PIONEER CX 3110 Service Manual
PIONEER CORPORATION 4-1, Meguro 1-Chome, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8654, Japan
PIONEER ELECTRONICS (USA) INC. P.O.Box 1760, Long Beach, CA 90801-1760 U.S.A.
PIONEER EUROPE NV Haven 1087 Keetberglaan 1, 9120 Melsele, Belgium
PIONEER ELECTRONICS ASIACENTRE PTE.LTD. 253 Alexandra Road, #04-01, Singapore 159936
C PIONEER CORPORATION 2003
K-ZZA. DEC. 2003 printed in Japan
ORDER NO.
CRT3178
CD MECHANISM MODULE(S10.1)
CX-3110
Model Service Manual CD Mechanism Module
DEH-1600/XU/UC CRT3173 CXK5602
DEH-16/XU/UC
DEH-6/XU/UC
DEH-1630R/XU/EW CRT3174
DEH-1600R/XU/EW
DEH-1600RB/XU/EW
DEH-1610/XU/EE CRT3175
DEH-1650/XU/ES CRT3176
DEH-1650B/XU/ES
DEH-1650/XU/CN
- This service manual describes the operation of the CD mechanism module incorporated in models list-
ed in the table below.
- When performing repairs use this manual together with the specific manual for model under repair.
CONTENTS
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS ...........................................2
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS.................................19
3. DISASSEMBLY .........................................................21
2
1
234
12
34
F
E
D
C
B
A
CX-3110
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
Recently, Many CD LSIs have been one-chip LSIs where RF amplifier, DSP, audio DAC, post filter, and other circuits are
integrated.
This product uses this type CD LSI, UPD63712AGC, which includes all functions necessary for CD player control.
Basically, this system outputs the analog signal, and the digital output can be supported.
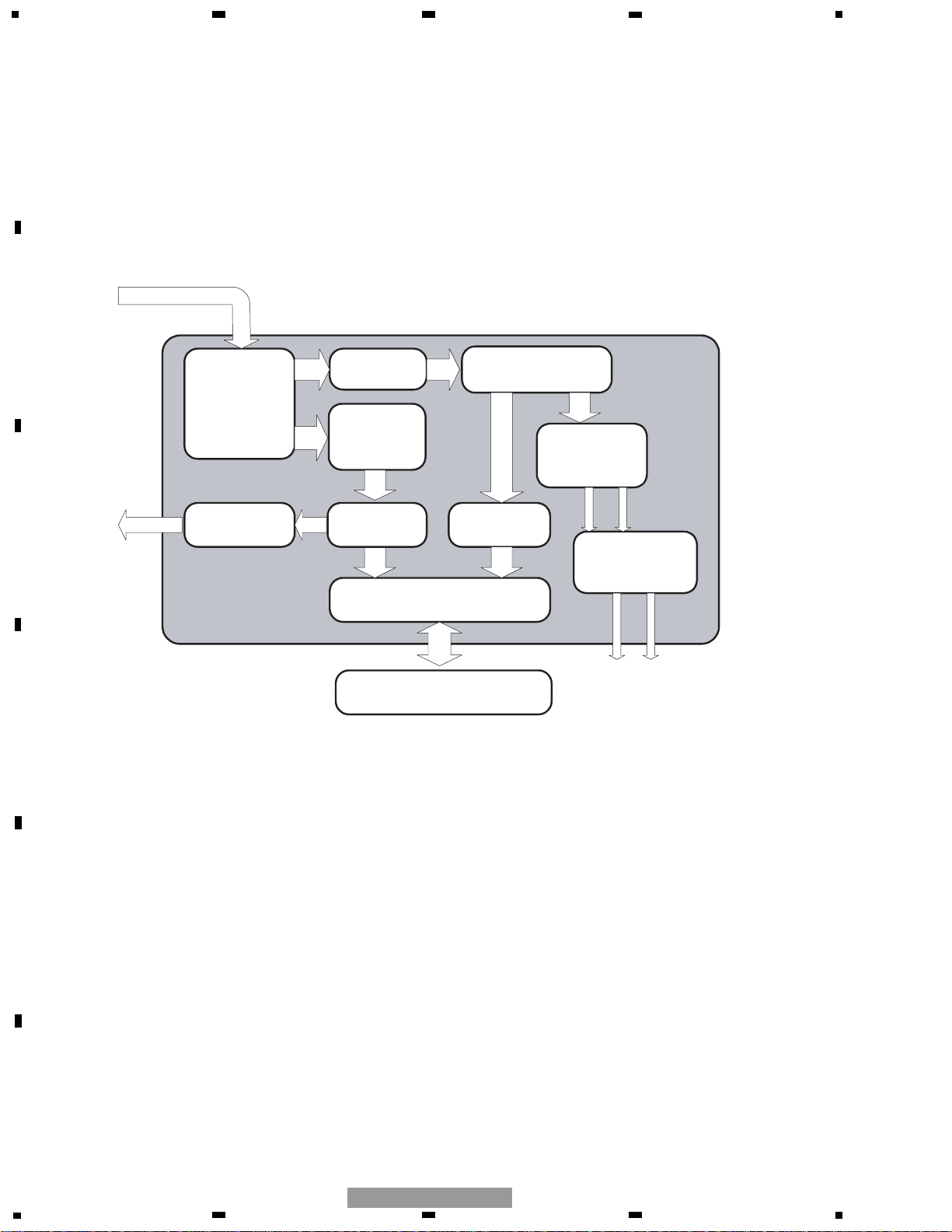
Fig.1.0.1 Block diagram of CD LSI UPD63712AGC
A-F
UPD63712AGC
EFM
Digital signal
processing
RF amplifier
A/D converter
1 bit,
Audio DAC
Drive output
Servo
PWM output
Digital servo
CD-TEXT
Post filter
(SCF)
MPU interface
Microcomputer
Analog output
for system control
3
5
6
7
8
F
E
D
C
B
A
5
6
7
8
CX-3110
1.1 PREAMPLIFIER BLOCK (UPD63712AGC: IC201)
In the preamplifier block, the pickup output signals are processed to generate signals that are used for the next-stage
blocks: the servo block, demodulator, and control.
After I/V-converted by the preamplifier with built-in photo detectors (inside the pickup), the signals are applied to the
preamplifier block in the CD LSI UPD63712AGC (IC201). After added by the RF amplifier in this block, these signals are
used to produce necessary signals such as RF, FE, TE, and TE zero-cross signals.
The CD LSI employs a single power supply system of + 3.3V. Therefore, the REFO (1.65V) is used as the reference voltage both for this CD LSI and the pickup. The LSI produces the REFO signal by using the REFOUT via the buffer amplifier and outputs from the pin 90. All the measurements should be made based on this REFO.
Caution: Be careful not to short the REFO and GRD when measuring.
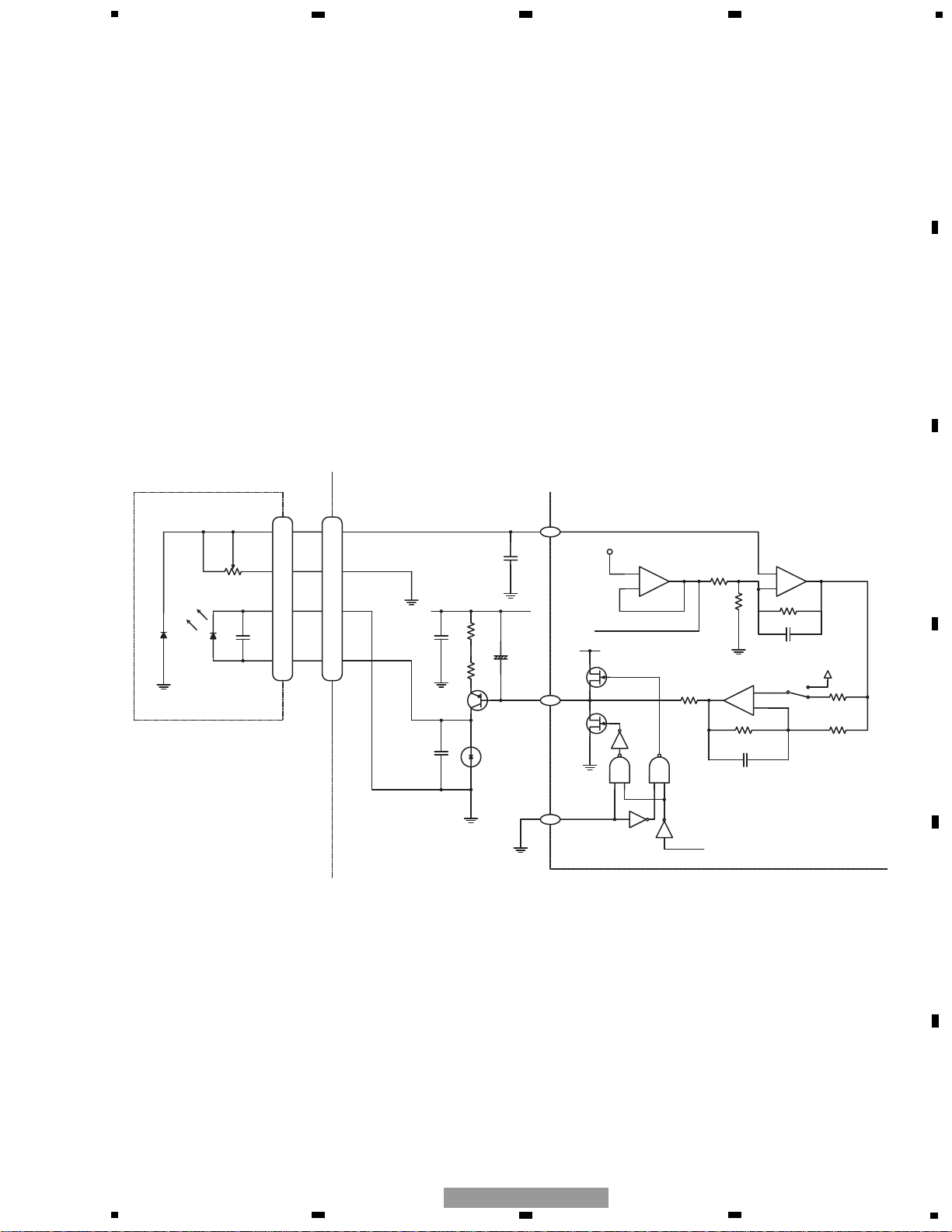
1.1.1 APC (Automatic Power Control)
A laser diode has extremely negative temperature characteristics in optical output at constant-current drive. To keep
the output constant, the LD current is controlled by monitor diodes. This is called the APC circuit. The LD current is
calculated at about 30mA, which is the voltage between LD1 and V+3A divided by 7.5 (ohms).
Fig. 1.1.1 APC
Pickup Unit
MD
VR
LD-
LD+
5
7
15
14 14
CD CORE UNIT
5
7
15
PD
2
100 p
100/16
1R5 x 5
R1 R1
+
2SB1132
LD
1
REG 1.25V
APC REG 1.25V
+
-
6.5 k
1 k
110 k
+
-
1 k
150 k
3 p
Vref
APN
+
-
100 k
100 k
1SS355
PN
3
UPD63712AGC
LDS
3 p
4
1
234
12
34
F
E
D
C
B
A
CX-3110
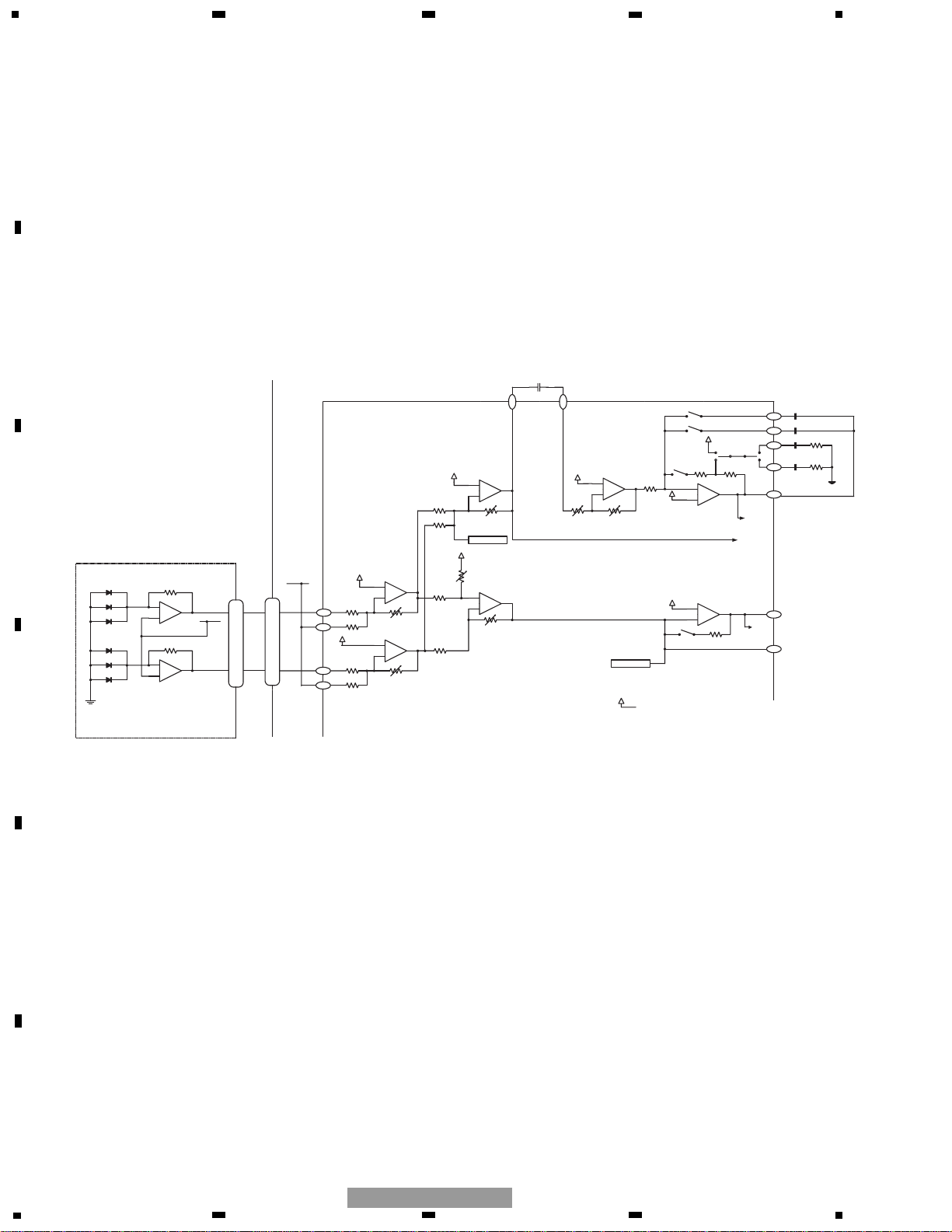
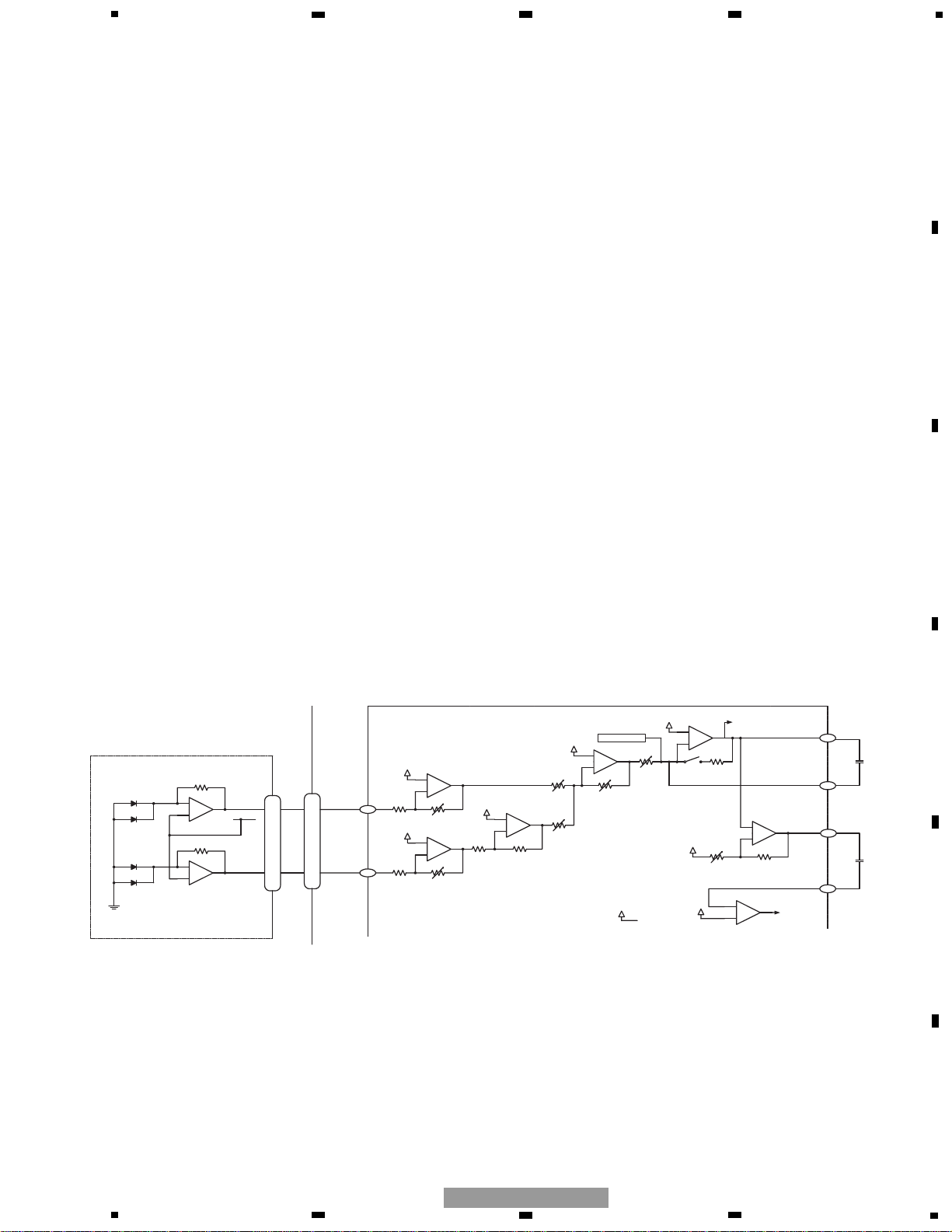
1.1.2 RF and RFAGC amplifiers
The photo-detector outputs (A + C) and (B + D) are added, amplified, and equalized inside this LSI, and then provided
as the RF signal from the RFI terminal. The RF signal can be used for eye-pattern check.
The low frequency component of the RFI voltage is:
RFO = (A + B + C + D) x 2
The RFO is used for the FOK generation circuit and RF offset adjustment circuit.
The RFI output from the pin 71 is A/C-coupled outside this LSI, and returned to the pin 76 of this LSI. The signal is
amplified in the RFAGC amplifier to obtain the RFAGC signal. This LSI is equipped with the RFAGC auto-adjustment
function as explained below. This function automatically controls the RFO level to keep at 1.5V by switching the feedback gain for the RFAGC amplifier.
The RFO signal is also used for the EFM, DFCT, MIRR, and RFAGC auto-adjustment circuits.
Fig. 1.1.2 RF/AGC/FE
CD CORE UNIT
Pickup Unit
P2
P4
P8
P3
P7
P9
VREF
A+C
13
B+D
VREF
13
6
6
A
C
D
B
UPD63712AGC
82
83
85
84
+
-
15.2 k
15.2 k
+
-
10 k
8.8 k
10 k
+
-
10 k
8.8 k
10 k
44 k 20 k 11.75 k
RFOFF setup
R2
61 k
+
-
140 k
61 k
R1
78
RFO
77
AGCI
+
-
FEOFF setup
VREF
3.55 k
RF-
RF2-
EQ2
5 k 5 k
+
To DEFECT/A3T detection
For RFOK generation
+
-
EQ1
AGCO
FEO
FE A/D
FE-
2 p
74
3 p
75
20 p
1.2 k
72
47 p
1.2 k
73
76
93
92
5
5
6
7
8
F
E
D
C
B
A
5
6
7
8
CX-3110
1.1.3 Focus error amplifier
The photo-detector outputs (A + C) and (B + D) are applied to the differential amplifier and the error amplifier to obtain
the (A + C - B - D) signal, which is then provided from the pin 93 as the FE signal.
The low frequency component of the FE voltage is:
FE = (A + C - B - D) x 8.8k/10k x 111k/61k x 160k/72k
= (A + C - B - D) x 3.55
The FE output shows 1.5Vp-p S-shaped curve based on the REFO. For the next-stage amplifiers, the cutoff frequency
is 14.6kHz.
1.1.4 RFOK
The RFOK circuit generates the RFOK signal, which indicates focus-close timing and focus-close status during the play
mode, and outputs from the pin 6. This signal is shifted to "H" when the focus is closed and during the play mode.
The DC level of the RFI signal is peak-held in the digital block and compared with a certain threshold level to generate
the RFOK signal. Therefore, even on a non-pit area or a mirror-surface area of a disc, the RFOK becomes "H" and the
focus is closed.
This RFOK signal is also applied to the microcomputer via the low-pass filer as the FOK signal, which is used for protection and RF amplifier gain switching.
1.1.5 Tracking error amplifier
The photo-detector outputs E and F are applied to the differential amplifier and the error amplifier to obtain the (E - F)
signal, and then provided from the pin 96 as the TE signal.
The low frequency component of the TE voltage is:
TEO = (E - F) x 63k/112k x 160k/160k x 181k/45.4k x 160k/80k
= (E - F) x 4.48
The TE output provides the TE waveform of about 1.16Vp-p based on the REFO. For the next-stage amplifiers, the cutoff frequency is 21.1kHz.
Fig. 1.1.3 TE
Pickup Unit
P10
E
F
UPD63712AGC
87
86
112 k
112 k
+
-
+
-
63 k
63 k
+
-
160 k 160 k
45.4 k
45.4 k
TEOFF setup
+
-
161 k
80 k
VREF
TE A/D
+
-
160 k
+
-
60 k20 k
-
Inside TEC
+
TEO
96
33 p
TE-
95
TE2
97
R1
TEC
98
CD CORE UNIT
P5
P1
P6
VREF
E
11
11
F
9
9
6
1
234
12
34
F
E
D
C
B
A
CX-3110
1.1.6 Tracking zero-cross amplifier
The tracking zero-cross signal (hereinafter TEC signal) is obtained by amplifying the TE signal 4 times, and used to
detect the tracking-error zero-cross point.
By using the information on this point, the following two operations can be performed:
1. Track counting in the carriage move and track jump modes
2. Sensing the lens-moving direction at the moment of the tracking close (The sensing result is used for the tracking
brake circuit as explained below.)
The frequency range of the TEC signal is between 300Hz and 20kHz.
TEC voltage = TE level x 4
The TEC level can be calculated at 4.64V. This level exceeds the D range of the operation amplifier, and the signal gets
clipped. However, it can be ignored because the CD LSI only uses the signal at the zero-cross point.
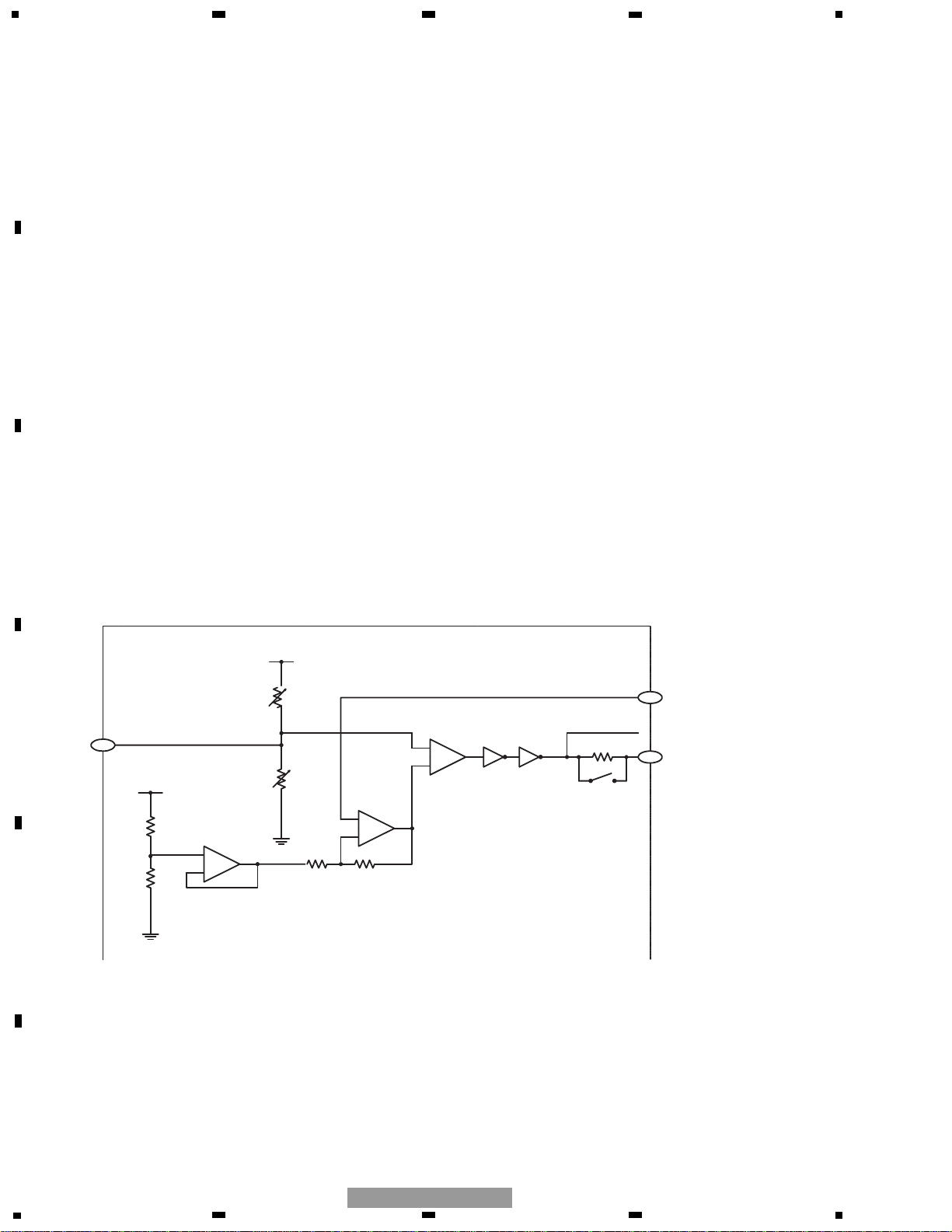
1.1.7 EFM
The EFM circuit converts the RF signal into a digital signal expressed in binary digits 0 and 1. The AGCO output from
the pin 76 is A/C-coupled in the peripheral circuit, fed back to the LSI from the pin 71, and sent to the EFM circuit inside
the LSI.
On scratched or dirty discs, part of the RF signal recorded may be missing. On other discs, part of the RF signal
recorded may be asymmetric, which was caused by dispersion in production quality. Such lack of information cannot
be completely eliminated by this AC coupling process. Therefore, by utilizing the fifty-fifty occurrence ratio of binary
digits (0 and 1) in the EFM signal, the EFM comparator reference voltage ASY is controlled, so that the comparator
level always stays around the center of the RFO signal. The reference voltage ASY is made from the EFM comparator
output via the low-pass filter. The EFM signal is put out from the pin 68.
Fig. 1.1.4 EFM
UPD63712AGC
RFI
71
40 k
40 k
Vdd
Vdd
ASY
40 k
EFM signal
+
40 k
+
-
+
-
1.5 k 7.5 k
-
2 k
69
EFM
68
7
5
6
7
8
F
E
D
C
B
A
5
6
7
8
CX-3110
1.2 SERVO BLOCK (UPD63712AGC: IC201)
The servo block controls the servo systems for error signal equalizing, in-focus, track jump and carriage move and so
on. The DSP block is a signal-processing block, where data decoding, error correction, and compensation are performed.
After A/D-converted, the FE and TE signals (generated in the preamplifier block) are applied to the servo block and
used to generate the drive signals for the focus, tracking, and carriage servos.
The EFM signal is decoded in the DSP block, and finally sent out as the audio signal after D/A-converted. In this
decoding process, the spindle servo error signal is generated, supplied to the spindle servo block, and used to generate the spindle drive signal.
The drive signals for focus, tracking, carriage, and spindle servos (FD, TD, SD, and MD) are provided as PWM3 data,
and then converted to the analog data by the low-pass filter in the driver IC BA5835FP (IC301). These analog drive signals can be monitored by the FIN, TIN, CIN, and SIN signals respectively. Afterwards, the signals are amplified and
applied to each servo's actuator and motor.
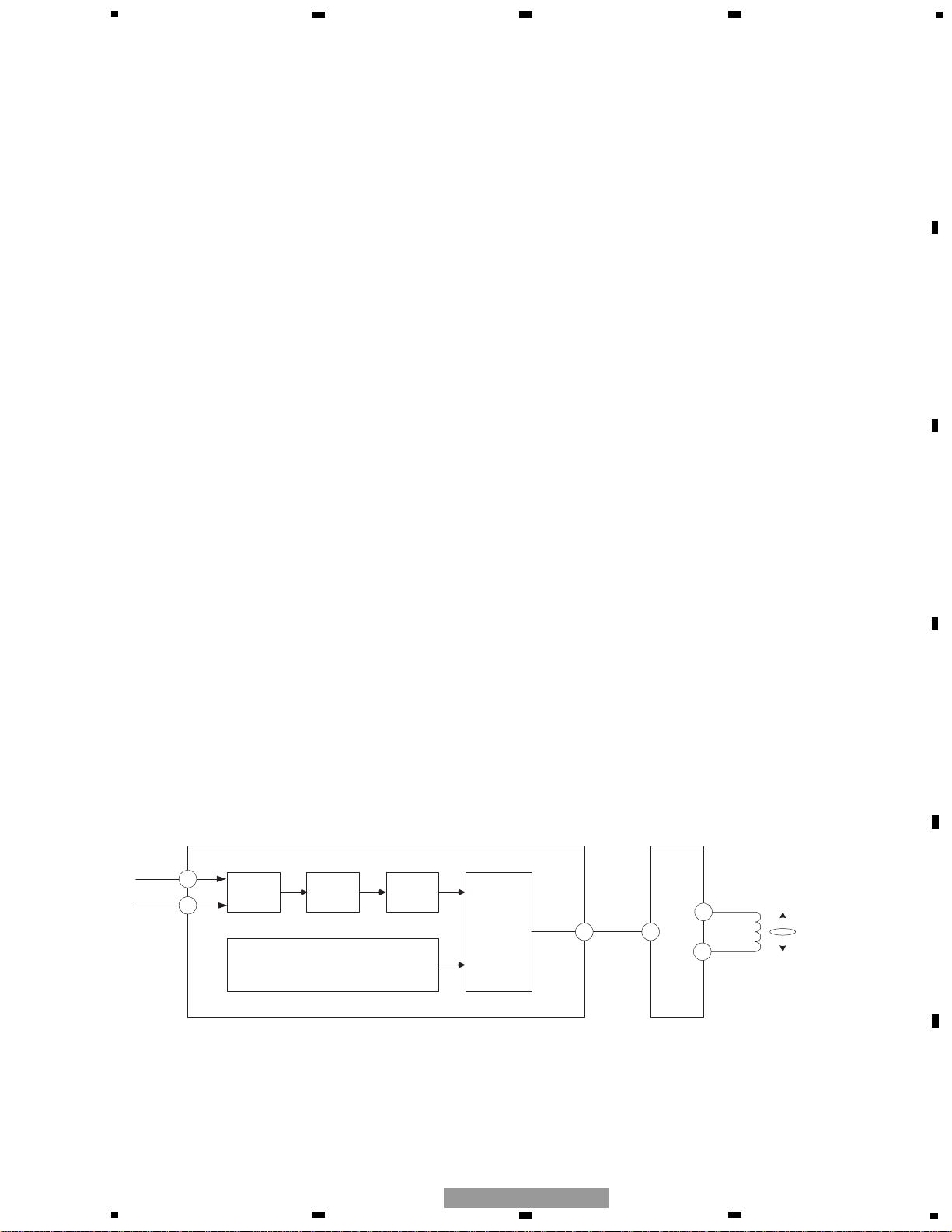
1.2.1 Focus servo system
In the focus servo system, the digital equalizer block works as its main equalizer. The figure 1.2.1 shows the block diagram of the focus servo system.
To close the focus loop circuit, the lens should be moved to within the in-focus range. While moving the lens up and
down by using the focus search triangular signal, the system tries to find the in-focus point. In the meantime, the spindle motor rotation is kept at the prescribed one by using the kick mode.
The servo LSI monitors the FE and RFOK signals and automatically performs the focus close operations at an appropriate timing. The focus loop will close when the following three conditions are satisfied at the same time:
1) The lens moves toward the disc surface.
2) The RFOK signal is shifted to "H".
3) The FE signal is zero-crossed. At last, the FE signal comes to the zero level (or REFO).
When the focus loop is closed, the FSS bit is shifted from "H" to "L". The microcomputer starts monitoring the RFOK
signal obtained through the low-pass filter 10msec after that.
If the RFOK signal is detected as "L", the microcomputer will take several actions including protection.
The timing chart for focus close operations is shown in fig. 1.2.2. (This shows the case where the system fails focus
close.)
In the test mode, the S-shaped curve, search voltage, and actual lens movement can be confirmed by pressing the
focus close button when the focus mode selector displays 01.
Fig. 1.2.1 Block diagram of the focus servo system
UPD63712AGC
A+C
B+D
82
85
FE
AMP
FOCUS SEARCH
TRIANGULAR
WAVE GENERATOR
A/D
DIG.
EQ
CONTROL
PWM
BA5835FP
FOP
FD
52
6
12
FOM
11
LENS
8
1
234
12
34
F
E
D
C
B
A
CX-3110
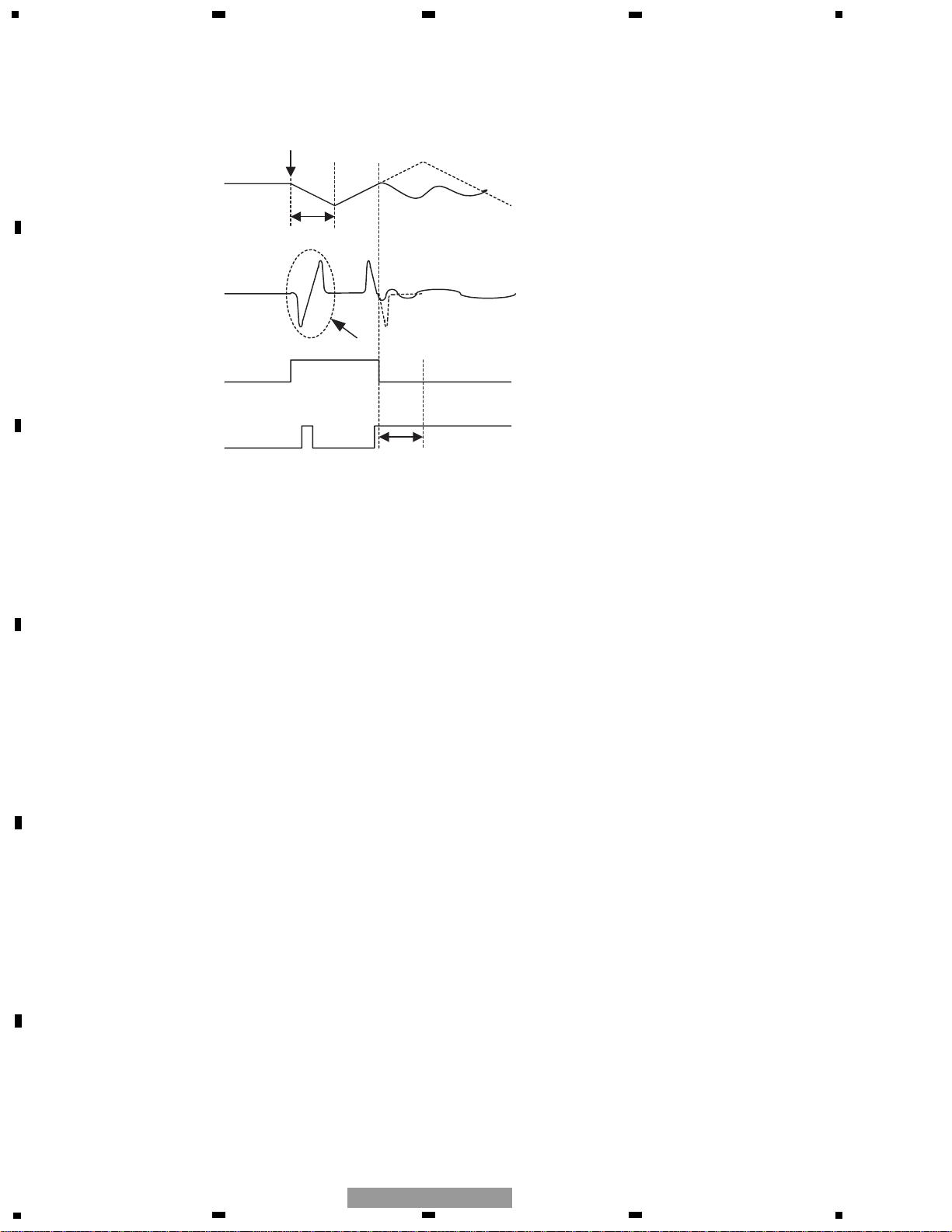
Fig. 1.2.2 Timing chart for focus close operations
1.2.2 Tracking servo system
In the tracking servo system, the digital equalizer block is used as its main equalizer. The figure 1.2.3 shows the block
diagram of the tracking servo system.
(a) Track jump
Track jump operation is automatically performed by the auto-sequence function inside the LSI with a command from
the microcomputer. In the search mode, the following five track jump modes are available: 1, 4, 10, 32, and 32*3
In the test mode, 1, 32, and 32*3 track jump modes, and carriage move mode are available and can be switched by
selecting the mode.
For track jumps, first, the microcomputer sets about half the number of tracks to be jumped as the target. (Ex. For 10
track jumps, it should be 5 or so.) Using the TEC signal, the microcomputer counts up tracks. When the counter
reaches the target set by the microcomputer, a brake pulse is sent out to stop the lens. The pulse width is determined
by the microcomputer. Then, the system closes the tracking loop and proceeds to the normal play. At this moment, to
make it easier to close the tracking loop, the brake circuit is kept ON for 50msec after the brake pulse, and the tracking
servo gain is increased.
In the normal operation mode, the FF/REW operation is realized by continuously repeating single jumps about 10
times faster than the normal single jump operation.
(b) Brake circuit
The brake circuit stabilizes the servo-loop close operation even under poor conditions, especially in the setting-up
mode or track jump mode. This circuit detects the lens-moving direction and emits only the drive signal for the opposite direction to slow down the lens. Thus, this makes it easier to close the tracking servo loop. The off-track direction
is detected from the phases of the TEC and MIRR signals.
Output from FD terminal
FE controlling signals
FSS bit of SRVSTS1 resistor
RFOK signals
Search start
A blind period
The broken line in the figure is assumed in the case
without focus servo.
You can ignore this for blind periods.
The status of focus close is judged from the statuses
of FSS and RFOK after about 10mS.
 Loading...
Loading...