Page 1
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
16M-BIT, 32M-BIT, AND 64M-BIT
SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH
4KB SECTORS AND DUAL OUTPUT SPI
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 1 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 2

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Table of Contents-
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................................... 4
2. FEATURES................................................................................................................................. 4
3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 208-MIL....................................................................................... 5
4. PIN CONFIGURATION WSON 6X5-MM.................................................................................... 5
5. PIN CONFIGURATION PDIP 300-MIL.......................................................................................6
6. PIN DESCRIPTION SOIC 208-MIL, PDIP 300-MIL, AND WSON 6X5-MM............................... 6
7. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 300-MIL....................................................................................... 7
8. PIN DESCRIPTION SOIC 300-MIL ............................................................................................ 7
8.1 Package Types............................................................................................................... 8
8.2 Chip Select (/CS)............................................................................................................ 8
8.3 Serial Data Output (DO) ................................................................................................. 8
8.4 Write Protect (/WP)......................................................................................................... 8
8.5 HOLD (/HOLD) ............................................................................................................... 8
8.6 Serial Clock (CLK).......................................................................................................... 8
8.7 Serial Data Input / Output (DIO) ..................................................................................... 8
9. BLOCK DIAGRAM......................................................................................................................9
10. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................. 10
10.1 SPI OPERATIONS ....................................................................................................... 10
10.1.1 SPI Modes....................................................................................................................10
10.1.2 Dual Output SPI............................................................................................................10
10.1.3 Hold Function ...............................................................................................................10
10.2 WRITE PROTECTION.................................................................................................. 11
10.2.1 Write Protect Features..................................................................................................11
11. CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS................................................................................... 12
11.1 STATUS REGISTER....................................................................................................12
11.1.1 BUSY............................................................................................................................12
11.1.2 Write Enable Latch (WEL)............................................................................................12
11.1.3 Block Protect Bits (BP2, BP1, BP0)..............................................................................12
11.1.4 Top/Bottom Block Protect (TB).....................................................................................12
11.1.5 Reserved Bits...............................................................................................................12
11.1.6 Status Register Protect (SRP)......................................................................................13
11.1.7 Status Register Memory Protection..............................................................................14
11.2 INSTRUCTIONS...........................................................................................................16
11.2.1 Manufacturer and Device Identification.........................................................................16
11.2.2 Instruction Set
11.2.3 Write Disable (04h).......................................................................................................18
(1)
...........................................................................................................17
- 2 -
Page 3

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.4 Write Enable (06h)........................................................................................................18
11.2.5 Read Status Register (05h)..........................................................................................19
11.2.6 Write Status Register (01h) ..........................................................................................20
11.2.7 Read Data (03h)...........................................................................................................21
11.2.8 Fast Read (0Bh)...........................................................................................................22
11.2.9 Fast Read Dual Output (3Bh).......................................................................................23
11.2.10 Page Program (02h)...................................................................................................24
11.2.11 Sector Erase (20h) .....................................................................................................25
11.2.12 Block Erase (D8h) ......................................................................................................26
11.2.13 Chip Erase (C7h)........................................................................................................27
11.2.14 Power-down (B9h)......................................................................................................28
11.2.15 Release Power-down / Device ID (ABh).....................................................................29
11.2.16 Read Manufacturer / Device ID (90h).........................................................................31
11.2.17 JEDEC ID (9Fh)..........................................................................................................32
12. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (PRELIMINARY)
12.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)
.................................................................................... 33
12.2 Operating Ranges......................................................................................................... 33
12.3 Endurance and Data Retention....................................................................................34
12.4 Power-up Timing and Write Inhibit Threshold.............................................................. 34
12.5 DC Electrical Characteristics........................................................................................ 35
12.6 AC Measurement Conditions........................................................................................ 36
12.7 AC Electrical Characteristics ........................................................................................ 37
12.8 AC Electrical Characteristics (cont’d)...........................................................................38
12.9 Serial Output Timing..................................................................................................... 39
12.10 Input Timing................................................................................................................. 39
12.11 Hold Timing ................................................................................................................. 39
13. PACKAGE SPECIFICATION.................................................................................................... 40
13.1 8-Pin SOIC 208-mil (Package Code SS)......................................................................40
13.2 8-Pin PDIP 300-mil (Package Code DA)...................................................................... 41
13.3 8-contact 6x5 WSON.................................................................................................... 42
13.4 8-contact 6x5 WSON Cont’d. ....................................................................................... 43
13.5 16-Pin SOIC 300-mil (Winbond Package Code SF)..................................................... 44
14. ORDERING INFORMATION
(1)
................................................................................................. 45
(4)
....................................................... 33
15. REVISION HISTORY................................................................................................................46
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 3 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 4

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The W25X16 (16M-bit), W25X32 (32M-bit), and W25X64 (64M-bit) Serial Flash memories provide a
storage solution for systems with limited space, pins and power. The 25X series offers flexibility and
performance well beyond ordinary Serial Flash devices. They are ideal for code download applications
as well as storing voice, text and data. The devices operate on a single 2.7V to 3.6V power supply
with current consumption as low as 5mA active and 1µA for power-down. All devices are offered in
space-saving packages.
The W25X16/32/64 array is organized into 8,192/16,384/32,768 programmable pages of 256-bytes
each. Up to 256 bytes can be programmed at a time using the Page Program instruction. Pages can
be erased in groups of 16 (sector erase), groups of 256 (block erase) or the entire chip (chip erase).
The W25X16/32/64 has 512/1024/2048 erasable sectors and 32/64/128 erasable blocks respectively.
The small 4KB sectors allow for greater flexibility in applications that require data and parameter
storage. (See figure 2.)
The W25X16/32/64 supports the standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI), and a high performance
dual output SPI using four pins: Serial Clock, Chip Select, Serial Data I/O and Serial Data Out. SPI
clock frequencies of up to 75MHz are supported allowing equivalent clock rates of 150MHz when
using the Fast Read Dual Output instruction. These transfer rates are comparable to those of 8 and
16-bit Parallel Flash memories.
A Hold pin, Write Protect pin and programmable write protect, with top or bottom array control
features, provide further control flexibility. Additionally, the device supports JEDEC standard
manufacturer and device identification.
2. FEATURES
• Family of Serial Flash Memories
– W25X16: 16M-bit / 2M -byte (2,097,152)
– W25X32: 32M-bit / 4M-byte (4,194,304)
– W25X64: 64M-bit / 8M-byte (8,388,608)
– 256-bytes per programmable page
– Uniform 4K-byte Sectors / 64K-byte Blocks
• SPI with Single or Dual Outputs
– Clock, Chip Select, Data I/O, Data Out
– Optional Hold function for SPI flexibility
• Data Transfer up to 150M-bits / second
– Clock operation to 75MHz
– Fast Read Dual Output instruction
– Auto-increment Read capability
• Flexible Architecture with 4KB sectors
– Sector Erase (4K-bytes)
– Block Erase (64K-byte)
– Page program up to 256 bytes <2ms
– Up to 100,000 erase/write cycles
– 20-year retention
• Low Power Consumption, Wide
Temperature Range
– Single 2.7 to 3.6V supply
– 5mA active current, 1µA Power-down (typ)
– -40° to +85°C operating range
• Software and Hardware Write Protection
– Write-Protect all or portion of memory
– Enable/Disable protection with /WP pin
– Top or bottom array protection
• Space Efficient Packaging
– 8-pin SOIC 208-mil (W25X16)
– 8-pin PDIP 300-mil (W25X16)
– 8-pin WSON 6x5-mm (W25X16)
– 16-pin SOIC 300-mil (W25X16, W25X32 &
W25X64)
- 4 -
Page 5
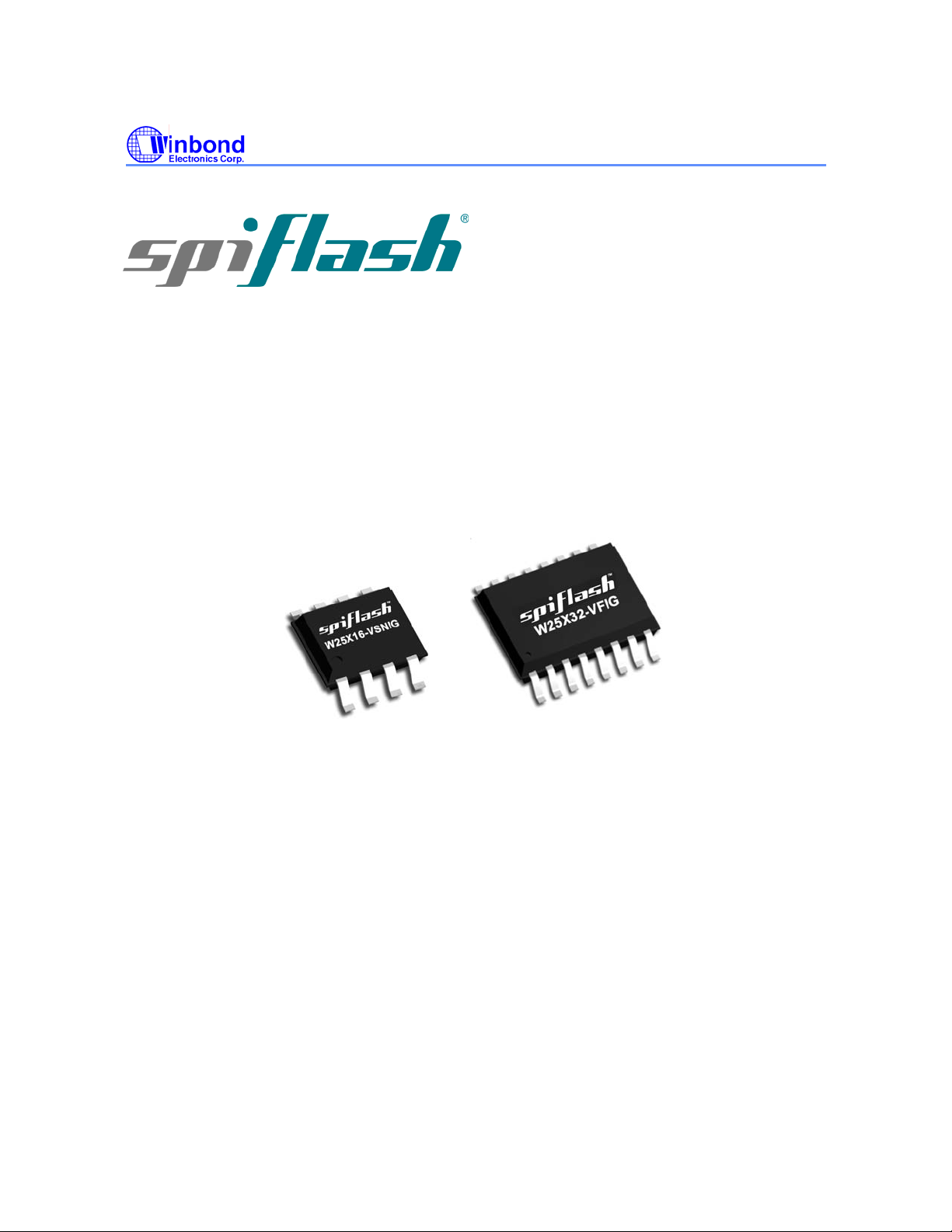
3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 208-MIL
Figure 1a。W25X16 Pin Assignments, 8-pin SOIC (Package Code SS)
4. PIN CONFIGURATION WSON 6X5-MM
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Figure 1b。W25X16 Pin Assignments, 8-pin WSON (Package Code ZP)
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 5 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 6
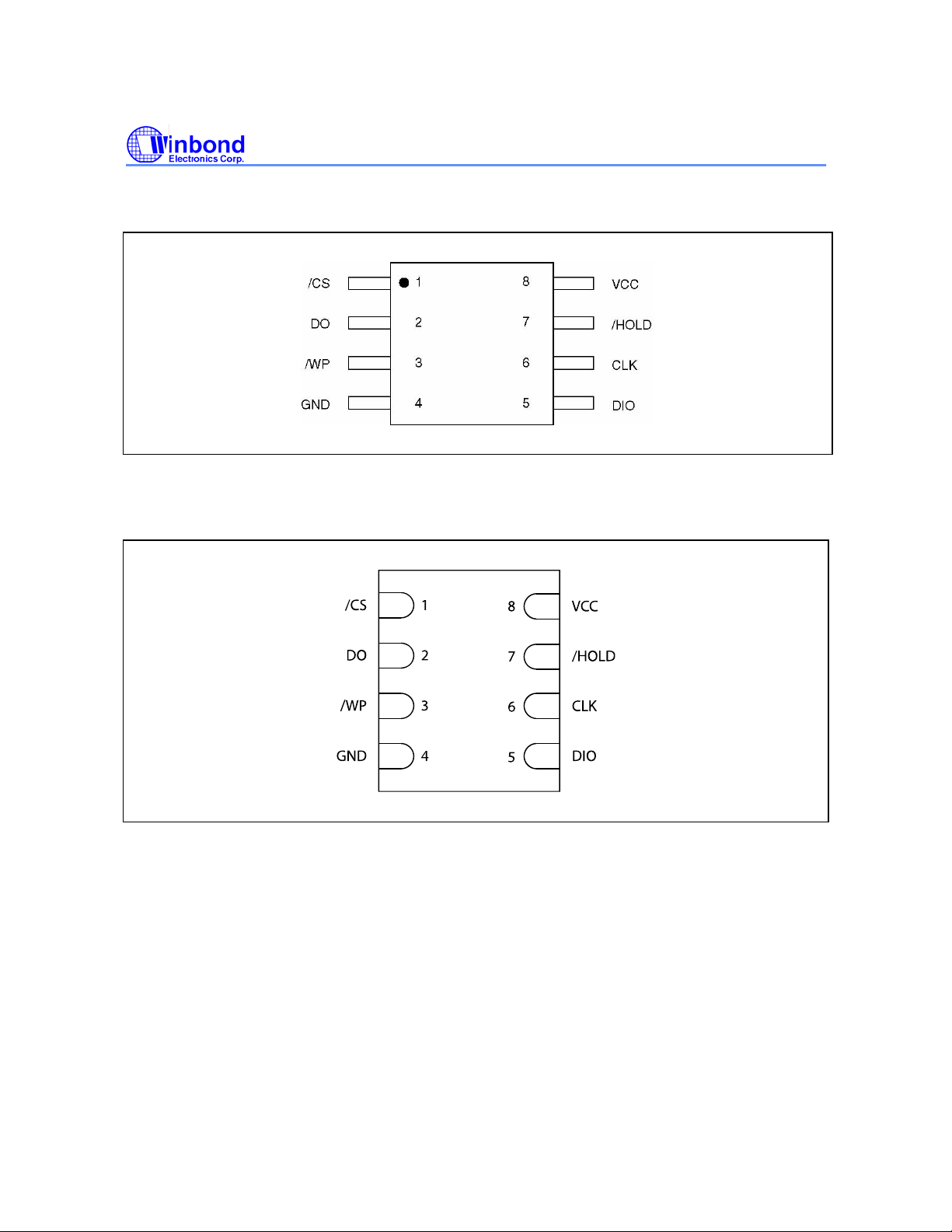
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
5. PIN CONFIGURATION PDIP 300-MIL
Figure 1c。W25X16 Pin Assignments, 8-pin PDIP (Package Code DA)
6. PIN DESCRIPTION SOIC 208-MIL, PDIP 300-MIL, AND WSON 6X5-MM
PAD NO. PAD NAME I/O FUNCTION
1 /CS I Chip Select Input
2 DO O Data Output
3 /WP I Write Protect Input
4 GND Ground
5 DIO I/O Data Input / Output
6 CLK I Serial Clock Input
7 /HOLD I Hold Input
8 VCC Power Supply
- 6 -
Page 7
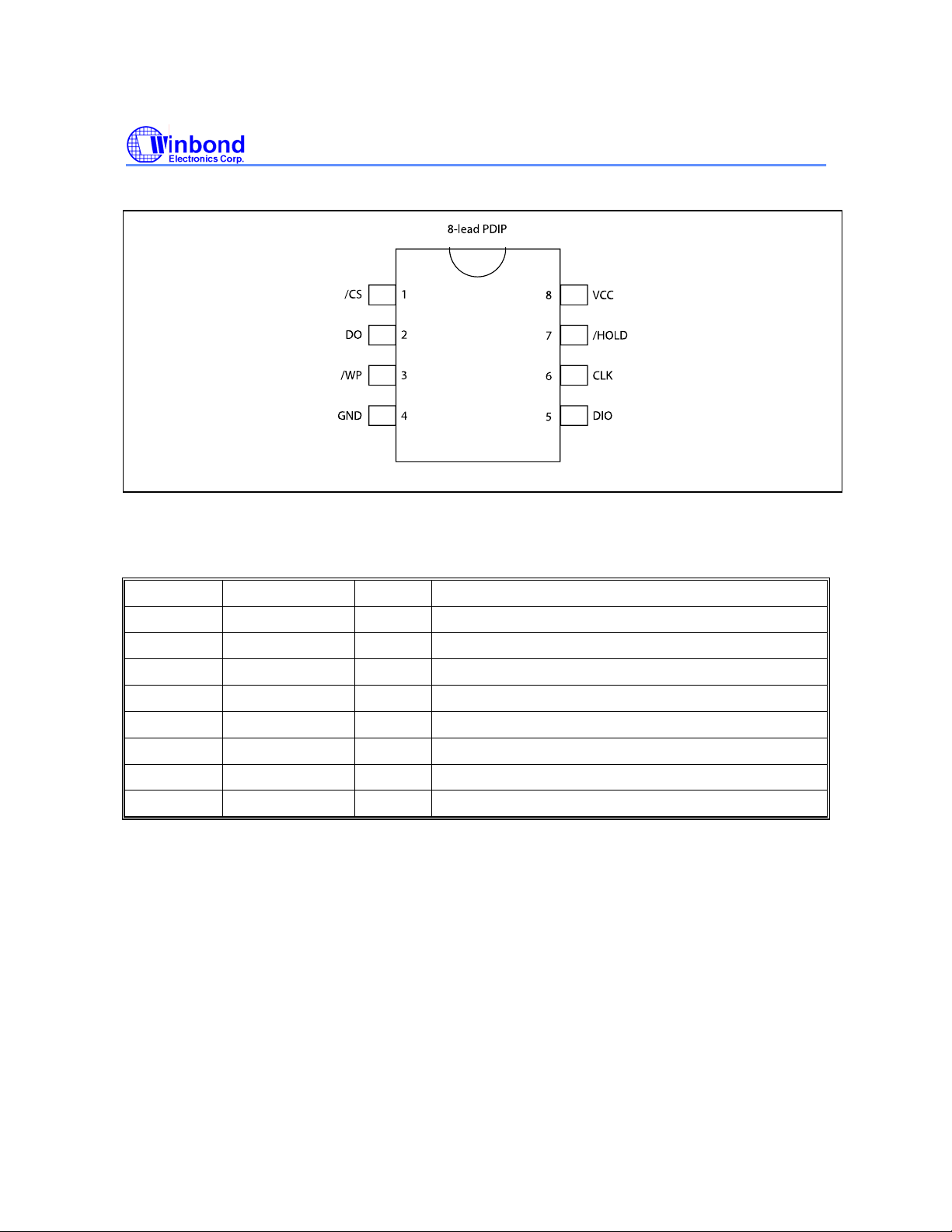
7. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 300-MIL
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Figure 1d. W25X16, W25X32 and W25X64 Pin Assignments, 16-pin SOIC 300-mil (Package Code SF)
8. PIN DESCRIPTION SOIC 300-MIL
PAD NO. PAD NAME I/O FUNCTION
1 /HOLD I Hold Input
2 VCC Power Supply
3 N/C No Connect
4 N/C No Connect
5 N/C No Connect
6 N/C No Connect
7 /CS I Chip Select Input
8 DO O Data Output
9 /WP I Write Protect Input
10 GND Ground
11 N/C No Connect
12 N/C No Connect
13 N/C No Connect
14 N/C No Connect
15 DIO I Data Input / Output
16 CLK I Serial Clock Input
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 7 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 8

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
8.1 Package Types
At the time this datasheet was published not all package types had been finalized. Contact Winbond
to confirm availability of these packages before designing to this specification. W25X16 is offered in
an 8-pin plastic 208-mil width SOIC (package code SS), 6x5-mm WSON (package code ZP) and 300mil DIP (package code DA) as shown in figure 1a, 1b, and 1c, respectively. The W25X16, W25X32
and W25X64 are offered in an 16-pin plastic 300-mil width SOIC (package code SF) as shown in
figure 1d. Package diagrams and dimensions are illustrated at the end of this datasheet.
8.2 Chip Select (/CS)
The SPI Chip Select (/CS) pin enables and disables device operation. When /CS is high the device is
deselected and the Serial Data Output (DO) pin is at high impedance. When deselected, the devices
power consumption will be at standby levels unless an internal erase, program or status register cycle
is in progress. When /CS is brought low the device will be selected, power consumption will increase
to active levels and instructions can be written to and data read from the device. After power-up, /CS
must transition from high to low before a new instruction will be accepted. The /CS input must track
the VCC supply level at power-up (see “Write Protection” and figure 20). If needed a pull-up resister
on /CS can be used to accomplish this.
8.3 Serial Data Output (DO)
The SPI Serial Data Output (DO) pin provides a means for data and status to be serially read from
(shifted out of) the device. Data is shifted out on the falling edge of the Serial Clock (CLK) input pin.
8.4 Write Protect (/WP)
The Write Protect (/WP) pin can be used to prevent the Status Register from being written. Used in
conjunction with the Status Register’s Block Protect (BP2, BP1, and BP0) bits and Status Register
Protect (SRP) bits, a portion or the entire memory array can be hardware protected. The /WP pin is
active low.
8.5 HOLD (/HOLD)
The /HOLD pin allows the device to be paused while it is actively selected. When /HOLD is brought
low, while /CS is low, the DO pin will be at high impedance and signals on the DIO and CLK pins will
be ignored (don’t care). When /HOLD is brought high, device operation can resume. The /HOLD
function can be useful when multiple devices are sharing the same SPI signals. (“See Hold function”)
8.6 Serial Clock (CLK)
The SPI Serial Clock Input (CLK) pin provides the timing for serial input and output operations. ("See
SPI "Operations")
8.7 Serial Data Input / Output (DIO)
The SPI Serial Data Input/Output (DIO) pin provides a means for instructions, addresses and data to
be serially written to (shifted into) the device. Data is latched on the rising edge of the Serial Clock
(CLK) input pin. The DIO pin is also used as an output when the Fast Read Dual Output instruction is
executed.
- 8 -
Page 9
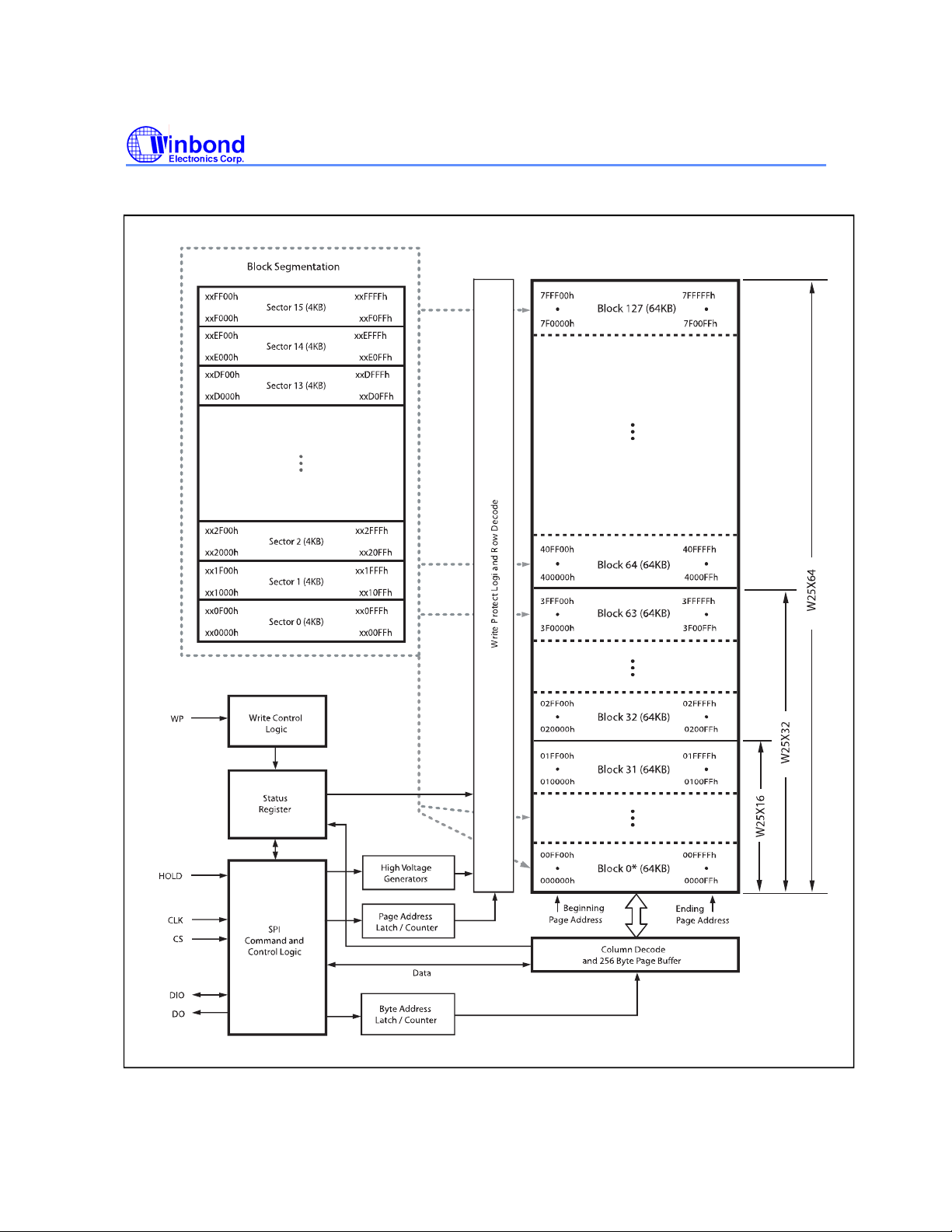
9. BLOCK DIAGRAM
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Figure 2. W25X16, W25X32 and W25X64 Block Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 9 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 10

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
10. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
10.1 SPI OPERATIONS
10.1.1 SPI Modes
The W25X16/32/64 is accessed through an SPI compatible bus consisting of four signals: Serial Clock
(CLK), Chip Select (/CS), Serial Data Input/Output (DIO) and Serial Data Output (DO). Both SPI bus
operation Modes 0 (0,0) and 3 (1,1) are supported. The primary difference between Mode 0 and Mode
3 concerns the normal state of the CLK signal when the SPI bus master is in standby and data is not
being transferred to the Serial Flash. For Mode 0 the CLK signal is normally low. For Mode 3 the CLK
signal is normally high. In either case data input on the DIO pin is sampled on the rising edge of the
CLK. Data on the DO and DIO pins are clocked out on the falling edge of CLK.
10.1.2 Dual Output SPI
The W25X16/32/64 supports Dual output operation when using the "Fast Read with Dual Output" (3B
hex) instruction. This feature allows data to be transferred from the Serial Flash memory at twice the
rate possible with the standard SPI. This instruction is ideal for quickly downloading code from Flash
to RAM upon power-up (code-shadowing) or for applications that cache code-segments to RAM for
execution. The Dual output feature simply allows the SPI input pin to also serve as an output during
this instruction. All other operations use the standard SPI interface with single output signal.
10.1.3 Hold Function
The /HOLD signal allows the W25X16/32/64 operation to be paused while it is actively selected (when
/CS is low). The /HOLD function may be useful in cases where the SPI data and clock signals are
shared with other devices. For example, consider if the page buffer was only partially written when a
priority interrupt requires use of the SPI bus. In this case the /HOLD function can save the state of the
instruction and the data in the buffer so programming can resume where it left off once the bus is
available again.
To initiate a /HOLD condition, the device must be selected with /CS low. A /HOLD condition will
activate on the falling edge of the /HOLD signal if the CLK signal is already low. If the CLK is not
already low the /HOLD condition will activate after the next falling edge of CLK. The /HOLD condition
will terminate on the rising edge of the /HOLD signal if the CLK signal is already low. If the CLK is not
already low the /HOLD condition will terminate after the next falling edge of CLK.
During a /HOLD condition, the Serial Data Output (DO) is high impedance, and Serial Data
Input/Output (DIO) and Serial Clock (CLK) are ignored. The Chip Select (/CS) signal should be kept
active (low) for the full duration of the /HOLD operation to avoid resetting the internal logic state of the
device.
- 10 -
Page 11

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
10.2 WRITE PROTECTION
Applications that use non-volatile memory must take into consideration the possibility of noise and
other adverse system conditions that may compromise data integrity. To address this concern the
W25X16/32/64 provides several means to protect data from inadvertent writes.
10.2.1 Write Protect Features
• Device resets when VCC is below threshold.
• Time delay write disable after Power-up.
• Write enable/disable instructions.
• Automatic write disable after program and erase.
• Software write protection using Status Register.
• Hardware write protection using Status Register and /WP pin.
• Write Protection using Power-down instruction.
Upon power-up or at power-down the W25X16/32/64 will maintain a reset condition while VCC is
below the threshold value of V
reset, all operations are disabled and no instructions are recognized. During power-up and after the
VCC voltage exceeds V
delay of tPUW. This includes the Write Enable, Page Program, Sector Erase, Block Erase, Chip Erase
and the Write Status Register instructions. Note that the chip select pin (/CS) must track the VCC
supply level at power-up until the VCC-min level and t
resister on /CS can be used to accomplish this.
WI, all program and erase related instructions are further disabled for a time
WI, (See Power-up Timing and Voltage Levels and Figure 20). While
VSL time delay is reached. If needed a pull-up
After power-up the device is automatically placed in a write-disabled state with the Status Register
Write Enable Latch (WEL) set to a 0. A Write Enable instruction must be issued before a Page
Program, Sector Erase, Chip Erase or Write Status Register instruction will be accepted. After
completing a program, erase or write instruction the Write Enable Latch (WEL) is automatically
cleared to a write-disabled state of 0.
Software controlled write protection is facilitated using the Write Status Register instruction and setting
the Status Register Protect (SRP) and Block Protect (TB, BP2, BP1, and BP0) bits. These Status
Register bits allow a portion or all of the memory to be configured as read only. Used in conjunction
with the Write Protect (/WP) pin, changes to the Status Register can be enabled or disabled under
hardware control. See Status Register for further information.
Additionally, the Power-down instruction offers an extra level of write protection as all instructions are
ignored except for the Release Power-down instruction.
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 11 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 12

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11. CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS
The Read Status Register instruction can be used to provide status on the availability of the Flash
memory array, if the device is write enabled or disabled, and the state of write protection. The Write
Status Register instruction can be used to configure the devices write protection features. See Figure 3.
11.1 STATUS REGISTER
11.1.1 BUSY
BUSY is a read only bit in the status register (S0) that is set to a 1 state when the device is executing
a Page Program, Sector Erase, Block Erase, Chip Erase or Write Status Register instruction. During
this time the device will ignore further instructions except for the Read Status Register instruction (see
t
W, tPP, tSE, TBE, and tCE in AC Characteristics). When the program, erase or write status register
instruction has completed, the BUSY bit will be cleared to a 0 state indicating the device is ready for
further instructions.
11.1.2 Write Enable Latch (WEL)
Write Enable Latch (WEL) is a read only bit in the status register (S1) that is set to a 1 after executing
a Write Enable Instruction. The WEL status bit is cleared to a 0 when the device is write disabled. A
write disable state occurs upon power-up or after any of the following instructions: Write Disable, Page
Program, Sector Erase, Block Erase, Chip Erase and Write Status Register.
11.1.3 Block Protect Bits (BP2, BP1, BP0)
The Block Protect Bits (BP2, BP1, and BP0) are non-volatile read/write bits in the status register (S4,
S3, and S2) that provide Write Protection control and status. Block Protect bits can be set using the
Write Status Register Instruction (see t
array can be protected from Program and Erase instructions (see Status Register Memory Protection
table). The factory default setting for the Block Protection Bits is 0, none of the array protected. The
Block Protect bits can not be written to if the Status Register Protect (SRP) bit is set to 1 and the Write
Protect (/WP) pin is low.
W in AC characteristics). All, none or a portion of the memory
11.1.4 Top/Bottom Block Protect (TB)
The Top/Bottom bit (TB) controls if the Block Protect Bits (BP2, BP1, BP0) protect from the Top
(TB=0) or the Bottom (TB=1) of the array as shown in the Status Register Memory Protection table.
The TB bit is non-volatile and the factory default setting is TB=0. The TB bit can be set with the Write
Status Register Instruction provided that the Write Enable instruction has been issued. The TB bit can
not be written to if the Status Register Protect (SRP) bit is set to 1 and the Write Protect (/WP) pin is
low.
11.1.5 Reserved Bits
Status register bit location S6 is reserved for future use. Current devices will read 0 for this bit
location. It is recommended to mask out the reserved bit when testing the Status Register. Doing this
will ensure compatibility with future devices.
- 12 -
Page 13
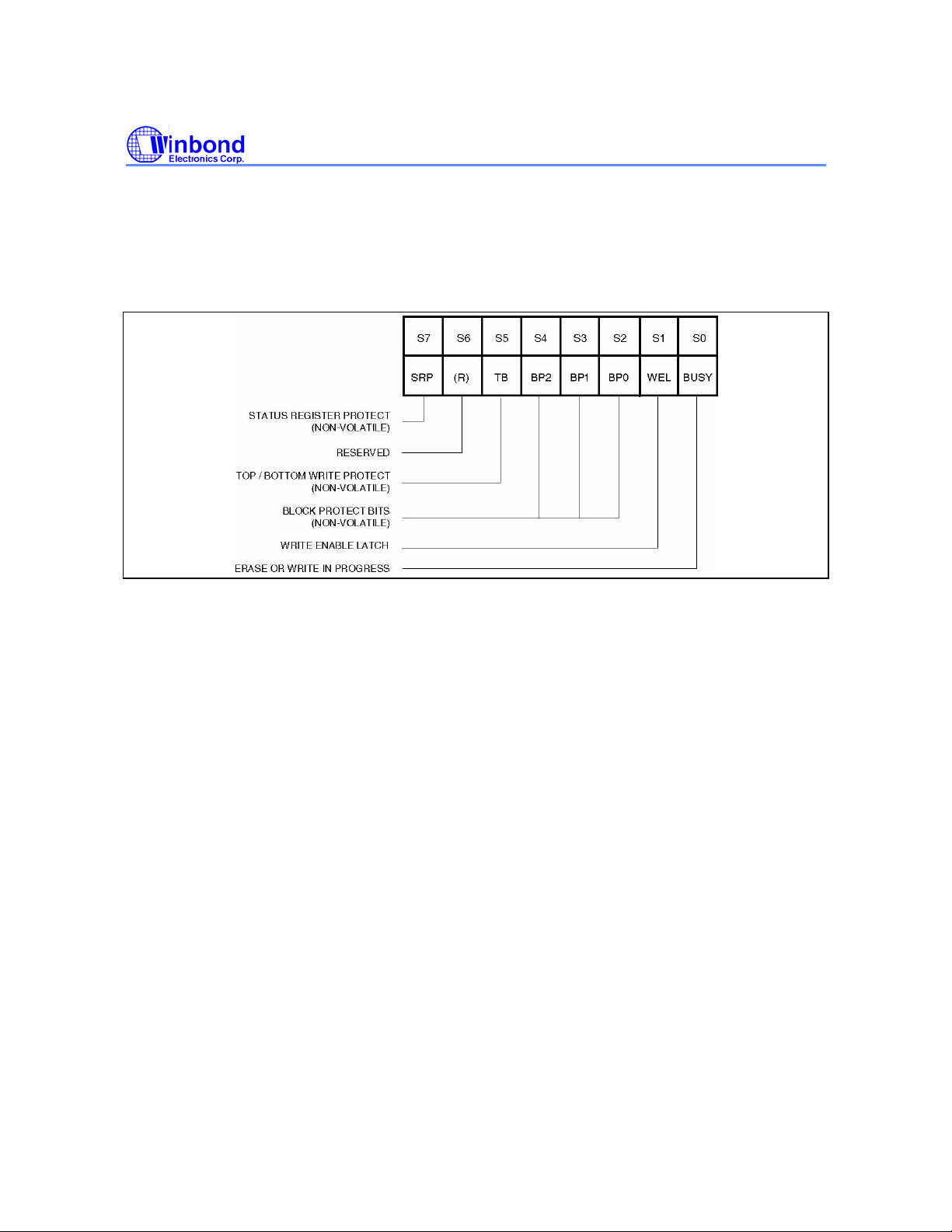
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.1.6 Status Register Protect (SRP)
The Status Register Protect (SRP) bit is a non-volatile read/write bit in status register (S7) that can be
used in conjunction with the Write Protect (/WP) pin to disable writes to status register. When the SRP
bit is set to a 0 state (factory default) the /WP pin has no control over status register. When the SRP
pin is set to a 1, the Write Status Register instruction is locked out while the /WP pin is low. When the
/WP pin is high the Write Status Register instruction is allowed.
Figure 3. Status Register Bit Locations
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 13 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 14
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
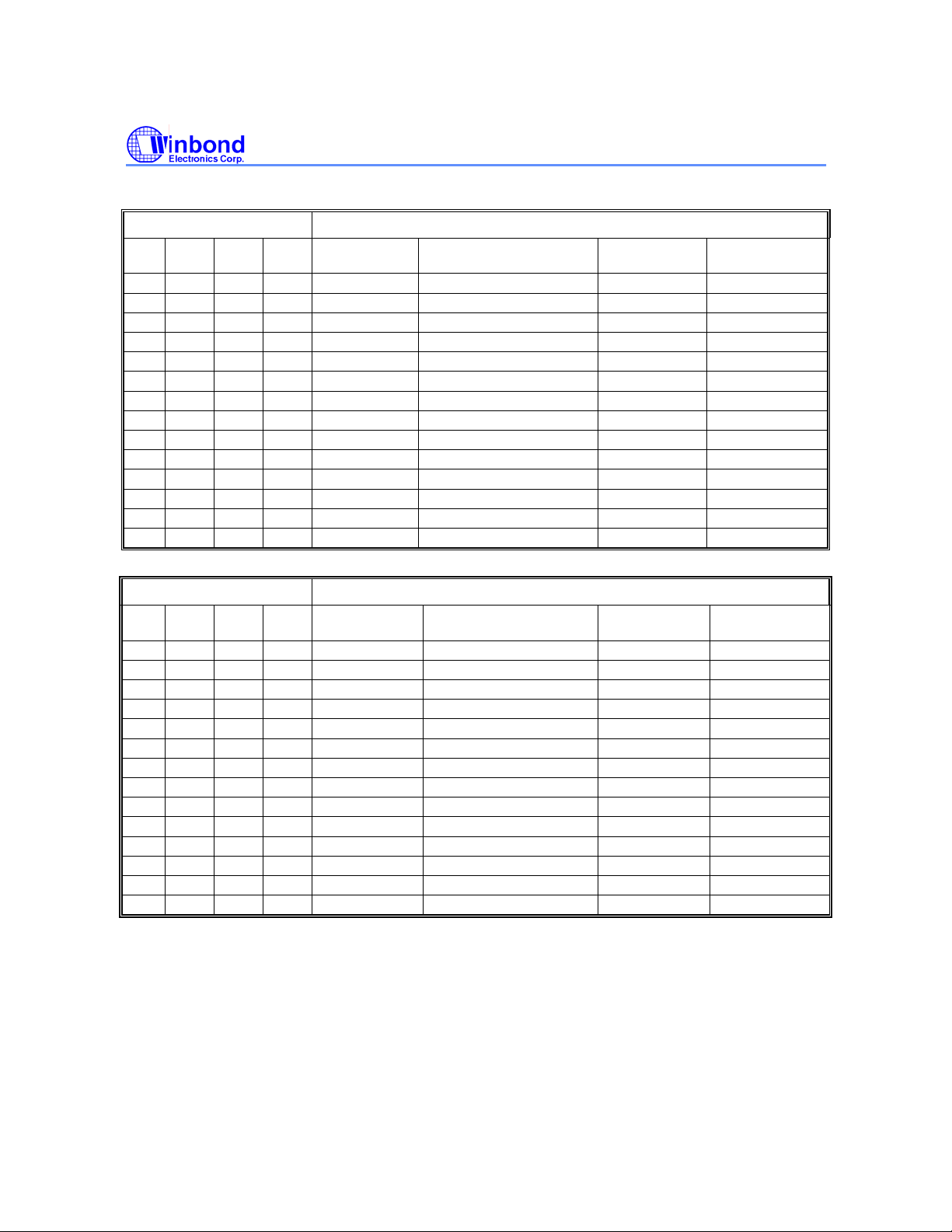
11.1.7 Status Register Memory Protection
STATUS REGISTER
TB BP2 BP1 BP0 BLOCK(S) ADDRESSES
x 0 0 0 NONE NONE NONE NONE
0 0 0 1 126 and 127 7E0000h - 7FFFFFh 1M -bit Upper 1/64
0 0 1 0 124 and 127 3C0000h - 7FFFFFh 2M-bit Upper 1/32
0 0 1 1 120 thru 127 780000h - 7FFFFFh 4M-bit Upper 1/16
0 1 0 0 112 thru 127 700000h - 7FFFFFh 8M-bit Upper 1/8
0 1 0 1 96 thru 127 600000h - 7FFFFFh 16M-bit Upper 1/4
0 1 1 0 64 thru 127 500000h - 7FFFFFh 32M-bit Upper 1/2
1 0 0 1 0 and 1 000000h - 01FFFFh 1M-bit Lower 1/64
1 0 1 0 0 thru 3 000000h - 03FFFFh 2M-bit Lower 1/32
1 0 1 1 0 thru 7 000000h - 07FFFFh 4M-bit Lower 1/16
1 1 0 0 0 thru 15 000000h – 0FFFFFh 8M-bit Lower 1/8
1 1 0 1 0 thru 31 000000h – 1FFFFFh 16M-bit Lower 1/4
1 1 1 0 0 thru 63 000000h – 3FFFFFh 16M-bit Lower 1/4
x 1 1 1 0 thru 127 000000h - 7FFFFFh 64M-bit ALL
STATUS REGISTER
TB BP2 BP1 BP0 BLOCK(S) ADDRESSES
x 0 0 0 NONE NONE NONE NONE
0 0 0 1 63 3F0000h - 3FFFFFh 512K-bit Upper 1/64
0 0 1 0 62 and 63 3E0000h - 3FFFFFh 1M-bit Upper 1/32
0 0 1 1 60 thru 63 3C0000h - 3FFFFFh 2M-bit Upper 1/16
0 1 0 0 56 thru 63 380000h - 3FFFFFh 4M-bit Upper 1/8
0 1 0 1 48 thru 63 300000h - 3FFFFFh 8M-bit Upper 1/4
0 1 1 0 32 thru 63 200000h - 3FFFFFh 16M-bit Upper 1/2
1 0 0 1 0 000000h - 00FFFFh 512K-bit Lower 1/64
1 0 1 0 0 and 1 000000h - 01FFFFh 1M-bit Lower 1/32
1 0 1 1 0 thru 3 000000h - 03FFFFh 2M-bit Lower 1/16
1 1 0 0 0 thru 7 000000h - 07FFFFh 4M-bit Lower 1/8
1 1 0 1 0 thru 15 000000h – 0FFFFFh 8M-bit Lower 1/4
1 1 1 0 0 thru 31 000000h – 1FFFFFh 16M-bit Lower 1/2
x 1 1 1 0 thru 63 000000h - 3FFFFFh 32M-bit ALL
(1)
W25X64 (64M-BIT) MEMORY PROTECTION
DENSITY
(KB)
(1)
W25X32 (32M-BIT) MEMORY PROTECTION
DENSITY
(KB)
PORTION
PORTION
- 14 -
Page 15
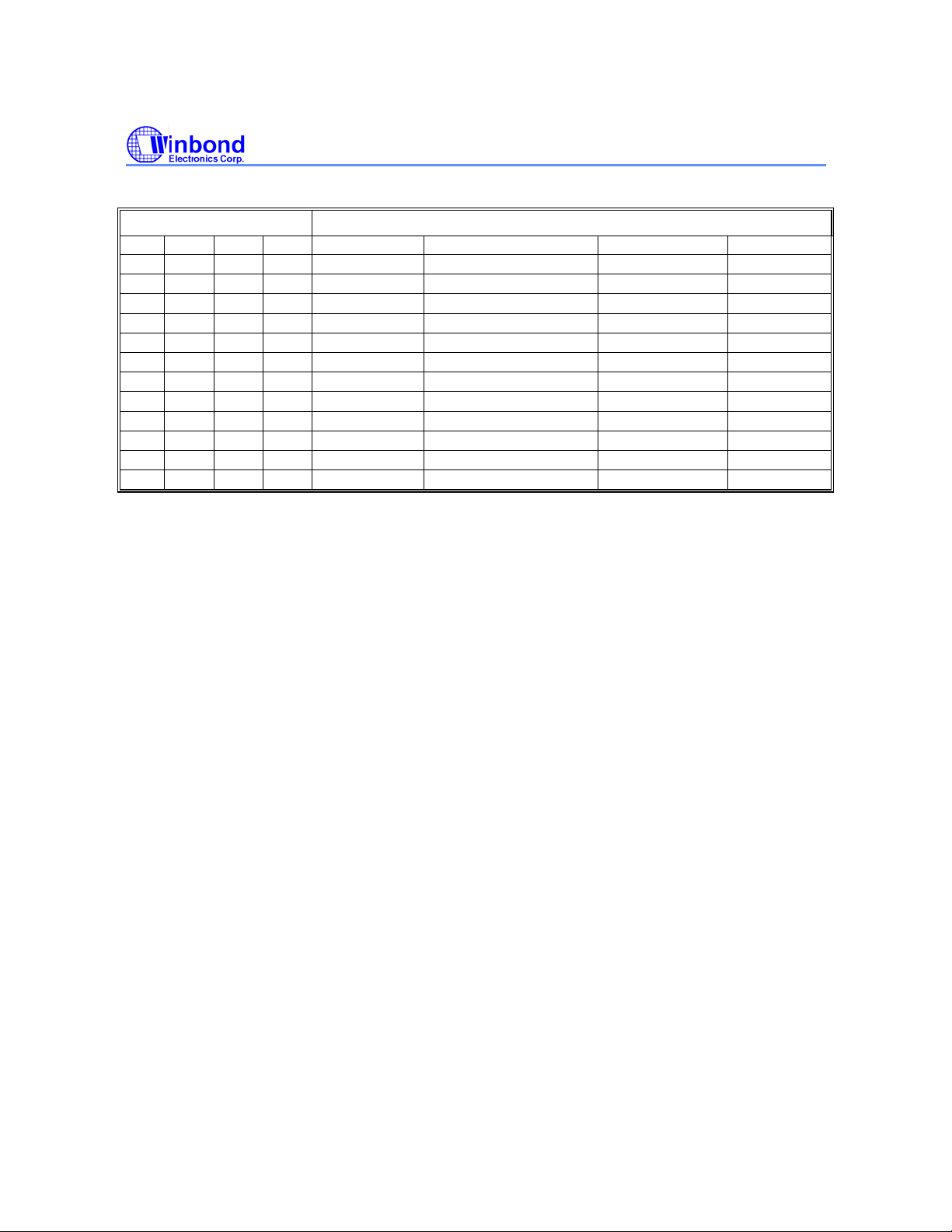
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
STATUS REGISTER
TB BP2 BP1 BP0 BLOCK(S) ADDRESSES DENSITY (KB) PORTION
x 0 0 0 NONE NONE NONE NONE
0 0 0 1 31 1F0000h - 1FFFFFh 512K-bit Upper 1/32
0 0 1 0 30 and 31 1E0000h - 1FFFFFh 1M-bit Upper 1/16
0 0 1 1 28 thru 31 1C0000h - 1FFFFFh 2M-bit Upper 1/8
0 1 0 0 24 thru 31 180000h - 1FFFFFh 4M-bit Upper 1/4
0 1 0 1 16 thru 31 100000h - 1FFFFFh 8M-bit Upper 1/2
1 0 0 1 0 000000h - 00FFFFh 512K-bit Lower 1/32
1 0 1 0 0 and 1 000000h - 01FFFFh 1M-bit Lower 1/16
1 0 1 1 0 thru 3 000000h - 03FFFFh 2M-bit Lower 1/8
1 1 0 0 0 thru 7 000000h - 07FFFFh 4M-bit Lower 1/4
1 1 0 1 0 thru 15 000000h - 0FFFFFh 8M-bit Lower 1/2
x 1 1 x 0 thru 31 000000h - 1FFFFFh 16M-bit ALL
Note:
1. x = don’t care
(1)
W25X16 (16M-BIT) MEMORY PROTECTION
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 15 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 16

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2 INSTRUCTIONS
The instruction set of the W25X16/32/64 consists of fifteen basic instructions that are fully controlled
through the SPI bus (see Instruction Set table). Instructions are initiated with the falling edge of Chip
Select (/CS). The first byte of data clocked into the DIO input provides the instruction code. Data on
the DIO input is sampled on the rising edge of clock with most significant bit (MSB) first.
Instructions vary in length from a single byte to several bytes and may be followed by address bytes,
data bytes, dummy bytes (don’t care), and in some cases, a combination. Instructions are completed
with the rising edge of edge /CS. Clock relative timing diagrams for each instruction are included in
figures 4 through 19. All read instructions can be completed after any clocked bit. However, all
instructions that Write, Program or Erase must complete on a byte boundary (CS driven high after a
full 8-bits have been clocked) otherwise the instruction will be terminated. This feature further protects
the device from inadvertent writes. Additionally, while the memory is being programmed or erased, or
when the Status Register is being written, all instructions except for Read Status Register will be
ignored until the program or erase cycle has completed.
11.2.1 Manufacturer and Device Identification
MANUFACTURER ID (M7-M0)
Winbond Serial Flash
Device ID (ID7-ID0)
Instruction ABh, 90h
W25X16 14h
W25X32 15h
W25X64 16h
EFH
(ID15-ID0)
9Fh
3015h
3016h
3017h
- 16 -
Page 17

11.2.2 Instruction Set
(1)
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
INSTRUCTION
NAME
BYTE 1
CODE
BYTE 2 BYTE 3 BYTE 4 BYTE 5 BYTE 6 N-BYTES
Write Enable 06h
Write Disable 04h
Read Status
Register
Write Status
Register
05h (S7–S0)
01h S7–S0
(1)
(2)
Read Data 03h A23–A16 A15–A8 A7–A0 (D7–D0) (Next byte) continuous
Fast Read 0Bh A23–A16 A15–A8 A7–A0 dummy (D7–D0)
I/O =
Fast Read Dual
Output
3Bh A23–A16 A15–A8 A7–A0 dummy
(D6,D4,D2,D0)
O =
(D7,D5,D3,D1)
Page Program 02h A23–A16 A15–A8 A7–A0
Block Erase
(64KB)
Sector Erase
(4KB)
D8h A23–A16 A15–A8 A7–A0
20h A23–A16 A15–A8 A7–A0
(3)
(D7–D0) (Next byte)
(Next Byte)
continuous
(one byte
per 4 clocks,
continuous)
Up to 256
bytes
Chip Erase C7h
Power-down B9h
Release Powerdown / Device ID
Manufacturer/
Device ID
(3)
ABh dummy dummy dummy (ID7-ID0)
90h dummy dummy 00h (M7-M0) (ID7-ID0)
JEDEC ID 9Fh
(M7-M0)
Manufacturer
(ID15-ID8)
Memory
Type
(ID7-ID0)
Capacity
(4)
Notes:
1. Data bytes are shifted with Most Significant Bit first. Byte fields with data in parenthesis “( )” indicate data being
read from the device on the DO pin.
2. The Status Register contents will repeat continuously until /CS terminates the instruction.
3. See Manufacturer and Device Identification table for Device ID information.
4. The Device ID will repeat continuously until /CS terminates the instruction.
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 17 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 18

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.3 Write Disable (04h)
The Write Enable instruction (Figure 4) sets the Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit in the Status Register to
a 1. The WEL bit must be set prior to every Page Program, Sector Erase, Block Erase, Chip Erase
and Write Status Register instruction. The Write Enable instruction is entered by driving /CS low,
shifting the instruction code “06h” into the Data Input (DI) pin on the rising edge of CLK, and then
driving /CS high.
Figure 4. Write Disable Instruction Sequence Diagram
11.2.4 Write Enable (06h)
The Write Disable instruction (Figure 5) resets the Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit in the Status Register
to a 0. The Write Disable instruction is entered by driving /CS low, shifting the instruction code “04h”
into the DIO pin and then driving /CS high. Note that the WEL bit is automatically reset after Power-up
and upon completion of the Write Status Register, Page Program, Sector Erase, Block Erase and
Chip Erase instructions.
Figure 5. Write Enable Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 18 -
Page 19

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.5 Read Status Register (05h)
The Read Status Register instruction allows the 8-bit Status Register to be read. The instruction is
entered by driving /CS low and shifting the instruction code “05h” into the DIO pin on the rising edge of
CLK. The status register bits are then shifted out on the DO pin at the falling edge of CLK with most
significant bit (MSB) first as shown in figure 6. The Status Register bits are shown in figure 3 and
include the BUSY, WEL, BP2-BP0, TB and SRP bits (see description of the Status Register earlier in
this datasheet).
The Status Register instruction may be used at any time, even while a Program, Erase or Write Status
Register cycle is in progress. This allows the BUSY status bit to be checked to determine when the
cycle is complete and if the device can accept another instruction. The Status Register can be read
continuously, as shown in Figure 6. The instruction is completed by driving /CS high.
Figure 6. Read Status Register Instruction Sequence Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 19 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 20

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.6 Write Status Register (01h)
The Write Status Register instruction allows the Status Register to be written. A Write Enable
instruction must previously have been executed for the device to accept the Write Status Register
Instruction (Status Register bit WEL must equal 1). Once write enabled, the instruction is entered by
driving /CS low, sending the instruction code “01h”, and then writing the status register data byte as
illustrated in figure 7. The Status Register bits are shown in figure 3 and described earlier in this
datasheet.
Only non-volatile Status Register bits SRP, TB, BP2, BP1 and BP0 (bits 7, 5, 4, 3 and 2) can be
written to. All other Status Register bit locations are read-only and will not be affected by the Write
Status Register instruction.
The /CS pin must be driven high after the eighth bit of the last byte has been latched. If this is not
done the Write Status Register instruction will not be executed. After /CS is driven high, the self-timed
Write Status Register cycle will commence for a time duration of t
the Write Status Register cycle is in progress, the Read Status Register instruction may still accessed
to check the status of the BUSY bit. The BUSY bit is a 1 during the Write Status Register cycle and a
0 when the cycle is finished and ready to accept other instructions again. After the Write Register
cycle has finished the Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit in the Status Register will be cleared to 0.
The Write Status Register instruction allows the Block Protect bits (TB, BP2, BP1 and BP0) to be set
for protecting all, a portion, or none of the memory from erase and program instructions. Protected
areas become read-only (see Status Register Memory Protection table). The Write Status Register
instruction also allows the Status Register Protect bit (SRP) to be set. This bit is used in conjunction
with the Write Protect (/WP) pin to disable writes to the status register. When the SRP bit is set to a 0
state (factory default) the /WP pin has no control over the status register. When the SRP pin is set to a
1, the Write Status Register instruction is locked out while the /WP pin is low. When the /WP pin is
high the Write Status Register instruction is allowed.
W (See AC Characteristics). While
Figure 7. Write Status Register Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 20 -
Page 21

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.7 Read Data (03h)
The Read Data instruction allows one more data bytes to be sequentially read from the memory. The
instruction is initiated by driving the /CS pin low and then shifting the instruction code “03h” followed
by a 24-bit address (A23-A0) into the DIO pin. The code and address bits are latched on the rising
edge of the CLK pin. After the address is received, the data byte of the addressed memory location
will be shifted out on the DO pin at the falling edge of CLK with most significant bit (MSB) first. The
address is automatically incremented to the next higher address after each byte of data is shifted out
allowing for a continuous stream of data. This means that the entire memory can be accessed with a
single instruction as long as the clock continues. The instruction is completed by driving /CS high. The
Read Data instruction sequence is shown in figure 8. If a Read Data instruction is issued while an
Erase, Program or Write cycle is in process (BUSY=1) the instruction is ignored and will not have any
effects on the current cycle. The Read Data instruction allows clock rates from D.C. to a maximum of
f
R (see AC Electrical Characteristics).
Figure 8. Read Data Instruction Sequence Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 21 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 22

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.8 Fast Read (0Bh)
The Fast Read instruction is similar to the Read Data instruction except that it can operate at the
highest possible frequency of F
eight “dummy” clocks after the 24-bit address as shown in figure 9. The dummy clocks allow the
devices internal circuits additional time for setting up the initial address. During the dummy clocks the
data value on the DIO pin is a “don’t care”.
R (see AC Electrical Characteristics). This is accomplished by adding
Figure 9. Fast Read Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 22 -
Page 23

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.9 Fast Read Dual Output (3Bh)
The Fast Read Dual Output (3Bh) instruction is similar to the standard Fast Read (0Bh) instruction
except that data is output on two pins, DO and DIO, instead of just DO. This allows data to be
transferred from the W25X16/32/64 at twice the rate of standard SPI devices. The Fast Read Dual
Output instruction is ideal for quickly downloading code from Flash to RAM upon power-up or for
applications that cache code-segments to RAM for execution.
Similar to the Fast Read instruction, the Fast Read Dual Output instruction can operate at the highest
possible frequency of FR (see AC Electrical Characteristics). This is accomplished by adding eight
“dummy” clocks after the 24-bit address as shown in figure 10. The dummy clocks allow the device's
internal circuits additional time for setting up the initial address. The input data during the dummy
clocks is “don’t care”. However, the DIO pin should be high-impedance prior to the falling edge of the
first data out clock.
Figure 10. Fast Read Dual Output Instruction Sequence Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 23 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 24

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.10 Page Program (02h)
The Page Program instruction allows up to 256 bytes of data to be programmed at previously erased
to all 1s (FFh) memory locations. A Write Enable instruction must be executed before the device will
accept the Page Program Instruction (Status Register bit WEL must equal 1). The instruction is
initiated by driving the /CS pin low then shifting the instruction code “02h” followed by a 24-bit address
(A23-A0) and at least one data byte, into the DIO pin. The /CS pin must be held low for the entire
length of the instruction while data is being sent to the device. The Page Program instruction
sequence is shown in figure 11.
If an entire 256 byte page is to be programmed, the last address byte (the 8 least significant address
bits) should be set to 0. If the last address byte is not zero, and the number of clocks exceed the
remaining page length, the addressing will wrap to the beginning of the page. In some cases, less
than 256 bytes (a partial page) can be programmed without having any effect on other bytes within the
same page. One condition to perform a partial page program is that the number of clocks can not
exceed the remaining page length. If more than 256 bytes are sent to the device the addressing will
wrap to the beginning of the page and overwrite previously sent data.
As with the write and erase instructions, the /CS pin must be driven high after the eighth bit of the last
byte has been latched. If this is not done the Page Program instruction will not be executed. After /CS
is driven high, the self-timed Page Program instruction will commence for a time duration of tpp (See
AC Characteristics). While the Page Program cycle is in progress, the Read Status Register
instruction may still be accessed for checking the status of the BUSY bit. The BUSY bit is a 1 during
the Page Program cycle and becomes a 0 when the cycle is finished and the device is ready to accept
other instructions again. After the Page Program cycle has finished the Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit
in the Status Register is cleared to 0. The Page Program instruction will not be executed if the
addressed page is protected by the Block Protect (BP2, BP1, and BP0) bits (see Status Register
Memory Protection table).
Figure 11. Page Program Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 24 -
Page 25

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.11 Sector Erase (20h)
The Sector Erase instruction sets all memory within a specified sector (4K-bytes) to the erased state
of all 1s (FFh). A Write Enable instruction must be executed before the device will accept the Sector
Erase Instruction (Status Register bit WEL must equal 1). The instruction is initiated by driving the /CS
pin low and shifting the instruction code “20h” followed a 24-bit sector address (A23-A0) (see Figure
2). The Sector Erase instruction sequence is shown in figure 12.
The /CS pin must be driven high after the eighth bit of the last byte has been latched. If this is not
done the Sector Erase instruction will not be executed. After /CS is driven high, the self-timed Sector
Erase instruction will commence for a time duration of t
Erase cycle is in progress, the Read Status Register instruction may still be accessed for checking the
status of the BUSY bit. The BUSY bit is a 1 during the Sector Erase cycle and becomes a 0 when the
cycle is finished and the device is ready to accept other instructions again. After the Sector Erase
cycle has finished the Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit in the Status Register is cleared to 0. The Sector
Erase instruction will not be executed if the addressed page is protected by the Block Protect (TB,
BP2, BP1, and BP0) bits (see Status Register Memory Protection table).
SE (See AC Characteristics). While the Sector
Figure 12. Sector Erase Instruction Sequence Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 25 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 26

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.12 Block Erase (D8h)
The Block Erase instruction sets all memory within a specified block (64K-bytes) to the erased state of
all 1s (FFh). A Write Enable instruction must be executed before the device will accept the Block
Erase Instruction (Status Register bit WEL must equal 1). The instruction is initiated by driving the /CS
pin low and shifting the instruction code “D8h” followed a 24-bit block address (A23-A0) (see Figure
2). The Block Erase instruction sequence is shown in figure 13.
The /CS pin must be driven high after the eighth bit of the last byte has been latched. If this is not
done the Block Erase instruction will not be executed. After /CS is driven high, the self-timed Block
Erase instruction will commence for a time duration of t
Erase cycle is in progress, the Read Status Register instruction may still be accessed for checking the
status of the BUSY bit. The BUSY bit is a 1 during the Block Erase cycle and becomes a 0 when the
cycle is finished and the device is ready to accept other instructions again. After the Block Erase cycle
has finished the Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit in the Status Register is cleared to 0. The Block Erase
instruction will not be executed if the addressed page is protected by the Block Protect (TB, BP2, BP1,
and BP0) bits (see Status Register Memory Protection table).
BE (See AC Characteristics). While the Block
Figure 13. Block Erase Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 26 -
Page 27

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.13 Chip Erase (C7h)
The Chip Erase instruction sets all memory within the device to the erased state of all 1s (FFh). A
Write Enable instruction must be executed before the device will accept the Chip Erase Instruction
(Status Register bit WEL must equal 1). The instruction is initiated by driving the /CS pin low and
shifting the instruction code “C7h”. The Chip Erase instruction sequence is shown in figure 14.
The /CS pin must be driven high after the eighth bit has been latched. If this is not done the Chip
Erase instruction will not be executed. After /CS is driven high, the self-timed Chip Erase instruction
will commence for a time duration of t
progress, the Read Status Register instruction may still be accessed to check the status of the BUSY
bit. The BUSY bit is a 1 during the Chip Erase cycle and becomes a 0 when finished and the device is
ready to accept other instructions again. After the Chip Erase cycle has finished the Write Enable
Latch (WEL) bit in the Status Register is cleared to 0. The Chip Erase instruction will not be executed
if any page is protected by the Block Protect (BP2, BP1, and BP0) bits (see Status Register Memory
Protection table).
CE (See AC Characteristics). While the Chip Erase cycle is in
Figure 14. Chip Erase Instruction Sequence Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 27 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 28

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.14 Power-down (B9h)
Although the standby current during normal operation is relatively low, standby current can be further
reduced with the Power-down instruction. The lower power consumption makes the Power-down
instruction especially useful for battery powered applications (See ICC1 and ICC2 in AC
Characteristics). The instruction is initiated by driving the /CS pin low and shifting the instruction code
“B9h” as shown in figure 15.
The /CS pin must be driven high after the eighth bit has been latched. If this is not done the Powerdown instruction will not be executed. After /CS is driven high, the power-down state will entered
within the time duration of t
Release from Power-down / Device ID instruction, which restores the device to normal operation, will
be recognized. All other instructions are ignored. This includes the Read Status Register instruction,
which is always available during normal operation. Ignoring all but one instruction makes the Power
Down state a useful condition for securing maximum write protection. The device always powers-up in
the normal operation with the standby current of ICC1.
DP (See AC Characteristics). While in the power-down state only the
Figure 15. Deep Power-down Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 28 -
Page 29

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.15 Release Power-down / Device ID (ABh)
The Release from Power-down / Device ID instruction is a multi-purpose instruction. It can be used to
release the device from the power-down state, obtain the devices electronic identification (ID) number
or do both.
When used only to release the device from the power-down state, the instruction is issued by driving
the /CS pin low, shifting the instruction code “ABh” and driving /CS high as shown in figure 16. After
the time duration of t
instructions will be accepted. The /CS pin must remain high during the tRES1 time duration.
When used only to obtain the Device ID while not in the power-down state, the instruction is initiated
by driving the /CS pin low and shifting the instruction code “ABh” followed by 3-dummy bytes. The
Device ID bits are then shifted out on the falling edge of CLK with most significant bit (MSB) first as
shown in figure 17. The Device ID values for the W25X16, W25X32, AND W25X64 are listed in
Manufacturer and Device Identification table. The Device ID can be read continuously. The instruction
is completed by driving /CS high.
When used to release the device from the power-down state and obtain the Device ID, the instruction
is the same as previously described, and shown in figure 15, except that after /CS is driven high it
must remain high for a time duration of t
device will resume normal operation and other instructions will be accepted.
RES1 (See AC Characteristics) the device will resume normal operation and other
RES2 (See AC Characteristics). After this time duration the
If the Release from Power-down / Device ID instruction is issued while an Erase, Program or Write
cycle is in process (when BUSY equals 1) the instruction is ignored and will not have any effects on
the current cycle
Figure 16. Release Power-down Instruction Sequence
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 29 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 30

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Figure 17. Release Power-down / Device ID Instruction Sequence Diagram
- 30 -
Page 31

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.16 Read Manufacturer / Device ID (90h)
The Read Manufacturer/Device ID instruction is an alternative to the Release from Power-down /
Device ID instruction that provides both the JEDEC assigned manufacturer ID and the specific device
ID.
The Read Manufacturer/Device ID instruction is very similar to the Release from Power-down / Device
ID instruction. The instruction is initiated by driving the /CS pin low and shifting the instruction code
“90h” followed by a 24-bit address (A23-A0) of 000000h. After which, the Manufacturer ID for Winbond
(EFh) and the Device ID are shifted out on the falling edge of CLK with most significant bit (MSB) first
as shown in figure 18. The Device ID values for the W25X16, W25X32, AND W25X64 are listed in
Manufacturer and Device Identification table. If the 24-bit address is initially set to 000001h the Device
ID will be read first and then followed by the Manufacturer ID. The Manufacturer and Device IDs can
be read continuously, alternating from one to the other. The instruction is completed by driving /CS
high.
Figure 18. Read Manufacturer / Device ID Diagram
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 31 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 32

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
11.2.17 JEDEC ID (9Fh)
For compatibility reasons, the W25X16/32/64 provides several instructions to electronically determine
the identity of the device. The Read JEDEC ID instruction is compatible with the JEDEC standard for
SPI compatible serial memories that was adopted in 2003.
The instruction is initiated by driving the /CS pin low and shifting the instruction code “9Fh”. The
JEDEC assigned Manufacturer ID byte for Winbond (EFh) and two Device ID bytes, Memory Type
(ID15-ID8) and Capacity (ID7-ID0) are then shifted out on the falling edge of CLK with most significant
bit (MSB) first as shown in figure 19. For memory type and capacity values refer to Manufacturer and
Device Identification table.
Figure 19. Read JEDEC ID
- 32 -
Page 33

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
12. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (PRELIMINARY)
12.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
PARAMETERS SYMBOL CONDITIONS RANGE UNIT
(1)
(4)
Supply Voltage VCC –0.6 to +4.0 V
Voltage Applied to Any Pin VIO Relative to Ground –0.6 to VCC +0.4 V
Storage Temperature TSTG –65 to +150
Lead Temperature TLEAD See Note
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage VESD Human Body Model
(3)
–2000 to +2000 V
(2)
°C
°C
Notes:
1. This device has been designed and tested for the specified operation ranges. Proper operation
outside of these levels is not guaranteed. Exposure beyond absolute maximum ratings (listed
above) may cause permanent damage.
2. Compliant with JEDEC Standard J-STD-20C for small body Sn-Pb or Pb-free (Green) assembly
and the European directive on restrictions on hazardous substances (RoHS) 2002/95/EU.
3. JEDEC Std JESD22-A114A (C1=100 pF, R1=1500 ohms, R2=500 ohms).
4. See preliminary designation at the end of this datasheet.
12.2 Operating Ranges
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS
= 50MHz, fR = 33MHz
F
R
Supply Voltage
Ambient Temperature,
Operating
Note:
1. VCC voltage during Read can operate across the min and max range but should not exceed ±10% of the
programming (erase/write) voltage.
2. Commercial temperature only applies to Fast Read (F
Industrial temperature applies to all other parameters.
(1)
VCC
T
A
F
= 70MHz, fR = 33MHz
R0
F
= 75MHz, fR = 33MHz
R1
Commercial
(2)
Industrial
& FR1) and 100K cycles endurance for 4K byte sectors .
R0
SPEC
MIN MAX
2.7
3.0
3.0
0
–40
3.6
3.6
3.6
+70
+85
UNIT
V
°C
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 33 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 34

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
12.3 Endurance and Data Retention
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
Erase/Program Cycles 4KB sector, 64KB block or full chip. 100,000 cycles
Data Retention Full Temperature Range 20 years
12.4 Power-up Timing and Write Inhibit Threshold
PARAMETER SYMBOL
VCC (min) to /CS Low tVSL
Time Delay Before Write Instruction tPUW
Write Inhibit Threshold Voltage VWI
Note:
1. These parameters are characterized only.
(1)
10 µs
(1)
1 10 ms
(1)
1 2 V
SPEC
MIN MAX
UNIT
Figure 20. Power-up Timing and Voltage Levels
- 34 -
Page 35

12.5 DC Electrical Characteristics
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS
SPEC
UNIT
MIN TYP MAX
Input Capacitance CIN
Output Capacitance Cout
(1)
VIN = 0V
(1)
VOUT = 0V
(2)
6 pf
(2)
8 pf
Input Leakage ILI ±2 µA
I/O Leakage ILO ±2 µA
Standby Current ICC1
Power-down Current ICC2
/CS = VCC,
VIN = GND or VCC
/CS = VCC,
VIN = GND or VCC
25 50 µA
<1 5 µA
Current Read Data /
Dual Output Read
(2)
1MHz
ICC3
C = 0.1 VCC / 0.9 VCC
DO = Open
5/8 10/12 mA
Current Read Data /
Dual Output Read
33MHz
(2)
CC3
I
C = 0.1 VCC / 0.9 VCC
DO = Open
10/10 15/20 mA
Current Read Data /
Dual Output Read
50MHz
(2)
CC3
I
C = 0.1 VCC / 0.9 VCC
DO = Open
10/15 15/20 mA
Current Read Data /
Dual Output Read
75MHz
(2)
Current Page
Program
Current Write Status
Register
Current Sector/Block
Erase
CC3
I
CC4 /CS = VCC 20 25 mA
I
I
CC5 /CS = VCC 8 12 mA
CC6 /CS = VCC 20 25 mA
I
C = 0.1 VCC / 0.9 VCC
DO = Open
15/20 20/25 mA
Current Chip Erase ICC7 /CS = VCC 20 25 mA
Input Low Voltage VIL –0.5 VCC x 0.3 V
Input High Voltage VIH VCC x0.7 VCC +0.4 V
Output Low Voltage VOL IOL = 1.6 mA 0.4 V
Output High Voltage VOH IOH = –100 µA VCC –0.2 V
Notes:
1. Tested on sample basis and specified through design and characterization data. TA=25° C, VCC 3V.
2. Checker Board Pattern.
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 35 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 36

12.6 AC Measurement Conditions
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
PARAMETER SYMBOL
MIN MAX
Load Capacitance
C
Load Capacitance for FR
only
1
L
SPEC
UNIT
30
pF
15
Input Rise and Fall Times TR, TF 5 ns
Input Pulse Voltages VIN 0.2 VCC to 0.8 VCC V
Input Timing Reference Voltages IN 0.3 VCC to 0.7 VCC V
Output Timing Reference Voltages OUT 0.5 VCC to 0.5 VCC V
Note:
1. Output Hi-Z is defined as the point where data out is no longer driven.
Figure 21. AC Measurement I/O Waveform
- 36 -
Page 37

12.7 AC Electrical Characteristics
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
DESCRIPTION SYMBOL ALT
UNIT
MIN TYP MAX
Clock frequency
SPEC
for all instructions, except Read Data (03h)
F
f
R
C
D.C. 50 MHz
2.7V-3.6V VCC & Industrial Temperature
Clock frequency
for all instructions, except Read Data (03h)
(4)
F
fC0 D.C. 70 MHz
R0
3.0V-3.6V VCC & Commercial Temperature
Clock frequency, for Fast Read (0Bh, 3Bh) only
3.0V-3.6V VCC & Commercial Temperature
(4)
fC1 D.C. 75 MHz
F
R1
Clock freq. Read Data instruction 03h fR D.C. 33 MHz
Clock High, Low Time, for Fast Read (0Bh, 3Bh) /
other instructions except Read Data (03h)
Clock High, Low Time for Read Data (03h)
instruction
Clock Rise Time peak to peak tCLCH
Clock Fall Time peak to peak tCHCL
tCLH,
tCLL
tCRLH,
tCRLL
(1)
6/7 ns
8 ns
(1)
(2)
0.1 V/ns
(2)
0.1 V/ns
/CS Active Setup Time relative to CLK tSLCH tCSS 5 ns
/CS Not Active Hold Time relative to CLK tCHSL 5 ns
Data In Setup Time tDVCH tDSU 2 ns
Data In Hold Time tCHDX tDH 5 ns
/CS Active Hold Time relative to CLK tCHSH 10 ns
/CS Not Active Setup Time relative to CLK tSHCH 0 ns
/CS Deselect Time tSHSL tCSH 100 ns
Output Disable Time tSHQZ
(2)
tDIS 7 ns
Clock Low to Output Valid
t
CLQV tV 7 / 6 ns
2.7V-3.6V / 3.0V-3.6V
Output Hold Time tCLQX tHO 0 ns
Continued – next page
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 37 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 38

12.8 AC Electrical Characteristics (cont’d)
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
DESCRIPTION SYMBOL ALT
UNIT
MIN TYP MAX
/HOLD Active Setup Time relative to CLK tHLCH 5 ns
/HOLD Active Hold Time relative to CLK tCHHH 5 ns
/HOLD Not Active Setup Time relative to CLK tHHCH 5 ns
/HOLD Not Active Hold Time relative to CLK tCHHL 5 ns
SPEC
/HOLD to Output Low-Z tHHQX
/HOLD to Output High-Z tHLQZ
Write Protect Setup Time Before /CS Low tWHSL
Write Protect Hold Time After /CS High tSHWL
/CS High to Power-down Mode tDP
/CS High to Standby Mode without Electronic
(2)
tLZ 7 ns
(2)
tHZ 12 ns
(3)
20 ns
(3)
100 ns
(2)
3 µs
(2)
tRES1
3 µs
Signature Read
/CS High to Standby Mode with Electronic
tRES2
(2)
1.8 µs
Signature Read
Write Status Register Time tW 10 15 ms
Byte Program Time (First Byte)
Additional Byte Program Time (After First Byte)
(5)
t
(5)
t
100 150 µs
BP1
6 12 µs
BP2
Page Program Time tPP 1.5 3 ms
Sector Erase Time (4KB) tSE 150 300 ms
Block Erase Time (64KB) tBE 1 2 s
Chip Erase Time W25X16
Chip Erase Time W25X32
Chip Erase Time W25X64
Notes:
1. Clock high + Clock low must be less than or equal to 1/f
2. Value guaranteed by design and/or characterization, not 100% tested in production.
3. Only applicable as a constraint for a Write Status Register instruction when Sector Protect Bit is set to 1.
4. Commercial temperature only applies to Fast Read (F
t
5. For multiple bytes after first byte within a page,
= number of bytes programmed.
BPN
= t
tCE 15
25
35
C.
& FR1). Industrial temperature applies to all other parameters.
R0
BP1 + tBP2 * N
(typical) and t
BPN
= t
BP1 + tBP2 * N
40
80
160
(max), where N
s
s
s
- 38 -
Page 39

12.9 Serial Output Timing
12.10 Input Timing
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
12.11 Hold Timing
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 39 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 40

13. PACKAGE SPECIFICATION
13.1 8-Pin SOIC 208-mil (Package Code SS)
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
SYMBOL
MILLIMETERS INCHES
MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 1.75 2.16 0.069 0.085
A1 0.05 0.25 0.002 0.010
A2 1.70 1.91 0.067 0.075
b 0.35 0.48 0.014 0.019
C 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
D
5.18 5.38 0.204 0.212
E 7.70 8.10 0.303 0.319
E1 5.18 5.38 0.204 0.212
e 1.27 BSC 0.050 BSC
L 0.50 0.80 0.020 0.031
θ
o
8
0
o
0
o
8
o
y --- 0.10 --- 0.004
Notes:
1. Controlling dimensions: inches, unless otherwise specified.
2. BSC = Basic lead spacing between centers.
3. Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash protrusions and should be measured from the bottom of the package.
4. Formed leads shall be planar with respect to one another within .0004 inches at the seating plane.
- 40 -
Page 41

13.2 8-Pin PDIP 300-mil (Package Code DA)
D
8
1
E
5
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
1
4
B
B
1
S
E
c
2
A
A
A
L
e
1
Symbol
A
A
A
B
B
c
D
E
E
e
L
α
e
S
Dimension in inch Dimension in mm
Nom
Min
0.010
1
0.130
0.125
2
0.016
0.018
1
1
1
A
0.060 1.52
0.010
0.008
0.360 0.380
0.3000.290
0.245
0.250
0.120
0.130
015
0.335 8.51
0.355
Base Plane
1
Seating Plane
Max Max
Min
0.175
0.25
0.135
3.18
0.41
0.022
0.0640.058
0.20
0.014
0.310
7.37
6.22
0.255
0.110
2.29 2.54 2.790.090 0.100
3.05
0.140
0.375
0.045
Nom
3.30
0.46
0.25
9.14
7.62
3.30
9.02
4.45
3.43
0.56
1.631.47
0.36
9.65
7.87
6.486.35
3.56
150
9.53
1.14
α
e
A
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 41 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 42

13.3 8-contact 6x5 WSON
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
- 42 -
Page 43

13.4 8-contact 6x5 WSON Cont’d.
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 43 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 44

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
13.5 16-Pin SOIC 300-mil (Winbond Package Code SF)
SYMBOL
MILLIMETERS INCHES
MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 2.36 2.64 0.093 0.104
A1 0.10 0.30 0.004 0.012
b 0.33 0.51 0.013 0.020
C 0.18 0.28 0.007 0.011
(3)
D
10.08 10.49 0.397 0.413
E 10.01 10.64 0.394 0.419
(3)
E1
7.39 7.59 0.291 0.299
(2)
e
1.27 BSC 0.050 BSC
L 0.39 1.27 0.015 0.050
θ
o
8
0
o
0
o
8
o
y --- 0.076 --- 0.003
Notes:
1. Controlling dimensions: inches, unless otherwise specified.
2. BSC = Basic lead spacing between centers.
3. Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash protrusions and should be measured from the bottom of the package.
- 44 -
Page 45

14. ORDERING INFORMATION
(1)
W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Notes:
1. Only the 2nd letter is used for the part marking.
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 45 - Preliminary - Revision B
Page 46

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
15. REVISION HISTORY
VERSION DATE PAGE DESCRIPTION
A 02/13/06 New Create
Added W25X64 in the product family of
W25X16/32/64.
Added 300mil PDIP package.
Added 6x5 mm WSON package.
Updated Endurance and Data Retention
table (11.3), ICC’s in DC Parameter table
B 06/28/06
1-4, 6, 32-36,
41, 42
(11.5 & 11.6).
Reduced tPP (max) from 5mS to 3mS.
Changed tSHCH from 5nS to 0nS.
Added byte programming parameters (tBP1
& tBPn.
Added additional byte programming
parameter, tBP2 and moved multiple byte
programming tBPn with formula to foot note.
Preliminary Designation
The “Preliminary” designation on a Winbond datasheet indicates that the product is not fully
characterized. The specifications are subject to change and are not g
authorized sales representative should be consulted for current information before using this product.
uaranteed. Winbond or an
Trademarks
Winbond and spiFlash are trademarks of Winbond
Electronics Corporation All other marks are the property of their respective owner.
Important Notice
Winbond products are not designed, intended, authorized or warranted for use as components
in systems or equipment intended for surgical implantation, atomic energy control
instruments, airplane or spaceship instruments, transportation instruments, traffic signal
instruments, combustion control instruments, or for other applications intended to support or
sustain life. Further more, Winbond products are not intended for applications wherein failure
of Winbond products could result or lead to a situation wherein personal injury, death or
severe property or environmental damage could occur.
Winbond customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so at their
own risk and agree to fully indemnify Winbond for any damages resulting from such improper
use or sales.
- 46 -
Page 47

W25X16, W25X32, W25X64
Headquarters
No. 4, Creation Rd. III,
Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, Taiwan
TEL: 886-3-5770066
FAX: 886-3-5665577
http://www.winbond.com.tw/
Taipei Office
9F, No.480, Rueiguang Rd.,
Neihu District, Taipei, 114,
Taiwan, R.O.C.
TEL: 886-2-8177-7168
FAX: 886-2-8751-3579
Please note that all data and specifications are subject to change without notice.
All the trademarks of products and companies mentioned in this datasheet belong to their respective owners.
Winbond Electronics Corporation America
2727 North First Street, San Jose,
CA 95134, U.S.A.
TEL: 1-408-9436666
FAX: 1-408-5441798
Winbond Electronics Corporation Japan
7F Daini-ueno BLDG, 3-7-18
Shinyokohama Kohoku-ku,
Yokohama, 222-0033
TEL: 81-45-4781881
FAX: 81-45-4781800
Winbond Electronics (Shanghai) Ltd.
27F, 2299 Yan An W. Rd. Shanghai,
200336 China
TEL: 86-21-62365999
FAX: 86-21-62365998
Winbond Electronics (H.K.) Ltd.
Unit 9-15, 22F, Millennium City,
No. 378 Kwun Tong Rd.,
Kowloon, Hong Kong
TEL: 852-27513100
FAX: 852-27552064
Publication Release Date: June 28, 2006
- 47 - Preliminary - Revision B
 Loading...
Loading...