Page 1

WRC-CANR-DF-DN
and
WRC-CANR-DF-SM
Series IV
CAN-Bus Fiber Optic Bus Extender
User’s Manual
Revision 4.03
W
estern Reserve Controls, Inc.
Page 2

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANX-DF-DN and -SM Series IV User’s Manual
Revision 4.03
Although every effort has been made to insure the accuracy of this document, all information is subject to
change without notice. WRC takes no liability for any errors in this document or for direct, indirect,
incidental or consequential damage resulting from the use of this manual.
Document PUB 14.2
Rev 4.03
January 2012
Copyright © 1998-2012 WRC
Western Reserve Controls, Inc.
1485 Exeter Road
Akron OH 44306
330-733-6662 (Phone)
330-733-6663 (FAX)
sales@wrcakron.com (Email)
http://www.wrcakron.com (Web)
SmartMux-Lite, CAN-Bus Extender and WRC are trademarks of Western Reserve Controls, Inc.
DeviceNet is a trademark of ODVA, Inc.
SDS is a trademark of the Honeywell, Inc.
All other trademarks are property of their respective companies.
Label Markings
і
Page 3

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANX-DF-DN and -SM Series IV User’s Manual
Revision 4.03
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1. S
1.2. F
1.3. B
1.4. R
ERIES IV SPECIFIC FEATURES
EATURES
ASIC OPERATION
EFERENCE DOCUMENTS
...................................................................................................................................... 2
........................................................................................................................... 2
................................................................................................................ 3
........................................................................................................ 1
2. QUICK START ...................................................................................................................................... 4
3. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................................................. 5
4. HARDWARE INSTALLATION AND CONFIGURATION ...................................................................... 6
4.1. O
4.2. LED O
4.3. DIP S
4.4. P
4.5. CAN N
VERVIEW
OWER REQUIREMENTS
...................................................................................................................................... 6
PERATION
WITCH SETTINGS
............................................................................................................................. 6
.................................................................................................................... 8
.................................................................................................................. 9
ETWORK CABLING AND CONFIGURATION
................................................................................ 9
4.5.1. Cable Lengths ........................................................................................................................... 9
4.5.2. Network Termination ............................................................................................................... 10
4.5.3. CAN-Bus Connection Wiring ................................................................................................... 11
4.5.4. Alternate Connector Options ................................................................................................... 12
4.6. F
IBER CABLE
................................................................................................................................. 13
5. OPERATION ....................................................................................................................................... 14
5.1. A
PPLICATION NOTES
..................................................................................................................... 14
6. ADDITIONAL WRC PRODUCTS ....................................................................................................... 17
7. TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................................................................ 19
8. SUMMARY OF CHANGES TO SERIES IV FROM REV 2 AND SERIES III ...................................... 21
8.1. DIP S
8.2. T
8.3. O
8.4. 2.2
8.5. S
8.6. E
WITCH BAUD RATE SETTINGS
ERMINATING RESISTORS
PERATION AND FUNCTIONALITY
KM MULTIMODE FIBER LINK AND DIAGNOSTICS
INGLE-MODE FIBER LINK AND DIAGNOSTICS
NHANCED
CAN S
.............................................................................................................. 21
UPPORT
............................................................................................................ 22
............................................................................................... 21
................................................................................................... 21
(WRC-CANR-DF-DN) ...................................... 21
(WRC-CANR-DF-SM) ............................................. 22
8.7. FIELD PROGRAMMABLE UPDATES ............................................................................................... 22
ii
Page 4

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANX-DF-DN and -SM Series IV User’s Manual
Revision 4.03
LIST OF TABLES
T
ABLE
4-1 M
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
ODULE STATUS
4-2 L
OCAL DEVICE’S NETWORK STATUS
4-3 R
EMOTE DEVICE’S NETWORK STATUS
4-4 D
IAGNOSTIC STATUS
4-5 B
AUD RATE SETTINGS FOR SWITCHES
4-6 N
ETWORK MAXIMUM LENGTHS - DEVICENET
4-7 N
ETWORK MAXIMUM LENGTHS -
4-8 T
ERMINATING RESISTORS
4-9 D
EVICENET CABLE SPECIFICATIONS
4-10 SDS
6-1 A
6-2 A
CABLE SPECIFICATIONS
DDITIONAL
DDITIONAL
LED (
WRC P
WRC P
LABELED
LEDS (
MS) ............................................................................................. 7
LEDS (
LABELED
LABELED
LEDS (
LABEL
NSA) ............................................................. 7
NSB) .............................................................. 7
DNG)................................................................................... 8
............................................................................................ 9
................................................................................. 10
SDS ........................................................................................... 10
............................................................................................................ 11
.............................................................................................. 12
....................................................................................................... 12
RODUCTS AVAILABLE FROM PROSOFT TECHNOLOGY
RODUCTS AVAILABLE FROM
WRC .................................................................. 17
...................................... 17
LIST OF FIGURES
F
IGURE
1-1 T
F
IGURE
F
IGURE
F
IGURE
F
IGURE
F
IGURE
F
IGURE
YPICAL FIBER OPTIC BUS EXTENSION APPLICATION
4-1 WRC-CANR-DF-DN CAN-B
4-2 D
EVICENET NETWORK SIDE A CABLE CONNECTOR – MALE (PINS
4-3 SDS M
5-1 CANR-DF
5-2 CANR-DF
5-3 S
INI CONNECTOR
AMPLE
CANR-DF S
ON A DROP LINE
ON MULTIPLE DROP LINES
ETUP
US EXTENDER
.............................................................................................................. 12
......................................................................................................... 15
.......................................................................................... 15
......................................................................................................... 16
........................................................................ 3
................................................................................. 6
) ................................................ 11
iii
Page 5

Westrn Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.1 Revision 4.03
1. Overview
The WRC-CANR-DF Fiber Optic CAN Bus Extenders convert a copper cable medium CAN-Bus
network to a fiber optic medium. The WRC-CANR-DF-DN uses multimode fiber optic cable, while the
WRC-CANR-DF-SM uses single-mode fiber optic cable. Both are always used in pairs with a length of
fiber media in between. The primary purposes of this type of configuration is to extend the maximum
length defined for one continuous network cable bus up to 2.2km (for multimode with WRC-CANR-DFDN) or 12km (for single-mode with WRC-CANR-DF-SM) and to provide network protection from external,
high-energy electrical interference, such as lightning storms, arc welders, etc. They can be connected in a
bus trunk line or drop line.
A WRC-CANR can be used for quite a number of helpful purposes, including
• To provide an electrically-isolated fiber transmission segment to your CAN bus for more
secure network in high-energy environmental conditions
• to extend the network beyond its absolute maximum at the slowest speed
• to implement a longer network for a given baud rate (e.g., pushing a 500K baud network
beyond 100 m for DeviceNet)
• to provide higher speed baud rates for a given network length
• to extend the length of the drop cable (e.g., longer drops than 6 m for DeviceNet)
• to provide 2600V electrical isolation between the 2 sub-nets
• to create a unique network topology instead of a conventional bus structure, such as a
star configuration
The Extenders are transparent to the other nodes on the bus. They receive and actively retransmit (store-and-forward) each message received at either side of the network without interpreting the
message or acting upon it. The Fiber Extenders perform all appropriate CAN Bus arbitration on the copper
bus as it re-transmits the message.
The WRC-CANR-DF-DN and WRC-CANR-DF-SM are members of WRC’s family of products that
extend the system communications lengths for DeviceNet, CANopen, SDS (Smart Distributed System),
J1939 and other CAN, V2.0, Part A or Part B, serial bus systems. By allowing the user to extend the bus
length for any given speed, they assist the user in cost-effectively implementing I/O or other nodes on
these buses at remote locations that would be more difficult or more expensive to do otherwise.
The unit derives its power through the copper network connector on Side A.
1.1. Series IV Specific Features
The Series IV WRC-CANR provides enhancements over previous the previous Series III
products, including:
* Single Mode Fiber Cable Option is now available.
1
Page 6

Westrn Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.1 Revision 4.03
* Expanded DIP Switch settings allow selection for CAN-bus (including CANopen) speeds up to 1 M
Baud in addition to the standard DeviceNet Baudrates
* 9.6K, 10K, 20K, 40K, 50K, 100K 125K, 250K, 500K, 800K and 1M baud
* Improved Reverse voltage protection and CAN data lines noise immunity
* Increased message internal buffers – Automatic Memory Technology (AMT) operation
* Eliminates the distinction between WRC’s earlier version Type 1 and Type 2 CANR
* WARNING: Series IV F/W Revision 4.002 is not backward compatible.
1.2. Standard Features
The WRC-CANR-DF-DN and WRC-CANR-DF-SM have the following features:
* Extends CAN-Bus cable lengths - trunk line or drop lines
* Expands the usable applications for CAN-Bus systems
* Allows operation at higher speeds for specific distances
* Provides superior electrical interference protection to copper cables
* Switch-selectable Autobaud or fixed baud rate operation
* Automatic speed selection - no configuration required
* Isolates the two sections of the copper bus
* Transparent to the Master and Slave devices on the bus
* No address selection needed
* No configuration parameters
* DeviceNet; SDS; CANopen; J1939; CAN, V2.0, Part A and Part B compatible
* Powered from the 24Vdc supplied by bus network or the user
* Sealed NEMA-4X enclosure
* Standard round, mini-style M18 connector with male pins for copper cable
* For WRC-CANR-DF-DN: Standard Fiber Optic ST female connector, 62.5/125µm technology
* For WRC-CANR-DF-SM: Standard Fiber Optic ST female connector, 9/125µm technology
* Standard CAN chips manage bus error detection
* Standard CAN chips handle message bus contention
* Less than 900 µsec latency
* Jumper-selectable termination built in on cable side
* 4 bi-color (red/green) status LEDs
* 2 green fiber transmit and receive LEDs
1.3. Basic Operation
Two CANR-DF units are included in an order and both are required for each application – both
units are identical. It does not matter which is placed in which position with respect to the network topology
or other devices on the network.
There are two bus connections for each CANR-DF, referred to as the Copper Cable Network Side
(Side A) and Fiber Cable Network Side (Side B). The CAN Bus copper cable is connected to side A of the
CANR-DF receives its power from side A.
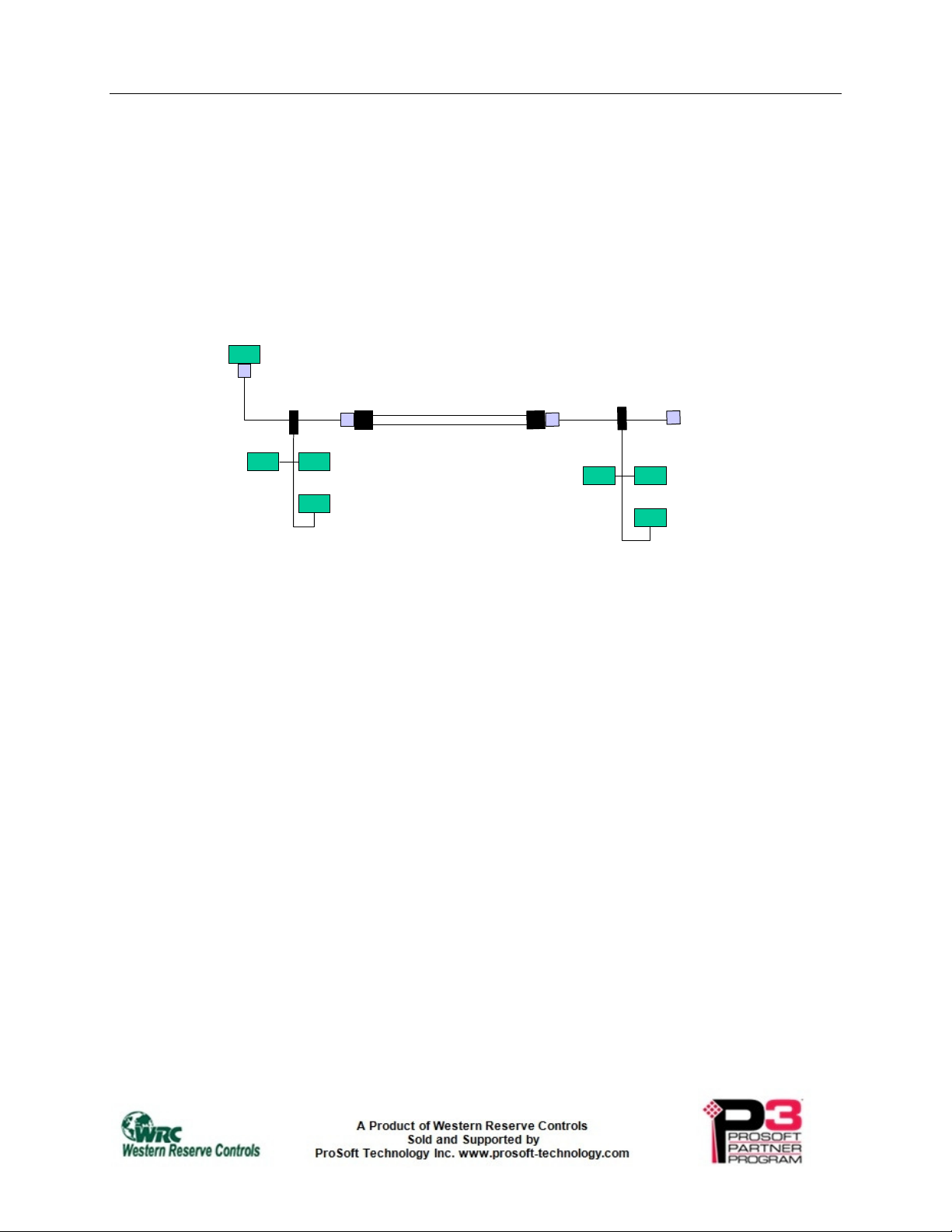
Figure 1-1 shows a typical application.
Whenever a message is transmitted on the Bus to which CANR-DF is connected, CANR-DF
receives the message on the side where it was initiated and performs a store-and-forward of the message
to the other side. This action is performed in each direction and is performed for any valid CAN message
independent of who generated it or to whom it is intended.
There is approximately a 900 µsec propagation delay of the message through the CANR-DF.
2
Page 7
Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
The CANR-DF is not addressed as a specific device on the Bus and cannot be interrogated by
other nodes. It is transparent to all other nodes on the bus.
Fiber-optic extenders -
especially useful for outdoor applications
Host PLC
Host PLC
Up to 2.2 km
Extender
Extender
Figure 1-1 Typical fiber optic bus extension application
Extender
Extender
1.4. Reference Documents
The following documents are referenced in this User’s Manual
* ODVA DeviceNet Specification
* Honeywell Micro Switch Specification GS 052 104, “SDS Smart Distributed System Physical
Layer Specification”, release date 12/8/1994
3
Page 8

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
2. Quick Start
To quickly and easily install your CAN-Bus Fiber Optic Extenders in your DeviceNet system, follow
the instructions below. For more details, see Section 4.
WARNING: Series IV F/W Revision 4.002 is not backward compatible.
1. These units are used in pairs. You need two (2) CANR-DF units and two (2) 62.5/125µµµµm, multi-
mode fiber cable lengths or two (2) 9/125µµµµm single mode fiber cable lengths with ST male
connectors.
2. Leave the DIP switches on the 8-position switch block SW1 in the factory setting position of FF or all
OPEN positions to set the baudrate of each CANR-DF to Autobaud.
3. Using on-board jumper W1, terminate CAN-Bus network, as appropriate. (This is especially critical at
the higher baud rates.)
• For trunk lines, install W1.
• For drop lines, remove W1.
4. Connect the fiber cables to the CANR of one unit. Make sure they are clearly marked on both ends
to differentiate between the two lines.
5. Make sure that there is power on the CAN-Bus Network and plug the Network cable with a 5-pin
round female MINI connector into the CAN-Bus Extender.
6. The CANR-DF Extender will undergo its initialization sequence, flashing the LEDs. After
approximately 5 seconds, the Module Status LED (labeled “MS”) will go on solid green and network
LEDs (labeled “NSA” and “NSB”) will flash green. The DGN led might stay solid red until the fiber
cables are connected to the other CANR and both CANRs are powered up.
7. Repeat steps 2-6 above for the second CANR-DF.
Note: Be sure to connect the fiber from the TX port on one device to the RX port on the other.
8. Connect the desired network devices to both sides of the copper CAN bus.
9. Both Network A and B Status LEDs (NSA and NSB) will go on solid on each unit once a valid CAN
message is received into either side of the Extender and the baudrate auto-detect has been
successfully performed.
10. You may observe the small green LEDs marked RXF and TXF, next to the fiber ports, illuminate when
data is received or transmitted.
11. The CAN-Bus Extenders are now operating on the network and they are ready operate in the CAN
network.
12. If any of the LED’s – marked DGN, NSA and NSB – blink red, this indicates that the internal message
buffer on the CANR-DF has been filled before the device could transfer all previously received
messages out the other side. Some messages may be lost. Slowing down the scan rate should help
eliminate this.
4
Page 9

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
3. General Specifications
Product: WRC-CANR-DF-DN and WRC-CANR-DF-SM, Series IV CAN-Bus Extender
Description: Electrical Extender to extend the cable distances of CAN-based protocol
Device Type: Communications Extender
Product Revision: 4.xx WARNING: Series IV F/W Revision 4.002 is not backward compatible
DeviceNet Conformance: Designed to conform to the ODVA DeviceNet Specification
Baud rate: 9.6K, 10K, 20K, 40K, 50K, 100K 125K, 250K, 500K, 800K and 1M baud fixed
Address selection: Not applicable
Bus Connection: Used On Device: Woodhead # 1R5006A17A120, male pins, male threads
CAN-Bus Cable: See accessories list
Fiber Optic Cable: For WRC-CANR-DF-DN:
For WRC-CANR-DF-SM:
Fiber Cable Length: DN: 2200 meters (max)
SM: 12k meters (max)
Fiber Connection: Used On Device: ST female
Fiber Cable: ST male
Status Indicators: MS - Module Status: green/red bi-color LED
NSA - Copper Network A Status: green/red bi-color LED
NSB - Fiber Network B Status: green/red bi-color LED
DGN - Diagnostic Data: green/red bi-color LED
TXF - Fiber Transmit Active: green LED
RXF - Fiber Receive Active: green LED
Voltage Isolation: Provided by fiber cable system
Maximum power: Voltage: 11 - 25 Vdc
Current: 110 mA @ 11 Vdc - 60 mA @ 25 Vdc
Power: 1.5 W
Mounting: Panel-mount, 4 screws
Size: Length: 5.11” (130 mm)
Depth: 2.27” (57.7 mm)
Height: 3.70” (94.0 mm)
Operating Temp: 0-70 ºC
Humidity: 0-95% RH, non-condensing
Agency Approvals and Agency: CE
Certifications:
and Fiber Optic Converter
products and convert the copper network to a fiber optic link.
or auto-detect baud rate on DeviceNet
• 62.5/125µm, multi-mode, ST termination
• 9/125µm single mode, ST termination
5
Page 10
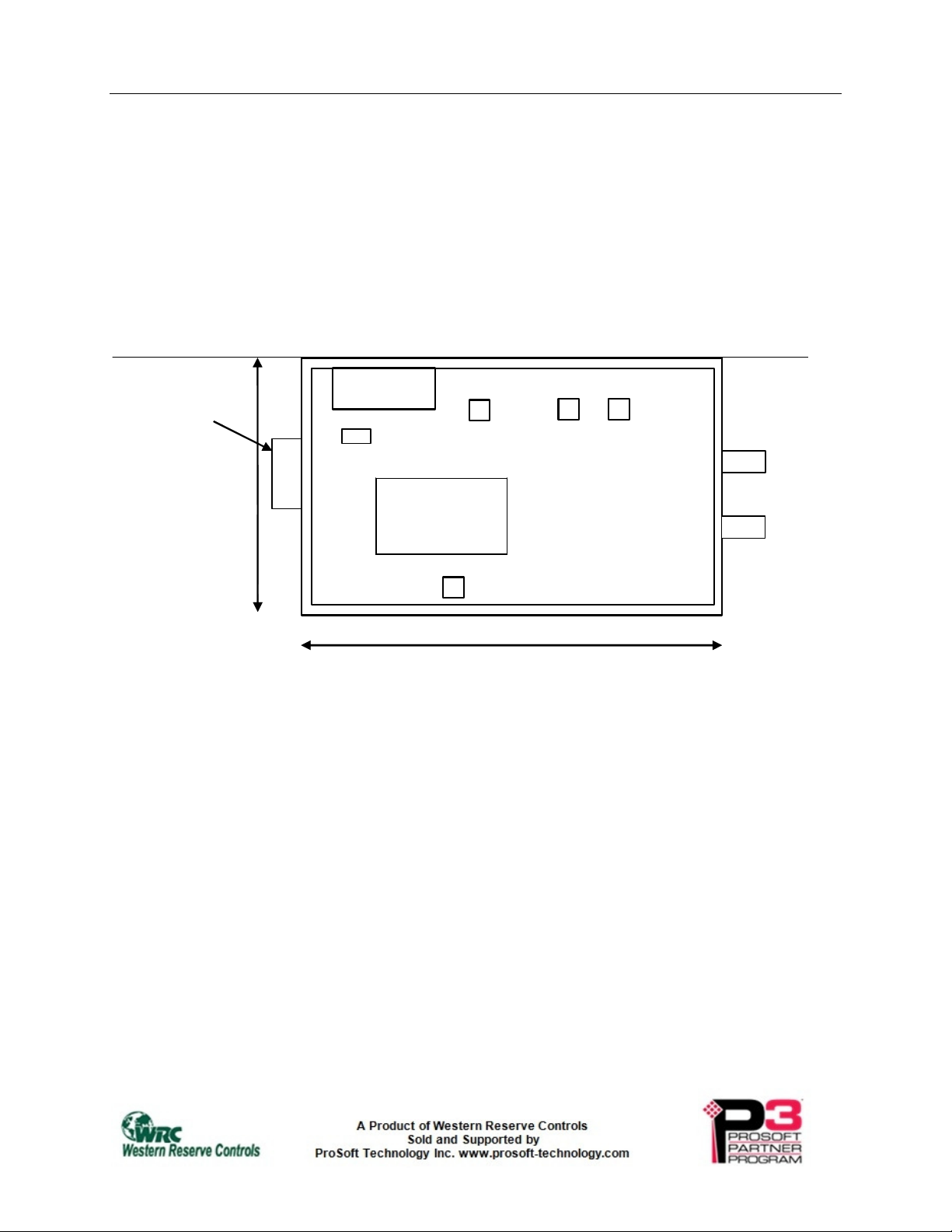
Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
MS
DeviceNet
ST Fiber
Connectors
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
4. Hardware Installation and Configuration
4.1. Overview
A CAN-Bus Extender is a single device connected to two parts of a single CAN-Bus network. The
CANR-DF is a NEMA-4X enclosure and is panel mounted.
Male, Mini
W1
NETWORK A
NSA
DGN
2.27” ( 57,7 mm)
--NET A- --NET B-1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SW1
OPEN
NSB
NETWORK B
5.11” (130 mm)
Figure 4-1 WRC-CANR-DF-xx CAN-Bus Extender (2 per)
4.2. LED Operation
A WRC-CANR-DF-DN Multiplexer has six (6) LEDs that provide visual status information to the
user about the product and the DeviceNet network. The LED’s definitions are summarized as follows and
more thoroughly in the tables below in Table 4-1, Table 4-2 and Table 4-4.
•
MS
– Module Status – indicates the general health of the unit and its ability to Store-and-Forward
messages.
•
NSA
– Network Status A – indicates the condition of the CAN bus connection of this Local unit.
•
NSB
– Network Status B – indicates the condition of the Remote unit’s CAN bus operation on the
other end of the fiber cable.
•
DGN
– Diagnostic – indicates status of the fiber-optic link.
•
RXF
– Receive Fiber – green indicates electrical signals being received by the CANR.
•
TXF
– Receive Fiber – green indicates electrical signals being sent by the CANR.
6
Page 11

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Table 4-1 Module Status LED (labeled MS)
LED State Module Status Meaning
OFF No Power There is no power through DeviceNet.
Green Device Operational WRC-CANR is operating normally.
Flashing Red Minor Fault
Red Unrecoverable Fault WRC-CANR may be damaged.
Flashing Red/Green Device Self-Testing WRC-CANR is in self-test mode.
Table 4-2 Local Device’s Network Status LEDs (labeled NSA)
LED State Module Status Meaning
OFF No Power / Not on-line
Flashing Green Idle
Fast Flashing Green Autobaud selection
Green On-line
Flashing Red CAN controller buffer overflow
Red Critical link failure (Bus Off)
Advanced Memory Technology (AMT)
buffers space exceeded.
WRC-CANR has no power or device is not
operating.
WRC-CANR has not received a valid
message for 0.5 sec.
The WRC-CANR is waiting for a valid
message to fix the baudrate.
WRC-CANR is operating normally and
receiving messages.
There is more traffic on the network than
the system can handle.
WRC-CANR has detected an error that
makes it incapable of communicating on
the link.
Table 4-3 Remote Device’s Network Status LEDs (label NSB)
LED State Module Status Meaning
OFF No Power / Not on-line
Flashing Green Idle
Fast Flashing Green Autobaud selection
Green On-line
Flashing Red CAN controller buffer overflow
Red
Critical CAN link failure
(Bus Off)
7
WRC-CANR has no power or device is not
WRC-CANR has not received a valid
message for 0.5 sec.
The WRC-CANR is waiting for a valid
message to fix the baudrate.
WRC-CANR is operating normally and
receiving messages.
There is more traffic on the network than
the system can handle.
WRC-CANR has detected an error that
makes it incapable of communicating on
the CAN bus.
operating.
Page 12

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Table 4-4 Diagnostic Status LEDs (labeled DNG)
LED State Module Status Meaning
OFF Normal Normal operation.
Green Fiber Link OK Serial link to fiber network operating.
Red Time-out
Flashing Red Communications error
The Green TXF and RXF LED’s are illuminated when data is actively transmitted out to the fiber
link.
Unit has not received a serial message
(status or can) from the fiber link.
Internal FIFO stack has overflowed on the
fiber link interface.
4.3. DIP Switch Settings
The WRC-CANR-DF has an 8-pole DIP switch.
• Switch positions 1-4 are used to set the baud rate of the CANR on which it is located
(the local unit).
• Switch positions 5-8 are used to set the baud rate on the CANR at the other end of
the fiber cable (the Remote Device).
The baud rates can be set independently, or one side can take its baud rate from the other side
(in the “Remote” setting).
The Autobaud detects from DeviceNet bauds.
For CANopen speeds, select the fix baudrate setting.
When both the CANR units are set to all open switch positions (remote-remote) it scans through
DeviceNet baudrates.
8
Page 13
Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
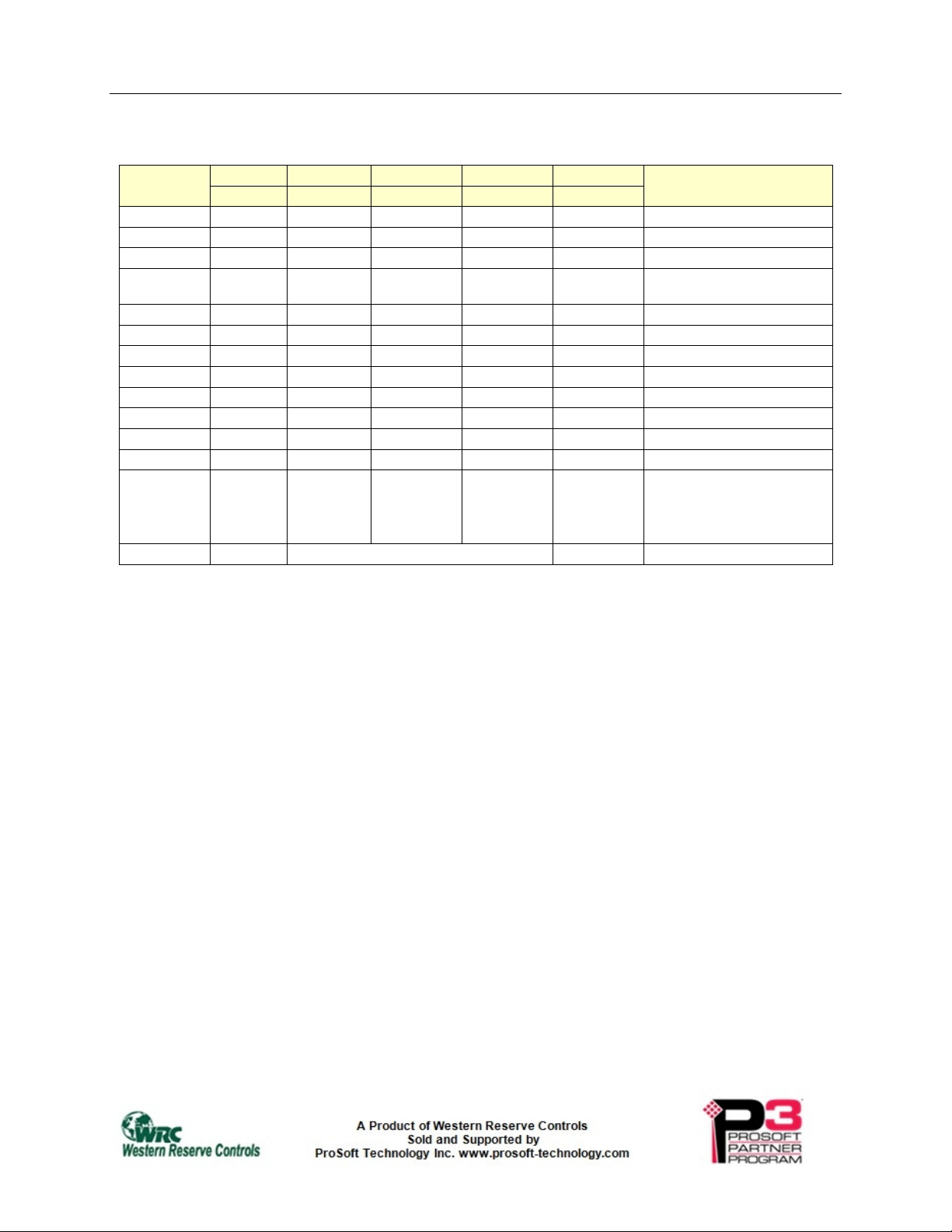
Table 4-5 Baud Rate Settings for Switches
Baud rate
125K CLOSED CLOSED CLOSED CLOSED Fixed
250K CLOSED CLOSED CLOSED
500K CLOSED CLOSED
Autobaud CLOSED CLOSED
9.6K CLOSED
10K CLOSED
20K CLOSED
40K CLOSED
50K
100K
800K
1M
Remote
Autobaud ALL OTHER SWITCH POSITIONS Autobaud
Local Position 1 Position 2 Position 3 Position 4
Remote Position 5 Position 6 Position 7 Position 8
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN OPEN
OPEN OPEN OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN
CLOSED CLOSED CLOSED Fixed
CLOSED CLOSED
CLOSED
CLOSED
CLOSED CLOSED Fixed
CLOSED
OPEN
OPEN OPEN
CLOSED Fixed
OPEN
CLOSED Fixed
OPEN
CLOSED Fixed
Meaning
Fixed
Autobaud for DeviceNet
Bauds (125k,250k,500k)
Fixed
Fixed
Fixed
Fixed
Takes baud rate from the
opposite end device. If
both sides are remote,
Autobaud from either side.
4.4. Power Requirements
The WRC-CANR-DF CAN-Bus Extender subsystems are powered from the 11-25 Vdc provided
by the DeviceNet network. The WRC-CANR consumes 60 mA of current at 25 Vdc, or 1.5 Watts, typical.
See Section 3.
4.5. CAN Network Cabling and Configuration
This section provides general guidelines for connecting DeviceNet and SDS systems. You can
find detailed specifications in the referenced ODVA DeviceNet and Honeywell SDS specifications.
4.5.1. Cable Lengths
The following provide cable length limits for DeviceNet and SDS systems. These numbers apply
independently to each physical section of the CAN (copper) network.
9
Page 14

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Table 4-6 Network Maximum Lengths - DeviceNet
Trunk Line Length Drop Length
Baud Rate
125 Kbits/s 500 m 1640 ft 6 m 20 ft 156 m 512 ft.
250 Kbits/s 250 m 820 ft 6 m 20 ft 78 m 256 ft.
500 Kbits/s 100 m 328 ft 6 m 20 ft 39 m 128 ft.
DeviceNet has a limit of 64 nodes per network for any baud rate.
Maximum Distance Maximum Cumulative
Meters Feet Meters Feet Meters Feet
Table 4-7 Network Maximum Lengths - SDS
Trunk Line Length
Baud Rate
125 Kbits/s 457.2 1500 3.6 12 64
250 Kbits/s 182.8 600 1.8 6 64
500 Kbits/s 91.4 300 0.9 3 64
1 Mbits/s 22.8 75 0.3 1 32
SDS has a limit of 32 nodes per network for any baud rate.
Note:
The CANR-DF CAN bus extender does not enable the user to add more nodes. In addition,
it is transparent to the network and does not count as an addressed device.
(maximum)
Meters Feet Meters Feet
Drop Length
(maximum)
No. of
Nodes
4.5.2. Network Termination
A CAN-Bus system
controller and the
to match impedance and eliminate reflections, even if only two nodes are present. Follow the information
below when using a CANR-DF.
The CANR Series IV has a built-in terminator, which can be selectively included or omitted from
the network. To include the on-board terminator (on the DeviceNet side), install jumper W1; or remove the
W1 jumper if the on-board terminator in not desired. The CANR is shipped from the factory with the
jumper installed. See Figure 4-1 for the location of the jumper.
last
node device or WRC CAN-Bus Extender on the network must always be terminated
must be terminated at each end of a copper trunk line
. The host
Trunk line use:
For the purpose of network termination, the CANR-DF is treated as the last node on the copper
section of the trunk network (side A) to which it is connected. Therefore, when a CANR-DF is used directly
in a trunk line, it must be terminated on side A. The terminating resistor built into the CANR-DF at W1
must be installed, or another terminator at the end of the line could be used in the place of the W1
terminator.
Drop line use:
10
Page 15

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
When CANR-DF is used in a drop line (the Network A side is toward the main trunk), the Network
A connection must
jumper plug at W1.
Some specifications for the terminating resistor are:
Important: Per the DeviceNet and SDS specs -- do not terminate devices on drop lines.
not be terminated
Table 4-8 Terminating Resistors
DeviceNet SDS
121 ohm 120 ohm
1% metal film 2%
1/4 watt 1/4 watt
. The user must remove the built-in terminator by removing the
4.5.3. CAN-Bus Connection Wiring
The CANR-DF uses the round, mini-style connector on the copper side A and standard ST
connectors on the fiber side B.
Figure 4-2
DeviceNet
3
4
5
Network Side A cable connector – Male (pins)
2
1
11
Page 16

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Pin # Function Wire color
1 Drain bare
2 V+ red
3 V- black
4 CAN_H white
5 CAN_L blue
Table 4-9
Pin # Function Wire color
1 Drain Bare
2 V+ Brown
3 GND Blue
4 CAN_H Black
5 CAN_L White
DeviceNet
Figure 4-3
cable specifications
SDS
Mini Connector
Table 4-10 SDS cable specifications
4.5.4. Alternate Connector Options
Cable sets may be purchased from an appropriate vendor or custom-made. Turck supplies
individual connectors that may be used to build custom DeviceNet or SDS copper cables. Turck part
number B 4151-0/16 is a 5-pin, 600V, 9A connector that mates with a number of cables that may be used
for the Network A side on the CANR. Contact WRC or your local Turck dealer.
12
Page 17

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
4.6. Fiber Cable
The WRC-CANR-DF-DN employs fiber optic driver and receiver that are capable of operating
62.5/125µm multi-mode cable a distance of 2200 meters. They use ST connectors. The Series IV WRCCANR-DF-SM can operate with 9/125µm single mode fiber optic cable.
Two fiber cables are required. Each fiber cable is connected between TX of one CANR and RX of
the other.
For custom applications using different fiber cable technology, contact WRC.
13
Page 18

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
5. Operation
Each CANR system receives CAN messages and then packs and transmits the messages over
the fiber link to the other CANR, which produces the messages onto its CAN bus network. The CANR pair
provides electrical isolation between the two CAN sub-networks. It has no CAN address and is logically
transparent to the CAN network protocol. The CANR does not interpret nor act on the CAN messages.
The CAN Bus is connected to the A Side of the CANR-DF and receives its power from the Bus.
Whenever a message is transmitted on the Bus to which the CANR-DF pair is connected, one
CANR-DF receives the message on the side where it was initiated and performs a store-and-forward of
the message to the other side. This action is performed for any valid CAN message independent of who
generated it or to whom it is intended.
There is a propagation delay of the message through the CANR-DF system, consisting of 2 parts:
each CANR introduces approximately a 75 µsec delay, and the transmission time on the fiber link (in both
directions) introduces additional delay.
The CANR Series IV also has the capability for each unit to monitor and report on the status of the
other unit in the pair. The NSB LED on one unit reflects the status of the other unit. In this manner you can
determine the operating status of both units by observing just one of them.
Also the CANR allows you set up the baud rate for both units from just one. See the section on
switch settings, 4.3 above, for more details.
5.1. Application Notes
NOTE: CANR-DF’S ARE ALWAYS USED IN PAIRS!
To help insure ease of installation and reliable operation of your system, the following guidelines
should be followed CANR-DF installation in your CAN network.
Proper CAN bus termination is critical to reliable operation of the network. Set the W1 jumpers
on the CANR’s appropriately.
Other than improper terminators, the most common problem is correct fiber cable connection
and termination. Make sure one cable connects TX on one to RX on the other and vice versa.
Also confirm that the fiber itself is good quality and the ends are correctly polished and
terminated with ST connectors.
Use the on-board LEDs to help determine the health of the fiber cable interconnection.
In Autobaud applications, the baud rate that each device selects will be defined by the first
valid message received from either the CAN-Bus or via the fiber connection from the other
device.
Although multiple CANR’s can be used in series, use only one CANR-DF pair in any network
section. That is, only use one CANR-DF pair per trunk line or drop line.
CANR-DF is not a grounded device and the Bus shield is not connected electrically to the
device. Therefore, follow appropriate wiring practices to eliminate noise and other problems.
Example of a valid drop line applications are shown in the following figures. See Figure 1-1 for an
example trunk line application.
14
Page 19

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Linear Bus Topology - extended fiber drop
Terminator
Terminator
Tap
Tap
Terminator
Terminator
Drop Line
Drop Line
Nodes
Nodes
Zero Drop
Zero Drop
Short Drops
Short Drops
Figure 5-1 CANR-DF on a drop line
Linear Bus Topology - multiple fiber drops
Terminator
Terminator
Nodes
Nodes
Drop Line
Drop Line
Taps
Taps
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
2.2km Fiber
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Terminator
Terminator
2.2km Fiber
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Zero Drop
Zero Drop
Short Drops
Short Drops
Fiber Extender
Fiber Extender
Figure 5-2 CANR-DF on multiple drop lines
15
Page 20

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Figure 5-3 Sample CANR-DF Setup
16
Page 21

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
6. Additional WRC Products
The following WRC products and components are also available.
Table 6-1 Additional WRC Products Available from ProSoft Technology
Part WRC Part Number
DeviceNet to Serial I/O Gateway 1782-JDC
DeviceNet to Modbus Gateway 1782-JDM
DeviceNet to Optomux Gateway 1782-JDO
DeviceNet to Pamux Gateway 1782-JDP
DeviceNet to Serial Gateway, open frame 1799wr-DASCII
DeviceNet/CAN Software Utility DNspector™
DeviceNet, CANopen Extender, DIN mount WRC-CANX-DIN-DN
DeviceNet, CANopen Extender, DIN mount WRC-CANX-DIN-C7
DeviceNet, CANopen Extender, NEMA box WRC-CANX-NEM-DN
DeviceNet, CANopen Extender, Fiber Optic, NEMA box,
ulti-mode fiber
DeviceNet, CANopen Extender, Fiber Optic, NEMA box,
single-mode fiber
Table 6-2 Additional WRC Products Available from WRC
Part WRC Part Number
WRC-CANR-DF-DN
WRC-CANR-DF-SM
DIN rail WRC 50022
Terminating resistor, axial lead RM121DN
Connector, 5-pin mini-round for CANX, CANR B 4151-0/16 (Turck)
Discrete I/O block – 4 channels 1782-JDB4
Discrete I/O block – 8 channels 1782-JDB8
Analog Input block – 4 channels, 10-bit 1782-JDA4
Analog I/O block – 8 channels, 12-bit 1782-JDA8
Discrete I/O block – 24 channels W2-JDB24
Discrete I/O block – 48 channels W2-JDB48
Discrete I/O, Analog Input block – 24 DIO, 32 AI W2-JDA24
Discrete I/O, Analog Input block – 48 DIO, 32 AI W2-JDA48
Analog I/O block - 32 channels W2-JDAIO
17
Page 22

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Table 6-2 Additional WRC Products continued:
Discrete and Analog I/O block – 24 DIO, 32 AIO W2-JDAIO24
Discrete and Analog I/O block – 48IO, 32 AIO W2-JDAIO48
Discrete I/O block – 8 DIs, 8 DOs, 4 AIs W5-JDB16x
The following components can be used with a WRC-CANR CAN-Bus Extender for replacements or spare
parts, or as complementary devices as a part of your DeviceNet system.
Part WRC P/N Equivalent Mfr. Part Number
• CANX-NEM Cable n/a Various manufacturers’ Mini-Style Connector
Examples:
Cable assy. w/ male threads, male pins:
Turck RSM 570-*M/630 (“trunk line”)
Turck RSM 571-*M/630 (“drop line”)
• DIN rail (1 meter) WRC 50022 Phoenix Contact NS 35/7,5 0801733 (2 m)
Allen-Bradley 199-DR1 (1 m)
• Terminating resistor RM121DN 121Ω,1%, metal film, axial lead resistor
WRC also provides discrete and analog I/O signal conditioning and multiplexing on DeviceNet, as well as
communication gateways.
18
Page 23

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
7. Troubleshooting
This section identifies some of the common problem observed when commissioning or operating
a CANR-DF Extender.
Problem:
DeviceNet devices will not communicate on the network
Module Status LED is solid Green
Network Status LEDs are flashing Green at ½ second intervals
Meaning
No transmissions have been received by the CANX for 0.5 seconds.
Possible Solutions:
1. Network cables are broken or disconnected.
2. Network is not properly terminated.
3. All devices have stopped trying to communicate on the network.
4. Power has been lost on the B Side subnetwork.
Problem:
DeviceNet devices will not communicate on the network
Module Status LED is solid Green
Network Status LEDs are flashing Green quickly
Meaning
The CANR is in autobaud and is waiting for a valid message to fix its baud rate.
Possible Solutions:
1. Network cables are broken or disconnected.
2. Network is not properly terminated.
3. All devices have stopped trying to communicate on the network.
Problem:
Some messages are missed on network.
Module Status LED is solid Green
NSA and NSB LEDs are flashing Red
Meaning
Internal CAN buffers are full. Network has more traffic than it can handle.
Possible Solutions:
1. Reduce the scan rate from the Master.
2. Reduce the COS frequency on I/O devices.
3. Decrease the assembly sizes of I/O connections.
4. Recalculate the network traffic and bandwidth without the CANX.
Problem:
Some messages are missed on network.
Module Status LED is flashing Red
Meaning
Internal AMT buffers are full. Network has more traffic than it can handle.
Possible Solutions:
1. Reduce the scan rate from the Master.
2. Reduce the COS frequency on I/O devices.
3. Decrease the assembly sizes of I/O connections.
4. Recalculate the network traffic and bandwidth without the CANX.
19
Page 24

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
Problem:
Device will not communicate on the network
Module Status LED is solid Green
Network Status LED is flashing Green
Possible Solutions:
1. CANR does not see CAN messages on the network.
2. Network does not have a terminating resistor. Add a 121 ohm resistor across the
CAN_H and CAN_L signals at the first and last nodes.
3. Network cable is broken or disconnected.
4. Network cable is miswired.
Problem:
Device will not communicate on the network
DGN is solid red or off
Possible Solutions:
1. Fiber Link is broken or not connected
2. Reterminate, Replace or Reconnect the optical fiber.
20
Page 25

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
8. Summary of Changes to Series IV from Rev 2 and
Series III
To facilitate implementation of the new Series III CANR products for customers that are currently
users of the CANR Revision 2.xx products, this section summarizes the product changes from Rev 2 to
Series 3.
8.1. DIP Switch Baud Rate Settings
Several new options exist for setting the baud rate on the CANR Series IV.
• Like the Series III, the Series IV has an 8-position DIP switch block. All 8 switches are
defined and used.
• The Series IV unit is compatible with all CANopen baud rates. These baud rates are fixed
by setting the 8 position dip switch to the appropriate configuration.
• See Section 4.3 for details.
8.2. Terminating Resistors
The Series IV has an on-board terminating resistor on the CAN connection that can be selectively
included or excluded from the network circuit. With jumpers W 1, the CANR puts a 121-ohm resistor
across the CAN_H and CAN_L lines on sub-network side A. See Section 4.5.2 and Table 4-8 for the
location of this jumper.
8.3. Operation and Functionality
The Rev 2 version CANR required one Type 1 and one Type 2 unit per connection. The Series III
and IV products now make no differentiation – there is only one design. Therefore, you do not need to be
concerned with “matching pairs”.
Important: The Series III and IV products are not backwards compatible with the previous
versions
and a Series III or IV on the other end. The same is true with networks with a Series III on one end and a
Series IV on the other:
.
You cannot implement a network which consists of a Revision 2 product on one end of the fiber
this will not perform
.
8.4. 2.2km Multimode Fiber Link and Diagnostics (WRC-CANRDF-DN)
The WRC-CANDF-DN Series III and IV have the following fiber serial link improvements:
• Extends your applications for up to 2.2km at any CAN baud rate.
o This significantly increases opportunities for mining, tank farm, remote out-
buildings, and other similar applications.
21
Page 26

Western Reserve Controls WRC-CANR-DF-DN and –SM User’s Manual
PUB 14.2 Revision 4.03
• Additional diagnostics:
o A “heartbeat” feature has been added to the fiber link on Series III and IV WRC-
CANR-DF-DN units. A heartbeat message is generated between the 2 CANR
units when no CAN activity is present for approximately 0.5 sec, allowing each
unit to confirm the status of the link.
o The NSB LED indicates the health of the fiber connection for both normal traffic
and the heartbeat.
8.5. 12km Single-mode Fiber Link and Diagnostics (WRCCANR-DF-SM)
The WRC-CANR-DF-SM Series IV can be used with single-mode fiber optic cable and has the
following fiber serial link characteristics:
• Extends your applications for up to 12km at any CAN baud rate.
o This significantly increases opportunities for applications requiring longer range
network extension than can be accomplished using single mode fiber.
• Additional diagnostics:
o As with the mulitmode fiber, a “heartbeat” feature has been added to the fiber link
on WRC-CANR-DF-SM Series IV units. A heartbeat message is generated
between the 2 CANR units when no CAN activity is present for approximately 0.5
sec, allowing each unit to confirm the status of the link.
o The NSB LED indicates the health of the fiber connection for both normal traffic
and the heartbeat.
8.6. Enhanced CAN Support
The CANR now supports CAN 2.0 Part B, as well as Part A. It also can operate up to 1M Baud
and with CANopen baud rates. (See factory for details.)
8.7. Field Programmable Updates
The CANR Series III and IV units have their programs held in flash memory, which can be
updated in the field. Contact the factory for details.
22
 Loading...
Loading...