Page 1

I
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright 2014 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or computer
language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to the contents
hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Any
software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the programs prove defective following
their purchase, the buyer (and not this company, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all
necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential damages resulting from any defect in the
software. Further, this company reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to
time in the contents hereof without obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in
a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference
by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reori
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
ent or relocate the receiving antenna.
connected.
FCC Caution:
To assure continued compliance, (example-use only shielded interface cables when connecting to computer or
peripheral devices) any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the Following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference
(2) This Device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
II
Page 3

Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled environment. In order to
avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity to the antenna
shall not be less than 20 cm (8 inches) during normal operation.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE OF THE EUROPEAN
PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL OF 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication terminal
Equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE).
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) As of April 8, 2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However, special
attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with electrical
equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be allowed at all times to
ensure the safe use of the equipment.
National Restrictions
This device is intended for home and office use in all EU countries (and other countries following the EU
directive 1999/5/EC) without any limitation except for the countries mentioned below:
Country Restriction Reason/remark
Bulgaria None
Outdoor use limited to 10
France
Italy None
Luxembourg None
Norway Implemented
Russian
Federation
mW e.i.r.p. within the band
2454-2483.5 MHz
None Only for indoor applications
General authorization required for outdoor use and
public service
Military Radiolocation use. Refarming of the 2.4 GHz
band has been ongoing in recent years to allow current
relaxed regulation. Full implementation planned 2012
If used outside of own premises, general authorization is
required
General authorization required for network and service
supply(not for spectrum)
This subsection does not apply for the geographical area
within a radius of 20 km from the centre of Ny-Ålesund
Note: Please don’t use the product outdoors in France
WEEE regulation
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of
hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic
equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of
WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
III
Page 4

Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET 0ESV802.11n Wireless Range Extender
Model: WNAP-1110
Rev: 2.0 (February, 2014)
Part No. EM-WNAP-1110v2_v2.0 (2081-E10350-002)
IV
Page 5

CONTENTS
Chapter 1. Product Introduction.........................................................................................................10
1.1 Package Contents...............................................................................................................10
1.2 Product Description.............................................................................................................10
1.3 Product Features................................................................................................................. 11
1.4 Product Specifications.........................................................................................................12
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation ........................................................................................................ 14
2.1 Hardware Description..........................................................................................................14
2.1.1 The Front Panel ......................................................................................................14
2.1.2 The Rear Panel.......................................................................................................15
Chapter 3. Connecting the AP ............................................................................................................ 17
3.1 System Requirements......................................................................................................... 17
3.2 Installing the AP .................................................................................................................. 17
Chapter 4. Quick Installation Guide ...................................................................................................21
4.1 Manual Network Setup - TCP/IP Configuration ..................................................................21
4.1.1 Configuring the IP Address Manually .....................................................................21
4.2 Starting Setup in Web UI..................................................................................................... 25
Chapter 5. Configuring the AP............................................................................................................ 29
5.1 Status ..................................................................................................................................29
5.2 Quick Setup......................................................................................................................... 31
5.3 Operation Mode ..................................................................................................................31
5.3.1 Operation Mode – Access Point .............................................................................32
5.3.2 Operation Mode – Multi-SSID................................................................................. 34
5.3.3 Operation Mode – Repeater (Range Extender) .....................................................38
5.3.4 Operation Mode – Bridge with AP ..........................................................................44
5.3.5 Operation Mode – Client......................................................................................... 49
5.4 WPS ....................................................................................................................................52
5.5 Network ...............................................................................................................................56
5.5.1 LAN.........................................................................................................................56
5.6 Wireless...............................................................................................................................58
5.6.1 Wireless Settings ....................................................................................................58
5.6.2 Wireless Security ....................................................................................................60
5.6.3 Wireless MAC Filtering ...........................................................................................65
5.6.4 Wireless Advanced .................................................................................................68
5.6.5 Antenna Alignment..................................................................................................69
V
Page 6

5.6.6 Throughput Monitor ................................................................................................70
5.6.7 Wireless Statistics...................................................................................................71
5.7 DHCP ..................................................................................................................................72
5.7.1 DHCP Settings........................................................................................................ 72
5.7.2 DHCP Clients List................................................................................................... 74
5.7.3 Address Reservation ..............................................................................................75
5.8 System Tools....................................................................................................................... 77
5.8.1 SNMP......................................................................................................................77
5.8.2 Time Settings.......................................................................................................... 79
5.8.3 Diagnostic ...............................................................................................................81
5.8.4 Ping Watch Dog......................................................................................................84
5.8.5 Firmware Upgrade..................................................................................................84
5.8.6 Factory Defaults...................................................................................................... 85
5.8.7 Backup & Restore...................................................................................................86
5.8.8 Reboot ....................................................................................................................87
5.8.9 Password ................................................................................................................87
5.8.10 System Log.............................................................................................................89
5.8.11 Statistics.................................................................................................................. 92
Chapter 6. Quick Connection to a Wireless Network....................................................................... 94
6.1 Windows XP (Wireless Zero Configuration)........................................................................94
6.2 Windows 7 (WLAN AutoConfig) ..........................................................................................96
6.3 Mac OS X 10.x ....................................................................................................................99
6.4 iPhone / iPod Touch / iPad................................................................................................ 101
Appendix A: Planet Smart Discovery Utility...................................................................................... 105
Appendix B: Factory Default Settings................................................................................................ 106
Appendix C: Troubleshooting .............................................................................................................107
Appendix D: Specifications.................................................................................................................109
Appendix E: Glossary .......................................................................................................................... 110
VI
Page 7

FIGURE
FIGURE 2-1 WNAP-1110 FRONT PANEL.................................................................................................14
FIGURE 2-2 WNAP-1110 REAR PANEL...................................................................................................15
FIGURE 3-1 ADJUST THE DIRECTION OF THE ANTENNA .............................................................................18
FIGURE 3-2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION OF THE WNAP-1110 WIRELESS AP.............................................. 19
FIGURE 3-3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION OF THE WNAP-1110 WIRELESS AP.............................................. 19
FIGURE 4-1 TCP/IP SETTING.................................................................................................................22
FIGURE 4-2 WINDOWS STAR T MENU ......................................................................................................23
FIGURE 4-3 SUCCESSFUL RESULT OF PING COMMAND .............................................................................23
FIGURE 4-4 FAILED RESULT OF PING COMMAND ......................................................................................24
FIGURE 4-5 LOGIN THE AP.....................................................................................................................25
FIGURE 4-6 LOGIN WINDOW .................................................................................................................. 25
FIGURE 4-7 WNAP-1110 QUICK SETUP.................................................................................................26
FIGURE 4-8 QUICK SETUP – OPERATION MODE ...................................................................................... 26
FIGURE 4-9 QUICK SETUP – WIRELESS ..................................................................................................27
FIGURE 4-10 QUICK SETUP – NETWORK ................................................................................................ 27
FIGURE 4-11 QUICK SETUP – FINISH ......................................................................................................28
FIGURE 4-12 BASIC WIRELESS INTERNET CONNECTION ..........................................................................28
FIGURE 5-1 MAIN MENU ........................................................................................................................29
FIGURE 5-2 STATU S...............................................................................................................................30
FIGURE 5-3 OPERATION MODE...............................................................................................................31
FIGURE 5-4 WIRELESS – AP MODE ........................................................................................................ 33
FIGURE 5-5 TOPOLOGY – AP MODE .......................................................................................................33
FIGURE 5-6 OPERATION MODE – MULTI-SSID ........................................................................................ 34
FIGURE 5-7 TOPOLOGY – MULTI-SSID ...................................................................................................36
FIGURE 5-8 MULTI-SSID – ENABLE VLAN..............................................................................................36
FIGURE 5-9 MULTI-SSID – VLAN TOPOLOGY .........................................................................................38
FIGURE 5-10 OPERATION MODE - REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER)...........................................................39
FIGURE 5-11 TOPOLOGY – UNIVERSAL REPEATER .................................................................................. 39
FIGURE 5-12 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – UNIVERSAL REPEATER.................................................... 40
FIGURE 5-13 TOPOLOGY – WDS REPEATER...........................................................................................40
FIGURE 5-14 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – WDS REPEATER ............................................................41
FIGURE 5-15 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – SURVEY.........................................................................42
FIGURE 5-16 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – AP LIST ......................................................................... 43
FIGURE 5-17 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – FINISH SETTING..............................................................43
FIGURE 5-18 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – SECURITY ......................................................................44
FIGURE 5-19 REPEATER (RANGE EXTENDER) – STATUS ..........................................................................44
FIGURE 5-20 OPERATION MODE - BRIDGE WITH AP ................................................................................45
FIGURE 5-21 TOPOLOGY - BRIDGE WITH AP ........................................................................................... 46
VII
Page 8

FIGURE 5-22 BRIDGE WITH AP – SURVEY ...............................................................................................47
FIGURE 5-23 BRIDGE WITH AP – AP LIST ...............................................................................................47
FIGURE 5-24 BRIDGE WITH AP – FINISH SETTING ...................................................................................48
FIGURE 5-25 BRIDGE WITH AP – STATUS ................................................................................................48
FIGURE 5-26 WIRELESS - CLIENT...........................................................................................................49
FIGURE 5-27 TOPOLOGY – CLIENT MODE ............................................................................................... 50
FIGURE 5-28 CLIENT – SURVEY .............................................................................................................50
FIGURE 5-29 CLIENT – AP LIST .............................................................................................................. 51
FIGURE 5-30 CLIENT – FINISH SETTING.................................................................................................. 51
FIGURE 5-31 CLIENT – STATU S .............................................................................................................. 52
FIGURE 5-32 WPS................................................................................................................................52
FIGURE 5-33 HARDWARE WPS BUTTON.................................................................................................53
FIGURE 5-34 SOFTWARE WPS BUTTON ................................................................................................. 53
FIGURE 5-35 ADD A NEW DEVICE ............................................................................................................54
FIGURE 5-36 NEW DEVICE CONNECT SUCCESSFULLY............................................................................... 55
FIGURE 5-37 THE NETWORK MENU ........................................................................................................56
FIGURE 5-38 LAN SETTINGS .................................................................................................................56
FIGURE 5-39 WIRELESS MENU ...............................................................................................................58
FIGURE 5-40 WIRELESS SETTINGS......................................................................................................... 58
FIGURE 5-41 WIRELESS SECURITY ........................................................................................................ 60
FIGURE 5-42 WIRELESS SECURITY – WEP.............................................................................................61
FIGURE 5-43 WIRELESS SECURITY - WPA/WPA2 ENTERPRISE...............................................................62
FIGURE 5-44 WIRELESS SECURITY - WPA/WPA2 PERSONAL..................................................................63
FIGURE 5-45 WIRELESS MAC ADDRESS FILTERING ................................................................................65
FIGURE 5-46 ADD OR MODIFY WIRELESS MAC ADDRESS FILTERING ENTRY ............................................ 66
FIGURE 5-47 WIRELESS MAC ADDRESS FILTERING ................................................................................67
FIGURE 5-48 WIRELESS ADVANCED ....................................................................................................... 68
FIGURE 5-49 ANTENNA ALIGNMENT........................................................................................................69
FIGURE 5-50 THROUGHPUT MONITOR ....................................................................................................70
FIGURE 5-51 THE AP ATTACHED WIRELESS STATIONS ..............................................................................71
FIGURE 5-52 THE DHCP MENU..............................................................................................................72
FIGURE 5-53 DHCP SETTINGS ..............................................................................................................73
FIGURE 5-54 DHCP CLIENTS LIST......................................................................................................... 74
FIGURE 5-55 ADDRESS RESERVATION .................................................................................................... 75
FIGURE 5-56 ADD AN ADDRESS RESERVATION ENTRY ............................................................................. 76
FIGURE 5-57 MODIFY AN ADDRESS RESERVATION ENTRY........................................................................ 76
FIGURE 5-58 THE SYSTEM TOOLS MENU ................................................................................................ 77
FIGURE 5-59 THE SYSTEM TOOLS MENU ................................................................................................ 78
FIGURE 5-60 TIME SETTINGS ................................................................................................................. 79
FIGURE 5-61 DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS...........................................................................................................81
VIII IX
Page 9

FIGURE 5-62 DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS ....................................................................................................... 83
FIGURE 5-63 PING WATCH DOG ............................................................................................................. 84
FIGURE 5-64 FIRMWARE UPGRADE ........................................................................................................85
FIGURE 5-65 RESTORE FACTORY DEFAULT............................................................................................. 86
FIGURE 5-66 BACKUP & RESTORE CONFIGURATION ................................................................................86
FIGURE 5-67 REBOOT THE AP ...............................................................................................................87
FIGURE 5-68 PASSWORD .......................................................................................................................88
FIGURE 5-69 SYSTEM LOG ....................................................................................................................89
FIGURE 5-70 MAIL ACCOUNT SETTINGS..................................................................................................90
FIGURE 5-71 STATI STICS .......................................................................................................................92
FIGURE 6-1 WIRELESS ZERO CONFIGURATION........................................................................................94
FIGURE 6-2 VIEW AVAILABLE WIRELESS NETWORKS ............................................................................... 94
FIGURE 6-3 CHOOSE A WIRELESS NETWORK ...........................................................................................95
FIGURE 6-4 ENTER THE ENCRYPTION KEY...............................................................................................95
FIGURE 6-5 WIRELESS NETWORK CONNECTED.......................................................................................96
FIGURE 6-6 WLAN AUTOCONFIG ........................................................................................................... 96
FIGURE 6-7 WLAN AUTOCONFIG WINDOW .............................................................................................97
FIGURE 6-8 WLAN AUTOCONFIG – TYPE THE NETWORK SECURITY KEY ................................................... 98
FIGURE 6-9 WLAN AUTOCONFIG – CONNECTING.................................................................................... 98
FIGURE 6-10 WLAN AUTOCONFIG – CONNECTED ..................................................................................99
FIGURE 6-11 THE AIRPORT NETWORK CONNECTION ICON....................................................................... 99
FIGURE 6-12 THE AIRPORT NETWORK CONNECTION MENU ...................................................................100
FIGURE 6-13 THE AIRPORT NETWORK CONNECTION – ENTER PASSWORD..............................................100
FIGURE 6-14 THE AIRPORT NETWORK CONNECTION – CONNECTED....................................................... 101
FIGURE 6-15 THE WI-FI SETTINGS IN IPHONE/IPOD TOUCH/IPAD...........................................................101
FIGURE 6-16 GENERAL SETTINGS ........................................................................................................ 102
FIGURE 6-17 GENERAL SETTINGS – NOT CONNECTED ..........................................................................102
FIGURE 6-18 GENERAL SETTINGS – WI-FI ON ......................................................................................103
FIGURE 6-19 GENERAL SETTINGS – ENTER PASSWORD.........................................................................104
FIGURE 6-20 GENERAL SETTINGS – WI-FI NETWORK CONNECTED ........................................................104
Page 10

Chapter 1. Product Introduction
1.1 Package Contents
The following items should be contained in the package:
WNAP-1110 Wireless Range Extender
Power Adapter
Passive PoE Injector
4dBi Antenna x1
Quick Installation Guide
CD-ROM (User’s Manual included)
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
If there is any item missing or damaged, please contact the seller immediately.
1.2 Product Description
PLANET 802.11n Wireless Access Point (WNAP-1110) features 802.11n radio with 1T1R MIMO technology. It is
also backward compliant with 802.11b/g standard. Compared with simple Access Point, the WNAP-1110 offers
more powerful, flexible capability for wireless client to access Internet.
The WNAP-1110 provides multiple operation modes including AP (Multi-SSID), Client, Repeater, Universal
Repeater (Range Extender), and WDS Bridge (Point to Point and Point to Multiple Points) that can play different
roles in different situations. To secure the wireless communications, the WNAP-1110 supports 64/128/152-bit
WEP encryption, WiFi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK). Furthermore, in order to simplify
the security settings, the WNAP-1110 supports WPS configuration with the PBC/PIN type. Your whole wireless
network can be secured within a few seconds.
Being an Access Point, the WNAP-1110 supports the VLAN function to allow multiple SSIDs (Four sets of SSID
and tagging VID) to access Internal VLAN topology via the VLAN Switch function. Moreover, WMM capability
can provide better service to selected traffic or application, which utilizes the network usage. In the wireless
security aspect, the WNAP-1110 supplies MAC address filtering which prevents possible hackers attack.
The WNAP-1110 provides a total solution for the Small Office and the SOHO users. With the MIMO 11n wireless
technology, it’s easy to combine the wireless devices with the existing wired network.
-10-
Page 11

1.3 Product Features
Standard Compliant Hardware Interface
150Mbps wireless transmission rate with MIMO technology
IEEE 802.11n, 802.11b/g standard compliant
1 x 10/100Base-TX Port with Passive PoE supported
Secure Network Connection
Advanced security: 64/128/152-bit WEP, WPA/WPA2, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (TKIP/AES
encryption) and 802.1X Radius Authentication
Easy setup secure wireless connection by one-touch WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) button
Supports MAC address filtering
Supports multiple SSIDs to allow users to access different networks through a single AP
Wireless Network Range Extender
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Multiple wireless modes: AP, WDS, Repeater, Universal Repeater, Client
Supports WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia), wireless QoS
Supports wireless roaming
Easy Installation & Management
Flexible deployment with passive PoE/PD supported
Web-based UI and Quick Setup Wizard for easy configuration
SNMP-based management interface
-11-
Page 12
1.4 Product Specifications
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Product
Hardware Specifications
Interface PoE LAN Port:
PoE Passive PoE (Up to 30 meters)
Antenna Detachable 4dBi antenna x1
Button
LED Indicators PWR/SYS/LAN/WLAN/WPS LED
Material Plastic
Dimensions (W x D x H) 174 x 110 x 23 mm
Weight 250g
Power Requirements 9V DC, 0.85A or Passive PoE
Power Consumption 2W (max.)
Wireless interface Specifications
Standard Compliance with IEEE 802.11b/g/n
Frequency Band 2.4~2.4835GHz
Extended Frequency DSSS
Modulation Type DBPSK, DQPSK, QPSK, CCK and OFDM (BPSK/ QPSK/ 16-QAM/ 64-QAM)
Data Transmission Rates
Frequency Band
Channel Width 20 or 40MHz
Transmission Distance
Max. RF Power
(Intentional Radiator)
Receive Sensitivity
WNAP-1110
150Mbps 802.11n Wireless Range Extender
1 x 10/100Mbps Auto MDI/MDI-X RJ45 port
※ Passive PoE/PD Port
WPS Button Press the WPS button on the front panel of the device.
Reset Button Press for about 5 seconds to reset the device to factory default.
IEEE 802.11n: up to 150Mbps(Dynamic)
IEEE 802.11g: 54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6Mbps (Dynamic)
IEEE 802.11b: 11/5.5/2/1Mbps (Dynamic)
America/ FCC: 2.414~2.462GHz (11 Channels)
Europe/ ETSI: 2.412~2.472GHz (13 Channels)
Japan/ TELEC: 2.412~2.484GHz (14 Channels)
Indoor up to 100m
Outdoor up to 300m (it is limited to the environment)
IEEE 802.11b: 18dBm
IEEE 802.11g: 15dBm
IEEE 802.11n: 15dBm
130M: -70dBm@10% PER
108M: -72dBm@10% PER
54M: -74dBm@10% PER
11M: -86dBm@8% PER
6M: -91dBm@10% PER
1M: -91dBm@8% PER
Wireless Management Features
Wireless Modes AP (Multi-SSID)
-12-
Page 13
Encryption Security
Wireless Security
Wireless Advanced
Max. Supported Clients
System Management
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
WDS
Repeater (WDS+AP)
Universal Repeater (AP+Client)
Client
WEP (64/128/152-bit)
WPA-PSK (TKIP) / WPA2-PSK (AES)
WPA (TKIP) / WPA2 (AES)
802.1x Authentication
Enable/Disable SSID Broadcast
Wireless LAN ACL (Access Control List) MAC filtering
AP Isolation: Enable it to isolate each connected wireless client to let them cannot access
mutually.
Supports 802.11e WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)
Wired: 32
Wireless: 20
Web-based (HTTP) management interface
Supports SNMP v1/v2
Supports Planet Smart Discovery
Supports Scheduling Reboot
System Log
-13-
Page 14
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation
Please follow the instructions below to build the wireless network connection between WNAP-1110 and your computers.
2.1 Hardware Description
2.1.1 The Front Panel
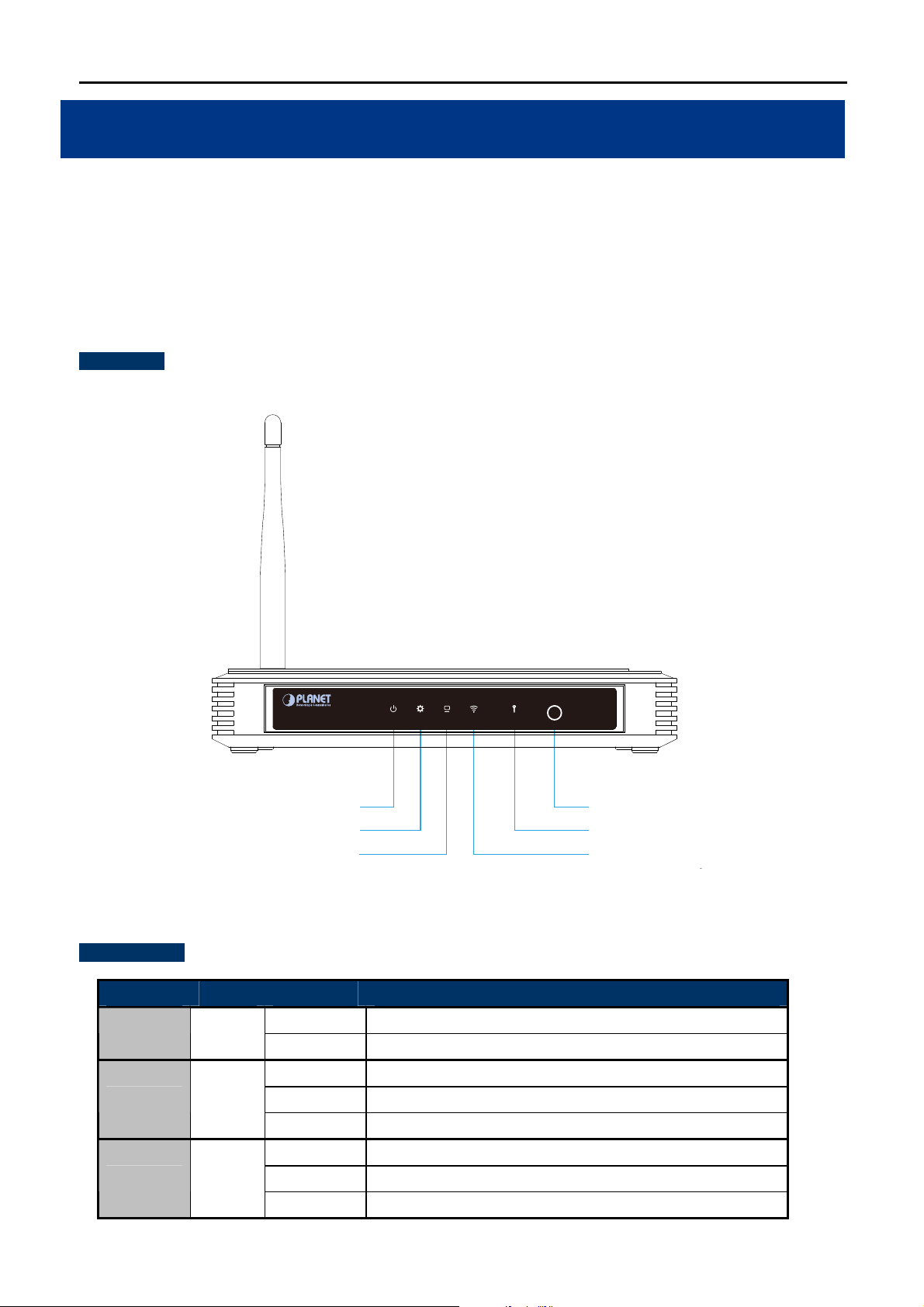
The front panel provides a simple interface monitoring the AP. Figure 2-1 shows the front panel of WNAP-1110.
Front Panel
LAN WLANSYSPWR WPS WPS
WNAP-1110
System LED
LAN LED
Figure 2-1 WNAP-1110 Front Panel
LED definition
Object Color State Description
PWR Green
SYSTEM Green
On
Off
On
Flash
Off
Device power on
Device power off
Device is initialising
The device is working properly
The device has a system error
WPS
WPS ButtonPower LED
WPS LED
Wireless LED
LAN Green
On
Flash
Off
There is a device linked to the corresponding port but no activity
Packets are transmitting or receiving
LAN port is not connected
-14-
Page 15
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
WLAN Green
WPS Green
Flash
Off
On
Slow Flash
Quick Flash
The Wireless function is enabled
The Wireless function is disabled
A wireless device has been successfully added to the network by
function.
WPS
A wireless device is connecting to the network by
This process will last in the first 2 minutes.
A wireless device failed to be added to the network by
function.
WPS
function.
WPS
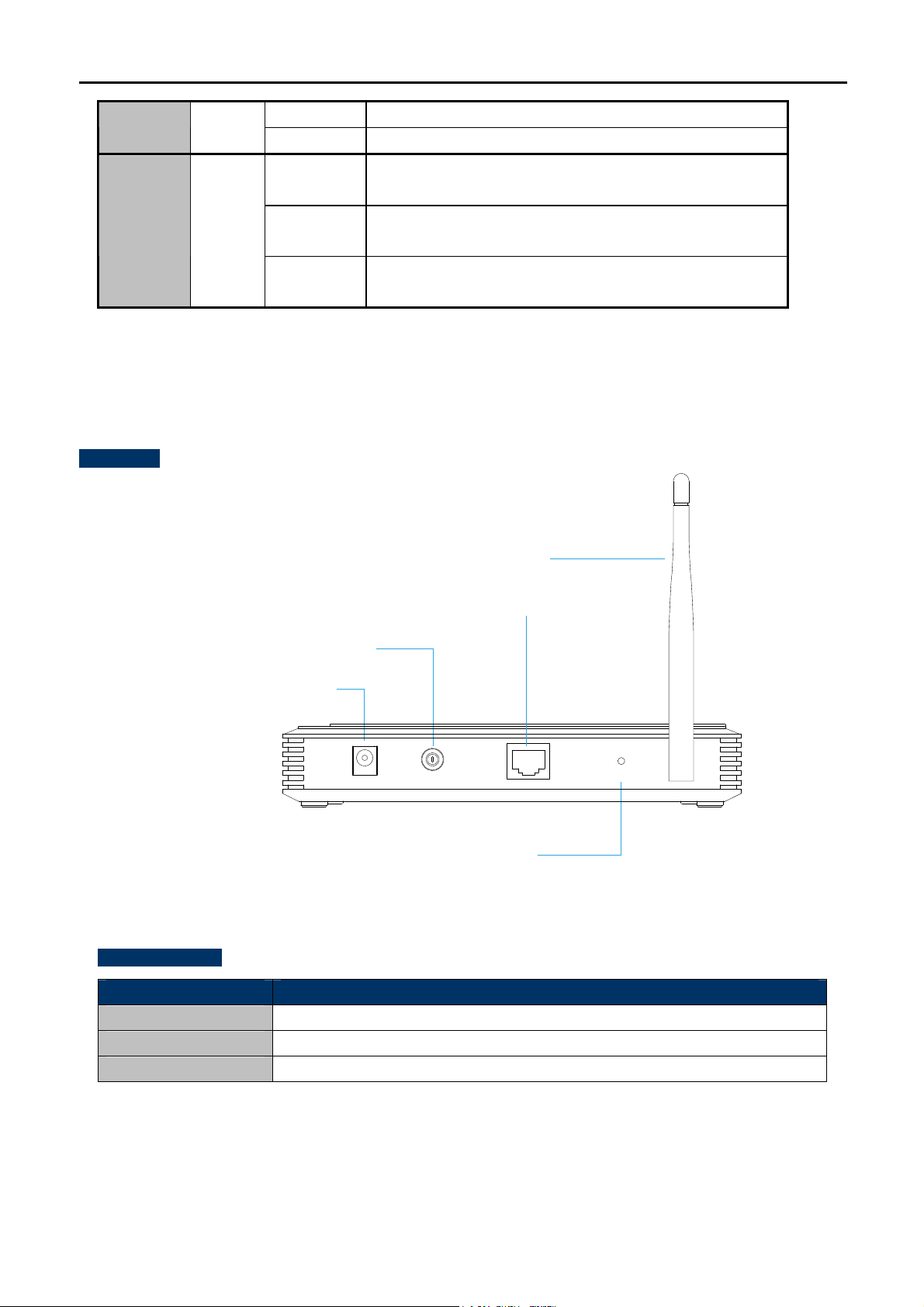
2.1.2 The Rear Panel
The rear panel of the WNAP-1110 consists of buttons, connection port, and power connector. Figure 2-2 shows
the hardware interface of WNAP-1110.
Rear Panel
4dBi Antenna
Button definition
Object Description
WPS
Power ON/OFF
Reset
10/100Mbps LAN Port
Power ON/OFF Button
Power Connector
9V DC Input
POWER ON/OFF LAN
Reset Button
(Press and hold the Reset button for
about 5 seconds for factory default)
Figure 2-2 WNAP-1110 Rear Panel
Press the button for less than 3 seconds for WPS configuration.
Press the button to power on the device.
Press and hold the button for about 5 seconds to the factory default setting.
Reset
-15-
Page 16
H/W Interface definition
Object Description
Antenna
LAN (Passive PoE)
LAN
Power Connector
The WNAP-1110 supports only 9VDC power adapter or passive POE injector (RJ45 pin
4, 5: +; pin 7, 8: -). It cannot work with IEEE 802.3af PSE for its power source.
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Detachable 4dBi Antenna with RP-SMA (male) connector.
10/100Mbps RJ-45 port, Auto MDI/ MDI-X & Passive PoE supported
Connect LAN port to the PoE injector to power on the device.
10/100Mbps RJ-45 port, Auto MDI/ MDI-X
Connect this port to the LAN port of the Router or Ethernet Switch.
Connect this port to the 9V DC power adapter to power on the device.
!
At the same time, either 9V DC adapter from the DC-jack or passive PoE injector from
the UTP LAN port can be connected to the device at one time. Use of two power sources
will damage the device permanently.
-16-
Page 17
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Chapter 3. Connecting the AP
3.1 System Requirements
Broadband Internet Access Service (DSL/Cable/Ethernet connection)
One DSL/Cable Modem that has an RJ-45 connector (not necessary if the AP is connected directly to
the Ethernet.)
PCs with a working Ethernet adapter and an Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors
Subscribers can utilize Windows 98/ME, NT4.0, 2000/XP, Windows Vista / Win 7, MAC OS 9 or later,
Linux, UNIX or other platforms compatible with TCP/IP protocols
The above PC is installed with a Web browser
It is recommended to use Internet Explore 7.0 or above to access the AP.
3.2 Installing the AP
Before installing the AP, make sure your PC is connected to the Internet through the broadband service
successfully at this moment. If there is any problem, please contact your local ISP. After that, please install the
AP according to the following steps. Don't forget to pull out the power plug and keep your hands dry.
Step 1. Power off your PC, Cable/DSL Modem, and the AP.
Step 2. Locate an optimum location for the AP. The best place is usually at the center of your wireless
network.
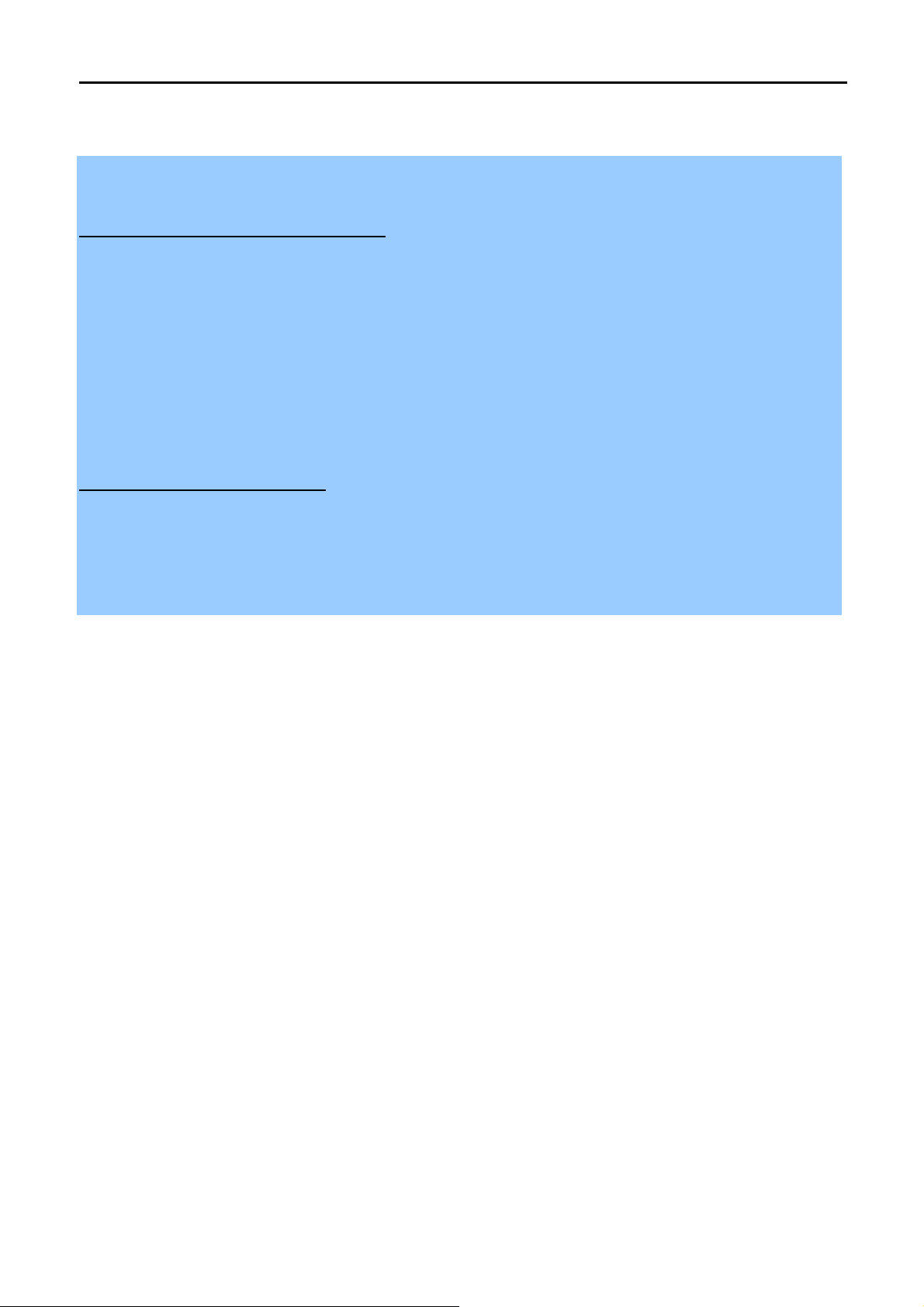
Step 3. Adjust the direction of the antenna. Normally, upright is a good direction.
-17-
Page 18
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 3-1 Adjust the direction of the antenna
Step 4. Connect the Power Source to the WNAP-1110. Only choose one of the following methods for the
suitability of AP’s location; otherwise, it will cause damage to the WNAP-1110.
Method A -- Hard to find the power socket
(1) Connect the Ethernet cable to the LAN port of the PC, and plug the other end of the Ethernet cable into the
LAN port of the PoE injector.
(2) Use another Ethernet cable (8-wire patch cable) to connect the LAN port of the WNAP-1110 and the PoE
port of the PoE Injector.
※ The 8-wire patch cable should not exceed 30 meters in length.
(3) Connect the power adapter to the DC port of the PoE injector, and plug the other end of the power adapter
into an electrical outlet.
Method B -- Power Socket nearby
(1) Connect the Ethernet cable to the LAN port of the PC, and plug the other end of the Ethernet cable into the
LAN port of the WNAP-1110.
(2) Connect the power adapter into the POWER port of the WNAP-1110 in the rear panel, and plug the other
end of the power adapter into an electrical outlet.
-18-
Page 19
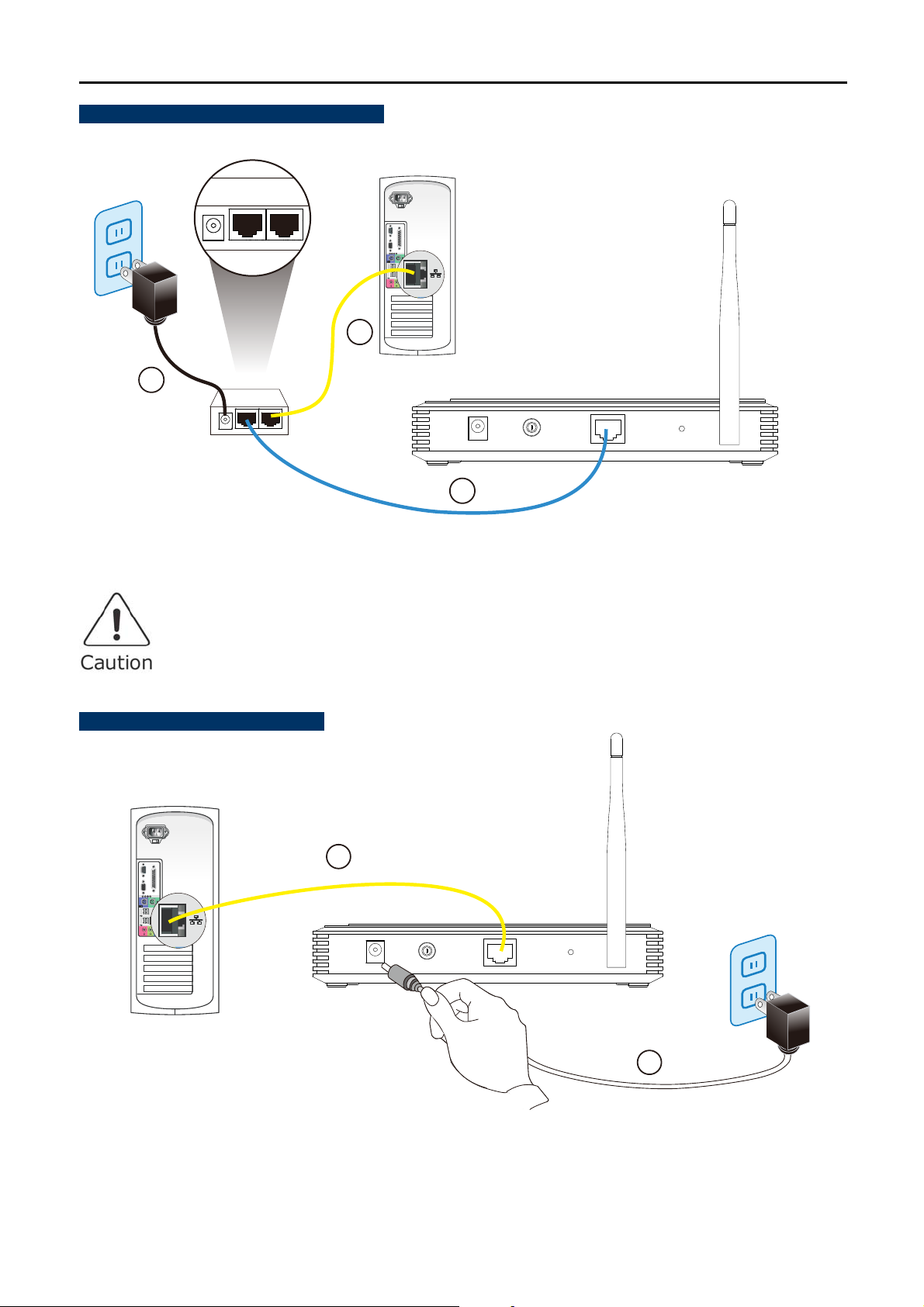
Method A – Hard to find the power socket
POWER
PoE
LAN
Power
1
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
3
PoE
POWER
PoE Injector
Check connection before powering on. Wrong connection may cause device
malfunction, say, your PC or other Ethernet device.
Method B – Power Socket nearby
LAN
Figure 3-2 Hardware Installation of the WNAP-1110 Wireless AP
PC
POWER ON/OFF LAN
2
Reset
PC
1
POWER ON/OFF LAN
Reset
2
Figure 3-3 Hardware Installation of the WNAP-1110 Wireless AP
-19-
Power
Page 20
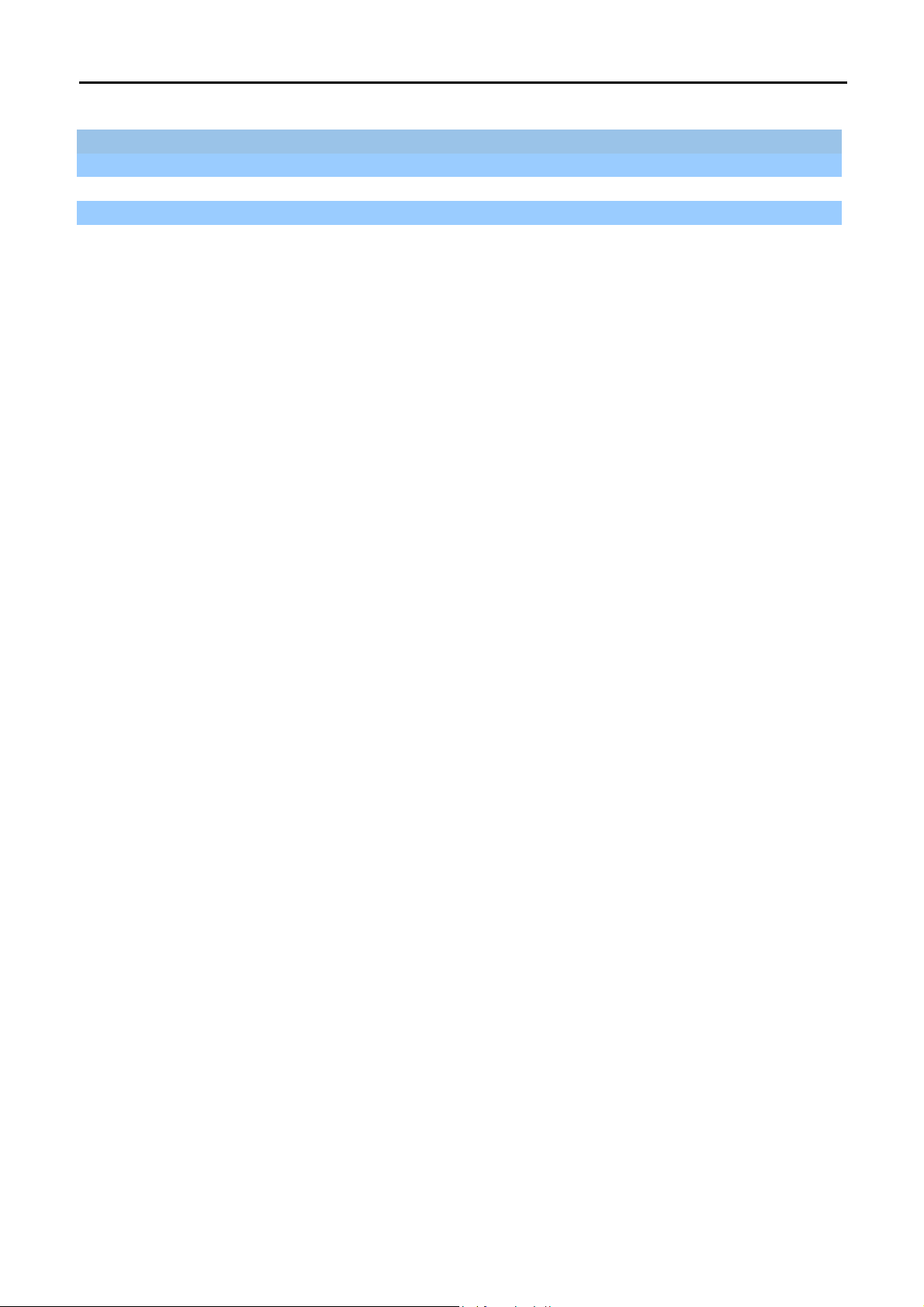
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Step 5. Connect the power adapter to the power socket on the AP, and the other end into an electrical outlet.
Then power on the AP.
Step 6. Power on your PC and Cable/DSL Modem.
-20-
Page 21

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Chapter 4. Quick Installation Guide
This chapter will show you how to configure the basic functions of your AP using Quick Setup within minutes.
A computer with wired Ethernet connection to the Wireless AP is required for the first-time
configuration.
4.1 Manual Network Setup - TCP/IP Configuration
The default IP address of the WNAP-1110 is 192.168.1.253. And the default Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0.
These values can be changed as you want. In this guide, we use all the default values for description.
Connect the WNAP-1110 to your PC with an Ethernet cable plugging in LAN port on one side and in LAN port of
PC on the other side. Please power on the WNAP-1110 by PoE switch through the PoE port.
In the following sections, we’ll introduce how to install and configure the TCP/IP correctly in Windows 7. And
the procedures in other operating systems are similar. First, make sure your Ethernet adapter is working, and
refer to the Ethernet adapter manual if needed.
4.1.1 Configuring the IP Address Manually
Summary:
Set up the TCP/IP Protocol for your PC.
Configure the network parameters. The IP address is 192.168.1.xxx (if the default IP address of the
WNAP-1110 is 192.168.1.253, and the DSL router is 192.168.1.254, the "xxx" can be configured to any
number from 1 to 252), and Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0.
1 Select Use the following IP address radio button, and then configure the IP address of the PC.
2 For example, as the default IP address of the WNAP-1110 is 192.168.1.253 and the DSL router is
192.168.1.254, you may choose from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.252.
-21-
Page 22
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 4-1 TCP/IP Setting
Now click OK to save your settings.
Now, you can run the Ping command in the command prompt to verify the network connection between your
PC and the AP. The following example is in Windows 7 OS. Please follow the steps below:
1. Click on Start > Run.
2. Type “cmd” in the Search box.
-22-
Page 23
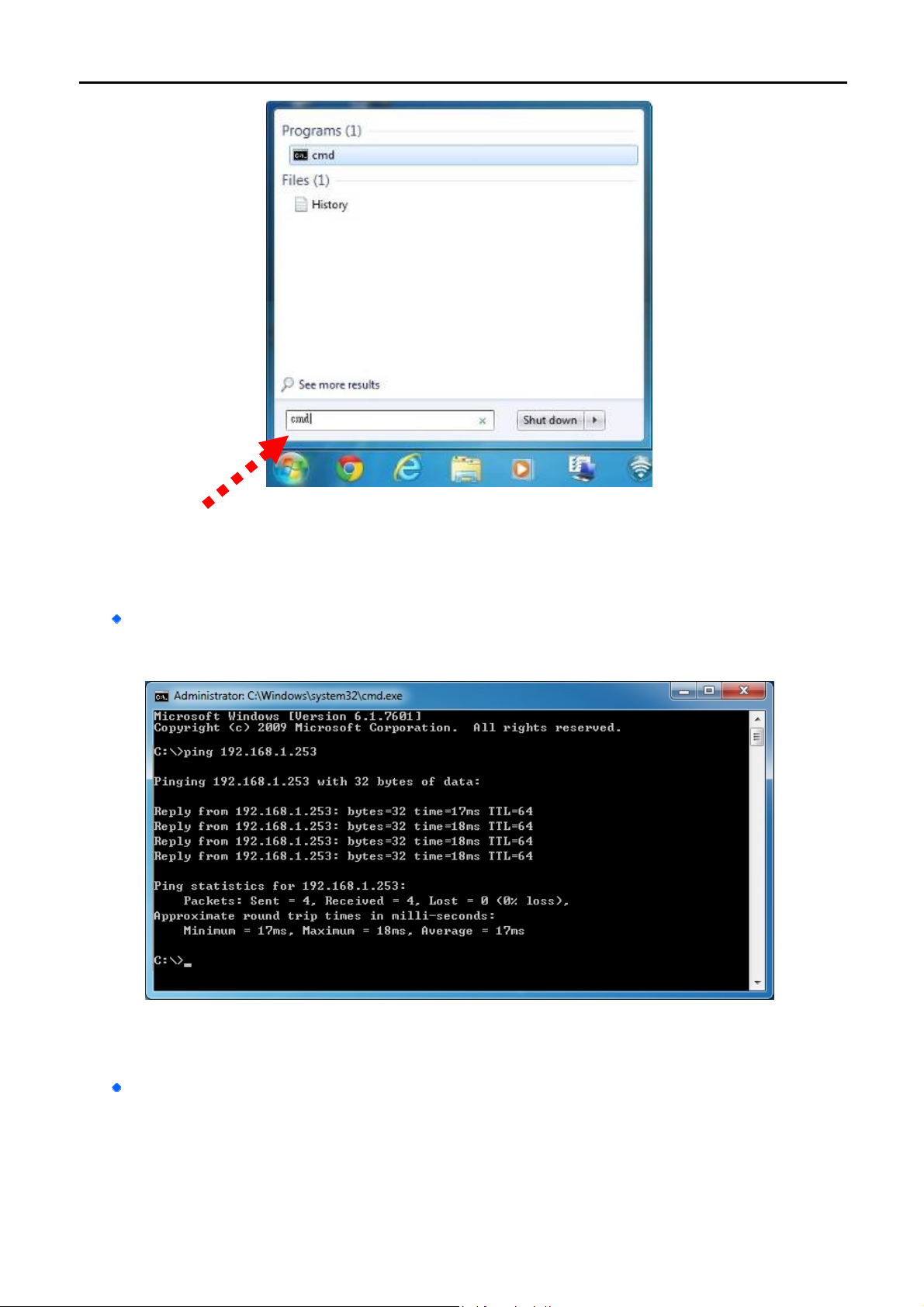
Figure 4-2 Windows Start Menu
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
3. Open a command prompt, and type ping 192.168.1.253, and then press Enter.
If the result displayed is similar to Figure 4-3, it means the connection between your PC and the AP
has been established well.
Figure 4-3 Successful result of Ping command
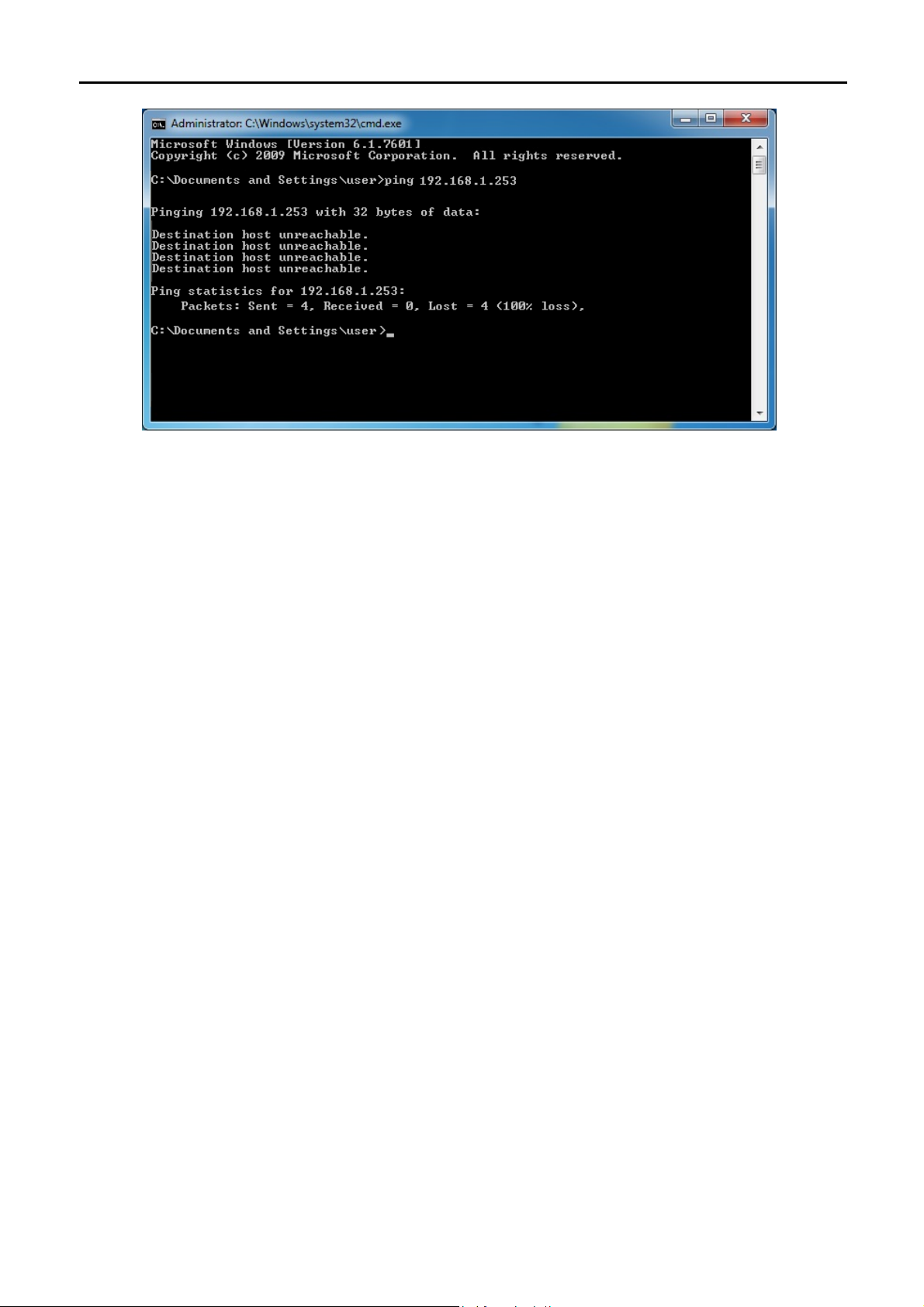
If the result displayed is similar to Figure 4-4, it means the connection between your PC and the AP
has failed.
-23-
Page 24
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 4-4 Failed result of Ping command
If the address is 0.0.0.0, check your adapter installation, security settings, and the settings on your AP. Some
firewall software programs may block a DHCP request on newly installed adapters.
-24-
Page 25
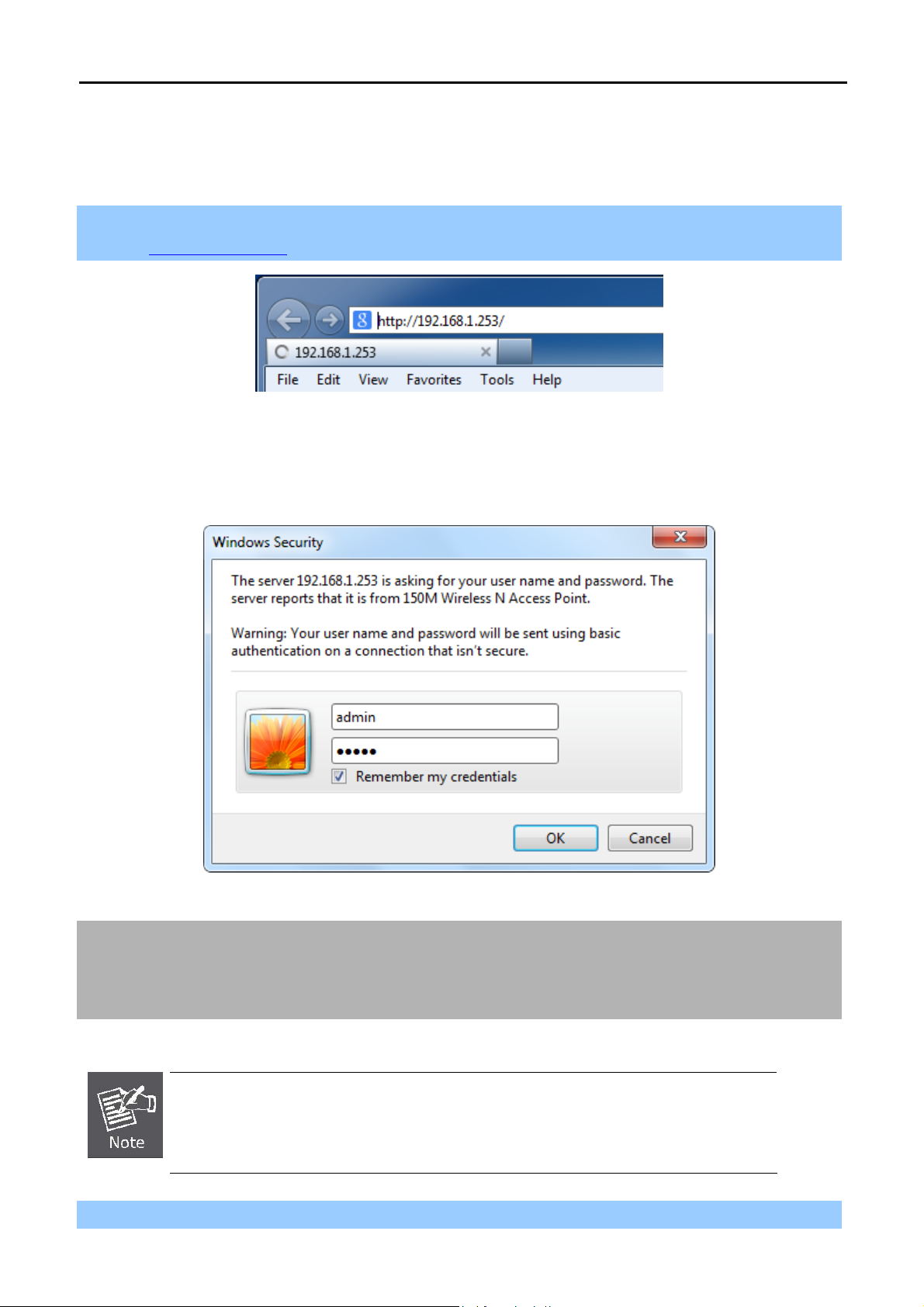
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
4.2 Starting Setup in Web UI
It is easy to configure and manage the WNAP-1110 with web browser.
Step 1. To access the configuration utility, open a web-browser and enter the default IP address
http://192.168.1.253 in the address field of the browser.
Figure 4-5 Login the AP
After a moment, a login window will appear. Enter admin for the User Name and Password, both in lower case
letters. Then click the OK button or press the Enter key.
Figure 4-6 Login Window
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: admin
Default SSID: WNAP-1110
Default Wireless Password: PIN code (refer to the label on the bottom of the WNAP-1110.)
If the above screen does not pop up, it may mean that your web-browser has been set to
a proxy. Go to Tools menu>Internet Options>Connections>LAN Settings, in the screen
that appears, cancel the Using Proxy checkbox, and click OK to finish it.
Step 2. After successfully login, you can click the Quick Setup to quickly configure your AP.
-25-
Page 26
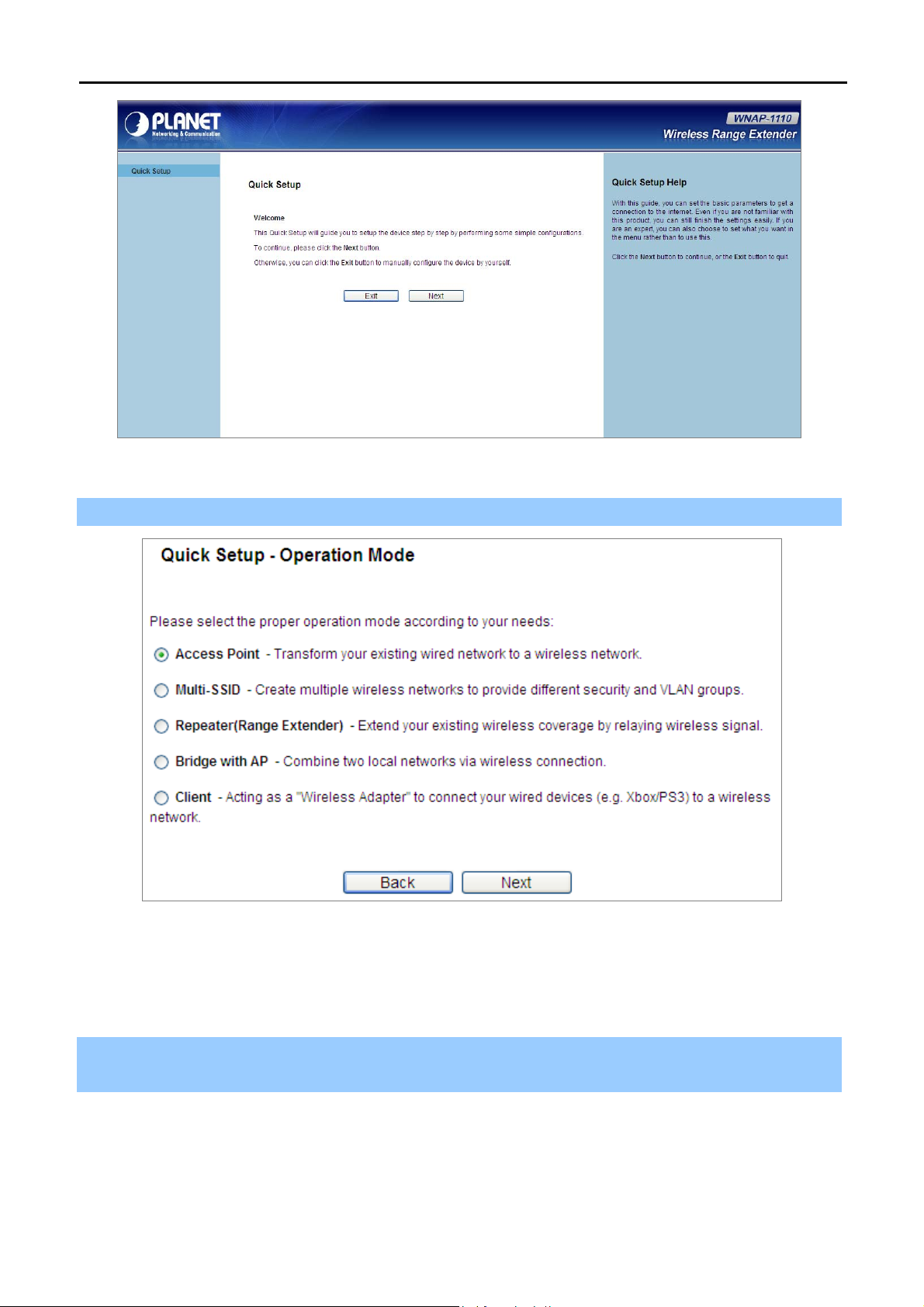
Figure 4-7 WNAP-1110 Quick Setup
Step 3. Select the proper operation mode according to your needs.
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 4-8 Quick Setup – Operation Mode
Click Next, and then Wireless Setting page will appear, shown in Figure 4-9.
Step 4. Enter a string of up to 32 characters into the SSID field. Then select one of the supported
security options and configure the password for your wireless network.
-26-
Page 27
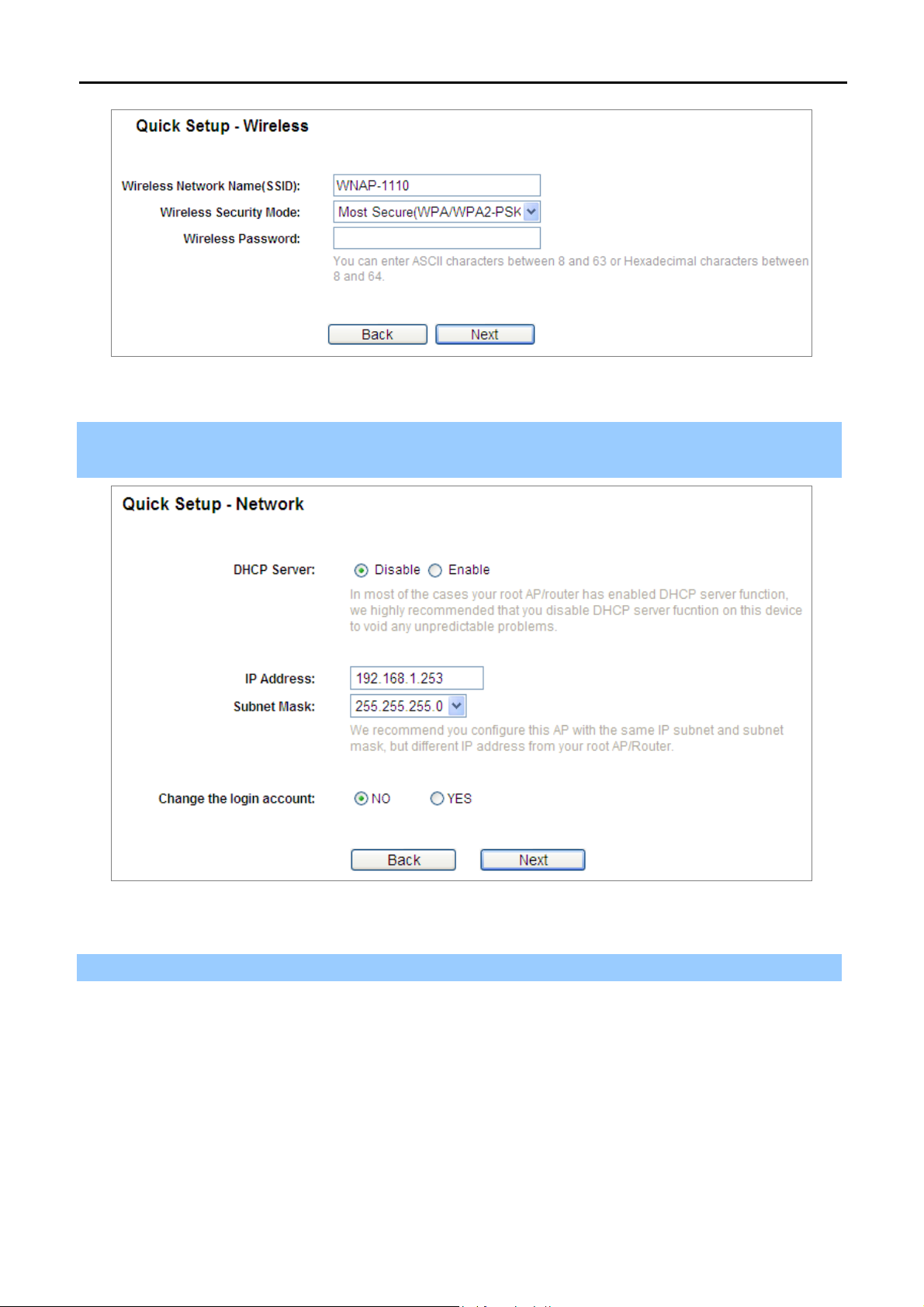
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 4-9 Quick Setup – Wirel
ess
Step 5. Click Next to continue. The Network settings page will appear as shown in Figure 4-10.
You can configure the IP parameters of LAN on this page.
Figure 4-10 Quick Setup – Network
Step 6. Click the Next button. You will then see the Finish page.
-27-
Page 28

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 4-11 Quick Setup – Finish
Step 7. Once the basic configuration is done, connect the WNAP-1110 with the xDSL modem/ router
through the Ethernet cable. Then, you will be able to surf the Internet using the wireless client through the
WNAP-1110.
Figure 4-12 Basic Wireless Internet Connection
-28-
Page 29

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Chapter 5. Configuring the AP
This chapter delivers a detailed presentation of AP’s functionalities and features under main menu below,
allowing you to manage the AP with ease.
Figure 5-1 Main Menu
5.1 Status
On this page, you can view information about the current running status of the WNAP-1110, including LAN
interface, wireless interface settings and status, and firmware version information.
-29-
Page 30
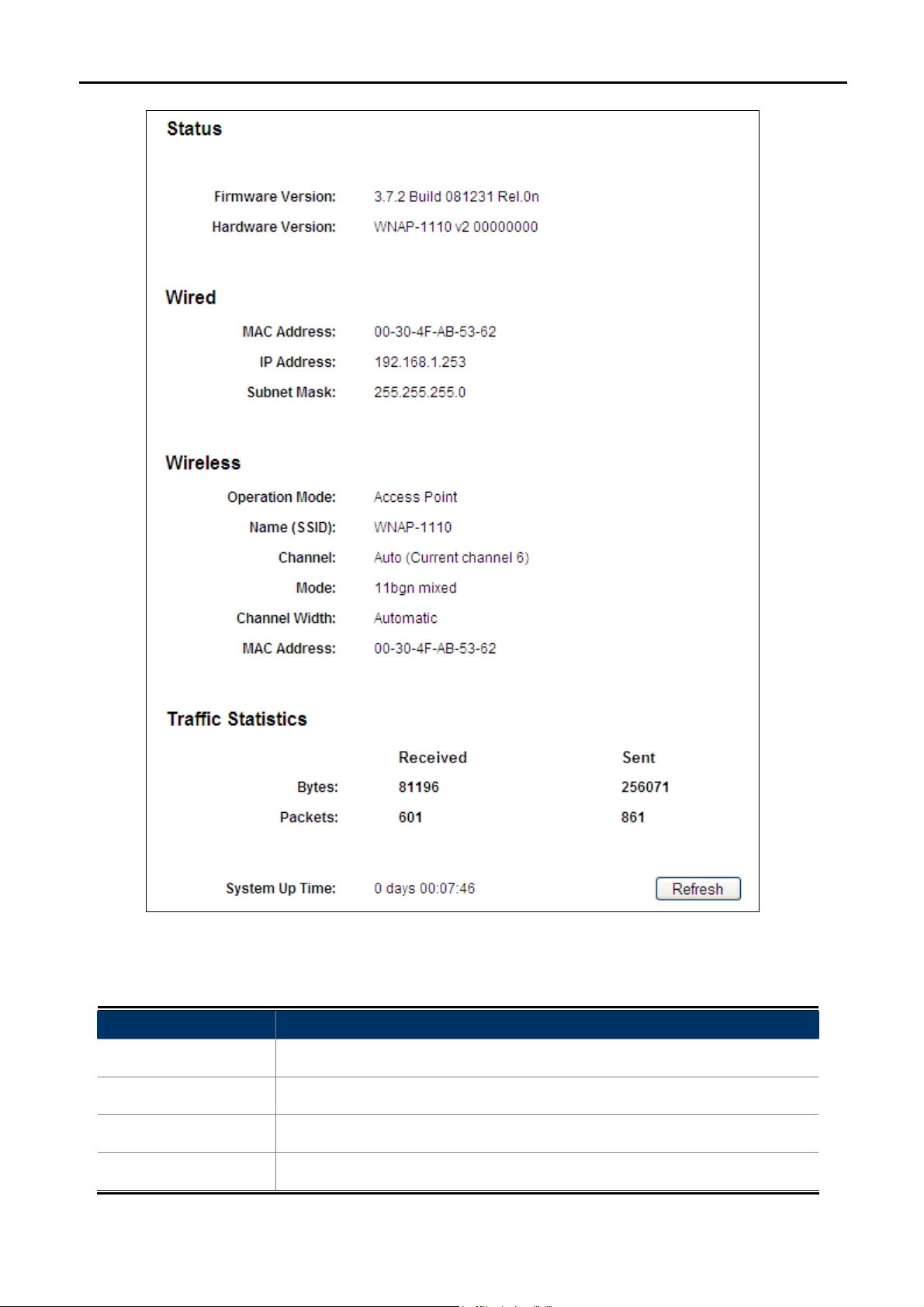
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-2 Status
This section allows you to view the AP’s basic info listed below:
Object Description
Firmware Version
Hardware Version
MAC Address
Displays the current firmware version.
Displays the current hardware version.
Displays AP’s LAN MAC address.
IP Address Displays LAN IP address.
-30-
Page 31

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Subnet Mask
Operation Mode
Name (SSID)
Channel
Mode
Channel Width
MAC Address
Traffic Statistics
System Up Time
Displays LAN subnet mask.
Displays AP’s current operation mode.
Displays AP’s SSID.
Displays AP’s current channel.
Displays AP’s current wireless mode.
Displays AP’s current wireless channel width.
Displays AP’s Wireless MAC address.
Displays the AP's traffic statistics.
Displays the System Up Time.
5.2 Quick Setup
Please refer to Chapter 4.2 Starting Setup in Web UI.
5.3 Operation Mode
Figure 5-3 Operation Mode
-31-
Page 32

The page includes the following fields:
A
Object Description
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
AP
Multi-SSID
Repeater(Range
Extender)
Bridge with AP
Client
In this mode, the device will act as a wireless central hub for your wireless LAN
clients, giving a wireless extension for your current wired network.
In this mode, the device can create up to 4 wireless networks labeled with
different SSIDs and assign each SSID with different security or VLAN, especially
for the situation when the various access policies and functions are required.
In this mode, the device can copy and reinforce the existing wireless signal to
extend the coverage of the signal, especially for a large space to eliminate
signal-blind corners.
In this mode, the device can be used to combine multiple local networks together
to the same one via wireless connections, especially for a home or office where
separated networks can't be connected easily together with a cable.
In this mode, the device can be connected to another device via Ethernet port
and act as an adaptor to grant your wired devices access to a wireless network,
especially for a Smart TV, Media Player, or game console only with an Ethernet
port.
Be sure to click the Save button to save your settings on this page.
The device will reboot automatically after you click the Save button.
When you change the operation mode to Client/Repeater, WPS function will stay disabled.
Please manually enable this function if needed when you switch back to
Point/Multi-SSID/Bridge mode.
ccess
5.3.1 Operation Mode – Access Point
Choose menu “Quick Setup → Next → Access Point”, or “Operation Mode → Access Point” to configure
the device as a general wireless access point.
-32-
Page 33

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-4 Wireless – AP Mode
For the definition of each field on this page, please refer to Chapter 5.6.1 Wireless Setting
Example of quickly set up a wireless network using AP Mode:
To configure each wireless parameter, please go to the “Wireless →
Wireless Settings” page.
.
Figure 5-5 Topology – AP Mode
Step 1. Create an easy-to-remember name for your wireless network, write it into Wireless Network
Name (SSID).
-33-
Page 34

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Step 2. Select the Most Secure (WPA/WPA2-PSK) encryption mode and enter a password below to prevent
unauthorized access to your AP.
Step 3. Click Next and you will then come to the Network Setting page for further configuration.
Step 4. Refer to Step 5 of Chapter 4.2 to continue the setting. Then, refer to Chapter 6 to quickly connect to a
wireless Network.
5.3.2 Operation Mode – Multi-SSID
Choose menu “Quick Setup → Next → Multi-SSID”, or “Operation Mode → Multi-SSID” to configure the
device as a general wireless access point with multiple SSIDs.
Figure 5-6 Operation Mode – Multi-SSID
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Enable VLAN
Check this box and then you can change the VLAN ID of each SSID. If you want
to configure the Guest and Internal networks on VLAN, the switch you are using
must support VLAN. As a prerequisite step, configure a port on the switch for
handling VLAN tagged packets as described in the IEEE802.1Q standard, and
enable this field.
SSID (1-4)
Up to 4 SSIDs for each BSS can be entered in the field like SSID1 ~ SSID4. The
name can be up to 32 characters. The same name (SSID) must be assigned to
all wireless devices in your network. If Enable VLAN is checked, the wireless
stations connecting to SSID of a different VLANID cannot communicate with each
-34-
Page 35

other.
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
VLAN ID (1-4)
Channel
Mode
Provide a number between 1 and 4095 for VLAN. This will cause the AP to send
packets with VLAN tags. The switch connecting with the AP must support VLAN
IEEE802.1Q frames. The wireless stations connecting to the SSID of a specified
VLANID can communicate with the PC connecting to the port with the same
VLANID on the Switch.
Determines the operating frequency to be used. It is not necessary to change the
wireless channel unless you notice interference problems with another nearby
access point.
This field determines the wireless mode which the device works on.
11b only - Only 802.11b wireless stations can connect to the AP.
11g only - Only 802.11g wireless stations can connect to the AP.
11n only - Only 802.11n wireless stations can connect to the AP.
11bg mixed - Both 802.11b and 802.11g wireless stations can connect to the AP.
11bgn mixed - All 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n wireless stations can connect to
the AP.
Channel Width
Determines the channel width to be used. It is unnecessary to change the default
value unless required.
Enable Wireless Radio
Select or deselect this check box to allow or deny wireless stations to access the
AP.
Enable SSID Broadcast
Select or deselect this check box to allow or deny the AP to broadcast its name
(SSID) on the air. If it’s allowed, when wireless clients survey the local area for
wireless networks to associate with, they will detect the SSID broadcast by the
AP.
You are suggested to implement Multi-SSID function with a switch that supports Tag VLAN feature.
-35-
Page 36

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Example of how to configure Multi-SSID Mode. Please take the following steps:
To configure each wireless parameter, please go to the “Wireless →
Figure 5-7 Topology – Multi-SSID
1. Configuring the Access Point
Wireless Settings” page.
Figure 5-8 Multi-SSID – Enable VLAN
Step 1. Select the checkbox “Enable VLAN” to enable VLAN function for this access point.
-36-
Page 37

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Step 2. Configure the SSID and its corresponding VLAN ID. The detailed parameters are shown as the figure
above.
Step 3. STA1, STA2, STA3 and STA4 join to the wireless network with SSID1, SSID2, SSID3 and SSID4,
respectively.
Step 4. Click Save to apply the current security settings for the selected SSID.
1. The wireless STAs, joined to the network with different VLAN IDs, cannot communicate with
each other, for example, STA1 and STA2.
2. The wireless STAs, joined to the network with the same VLAN ID, can communicate with
each other, for example, STA1 and STA3.
3. All wireless STAs can log on to the Web management page of the WNAP-1110 and manage
the access point, for example, STA1, STA2, STA3 and STA4.
4. All the packets received in the wired network from the wireless STA will be added a
corresponding VLAN Tag of the wireless STA, unless the VLAN ID of the wireless network is
set to 1.
2. Configuring the Switch
Step 1. Enable 802.1Q Tag VLAN function on the switch.
Step 2. Make sure the Untag frames are forwarded.
The following table shows the detailed configuration of the switch
Port VLAN ID PVID Egress Rule Processing mode of Untag Frames
1 1 1 Untag
2 2 2 Untag
3 3 3 Untag
4 4 4 Untag
5 Port 5 belongs to all VLANs 1 Tag
Forwarding
Forwarding
Forwarding
Forwarding
Forwarding
Step 3. Connect PC1, PC2, PC3 and PC4 to port1, port2, port3 and port4 of the switch, respectively. The
corresponding VLAN IDs of the four ports are 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Step 4. Configure port5 of the switch to be the member of VLAN1, VLAN2, VLAN3 and VLAN4 and connect it
to the LAN port of the WNAP-1110.
Step 5. Configure the VLAN ID of the PC that can log on to the Web management page of the WNAP-1110 via
-37-
Page 38
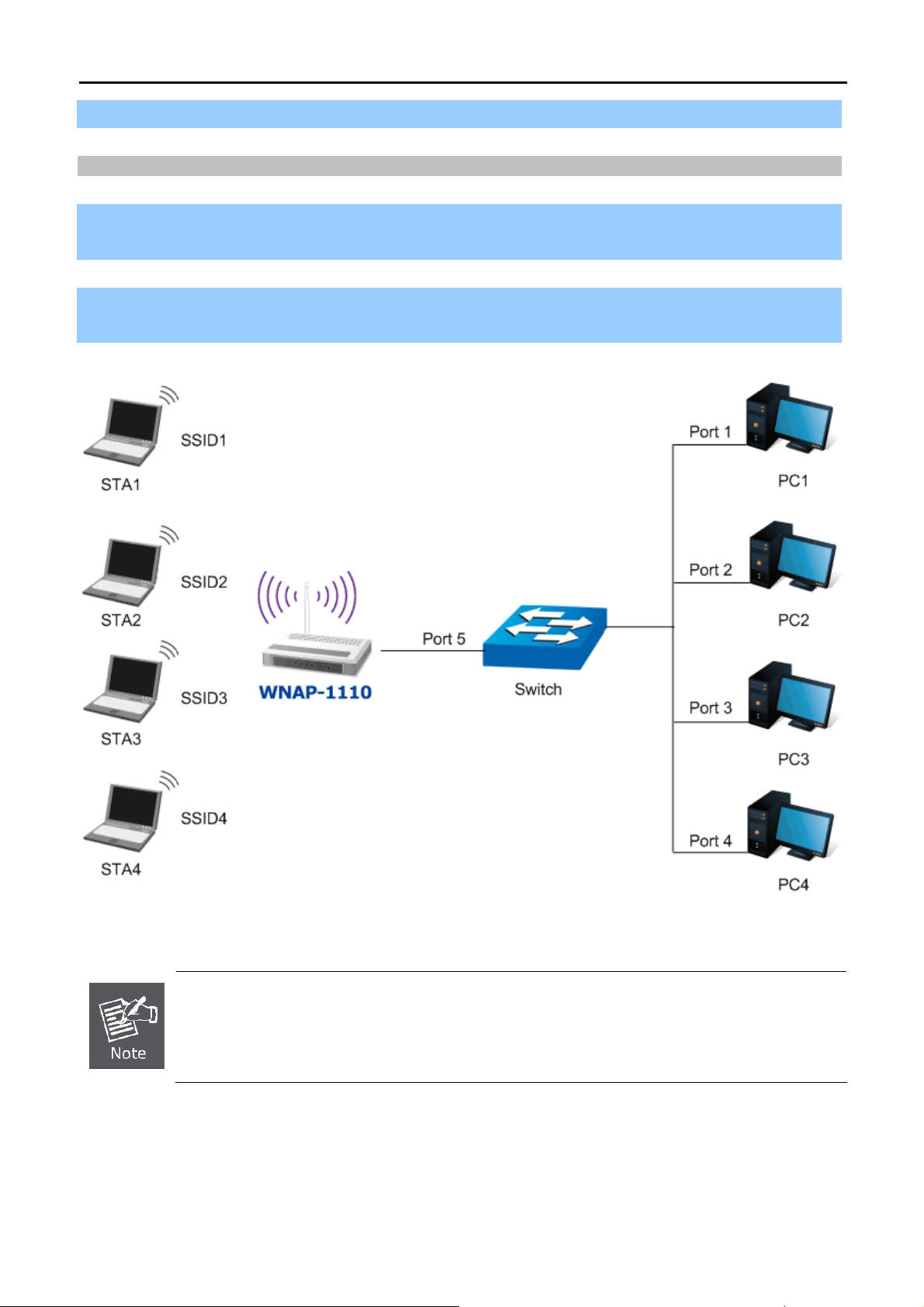
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
the LAN port equal to the PVID of port 5.
3. Verifying the communication status after the above configuration is completed.
Step 1. If VLAN ID of the PC connected to the switch is different from the VLAN ID of the wireless STA, the
two cannot communicate with each other, for example, PC1 and STA2.
Step 2. If the PC connected to the switch and the wireless STA have the same VLAN ID, the two can
communicate with each other, for example, PC2 and STA2.
Figure 5-9 Multi-SSID – VLAN Topology
If the LAN port of the WNAP-1110 is not connected to a switch but directly to a PC,
1. The PC can directly log on to the Web management page of the WNAP-1110 and manage
the access point.
2. Only the wireless STA with its VLAN ID set to 1 can communicate with the wired PC.
5.3.3 Operation Mode – Repeater (Range Extender)
Choose menu “Quick Setup → Next → Repeater (Range Extender)”, or “Operation Mode → Repeater
(Range Extender)” to configure the device as a general wireless access point with multiple SSIDs.
-38-
Page 39

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
In this mode, the product can extend the coverage of another wireless Access Point or Router. The universal
repeater mode is for the wireless Access Point or Router which does not support WDS function.
Figure 5-10 Operation Mode - Repeater (Range Extender)
1. Universal Repeater
This mode allows the AP with its own BSS to relay data to a root AP to which it is associated with WDS disabled.
The wireless repeater relays signal between its stations and the root AP for greater wireless range.
Figure 5-11 Topology – Universal Repeater
-39-
Page 40

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-12 Repeater (Range Extender) – Universal Repeater
2. WDS Repeater
This mode allows the AP with its own BSS to relay data to a root AP to which it is associated with WDS enabled.
The wireless repeater relays signal between its stations and the root AP for greater wireless range.
Figure 5-13 Topology – WDS Repeater
-40-
Page 41

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-14 Repeater (Range Extender) – WDS Repeater
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Repeater Mode
Choose mode for repeater.
WDS Repeater - In WDS Repeater mode, the AP with WDS enabled will
Universal Repeater - In Universal Repeater mode, the AP with WDS
relays data to an associated root AP. AP function is enabled
meanwhile. The wireless repeater relays signal between its stations
and the root AP for greater wireless range. Please input the MAC
address of root AP in the field "MAC of AP".
disabled will relays data to an associated root AP. AP function is
enabled meanwhile. The wireless repeater relays signal between its
stations and the root AP for greater wireless range. Please input the
MAC address of root AP in the field "MAC of AP".
Wireless Name of Root
AP
MAC Address of Root
AP
Survey
Region
The SSID of the AP your device is going to connect to as a client. You can also use the
search function to select the SSID to join.
The BSSID of the AP your device is going to connect to as a client. You can also
use the search function to select the BSSID to join.
Click this button; you can search the AP which runs in the current channel.
Select your region from the pull-down list. This field specifies the region where the
wireless function of the device can be used. It may be illegal to use the wireless
-41-
Page 42

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
function of the device in a region other than one of those specified in this field. If
your country or region is not listed, please contact your local government agency
for assistance.
Channel Width
Enable Wireless Radio
The bandwidth of the wireless channel.
The wireless radio of the AP can be enabled or disabled to allow or deny wireless
stations to access. If enabled, the wireless stations will be able to access the AP,
otherwise, wireless stations will not be able to access the AP.
Example of how to configure Repeater Mode. The procedure of Universal Repeater and WDS Repeater
modes are the same. Please take the following steps:
To configure each wireless parameter, please go to the “Wireless → Wireless Settings” page.
Step 1. Select one of the Repeater Modes, and then click “Survey”.
Figure 5-15 Repeater (Range Extender) – Survey
Step 2. Click “Connect” to choose the root AP from the list to repeat the signal. If the root AP is not listed in
the table, click “Refresh” to update the list.
-42-
Page 43

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-16 Repeater (Range Extender) – AP List
Step 3. The selected AP’s wireless name and MAC address will be automatically filled in the relevant fields.
Figure 5-17 Repeater (Range Extender) – Finish Setting
Step 4. Go to Wireless Security page to configure the repeater's security as the same as the root AP's.
-43-
Page 44

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-18 Repeater (Range Extender) – Security
Step 5. You can go to Status page to check the repeater’s signal.
Figure 5-19 Repeater (Range Extender) – Status
5.3.4 Operation Mode – Bridge with AP
Choose menu “Quick Setup → Next → Bridge with AP”, or “Operation Mode → Bridge with AP” to
configure the device as a general wireless access point with multiple SSIDs.
In this mode, the product can extend the coverage of another wireless Access Point or Router. The universal
repeater mode is for the wireless Access Point or Router which does not support WDS function.
-44-
Page 45

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-20 Operation Mode - Bridge with AP
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Wireless Name of
Remote AP
MAC Address of
Remote AP
Survey
Key type
The SSID of the AP your device is going to connect to as a client. You can also
use the search function to select the SSID to join.
The BSSID of the AP your device is going to connect to as a client. You can also
use the search function to select the BSSID to join.
Click Survey button, you can search the AP which runs in the current channel.
This option should be chosen according to the AP's security configuration. It is
recommended that the security type is the same as your AP's security type
Password
If the AP your device is going to connect needs password, you need to fill the
password in this blank.
Local Wireless Name
Enter a value of up to 32 characters. The same Name (SSID) must be assigned
to all wireless devices in your network.
Region
Channel
Select your region from the pull-down list. This field specifies the region where
the wireless function of the AP can be used. It may be illegal to use the wireless
function of the AP in a region other than one of those specified in this filed. If your
country or region is not listed, please contact your local government agency for
assistance.
This field determines which operating frequency will be used. It is not necessary
to change the wireless channel unless you notice interference problems with
another nearby access point.
-45-
Page 46

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Mode
Channel Width
Enable Wireless Radio
This field determines the wireless mode which the AP works on.
The bandwidth of the wireless channel.
The wireless radio of the AP can be enabled or disabled to allow or deny wireless
stations to access. If enabled, the wireless stations will be able to access the AP,
otherwise, wireless stations will not be able to access the AP.
Enable SSID Broadcast
If you select the Enable SSID Broadcast checkbox, the AP will broadcast its
name (SSID) on the air.
Disable Local Wireless
Access
If you select the Disable Local Wireless Access checkbox, the AP will deny
wireless stations to access, allowing only wired network while bridging with
remote AP.
Example of how to configure Bridge with AP Mode. Please take the following steps:
To configure each wireless parameter, please go to the “Wireless → Wireless Settings” page.
Step 1. Click “Survey”.
Figure 5-21 Topology - Bridge with AP
-46-
Page 47

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-22 Bridge with AP – Survey
Step 2. Click “Connect” to choose the root AP from the list. If the root AP is not listed in the table, click
“Refresh” to update the list.
Figure 5-23 Bridge with AP – AP List
Step 3. The selected AP’s wireless name and MAC address will be automatically filled in the relevant fields.
Select the root AP’s security key type and enter the password to finish the setting.
-47-
Page 48

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-24 Bridge with AP – Finish Setting
Step 4. Click “Save” to save and apply the setting.
Step 5. You can go to Status page to check the repeater’s signal.
Figure 5-25 Bridge with AP – Status
-48-
Page 49

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.3.5 Operation Mode – Client
Choose menu “Quick Setup → Next → Client”, or “Operation Mode → Client” to configure the device as a
general wireless access point with multiple SSIDs.
In this mode, the product can extend the coverage of another wireless Access Point or Router. The universal
repeater mode is for the wireless Access Point or Router which does not support WDS function.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Wireless Name of Root
AP
MAC Address of Root
AP
Survey
Region
The SSID of the AP your device is going to connect to as a client. You can also
use the search function to select the SSID to join.
The BSSID of the AP your device is going to connect to as a client. You can also
use the search function to select the BSSID to join.
Click Survey button, you can search the AP which runs in the current channel.
Select your region from the pull-down list. This field specifies the region where
the wireless function of the AP can be used. It may be illegal to use the wireless
function of the AP in a region other than one of those specified in this filed. If your
country or region is not listed, please contact your local government agency for
assistance.
Figure 5-26 Wireless - Client
Channel Width
Enable Wireless Radio
The bandwidth of the wireless channel.
The wireless radio of the AP can be enabled or disabled to allow or deny wireless
-49-
Page 50

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
stations to access. If enabled, the wireless stations will be able to access the AP,
otherwise, wireless stations will not be able to access the AP.
Example of how to configure Client Mode. Please take the following steps:
To configure each wireless parameter, please go to the “Wireless → Wireless Settings” page.
Step 1. Click “Survey”.
Figure 5-27 Topology – Client Mode
Figure 5-28 Client – Survey
-50-
Page 51

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Step 2. Click “Connect” to choose the root AP from the list. If the root AP is not listed in the table, click
“Refresh” to update the list.
Figure 5-29 Client – AP List
Step 3. The selected AP’s wireless name and MAC address will be automatically filled in the relevant fields.
Click “Save” and “click here” to save and apply the setting.
Figure 5-30 Client – Finish Setting
-51-
Page 52

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Step 4. You can go to Status page to check the repeater’s signal.
Figure 5-31 Client – Status
5.4 WPS
This section will guide you to adding a new wireless device quickly to an existing network by WPS (Wi-Fi
Protected Setup) function.
Step 1. Choose menu “WPS”, and you will see the next screen (shown in Figure 5-32 ). Click “Enable WPS”
button to enable the WPS functio
n.
Figure 5-32 WPS
The pa
ge includes the following fields:
Object Description
WPS Status
Current PIN
Restore PIN
Enable or disable the WPS function here.
The current value of the AP's PIN displayed here. The default PIN of the AP can
be found in the label or User Guide.
Restore the PIN of the AP to its default.
-52-
Page 53

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Gen New PIN
Click this button, and then you can get a new random value for the AP's PIN. You
can ensure the network security by generating a new PIN.
Add device
You can add the new device to the existing network manually by clicking this
button.
Step 2. To add a new device:
If the wireless adapter supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS), you can establish a wireless connection between
wireless adapter and AP using either Push Button Configuration (PBC) method or PIN method.
To build a successful connection by WPS, you should also do the corresponding configuration
of the new device for WPS function.
Step 1 By Push Button Configuration (PBC)
If the wireless adapter supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup and the Push Button Configuration (PBC) method, you
can add it to the network by PBC with the following two methods.
Step 1: Press the WPS/Reset Button on the front panel of the AP.
Figure 5-33 Hardware WPS Button
Or you can keep the default WPS Status as Enabled and click the Add device button in Figure 5-34, and then
the following screen will appear.
Figure 5-34 Software WPS Button
-53-
Page 54

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Choose Press the button of the new device in two minutes, and click Connect.
When pressing and holding the WPS/Reset Button on the AP for more than 5 seconds, you
will reset the AP.
Step 2: Press and hold the WPS Button equipped on the adapter directly for 2 or 3 seconds. Or you can click
the WPS button with the same function in the configuration utility of the adapter.
Step 3: Wait for a while until the next screen appears. Click Finish to complete the WPS configuration.
Step 2 By PIN
If the new device supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup and the PIN method, you can add it to the network by PIN with
the following two methods.
Method One: Enter the PIN of your Wireless adapter into the configuration utility of the AP
Step 1: Keep the default WPS Status as Enabled and click the Add device button in Figure 5-35, then the
following screen will appear.
Figure 5-35 Add a new device
Step 2: Choose Enter the new device's PIN and enter the PIN code of the wireless adapter in the field
behind PIN in the above figure. Then click Connect.
The PIN code of the adapter is always displayed on the WPS configuration screen.
-54-
Page 55

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Step 3: For the configuration of the wireless adapter, please choose the option that you want to enter PIN
into the AP in the configuration utility of the WPS, and click Next.
Method Two: Enter the PIN of the AP into the configuration utility of your Wireless adapter
Step 1: Get the Current PIN code of the AP in Figure 5-32 (each AP has its unique PIN code).
Step 2: For the configuration of the wireless adapter, please choose the option that you want to enter the PIN
of the AP in the configuration utility of the Wireless adapter, and enter it into the field. Then click
Next
.
The default PIN code of the AP can be found in WPS configuration screen as shown in Figure
5-32.
Step 3. You will see the following screen when the new device has successfully connected to the network.
Figure 5-36 New de
1. The WPS LED on the AP will light green for about 5 minutes if the device has been
successfully added to the network.
vice connect successfully
2. The WPS function cannot be configured if the Wireless Function of the AP is disabled.
Please make sure the Wireless Function is enabled before configuring the WPS.
-55-
Page 56

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.5 Network
There are three submenus under the Network menu (shown in Figure 5-37): WAN, LAN, and MAC Clone.
Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
Figure 5-37 The Network menu
5.5.1 LAN
Choose menu “Network→LAN” to configure the IP parameters of the LAN on the screen as shown below:
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
MAC Address
The physical address of the AP, as seen from the LAN. The value can't be
changed.
Type
Select Dynamic IP to get IP address from DHCP server or select Static IP to
configure IP address manually from the drop-down list.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of your AP or reset it in dotted-decimal notation (factory
default: 192.168.1.1).
Subnet Mask
An address code that determines the size of the network. Normally use
255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask.
Figure 5-38 LAN Settings
-56-
Page 57

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Gateway
The gateway should be in the same subnet as your IP address.
A. If you change the IP Address of LAN, you must use the new IP Address to login the AP.
B. If the new LAN IP Address you set is not in the same subnet, the IP Address pool of the
DHCP server will change accordingly at the same time while the Virtual Server and DMZ
Host will not take effect until they are re-configured.
-57-
Page 58

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.6 Wireless
There are five submenus under the Wireless menu (shown in Figure 5-39): Wireless Settings, Wireless
Security, Wireless MAC Filtering, Wireless Advanced and Wireless Statistics. Click any of them, and you
will be able to configure the corresponding function.
Figure 5-39 Wireles
s menu
5.6.1 Wireless Settings
Choose menu “Wireless→Wireless Settings” to configure the basic settings for the wireless network on this
page.
The page includes the following fields:
Figure 5-40 Wireless Settings
-58-
Page 59

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Object Description
Wireless Network Name
(SSID)
Region
Channel
Enter a value of up to 32 characters. The same name of SSID (Service Set
Identification) must be assigned to all wireless devices in your network.
Considering your wireless network security, the default SSID is set to be
WNAP-1110. This value is case-sensitive. For example, PLANET is NOT the same
as planet.
Select your region from the pull-down list. This field specifies the region where the
wireless function of the AP can be used. It may be illegal to use the wireless
function of the AP in a region other than one of those specified in this field. If your
country or region is not listed, please contact your local government agency for
assistance. Please be note that selecting the incorrect country may cause
interference to other devices and violate the applicable law.
This field determines which operating frequency will be used. The default channel
is set to Auto, so the AP will choose the best channel automatically. It is not
necessary to change the wireless channel unless you notice interference
problems with another nearby access point.
Mode
Channel width
Enable Wireless Radio
Enable SSID Broadcast
Select the desired mode. The default setting is 11bgn mixed.
11b only, 11g only, 11n only, 11bg mixed, 11bgn mixed.
It is strongly recommended that you set the Mode to 802.11b&g&n, and all of
802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n wireless stations can connect to the AP.
Select any channel width from the pull-down list. The default setting is Auto, which
can adjust the channel width for your clients automatically.
The wireless radio of this AP can be enabled or disabled to allow wireless stations
access.
When wireless clients survey the local area for wireless networks to associate
with, they will detect the SSID broadcast by the AP. If you select the Enable SSID
Broadcast checkbox, the Wireless AP will broadcast its name (SSID) on the air.
If 11b only, 11g only, or 11bg mixed is selected in the Mode field, the Channel Width selecting field
will turn grey and the value will become 20M, which is unable to be changed.
-59-
Page 60

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.6.2 Wireless Security
Choose menu “Wireless→Wireless Security” to configure the security settings of your wireless network.
Figure 5-41 Wireless Security
The AP supports the following wireless security modes:
Object Description
Disable Security
If you do not want to use wireless security, select this check box, but it’s strongly
recommended to choose one of the following modes to enable security.
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a security protocol, specified in the IEEE
Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) standard, 802.11b, that is designed to provide a wireless
local area network (WLAN) with a level of security and privacy comparable to what
-60-
Page 61
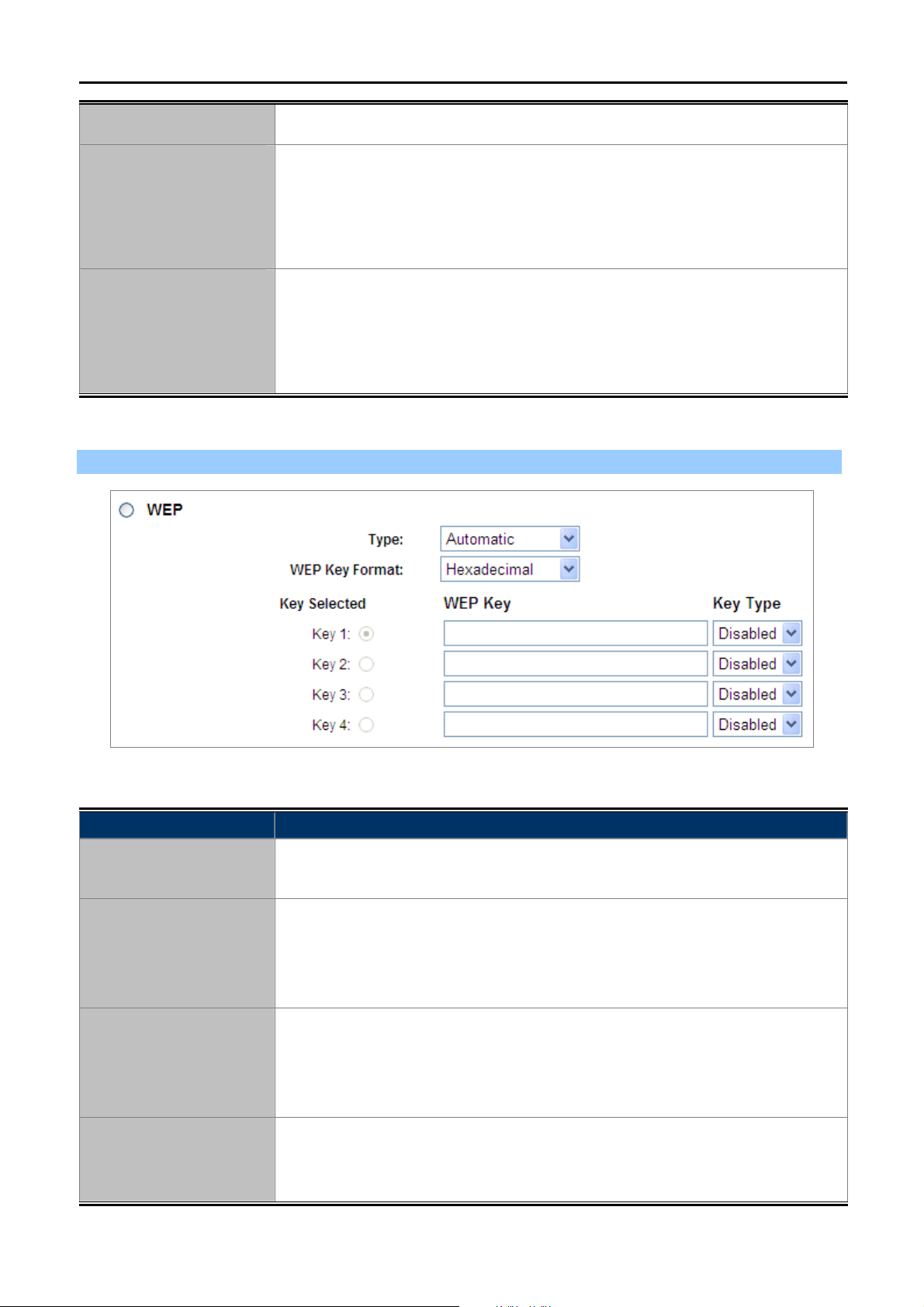
is usually expected of a wired LAN.
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
WPA/WPA2 - Personal
WPA/WPA2 - Enterprise
A. WEP
WPA-Personal (a.k.a. WPA-PSK) is a common method to secure wireless
networks. In the Personal mode, a pre-shared key or passphrase is used for
authentication. This pre-shared key is then dynamically sent between the AP and
clients.
WPA-Enterprise (a.k.a. WPA-802.1x, RADIUS) includes all of the features of
WPA-Pers
appropriate i
should only be used when
onal (WPA-PSK) plus support for 802.1x RADIUS authentication and is
n those cases where a RADIUS server is deployed. WPA-Enterprise
a RADIUS server is connected for client authentication.
Object Description
WEP
Type
WEP Key Format
WEP Key
Figure 5-42 Wireless Security – WEP
It is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard. If you select this check box, you will find
a notice in red as show in Figure 5-42 Wireless Security – WEP.
you can choose the type for the WEP security on the pull-down list. The default
setting is Automatic, which can select Open System or Shared Key
authentication type automatically based on the wireless station's capability and
request.
Hexadecimal and ASCII formats are provided. Hexadecimal format stands for
any combination of hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-F) in the specified length.
ASCII format stands for any combination of keyboard characters in the specified
length.
Select which of the four keys will be used and enter the matching WEP key that
you create. Make sure these values are identical on all wireless stations in your
network.
-61-
Page 62

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Key Type
You can select the WEP key length (64-bit, or 128-bit, or 152-bit.) for encryption.
"Disabled" means this WEP key entry is invalid.
64-bit You can enter 10 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
128-bit You can enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
152-bit You can enter 32 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
If you do not set the key, the wireless security function is still disabled even if you have selected
Shared Key as Authentication Type.
B. WPA/WPA2 – Enterprise
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 5 ASCII
characters.
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 13 ASCII
characters.
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 16 ASCII
characters.
Figure 5-43 Wireles
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
WPA/WPA2
Version
It is based on Radius Server.
You can choose the version of the WPA security on the pull-down list. The default
setting is Automatic, which can select WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) or WPA2
(WPA version 2) automatically based on the wireless station's capability and
request.
Encryption
You can select either Automatic, or TKIP or AES.
s Security - WPA/WPA2 Enterprise
-62-
Page 63

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Radius Server IP
Radius Port
Radius Password
Group Key Update
Period
Enter the IP address of the Radius Server.
Enter the port that radius service used.
Enter the password for the Radius Server.
Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30 or
above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
If you check the WPA/WPA2 radio button and choose TKIP encryption, you will find a notice in red
as shown in Figure 5-43.
C. WPA/WPA2 – Personal
Figure 5-44 Wireles
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Version
It’s the WPA/WPA2 authentication type based on pre-shared passphrase.
You can choose the version of the WPA-PSK security on the drop-down list. The
default setting is Automatic, which can select WPA-PSK (Pre-shared key of
WPA) or WPA2-PSK (Pre-shared key of WPA) automatically based on the
wireless station's capability and request.
Encryption
PSK Password
When WPA-PSK or WPA is set as the Authentication Type, you can select either
Automatic, or TKIP or AES as Encryption.
You can enter ASCII characters between 8 and 63 characters or 8 to 64
Hexadecimal characters.
s Security - WPA/WPA2 Personal
Group Key Update
Period
Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30 or
above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
-63-
Page 64

Be sure to click the Save button to save your settings on this page.
If you check the WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK radio button and choose TKIP encryption, you will find a
notice in red as shown in Figure 5-44.
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
-64-
Page 65

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.6.3 Wireless MAC Filtering
Choose menu “Wireless→MAC Filtering”, and you can control the wireless access by configuring the Wireless
MAC Address Filtering function, shown in Figure 5-45. This function is not available when the operation is set to
Client.
Figure 5-45 Wireless MAC
Address Filtering
Wireless MAC Filtering:Click the Enable button to enable the Wireless MAC Address Filtering. The
default setting is disabled.
Filtering Rules:Select "Allow the stations specified by any enabled entries in the list to access.” if you
only want selected computers to have network access and all other computers not to have network access.
Select "Deny the stations specified by any enabled entries in the list to access." if you want all computers
to have network access except those computers in the list.
Add New…:Click “Add New…” to create a user profile to which wireless network access is denied or
allowed.
To add a Wireless MAC Address filtering entry, click the Add New… button. The "Add or Modify Wireless
MAC Address Filtering entry" page will appear, shown in Figure 5-46:
-65-
Page 66

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-46 Add or Modify Wirele
ss MAC Address Filtering entry
Object Description
MAC Address
Description
Status
The wireless station's MAC address that you want to filter.
A simple description of the wireless station.
The status of this entry either Enabled or Disabled.
To add or modify a MAC Address Filtering entry, follow these instructions:
Step 1. Enter the appropriate MAC Address into the MAC Address field. The format of the MAC Address is
XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX (X is any hexadecimal digit). For example, 00-30-4F-11-22-33.
Step 2. Enter a simple description of the wireless station in the Description field. For example, Wireless
station A.
Step 3. Status - Select Enabled or Disabled for this entry on the Status pull-down list.
Step 4. Click the Save button to save this entry.
To modify or delete an existing entry:
Step 1. Click the Modify in the entry you want to modify. If you want to delete the entry, click the Delete.
Step 2. Modify the information.
Step 3. Click the Save button.
Click the Enable All button to make all entries enabled
Click the Disabled All button to make all entries disabled.
Click the Delete All button to delete all entries
Click the Next button to go to the next page
-66-
Page 67

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Click the Previous button to return to the previous page.
For example, if you desire that the wireless station 1 with MAC address 00-30-4F-11-22-33 and the wireless
station 2 with MAC address 00-30-4F-A8-FF-FF are able to access the AP, but all the other wireless stations
cannot access the AP, you can configure the Wireless MAC Address Filtering list by following the steps
below:
Step 1. Click the Enable button to enable this function.
Step 2. Select the radio button: Deny the stations not specified by any enabled entries in the list to
access for Filtering Rules.
Step 3. Delete all or disable all entries if there are any entries already.
Step 4. Click the Add New... button and enter the MAC address 00-30-4F-11-22-33 /00-30-4F-A8-FF-FF in the
MAC Address field, then enter wireless station 1/2 in the Description field, while selecting Enabled in
the Status pull-down list. Finally, click the Save and the Back button.
The filtering rules that configured should be similar to the following list:
Figure 5-47 Wireless MAC Address Filtering
-67-
Page 68

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.6.4 Wireless Advanced
Choose menu “Wireless→Wireless Advanced”, and you can configure the advanced settings of your wireless
network.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Beacon Interval
Enter a value between 20-1000 milliseconds for Beacon Interval here. The
beacons are the packets sent by the AP to synchronize a wireless network.
Beacon Interval value determines the time interval of the beacons. The
default value is 100.
RTS Threshold
Here you can specify the RTS (Request to Send) Threshold. If the packet is
larger than the specified RTS Threshold size, the AP will send RTS frames to
a particular receiving station and negotiate the sending of a data frame. The
default value is 2346.
Fragmentation
Threshold
This value is the maximum size determining whether packets will be
fragmented. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low may result in poor
Figure 5-48 Wireless Advanced
DTIM Interval
network performance since excessive packets. 2346 is the default setting
and is recommended.
This value determines the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message
(DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next window
for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the AP has buffered
broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next
DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. You can specify the value between 1-255
-68-
Page 69

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Beacon Intervals. The default value is 1, which indicates the DTIM Interval is
the same as Beacon Interval.
Enable WMM
WMM function can guarantee the packets with high- priority messages being
transmitted preferentially. It is strongly recommended enabled.
Enable Short GI
This function is recommended for it will increase the data capacity by
reducing the guard interval time.
Enabled AP Isolation
This function can isolate wireless stations on your network from each other.
Wireless devices will be able to communicate with the AP but not with each
other. To use this function, check this box. AP Isolation is disabled by default.
If you are not familiar with the setting items on this page, it's strongly recommended to keep
the provided default values; otherwise, it may result in low wireless network performance.
5.6.5 Antenna Alignment
The Align Antenna utility allows the user to point and optimize the antenna in the direction of the maximum link
signal. Choose menu “Wireless→Antenna Alignment”, and you can align the remote site by reference to the
RSSI value of the remote AP. You can observe the remote AP’s signal strength changes while changing the
antenna's direction.
Figure 5-49 Antenna Alignment
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Remote AP RSSI
Signal percent
Remote AP's signal strength value.
The ratio of RSSI to RSSI RANGE in percentage.
-69-
Page 70

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
RSSI RANGE
The "RSSI Range" slider bar allows the range of the meter to be either
increased or reduced. If the range is reduced, the Signal Percent change will
be more sensitive to signal fluctuations as RSSI Range slider actually
changes an offset of the maximum indicator value thus the scale itself.
You can drag the Slider to set or input the RSSI RANGE value.
The Antenna Alignment only works after you have established connection to remote AP in
client mode.
5.6.6 Throughput Monitor
Choose menu “Wireless→Throughput Monitor” to help you to monitor the current wireless throughput.
Figure 5-50 Throughput Monitor
Click the Start button to start wireless throughput monitor.
Click the Stop button to stop wireless throughput monitor.
-70-
Page 71
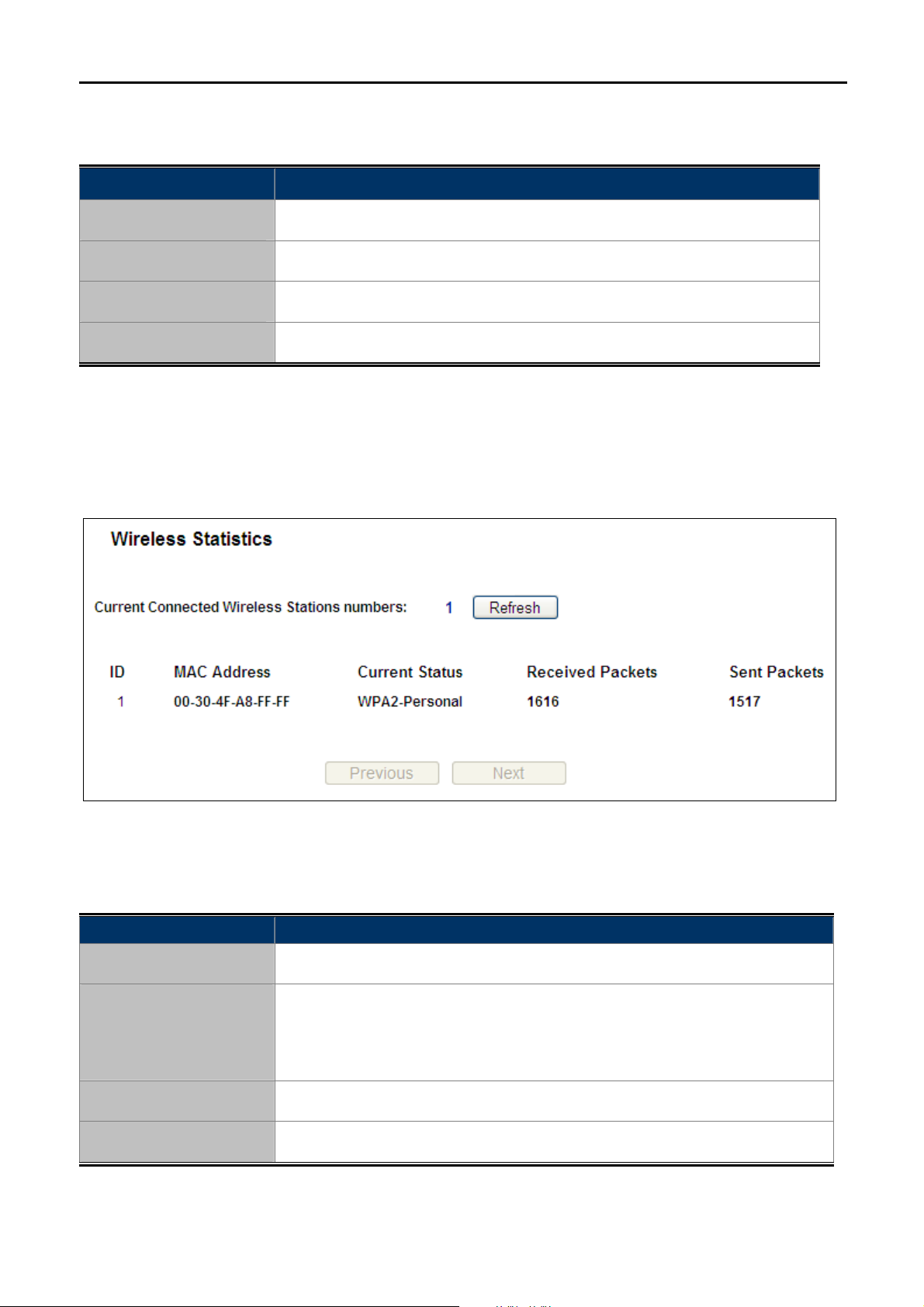
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Rate
Run Time
Transmit
Receive
The Throughput unit.
How long this function is running.
Displays the wireless transmitting rate information.
Displays the wireless receiving rate information.
5.6.7 Wireless Statistics
Choose menu “Wireless→Wireless Statistics”, and you can see the MAC Address, Current Status, Received
Packets and Sent Packets for each connected wireless station.
Figure 5-51 The AP attached wireless stations
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
MAC Address
Current Status
The connected wireless station's MAC address
The connected wireless station's running status, one of STA-AUTH /
STA-ASSOC / STA-JOINED / WPA / WPA-PSK / WPA2 / WPA2-PSK /
AP-UP / AP-DOWN / Disconnected
Received Packets
Sent Packets
Packets received by the station
Packets sent by the station
-71-
Page 72

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
You cannot change any of the values on this page. To update this page and to show the current connected
wireless stations, click on the Refresh button.
If the numbers of connected wireless stations go beyond one page, click the Next button to go to the next page
and click the Previous button to return to the previous page.
This page will be refreshed automatically every 5 seconds.
5.7 DHCP
There are three submenus under the DHCP menu (shown in Figure 5-52): DHCP Settings, DHCP Clients List
and Address Reservation. Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
Figure 5-52 The DHCP
menu
5.7.1 DHCP Settings
Choose menu “DHCP→DHCP Settings” and you can configure the DHCP Server on the page (shown in
Figure 5-53).The AP is set up by default as a DHCP (Dynamic
provides the TCP/IP configuration for all the PC(s) that are connected to the AP on the LAN.
Host Configuration Protocol) server, which
-72-
Page 73

Figure 5-53 DHCP Settings
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
The p
age includes the following fields:
Object Description
DHCP Server
Start IP Address
End IP Address
Address Lease Time
Enable or Disable the DHCP server. If you disable the Server, you must have
another DHCP server within your network or else you must configure the
computer manually.
Specify an IP address for the DHCP Server to start with when assigning IP addresses.
192.168.1.100 is the default start address.
Specify an IP address for the DHCP Server to end with when assigning IP
addresses. 192.168.1.199 is the default end address.
The Address Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be
allowed connection to the AP with their current dynamic IP Address. Enter the
amount of time in minutes and the user will be "leased" this dynamic IP
Address. After the time is up, the user will be automatically assigned a new
dynamic IP address. The range of the time is 1 ~ 2880 minutes. The default
Default Gateway
Default Domain
Primary DNS
value is 120 minutes.
(Optional.) Suggest to input the IP address of the LAN port of the AP, default
value is 192.168.1.1
(Optional.) Input the domain name of your network.
(Optional.) Input the DNS IP address provided by your ISP. Or consult your
ISP.
-73-
Page 74

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Secondary DNS
(Optional.) Input the IP address of another DNS server if your ISP provides
two DNS servers.
To use the DHCP server function of the AP, you must configure all computers on the LAN as
"Obtain an IP Address automatically" mode.
5.7.2 DHCP Clients List
Choose menu “DHCP→DHCP Clients List”, and you can view the information about the clients attached to
the AP in the next screen (shown in ).
Figure 5-54
Figure 5-54 DHCP Clients List
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
ID
Client Name
MAC Address
Assigned IP
Lease Time
The index of the DHCP Client
The name of the DHCP client
The MAC address of the DHCP client
The IP address that the AP has allocated to the DHCP client.
The time of the DHCP client leased. After the dynamic IP address has expired,
a new dynam
ic IP address will be automatically assigned to the user.
You cannot change any of the values on this page. To update this page and to show the current attached
devices, click the Refresh button.
-74-
Page 75
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.7.3 Address Reservation
Choose menu “DHCP→Address Reservation”, and you can view and add a reserved address for clients via
the next screen (shown in Figure 5-55). When you specify a reserved IP address for a PC on the LAN, that
PC
will always receive the same IP address each time when it accesses the DHCP server. Reserved IP addresses
should be assigned to the servers that require permanent IP settings.
Figure 5-55 Address Re
servation
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
ID
MAC Address
Reserved IP Address
Status
Modify
Displays the index of the DHCP client.
The MAC address of the PC for which you want to reserve IP address.
Displays the IP address that the AP is reserved.
The status of this entry either Enabled or Disabled.
To modify or delete an existing entry.
To Reserve IP addresses:
Step 1. Click the Add New … button.
Step 2. Enter the MAC address (in XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX format.) and IP address in dotted-decimal notation
of the computer you wish to add.
Step 3. Click the Save button when finished.
-75-
Page 76

Figure 5-56 Add an Address Reservation Entry
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
MAC Address
Assigned IP Address
Status
The MAC address of the PC for which you want to reserve IP address.
The IP address of the AP reserved.
The status of this entry either Enabled or Disabled.
To modify or delete an existing entry:
Step 1. Click the Modify in the entry you want to modify. If you want to delete the entry, click the Delete.
Step 2. Modify the information.
Step 3. Click the Save button.
Figure 5-57 Modify an Address Reservation Entry
Click the Enable/ Disabled All button to make all entries enabled/disabled
Click the Delete All button to delete all entries
Click the Next button to go to the next page and click the Previous button to return to the previous page.
-76-
Page 77

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.8 System Tools
Choose menu “System Tools”, and you can see the submenus under the main menu: SNMP, Time Settings,
Diagnostic, Ping Watch Dog, Firmware Upgrade, Factory Defaults, Backup & Restore, Reboot,
Password, System Log and Statistics. Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding
function. The detailed explanations for each submenu are provided below.
Figure 5-58 The System Tools menu
5.8.1 SNMP
Choose menu “System Tools→SNMP” to enable this function to allow the network management station to
retrieve statistics and status from the SNMP agent in this AP. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is
a popular network monitoring and management protocol, used to refer to a collection of specifications for
network management that includes the protocol itself.
-77-
Page 78

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-59 The System Tools menu
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
SNMP Agent
Select the radio button before Enable will enable this function if you want to
have remote control through SNMPv1/v2 agent with MIB-II. Select the radio
button before Disable will disable this function. The default setting is Disable.
SysContact
SysName
SysLocation
Get Community
The textual identification of the contact person for this managed node.
An administratively-assigned name for this managed node.
The physical location of this node.
Enter the community name that allows Read-Only access to the AP's SNMP
information. The community name can be considered a group password. The
default setting is “public”.
Get Source
Get source defines the IP address or subnet for management systems that can
read information from this 'get' community device.
Set Community
Set Source
Enter the community name that allows Read/Write access to the AP's SNMP
information. The community name can be considered a group password. The
default setting is “private”.
Set source defines the IP address or subnet for management systems that can
control this 'set' community device.
-78-
Page 79

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
A restricted source can be a specific IP address (e.g. 10.10.10.1), or a subnet - represented
as IP/BITS (e.g. 10.10.10.0/24). If an IP address of 0.0.0.0 is specified, the agent will accept
all requests under the corresponding community name.
5.8.2 Time Settings
Choose menu “System Tools→Time Settings”, and you can configure the system time and the auto reboot
time on the following screen. Click the "GET GMT" to update the time from the Internet with the pre-defined
servers or entering the customized server (IP Address or Domain Name) in the above frames.
Figure 5-60 Time Settings
-79-
Page 80

The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Time Zone
Date
Time
NTP Server Prior
Enable Daylight Saving
Auto Reboot Setting
Start Time
Reboot Plan
Select your local time zone from this pull down list.
Enter your local date in MM/DD/YY into the right blanks.
Enter your local time in HH/MM/SS into the right blanks.
Enter the address for the NTP Server, then the AP will get the time from the
NTP Server preferentially. In addition, the AP builds in some common NTP
Servers, so it can get time automatically once it connects the Internet.
Check this option if your location observes daylight saving time.
Enable this option to enable auto reboot function to clear the memory buffer
regularly.
Enter the Start Time (24-hour format) to enable the auto reboot function to
take effect.
Choose “Everyday” or "Weekday" in the Reboot Plan field to schedule your
auto reboot frequency.
Weekday
When you choose “Weekday” as reboot plan, you need to select at least one
day of a week for the plan.
To configure the system manually:
Step 1. Select your local time zone.
Step 2. Enter date and time in the right blanks.
Step 3. Click Save to save the configuration.
To configure the system automatically:
Step 1. Select your local time zone.
Step 2. Enter the IP address for NTP Server Prior.
Step 3. Click the Get GMT button to get system time from Internet if you have connected to the Internet.
To enable Auto Reboot:
Step 1. Select the Auto Reboot Setting checkbox.
Step 2. Enter the Start Time (24-hour format) to enable this function to take effect. For example, if you
want this function to work at 18:00 every Sunday, you need to choose "Weekday" in the Reboot
Plan field, and select the "Sun" checkbox in the Weekday field. If you want this function to work
at 18:00 every day, you just need to choose "Every day" in the Reboot Plan field.
Step 3. Click the Save button to effect this function.
-80-
Page 81

1. This setting will be used for some time-based functions such as firewall functions. These
time dependant functions will not work if time is not set. So, it is important to specify time
settings as soon as you successfully login to the Device.
2. The time will be lost if the Device is turned off.
3. The Device will automatically obtain GMT from the Internet if it is configured accordingly.
4. In daylight saving configuration, start time and end time will be within one year and start
time will be earlier than end time.
5. After you enable daylight saving function, it will take action in one minute.
6. The Auto Reboot setting will only take effect when the Internet connection is accessible
and the GMT time is configured correctly.
7. You must select at least one day when choosing "Weekday" as your reboot plan.
8. When choosing "Every day" as your reboot plan, the "Weekday" will be grayed out
(disabled), which means Every day will auto reboot at the time that you scheduled.
5.8.3 Diagnostic
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Choose menu “System Tools → Diagnostic”, and you can transact Ping or Traceroute function to check
connectivity of your network in the following screen.
Figure 5-61 Diagnostic Tools
-81-
Page 82

The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Diagnostic Tool
IP Address/Domain Name
Pings Count
Ping Packet Size
Ping Timeout
Traceroute Max TTL
Check the radio button to select one diagnostic tool.
Ping - This diagnostic tool troubleshoots connectivity, reachability,
and name resolution to a given host or gateway.
Traceroute - This diagnostic tool tests the performance of a
connection.
Type the destination IP address (such as 74.125.153.103) or Domain name
(such as http://www.google.com)
The number of Ping packets for a Ping connection.
The size of Ping packet.
Set the waiting time for the reply of each Ping packet. If there is no reply in the
specified time, the connection is overtime.
The max. number of hops for a Traceroute connection.
Click Start to check the connectivity of the Internet.
You can use ping or traceroute to test both numeric IP address or domain name. If pinging or
tracerouting the IP address is successful, but pinging or tracerouting the domain name is not,
you might have a name resolution problem. In this case, ensure that the domain name you
are specifying can be resolved by using Domain Name System (DNS) queries.
The Diagnostic Results page displays the result of diagnosis.
If the result is similar to the following screen, the connectivity of the Internet is fine.
-82-
Page 83

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-62 Diagnostic Results
Only one user can use this tool at one time. Options “Number of Pings”, “Ping Size” and “Ping Timeout”
are used for Ping function. Option “Tracert Hops” is used for Tracert function.
-83-
Page 84

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.8.4 Ping Watch Dog
Choose menu “System Tools → Ping Watch Dog” to allow you to continuously monitor the particular
connection between the AP to a remote host. It makes this AP continuously ping a user defined IP address (it
can be the Internet gateway, for example). If it is unable to ping under the user defined constraints, this device
will automatically reboot.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Enable
IP Address
Turn on/off Ping Watch Dog.
The IP address of the target host where the Ping Watch Dog Utility is sending
ping packets.
Interval
Delay
Fail Count
Time interval between two ping packets which are sent out continuously.
Time delay before first ping packet is sent out when the device is restarted.
Upper limit of the ping packet the device can drop continuously. If this value is
overrun, the device will restart automatically.
Figure 5-63 Ping Watch Dog
5.8.5 Firmware Upgrade
Choose menu “System Tools → Firmware Upgrade”, and you can update the latest version of firmware for
the AP in the following screen.
-84-
Page 85

The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-64 Firmware Upgrade
Firmware Version
Hardware Version
To upgrade the AP's firmware, follow these instructions below:
Step 1. Download a more recent firmware upgrade file from the Planet
Step 2. Type the path and file name of the update file into the File field. Or click the Browse… button to
locate the update file.
Step 3. Click the Upgrade button.
New firmware versions posted on the website of PLANET Technology can be downloaded for
free. There is no need to upgrade the firmware unless the new firmware has a new feature
you want to use. However, when experiencing problems caused by the AP rather than the
configuration, you can try to upgrade the firmware.
When you upgrade the AP's firmware, you may lose its current configurations, so before
This displays the current firmware version.
This displays the current hardware version. The hardware version of the
upgrade file must accord with the AP’s current hardware version.
website
upgrading the firmware please write down some of your customized settings to avoid losing
important settings.
Do not turn off the AP or press the Reset button while the firmware is being upgraded;
otherwise, the AP may be damaged.
The AP will reboot after the upgrading has been finished.
5.8.6 Factory Defaults
Choose menu “System Tools → Factory Defaults”, and you can restore the configurations of the AP to
factory defaults in the following screen
-85-
Page 86

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 5-65 Restore Factory Default
Click the Restore button to reset all configuration settings to their default values.
Default IP Address: 192.168.1.253
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: admin
Default SSID: WNAP-1110
Default Wireless Password: PIN code (refer to the label on the bottom of the WNAP-1110.)
Any settings you have saved will be lost when the default settings are restored.
5.8.7 Backup & Restore
Choose menu “System Tools → Backup & Restore”, and you can save the current configuration of the AP as
a backup file and restore the configuration via a backup file as shown in Figure 5-66.
Figure 5-66 Backup & Restore Co
nfiguration
Click the Backup button to save all configuration settings as a backup file in your local computer.
To restore the AP's configuration, follow these instructions.
Step 1. Click the Browse… button to locate the update file for the AP, or enter the exact path to the
Setting file in the text box.
Step 2. Click the Restore button.
-86-
Page 87

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
The current configuration will be covered by the uploading configuration file. The upgrade
process lasts for 20 seconds and the AP will restart automatically. Keep the AP power on
during the upgrading process to prevent any damage.
5.8.8 Reboot
Choose menu “System Tools → Reboot”, and you can click the Reboot button to reboot the AP via the next
screen.
Figure 5-67 Reboot the AP
Some settings of the AP will take effect only after rebooting, which include
Change the LAN IP Address (system will reboot automatically).
Change the DHCP Settings.
Change the Wireless configurations.
Upgrade the firmware of the AP (system will reboot automatically).
Restore the AP's settings to factory defaults (system will reboot automatically).
Update the configuration with the file (system will reboot automatically.
5.8.9 Password
Choose menu “System Tools → Password”, and you can change the factory default user name and
password of the AP in the next screen as shown in Figure 5-68.
-87-
Page 88

Figure 5-68 Password
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
It is strongly
recommended that you should change the factory default user name and password of the AP,
because all users who try to access the AP's Web-based utility or Quick Setup will be prompted for the AP's
default user name and password.
The new user name and password must not exceed 14 characters in length and not include
any spaces. Enter the new Password twice to confirm.
Click the Save button when finished.
Click the Clear All button to clear all.
-88-
Page 89

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.8.10 System Log
Choose menu “System Tools → System Log”, and you can view the logs of the AP.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Auto Mail Feature
Mail Settings
Indicates whether auto mail feature is enabled or not.
Set the receiving and sending mailbox address, server address, validation
information as well as the timetable for Auto Mail Feature, as shown in Figure
5-70 .
Log Type
By selecting the log type, only logs of this type will be shown.
Figure 5-69 System Log
-89-
Page 90

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Log Level
Refresh
Save Log
Mail Log
Clear Log
Previous
Next
By selecting the log level, only logs of this level will be shown.
Click the Refresh button to show the latest log list.
Click the Save Log button to save all the logs in a txt file.
Click the Mail Log to send an email of current logs manually according to the
address and validation information set in Mail Settings. The result will be shown
in the later log soon.
Click the Clear Log button to delete all the logs from the system permanently,
not just from the page.
Click the Previous button return to the previous page.
Click the Next button to go to the next page
Figure 5-70 Mail Acc
Click Save to keep your settings.
Click Back to return to the previous page.
ount Settings
-90-
Page 91

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
From Your mail box address. The AP would connect it to send logs.
To Recipient’s address. The destination mailbox where the logs would be
received.
SMTP Server Your SMPT server. It corresponds with the mailbox filled in the From field. You
can log on the relevant website for Help if you are not clear with the address.
Authentication Most SMTP Server requires Authentication. It is required by most mailboxes
that need User Name and Password to log in.
User Name Your mail account name filled in the From field. The part behind @ is
excluded.
Password Your mail account password.
Confirm The Password Enter the password again to confirm.
Enable Auto Mail
Feature
Select it to mail logs automatically. You could mail the current logs either at a
specified time everyday or by intervals, but only one could be the current
effective rule.
Everyday, at specified time, the Device will automatically send the log to
specified mailbox.
Every few hours, such as 2 hours, the Device will automatically send the
log to specified mailbox.
Only when you select Authentication, you have to enter the User Name and Password in the
following fields.
-91-
Page 92

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
5.8.11 Statistics
Choose menu “System Tools → Statistics”, and you can view the statistics of the AP, including total traffic
and current traffic of the last Packets Statistic Interval.
Figure 5-71 Statistics
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Current Statistics Status
Enable or Disable. The default value is disabled. To enable, click the Enable
button. If disabled, the function of DoS protection in Security settings will be
disabled.
Packets Statistics Interval
(5-60)
The default value is 10. Select a value between 5 and 60 seconds in the
pull-down list. The Packets Statistic interval indicates the time section of the
packets statistic.
Sorted Rules
Choose how displayed statistics are sorted.
Select the Auto-refresh checkbox to refresh automatically.
Click the Refresh button to refresh immediately.
Click Reset All to reset the values of all the entries to zero.
Click Delete All to delete all entries in the table.
-92-
Page 93

Statistics Table:
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
IP/MAC Address
Packets
Total
Bytes
Packets
Bytes
ICMP Tx
Current
UDP Tx
The IP and MAC address are displayed with related statistics.
The total number of packets received and transmitted by the AP.
The total number of bytes received and transmitted by the AP.
The total number of packets received and transmitted in the last Packets
Statistic interval seconds.
The total number of bytes received and transmitted in the last Packets
Statistic interval seconds.
The number of the ICMP packets transmitted to WAN per second at the
specified Packets Statistics interval. It is shown like “current transmitting
rate / Max transmitting rate”.
The number of UDP packets transmitted to the WAN per second at the
specified Packets Statistics interval. It is shown like “current transmitting
rate / Max transmitting rate”.
The number of TCP SYN packets transmitted to the WAN per second at
TCP SYN Tx
the specified Packets Statistics interval. It is shown like “current
transmitting rate / Max transmitting rate”.
Reset
Reset the value of he entry to zero.
Modify
Delete
Delete the existing entry in the table.
There would be 5 entries on each page. Click Previous to return to the previous page and Next to the next
page.
-93-
Page 94

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Chapter 6. Quick Connection to a Wireless Network
6.1 Windows XP (Wireless Zero Configuration)
Step 1: Right-click on the wireless network icon displayed in the system tray
Figure 6-1 Wireless Zero Configuration
Step 2: Select [View Available Wireless Networks]
Figure 6-2 View Available Wireless Networks
Step 3: Highlight and select the wireless network (SSID) to connect
(1) Select SSID [PLANET]
(2) Click the [Connect] button
-94-
Page 95

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 6-3 Choose a wireless network
Step 4: Enter the encryption key of the Wireless AP
(1) The Wireless Network Connection box will appear
(2) Enter the encryption key that is configured in Section 5.6.2
(3) Click the [Connect] button
Figure 6-4 Enter the encryption key
Step 5: Check if “Connected” is displayed
-95-
Page 96

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 6-5 Wireless Network Connected
Some laptops are equipped with a “Wireless ON/OFF” switch for the internal wireless LAN.
Make sure the hardware wireless switch is switch to “ON” position.
6.2 Windows 7 (WLAN AutoConfig)
WLAN AutoConfig service is built-in in Windows 7 that can be used to detect and connect to wireless network.
This built-in wireless network connection tool is similar to wireless zero configuration tool in Windows XP.
Step 1: Right-click on the network icon displayed in the system tray
Figure 6-6 WLAN AutoConfig
Step 2: Highlight and select the wireless network (SSID) to connect
(1) Select SSID [PLANET]
-96-
Page 97
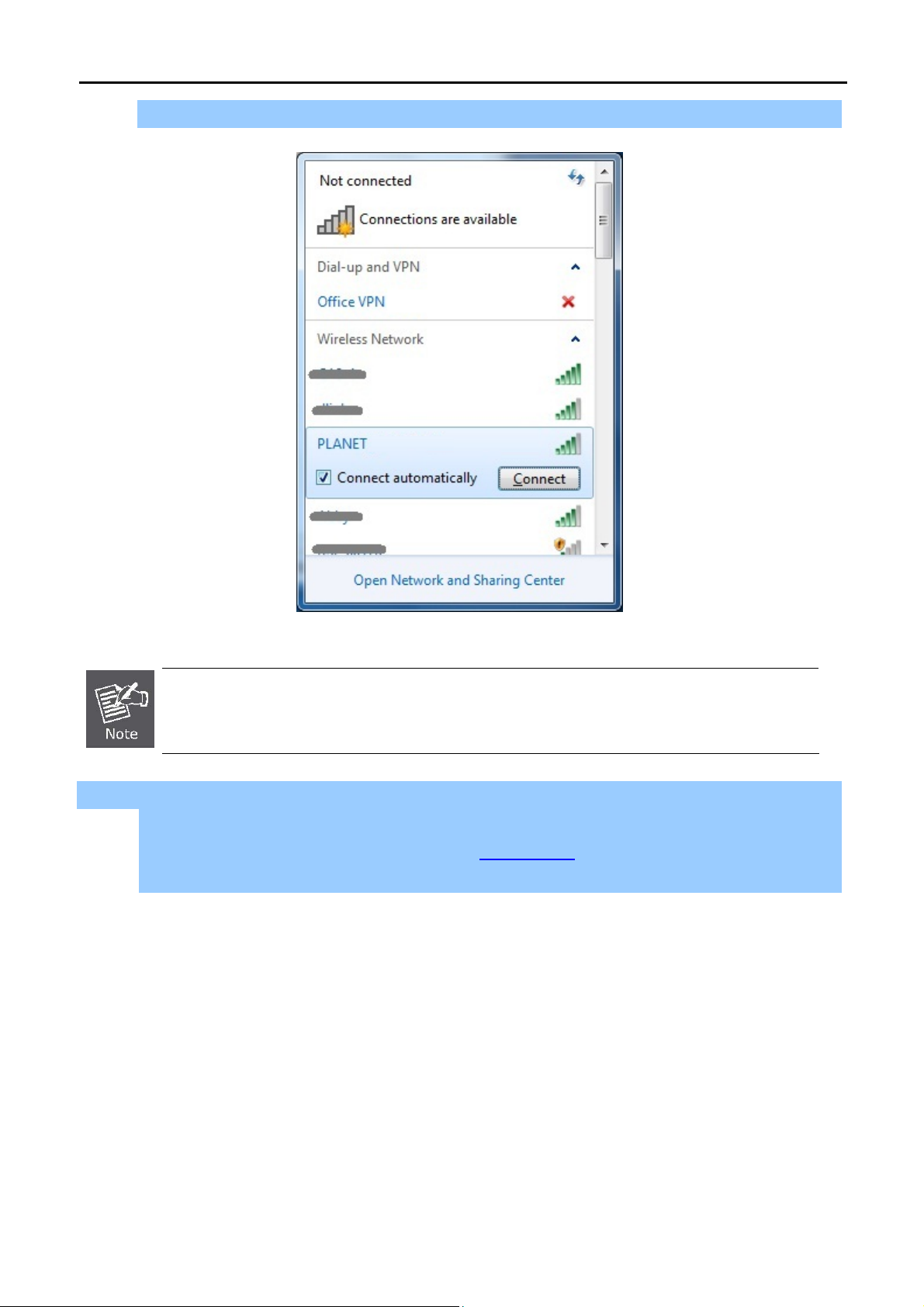
(2) Click the [Connect] button
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 6-7 WLAN AutoConfig window
If you will be connecting to this Wireless AP in the future, check [Connect automatically].
Step 4: Enter the encryption key of the Wireless AP
(1) The Connect to a Network box will appear
(2) Enter the encryption key that is configured in Section 5.6.2
(3) Click the [OK] button
-97-
Page 98
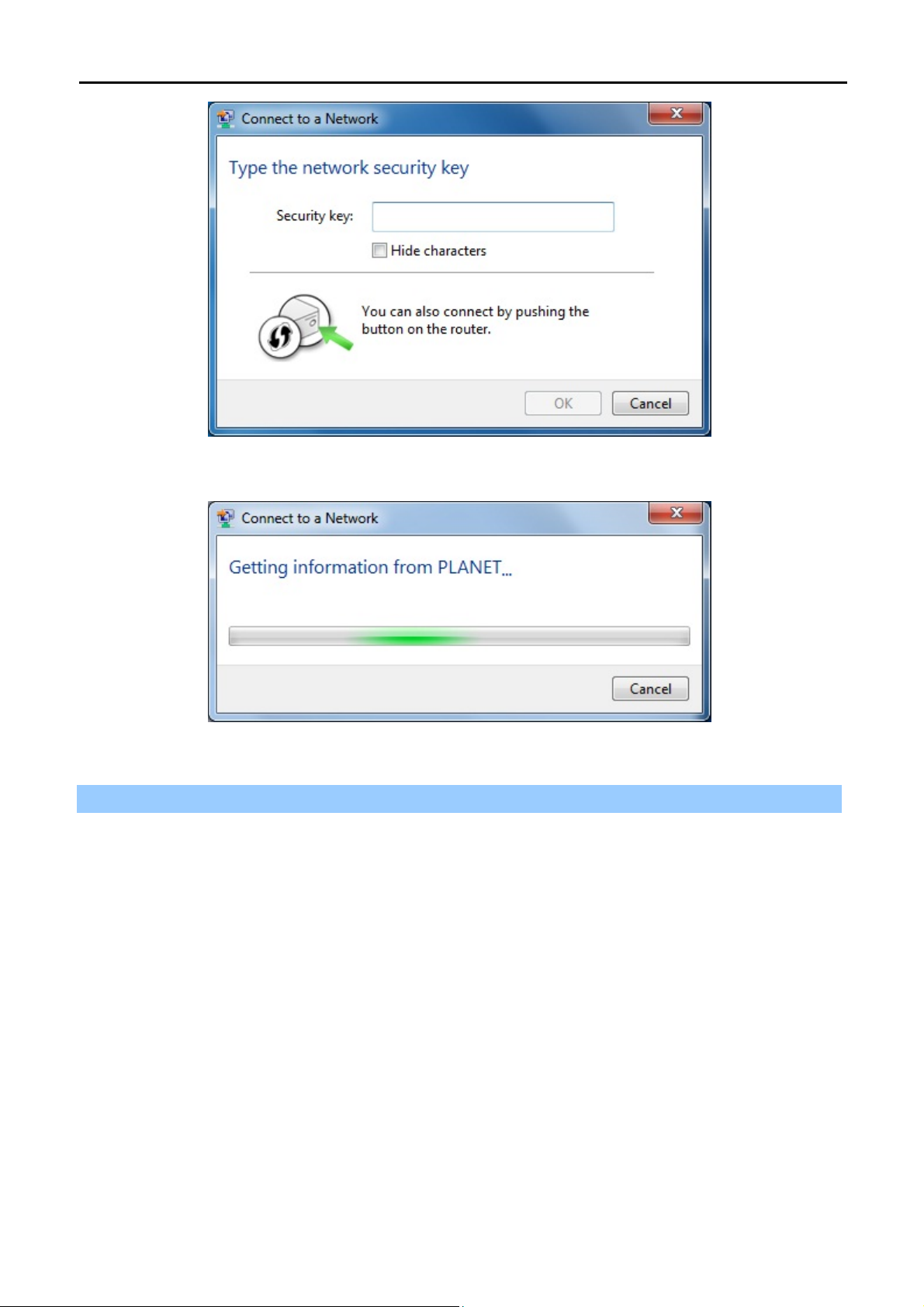
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 6-8 WLAN AutoConfig – type the network security key
Figure 6-9 WLAN AutoConfig – connecting
Step 5: Check if “Connected” is displayed
-98-
Page 99

User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 6-10 WLAN AutoConfig – Connected
6.3 Mac OS X 10.x
Step 1: Right-click on the network icon displayed in the system tray
The AirPort Network Connection menu will appear
Figure 6-11
Step 2: Highlight and select the wireless network (SSID) to connect
The AirPort Network Connection icon
(1) Select and SSID [PLANET]
(2) Double-click on the selected SSID
-99-
Page 100

Figure 6-12 The AirPort Network Connection menu
Step 4: Enter the encryption key of the Wireless AP
(1) Enter the encryption key that is configured in Section 5.6.2
(2) Click the [OK] button
User’s Manual of WNAP-1110
Figure 6-13 The AirPort Network Connection – enter password
If you will connect this Wireless AP in the future, check [Remember this
network].
Step 5: Check if the AirPort is connected to the selected wireless network.
If “Yes”, then there will be a “check” symbol in the front of the SSID.
-100-
 Loading...
Loading...