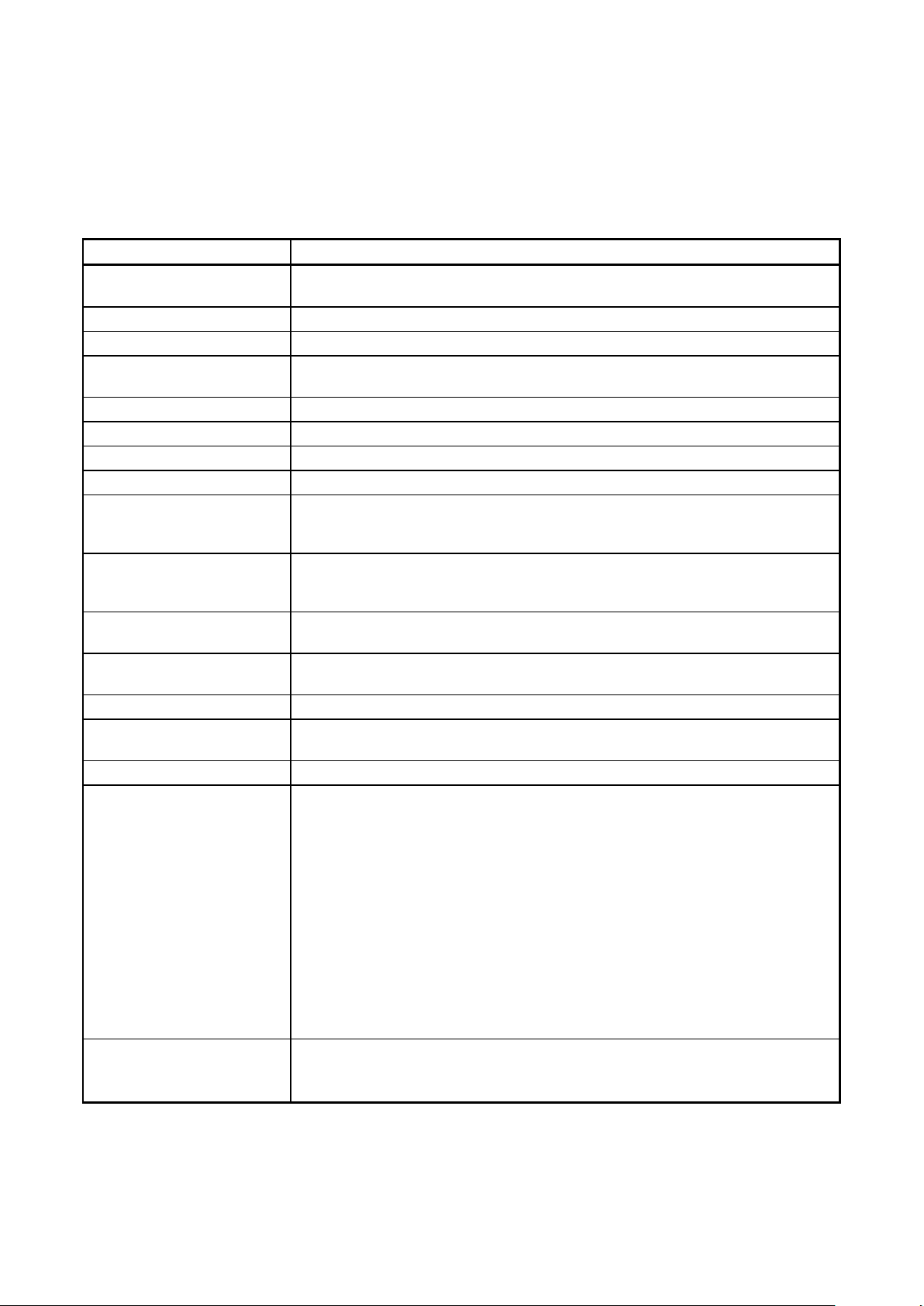
Term
Meaning
E1/E20/E2/E2 Lite
Abbreviation of “the E1, E20, E2, or E2 emulator Lite”
J-Link
SEGGER-produced debug probe for MCUs
Tool used
General term for the tool used by the customer, whether an E1, E20, E2, E2 Lite, or
Target MCU
The Renesas Electronics MCU with on-chip flash memory which is in use by the user
Target system
User-designed board on which the target MCU is mounted
Input clock
A clock from an oscillator or a resonator which is externally input to the target MCU
Parameter file
Parameter files include information required to program the flash memory of the
ID code
Authentication code used in flash programming and in on-chip debugging. For
RPI file
RPI files are image files generated by the RFP that combine usable HEX files and
RPE file
An encrypted program file that has been generated by the encryption utility program
3. Terminology
The meanings of the terms used in the Renesas Flash Programmer manual are as follows.
RFP Abbreviation of “Renesas Flash Programmer”, software for programming flash
memory
J-Link.
MCU Abbreviation of “microcontroller unit”
Project file Project files hold the data required to write programs. In the RFP, a project file holds
the settings related to the programming environment, such as target MCU settings
and command option specifications. Project files have the filename extension *.rpj.
(1/2)
target MCU, and are created by acquiring information from the MCU. Parameter files
have the extension *.fcf.
details, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
Lock bit One of the safety functions of the MCU. For details, refer to the user’s manual of the
target MCU.
HEX file Program file without flash option data
flash options data.
Program file “Program file” refers to a file that contains a program to be written to the MCU. The
RFP supports the following program file formats.
a. HEX files in Intel HEX format
b. HCUHEX files in Intel HEX format
c. HEX files in Motorola S format
d. HCUHEX files in Motorola S format
e. RPI files
Refer to section 1.5.1, RPI File.
The only supported character code is ASCII (one byte). Unicode (two bytes) is not
supported.
f. RPE files
Refer to section 1.5.2, RPE File.
COMx COMx is a serial interface port of the host PC.
When writing data to the target system by using a serial interface of the host PC,
select COMx as the tool to be used. Any value from 1 to 256 can be specified for x.
Page 6
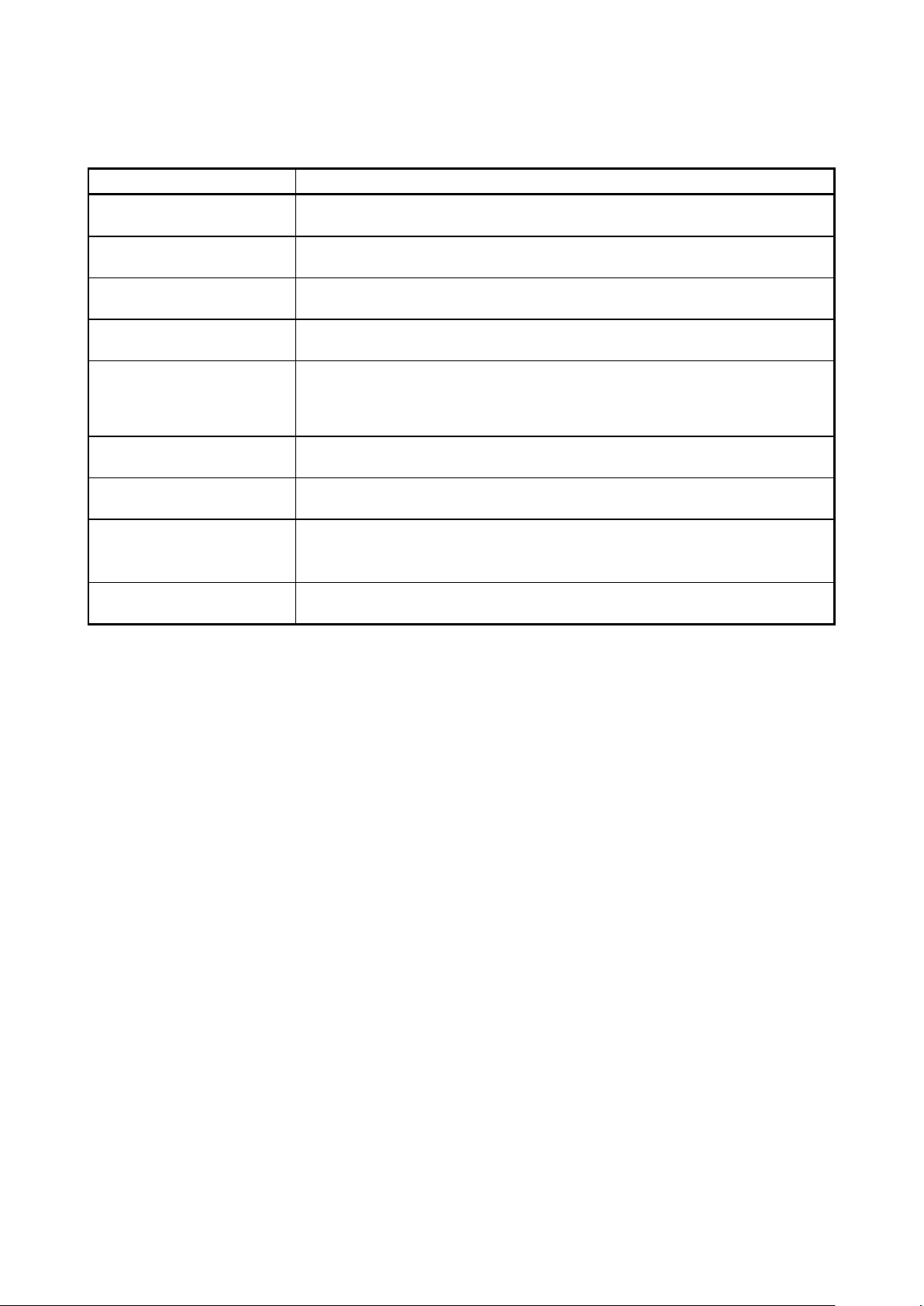
Term
Meaning
USB Direct
USB Direct is a method of writing to the MCU in the USB boot mode by using the
OTP
A security function of the MCU. For details, refer to the user’s manual of the target
Access window (AW)
This is also referred to as the “flash shield window”. The specified range is selected
DLM
Management to maintain security in the entire life cycle of the device (device life-
Authentication code
A collective term for authentication codes, including ID codes, passwords, and
USB interface port of the host PC.
FINE FINE is a single- or dual-line communications interface operating through the FINE
pin or pins of an MCU. Some of our MCUs support writing via single line FINE.
ID authentication mode One of the security functions of the MCU. Connection of the flash programmer is
protected by ID authentication.
MCU.
as the access window (and window area), and functionality in other ranges is
restricted to a degree which depends on the operating mode. For details, refer to
the user’s manual of the target MCU.
Flash options Flash options are settings which determine the state after the MCU is reset, and is
a general term for settings which must be specified separately from the HEX file.
TSIP Dedicated hardware secure IP (trusted secure IP) for managing the encryption key.
For details, contact a Renesas Electronics sales office.
(2/2)
cycle management).
For details, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
DLM keys.
Page 7
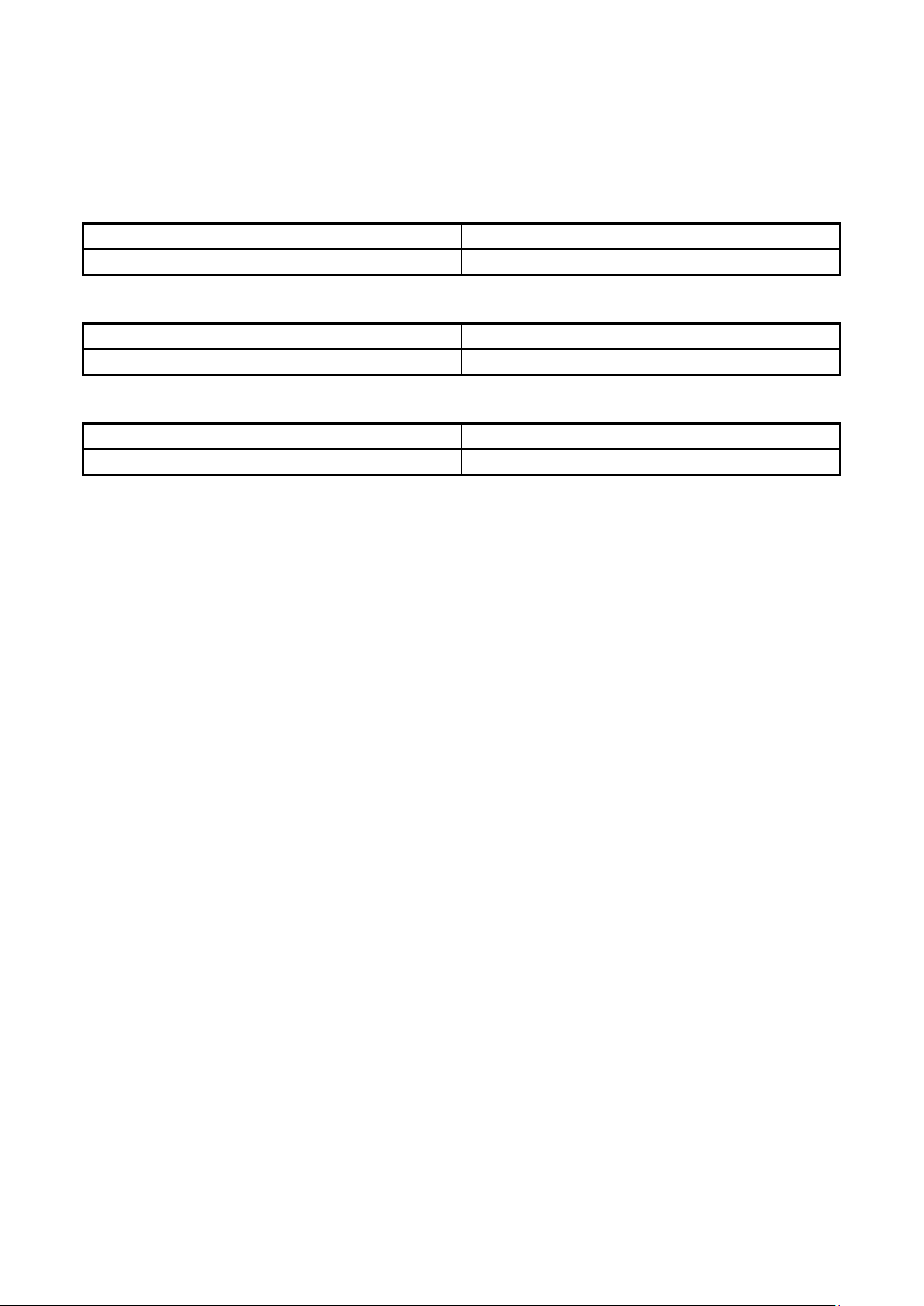
Term in This Application
To be Replaced with
Access window (AW)
Flash shield window
Term in This Application
To be Replaced with
4. Replacing Terms
Some terms used in this application should be replaced as shown in the table below, depending on the MCU
to be used.
USB Direct USB interface mode
• When an RL78 is to be used:
Term in This Application To be Replaced with
• When an RH850 with an extended user area is to be used:
User Boot Area Extended user area
All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 8

Table of Contents
1. Overview .......................................................................................................................... 10
1.1 Features ................................................................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Supported Microcontrollers ...................................................................................................................... 10
1.3 System Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 11
1.3.1 Connection with the Target System ............................................................................................... 11
1.4 Operating Environment ............................................................................................................................ 12
1.4.1 Hardware Environment .................................................................................................................. 12
1.4.2 Software Environment .................................................................................................................... 12
1.5 Formats of Program Files ........................................................................................................................ 13
1.5.1 RPI File ........................................................................................................................................... 13
1.5.2 RPE File ......................................................................................................................................... 13
1.6 Relative Paths for Files ............................................................................................................................ 13
2. Descriptions of Functions ................................................................................................ 14
2.1 Main Window ........................................................................................................................................... 14
2.2 Creating a New Project ............................................................................................................................ 15
2.2.1 [Create New Project] Dialog Box.................................................................................................... 15
2.2.2 [Tool Details] Dialog Box ................................................................................................................ 17
2.2.3 [Set Clock] Dialog Box ................................................................................................................... 20
2.2.4 [Authentication] Dialog Box ............................................................................................................ 21
2.3 Operating the Tabbed Pages ................................................................................................................... 22
2.3.1 [Operation] Tabbed Page ............................................................................................................... 23
2.3.2 [Operation Settings] Tabbed Page ................................................................................................. 25
2.3.3 [Block Settings] Tabbed Page ........................................................................................................ 29
2.3.4 [Flash Option] Tabbed Page .......................................................................................................... 31
2.3.5 [Connect Settings] Tabbed Page ................................................................................................... 36
2.3.6 [Unique Code] Tabbed Page .......................................................................................................... 37
2.3.7 [User Keys] Tabbed Page .............................................................................................................. 41
2.4 Menu Bar.................................................................................................................................................. 42
2.4.1 [File] Menu ...................................................................................................................................... 42
2.4.2 [Device Information] Menu ............................................................................................................. 45
2.4.3 [Help] Menu .................................................................................................................................... 50
2.5 Simple Use of Project Files from a Command Line ................................................................................. 51
2.5.1 Exit Code ........................................................................................................................................ 51
2.5.2 Restriction ...................................................................................................................................... 51
2.5.3 Command-line Syntax .................................................................................................................... 51
2.5.4 Start Options .................................................................................................................................. 52
2.5.5 Example of Command-line Statements ......................................................................................... 56
2.6 Command Line for Linux or Windows ...................................................................................................... 56
2.7 Encryption Utility Program ....................................................................................................................... 57
2.7.1 Exit Code ........................................................................................................................................ 57
2.7.2 Command-line Syntax .................................................................................................................... 57
2.7.3 Start Options .................................................................................................................................. 57
2.8 Renesas Flash Programmer Utility Program ........................................................................................... 58
2.8.1 Exit Code ........................................................................................................................................ 58
2.8.2 Command-line Syntax .................................................................................................................... 58
2.8.3 List of Commands .......................................................................................................................... 59
2.8.4 Start Options .................................................................................................................................. 59
3. Operating the RFP ........................................................................................................... 61
3.1 Flow of Operations ................................................................................................................................... 62
Page 9

4. Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................... 71
4.1 Problems during Startup .......................................................................................................................... 71
4.2 Problems during Operation ...................................................................................................................... 72
4.3 Problems during Communications ........................................................................................................... 77
4.4 Error Messages ........................................................................................................................................ 78
5. Points for Caution ............................................................................................................ 84
5.1 Manipulating the User Boot Mat .............................................................................................................. 84
5.2 Host PC .................................................................................................................................................... 84
5.3 USB-to-Serial Converter .......................................................................................................................... 84
5.4 Check before Connection ........................................................................................................................ 84
5.5 Erase Chip of the RH850 Family ............................................................................................................. 84
5.6 Connecting through a COM Port or USB Direct ...................................................................................... 85
5.7 Auto-padding with 0xFF ........................................................................................................................... 85
5.8 Verification after Protecting the MCU ...................................................................................................... 85
5.9 MCUs Supporting a Dual-Bank Structure ................................................................................................ 85
Page 10

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 1. Overview
1. Overview
The Renesas Flash Programmer (hereafter referred to as the RFP) is software that uses an E1 emulator
(hereafter referred to as the E1), E20 emulator (hereafter referred to as the E20), E2 emulator (hereafter
referred to as the E2), or E2 emulator Lite (hereafter referred to as the E2 Lite) via a serial or USB interface or
a J-Link debug probe (hereafter referred to as the J-Link) to erase, write, and verify programs on a target
system on which a Renesas Electronics MCU with on-chip flash memory is mounted.
1.1 Features
• Writing controlled by the host PC
• High-speed writing by using an emulator
• Simple operation for writing with a simple GUI specific to development
• Automatic writing from a command line
• Programming of a unique code to a designated area of flash memory
• Support of encrypted program files
1.2 Supported Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers supported by the RFP are listed on the Web page at the following link:
https://www.renesas.com/rfp
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 10 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 11
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 1. Overview
+
Renesas
Flash Programmer
Serial cable (RS-232C)
USB cable
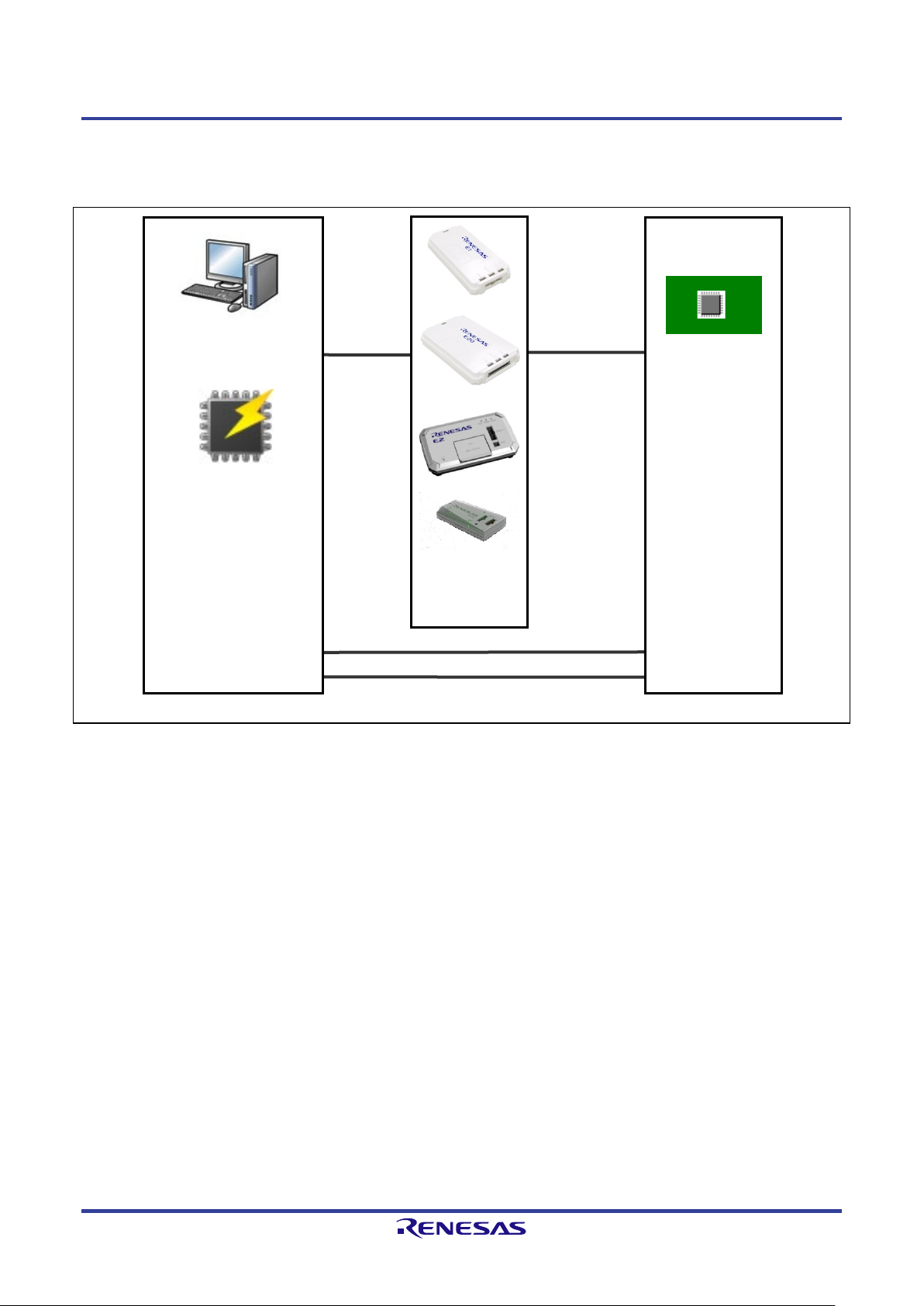
1.3 System Overview
An overview of the RFP system is illustrated in the following diagram.
E1
PC
USB cable
E20
E2
E2 Lite
J-Link
Target cable
Target system
Figure 1-1 RFP Connection Image
1.3.1 Connection with the Target System
For examples of programming circuits by using the E1, E20, E2, or E2 Lite, refer to the user’s manuals for the
individual products.
For examples of programming circuits by using the USB, refer to the hardware manual of the target MCU you
are using.
Examples of programming circuits by using the serial interface of the host PC are provided on the web page at
the following link.
https://www.renesas.com/rfp
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 11 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 12

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 1. Overview
1.4 Operating Environment
1.4.1 Hardware Environment
(1) Host PC
• Processor: 1 GHz or faster
• Main memory: At least 1 Gbyte (2 Gbytes or more when using 64-bit Windows); 2 Gbytes or more
recommended
• Display: 1,024 x 768 or higher
• Interface: USB 2.0 (when using E1, E20, E2, E2 Lite, USB Direct, or J-Link)
Serial interface (RS-232C, when using COMx)
(2) Tools supported
• E1
• E20
• E2
• E2 Lite
• J-Link
Note: The following restrictions apply to the J-Link.
Target MCUs: RA series
Communications method: 2-wire UART
Communications rates: 115200 bps or 9600 bps
Remark: The supported target MCUs differ with the tool. For the target MCUs supported by the different
tools, refer to List of MCUs Supported by Renesas Flash Programmer V3.
1.4.2 Software Environment
(1) OSs supported
• Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Windows 8.1 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Windows 10 (32-bit and 64-bit)
• Linux (Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, x64/ARM32/ARM64)
• Linux (Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, x64/ARM32/ARM64)
Remarks: 1. We recommend having the latest service pack or version of Windows installed.
2. The GUI (RFPV3.exe) does not run under Linux.
(2) Required software
• Windows: Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 or a later version
• Linux: Refer to the guide “rfp_cli.md”, which is separately provided. Note that this is a markdown-format
English file.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 12 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 13

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 1. Overview
1.5 Formats of Program Files
For a HEX file to be readable by the RFP, it must have the correct format and satisfy the following conditions.
If a program file with a non-supported format is read, an error will occur.
(1) Intel HEX format
• The format file ends with the end record.
• All lines consist solely of record types 00 to 05.
(2) Motorola S format
• The format file ends with the end record (S7, S8, or S9).
• All lines consist solely of record types S0 to S9 (excluding S4).
1.5.1 RPI File
An RPI file is an image file that the RFP can generate. An RPI file combines program code and flash options
data. Refer to section 2.4.1 for the generation of these files.
1.5.2 RPE File
An RPE file is a file generated by using the encryption utility program to encrypt a program file. Refer to
section 2.7 for the generation of such files.
1.6 Relative Paths for Files
When the following files are registered in a project, the RFP automatically uses relative paths in saving the
files under the project directory.
• Program file
• Unique code file
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 13 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 14
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
2. Descriptions of Functions
This chapter describes the window structure and functions of the RFP.
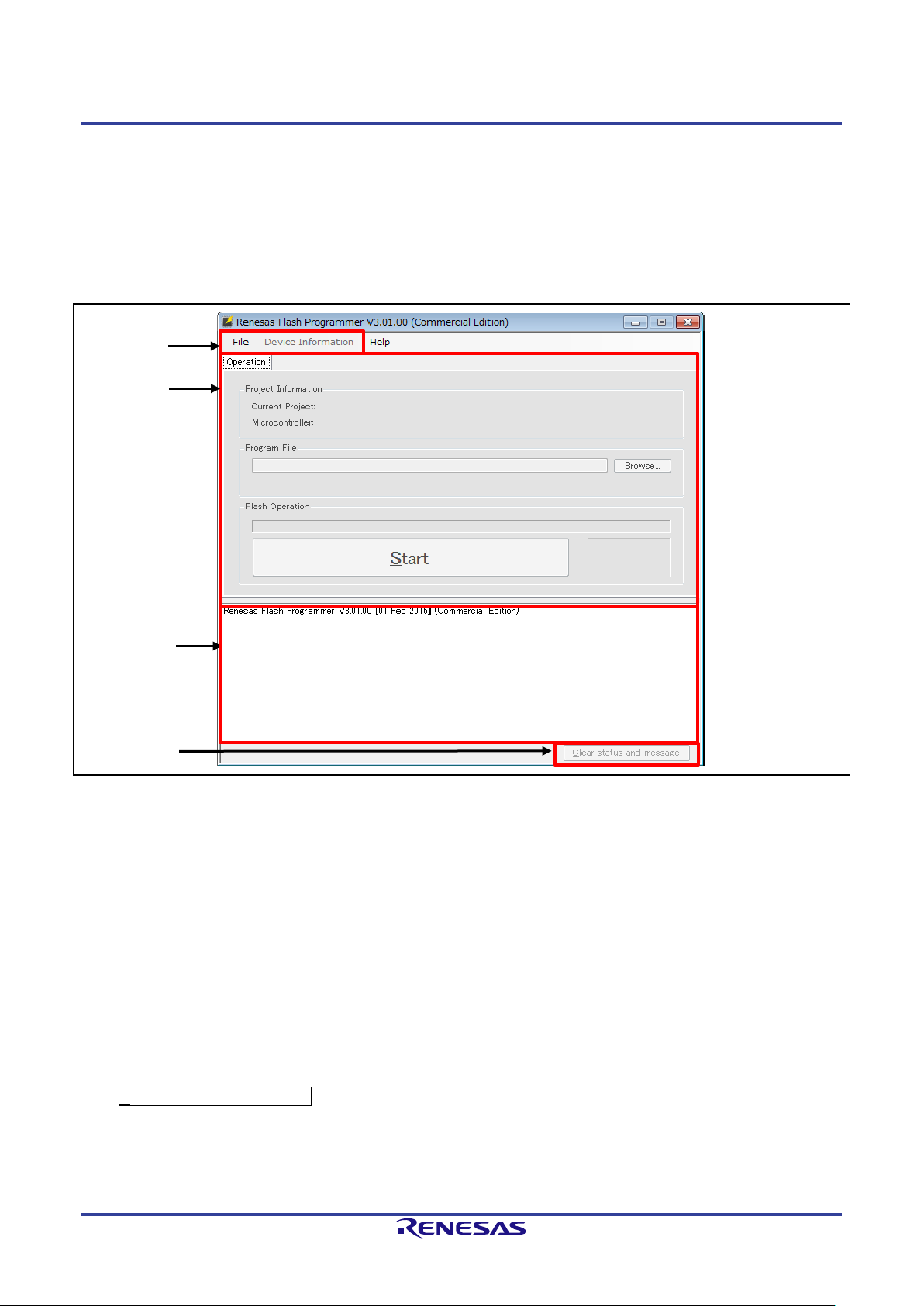
2.1 Main Window
After the RFP is started, the main window as shown below will appear.
Figure 2-1 Main Window
(1) Menu bar
For the menu bar, refer to section 2.4, Menu Bar.
(2) Tabbed pages
Operations on the tabbed pages enable controlling the RFP for writing, setting options, and so on. For details
on the individual tabbed pages, refer to section 2.3, Operation of the Tabbed Pages.
(3) Log output panel
The version information of RFP and the contents and results of command execution are displayed here.
Caution: Log entries older than the 1500th line are automatically removed.
(4) Clear status and message
Pressing this button clears the contents of the log output window and the status information on the [Operation]
tabbed page.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 14 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 15

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
2.2 Creating a New Project
2.2.1 [Create New Project] Dialog Box
Selecting [File] → [Create a new project] in the menu bar makes the [Create New Project] dialog box appear.
The configuration of the dialog box is shown below.
Figure 2-2 [Create New Project] Dialog Box
(1) Microcontroller
Select the type of target MCU to be used.
(2) Project Name and Project Folder
Specify the name of a project which is to be newly created and the project folder which will hold the created
project file.
Remark: Since the project name is used in the file name, characters that are not usable in file names cannot
be used.
(3) Communication
Set up communications with the target MCU.
• “Tool”
Select the tool to be used for connection with the target MCU.
Caution: For the USB connection of RX65x, RX66x, RX72x, RA, RE devices with Renesas SynergyTM, select
“COM”, since serial communications are performed through a virtual USB COM port.
Remark: The usable tools may differ with the selected target MCU.
• “Interface”
When this item is selectable, select the method for communicating with the target MCU.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 15 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 16
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
• Tool Details…
Make detailed settings for the tool to be used. The tool in use and the setting for the supply of power
supply are shown to the right of Tool Details…. For details on Tool Details…, refer to section 2.2.2, [Tool
Details] Dialog Box.
(4) Wide Voltage
When “Wide Voltage” is selected, each command can be executed with the target microcontroller set to wide
voltage mode. When writing to the target MCU proceeds with a voltage lower than 2.4 V, deselect this
checkbox. For details on the wide voltage mode, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
Remark: “Wide Voltage” is not displayed for those target MCUs which do not support it.
(5) Connect
Clicking on Connect enables connection with the target MCU.
At this time, the following dialog boxes might be displayed according to the type of the target MCU; enter a
value in each dialog box to continue processing to make the connection.
• [Set Clock] dialog box
• [Authentication] dialog box
For details on these dialog boxes, refer to sections 2.2.3, [Set Clock] Dialog Box, and 2.2.4,
[Authentication] Dialog Box.
Caution: If the connection is made with incorrect settings, the tool or the target system might be damaged.
For details, refer to chapter 5, Points for Caution.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 16 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 17
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(3)
(4)
(1)
(2)
(5)
(6)
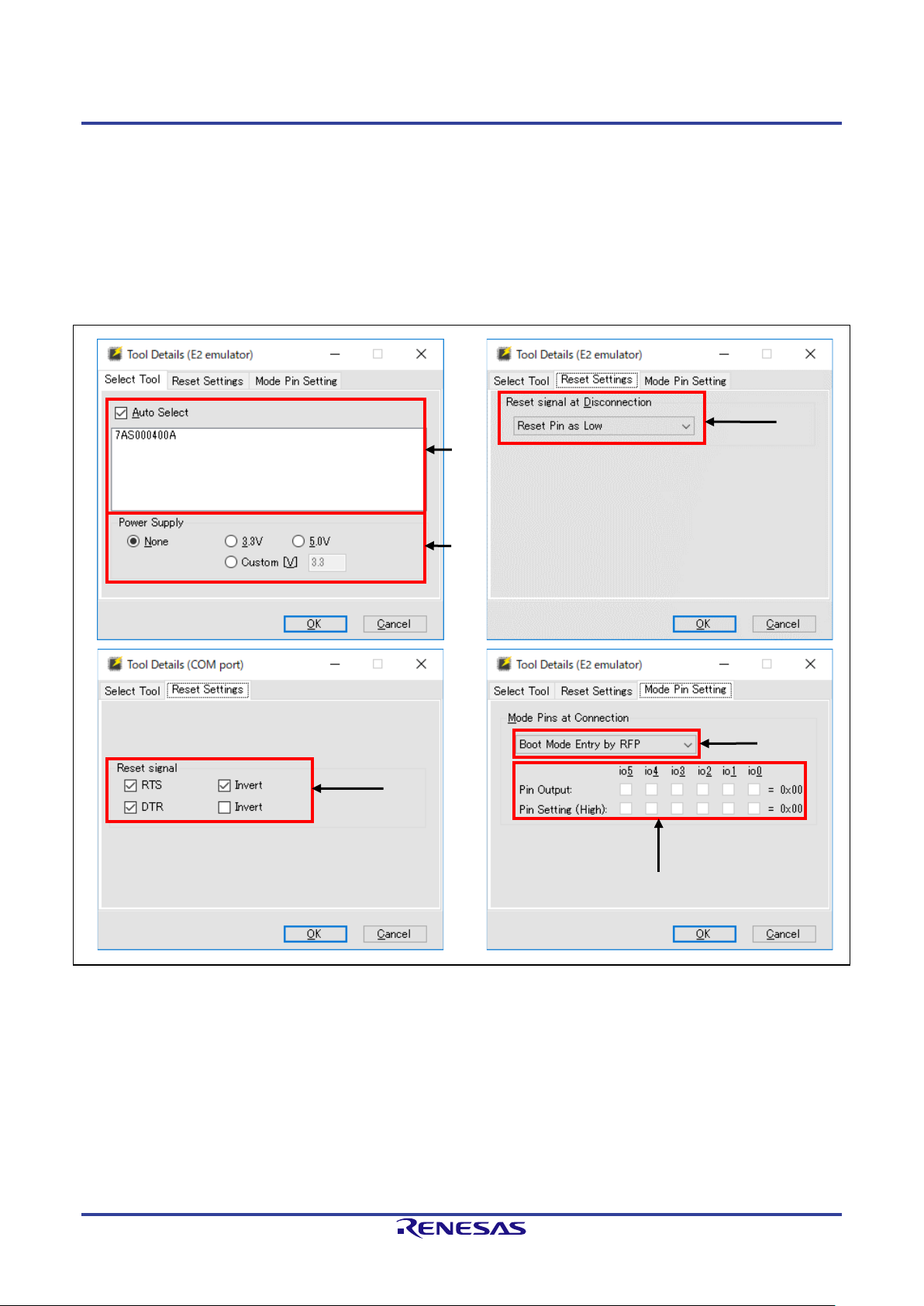
2.2.2 [Tool Details] Dialog Box
The [Tool Details] dialog box consists of the following tabbed pages.
• [Select Tool] tabbed page
• [Reset Settings] tabbed page
• [Mode Pin Setting] tabbed page
The [Mode Pin Setting] tabbed page is only displayed when the E1, E20, E2, or E2 Lite is selected.
Figure 2-3 [Tool Details] Dialog Box
(1) [Select Tool]
Tools which are currently available are shown; select the tool to be used.
When the “Auto Select” checkbox is selected, the tool which is shown at the top of the list is automatically
selected. To directly select the tool to be used, deselect the “Auto Select” checkbox and select a tool from the
list.
Remark: For the E1, E20, E2, or E2 Lite, the serial number of the emulator is shown.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 17 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 18

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(2) Power Supply
Select the power-supply function of the tool.
Select “None” if no power is to be supplied from the tool in use.
Specify the voltage when the tool in use is to supply power.
For the power-supply function, refer to the user’s manual of the tool you are using.
Caution: Do not use the power-supply function from the tool in processing for mass-production; instead,
supply power which matches the MCU’s specifications from the target system. Since the voltage
supplied from the tool depends on the performance of the USB power supply of the host PC, its
precision cannot be guaranteed.
Remark: [Custom] only appears in the [Tool Details] dialog box when the E2 emulator is selected. A voltage
within the range from 1.8 V to 5.5 V can be specified.
(3) Setting of RESET
Sets the operation of the reset signal when the RFP is disconnected from the target MCU.
• Reset Pin as Low
After the RFP is disconnected from the target MCU, the low level continues to be output from the RESET
pin.
• Reset Pin as Hi-Z
After the RFP is disconnected from the target MCU and the RESET pin has been at the low level, the
RESET pin enters the hi-Z state. This setting is used when the user wishes to operate the target MCU on
completion of processing with the RFP.
(4) Settings for reset signals
Make settings for pins to be used for the output of reset signals to the target MCU.
Remark: Reset signals are only displayed when the COM port is selected for the tool.
• Selection of the RTS or DTR signal
Selected: The signal is used as a reset signal.
Deselected: The signal is not used as a reset signal.
• Logic of the signal
Selected: The RTS or DTR signal outputs the high level when the device is reset.
Deselected: The RTS or DTR signal outputs the low level when the device is reset.
(5) Setting of entry to boot mode
Make settings for pins when the target MCU is connected.
• “Boot Mode Entry by RFP”
The settings of “Pin Output” and “Pin Setting” according to the recommended circuits of the tool in use are
made automatically.
Remark: For the recommended circuit, refer to the user’s manual and the additional document of the tool
you are using.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 18 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 19
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
14 Pins
38 Pins
Pin Name (RX Family)
1
15
io4 2 ―
GND
3
21
io5 4 3
io0 5 11
TxD 6 1
io1 7 8
io3 8 14
VCC
9
17 ― 10 2 io2
11
19
RxD
12 ― GND
13 9 RESET
14 5 GND
• “Boot Mode Entry by User”
Manually make the settings for “Pin Output” and “Pin Setting”.
Remark: “Boot Mode Entry by User” might not be selectable depending on the target MCU or tool in use and
the communications interface.
(6) Setting of outputs
Selecting “Boot Mode Entry by User” for boot mode entry enables the setting of outputs.
The boxes set the output of the io0 to io5 pins of the tool in use when the target MCU is connected.
• Pin Output
Selected: The target pin is used as an output pin.
Deselected: The target pin is used as hi-Z.
• Pin Setting (High)
Selected: The high level is output.
Deselected: The low level is output.
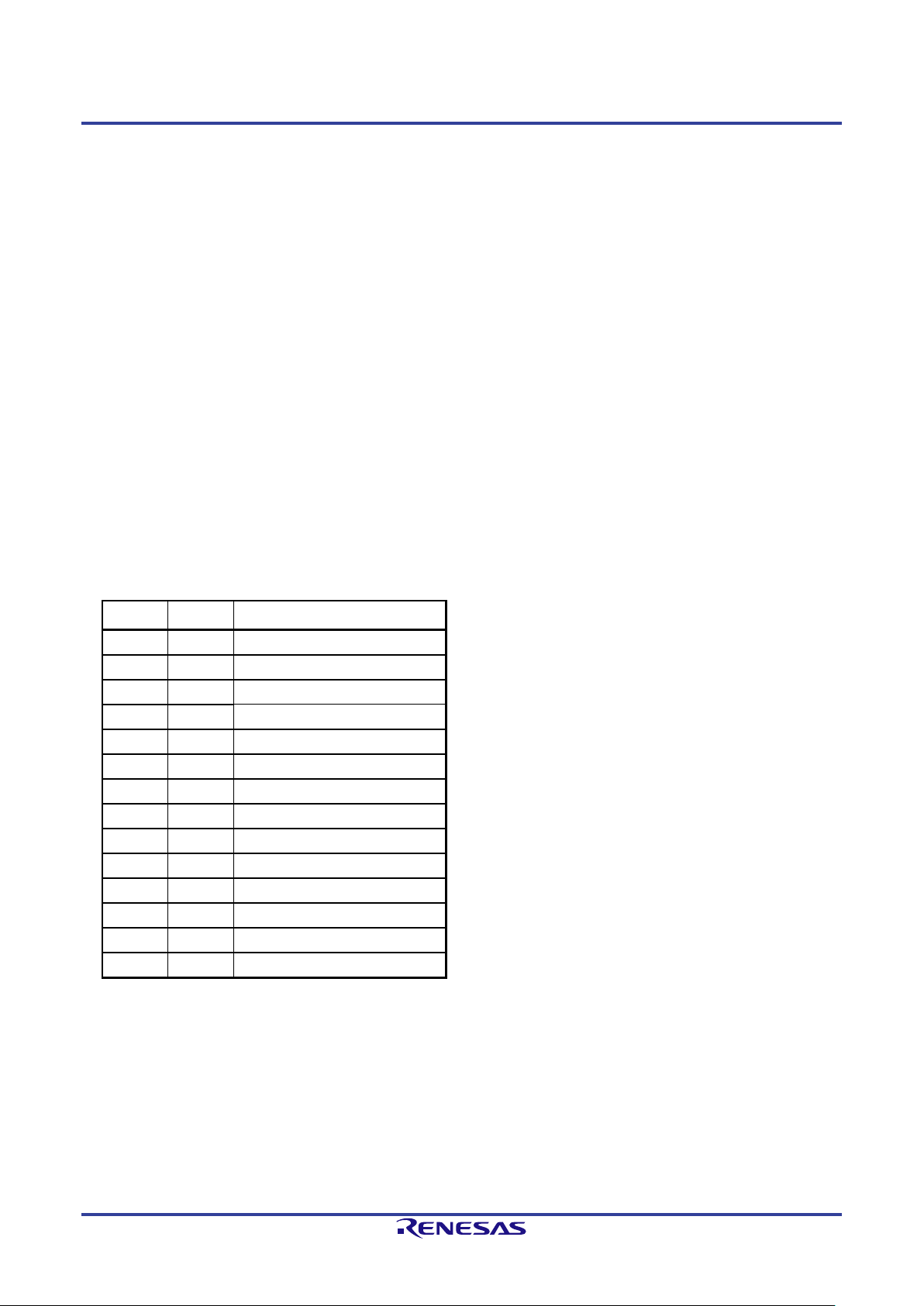
For pin assignments of io0 to io5 in the E1, E20, E2, and E2 Lite, refer to table 2-1 and table 2-2.
Table 2-1 Pin Assignments for the E1, E20, E2, and E2 Lite
Remark: TxD and RxD are signal names of the MUC side.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 19 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 20
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
20 Pins
Pin Name (RA Family)
Pin Name (RE Family)
Remark
1
VCC
VCC
2 ―
RxD
3 GND
GND
4 io4
io4 / TxD
E2 Lite cannot use
5
GND
GND
6 TxD ― 7 ― ― 8 RxD
― 9
GND
GND
10
RESET
RESET
11 ― ― 12
io3
io3
E2 Lite cannot use
13 ― ― 14
io1
io1
E2 Lite cannot use
15
GND
GND
16
io5
io5
E2 Lite cannot use
17
GND
GND
18
io0
io0
E2 Lite cannot use
19
GND
GND
20
io2
io2
E2 Lite cannot use
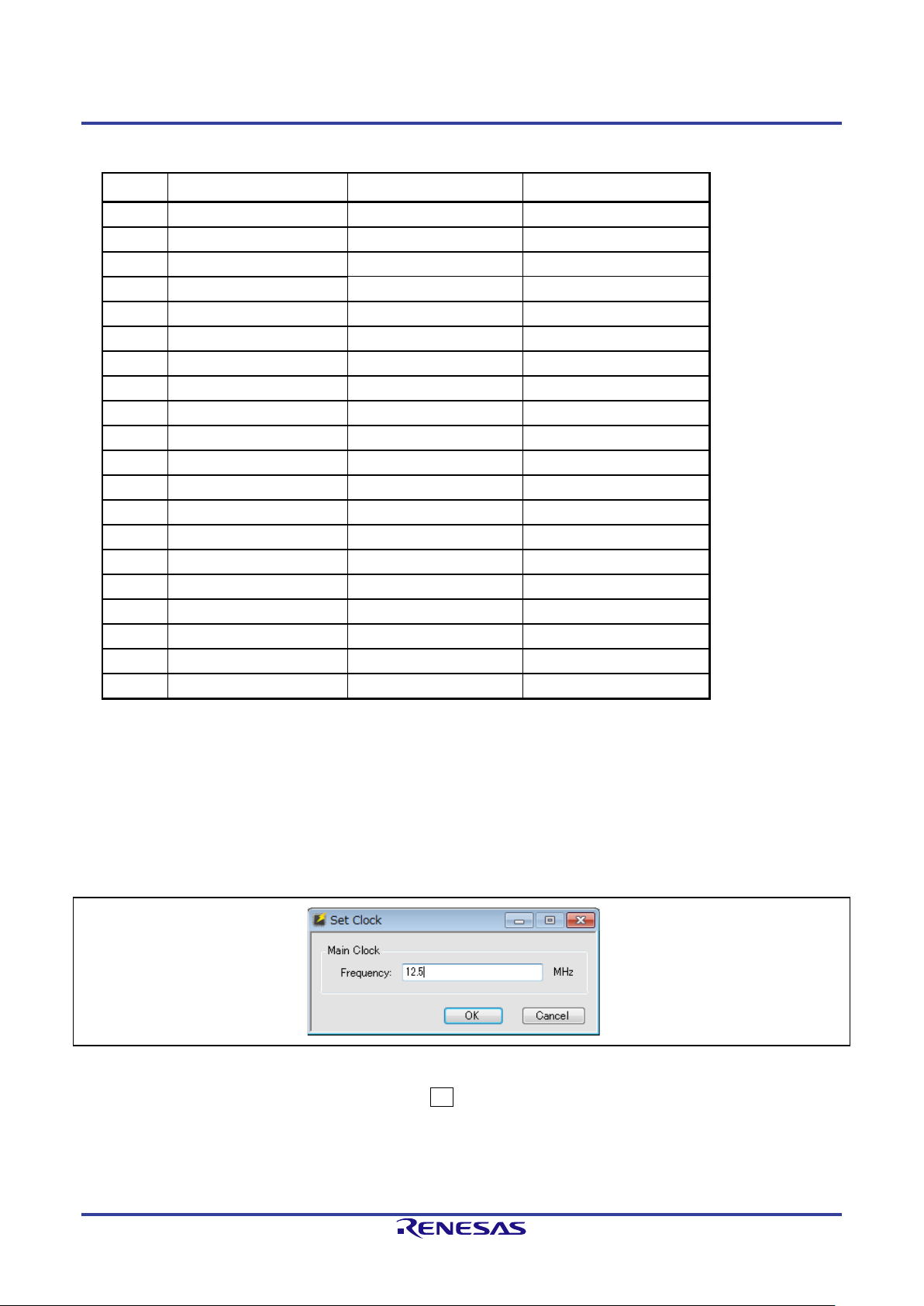
Table 2-2 Pin Assignments for the E2, and E2 Lite
Remark
- TxD and RxD are signal names of the MUC side.
- E2 Lite does not support the RE family.
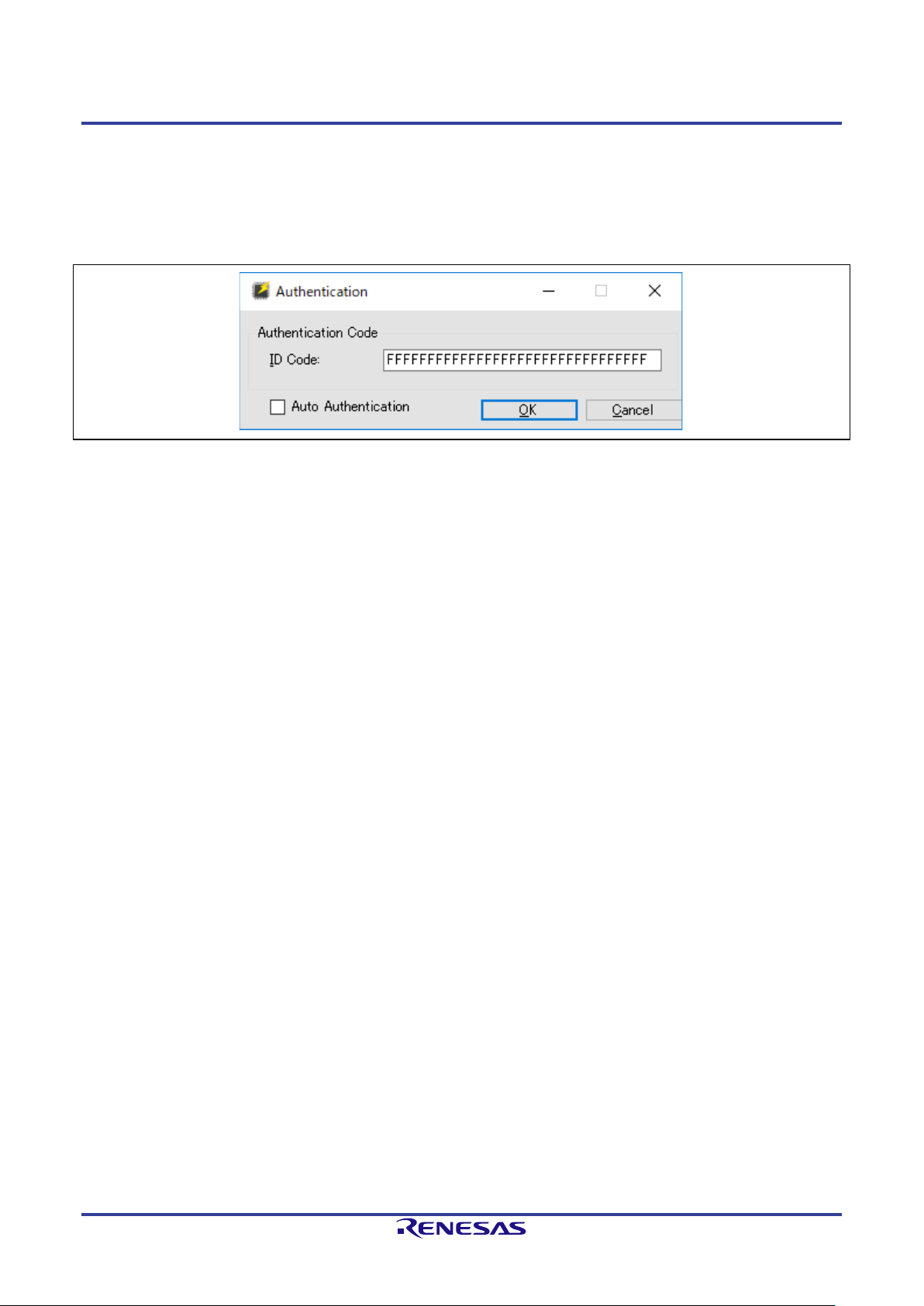
2.2.3 [Set Clock] Dialog Box
The input clock must be set to suit the type of the target MCU.
If setting of the input clock is required, the [Set Clock] dialog box will appear.
Figure 2-4 [Set Clock] Dialog Box
Enter the frequency of the input clock and click on OK.
The value for frequency is entered in MHz. If you want to enter a value in smaller units than MHz, use a
decimal point.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 20 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 21
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
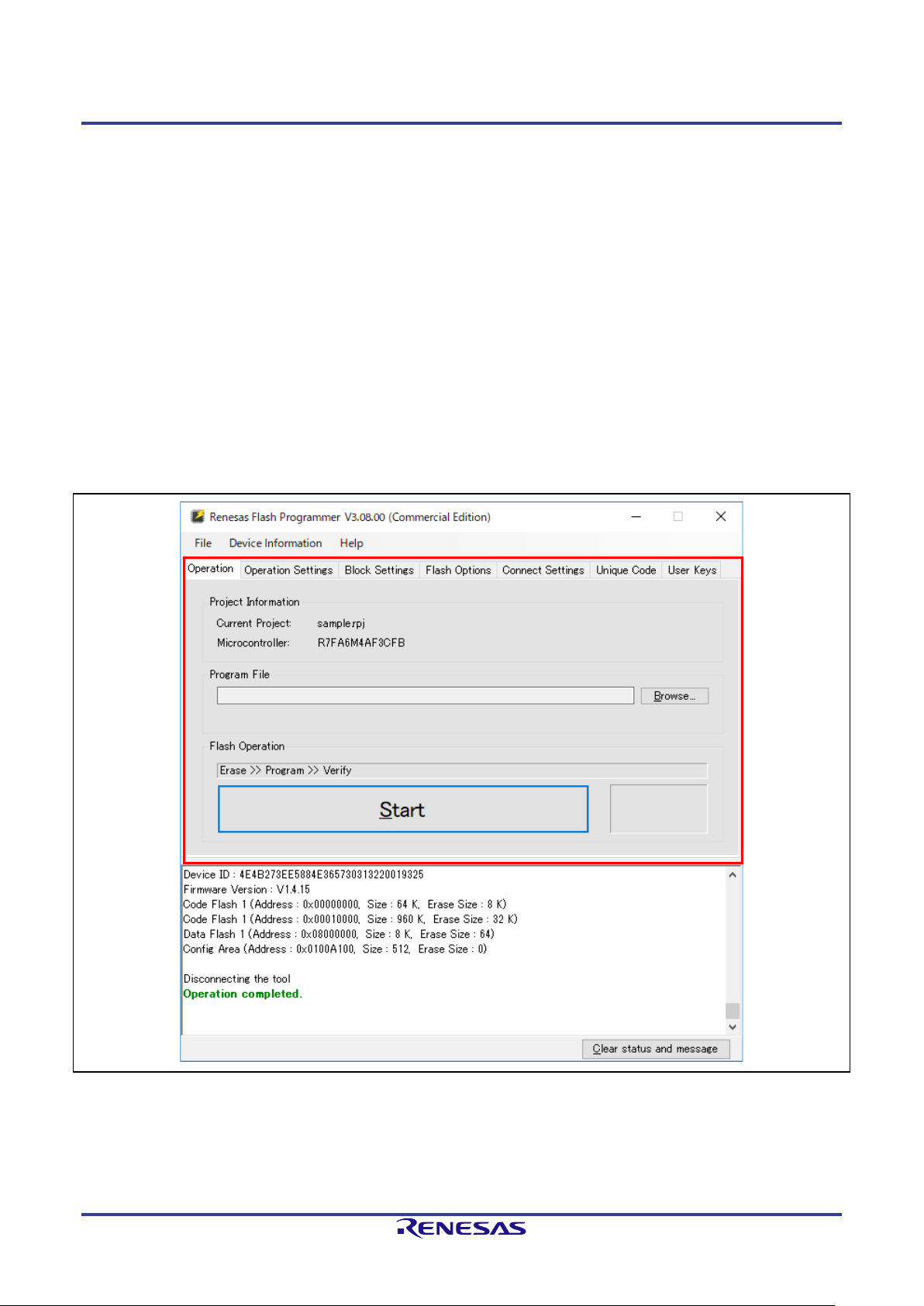
2.2.4 [Authentication] Dialog Box
If entering an authentication code is required, the [Authentication] dialog box will appear.
Remark: Whether or not there is an authentication code function depends on the target MCU.
Figure 2-5 [Authentication] Dialog Box
• Authentication Code
Enter the authentication code in hexadecimal notation (0 to 9 and A to F).
• Auto Authentication
When this checkbox is selected, the authentication code is saved in the project file and authentication
automatically proceeds from the next time the project is opened.
Caution
- If the value of the input field takes up fewer than the number of effective bytes, the RFP
automatically pads the input data with 0xFF after the input value.
- When an RX-family device is connected via the RFP, input the value in the order ID1, ID2, ..., ID16.
However, for a device with control code, enter the value of the code as the first of the effective
bytes.
Example:
When the number of effective bytes = 16, control code = 0x45, ID code = ID1=0x01, ID2=0x02,
ID3=0x03, ID4=0x04, ID5=0x05, ID6=0x06, ID7=0x07, ID8=0x08, ID9=0x09, ID10=0x0A,
ID11=0x0B, ID12=0x0C, ID13=0x0D, ID14=0x0E, and ID15=0x0F, the value will be
‘450102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F’.
- When RX72x, RX71x, RX66x, RX65x, or RX64x device is connected via a debug tool which has
been specified with the CS+ or e2 studio, the order for input of the authentication code changes to
that shown below.
ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID8 ID7 ID6 ID5 ID12 ID11 ID10 ID9 ID16 ID15 ID14 ID13
- When an RA-family, Renesas Synergy-family, or RE-family device is connected to the RFP, input
values to be specified for registers of the target MCU in order of bits 127 to 0 in byte units. Since the
input specification may also differ with the tool, confirm the input specification of the tool you will be
using.
Remark: The default authentication code in some target MCUs at the time of shipment is all FFs. For details,
refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 21 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 22
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.3 Operating the Tabbed Pages
When “Create New Project” is completed normally, the main window of the RFP is displayed.
Operating the tabbed pages in the main window allows you to make detailed settings of the RFP.
The tabbed pages consist of the seven listed below.
• [Operation] tabbed page
• [Operation Settings] tabbed page
• [Block Settings] tabbed page
• [Flash Option] tabbed page
• [Connect Settings] tabbed page
• [Unique Code] tabbed page
• [User Keys] tabbed page
The following describes the configuration and operation of each tabbed page.
Figure 2-6 Main Window
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 22 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 23
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
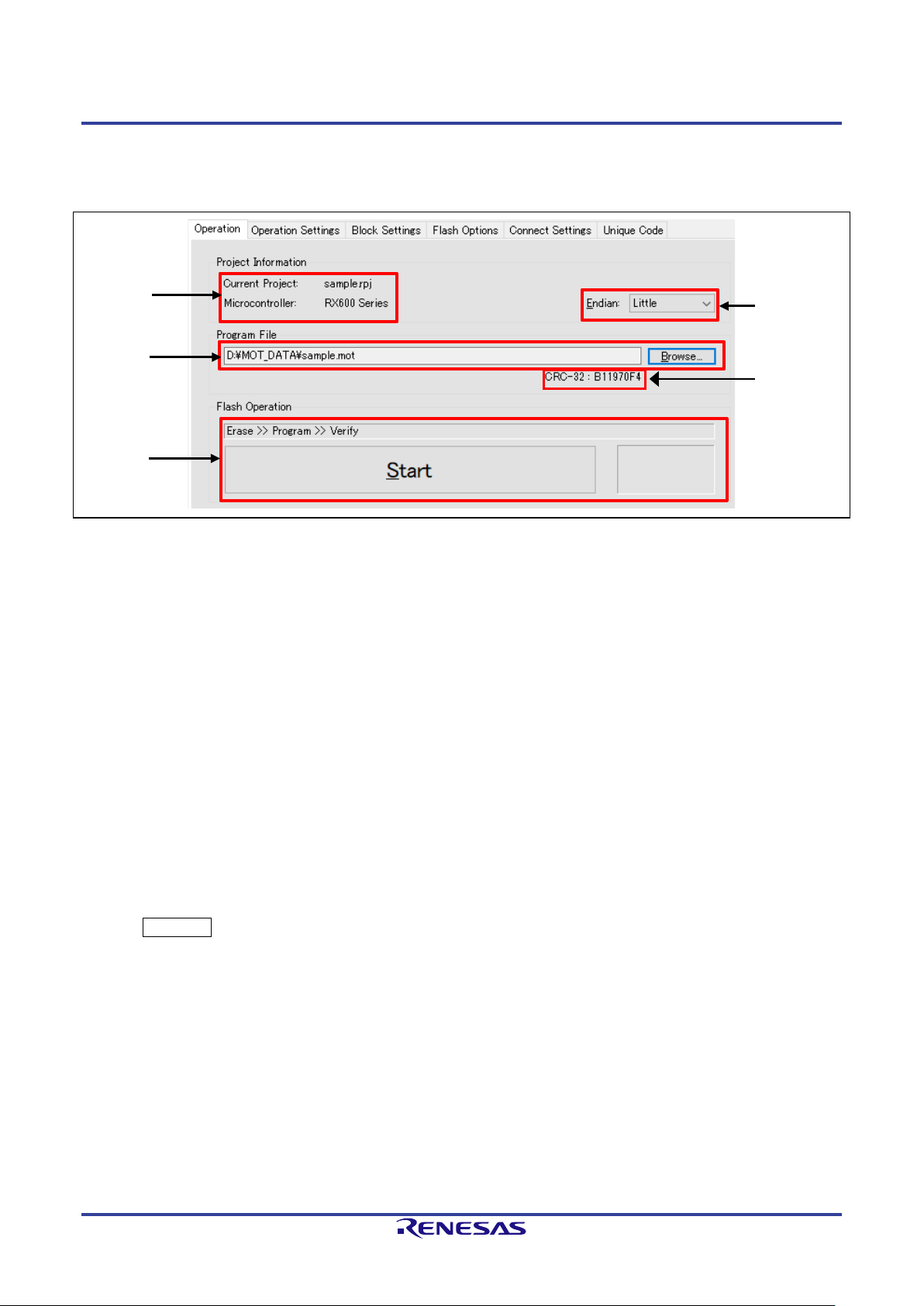
2.3.1 [Operation] Tabbed Page
The [Operation] tabbed page shows information on the project and flash operation.
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
Figure 2-7 [Operation] Tabbed Page
(1) Project Information
Information on the selected project is shown.
(2) Endian
Select the endianness for the data of the program file.
This item does not appear for target MCUs which do not support changing the endianness in the RFP.
• “Little”
Set the handling of files for programming as little endian.
• “Big”
Set the handling of files for programming as big endian.
(3) Program File
Set the path to a file to be programmed in the flash memory of the target MCU.
Click on Browse… to select a file.
Multiple files for programming are also selectable simultaneously. Refer to 2.3.1.1, Selecting Multiple Program
Files, for details.
(4) File Check Sum
CRC-32 check sum of the selected program file is displayed.
Caution: This CRC-32 is a check sum for whole of file, not for HEX data. The file check sum is different from
the check sum of the one obtained from MCU.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 23 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 24
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
Immediately after the RFP has been started or after clicking on the Clear button under the
A command is being executed.
(1)
(2)
(5) Flash Operation
Clicking on Start leads to the execution of commands to handle the processing shown above Start.
Information on the state is indicated with color and characters in the status display to the right of Start. For the
status display, refer to table 2-3.
The type of flash operation can be changed on the [Operation Settings] tabbed page. For the [Operation
Settings] tabbed page, refer to section 2.3.2, [Operation Settings] Tabbed Page.
Table 2-3 State Information
output panel
A command has been executed and ended normally.
Processing has stopped during the execution of a command.
Processing failed after the execution of a command.
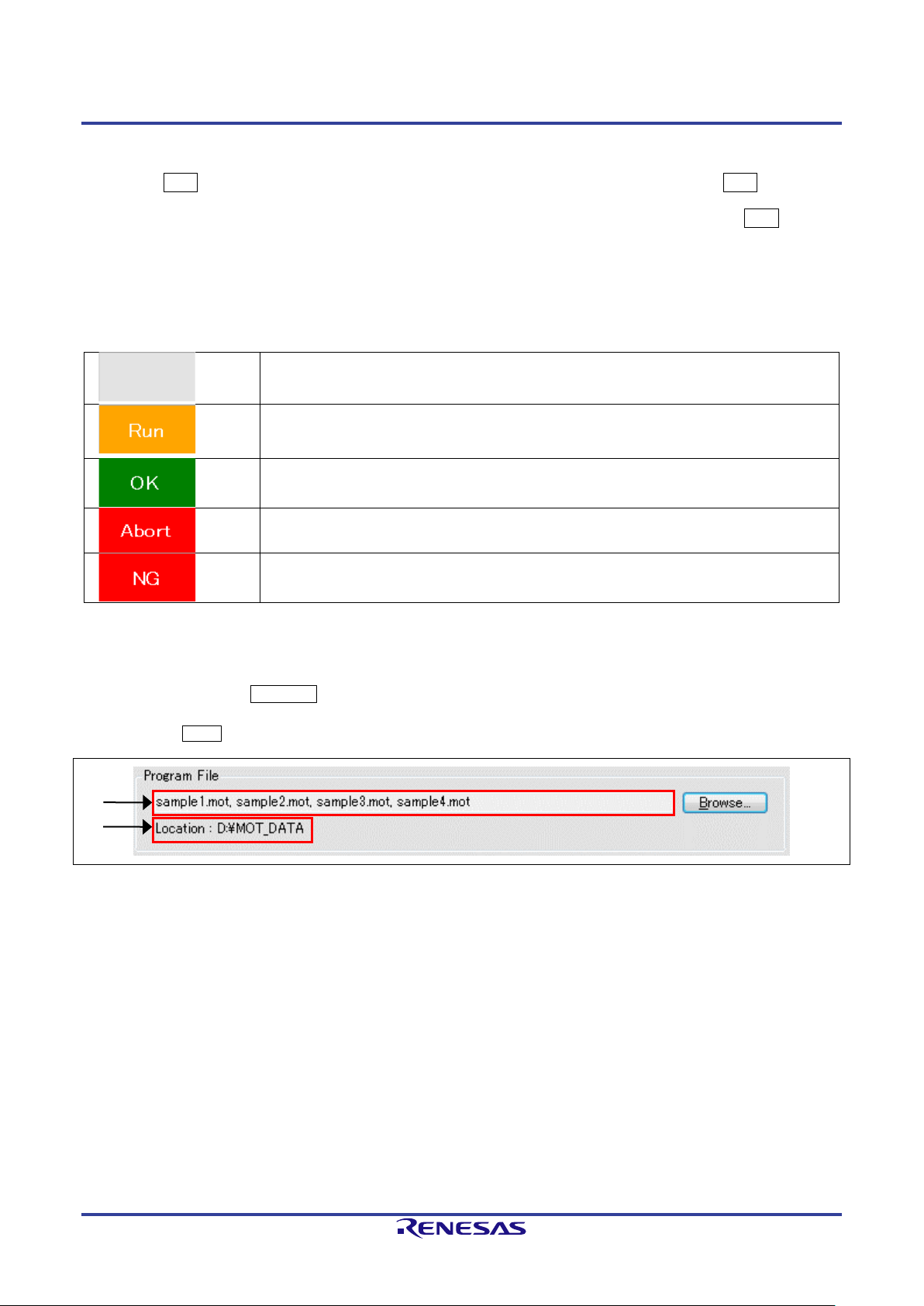
2.3.1.1 Selecting Multiple Program Files
When selecting multiple files, specify all desired files beforehand then press the [Start] button to run the actual
programming. Selecting Browse… opens the [Specify a program file] dialog box. The files can be recorded by
selecting them by mouse or by using the CTRL or SHIFT keys with the mouse or mouse and cursor keys, and
then selecting Open.
Figure 2-8 [Program File] Group Box after the Selection of Multiple Files for Programming
(1) Program Files
Only the file names are displayed when multiple files have been selected. That is, the path is separately
displayed.
(2) File Information
The path to the files for programming is displayed.
Caution
- An error occurs if an RPI, HCUHEX, or RPE file is specified in the selection of multiple files.
- An error occurs when writing to the flash area in cases of overlapping between the addresses of the
data files for programming.
- The selected multiple files must be in the same folder.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 24 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 25

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.3.2 [Operation Settings] Tabbed Page
Settings for the flash operation can be changed on the [Operation Settings] tabbed page.
Remark: Some items will not be shown according to the selected program file or the type of the target MCU.
(3)
(1)
(4)
(5)
(2)
(6)
Figure 2-9 [Operation Settings] Tabbed Page
(1) Command
Specify the type of processing that will proceed after clicking on Start in the main window.
When multiple operations are specified for “Command”, each operation is executed from the top item in order.
The following five types of processing can be specified for “Command”, and are described in more detail
following the summaries below.
• Erase
Erase the flash area.
The range of areas to be erased conforms to the setting made with “(3) Erase Option”.
• Program
Program the flash area.
The operation reflects the setting made under “(4) Program & Verify Option”.
• Verify
Perform verification.
The operation reflects the setting made under “(4) Program & Verify Option”.
• Program Flash Options
Set flash options such as “Lockbit”, “OTP”, “Access Window”, “Option Bytes”, and “Security”.
The programming setting conforms to the settings made on the [Block Settings] and [Flash Option] tabbed
pages.
Note, however, that this command is not displayed if an HCUHEX file, RPI file, or RPE file generated by
encrypting an HCUHEX file or RPI file is selected, in which case the flash options are always programmed.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 25 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 26

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
• Verify Flash Options
Select whether or not to verify values in the flash option area.
• Checksum
Acquire the checksum.
The checksum is calculated by the method selected under “(5) Checksum Type”.
Remark: The results are output in units of areas of flash memory. Use the verify command if you want to
check the consistency of data in units of blocks.
(2) Fill with 0xFF
Select the method for handling ranges for which files have no data in each area of flash memory.
• When this option is selected
Programming: The value 0xFF is programmed to bytes in ranges for which the program file has no data.
Verifying: Ranges containing no data from a program file are regarded as having the value 0xFF for
comparison.
• When this option is not selected
Programming: Ranges for which the program file has no data are not programmed.
Verifying: Ranges for which the program file has no data are not verified.
Caution: Even if “Fill with 0xFF” is not selected, this action always applies for the minimum unit of
programming by the MCU.
(3) Erase Option
Set options when “Erase” is selected for “Command”.
• Erase Selected Blocks
Erase only those blocks selected on the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
For the [Block Settings] tabbed page, refer to section 2.3.3, [Block Settings] Tabbed Page.
• Erase All Blocks
Erase all blocks.
Caution: Erasure processing may be skipped for certain blocks reserved by the MCU due to security
functions and so on.
• Erase Chip
Erase all blocks and clear the flash options.
Caution: This processing does not restore the MCU to its state at shipment. If correct settings are not
programmed for the flash options after erasing the chip, the MCU will not operate.
When this processing is used on an RH850 family product, be sure to refer to chapter 5, Points for
Caution.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 26 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 27

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(4) Program & Verify Option
Set options here when you have selected “Program” or “Verify” for “Command”.
• Erase Before Program
The range where data are to be programmed is erased beforehand if this option is selected.
Caution: The range to be erased depends on the minimum unit of erasing by the MCU.
• Verification type
Select the type of verification as one of the following items. Depending on the target MCU, only one type
may be available.
Verify by reading the device
Data are acquired with a read command from the MCU and the RFP handles comparison.
Comparison cannot proceed if the MCU is in a state such that reading is prohibited.
Verify in the device
Data are re-sent to the MCU in response to the verify command and the MCU side handles
comparison.
Depending on the specifications of the verify command, the range for comparison may extend beyond
the programmed data, and this may lead to an error in verification if “Fill with 0xFF” was not selected.
• Skip ID Code Verify
In general, do not select the checkbox when this feature is displayed as an option. However, use this
feature in cases of the following type.
The security settings of the MCU may make reading of the ID code impossible since the ID code in the
MCU is protected. This may lead to an error may occur in verification processing. To avoid errors of this
type, select this checkbox to use the feature.
For details, refer to section 5.8, Verification after Protecting the MCU.
(5) Checksum Type
Select the type of calculation when “Checksum” is selected for “Command”.
The available types of calculation differ according to the target MCU.
• Calculate block selection range
Applies to: RL78
When this option is selected
The range of calculation is limited to blocks that are selected in the [P.V] column on the [Block Settings]
tabbed page.
When this option is not selected
The result for the whole area of the flash memory is output.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 27 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 28

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(6) Error Settings
Select the method for handling cases where the program file attempts access to data which is out of the range
of memory in the MCU.
• Enable address check of program file
When this option is selected
In case of attempted access to data that are out of the range of memory, the RFP outputs an error
message and stops processing.
When this option is not selected
In case of attempted access to data that are out of the range of memory, the RFP outputs a warning
message, ignores that data, and continues processing.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 28 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 29

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.3.3 [Block Settings] Tabbed Page
The blocks for operations can be set on the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
Remark: The columns to be displayed differ according to the type of the target MCU.
(1)
(2) (3) (4)
Figure 2-10 [Block Settings] Tabbed Page
(1) Information on the block areas
Information on the ranges of the block areas for the target MCU is shown.
Caution: Common area names and block numbers are used in the RFP; note that they may differ from those
described in the user’s manuals of the target MCUs.
(2) Erase column
Specify blocks to be erased.
When “Erase Selected Blocks” is selected for “Erase Option” on the [Operation Settings] tabbed page, blocks
with checkboxes selected in the Erase column are to be erased.
(3) P.V column
Specify blocks to be programmed or verified.
Blocks with checkboxes selected in the P.V column are to be programmed or verified.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 29 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 30

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(4) Setting functions in units of blocks
Specify blocks for the setting of security or safety functions.
While “Program Flash Option” is selected, the settings are only reflected in the MCU when the type of setting
is enabled on the [Flash Option] tabbed page.
• Lockbit column
Select blocks for which the lock bit is to be set.
A lock bit is set for blocks with the checkbox selected.
• OTP column
Select blocks to be set as OTP.
Blocks with the checkbox selected are set as OTP.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 30 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 31

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.3.4 [Flash Option] Tabbed Page
The flash options of the MCU can be set in the [Flash Option] tabbed page.
Remark: Only those items the target MCU supports are shown. For the meanings and details of the settings
of the individual items, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU in use.
Figure 2-11 [Flash Option] Tabbed Page
(1) Lock-Bit
Specify lock bits.
The blocks for which the lock bit is to be set are selected on the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
(2) OTP
Specify OTP.
The blocks to be set as OTP are selected on the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
(3) Access Window
Specify access window.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: Access window is not set.
“Set”: The setting of access window is enabled.
• “Start Block/End Block”
Select the start or end block from the pull-down menu.
• “Operation Setting”
“Prohibit outside the range”: Programming or erasing of blocks outside the range from the start block to
the end block is prohibited.
“Prohibit inside the range”: Programming or erasing of blocks within the range from the start block to
the end block is prohibited.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 31 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 32

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
• “Disable Rewriting”
“No”: Making changes within the access window is not disabled.
“Yes”: Making changes within the access window is disabled.
(4) Option Bytes
Change the settings of option bytes.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: Option bytes are not set.
“Set”: The setting of option bytes is enabled.
• “Enable Extended Option Bytes”
“Disable”: Operations on the extended option bytes (OPBT8 and above) are disabled.
“Enable”: Operations on the extended option bytes (OPBT8 and above) are enabled.
Caution: Since the extended option bytes contain important settings for the MCU, take care with the data to
be programmed if you enable this operation. Normally use this option as “disabled” unless you have
a particular reason to do otherwise.
• “OPBT0∼OPBT7”
Enter the settings for option bytes in units of four bytes in hexadecimal notation (bit31....bit0).
• “OPBT8” or later
Enter the settings for extended option bytes in units of four bytes in hexadecimal notation (bit31....bit0).
(5) ICU-S
Set ICU-S.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: ICU-S is not set.
“Set”: The ICU-S function is enabled.
Caution: Once the ICU-S function is set for the MCU, it cannot be canceled by the RFP.
(6) Security
Set security functions.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: The security function is not set.
“Set”: The security function is enabled.
• “Enable ID Code Authentication”
“No”: The ID authentication function is disabled.
“Yes”: The ID authentication function is enabled.
• “Disable Block Erase / Disable Program / Disable Read / Disable Rewriting boot cluster / Disable Initialize
Command”
“No”: The security function is not set for the target command.
“Yes”: The use of the target command is prohibited.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 32 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 33

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
Caution
- Once the Disable Block Erase, Disable Rewriting boot cluster, or Disable Initialize Command
functions has been set for an MCU, the setting cannot be reversed.
- Even if the security setting is “No”, the security setting for the MCU is not reversed.
(7) Connection prohibited
Make the setting for disabling connection in serial programming mode or both the debugger and serial
programming mode.
• “Disable Serial Programming”
“Do Nothing”: Serial programming is not disabled.
“Set”: Connection in serial programming mode is disabled.
• “Disable Debugger and Serial Programming”
“Do Nothing”: Debugger and serial programming are not disabled.
“Set”: Connection in debugger and serial programming mode is disabled.
Caution: Once the Connection Prohibited function is set for an MCU, the setting cannot be reversed.
(8) Security Code
Set the ID code or the access password.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: An ID code or access password is not set.
“Set”: The setting of an ID code or access password is enabled.
• “ID Code”
Enter the ID code in hexadecimal notation.
• “Code Flash Access Password”
Enter the code flash access password in hexadecimal notation.
• “Data Flash Access Password”
Enter the data flash access password in hexadecimal notation.
(9) DLM
Make the setting for DLM transitions.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: A transition of the DLM state is not to be set.
“Set”: The setting of DLM transitions is enabled.
• “Target State”
Select the destination of the DLM transition from the pull-down menu.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 33 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 34

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(10) DLM Keys
Specify the DLM key file for use in DLM authentication which is to be set for the target MCU.
For details on how to generate DLM keys, refer to section 2.8, Renesas Flash Programmer Utility Program.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: A DLM key is not to be set.
“Set”: The setting of a DLM key is enabled.
• DLM key file
Open the [Open] dialog box by clicking on …, and specify a DLM key file.
Remark: If a DLM key file is not specified, programming of the flash memory will not proceed.
(11) Boundary
Set the size of the secure and non-secure areas of the target MCU.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: Boundaries are not to be set.
“Set”: The setting of boundaries is enabled.
• “Secure [KB]”
Enter the size of the secure area in KB units.
• “NSC [KB]”
Enter the size of the non-secure callable area in KB units.
Note: Confirm the specifiable sizes in the user’s manual of the target MCU since limits will apply.
(12) Flash Read Protection
Make the setting for flash read protection.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: Flash read protection is not to be set.
“Set”: The setting for flash read protection is enabled.
• “Start Block/End Block”
Select the start or end block from the pull-down menu.
Remark: To enable reading of all blocks, select “Permitted All Blocks”.
• “Disable Rewriting”
“No”: Rewriting of flash read protection is not disabled.
“Yes”: Rewriting of flash read protection is disabled.
(13) Extra Option
Make the setting for an extra option.
• “Set Option”
“Do Nothing”: An extra option is not to be set.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 34 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 35

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
“Set”: The setting of an extra option is enabled.
• “Disable Rewriting”
“No”: Rewriting of an extra option is not disabled.
“Yes”: Rewriting of an extra option is disabled.
Caution: Once the Extra Option function is set for an MCU, the setting cannot be reversed.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 35 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 36

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.3.5 [Connect Settings] Tabbed Page
The information required to connect the MCU can be set on the [Connect Settings] tabbed page.
Remark: The items displayed differ according to the type of the target MCU.
(1)
(4)
(6)
Figure 2-12 [Connect Settings] Tabbed Page
(1) Communication
Change the settings for communications.
For details, refer to section 2.2.1, [Create New Project] Dialog Box.
(2) Speed
Select the bit rate for use in communications with the target MCU.
The available bit rates differ according to the environment of the target MCU and the target system.
(2)
(3)
(5)
Caution: The speed is only directly specifiable for a COM connection. Since using this may lead to the RFP
being unable to detect a bit-rate error, set the speed only after confirming that it will not cause a
problem.
Remark: The maximum rate that the E2 Lite can support is 1.5 Mbps. However, only rates which are
selectable from the external clock of the target MCU or system are displayed for the RX family. The
baud rate which was selected for the E1, E20, or E2 emulator might not be selectable.
(3) Wide Voltage
For details, refer to section 2.2.1, [Create New Project] Dialog Box.
(4) Main Clock
Change the frequency of the input clock from that which was set when the project was created.
(5) Device Authentication
When “Auto Authentication” is set to “Yes” in the dialog box which is displayed in response to clicking on the
Settings… button, the ID code or access password that has been entered is used for authentication. To
change the value used for automatic authentication, enter a new value.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 36 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 37

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Remark: If “Auto Authentication” is set to “No”, the ID code or access password will not be saved in the
project file.
(6) RH850 SVR Setting
Make the settings to control the SVR parameters while the RFP is connected to the target MCU.
• “Override SVR parameters”
When this item is selected, the RFP is connected to the target MCU after forcibly changing the SVR
settings of the target MCU.
“Using program files”: Parameters in the program file are used.
“Disable SVR”: The SVR facilities are disabled.
Caution: Caution is required since the SVR settings are for the power supply. For details, refer to the user’s
manual of the target MCU.
2.3.6 [Unique Code] Tabbed Page
The [Unique Code] feature is for the embedding in a specified area of a unique code for the loaded program
file. The feature becomes effective when a unique code and specified area are written to a unique code file,
and the file name is set on the [Unique Code] tabbed page. A unique code file can contain a single
specification of an area and multiple unique codes, with an index for each of the unique codes. The next index
will be specified when a [Program] command ends normally; however, no index will be specified when a
[Flash Option Program] command ends normally.
Figure 2-13 [Unique Code] Tabbed Page
(1) Enabling or Disabling the Use of Unique Codes
Usage or non-usage of the unique code feature can be set in this checkbox.
Check the box to select the use of unique codes.
(2) Unique Code File
Open the [Open] dialog box by clicking on Browse…, and specify a unique code file.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 37 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 38

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(3) Specifying a Range
Specify a range of indices in the unique code file.
• “All”
Obtain the first and last indices from the unique code file. This starts from the first index when the RFP is
rebooted.
• “Continue from previous/User Specified”
The first and last indices are directly specifiable. Even if the RFP is rebooted, it will start from the previous
point.
“Next Index”: The next index is displayed or specified. The corresponding unique code will be shown
under the box.
“Final Index”: The last index of the range is displayed or specified. The corresponding unique code will
be shown under the box.
(4) Operation Setting
• Allow the overwriting of data
When embedding a unique code for a loaded program file, this button is used to allow or prohibit the
overwriting of data if the area where the code is to be embedded already contains data (contention). Put a
checkmark in the box to allow this and remove the checkmark to prohibit it.
[Remark] If the checkmark is removed, an error message is displayed and the process is cancelled, in cases
of contention with existing data during embedding of the unique code.
2.3.6.1 Unique Code Files
This section describes unique code files.
(1) Filename Extension
*.ruc
(2) File Format
A unique code file is a text file. A file consists of a header and a code part. Write a list of the combinations of
indices and unique codes after the header, which defines the location where the unique code is to be
embedded. The only supported formats for the codes are ASCII (one byte) character codes. Unicode is not
supported.
• Comment line
Line starting with “//” are considered as comments and ignored in processing. Lines consisting only of
blanks are also ignored.
• Separating characters
Tabs, spaces, or commas can be used as separating characters in the header definitions and the settings
of the indices and unique codes.
• Header part
The header part has the following definitions that are case-insensitive.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 38 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 39

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
Item
Definition of Unique Code
Specifying the format
format <hex | ascii>
Specifying the address
address <address>
Specifying the size
size <size>
<size>: Specify a size in bytes (range: 1 to 2048)
Item
Unique code definition
Declaration of unique codes
index data
Indices and unique codes
<index> <unique code>
Table 2-4 Header Definitions
Description
Specify the format of the unique codes.
<hex>: Hexadecimal numerals
<ascii>: ASCII characters (0x20 to 0x7e)
Specify the address where the unique code is to start as a
hexadecimal number preceded by “0” or “H”.
Specify the size of each unique code.
Remark: An area specification (area) was necessary for the earlier versions. It is now ignored even if there is a
statement in the file.
• Codes
The list of unique codes consists of indices and codes, with only one code and index per line. Indices need
not be prefixed by padding with“0” as in the example. They are assumed to be base-10 ordinal numbers in
ascending order.
Table 2-5 Code Definitions
(header of code part)
• Limit on size
The size of a unique code file should be no greater than 2 GB.
Description
Declares that unique codes follow from the next line.
This is case-insensitive.
Each line specifies an index and a unique code.
<index>: Specifies an index (integer in the range 0 to 2147483647)
<unique code>: Specifies a unique code (big endian format, with the
format and size specified in the header)
If the format is ascii
<unique code> A unique code can be enclosed in double quotation
marks. If the code includes a space at its beginning or end, the
quotation marks are required to distinguish such spaces from
separating characters. If the code itself includes consecutive double
quotation marks, they are handled as one double quotation mark.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 39 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 40

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(3) Example of a File
//Sample unique code file
format hex
address 0xf000
size 6
index data
000001 abcdef000001
000002 abcdef000002
000003 abcdef000003
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 40 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 41

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(1)
(2)
(4)
(3)
2.3.7 [User Keys] Tabbed Page
The [User Keys] feature is for storing the encrypted user keys in the TSIP. For the type of user keys and the
features, refer to the user’s manual of the boot firmware.
Remark: Whether or not a user key function is available depends on the target MCU.
Figure 2-14 [User Keys] Tabbed Page
(1) Write User Keys
Usage or non-usage of the feature for writing the user key can be set in this checkbox.
Check the box to select the use of user keys.
(2) Specifying a user key file
Specify a user key file or the address to which the file is to be written.
For details on how to generate user key files, refer to section 2.8, Renesas Flash Programmer Utility Program.
• “Encrypted Key File”
Open the [Open] dialog box by clicking on …, and specify a user key file.
• “Address”
Enter the address to which the user key file is to be written.
• “Add Key”
Register the user key file in the list of key files by clicking on the Add Key button.
(3) Removing user key files
When a file to be removed is selected from a list of key files, clicking on the Remove Selected Keys button
removes the file from the list.
(4) List of key files
Information on key files is displayed in a list.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 41 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 42

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.4 Menu Bar
2.4.1 [File] Menu
Menu items for processing related to projects can be selected.
• [New Project]
Create a new project.
For details, refer to section 2.2, Creating a New Project.
• [Open Project]
Open an existing project file.
• [Save Project]
Save the changes to the current project.
• [Save Image File]
Saves an image file (RPI file) that is a combination of a program file and flash options.
Select [Save Image File] from the [File] menu. This opens the [Save As] dialog box. Specify where the
image file is to be saved.
Cautions:
- The memory ranges are in accord with those selected in the P.V column on the [Block Settings]
tabbed page.
- The setting of [Fill with 0xFF] on the [Operation Settings] tabbed page is applicable.
- Data which exceed the address range of the MCU in use are not deleted.
- Only values which represent valid settings can be saved as flash options.
• [File Checksum]
The checksum of the program file is displayed in the [Log output] panel.
Remark: For the checksum operation, use the method specified on the [Operation Settings] tabbed page.
• [Set File Password]
The password for decrypting an RPE file is encrypted and saved on the host PC. For details, refer to
section 2.4.1.1, [File Password] Dialog Box (for Setting a Password).
• [Recently used projects]
The names of project files that have recently been used are displayed. The name of the most recently used
file is displayed at the top of the menu.
• [Exit]
Exit the RFP.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 42 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 43

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(1)
(3)
2.4.1.1 [File Password] Dialog Box (for Setting a Password)
Selecting [File] → [Set File Password] in the menu bar makes the [File Password] dialog box appear, allowing
you to set the password for use in decryption. The password for decrypting an RPE file is encrypted and
saved on the host PC.
Remark: You must run the RFP as an administrator to set a file password. The password cannot be set
without administrator rights.
(2)
Figure 2-15 [File Password] Dialog Box (for Setting a Password)
(1) [Save Password]
• When the checkbox is selected
The password is saved on the host PC.
• When the checkbox is deselected
The password is deleted from the host PC.
(2) Entering a password
Enter a password made up of alphanumeric characters and symbols (up to 64 characters).
Remark: The alphanumeric characters are handled as case-sensitive; the usable symbols are as follows.
!, @, #, $, ^, &, *, (, ), _, -, +, =, [, ], {, }, ;, :, <, >, |, ., /, ?
(3) [Show]
When this checkbox is selected, the password being entered is shown.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 43 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 44

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(2)
2.4.1.2 [File Password] Dialog Box (for Entering a Password)
When an RPE file is decrypted, the [File Password] dialog box appears to allow the entry of a password if a
password has not been saved on the host PC or decryption of the file has failed.
Remark: The password that has been entered is only retained while the RFP is running.
(1)
Figure 2-16 [File Password] Dialog Box (for Entering a Password)
(1) Entering a password
Enter a password made up of alphanumeric characters and symbols (up to 64 characters).
Remark: The alphanumeric characters are handled as case-sensitive; the usable symbols are as follows.
!, @, #, $, ^, &, *, (, ), _, -, +, =, [, ], {, }, ;, :, <, >, |, ., /, ?
(2) [Show]
When this checkbox is selected, the password being entered is shown.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 44 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 45

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.4.2 [Device Information] Menu
Processing for device information can be selected.
Caution: Selecting items from the [Device Information] menu leads to transfer to and from the target MCU to
acquire information. Before selecting an item, check the connection between the host PC and the
target MCU. If a connection is not found, an error will occur.
Remark: Some menu items will not be usable according to the type of the target MCU.
• [Read Device Information]
Read information on the device while a target MCU is connected.
The information that has been read is displayed in the log output panel.
• [Read Memory…]
Connect the target MCU and read and save the contents of the flash areas.
For details, refer to section 2.4.2.1, Read Memory.
• [Read Block Information]
Connect the target MCU and read the information on the blocks.
The read block information can be reflected in the current project.
For details, refer to section 2.4.2.2, Read Block Information.
• [Read Flash Option]
Connect the target MCU and read the flash options.
The read flash option information can be reflected in the current project.
For details, refer to section 2.4.2.3, Read Flash Option.
• [Blank Check]
Connect the target MCU for blank checking.
• [Initialize Device]
For a connected target MCU, initialize the settings for flash memory, boundaries and so on, and cause the
DLM state to change to SSD.
• [DLM Transition…]
Cause a transition of a connected target MCU to the DLM state.
For details, refer to section 2.4.2.4, DLM Transition.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 45 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 46

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.4.2.1 Read Memory
When [Device Information] → [Read Memory] is selected from the menu bar, the [Save As] dialog box will
appear. Specify the file and folder where the data that have been read are to be stored.
Clicking on the Save button shows the [Read Memory Information] dialog box. Specify the range of the flash
area to be read.
Remark: The Motorola S format or the Intel HEX format is selectable as the file format for saving.
(1)
(2)
(3)
(5)
Figure 2-17 [Read Memory Information] Dialog Box
(1) Area list
Select the area to be read or all areas.
(2) Area information
Information on the area that has been selected from the list of areas or on all areas is shown.
(3) Skip blank areas
(4)
Reading of blank areas of the MCU is skipped if this checkbox is selected.
Remark: The size of the area for judging whether a range is blank or not differs according to the target MCU.
Furthermore, in some target MCUs, selecting this option will significantly increase time for reading.
(4) Select Address
Change items when only a specific range is to be read.
(5) Read
Connect the target MCU, start reading the range specified in “Select Address”, and save the data in the
specified file and folder.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 46 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 47

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
(2)
(3)
(1)
(4)
2.4.2.2 Read Block Information
When [Device Information] → [Read Block Information] is selected from the menu bar, the [Read Block
Information] dialog box will appear after connecting the target MCU, and information on blocks, including lock
bits, OTP flags, and access window, will be read. Note that the columns to be shown differ according to the
type of the target MCU in use.
Figure 2-18 [Read Block Information] Dialog Box
(1) Information on block areas
Information on the block areas for the target MCU is shown.
(2) “NotBlank” Column
Information on blank blocks in the target MCU is shown.
Blocks with check marks are not blank.
(3) Information on options in units of blocks
Information on the target MCU in units of blocks is shown.
For details on each item, refer to section 2.3.3, [Block Settings] Tabbed Page.
(4) Reflecting read information
Clicking on OK reflects the read contents of the checked items in the corresponding columns of the [Block
Settings] tabbed page.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 47 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 48

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.4.2.3 Read Flash Option
When [Device Information] → [Read Flash Option] is selected from the menu bar, the [Read Flash Option]
dialog box will appear after connecting the target MCU and information on Option Bytes and Security will be
read out. Note that the items to be shown differ according to the type of the target MCU in use.
(1)
Figure 2-19 [Read Flash Option] Dialog Box
(1) Reflecting the set information
Selecting the checkbox and clicking on OK reflects the read contents on the [Flash Option] tabbed page.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 48 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 49

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.4.2.4 DLM Transition
In the dialog box that is displayed by selecting [Device Information] → [DLM Transition] from the menu bar,
selecting the target DLM state and clicking on Transition cause the required transition of the DLM state.
Figure 2-20 [DLM Transition] Dialog Box
• Target DLM State
Caution: Returning to a state may not be possible depending on the state of DLM for the target. For details,
refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
• Use Unique ID authentication
When this checkbox is selected, the unique ID authentication feature is enabled.
Caution: This item is only displayed when the DLM state of the MCU is “RMA_REQ”.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 49 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 50

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.4.3 [Help] Menu
The loading of a license file and the version of the RFP can be confirmed from this menu.
• [Activate License]
Refer to the documentation which comes with the product for the usage of this menu item.
• [Deactivate License]
This menu item is only available for the Commercial Edition.
Use this menu to release authentication of the license.
• [About]
The [About] message box is opened and displays the RFP version number.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 50 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 51

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
RFPV3.exe
A name of a file to be executed.
Option…
Option names prefixed by a slash (/).
2.5 Simple Use of Project Files from a Command Line
RFPV3.exe can be run from the command line, with options prefixed by ‘/’.
An option may have one or more parameters; the number of parameters is determined by the option.
The name of a project file can be specified.
2.5.1 Exit Code
When the operation was successful, exit code 0 is returned.
Otherwise, 1 is returned.
2.5.2 Restriction
When command-line statements specifying the same project file are started at the same time, the same value
may be written as the index of the unique code.
2.5.3 Command-line Syntax
The command-line syntax is as follows:
RFPV3.exe [Option...] [ProjectFile] [Option…]
RFPV3.Console.exe [Option...] [ProjectFile] [Option…]
The following table gives descriptions of each item.
Table 2-6 Command-line Syntax
Item Description
RFPV3.Console.exe A name of a file to be executed with the standard output facility. This
file always starts the RFP in silent mode.
• Specify parameters as required.
• If [Option…] is omitted, operation of the RFP is the default.
• Options and parameters are not case sensitive.
• Absolute or relative paths can be used for the name of the file.
ProjectFile Specifies the name of a project file.
• If this item is omitted, operation of the RFP is as follows.*
When there is a project that has been recently used, that project
will be opened. When no such project has been set up yet, the
RFP is started without opening a project.
• Absolute or relative paths can be used for the name of the file.
Note: An error will occur if RFPV3.Console.exe is used.
Caution: Pathnames that include spaces must be enclosed in double-quotation marks (").
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 51 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 52

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
silent
None
None
Starts the RFP in silent mode. After the specified project file
encoding
Encode
UTF8
Specifies the character encoding for the log file.
lang
jp/en
Automatically
Specifies the language for display of the RFP.
2.5.4 Start Options
The following lists start options for the RFP. If a command that cannot be used with the specified project file is
specified, the E0000017 error message will be displayed.
Table 2-7 Start Options
Option Parameter Default Description
is opened and processing which is equivalent to execution
in response to pressing the [Start] button once is done, the
RFP is closed. If the device requires ID authentication,
automatic ID authentication is performed. When no project
file is specified, this option is ignored.
• Silent mode
In this mode, the GUI, progress bars, and dialog boxes
are not displayed.
log File Path None Saves a log in a file. If the specified file already exists, the
log is appended to the contents of the file. Encoding in
saving of the log depends on the encoding option.
If a parameter other than UTF8 or ASCII is specified for
Encode, an error will occur.
force None None A facility for interlinking with the CS+ integrated
development environment from Renesas.
• When a project file is specified, the project file is loaded
and the RFP is started.
• When no project file is specified, the specified path is
used and the dialog box for creating a new project is
opened.
Note that this option is ignored both in silent mode and
when no project file is specified.
selected by
default
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 52 of 87
Apr.01.21
• jp: Japanese
• en: English
Page 53

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
Option
Parameter
Default
Description
bin
Address
None
Used to specify one or more binary files. If the addresses of
auth
IDType:IDCode
Setting in
Specifies the ID code for use in authentication. One or more
userkey
Setting in
Used to specify one or more user key files. Flash memory in
The following options for the command can only be specified in silent mode.
Table 2-8 Start Options Specific to Silent Mode (1/2)
file File Path Setting in
the project
File Path
tool SerialNo Setting in
the project
the project
blankcheck blank/notblank None Performs blank checking. Note that this command is
Address
File Path
the project
Used to specify one or more program files. Flash memory in
the target device is programmed by replacing the program
file specified as the parameter with the program file in the
project file.
Refer to the caution in section 2.3.1.1.
the data files for programming are overlapped, no error
occurs and the data files are overwritten in the order of
execution of the commands.
Selects the tool specified in the project.
• SerialNo:
Emulator: Serial No. on the body
COM: “COMx”
USB: USB instance path*
e.g. "VID_045B&PID_0025¥6&3234B9D9&0&3"
Note: The USB instance path must be enclosed in doublequotation marks (").
auth options can be specified.
• IDType:
Specifies the character string that identifies each ID
code. If a parameter other than id, cfpw, dfpw, seckey,
nonseckey, or rmakey is specified, an error will occur.
• IDCode:
Specifies the ID code for use in authentication as a
hexadecimal number.
executed first and an error occurs if the device does not
support it.
• Specifying blank:
Execution of the command is only successful when the
flash memory in the device is blank.
• Specifying notblank:
Execution of the command is only successful when the
flash memory in the device is not blank.
the target device is programmed by replacing the user key
file specified as the parameter with the user key file in the
project file.
If the addresses of the user key files are overlapped, an
error occurs.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 53 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 54

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
Option
Parameter
Default
Description
read32
Address
None
Reads memory of the device in 32-bit units and saves the
Table 2-9 Start Options Specific to Silent Mode (2/2)
Caution: Only one of the following options can be specified.
Remark: The read, read32, write32, and writebit options are not supported for devices of the RL78 family.
read Format
Address
Size
File Path
Size
write32 Address
Data…
None Reads memory of the device.
• Format: Select one of the following formats for saving
data in the file:
srec: S-record
hex: Intel hex
bin: Binary file
• Address: Specify the start address as a hexadecimal
number.
• Size: Specify the size for acquisition as a decimal
number.
• File Path: Specify the name of the destination file for
saving.
result in a log. The endianness is specified by the settings
for the project. If the endianness is not specified for the
project, little endian will be used.
• Address: Specify the start address as a hexadecimal
number.
• Size: Specify the size for acquisition as a decimal
number (multiples of 4 up to 1024 are specifiable).
None Writes data to the device in 32-bit units. The endianness is
specified by the settings for the project. If the endianness is
not specified for the project, little endian will be used.
• Address: Specify the start address as a hexadecimal
number.
• Data…: Specify the 4-byte data to be written in
hexadecimal. When multiple data are to be specified,
separate them with spaces (up to 64 units of 4-byte data
are specifiable).
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 54 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 55

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
writebit
Address
None
Writes data to the device in 1-bit units. The endianness is
dlm
State
None
Causes a transition of the DLM state. Refer to the
BitPos
BitData
Command Command Setting in
the project
specified by the settings for the project. If the endianness is
not specified for the project, little endian will be used.
• Address: Specify the start address as a hexadecimal
number.
• BitPos: Specify the start bit number (0 to 31). For 4-byte
data, the most significant bit is 31 and the least
significant bit is 0.
• BitData: Specify the data to be written in binary. Write
the bit data in descending order from the specified bit
number to the least significant bit (up to 32 characters
are specifiable).
Specifies processing to be executed. This depends on the
settings in the project. When the read option is specified, the
command option is ignored.
Select the commands to be executed from among the
following. Some commands can be specified in combination
but their order is ignored.
• Commands
e: Erase
p: Program*
v: Verify
o: Program Flash Options*
y: Verify Flash Options
s: Checksum
e.g. /command epv
Note: When the selected file is an HCUHEX file, RPI file, or
RPE file generated by encrypting an HCUHEX file or RPI
file, p forcibly includes o. Executing o on its own is not
possible.
initialize None None Initializes the device.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 55 of 87
Apr.01.21
cautionary note in section 2.4.2.4.
• State:
SSD, NSECSD, DPL, LCK_DBG, LCK_BOOT, or
RMA_REQ
Page 56

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
2.5.5 Example of Command-line Statements
The following is an example of command-line statements in a batch file.
• Example of a whole file
RFPV3.exe /silent "d:\rfp\project\sample.rpj" /file "d:\rfp\hex\sample_1.hex" /file
"d:\rfp\hex\sample_2.hex" /log "d:\rfp\log\sample.log"
ECHO Result Code: %ErrorLevel%
PAUSE
• Example of the [write32] option
The following command writes 0x01020304 and 0x05060708 to addresses 0xFF200000 and 0xFF200004,
respectively.
RFPV3.exe /silent "d:\rfp\project\sample.rpj" /write32 FF200000 01020304 05060708
• Example of the [writebit] option
The following command writes 0xAAAA to the 16 lower-order bits (bits 15 to 0) of address 0xFF200000.
RFPV3.exe /silent "d:\rfp\project\sample.rpj" /writebit FF200000 15 1010101010101010
2.6 Command Line for Linux or Windows
Programming can be controlled from the command line alone without the use of project files.
Regarding the usage of the command line, refer to the separate guide in the directory where the RFP has
been installed: “Doc\rfp_cli.md”.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 56 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 57

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
file
Specifies the file to be input (this specification is mandatory).
decrypt
Decrypts an encrypted file (RPE).
nooverwrite
Prohibits overwriting of output files.
2.7 Encryption Utility Program
rpe.exe, which is bundled with this product, can be used to encrypt or decrypt program files.
Remark: rpe.exe is stored in the same location as that for RFPV3.exe in the folder where the RFP has been
installed.
2.7.1 Exit Code
When the operation was successful, exit code 0 is returned.
Otherwise, 1 is returned.
2.7.2 Command-line Syntax
The command-line syntax is as follows:
rpe <file> /password <password> [options...]
2.7.3 Start Options
The following lists start options for the encryption utility program.
Table 2-10 Start Options
Option Description
• The file can be specified as a relative path from the working directory.
• Files to be encrypted: Intel Hex, S-Record, HCUHEX, and RPI
• Files to be decrypted: RPE
password Specifies the password for use in encrypting or decrypting the file (this specification is
mandatory).
If the password includes symbols, enclose each in double-quotation marks (").
If this option is not specified, the file is encrypted.
output Specifies the destination for output of a file.
If this option is not specified, the directory holding the input files is used.
• The file can be specified as a relative path from the working directory.
? Displays help information on the options.
Caution: Pathnames that include spaces must be enclosed in double-quotation marks (").
Remark: Enter a password made up of alphanumeric characters and symbols (up to 64 characters). The usable symbols
are as follows.
!, @, #, $, ^, &, *, (, ), _, -, +, =, [, ], {, }, ;, :, <, >, |, ., /, ?
Example:
> rpe "out.hex" /password "0123456789"
> rpe "out.hex" /password "0123456789" /output "out.rpe"
> rpe "out.rpe" /decrypt /password "0123456789" /output "D:\outputdir\"
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 57 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 58

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
rfp-util.exe
A name of a file to be executed.
options…
Option names prefixed by a slash (/) or a hyphen (-).
2.8 Renesas Flash Programmer Utility Program
rfp-util.exe, which is bundled with this product, can be used to run the following processing.
Remark: rfp-util.exe is stored in the same location as RFPV3.exe; that is, in the folder where the RFP has
been installed.
• Encryption with the use of user factory programming keys (UFPKs) as DLM keys and user keys
• Generation of random UFPKs and initialization vectors (IVs)
• Output of UFPK files for the Renesas Key Wrapping Service
• Generation of Renesas key files
• Generation of RMA authentication codes with unique IDs
2.8.1 Exit Code
When the operation was successful, exit code 0 is returned.
Otherwise, 1 is returned.
2.8.2 Command-line Syntax
The command-line syntax is as follows:
rfp-util [command] [options...]
The following table gives descriptions of each item.
Table 2-11 Command-line Syntax
Item Description
command Command names prefixed by a slash (/) or a hyphen (-).
command: genufpk, genkey, or calcresponse
• Specify parameters as required.
• Options and parameters are not case sensitive.
• Absolute or relative paths can be used for the name of the file.
? Displays help information on the options.
Caution: Pathnames that include spaces must be enclosed in double-quotation marks (").
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 58 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 59

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
genufpk
Generates a UFPK file.
calcresponse
Calculates a response value for use in challenge-and-response
Option
Parameter
Description
nooverwrite
None
If an output file already exists, an error will occur.
Option
Parameter
Description
2.8.3 List of Commands
The following table gives descriptions of each command.
Table 2-12 List of Commands
Command Description
When generation was successful, the generated UFPK is displayed in
the console.
genkey Generates a Renesas key file.
When generation was successful, a wrapped UFPK (W-UFPK), IV,
and encrypted key (including a message authentication code, MAC)
are displayed in the console.
authentication and outputs it to the console.
2.8.4 Start Options
The following lists start options for the key encryption utility program.
Remark: A hexadecimal data or binary file can be specified for the parameters indicated as Hex data. To
specify a file, use the path to the file with “file=” as a prefix.
Table 2-13 Common Options
output File path Specifies the name of a file to be output.
If this option is omitted, the execution result is output to the console.
Table 2-14 genufpk Command Option
ufpk Hex data Specifies the output of 32 bytes of binary data.
If this option is omitted, a random value is used for ufpk.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 59 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 60

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 2. Descriptions of Functions
Option
Parameter
Description
ufpk
File path
Specifies a UFPK file used in encryption.
key
Hex data
challenge
Hex data
Specifies a challenge value (the unique ID of the device is usually specified).
Table 2-15 genkey Command Options
iv Hex data Specifies an IV for use in encryption. The data size is 16 bytes.
If this option is omitted, a random value is used for IV.
wufpk File path Specifies a W-UFPK file obtained from the Renesas Key Wrapping Service.
• When the userkey option is not specified
Specifies the DLM key data. The data size is 16 bytes.
• When the userkey option is specified
Specifies the user key data. For the key data format and data size, refer
to the user’s manual of the boot firmware.
Note that this tool does not check the user key size.
userkey XX Generates a user key. Specify the type of user key as a one-byte
hexadecimal parameter. For the values to be entered, refer to the user’s
manual of the boot firmware.
If this option is omitted, a DLM key is generated.
Table 2-16 calcresponse Command Options
Option Parameter Description
The data size is 16 bytes.
key Hex data Specifies the DLM key data. The data size is 16 bytes.
Example:
(genufpk)
> rfp-util /genufpk /output "D:\example\ufpk.key"
(genkey)
> rfp-util /genkey /ufpk file="D:\example\ufpk.key" /wufpk file="D:\example\ufpk_enc.key" /key
"000102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F" /output "D:\example\abc.rkey"
(calcresponse)
> rfp-util /calcresponse /challenge "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ012345" /key
"000102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F"
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 60 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 61

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
Create a new project file.
Open a created workspace.
Execute a command.
Create a new project file.
Select an existing project file.
Set up a project.
Connect the host and emulator.
Connect the target system.
Start the RFP.
Terminate the host and emulator.
3. Operating the RFP
This chapter describes the basic operation of the RFP (the flow until a file is programmed) so that the user
understands the series of basic operations using the RFP from activation of the system to programming of the
target MCU.
The operations of creating, erasing, programming, and verifying a new project file are explained here. The
conditions for the series of operations used in the examples are as follows.
• Target MCU: R5F104PJ (RL78/G14)
• Tool used: E1 emulator
• Connection method: 1-wire UART (single-wire UART)
• Communications speed: 1,000,000 bps
• Clock supply: No external clock (internal clock oscillator)
• Power supply: E1 (5.0 V, from USB VBUS)
• Flash options: Not used
Use a project file you
have used before.
Figure 3-1 Flow of Operations
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 61 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 62

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
3.1 Flow of Operations
(1) Connecting the system
Connect the USB port of the host PC to the tool you will be using via the USB cable.
(2) Connecting the target system
Connect the target cable of the tool to the target system.
Caution: If power is to be supplied on the target system, be sure to connect the tool in use to the target
system before switching the power on.
(3) Creating a project file
(1) When the RFP is started, the main window opens.
When [File] → [Create a new project] is selected from the menu bar, the [Create New Project] dialog box
will appear.
Figure 3-2 File Menu
(2) Select “RL78” for [Microcontroller].
Enter any project name (in this example, “sample”) for [Project Name] and specify any folder (e.g.
D:\rfp\sample) for [Project Folder].
Select “E1” for [Tool]. For the RL78 family, [Interface] is fixed to “1 wire UART”.
Clicking on the Tool Details… button opens the [Tool Details] dialog box.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 62 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 63

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
Figure 3-3 [Create New Project] Dialog Box
(3) Select the [Select Tool] tabbed page and the [Auto Select] checkbox.
After that, select “5.0V (USB VBUS)” in [Power Supply].
Click on OK.
Figure 3-4 [Select Tool] Tabbed Page
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 63 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 64

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(4) Information on the specified tool is displayed.
Check the contents (in this example, “Num: AutoSelect Power: 5.0V (USB VBUS)”) and click on Connect.
A project is created and the Main Window is shown.
Caution: Clicking on Connect starts the connection to the target MCU.
Figure 3-5 [Create New Project] Dialog Box
(5) When a project is created, the display of the main window changes with the addition of new tabbed pages.
Check the information displayed in Project Information.
Figure 3-6 Main Window
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 64 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 65

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(4) Detailed settings of the RFP
Operate the tabbed windows to make detailed settings of the RFP.
(1) Set the [Operation Settings] tabbed page.
Refer to “Command” and check that the “Erase”, “Program”, and “Verify” checkboxes have been selected,
then click on the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
Figure 3-7 [Operation Settings] Tabbed Page
(2) Set the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
Check that all checkboxes in the “Erase” and “P.V” columns have been selected.
Then click on the [Connect Settings] tabbed page.
Figure 3-8 [Block Settings] Tabbed Page
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 65 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 66

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(3) Set the [Connect Settings] tabbed page.
Specify 1,000,000 bps for “Speed”, then click on the [Operation] tab.
Figure 3-9 [Connect Settings] Tabbed Page
(4) Check that the commands above Start are displayed as “Erase >> Program >> Verify”.
Figure 3-10 Main Window
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 66 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 67

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(5) Selecting a program file
Click on Browse… in “Program File” on the [Operation] tabbed page and select a program file from among
those displayed in the dialog box (in this example, “C:\RFP_ProgramFile\sample.hex”).
Check that the path to the program file selected in the “Program File” box is indicated.
Figure 3-11 [Operation] Tabbed Page
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 67 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 68

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(6) Executing a command
(1) Click on Start to execute the commands indicated above Start.
When sending of the commands is started, the [Progress Report] dialog box will appear.
Figure 3-12 Main Window
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 68 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 69

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(2) The [Progress Report] dialog box shows the state of command execution.
The state information is changed to “Run” and details of the processing are output as a log in the log
output panel of the main window.
When command execution is completed, the [Progress Report] dialog box is automatically closed and the
main window is displayed.
Figure 3-13 [Progress Report] Dialog Box
(3) When command processing is completed normally, the message “Operation completed.” is displayed in
the log output panel and the state information is displayed as “OK”.
Figure 3-14 Main Window
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 69 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 70

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 3. Operating the RFP
(7) Exiting the system
(1) Remove the target cable of the tool in use from the target system.
Caution: If VDD is being supplied on the target system, turn off the supply power before removing the target
cable of the tool in use from the target system.
(2) If you do not need to program another target MCU, select [File] → [Exit] and exit the RFP. Since all
settings that you have made are saved in the project file, they can be reused when the RFP is restarted.
When you intend to continue to program other target MCUs, connect the target system (step (2)) and
execute the required commands (step (6)).
Figure 3-15 Main Window
(3) Remove the USB cable from the tool.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 70 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 71

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
4. Troubleshooting
This chapter explains how to troubleshoot the RFP.
Remark If an error occurs during the sequence of a procedure, refer to this chapter and the user’s manual of
the target MCU. Also refer to the user’s manual of the tool you are using and execute diagnostic
tests. If this still does not resolve the problem, refer to the FAQ (at <https://www.renesas.com/rfp> ->
Design Support -> FAQ). If you are using the product version of the RFP, contact Renesas via the
Renesas website (http://www.renesas.com/contact) after writing down the PID number printed on
the back of the CD case for the RFP.
4.1 Problems during Startup
This section explains how to troubleshoot problems that might occur in the processes from installation to
startup.
(1) When the tool is connected to the host PC via a USB interface, plug and play does not recognize
the driver.
Cause:
The USB connector might not be inserted properly into the USB port of the host PC.
Action:
Check that the USB connector is fully inserted into the USB port of the host PC. Alternatively, disconnect the
USB connector, and then insert the USB connector again after a while.
(2) The tool is connected to the host PC but the power LED on the tool is not turned on.
Cause:
The USB port of the tool or the host PC might be defective.
Action:
Check the tool for defects by using the diagnostic tool for the tool in use. If you find a defect, consider repairs.
If there is no defect, try connecting the tool to another host PC.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 71 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 72

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
4.2 Problems during Operation
This section describes troubleshooting for problems that may occur during operation.
(1) When an error produces the message ‘E3000105 There is no response from the device.’
Cause 1:
The connection with the target system might be wrong.
Action 1:
(1) Check that the connection with the target system is in accord with the recommended circuits shown in the
user’s manual of the tool in use. Also check that all required pins of the tool have been connected.
(2) For the RL78 family, check that the EMVDD pins of the E1, E20, E2, or E2 Lite have been correctly
connected.
Cause 2:
The operating mode of the target MCU might be wrong.
Action 2:
(1) Refer to the user’s manual for the target MCU and check that all required mode pins are being handled
correctly.
(2) For the RX family, check that the settings for I/O signals in the [Tool Details] dialog box match the wiring of
the target system.
Cause 3:
The wrong MCU might be selected in the [Create New Project] dialog box.
Action 3:
Select the same MCU as the target MCU.
Cause 4:
The target MCU might not be receiving a clock signal.
Action 4:
Check the clock supply on the target system.
Cause 5:
Power might not be being supplied normally to the target MCU.
Action 5:
(1) Check the power supply setting.
(2) If the power is being supplied from the tool in use, the power might not be sufficient. In such cases, supply
power from the target system. Confirm that the supply of power on the target system is possible.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 72 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 73

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
(2) When USB Direct of the RX device does not work
Cause:
The wrong driver may be being recognized as the driver for booting via the USB. “Generic Boot USB Direct”
should normally be recognized.
Action:
Install the correct driver through the following steps (Windows 7 is used in this example).
(1) When the wrong driver is being recognized, Windows Device Manager will show the following state.
Figure 4-1 Device Manager
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 73 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 74

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
(2) When you select “Update Driver Software”, the following dialog box is displayed. Select “Browse my
computer for driver software”.
Figure 4-2 Update Driver Software
(3) Select “Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer”.
Figure 4-3 Update Driver Software
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 74 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 75

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
(4) The dialog box below is shown. If “Generic Boot USB Direct” is not displayed, use the RFP installer to re-
install the USB driver for the USB boot MCU Type A. Select “Generic Boot USB Direct” and click on Next.
Figure 4-4 Update Driver Software
(5) Installation of the driver for booting via the USB is finished.
Figure 4-5 Update Driver Software
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 75 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 76

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
(3) Forgetting the ID code of the RX or entering the wrong ID code
Action:
Refer to the address in the program file at which the ID code was set.
For details, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
When the control code for the ID code is set so that the whole flash memory is erased after consecutively
entering a wrong ID code three times, you can program the flash memory after returning to boot mode.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 76 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 77

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
4.3 Problems during Communications
This section describes troubleshooting for problems that may occur during communications with the tool or the
MCU.
(1) When the following errors occur while the tool is connected
• E3000203: An error occurred while connecting to the tool.
• E3000204: An error occurred while communicating with the tool.
• E3000205: An error occurred while updating the tool firmware.
• E3000206: An error occurred while initializing the tool.
Action 1:
When using USB Direct, Refer to section 4.2, Problems during Operation.
Action 2:
The tool you are using might have locked up. Try disconnecting and then reconnecting the USB cable.
Action 3:
The host PC might be unstable or the USB port might be broken. Restart the host PC or connect the tool to a
USB port other than that you are trying to use.
Action 4:
On the E1, E20, or E2, the tool might be damaged. Refer to the user’s manual of the tool you are using and
run the self-diagnostic test.
(2) When the following errors occur during communications
• E300010C: Received data from the device is corrupted.
• E4000004: A framing error occurred while receiving data.
• E4000005: A parity error occurred while receiving data.
• E4000006: An overrun error occurred while receiving data.
• E1000004: A transmission data error occurred in the device.
Action:
The setting of the target MCU might be wrong or communications might not be stable. Check the following
items.
• Check that there is no noise on the communications line.
• Check that the tool in use is properly connected with the target system.
• Check that unused pins are being handled correctly.
• Confirm that the correct input clock and transfer rate are selected. Stable programming might be achieved
by setting a lower value for the transfer rate.
Remark Good communications may not be possible if you are using a USB-to-serial converter, a self-made
cable, a self-made extension cable, or the like for connection with a tool.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 77 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 78

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
E0000002
Message
The project file is not correct.
Description
This error occurs when you attempt to open a corrupted project file.
E0000003
Message
No program file has been specified.
Description
Change the folder to a location to which the project file can be written.
E0000005
Message
The project file pathname exceeds 260 characters.
Description
The pathname exceeds the available number of characters.
E0000007
Message
The specified crystal frequency is out of range. Valid values are between x.xx and
Description
The value entered exceeds the valid range.
E0000009
Message
The input is not correct.
Description
Select one or more commands on the [Operation Settings] tabbed page.
E0000012
Message
No blocks have been selected for the current operation.
Description
Check one or more blocks for the operation on the [Block Settings] tabbed page.
E0000015
Message
The parameter file is not correct.
Description
The project might have been damaged.
E0000016
Message
The program file is not correct.
Description
The command entered was wrong.
4.4 Error Messages
This section describes error messages generated while the RFP is in use.
Table 4-1 Error Messages
E0000001 Message The specified program file doesn't exist.
Description This error code and message are displayed when the last specified program file
was not found.
Specify a new program file.
Description To start processing, a program file must be specified.
E0000004 Message The project file cannot be generated.
Change the project name or the location.
E0000006 Message The project file name or location is not correct.
Description Change the project name or the location.
x.xx.
Refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU and enter a correct value.
Description The value entered is wrong. Enter the value again in the correct format.
E0000011 Message There is no flash operation specified under "Command" on the "Operation Setting"
tabbed page.
E0000013 Message No flash options have been set.
Description There are no target options when flash options are to be programmed.
Change at least one setting to [Set] on the [Flash Option] tabbed page.
Description This error occurs when a program file that is corrupted, is in a non-supported
format, or contains entries in a non-supported format is specified.
E0000017 Message The specified command line option cannot be used in this project file.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 78 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 79

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
E0000018
Message
The combination of file type is incorrect.
Description
This error occurs when an RPI, HCUHEX, or RPE file is included in a multiple
E0000030
Message
The project file cannot be opened.
Description
Create a new project.
E0000031
Message
The project file cannot be opened.
Description
This error occurs in response to an attempt to open a corrupted, non-supported, or
E0000101
Message
No unique code file specified.
Description
This error occurs when a definition file is not specified on the unique code tabbed
Description
Processing cannot be continued since there is not enough memory in the host PC.
E3000008
Message
This file is corrupt and cannot be opened (line X).
Description
This error occurs when a program file which contains a line that is corrupted, is in a
E3000101
Message
The data at 0xXXXXXXXX already exist and cannot be overwritten.
Description
This error occurs when an attempt is made to handle data having overlapping
E3000103
Message
The format of option data is invalid.
Description
The target MCU does not support the format of the option data in the specified
E3000104
Message
The data address is outside the 32-bit address space.
Description
This error occurs when processing of data beyond the 32-bit address space is
program file selection.
E0000020 Message The program file exceeds the flash memory size of target device.
Description This error occurs when a file that includes data that are out of the range of memory
in the MCU has been selected.
If you do not wish this situation to produce an error, e.g. ignoring the data beyond
the range of the memory does not create a problem, it can be changed to a
warning.
Regarding changing error messages to warnings, refer to “(6) Error Settings” in
section 2.3.2, [Operation Settings] Tabbed Page.
This file was created with an unsupported version.
This file was created with an older version and contains settings that can not be
converted.
Description Create a new project.
E0000039 Message The project file cannot be opened.
non-existent project file.
page.
E0000102 Message The unique code file is not correct.
Description This error occurs when the specified unique code file is corrupted or is not in the
correct format.
EF000001 Message Not enough memory.
non-supported format, or contains entries in a non-supported format is specified.
Check the format of the program file.
addresses.
Check for data having overlapped addresses in the program file.
program file.
attempted.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 79 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 80

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
E3000105
Message
The device is not responding.
Description
This error occurs when there is no response from the target MCU during connection
E3000106
Message
This device is not supported.
Description
An attempt was made to connect a non-supported target MCU.
E3000107
Message
This device does not match the connection parameters.
Description
An attempt was made to connect an MCU which does not match the target MCU
E3000108
Message
There is no data in the operation range.
Description
This error occurs when there are no data in the range of memory of the MCU
E300010A
Message
The data at address 0xXXXXXXXX do not match.
Description
The data in the program file might be different from that programmed in the target
E300010B
Message
The option data do not match.
Description
The flash option data in the program file might be different from that programmed in
E300010C
Message
Data received from the device are corrupted.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E300010D
Message
The device sent an unrecognized response. (0xXX)
Description
This error occurs when unexpected data were received from the MCU.
E3000201
Message
Cannot find the specified tool.
Description
This error occurs when the tool specified by a project could not be found.
E3000202
Message
The specified tool is already in use.
Description
This error occurs when the specified tool is already in use by another program.
E3000203
Message
An error occurred while connecting to the tool.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E3000204
Message
An error occurred while communicating with the tool.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E3000205
Message
An error occurred while updating the tool firmware.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E3000206
Message
An error occurred while initializing the tool.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E3000207
Message
Power is not being supplied to the user system.
Description
Turn on the target system before connecting the tool. Check the connection of the
to the target system.
Refer to section 4.2, Problems during Operation, and section 5, Points for Caution.
that was acquired when the project was created.
Check that the target MCU is correct or re-create the project.
This error may also occur in response to changing the operating mode of the MCU
or the allocation in the flash memory.
Refer to section 5.9, MCUs Supporting a Dual-Bank Structure.
specified by the program file.
MCU.
the target MCU.
This error will occur when the flash option data is reflected in the MCU after a reset.
Check that the MCU was reset before connection.
Refer to section 5.6, Connecting through a COM Port or USB Direct.
tool after you have turned the target system on.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 80 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 81

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
E4000001
Message
Power is already been supplied on the user system.
Description
This error occurs when the power-supply function of the tool is selected for use but
E4000002
Message
Cannot release a reset signal.
Description
This error occurs when the reset signal of the target MCU going to the high level
E4000003
Message
A timeout error occurred.
Description
This error occurs when a problem in communications between the target MCU and
E4000004
Message
A framing error occurred while receiving data.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E4000005
Message
A parity error occurred while receiving data.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E4000006
Message
An overrun error occurred while receiving data.
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
a power-supply voltage that is already present is detected on the user board. Check
the power-supply setting.
has not been detected while the E1, E20, E2, or E2 Lite is in use and the target
MCU is connected.
Check the reset signal of the target MCU.
the RFP (host PC) arises for some reason, resulting in a timeout.
The RFP allows you to set the bit rate, but communications cannot proceed if the
specified bit rate does not match the actual settings of the target MCU.
Check the following points.
(1) Bit rate: Check the operating frequency of the MCU to see if the bit rate exceeds
the allowable communications rate and if the bit rate is appropriate.
(2) Clock settings: Check if the clock settings for the MCU in the RFP match the
actual clock of the target MCU.
(3) Connection between the target system and the PC: Good communications may
not be possible if you are using a USB-to-serial converter, a self-made cable, a selfmade extension cable, or the like for connection with a tool.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 81 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 82

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
E1000002
Message
A fatal error occurred during control of the flash memory. (Response XX:XX)
Description
E1000004
Message
A transmission data error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
Refer to section 4.3, Problems during Communications.
E1000005
Message
An input frequency error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error occurs when the value specified for the input clock signal cannot be used
E1000006
Message
A frequency error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error occurs when the MCU failed to make the clock settings.
E1000007
Message
An authentication code error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error occurs when an ID code different from that set in the target MCU is
E1000008
Message
An address error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
E1000009
Message
A baudrate error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error occurs when a bit rate which the MCU cannot generate is selected.
E100000A
Message
A sequencer error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error will occur in the following cases.
E100000C
Message
A serial programming connection is prohibited for this device.
Description
This error occurs when the security setting to prohibit connection has been made.
E100000D
Message
A flow error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
E100000E
Message
A protection error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
Execution of a specified command might have failed because the security setting to
E100000F
Message
A blank error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
Table 4-2 Error Messages Due to Errors in the MCU
−
in the MCU.
For details, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
Check the value of the input clock or the settings of the target MCU.
For details, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
entered (the message is the same for an incorrect access password).
If you have forgotten the configured ID code, connection to the MCU for serial
programming is basically disabled. However, erasure of the whole flash memory is
enabled as an exception in some MCUs; for details, refer to the user’s manual of
the target MCU.
−
Check the settings for the bit rate and the clock.
• When an operation is attempted in an area reserved by the security function of
the MCU
• When the MCU is malfunctioning
The serial programming function then cannot be used.
−
prohibit it in the target MCU has already been made. Although some security flags
can be cleared by erasing the chip, others cannot.
For details, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU.
−
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 82 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 83

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 4. Troubleshooting
E1000010
Message
A verification error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
E1000011
Message
A write error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error will occur in the following cases.
E1000012
Message
An erasure error occurred in the device. (Response XX:XX)
Description
This error code and message are displayed when erasure of data in the flash
• Different data might have been written to the program file and the target MCU.
• There might have been a failure in verification due to a defect in the flash
memory.
• An attempt might have been made to overwrite an area already containing data
with different data.
• There might have been a failure in programming due to a defect in the flash
memory.
memory of the MCU was attempted but failed. Possible causes of the error (failure
to erase) include:
(1) The power-supply voltage for the MCU not being correct.
(2) The MCU being unable to operate properly because of the pin settings.
(3) The MCU having been damaged for some reason.
(4) Communication between the MCU and the PC having failed*, so the command
was not executed.
Check the items (1) through (4) above.
*Good communications may not be possible if you are using a USB-to-serial
converter, a self-made cable, a self-made extension cable, or the like for connection
with a tool.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 83 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 84

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 5. Points for Caution
5. Points for Caution
This chapter describes points for caution regarding the RFP.
5.1 Manipulating the User Boot Mat
Applies to: RX610
If a valid ID code has not been set before the MCU is connected (i.e. the device is not protected),
manipulation of the user boot mat is not possible on completion of the connection. To enable manipulation of
the user boot mat, set a valid ID code before connecting the MCU.
5.2 Host PC
Applies to: All MCUs
Some tools (the E1, E20, E2, E2 Lite, serial interface, and USB interface) may not work with the host PC you
are using. Check the connection between the tool and the host PC. If the tool still does not work, you may
need to use a different host PC.
5.3 USB-to-Serial Converter
Applies to: All MCUs
We do not recommend the use of a USB-to-serial converter because it may cause delays in timing and data
being lost due to the specifications of the converter. Check the operation of the USB-to-serial converter you
are using. If timing is delayed or data are being lost, you may consider using a different USB-to-serial
converter.
5.4 Check before Connection
Applies to: All MCUs
Connection of the target MCU in the cases listed below may damage the tool in use or the target system due
to conflicts between signals. Be sure to check that the settings and circuit connection are correct.
• The type of the target MCU to be connected was mistaken.
• The wrong recommended circuit was used for the target MCU or the circuit being used was in error.
• The output setting of an I/O port pin was wrong while the setting is for manual entry to boot mode.
• The power-supply setting of the tool was wrong.
5.5 Erase Chip of the RH850 Family
Applies to: RH850
When a chip is erased, the configuration data are cleared after all other data have been erased. In other
words, the option settings of the MCU are all erased. Since all settings, including the settings at the time of
shipment, are erased at this time, be sure to make the required settings at the same time.
In addition, processing to clear the configuration data is prohibited in some MCUs. When you wish to erase a
chip, refer to the user’s manual of the target MCU in use and determine whether or not processing to clear the
configuration data can be used.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 84 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 85

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 5. Points for Caution
5.6 Connecting through a COM Port or USB Direct
Applies to: RX, RH850, Renesas SynergyTM, RA, RE
When the connection is through a COM port or USB Direct, the RFP does not control the reset pin of the
MCU. Reset the MCU in advance when connecting with a target MCU.
5.7 Auto-padding with 0xFF
Applies to: All MCUs
When an amount of data is less than the minimum unit for writing to a flash memory, the data are always
padded with 0xFF before writing especially when writing to the configuration setting area.
5.8 Verification after Protecting the MCU
Applies to: RH850, RX72T, RX71x, RX66x, RX64x
Setting the following protection functions of the MCU restricts the verification function.
• ID code protection
Proceeding with verification (“Verify by reading the device”) without issuing a reset after the ID code
protection bit has been set (written) will cause a protection error. To avoid this type of error, be sure to
reset the MCU after setting (writing to) the ID code protection bit. The RFP enters the ID authentication
mode and verification is enabled.
• Read command protect (Reading prohibited)
After the read command protection bit has been set, the ID code written to the MCU cannot be verified.
However, the setting of the read command protection bit becomes effective immediately after a new setting
has been written.
5.9 MCUs Supporting a Dual-Bank Structure
Applies to: RX
For MCUs that support a dual-bank structure, the RFP recognizes MCUs in the dual and linear modes as
different MCUs. Thus, when the bank mode of an MCU has been changed, the error “E3000107 This device
does not match the connection parameters.” will occur. In the RFP, newly create and change projects if you
change the bank mode.
The bank mode for the MCU is changed by the following actions.
• Resetting the MCU after a setting for bank mode which differs from the current setting has been written to
the Bank Mode Select bit
• Resetting the MCU after selecting [Erase Chip] to erase a chip that is currently in dual mode
[How to switch a chip from the linear mode to the dual mode]
The following describes the steps in switching a chip from the linear mode to the dual mode.
• 1. Connect the MCU in the linear mode and create a new project for the linear mode.
• 2. Select the erasure option as [Erase Chip] to erase the chip.
• 3. Program the option-setting memory with a file that specifies the dual mode.
• 4. Reset the MCU.
R20UT4813EJ0200 Rev.2.00 Page 85 of 87
Apr.01.21
Page 86

Published by: Renesas Electronics Corporation
Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08 User’s Manual
Publication Date: Rev.2.00 Apr.01.21
Page 87

Renesas Flash Programmer V3.08
R20UT4813EJ0200
 Loading...
Loading...