Page 1

A Guide to Quark Publishing
Platform 9.5.1
Page 2

ÍNDICE
Índice
Introduction...................................................................................................8
Where we're coming from.....................................................................................................8
Conventions in this book.......................................................................................................8
About Quark Publishing Platform............................................................10
Platform concepts................................................................................................................11
Platform components...........................................................................................................12
Platform architecture..........................................................................................................13
Platform features.................................................................................................................14
Configuration..............................................................................................16
Administration client...........................................................................................................16
System area............................................................................................................................17
Content Model area................................................................................................................17
Workflow area........................................................................................................................17
Users and Groups area...........................................................................................................17
Configuring storage options................................................................................................17
Adding repositories................................................................................................................18
Deleting repositories..............................................................................................................18
Working with content types................................................................................................18
Working with collection types...............................................................................................20
Working with attributes......................................................................................................20
Defining attributes.................................................................................................................20
Adding constraints to attributes.............................................................................................26
Working with relationships.................................................................................................28
Working with workflows.....................................................................................................29
Creating a workflow..............................................................................................................29
Working with statuses............................................................................................................30
Working with forms.............................................................................................................31
Defining Roles and Privileges.............................................................................................32
Roles and Privileges..............................................................................................................32
Creating and deleting users ...............................................................................................33
Managing user lists with LDAP............................................................................................34
Creating and deleting groups..............................................................................................38
Configuring Redline colors.................................................................................................39
Maintenance and asset management.........................................................41
Monitoring user activity and logging off users.................................................................41
ii | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 3

Deleting assets......................................................................................................................42
Archiving assets....................................................................................................................42
Restoring assets....................................................................................................................43
User interface...............................................................................................45
Roles, views, and content structure overview....................................................................45
The Workspace Browser window.......................................................................................45
Workspace Browser window...............................................................................................45
Workspace toolbar.................................................................................................................47
View display options..............................................................................................................51
Icon columns..........................................................................................................................56
Preview pane..........................................................................................................................57
Menus (Quark Publishing Platform Client)......................................................................58
Quark Publishing Platform Client menu (Mac OS only).......................................................59
File menu...............................................................................................................................59
Edit menu...............................................................................................................................59
View menu.............................................................................................................................60
Actions menu.........................................................................................................................60
Go To menu...........................................................................................................................61
Search menu...........................................................................................................................61
Window menu (Mac OS).......................................................................................................62
Help menu..............................................................................................................................62
Menus (QCD).......................................................................................................................62
QuarkCopyDesk menu (Mac OS only)..................................................................................62
Platform menu.......................................................................................................................62
Menus (QXP)........................................................................................................................63
QuarkXPress menu (Mac OS only).......................................................................................63
Utilities menu.........................................................................................................................63
Window menu........................................................................................................................64
Platform menu.......................................................................................................................64
ÍNDICE
Client tasks ..................................................................................................66
Understanding how Quark Publishing Platform works..................................................66
Quark Publishing Platform Server and Quark Publishing Platform client applications........66
Administering a Quark Publishing Platform workflow.........................................................66
Using XML Author with Quark Publishing Platform...........................................................66
Assigning and managing assets from QXP...........................................................................67
Routing and tracking..............................................................................................................71
Automating output and export...............................................................................................71
Archiving and restoring.........................................................................................................71
Logging on............................................................................................................................72
Creating assets (QCD and QXP)........................................................................................73
Working with collections.....................................................................................................73
Working with collection templates........................................................................................73
Creating a collection..............................................................................................................74
Editing collections.................................................................................................................81
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | iii
Page 4

ÍNDICE
Duplicating a collection.........................................................................................................82
Deleting a collection..............................................................................................................82
Appending content (QCD and QXP).................................................................................83
Checking in assets................................................................................................................83
Check In command................................................................................................................83
Check In Other command .....................................................................................................85
Check in multiple assets........................................................................................................85
Check In Project With Pictures (QXP only)..........................................................................86
Assigning assets....................................................................................................................86
Assigning assets: Quark Publishing Platform Client.............................................................87
Assigning assets: QXP...........................................................................................................88
Performing a search.............................................................................................................88
Using the Quick Search feature.............................................................................................90
Performing a nested search....................................................................................................91
Performing a full-text search.................................................................................................92
Performing a collection search..............................................................................................93
Search from here....................................................................................................................94
Working with saved searches.................................................................................................94
Managing searches.................................................................................................................94
Specifying search result display options ...............................................................................95
Checking out assets..............................................................................................................95
Checking out an asset: Quark Publishing Platform Client....................................................96
Checking out an asset: QCD..................................................................................................96
Checking out an article or project: QXP................................................................................96
Checking out a project with attachments: QXP.....................................................................96
Checking out and editing pictures: QXP & QCD..................................................................97
Using Advanced search: QCD and QXP ..............................................................................97
Cancelling a Checkout ..........................................................................................................98
Working with templates......................................................................................................98
Attaching content to layouts...............................................................................................98
Primary and secondary attachments......................................................................................99
Attaching article components by dragging..........................................................................100
Attaching articles by dragging.............................................................................................100
Attaching articles by assigning............................................................................................102
Attaching text files to layouts..............................................................................................102
Attaching pictures to layouts...............................................................................................103
Attaching App Studio assets................................................................................................103
Attaching multimedia assets to reflow articles....................................................................103
Tracking attachments...........................................................................................................103
Detaching components.........................................................................................................104
Attaching digital assets to layouts.......................................................................................104
Replacing article geometry...............................................................................................105
Working with libraries......................................................................................................105
Using Read-Only to view an asset....................................................................................106
Publishing assets................................................................................................................106
Viewing and editing attribute information......................................................................107
iv | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 5

Saving a revision of an asset..............................................................................................108
Customizing the search results pane................................................................................108
Setting Quark Publishing Platform Client preferences.................................................109
General pane........................................................................................................................109
Workspace pane...................................................................................................................111
Startup Mode pane...............................................................................................................112
Archive pane........................................................................................................................113
Setting Quark Publishing Platform preferences: QXP .................................................114
QXP preferences: General pane...........................................................................................114
QXP preferences: Workspace pane......................................................................................116
QXP preferences: Project and Attachments pane................................................................118
QXP preferences Article pane.............................................................................................119
QXP preferences: Alerts pane..............................................................................................119
Setting Quark Publishing Platform preferences: QCD..................................................121
QCD preferences: General pane..........................................................................................121
QCD preferences: Workspace pane.....................................................................................124
QCD preferences: Article pane............................................................................................125
QCD preferences: Alerts pane.............................................................................................126
ÍNDICE
Redlining....................................................................................................127
Using Redline controls.......................................................................................................127
Notes...........................................................................................................129
Working with notes............................................................................................................129
Opening and closing notes...................................................................................................129
Showing and hiding notes....................................................................................................129
Deleting notes......................................................................................................................129
Converting between notes and text......................................................................................130
Viewing notes by author, date, name, or color....................................................................130
Moving and resizing notes...................................................................................................130
Printing notes.......................................................................................................................130
Notes in PDFs......................................................................................................................130
Web Client.................................................................................................131
Logging on with Quark Publishing Platform Web Client.............................................131
Changing password...........................................................................................................132
Customize search results display......................................................................................132
Searching in Web Client....................................................................................................133
Archiving and Restoring in Web Client...........................................................................133
Using display options.........................................................................................................133
Previewing assets with Quark Publishing Platform Web Client...................................135
Using the Publish features.................................................................................................135
Editing asset attributes......................................................................................................135
Viewing asset revisions......................................................................................................136
Viewing relationship information.....................................................................................137
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | v
Page 6

ÍNDICE
Creating articles in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client........................................137
Creating projects from templates in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client............138
Editing articles in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client...........................................138
Editing text components......................................................................................................139
Editing picture components.................................................................................................141
Managing components.........................................................................................................141
Finding and replacing text in articles...................................................................................142
Adjusting background color for editing...............................................................................143
Changing text size for editing..............................................................................................144
Working with Rubi...............................................................................................................144
Working with Grouped Characters......................................................................................145
Using notes in articles..........................................................................................................146
Editing projects in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client..........................................146
Callouts in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client.......................................................146
Checking in Other files......................................................................................................146
Editing Other Files............................................................................................................147
Using the Web Client Preview pane.................................................................................147
Setting Quark Publishing Platform Web Client preferences.........................................147
Script Manager .........................................................................................150
Quark Publishing Platform Script Manager configuration..........................................150
Working with Quark Publishing Platform Script Manager..........................................150
Logging on with Quark Publishing Platform Script Manager.............................................151
Creating a script...................................................................................................................152
Importing a script.................................................................................................................152
Deleting and exporting scripts.............................................................................................153
Writing, editing, and triggering a script..........................................................................154
Accessing Quark Publishing Platform Server objects.........................................................154
Loading a script in a script...................................................................................................154
Logging and debugging scripts............................................................................................154
Using utility methods in scripts...........................................................................................155
Triggering a script................................................................................................................156
Quark Publishing Platform event-based script example......................................................157
Executing a script manually.................................................................................................158
Privileges....................................................................................................159
Content privileges..............................................................................................................160
Content privileges: General.................................................................................................160
Content privileges: Edit Attributes......................................................................................161
Content privileges: Job Jackets............................................................................................161
Content privileges: Edit Redlining......................................................................................162
Content privileges: Article Components..............................................................................162
Content privileges: Edit Pictures.........................................................................................162
Content privileges: Editing..................................................................................................162
Application privileges........................................................................................................163
Application privileges: Administration...............................................................................163
vi | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 7

Application privileges: Workspace......................................................................................163
Glossary......................................................................................................165
Legal notices..............................................................................................175
ÍNDICE
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | vii
Page 8

INTRODUCTION
Introduction
Quark® Publishing Platform™ is a collection of networked applications for creative workgroups.
This Guide provides a high-level introduction to the Quark Publishing Platform Client application
and the functionality Quark Publishing Platform adds to QuarkXPress® and QuarkCopyDesk®.
You can use this Guide to learn what each feature is, what it's for, how you can put it to work for
you, and where you can find it. For information about using Quark Publishing Platform with XML
Author, see the Quark XML Author for Quark Publishing Platform documentation.
Where we're coming from
This book assumes you are familiar with your computer and know how to:
• Launch an application
• Open, save, and close files
• Use menus, dialog boxes, and palettes
• Use the mouse, keyboard commands, and modifier keys
If you needhelp performing any of these tasks, consultthe documentationresources (user or reference
guides) provided with your computer.
Conventions in this book
Formatting conventions in this guide highlight information to help you quickly find what you need.
• Bold type style: The names of all dialog boxes, fields, and other controls are set in bold type. For
example: "Click Storage in the Administration pane."
• References: In descriptionsof features, parenthetical references guide you inaccessing those features.
For example: "The System Storage controls (Administration pane) let you designate asset storage."
• Arrows: You will often see arrows (>), which map the path to a feature. For example: "Choose
Administration > User Profiles to add a user."
• Icons: Although many tools and buttons are referenced by name, which you can see by displaying
ToolTips, in some cases icons are shown for easy identification.
• Cross-platform issues: Somelabels, buttons,key combinations, and other aspects of QuarkPublishing
Platform client applications differ between Mac OS® and Windows® because of user interface
conventions or other factors. In such cases, both the Mac OS and Windows versions are presented,
separated by a slash, with the Mac OS version presented first. For example, if the Mac OSversion of
8 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 9

INTRODUCTION
a button is labeled Select, and the Windows version is labeled Browse, you are directed to "Click
Select/Browse." More complex cross-platform differences are mentioned in notes or parenthetical
statements.
Notes provide helpful information about particular features and general techniques for using the
software.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 9
Page 10

ABOUT QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM
About Quark Publishing Platform
Quark Publishing Platform is a highly configurable solution for complete, automated, end-to-end
multichannel publishing.Quark Publishing Platform is purpose-built to support end-to-end publishing
needs, from complete manual publishing systems to highly automated workflows.
The Platform consists of a set of core modules that can be combined in various ways and integrated
with third-party systems to accommodate almost any workflow. Its capabilities can be described in
terms of content creation, management, publishing, and delivery.
Create
Quark Publishing Platform lets you:
• Design professional templates for different publications
• Author structured content in the familiar Microsoft Word environment
• Integrate content from databases with other forms of content
• Utilize multimedia content such as video, audio, and slideshows
Manage
Quark Publishing Platform provides:
• Workflow and collaboration tools
• Task and update notifications
• Component management
• Automated checks
• Version control
Publish
With Quark Publishing Platform, you can:
• Automatically assemble componentsof varioustypes from various sources into sophisticated layouts
• Automatically publish those layouts in a variety of formats for a variety of devices
Deliver
The automation features built into Quark Publishing Platform make it easyfor you to deliver content
to your content consumers in both public and secure environments.
10 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 11

Platform concepts
In order to use Quark Publishing Platform effectively, you should understand some of the key
concepts that it uses.
Assets: An asset is a unit of independent content. Quark Publishing Platform stores, tracks, and
manages assets along with their metadata. The Platformalso provides version control of assets, with
both major and minor versions. Versioning policy can be configured for each content type within a
collection. The Platform also supports multiple renditions of assets (such as previews, thumbnails,
XML representations, and so forth), storing renditions along with each version of their original
assets. Assets are stored in a configurable repository; the default repository on a file server, but
pluggable third-party repositories are also supported.
Content types: Every asset has a content type. The content type concept is a unified mechanism for
associating metadata, workflows, relationships, privileges, and rendering and publishing actions
with different types of content. The Platform can automatically detect a variety of different content
types, including pictures, QuarkXPress projects, DITA topics, and DITA for Business Documents.
Assigning content types to assets allows the Platform to apply different lifecycles, workflows, and
publishing requirements to different types of content. Content types are hierarchical, with child
content types inheriting from their parents, for easy and logical configuration. Child content types
can be fine-tuned by associating specific metadata and publishing activities with them. In addition
to the standard set of content types, the Platform allows you to define your own and provides an
auto-detection mechanism for so that they can be automatically recogized.
ABOUT QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM
Attributes: Assets can have attributes, which are containers for metadata that model the intrinsic
properties of those assets. The selection of attributes for an asset is determined by its content type.
You can use attributes to drive custom workflows and publishing processes, and to reflect
system-managed state. Attributes are created globally and can be applied to one or more content
types.
Relationships: A relationship links two assets with one another, with one asset being the parent and
the other being the child, and hassome associated metadata. There are different types of relationships,
with different sets of associated metadata. Relationships can be specific to a particular version of a
child asset, or can apply to all versions. Relationships enable component-content management use
cases. There are predefined relationships between QuarkXPress projects and article components,
and betweenQuarkCopyDesk articlecomponents and pictures, and there is a predefined relationship
for XML component references. You can also create your own relationships.
Component management and referencing features are available both for XML content and for
QuarkXPress/QuarkCopyDesk components.In thiscontext, an asset can be a single topic, a concept,
an image, or a media file. Aggregated documents (including DITA maps and QuarkXPress layouts)
are also modeled as assets. The content type of an asset determines its role.
The Platform uses asset relationships to model content-component references. For cases of content
reuse, the Platform creates multiple relationships, which define suchthings as a component’s location,
its update status, and so forth. You canselectively burst content when you check it into the Platform,
for easy reuse. You can pin content to a particular version, or be automatically updated when the
master version of the content changes.
Collections: A collection is a generic hierarchy that you can use to organize assets. You can model
departmental hierarchies,folders, or jobs. You can then map one ormore workflows to each collection,
and the assets in each collection will follow that collection's workflow. Collections also have users
associated with them, and different users can have different roles in different collections. You can
apply collection-specific routing rules and revision control settings, and assign collection-specific
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 11
Page 12

ABOUT QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM
attributes, and search on a collection-specific basis.A collection'sJob Jackets file defines theresources
available for the projects and articles in that collection.
Workflows: A workflow helps you to manage the lifecycle of assets by providing a named, ordered
set of statuses for those assets to move through. A status-based auto-routing feature helps keep
everything on track. You can create different workflows for different content types, use different
forms to present attributes in different workflows, and color-code the statuses in aworkflow foreasy
identification. Each workflow can have its own QuarkXPress/QuarkCopyDesk redlining settings
and Job Jacket rule evaluations, and you can apply status-based constraints for each attribute.
Publishing Services: The Publishing Service Framework is a server-sideframework that automates
publishing and delivery tasks. You can create configurable and extensible publishing processes that
use a variety of renderers, including third-party renderers.
• A Publishing Process is a pipeline consisting of re-usable Activitiesthat encapsulate common tasks
such as resolving XML component references and QuarkXPress attachments, applying
transformations, submitting content to the appropriate rendering engine, packaging and collecting
the output, and delivering the rendered output to a CMS or via FTP or HTTP.
• A Publishing Channel is a specific configuration of a publishing process that can be mapped to
specific content types. The Platform ships witha library of commonly required Activities and several
pre-configured Publishing Channels.
• An SDK for developing custom Activities is also available.
Platform components
Quark Publishing Platform consists of a set of core modules that can be combined in various ways
with each other and with other systems. Depending on the needs of your organization, you may
choose to use some or all of these modules.
Quark Publishing Platform Server: The heart of Quark Publishing Platform. The Server manages
content, controls and coordinates workflows, provides a hierarchical scheme for organizing assets
and tracks the relationships between those assets, implements automated versioning, and lets you
keep track of users and their permissions. A Web-based administrative interface lets you control and
configure the Server.
Quark Publishing Platform Clients: A Platform client is any application that can talk to Quark
Publishing Platform Server. Available clients include QuarkXPress for Quark Publishing Platform,
Quark XML Author for Quark Publishing Platform, Quark Publishing Platform Web Client,
QuarkCopyDesk for Quark Publishing Platform, and desktop client for Mac and Windows. You can
also implement and integrate your own clients with the Quark Publishing Platform SDK. A sample
client for iOS "Gateway Starter App" is also included with the SDK.
• Quark XML Author for Platform: For XML content authoring and reuse in Microsoft Word.
• QuarkXPress: For template development, custom layout, content authoring, and layout and content
review.
• QuarkCopyDesk: For content authoring and review.
• Quark Publishing Platform Web Client: For content authoring and review in a Web browser.
• Quark Publishing Platform Client: A generic desktop client, available for Windows and Mac OS.
12 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 13
ABOUT QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM
Work-in-Progress Repository: A repository that provides versioning and component management
capabilities for XML assets, QuarkXPress assets, and QuarkCopyDesk assets. Once a publication
is finalized, the published files can be archived in a system of record.
Quark Publishing Platform Renderer: QuarkXPress Server, an engine that produces published
files from component assets. QuarkXPress Server can produce outputin avariety of formats, including
PDF, ePub, and AVE (for deployment to the iPad and other devices).
DITA Open Toolkit: An engine thatproduces published files from XML content thatuses the DITA
schema. Working with an XSL-FO processor such as Antenna House, the DITA Open Toolkit can
produce output in PDF, HTML, RTF, and HTML Help formats.
Quark Publishing Platform Script Manager: A scripting engine that allows you to build
sophisticated custom functionality into Quark Publishing Platform Server without having to know
a programming language.
Quark Publishing Platform SDK and REST interface: Robust interfaces that allow you to easily
develop your own custom Quark Publishing Platform clients.
In addition to the clients listed above, Quark Publishing Platform can support custom mobile client
applications. The Platform includes the source code for a sample mobile application called the
Gateway iOS Starter App, which demonstrates how to create a custom Platform client for iPhone
or iPad.
Platform architecture
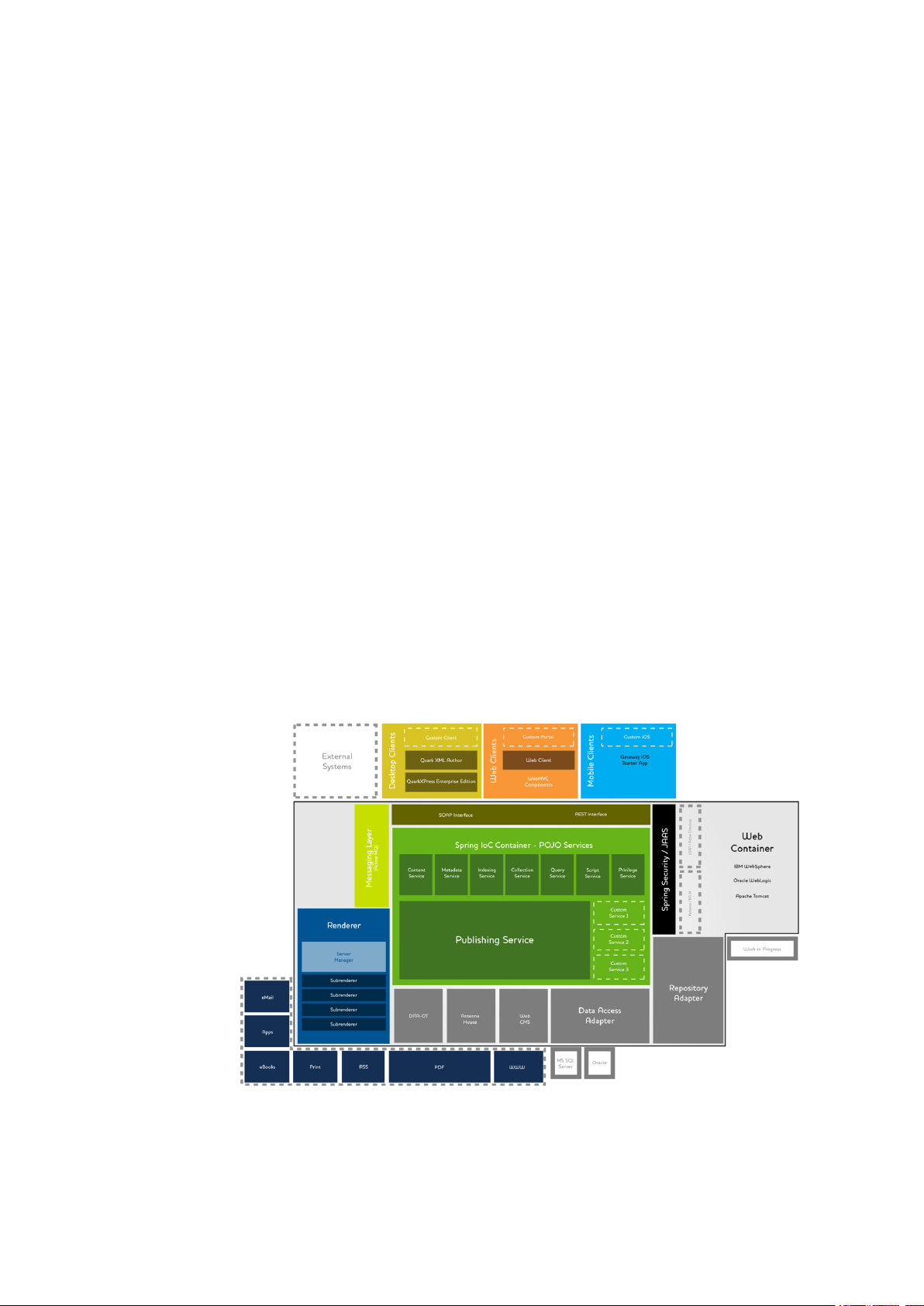
Quark Publishing Platform is built using open industry standards such as SOA and the Spring
framework, to allow easy integration with existing business systems. The architecture of Quark
Publishing Platform is shown in the following diagram.
Quark Publishing Platform architecture
At the center is Quark Publishing Platform Server, which is a Spring-based Java applicationrunning
in a Web container. This application has a number of services, hosted using the Spring framework,
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 13
Page 14

ABOUT QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM
which it uses to perform various operations such as querying, honoring privileges, and maintaining
metadata. You can also write your own custom services for business system integration.
The Publishing Service provides a component-aware publishing framework that can integrate with
multiple renderers and delivery systems to publish content in multiple formats, including PDF,
eBooks, iPad content, RSS feeds , syndications, and so forth.
At the top of the diagram arethe QuarkPublishing Platform client applications. These include desktop
applications (such as QuarkXPress, QuarkCopyDesk, and Quark XML Author), Web applications
(including the Web client and Web administrator), and mobile clients such as the Gateway iOS
Starter App. Such client applications can communicate with Quark Publishing Platform Server via
SOAP or the REST interface, whichever is a better fit.
Also within the Web container are any adapters that are necessary for Quark Publishing Platform
Sever to talk to the Work-in-Progress repository or databases. Other adapters connect Quark Publishing
Platform Server with output technologies such as the DITA Open Toolkit and the Antenna House
XSL-FO formatter.
The Web container also hosts Quark Publishing Platform Renderer, which provides output in a
variety of formats (shown in the boxes around the lower left corner). The Renderer includes a load
balancer called Server Manager and some number of subrenderers running separately to handle
requests as efficiently as possible.
Messaging within the system is handled with Java Message Service (JMS) messages, managed by
ActiveMQ.
The Platform can securely communicate with external resources such as LDAP servers using either
Kerberos or NTLM encryption. This enables the Platform to support single sign-on and domain
users.
Platform features
In addition to the features already discussed, Quark Publishing Platform offers the following.
• Powerful content reuse features: You can easily use and reuse assets and XML content in an
interface that allows you to preview your changes as they will look at outlook without leaving
Microsoft Word. For more information, see the documentation for Quark XML Author for Quark
Publishing Platform.
• Versatile automation features: Using the Quark Publishing Platform publishing framework, you
can create publishing channels (for automatically building output) and delivery channels (for
delivering published content to its destination).
• Workflow management: Quark Publishing Platform lets you construct workflows that can
automatically route files to the appropriate parties based on their statuses, notify those parties of
their assigned tasks, add comments to drafts of document, track and review changes, and divide the
work on a single document so that different users can work on it simultaneously.
• Collections hierarchy: The Work-in-Progress repository can be organized into whatever kind of
hierarchy works for your organization.
• Sophisticated query engine: Quark Publishing Platform clients can take advantage of a powerful
query engine, including metadata search and full-textsearch, using an intuitive user interface. Queries
can be named, saved, and shared among users.
14 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 15

ABOUT QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM
• Server-side scripting: Quark Publishing Platform Server comes pre-configured with the Rhino
scripting enginefor JavaScript. Scripting is implemented using the Apache Bean Scripting Framework
(BSF). All services, data transfer objects (DTOs), and JMS messages are available to the script
engines. Scripts are executed on the server in a separate thread of the server process for maximum
safety and efficiency. Scripts can be triggered manually, by a schedule, or by a server-side event.
For more information, see "Script Manager ."
• Directory server integration: You can import users from LDAP servers to enable single sign-on.
For more information, see "Managing user lists with LDAP."
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 15
Page 16
CONFIGURATION
Configuration
Administration client
Users with the Administration role can configure and maintain a Quark Publishing Platform
workgroup's workflow. In addition to establishing structure for users and the content they generate,
Administrators controlsecurity, setdefaults, specifystorage locations,and customize the parameters
for tracking every asset in their workflow.
To administer Quark Publishing Platform Server, navigate to the following URL in a Web browser:
http://[IP address of Platform Server computer]:61400/admin
You can also display the administration from the home page, which is http://[IP address of Platform
Server computer]:61400
The Quark Publishing Platform Web Administrator displays.
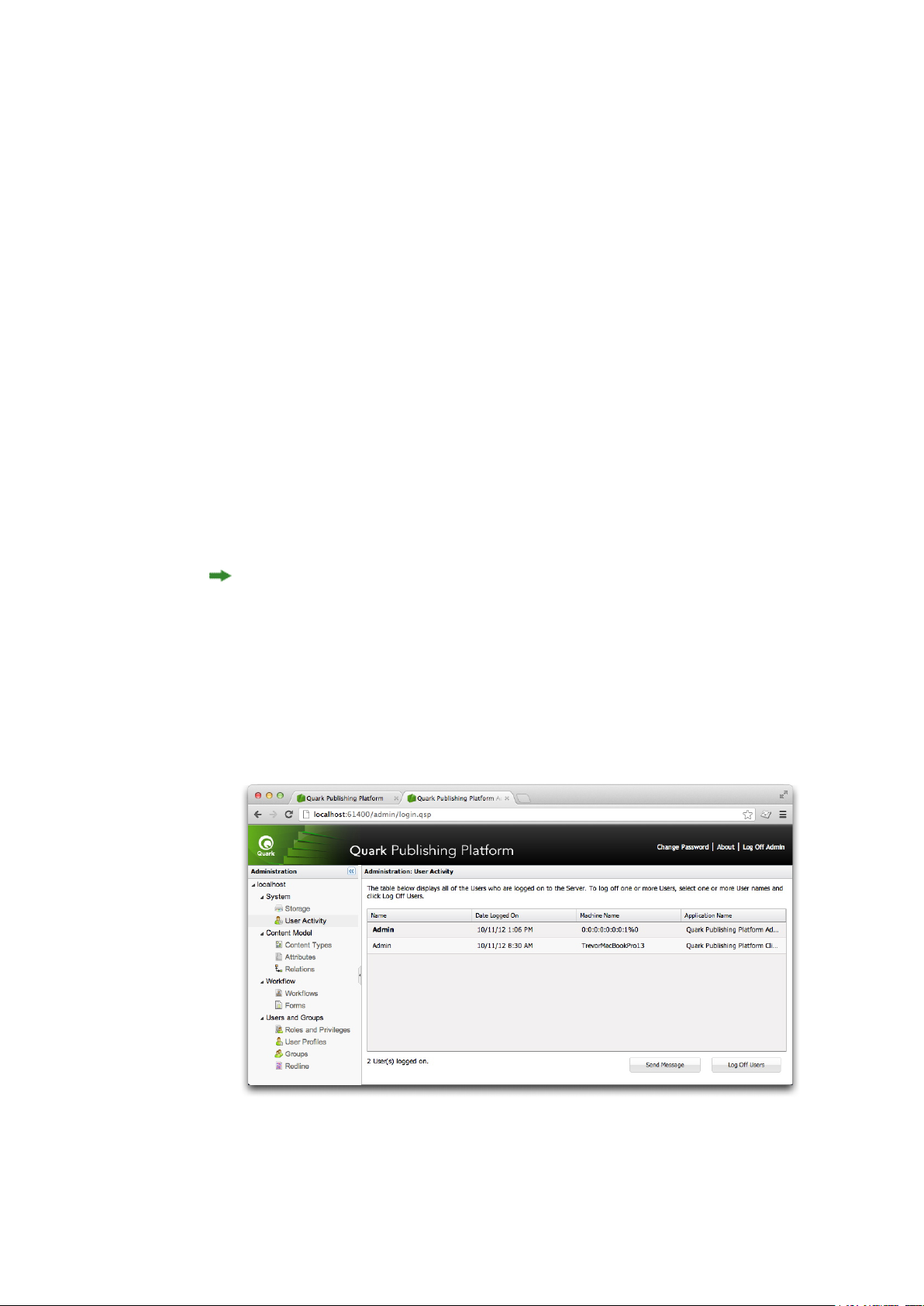
When you select User Activity, the admin client displays the list of all logged-on users, including
each user's name, the time and date each user logged on, each user's machine name, and each user's
application. If you need to log off a user, select the user's name in the list and click Log Off Users.
You can also log off users and send a message to a logged-on user.
Admin client running in Web client
16 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 17

System area
The System area includes the following controls:
• Storage: Use this control to specify one or more storage folders for assets and to establish rules for
storing different file types. For more information, see "Configuring storage options."
•
User Activity: Lets you view logged-on users. For more information, see "Administration client."
Content Model area
The Content Model area includes the following controls:
• Content Types: Use these controls to specify which types of content the Platform is managing. For
more information, see "Working with content types."
• Attributes (also called "metadata" or "headers"):Use these controls to create and configureattributes
that can be associated with assets, articlecomponents, collectiontypes, and layout types. For example,
you could create an attribute called "Image approved" for picture file types. When a user approves
an image, he or she can check "Image approved" for the picture. When another user searches for
approved pictures,the usercan includethe "Image approved" attribute in the search criteria and limit
the search results to approved images. For more information, see "Defining attributes."
CONFIGURATION
• Relations: Use these controls to configure the relationships available between Platform assets. For
more informaiton, see "Working with relationships."
Workflow area
The Workflow area includes the following controls:
• Workflow Definition: Use these controls to createand configure workflows. For moreinformation,
see "Working with workflows."
Users and Groups area
The Users and Groups area includes the following controls:
• Roles and Privileges: Use these controls to create, delete, rename, and modify roles and their
associated privileges. For details about setting privileges, see "Privileges." For example, you can
create a role called "Editorial," and assign this role to your writers and editors. All users with this
role will have the same privileges to perform editorial functions.
• User Profiles: Use these controls to create a user, assign a role to the user, assign a password, and
enable or disable the user's ability to log on. You can also delete, rename, and modify user accounts.
• Groups: Use these controls tocombine user profiles into groups to whichassets can be routed. When
you route an assignment to a group, that asset appears in the assignments for everyone in that group.
The firstperson in the group who checks out the assetgains controlof that asset. You can also delete,
rename, and modify groups.
• Redline: Use these controls to specify default redline tracking colors for each user.
Configuring storage options
In versions of Quark Publishing Platform prior to 9.5, you could set up separate repositories for
different file types. In version 9.5 and later, you can simply set up a single repository for all asset
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 17
Page 18
CONFIGURATION
types. You can add additional repositories if you need additional space, and change the priority of
your repositories to control which one new assets are written into.
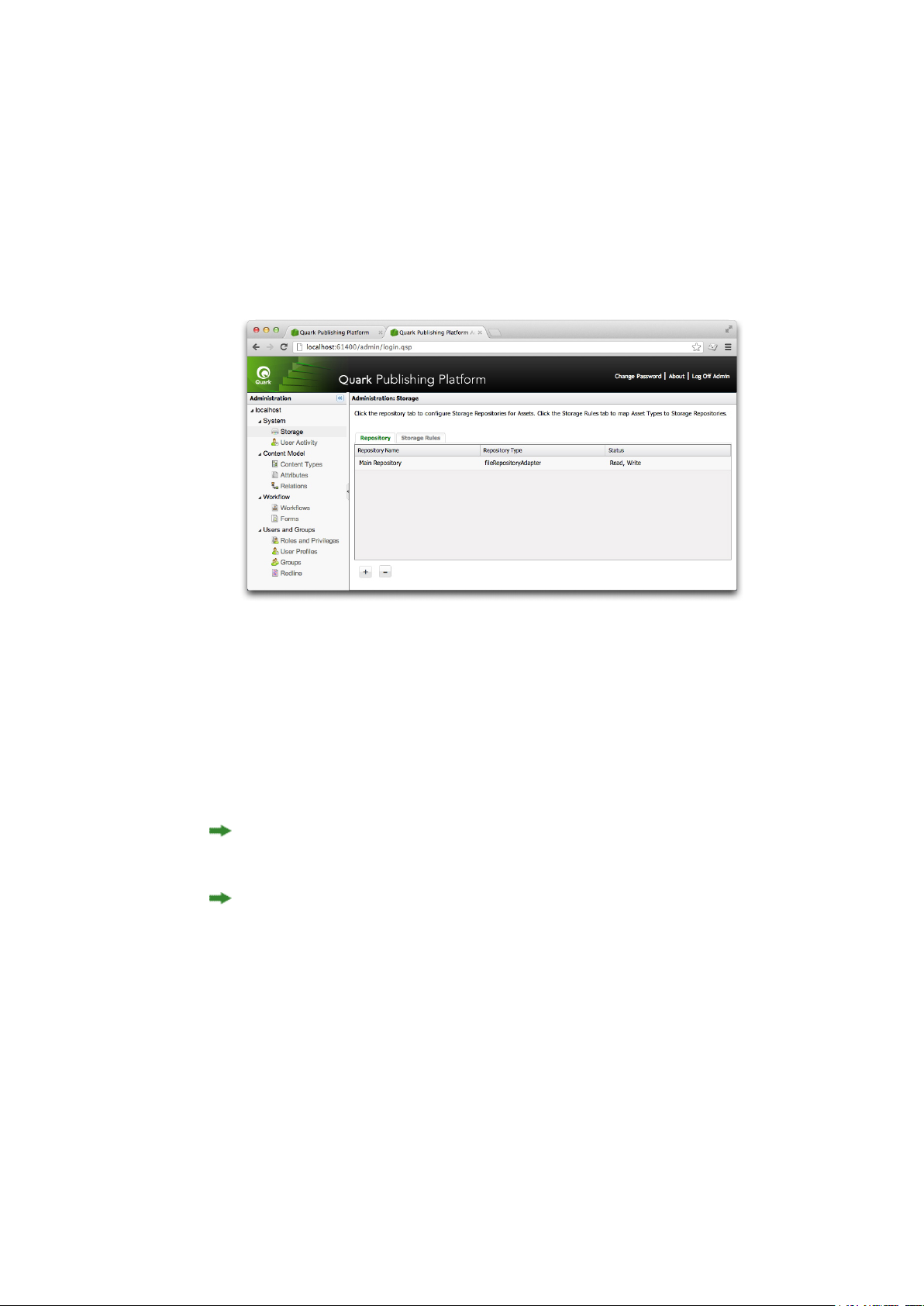
To configure storage options, click Storage.
Adding repositories
To add a storage repository:
1
Click the Repository tab in the Administration: Storage window.
Use the Repository tab of the Administration: Storage area to view and manage the folders where
Quark Publishing Platform assets are stored.
2
Click + to display the New Repository dialog box.
3
Enter a name for the repository in the Name field.
4
To specify a specific file system directory, choose fileRepositoryAdapter and then specify a URL
in the URL field (for example: /Users/Name/QPP Repository for Mac OS, or C:\QPP Repository
for Windows).
For information about creating a SharePoint repository, see the Quark Publishing Platform SharePoint
Adapter ReadMe.
The storage location must include read/write permissions.
Deleting repositories
To remove a storage repository, click the Repository tab in the Administration: Storage window,
select the repository you want to remove, then click – (minus sign). A warning message prompts
you to confirm the deletion.
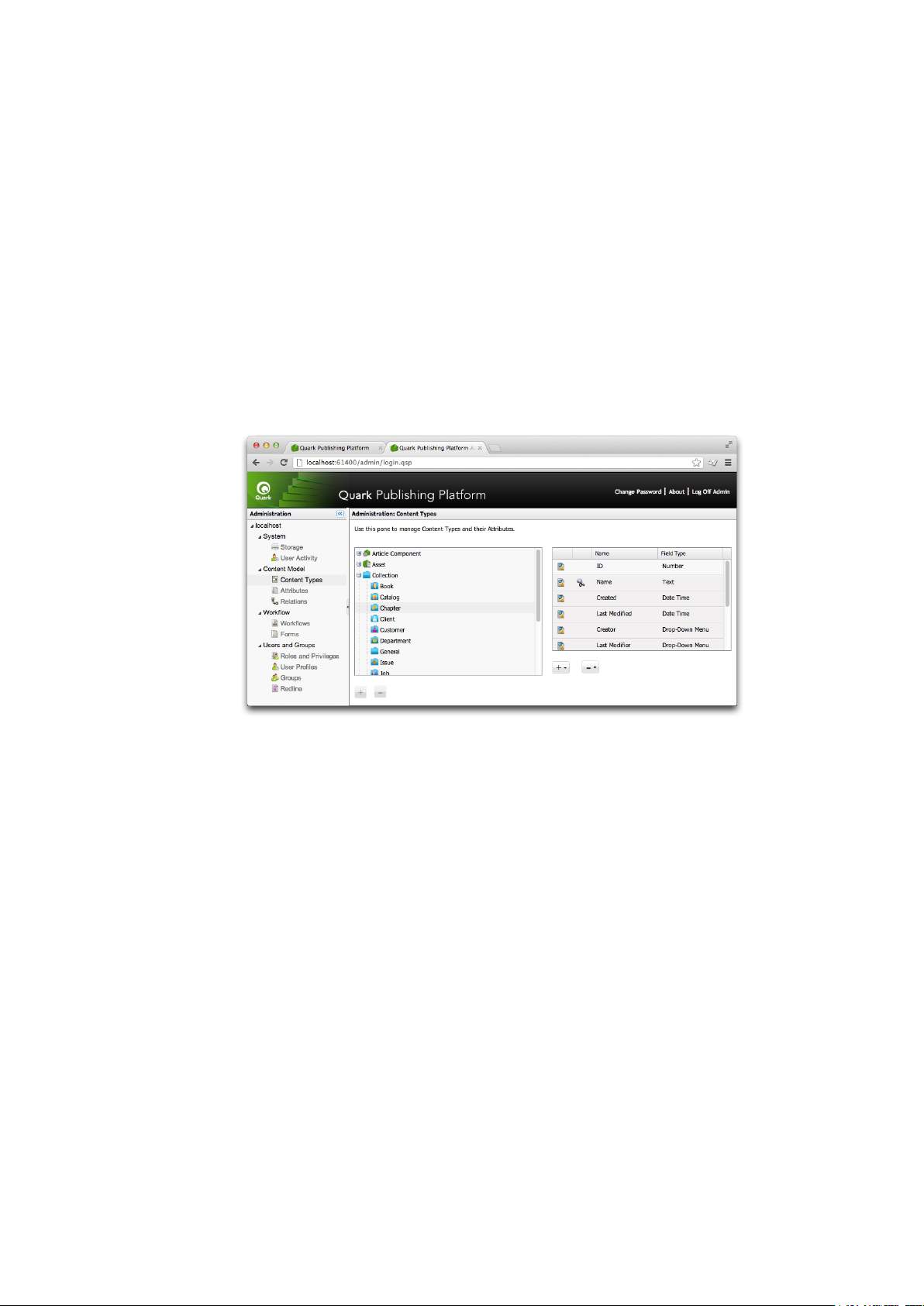
Working with content types
Quark Publishing Platform supports a variety of different types of content, including QuarkXPress
projects, QuarkCopyDesk articles, picture files, multimedia files, and XML files. TheContent Types
18 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 19
CONFIGURATION
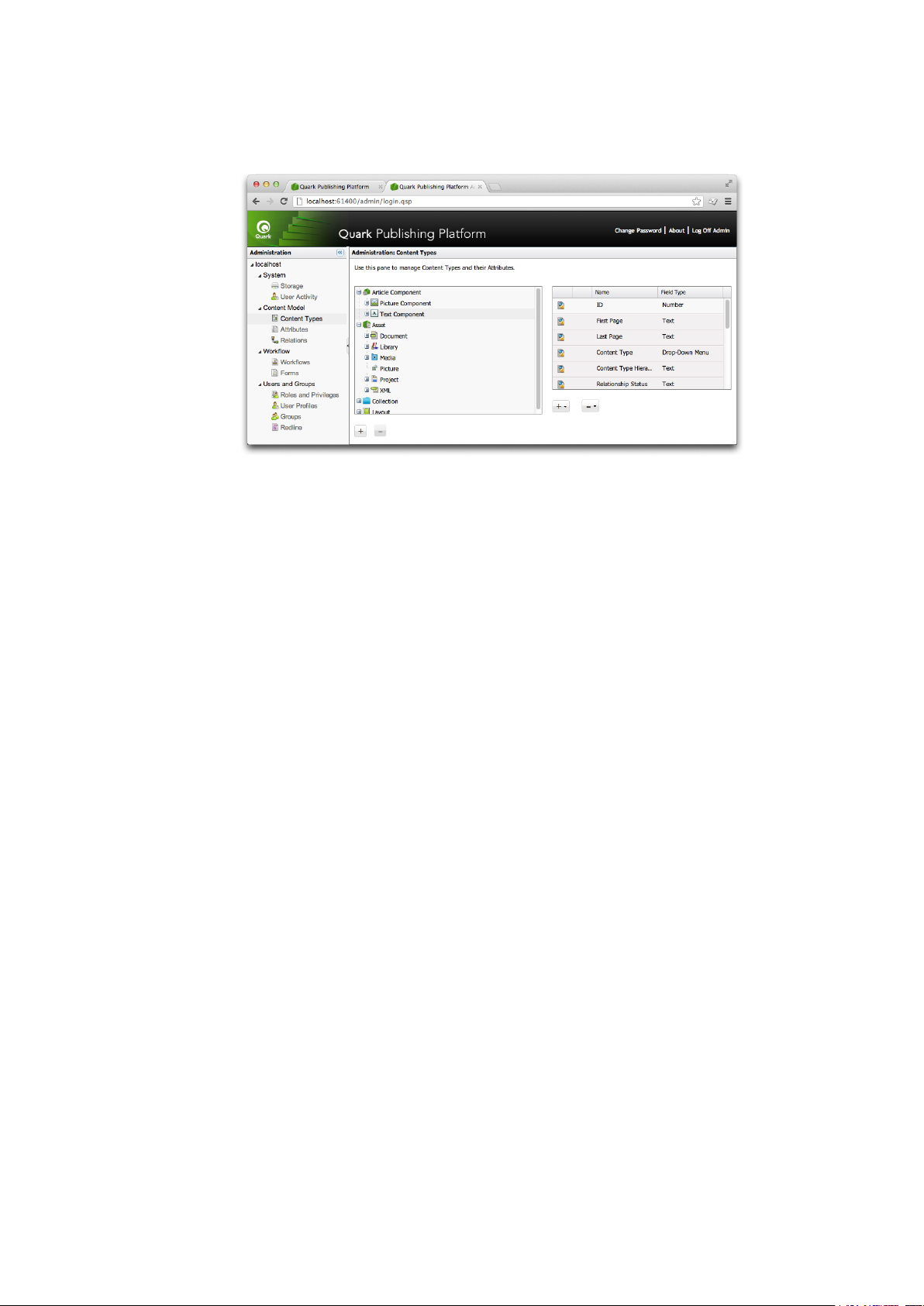
pane lets you control the way in which information about each of these content types display in
Quark Publishing Platform user interfaces.
Content Types pane
Different types of content have different attributes. For example, the list of attributes for a picture
includes values for "Pixel width," "Pixel height," and "Resolution," and the list of attributes for a
text componentincludes values for "Word count" and "Line count." Some attributes, such as "Checked
out duration," are relevant only to QuarkPublishing Platform,and are stored only in Quark Publishing
Platform.
For XML files that adhere to the DITA and BusDocs schemas, Quark Publishing Platform provides
access to specific file-level element and attribute values. For example, you can use the Quark
Publishing Platform user interface to view the values of a DITA XML file's <title> and <author>
elements without having to open the file.
By default, Quark Publishing Platform is configured to provide access to a variety of attributes for
four categories of content types:
• Article components
• Assets (of various types)
•
Quark Publishing Platform collection types (for more information, see "Working with collection
types")
• QuarkXPress layouts
You can create new content types for asset, text components, and picture components. You can also
create new collection types. To add a new content type, select an eligible parent content type, then
click the plus button under the content type list on the left.
You can add new attributes to any content type. These can be existing attributes from the Attributes
pane, or entirely new attributes.
• To add an existing attribute to the selected content type, click the plus button under the attribute list
on the right and choose Select from Existing.
• To createa new attribute, click the plus button under the attribute list on the right and choose Create
New. (For more information, see "Understanding attribute types.") Any new attributes you create
are automatically added to the attribute list displayed in the Attributes pane.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 19
Page 20
CONFIGURATION
There are two ways to disassociate an attribute from a content type:
• To permanently delete the attribute, select it, click the minus button under the attribute list on the
right, and choose Delete.
• To disassociate the attribute from the selected content type but leave it in the attribute pool, select
the attribute, click the minus button under the attributelist on the right, and choose RemoveMapping.
Working with collection types
A collection type is similar to an asset type in that it has a particular set of attributes. By applying a
collection type to a collection, you enable users to view and edit attributes for that collection and
create a form for editing those attributes.
To configure a collection type, expand the Collection category in the content type tree and select
the collection type you want to configure.
Configuring a collection type
For more information, see "Working with collection types."
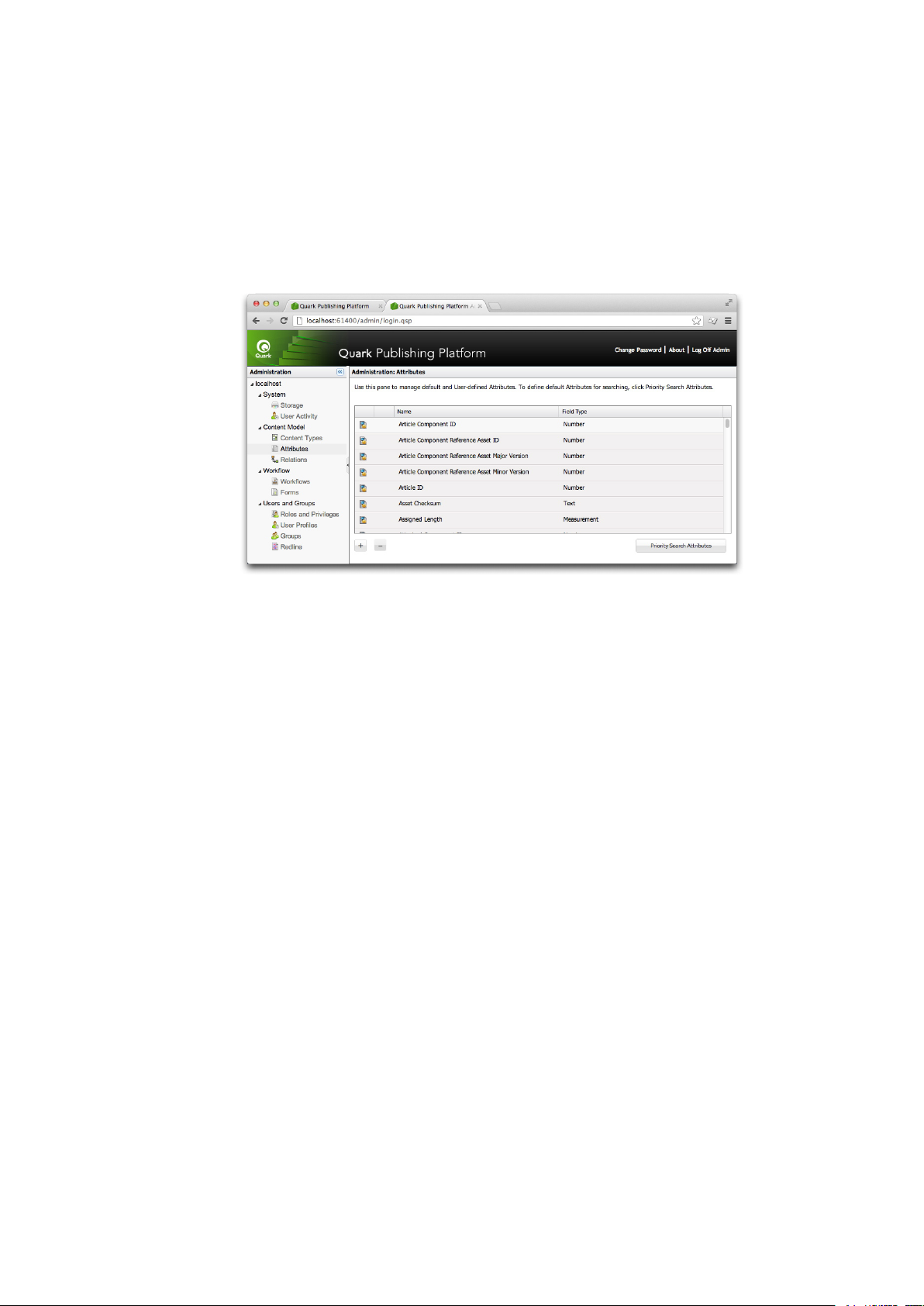
Working with attributes
Each content type has its own set of attributes. For convenience, all attributes are listed in the
Attributes pane. You can assign attributes to content types in the Content Types pane. For more
information, see "Working with content types."
Defining attributes
Each asset in Quark Publishing Platform has a correspondingset of attributes that describes the asset
and its status in the Quark Publishing Platform workflow. Each content type can have its own set of
attributes. These attributes include system-generated information such as the date and time of the
last modification, default Quark Publishing Platform attributes such as Checked Out By, and any
custom attributes you create to meet the needs of your workflow. For example, you could create an
attribute called Image approved for picture file types. When a user approves an image, he or she
could check Image approved for the picture. When another user searches for approved pictures,
the usercould include the Image approved attribute in the search criteria and limit the search results
to approved images.
20 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 21
CONFIGURATION
You can create eight kinds of attribute types: Text, Date, Time, Number, Measurement, Check
Box, Drop-down Menu, and Date Time. Each attribute type can have a default value. For each
attribute, you can limit access so that only users with the privileges to edit "limited-access" fields
can edit the attribute values. Attributes are defined at the server level, so each attribute can be used
by multiple asset types and collection types.
To create, delete, and modify attributes, click Attributes in the navigation pane. The right pane
displays the list of attributes available in the system.
Use the Attributes pane to create, edit, and delete attributes that help identify Quark Publishing
Platform assets.
Creating an attribute
To create an attribute:
1
Click + (plus sign) to display the Create Attribute dialog box.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 21
Page 22
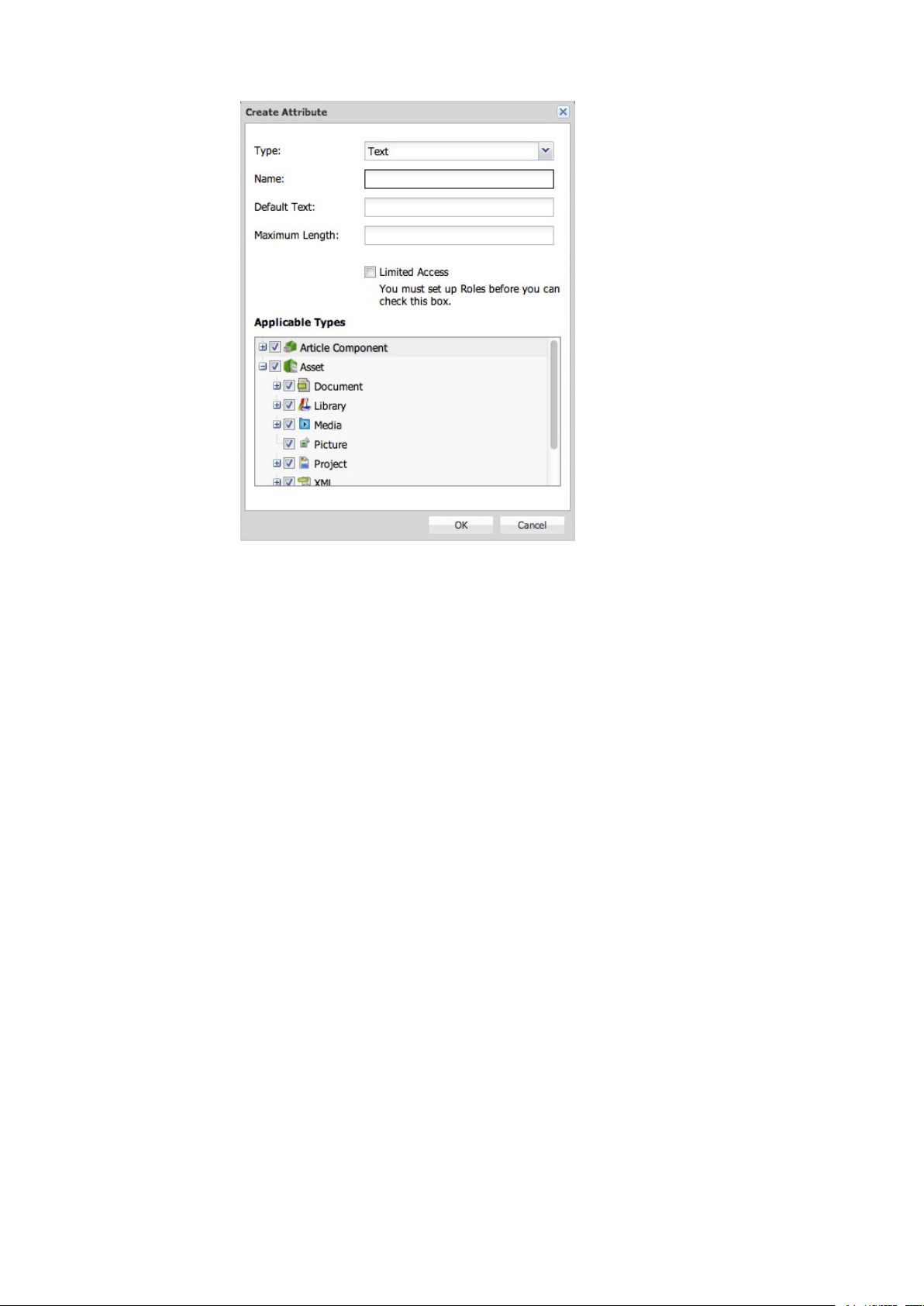
CONFIGURATION
Specify the attribute name and type in the Create Attribute dialog box.
2
Choose an attribute type from the Type drop-down menu. (For more information about attribute
types, see "Understanding attribute types.")
3
Enter a name for the attribute in the Name field.
4
To allow only users with the "Edit normal- and limited-access fields" privilege to access the
attribute, check "Limited Access." For more information, see "Defining Roles and Privileges."
5
Configure theremaining controls.These controlsvary dependingon which attribute type is selected.
For more information, see "Understanding attribute types."
6
To control which content types the attribute is applicable to, check the appropriate boxes in the
Applicable Types list.
Understanding attribute types
There are eight kinds of attributes: Text, Date, Time, Number, Measurement, Check Box,
Drop-down Menu, and Date Time.
Text
Use the Text attribute type to create text attributes.
• Enter a default value in the Default Text field.
• To indicate the maximum length of text in the field, enter a value in the Maximum Length field.
Date
Use the Date attribute type to create date attributes.
• Enter a default date in the Default Date field.
22 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 23

CONFIGURATION
• To constrain users to a particular date range, enter a starting date in the Start Date field and an
ending date in the End Date field.
Time
Use the Time attribute type to create attributes where users can enter times.
• Enter a default time in the Default Time field.
• To constrain users to a particular time range, choose a starting time from the Start Time drop-down
menu and an ending time from the End Time drop-down menu.
Time values are determined by the Quark Publishing Platform user's locale setting.
Number
Use the Number attribute type to create attributes where users can enter only numbers.
• Enter a default number in the Default Value field.
• To constrain users to a particular numeric range, enter a minimum number in the Minimum Value
field and a maximum value in the Maximum Value field.
Measurement
Use the Measurement attribute type to create attributes where users can enter only measurements.
• Enter a default number in the Default Value field.
• Use the Units drop-down menu to specify the unified unit of measure (for example, Picas or
Millimeters).
• To constrain users toa particular measurement range, enter a minimum value inthe MinimumValue
field and a maximum value in the Maximum Value field.
Check box
Use the Check Box attribute type to create check box attributes. To display the attribute with a
checkmark by default, check Checked by Default.
Drop-down Menu
Use the Drop-down Menu attribute type to create drop-down menu attributes.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 23
Page 24
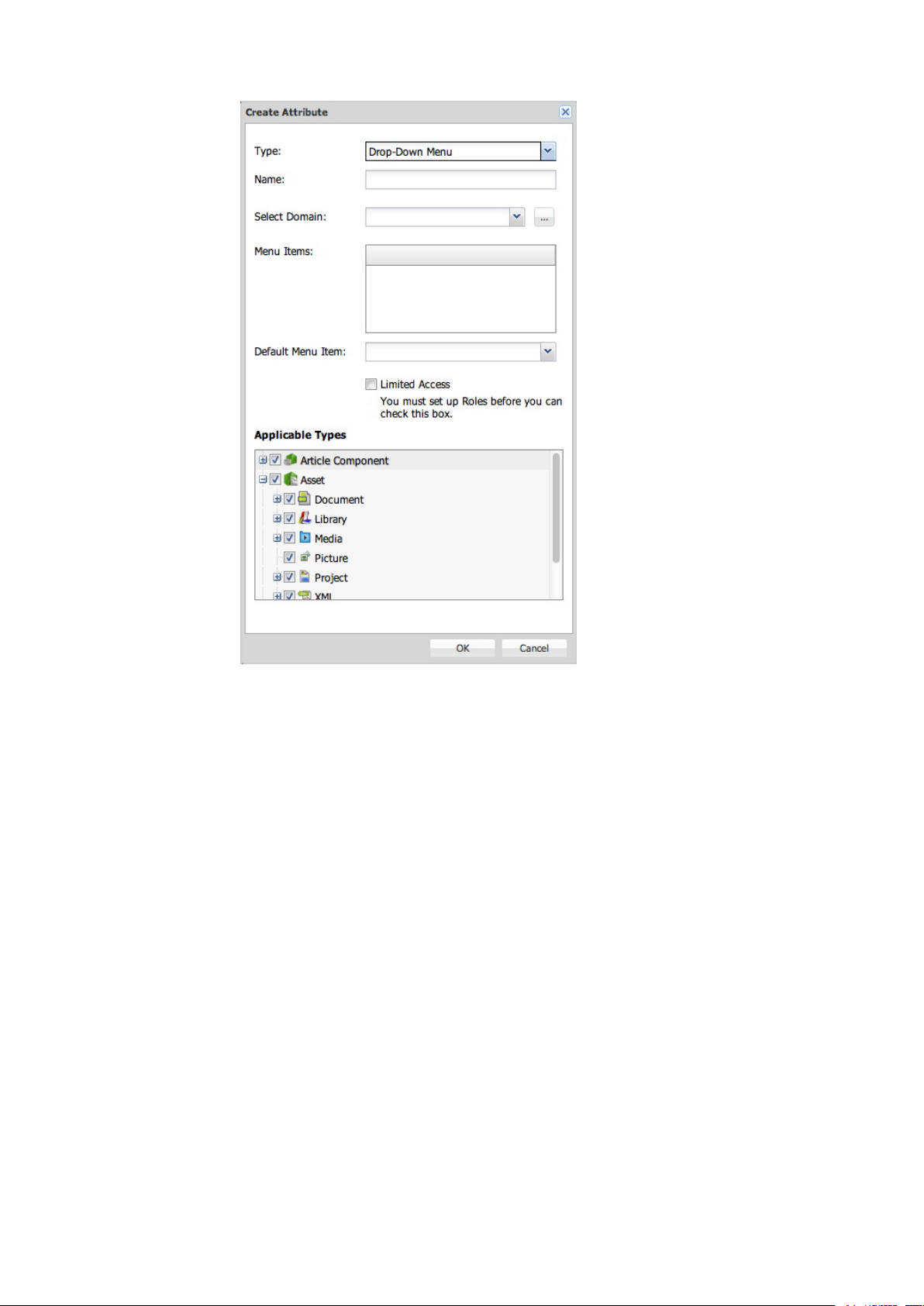
CONFIGURATION
Choose Drop-down Menu from the Type drop-down menu to create a Drop-down Menu attribute
type.
Drop-down menu attributes can display lists of values called attribute domains. For example, if you
create a drop-down menu attribute that requires the list of users on your system, you can use the
existing list of users with the attribute rather than entering all the names manually.
1
To assign an attribute domain to a drop-down menu attribute, choose the attribute domain from the
Select Domain drop-down menu. The attribute domain's contents display in the Menu Items list.
2
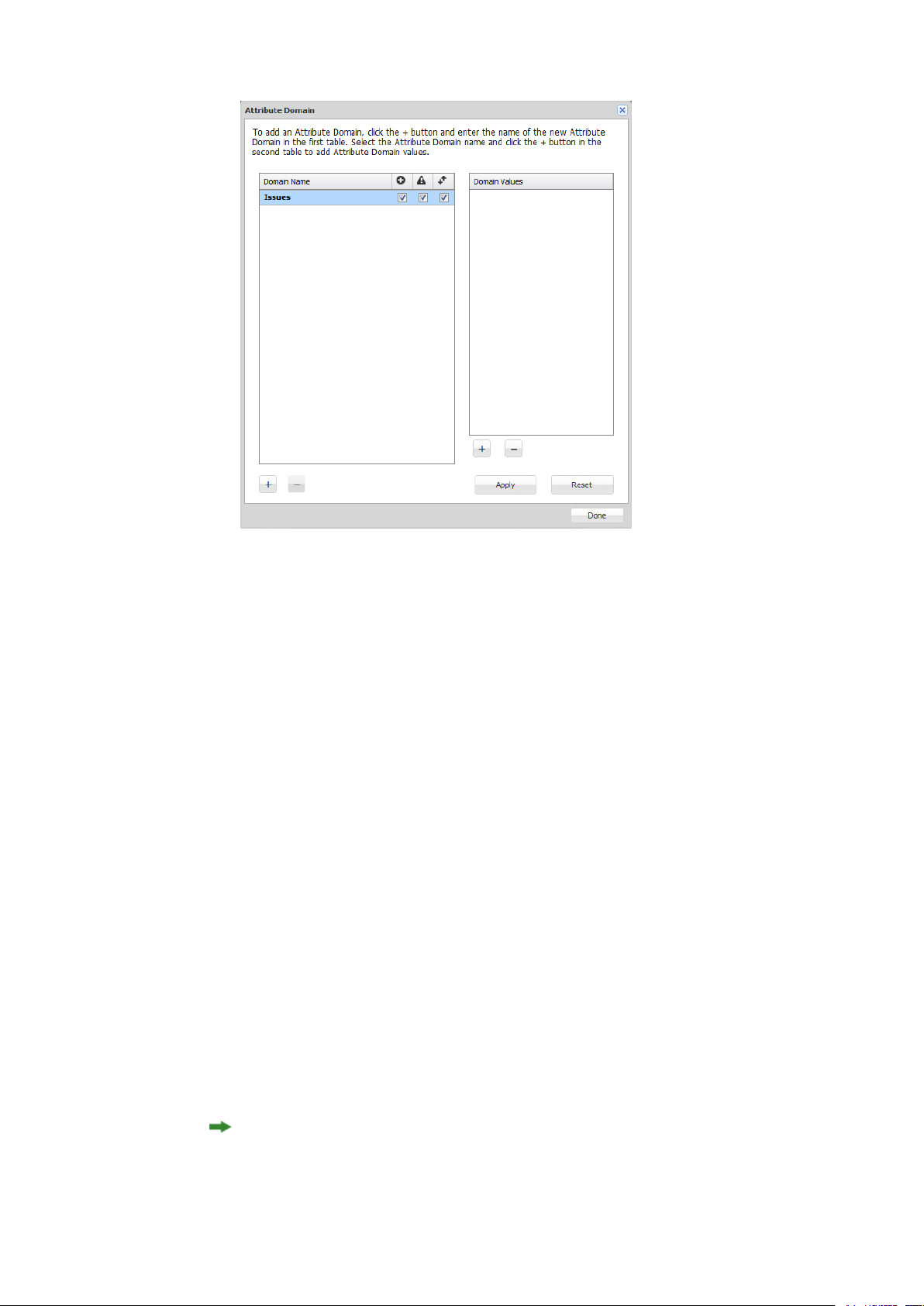
To create a custom attribute domain, click … to the right of the Select Domain drop-down menu.
The Attribute Domain dialog box displays.
24 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 25
CONFIGURATION
Use the controls in the Attribute Domain dialog box to create and view lists that you can add to
drop-down menu attributes.
The Domain Name list includes the available attribute domains. The Domain Values column lists
the values for the selected attribute domain.
3
To add an attribute domain, click + (plus sign) below the Domain Name column.
4
Toenable usersto add entries to the drop-down menuattribute, checkthe box in the Allow Expansion
column.
5
Towarn users when they add an entryto the drop-down menu attribute, check thebox in the Display
Warning column.
6
Toalphabetically sortitems in the drop-down menu attribute, checkthe boxin the Sort Items column.
7
To rename the domain name, double-click its name.
8
Toadd valuesto theselected attribute domain, click + (plus sign) below the Domain Values column.
9
Click Done to close the Attribute Domain dialog box and continue creating your drop-down menu
attribute.
Date Time
Use the Date Time attribute type to create attributes for tracking both dates and times.
• Enter a default date and time in the Default Date field.
• To constrain users to a particular date/time range, enter a starting date and time in the Start Date
field and an ending date and time in the End Date field.
Time values are determined by the Quark Publishing Platform user's locale setting.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 25
Page 26
CONFIGURATION
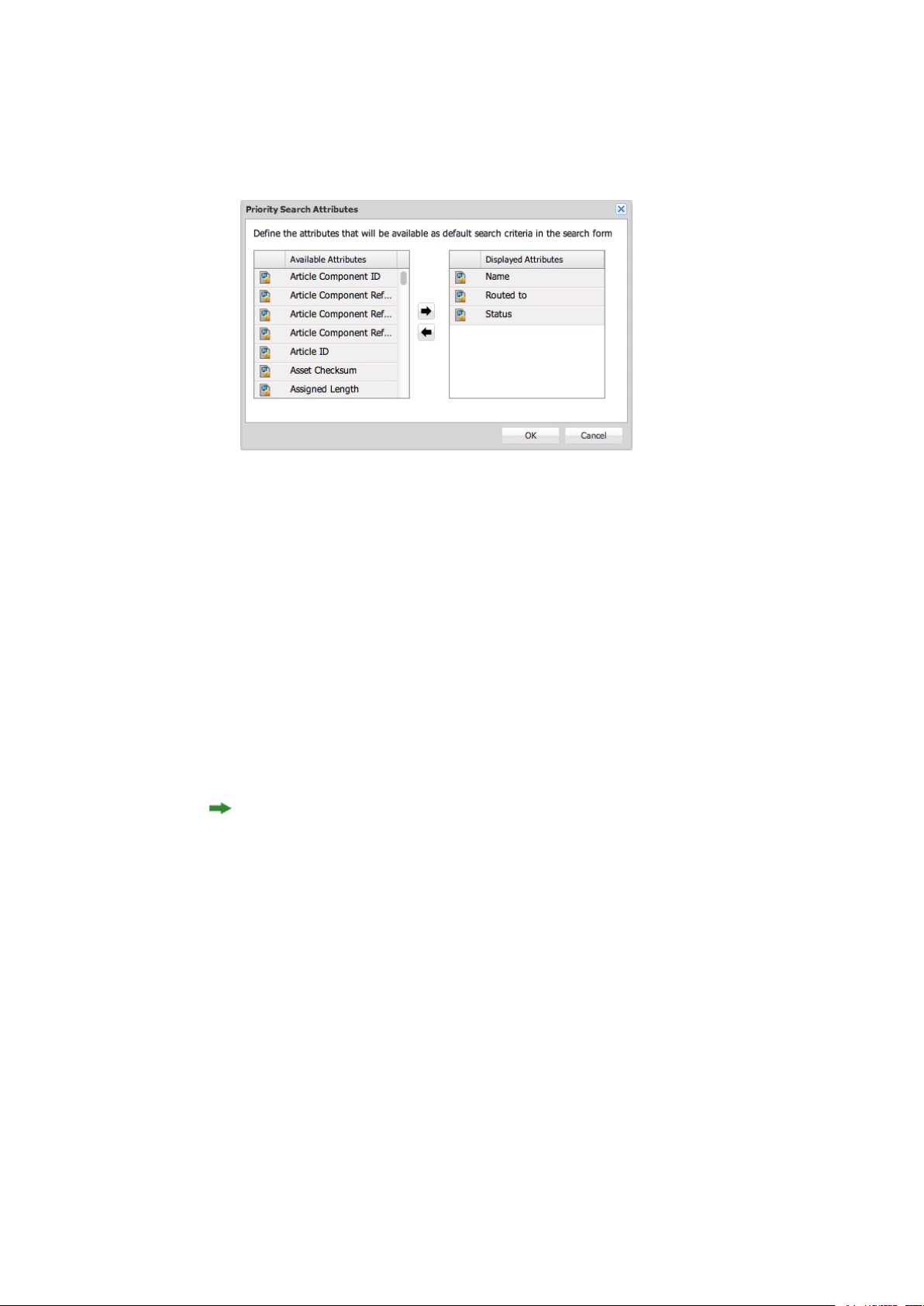
Setting priority search attributes
Priority search attributes display at the top of the list of search criteria in the search controls. After
the priority search attributes, all search attributes display alphabetically.
Priority Search Attributes dialog box
Todesignate priority search attributes, click Attributes in the navigationpane, and then click Priority
Search Attributes. The Priority Search Attributes dialog box displays. To add an attribute to the
list, select it in the list on the left and then click the right arrow button.
Adding constraints to attributes
Users can edit asset attributes when theycheck in an asset, when they savea revision, and by selecting
an asset and clicking Edit Attributes. Constraints let a Quark Publishing Platform administrator
place some controls on how users edit attributes at these times. For example, if you want users with
the Editor role to explicitly approve an asset when it reaches Final status, you can use the Require
Value constraint to require these users to indicate that the asset is approved or not approved. If a
user does not enter a value, "Errors found" displays in red at the bottom of the Check In, Save
Revision, or Edit Attribute dialog box. The attribute is also highlighted in red, and the user cannot
proceed until he or she provides a value.
Only user-modifiable attributes can be constrained. In addition, you cannot constrain the Workflow
and Collection attributes because privileges determine whether these attributes can be modified.
To constrain an attribute for a particular workflow:
1
Click Workflows. The Workflows pane displays.
2
Select a workflow in the Workflow Name list.
3
Click the Attribute Constraints tab.
4
Select the attribute you want to constrain and click Add Constraints. The Add Constraints dialog
box displays.
26 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 27
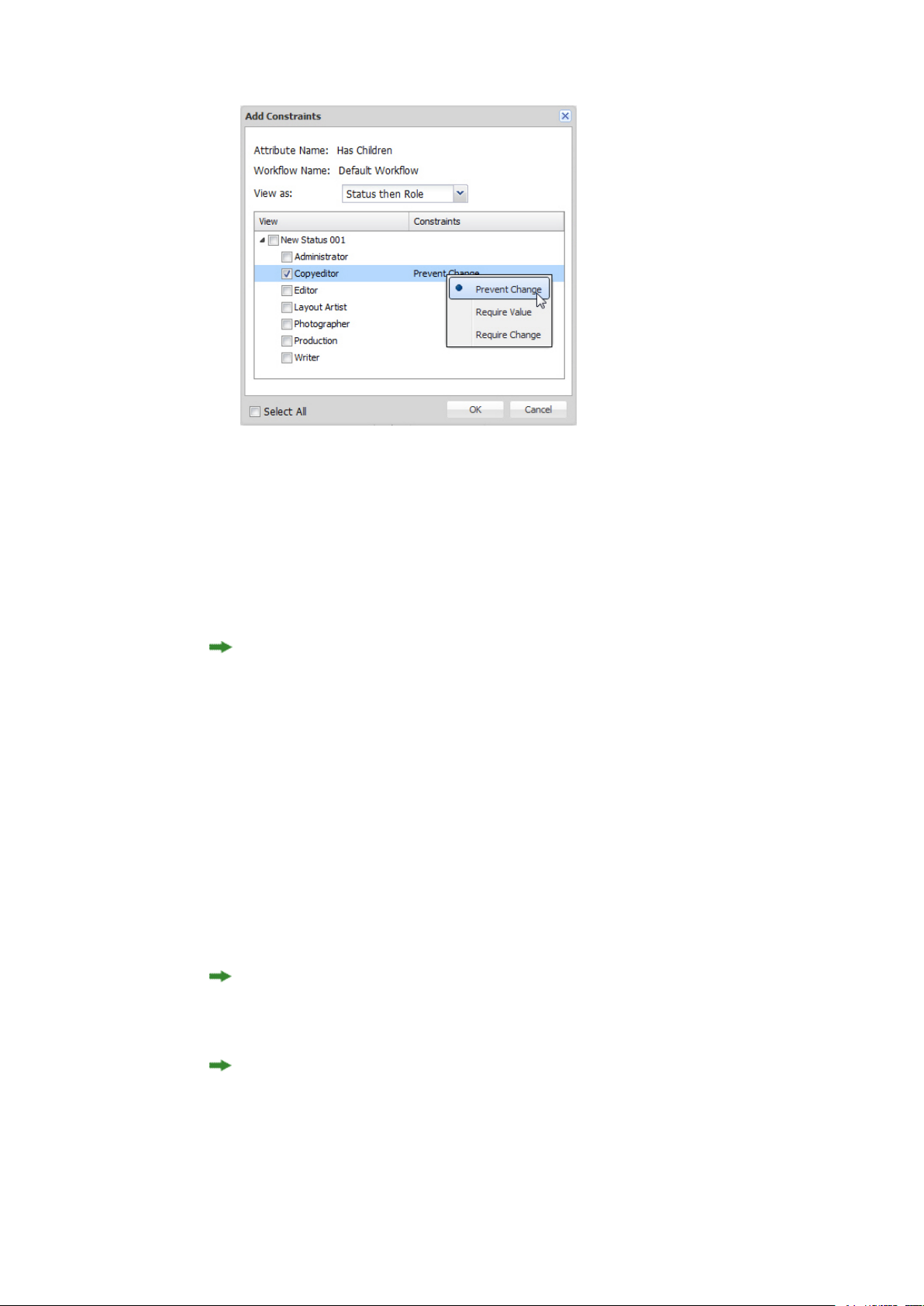
Add Constraints dialog box
5
Choose an option from the View as drop-down menu. This value controls how the information in
the list of statuses and roles displays while you establish a constraint. Options include:
CONFIGURATION
• Status then Role: Displays a hierarchical list with statusesas mainheadings and roles as subheadings.
You can apply the constraint to individual roles at specific statuses.
• Role then Status: Displays a hierarchical list with rolesas mainheadings and statuses as subheadings.
You can apply the constraint to individual statuses for specific roles.
If you change the View as option, the active setting will be retained, but will display according to
the View as drop-down menu hierarchy.
6
Check the box for the status or user role the constraint is for.
7
When you check a role or status in the list, the constraint types become available for the selected
line in the list. There are three kinds of constraints:
• Prevent Change: Prevents users from altering the attribute's value.
• Require Value: Prevents users from leaving an attribute's value unspecified.
• Require Change: Forces users to change the attribute value.
8
To display the status only, check Select All. You can apply the constraint to all or none of the roles
at specific statuses. Unchecking Select All displays the roles only.
Constraints are applied based on the user's role and the asset's status at the time the Check in, Save
Revision, or Edit Attribute dialog box is displayed. The constraints in effect in these dialog boxes
remain the same even if you change the value of the Status drop-down menu.
You can use constraints to enforce automatic routing according to status. For example, you can set
up automatic routing for a collection at the status level and use Prevent Change (in the Add
Constraints dialog box) to disable modifications of the Route to drop-down menu in the Check In
dialog box. This will cause assets to be rerouted when their status changes and prevent users from
changing the routing of the asset.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 27
Page 28
CONFIGURATION
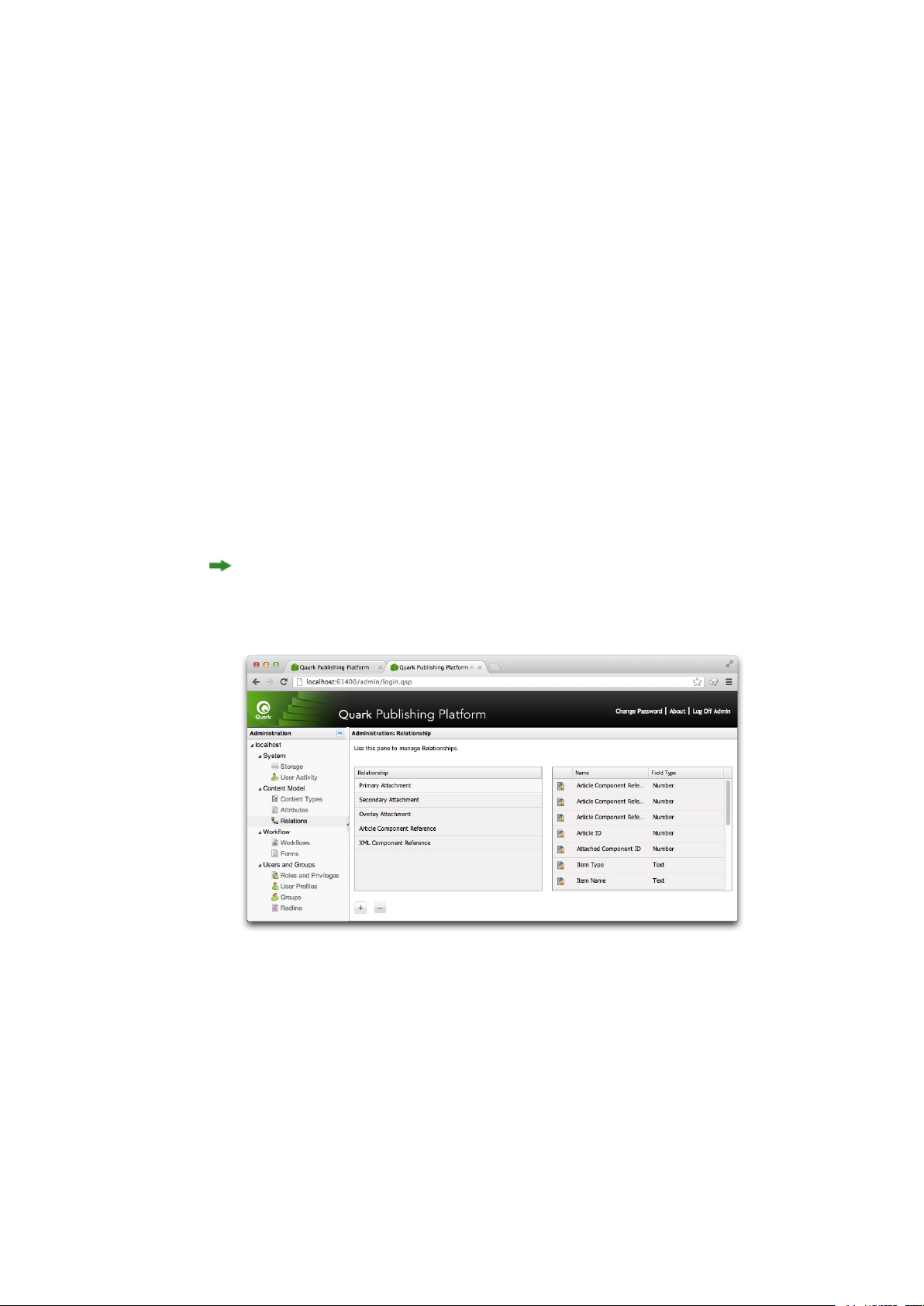
Working with relationships
A relationship is an object that storesthe metadata for the association between two objects. Whenever
you assign an article froma QuarkXPress layout, drag a picture into a layout, or create an interactive
object with App Studio, a relationship object is created to store information about the link you've
just created.
For example, if you draga picture into a QuarkXPress layout, a relationship is created. Among other
things, that relationship stores the IDs of both the picture and the layout. This makes it easy to find
out which layouts are using a given picture, or how many pictures are attached to a given layout.
There are six types of relationship:
•
Primary attachment: Stores information about a primary attachment.
•
Secondary attachment: Stores information about a secondary attachment.
•
Overlay attachment: Stores an information about an App Studio or ePub attachment.
•
Article component reference: Stores informationabout the association between anarticle component
and a linked asset such as a picture.
•
XML component reference: Stores information about a reference from one XML file to another.
•
Custom: Developers can create their own relationship types for custom applications.
For more information about attachments, see "Primary and secondary attachments."
Administrators can view the fields assigned to each type of relationship in the Relations pane.
Relations pane
Administrators can also add custom relationship types and assign atributes to them. To view or edit
the attributes associated with a relationship type, double-click the relationship type.
In Quark Publishing Platform Web client, users can view the relationships for an asset by displaying
that assetin ListView with Relationship Status. Other Platform clients can view relationships with
Relationship View.
28 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 29
Working with workflows
In Quark Publishing Platform terminology, a workflow is a set of steps that helps you to publish a
document. You define workflows at the server level and then apply them to collections.
Each workflow has the following characteristics:
• A name.
• A list of the asset types to which it applies.
• A set of statuses, in a particular order. The order of the statusesreflects the order of thesteps necessary
for completing the workflow. For example, you might specify that assets begin with a status called
"Assigned," followedby "In Progress," "In Review," and "Completed." Youcan specifythat an asset
with the "Completed" status automatically routes to an editorfor final approval (for more information,
see "Setting up auto routing"). You can also enable or disable Redline tracking, check-in layout
evaluation, and output layout evaluation for each status.
• A list of asset attributes. Attributes are defined at the server level, so you can use an attribute in any
number of workflows. You can define constraints for some attributes at the workflow level.
• An attribute form for each asset type. (The attribute form displays when you check an asset in.)
CONFIGURATION
Creating a workflow
To create a workflow:
1
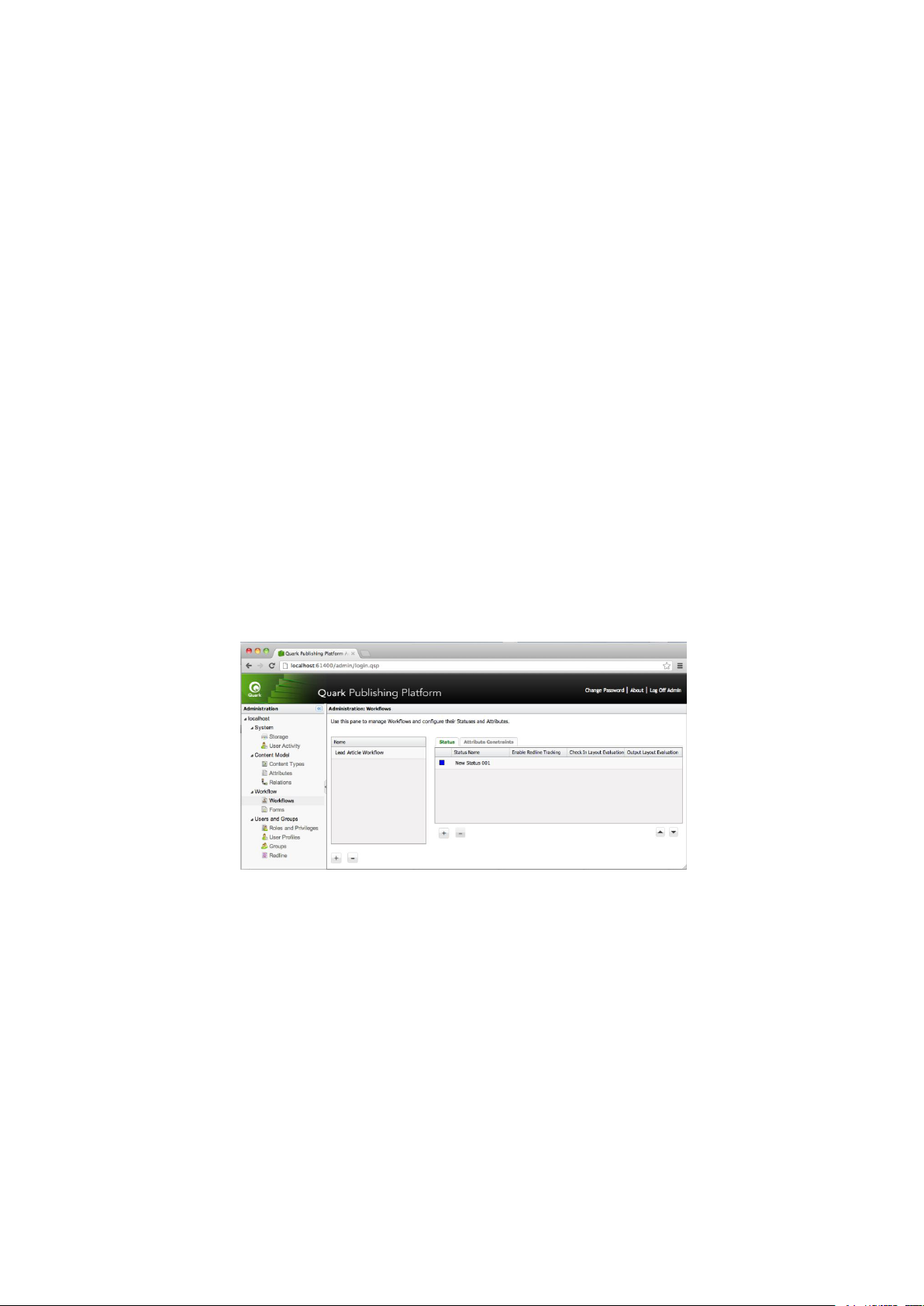
Click Workflows. The Administration: Workflows screen displays.
Administration: Workflows screen
2
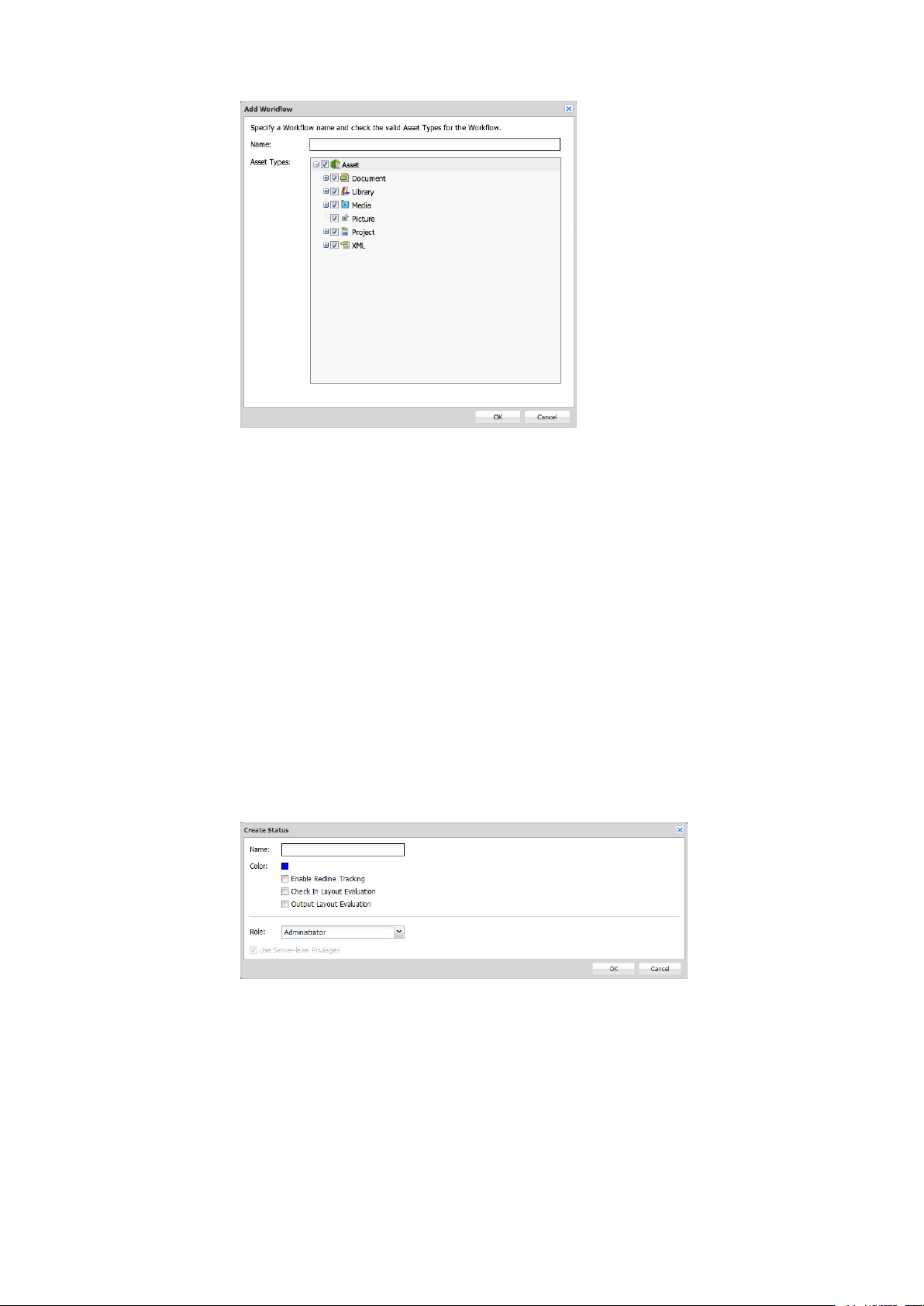
To create a workflow, click + under the Name list. The Add Workflow dialog box displays.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 29
Page 30
CONFIGURATION
Add Workflow dialog box
3
Enter a name for the workflow in the Name field.
4
Under Asset Types, check the asset types you want this workflow to be available for.
5
Click OK.
For information on configuring a workflow, see the following topics.
Working with statuses
Each workflow has its own sequence of statuses. To work with a workflow's statuses:
1
Click Workflows. The Workflows pane displays.
2
Select a workflow in the Workflow Name list.
3
Click the Status tab.
4
To add a status, click + in the Status tab. The Create Status dialog box displays.
Create Status dialog box
5
Enter a name for the status in the Name field.
6
Use the Color control to associate a color with the status. This color displays in the Status icon
column in the Workspace window.
7
To enable redline tracking for articles with this status in this workflow, check Enable Redline
Tracking.
30 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 31

CONFIGURATION
8
To automatically evaluate layouts with this status in this workflow when their projects are checked
in, check Check In Layout Evaluation.
9
To automatically evaluate layouts with this status in this workflow when they are sent to output,
check Output Layout Evaluation.
10
You can give a status an associated set of privileges based on the role privilegesdefined at the server
level, or you can custom design a set of privileges for the status.
• You can specify that a status grants the privileges defined for a particular role at the server level by
choosing an option from the Role drop-down menu and checking Use Server-level Privileges.
• You can choose an option from the Role drop-down menu and then modify the settings in the
Privileges list. This does not affect the role privileges settings at the server level; rather, it creates
an exception for privileges when assets reach the chosen status.
11
Click OK.
12
Use the arrows at the bottom right of the Status area to set up the statuses so that they occur in the
proper order (from top to bottom).
To delete a status, select it in the Status tab and click -.
To edit a status, double-click its name in the Status tab.
To duplicate a status, Option+click/right-click the status and choose Duplicate from the context
menu.
Working with forms
The Asset Form tab of the Forms pane lets you edit the asset forms for each of the content types.
The Collection Form tab lets you edit the forms associated with the various collection types. To
configure a form:
1
Click Forms in the navigation pane. The Forms pane displays.
Forms pane
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 31
Page 32

CONFIGURATION
2
Click the Asset Form or Collection Form tab.
3
Select a content type or collection type in the tree on the left and click Form Designer. The Form
Designer dialog box displays.
Form Designer dialog box
4
To display all attributes in a default layout, check Use the Default View for All Fields. To add
individual attributes, drag them from the Attribute Name list to the grid. To remove an attribute,
click its close box at the upper left. Use each attribute's handles to move and resize the attribute in
the grid.
5
Click Save.
Defining Roles and Privileges
All users must belong to a role. A role defines the Quark Publishing Platform privileges for its
members.
Roles and Privileges
A role specifies a set of privileges for working within Quark Publishing Platform applications. Each
Quark Publishing Platform user belongs to at least one role. To create, delete, rename, and modify
roles and their associated privileges, click Roles and Privileges.
32 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 33

CONFIGURATION
Define classificationsfor differentworkgroup members in the Administration: Roles and Privileges
area.
• To add a role, click + (plus sign). A new role displays in the Roles column. The role's content-type
privileges display in a tree in the Content Privileges tab, and the role'savailable application-specific
privileges display in a tree in the Application Privileges tab. Check privileges to enable them, and
uncheck privileges to disable them. For detailed descriptions of the available resources, see
"Privileges."
• To change the name of a role, Control+click/right-click the role, then choose Rename Role from
the context menu. You can also use the toolbar or the contextual menu to rename a role.
• To make a copy of a role, Control+click/right-click the role, then chooseDuplicate from the context
menu.
• To delete a role, click – (minus sign). An alert asks you to confirm the deletion. If users are assigned
to the role, you can assign them to a different role at this time.
Creating and deleting users
To create and delete user profiles, click User Profiles.
Use the Administration: User Profiles window to add and delete users and override user-role
settings.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 33
Page 34

CONFIGURATION
• To create a user profile, click +. In the Create User Profile dialog box, enter a user name and
password, enter the user's last name and first name, choose a role, and enter the user's e-mail address
and phone number. To prevent the user from logging on (for example, if the user is on extended
leave), check Disable Log On.
Specify a user's name, role, password, and access in the Create User Profile dialog box.
You can edit a user name by double-clicking it or using the contextual menu.
When you add users, you can pull them from your Lightweight Directory Application Protocol
(LDAP) list. See "Managing user lists with LDAP" for instructions. You can add Quark Publishing
Platform users in addition to users you manage through the LDAP service.
• To delete a user profile, select the profile and click–(minus sign). An alert prompts you to confirm
the deletion. If the user had assets routed to him or her, you can reroute the assets at this time.
• To duplicate a user profile, select the user profile and choose Duplicate from the contextual menu.
Managing user lists with LDAP
Many system administrators use directory services to manage users on an enterprise network, such
as Lightweight Directory Application Protocol (LDAP). The LDAP protocol provides global
management over user names and passwords. Quark Publishing Platform administrators are not
required to use LDAP, but if they rely on LDAP for other systems, such as e-mail, then Quark
Publishing Platform can be configured so that Quark Publishing Platform users can log on to Quark
Publishing PlatformServer with the same domainusername andpassword they use for other systems
on their enterprise network.
The LDAP service must exist within the same domain as your Quark Publishing Platform Server.
Quark Publishing Platform Server is the only Quark Publishing Platform application that maintains
communication with the LDAP service.
Quark Publishing Platform Server works with LDAP v3, and X.500 DAP is not required for or
supported by this implementation.
34 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 35

Refer to the Quark Publishing Platform Administration Guide and Quark Publishing Platform
ReadMe for more information about integrating LDAP and Quark Publishing Platform Server.
Before you can integrate Quark Publishing Platform Server with an LDAP Directory Server, you
must create an LDAP profile and map the LDAP attributes to Quark Publishing Platform user
attributes. The topics below explain how to do this.
Managing LDAP profiles
Before you can import LDAP users into Quark Publishing Platform, you must create an LDAP
profile. An LDAP profile lets you supply the Active Directory Server credentials that are necessary
to allow you to import LDAP users.
To create an LDAP profile:
1
Click User Profiles.
2
Click Manage LDAP Profiles. The Manage LDAP Profile dialog box displays.
CONFIGURATION
Manage LDAP Profile dialog box
3
Click the + button under the LDAP Profiles list to create a new LDAP profile.
4
Enter a name for the LDAP profile in the Profile Name field.
5
Choose the LDAP server's authentication method from the Authentication Type drop-down menu.
Valid values include Kerberos, Digest-MD5, and Simple.
6
Enter the realm name in the Realm field.
The convention is to enter realm names in upper-case letters.
Each profile must have a unique realm name.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 35
Page 36
CONFIGURATION
7
Enter the user name and password of a user who has read access to the Directory Server (that is, the
designated name in the Directory Server). This user authentication will be used to retrieve the list
of users from the Directory Server.
8
To add an LDAP server to the profile, click the + button under the Servers list.
9
Click Apply.
10
Click Done.
Mapping LDAP attributes
Before you can import LDAP users into Quark Publishing Platform, you must map the LDAP
attributes to Quark Publishing Platform user attributes.
To map LDAP attributes:
1
Click User Profiles.
2
Click LDAP Attribute Mapping. The LDAP Attribute Mapping dialog box displays.
LDAP Attribute Mapping dialog box
3
For each field in the dialog box, specify the corresponding LDAP field.
4
Click OK.
Importing LDAP users
To import users from your LDAP service:
1
Click User Profiles.
2
Click Import Users From LDAP. The Import Users From LDAP dialog box displays.
36 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 37

CONFIGURATION
Use the Import Users From LDAP dialog box to add users to your Quark Publishing Platform user
list.
3
The search controls at the top of the dialog box let you specify which users you want to be able to
import. To create a search:
• Choose the name of the appropriate LDAP profile from the Profile Name drop-down menu.
• Enter the search criteria in the Search Criteria field. For example, to import all LDAP users that
meet the criteria samaccountname=*, enter samaccountname=*
• Enter the base string in the Base String field. In this string, ou is an abbreviation for "organizational
unit" and dc is short for "domain component." This string represents the search base used to search
for users in the Active Directory server computer's hierarchy.
• Click Save to save the search and provide a name for the search in the dialog box that displays.
4
Choose the search to execute. The matching users are listed on the left.
5
Select one or more names from the LDAP Users list on the left and click the right arrow to add
selected users to the Platform Users list on the right. The Assign Role dialog box displays.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 37
Page 38
CONFIGURATION
Use the Assign Role dialog box to assign a Quark Publishing Platform user to a role.
6
Choose a role from the Role drop-down menu in the Assign Role dialog box and then click OK.
You can change the search criteria, execute more searches, and continue to add users until you click
OK in the Import Users from LDAP dialog box.
7
Click OK. The users in the list on the right are imported.
If you duplicate a Quark Publishing Platform user that you imported from your LDAP service, the
duplicated user is not connected to your LDAP service (that is, it's like creating a new user).
You cannot have two Quark Publishing Platform users with the same name. If you attempt to add a
user name that is the same as an existing user name, you will not be allowed to add the duplicate
user name.
A Quark Publishing Platform administrator must have the "Manage LDAP Users" privilege for the
Import Users from LDAP functionality to be available.
Creating and deleting groups
If you combine users into groups, you can route an asset to a group, and any user in that group can
check out the asset and work on it. To create and delete groups, click Groups.
38 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 39

CONFIGURATION
Use the Administration: Groups screen to create, edit, and delete groups of users.
• To create a group, click + (plus sign). In the resulting dialog box, enter a group name. Use the ->
arrow to add users to the group and the <- arrow to delete users from the group.
Specify group members through the Create Group dialog box.
You can edit a group name by double-clicking it, using the toolbar, or using the contextual menu.
• To delete a group, select the group and click – (minus sign). An alert prompts you to confirm the
deletion.
• To edit a group, double-click the group name.
Configuring Redline colors
For users with redline privileges, administrators specify colors that identify each user's changes.
To specify redline colors:
1
Click Redline. The Redline pane displays.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 39
Page 40

CONFIGURATION
The Redline screen lets you assign redline colors to users.
2
Select a user from the User Name list, then click the box in the Redline Color list to display the
Colors dialog box. Use the controls in the Colors dialog box to specify a specific color to be applied
to text when the user enters text with redlining enabled.
Alternatively, you can check Display All Redline Deletions in One Color to use a single color for
identifying deletions by all users.
3
Click Apply.
QuarkXPress and QuarkCopyDesk users can specify default redline colorsand styles to differentiate
insertions and deletions in WYSIWYG, Full Screen, and Galley views. However, when a
QuarkXPress or QuarkCopyDesk user is logged on to Quark Publishing Platform and working on
an article tracked by Quark Publishing Platform, the colors assigned by the administrator override
the colors specified in the Preferences dialog box. See A Guide to QuarkCopyDesk for information
about using the Redline feature outside of a Quark Publishing Platform workflow.
You can turn the Redline feature on and off on a status-by-status basis. For more information, see
"Working with statuses."
40 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 41

MAINTENANCE AND ASSET MANAGEMENT
Maintenance and asset management
Quark Publishing Platform provides remote server monitoring and other tools to promote effective
server maintenance. Using the Quark Publishing Platform Client, administrators perform asset
management functions to archive completed projects, restore archives, and so forth. This chapter
explains how to use these tools.
Monitoring user activity and logging off users
When you select the server name in the Quark Publishing Platform Web Administrator, information
about Quark Publishing Platform Server and the users loggedon to it displays. To use this information:
1
Click User Activity. The displayed list includes the number of users who are currently logged on
to Quark Publishing Platform Server, their names, the time and date eachuser logged on, each user's
machine name, and each user's application (including Quark Publishing Platform Script Manager).
User Activity pane
2
To log off a user, select the user and click Log Off Users. You can select multiple users to log off
more than one at a time.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 41
Page 42

MAINTENANCE AND ASSET MANAGEMENT
Deleting assets
You can delete assets using Quark Publishing Platform Client, QuarkCopyDesk, QuarkXPress, or
Quark PublishingPlatform Web Client. Your preference settings determine how the deletion process
for checked-out and attached assets works for each application.
To specify how Quark Publishing Platform Client, QuarkCopyDesk, QuarkXPress, or Quark
Publishing Platform Web Client responds when you attempt to delete checked-out assets and assets
attached to QuarkXPress projects, use the Checked-out Assets and Attached Assets drop-down
menus in the Asset Deletion Options area of the respective Preferences dialog box. The controls
are identical for both options. Choose Delete Asset Without Warning to delete checked-out or
attached assets without displaying a warning. Choose Never Allow Deletion to prevent the deletion
of checked-out or attached assets. Choose Ask Before Deleting to display an alert so youcan decide
each time you delete a checked-out or attached asset.
To delete assets:
1
Display the search results pane and select one or more assets you want to delete.
2
Click Delete in the Quark Publishing Platform Client Workspace toolbar. If the selected assets are
not checked out or attached to a QuarkXPress project, they are deleted. If the selected assets are
checked out or attached, the delete process continues according to your preference settings.
Archiving assets
You can use Quark Publishing Platform Client to archive Quark Publishing Platform assets when
you're finished with them, and Quark Publishing Platform provides a restoremechanism if you need
to reintroduce these assets to your Quark Publishing Platform workflow. Archiving assets requires
the "Enable Asset Archiving" privilege.
To archive assets:
1
Display the Workspace pane and select one or more assets to archive.
2
Choose Actions > Archive or click Archive in the Quark Publishing Platform Client Workspace
toolbar. The Archive dialog box displays.
3
Specify a folder for storing the archives, enter an archive name, and then click Archive/Save.
4
The selected assets are copied to the location you specify, and the attribute information for these
assets is combined in a single XML file.
If you check Delete Assets Afterwards in the Archive pane of the Preferences dialog box (Quark
Publishing Platform Client > Preferences), Quark Publishing Platform asks you if you want to
delete the assets after a successful archive operation. If Delete Assets Afterwards is unchecked, the
original assets remain on Quark Publishing Platform Server.
Quark PublishingPlatform confinesan archivefile and its corresponding XML file to a single folder.
When you name the XML file and the folderthat containsit, you can identify archive characteristics,
such as the date the archive was created. Using descriptive names will help you identify the archive
if you need to restore the assets later.
42 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 43

Your archive preferences are stored on Quark Publishing Platform Server, so your user log-on name
determines the archive preferences, regardless of theworkstation you use to archive assets. However,
archive log files are stored in the same folder where you store archive files.
Restoring assets
You can restore Quark Publishing Platform assets that have been archived if you have the "Enable
Asset Archiving" privilege.
In versions 9 and later of QuarkPublishing Platform,restoring a project also restores the corresponding
versions of all assets attached to that project, and all of those assets are attached to the project.
However, if you revert to a previous version of a project, any attached assets are detached.
To restore assets:
1
Display theWorkspace pane and choose Actions > Restore or click Restorein theQuark Publishing
Platform Client Workspace toolbar. The Restore dialog box displays.
MAINTENANCE AND ASSET MANAGEMENT
On Mac OS, you can add the Restore button to your Workspace toolbar.
Use the Restore dialog box to locate the archive file you want to restore.
2
Select the XML file that corresponds to the archived assets you want to restore, then click Restore.
Using descriptive names for the archive folder and XML file when you create the archive will help
you identify assets for restoration.
If one or more of the attributes for the archived assets are no longer part of the server configuration,
you can choose alternative attributes in many cases. However, when switching attributes is not
possible, the restore process skips to the next archived file. You will need to re-create the missing
attribute to restore these skipped assets.
If an asset with the same name and file type is already checked in to Quark Publishing Platform
Server, an error occurs and identifies the asset in the log file.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 43
Page 44

MAINTENANCE AND ASSET MANAGEMENT
Your "Restore" log files are stored in the same folder where you store archive files. If you do not
have write access to the folder where you store archive files, Quark Publishing Platform Server will
prompt you to specify a location.
44 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 45

User interface
Users can access their Quark Publishing Platform workflow through the Quark Publishing Platform
Client application, Quark Publishing Platform Web Client, and (using XTensions® software)
QuarkCopyDesk and QuarkXPress. This chapter provides an overview of the Quark Publishing
Platform user interface on both Mac OS and Windows. To learn how to perform application-specific
tasks, see the other chapters in this document.
USER INTERFACE
Roles, views, and content structure overview
Before you can use Quark Publishing Platform,you mustlog on to the server. Bydefault, the Platform
includes an existing user named "Admin" with a case-sensitivepassword of"Admin." Administrators
use this name and password to log on for the first time, and Quark recommends enhancing
administrative security by changing the password the first time you log on.
For all users, the name and password you use to log on are associated with a particular role. This
role determines which privileges you have and which functions are available to you. Consequently,
your view of the Quark Publishing Platform user interface may be different from someone else's.
See "Privileges" to learn about specific privileges for a role.
The Workspace Browser window
The Workspace Browser window displays when you log on to Quark Publishing Platform from
any Quark Publishing Platform client application.
Workspace Browser window
You can use the Workspace navigation pane to work with files in Quark Publishing Platform.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 45
Page 46

USER INTERFACE
Workspace pane
You can control what displays in the main area on the right by clicking items in the Workspace
navigation pane on the left.
• Quick Search: Use the Quick Search field to search for Quark Publishing Platform assets according
to asset name, text within an asset, or a combination of asset name and text content.
• Favorites: Drag frequently used collections and searches to this area, and they will be available in
every Quark Publishing Platform client you use. (In Quark Publishing Platform Web Client, you
can Option+click/right-click an asset and use the context menu to add it to or remove it from the
Favorites area.)
• Assignments: Displays all assets that are routed to you.
• Attachments (QuarkXPress only): Displays all assets that are attached to the active layout.
• Depth (QuarkXPress only): Displays articles with text components that can fit in the selected text
box (within a certain range). For more information, see "QXP preferences: Workspace > Workspace
Browser."
• My Searches: Displays all of your searches. Click a search to see its results in the search results
pane. To duplicate, delete or reload a search, Option+click/right-click it and choose Duplicate
Search, DeleteSearch or Reload Search. You can also Option+click/right-click a search and choose
Manage Searches in order to edit, share, duplicate, rename and delete searches.
• Shared Searches: Displays all of the shared searches that you have access to. Click a search to see
its results on the search results pane.
• Unsaved Searches: Displays all unsaved searches that you have created. To delete an unsaved
search, Option+click/right-click it and choose Delete Search.
• Collections: Displays, in tree format, all of the collections that the active user has access to. You
can add an asset to a collection by dragging the asset onto the collection from elsewhere in the
collections hierarchy, from the search results area, or from the file system.
The options for Quark Publishing Platform Web Client are slightly different. For more information,
see "Quark Publishing Platform Web Client."
46 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 47

Assign
Check Out
USER INTERFACE
Workspace toolbar
The Workspace toolbar provides the commands listed in this section. The overflow menu on the
right side of the toolbar includes many other commands.
On Windows, the controls in the Workspace toolbar are presented using the Windows ribbon
interface. This provides additional features, including the Quick Access Toolbar feature.
DescriptionButton
Use the Assign drop-down menu todisplay theassignment options:Text File, Graphic, QuarkCopyDesk Article,
QuarkCopyDesk Article Template, QuarkXPress Project, and QuarkXPress Project Template.
QuarkCopyDesk Article displays a submenu with options to create an assignment based on an existing article
or based on default specifications from your Quark Publishing Platform Server.
Click this button to open and display the asset selected in the Workspace Browser window. The button
accommodates different conditions. If you select a checked-in asset, this button checks the asset out. If you select
an assetthat youhave checked-out,this buttonopens it. If you select an asset that you have open,this buttonbrings
that asset's window to the front.
When you check out a file, Quark Publishing Platform automatically copies the asset to your computer, stores it
in a folder that you have designated for storing checked-out assets (or, if this is your first checkout, prompts you
to designate the folder), and opens the asset.
Cancel
Checkout
Read Only
Get
Get Collection
Click Cancel Checkout to cancel an asset checkout without updating Quark Publishing Platform Server with a
revision. However, if you made any changes, an alert notifies you that your changes might be lost. If you saved a
revision of the asset on Quark Publishing Platform Server, the revision becomes the current version.
Click Read Only to display an asset with read-only access. You can view the asset's contents, but you cannot
change the asset.
Click Get to move a copy of the selected asset to your computer. If you have the privilege to check in new files,
you can rename the asset and check it in.
Click Get Collection to move a copy of the selected collection to your computer.
Click Check In to check in a checked-out asset selected in the search results pane.
Check In
Check In Other
(MAC OS client) Click Check In Other to display the Check In Other File dialog box. This dialog box lets you
navigate to oneor more assets stored locally or on anetwork. You can specify anasset's attributes before checking
in the asset. This dialog also lets you choose folders on the disk to be checked in along with its content and any
sub folders and their contents.
(Windows client ) Use the Check In Other drop-down menu to display the options: Check In File and Check In
Folder. Click Check In File to display the Check In Other File dialog box. This dialog box lets you navigate to
one or more assets stored locally or on a network. You can specify an asset's attributes before checking in the
asset. Click Check In Folder to check in a folder and all of its subfolders.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 47
Page 48

USER INTERFACE
Save Revision
Publish
ePUB
DescriptionButton
Click Save Revision to display the Save Revision dialog box and update Quark Publishing Platform Server with
the most current content from the selected asset.
Click Publish to publish the selected asset in one of a variety of formats.
Click Publish as PDF to publish the selected asset in PDF format.Publish as PDF
Click Publish as Adobe Flash to publish the selected asset in SWF (Flash) format.Publish as SWF
Click Publish as ePUB to publish the selected asset in ePUB format.Publish as
Click Publish as AVE to publish the selected asset in AVE (App Studio) format.Publish as AVE
Text Format
HTML
QuarkXPress
Project
Publish as App
Studio Article
Refresh
Edit Attributes
Displays
Click Publish as Rich Text Format to publish the selected asset in RTF format.Publish as Rich
Click Publish as HTML to publish the selected asset in HTML format.Publish as
Click Publish as QuarkXPress Project to publish the selected asset as a QuarkXPress project.Publish as
Click Publishas App Studio Article to publish the selectedasset asan HTML5article. Note that you must supply
App Studio Publishing Portal credentials in QuarkXPress Server in order to be able to upload App Studio articles
to the Portal; for more information, see A Guide to QuarkXPress Server.
When you click Refresh, Quark Publishing Platform performs the active search again and refreshes the search
results pane.
Click Edit Attributes to display the Edit Attributes dialog box for the asset selected in the window. Attributes
are known as metadata in other systems, and they were called "headers" in earlier versions of Quark Publishing
Platform. If you have the privilege and an attribute is available, you can change the attribute value in this dialog
box and then click Update.
Use the Displays drop-down menu to control how assets display in the search results pane. For more information,
see "View display options."
For users who have the "Enable Enhanced Search Displays in Workspace Browser" privilege, this menu also
includes Project, Project and Page, Collections, and Relationships options for asset searches. Also, the dialog
box that displays when you choose Custom includes Group By and Attachment tabs.
Click New Search to create a search with new search criteria.
New Search
48 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 49

Saved Searches
Preview
Selection
Information
Relationship
Information
USER INTERFACE
DescriptionButton
Use theSaved Searches drop-down menu to executesaved searches.The Saved Searches list also includesshared
searches from other users. Choose Manage to display the Manage Saved Searches dialog box, which lets you
add, edit, share, duplicate, and delete search operations.
Click Preview to display a large preview of the selected image, QuarkCopyDesk article, or QuarkXPress project.
The preview window also displays navigation controls for previewing different pages of the asset.
By default, Quark Publishing Platform asset previews include the first five pages of a PDF and the first 20 pages
of a QuarkXPress project or QuarkCopyDesk article. Quark Publishing Platform administrators can adjust the
number of pages in a preview by editing configuration files. See A Guide to Quark Publishing Platform
Administration for details.
Click SelectionInformation to display theSelection Information dialog box. This dialog box contains information
about the selected asset or assets, such as whether you can check out the assets or delete components.
Click Relationship Information to view the primary attachments, secondary attachments (if any), and revision
number for the asset selected in the window. For files, the Relationship Information dialog box also displays
Layout Name, Page Name, Page Index &, and Component Name. For QuarkCopyDersk files, it displays
Component Name. For XML files, it displays XPath.
View Revisions
Index Again
Delete
Asset
Information
Click View Revisions to display the Revisions dialog box. This dialog box contains information about the revisions
tracked by Quark Publishing Platform Server for the selected asset. You can print a revision, open a read-only
copy of a revision, delete a revision, or revert to an earlier version to designate a revision as the current version.
Click Index Again to receive updated previews from QuarkXPress Server for articles and projects.
Click Delete to remove the selected asset from Quark Publishing Platform Server.
Click AssetInformation to display the MoreInfo window, which listsall the attributes and valuesfor theselected
asset.
Click View Slideshow to display a slideshow of the selected assets.
View Slideshow
Duplicate
Click Duplicate Item to create a copy of the selected asset on Quark Publishing Platform Server.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 49
Page 50

USER INTERFACE
Export Search
Results
Archive
Restore
DescriptionButton
You can export the results of a search as an HTML file, an XML file, a tab-delimited file, or a comma-delimited
file.
Click Archive to display the Archive dialog box to choose the archive location for the selected asset. For more
information, see "Archiving assets" and "Restoring assets."
Click Restore to display the Restore dialog box to restore one or more archived assets. For more information, see
"Archiving assets" and "Restoring assets."
Click Print to print the search results.
Print
Print Preview
Customize
(Windows only) Click Print Preview to display a preview of printed output.
On Mac OS, click Customize to display the Workspace toolbar icon controls. Clicking Customize has the same
effect as control-clicking the Workspace toolbar and choosing Customize Toolbar.
Compact View (Mac OS only)
Click Compact View to reduce the size of the Workspace Browser window and include fewer
controls. Many of the other controls automatically move to the overflow menu, and the window
identifies the name of the active application. For example, if you choose Compact View and then
switch to TextEdit, the Quark Publishing Platform Client window displays the name of the active
application and provides buttons for checking in assets, checking out assets, viewing revisions of
assets, and searching for other assets.
Customizing the Workspace toolbar
You can customize your display on Mac OSby control-clickingthe Workspace toolbar and choosing
Customize Toolbar. A window displays that allows you to add an icon by dragging it to the toolbar
or remove an icon by dragging it from the toolbar. You can add the Customize icon to more quickly
access this window. You can also add spacing and dotted-line separators to the Workspace toolbar.
On Mac OS, use the Show drop-down menu at the bottom of the window to display controls (such
as the Check In button) with text and icons, text only, or icons only. You can also control the size
of the icons.
On Windows, you can add a command to the Quick Access Toolbar by right-clicking the command.
50 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 51
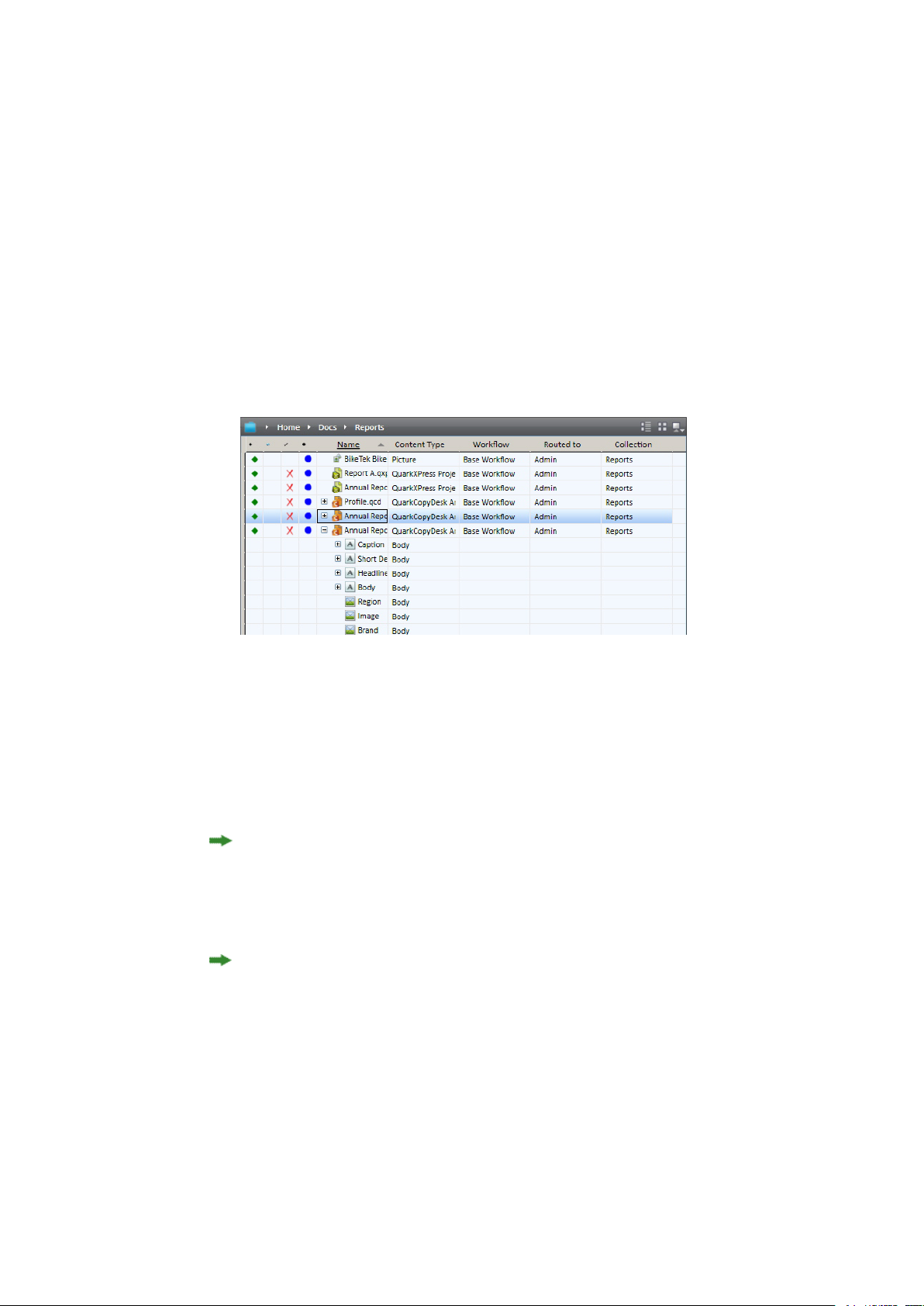
If you decrease the size of the Workspace Browser window, increase the size of icons, and display
icons and text, the Workspace toolbar automatically generates an overflow menu that displays on
the right side of the palette to include the controls that don't fit on the toolbar.
View display options
Viewdisplay options let you control how assetsdisplay in the workspace. These options areavailable
from the View menu (Mac OS only) and from the icons above the workspace area in the Workspace
Browser window.
Name view
The Name submenu includes the following options.
Choose List View to display assets in a list format.
USER INTERFACE
List view
In list views, you can show and hide all columns except the Name column.
• To sort (or reverse sort) the search results according to a column, click the column title.
• To show or hide a column, Control+click/right-click the column title and choose the attribute.
• To show or hide multiple attributes, Control+click/right-click the column title and choose Customize
Current View. The Configure Columns tab includes all the attribute fields for you to show or hide.
You can add the Thumbnails column to display thumbnail asset previews.
• To reposition a column, click and drag the column title.
• To resize a column, click and drag the column edge.
Quark Publishing Platform assets that match your search criteria but are not attached to projects are
listed below Unattached. Quark Publishing Platform assets that match your search criteria but are
attached to projects that have never beenchecked in to the Platform Server arelisted below Attached
to other projects. Attached assetscan display below multiple projects if theyare attached to multiple
projects.
Choose Relationship View to display the relationships between assets. This lets you determine
which assets are used by other assets.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 51
Page 52

USER INTERFACE
Relations view
Choose Thumbnails to display small previews of assets. You can display the color of an asset's
status in the border of the thumbnail preview by checking the Show Status Color around
Thumbnails preference (Quark Publishing Platform Client > Preferences > Workspace). The
status color border displays when you choose Thumbnails, Filmstrip, or Detailed Thumbnails
View from the Displays > Name submenu.
Thumbnails view
Choose Filmstrip to display a large preview of the selected asset with all other assets below it.
52 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 53
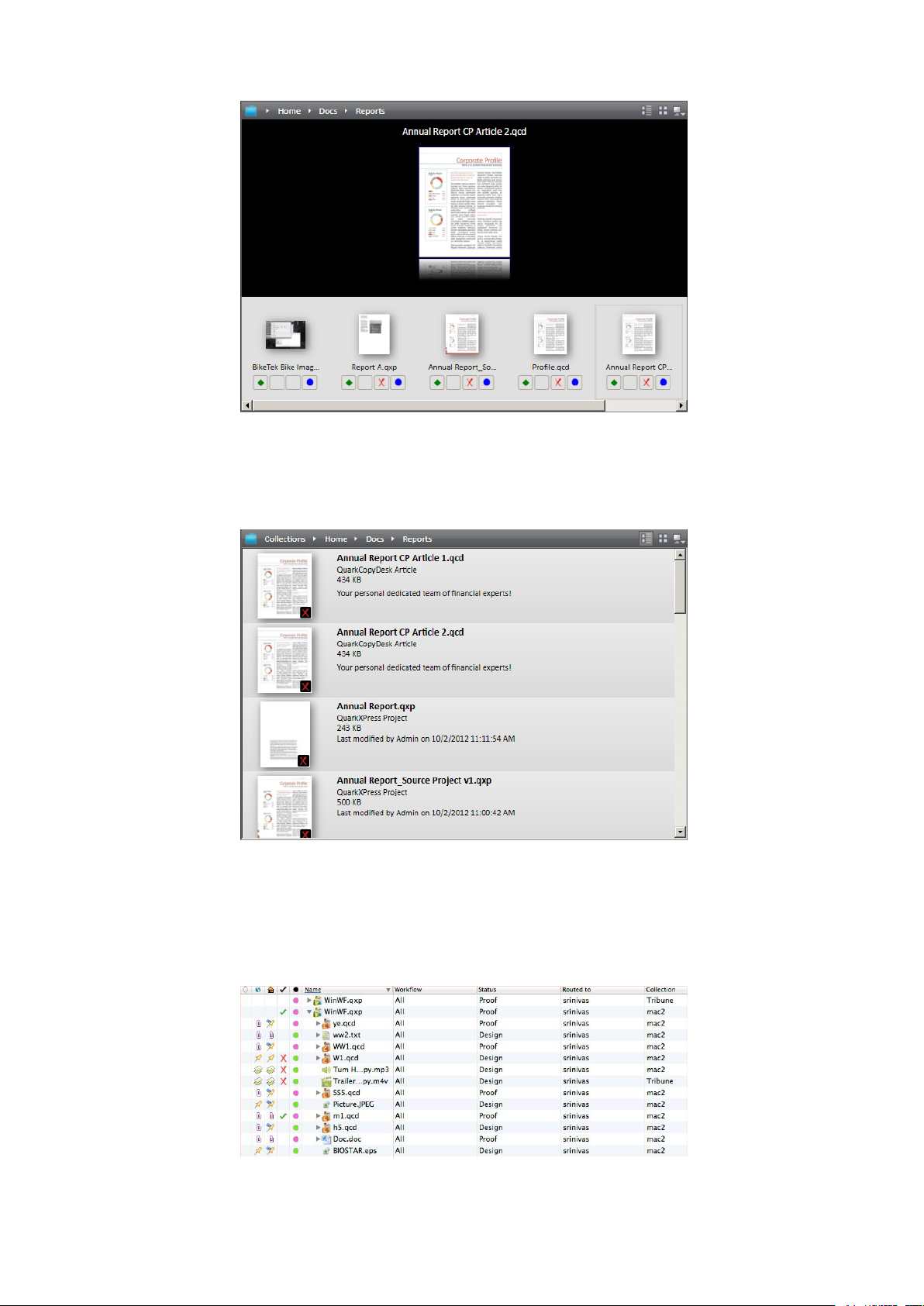
USER INTERFACE
Filmstrip view
Choose Snippet View to display a thumbnail preview for each asset, with a thumbnail preview and
other asset information to the right of the preview.
Snippet view
Project view
Project view displays search results in ahierarchical structure with QuarkXPress projectsat the top.
Articles and pictures attached to each project are listed below their respective projects.
Project view
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 53
Page 54
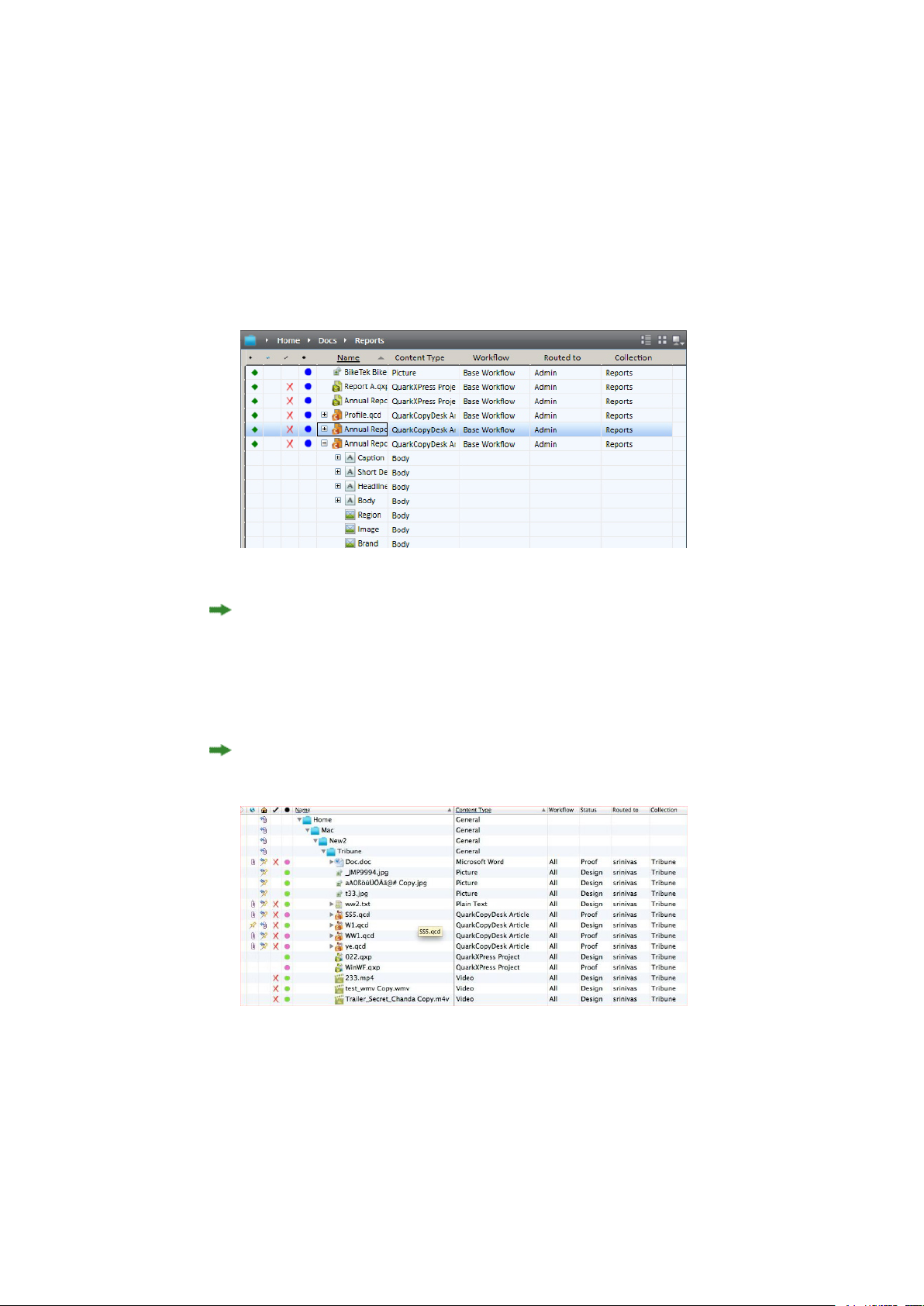
USER INTERFACE
Project and Page view
Project and Page view displays search results in a hierarchical structure with QuarkXPress projects
at thetop. Each page is listed below its respective layout. Articles and pictures in the layout are listed
below their respective pages.
If one item attached to a layout matches the search, the project and all the other attachments of the
project also display.
An article or picture can display below more than one page if it is attached to multiple pages in a
project.
Project and Page view
This view is not available when you are browsing collections. To see the assets attached to a project,
use List View with Attachments.
Collections view
Collections displays search results in the hierarchical structure of the collections tree.
This view is not available when you are browsing collections.
Collections view
Custom view
Custom view displays search results in a hierarchical structure based on fourlevels of attributes you
specify. Choosing Custom displays a window with three tabs: Configure Columns, Group By,
and Explore By.
54 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 55

USER INTERFACE
Use the Configure Columns tab to specify the attributes you want to display as columns in the
search result.
Use the Group By tab to specify up to four hierarchical groups within which you can group your
search results. This option is not available in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 55
Page 56

USER INTERFACE
Use the Explore By tab to display QuarkXPress projects and attached assets or to display assets in
the collections hierarchy. This option is not available in Quark Publishing Platform Web Client.
List View with Relationships
List View with Relationships displays assets in a list view where you can expand projects to see
their relationships, and expand articles to see their components.
List View with Relationships view
List View with Relationship Status
List View with Relationship Status displays assets in a list view where you can expand projects
to see their relationships and view their statuses.
Icon columns
In QuarkPublishing PlatformClient andQuarkCopyDesk, the Workspace Browser window displays
four icon columns that provide information about each asset. The Workspace Browser window in
QuarkXPress displaysa fifth icon column calledLocal Attachment. These icons display in columns
on the left side of the Search Results list in all extended views and List View, as well as under each
asset's icon in Thumbnails View and Filmstrip View. In order from left to right, the icons are as
follows:
• Clear Diamonds: A diamond indicates each asset's status, relative to the last search performed in
the Workspace Browser window. A green diamond indicates the asset has been added to the list
since the current search was executed. A white diamond indicates that an asset's attributes have
been updated since the current search was executed, but the asset still meets the search criteria. A
gray diamond and gray shade to the line indicate that another user changed the asset's attributes
and the attributes no longer match the search criteria. However, if you made the same change to the
asset's attributes, the asset would simply be removed from the Workspace Browser window. If you
56 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 57

USER INTERFACE
click the Clear Diamonds icon at the top of the column, all diamonds are removed, the Workspace
Browser window is updated, and the assets no longer matching the search are removed from the
display.
Press Option/Alt while clicking the Clear Diamonds icon at the top of the column to lock or unlock
the ClearDiamonds column. When the Clear Diamonds column is locked , assetattribute changes
do not display in the Clear Diamonds column.
Clicking the diamond next to an asset name removes the diamond for that asset, but the rest of the
Clear Diamonds column in the Workspace Browser window does not change.
• Global Attachment: A symbol indicates whether each asset is attached to a QuarkXPress project
as a primary or secondary attachment. Select an attachment in the Workspace Browser window
and click Attachment Information to determine attachment status. You can also position your
mouse over the Global Attachment icon for the asset to display a tooltip (for example, "Indirect
Picture Attachment" and "Secondary Global Attachment").
• Local Attachment (QuarkXPress only): A symbol indicates any local attachments for the active
project (that is, "local" project). Select an attachment in the Workspace Browser window and click
Attachment Information to determine attachment status. You can also position your mouse over
the Local Attachment icon to display a tooltip (for example, "Unattached Secondary Attachment"
and "Secondary Local Attachment").
• Checked Out: A symbol indicates whether assets are checked out. If an asset is checked out by the
logged-on user, a green checkmark displays. If an asset is checked out by another user, a red
checkmark displays. If the logged-on user cannot check out the asset, a red X displays.
• Status: A color-coded circle indicates the Quark Publishing Platform status for the selected asset.
Your Quark Publishing Platform administrator defines these statuses and associates a color with
each status. A tooltip for each color-coded circle displays the status name.
Preview pane
The Preview pane on theright sideof theWorkspacewindow displaysadditional informationabout
the selected asset.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 57
Page 58

USER INTERFACE
Preview pane
The Preview area displays a preview of the selected asset. If the asset is a project or article, the
Preview area displays a spread preview of all pages. If the asset is a project, the Preview area can
display a preview of every layout in the project. If the project has multiple Print, Interactive, and/or
App Studio layouts, a tab displays at the top for each layout.
You cannot preview projects that contain Web layouts in the Preview area.
Beneath this area are the following tabs:
• Asset Preview Info: Displays an overview of the asset's attributes.
• Asset Information: Displays all of the asset's attributes.
• Relationship Information: Displays information about the asset's attachments.
• Selection Information: Displays information about what you can and cannot do with the asset.
• The Revisions area displays the number of asset revisions. Click Revisions to display the Revisions
dialog box. This dialog box allows you to see the full list of revisions, view a read-only copy of a
revision, revert to a previous revision, or print the asset revision list.
If articles or projects do not display in the Preview Pane, select the assets and click Index Again
in the Workspace toolbar to receive updated asset previews from QuarkXPress Server.
Menus (Quark Publishing Platform Client)
The commandsin the Quark Publishing Platform Client application window's menus vary depending
on the active application, the user's role, and the pane selected on the left side of the window.
58 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 59

Only the Mac OS version of the Quark Publishing Platform Client application has menus. On
Windows, use the ribbon interface.
Quark Publishing Platform Client menu (Mac OS only)
The Quark Publishing Platform Client menu includes the following commands:
• About Quark Publishing Platform Client: Displays information about Quark Publishing Platform
Client, including the version number.
• Preferences: Enables you to specify default settings and customize the way Quark Publishing
Platform Client performs on your workstation.
• Log On/Log Off: The Log On command displays the Log On dialog box. The Log Off command
logs off the user but does not exit the application.
• Quit Quark Publishing Platform Client: Exits the application.
If you click the close icon in the upper-left corner of the Quark Publishing Platform Client window
on Mac OS, the window closes. Clickthe Quark Publishing Platform Client icon inthe Dock to open
a new window.
USER INTERFACE
This menu also contains some commands supplied by Mac OS.
File menu
The File menu provides commands for printing the Quark Publishing Platform Client window on
Mac OS and Windows, as well as the Quit and Log Off commands on Windows.
• New Window: Displays a new Workspace Browser window.
• Page Setup: Lets you configure the printed version of the active window.
• Print: Prints the active window.
• Close: Closes the active Workspace Browser window.
• Export Search Results: Lets you export the search results displayed in the search results pane as
an HTML file, an XML file, a tab-delimited file, or a comma-delimited file.
Edit menu
The Edit menu includes the following commands:
• Undo <Last Operation>: Reverses the last operation performed on content.
• Redo <Last Operation>: Reverses the last Undo command performed on content.
• Cut: Removes the selected content and stores it on the Clipboard.
• Copy: Copies the selected content and stores it on the Clipboard.
• Paste: Pastes the Clipboard content at the text insertion point.
• Select None: Deselects all the contents of the active document, Workspace window, or field.
• Select All: Selects all the contents of the active document, Workspace window, or field.
• Rename: Lets you rename the selected item.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 59
Page 60

USER INTERFACE
• Add: Adds a new instance of the selected item.
• Edit: Lets you edit the selected item.
• Duplicate: Makes a copy of the selected item.
• Program Language: Lets you change the language of the Quark Publishing Platform interface.
• Delete Selection: Removes the selected content or item.
• Special Characters: Displays the Character Palette with the character options for available fonts.
View menu
The View menu includes the following commands:
•
Displays submenu: Use this submenu to control how assets display. For moreinformation, see"View
display options."
• Compact: Use this command to change the Workspace display from Expanded View to Compact
View.
• Navigation Pane: Use this command to show or hide the navigation pane on the left.
Actions menu
The Actions menu includes the following commands: for assigning assets, checking assets in and
out, opening copies of assets, opening read-only versions of assets, viewing asset information,
viewing asset revisions, editing asset attributes, and checking in assets in third-party file formats
that cannot be opened with File > Open in QuarkXPress or QuarkCopyDesk.
• Assign: Use the Assign drop-down menu to display six assignment options: Text File, Graphic,
QuarkCopyDesk Article, QuarkCopyDesk Article Template, QuarkXPress Project, and
QuarkXPress Project Template. QuarkCopyDesk Article displays a submenu with options to
create an assignment based on an existing articleor based on default specifications from your Quark
Publishing Platform Server.
• Check In: Click Check In to check in a checked-out asset selected in the Workspace Browser
window.
• Check In Other: Click Check In Other to display the Check In Other File dialog box. Thisdialog
box lets you navigate to one or more assets stored locallyor on a network. You can specify an asset's
attributes before checking in the asset.
• Check Out: Click Check Out to open and display the asset selected in the Workspace Browser
window.
• Read Only: Click Read Only to display an asset with read-only access. You can view the asset's
contents, but you cannot change the asset.
• Get: Click Get to move a copy of the selected asset to your computer. If you have the privilege to
check in new files, you can rename the asset and check it in.
• Publish > Publish as ePUB: Click Publish as ePUB to create an ePUB document fom a layout's
Reflow view.
• Publish > Publish as App Studio Article: ClickPublish as App Studio Article to create anHTML5
App Studio article from a layout and upload it to the App Studio Publishing Portal. Note that you
must supply App Studio Publishing Portal credentials in QuarkXPress Server in order to be able to
upload App Studio articles to the Portal; for more information, see A Guide to QuarkXPress Server.
60 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 61

USER INTERFACE
• Publish > Publish as Adobe® Flash®: Click Publish as Adobe® Flash® to create a SWF (Flash)
version of a layout.
• Publish > Publish as PDF: Click Publish as PDF to create a PDF version of an article or layout.
• Publish > Publish as AVE: Click Publish as AVE to create an App Studio issue from a layout.
• Publish > Publish as QuarkXPress Project: Click Publish as QuarkXPress Project to create a
QuarkXPress project from a layout.
• Publish > Publish as RTF: Click Publish as RTF to create an RTF file from a layout.
• Cancel Checkout: Click Cancel Checkout to cancel an asset checkout without updating Quark
Publishing Platform Server with a revision. However, if you madeany changes, an alert notifies you
that your changes might be lost. If you saved a revision of the asset on Quark Publishing Platform
Server, the revision becomes the current version.
• Edit Attributes: Click Edit Attributes to display the Edit Attributes dialog box for the asset
selected in the window. Attributes are known as metadata in other systems, and they were called
"headers" in earlier versions of Quark Publishing Platform. If you have the privilege and an attribute
is available, you can change the attribute value in this dialog box and then click Update.
• View Revisions: Click View Revisions to display the Revisions dialog box. This dialog box contains
information about the revisions tracked by Quark Publishing Platform Server for the selected asset.
You can print a revision, open a read-only copy of a revision, or revert to an earlier version to
designate a revision as the current version.
• Asset Information: Click Asset Information to display the More Info window, which lists all the
attributes and values for the selected asset.
• Edit Collection Template: Click Edit Collection Template to edit collection templates.
• Restore: Click Restore to display the Restore dialog box to restore one or more archived assets.
• Archive: Click Archive to display the Archive dialog box to choose the archive location for the
selected asset.
Go To menu
When the Workspace pane is selected, you can choose Go To > Assignments to display all assets
routed to you.
If you have administrator privileges, you can use the Go To menu to navigate to the various
administration panes.
Search menu
The Search menu includes the following commands:
• New Search: Creates a search.
• Saved Searches submenu: Choose a search from the Saved Searches submenu to perform a search
with predefined criteria. Choose Manage to display the Manage Saved Searches dialog box. This
dialog box lets you view and modify saved searches, as well as view and share searches.
• Shared Searches: Choose a search from the Shared Searches submenu to use searches that have
been shared with you. The name of the user who shared the search displays in parentheses.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 61
Page 62

USER INTERFACE
Menus (QCD)
Window menu (Mac OS)
The Window menu includes the following commands:
• Minimize: Stores the active window in the dock.
• Zoom: Displays the active window on your entire monitor.
• Bring All to Front: Brings all active Quark Publishing Platform Client windows to the front.
• The area at the bottom of the Window menu identifies the active window with a checkmark and
lists all other open windows.
Help menu
The Help menu displays the Quark Publishing Platform Help file.
See A Guide to QuarkCopyDesk for a detailed explanation of QuarkCopyDesk menu commands.
The informationbelow applies only to QuarkCopyDesk in a Quark PublishingPlatform environment.
When you Control+click/right-click in the layout or on an item, the Platform submenu makes it
easy to get to the commands that are appropriate in the current setting.
QuarkCopyDesk menu (Mac OS only)
The QuarkCopyDesk menu is a part of QuarkCopyDesk for Mac OS. This menu includes the
following Quark Publishing Platform related commands:
• Preferences > Quark Publishing Platform: Enables you to specify default settings and customize
the way QuarkCopyDesk works on your computer. Use the Quark Publishing Platform area to
specify Quark Publishing Platform specific parameters. See "Setting Quark Publishing Platform
preferences — QuarkCopyDesk" for more information.
Platform menu
The Platform menu displays when you install the Quark Publishing Platform XTensions software
module in the "XTensions" folder in your QuarkCopyDesk application folder. This menu includes
the following commands:
• Check Out Article: Displays the Check Out dialog box. This dialog box allows you to check out
a QuarkCopyDesk article, article template, or compatible third-party asset.
• Check In Article: Displays the Check In dialog box. This dialog box allows you to check in a
QuarkCopyDesk article.
You can check in a QuarkCopyDesk template by choosing QuarkCopyDesk Template from the
Content Type drop-down menu in the Check In dialog box.
• Cancel Article Check Out: Removes a checked-out asset from your computer and makes it available
for others to check out. An alert displays, allowing you to save or discard any changes made since
your checkout. Also, if you saved a revision on Quark Publishing Platform Server, it becomes the
current version when you cancel a checkout.
62 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 63

USER INTERFACE
• Save Article Revision: Displays the Save Revision dialog box. This dialog box allows youto update
Quark Publishing Platform Server to reflect recent changes while leaving the article open for more
editing.
• Attach Picture: Displays a dialog box that makes it easy for you to attach a picture to the selected
checked-out picture component or direct attachment. By default, all pictures routed to you display,
but you can also browse and search for other pictures.
• Replace Picture: Displays a dialog box that makes it easy for you to replace the picture in the
selected checked-out picture component or direct attachment with a new picture. By default, all
pictures routed to you display, but you can also browse and search for other pictures.
• Edit Article Attributes: Displays the Edit Article Attributes dialog box. This dialog box allows
you to view and change attribute information for the active QuarkCopyDesk article.
• View Revisions > Article: Ifyou havean articlechecked out and displayed on screen, this command
displays the Revisions dialog box. This dialog box allows you to display a read-only version of the
article, revert the article to an earlier revision, and print the contents of the Revisions dialog box.
• View Revisions > For All Articles: If you have the privilegeand nochecked-out articlesare displayed
on screen, this command displays the Revisions dialog box. This dialog box allows you to view
article names, display read-only versions of articles, revert an article to an earlier revision, and print
the contents of the Revisions dialog box.
• Workspace Browser: Displays or hides the Workspace Browser window.
• Log On/Log Off: Logs the user on to or off of a Quark Publishing Platform Server.
Menus (QXP)
See A Guide to QuarkXPress for a detailed explanation of QuarkXPress menu commands. The
information below applies only to QuarkXPress in a Quark Publishing Platform environment
When you Control+click/right-click in the layout or on an item, the Platform submenu makes it
easy to get to the commands that are appropriate in the current setting.
QuarkXPress menu (Mac OS only)
The QuarkXPress menu is a part of QuarkXPress for Mac OS. This menu includes the following
Quark Publishing Platform related commands:
• Preferences > Quark Publishing Platform: Enables you to specify default settings and customize
the wayQuark Publishing Platform-related tasks are performed within QuarkXPress on your computer.
Use the Quark Publishing Platform area to specifyQuark Publishing Platform specific parameters.
Utilities menu
If Quark Publishing Platform XTensions software is installed in the "XTensions" folder in your
QuarkXPress application folder, the Utilities menu includes the following command.
•
Redline: Displays the Redline palette. For more information, see "Redlining."
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 63
Page 64

USER INTERFACE
Window menu
If Quark Publishing Platform XTensions software is installed in the "XTensions" folder in your
QuarkXPress application folder, the Window menu includes the following command.
• Article: Displays the Articles palette.
• Project Attachments: Displays the Project Attachments palette, which lists the assets attached to
the active layout.
Platform menu
If Quark Publishing Platform XTensions software is installed in the "XTensions" folder in your
QuarkXPress application folder, the Platform menu displays in QuarkXPress. This menu includes
the following commands:
• Check Out > Project: Displays the Check Out dialog box. This dialog box allows you to search
for and check out a QuarkXPress project or template (or open a read-only version of a QuarkXPress
project or template).
• Check Out > Article: Lets you check out the article selected in the layout.
• Check Out > Picture: Lets you check out the picture attached to the selected picture box.
• Check Out > Library: Lets you check out a library.
• Check In > Project: Displays the CheckIn Project dialog box.This dialogbox allowsyou to check
in the active QuarkXPress project.
If you also have one or more attached articles checked out when you choose Check In Project, all
articles are checked in along with the project.
You can check in a QuarkXPress template by choosing Project Template from the Content Type
drop-down menu in the Check In dialog box.
• Check In > Project With Pictures: Displays the Check In dialog box with attached and imported
pictures displayedin a list on the left. This dialog boxallows youto check in the active QuarkXPress
project and its pictures.
• Check In > All Local Pictures: Lets you check in all pictures that have been locally imported into
the active layout. The pictures are not attached to the layout.
• Check In > Article: Lets you check in the article selected in the layout.
• Check In > Picture: Lets you check in the picture attached to the selected picture box.
• Check In > Library: Lets you check in the frontmost library.
• Cancel Checkout > Project, Cancel Checkout > Article, Cancel Checkout > Picture, Cancel
Checkout > Library: Removes the asset from your computer and makes it available for others to
check out.
• Save Revision > Project, Save Revision > Article: Updates QuarkPublishing PlatformServer with
your most current changes while leaving the project or article open for more editing.
• Save Revision > Picture: Saves a revision of the picture attached to the selected picture box.
• Save Revision > Library: Saves a revision of the frontmost library (if it has been checked out from
Quark Publishing Platform).
64 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 65

USER INTERFACE
• Assign as Article: Assigns the selected text and/or picture boxes as an article.
• Assign as Picture: Assigns the picture in the selected box as a direct attachment.
• Attach Picture: Displays a dialog box that makes it easy for you to attach a picture to the selected
picture box or checked-out picture component. By default, all pictures routed to you display, but
you can also browse and search for other pictures.
• Replace Picture: Displays a dialog box that makes it easy for you to replace the picture in the
selected checked-out picture component or direct attachment with a new picture. By default, all
pictures routed to you display, but you can also browse and search for other pictures.
• Detach: Detaches any articles or pictures assigned to the selected boxes.
• Add Component: To add a new component to an article in the active layout, select one or more
boxes and choose this option. If the layout contains more than one article, the Select Article dialog
box lets you choose which article you want to add to.
• Edit Attributes > Project, Edit Attributes > Article, Edit Attributes > Picture: Displaysthe Edit
<Project/Article/Picture> Attributes dialog box. This dialog box allows you to view and change
attribute information for the active QuarkXPress project, QuarkCopyDesk article, or picture.
• View Revisions > Project, View Revisions > Article: If you have the privilege, this command
displays the Revisions dialog box. This dialog box allows you to view project names or article
information, display read-only versions of projects or the active article, revert a project or article to
an earlier revision, and print the contents of the Revisions dialog box.
• View Revisions > Picture: If you have the privilege, this command displays the Revisions dialog
box for the picture attached to the active picture box.
• View Revisions > For All Projects: If you have the privilege and no checked-out projects are
displayed on screen, this command displays the Revisions dialog box. This dialog box allows you
to view project names, display read-only versions of projects, revert a project to an earlier revision,
and print the contents of the Revisions dialog box.
• Update > Update All: Updates all content and geometry in the active project.
• Update > Content: Updates all the content in the active box or boxes to include the current content
of attached assets stored on Quark Publishing Platform Server.
• Update > All Content: Updates all the content in the active QuarkXPress project to include the
current content of attached assets stored on Quark Publishing Platform Server.
• Update > Geometry: UpdatesQuark PublishingPlatform Serverto include the current page geometry
of the active box or boxes. Thisenables a QuarkCopyDesk user who is working on an article attached
to the active box or boxes to have exact copyfit information for the assignment.
• Update > All Geometry: Updates Quark Publishing Platform Server to include the current page
geometry of the active QuarkXPress project.
• Workspace Browser: Displays and hides the Workspace Browser window.
• Log On/Log Off: Logs the user on to or off of Quark Publishing Platform.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 65
Page 66

CLIENT TASKS
Client tasks
Many Quark Publishing Platform operations work the same way in all Quark Publishing Platform
client applications.Following a brief overview of the QuarkPublishing Platform workflow concepts,
this chapter explains how to log on to a Quark Publishing Platform Server, change your password,
check assets in and out, assign assets, search for assets, get read-only copies of assets, save revisions
of assets, and set application preferences.
Understanding how Quark Publishing Platform works
Quark Publishing Platform provides the tools forteams of people to integrate their writing,designing,
and editing skills and produce content for audiences to view and read. This section describes how
Quark Publishing Platform works in practice.
An ideal publishing workflow looks like a linear progression from start to finish. But in truth, the
process often requires changes, and Quark Publishing Platform accommodates these changes.
Quark Publishing Platform Server and Quark Publishing Platform client applications
The full Quark Publishing Platform software suite includes a Quark Publishing Platform Server that
tracks all assets and a collection of client applications for writers, designers, artists, editors, and
managers to work on assets. Quark Publishing Platform users transfer assets to one another using
client applications, and Quark Publishing Platform Server dynamically maintains a record of this
activity for all Quark Publishing Platform users to see.
Administering a Quark Publishing Platform workflow
The Quark Publishing Platform administratordefines the workflows for Quark Publishing Platform,
creates the list of users, and assigns each user to a specific role that governs the privileges available
to that user. The Quark Publishing Platform administrator also controls where assets are stored, the
progression of steps in each workflow, default specifications for new assets, and the attributes
(descriptive metadata fields such as name and due date) that are attached to every asset in Quark
Publishing Platform. All Quark Publishing Platform users can track assets based on these attributes.
Using XML Author with Quark Publishing Platform
With the Quark XML Author for Quark Publishing Platform, you can create XML content in the
familiar Microsoft Word interface, and use the Platform to store it and generate output. You can also
break your content down into components and reuse them, as needed, for maximum efficiency. For
more information, see the XML Author for Quark Publishing Platform documentation.
66 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 67

Assigning and managing assets from QXP
A Quark Publishing Platform workgroup for a brochure might include a QuarkXPress userresponsible
for page layout, a QuarkCopyDesk user who writes the brochure copy, a graphic artist who uses an
image-editing application,and aremote editorialmanager whouses QuarkPublishing PlatformWeb
Client to work on text through a Web browser.
Quark Publishing Platform users with an alternate workflow might rely almost entirely on Quark
XML Author.
Quark Publishing Platform Server is the central repository of Quark Publishing Platform. Quark
Publishing Platform users connect to Quark Publishing Platform Server from Quark Publishing
Platform clients, which include Quark Publishing Platform Client, QuarkXPress (with Quark
Publishing Platform XTensions software), QuarkCopyDesk (with Quark Publishing Platform
XTensions software), XML Author (with the XML Author Quark Publishing Platform Adapter),
and a Web browser with Quark Publishing Platform Web Client and Quark Publishing Platform
Web Admin.
CLIENT TASKS
Let's consider a sample workflow. Notethat this is only asample; different organizations set up their
Quark Publishing Platform workflows in different ways. In this workflow, the QuarkXPress user
often works as the content manager through which all other work flows.
The layout artist uses QuarkXPressto create the page layoutby drawing boxes for text and graphics.
Once the layout artist has created the page, he or she checks it in to Quark Publishing Platform
Server. The layout is now backed up on the server, and every time the layout artist checks it out and
back in, a new revision is created.
The layout artist checks in the layout.
Using Quark Publishing Platform, the layout artist assigns articles to QuarkCopyDesk users and
picture boxes to artists working in image-editing applications. The writers and artists receive
notification of these assignments, which can also include instructions and other useful information
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 67
Page 68

CLIENT TASKS
in theattributes forthe asset. Here, a designer has been assigned to create a picture asset, and a writer
has been assigned to write the brochure text.
The designer receives the picture assignment, and the writerchecks outthe article in QuarkCopyDesk.
It is important to note that anarticle created from a layout comes withgeometry, which is a description
of the article's size and shape within the layout. Geometry tells the writer exactly how much space
he or she has to fill.
Having received their assignments, writers and artists can now do their part to complete the layout.
The designer creates the picture, and the writer writes the text.
The designer creates a picture to the layout artist's specifications, and the writer writes an article of
the appropriate length.
Next, the designer and writer check in their work to update Quark Publishing Platform Server. Now,
like the layout, the picture and article are backed up in a central location, and revisions of the assets
will be saved. When the layout artist refreshes the layout, the layout updates to show the work of
the designer and the writer.
68 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 69

CLIENT TASKS
Once checked in, pictures and articles can be viewed in the layout with which they are associated.
So far we've been looking at a linear workflow. However, workflows are not always linear. For
example, what happens if the layout artistdecides that the picture should be largerand the text should
be shorter? If a layout artist changes the size of a text box in an assigned article, Quark Publishing
Platform can automatically update the page geometry to reflect the new size of the box. The writer
can then add or remove text to fit the updated page design.
The layout artist updates the layout in Quark Publishing Platform. This automatically updates the
geometry in the article. Quark Publishing Platform notifies the writer of the change.
The writer updates the text to fit the available space, checks in the article, and all is well.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 69
Page 70

CLIENT TASKS
The writer updates the text to match the updated geometry and checks in the article. The layout
updates to show the updated text.
Now, let's assume the copy editor assigned to fact checking is in another location, and does not have
access to the network where Quark Publishing Platform Server is running. The copy editor can
simply launch a Web browser, log in through Quark Publishing Platform Web Client, check out the
story,and dothe copyediting.And becauseQuark Publishing Platform Web Client is aware of article
geometry, the copy editor knows exactly how much space is available.
The remote editor copyedits the article using Quark Publishing Platform Web Client.
As mentioned above, this layout-driven workflow is only one option. An organization might instead
choose to use a content-driven workflow, where the designer and writer do their work first, and the
layout artist then designs the layout to fit the content. In such a workflow, the designer creates a
picture and checks it inwith Quark Publishing Platform Client, and the writer creates an article from
scratch in QuarkCopyDesk and then checks it in with the Quark Publishing Platform XTensions
software.
When this is done, the layout artist creates alayout andattaches the pictureto the layout by dragging
the file icons from the Workspace Browser window to a picture box, thus creating a relationship
between the layout and the picture. The layout artist can use the same method to attach the text of
the article to a text box.
70 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 71

In addition, QuarkXPress users can attach the same article in separate QuarkXPress projects. The
first attachment is called the "primary attachment," or and all other attachments are "secondary
attachments." If the article content changes, all instances are updated.
While workingon an assignment, a Quark Publishing Platform user can update the entire workgroup
with the status of that assignment by using the Save Revision command. This command updates
Quark Publishing Platform Server with the most current version of the assignment. For example, if
a QuarkCopyDesk user finishes four of five sections in a brochure assignment and then chooses
Save Revision, the editor can open a read-only copy of the text and preview it before the assignment
is complete.
Routing and tracking
Many Quark Publishing Platform workflows include a sequence of hand-offs from one team member
to another. In Quark Publishing Platform, this is calledrouting. For example, when a QuarkCopyDesk
user completes an assignment, he or she might route the asset to an editor who reads first drafts.
Using Quark Publishing Platform Web Client or QuarkCopyDesk, this first-draft editor might finish
the job and route the asset to a copy editor, who in turn might route it to a managing editor. As the
asset moves from workgroup member to workgroup member, other team members can track the
asset's movement using the Quark Publishing Platform search interface.
CLIENT TASKS
The Quark Publishing Platform Copytasting feature lets users view the first 255 characters in a
QuarkCopyDesk articlein the Workspace Browser window. Userscan also view a list of all revisions
of an asset, open a read-only copy of any revision, open a read-only copy of any current asset, and
Get (retrieve) a fully editable copy of any asset tracked by Quark Publishing Platform.
Automating output and export
Organizations often report that the final step in the publishing process — output — requires too
much time and money to accommodate last-minute changes. Quark Publishing Platform users can
streamline much of the output process by using the Quark Job Jackets controls within QuarkXPress
and Quark Publishing Platform Server to eliminate problems before the output stage.
For final output, Quark Publishing Platform provides three ways to automate tasks.
• Within QuarkXPress and QuarkCopyDesk, users can create output styles that specify every aspect
of output. With an output style, a single action can trigger output for one or more assets.
• Working with Automation Services or the Quark Publishing Platform Script Manager application
for Quark Publishing Platform Server, administrators can write automation profiles or scripts that
automate output based on conditions within the Quark Publishing Platform workflow. For example,
when a user changes the status of a QuarkXPress project to "Ready for Output," an automation
profile or script can output or export the project in any of the supported formats (PostScript®, PDF,
PDF/X–1a,PDF/X–3, SWF, PPML, XML, or native QuarkXPress or QuarkCopyDesk format).
Automation Services can also transform content from one format to another and upload content to
a Web server.
• If an organization requires more automation, the open architecture of Quark Publishing Platform
allows third-party developers to fine-tune the output process with XTensions software.
Archiving and restoring
When a project is complete, all the assets can be gathered for archiving within the file system. If the
designer needs to revise the brochure or create a similar project in the future, he or she can use the
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 71
Page 72

CLIENT TASKS
Quark Publishing Platform Restore function to access the content. For more information, see
"Archiving assets" and "Restoring assets."
Logging on
You must log on to a Quark Publishing Platform Server to access assets on that server.
The LogOn dialog box displays when you launch the Quark Publishing Platform Client application,
QuarkCopyDesk, or QuarkXPress. Quark Publishing Platform Web Client users log on through the
Quark Publishing Platform Welcome screen that displays in the Internet browser window when the
user enters the correct URL. If you do not log on at launch, note that Log On displays in the Quark
Publishing Platform Client menu for Quark Publishing Platform Client, the Platform menu for
QuarkXPress and QuarkCopyDesk, and the Welcome screen of Quark Publishing Platform Web
Client.
Use the Log On dialog box to access your Quark Publishing Platform Server and, if necessary,
change your password.
• The values in the User Name and Password field are defined for each user by the Quark Publishing
Platform administrator. For Quark Publishing Platform sites that use Lightweight Directory
Application Protocol (LDAP) to manage user lists, Quark Publishing Platform users log on with
their network user names and passwords. Log-on passwords may or may not be case-sensitive,
depending on the Quark Publishing Platform administrator's specifications.
• The Server Name drop-down menu displays Enter the Server Name by default. But after you have
logged on to one or more Quark Publishing Platform Servers, the Server Name drop-down menu
displays themachine namesand IP addresses of separate Quark Publishing Platform Servers (if your
site runs more than one Quark Publishing Platform Server). Choose an option from the drop-down
menu or enter the Quark Publishing Platform Server's IP address and port number in the fields that
display.
• The Protocol controls let you choose whether to use HTTP or HTTPS for communication with
Quark Publishing Platform Server. If you're not sure which to use, askyou Quark Publishing Platform
administrator.
• To automatically enter your user name and password the next time you log on, check Remember
Me.
72 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 73

• To bypass the Log On dialog box the next time you log on, check Do Not Show This Dialog Box
Again and Remember Me. If you want the Log On dialog box to display again the next time you
choose the command, choose QuarkPublishing Platform Client > Preferences, click the Startup
Mode icon, and uncheck Do Not Display Log On Dialog Box.
• To change your password, click the Change Password button. Enter your old password, your new
password, and confirmation of your new password.
Creating assets (QCD and QXP)
In addition to creating QuarkCopyDesk articles and QuarkXPress projects according to application
defaults (File > New), QuarkCopyDesk and QuarkXPress users who are logged on can create assets
with defaultsettings defined in Quark Publishing Platform Server. For QuarkCopyDesk, the command
is File > New > Article From Server Ticket. For QuarkXPress, the command is File > New >
Project from Server Ticket.
When you choose either of these commands, a New Article/Project from Server Ticket dialog box
displays. Choose the collection where you want to store the asset from the Collection drop-down
menu, then choose the Job Ticket that should define the characteristics of the new article or project.
If thereis morethan oneJob Jacketsfile associated with the collection, you can select the Job Jackets
file and Job Ticket template you want to use. (The default Job Jackets file for the collection displays
in bold.) When you're finished, click Continue. Quark Publishing Platform creates an article or
project using the Job Ticket template you select.
CLIENT TASKS
When creating a new article from Job Ticket, QuarkCopyDesk uses the dimensions and margins
defined in that Job Jackets file's default Print Layout resource. (Resources that are not required for
article creation are ignored.) If there is no such resource, QuarkCopyDesk displays a dialog box
where you can specify page dimensions and margins. In any case, only one master page is used.
You can also create projects and articles from templates in Quark Publishing Platform. For more
information, see "Working with templates."
In QuarkXPress and QuarkCopyDesk, you can also create Quark Publishing Platform assets by
attaching or importing text or picture content and updating the Quark Publishing Platform Server.
If you want to create a file based on a checked-out article or project, choose File > Save As to create
an asset outside of Quark Publishing Platform. If you want to check in the asset, you must have the
privilege to check in new files.
Working with collections
A collection is a group of related assets. Each collection can have one or more associated workflows
(optionally with automatic routing rules), a set of Job Jackets, a number of associated users and
groups, and revision settings for each asset type. A Quark Publishing Platform server contains a
hierarchy of collections.
Working with collection templates
Collection templates make it easier to create and maintain collections. For example, assume you
have several publications, and each publication needs its own identically configured "Images"
subcollection. Rather than creating each "Images" collection manually from scratch, you can create
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 73
Page 74

CLIENT TASKS
an "Images Template" collection template, then create each "Images" collection from that template.
If you later need to add a user or make a change to the auto routing rules used by the "Images"
subcollections, you can simply make the change to the "Images Template" collection template, and
the change is automatically applied to all collections that use that collection template.
To create a collection template, Option+click/right-click a collection and choose New Collection
Template, then configure the template the way you want it (for more information, see "Creating a
collection").
Collection template icons are different from collection icons.
To create a collection from a collection template, Option+click/right-click a collection and choose
New Collection From Template, then choose a collection template in the New Collection From
Template dialog box and click Continue. Quark Publishing Platform creates a collection from the
template you indicate, as a child of the collection you clicked. Note that you cannot change any of
the settings of the new collection (exceptfor the name), because the collection pulls all ofits settings
from the collection template.
To determine which collection template a collection is based on, look at its Collection Template
attribute. To see which collections are based on a collection template, click that collection template
in the collection tree. The collections based on that collection template display in the Collections
pane.
Tobreak the link between a collection and its collectiontemplate, Option+click/right-clicka collection
and chooseEdit Collection, then uncheck Link to Collection Templateand click OK. The collection
retains all of the template's settings, but loses its link to the collection template. Any changes you
make to the collection template after this will not be applied to the collection.
There is no way to relink a collection with a collection template.
It's generally a good idea to create a collection named "Collection Templates" at the root level of
your collections hierarchy, and store all of your collection templates in that collection.
You cannot check assets into a collection template.
Creating a collection
To create a new collection, Control-click/right-click the new collection's parent and choose New
Collection from the context menu. The New Collection dialog box displays. Enter a name for the
collection in the Collection Name field, then choose a collection type from the Collection Type
drop-down menu. The attribute form for theselected collectiontype displays. (For more information,
see "Working with collection types.") The new collection will be inserted as a child of the collection
you click.
74 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 75

CLIENT TASKS
Use the New Collection dialog box to set up a collection.
By default, a new collection inherits all of the characteristics of its parent collection except for its
name and attributes. However, you can change these characteristics if you want.
To edit an existing collection, Control-click/right-click a collection and choose Edit Collection.
Adding workflows to a collection
Each collection can have one or more workflows. You can use the same workflow for all assets in
a collection, or use different workflows for different asset types. Users can switch an asset to a
different workflow at any time.
Only users with the appropriate privileges can add workflows to a collection or change an asset to
a different workflow. For more information, see "Privileges."
To add workflows to a collection:
1
Control+click/right-click the collection and choose Edit Collection. The Edit Collection dialog
box displays.
2
Click Workflows in the list on the left. The Workflows pane displays.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 75
Page 76

CLIENT TASKS
Workflows pane
3
To add a workflow, click +. The Workflow Mapping dialog box displays.
Workflow Mapping dialog box
4
To add a workflow to the collection, select it in the list on the left and then click the right arrow
button. To remove a workflow from the collection, select it in the list on the right and then click the
left arrow button.
5
Click OK.
Adding users to a collection
Each collection can have its own list of users. To add users to a collection:
1
Control+click/right-click the collection and choose Edit Collection. The Edit Collection dialog
box displays.
76 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 77

2
Click User Profiles in the list on the left. The User Profiles pane displays.
CLIENT TASKS
User Profiles pane
3
To add a user, click +. The User Mapping dialog box displays.
User Mapping dialog box
4
To add a user to the collection, select it in the list on the left and then click the right arrow button.
To remove a user from the collection, select it in the list on the right and then click the left arrow
button.
5
Click OK to return to the Edit Collection dialog box.
6
To change a user's role within this collection, choose a different user role for that user from the
drop-down menu in the Role column.
7
Click OK.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 77
Page 78

CLIENT TASKS
Adding groups to a collection
Each collection can have its own list of groups. To add groups to a collection:
1
Control+click/right-click the collection and choose Edit Collection. The Edit Collection dialog
box displays.
2
Click Groups in the list on the left. The Groups pane displays.
Groups pane
3
To add a group, click +. The Manage Groups dialog box displays.
Manage Groups dialog box
4
To add a group to the collection, select it in the list on the left and then click the right arrow button.
To remove a group from the collection, select it in the list on the right and then click the left arrow
button.
5
Click OK.
78 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 79

Setting up auto routing
Routing rules let you automatically route assets to a particular user or group when those assets reach
a certain status.
You must create workflows, users and/or groups, and statuses before you can specify workflow
routing.
To set up automatic routing:
1
Control+click/right-click the collection and choose Edit Collection. The Edit Collection dialog
box displays.
2
Click Auto Routing in the list on the left. The Auto Routing pane displays.
CLIENT TASKS
Auto Routing pane
3
You can use this pane to set up auto routing for any of the workflows associated with this collection.
Choose the workflow you want to configure from the Workflow drop-down menu. The sequence
of statuses for that workflow displays.
4
Select a status name and click the Destination column to choose the user or group to whom assets
with this status should be routed.
• To specify that these assets should retain their current Route to value from the previous status,
choose No Auto Routing.
• To specify that these assets should not be routed to a specific user or group, choose No Group or
User.
• To specify that these assets should be routed to a specific group, choose the group name.
• To specify that these assets should be routed to a specific user, choose the user name.
5
Click OK.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 79
Page 80
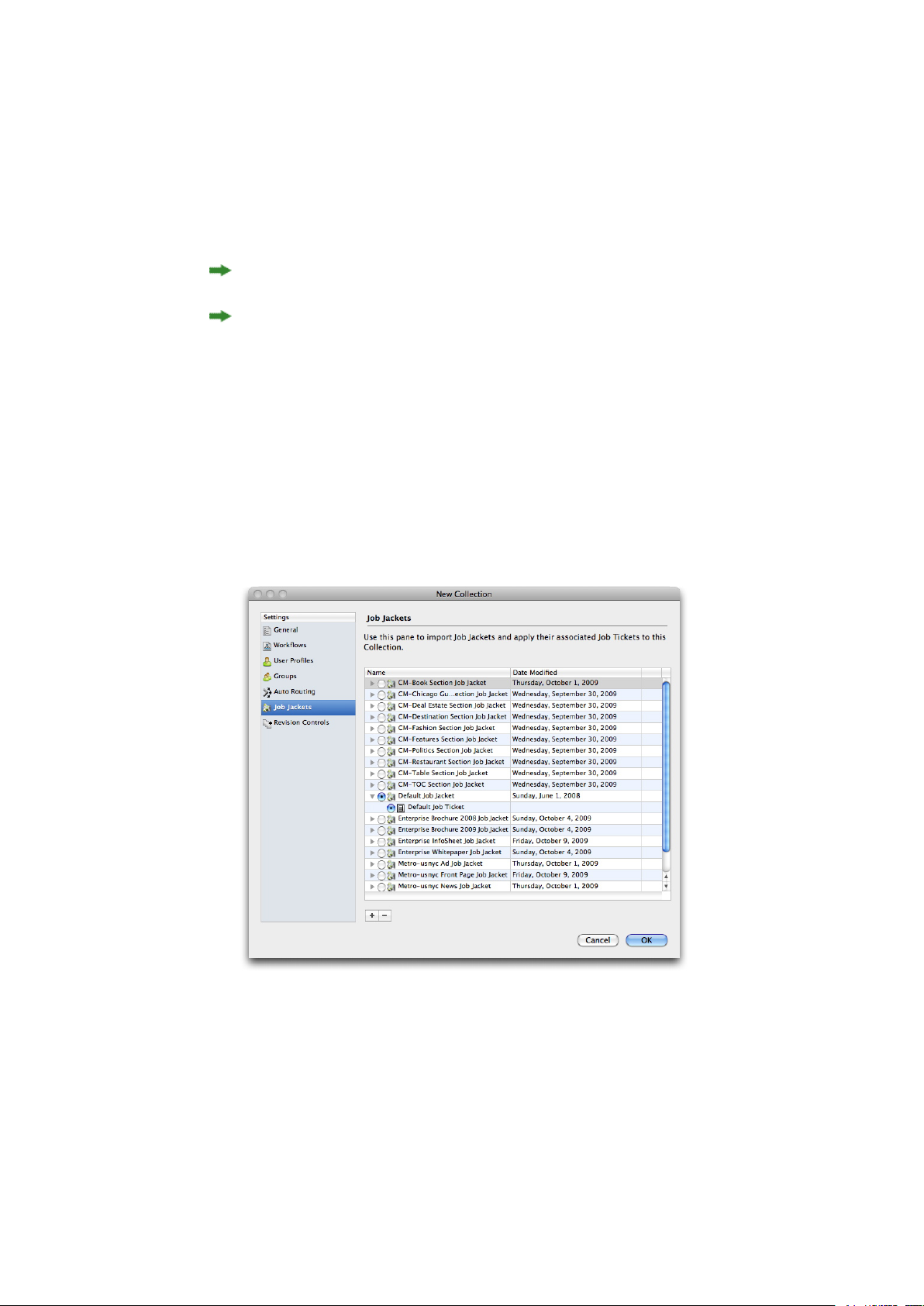
CLIENT TASKS
Setting up Job Jackets
A Job Ticket is a package of QuarkXPress resources (preferences, style sheets, colors, and so forth).
A Job Jackets file is a containerfor Job Tickets. InQuarkXPress, you can pre-configure a new project
by creating that project from a Job Ticket that contains the desired resources.
In Quark Publishing Platform, you can use a Job Jackets file to define a Job Ticket with a collection
of default resources for each collection.
Job Jackets files must be created in QuarkXPress. Formore information,see A Guide to QuarkXPress.
When you are configuring resources (for example, style sheets, colors, and H&Js) at the collections
level, make sure you do not havemore than 80 resources per Job Ticket. A larger number of resources
can hinder performance in QuarkCopyDesk, QuarkXPress, and Quark Publishing Platform Web
Client. If you require more than 80resources per Job Ticket,you can improve performance by adding
unique resources through separate Job Tickets for each collection.
To assign Job Jackets:
1
Control+click/right-click the collection and choose Edit Collection. The Edit Collection dialog
box displays.
2
Click Job Jackets in the list on the left. The Job Jackets pane displays.
Job Jackets pane
3
To import a Job Jackets file, click +, navigate to the target Job Jackets file, and then click Open.
4
To specify which Job Jackets file to use with the collection, select the Job Jackets file.
5
To specify which Job Ticket to use with the collection, expand its Job Jackets file and then select
the Job Ticket.
80 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 81

Controlling asset revision handling
To specify asset revision parameters for a collection:
1
In the Workflow navigation pane, Control-click/right-click the collection and choose Edit Collection.
The Edit Collection dialog box displays.
2
Click Revision Controls. The Revision Controls pane displays.
CLIENT TASKS
Revision Controls pane.
3
You can specifydifferent parameters for different filetypes. Forexample, youmight choose to retain
all versions of text files because they have relatively small file sizes, but you might save only the
original picture and the most recent revision for larger picture files. Choose an option from the Asset
Type drop-down menu.
4
Tocontrol thedefault versioningfor assetcheck-in, clickMajor or Major and Minor under Create
a Version.
5
Configure revision settings for the chosen asset type:
• To retain every revision of the chosen asset type, click Keep All.
• To limit automatic revision retention to a specific number of early and recent versions, click By
Number and then enter values in the Keep first and keep last fields.
• To limit automatic revision retention to a specific number of days, click By Days and then enter
values in the Keep first and keep last fields.
Editing collections
To edit a collection, Control-click/right-click the collection in the Workspace navigation pane and
choose Edit Collection from the context menu. The Edit Collection dialog box displays. This dialog
box is very similar to the New Collection dialog box (see "Creating a collection").
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 81
Page 82
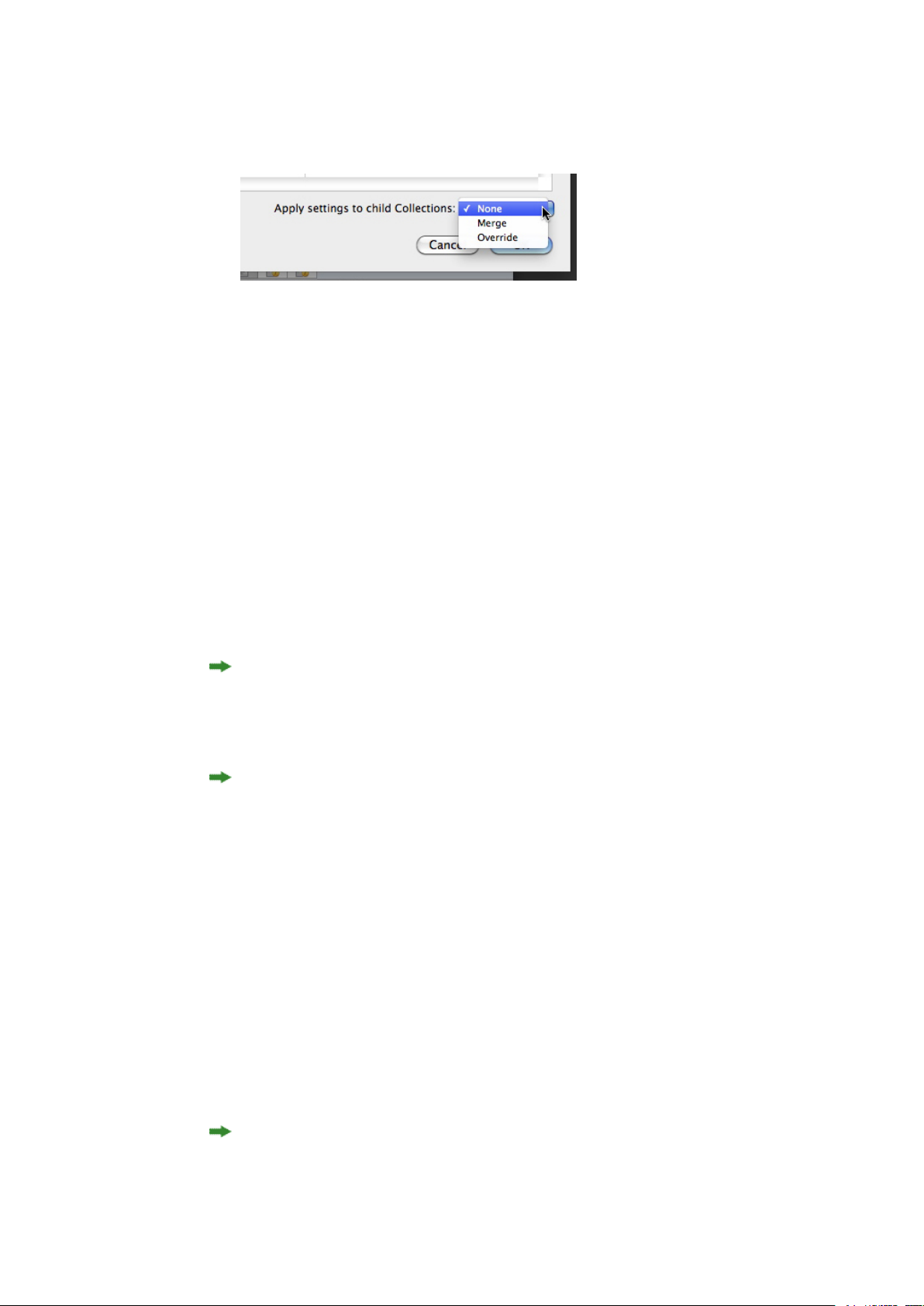
CLIENT TASKS
All of the panes in the Edit Collections dialog box include the Apply settings to child Collections
drop-down menu.
Apply settings to child Collections drop-down menu
You can use the options in this drop-down menu to control how the changes you make in each pane
affect the active collection's child collections.
• None: No changes are made to child collections.
• Merge: This option adds the parent collection's settings to all of its child collections. Only settings
that are not already present in child collections are added to the child collections. For example, if a
child collection has a workflow named "W1," and you assign a workflow named "W2" to the parent
collection, then after the operation the child collection has both the "W1" and "W2" workflows. If
a user has different roles assigned in the child collection and the parent collection,the role assignment
for the child collection is not changed.
• Override: This option overrides all settings for child collections with the new settings for the parent
collection. For example, if a child collection has aworkflow named"W1," and you assign a workflow
named "W2" to the parent collection, then after the operation the child collection has only the "W2"
workflow.
If someone make changes to a collection, an asterisk displays in the label for the Collections area
in the Workspace navigation pane, and the collection's name displays in italics for everyone except
the user who made the change. To update the collection, Control-click/right-click the collection in
the Workspace navigation pane and choose Refresh Collection from the context menu.
If you want to change a collection that is based on a collection template, you must change the
collection template or unlink the collection from the collection template. For more information, see
"Working with collection templates."
Duplicating a collection
When you duplicate a collection, Quark Publishing Platform creates a duplicate of that collection,
but not of the assets the collection contains. You can specify whether you want to simply duplicate
the collection or also duplicate the hierarchy inside the collection.
To duplicate a collection, Control-click/right-click the collectionin the Workspace navigation pane
and choose Duplicate Collection from the context menu.
Deleting a collection
To delete a collection, Control-click/right-click the collection in the Workspace navigation pane
and choose Delete Collection from the context menu.
You cannot delete a collection if it or any of its subfolders contains assets.
82 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 83

Appending content (QCD and QXP)
In QuarkXPress and QuarkCopyDesk, you can use the Append Content button in the
Workspace Browser window toolbar to add textfrom an article component to an article component
or a QuarkXPress text box. To use the Append Content button:
1
Select a text box in QuarkXPress or text component in QuarkCopyDesk.
2
Select a text component or article in the Workspace Browser window.
3
Click the Append Content button in the Workspace Browser toolbar. The text flows into the text
box or text component.
(Mac OS only) If the Append Content button is not visible, add it to the toolbar. For more
information, see "Customizing the Workspace toolbar."
If you are working in QuarkXPress and select an article that contains multiple components in step
5, the Select Text Component dialog box displays, which allows you to select a text component. If
you are working in QuarkCopyDesk, text in all the components is appended. Picture components
are not appended.
CLIENT TASKS
The appended text is no longer linked to the article component from which it was appended. If you
change the text in the original article component, the change is not updated in the text box or text
component.
If you selected text before clicking Append Content, the appended content replaces the selected
text.
Checking in assets
Although the fields in the Check In dialog box may vary, the check-in process is fundamentally the
same for all Quark Publishing Platform clientapplications. Thesteps vary slightly if youare checking
in an asset you have checked out or if you are checking in an asset for the first time. You can also
use the Check In Other command to check in new QuarkCopyDesk articles, QuarkXPress layouts,
and files in third-party formats.
Check In command
The Check In command is available as a menu command and an icon.
1
Open the asset you want to check in to Quark Publishing Platform Server.
2
Choose Actions > Check In or select the checked-out asset in the Quark Publishing Platform Client
toolbar and click the Check In button. The Check In dialog box displays.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 83
Page 84
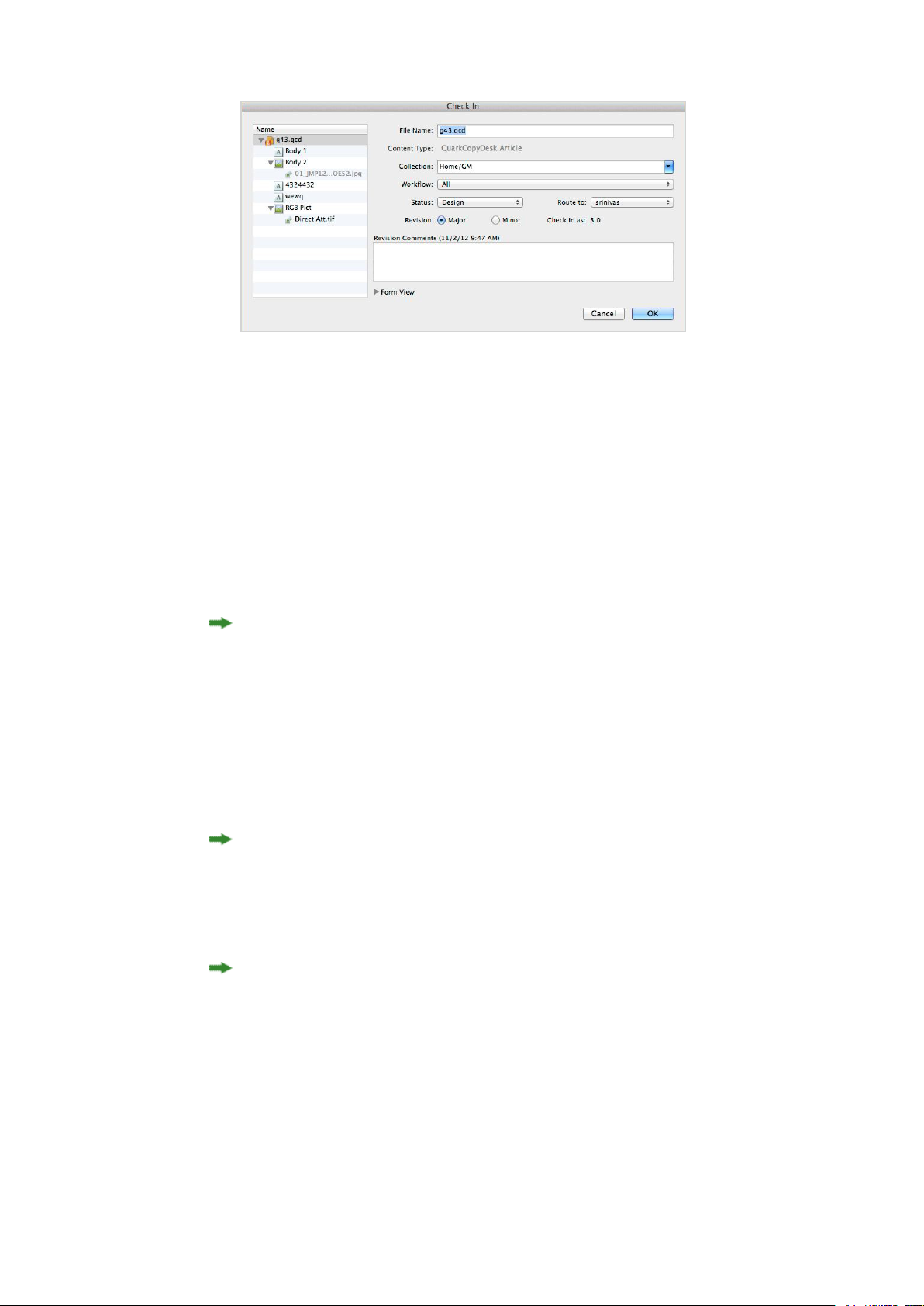
CLIENT TASKS
Use the Check In dialog box to add an asset to Quark Publishing Platform Server (or return a
checked-out asset to Quark Publishing Platform Server control).
The Name list on the left shows all of the components that will be checked in along with this asset.
For example, if you're checking in an article with a picture component and two text components,
the Name list displays an item for the article, plus two child items for the text components, plus a
child item for the picture component. In addition, the picture component has a child item for the
picture in the picture component.
You can supply different attribute values for each item. If you do not specify values for the child
items, the child items inherit the values specified for the parent item.
3
Choose a target collection from the Collection drop-down menu.
You can use the search field to find a collection quickly. Mouse over each search result to see its
collection path.
4
Choose a workflow from the Workflow drop-down menu.
5
To indicate the asset's current status, choose an option from the Status drop-down menu.
6
Tosend the asset to a particular user or group, choose an optionfrom the Route to drop-down menu.
(Note that if your workflow relies on automatic status-based routing, the Route to drop-down menu
value might change automatically when you choose an option from the Status drop-down menu.)
If you do not choose any name from the Route to drop-down menu when you check in an asset for
the first time, the asset is routed to the active user.
7
To specify whether the asset is saved with a major or minor version number, click Major or Minor
under Revision.
Access to the Minor option is controlled by privileges.
8
Use the Revision Comment field to enter a revision comment for the version of the asset you are
checking in. The revision comment will bestored with the asset. Depending on thepreference setting
of the user who checks out the asset, the revision comment displays during the check-out process.
The revision comment also displays when you view revisions of the asset.
9
Modify any other available attribute fields as appropriate. Note that access to these attribute fields
is determined by your privileges.
84 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 85
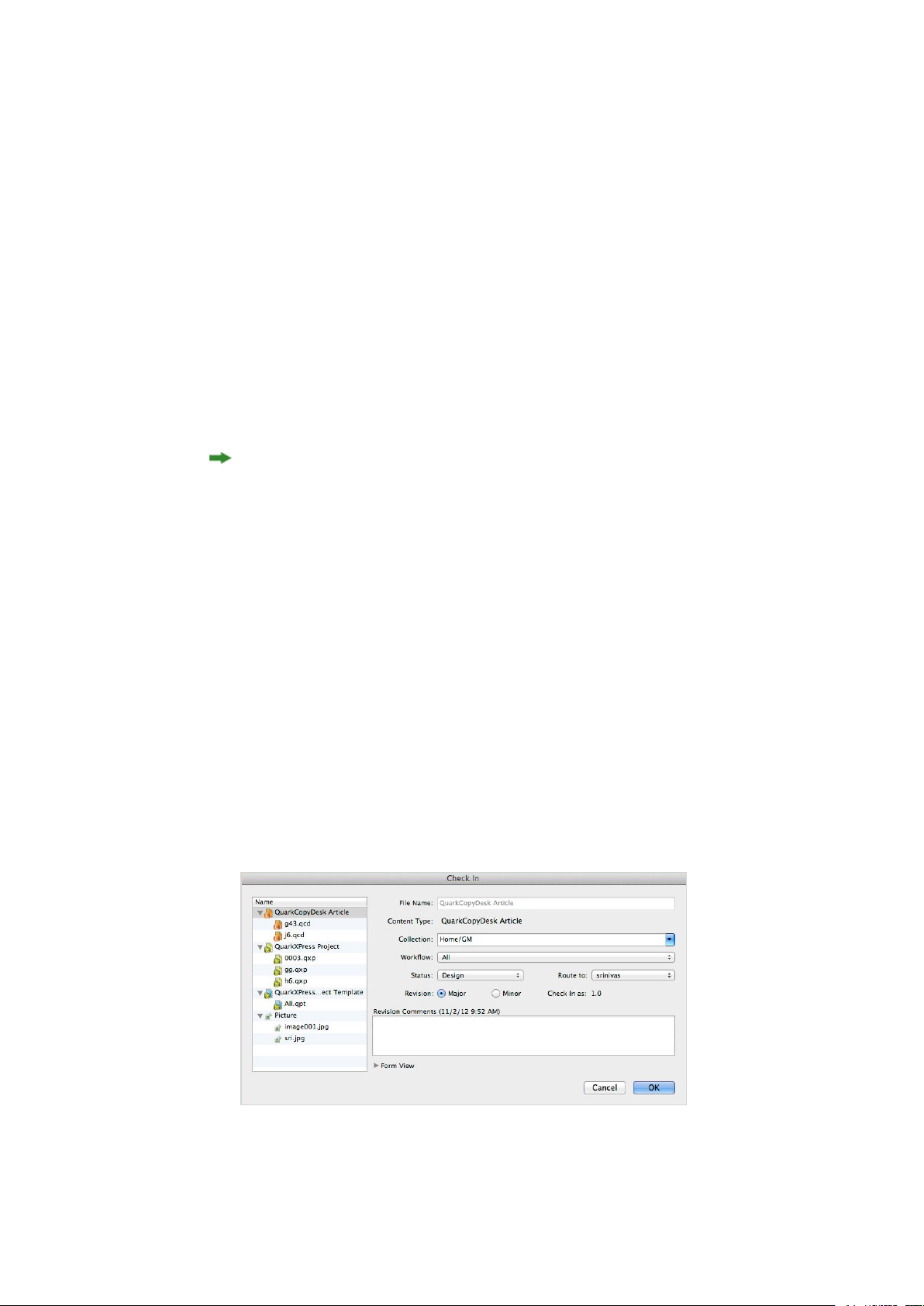
10
Click OK. Depending on your preferences, when the check-in process completes, Quark Publishing
Platform Server may delete the local copy of the asset.
Check In Other command
The CheckIn Other command lets youcheck innew QuarkCopyDeskarticles, QuarkXPresslayouts,
and files in third-party formats.
(MAC OS client) To use the Check In Other command, click the Check In Other button. (Quark
Publishing Platform Client users can also choose Actions > Check In Other). Then navigate to the
target asset and follow the procedure in the "Check In command" section. Click Check In Folder
to check in a folder and all of its subfolders.
(Windows client ) To use the Check In Other command, click theCheck In Other and the drop-down
menu displays the options: Check In File and Check In Folder. Click Check In File to display the
Check In Other File dialog box.Then navigate to the target asset and follow the procedure in the
"Check In command" section. Click Check In Folder to check in a folder and all of its subfolders.
The Last Modified and Last Modifier attributes indicate the name of the user who checks in a file,
as well as the time and date the file is checked in.
CLIENT TASKS
Check in multiple assets
You can check in multiple assets in one check-in process with Quark Publishing Platform Client,
QuarkXPress, and QuarkCopyDesk. The process is different if you are checking in assets you have
checked out or if you are using the Check In Other command to check in new assets.
1
To check in new assets using Quark Publishing Platform Client, (MAC OS client) Click Check In
Other or choose Actions > Check In Other. (Windows client ) Use the Check In Other drop-down
menu to display the options: Check In File and Check In Folder. In QuarkCopyDesk and
QuarkXPress, display the Workspace Browser window and click Check In Other. A directory
dialog box displays for you to select one or more assets.
2
You can select a range of assets or non-consecutive assets in the list. To select a range of assets,
press Shift, select the first asset in the range, select the last asset in the range, then click Open. To
select non-consecutive assets in the list, press Command/Ctrl, select an asset, select one or more
other assets you want to check in, then click Open.
The Check In dialog box lists the assets on the left. Articles, pictures, and other files are listed in
separate groups.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 85
Page 86

CLIENT TASKS
3
Select an asset in the list on the left, and modify the attribute information on the right.
The assetselection onthe left determines the attribute options on the right. You can specify attributes
once for multiple assets in a group.
4
After you specify attributes for the assets, click OK.
5
To check in multiple assets you have checked out, select the assets in the Workspace Browser
window and click Check In. The Check In dialog box displayssequentially for each asset. If Quark
Publishing PlatformClient users select checked-out QuarkXPress projects or QuarkCopyDesk articles
in addition to other checked-out files, the articles and projects are not included in the sequence of
Check In dialog box displays. See "Check In command" for more information about the Check In
dialog box.
In Quark Publishing Platform Client, QuarkXPress, and QuarkCopyDesk, you can also check assets
into acollection by dragging the assets from the file system to thecollection's iconin theWorkspace
Browser window.
Check In Project With Pictures (QXP only)
If a checked-out project contains imported pictures, you can attach the pictures and check them in
when you check in the project by choosing Platform > Check In Project With Pictures. This
command allows you to specify Quark Publishing Platform attributes for eachimported picture. See
"Check in multiple assets" for more information about the Check In dialog box for multiple assets.
1
In QuarkXPress, open a project that contains at least one imported picture.
2
Choose Platform > Check In Project With Pictures.The Check In dialog box displays with the
project name and picture names in separate groups on the left. If the project contains only one
imported picture, the picture name displays below the layout name.
3
Click the project name at the top of the list. The available attributes apply to the project.
4
Click one or more pictures in the Pictures group. The available attributes apply to the pictures.
5
Follow the instructions in the "Check In command" section to check in the project and its imported
pictures.
Assigning assets
Assignments make it easy for each user to know which jobs they should be working on. When you
check in an asset, you can assign it to a particular user or group, or to No One. When you assign an
asset, the following things happen:
• A dialog box displays for the user to whom the asset is routed, indicating that the asset is assigned
to them.
• The asset is listed in the Assignments area in the Workflow navigation pane for the user to whom
the asset is routed.
If the asset is routed to a group, the above is true for every user in that group.
86 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 87
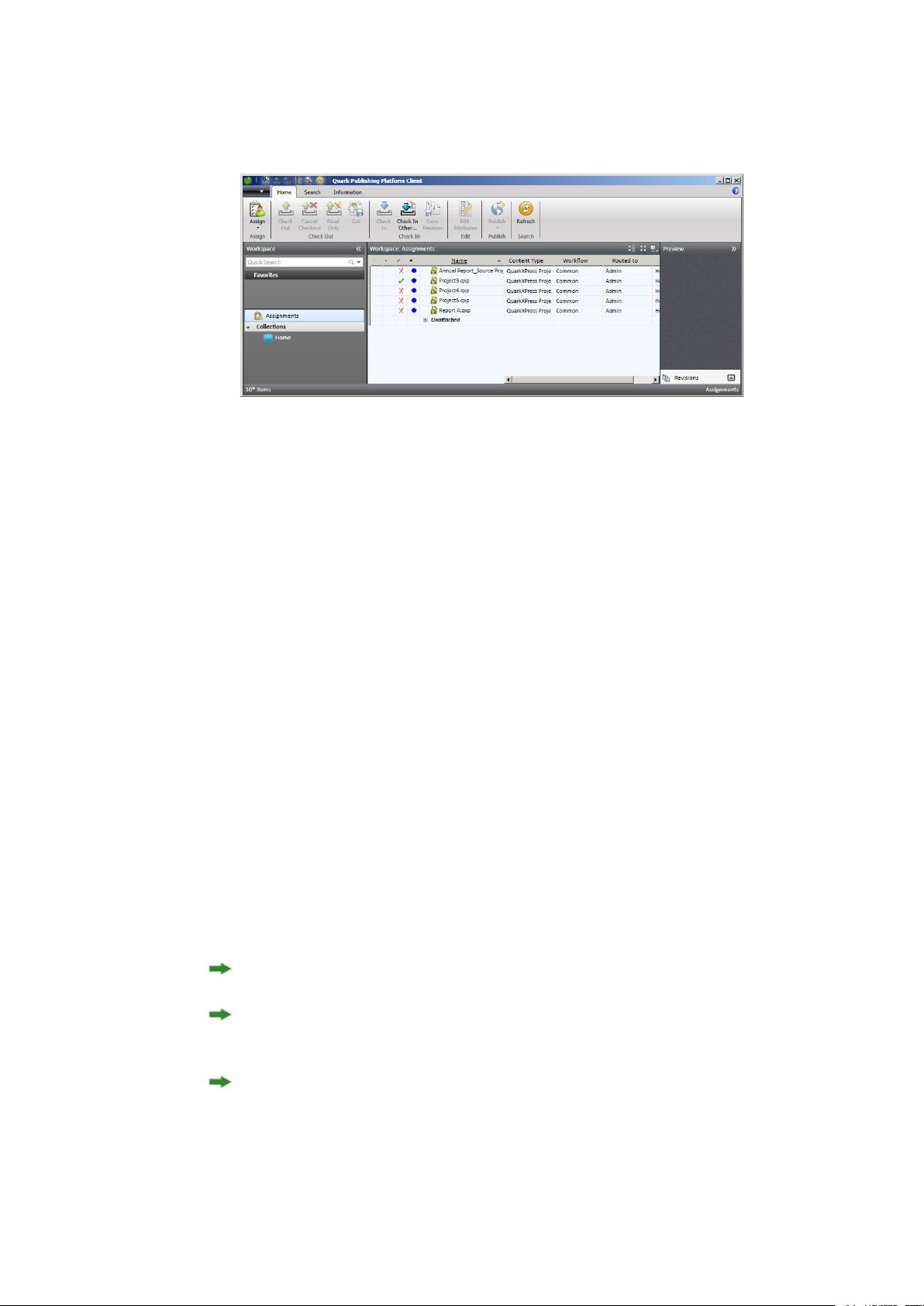
Each user can view the assets assigned to them from any Quark Publishing Platform client in the
Assignments area in the Workflow navigation pane.
Assignments displayed in the Workspace Browser window
Assigning assets: Quark Publishing Platform Client
Quark Publishing Platform Client users can make seven kinds of assignments from the Actions >
Assign submenu.
CLIENT TASKS
To make an assignment from Quark Publishing Platform Client:
1
Click Workspace in the Quark Publishing Platform Client window.
2
To assign a text file, choose Text File.
3
To assign a graphic file, choose Graphic.
4
To assign a QuarkCopyDesk article based on Quark Publishing Platform Server default settings,
choose QuarkCopyDesk Article > From Defaults.
5
To assign a QuarkCopyDesk article based on an existing QuarkCopyDesk article, choose
QuarkCopyDesk Article > From Article.
6
Toassign aQuarkCopyDesk articlebased on a QuarkCopyDesk template, choose QuarkCopyDesk
Article Template.
7
To assign a QuarkXPress project based on an existing QuarkXPress project, choose QuarkXPress
Project.
8
Toassign a QuarkXPress project based on anexisting QuarkXPress template, choose QuarkXPress
Project Template.
You can click the Assign button in the Workspace toolbar to access the Assign submenu.
When you create a graphic assignment, Quark Publishing Platform Client checks in a placeholder
image that can be opened in an image-editing application and replaced with picture content.
The Content Creator field is empty when you check in a placeholder.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 87
Page 88

CLIENT TASKS
Assigning assets: QXP
When you route an asset to another user, you effectively assign it to that user. But Assign is also a
specific command in the Workspace Browser window. To assign an asset from QuarkXPress:
1
Open or display a QuarkXPress project.
2
Draw a box.
3
Display the Workspace Browser window (Platform menu).
4
Do one of the following things:
• With the box selected, click the Workspace Browser window and choose Assign. (If you are
assigning from picture boxes, you can select more than one.)
• Choose Platform > Assign as Article or Platform > Assign as Picture.
• Control+click/right-click the box and choose Platform > Assign as Article or Assign as Picture
from the context menu.
• Click Assign in the Project Attachments palette.
5
If you choose Assign as Picture, the Assign Picture Options dialog box displays with options to
assign a picture asset or a picture component of a QuarkCopyDesk article. Choose an option and
click OK. The Check In dialog box displays.
If you selected a box containing text before choosing Assign, the Check In dialog box displays.
Follow the instructions for "Check In command."
You can enter asset attribute information in the Check In dialog box.
You can assign an article as a QuarkCopyDesk article or a QuarkCopyDesk article template by
choosing an option from the Content Type drop-down menu in the Check In dialog box.
To display the Assign Picture dialog box when you drag a picture from the Workspace Browser
window toa boxin a QuarkXPress project, uncheck Attaching a picture under Do not show Assign
dialog box when in the Attachments tab of the Alerts pane in the Preferences dialog box.
If you duplicate a picture box that contains an attached picture, the picture attachment displays as
two separate attachments in the Project Attachments palette after you save a revision of the project
or check it in.
To see which projects and articles are assigned to you, choose Platform > Workspace Browser.
Performing a search
You can use a variety of methods to search for assets and collections in Quark Publishing Platform.
You can click Assignments in the Workspace navigation pane to display all assets routed to you.
You can click New Search to specify parameters for a new search. And you can choose from
predefined search operations that you have created or that other users have shared with you.
To create a search:
88 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 89

CLIENT TASKS
1
In the Quark Publishing Platform Client, click the Workspace navigation pane.
2
Click New Search in the toolbar. Alternatively, you can Option+click/right-click a saved search in
the Workspace navigation pane and choose New Search from the context menu.
A new, unsaved search
3
Use the drop-down menus at the top of the window to specify search criteria.
• Choose a file type and collection from the two drop-down menus in the Find Items search criteria
row. To search the subcollections of the selected collection as well as the selected collection itself,
check the box on the right end of the row.
• Use the controls in the Where row to narrow the search. To add a row of search options and further
narrow the search, click +.
• To specify inclusive or exclusive criteria, choose And or Or. Choosing And narrows your search.
Choosing Or widens your search.
• To delete a row, click the – (minus symbol) button for that row.
When you finish defining your search criteria, you can click Count to see how many assets match
the criteria.
If the Count value is too high, you can refine your search and save time by displaying a smaller
search.
4
If you plan to save this search and use it to search for different values, you can use the Ask feature.
To use this feature, choose an attribute from the drop-down menu, then click the gray Ask icon .
The Ask icon displays orange .
When someone executes the search, the Ask dialog box will display.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 89
Page 90

CLIENT TASKS
Ask dialog box
5
To add a saved search to the conditions of a search, click New Search, add a row in the search
criteria, chooseAsset matches search or Asset does not match search from the attributedrop-down
menu, and then choose a saved search from thedrop-down menuto theright of the attribute drop-down
menu. You can add as many conditions as you want on subsequent rows.
If you choose Asset matches search or Asset does not match search, searches that contain an
"Ask" parameter are not included in the list.
6
To execute the search, click Go.
To save a search for future use, click Save and specify a name for the search. The search name is
added tothe My Searches area of the Workspace navigation pane and the Search drop-down menu.
To execute a search again, Control+click/right-click the search in the Workspace navigation pane
and choose Reload Search from the context menu or click Refresh in the toolbar.
In QuarkXPressand QuarkCopyDesk, if you add the Save as PDF button to theWorkspace Browser
toolbar, you can create a PDFof your search results display. See "Customizing the Workspace toolbar"
to learn how to add the Save as PDF button.
Using the Quick Search feature
You can quickly find Quark Publishing Platform assets with the Quick Search feature, regardless
of the active application. To use the Quick Search feature, click the magnifier icon at the top of the
Workspace navigation pane.
Use the Quick Search control to search for assets according to text contained in the assets.
Choose an option from the drop-down menu.
90 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 91

• Choose Name to search according to asset name exclusively.
• Choose Content to search according to asset content exclusively.
• Choose Name and Content to search according to asset name and content.
Performing a nested search
You can narrow a search by creating a nested hierarchy of search conditions. In the example below,
the search uses a nested search to look for all assets routed to Tracy or Pat.
1
Click New Search.
2
To add a row of search options, click +.
3
To add a nested condition, choose Asset matches condition from the Where drop-down menu. The
Asset matches condition dialog box displays.
CLIENT TASKS
Asset matches condition dialog box
4
Specify an attribute and choose a condition. You can click + in the Asset matches condition dialog
box to combine multiple conditions.
You can also click the Ask icon in the Asset matches condition dialog box to display a prompt
when a user performs a conditional search.
5
After you specify parameters in the Asset matches condition dialog box, click Join.
Nested search
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 91
Page 92

CLIENT TASKS
The Nested icon displays when you specify a nested search.
Performing a full-text search
The Quick Search control lets you search for assets according to text contained in the assets.
1
Click the Quick Search control to display the Quick Search drop-down menu.
Use the Quick Search control to search for assets according to text contained in the assets.
2
Choose Content to search according to asset content exclusively. Choose Name and Content to
search according to asset name and content.
3
Enter text in the Quick Search field and press Enter. The Workspace Browser window displays
the results of your Quick Search. The search is also displayed in the Unsaved Searches area in the
Workspace navigation pane.
By default, only assets with all the text you enter in the Quick Search field are returned.
4
To refine your full-text search, you can use the following in the Quick Search field:
• Phrase search: You can specify exact wording for more than one word by enclosing your phrase
in quotation marks, such as "Bike History." A space between words in a phrase functions like the
"AND" operator, and all the words in quotation marks must be together to display in the search
results.
• Proximity search: Use "~<number of words>" after a phrase search to specify the number of words
that can exist between the words in your phrase. For example, if you enter "Bike History" ~10, the
search will find instances of "Bike" and "History" within 10 words of each other.
• Wildcard search (single character): Use "?" to specify a search with a single wildcard character,
such as "r?de" to find "ride" and "rode."
• Wildcard search (multiple characters): Use"*" to specify a search with multiplewildcard characters,
such as "ride*" to find "rider" and "riders."
• Fuzzy search: Use "~" to specify a search with a range of possibilities for a single word, such as
"gearing~" to find "hearing," "gears," and "gearing."
• Boolean operators (AND): You can narrow a search by using the "AND," "&&," and "+" operators
to search for exact word combinations. For example, you can search for "Bike" and "History" by
entering Bike AND History in the Quick Search field. Use "+" before search terms to search for
one mandatory term and another possible term. For example, use +Bike History to find instances
where "Bike" exists and "History" might or might not exist.
Boolean operators must be entered in ALL CAPS.
92 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 93

• Boolean operators (OR): You can expand a search by using the "OR" operator to search for one or
more words. For example, if you enter "Bike" OR "History" in the Quick Search field, the results
can include one or both words.
By default, a space between search terms works like the "AND" operator.
• Boolean operators (NOT): You can limit a search by excluding certain words after "NOT" in the
Quick Search field. For example, if you enter "Bike History" NOT "History of Skiing," the search
results will not include the "History of Skiing" text string combinations.
You can use "!" or "-" instead of "NOT."
You cannot use the "NOT" operator with a single term, such as NOT "Bike History."
Performing a collection search
You can use a collection search to locate a collection that has specific attributes. To perform a
collection search:
CLIENT TASKS
1
Click the Workspace navigation pane.
2
Click New Search in the toolbar. In Quark Publishing Platform Web Client, click New Search in
your browser window.
3
In the Find Items drop-down menu, click Collections to make collection options available.
4
To search a particular collection, choose the collection's name from the following drop-down menu.
You can also type the collection's name in the Quick Search field.
5
To search the selected collection's subcollections, check the box at the end of the first row.
6
Use the drop-down menus at the top of the window to specify search criteria.
• Use the controls in the Where row to narrow the search. To add a row of search options and further
narrow the search, click +.
• To specify inclusive or exclusive criteria, choose And or Or. Choosing And narrows your search.
Choosing Or widens your search.
• To delete a row, click the – (minus symbol) button for that row.
When you finish defining your search criteria, you can click Count to see how many collections
match the criteria.
If the Count value is too high, you can refine your search and save time by displaying a smaller
search.
7
To execute the search, click Go.
Not all view options are available for the results of collection searches.
To save a search for future use, click Save and specify a name for the search. The search name is
added tothe My Searches area of the Workspace navigation pane and the Search drop-down menu.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 93
Page 94

CLIENT TASKS
To execute a search again, Control+click/right-click the search in the Workspace navigation pane
and choose Reload Search from the context menu or click Refresh in the toolbar.
In QuarkXPressand QuarkCopyDesk, if you add the Save as PDF button to theWorkspace Browser
toolbar, you can create a PDFof your search results display. See "Customizing the Workspace toolbar"
to learn how to add the Save as PDF button.
Search from here
To create a search that starts from a particular collection, Option+click/right-click that collection
and choose Search from Here. QuarkPublishing Platform creates an unsaved search in that collection
and includes its subcollections.
You can limit the search to that particular collection by unchecking Search this Collection and its
Subcollections (on the right end of the first row in the search interface).
Working with saved searches
To save the active search for future use, click Save and specify a name for the search. The search
name isadded to the My Searches area of the Workspace navigation pane and the Search drop-down
menu.
To return to an unsaved search, click the search in the Unsaved Searches area in the Workspace
navigation pane. Unsaved searches are named "New Search XX," where XX is a number.
To execute a saved search, click the search in the Saved Search area in the Workspace navigation
pane. To re-execute a saved search, Control+click/right-click the search and choose Reload Search
from the context menu.
Managing searches
Use the Manage Saved Searches dialog box to create, edit, share, duplicate, rename, and delete
searches. To display this dialog box, click Saved Searches in the Workspace toolbar and choose
Manage (Mac OS only) or choose Search > Saved Searches > Manage.
Use the Manage Saved Searches dialog box to create, modify, duplicate, share, anddelete searches.
94 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 95

CLIENT TASKS
• To create a search, click New. The Edit Search dialog box displays. Enter a name in the Search
Name field, and then specify searchcriteria according to the instructions for "Performing a search."
Click Save, then click Done to close the Manage Saved Searches dialog box.
• To editan existing search, select a search in the Manage Saved Searches dialog box and click Edit.
The Edit Search dialog box displays. Update the criteria, then click Save. Click Done to close the
Manage Saved Searches dialog box.
• To share a search with other members of your Quark Publishing Platform workgroup, select the
search name and click Share. Then use the controls in the Select the Users to share the saved
searches with dialog box to choose the users with whom you want to share the search.
• To duplicate a search, select the search name and click Duplicate. A new search with the word
"Copy" added to the name displays in the Saved Searches area.
• To rename a search, select the search name and click Rename. The search name becomes editable.
• To delete a search, select the search name and click Delete.
Only the user who shares a search can modify it. Other users can delete the shared search from their
lists, but they cannot edit the search.
Specifying search result display options
Use the View > Displays submenu (Mac OS only), the Display drop-down menu in the Workspace
window, or the buttons at the top of the pane to specify how search results display. For more
information about asset display options, see "View display options."
Some of these options are not available for collections searches. For more information, see
"Performing a collection search."
Quark Publishing Platform assets that match your search criteria but are attached to QuarkXPress
projects that have never been checked in to the Platform are listed under the Attached to other
projects attribute (in the Name attribute column).Attached assets can display under multiple projects
if they are attached to multiple projects.
If an item attached to a project matches the search, the project and all the other assets attached to the
project also display.
An article or picture can display under more than one page if it is attached to multiple pages in a
project.
If you change the view display options for a saved search or collection, the new options are saved
for you for that particular collection or search.
Checking out assets
To check out an asset, use one of the following methods.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 95
Page 96
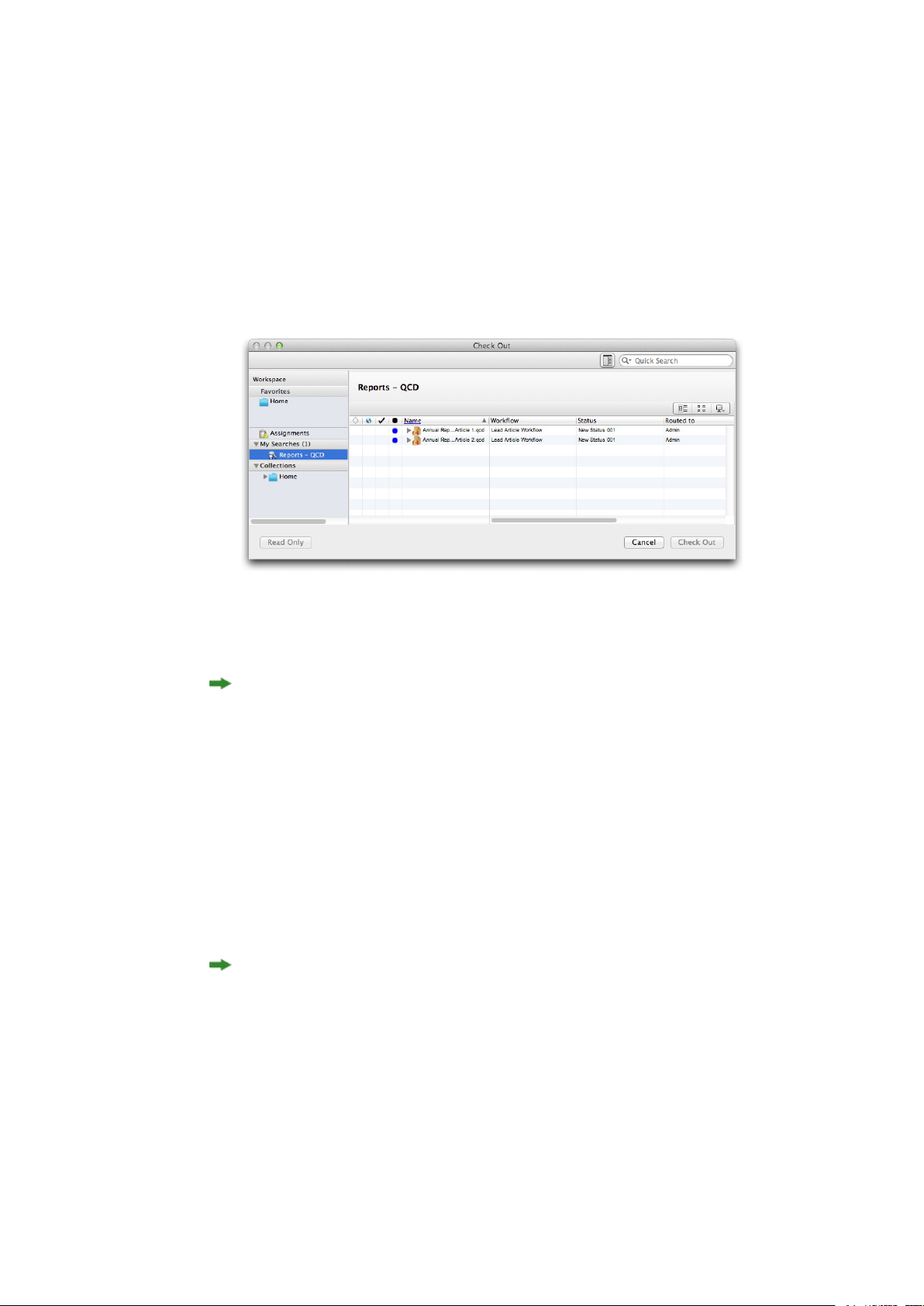
CLIENT TASKS
Checking out an asset: Quark Publishing Platform Client
To check out an asset in Quark Publishing Platform Client, click the Check Out icon in the Quark
Publishing Platform Client Workspace toolbar or choose the Check Out command in the Actions
menu.
Checking out an asset: QCD
To check out an article in QuarkCopyDesk, display the article in the Workspace Browser window
and click Check out, Open, or Display. Or, you can choose Platform > Check Out Article. The
Check Out dialog box displays with the user's assignments displayed by default.
Select the search and asset options in the Check Out dialog box.
Choose a saved search from the My Searches area. Then select the asset in the list and click Check
Out.
You can select an article in the Workspace Browser window, and click Read-Only to open a
read-only copy of the article.
Checking out an article or project: QXP
To check out an article in QuarkXPress, you begin by checking out the project to which the article
is attached. You can select the text box in the active project that contains the article and choose
Check Out Article (Platform menu) or Control+click/right-click the box and choose Platform >
Check Out Article . You can also click the Check Out button in the Workspace Browser window.
To check out aproject in QuarkXPress, choose Check Out > Project (Platform menu). Then select
the target project asset in the Check Out dialog box and click Check Out. You can also click the
Check Out, Open, or Display button in the Workspace Browser window.
You can select a project and click Read-Only to open a read-only copy of the project.
Checking out a project with attachments: QXP
When you check out a project, you can check out the project's attachments at the same time with a
single operation.
1
Display a Workspace Browser window in QuarkXPress.
2
Click the Check Out with Attachments icon and drag it to the toolbar of the Workspace Browser
window.
96 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 97
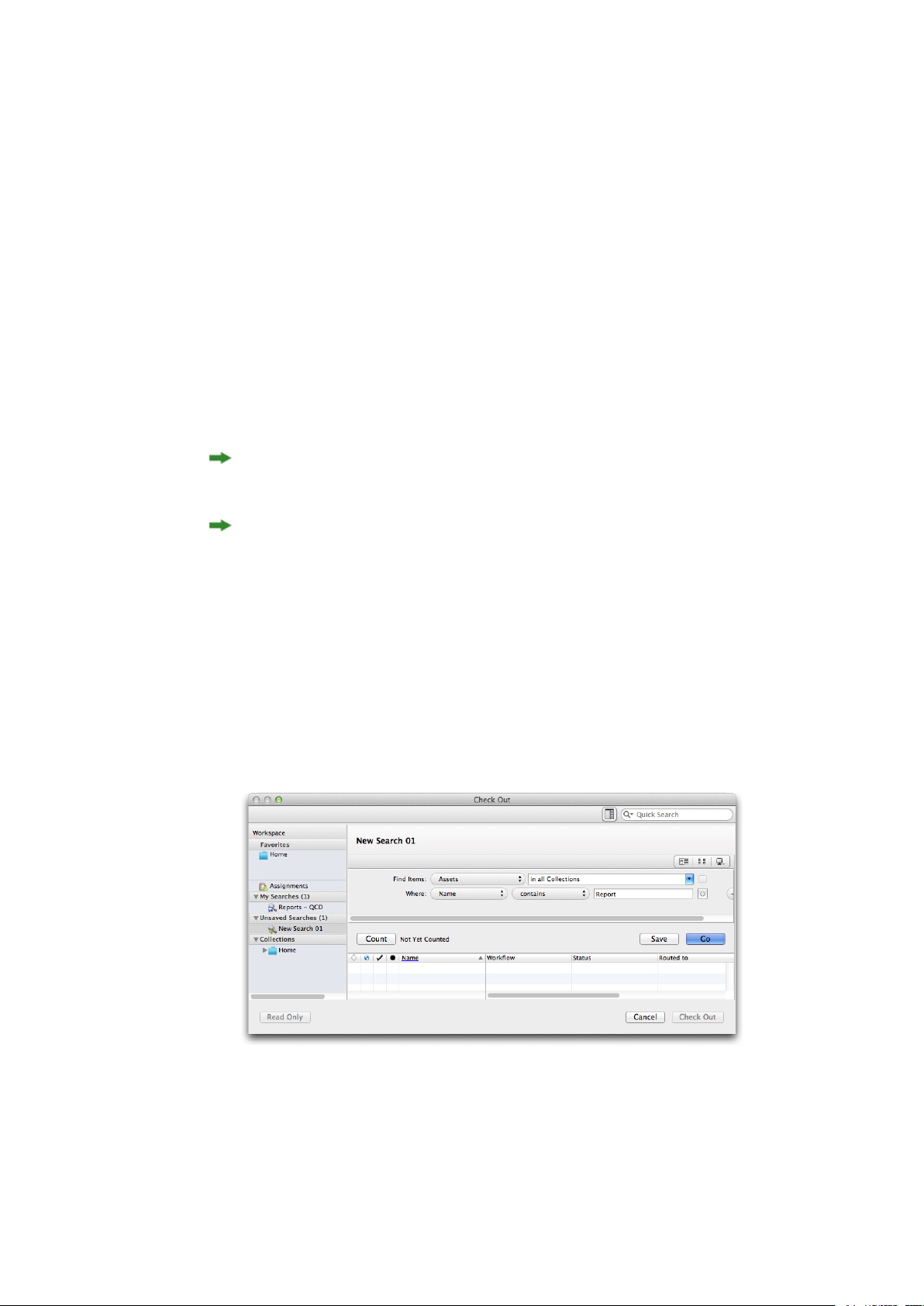
3
Select a project in theWorkspace Browser window that contains attachments and click Check Out
with Attachments.The project and its attachments are checked out.
Checking out and editing pictures: QXP & QCD
You can check out and edit attached pictures in QuarkXPress by choosing Platform > Check Out
Picture. After a picture is checked out, it is located in the folder you specify for storing checked-out
files (QuarkXPress/Edit > Preferences > Quark Publishing Platform > General). If QuarkVista
XTensions software is installed, you can choose Window > Picture Effects to display the Picture
Effects palette and apply picture effects to the attached picture.
If the Edit Original XTensions software is installed,you can also check out and edit attached pictures.
Double-click a box that contains an attached picture to display the Edit Original dialog box and
check out the picture in the background.
You can also Control-click/right-click a picture box that contains an attached picture and choose
Edit Original from the context menu.
Whether you use Edit Original or Platform > Check Out Picture, you must check in the picture or
save a revision to update Quark Publishing Platform Server.
CLIENT TASKS
You can also choose Platform > View Picture Revisions to view revisions of the image or revert
to a previous version.
In QuarkXPress, you can also check out pictures that are not attached to a layout. When you check
out such a picture, it opens in the default image-editing application.
Using Advanced search: QCD and QXP
You can create a search by choosing Advanced Search from the drop-down menu attached to the
Quick Search field. You can use this search once, or you can save it with your other searches.
1
Choose Advanced Search. The advanced search interface displays.
Use the advanced search mode to specify search criteria.
2
To save the search, enter a name in the Search Name field, specify search criteria, and click Save
to execute and save the search. If you do not want to save the search, click Go after you specify
criteria.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 97
Page 98

CLIENT TASKS
3
Select a file and click Check Out.
Cancelling a Checkout
To cancel a checkout of an asset, select the asset in the Workspace window and click Cancel
Checkout. The asset is removed from your computer and any changes made since checkout are
discarded. However, if you made any changes, an alert notifies you that your changes may be lost.
If you saved a revision of the asset on Quark Publishing Platform Server, the revision becomes the
current version.
Working with templates
In order to maintain consistency in your workgroup, you can create articles from article templates
and create projects from project templates.
• To create an article template, design an article in QuarkCopyDesk, choose File > Save As, and
choose Article Template from the Type drop-down menu before you click Save. QuarkCopyDesk
article templates have a suffix of .qct.
• To create a project template, design a layout in a QuarkXPress project, choose File > Save As, and
choose Project Template from the Type drop-down menu before you click Save. QuarkXPress
project templates have a suffix of .qpt.
You can check article templates andproject templatesinto Quark Publishing Platform like you would
articles and projects.
To create a new project from a template in QuarkXPress, choose File > New > Project from Server
Template. In the dialog box that displays, you can choose any project template available to you in
Quark Publishing Platform.
To create a new article from a template in QuarkCopyDesk, choose File > New > Article from
Server Template. In the dialog box that displays, you can choose any article template available to
you in Quark Publishing Platform.
You can use Quark Publishing Platform article templates to create and replace geometry in
QuarkXPress layouts. For more information, see "Attaching articles by dragging."
Attaching content to layouts
In some workflows, content is created in QuarkCopyDesk or another application, and then added to
a layout by a layout artist. In other workflows, the layout iscreated first, and then boxes in the layout
are assignedto contentcontributors asarticles. Bothadding contentfrom QuarkPublishing Platform
to a layout and assigning articles from a layout are examples of attaching content to a layout.
When you attach an asset to a layout, the Assign dialog box may display, depending on whether the
asset is attached as a primary or secondary attachment to the layout (see "Primary and secondary
attachments"). You can use this dialog box to make any necessary changes to the asset's metadata.
For example, you might change the status to indicate that it is now in layout, or add to the revision
comment.
To see which assets are attached to the active layout in QuarkXPress, click Attachments in the
Workspace navigation pane of the Workspace Browser palette.
98 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
Page 99

If you attach an asset to a layout in a project that has not yet been checked in to Quark Publishing
Platform, that asset is referred to as a local asset. Once you have checked the project in, the asset is
referred to as a global asset.
Primary and secondary attachments
There are two kinds of attachments: primary attachments and secondary attachments. An article can
be a secondary attachment to layouts in multiple projects, but can be a primary attachment for only
one layout. The layout that has an article as a primary attachment determines the article's geometry.
You cannot edit secondary attachments directly, but you can update them to reflect changes to the
contents of the primary attachment.
If an article is a primary attachmentfor a layout, Quark Publishing Platform sendsnotifications when
certain modifications are made to that article.
• When a layout artist alters the geometry of such an article and then chooses Platform > Update All
Geometry, an alert displays for the QuarkCopyDesk user who is working on the text of the article,
allowing that person to update the article with the latest geometry from the layout. This allows the
QuarkCopyDesk user to respond to any changes in component size. Geometry is also updated at
check-in and check-out when the QuarkXPress user checks in the project if Auto update geometry
on: Check In and Auto update geometry on: Check Out are checked in the Project and
Attachments preferences pane in QuarkXPress.
CLIENT TASKS
• If a layout artist updates the geometry for an article, but then cancels the checkout of the project, the
geometry is updated to restore it to its original settings if your preferences allow it to.
• If a QuarkCopyDesk user updates the content of such an article and then saves a revision, Content
Differs displays in the Update State column of the Workspace Browser window for that article.
A QuarkXPress user can then update the content by Control+clicking/right-clicking the article and
choosing Update Content, clicking the Update Content button in the toolbar of the Workspace
Browser window, or double-clicking the asset's icon in the Attachments view in the Workspace
Browser window. This allows the QuarkXPress user to respond to any changes in text or picture
content. Article content is automatically updated when you check out a project if Auto update
content on: Check-Out is checked in the Project and Attachments preferences pane in
QuarkXPress. Article content is automatically updated when you save a revision of a project, check
in a project, or output a project if Auto update content on: Check-Out Check-In/Save
Revision/Output is checked in the same pane.
Pictures are always secondary attachments, because they do not have geometry. Unlike articles,
though, pictures can be attached multiple times in the same layout.
A QuarkXPress user can also update geometry with the Update Geometry drop-down menu icon
in the Workspace Browser window and by Control+clicking/right-clicking the asset icon and
choosing an option from the Update Geometry submenu.
When a layout artist updates an article's geometry, Geometry Differs displays in the Update State
column of the Workspace Browser window for that article.
To override an article or component's primary attachment, press Shift and then drag the article or
component to a layout. This makes the article or component a primary attachment to the current
layout, and converts the old primary attachment into a secondary attachment.
A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1 | 99
Page 100

CLIENT TASKS
Attaching article components by dragging
To attach a single article component by dragging, drag the article component from the Workspace
Browser window to a text or picture box. If the type of the target box does not match the component
type, you can press Command/Ctrl to force the box to accept the content.
To attach multiple components, drag them from the Workspace Browser window to a blank part
of the page.
You can also drag and drop multiple components by dragging them to a group of boxes. A dialog
box allows you to map the components to the appropriate boxes.
When you attach a component to a layout, Quark Publishing Platform assigns the component's type
and name to the component's box (whether or not the component has geometry). QuarkXPress users
can view a box's component information in the Component tab of the Modify dialog box (Item
menu).
Attaching articles by dragging
You can attach an article by dragging either an article or an article template to a layout. The topics
below explain how.
To cancel a drag-and-drop operation, press Escape before you release the mouse button.
Dragging articles
The following table explains what happens when you drag an article to various targets in a layout.
Blank area on the page
One of two or more selected
boxes without attachments
Box without attachment
ResultTarget
Quark Publishing Platform creates boxes for all of the components in the article. If the article has
geometry, Quark Publishing Platform uses that geometry (including any relative geometry) when it
creates the boxes for the components. If the article has text or pictures, they are added to the layout.
Text box links are maintained.
The Assign dialog box displays. The list on the left side of the Assign dialog box lets you change the
attributes of all of the components from a single dialog box. When you click OK, the entire article
is attached to the layout.
Quark Publishing Platform attempts to map the components in the article to the selected boxes based
on content type, component type, andcomponent name.If itcannot, itdisplays theMap Components
to Boxes dialog box (see below) so that you can manually map the content to the boxes.
The Assign dialog box displays. The list on the left side of the Assign dialog box lets you change the
attributes of all of the components from a single dialog box. When you click OK, the mapped
components are attached to the layout.
If you press Option/Alt, the existing box is ignored and everything works as if you had dragged the
article to a blank area on the page.
If the article has one component, Quark Publishing Platform attempts to map the component to the
box. If the articlehas multiplecomponents, QuarkPublishing Platformdisplays theSelect Component
dialog box so that you can specify which component should be mapped to the box.
The Assign dialog box displays. When you click OK, the component is attached to the layout.
If you press Option/Alt, the existing box is ignored and everything works as if you had dragged the
article to a blank area on the page.
Nothing happens.Box with attachment
If you press Option/Alt, the existing box is ignored and everything works as if you had dragged the
article to a blank area on the page.
100 | A GUIDE TO QUARK PUBLISHING PLATFORM 9.5.1
 Loading...
Loading...