Page 1

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
Rev. GC65_Hardware_Design_V2.0
Date: 2014-01-09
www.quectel.com
Page 2

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
Our aim is to provide customers with timely and comprehensive service. For any
assistance, please contact our company headquarters:
Quectel Wireless Solutions Co., Ltd.
Room 501, Building 13, No.99, Tianzhou Road, Shanghai, China, 200233
Tel: +86 21 5108 6236
Mail: info@quectel.com
Or our local office, for more information, please visit:
http://www.quectel.com/support/salesupport.aspx
For technical support, to report documentation errors, please visit:
http://www.quectel.com/support/techsupport.aspx
GENERAL NOTES
QUECTEL OFFERS THIS INFORMATION AS A SERVICE TO ITS CUSTOMERS. THE INFORMATION
PROVIDED IS BASED UPON CUSTOMERS’ REQUIREMENTS. QUECTEL MAKES EVERY EFFORT
TO ENSURE THE QUALITY OF THE INFORMATION IT MAKES AVAILABLE. QUECTEL DOES NOT
MAKE ANY WARRANTY AS TO THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN, AND DOES NOT ACCEPT
ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY INJURY, LOSS OR DAMAGE OF ANY KIND INCURRED BY USE OF OR
RELIANCE UPON THE INFORMATION. ALL INFORMATION SUPPLIED HEREIN ARE SUBJECT TO
CHANGE WITHOUT PRIOR NOTICE.
COPYRIGHT
THIS INFORMATION CONTAINED HERE IS PROPRIETARY TECHNICAL INFORMATION OF
QUECTEL CO., LTD. TRANSMITTABLE, REPRODUCTION, DISSEMINATION AND EDITING OF THIS
DOCUMENT AS WELL AS UTILIZATION OF THIS CONTENTS ARE FORBIDDEN WITHOUT
PERMISSION. OFFENDERS WILL BE HELD LIABLE FOR PAYMENT OF DAMAGES. ALL RIGHTS ARE
RESERVED IN THE EVENT OF A PATENT GRANT OR REGISTRATION OF A UTILITY MODEL OR
DESIGN.
Copyright © Quectel Wireless Solutions Co., Ltd. 2014. All rights reserved.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 1 / 76
Page 3
GC65 Hardware Design
About the Document
History
Revision Date Author Description
1.0 2013-12-09 King HAO Initial
GSM/GPRS Module Series
2.0 2014-01-09 King HAO
1. Update Figure 2:Pin assignment.
2. Modified the mechanical dimensions and the
recommended footprint of the module in Chapter 6.
3. Update the function of SIM card detection.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 2 / 76
Page 4

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
Contents
About the Document ................................................................................................................................... 2
Contents ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
Table Index ................................................................................................................................................... 5
Figure Index ................................................................................................................................................. 6
1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.1. Safety Information ................................................................................................................... 8
2 Product Concept ................................................................................................................................ 10
2.1. General Description ............................................................................................................... 10
2.2. Directives and Standards ...................................................................................................... 10
2.3. Key Features ......................................................................................................................... 11
2.4. Functional Diagram ............................................................................................................... 13
2.5. Evaluation Board ................................................................................................................... 14
3 Application Interface ......................................................................................................................... 15
3.1. Pin of Module ......................................................................................................................... 16
3.2. Operating Modes ................................................................................................................... 21
3.3. Power Supply ........................................................................................................................ 22
3.4. Power On and Down Scenarios ............................................................................................ 24
3.5. Power Saving Technology ..................................................................................................... 31
3.6. RTC Backup .......................................................................................................................... 32
3.7. Serial Interfaces ..................................................................................................................... 34
2.2.1. FCC Statement ............................................................................................................... 10
2.2.2. FCC Radiation Exposure Statement .............................................................................. 11
3.1.1. Pin Assignment .............................................................................................................. 16
3.1.2. Pin Description ............................................................................................................... 17
3.3.1. Power Features of Module ............................................................................................. 22
3.3.2. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop ...................................................................................... 22
3.3.3. Reference Design for Power Supply .............................................................................. 23
3.3.4. Monitor Power Supply .................................................................................................... 24
3.4.1. Power On ....................................................................................................................... 24
3.4.2. Power Down ................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.2.1. Power Down Module by the PWRKEY Pin ....................................................... 27
3.4.2.2. Power Down Module by AT Command ............................................................. 28
3.4.2.3. Over-voltage or Under-voltage Automatic Shutdown ........................................ 28
3.4.2.4. Emergency Shutdown by EMERG_OFF Pin .................................................... 29
3.4.3. Restart ............................................................................................................................ 30
3.5.1. Minimum Functionality Mode ......................................................................................... 31
3.5.2. Sleep Mode .................................................................................................................... 31
3.5.3. Wake Up Module from Sleep Mode ............................................................................... 32
3.5.4. Summary of State Transition .......................................................................................... 32
3.7.1. UART Port ...................................................................................................................... 36
3.7.1.1. The Features of UART Port ............................................................................... 36
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 3 / 76
Page 5

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.7.1.2. The Connection of UART .................................................................................. 37
3.7.2. Debug and Upgrade Port ............................................................................................... 38
3.7.3. UART Application ........................................................................................................... 39
3.8. Audio Interfaces ..................................................................................................................... 41
3.8.1. Decrease TDD Noise and Other Noises ........................................................................ 42
3.8.2. Microphone Interfaces Design ....................................................................................... 43
3.8.3. Receiver Interface Design .............................................................................................. 44
3.8.4. Earphone Interface Design ............................................................................................ 46
3.8.5. Audio Characteristics ..................................................................................................... 46
3.9. SIM Card Interface ................................................................................................................ 47
3.9.1. SIM Card Application ...................................................................................................... 47
3.9.2. SIM Cassette .................................................................................................................. 49
3.10. PCM Interface ........................................................................................................................ 52
3.11. Behaviors of the RI ................................................................................................................ 52
3.12. Network Status Indication ...................................................................................................... 53
4 Antenna Interface ............................................................................................................................... 55
4.1. RF Reference Design ............................................................................................................ 55
4.2. RF Output Power ................................................................................................................... 56
4.3. RF Receiving Sensitivity ........................................................................................................ 56
4.4. Operating Frequencies .......................................................................................................... 57
4.5. RF Cable Soldering ............................................................................................................... 57
5 Electrical, Reliability and Radio Characteristics ............................................................................ 58
5.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings................................................................................................... 58
5.2. Operating Temperature ......................................................................................................... 59
5.3. Power Supply Ratings ........................................................................................................... 59
5.4. Current Consumption ............................................................................................................ 60
5.5. Electro-static Discharge ........................................................................................................ 61
6 Mechanical Dimensions .................................................................................................................... 63
6.1. Mechanical Dimensions of Module ....................................................................................... 63
6.2. Recommended Footprint ....................................................................................................... 65
6.3. Top View of the Module ......................................................................................................... 66
6.4. Bottom View of the Module ................................................................................................... 66
7 Storage and Manufacturing .............................................................................................................. 67
7.1. Storage .................................................................................................................................. 67
7.2. Soldering ............................................................................................................................... 68
7.3. Packaging .............................................................................................................................. 69
7.3.1. Tape and Reel Packaging .............................................................................................. 69
8 Appendix A Reference ....................................................................................................................... 71
9 Appendix B GPRS Coding Scheme ................................................................................................. 75
10 Appendix C GPRS Multi-slot Class .................................................................................................. 77
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 4 / 76
Page 6

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Table Index
TABLE 1: MODULE KEY FEATURES ................................................................................................................ 11
TABLE 2: CODING SCHEMES AND MAXIMUM NET DATA RATES OVER AIR INTERFACE ........................ 13
TABLE 3: PIN DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................................................... 17
TABLE 4: OVERVIEW OF OPERATING MODES ............................................................................................. 21
TABLE 5: SUMMARY OF STATE TRANSITION ............................................................................................... 32
TABLE 6: LOGIC LEVELS OF THE UART INTERFACES ................................................................................ 35
TABLE 7: PIN DEFINITION OF THE UART INTERFACES .............................................................................. 35
TABLE 8: PIN DEFINITION OF AUDIO INTERFACE ....................................................................................... 41
TABLE 9: TYPICAL ELECTRET MICROPHONE CHARACTERISTICS ........................................................... 46
TABLE 10: TYPICAL AUDIO OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS .......................................................................... 46
TABLE 11: PIN DEFINITION OF THE SIM INTERFACE .................................................................................. 47
TABLE 12: PIN DESCRIPTION OF AMPHENOL SIM CARD HOLDER ........................................................... 50
TABLE 13: PIN DESCRIPTION OF MOLEX SIM CARD HOLDER .................................................................. 51
TABLE 14: BEHAVIOURS OF THE RI .............................................................................................................. 52
TABLE 15: WORKING STATE OF THE NETLIGHT .......................................................................................... 53
TABLE 16: PIN DEFINITION OF THE RF_ANT ................................................................................................ 55
TABLE 17: THE MODULE CONDUCTED RF OUTPUT POWER .................................................................... 56
TABLE 18: THE MODULE CONDUCTED RF RECEIVING SENSITIVITY ....................................................... 56
TABLE 19: THE MODULE OPERATING FREQUENCIES ................................................................................ 57
TABLE 20: ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .................................................................................................. 58
TABLE 21: OPERATING TEMPERATURE ........................................................................................................ 59
TABLE 22: THE MODULE POWER SUPPLY RATINGS .................................................................................. 59
TABLE 23: THE MODULE CURRENT CONSUMPTION .................................................................................. 60
TABLE 24: THE ESD ENDURANCE (TEMPERATURE: 25℃, HUMIDITY: 45 %) ........................................... 62
TABLE 25: RELATED DOCUMENTS ................................................................................................................ 71
TABLE 26: TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ...................................................................................................... 72
TABLE 27: DESCRIPTION OF DIFFERENT CODING SCHEMES .................................................................. 75
TABLE 28: GPRS MULTI-SLOT CLASSES ...................................................................................................... 77
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 5 / 76
Page 7

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure Index
FIGURE 1: MODULE FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM ............................................................................................... 14
FIGURE 2: PIN ASSIGNMENT ......................................................................................................................... 16
FIGURE 3: VOLTAGE DROP DURING TRANSMITTING ................................................................................. 22
FIGURE 4: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR THE VBAT INPUT ........................................................................... 23
FIGURE 5: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR POWER SUPPLY ............................................................................ 24
FIGURE 6: REFERENCE DIAGRAM FOR SWITCHING POWER CONVERTER ........................................... 24
FIGURE 7: TURN ON THE MODULE WITH AN OC DRIVER .......................................................................... 25
FIGURE 8: TURN ON THE MODULE WITH A BUTTON .................................................................................. 25
FIGURE 9: TURN-ON TIMING .......................................................................................................................... 26
FIGURE 10: TURN-OFF TIMING ...................................................................................................................... 27
FIGURE 11: AN OC DRIVER FOR EMERG_OFF ............................................................................................ 29
FIGURE 12: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR EMERG_OFF BY BUTTON .......................................................... 29
FIGURE 13: TIMING OF RESTARTING SYSTEM ............................................................................................ 30
FIGURE 14: TIMING OF RESTARTING SYSTEM AFTER EMERGENCY SHUTDOWN ................................ 30
FIGURE 15: RTC SUPPLIED FROM A NON-CHARGEABLE BATTERY ......................................................... 33
FIGURE 16: RTC SUPPLIED FROM A RECHARGEABLE BATTERY ............................................................. 33
FIGURE 17: RTC SUPPLIED FROM A CAPACITOR ....................................................................................... 33
FIGURE 18: CHARGING CHARACTERISTICS OF SEIKO’S XH414H-IV01E ................................................ 34
FIGURE 19: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR FULL-FUNCTION UART ................................................................ 37
FIGURE 20: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR UART PORT ................................................................................... 38
FIGURE 21: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR UART PORT WITH HARDWARE FLOW CONTROL .................... 38
FIGURE 22: THE CONNECTION OF FIRMWARE DEBUGGING AND UPGRADE......................................... 39
FIGURE 23: LEVEL MATCH DESIGN FOR 3.3V SYSTEM .............................................................................. 39
FIGURE 24: LEVEL MATCH DESIGN FOR 5V SYSTEM ................................................................................. 40
FIGURE 25: LEVEL MATCH DESIGN FOR RS-232 ......................................................................................... 41
FIGURE 26: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR AIN1&AIN2 ..................................................................................... 43
FIGURE 27: REFERENCE RECEIVER INTERFACE DESIGN OF AOUT1 ..................................................... 44
FIGURE 28: SPEAKER INTERFACE WITH AMPLIFIER CONFIGURATION OF AOUT1................................ 44
FIGURE 29: REFERENCE RECEIVER INTERFACE DESIGN OF AOUT2 ..................................................... 45
FIGURE 30: SPEAKER INTERFACE WITH AMPLIFIER CONFIGURATION OF AOUT2................................ 45
FIGURE 31: EARPHONE INTERFACE DESIGN .............................................................................................. 46
FIGURE 32: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR 8-PIN SIM CARD HOLDER .......................................................... 48
FIGURE 33: REFERENCE CIRCUIT FOR 6-PIN SIM CARD HOLDER .......................................................... 49
FIGURE 34: AMPHENOL C707 10M006 512 2 SIM CARD HOLDER .............................................................. 50
FIGURE 35: MOLEX 91228 SIM CARD HOLDER ............................................................................................ 51
FIGURE 36: RI BEHAVIOUR OF VOICE CALLING AS A RECEIVER ............................................................. 52
FIGURE 37: RI BEHAVIOUR AS A CALLER ..................................................................................................... 53
FIGURE 38: RI BEHAVIOUR OF URC OR SMS RECEIVED ........................................................................... 53
FIGURE 39: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR NETLIGHT ..................................................................................... 54
FIGURE 40: REFERENCE DESIGN FOR RF .................................................................................................. 55
FIGURE 41: RF SOLDERING SAMPLE ........................................................................................................... 57
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 6 / 76
Page 8

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
FIGURE 42: GC65 MODULE TOP AND SIDE DIMENSIONS (UNIT: MM) ....................................................... 63
FIGURE 43: GC65 MODULE BOTTOM DIMENSIONS (UNIT: MM) ................................................................ 64
FIGURE 44: RECOMMENDED FOOTPRINT (UNIT: MM) ................................................................................ 65
FIGURE 45: TOP VIEW OF THE MODULE ...................................................................................................... 66
FIGURE 46: BOTTOM VIEW OF THE MODULE .............................................................................................. 66
FIGURE 47: THE PICTURE OF PRINTING PASTE ......................................................................................... 68
FIGURE 48: RAMP-SOAK-SPIKE REFLOW PROFILE .................................................................................... 69
FIGURE 49: DIMENSIONS OF TAPE ............................................................................................................... 70
FIGURE 50: DIMENSIONS OF REEL ............................................................................................................... 70
FIGURE 51: RADIO BLOCK STRUCTURE OF CS-1, CS-2 AND CS-3 ........................................................... 75
FIGURE 52: RADIO BLOCK STRUCTURE OF CS-4 ....................................................................................... 76
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 7 / 76
Page 9
GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
1
This document defines the GC65 module and describes its hardware interface which are connected with
your application and the air interface.
This document can help you quickly understand module interface specifications, electrical and
mechanical details. Associated with application notes and user guide, you can use GC65 module to
design and set up mobile applications easily.
Introduction
1.1. Safety Information
The following safety precautions must be observed during all phases of the operation, such as usage,
service or repair of any cellular terminal or mobile incorporating GC65 module. Manufacturers of the
cellular terminal should send the following safety information to users and operating personnel and to
incorporate these guidelines into all manuals supplied with the product. If not so, Quectel does not take on
any liability for your failure to comply with these precautions.
Full attention must be given to driving at all times in order to reduce the risk of an
accident. Using a mobie while driving (even with a handsfree kit) cause distraction
and can lead to an accident. You must comply with laws and regulations restrcting
the use of wireless devices while driving.
Switch off the cellular terminal or mobile before boarding an aircraft. Make sure it
switched off. The operation of wireless appliances in an aircraft is forbidden to
prevent interference with communication systems. Consult the airline staff about
the use of wireless devices on boarding the aircraft. If your device offers a Flight
Mode which must be enabled prior to boarding an aircraft.
Switch off your wireless device when in hospitals or clinics or other health care
facilities. These requests are desinged to prevent possible interference with
sentitive medical equipment.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 8 / 76
Page 10
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
GSM cellular terminals or mobiles operate over radio frequency signal and cellular
network and cannot be guaranteed to connect in all conditions, for example no
mobile fee or an invalid SIM card. While you are in this condition and need
emergent help, please remember using emergency call. In order to make or
receive call, the cellular terminal or mobile must be switched on and in a service
area with adequate cellular signal strength.
Your cellular terminal or mobile contains a transmitter and receiver. When it is ON ,
it receives and transmits radio frequency energy. RF interference can occur if it is
used close to TV set, radio, computer or other electric equipment.
In locations with potencially explosive atmospheres, obey all posted signs to turn
off wireless devices such as your phone or other cellular terminals. Areas with
potencially exposive atmospheres including fuelling areas, below decks on boats,
fuel or chemical transfer or storage facilities, areas where the air contains
chemicals or particles such as grain, dust or metal powders.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 9 / 76
Page 11

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
2
Product Concept
2.1. General Description
GC65 is a Quad-band GSM/GPRS engine that works at frequencies of GSM850MHz, GSM900MHz,
DCS1800MHz and PCS1900MHz. The GC65 features GPRS multi-slot class 10 and supports the GPRS
coding schemes CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4. For more details about GPRS multi-slot classes and coding
schemes, please refer to the Appendix B&C.
With a tiny profile of 19mm×16.9mm×2.35mm, the module can meet almost all the requirements for M2M
applications, including Vehicles and Personal Tracking, Security System, Wireless POS, Industrial PDA,
Smart Metering, and Remote Maintenance & Control, etc.
GC65 is an SMD type module, which can be easily embedded into applications through its 44-pin pads. It
provides abundant hardware interfaces like Audio and UART Interface.
Designed with power saving technique, the current consumption of GC65 is as low as 1.3mA in sleep
mode when DRX is 5.
GC65 is integrated with Internet service protocols, such as TCP/UDP, HTTP and PPP. Extended AT
commands have been developed for you to use these Internet service protocols easily.
The module fully complies with the RoHS directive of the European Union.
2.2. Directives and Standards
The GC10 module is designed to comply with the FCC statements. FCC ID: XMR201403GC65
The Host system using GC65, should have label indicated FCC ID: XMR201403GC65.
2.2.1. FCC Statement
1. This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following conditions:
a) This device may not cause harmful interference.
b) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 10 / 76
Page 12

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
2. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void
the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
2.2.2. FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator and
your body as well as kept minimum 20cm from radio antenna depending on the Mobile status of this
module usage. This module should NOT be installed and operating simultaneously with other radio.
The manual of the host system, which uses GC65, must include RF exposure warning statement to
advice user should keep minimum 20cm from the radio antenna of GC65 module depending on the
Mobile status.
Note: If a portable device (such as PDA) uses GC65 module, the device needs to do permissive change
and SAR testing.
The following list of antenna is indicating the maximum permissible antenna gain.
Part Number
3R007A
Frequency
Range (MHz)
PCS1900:1850~1990
GSM850:824-894
Peak Gain
XZ-V)
1 dBi typ. 1 dBi typ. 3 max 50Ω
Average Gain
VSWR Impedance
XZ-V)
2.3. Key Features
The following table describes the detailed features of GC65 module.
Table 1: Module Key Features
Feature Implementation
Power Supply
Power Saving
Frequency Bands
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 11 / 76
Single supply voltage: 3.3V~4.6V
Typical supply voltage: 4.0V
Typical power consumption in sleep mode: 1.3 mA@ DRX=5
1.1 mA@ DRX=9
Quad-band: GSM850/GSM900/DCS1800/PCS1900
The module can search these frequency bands automatically
The frequency bands can be set by AT command
Page 13
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Compliant to GSM Phase 2/2+
Transmitting Power
GPRS Connectivity
Class 4 (2W) at GSM850/GSM900
Class 1 (1W) at DCS1800/PCS1900
GPRS multi-slot class 10
GPRS mobile station class B
Normal operation: -35°C~ +80°C
Temperature Range
Restricted operation: -40°C ~ -35°C and +80°C ~ +85°C 1)
Storage temperature: -45°C ~ +90°C
GPRS data downlink transfer: max. 85.6kbps
GPRS data uplink transfer: max. 42.8kbps
DATA GPRS
Coding scheme: CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4
Internet service protocols TCP/UDP, PPP, HTTP
Support Packet Broadcast Control Channel (PBCCH)
USSD Support Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
SMS
MT/MO, Text and PDU mode
SMS storage: SIM card
SIM Interface Support SIM card: 1.8V/3.0V
Speech codec modes:
Half Rate (ETS 06.20)
Full Rate (ETS 06.10)
Audio Features
Enhanced Full Rate (ETS 06.50/06.60/06.80)
Echo Suppression
Echo Cancellation
Noise Reduction
UART Port:
Seven lines on UART port interface
Used for AT command, GPRS data
Support fixed baud rate from 2400bps to 460800bps
UART Interfaces
Support autobauding from 4800bps to 115200bps
Debug Port:
Two lines on debug port interface DBG_TXD and DBG_RXD
Used for firmware debugging and log output
Used for firmware upgrade
The baud rate is fixed at 921600bps
Phonebook Management Support phonebook types: SM/ON/FD/LD
SIM Application Toolkit Support SAT class 3, GSM 11.14 Release 99
Real Time Clock Supported
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 12 / 76
Page 14
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Physical Characteristics
Size: 19±0.15×16.9±0.15×2.35±0.2mm
Weight: Approx.1.3g
Firmware Upgrade Firmware upgrade via debug port
Antenna Interface Connected to antenna pad with 50 Ohm impedance control
NOTE
When the module works within this temperature range, the deviations from the GSM specification may
occur. For example, the frequency error or the phase error will be increased.
Table 2: Coding Schemes and Maximum Net Data Rates over Air Interface
Coding Scheme 1 Timeslot 2 Timeslot 4 Timeslot
CS-1 9.05kbps 18.1kbps 36.2kbps
CS-2 13.4kbps 26.8kbps 53.6kbps
CS-3 15.6kbps 31.2kbps 62.4kbps
CS-4 21.4kbps 42.8kbps 85.6kbps
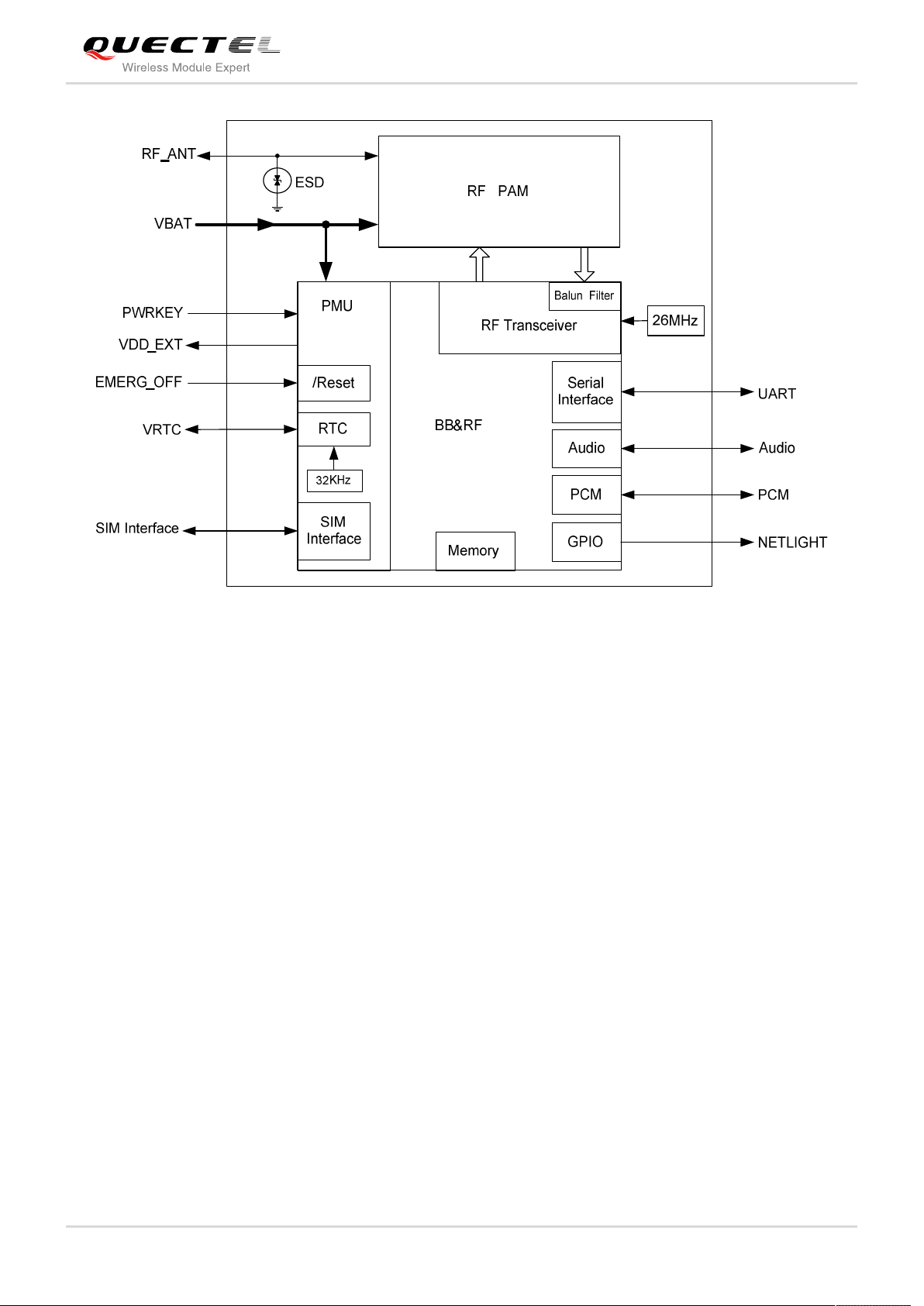
2.4. Functional Diagram
The following figure shows a block diagram of GC65 and illustrates the major functional parts.
Radio frequency part
Power management
Memory
The peripheral interface
—Power supply
—Turn-on/off interface
—UART interfaces
—Audio interfaces
—SIM interface
—PCM interface
—RTC interface
—RF interface
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 13 / 76
Page 15
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 1: Module Functional Diagram
2.5. Evaluation Board
In order to help you to develop applications with GC65, Quectel supplies an evaluation board (EVB) with
RS-232 to USB cable, power adapter, antenna, firmware upgrade cable (UART to USB cable) and other
peripherals to control or test the module. For details, please refer to the document [11].
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 14 / 76
Page 16

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
3
The module adopts 44-pin pads with LCC package. The following chapters provide detailed descriptions
about these pins below.
Power supply (Please refer to chapter 3.3)
Power on/down (Please refer to chapter 3.4)
Power saving technology (Please refer to chapter 3.5)
RTC (Please refer to chapter 3.6)
Serial interfaces (Please refer to chapter 3.7)
Audio interfaces (Please refer to chapter 3.8)
SIM interface (Please refer to chapter 3.9)
PCM interface (Please refer to chapter 3.10)
Application Interface
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 15 / 76
Page 17
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
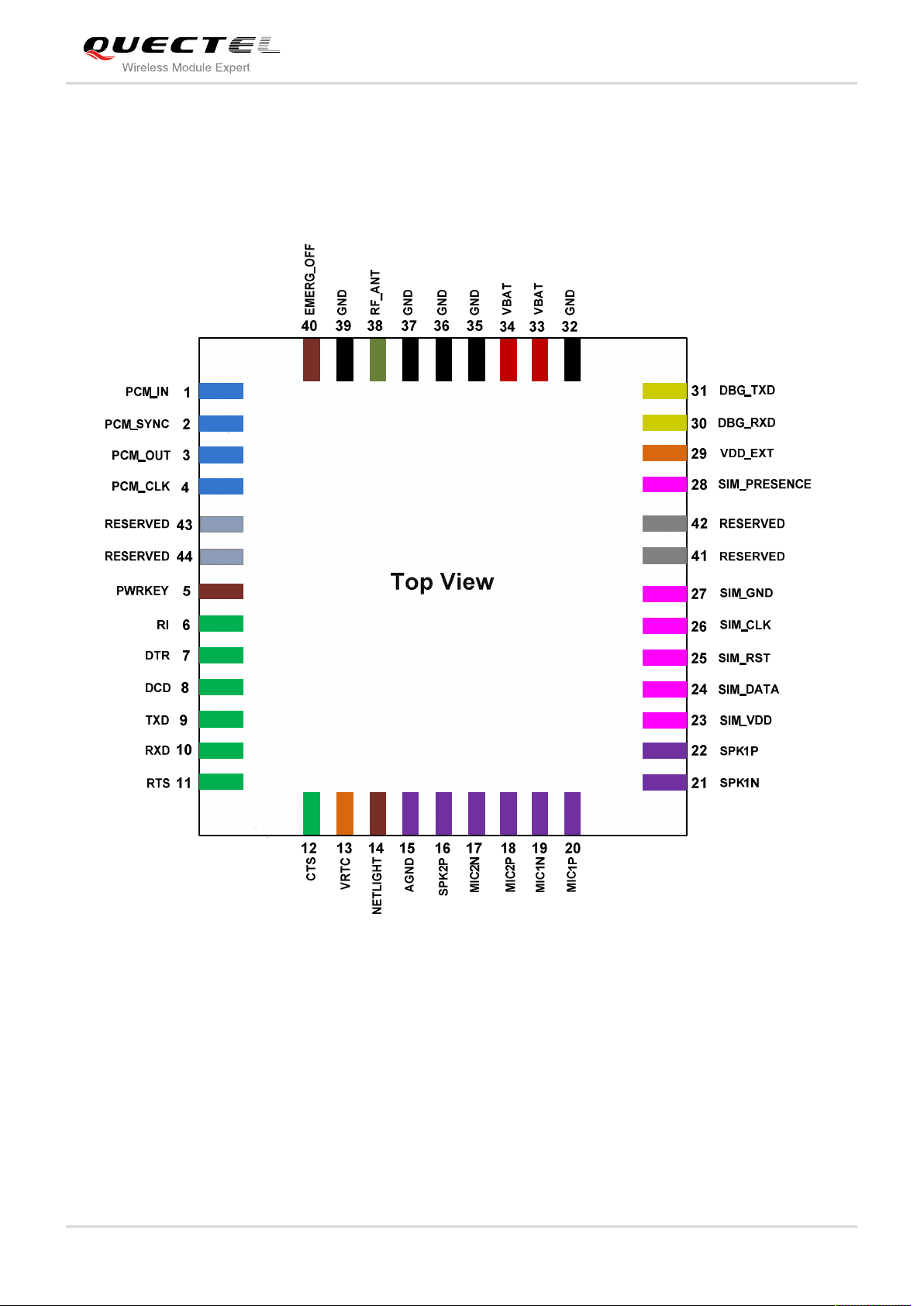
3.1. Pin of Module
3.1.1. Pin Assignment
Figure 2: Pin Assignment
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 16 / 76
Page 18
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.1.2. Pin Description
Table 3: Pin Description
Power Supply
Pin Name
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
VBAT 33,34 I
VRTC 13 I/O
VDD_EXT 29 O
Main power supply of
module:
VBAT=3.3V~4.6V
Power supply for RTC
when VBAT is not
supplied for the system.
Charging for backup
battery or golden
capacitor when the VBAT
is applied.
Supply 3.0V voltage for
external circuit.
Vmax= 4.6V
Vmin=3.3V
Vnorm=4.0V
VImax=3.3V
VImin=2.0V
VInorm=2.8V
VOmax=2.9V
VOmin=2.7V
VOnorm=2.8V
Iout(max)=1.35mA
Iin=70uA
Vmax=3.1V
Vmin=2.9V
Vnorm=3.0V
Imax=20mA
Make sure that supply
sufficient current in a
transmitting burst
typically rises to 1.6A.
Recommended to be
connected to a backup
battery or a golden
capacitor. If unused,
keep this pin open.
Recommend to add a
2.2 or 4.7uF bypass
capacitor, when using
this pin for power
supply. If unused,
keep this pin open.
GND
Turn on/off
Pin Name
PWRKEY 5 I
Emergency Shutdown
Pin Name
32,35,
36,37,
39
Pin
NO.
Pin
NO.
Ground
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
Power on/off key.
PWRKEY should be
pulled down for a
moment to turn on or
VILmax=2.0V
VIHmin=2.3V
VImax=3.3V
Recommend to add an
OC driver circuit to
control this pin.
turn off the system.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 17 / 76
Page 19

VOHmax=
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Emergency off. Pulled
EMERG_
OFF
40 I
down for at least 10ms,
which will turn off the
module in case of
emergency. Use it only
when shutdown via
PWRKEY or AT
command cannot be
VILmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VIHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
Pulled up to VDD_EXT
internally. OC/OD
driver required in
cellular device
application. If unused,
keep this pin open.
achieved.
Module Indicator
Pin Name
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
NETLIGHT 14 O Network status indication
Audio Interfaces
Pin Name
MIC1P
MIC1N
SPK1P
SPK1N
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
19,20 I
21,22 O
Channel 1 positive and
negative voice input
Channel 1 positive and
negative voice output
VOLmin=0V
VOLmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VOHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VDD_EXT
If unused, keep this
pin open.
Main audio channel.
Recommended to add
ESD protection
components at the
MIC1P/N lines. If
unused, keep these
pins open.
MIC2P
MIC2N
17,18 I
SPK2P 16 O
AGND 15 Audio analog ground.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 18 / 76
Channel 2 positive and
negative voice input
Channel 2 single-ended
voice output
For Audio DC
characteristics refer
to Chapter 3.9.
Auxiliary audio
channel.
Recommended to add
ESD protection
components at the
MIC2P/N lines. If
unused, keep these
pins open.
Separate ground
connection for external
audio circuits.
Page 20

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
UART Port
Pin Name
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
RI 6 O Ring indication
DTR 7
I
Data terminal ready
DCD 8 O Data carrier detection
TXD 9 O Transmit data
RXD 10 I Receive data
RTS 11 I Request to send
CTS 12 O Clear to send
Debug Port
Pin Name
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
VILmin=0V
VILmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VIHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VIHmax=
VDD_EXT
VOLmin=0V
VOLmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VOHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VOHmax=
VDD_EXT
If only use TXD, RXD
and GND to
communicate,
recommended
connecting RTS to
GND via a 0R resistor
and keeping other pins
open.
DBG_TXD 31 O
DBG_RXD 30 I
SIM Interface
Pin Name
SIM_VDD 23 O
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
Used for firmware
debugging and upgrade.
The baud rate is fixed at
921600bps.
Power supply for SIM
card
VILmin=0V
VILmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VIHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VIHmax=
VDD_EXT
VOLmin=0V
VOLmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VOHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VOHmax=
VDD_EXT
The voltage can be
selected by software
automatically. Either
1.8V or 3V.
If unused, keep these
pins open.
All signals of SIM
interface should be
protected against ESD
with a TVS diode
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 19 / 76
Page 21
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
SIM_DATA 24 O SIM data
SIM_ RST 25 I/O SIM reset
SIM_CLK 26 O SIM clock
SIM_GND 27 SIM ground
VILmin=0V
VILmax=
SIM_
PRESENCE
28
I
SIM card detection
0.3×VDD_EXT
VIHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VIHmax=
VDD_EXT
PCM Interface
Pin Name
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
VILmin=0V
PCM_ IN 1 I PCM data input
VILmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VIHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
VIHmax=
VDD_EXT
PCM_SYNC 2
PCM frame
O
synchronization
VOLmin=0V
PCM_ OUT 3 O PCM data output
VOLmax=
0.3×VDD_EXT
VOHmin=
0.7×VDD_EXT
PCM_ CLK 4 O PCM clock
VOHmax=
VDD_EXT
array. Maximum trace
length is 100mm from
the module pad to SIM
card holder.
SIM_PRESENCE
must be pulled up by
an external resistor
when SIM card
detection function is
used.
PCM function is not
supported at present.
If unused, keep these
pins open.
RF Interface
Pin Name
RF_ANT 38 I/O RF antenna pad Impedance of 50Ω
Pin
NO.
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
Please refer to
Chapter 4
Other Interface
Pin Name
RESERVED
Pin
NO.
41,42,
43,44
I/O Description DC Characteristics Comment
Please keep these
pins open.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 20 / 76
Page 22
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.2. Operating Modes
The table below briefly summarizes the various operating modes in the following chapters.
Table 4: Overview of Operating Modes
Mode Function
The module will automatically go into sleep mode if DTR is
set to high level and there is no interrupt (such as GPIO
GSM/GPRS
Sleep
GSM Idle
interrupt or data on UART port). In this case, the current
consumption of module will reduce to the minimal level.
During sleep mode, the module can still receive paging
message and SMS from the system normally.
Software is active. The module has registered to the GSM
network, and the module is ready to send and receive
GSM data.
Normal Operation
Mode
Power Down Mode
GSM connection is ongoing. In this mode, the power
GSM Talk
consumption is decided by the configuration of Power
Control Level (PCL), dynamic DTX control and the working
RF band.
GPRS Idle
The module is not registered to GPRS network. The
module is not reachable through GPRS channel.
The module is registered to GPRS network, but no GPRS
GPRS Standby
PDP context is active. The SGSN knows the Routing Area
where the module is located at.
The PDP context is active, but no data transfer is ongoing.
GPRS Ready
The module is ready to receive or send GPRS data. The
SGSN knows the cell where the module is located at.
There is GPRS data in transfer. In this mode, power
GPRS Data
consumption is decided by the PCL, working RF band and
GPRS multi-slot configuration.
Normal shutdown by sending the “AT+QPOWD=1” command, using the
PWRKEY or the EMERG_OFF1) pin. The power management ASIC
disconnects the power supply from the base band part of the module, and
only the power supply for the RTC is remained. Software is not active. The
UART interfaces are not accessible. Operating voltage (connected to VBAT)
remains applied.
“AT+CFUN” command can set the module to a minimum functionality mode
Minimum Functionality
Mode
without removing the power supply. In this case, the RF part of the module
will not work or the SIM card will not be accessible, or both RF part and SIM
card will be disabled, but the UART port is still accessible. The power
consumption in this case will be reduced.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 21 / 76
Page 23
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
NOTE
Use the EMERG_OFF pin only when failing to turn off the module by the command “AT+QPOWD=1” and
the PWRKEY pin. For more details, please refer to Section 3.4.2.4.
3.3. Power Supply
3.3.1. Power Features of Module
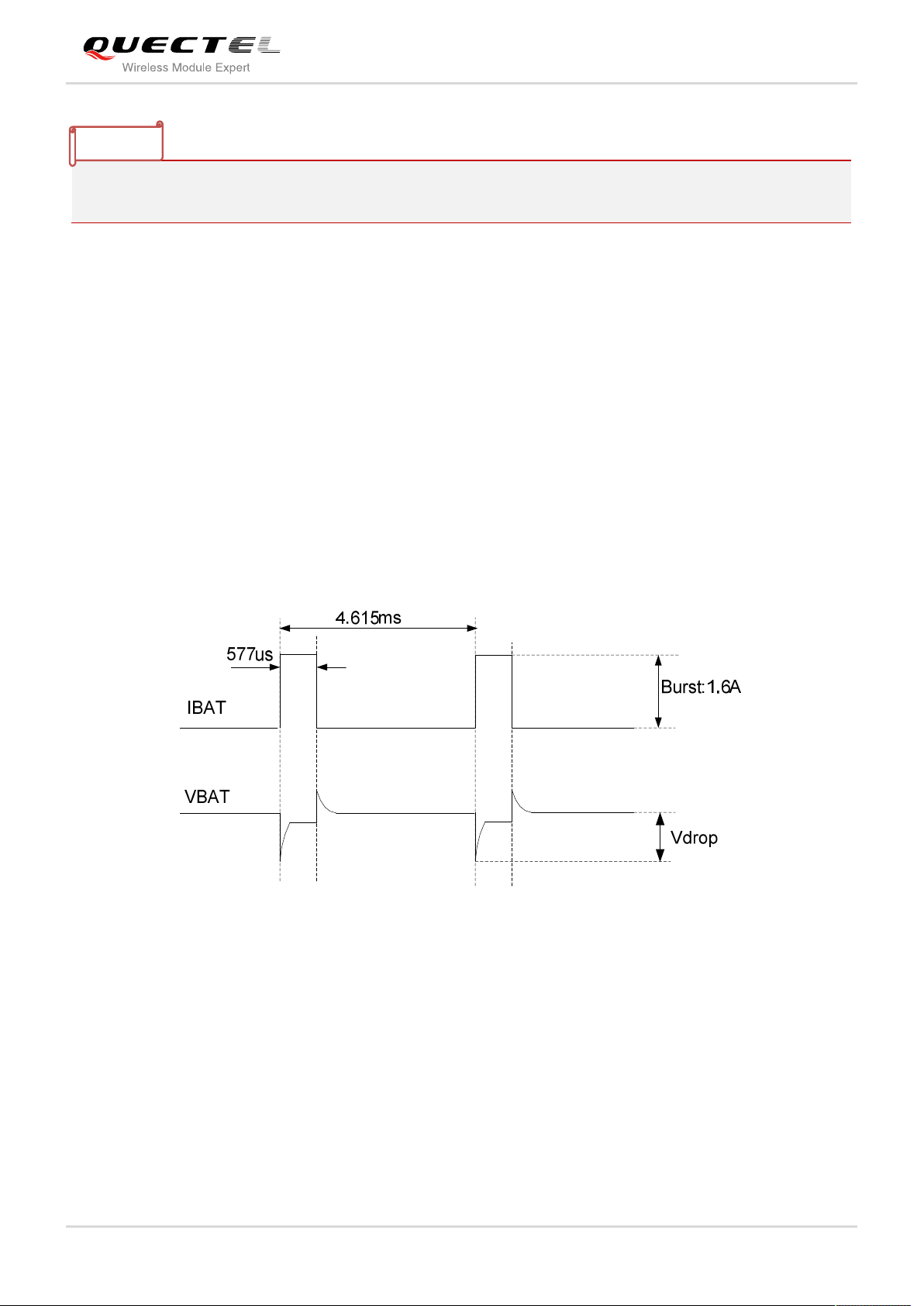
The power supply is one of the key issues in designing GSM terminals. Because of the 577us radio burst
in GSM every 4.615 ms, power supply must be able to deliver high current peaks in a burst period. During
these peaks, drops on the supply voltage must not exceed minimum working voltage of module.
For GC65 module, the max current consumption could reach to 1.6A during a transmit burst. It will cause
a large voltage drop on the VBAT. In order to ensure stable operation of the module, it is recommended
that the max voltage drop during the transmit burst does not exceed 400mV.
Figure 3: Voltage Drop during Transmitting
3.3.2. Decrease Supply Voltage Drop
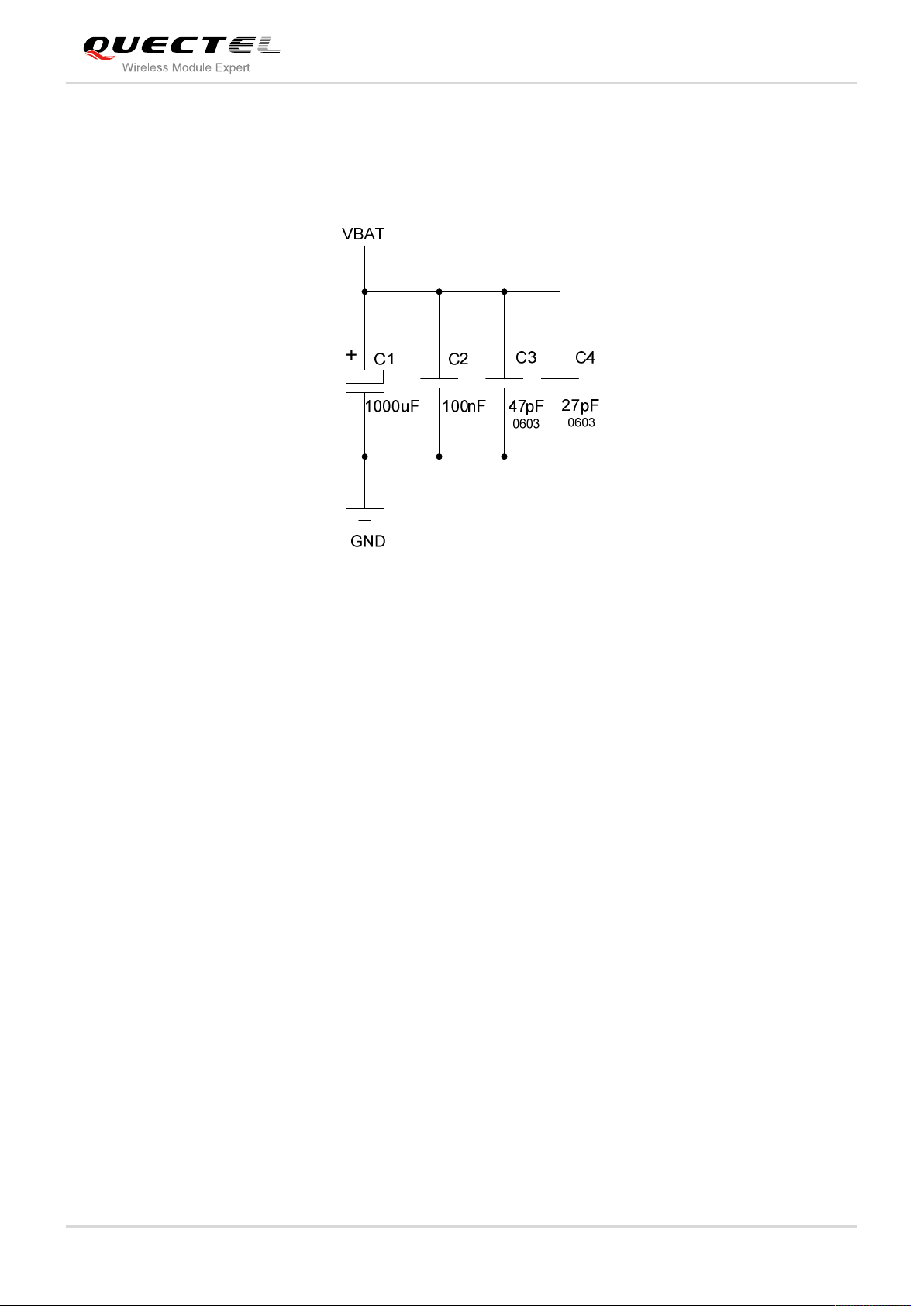
The power supply range of the module is 3.3V to 4.6V. Make sure that the input voltage will never drop
below 3.3V even in a transmitting burst. If the power voltage drops below 3.3V, the module could turn off
automatically. For better power performance, it is recommended to place a 1000uF tantalum capacitor
with low ESR and ceramic capacitor 100nF, 47pF and 27pF near the VBAT pin. The reference circuit is
illustrated in Figure 4.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 22 / 76
Page 24
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The VBAT route should be wide enough to ensure that there is not too much voltage drop during transmit
burst. The width of trace should be no less than 2mm and the principle of the VBAT route is the longer
route, the wider trace.
Figure 4: Reference Circuit for the VBAT Input
3.3.3. Reference Design for Power Supply
The power design for the module is very important, since the performance of power supply for the module
largely depends on the power source. The power supply is capable of providing the sufficient current to
2A at least. If the voltage drop between the input and output is not too high, it is suggested to use a LDO
as module’s power supply. If there is a big voltage difference between the input source and the desired
output (VBAT), a switching power converter is recommended to be used as a power supply.
Figure 5 shows a reference design for +5V input power source. The designed output for the power supply
is 4.16V and the maximum load current is 3A. In addition, in order to get a stable output voltage, a zener
diode is placed close to the pins of VBAT. As to the zener diode, it is suggested to use a zener diode
whose reverse zener voltage is 5.1V and dissipation power is more than 1 Watt.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 23 / 76
Page 25

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 5: Reference Circuit for Power Supply
If a switching power converter is used, please follow the diagram to design the circuit, it is beneficial to
maintain stable power supply for the module.
Figure 6: Reference Diagram for Switching Power Converter
3.3.4. Monitor Power Supply
To monitor the supply voltage, you can use the “AT+CBC” command which includes three parameters:
charging status, remaining battery capacity and voltage value (in mV). It returns the 0-100 percent of
battery capacity and actual value measured between VBAT and GND. The voltage is automatically
measured in period of 5s. The displayed voltage (in mV) is averaged over the last measuring period
before the “AT+CBC” command is executed.
For details, please refer to document [1].
3.4. Power On and Down Scenarios
3.4.1. Power On
The module can be turned on by driving the pin PWRKEY to a low level voltage, after booting successfully,
PWRKEY pin can be released. You may monitor the status of the NETLIGHT pin to judge whether the
module is power-on or not. When NETLIGHT pin outputs a signal with certain frequency, it indicates the
module is turned on successfully. The NETLIGHT pin will keep in low level all the time after the module is
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 24 / 76
Page 26

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
turned off. An OC driver circuit is suggested to control the PWRKEY. A simple reference circuit is
illustrated as below:
Figure 7: Turn On the Module with an OC Driver
NOTE
GC65 module is set to autobauding mode (AT+IPR=0) by default. In the autobauding mode, URC “RDY”
is not reported to the host controller after module is powered on. When the module receives AT command,
it will be powered on after a delay of 5~6 seconds. Host controller should first send the “AT” string in order
that the module can detect baud rate of host controller, and it will continuously send 1~5 “AT” string until
receiving “OK” string from the module. Then enter “AT+IPR=x;&W” to set a fixed baud rate for the module
and save the configuration to flash memory of the module. After these configurations, the URC “RDY”
would be received from the UART port of the module every time when the module is powered on. For
more details, refer to the section “AT+IPR” in document [1].
The other way to control the PWRKEY is through a button directly. A TVS component is indispensable to
be placed nearby the button for ESD protection. For the best performance, the TVS component must be
placed nearby the button. When pressing the key, electrostatic strike may generate from finger. A
reference circuit is shown in the following figure:
Figure 8: Turn On the Module with a Button
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 25 / 76
Page 27

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The turn-on timing is illustrated as the following figure:
T
1
VBAT
EMERG_OFF
(INPUT)
PWRKEY
(INPUT)
>10ms
VDD_EXT
(OUTPUT)
>1s
VIL< 2.0V
V
> 2.3V
IH
NETLIGHT
(OUTPUT)
MODULE
STATUS
OFF
>910ms
BOOTING
RUNNING
Figure 9: Turn-on Timing
NOTES
1. Make sure that VBAT is stable before pulling down PWRKEY pin. At least 30ms for T1 is
recommended.
2.
EMERG_OFF should be floated when it is unused.
You can monitor the status of the NETLIGHT pin to judge whether the module is power-on. After the
NETLIGHT pin goes to pulse, PWRKEY can be released. If the NETLIGHT pin is ignored, pull the
PWRKEY pin to low level for more than 2 seconds to turn on the module.
3.4.2. Power Down
The following procedures can be used to turn off the module:
Normal power down procedure: Turn off module by the PWRKEY pin.
Normal power down procedure: Turn off module by command “AT+QPOWD”.
Over-voltage or under-voltage automatic shutdown: Take effect when over-voltage or under-voltage
is detected.
Emergent power down procedure: Turn off module by the EMERG_OFF pin.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 26 / 76
Page 28

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
After power down, no further AT commands can be executed, only the RTC is still active. The power
down mode can be indicated by the VDD_EXT pin (the NETLIGHT pin can also be used.), which is a low
level voltage in this mode.
3.4.2.1. Power Down Module by the PWRKEY Pin
It is a safe way to turn off the module by driving the PWRKEY to a low level voltage for a certain time. The
power down scenario is illustrated in Figure 10:
Figure 10: Turn-off Timing
The power down procedure causes the module to log off from the network and allows the firmware to
save important data before completely disconnecting the power supply.
Before the completion of the power down procedure, the module sends the result code, shown as below:
NORMAL POWER DOWN
NOTE
When autobauding is active and DTE&DCE are not correctly synchronized after start-up, this result code
will not appear. It is recommended to set a fixed baud rate for the module.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 27 / 76
Page 29

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.4.2.2. Power Down Module by AT Command
It is also a safe way to turn off the module via AT command “AT+QPOWD=1”. This command will let the
module log off from the network and allow the firmware to save important data before completely
disconnecting the power supply.
Before the completion of the power down procedure, the module sends the result code, shown as below:
NORMAL POWER DOWN
Please refer to the document [1] for details about the AT command “AT+QPOWD”.
3.4.2.3. Over-voltage or Under-voltage Automatic Shutdown
The module will constantly monitor the voltage applied on the VBAT, if the voltage is≤3.5V, the following
URC will be presented:
UNDER_VOLTAGE WARNING
If the voltage is≥4.5V, the following URC will be presented:
OVER_VOLTAGE WARNING
The normal input voltage range is from 3.3V to 4.6V. If the voltage is >4.6V or <3.3V, the module would
automatically shut down itself.
If the voltage is <3.3V, the following URC will be presented:
UNDER_VOLTAGE POWER DOWN
If the voltage is >4.6V, the following URC will be presented:
OVER_VOLTAGE POWER DOWN
NOTE
When autobauding is active and DTE&DCE are not correctly synchronized after start-up, this result code
will not appear. It is recommended to set a fixed baud rate for the module.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 28 / 76
Page 30

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.4.2.4. Emergency Shutdown by EMERG_OFF Pin
The module can be shut down by driving the pin EMERG_OFF to a low level voltage over 10ms and then
releasing it. The EMERG_OFF line can be driven by an OC/OD driver or a button. The circuit is illustrated
as the following figures:
Figure 11: An OC Driver for EMERG_OFF
S2
EMERG_OFF
TVS2
Close to S2
Figure 12: Reference Circuit for EMERG_OFF by Button
Be cautious to use the pin EMERG_OFF. It should only be used under emergent situation. For instance, if
the module is unresponsive or abnormal, the pin EMERG_OFF could be used to shut down the system.
Although turning off the module by EMERG_OFF is fully tested and no error is detected, this operation is
still a big risk as it could cause to destroy the code or data area of the flash memory in the module.
Therefore, it is recommended that PWRKEY or AT command should always be the preferential way to
turn off the system.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 29 / 76
Page 31

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.4.3. Restart
You can restart the module by driving the PWRKEY to a low level voltage for a certain time, which is
similar to the way of turning on module. Before restarting the module, at least 500ms should be delayed
after detecting the low level of VDD_EXT. The restart timing is illustrated as the following figure:
Figure 13: Timing of Restarting System
The module can also be restarted by the PWRKEY after emergency shutdown.
Figure 14: Timing of Restarting System after Emergency Shutdown
NOTE
Before pulling down the EMERG_OFF pin, please ensure that the PWRKEY pin has been released.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 30 / 76
Page 32

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.5. Power Saving Technology
Based on system requirements, there are several actions to drive the module to enter into low current
consumption state. For example, “AT+CFUN” can be used to set module into minimum functionality mode
and DTR hardware interface signal can be used to lead system to sleep mode.
3.5.1. Minimum Functionality Mode
Minimum functionality mode reduces the functionality of the module to a minimum level. The consumption
of the current can be minimized when the slow clocking mode is activated at the same time. The mode is
set with the “AT+CFUN” command which provides the choice of the functionality levels <fun>=0,1,4.
0: Minimum functionality.
1: Full functionality (default).
4: Disable both transmitting and receiving of RF part.
If the module is set to minimum functionality by “AT+CFUN=0”, the RF function and SIM card function
would be disabled. In this case, the UART port is still accessible, but all AT commands related with RF
function or SIM card function will not be available.
If the module has been set by the command with “AT+CFUN=4”, the RF function will be disabled, but the
UART port is still active. In this case, all AT commands related with RF function will not be available.
After the module is set by “AT+CFUN=0” or “AT+CFUN=4”, it can return to full functionality by
“AT+CFUN=1”.
For detailed information about “AT+CFUN”, please refer to the document [1].
3.5.2. Sleep Mode
The sleep mode is disabled by default. You can enable it by “AT+QSCLK=1”. On the other hand, the
default setting is “AT+QSCLK=0” and in this mode, the module cannot enter into sleep mode.
When the module is set by the command “AT+QSCLK=1”, you can control the module to enter into or exit
from the sleep mode through pin DTR. When DTR is set to high level, and there is no on-air or hardware
interrupt such as GPIO interrupt or data on UART port, the module will enter into sleep mode
automatically. In this mode, the module can still receive voice, SMS or GPRS paging from network, but
the UART port does not work.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 31 / 76
Page 33

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.5.3. Wake Up Module from Sleep Mode
When the module is in the sleep mode, the following methods can wake up the module:
If the DTR pin is set to low level, it would wake up the module from the sleep mode.
Receive a voice or GPRS data from network to wake up module.
Receive an SMS from network to wake up module.
NOTE
DTR pin should be kept in low level during communication between the module and DTE.
3.5.4. Summary of State Transition
Table 5: Summary of State Transition
Next Mode
Current Mode
Power Down Normal Mode Sleep Mode
Power Down Use PWRKEY
Use AT command
“AT+QSCLK=1” and pull up
DTR
Normal Mode
Sleep Mode
AT+QPOWD, use PWRKEY
pin, or use EMERG_OFF pin
Use PWRKEY pin, or use
EMERG_OFF pin
Pull down DTR or
incoming voice call or
SMS or GPRS data
3.6. RTC Backup
The RTC (Real Time Clock) can be supplied by an external capacitor or battery (rechargeable or
non-chargeable) through the pin VRTC. A 2.2K resistor has been integrated in the module for current
limiting. A coin-cell battery or a super-cap can be used to backup power supply for RTC.
The following figures show various sample circuits for RTC backup.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 32 / 76
Page 34

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 15: RTC Supplied from a Non-chargeable Battery
Figure 16: RTC Supplied from a Rechargeable Battery
Figure 17: RTC Supplied from a Capacitor
The following figure shows the charging characteristics of a coin-type rechargeable battery
XH414H-IV01E from Seiko.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 33 / 76
Page 35

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 18: Charging Characteristics of Seiko’s XH414H-IV01E
3.7. Serial Interfaces
The module provides two universal asynchronous serial ports: UART port and debug port. The module is
designed as a DCE (Data Communication Equipment), following the traditional DCE-DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment) connection. Autobauding function supports baud rate from 4800bps to 115200bps.
The UART port:
TXD: Send data to RXD of DTE.
RXD: Receive data from TXD of DTE.
RTS: Request to send.
CTS: Clear to send.
DTR: DTE is ready and inform DCE (this pin can wake the module up).
RI: Ring indicator (when the call, SMS, data of the module are coming, the module will output signal
to inform DTE).
DCD: Data carrier detection (the validity of this pin demonstrates the communication link is set up).
NOTE
The module disables hardware flow control by default. When hardware flow control is required, RTS and
CTS should be connected to the host. AT command “AT+IFC=2,2” is used to enable hardware flow
control. AT command “AT+IFC=0,0” is used to disable the hardware flow control. For more details, please
refer to the document [1].
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 34 / 76
Page 36

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The Debug port:
DBG_TXD: Send data to the COM port of computer.
DBG_RXD: Receive data from the COM port of computer.
The logic levels are described in the following table:
Table 6: Logic Levels of the UART Interfaces
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VIL 0 0.3×VDD_EXT V
VIH 0.7×VDD_EXT VDD_EXT V
VOL 0 0.3×VDD_EXT V
VOH 0.7×VDD_EXT VDD_EXT V
Table 7: Pin Definition of the UART Interfaces
Interfaces Pin Name Pin NO. Description
TXD 9 Transmit data
RXD 10 Receive data
RTS 11 Request to send
UART Port
CTS 12 Clear to send
DTR 7 Data terminal ready
DCD 8 Data carrier detection
RI 6 Ring indication
DBG_TXD 31 Transmit data
Debug Port
DBG_RXD 30 Receive data
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 35 / 76
Page 37

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.7.1. UART Port
3.7.1.1. The Features of UART Port
Seven lines on UART interface.
Contain data lines as TXD and RXD, hardware flow control lines as RTS and CTS, other control lines
as DTR, DCD and RI.
Used for AT command, GPRS data, etc.
Support the following communication baud rates: 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400,
57600, 115200, 230400 and 460800bps.
The default setting is autobauding mode. Support the following baud rates for autobauding function:
4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 and 115200bps.
The module disables hardware flow control by default. AT command “AT+IFC=2,2” is used to enable
hardware flow control.
After setting a fixed baud rate or autobauding, please send “AT” string at that rate. The UART port is
ready when it responds “OK”.
Autobauding allows the module to detect the baud rate by receiving the string “AT” from the host or PC
automatically, which gives module flexibility without considering which baud rate is used by the host
controller. Autobauding is enabled by default. To take advantage of the autobauding mode, special
attention should be paid according to the following requirements:
1. Synchronization between DTE and DCE
When DCE (the module) powers on with the autobauding enabled, it is recommended to wait 5~6
seconds before sending the first “AT” characters. After receiving the “OK” response, DTE and DCE are
correctly synchronized.
If the host controller needs URC in the mode of autobauding, it must be synchronized firstly. Otherwise
the URC will be discarded.
2. Restrictions on autobauding operation
The UART port has to be operated at 8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit (factory setting).
The Unsolicited Result Codes like “RDY”, “+CFUN: 1” and “+CPIN: READY” will not be indicated
when the module is turned on with autobauding enabled and not be synchronized.
Any other unsolicited result codes will be sent at the previous baud rate before the module detects
the new baud rate by receiving the “AT” string. The DTE may receive unknown characters after
switching to new baud rate.
It is not recommended to switch to autobauding from a fixed baud rate.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 36 / 76
Page 38

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
NOTE
To ensure reliable communication and avoid any problems caused by undetermined baud rate between
DCE and DTE, it is strongly recommended to configure a fixed baud rate and save it instead of using
autobauding after start-up. For more details, please refer to the section “AT+IPR” in document [1].
3.7.1.2. The Connection of UART
The connection between module and host by UART port is very flexible. Three connection styles are
illustrated as below.
Reference design for Full-Function UART connection is shown as below when it is applied in
modulation-demodulation.
Figure 19: Reference Design for Full-Function UART
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 37 / 76
Page 39

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Three-line connection is shown as below:
Figure 20: Reference Design for UART Port
UART port with hardware flow control is shown as below. This connection will enhance the reliability of the
mass data communication.
Figure 21: Reference Design for UART Port with Hardware Flow Control
3.7.2. Debug and Upgrade Port
Debug port:
Two lines: DBG_TXD and DBG_RXD
Debug port is used for firmware debugging and upgrading, its baud rate must be configured as
921600bps.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 38 / 76
Page 40

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 22: The Connection of Firmware Debugging and Upgrade
NOTE
Because the debug port uses a high baud rate 921600bps configuration, when connecting a PC for
debugging and upgrading, the UART to USB mode is recommended. The test points for debug UART is
recommended to be reserved, for detailed design, please refer to the document [12].
3.7.3. UART Application
VDD_EXT is the reference voltage level for UART of GC65, the 1K resistors is recommended to be added
on the UART lines, the reference circuit is shown as below. This circuit is also applicable in 2.8V or 3.0V
systems.
Figure 23: Level Match Design for 3.3V System
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 39 / 76
Page 41

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The reference design for 5V level match is shown as below. The connection of dotted line can be referred
to the connection of solid line. Please pay attention to the direction of signal. Input dotted line of module
should be referred to input solid line of the module. Output dotted line of module should be referred to
output solid line of the module.
As to the circuit below, VDD_EXT supplies power for the I/O of module, while VCC_MCU supplies power
for the I/O of the peripheral.
Figure 24: Level Match Design for 5V System
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 40 / 76
Page 42

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The following circuit shows a reference design for the communication between module and PC. A RS232
level shifter IC or circuit must be inserted between module and PC, since the UART port does not support
the RS232 level, but the CMOS level only.
Figure 25: Level Match Design for RS-232
NOTE
For three-line UART port, the UART to USB mode can also be used.
3.8. Audio Interfaces
The module provides two analogy audio input channels and two analogy audio output channels.
Table 8: Pin Definition of Audio Interface
Interfaces Pin Name Pin NO. Description
MIC1P 20 Channel 1 microphone positive input
AIN1/AOUT1
MIC1N 19 Channel 1 microphone negative input
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 41 / 76
Page 43

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
SPK1P 22 Channel 1 audio positive output
SPK1N 21 Channel 1 audio negative output
MIC2P 18 Channel 2 microphone positive input
MIC2N 17 Channel 2 microphone negative input
AIN2/AOUT2
SPK2P 16 Channel 2 audio single-ended output
AGND 15 Form a pseudo-differential pair with SPK2P
AIN1 and AIN2 can be used for input of microphone. An electret microphone is usually used. AIN1 and
AIN2 are both differential input channels.
AOUT1 is used for output of the receiver. This channel is typically used for a receiver built into a handset.
AOUT1 channel is a differential channel. If it is used as a speaker, an amplifier should be employed.
AOUT2 is used for output of earphone, which can be used as a single-ended channel. SPK2P and AGND
can establish a pseudo differential mode.
All of these two audio channels support voice and ringtone output, and so on, and can be switched by
“AT+QAUDCH” command. For more details, please refer to the document [1].
Use AT command “AT+QAUDCH” to select audio channel:
0--AIN1/AOUT1 (main audio channel), the default value is 0.
1--AIN2/AOUT2 (auxiliary audio channel), this channel is used for earphone.
For each channel, you can use AT+QMIC to adjust the input gain level of microphone. You can also use
“AT+CLVL” to adjust the output gain level of receiver. “AT+QSIDET” is used to set the side-tone gain level.
For more details, please refer to the document [1].
3.8.1. Decrease TDD Noise and Other Noises
The 47pF capacitor is applied for filtering out 900MHz RF interference when the module is transmitting at
GSM900MHz. Without placing this capacitor, TDD noise could be heard. Moreover, the 10pF capacitor
here is for filtering out 1800MHz RF interference. However, the resonant frequency point of a capacitor
largely depends on the material and production technique. Therefore, you would have to discuss with its
capacitor vendor to choose the most suitable capacitor for filtering out GSM850MHz, GSM900MHz,
DCS1800MHz and PCS1900MHz separately.
The severity degree of the RF interference in the voice channel during GSM transmitting period largely
depends on the application design. In some cases, GSM900 TDD noise is more severe; while in other
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 42 / 76
Page 44

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
cases, DCS1800 TDD noise is more obvious. Therefore, you can have a choice based on test results.
Sometimes, even no RF filtering capacitor is required.
The capacitor which is used for filtering out RF noise should be close to audio interface. Audio alignment
should be as short as possible.
In order to decrease radio or other signal interference, the position of RF antenna should be kept away
from audio interface and audio alignment. Power alignment and audio alignment should not be parallel,
and power alignment should be far away from audio alignment.
The differential audio traces have to be placed according to the differential signal layout rule.
3.8.2. Microphone Interfaces Design
AIN1 and AIN2 channels come with internal bias supply for external electret microphone. A reference
circuit is shown in the following figure.
Figure 26: Reference Design for AIN1&AIN2
NOTE
The ESD protection components on the MIC channels are strongly recommended.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 43 / 76
Page 45

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.8.3. Receiver Interface Design
Figure 27: Reference Receiver Interface Design of AOUT1
Figure 28: Speaker Interface with Amplifier Configuration of AOUT1
Texas Instruments TPA6205A1 is recommended for a suitable differential audio amplifier. There are
plenty of excellent audio amplifiers in the market.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 44 / 76
Page 46

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 29: Reference Receiver Interface Design of AOUT2
Figure 30: Speaker Interface with Amplifier Configuration of AOUT2
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 45 / 76
Page 47

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.8.4. Earphone Interface Design
Figure 31: Earphone Interface Design
3.8.5. Audio Characteristics
Table 9: Typical Electret Microphone Characteristics
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Working Voltage 1.2 1.5 2.0 V
Working Current 200 500 uA
External Microphone Load Resistance 2.2 kΩ
Table 10: Typical Audio Output Characteristics
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Load resistance
16
Ω
Single-ended
AOUT1
Ref level 0 1.3 Vpp
(SPK1)
Load resistance 16 Ω
Differential
Ref level 0 2.6 Vpp
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 46 / 76
Page 48

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
AOUT2
(SPK2)
Single-ended
Maximum Driving Current
Limit of SPK1 and SPK2
Load resistance 32 Ω
Reference level 0 1.0 Vpp
SPK1 80 mA
SPK2 25 mA
3.9. SIM Card Interface
3.9.1. SIM Card Application
The SIM interface supports the functionality of the GSM Phase 1 specification and also supports the
functionality of the new GSM Phase 2+ specification for FAST 64 kbps SIM card, which is intended to use
with a SIM application Tool-kit.
The SIM interface is powered by an internal regulator in the module. Both 1.8V and 3.0V SIM Cards are
supported.
Table 11: Pin Definition of the SIM Interface
Pin Name Pin NO. Description
23 SIM_VDD Supply power for SIM card. Automatic detection of SIM card voltage.
24 SIM_RST SIM card reset.
25 SIM_DATA SIM card data I/O.
26 SIM_CLK SIM card clock.
27 SIM_GND SIM card ground.
28 SIM_PRESENCE SIM card detection
Figure 32 is the reference circuit for SIM interface, and here an 8-pin SIM card holder is used.
The pin SIM_PRESENCE is used to detect whether the tray of the Molex SIM socket, which is used for
holding SIM card, is presented in the card socket. When the tray is inserted in the socket,
SIM_PRESENCE is in low level. Regardless of the SIM card is in the tray or not, the change of
SIM_PRESENCE level from high to low prompts the module to initialize SIM card. In default configuration,
SIM card detection function is disabled. Customer’s application can use “AT+QSIMDET=1,0” and
“AT+QSIMDET=0,0” to switch on and off the SIM card detection function. For details of this AT command,
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 47 / 76
Page 49

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
please refer to document [1]. When “AT+QSIMDET=1,0” is set and the tray with SIM card is removed
from SIM socket, the following URC will be presented:
+CPIN: NOT INSERTED
When the tray with SIM card is inserted into SIM socket again and the module finishes
reinitializing SIM card, the following URC will be presented:
+CPIN: READY
Call Ready
Figure 32: Reference Circuit for 8-pin SIM Card Holder
NOTE
1. Please do not use “AT+QSIMDET=1,1” when circuit in Figure 32 is adopted, which can cause to
reinitialize SIM card.
2. When SIM card detection function is used, SIM_PRESENCE pin must be pulled up by an external
resistor. If unused, please keep this pin open.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 48 / 76
Page 50

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The reference circuit for a 6-pin SIM card socket is illustrated as the following figure:
Figure 33: Reference Circuit for 6-pin SIM Card Holder
In order to enhance the reliability and availability of the SIM card in application. Please follow the criteria
below in the SIM circuit design.
Keep layout of SIM card as close as possible to the module. Assure the possibility of the length of the
trace is less than 100mm.
Keep SIM card signal away from RF and VBAT alignment.
Assure the ground between module and SIM cassette short and wide. Keep the width of ground no
less than 0.5mm to maintain the same electric potential. The decouple capacitor of SIM_VDD is less
than 1uF and must be near to SIM cassette.
To avoid cross talk between SIM_DATA and SIM_CLK. Keep them away with each other and shield
them with surrounded ground.
In order to offer good ESD protection, it is recommended to add TVS such as WILL
(http://www.willsemi.com/) ESDA6V8AV6. The 22Ω resistors should be connected in series between
the module and the SIM card so as to suppress the EMI spurious transmission and enhance the ESD
protection. Please to be noted that the SIM peripheral circuit should be close to the SIM card socket.
Place the RF bypass capacitors (33pF) close to the SIM card on all signals line for improving EMI.
3.9.2. SIM Cassette
As to the 6-pin SIM card holder, it is recommended to use Amphenol C707 10M006 512 2. Please visit
http://www.amphenol.com for more information.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 49 / 76
Page 51

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 34: Amphenol C707 10M006 512 2 SIM Card Holder
Table 12: Pin Description of Amphenol SIM Card Holder
Name Pin Description
SIM_VDD C1 SIM card power supply
SIM_RST C2 SIM card reset
SIM_CLK C3 SIM card clock
GND C5 Ground
VPP C6 Not connected
SIM_DATA C7 SIM card data I/O
For 8-pin SIM card holder, it is recommended to use Molex 91228. Please visit http://www.molex.com for
more information.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 50 / 76
Page 52

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 35: Molex 91228 SIM Card Holder
Table 13: Pin Description of Molex SIM Card Holder
Name Pin Description
SIM_VDD C1 SIM card power supply
SIM_RST C2 SIM card reset
SIM_CLK C3 SIM card clock
SIM_PRESENCE C4 SIM card presence detection
GND C5 Ground
VPP C6 Not connect
SIM_DATA C7 SIM card data I/O
SIM_DETECT C8
Pull down GND with external circuit. When the
tray is presented, C4 is connected to C8.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 51 / 76
Page 53

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
3.10. PCM Interface
GC65 has reserved PCM interface, it is used as digital audio transmission between module and customer
device. This interface composes PCM_CLK, PCM_SYNC, PCM_IN and PCM_OUT signal lines. PCM
function is not supported at present.
3.11. Behaviors of the RI
Table 14: Behaviours of the RI
State RI Response
Standby HIGH
Change to LOW, then:
1. Change to HIGH when call is established.
Voice Call
2. Use ATH to hang up the call, RI changes to HIGH.
3. Calling part hangs up, RI changes to HIGH first, and changes to LOW for
120ms indicating “NO CARRIER” as an URC, then changes to HIGH again.
4. Change to HIGH when SMS is received.
SMS
URC
When a new SMS comes, the RI changes to LOW and holds low level for about
120ms, then changes to HIGH.
Certain URCs can trigger 120ms low level on RI. For more details, please refer to the
document [10].
If the module is used as a caller, the RI would maintain high unless the URC or SMS is received. On the
other hand, when it is used as a receiver, the timing of the RI is shown below:
Figure 36: RI Behaviour of Voice Calling as a Receiver
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 52 / 76
Page 54

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 37: RI Behaviour as a Caller
Figure 38: RI Behaviour of URC or SMS Received
3.12. Network Status Indication
The NETLIGHT signal can be used to drive a network status indicator LED. The working state of this pin is
listed in the following table:
Table 15: Working State of the NETLIGHT
State Module Function
Off The module is not running.
64ms On/ 800ms Off The module is not synchronized with network.
64ms On/ 2000ms Off The module is synchronized with network.
64ms On/ 600ms Off The GPRS data transmission after dialing the PPP connection.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 53 / 76
Page 55

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
A reference circuit is shown as below:
Figure 39: Reference Design for NETLIGHT
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 54 / 76
Page 56

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
4
The Pin 38 is the RF antenna pad. The RF interface has an impedance of 50Ω.
Table 16: Pin Definition of the RF_ANT
Pin Name Pin NO. Description
GND 37 Ground
RF_ANT 38 RF antenna pad
GND 39 Ground
Antenna Interface
4.1. RF Reference Design
The reference design for RF is shown as below:
Figure 40: Reference Design for RF
GC65 provides an RF antenna pad for antenna connection. The RF trace in host PCB connected to the
module RF antenna pad should be coplanar waveguide line or microstrip line, whose characteristic
impedance should be close to 50Ω. GC65 comes with grounding pads which are next to the antenna pad
in order to give a better grounding. Besides, a ∏ type match circuit is suggested to be used to adjust the
RF performance.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 55 / 76
Page 57

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
To minimize the loss on the RF trace and RF cable, take design into account carefully. It is recommended
that the insertion loss should meet the following requirements:
GSM850/EGSM900 is <1dB.
DCS1800/PCS1900 is <1.5dB.
4.2. RF Output Power
Table 17: The Module Conducted RF Output Power
Frequency Max. Min.
GSM850 33dBm±2dB 5dBm±5dB
EGSM900 33dBm±2dB 5dBm±5dB
DCS1800 30dBm±2dB 0dBm±5dB
PCS1900 30dBm±2dB 0dBm±5dB
4.3. RF Receiving Sensitivity
Table 18: The Module Conducted RF Receiving Sensitivity
Frequency Receive Sensitivity
GSM850 < -108dBm
EGSM900 < -108dBm
DCS1800 < -108dBm
PCS1900 < -108dBm
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 56 / 76
Page 58

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
4.4. Operating Frequencies
Table 19: The Module Operating Frequencies
Frequency Receive Transmit ARFCH
GSM850 869~894MHz 824~849MHz 128~251
EGSM900 925~960MHz 880~915MHz 0~124, 975~1023
DCS1800 1805~1880MHz 1710~1785MHz 512~885
PCS1900 1930~1990MHz 1850~1910MHz 512~810
4.5. RF Cable Soldering
Soldering the RF cable to RF pad of module correctly will reduce the loss on the path of RF, please refer
to the following example of RF soldering.
Figure 41: RF Soldering Sample
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 57 / 76
Page 59

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
5
Electrical, Reliability and Radio
Characteristics
5.1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings for power supply and voltage on digital and analog pins of module are listed in
the following table:
Table 20: Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VBAT -0.3 5.0 V
Peak current of power supply 0 2 A
RMS current of power supply (during one TDMA- frame) 0 0.8 A
Voltage at digital pins -0.3 3.3 V
Voltage at analog pins -0.3 3.3 V
Voltage at digital/analog pins in power down mode -0.25 0.25 V
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 58 / 76
Page 60

50
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
5.2. Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is listed in the following table:
Table 21: Operating Temperature
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Normal Temperature -35 +25 +80
Restricted Operation -40 ~ -35 +80 ~ +85
Storage Temperature -45 +90
℃
℃
℃
5.3. Power Supply Ratings
Table 22: The Module Power Supply Ratings
Parameter Description Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Voltage must stay within the
min/max values, including
voltage drop, ripple, and
spikes.
Maximum power control level
on GSM850 and GSM900.
3.3 4.0 4.6 V
400 mV
VBAT
Supply voltage
Voltage drop
during
transmitting
burst
Voltage ripple
Average supply
current
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 59 / 76
Maximum power control level
on GSM850 and GSM900
@ f<200kHz
@ f>200kHz
Power down mode
Sleep mode @ DRX=5
Minimum functionality mode
AT+CFUN=0
Idle mode
Sleep mode
AT+CFUN=4
Idle mode
120
1.3
21
0.8
21
20
mV
mV
uA
mA
mA
mA
mA
Page 61

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
IVBAT
Peak supply
current (during
transmission
slot)
NOTES
1)
1.
Power control level PCL 5.
2)
2.
Power control level PCL 0.
Sleep mode 0.8 mA
Talk mode
GSM850/EGSM9001)
DCS1800/PCS19002)
DATA mode, GPRS (3Rx/2Tx)
GSM850/EGSM9001)
DCS1800/PCS19002)
DATA mode, GPRS (4Rx/1Tx)
GSM850/EGSM9001)
DCS1800/PCS19002)
Maximum power control level
on GSM850/GSM900.
1.6 1.8 A
211/208
156/165
372/367
245/285
224/220
162/182
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
5.4. Current Consumption
The values of current consumption are shown as below:
Table 23: The Module Current Consumption
Condition Current Consumption
Voice Call
GSM850 @power level #5 <300mA,Typical 211mA
@power level #12,Typical 86mA
@power level #19,Typical 64mA
GSM900 @power level #5 <300mA,Typical 208mA
@power level #12,Typical 85mA
@power level #19,Typical 64mA
DCS1800 @power level #0 <250mA,Typical 156mA
@power level #7,Typical 75mA
@power level #15,Typical 64mA
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 60 / 76
Page 62

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
PCS1900 @power level #0 <250mA,Typical 165mA
@power level #7,Typical 80mA
@power level #15,Typical 64mA
GPRS Data
DATA mode, GPRS ( 3 Rx/2 Tx ) CLASS 10
GSM850 @power level #5 <550mA,Typical 372mA
@power level #12,Typical 132mA
@power level #19,Typical 90mA
EGSM 900 @power level #5 <550mA,Typical 367mA
@power level #12,Typical 134mA
@power level #19,Typical 92mA
DCS 1800 @power level #0 <450mA,Typical 245mA
@power level #7,Typical 113mA
@power level #15,Typical 90mA
PCS 1900 @power level #0 <450mA,Typical 285mA
@power level #7,Typical 121mA
@power level #15,Typical 90mA
DATA mode, GPRS ( 4 Rx/1 Tx ) CLASS 10
GSM850 @power level #5 <350mA,Typical 224mA
@power level #12,Typical 103mA
@power level #19,Typical 82mA
EGSM 900 @power level #5 <350mA,Typical 220mA
@power level #12,Typical103mA
@power level #19,Typical 82mA
DCS 1800 @power level #0 <300mA,Typical 162mA
@power level #7,Typical 96mA
@power level #15,Typical 85mA
PCS 1900 @power level #0 <300mA,Typical 182mA
@power level #7,Typical 100mA
@power level #15,Typical 85mA
5.5. Electro-static Discharge
Although the GSM engine is generally protected against Electro-static Discharge (ESD), ESD protection
precautions should still be emphasized. Proper ESD handling and packaging procedures must be applied
throughout the processing, handling and operation of any applications using the module.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 61 / 76
Page 63

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
The measured ESD values of module are shown as the following table:
Table 24: The ESD Endurance (Temperature: 25℃, Humidity: 45 %)
Tested Point Contact Discharge Air Discharge
VBAT/GND
±6KV ±12KV
RF_ANT ±4KV ±12KV
RXD/TXD ±2KV ±4KV
Others ±0.5KV ±1KV
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 62 / 76
Page 64

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
6
This chapter describes the mechanical dimensions of the module.
Mechanical Dimensions
6.1. Mechanical Dimensions of Module
Figure 42: GC65 Module Top and Side Dimensions (Unit: mm)
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 63 / 76
Page 65

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 43: GC65 Module Bottom Dimensions (Unit: mm)
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 64 / 76
Page 66

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
6.2. Recommended Footprint
k
ee
po
ut
ar
ea
Figure 44: Recommended Footprint (Unit: mm)
NOTES
1. In order to maintain the module, keep about 3mm between the module and other components in the
host PCB.
2. Keep out area in above figure is forbidden to pour ground copper. Since the RF test point is in this
area, please avoid generating parasitic capacitance between RF test point and ground.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 65 / 76
Page 67

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
6.3. Top View of the Module
Figure 45: Top View of the Module
6.4. Bottom View of the Module
Figure 46: Bottom View of the Module
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 66 / 76
Page 68

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
7
Storage and Manufacturing
7.1. Storage
GC65 module is distributed in a vacuum-sealed bag. The restriction for storage is shown as below.
Shelf life in the vacuum-sealed bag: 12 months at environments of <40℃ temperature and <90%RH.
After the vacuum-sealed bag is opened, devices that need to be mounted directly must be:
Mounted within 72 hours at the factory environment of ≤30℃ temperature and <60% RH.
Stored at <10% RH.
Devices require baking before mounting, if any circumstance below occurs.
When the ambient temperature is 23℃±5℃, humidity indication card shows the humidity is >10%
before opening the vacuum-sealed bag.
If ambient temperature is <30℃ and the humidity is <60%, the devices have not been mounted
during 72hours.
Stored at >10% RH after opening the vacuum-sealed bag.
If baking is required, devices should be baked for 48 hours at 125℃±5℃.
NOTE
As plastic container cannot be subjected to high temperature, devices must be removed before high
temperature (125℃) bake. If shorter bake times are desired, please refer to the IPC/JEDECJ-STD-033 for
bake procedure.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 67 / 76
Page 69

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
7.2. Soldering
The squeegee should push the paste on the surface of the stencil that makes the paste fill the stencil
openings and penetrate to the PCB. The force on the squeegee should be adjusted so as to produce a
clean stencil surface on a single pass. To ensure the module soldering quality, the thickness of stencil at
the hole of the module pads should be 0.2 mm for GC65.
Figure 47: The Picture of Printing Paste
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 68 / 76
Page 70

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
It is suggested that peak reflow temperature is from 235 ºC to 245ºC (for SnAg3.0Cu0.5 alloy). Absolute
max reflow temperature is 260ºC. To avoid damaging the module when it was repeatedly heated, it is
suggested that the module should be mounted after the first panel has been reflowed. The following
picture is the actual diagram which we have operated.
Figure 48: Ramp-Soak-Spike Reflow Profile
7.3. Packaging
The modules are stored inside a vacuum-sealed bag which is ESD-protected. It should not be opened
until the devices are ready to be soldered onto the application.
7.3.1. Tape and Reel Packaging
The reel is 330mm in diameter and each reel contains 250 modules.
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 69 / 76
Page 71

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Figure 49: Dimensions of Tape
Out direction
Plastic tray
Figure 50: Dimensions of Reel
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 70 / 76
Page 72

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
8
Table 25: Related Documents
SN Document Name Remark
[1] GC65_AT_Commands_Manual AT commands manual
[2] ITU-T Draft new recommendation V.25ter Serial asynchronous automatic dialing and control
[3] GSM 07.07
[4] GSM 07.10 Support GSM 07.10 multiplexing protocol
[5] GSM 07.05
Appendix A Reference
Digital cellular telecommunications (Phase 2+); AT
command set for GSM Mobile Equipment (ME)
Digital cellular telecommunications (Phase 2+); Use
of Data Terminal Equipment–Data Circuit
terminating Equipment (DTE–DCE) interface for
Short Message Service (SMS) and Cell Broadcast
Service (CBS)
Digital cellular telecommunications (Phase 2+);
[6] GSM 11.14
[7] GSM 11.11
[8] GSM 03.38
[9] GSM 11.10
[10] GSM_UART_AN UART port application note
[11] M10_EVB_UGD M10 EVB user guide
[12] GSM_FW_Upgrade_AN01 GSM Firmware upgrade application note
Specification of the SIM application toolkit for the
Subscriber Identity module–Mobile Equipment
(SIM–ME) interface
Digital cellular telecommunications (Phase 2+);
Specification of the Subscriber Identity module –
Mobile Equipment (SIM–ME) interface
Digital cellular telecommunications (Phase 2+);
Alphabets and language-specific information
Digital cellular telecommunications (Phase 2);
Mobile Station (MS) conformance specification; Part
1: Conformance specification
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 71 / 76
Page 73

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Table 26: Terms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
AMR Adaptive Multi-Rate
ARP Antenna Reference Point
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
BER Bit Error Rate
BOM Bill of Material
BTS Base Transceiver Station
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CS Coding Scheme
CSD Circuit Switched Data
CTS Clear to Send
DRX Discontinuous Reception
DCE Data Communications Equipment (typically module)
DTE Data Terminal Equipment (typically computer, external controller)
DTR Data Terminal Ready
DTX Discontinuous Transmission
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
EGSM Enhanced GSM
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
EMI Electromagnetic Interference
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
ETS European Telecommunication Standard
FCC Federal Communications Commission (U.S.)
FDMA Frequency Division Multiple Access
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 72 / 76
Page 74

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
FR Full Rate
FTP File Transfer Protocol
GMSK Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
HR Half Rate
HTTP Hypertext Transport Protocol
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
MO Mobile Originated
MS Mobile Station (GSM engine)
MT Mobile Terminated
PAP Password Authentication Protocol
PBCCH Packet Switched Broadcast Control Channel
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PDU Protocol Data Unit
PDP Packet Data Protocol
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
RF Radio Frequency
RMS Root Mean Square (value)
RTC Real Time Clock
RX Receive Direction
SIM Subscriber Identification Module
SMS Short Message Service
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
TDMA Time Division Multiple Access
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 73 / 76
Page 75

GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
TE Terminal Equipment
TX Transmitting Direction
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver &Transmitter
UDP User Datagram Protocol
URC Unsolicited Result Code
USSD Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Phonebook Abbreviations
FD SIM Fix Dialing Phonebook
LD SIM Last Dialing Phonebook (list of numbers most recently dialed)
ON SIM (or ME) Own Numbers (MSISDNs) List
SM SIM Phonebook
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 74 / 76
Page 76

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
9
Four coding schemes are used in GPRS protocol. The differences between them are shown in the
following table:
Table 27: Description of Different Coding Schemes
Scheme
CS-1 1/2 3 3 181 40 4 456 0 9.05
CS-2 2/3 3 6 268 16 4 588 132 13.4
CS-3 3/4 3 6 312 16 4 676 220 15.6
CS-4 1 3 12 428 16 - 456 - 21.4
Appendix B GPRS Coding Scheme
Radio
Block
excl.USF
and BCS
BCS Tail
Coded
Bits
Punctured
Bits
Code
Rate
USF
Pre-
coded
USF
Data
Rate
Kb/s
Radio block structure of CS-1, CS-2 and CS-3 is shown as the figure below:
USF
Rate 1/2 convolutional coding
Radio Block
456 bits
Puncturing
BCS
Figure 51: Radio Block Structure of CS-1, CS-2 and CS-3
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 75 / 76
Page 77

Radio Block
GSM/GPRS Module Series
GC65 Hardware Design
Radio block structure of CS-4 is shown as the following figure:
USF
Block
Code
No coding
BCS
456 bits
Figure 52: Radio Block Structure of CS-4
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 76 / 76
Page 78

GC65 Hardware Design
GSM/GPRS Module Series
10
Twenty-nine classes of GPRS multi-slot modes are defined for MS in GPRS specification. Multi-slot
classes are product dependant, and determine the maximum achievable data rates in both the uplink and
downlink directions. Written as 3+1 or 2+2, the first number indicates the amount of downlink timeslots,
while the second number indicates the amount of uplink timeslots. The active slots determine the total
number of slots the GPRS device can use simultaneously for both uplink and downlink communications.
The description of different multi-slot classes is shown in the following table:
Table 28: GPRS Multi-slot Classes
Multislot Class Downlink Slots Uplink Slots Active Slots
1 1 1 2
2 2 1 3
Appendix C GPRS Multi-slot Class
3 2 2 3
4 3 1 4
5 2 2 4
6 3 2 4
7 3 3 4
8 4 1 5
9 3 2 5
10 4 2 5
11 4 3 5
12 4 4 5
GC65_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 77 / 76
 Loading...
Loading...