REALTEK RTL8208 Datasheet

RTL8208
REALTEK SINGLE CHIP
OCTAL 10/100 MBPS
FAST ETHERNET TRANSCEIVER
RTL8208
1. Features........................................................................ 2
2. General Description .................................................... 2
3. Block Diagram............................................................. 3
4. Pin Assignments .......................................................... 4
5. Pin Description ............................................................ 6
5.1 Media Connection Pins .......................................... 6
5.2 Power and Ground Pins.......................................... 6
5.3 Miscellaneous Pins................................................. 7
5.4 RMII/SMII/SS-SMII Pins ...................................... 8
5.5 SMI (Serial Management Interface) Pins............... 9
5.6 LED Pins................................................................ 9
5.7 Mode Control Pins ............................................... 10
5.8 Reserved Pins....................................................... 11
6. Register Descriptions ................................................ 12
6.1 Register 0: Control ............................................... 12
6.2 Register1: Status................................................... 14
6.3 Register2: PHY Identifier 1 Register ................... 15
6.4 Register3: PHY Identifier 2 Register ................... 15
6.5 Register4: Auto-Negotiation Advertisement........ 16
6.6 Register5: Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability......... 17
6.7 Register6: Auto-Negotiation Expansion............... 18
7. Functional Description ............................................. 19
7.1 General................................................................. 19
7.1.1 SMI (Serial Management Interface) ............. 19
7.1.2 Port Pair Loop Back Mode (PP-LPBK)........ 19
7.1.3 PHY Address................................................ 20
7.1.4 Auto-Negotiation.......................................... 20
7.1.5 Full-Duplex Flow Control ............................ 20
7.2 Initialization and Setup......................................... 20
7.2.1 Reset ............................................................. 20
7.2.2 Setup and configuration................................ 20
7.3 10Base-T .............................................................. 20
7.3.1 Transmit Function......................................... 20
7.3.2 Receive Function .......................................... 21
7.3.3 Link Monitor................................................. 21
7.3.4 Jabber............................................................ 21
7.3.5 Loopback ...................................................... 21
7.4 100Base-TX ......................................................... 21
7.4.1 Transmit Function......................................... 21
7.4.2 Receive Function.......................................... 21
7.4.3 Link Monitor ................................................ 22
7.4.4 Baseline Wander Compensation................... 23
7.5 100Base-FX ......................................................... 23
7.5.1 Transmit Function......................................... 23
7.5.2 Receive Function.......................................... 23
7.5.3 Link Monitor ................................................ 24
7.5.4 Far-End-Fault-Indication (FEFI).................. 24
7.6 RMII/SMII/SS-SMII............................................ 24
7.6.1 RMII (Reduced MII) .................................... 25
7.6.2 SMII (Serial MII) ......................................... 25
7.5.3 SS-SMII (Source Synchronous -Serial MII) ....... 27
7.7 Power Saving and Power Down Mode ................ 28
7.7.1 Power Saving Mode ..................................... 28
7.7.2 Power Down Mode....................................... 28
7.8 LED Configuration .............................................. 28
7.8.1 LED Blinking Time ...................................... 28
7.8.2 Serial Stream Order...................................... 29
7.8.3 Bi-Color LED............................................... 30
7.9 2.5V Power Generation....................................... 31
8. Design and Layout Guide......................................... 32
8.1 General Guidelines............................................... 32
8.2 Differential Signal Layout Guidelines ................. 32
8.3 Clock Circuit........................................................ 32
8.4 2.5V power........................................................... 32
8.5 Power Planes........................................................ 32
8.6 Ground Planes...................................................... 32
8.7 Transformer Options ............................................ 32
9. Application information ........................................... 33
9.1 10Base-T/100Base-TX Application..................... 33
9.2 100Base-FX Application...................................... 34
10. Electrical Characteristics ....................................... 35
10.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings .............................. 35
10.2 Operating Range ................................................ 35
10.3 DC Characteristics ............................................. 35
10.4 AC Characteristics ............................................. 36
10.5 Digital Timing Characteristics ........................... 37
10.6 Thermal Data...................................................... 38
11. Mechanical Dimensions .......................................... 39
2001/01/07 1 Rev.1.923

RTL8208
1. Features
Supports 8-port integrated physical layer and
transceiver for 10Base-T and 100Base-TX
Up to 8 ports support of 100Base-FX
Reduced 100Base-FX interface (patented)
Robust baseline wander correction for improved
100BASE-TX performance
Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u
IEEE 802.3u compliant Auto-negotiation for 10/100
Mbps control
Hardware controlled Flow control advertisement ability
Supports RMII/SMII/SS-SMII interfaces
Multiple driving capabilities of RMII/SMII/SS-SMII
Supports 25MHz crystal as clock source for RMII with
50MHz REFCLK output for MAC
Very low power consumption
Supports port-pair loop mode (PP-LPBK mode)
Supports two Power reduction methods:
1. Power saving mode (cable detection)
2. Power down mode
Power-on auto reset function eliminates the need for
external reset circuits
Flexible LED display modes through 2-wire serial
LED control interface
128-pin PQFP
2.5V/3.3V power supply
0.25µm, CMOS technology
2. General Description
The RTL8208 is a highly integrated 8 port, 10Base-T/100Base-TX/FX, Ethernet transceiver implemented in 0.25µm CMOS
technology. It is currently the world’s smallest Octal-PHY chip package with many special patented features. Traditional SD pins
in 100Base-FX are omitted by Realtek patent to obtain fewer pin-count. Flexible hardware settings are provided to configure the
various operating modes of the chip. The RTL8208 consists of 8 separate and independent channels. Each channel consists of an
RMII/SMII/SS-SMII interface to MAC controller, and hardware pins are used to configure the interface for RMII, or SMII, or
SS-SMII mode. In RMII mode, another hardware pin is used to set port-pair loop mode (PP-LPBK mode), which can extend
physical transmission length or perform physical media transport operations without any switch controller. In addition, the
RTL8208 features very low power consumption, as low as 1.8 W (max.). Additionally, pin-outs are designed to provide
optimized direct routing can be implemented, which simplifies the layout work and reduces EMI noise issues.
2001/01/07 2 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
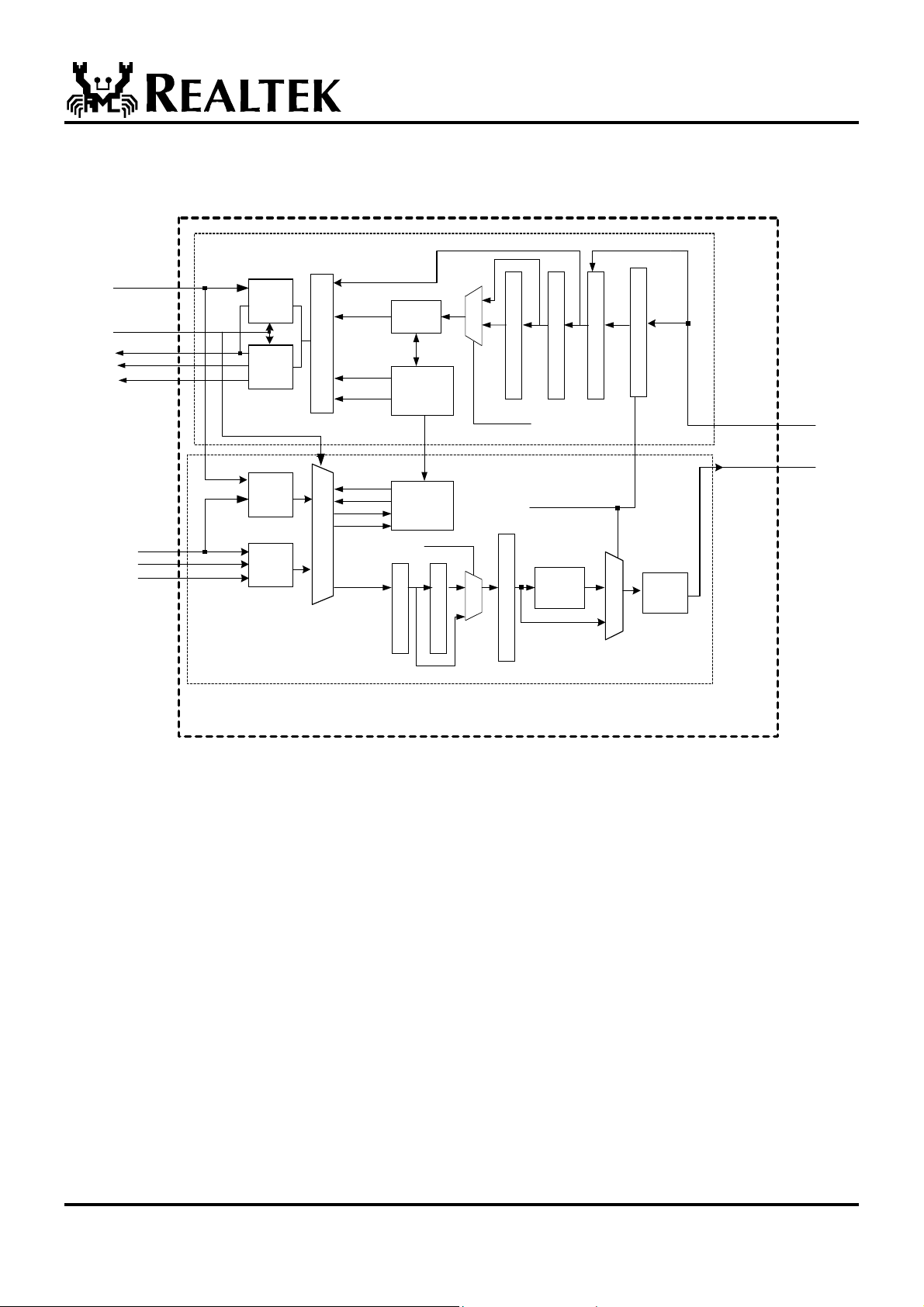
3. Block Diagram
SYNC
M ODE[1:0]
RXD0
RXD1
CRSD
V
TXD0
TXD1
TXE
N
SM II
RX
R M II
RX
SM II
TX
R M II
TX
RX FI FO
TXD[3:0
RXD[3:0
]
CR
S
RXD
V
CO
TX C L
L
TX E
K
TX E
N
R
]
4B /5
BDECOD
E
MACHIN
4B/ 5B
ENCODER
R
XSTA T
E
E
T
XSTA T
EMACHIN
E
B Y P-SC
RXCL
B Y P-D E SC
RX RECEIVER
R
R
SCA M B LE
K
L
R
EESCRAM BLE
SERI AL-TO-PARA LLE
R
FX enabl e
MLT
3ENCODE
R
L
PARA LLEL-TO-SERI A
CLOCK
FX input
RECOVERY
ADAPTIVE
TP input
EQU ALIZER
10/100
TX/FX
DRIVE
R
RX+/-
TX +/-
TX/FX out put
TX TRA N SM ITTER
2001/01/07 3 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
4. Pin Assignments
CRS_DV[3]
VDD
89
TX_EN[3]
88
TXD1[3]
TXD0[3]
868587
RXD1[3]
RXD0[3]
RTL8208
08042T1
050A TAIWAN
14
16
15
20
17
19
18
VSS
828481
21
RX_SYNC
TX_SYNC
22
23
VDD
798380
24
TX_EN[4]
TXD0[4]
78
77
26
25
CRS_DV[4]
TXD1[4]
76
28
27
RXD0[4]
747375
30
29
RXD1[4]
VSS
31
VDD
32
TX_EN[5]
TXD0[5]
707269
34
33
TXD1[5]
35
CRS_DV[5]
RXD0[5]
RXD1[5]
677168
66
65
37
36
38
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
TX_EN[6]
TXD0[6]
TXD1[6]
CRS_DV[6]
RXD0[6]
RXD1[6]
VSS
VDD
TX_EN[7]
TXD0[7]
TXD1[7]
CRS_DV[7]
RXD0[7]
RXD1[7]
LED_CLK
LED_DATA
REFCLK
RESET#
VDDAL
RXIN[7]
RXIP[7]
VSSA
TXOP[7]
TXON[7]
VDDAH
VDDAH
RXD1[0]
RXD0[0]
CRS_DV[0]
TXD1[0]
TXD0[0]
TX_EN[0]
MDIO
VCTRL
VDDAH
IBREF
VDDAL
RXIN[0]
RXIP[0]
VSSA
TXOP[0]
TXON[0]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXON[1]
TXOP[1]
VDD
VSS
VSS
MDC
TX_EN[2]
RXD1[1]
7
6
TXD0[2]
TXD1[2]
949693
9
8
CRS_DV[2]
RXD1[2]
RXD0[2]
919592
12
10
11
VSS
90
13
CRS_DV[1]
TX_EN[1]
TXD0[1]
RXD0[1]
TXD1[1]
989799
102
101
100
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
X1
X2
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
5
4
1
2
3
VSSA
RXIP[1]
RXIN[1]
VDDAL
VDDAL
RXIP[2]
RXIN[2]
VSSA
TXOP[2]
TXON[2]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXOP[3]
TXON[3]
VSSA
RXIP[3]
VDDAL
RXIN[3]
VDDAL
RXIP[4]
RXIN[4]
VSSA
TXOP[4]
TXON[4]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXOP[5]
TXON[5]
VSSA
RXIP[5]
RXIN[5]
VDDAL
VDDAL
RXIP[6]
RXIN[6]
VSSA
TXOP[6]
TXON[6]
2001/01/07 4 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
'I' stands for input; 'O' stands for output; 'A' stands for analog; ‘D’ stands for digital
Pin Name Pin# Type Pin Name Pin# Type
VSSA
RXIP[1]
RXIN[1]
VDDAL
VDDAL
RXIN[2]
RXIP[2]
VSSA
TXOP[2]
TXON[2]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXON[3]
TXOP[3]
VSSA
RXIP[3]
RXIN[3]
VDDAL
VDDAL
RXIN[4]
RXIP[4]
VSSA
TXOP[4]
TXON[4]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXON[5]
TXOP[5]
VSSA
RXIP[5]
RXIN[5]
VDDAL
VDDAL
RXIN[6]
RXIP[6]
VSSA
TXOP[6]
TXON[6]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXON[7]
TXOP[7]
VSSA
RXIP[7]
RXIN[7]
VDDAL
RESET#
REFCLK
LED_DATA/LEDMODE[1]
LED_CLK/LEDMODE[0]
RXD1[7]
RXD0[7]/DRIVE[0]
CRS_DV[7]/MODE[0]
TXD1[7]
TXD0[7]
TX_EN[7]
VDD
VSS
RXD1[6]/DISBLINK
RXD0[6]/DRIVE[1]
CRS_DV[6]/MODE[1]
TXD1[6]
TXD0[6]
TX_EN[6]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
AGND
AI
AI
AVDD
AVDD
AI
AI
AGND
AO
AO
AVDD
AVDD
AO
AO
AGND
AI
AI
AVDD
AVDD
AI
AI
AGND
AO
AO
AVDD
AVDD
AO
AO
AGND
AI
AI
AVDD
AVDD
AI
AI
AGND
AO
AO
AVDD
AVDD
AO
AO
AGND
AI
AI
AVDD
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
I
I
DVDD
DGND
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
I
I
RXD1[5]/LED_BLNK_TIME
RXD0[5]
CRS_DV[5]/TP_PAUSE
TXD1[5]
TXD0[5]
TX_EN[5]
VDD
VSS
RXD1[4]/PHY_ADDR[4]
RXD0[4]
CRS_DV[4]/RX_CLK
TXD1[4]
TXD0[4]
TX_EN[4]/TX_CLK
VDD
SYNC/TX_SYNC
RX_SYNC/RPT_MODE
VSS
RXD1[3]/PHY_ADDR[3]
RXD0[3]
CRS_DV[3]/FX_PAUSE
TXD1[3]
TXD0[3]
TX_EN[3]
VDD
VSS
RXD1[2]/TEST
RXD0[2]
CRS_DV[2]/FX_DUPLEX
TXD1[2]
TXD0[2]
TX_EN[2]
RXD1[1]
RXD0[1]
CRS_DV[1]/SEL_TXFX[1]
TXD1[1]
TXD0[1]
TX_EN[1]
VDD
VSS
RXD1[0]
RXD0[0]
CRS_DV[0]/SEL_TXFX[0]
TXD1[0]
TXD0[0]
TX_EN[0]
VSS
MDIO
MDC
X1
X2
VCTRL
VDDAH
IBREF
VDDAL
RXIN[0]
RXIP[0]
VSSA
TXOP[0]
TXON[0]
VDDAH
VDDAH
TXON[1]
TXOP[1]
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
I/O
O
I/O
I
I
I
DVDD
DGND
I/O
O
O
I
I
I
DVDD
I
I
DGND
I/O
O
I/O
I
I
I
DVDD
DGND
I/O
O
I/O
I
I
I
O
O
I/O
I
I
I
DVDD
DGND
O
O
I/O
I
I
I
DGND
I/O
I
I
O
I/O
AVDD
AO
AVDD
AI
AI
AGND
AO
AO
AVDD
AVDD
AO
AO
2001/01/07 5 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
5. Pin Description
In order to reduce pin count, and therefore size and cost, some pins have multiple functions. In those cases, the functions are
separated with a “/” symbol. Refer to the Pin Assignment diagram for a graphical representation.
'I' stands for input
'O' stands for output
'A' stands for analog signal
'D' stands for digital signal
'P' stands for power
'G' stands for ground
'Pu' stand for internal pull up (75K ohm)
'Pd' stand for internal pull down (75K ohm)
5.1 Media Connection Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
RXIP[7:0] 44,35,30,21,16,
7,2,121
RXIN[7:0] 45,34,31,20,17,
6,3,120
TXOP[7:0] 42,37,28,23,14,
9,128,123
TXON[7:0] 41,38,27,24,
13,10,127,124
AI Receiver Input: Differential positive signal shared by 100Base-TX,
100Base-FX, 10Base-T.
AI Receiver Input: Differential negative signal shared by 100Base-TX,
100Base-FX, 10Base-T.
AO Transmitter Output: Differential positive signal shared by
100Base-TX, 100Base-FX, 10Base-T.
AO Transmitter Output: Differential negative signal shared by
100Base-TX, 100Base-FX, 10Base-T.
5.2 Power and Ground Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
VDDAH 117 P
VDDAH 11,12,25,26,39,
40,125,126
VDDAL 119,4,5,18,19,3
2,33,46
VSSA 122,18,15,22,2
9,36,43
VDD 57,71,79,89,
103
VSS 58,72,82,90,
104,111
Power for IBREF
P 3.3V Power to analog: Used for transmitters and equalizers.
P 2.5V Power to analog: Used for PLL circuits.
G
Analog ground
P
Digital 2.5V power supply
G
Digital ground
2001/01/07 6 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
5.3 Miscellaneous Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
RESET# 47 I,
(Pu)
X1 114 I 25MHz Crystal X1 or 25MHz Oscillator clock input: When X1 is
X2 115 O
REFCLK 48 I/O
IBREF 118 A Reference Bias Resistor: This pin must be tied to analog ground through
VCTRL 116 O Voltage control: This pin controls a PNP transistor to generate the
Reset: This is an active low input. To complete the reset function, this
pin must be asserted low for at least 10ms.
pulled low, X2 must be floating. REFCLK will then be the chip clock
input.
25MHz Crystal X2
Reference clock:
If X1 is 25MHz active, REFCLK is a 50MHz output.
If X1 is pulled-low (disabled), REFCLK is the clock input as below:
50MHz 100ppm clock input for RMII mode.
125MHz 100ppm clock input for SMII/SS-SMII mode.
an external 1.96KΩ resistor when using a 1:1 transformer on Tx/Rx.
2.5V power supply for VDD and VDDAL pins.
2001/01/07 7 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
5.4 RMII/SMII/SS-SMII Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
TXD0[7:0] 55,63,69,77,
87,95,101,109
TXD1[7:0] 54,62,68,76,
86,94,100,108
TX_EN [7:0] 56,64,70,78,
88,96,102,110
RXD0[7:0] 52,60,66,74,
84,92,98,106
RXD1[7:0] 51,59,65,73,
83,91,97,105
CRS_DV[7:0] 53,61,67,75,
85,93,99,107
RX_CLK/
CRS_DV[4]
RX_SYNC
SYNC/
TX_SYNC
TX_CLK/
TX_EN[4]
75 O Receive Clock: In SS-SMII, CRS_DV[4] of RMII is used as
81 I/O
80 I Sync/Transmit Synchronous: In SMII, SYNC is a sync signal used
78 I Transmit Clock/Transmit Enable: In SS-SMII, TX_EN[4] of RMII
I
Transmit Data Input (bit 0):
In RMII, TXD0 and TXD1 are the di-bits input transmitted and driven
synchronously to REFCLK from MAC.
In SMII, TXD0 inputs the data that is transmitted and is driven
synchronously to REFCLK. In 100Mbps, TXD0 inputs a new 10-bit
segment starting with SYNC. In 10Mbps, TXD0 must repeat each
10-bit segment 10 times.
In SS-SMII, TXD0 behaves as SMII except synchronous to TX_CLK
instead of REFCLK and 10-bit segment starting with TX_SYNC
instead of SYNC.
I
Transmit Data Input (bit 1):
In RMII, TXD1 and TXD0 are the input di-bits synchronously to
REFCLK.
In SMII/SS-SMII, TXD1 is not used and should be tied either high or
low.
I
Transmit Enable:
In RMII , TX_EN indicates the di-bits on TXD is valid and is
synchronous to REFCLK.
In SMII/SS-SMII, TX_EN[7:0] are not used.
O
Receive Data Input (bit 0):
In RMII, RXD0 and RXD1 output di-bits synchronously to REFCLK.
In SMII, RXD0 outputs data or inband management information
synchronously to REFCLK. In 100Mbps, RXD0 outputs a new 10-bit
segment starting with SYNC. In 10Mbps, RXD0 must repeat each
10-bit segment 10 times.
In SS-SMII, RXD0 behaves as SMII except synchronous to RX_CLK
instead of REFCLK and 10-bit segment starting with RX_SYNC
instead of SYNC.
O
Receive Data Input (bit 1):
In RMII, RXD1 and RXD0 output di-bits synchronously to REFCLK.
In SMII/SS-SMII, RXD1is not used and they are driven low.
O
Carrier Sense and Data Valid:
In RMII, CRS_DV is asynchronous to REFCLK and asserts when the
medium is non-idle.
In SMII/SS-SMII, CRS_DV[7:0] are not used and driven low.
RX_CLK, which is a 125MHz clock output.
Receive Synchronous :
In SS-SMII, RX_SYNC is a sync signal used to delimit the 10-bit
segment of RXD0 for all ports.
to delimit a 10-bit segment of RXD0 and TXD0 for all ports.
In SS-SMII, TX_SYNC is a sync signal used to delimit the 10-bit
segment of TXD0 for all ports.
is used as TX_CLK, which is a 125MHz clock input from MAC.
2001/01/07 8 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
5.5 SMI (Serial Management Interface) Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
MDIO 112 I/O,
(Pu)
MDC 113 I,
(Pd)
Management Data I/O. Bi-directional data interface. A 1.5KΩ
pull-up resistor is required (as specified in IEEE802.3u).
The MAC controller access of the MII registers should be delayed at
least 700us after completion of the reset because of the internal reset
operation of the RTL8208
Management Data Clock. 0 to 25MHz clock sourced by MAC to
sample MDIO.
The MAC controller access of the MII registers should be delayed at
least 700us after completion of the reset because of the internal reset
operation of the RTL8208
5.6 LED Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
LED_DATA/
LEDMODE[1]
LED_CLK/
LEDMODE[0]
49 I/O LED_DATA outputs serial status bits that can be shifted into a shift
register to be displayed via LEDs. LED_DATA is output
synchronously to LED_CLK.
This pin is latched upon reset as LEDMODE[1]
LEDMODE[1:0] controls the forms of serial LED statuses.
See LED operation mode section.
50 I/O LED_CLK outputs the reference clock for the serial LED signals. This
pin is latched upon reset as LEDMODE[0]
2001/01/07 9 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
5.7 Mode Control Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
SEL_TXFX[1:0]/
CRS_DV[1:0]
PP-LPBK mode
/ RX_SYNC
PHY_ADDR[4:3]/
RXD1[4:3]
MODE[1:0]/
CRS_DV[6:7]
TP_PAUSE/
CRS_DV[5]
FX_PAUSE/
CRS_DV[3]
FX_DUPLEX/
CRS_DV[2]
DISBLINK/
RXD1[6]
LED_BLNK_TIME/
RXD1[5]
LEDMODE[1:0] 49,50 I,
99,107 I/O,
(Pd,Pd)
81 I/O,
(Pd)
73,83 I/O,
(Pd,Pu)
61,53 I/O,
(Pu,Pu)
67 I/O,
(Pu)
85 I/O,
(Pu)
93 I/O,
(Pu)
59 I/O,
(Pd)
65 I/O,
(Pu)
(Pd,Pd)
Select 10/100BaseTX or 100BaseFX: (default = 2’b00)
If RPT_MODE = 0:
2’b00: All 8 ports (port0~port7) are 10Base-T/100Base-TX.
2’b01: Port 7 is 100FX, other ports are 10Base-T/100Base-TX.
2’b10: Ports 6 & 7 are 100FX, other ports are 10Base-T/100Base-TX.
2’b11: All 8 ports are 100Base-FX.
If RPT_MODE =1:
2’b00: All 8 ports (port0~port7) are 10Base-T/100Base-TX.
2’b01: Port 7 and 5 are 100FX, others are 10Base-T/100Base-TX.
2’b10: Ports 1,3,5&7 are 100FX, others are 10Base-T/100Base-TX.
2’b11: All 8 ports are 100Base-FX.
Port Pair Loop Back mode: (default =0)
Upon power-on reset, this pin is input to assert PP-LPBK mode. When
set, all eight ports are port-pair looped back, acting like a signal
regeneration/transformation repeater.
Refer to the section covering PP-LPBK mode.
PHY Address: (default = 2’b01) These 2bits determine the highest
2bits of 5-bit PHY address upon reset.
Select RMII/SMII/SS-SMII mode: (default = 2’b11)
2’b1x: RMII
2’b00: SMII
2’b01: SS-SMII
Twisted Pair Pause capability: (default =1) Sets the Flow control
ability of Reg.4.10 for UTP ports upon power-on reset.
1: With flow control ability.
0: Without flow control ability
100Base-FX Flow control capability: (default =1) Forces the flow
control capability of Reg.4.10 and Reg.5.10 upon power-on reset.
1: With flow control ability in 100Base-FX.
0: Without flow control ability in 100Base-FX.
FX_DUPLEX: Force 100Base-FX Full Duplex Mode: (default =1)
This pin sets 100Base-FX duplex and affects those ports in
100Base-FX mode.
1=full duplex, 0=half duplex.
Upon reset, this pin sets the default values of Reg.0.8 of those ports in
100Base-FX.
Disable power-on reset LEDs blinking: (default = 0)
1=Disable power-on LED blinking
0=blink.
LED blink time: (default =1) Used to control blinking speed of
activity and collision LEDs.
1= 43ms
0= 120ms
LEDMODE[1:0]: (default = 00) Controls the forms of serial LED status.
LEDMODE Mode Output
2’b00 3-bit serial stream Col/Fulldup, Link/Act, Spd
2’b01 2-bit serial stream Spd, Link/Act
2’b10 3-bit for Bi-color LED Col/Fulldup, Link/Act, Spd
See LED operation mode section for more information.
2001/01/07 10 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
DRIVE[0]/
RXD0[7]
DRIVE[1]/
RXD0[6]
52 I/O,
(Pd)
60 I/O,
(Pd,Pd)
DRIVE[0]: Controls the output driving ability of SSMII RX_CLK.
1’b0: 12mA (default)
1’b1: 16mA
DRIVE[1]: Controls the output driving abilities of the
RMII/SMII/SS-SMII signals other than RX_CLK.
Drive [1:0] Output driving ability
2’b00 4mA (default)
2’b01 8mA
2’b10 12mA
2’b11 16mA
5.8 Reserved Pins
Pin Name Pin Ty pe Description
ENANAPAR/
RXD1[1]
TEST/
RXD1[2]
CPRST/
RXD1[0]
97 I/O,
(Pd)
91 I/O,
(Pd)
105 I/O,
(Pd)
Reserved for internal use. Must be kept floating.
TEST. Reserved for internal use. Must be kept floating.
Reserved for internal use. Must be kept floating.
2001/01/07 11 Rev.1.923
RTL8208
6. Register Descriptions
The first six registers of the MII are defined by the MII specification. Other registers are defined by Realtek Semiconductor Corp.
for internal use and are reserved for specific uses.
Register Description Default
0 Control Register 3100
1 Status Register 0F49
2 PHY Identifier 1 Register 001C
3 PHY Identifier 2 Register C883
4 Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register 05E1
5 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register 0001
6 Auto-Negotiation Expansion Register 0000
RO: Read Only
RW: Read/Write
LL: Latch Low until cleared
LH: Latch High until cleared
SC: Self Clearing
6.1 Register 0: Control
Reg. bit Name Description Mode Default
0.15 Reset 1=PHY reset. This bit is self-clearing. RW/SC 0
0.14 Loopback This will loopback TXD to RXD and ignore all the activities
on the cable media. Valid only for 10Base-T.
1=Enable loopback.
0=Normal operation.
0.13 Spd_Sel When Nway is enabled, this bit reflects the result of
Auto-negotiation. (Read only)
When Nway is disabled, this bit can be set by SMI*.
(Read/Write)
When 100FX is enabled, this bit =1 (Read only)
1=100Mbps.
0=10Mbps.
0.12 Auto Negotiation
Enable
0.11 Power Down 1=Power down. All functions will be disabled except
0.10 Isolate 1 = Electrically isolate the PHY from RMII/SMII/SS-SMII.
0.9 Restart Auto
Negotiation
0.8 Duplex Mode When Nway is enabled, this bit reflects the result of
0.[7:0] Reserved 0
*SMI: Serial Management Interface , which is composed of MDC,MDIO, allows MAC to manage PHY.
This bit can be set through SMI.(Read/Write)
When 100FX is enabled, this bit =0 (Read only)
1 = Enable Auto-negotiation process.
0 = disable Auto-negotiation process.
SMI.read/write function.
0=Normal operation.
PHY is still able to respond to MDC/MDIO.
0 = Normal operation
1=Restart Auto-Negotiation process.
0=Normal operation.
Auto-negotiation. (Read only)
When Nway is disabled, this bit can be set by SMI*.
(Read/Write)
When 100FX is enabled, this bit is determined by the
FX_DUPLEX pin. (Read/Write)
1=Full duplex operation.
0=Half duplex operation.
RW 0
RW 1
RW 1
or
0 for 100FX
RW 0
RW 0
RW/S C 0
RW 1
2001/01/07 12 Rev.1.923
 Loading...
Loading...