Page 1

C
M
S
a
3
_
w
_
r
D
s
w
n
E
LTE
Rev.
Date:
21
odule
EC21_H
2017-0
Ha
eries
rdware
-01
rd
Design
a
V1.4
e
e
ig
ww.quecte l.com
Page 2

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Our aim is to provide customers with timely and comprehensive service. For any
assistance, please contact our company headquarters:
Quectel Wireless Solutions Co., Ltd.
Office 501, Building 13, No.99, Tianzhou Road, Shanghai, China, 200233
Tel: +86 21 5108 6236
Email:info@quectel.com
Or our local office.For more information, please visit:
http://www.quectel.com/support/salesupport.aspx
For technical support, or to report documentation errors, please visit:
http://www.quectel.com/support/techsupport.aspx
Or email to: Support@quectel.com
GENERAL NOTES
QUECTEL OFFERS THE INFORMATION AS A SERVICE TO ITS CUSTOMERS. THE INFORMATION
PROVIDED IS BASED UPON CUSTOMERS’ REQUIREMENTS. QUECTEL MAKES EVERY EFFORT
TO ENSURE THE QUALITY OF THE INFORMATION IT MAKES AVAILABLE. QUECTEL DOES NOT
MAKE ANY WARRANTY AS TO THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN, AND DOES NOT ACCEPT
ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY INJURY, LOSS OR DAMAGE OF ANY KIND INCURRED BY USE OF OR
RELIANCE UPON THE INFORMATION. THE INFORMATION SUPPLIED HEREIN IS SUBJECT TO
CHANGE WITHOUT PRIOR NOTICE.
COPYRIGHT
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HERE IS PROPRIETARY TECHNICAL INFORMATION OF
QUECTEL CO., LTD. TRANSMITTING, REPRODUCTION, DISSEMINATION AND EDITING OF THIS
DOCUMENT AS WELL AS UTILIZATION OF THE CONTENT ARE FORBIDDEN WITHOUT
PERMISSION. OFFENDERS WILL BE HELD LIABLE FOR PAYMENT OF DAMAGES. ALL RIGHTS
ARE RESERVED IN THE EVENT OF A PATENT GRANT OR REGISTRATION OF A UTILITY MODEL
OR DESIGN.
Copyright © Quectel Wireless Solutions Co., Ltd. 2017. All rights reserved.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 1 / 94
Page 3
EC21 Hardware Design
About the Document
History
Revision Date Author Description
1.0 2016-04-15 Yeoman CHEN Initial
LTE Module Series
Yeoman CHEN/
1.1 2016-09-22
1.2 2016-11-04
Frank WANG/
Lyndon LIU
Lyndon LIU/
Michael ZHANG
1. Updated frequency bands in Table 1.
2. Updated transmitting power, supported maximum
baud rate of main UART, supported internet
protocols, supported USB drivers of USB interface,
and temperature range in Table 2.
3. Updated timing of turning on module in Figure 12.
4. Updated timing of turning off module in Figure 13.
5. Updated timing of resetting module in Figure 16.
6. Updated main UART supports baud rate in Chapter
3.11.
7. Added notes for ADC interface in Chapter 3.13.
8. Updated GNSS Performance in Table 21.
9. Updated operating frequencies of module in Table
23.
10. Added current consumption in Chapter 6.4.
11. Updated RF output power in Chapter 6.5.
12. Added RF receiving sensitivity in Chapter 6.6.
1. Added SGMII and WLAN interfaces in Table 2.
2. Updated function diagram in Figure 1.
3. Updated pin assignment (Top View) in Figure 2.
4. Added description of SGMII and WLAN interfaces in
Table 4.
5. Added SGMII interface in Chapter 3.17.
6. Added WLAN interface in Chapter 3.18.
7. Added USB_BOOT interface in Chapter 3.19.
8. Added reference design of RF layout in Chapter
5.1.4.
9. Added current consumption of EC21-V in Chapter
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 2 / 94
Page 4
EC21 Hardware Design
1.3 2017-01-24
Lyndon LIU/
Rex WANG
LTE Module Series
6.4.
10. Added note about SIMO in Chapter 6.6.
1. Updated frequency bands in Table 1.
2. Updated function diagram in Figure 1.
3. Updated pin assignment (top view) in Figure 2.
4. Added BT interface in Chapter 3.18.2.
5. Updated reference circuit of wireless connectivity
interfaces with FC20 module in Figure 29.
6. Updated GNSS performance in Table 24.
7. Updated module operating frequencies in Table 26.
8. Added EC21-AUV current consumption in Table 38.
9. Updated EC21-A conducted RF receiving sensitivity
of in Table 42.
10. Added EC21-J conducted RF receiving sensitivity in
Table 48.
1.4 2017-03-01 Geely YANG Deleted the LTE band TDD B41 of EC21-CT
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 3 / 94
Page 5

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Contents
About the Document ................................................................................................................................ 2
Contents .................................................................................................................................................... 4
Table Index ............................................................................................................................................... 6
Figure Index .............................................................................................................................................. 8
1 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 10
1.1. Safety Information ..................................................................................................................11
2 Product Concept ............................................................................................................................. 12
2.1. General Description .............................................................................................................. 12
2.2. Key Features ......................................................................................................................... 13
2.3. Functional Diagram ............................................................................................................... 15
2.4. Evaluation Board ................................................................................................................... 16
3 Application Interfaces ..................................................................................................................... 17
3.1. General Description .............................................................................................................. 17
3.2. Pin Assignment ..................................................................................................................... 18
3.3. Pin Description ...................................................................................................................... 19
3.4. Operating Modes .................................................................................................................. 28
3.5. Power Saving ........................................................................................................................ 28
3.5.1.
Sleep Mode.................................................................................................................. 28
3.5.1.1. UART Application ............................................................................................... 28
3.5.1.2. USB Application with USB Remote Wakeup Function ....................................... 29
3.5.1.3. USB Application with USB Suspend/Resume and RI Function .......................... 30
3.5.1.4. USB Application without USB Suspend Function ............................................... 31
3.5.2. Airplane Mode .............................................................................................................. 32
3.6. Power Supply ........................................................................................................................ 32
3.6.1. Power Supply Pins ....................................................................................................... 32
3.6.2. Decrease Voltage Drop ................................................................................................ 33
3.6.3. Reference Design for Power Supply ............................................................................ 34
3.6.4. Monitor the Power Supply ............................................................................................ 35
3.7. Turn on and off Scenarios ..................................................................................................... 35
3.7.1. Turn on Module Using the PWRKEY ........................................................................... 35
3.7.2. Turn off Module ............................................................................................................ 37
3.7.2.1. Turn off Module Using the PWRKEY Pin ........................................................... 37
3.7.2.2. Turn off Module Using AT Command ................................................................. 37
3.8. Reset the Module .................................................................................................................. 38
3.9. USIM Card Interface ............................................................................................................. 39
3.10. USB Interface ........................................................................................................................ 41
3.11. UART Interfaces .................................................................................................................... 43
3.12. PCM and I2C Interfaces ........................................................................................................ 45
3.13. ADC Function ........................................................................................................................ 48
3.14. Network Status Indication ..................................................................................................... 49
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 4 / 94
Page 6

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.15. STATUS ................................................................................................................................ 50
3.16. Behavior of the RI ................................................................................................................. 51
3.17. SGMII Interface ..................................................................................................................... 51
3.18. Wireless Connectivity Interfaces ........................................................................................... 54
3.18.1. WLAN Interface ........................................................................................................... 56
3.18.2. BT Interface* ................................................................................................................ 56
3.19. USB_BOOT Interface ............................................................................................................ 57
4 GNSS Receiver ................................................................................................................................ 58
4.1. General Description .............................................................................................................. 58
4.2. GNSS Performance .............................................................................................................. 58
4.3. Layout Guidelines ................................................................................................................. 59
5 Antenna Interfaces .......................................................................................................................... 60
5.1. Main/Rx-diversity Antenna Interface ..................................................................................... 60
5.1.1. Pin Definition ................................................................................................................ 60
5.1.2. Operating Frequency ................................................................................................... 60
5.1.3. Reference Design of RF Antenna Interface ................................................................. 61
5.1.4. Reference Design of RF Layout ................................................................................... 62
5.2.
GNSS Antenna Interface ....................................................................................................... 64
5.3. Antenna Installation .............................................................................................................. 65
5.3.1. Antenna Requirement .................................................................................................. 65
5.3.2. Recommended RF Connector for Antenna Installation ................................................ 66
6 Electrical, Reliability and Radio Characteristics .......................................................................... 68
6.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings .................................................................................................. 68
6.2. Power Supply Ratings ........................................................................................................... 68
6.3. Operating Temperature ......................................................................................................... 69
6.4. Current Consumption ............................................................................................................ 70
6.5. RF Output Power .................................................................................................................. 76
6.6. RF Receiving Sensitivity ....................................................................................................... 76
6.7. Electrostatic Discharge ......................................................................................................... 80
7 Mechanical Dimensions.................................................................................................................. 81
7.1. Mechanical Dimensions of the Module.................................................................................. 81
7.2. Recommended Footprint ....................................................................................................... 83
7.3. Design Effect Drawings of the Module .................................................................................. 84
8
Storage, Manufacturing and Packaging ........................................................................................ 85
8.1. Storage ................................................................................................................................. 85
8.2. Manufacturing and Soldering ................................................................................................ 86
8.3. Packaging ............................................................................................................................. 87
9 Appendix A References .................................................................................................................. 88
10 Appendix B GPRS Coding Schemes ............................................................................................. 92
11 Appendix C GPRS Multi-slot Classes ............................................................................................ 93
12 Appendix D EDGE Modulation and Coding Schemes .................................................................. 94
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 5 / 94
Page 7

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Table Index
TABLE 1: FREQUENCY BANDS OF EC21 SERIES MODULE ........................................................................ 12
TABLE 2: KEY FEATURES OF EC21 MODULE ............................................................................................... 13
TABLE 3: I/O PARAMETERS DEFINITION ....................................................................................................... 19
TABLE 4: PIN DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................................................... 19
TABLE 5: OVERVIEW OF OPERATING MODES ............................................................................................. 28
TABLE 6: VBAT AND GND PINS ....................................................................................................................... 33
TABLE 7: PWRKEY PIN DESCRIPTION .......................................................................................................... 35
TABLE 8: RESET_N PIN DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................................... 38
TABLE 9: PIN DEFINITION OF THE USIM CARD INTERFACE ...................................................................... 39
TABLE 10: PIN DESCRIPTION OF USB INTERFACE ..................................................................................... 41
TABLE 11: PIN DEFINITION OF THE MAIN UART INTERFACE ..................................................................... 43
TABLE 12: PIN DEFINITION OF THE DEBUG UART INTERFACE ................................................................. 43
TABLE 13: LOGIC LEVELS OF DIGITAL I/O .................................................................................................... 44
TABLE 14: PIN DEFINITION OF PCM AND I2C INTERFACES ....................................................................... 46
TABLE 15: PIN DEFINITION OF THE ADC ...................................................................................................... 48
TABLE 16: CHARACTERISTIC OF THE ADC .................................................................................................. 48
TABLE 17: PIN DEFINITION OF NETWORK CONNECTION STATUS/ACTIVITY INDICATOR ...................... 49
TABLE 18: WORKING STATE OF NETWORK CONNECTION STATUS/ACTIVITY INDICATOR ................... 49
TABLE 19: PIN DEFINITION OF STATUS ........................................................................................................ 50
TABLE 20: BEHAVIOR OF THE RI ................................................................................................................... 51
TABLE 21: PIN DEFINITION OF THE SGMII INTERFACE .............................................................................. 52
TABLE 22: PIN DEFINITION OF WIRELESS CONNECTIVITY INTERFACES ................................................ 54
TABLE 23: PIN DEFINITION OF USB_BOOT INTERFACE ............................................................................. 57
TABLE 24: GNSS PERFORMANCE ................................................................................................................. 58
TABLE 25: PIN DEFINITION OF THE RF ANTENNA ....................................................................................... 60
TABLE 26: MODULE OPERATING FREQUENCIES ........................................................................................ 60
TABLE 27: PIN DEFINITION OF GNSS ANTENNA INTERFACE ..................................................................... 64
TABLE 28: GNSS FREQUENCY ....................................................................................................................... 64
TABLE 29: ANTENNA REQUIREMENTS .......................................................................................................... 65
TABLE 30: ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .................................................................................................. 68
TABLE 31: POWER SUPPLY RATINGS ........................................................................................................... 68
TABLE 32: OPERATING TEMPERATURE ........................................................................................................ 69
TABLE 33: EC21-A CURRENT CONSUMPTION ............................................................................................. 70
TABLE 34: EC21-AUT CURRENT CONSUMPTION ........................................................................................ 71
TABLE 35: EC21-E CURRENT CONSUMPTION ............................................................................................. 72
TABLE 36: EC21-KL CURRENT CONSUMPTION ........................................................................................... 73
TABLE 37: EC21-V CURRENT CONSUMPTION ............................................................................................. 74
TABLE 38: EC21-AUV CURRENT CONSUMPTION ........................................................................................ 74
TABLE 39: GNSS CURRENT CONSUMPTION OF EC21 SERIES MODULE ................................................. 75
TABLE 40: RF OUTPUT POWER ..................................................................................................................... 76
TABLE 41: EC21-E CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY .................................................................. 76
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 6 / 94
Page 8

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
TABLE 42: EC21-A CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY .................................................................. 77
TABLE 43: EC21-V CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY .................................................................. 77
TABLE 44: EC21-AUT CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY ............................................................. 77
TABLE 45: EC21-AUTL CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY ........................................................... 78
TABLE 46: EC21-KL CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY ................................................................ 78
TABLE 47: EC21-CT CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY ................................................................ 78
TABLE 48: EC21-J CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY................................................................... 79
TABLE 49: EC21-AUV CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY ............................................................. 79
TABLE 50: ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................. 80
TABLE 51: RELATED DOCUMENTS ................................................................................................................ 88
TABLE 52: TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ...................................................................................................... 88
TABLE 53: DESCRIPTION OF DIFFERENT CODING SCHEMES .................................................................. 92
TABLE 54: GPRS MULTI-SLOT CLASSES ...................................................................................................... 93
TABLE 55: EDGE MODULATION AND CODING SCHEMES ........................................................................... 94
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 7 / 94
Page 9

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Figure Index
FIGURE 1: FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM ............................................................................................................... 16
FIGURE 2: PIN ASSIGNMENT (TOP VIEW) .................................................................................................... 18
FIGURE 3: SLEEP MODE APPLICATION VIA UART ....................................................................................... 29
FIGURE 4: SLEEP MODE APPLICATION WITH USB REMOTE WAKEUP .................................................... 30
FIGURE 5: SLEEP MODE APPLICATION WITH RI ......................................................................................... 31
FIGURE 6: SLEEP MODE APPLICATION WITHOUT SUSPEND FUNCTION ................................................ 31
FIGURE 7: POWER SUPPLY LIMITS DURING BURST TRANSMISSION ...................................................... 33
FIGURE 8: STAR STRUCTURE OF THE POWER SUPPLY ............................................................................ 34
FIGURE 9: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF POWER SUPPLY .............................................................................. 34
FIGURE 10: TURN ON THE MODULE USING DRIVING CIRCUIT ................................................................. 35
FIGURE 11: TURN ON THE MODULE USING KEYSTROKE .......................................................................... 36
FIGURE 12: TIMING OF TURNING ON MODULE ........................................................................................... 36
FIGURE 13: TIMING OF TURNING OFF MODULE ......................................................................................... 37
FIGURE 14: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF RESET_N BY USING DRIVING CIRCUIT ...................................... 38
FIGURE 15: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF RESET_N BY USING BUTTON ...................................................... 38
FIGURE 16: TIMING OF RESETTING MODULE ............................................................................................. 39
FIGURE 17: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF USIM CARD INTERFACE WITH AN 8-PIN USIM CARD
CONNECTOR .................................................................................................................................................... 40
FIGURE 18: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF USIM CARD INTERFACE WITH A 6-PIN USIM CARD CONNECTOR
........................................................................................................................................................................... 40
FIGURE 19: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF USB APPLICATION ......................................................................... 42
FIGURE 20: REFERENCE CIRCUIT WITH TRANSLATOR CHIP ................................................................... 44
FIGURE 21: REFERENCE CIRCUIT WITH TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT .............................................................. 45
FIGURE 22: PRIMARY MODE TIMING ............................................................................................................ 46
FIGURE 23: AUXILIARY MODE TIMING .......................................................................................................... 46
FIGURE 24: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF PCM APPLICATION WITH AUDIO CODEC .................................... 47
FIGURE 25: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF THE NETWORK INDICATOR .......................................................... 50
FIGURE 26: REFERENCE CIRCUITS OF STATUS ......................................................................................... 50
FIGURE 27: SIMPLIFIED BLOCK DIAGRAM FOR ETHERNET APPLICATION ............................................. 52
FIGURE 28: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF SGMII INTERFACE WITH PHY AR8033 APPLICATION ................. 53
FIGURE 29: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF WIRELESS CONNECTIVITY INTERFACES WITH FC20 MODULE
........................................................................................................................................................................... 55
FIGURE 30: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF USB_BOOT INTERFACE ................................................................ 57
FIGURE 31: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF RF ANTENNA INTERFACE ............................................................. 61
FIGURE 32: MICROSTRIP LINE DESIGN ON A 2-LAYER PCB ...................................................................... 62
FIGURE 33: COPLANAR WAVEGUIDE LINE DESIGN ON A 2-LAYER PCB .................................................. 62
FIGURE 34: COPLANAR WAVEGUIDE LINE DESIGN ON A 4-LAYER PCB (LAYER 3 AS REFERENCE
GROUND) .......................................................................................................................................................... 63
FIGURE 35: COPLANAR WAVEGUIDE LINE DESIGN ON A 4-LAYER PCB (LAYER 4 AS REFERENCE
GROUND) .......................................................................................................................................................... 63
FIGURE 36: REFERENCE CIRCUIT OF GNSS ANTENNA ............................................................................. 64
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 8 / 94
Page 10

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
FIGURE 37: DIMENSIONS OF THE UF.L-R-SMT CONNECTOR (UNIT: MM) ................................................ 66
FIGURE 38: MECHANICALS OF UF.L-LP CONNECTORS ............................................................................. 66
FIGURE 39: SPACE FACTOR OF MATED CONNECTOR (UNIT: MM) ........................................................... 67
FIGURE 40: MODULE TOP AND SIDE DIMENSIONS ..................................................................................... 81
FIGURE 41: MODULE BOTTOM DIMENSIONS (BOTTOM VIEW) ................................................................. 82
FIGURE 42: RECOMMENDED FOOTPRINT (TOP VIEW) .............................................................................. 83
FIGURE 43: TOP VIEW OF THE MODULE ...................................................................................................... 84
FIGURE 44: BOTTOM VIEW OF THE MODULE .............................................................................................. 84
FIGURE 45: REFLOW SOLDERING THERMAL PROFILE .............................................................................. 86
FIGURE 46: TAPE AND REEL SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................... 87
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 9 / 94
Page 11

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
1 Introduction
This document defines the EC21module and describes its air interface and hardware interface which are
connected with your application.
This document can help you quickly understand module interface specifications, electrical andmechanical
details, as well as other related information of EC21 module. Associated with application note and user
guide, you can use EC21 module to design and set up mobile applications easily.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 10 / 94
Page 12
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
1.1. Safety Information
The following safety precautions must be observed during all phases of the operation, such as usage,
service or repair of any cellular terminal or mobile incorporating EC21 module. Manufacturers of the cellular
terminal should send the following safety information to users and operating personnel, andincorporate
these guidelines into all manuals supplied with the product. If not so, Quectel assumes no liability for the
customer’s failure to comply with these precautions.
Full attention must be given to driving at all times in order to reduce the risk of an
accident. Using a mobile while driving (even with a handsfree kit) causes
distraction and can lead to an accident. You must comply with laws and regulations
restricting the use of wireless devices while driving.
Switch off the cellular terminal or mobile before boarding an aircraft. Make sure it is
switched off. The operation of wireless appliances in an aircraft is forbidden, so as
to prevent interference with communication systems. Consult the airline staff about
the use of wireless devices on boarding the aircraft, if your device offers an
Airplane Mode which must be enabled prior to boarding an aircraft.
Switch off your wireless device when in hospitals,clinics or other health care
facilities. These requests are designed to prevent possible interference with
sensitive medical equipment.
Cellular terminals or mobiles operatingover radio frequency signal and cellular
network cannot be guaranteed to connect in all conditions, for example no mobile
fee or with an invalid USIM/SIM card. While you are in this condition and need
emergent help, please remember using emergency call. In order to make or
receive a call, the cellular terminal or mobile must be switched on and in a service
area with adequate cellular signal strength.
Your cellular terminal or mobile contains a transmitter and receiver. When it is ON,
it receives and transmits radio frequency energy. RF interference can occur if it is
used close to TV set, radio, computer or other electric equipment.
In locations with potentially explosive atmospheres, obey all posted signs to turn
off wireless devices such as your phone or other cellular terminals. Areas with
potentially explosive atmospheres includefuelling areas, below decks on boats,
fuel or chemical transfer or storage facilities, areas where the air contains
chemicals or particles such as grain, dust or metal powders, etc.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 11 / 94
Page 13

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
2 Product Concept
2.1. General Description
EC21 is a series of LTE-FDD/LTE-TDD/WCDMA/GSM wireless communication module with receive
diversity. It provides data connectivity on LTE-FDD, LTE-TDD,DC-HSPA+, HSPA+, HSDPA, HSUPA,
WCDMA,EDGE andGPRSnetworks. It also provides GNSS
applications.EC21 contains tenvariants:EC21-E, EC21-A, EC21-V, EC21-AUT,
EC21-AU,EC21-AUV,EC21-AUTL, EC21-J, EC21-CT and EC21-KL. You can choose a dedicated type
based on the region or operator. The following table shows the frequency bands of EC21 series module.
1)
and voice functionality2) for your specific
Table 1: Frequency Bands of EC21 Series Module
Modules2) LTE Bands 3G Bands GSM
EC21-E
EC21-A
EC21-V
EC21-AUT
EC21-AU3)
EC21-AUV
EC21-AUTL
FDD:B1/B3/B5/B7/B8/B20
FDD:B2/B4/B12
FDD:B4/B13 N N Y
FDD:B1/B3/B5/B7/B28
FDD: B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B7/B8/
B28
TDD: B40
FDD: B1/B3/B5/B8/B28 B1/B5/B8 N Y N
FDD:B3/B7/B28 N N Y N
WCDMA:B1/B
5/B8
WCDMA:B2/B
4/B5
WCDMA:
B1/B5
WCDMA:
B1/B2/B5/B8
900/1800 Y
N Y
N Y
850/900/
1800/1900
Rxdiversity
Y
GNSS1)
GPS,
GLONASS,
BeiDou/
Compass,
Galileo,QZS
S
EC21-J
EC21-CT
EC21-KL
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 12 / 94
FDD: B1/B3/B8/B18/B19/B26 N N Y N
FDD:B1/B3/B5 N N N N
FDD:B1/B3/B5/B7/B8 N N Y N
Page 14
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
NOTES
1)
1.
GNSS function is optional.
2)
2.
EC21 series module (EC21-E, EC21-A, EC21-V, EC21-AUT, EC21-AU,EC21-AUV, EC21-AUTL,
EC21-J, EC21-CT and EC21-KL) includes Data-only and Telematics versions. Data-only version
does not support voice function, while Telematics version supports it.
3)
3.
B2 band on EC21-AU module does not support Rx-diversity.
4. Y = supported (including LTE and WCDMA). N = Not supported.
With a compact profile of 32.0mm ×29.0mm ×2.4mm, EC21 can meet almost all requirements for M2M
applications such as automotive, metering, tracking system, security, router, wireless POS, mobile
computing device, PDA phone,tablet PC, etc.
EC21 is an SMD type module which can be embedded into applications through its 144-pin pads,
including 80LCC signal pads and 64 other pads.
2.2. Key Features
The following table describes the detailed features of EC21 module.
Table 2: Key Features of EC21 Module
Features Details
Power Supply Supply voltage: 3.3V~4.3VTypical supply voltage: 3.8V
Class 4 (33dBm±2dB) for GSM900
Class 1 (30dBm±2dB) for DCS1800
Class E2 (27dBm±3dB) for GSM900 8-PSK
Transmitting Power
LTE Features
Class E2 (26dBm±3dB) for DCS1800 8-PSK
Class 3 (22.5dBm -3/+1dB) for WCDMA bands
Class 3 (22.5dBm -3/+1dB) for LTE-FDD bands
Class 3 (22.5dBm -3/+1dB) for LTE-TDD bands
Support up to non-CA CAT1
Support 1.4 to 20MHz RF bandwidth
SupportMIMO in DL direction
FDD: Max 5Mbps (UL), 10Mbps (DL)
TDD: Max 3.1Mbps(UL), 8.96Mbps(DL)
Support 3GPP R8 DC-HSPA+
WCDMA Features
Support 16-QAM, 64-QAM and QPSKmodulation
3GPP R6 CAT6 HSUPA: Max 5.76Mbps (UL)
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 13 / 94
Page 15
EC21 Hardware Design
GSMFeatures
Internet Protocol Features
LTE Module Series
3GPP R8 CAT24 DC-HSPA+: Max 42Mbps (DL)
R99:
CSD: 9.6kbps, 14.4kbps
GPRS:
Support GPRS multi-slot class 12 (12 by default)
Coding scheme: CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4
Maximum of four Rx time slots per frame
EDGE:
Support EDGE multi-slot class 12 (12 by default)
Support GMSK and 8-PSK for different MCS (Modulation and Coding
Scheme)
Downlink coding schemes: CS 1-4 and MCS 1-9
Uplink coding schemes: CS 1-4 and MCS 1-9
Support
TCP/UDP/PPP/FTP/HTTP/NTP/PING/QMI/HTTPS*/SMTP*/MMS*/FTPS*/
SSL*protocols
Support PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge
Handshake Authentication Protocol) protocols which are usually used for
PPP connections
Text and PDU mode
SMS
Point to point MO and MT
SMS cell broadcast
SMS storage: ME by default
USIM Interface Support USIM/SIM card: 1.8V, 3.0V
Support one digital audio interface: PCM interface
GSM: HR/FR/EFR/AMR/AMR-WB
Audio Features
WCDMA: AMR/AMR-WB
LTE: AMR/AMR-WB
Support echo cancellation and noise suppression
Used for audio function with external codec
Support 8-bit A-law*, μ-law*and 16-bit linear data formats
PCM Interface
Support long frame synchronization and short frame synchronization
Support master and slave modes, but must be the master in long frame
synchronization
Compliant with USB 2.0 specification (slave only);the data transfer rate can
reach up to 480Mbps
USB Interface
Used for AT command communication, data transmission, GNSS NMEA
output, software debugging, firmware upgradeand voice over USB*
SupportUSB drivers for Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows
8/8.1, Window 10, Linux 2.6 or later, Android 4.0/4.2/4.4/5.0/5.1/6.0
UART Interface
Main UART:
Used for AT command communication and data transmission
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 14 / 94
Page 16

EC21 Hardware Design
Baud rate reach up to 3000000bps, 115200bps by default
Support RTS and CTS hardware flow control
Debug UART:
Used for Linux console, log output
115200bps baud rate
SGMII Interface Support 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet connectivity
LTE Module Series
Wireless Connectivity
Interfaces
Support a low-power SDIO 3.0 interface for WLAN and UART/PCM
interface for Bluetooth*
Rx-diversity Support LTE/WCDMA Rx-diversity
GNSS Features
AT Commands
Network Indication
Antenna Interface
Physical Characteristics
Temperature Range
Gen8CLite of Qualcomm
Protocol: NMEA 0183
Compliant with 3GPP TS 27.007, 27.005 and Quectel enhanced AT
commands
Two pins including NET_MODE and NET_STATUS to indicate network
connectivity status
Including main antennainterface(ANT_MAIN), Rx-diversity antenna
interface (ANT_DIV) and GNSS antenna interface (ANT_GNSS)
Size: (32.0±0.15)×(29.0±0.15)×(2.4±0.2)mm
Weight: approx. 4.9g
Operation temperature range: -35°C ~ +75°C
Extended temperature range: -40°C ~ +85°C
1)
2)
Firmware Upgrade USB interfaceand DFOTA*
RoHS All hardware components are fully compliant with EU RoHS directive
NOTES
1. 1) Within operating temperature range, the module is 3GPP compliant.
2. 2) Within extended temperature range, the module remains the ability to establish and maintain a
voice, SMS, data transmission, emergency call, etc. There is no unrecoverable malfunction. There
are also no effects on radio spectrum and no harm to radio network. Only one or more parameters
like P
might reduce in their value and exceed the specified tolerances. When the temperature
out
returns to normal operating temperature levels, the module will meet 3GPP specificationsagain.
3. “*” means under development.
2.3. Functional Diagram
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 15 / 94
Page 17
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
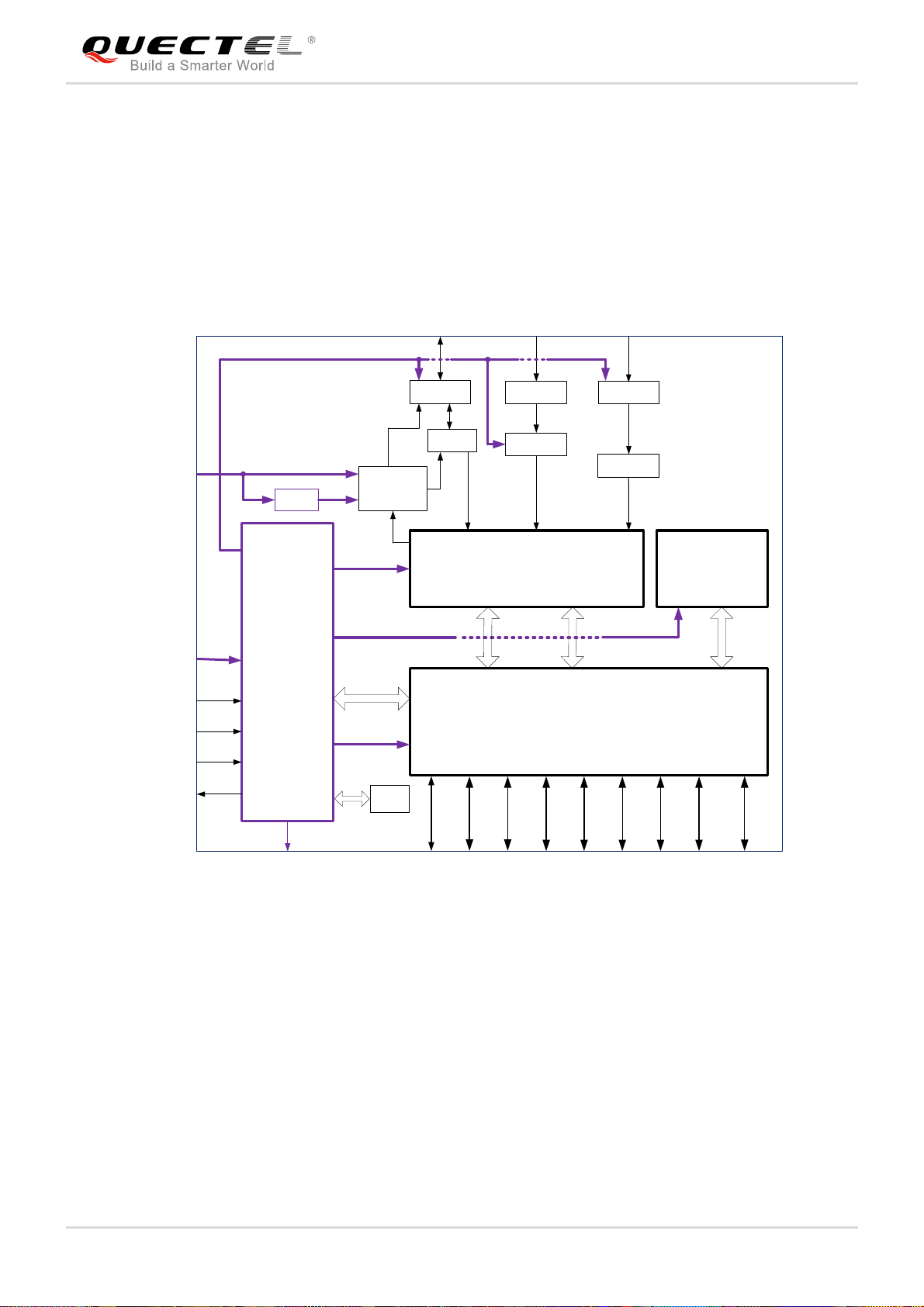
The following figure shows a block diagram of EC21 and illustrates the major functional parts.
Power management
Baseband
DDR+NAND flash
Radio frequency
Peripheral interfaces
ANT_MAIN ANT_DIVANT_GNSS
VBAT_RF
VBAT_BB
PWRKEY
RESET_N
ADCs
STATUS
APT
PMIC
Tx
Control
19.2M
PA
XO
Switch
Duplex
PRx DRx
SAW
LNA
Transceiver
IQ Control
Baseband
Switch
SAW
NAND
DDR2
SDRAM
VDD_EXT
USB
USIM
PCM
SGMII
WLAN
I2C
UART
GPIOs
BT
Figure 1: Functional Diagram
2.4. Evaluation Board
In order to help youdevelop applications with EC21, Quectel supplies an evaluation board (EVB), USB
data cable, earphone, antenna and other peripherals to control or test the module.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 16 / 94
Page 18

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3 Application Interfaces
3.1. General Description
EC21 is equipped with 80-pin SMT pads plus 64-pin ground pads and reserved pads that can
beconnected to cellular application platform. Sub-interfaces included in these pads are described in detail
in the following chapters:
Power supply
USIM interface
USB interface
UART interfaces
PCM interface
ADC interface
Status indication
SGMII interface
Wireless connectivity interfaces
USB_BOOT interface
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 17 / 94
Page 19

EC21 Hardware Design
3.2. Pin Assignment
The following figure shows the pin assignment of EC21 module.
LTE Module Series
Figure 2: Pin Assignment (Top View)
NOTES
1. 1)means that these pins cannot be pulled up before startup.
2)
2.
PWRKEY output voltage is 0.8V because of the diode drop in the Qualcomm chipset.
3. Pads 119~126 are SGMII function pins.
4. Pads 37~40, 118, 127 and 129~139 are wireless connectivity interfaces, among which pads 127 and
129~138 are WLAN function pins, and others are Bluetooth (BT) function pins. BT function is under
development.
5. Pads 24~27 are multiplexing pinsused for audio design on EC21 module and BT function on FC20
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 18 / 94
Page 20

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
module.
6. Keep all RESERVEDpins and unused pins unconnected.
7. GND pads 85~112 should be connected to ground in the design, and RESERVED pads 73~84should
not be designed in schematic and PCB decal.
※
8. “
” means these interface functions are only supported on Telematics version.
3.3. Pin Description
The following tables show the pin definition of EC21 module.
Table 3: I/O Parameters Definition
Type Description
IO Bidirectional
DI Digital input
DO Digital output
PI Power input
PO Power output
AI Analog input
AO Analog output
OD Open drain
Table 4: Pin Description
Power Supply
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
VBAT_BB 59,60 PI
VBAT_RF 57,58 PI
Power supply for
module baseband
part
Power supply for
module RF part
Vmax=4.3V
Vmin=3.3V
Vnorm=3.8V
Vmax=4.3V
Vmin=3.3V
Vnorm=3.8V
It must be able to provide
sufficient current up to
0.8A.
It must be able to provide
sufficient current up to
1.8A in a burst
transmission.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 19 / 94
Page 21

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Power supply for
external GPIO’s pull up
circuits.
VDD_EXT 7 PO
Provide 1.8V for
external circuit
Vnorm=1.8V
I
max=50mA
O
8,9,19,22,3
GND
6,46,48,50
~54,56,72,
Ground
85~112
Turn on/off
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
The output voltage is
0.8V because of the
diode drop in the
Qualcomm chipset.
PWRKEY 21 DI
Turnon/off the
module
RESET_N 20 DI Reset the module
V
max=2.1V
IH
V
min=1.3V
IH
V
max=0.5V
IL
max=2.1V
V
IH
V
min=1.3V
IH
V
max=0.5V
IL
Status Indication
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
STATUS 61 OD
Indicate the module
operating status
Indicate the module
NET_MODE 5 DO
network registration
mode
NET_
STATUS
6 DO
Indicate the module
network activity
status
The drive current
should be less than
0.9mA.
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
max=0.45V
OL
Require external
pull-up. If unused,
keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
Cannot be pulled up
before startup.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
USB Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
USB_VBUS 71 PI USB detection Vnorm=5.0V
USB_DP 69 IO
USB differential data
bus
Compliant with USB
2.0 standard
specification.
Require differential
impedance of 90ohm.
USB_DM 70 IO
USB differential data
bus
Compliant with USB
2.0 standard
specification.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 20 / 94
Require differential
impedance of 90ohm.
Page 22
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
USIM Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
USIM_GND 10
USIM_VDD 14 PO
USIM_DATA 15 IO
USIM_CLK 16 DO
USIM_RST 17 DO
USIM_
PRESENCE
13 DI
Specified ground for
USIM card
Power supply for
USIM card
Data signal of USIM
card
Clock signal of USIM
card
Reset signal of
USIM card
USIM card insertion
detection
For 1.8V USIM:
Vmax=1.9V
Vmin=1.7V
For 3.0V USIM:
Vmax=3.05V
Either 1.8V or 3.0V is
supported by the
module automatically.
Vmin=2.7V
I
max=50mA
O
For 1.8V USIM:
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
For 3.0V USIM:
V
max=1.0V
IL
V
min=1.95V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=2.55V
OH
For 1.8V USIM:
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
For 3.0V USIM:
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=2.55V
OH
For 1.8V USIM:
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
For 3.0V USIM:
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=2.55V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 21 / 94
Page 23

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
UART Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
V
RI 62 DO Ring indicator
DCD 63 DO
Data carrier
detection
CTS 64 DO Clear to send
RTS 65 DI Request to send
Data terminal
DTR 66 DI
ready,sleep mode
control
OL
V
OH
V
OL
VOHmin=1.35V
V
OL
V
OH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
max=0.45V
min=1.35V
max=0.45V
max=0.45V
min=1.35V
min=-0.3V
max=0.6V
min=1.2V
max=2.0V
min=-0.3V
max=0.6V
min=1.2V
max=2.0V
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
Pull-up by default. Low
level wakes up the
module.
If unused, keep it open.
TXD 67 DO Transmit data
RXD 68 DI Receive data
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
V
Debug UART Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
DBG_TXD 12 DO Transmit data
DBG_RXD 11 DI Receive data
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
V
ADC Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
General purpose
ADC0 45 AI
analog to digital
converter
General purpose
ADC1 44 AI
analog to digital
converter
Voltage range:
0.3V to VBAT_BB
Voltage range:
0.3V to VBAT_BB
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 22 / 94
If unused, keep it open.
If unused, keep it open.
Page 24
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
PCM Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
PCM_IN 24 DI PCM data input
PCM_OUT 25 DO PCM data output
PCM data frame
PCM_SYNC 26 IO
synchronization
signal
PCM_CLK 27 IO PCM clock
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
VOLmax=0.45V
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
In master mode, it is an
output signal.
In slave mode, it is an
input signal.
If unused, keep it open.
1.8V power domain.
In master mode, it is an
output signal.
In slave mode, it is an
input signal.
If unused, keep it open.
I2C Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
I2C serial clock.
I2C_SCL 41 OD
Used for external
codec
I2C serial data.
I2C_SDA 42 OD
Used for external
codec
External pull-up
resistor is required.
1.8V only.
If unused, keep it open.
External pull-up
resistor is required.
1.8V only.
If unused, keep it open.
SGMII Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
For 1.8V:
max=0.45V
V
EPHY_RST_N 119 DO Ethernet PHY reset
OL
V
min=1.4V
OH
For 2.85V:
V
max=0.35V
OL
V
min=2.14V
OH
1.8V/2.85V power
domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 23 / 94
Page 25
EC21 Hardware Design
EPHY_INT_N 120 DI
SGMII_
MDATA
SGMII_
MCLK
121 IO
122 DO
USIM2_VDD 128 PO
Ethernet PHY
interrupt
SGMII MDIO
(Management Data
Input/Output) data
SGMII MDIO
(Management Data
Input/Output) clock
SGMII MDIO pull-up
power source
V
min=-0.3V
IL
VILmax=0.6V
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
For 1.8V:
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.4V
OH
V
max=0.58V
IL
V
min=1.27V
IH
For 2.85V:
V
max=0.35V
OL
V
min=2.14V
OH
V
max=0.71V
IL
V
min=1.78V
IH
For 1.8V:
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.4V
OH
For 2.85V:
V
max=0.35V
OL
V
min=2.14V
OH
LTE Module Series
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V/2.85V power
domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V/2.85V power
domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
Configurable power
source.
1.8V/2.85V power
domain.
External pull-up for
SGMII MDIO pins.
If unused, keep it
open.
SGMII_TX_M 123 AO
SGMII_TX_P 124 AO
SGMII_RX_P 125 AI
SGMII_RX_M 126 AI
SGMII transmission
- minus
SGMII transmission
- plus
SGMII receiving
- plus
SGMII receiving
-minus
If unused, keep it
open.
If unused, keep it
open.
If unused, keep it
open.
If unused, keep it
open.
Wireless Connectivity Interfaces
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
SDC1_
DATA3
129 IO SDIO data bus D3
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 24 / 94
Page 26
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
SDC1_
DATA2
SDC1_
DATA1
SDC1_
DATA0
130 IO SDIO data bus D2
131 IO SDIO data bus D1
132 IO SDIO data bus D1
SDC1_CLK 133 DO SDIO clock
VILmin=-0.3V
VILmax=0.6V
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
SDC1_CMD 134 DO SDIO command
PM_ENABLE 127 DO
WAKE_ON_
WIRELESS
135 DI
External power
control
Wake up the host
(EC21 module) by
FC20 module.
WLAN function
WLAN_EN 136 DO
controlvia FC20
module
COEX_UART_
RX
137 DI
LTE/WLAN
coexistence signal
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
VILmin=-0.3V
VILmax=0.6V
VIHmin=1.2V
VIHmax=2.0V
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
Active low.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
Active high.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 25 / 94
Page 27

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
COEX_UART_
TX
WLAN_SLP_
CLK
138 DO
118 DO WLAN sleep clock
BT_RTS* 37 DI
BT_TXD* 38 DO
BT_RXD* 39 DI
BT_CTS* 40 DO
LTE/WLAN
coexistence signal
BT UART request to
send
BT UART transmit
data
BT UART receive
data
BT UART clear to
send
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
BT_EN* 139 DO
BTfunctioncontrolvia
FC20 module
V
max=0.45V
OL
V
min=1.35V
OH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
RF Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
ANT_DIV 35 AI
Diversity antenna
pad
50ohm impedance
If unused, keep it
open.
ANT_MAIN 49 IO Main antenna pad 50ohm impedance
ANT_GNSS 47 AI GNSS antenna pad 50 ohm impedance
If unused, keep it
open.
GPIO Pins
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Chara ct eristics Comment
1.8V power domain.
Cannot be pulled up
before startup.
Low level wakes up
the module.
If unused, keep it
WAKEUP_IN 1 DI Sleep mode control
V
min=-0.3V
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
open.
W_DISABLE# 4 DI Airplane mode VILmin=-0.3V 1.8V power domain.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 26 / 94
Page 28
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
control VILmax=0.6V
VIHmin=1.2V
V
max=2.0V
IH
Pull-up by default.
In low voltage level,
module can enter into
airplane mode.
If unused, keep it
open.
V
min=-0.3V
AP_READY 2 DI
Application
processor sleep
state detection
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
Other Interface Pins
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
V
min=-0.3V
USB_BOOT 115 DI
Force the module to
boot from USB port.
IL
V
max=0.6V
IL
V
min=1.2V
IH
V
max=2.0V
IH
1.8V power domain.
If unused, keep it
open.
RESERVED Pins
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
3, 18, 23,
28~34,
RESERVED
43, 55,
73~84,
113, 114,
Reserved
Keep these pins
unconnected.
116, 117,
140~144
NOTES
1. “*” means under development.
2. Pads 24~27 are multiplexing pins used for audio design on EC21 module and BT function on FC20
module.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 27 / 94
Page 29
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.4. Operating Modes
The table below briefly summarizes the various operating modes referred in the following chapters.
Table 5: Overview of Operating Modes
Mode Details
Normal
Idle
Operation
Talk/Data
Minimum
Functionality
Mode
Airplane
Mode
AT+CFUN command can set the module to a minimum functionality mode without
removing the power supply. In this case, both RF function and USIM card will be invalid.
AT+CFUN command or W_DISABLE# pin can set the module to airplane mode. In this
case, RF function will be invalid.
In this mode, the current consumption of the module will be reduced to the minimal level.
Sleep Mode
During this mode, the module can still receive paging message, SMS, voice call and
TCP/UDP data from the network normally.
Power down
Mode
In this mode, the power management unit shuts down the power supply. Software is not
active. The serial interface is not accessible. Operating voltage (connected to VBAT_RF
and VBAT_BB) remains applied.
3.5. Power Saving
Software is active. The module hasbeen registered onthe network, and
it is ready to send and receive data.
Network connection is ongoing. In this mode, the power consumption is
decided by network settingand data transfer rate.
3.5.1. Sleep Mode
EC21 is able to reduce its current consumption to a minimum value during the sleep mode. The following
section describes power saving procedure of EC21 module.
3.5.1.1. UART Application
If the host communicates with module via UART interface, the following preconditions can let the module
enter into sleep mode.
Execute AT+QSCLK=1 command to enable sleep mode.
Drive DTR to high level.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 28 / 94
Page 30

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
The following figure shows the connection between the module and the host.
Figure 3: Sleep Mode Application via UART
Driving thehost DTR to low level will wake up the module.
When EC21 has URC to report, RI signal will wake up the host. Refer to Chapter 3.16 for details
about RI behavior.
AP_READY will detect the sleep state of the host (can be configured to high level or low level
detection). Please refer to A T+QCFG=“apready”command for details.
NOTE
AT+QCFG=“apready”commandis under development.
3.5.1.2. USB Application with USB Remote Wakeup Function
If the host supports USB suspend/resume and remote wakeup functions, the following
threepreconditionsmust be mettolet the module enter into sleep mode.
Execute AT+QSCLK=1command to enable sleep mode.
Ensure the DTR is held in high level or keep it open.
The host’s USB bus, which is connected with the module’s USB interface, enters into suspended
state.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 29 / 94
Page 31

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
The following figure shows the connection between the module and the host.
Figure 4: Sleep Mode Application withUSB Remote Wakeup
Sending data to EC21through USB will wake up the module.
When EC21has URC to report, the module will send remote wake-up signals via USB bus so as to
wake up the host.
3.5.1.3. USB Application with USB Suspend/Resume and RI Function
If the host supports USB suspend/resume, but does not support remote wake-up function, the RI signal is
needed to wake up the host.
There are threepreconditions to let the module enter into the sleep mode.
Execute AT+QSCLK=1 command to enable sleep mode.
Ensure the DTR is held in high level or keep it open.
The host’s USB bus, which is connected with the module’s USB interface, enters into suspended
state.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 30 / 94
Page 32

EC21 Hardware Design
The following figure shows the connection between the module and the host.
Figure 5: Sleep Mode Application with RI
Sending data to EC21through USB will wake up the module.
When EC21has URC to report, RI signal will wake up the host.
LTE Module Series
3.5.1.4. USB Application without USB Suspend Function
If the host does not support USB suspend function, you should disconnect USB_VBUS with additional
control circuit to let the module enter into sleep mode.
Execute AT+QSCLK=1command to enable sleep mode.
Ensure the DTR is held in high level or keep it open.
Disconnect USB_VBUS.
The following figure shows the connection between the module and the host.
Figure 6: Sleep Mode Application without Suspend Function
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 31 / 94
Page 33

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Switching on the power switch to supply power to USB_VBUS will wake up the module.
NOTE
Please pay attention to the level match shown in dotted line between the module and thehost.Refer to
document [1] for more details about EC21 power management application.
3.5.2. Airplane Mode
When the module enters into airplane mode, the RF function does not work, and all AT commands
correlative with RF function will be inaccessible. This mode can be set via the following ways.
Hardware:
The W_DISABLE# pin is pulled up by default;driving it to low level will let the module enter into airplane
mode.
Software:
AT+CFUNcommand provides the choice of the functionality level.
AT+CFUN=0: Minimum functionality mode;both USIM and RF functions are disabled.
AT+CFUN=1: Full functionality mode (by default).
AT+CFUN=4: Airplane mode. RF function is disabled.
NOTES
1. The W_DISABLE# control function is disabled in firmware by default. It can be enabled by
AT+QCFG=“airplanecontrol” command. This commandis under development.
2. The execution of AT+CFUN command will not affect GNSS function.
3.6. Power Supply
3.6.1. Power Supply Pins
EC21 provides four VBAT pins for connection with the external power supply. There are two separate
voltage domains for VBAT.
Two VBAT_RF pins for module RF part.
Two VBAT_BB pins for module baseband part.
The following table shows the details of VBAT pins and ground pins.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 32 / 94
Page 34

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Table 6: VBAT and GND Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Description Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VBAT_RF 57,58
VBAT_BB 59,60
Power supply for module RF
part.
Power supply for module
baseband part.
3.3 3.8 4.3 V
3.3 3.8 4.3 V
8,9,19,22,36,46
GND
, 48,50~54,56,
Ground - 0 - V
72, 85~112
3.6.2. Decrease Voltage Drop
The power supply range of the module is from 3.3Vto4.3V. Please make sure that the input voltage will
never drop below 3.3V. The following figure shows the voltage drop during burst transmission in 2G
network.The voltage drop will be less in 3G and 4G networks.
Figure 7: Power Supply Limits during Burst Transmission
To decrease voltage drop, a bypass capacitor of about 100µF with low ESR should be used, and
amulti-layer ceramic chip (MLCC) capacitorarray should also be used to provide the low ESR. The main
power supply from an external application has to be a single voltage source and can be expanded to two
sub paths with star structure. The width of VBAT_BB trace should be no less than 1mm; andthe width of
VBAT_RF trace should be no less than 2mm.In principle, the longerthe VBAT trace is, the wider it will be.
Three ceramic capacitors (100nF, 33pF, 10pF) are recommended to be applied to the VBAT pins. These
capacitors should be placed close to the VBAT pins. In addition, in order to get a stable power source, it is
suggested that you should use a zener diode of which reverse zener voltage is 5.1V and dissipation
power is more than 0.5W. The following figure shows the star structure of the power supply.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 33 / 94
Page 35

EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 8: Star Structure of the Power Supply
3.6.3. Reference Design for Power Supply
LTE Module Series
Power design for the module is very important, asthe performance of the module largely depends on the
power source. The power supply is capable of providing sufficient current up to 2A at least. If the voltage
drop between the input and output is not too high, it is suggested that you shoulduse an LDO to supply
power for the module. If there is a big voltage difference between the input source and the desired output
(VBAT), a buck converter is preferred to be used as thepower supply.
The following figure shows a reference design for +5V input power source. The typical output of the power
supply is about 3.8V and the maximum load current is 3A.
Figure 9: Reference Circuit of Power Supply
NOTE
In order to avoid damaging internal flash, please do not switch off the power supply when the module
works normally. Only after the module is shutdown by PWRKEY or AT command, the power supply can be
cut off.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 34 / 94
Page 36

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.6.4. Monitor the Power Supply
AT+CBC command can be used to monitor the VBAT_BB voltage value. For more details, please refer to
document [2].
3.7. Turn on and off Scenarios
3.7.1. Turn on Module Using the PWRKEY
The following table shows the pin definition of PWRKEY.
Table 7: PWRKEY Pin Description
Pin Name Pin No. Description DC Characteristics Comment
max=2.1V
PWRKEY 21 Turn on/off the module
V
IH
V
min=1.3V
IH
V
max=0.5V
IL
The output voltage is 0.8V
because of the diode drop in
the Qualcomm chipset.
When EC21 is in power down mode, it can be turned on to normal mode by driving the PWRKEY pin to a
low level for at least 100ms. It is recommended to use an open drain/collector driver to control the
PWRKEY.After STATUS pin (require external pull-up) outputting a low level, PWRKEY pin can be
released. A simple reference circuit is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 10: Turn on the Module Using Driving Circuit
The other way to control the PWRKEY is using a button directly. When pressing the key, electrostatic
strike may generate from finger. Therefore, a TVS component is indispensable to be placed nearby the
button for ESD protection. A reference circuit is shownin the following figure.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 35 / 94
Page 37

EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 11: Turn on the Module Using Keystroke
The turn on scenario is illustrated in the following figure.
LTE Module Series
Figure 12: Timing of Turning on Module
NOTE
Please make sure that VBAT is stable before pulling down PWRKEY pin. The time between them is no
less than 30ms.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 36 / 94
Page 38

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.7.2. Turn off Module
The following procedures can be used to turn off the module:
Normal power down procedure: Turn off the module using the PWRKEY pin.
Normal power down procedure: Turn off the module using AT+QPOWD command.
3.7.2.1. Turn off Module Using the PWRKEY Pin
Driving the PWRKEY pin to a low level voltagefor at least 650ms, the module will execute power-down
procedure after the PWRKEY is released. The power-down scenario is illustrated inthe following figure.
Figure 13: Timing of Turning off Module
3.7.2.2. Turn off Module Using AT Command
It is also a safe way to use AT+QPOWDcommandto turn off the module, which is similar to turning off the
module via PWRKEY pin.
Please refer todocument [2] for details about AT+QPOWD command.
NOTE
In order to avoid damaging internal flash, please do not switch off the power supply when the module
works normally. Only after the module is shutdown by PWRKEY or AT command, the power supply can be
cut off.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 37 / 94
Page 39

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.8. Reset the Module
The RESET_N pin can be used to reset the module.The module can be reset by driving RESET_N to a
low level voltage for time between 150ms and 460ms.
Table 8: RESET_N Pin Description
Pin Name Pin No. Description DC Characteristics Comment
max=2.1V
V
IH
RESET_N 20 Reset the module
The recommended circuit is similar to the PWRKEY control circuit. An open drain/collector driver or button
can be used to control the RESET_N.
V
min=1.3V
IH
V
max=0.5V
IL
RESET_N
TBD
Reset pulse
4.7K
47K
Figure 14: Reference Circuit of RESET_N by Using Driving Circuit
Figure 15: Reference Circuit of RESET_N by Using Button
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 38 / 94
Page 40

EC21 Hardware Design
The reset scenario is illustrated inthe following figure.
Figure 16: Timing of Resetting Module
LTE Module Series
NOTES
1. Use RESET_N only when turning off the module by AT+QPOWD command and PWRKEY pin failed.
2. Ensure that there is no large capacitance on PWRKEY and RESET_N pins.
3.9. USIM Card Interface
The USIM card interface circuitrymeets ETSI and IMT-2000 SIM interface requirements. Both 1.8V and
3.0V USIM cards are supported.
Table 9: Pin Definition of the USIM Card Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
USIM_VDD 14 PO Power supply for USIM card
Either 1.8V or 3.0V is supported
by the module automatically.
USIM_DATA 15 IO Data signal of USIM card
USIM_CLK 16 DO Clock signal of USIM card
USIM_RST 17 DO Reset signal of USIM card
USIM_
PRESENCE
USIM_GND 10 Specified ground for USIM card
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 39 / 94
13 DI USIM card insertion detection
Page 41

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
EC21 supports USIM card hot-plug via the USIM_PRESENCE pin. The function supports low level and
high level detections, and is disabled by default. Please refer to document [2] about AT+QSIMDET
command for details.
The following figure shows a reference design for USIM card interface with an 8-pin USIM card connector.
Figure 17: Reference Circuit of USIM Card Interface with an 8-Pin USIM Card Connector
If USIM card detection function is not needed, please keep USIM_PRESENCE unconnected. Areference
circuit for USIM card interface with a 6-pin USIM card connector is illustrated inthe following figure.
Figure 18: Reference Circuit of USIM Card Interface with a6-Pin USIM Card Connector
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 40 / 94
Page 42

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
In order to enhance the reliability and availability of the USIM card in your application, please follow the
criteria below in USIM circuit design:
Keep layout of USIM card as close to the module as possible. Keep the trace length as less than
200mm as possible.
Keep USIM card signals away from RF and VBAT traces.
Assure the ground between the module and the USIM card connectorshort and wide. Keep the trace
width of ground and USIM_VDD no less than 0.5mm to maintain the same electric potential.
To avoid cross-talk between USIM_DATA and USIM_CLK, keep them away fromeach other and
shield them with surrounded ground.
In order to offer good ESD protection, it is recommended to add a TVSdiode array whose parasitic
capacitance should not be more than 50pF. The 22ohmresistors should be added in series between
the module and the USIM card so as to suppress EMI spurious transmission and enhance ESD
protection. The 33pFcapacitors are used for filtering interference of GSM900.Please note that the
USIM peripheral circuit should be close to the USIM card connector.
The pull-up resistor on USIM_DATA line can improve anti-jamming capability when long layout trace
and sensitive occasion areapplied, and should be placed close to the USIM card connector.
3.10. USB Interface
EC21 contains one integrated Universal Serial Bus (USB) transceiver which complies with the USB 2.0
specification and supports high-speed (480Mbps) and full-speed (12Mbps)modes. The USB interface is
used for AT command communication, data transmission, GNSS NMEA sentences output, software
debugging, firmware upgrade and voice over USB*. The following table shows the pin definition of USB
interface.
Table 10: Pin Description of USB Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
USB Signal Part
USB_DP 69 IO USB differential data bus (positive)
USB_DM 70 IO USB differential data bus (minus)
Require differential
impedance of 90Ω
Require differential
impedance of 90Ω
USB_VBUS 71 PI Used for detecting the USB connection Typical 5.0V
GND 72 Ground
For more details about the USB 2.0 specifications, please visit http://www.usb.org/home
.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 41 / 94
Page 43

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
The USB interface is recommended to be reserved for firmware upgrade in your design. The following
figure shows areference circuit of USB interface.
Figure 19: Reference Circuit of USB Application
In order to ensurethe integrity of USB data line signal, components R1, R2, R3 and R4 must be placed
close to the module, and alsothese resistors should be placed close to each other. The extra stubs of
trace must be as short as possible.
In order to ensure the USB interface design corresponding with the USB 2.0 specification, please comply
with the following principles:
It is important to route the USB signal traces as differential pairs with total grounding. The impedance
of USB differential trace is 90ohm.
Do not route signal traces under crystals, oscillators, magnetic devicesorRF signal traces. It is
important to route the USB differential traces in inner-layer with ground shielding onnot only upper
and lower layers but also right and left sides.
Pay attention to the influence of junction capacitance of ESD protection components on USB data
lines. Typically, the capacitance value should be less than 2pF.
Keep the ESD protection components to the USB connector as close as possible.
NOTES
1. EC21 module can only be used as a slave device.
2. “*” means under development.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 42 / 94
Page 44

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.11. UART Interfaces
The module provides two UART interfaces: the main UART interface and the debug UART interface. The
following shows their features.
The main UART interface supports 4800, 9600,19200,38400,
57600,115200,230400,460800,921600and 3000000bps baud rates, and the default is 115200bps.
The interface is used for data transmission and AT command communication.
The debug UART interface supports 115200bpsbaud rate. It is used forLinux console and log output.
The following tables show the pin definition of the main UART interface.
Table 11: Pin Definition of the Main UART Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
RI 62 DO Ring indicator
DCD 63 DO Data carrier detection
CTS 64 DO Clear to send
RTS 65 DI Request to send
1.8V power domain
DTR 66 DI Sleep mode control
TXD 67 DO Transmit data
RXD 68 DI Receive data
Table 12: Pin Definition of the Debug UART Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
DBG_TXD 12 DO Transmit data
1.8V power domain
DBG_RXD 11 DI Receive data
The logic levels are described in the following table.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 43 / 94
Page 45

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Table 13:Logic Levels of Digital I/O
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VIL -0.3 0.6 V
VIH 1.2 2.0 V
VOL 0 0.45 V
VOH 1.35 1.8 V
The module provides 1.8V UART interface. A level translator should be used if your application is
equipped with a 3.3V UART interface. A level translator TXS0108EPWR provided by Texas Instrumentis
recommended. The following figure shows areference design.
Figure 20: Reference Circuit with Translator Chip
Please visithttp://www.ti.com
for more information.
Another example with transistor translation circuit is shown as below. The circuit design of dotted line
section can refer to the design of solid line section, in terms of both module input and output circuit
designs; but please pay attention to the direction of connection.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 44 / 94
Page 46

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 21: Reference Circuit with Transistor Circuit
NOTE
Transistor circuit solution is not suitable for applications with high baud rates exceeding 460Kbps.
3.12. PCM and I2C Interfaces
EC21 provides one Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) digital interface for audio design, which supports the
following modes:
Primary mode (short frame synchronization, works as both master and slave)
Auxiliary mode (long framesynchronization, works as master only)
In primary mode, the data is sampled on the falling edge of the PCM_CLK and transmitted on the rising
edge.The PCM_SYNC falling edge represents the MSB. In this mode, PCM_CLK supports
128,256,512,1024 and2048kHz for different speech codecs.
In auxiliary mode, the data is also sampled on the falling edge of the PCM_CLK and transmitted on the
rising edge.But the PCM_SYNC rising edge represents the MSB. In this mode, PCM interface operates
with a 128kHz PCM_CLK and an 8kHz, 50% duty cycle PCM_SYNC only.
EC21 supports 8-bit A-law* andμ-law*, and also 16-bit linear data formats. The following figures show
theprimary mode’s timing relationship with 8kHz PCM_SYNC and 2048kHz PCM_CLK, as well asthe
auxiliary mode’s timing relationship with 8kHz PCM_SYNC and 128kHz PCM_CLK.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 45 / 94
Page 47

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 22: Primary Mode Timing
Figure 23: Auxiliary Mode Timing
The following table shows the pin definition of PCM and I2C interfaces which can be applied on audio
codec design.
Table 14: Pin Definition of PCM and I2C Interfaces
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
PCM_IN 24 DI PCM data input 1.8V power domain
PCM_OUT 25 DO PCM data output 1.8V power domain
PCM_SYNC 26 IO PCM data frame sync signal 1.8V power domain
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 46 / 94
Page 48

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
PCM_CLK 27 IO PCM data bit clock 1.8V power domain
I2C_SCL 41 OD I2C serial clock Require external pull-up to 1.8V
I2C_SDA 42 OD I2C serial data Require external pull-up to 1.8V
Clock and mode can be configured by AT command, and the default configuration is master mode using
short frame synchronization format with 2048kHzPCM_CLK and 8kHz PCM_SYNC.Please refer to
document [2] about AT+QDAIcommand for details.
The following figure shows areference design of PCM interface with external codec IC.
Figure 24: Reference Circuit of PCM Application with Audio Codec
NOTES
1. “*” means under development.
2. It is recommended to reserve RC (R=22ohm, C=22pF) circuit on the PCM lines, especially for
PCM_CLK.
3. EC21 works as a master device pertaining to I2C interface.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 47 / 94
Page 49

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.13. ADC Function
The module provides two analog-to-digital converters (ADC).AT+QADC=0 command can be used to read
the voltage value on ADC0 pin. AT+QADC=1command can be used to read the voltage value on ADC1
pin. For more details about these AT commands, please refer todocument [2].
In order to improve the accuracy of ADC, the trace of ADC should be surrounded by ground.
Table 15: Pin Definition of the ADC
Pin Name Pin No. Description
ADC0 45 General purpose analog to digital converter
ADC1 44 General purpose analog to digital converter
The following table describes the characteristic of the ADC function.
Table 16: Characteristic of the ADC
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
ADC0 Voltage Range 0.3 VBAT_BB V
ADC1 Voltage Range 0.3 VBAT_BB V
ADC Resolution 15 bits
NOTES
1. ADC input voltage must not exceed VBAT_BB.
2. It is prohibited to supply any voltage to ADC pins when VBAT is removed.
3. It is recommended to use resistor divider circuit for ADC application.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 48 / 94
Page 50

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.14. Network Status Indication
The network indication pins can be used to drive network status indicationLEDs. The module provides two
pins which are NET_MODE and NET_STATUS. The following tables describe thepin definition and logic
level changes in different network status.
Table 17: Pin Definition of Network ConnectionStatus/Activity Indicator
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
NET_MODE1) 5 DO
Indicate the module’s network
registrationstatus
1.8V power domain
NET_STATUS 6 DO
Indicate the module’s network activity
status
NOTE
1)
means that this pin cannot be pulled up before startup.
Table 18: Working State of Network Connection Status/Activity Indicator
Pin Name Logic Level Changes Network Status
Always High Registered on LTE network
NET_MODE
Always Low Others
Flicker slowly (200ms High/1800ms Low) Network searching
Flicker slowly (1800ms High/200ms Low) Idle
NET_STATUS
Flicker quickly (125ms High/125ms Low) Data transfer is ongoing
Always High Voice calling
A reference circuit is shown in the following figure.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 49 / 94
Page 51

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 25: Reference Circuit of the Network Indicator
3.15. STATUS
The STATUS pin is an open drain output for indicating the module’s operation status. You can connect it
to a GPIO of DTE with a pull up resistor, or as the LED indication circuit shown below. When the module is
turned on normally, the STATUS will present the low state. Otherwise, the STATUS will present
high-impedance state.
Table 19: Pin Definition of STATUS
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
STATUS 61 OD Indicate the module’s operation status Require external pull-up
The following figure shows different circuit designs of STATUS, and you can choose either one according
to your application demands.
Figure 26: Reference Circuits of STATUS
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 50 / 94
Page 52

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.16. Behavior of the RI
AT+QCFG=“risignaltype”,“physical” command can be usedto configure RI behavior.
No matter on which port URC is presented, URC will trigger the behavior of RI pin.
NOTE
URC can be output from UART port, USB AT port and USB modem port by AT+QURCCFG command.
The default port is USB AT port.
In addition, RI behavior can be configured flexibly. The default behavior of the RI is shown as below.
Table 20: Behavior of the RI
State Response
Idle RI keeps in high level
URC RI outputs 120ms low pulse when new URC returns
The RI behavior can be changed by AT+QCFG=“urc/ri/ring”command.Please refer to document [2] for
details.
3.17. SGMII Interface
EC21 includes an integrated Ethernet MAC with an SGMII interface and two management interfaces, key
features of the SGMII interface are shown below:
IEEE802.3 compliance
Full duplex at 1000Mbps
Half/full duplex for 10/100Mbps
Support VLAN tagging
Support IEEE1588 and Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
Can be used to connect to external Ethernet PHY like AR8033, or to an external switch
Management interfaces support dual voltage 1.8V/2.85V
The following table shows the pin definition of SGMII interface.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 51 / 94
Page 53

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Table 21: Pin Definition of the SGMII Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
Control Signal Part
EPHY_RST_N 119 DO Ethernet PHY reset 1.8V/2.85V power domain
EPHY_INT_N 120 DI Ethernet PHY interrupt 1.8V power domain
SGMII_MDATA 121 IO
SGMII_MCLK 122 DO
SGMII MDIO (Management Data
Input/Output) data
SGMII MDIO (Management Data
Input/Output) clock
1.8V/2.85V power domain
1.8V/2.85V power domain
Configurable power source.
USIM2_VDD 128 PO
SGMII MDIO pull-up power
source
1.8V/2.85V power domain.
External pull-up power source for
SGMII MDIO pins.
SGMII Signal Part
SGMII_TX_M 123 AO SGMII transmission-minus
SGMII_TX_P 124 AO SGMII transmission-plus
SGMII_RX_P 125 AI SGMII receiving-plus
SGMII_RX_M 126 AI SGMII receiving-minus
Connect with a 0.1uF capacitor,
close to the PHY side.
Connect with a 0.1uF capacitor,
close to the PHY side.
Connect with a 0.1uF capacitor,
close to EC21 module.
Connect with a 0.1uF capacitor,
close to EC21 module.
The following figure shows the simplified block diagram for Ethernet application.
SGMII
Module
Control
AR8033
MDI
Ethernet
Transformer
RJ45
Figure 27: Simplified Block Diagram for Ethernet Application
The following figure shows a reference design of SGMII interface with PHY AR8033 application.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 52 / 94
Page 54

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 28: Reference Circuit of SGMII Interface with PHY AR8033 Application
In order to enhance the reliability and availability in your application, please follow the criteria below in the
Ethernet PHY circuit design:
Keep SGMII data and control signals away from RF and VBAT trace.
Keep the maximum trace length less than 10inch and keep skew on the differential pairs less than
20mil.
The differential impedance of SGMII data trace is 100ohm±10%.
To minimize crosstalk, the distance between separate adjacent pairs that are on the same layer must
be equal to or larger than 40mil.
NOTE
For more information about SGMII application, please refer to document [5]and document[7].
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 53 / 94
Page 55

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.18. Wireless Connectivity Interfaces
EC21supports a low-power SDIO 3.0 interface for WLAN and a UART/PCM interface for BT.
The following table shows the pin definition of wireless connectivity interfaces.
Table 22: Pin Definition of Wireless Connectivity Interfaces
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
WLAN Part
SDC1_DATA3 129 IO SDIO data bus D3 1.8V power domain
SDC1_DATA2 130 IO SDIO data bus D2 1.8V power domain
SDC1_DATA1 131 IO SDIO data bus D1 1.8V power domain
SDC1_DATA0 132 IO SDIO data bus D0 1.8V power domain
SDC1_CLK 133 DO SDIO clock 1.8V power domain
SDC1_CMD 134 IO SDIO command 1.8V power domain
WLAN_EN 136 DO
Coexistence and Control Part
PM_ENABLE 127 DO External power control 1.8V power domain
WAKE_ON_
WIRELESS
COEX_UART_RX 137 DI LTE/WLAN&BT coexistence signal 1.8V power domain
COEX_UART_TX 138 DO LTE/WLAN&BT coexistence signal 1.8V power domain
WLAN_SLP_CLK 118 DO WLAN sleep clock
135 DI
WLAN function control via
FC20 module. Active high.
Wake up the host (EC21 module)
by FC20 module.
1.8V power domain
1.8V power domain
BT Part*
BT_RTS* 37 DI BT UART request to send 1.8V power domain
BT_TXD* 38 DO BT UART transmit data 1.8V power domain
BT_RXD* 39 DI BT UART receive data 1.8V power domain
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 54 / 94
Page 56

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
BT_CTS* 40 DO BT UART clear to send 1.8V power domain
PCM_IN1) 24 DI PCM data input 1.8V power domain
PCM_OUT1) 25 DO PCM data output 1.8V power domain
PCM_SYNC1) 26 IO PCM data frame sync signal 1.8V power domain
PCM_CLK1) 27 IO PCM data bit clock 1.8V power domain
BT_EN* 139 DO
WLAN function control via FC20
module. Active high.
1.8V power domain
NOTES
1. “*” means under development.
1)
2.
Pads 24~27 are multiplexing pins used for audio design on EC21 module and BT function on FC20
module.
The following figure shows a reference design of wireless connectivity interfaces with Quectel FC20
module.
Figure 29: Reference Circuit of Wireless Connectivity Interfaces with FC20 Module
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 55 / 94
Page 57
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
NOTES
1. FC20 module can only be used as a slave device,
2. When BT function is enabled on EC21 module, PCM_SYNC and PCM_CLK pins are only used to
output signals.
3. For more information about wireless connectivity interfaces, please refer to document [5].
3.18.1. WLAN Interface
EC21 provides a low power SDIO 3.0 interface and control interface for WLAN design.
SDIO interface supports the following modes:
Single data rate (SDR) mode (up to 200MHz)
Double data rate (DDR) mode (up to 52MHz)
As SDIO signals are very high-speed, in order to ensure the SDIO interface design corresponds with the
SDIO 3.0 specification, please comply with the following principles:
It is important to route the SDIO signal traces with total grounding. The impedance of SDIOsignal
trace is 50ohm (±10%).
Protect other sensitive signals/circuits (RF, analog signals, etc.) from SDIO corruption and protect
SDIO signals from noisy signals (clocks, DCDCs, etc.).
It is recommended to keep matching lengthbetween CLK and DATA/CMD less than 1mm and total
routing length less than 50mm.
Keep termination resistors within 15~24ohm on clock lines near the module and keep the route
distance from the module clock pins to termination resistors less than 5mm.
Make sure the adjacent trace spacing is 2x line width and bus capacitance is less than 15pF.
3.18.2. BT Interface*
EC21 supports a dedicated UART interface and a PCM interface for BTfunction application.
Further information about BT interface will be added in future version of this document.
NOTE
“*” means under development.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 56 / 94
Page 58

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
3.19. USB_BOOT Interface
EC21 provides a USB_BOOT pin. During development or factory production, USB_BOOT pin can force
the module to boot from USB port for firmware upgrade.
Table 23: Pin Definition of USB_BOOT Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
USB_BOOT 115 DI
Force the module to boot from USB
port
The following figure shows a reference circuit of USB_BOOT interface.
1.8V power domain.
Active high.
If unused, keep it open.
Figure 30: Reference Circuit of USB_BOOT Interface
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 57 / 94
Page 59

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
4 GNSS Receiver
4.1. General Description
EC21 includes a fully integrated global navigation satellite system solution that supports Gen8C-Liteof
Qualcomm (GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo and QZSS).
EC21 supports standard NMEA-0183 protocol, and outputs NMEA sentences at 1Hz data update ratevia
USB interface by default.
By default, EC21 GNSS engine is switched off. It has to be switched on via AT command. For more
details about GNSS engine technology and configurations, please refer to document [3].
4.2. GNSS Performance
The following table shows the GNSS performance of EC21.
Table 24: GNSS Performance
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
Cold start Autonomous -146 dBm
Sensitivity
(GNSS)
TTFF
(GNSS)
Reacquisition Autonomous -157 dBm
Tracking Autonomous -157 dBm
Cold start
@open sky
Warm start
@open sky
Autonomous 35 s
XTRA enabled 18 s
Autonomous 26 s
XTRA enabled 2.2 s
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 58 / 94
Page 60
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Hot start
@open sky
Accuracy
(GNSS)
NOTES
1. Tracking sensitivity: the lowest GNSS signal value at the antenna port on which the module can keep
on positioning for 3 minutes.
2. Reacquisition sensitivity: the lowest GNSS signal value at the antenna port on which the module can
fix position again within 3 minutes after loss of lock.
3. Cold start sensitivity: the lowest GNSS signal value at the antenna port on which the module fixes
position within 3 minutes after executing cold start command.
CEP-50
Autonomous 2.5 s
XTRA enabled 1.8 s
Autonomous
@open sky
<1.5 m
4.3. Layout Guidelines
The following layout guidelines should be taken into account in your design.
Maximize the distance among GNSS antenna, main antenna and the Rx-diversity antenna.
Digital circuits such as USIM card, USB interface, camera module, display connector and SD card
should be kept away from the antennas.
Use ground vias around the GNSS trace and sensitive analog signal traces to provide coplanar
isolation and protection.
Keep 50ohm characteristic impedance forthe ANT_GNSS trace.
Please refer to Chapter 5 for GNSS antenna reference design and antenna consideration.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 59 / 94
Page 61

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
5 Antenna Interfaces
EC21 antenna interfaces include a main antennainterface,anRx-diversity antenna interface which is used
toresist the fall of signals caused by high speed movement and multipath effect, and a GNSS antenna
interface. The antenna interfaceshave an impedance of 50ohm.
5.1. Main/Rx-diversityAntenna Interface
5.1.1. Pin Definition
The pin definition of main antenna and Rx-diversityantenna interfacesis shown below.
Table 25: Pin Definition of the RF Antenna
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
ANT_MAIN 49 IO Main antenna pad 50ohmimpedance
ANT_DIV 35 AI Receive diversityantenna pad 50ohm impedance
5.1.2. Operating Frequency
Table 26: Module Operating Frequencies
3GPP Band Transmit Receive Unit
B1 1920~1980 2110~2170 MHz
B2 (1900) 1850~1910 1930~1990 MHz
B3 (1800) 1710~1785 1805~1880 MHz
B4 1710~1755 2110~2155 MHz
B5 (850) 824~849 869~894 MHz
B7 2500~2570 2620~2690 MHz
B8 (900) 880~915 925~960 MHz
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 60 / 94
Page 62

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
B12 699~716 729~746 MHz
B13 777~787 746~756 MHz
B18 815~830 860~875 MHz
B19 830~845 875~890 MHz
B20 832~862 791~821 MHz
B26 814~849 859~894 MHz
B28 703~748 758~803 MHz
B40 2300~2400 2300~2400 MHz
5.1.3. Reference Design of RF Antenna Interface
Areference design of ANT_MAIN and ANT_DIVantenna pads is shown as below. It should reserve a
π-type matching circuit for better RF performance. The capacitors are not mounted by default.
Figure 31: Reference Circuit of RF Antenna Interface
NOTES
1. Keep a proper distance between the main antenna and the Rx-diversity antenna to improve the
receiving sensitivity.
2. ANT_DIV function is enabledby default.
3. Place the π-type matching components (R1, C1, C2, R2, C3, C4) as close to the antenna as
possible.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 61 / 94
Page 63

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
5.1.4. Reference Design of RF Layout
For user’s PCB, the characteristic impedance of all RF traces should be controlled as 50 ohm. The
impedance of the RF traces is usually determined by the trace width (W), the materials’ dielectric constant,
the distance between signal layer and reference ground (H), and the clearance between RF trace and
ground (S). Microstrip line or coplanar waveguide line is typically used in RF layout for characteristic
impedance control. The following are reference designs of microstrip line or coplanar waveguide line with
different PCB structures
.
Figure 32: Microstrip Line Design on a 2-layer PCB
Figure 33: Coplanar Waveguide Line Design on a 2-layer PCB
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 62 / 94
Page 64

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Figure 34: Coplanar Waveguide Line Design on a 4-layer PCB (Layer 3 as Reference Ground)
Figure 35: Coplanar Waveguide Line Design on a 4-layer PCB (Layer 4 as Reference Ground)
In order to ensure RF performance and reliability, the following principles should be complied with in RF
layout design:
Use impedance simulation tool to control the characteristic impedanceof RF tracesas 50ohm.
The GND pins adjacent to RF pins should not be hot welded, and should be fully connected to
ground.
The distance between the RF pinsand the RFconnector should be as short as possible, and all the
right angle traces should be changed to curved ones.
There should be clearance area under the signal pin of the antenna connector or solder joint.
The reference ground of RF traces should be complete. Meanwhile, adding some ground viasaround
RF traces and the reference ground could help to improve RF performance. The distance between
the ground vias and RF traces should be no less than two times the width of RF signal traces (2*W).
For more details about RF layout, please refer to document [6].
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 63 / 94
Page 65
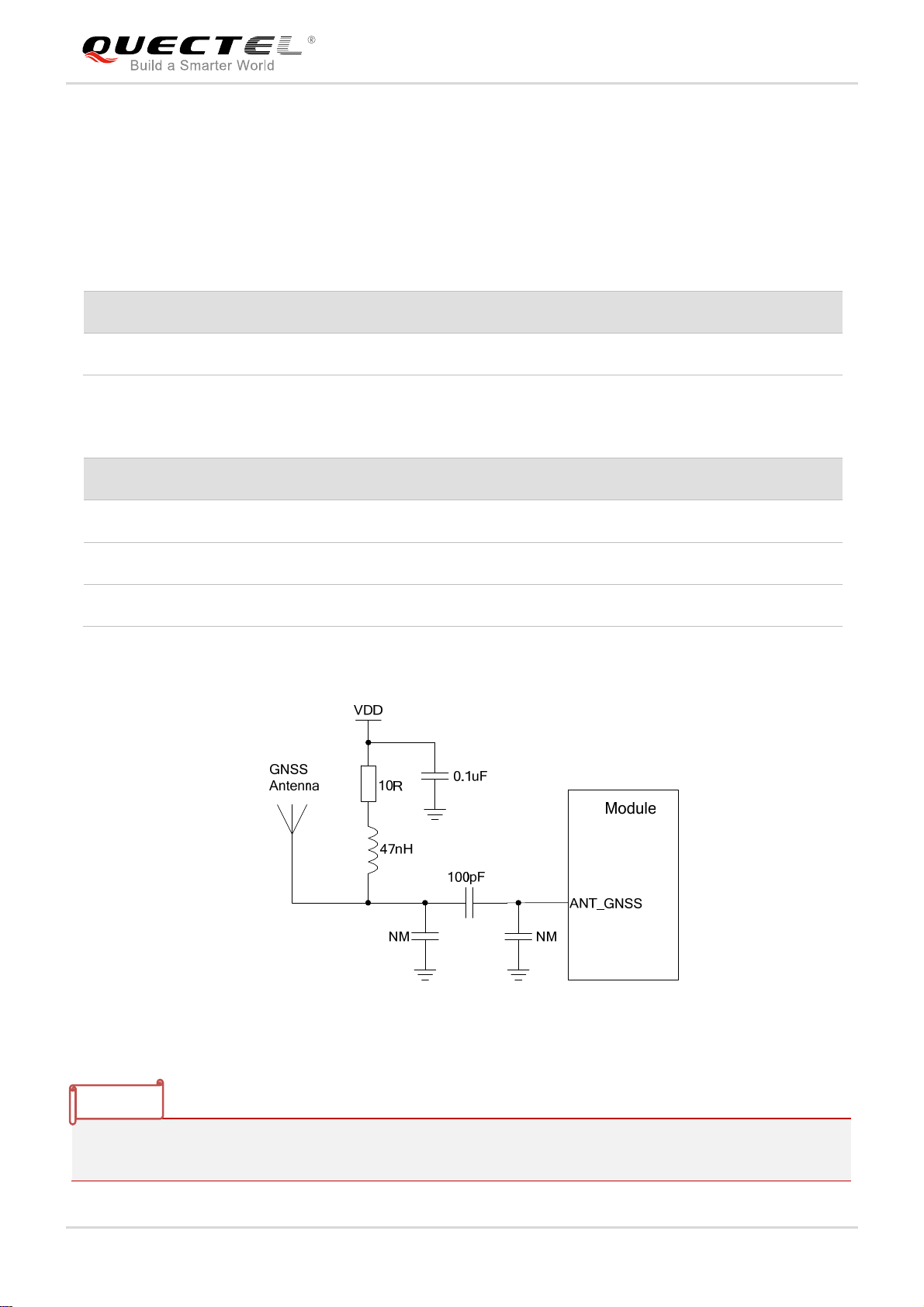
LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
5.2. GNSS Antenna Interface
The following tables show the pin definition and frequency specification of GNSS antenna interface.
Table 27: Pin Definition of GNSS Antenna Interface
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Description Comment
ANT_GNSS 47 AI GNSS antenna 50ohmimpedance
Table 28: GNSS Frequency
Type Frequency Unit
GPS/Galileo/QZSS 1575.42±1.023 MHz
GLONASS 1597.5~1605.8 MHz
BeiDou 1561.098±2.046 MHz
A reference design of GNSS antenna is shown as below.
Figure 36: Reference Circuit of GNSS Antenna
NOTES
1. An external LDO can be selected to supply power according to the active antenna requirement.
2. If the module is designed with a passive antenna, then the VDD circuit is not needed.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 64 / 94
Page 66

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
5.3. Antenna Installation
5.3.1. Antenna Requirement
The following table shows the requirements on main antenna, Rx-diversity antenna and GNSS antenna.
Table 29: Antenna Requirements
Type Requirements
Frequency range: 1561~1615MHz
Polarization: RHCP or linear
VSWR: <2 (Typ.)
GNSS
Passive antenna gain: >0dBi
Active antenna noise figure: <1.5dB
Active antenna gain: >-2dBi
Active antenna embedded LNA gain: 20dB (Typ.)
Active antenna total gain: >18dBi (Typ.)
GSM/WCDMA/LTE
VSWR: ≤2
Gain (dBi): 1
Max input power (W): 50
Input Impedance (ohm): 50
Polarization type: Vertical
Cable insertion loss: <1dB
(GSM900, WCDMA B5/B8,
LTE B5/B8/B12/B13/B18/B19/B20/B26/B28)
Cable insertion loss: <1.5dB
(GSM1800, WCDMA B1/B2/B4,LTE B1/B2/B3/B4)
Cable insertion loss <2dB
(LTE B7/B40)
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 65 / 94
Page 67

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
5.3.2. Recommended RF Connector for Antenna Installation
If RF connector is used for antenna connection, it is recommended to use UF.L-R-SMT connector
provided by HIROSE.
Figure 37: Dimensions of the UF.L-R-SMT Connector (Unit: mm)
U.FL-LP serial connectors listed in the following figure can be used to match the UF.L-R-SMT.
Figure 38:Mechanicalsof UF.L-LP Connectors
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 66 / 94
Page 68

EC21 Hardware Design
The following figure describes the space factor of mated connector.
LTE Module Series
Figure39:Space Factor of Mated Connector (Unit: mm)
For more details, please visit http://www.hirose.com
.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 67 / 94
Page 69

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
6 Electrical, Reliability and
RadioCharacteristics
6.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings for power supply and voltage on digital and analog pins of the module are
listed in the following table.
Table 30: Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VBAT_RF/VBAT_BB -0.3 4.7 V
USB_VBUS -0.3 5.5 V
Peak Current of VBAT_BB 0 0.8 A
Peak Current of VBAT_RF 0 1.8 A
Voltage at Digital Pins -0.3 2.3 V
Voltage at ADC0 0 VBAT_BB V
Voltage at ADC1 0 VBAT_BB V
6.2. Power Supply Ratings
Table 31: Power Supply Ratings
Parameter Description Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VBAT VBAT_BB and Voltage must stay within the 3.3 3.8 4.3 V
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 68 / 94
Page 70

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
VBAT_RF min/max values, including
voltage drop, ripple and
spikes.
I
VBAT
Voltage drop during
burst transmission
Peak supply current
(during
transmissionslot)
Maximum power control
level on GSM900
Maximum power control
level on GSM900
400 mV
1.8 2.0 A
USB_VBUS USB detection 3.0 5.0 5.25 V
6.3. Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is listed in the following table.
Table 32: Operating Temperature
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
OperationTemperature Range1) -35 +25 +75 ºC
ExtendedTemperature Range2) -40 +85 ºC
NOTES
1. 1)Within operation temperature range, the module is 3GPP compliant.
2)
2.
Within extended temperature range, the module remains the ability to establish and maintain a
voice, SMS, data transmission, emergency call, etc. There is no unrecoverable malfunction. There
are also no effects on radio spectrum and no harm to radio network. Only one or more parameters
like P
might reduce in their value and exceed the specified tolerances. When the temperature
out
returns to the normal operating temperature levels, the module will meet 3GPP specifications again.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 69 / 94
Page 71

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
6.4. Current Consumption
The values of current consumption are shown below.
Table 33: EC21-A Current Consumption
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
OFF state Power down 20 uA
I
VBAT
AT+CFUN=0 (USB disconnected)
1.0 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.8 mA
Sleep state
WCDMA PF=128 (USB disconnected) 2.3 mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.2 mA
LTE-FDD PF=128 (USB disconnected) 2.2 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) 21.6 mA
Idle state
(GNSS OFF)
WCDMA PF=64 (USB connected) 31.6 mA
LTE-FDDPF=64 (USB disconnected) 23.7 mA
LTE-FDDPF=64 (USB connected) 36.5 mA
WCDMA B2 HSDPA @22.09dBm 542.0 mA
WCDMA B2 HSUPA @22.28dBm 681.0 mA
WCDMA
WCDMA B4 HSDPA @21.94dBm 550.0 mA
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
WCDMA B4 HSUPA @21.81dBm 547.0 mA
WCDMA B5 HSDPA @22.13dBm 429.0 mA
WCDMA B5 HSUPA @22.48dBm 459.0 mA
LTE-FDD B2 @22.79dBm 709.0 mA
LTE
datatransfer(GNSS
LTE-FDD B4 @22.89dBm 710.0 mA
OFF)
LTE-FDD B12 @23.39dBm 679.0 mA
WCDMA voice call WCDMA B2 @23.67dBm 663.0 mA
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 70 / 94
Page 72

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
WCDMA B4 @23.36dBm 594.0 mA
WCDMA B5 @23.64dBm 522.0 mA
Table 34: EC21-AUT Current Consumption
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
OFF state Power down 20 uA
I
VBAT
AT+CFUN=0 (USB disconnected)
0.99 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.1 mA
Sleep state
WCDMA PF=128 (USB disconnected) 1.7 mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.9 mA
LTE-FDD PF=128 (USB disconnected) 2.4 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) 22.0 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB connected) 32.0 mA
Idle state
LTE-FDDPF=64 (USB disconnected) 23.6 mA
LTE-FDDPF=64 (USB connected) 33.6 mA
WCDMA data
(GNSS OFF)
WCDMA B1 HSDPA@22.59dBm 589.0 mA
WCDMA B1 HSUPA@22.29dBm 623.0 mA
WCDMA B5 HSDPA@22.22dBm 511.0 mA
WCDMA B5 HSUPA@21.64dBm 503.0 mA
LTE-FDD B1 @23.38dBm 813.0 mA
LTE-FDD B3 @22.87dBm 840.0 mA
LTE
datatransfer(GNSS
LTE-FDD B5 @23.12dBm 613.0 mA
OFF)
LTE-FDD B7 @22.96dBm 761.0 mA
LTE-FDD B28 @23.31dBm 650.0 mA
WCDMA B1 @24.21dBm 687.0 mA
WCDMA voice call
WCDMA B5 @23.18dBm 535.0 mA
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 71 / 94
Page 73

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Table 35: EC21-E Current Consumption
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
OFF state Power down TBD uA
I
VBAT
AT+CFUN=0 (USB disconnected)
TBD mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) TBD mA
Sleep state
WCDMA PF=128 (USB disconnected) TBD mA
FDD-LTE PF=64 (USB disconnected) TBD mA
FDD-LTE PF=128 (USB disconnected) TBD mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) TBD mA
Idle state
(GNSS OFF)
WCDMA PF=64 (USB connected) TBD mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) TBD mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB connected) TBD mA
GSM900 4DL/1UL @32.3dBm 220 mA
GSM900 3DL/2UL @32.18dBm 387 mA
GSM900 2DL/3UL @30.3dBm 467 mA
GPRS
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
EDGE
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
GSM900 1DL/4UL @29.4dBm 555 mA
DCS1800 4DL/1UL @29.6dBm 185 mA
DCS1800 3DL/2UL @29.1dBm 305 mA
DCS1800 2DL/3UL @28.8dBm 431 mA
DCS1800 1DL/4UL @29.1dBm 540 mA
GSM900 4DL/1UL @26dBm 148 mA
GSM900 3DL/2UL @26dBm 245 mA
GSM900 2DL/3UL @25dBm 338 mA
GSM900 1DL/4UL @25dBm 432 mA
DCS1800 4DL/1UL @26dBm 150 mA
DCS1800 3DL/2UL @25dBm 243 mA
DCS1800 2DL/3UL @25dBm 337 mA
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 72 / 94
Page 74

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
DCS1800 1DL/4UL @25dBm 430 mA
WCDMA B1 HSDPA@22.5dBm 659 mA
WCDMA B1 HSUPA@21.11dBm 545 mA
WCDMA
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
LTE
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
GSMvoice call
WCDMA B5 HSDPA@23.5dBm 767 mA
WCDMA B5 HSUPA@21.4dBm 537 mA
WCDMA B8 HSDPA@22.41dBm 543 mA
WCDMA B8 HSUPA@21.2dBm 445 mA
LTE-FDD B1 @23.45dBm 807 mA
LTE-FDD B3 @23.4dBm 825 mA
LTE-FDD B5 @23.4dBm 786 mA
LTE-FDD B7 @23.86dBm 887 mA
LTE-FDD B8 @23.5dBm 675 mA
LTE-FDD B20 @23.57dBm 770 mA
GSM900 PCL=5 @32.8dBm 336 mA
PCS1800 PCL=0 @29.3dBm 291 mA
WCDMA B1 @23.69dBm 683 mA
WCDMAvoice call
WCDMA B5 @23.61dBm 741 mA
WCDMA B8 @23.35dBm 564 mA
Table 36: EC21-KL Current Consumption
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
OFF state Power down 20 uA
0.98 mA
I
VBAT
AT+CFUN=0 (USB disconnected)
Sleep state
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.5 mA
LTE-FDD PF=128 (USB disconnected) 2.4 mA
Idle state
(GNSS OFF)
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 23.0 mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB connected) 34.0 mA
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 73 / 94
Page 75

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
LTE-FDD B1 @23.65dBm 765.0 mA
LTE-FDD B3 @23.2dBm 825.0 mA
LTE
datatransfer(GNSS
LTE-FDD B5 @23.2dBm 598.0 mA
OFF)
LTE-FDD B7 @23.7dBm 762.0 mA
LTE-FDD B8 @23.1dBm 569.0 mA
Table 37: EC21-V Current Consumption
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
OFF state Power down 20 uA
1.0 mA
Sleep state
AT+CFUN=0 (USB disconnected)
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.5 mA
LTE-FDD PF=128 (USB disconnected) 2.0 mA
I
VBAT
Idle state
(GNSS OFF)
LTE
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 22.0 mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB connected) 32.0 mA
LTE-FDD B4 @22.79dBm 752.0 mA
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
LTE-FDD B13 @23.26dBm 534.0 mA
Table 38: EC21-AUV Current Consumption
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
OFF state Power down 20 uA
AT+CFUN=0 (USB disconnected)
1.0 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.0 mA
I
VBAT
Sleep state
WCDMA PF=128 (USB disconnected) 1.6 mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 2.4 mA
LTE-FDD PF=128 (USB disconnected) 1.9 mA
Idle state
(GNSS OFF)
WCDMA PF=64 (USB disconnected) 24.0 mA
WCDMA PF=64 (USB connected) 34.0 mA
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 74 / 94
Page 76

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB disconnected) 24.0 mA
LTE-FDD PF=64 (USB connected) 34.0 mA
WCDMA B1 HSDPA@22.05dBm 586.0 mA
WCDMA B1 HSUPA@22.29dBm 630.0 mA
WCDMA
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
LTE
datatransfer(GNSS
OFF)
WCDMA voice call
WCDMA B5 HSDPA@22.43dBm 576.0 mA
WCDMA B5 HSUPA@22.43dBm 600.0 mA
WCDMA B8 HSDPA@22.44dBm 577.0 mA
WCDMA B8 HSUPA@21.78dBm 555.0 mA
LTE-FDD B1 @23.12dBm 721.0 mA
LTE-FDD B3 @23.04dBm 734.0 mA
LTE-FDD B5 @23.16dBm 669.0 mA
LTE-FDD B8 @23.21dBm 698.0 mA
LTE-FDD B28 @23.57dBm 790.0 mA
WCDMA B1 @22.72dBm 640.0 mA
WCDMA B5 @23.19dBm 638.0 mA
WCDMA B8 @23.27dBm 626.0 mA
Table 39: GNSS Current Consumption of EC21 Series Module
Parameter Description Conditions Typ. Unit
Cold start @Passive Antenna 58 mA
Lost state @Passive Antenna 58 mA
Instrument Environment 33 mA
OpenSky @Passive Antenna 35 mA
I
VBAT
(GNSS)
Searching
(AT+CFUN=0)
Tracking
(AT+CFUN=0)
OpenSky @Active Antenna 43 mA
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 75 / 94
Page 77

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
6.5. RF Output Power
The following table shows the RF output power of EC21 module.
Table 40: RF Output Power
Frequency Max. Min.
GSM900 33dBm±2dB 5dBm±5dB
DCS1800 30dBm±2dB 0dBm±5dB
DCS1800 26dBm±3dB 0dBm±5dB
WCDMA bands 22.5dBm+1/-3dB <-50dBm
LTE-FDD bands 22.5dBm+1/-3dB <-44dBm
LTE-TDD bands 22.5dBm+1/-3dB <-44dBm
NOTE
In GPRS 4 slots TX mode, the maximum output power is reduced by 3.0dB. Thedesign conforms to the
GSM specification as described in Chapter 13.16 of 3GPP TS 51.010-1.
6.6. RF Receiving Sensitivity
The following tables show the conducted RF receiving sensitivity of EC21 series module.
Table 41: EC21-E Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO1) 3GPP (SIMO)
GSM900 -109.0dBm / / -102.0dBm
DCS1800 -109.0dBm / / -102.0dbm
WCDMA Band1 -110.5dBm / / -106.7dBm
WCDMA Band5 -110.5dBm / / -104.7dBm
WCDMA Band8 -110.5dBm / / -103.7dBm
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 76 / 94
Page 78

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
LTE-FDD B1(10M) -98.0dBm -98.0dBm -101.5dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B3(10M) -96.5dBm -98.5dBm -101.5dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B5(10M) -98.0dBm -98.5dBm -101.0dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B7(10M) -97.0dBm -94.5dBm -99.5dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B8(10M) -97.0dBm -97.0dBm -101.0dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B20(10M) -97.5dBm -99.0dBm -102.5dBm -93.3dBm
Table 42: EC21-A Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
WCDMA B2 -110.0dBm / / -104.7dBm
WCDMA B4 -110.0dBm / / -106.7dBm
WCDMA B5 -110.5dBm / / -104.7dBm
LTE-FDD B2 (10M) -98.0dBm -98.0dBm -101.0dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B4 (10M) -97.5dBm -99.0dBm -101.0dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B12 (10M) -96.5dBm -98.0dBm -101.0dBm -93.3dBm
Table 43: EC21-V Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
LTE-FDD B4 (10M) -97.5dBm -99.0dBm -101.0dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B13 (10M) -95.0dBm -97.0dBm -100.0dBm -93.3dBm
Table 44: EC21-AUT Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
WCDMA B1 -110.0dBm / / -106.7dBm
WCDMA B5 -110.5dBm / / -104.7dBm
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 77 / 94
Page 79

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
LTE-FDD B1(10M) -98.5dBm -98.0dBm -101.0dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B3(10M) -98.0dBm -96.0dBm -100.0dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B5(10M) -98.0dBm -99.0dBm -102.5dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B7(10M) -97.0dBm -95.0dBm -98.5dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B28(10M) -97.0dBm -99.0dBm -102.0dBm -94.8dBm
Table 45: EC21-AUTL Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
LTE-FDD B3(10M) -98.0dBm -96.0dBm -100.0dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B7(10M) -97.0dBm -95.0dBm -98.5dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B28(10M) -97.0dBm -99.0dBm -102.0dBm -94.8dBm
Table 46: EC21-KL Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
LTE-FDD B1(10M) -98.0dBm -99.5dBm -100.5dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B3(10M) -97.0dBm -97.5dBm -99.5dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B5(10M) -98.0dBm -99.5dBm -100.5dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B7(10M) -96.0dBm -96.0dBm -98.5dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B8(10M) -97.0dBm -99.0dBm -101.0dBm -93.3dBm
Table 47: EC21-CT Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
LTE-FDD B1(10M) -98.0dBm -99.5dBm -100.5dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B3(10M) -97.0dBm -97.5dBm -99.5dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B5* (10M) TBD TBD TBD TBD
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 78 / 94
Page 80

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
Table 48: EC21-J Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
LTE-FDD B1 (10M) -97.5dBm -98.7dBm -100.2dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B3 (10M) -96.5dBm -97.1dBm -100.5dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B8 (10M) -98.4dBm -99.0dBm -101.2dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B18 (10M) -99.5dBm -99.0dBm -101.7dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B19 (10M) -99.2dBm -99.0dBm -101.4dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B26 (10M) -99.5dBm -99.0dBm -101.5dBm -93.8dBm
Table 49: EC21-AUV Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Primary Diversity SIMO 3GPP (SIMO)
WCDMA B1 -110.0dBm / / -106.7dBm
WCDMA B5 -111.0dBm / / -104.7dBm
WCDMA B8 -111.0dBm / / -103.7dBm
LTE-FDD B1 (10M) -97.2dBm -97.2dBm -100.2dBm -96.3dBm
LTE-FDD B3 (10M) -98.2dBm -98.7dBm -100.7dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B5 (10M) -99.2dBm -98.7dBm -101.7dBm -94.3dBm
LTE-FDD B8 (10M) -97.7dBm -97.2dBm -101.2dBm -93.3dBm
LTE-FDD B28 (10M) -97.0dBm -98.2dBm -101.2dBm -94.8dBm
NOTES
1)
1.
SIMO is a smart antenna technology that uses a single antenna at the transmitter side and two
antennas at the receiver side, which can improve RX performance.
2. “*” means under development.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 79 / 94
Page 81

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
6.7. Electrostatic Discharge
The module is not protected against electrostatic discharge (ESD) in general. Consequently, it is subject
to ESD handling precautions that typically apply to ESD sensitive components. Proper ESD handling and
packaging procedures must be applied throughout the processing, handling and operation of any
application that incorporates the module.
The following table shows the module’s electrostatic discharge characteristics.
Table 50: Electrostatic Discharge Characteristics
Tested Points Contact Discharge Air Discharge Unit
VBAT, GND ±5 ±10 kV
All Antenna Interfaces ±4 ±8 kV
Other Interfaces ±0.5 ±1 kV
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 80 / 94
Page 82

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
7 Mechanical Dimensions
This chapter describes the mechanical dimensions of the module.All dimensions are measured in mm.
7.1. Mechanical Dimensions of the Module
(29+/-0.15)
(32+/-0.15)
2.4+/-0.2
0.8
Figure40: Module Top and Side Dimensions
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 81 / 94
Page 83

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
32.0
1.90
1.30
3.85
2.49
1.8
2.15
5.96
1.6
1.7
6.75
0.82
4.88
4.4
3.2
1.05
1.15
3.4
3.35
3.5
1.30
2.0
2.0
3.0
2.8
1.10
1.10
4.8
3.23.43.2
1.8
29.0
0.8
3.5
1.9
2.4
3.45
1.5
Figure41: Module Bottom Dimensions (Bottom View)
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 82 / 94
Page 84
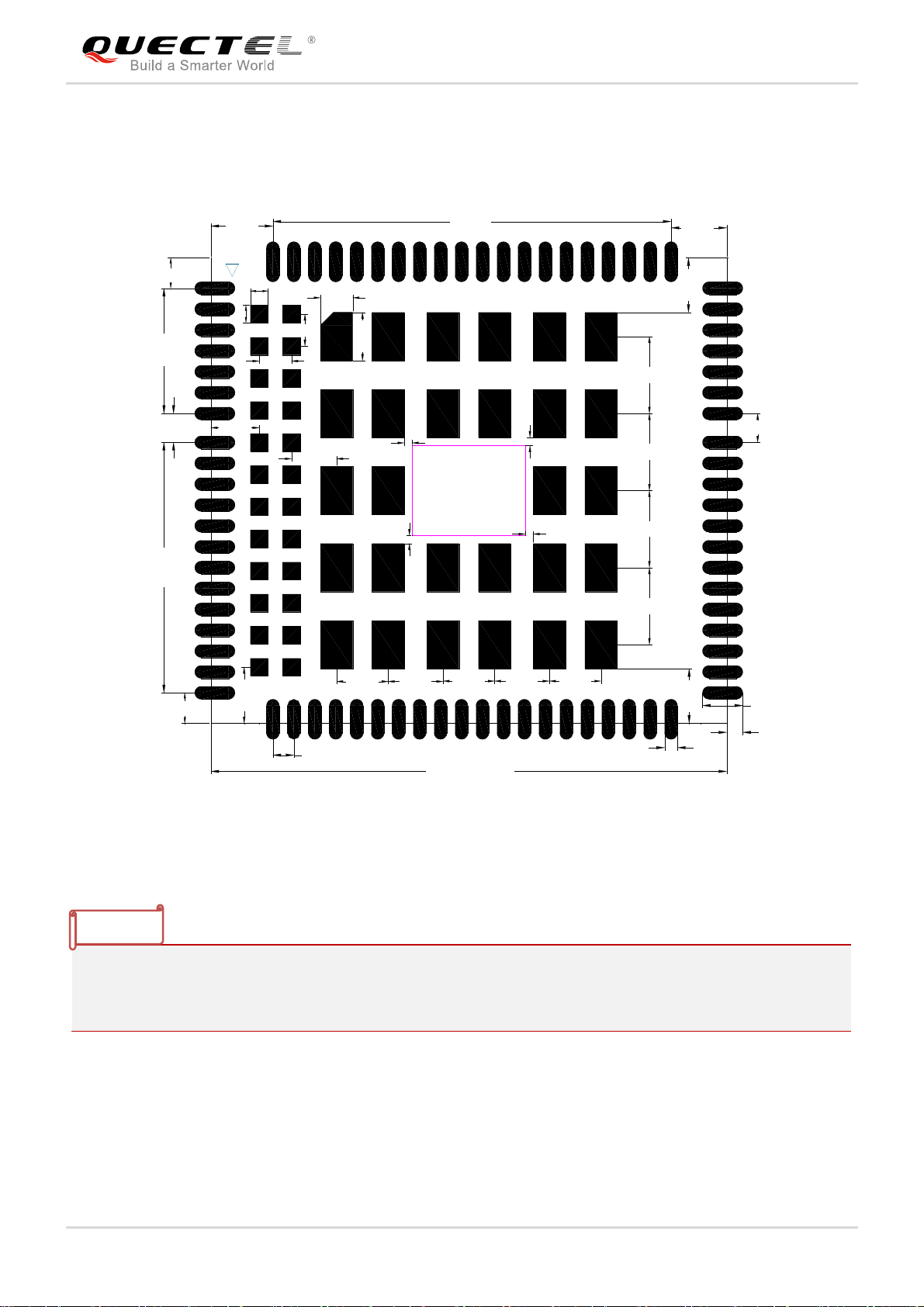
EC21 Hardware Design
7.2. Recommended Footprint
LTE Module Series
1.90
7.80
1.80
15.60
3.85
3.00
24.70
1.10
1.10
2.00
2.00
2.00
3.00
3.45
3.40
4.80
1.80
2.80
0.50
0.50
0.50
Keepout area
0.50
4.80
4.80
4.80
3.20 3.40 3.20
3.40
0.80
2.50
1.00
1.90
3.20 3.40
3.50
1.30
32.0
Figure42: Recommended Footprint (Top View)
NOTES
1. The keepout area should not be designed.
2. For easy maintenance of the module, please keep about 3mm between the module and other
components in thehost PCB.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 83 / 94
Page 85

d
e
t
i
c
t
n
g
t
T
o
u
t
e
r
s
e
e
C
e
LTE Mo
d
w
o
s
n
e
E
21 Hard
ule Serie
are Desig
7.3. Des
ign Effe
t Drawi
gsof th
Figure43:
e Modul
op Viewof
the Modul
Fi
ure 44: B
ttom View
of the Mod
ule
NOTE
Theseared
that you ge
EC21_Har
sign effect
from Quec
ware_Des
drawings of
el.
gn
EC21 mod
le. For mo
Confiden
e accurate
ial / Relea
pictures, pl
ed 84 / 94
ase refer t
the modul
Page 86

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
8 Storage, Manufacturing and
Packaging
8.1. Storage
EC21 is stored in a vacuum-sealed bag. The storage restrictionsareshown as below.
1. Shelf life in thevacuum-sealed bag: 12 months at <40ºC/90%RH.
2. After the vacuum-sealed bagis opened, devices that will be subjected to reflow soldering or other high
temperature processes must be:
Mounted within 72 hours at the factory environment of ≤30ºC/60%RH
Stored at <10%RH
3. Devices require baking before mounting, if any circumstances below occurs:
When the ambient temperature is 23ºC±5ºC and the humidity indicator card shows the humidity
is>10% before opening the vacuum-sealed bag.
Device mounting cannot be finished within 72 hours at factory conditions of ≤30ºC/60%RH.
4. If baking is required, devices may be baked for 48 hours at 125ºC±5ºC.
NOTE
As the plastic packagecannot be subjected to high temperature, it should be removed from devices before
high temperature (125ºC) baking. If shorter baking time is desired, please refer to IPC/JEDECJ-STD-033
for bakingprocedure.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 85 / 94
Page 87

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
8.2. Manufacturing and Soldering
Push the squeegee to apply the solder paste on the surface of stencil, thus making the paste fill the
stencil openings and then penetrate to the PCB. The force on the squeegee should be adjusted
properlyso as to produce a clean stencil surface on a single pass. To ensure the module soldering quality,
thethickness of stencil for the module is recommended to be 0.18mm. For more details, please refer
todocument [4].
It is suggested that the peak reflow temperature is from 235 to 245ºC (for SnAg3.0Cu0.5 alloy). The
absolute maximum reflow temperature is 260ºC. To avoid damage to the module caused by repeated
heating, it is suggested that the module should be mounted after reflow soldering for the other side of
PCB has been completed. Recommended reflow soldering thermal profile is shown below:
Figure 45: Reflow Soldering Thermal Profile
NOTE
During manufacturing and soldering, or any other processes that may contact the module directly, NEVER
wipe the module label with organic solvents, such as acetone, ethyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol,
trichloroethylene, etc.
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 86 / 94
Page 88

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
8.3. Packaging
EC21 is packaged in tape andreel carriers. One reel is 11.53m longand contains 250pcs modules. The
figure below shows the packagingdetails, measured in mm.
±0.3
44.00
±0.1
1.75
±0.15
20.20
32.5
33.5
48.5
2.00
±0.15
±0.15
±0.1
44.00
±0.1
4.00
±0.1
32.5± 0.15
33.5± 0.15
1
.
0
±
0
5
.
1
±0.15
29.3
±0.15
30.3
0.35± 0.05
4.2
±0.15
3.1
±0.15
±0.15
30.3
Cover tap
e
13
Direction of feed
100
+0.20
44.5
-0.00
Figure 46: Tape and Reel Specifications
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 87 / 94
Page 89

EC21 Hardware Design
9 Appendix A References
Table 51: Related Documents
SN Document Name Remark
LTE Module Series
[1] Quectel_EC21_Power_Management_Application_Note
[2] Quectel_EC25&EC21_AT_Commands_Manual EC25 and EC21 AT Commands Manual
[3] Quectel_EC25&EC21_GNSS_AT_Commands_Manual
[4] Quectel_Module_Secondary_SMT_User_Guide Module Secondary SMT User Guide
[5] Quectel_EC21_Reference_Design EC21 Reference Design
[6] Quectel_RF_Layout_Application_Note RF Layout Application Note
[7] Quectel_SGMII_Design_Application_Note SGMII Design Application Note
Table 52: Terms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
AMR Adaptive Multi-rate
EC21 Power Management Application
Note
EC25 and EC21GNSS AT Commands
Manual
bps Bits Per Second
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CS Coding Scheme
CSD Circuit Switched Data
CTS Clear To Send
DC-HSPA+ Dual-carrier High Speed Packet Access
DFOTA Delta Firmware Upgrade Over The Air
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 88 / 94
Page 90

EC21 Hardware Design
DL Downlink
DTR Data Terminal Ready
DTX Discontinuous Transmission
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
FDD Frequency Division Duplex
FR Full Rate
LTE Module Series
GLONASS
GLObalnayaNAvigatsionnayaSputnikovayaSistema, the Russian Global
Navigation Satellite System
GMSK Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
GNSS Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS Global Positioning System
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
HR Half Rate
HSPA High Speed Packet Access
HSDPA High Speed Downlink Packet Access
HSUPA High Speed Uplink Packet Access
I/O Input/Output
Inorm Normal Current
LED Light Emitting Diode
LNA Low Noise Amplifier
LTE Long Term Evolution
MIMO Multiple Input Multiple Output
MO Mobile Originated
MS Mobile Station (GSM engine)
MT Mobile Terminated
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 89 / 94
Page 91

EC21 Hardware Design
PAP Password Authentication Protocol
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PDU Protocol Data Unit
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
RF Radio Frequency
RHCP Right Hand Circularly Polarized
Rx Receive
LTE Module Series
SGMII Serial Gigabit Media IndependentInterface
SIM Subscriber Identification Module
SIMO Single Input Multiple Output
SMS Short Message Service
TDD Time Division Duplexing
TDMA Time Division Multiple Access
TD-SCDMA Time Division-Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access
TX Transmitting Direction
UL Uplink
UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
URC Unsolicited Result Code
USIM Universal Subscriber Identity Module
Vmax Maximum Voltage Value
Vnorm Normal Voltage Value
Vmin Minimum Voltage Value
VIHmax Maximum Input High Level Voltage Value
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 90 / 94
Page 92

EC21 Hardware Design
VIHmin Minimum Input High Level Voltage Value
VILmax Maximum Input Low Level Voltage Value
VILmin Minimum Input Low Level Voltage Value
VImax Absolute Maximum Input Voltage Value
VImin Absolute Minimum Input Voltage Value
VOHmax Maximum Output High Level Voltage Value
VOHmin Minimum Output High Level Voltage Value
VOLmax Maximum Output Low Level Voltage Value
VOLmin Minimum Output Low Level Voltage Value
LTE Module Series
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
WLAN Wireless Local Area Network
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 91 / 94
Page 93

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
10 Appendix B GPRS Coding Schemes
Table 53: Description of Different Coding Schemes
Scheme
Code Rate
USF
Pre-coded USF
Radio Block excl.USF and BCS
BCS
Tail
Coded Bits
Punctured Bits
Data Rate Kb/s
CS-1 CS-2 CS-3 CS-4
1/2 2/3 3/4 1
3 3 3 3
3 6 6 12
181 268 312 428
40 16 16 16
4 4 4 -
456 588 676 456
0 132 220 -
9.05 13.4 15.6 21.4
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 92 / 94
Page 94

LTE Module Series
EC21 Hardware Design
11 Appendix C GPRS Multi-slot Classes
Twenty-nine classes of GPRS multi-slot modes are defined for MS in GPRS specification. Multi-slot
classes are product dependent, and determine the maximum achievable data rates in both the uplink and
downlink directions. Written as 3+1 or 2+2, the first number indicates the amount of downlink timeslots,
while the second number indicates the amount of uplink timeslots. The active slots determine the total
number of slots the GPRS device can use simultaneously for both uplink and downlink communications.
The description of different multi-slot classes is shown in the following table.
Table 54: GPRS Multi-slot Classes
Multislot Class Downlink Slots Uplink Slots Active Slots
1 1 1 2
2 2 1 3
3 2 2 3
4 3 1 4
5 2 2 4
6 3 2 4
7 3 3 4
8 4 1 5
9 3 2 5
10 4 2 5
11 4 3 5
12 4 4 5
EC21_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 93 / 94
Page 95

E
h
r
p
d
u
d
S
S
S
S
S
s
x
S
E
m
h
E
1
9282245
5
e
d
C
m
k
k
k
k
0
k
k
k
k
k
k
8
4
o
w
n
s
n
E
LTE M
21 Hard
dule Sire
are Desig
12
Table 55:
Coding Sc
CS-1:
CS-2:
CS-3:
CS-4:
MCS-1
MCS-2
Ap
Co
DGE Mod
eme Mo
GM
GM
GM
GM
GM
GM
endi
ing
lation and
ulation
SK
SK
SK
SK
SK
SK
D
che
Coding Sc
Coding
/
/
/
/
C
B
DG
es
emes
Family
Mo
Timeslot
.05kbps
13.4kbps
15.6kbps
1.4kbps
.80kbps
11.2kbps
ulati
2 Ti
18.1
26.8
31.2
42.8
17.6
22.4
ona
eslot
bps
bps
bps
bps
kbps
bps
d
4 Timeslot
36.2kbps
53.6kbps
62.4kbps
85.6kbps
35.20kbps
44.8kbps
MCS-3
MCS-4
MCS-5
MCS-6
MCS-7
MCS-8
MCS-9
GM
GM
8-P
8-P
8-P
8-P
8-P
SK
SK
K
K
K
K
K
A
C
B
A
B
A
A
14.8kbps
17.6kbps
2.4kbps
9.6kbps
4.8kbps
4.4kbps
9.2kbps
29.6
35.2
44.8
59.2
89.6
108.
118.
bps
bps
bps
bps
bps
kbps
kbps
59.2kbps
70.4kbps
89.6kbps
118.4kbps
179.2kbps
217.6kbps
236.8kbps
EC21_Ha
dware_De
ign
Confid
ntial / Rele
ased94 /94
 Loading...
Loading...