Pioneer CX-3078 Service manual

PIONEER CORPORATION 4-1, Meguro 1-chome, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8654, Japan
PIONEER ELECTRONICS (USA) INC. P.O. Box 1760, Long Beach, CA 90801-1760, U.S.A.
PIONEER EUROPE NV Haven 1087, Keetberglaan 1, 9120 Melsele, Belgium
PIONEER ELECTRONICS ASIACENTRE PTE. LTD. 253 Alexandra Road, #04-01, Singapore 159936
PIONEER CORPORATION 2004
ORDER NO.
CRT3257
DVD MECHANISM MODULE(MS-3V1)
CX-3078
This service manual describes the operation of the DVD mechanism modules
incorporated in the models listed below.
When performing repairs use this manual together with the specific manual for the
model under repair.
Model No. Service Manual DVD Mechanism Module
AVH-P6600DVD/UC CRT3193 CXK6410
DVH-P5650/RC CRT3264 CXK6414
CONTENTS
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3. DISASSEMBLY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
K-ZZU. MAR. 2004 printed in Japan
1234
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
A
1 Front End Part (MN35103UB, MN35104UB:IC1501)
MN35103UB and MN35104UB are 1-chip LSI for DVD-Player. The connection of this LSI to the Driver IC,
SDRAM, Flash-ROM, Audio-DAC, etc. can configure the DVD-Player System.
This LSI contains Front End (SODC/FE) that performs RF signal /Servo /Decode processings, Back End
(AV decoder/BE) that performs the video decode processing such as MPEG1/MPEG2/JPEG and audio decode
processing such as DVD-Audio/AC-3/DTS/MP3, and the system controller (Siscon) for controlling the system.
Front End part realizes the arithmetic processing of optical head signal and RF signal processing,
the digital signal processing for DVD-ROM reproduction that conforms to DVD standards (16-8 Demodulation,
Error correction), the digital signal processing for CD-DA/CD-ROM (Error correction), AV decoder transmission,
servo control, spindle motor control and seek control.
Please take note that, since (FEP) and (SODC) with DVD mecha-module (MS3) of CX-3016 are integrated into
B
one chip at MN35103UB and MN35104UB, the waveforms of servo system on the front end which had
previously appeared at MS3, i.e., the waveforms of FE, TE and AS, cannot be seen anymore.
1.1 Analog Block (MN35103UB, MN35104UB:IC1501)
The analog block for IC1501 generates the servo signals including focus and tracking, processes addition of
RF signals, and controls the laser power of pickup.
The servo system contains focus operation amp, focus offset adjustment circuit, 3-beam tracking operation amp,
phase difference tracking detection circuit, tracking offset adjustment circuit, TE2 value-making circuit.
Also, RF signal processing system contains the functions of AGC and equalizer.
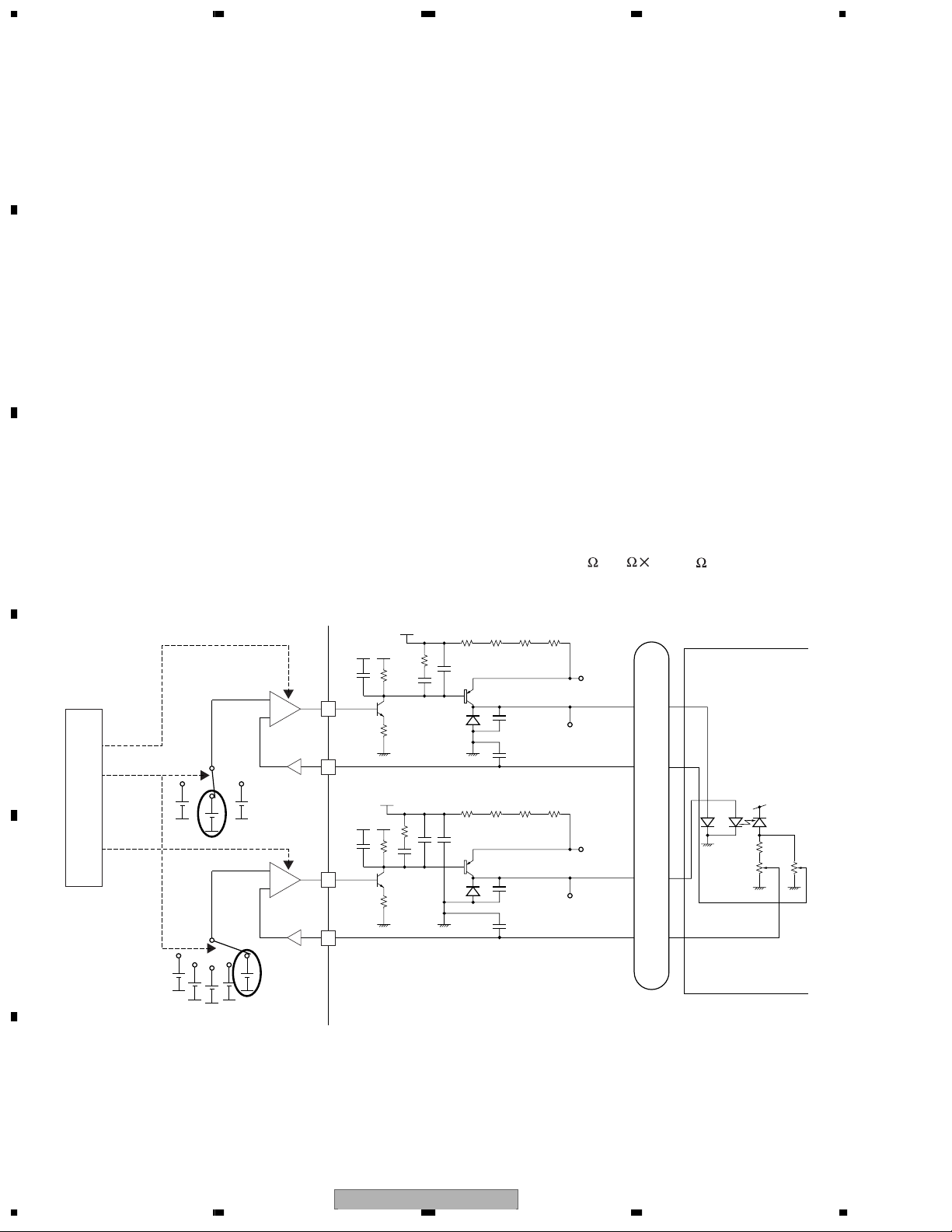
1.1.1 APC Circuit
The optical output for the laser diode (LD) has large minus temperature characteristics. Therefore, the constant
C
optical output cannot be obtained when LD is driven by the constant current. APC circuit controls the electric
current so as to provide constant output at the monitor diode (MD). MN35103UB and MN35104UB contain two
types of APC circuits, one for DVD and another for CD. The LD electric current for DVD (CD) can be obtained by
dividing the voltage measurements between DVDLD1 (CDLD1) and 5V by 15.6 (3.9 4=15.6 ). For DVD (CD),
the results are approx. 26mA (44mA).
+5V
+
+
D
LDONCD
LDPOWER
Reg.
LDONDVD
0.17V
–
–
0.25V0.18V
+
+
–
–
LPCO2
LPC2
+5V
+
LPCO1
E
LPC1
0.59V 0.18V
0.5V
0.25V
0.22V
3.9Ω 3.9Ω 3.9Ω 3.9Ω
+
3.9Ω 3.9Ω 3.9Ω 3.9Ω
+
CDLD1
CDLD0
DVDLD1
DVDLD0
CN1101
24
5
26
7
78LD
78MD
65LD
65MD
CDLDDVD
LD
PU unit
+5V
MD
F
CX-30782
1234
5678
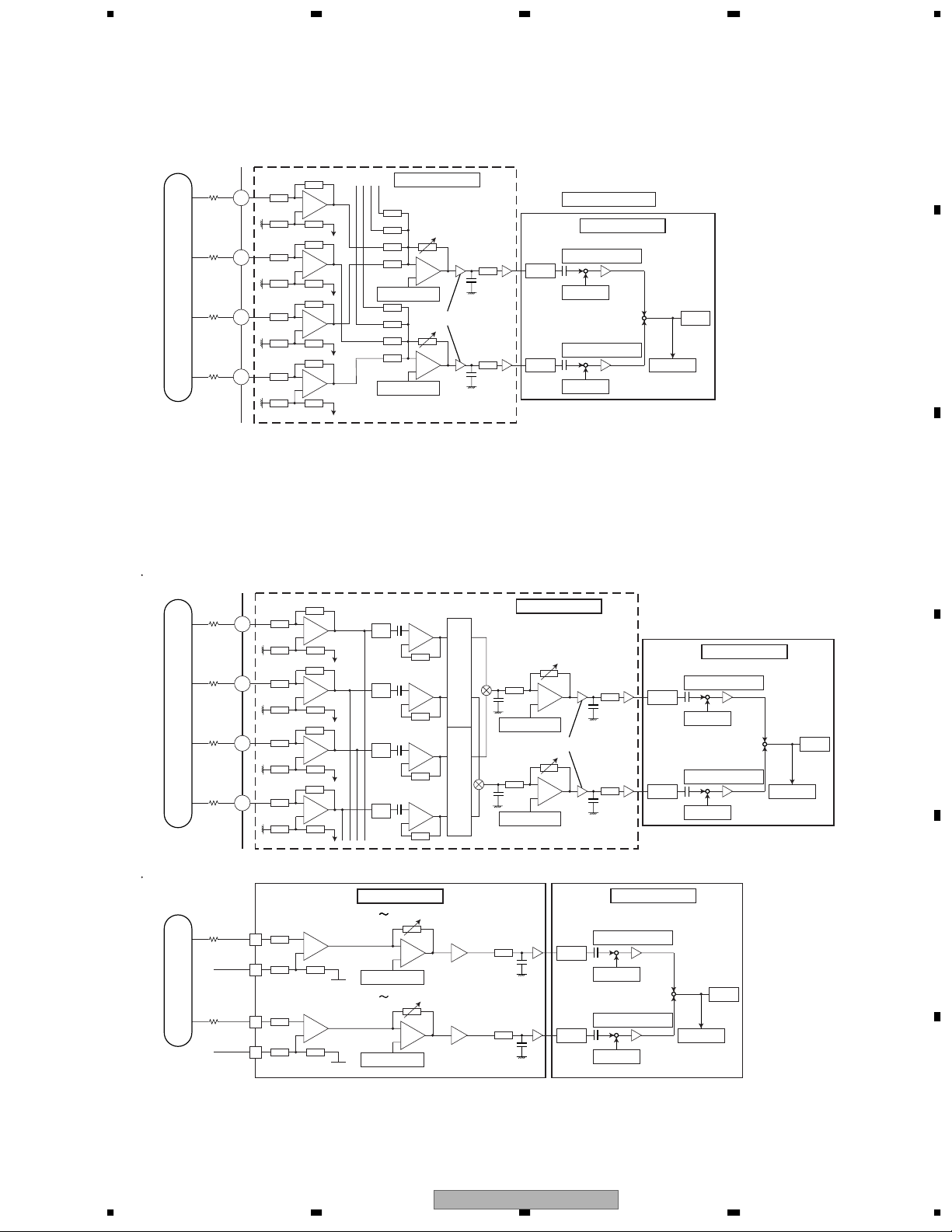
1.1.2 FE Generation Circuit
Focus Error (FE) Generation Circuit
Each of input signals from B1 to B4 which had been quartered by PU within the analog block is input to IC 1501
passing through the resistance and becomes a signal of FE
offset adjustment value. Then, the signal is AD-converted within the servo block and adds an offset cancel value
to become FE, generating a signal of FE=(FE+)
CN1101
VIN5
B1
B2
B3
B4
16
91
VIN6
15
92
VIN7
13
93
VIN8
11
94
–
+
–
+
OFFSET ADJ
–
+
–
+
OFFSET ADJ
-
(FE-).
Analog block
–
+
x1 or x4
–
+
+=
-
(B1+B3) and FE
1+(Pfbal/0x10000)
1+(Pfbal/0x10000)
+
FE
Pfepofs
1-(Pfbal/0x10000)
-
FE
Pfenofs
Servo block
+
+
-=-
(B2+B4) after adding a focus
FE
–
Dfesv
A
B
1.1.3 TE Generation Circuit
Trackings Error (TE) Generation Circuit
For DVD, TE is generated, with the application of a phase contrast method, from the phase difference of (B2+B4)
and (B1+B3). For CD, TE is generated, with the application of a 3-beam method, by sending the signal to the
variable amp set for the tracking offset adjustment via outer-attached resistance and then by AD-converting it to
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
-
C.
VHALF
VHALF
+
EQ
–
+
EQ
–
+
EQ
–
+
EQ
–
Analog block
-
6dB 15dB(3dB STEP)
0dB/12dB
–
+
OFFSET DAC
-
6dB 15dB(3dB STEP)
0dB/12dB
–
+
OFFSET DAC
PC
PC
G
G
Analog block
OFFSET ADJ
OFFSET ADJ
30kHz
30kHz
–
+
x1 or x4
–
+
1+(Pfbal/0x10000)
+
TE
1-(Pfbal/0x10000)
-
TE
Servo block
+
Pfepofs
+
Pfenofs
1+(Pfbal/0x10000)
+
TE
1-(Pfbal/0x10000)
-
TE
–
+
Pfepofs
+
Pfenofs
Dfesv
Servo block
TE
–
TE
Dfesv
make the formula of TE=A
DVD (TE from phase difference)
CN1101
VIN1
16
B1
B2
B3
B4
95
VIN2
15
96
VIN3
13
97
VIN4
11
98
CD (3-beam TE)
CN1101
17
A
VIN9
20kΩ
VREFH
10
C
VIN10
VREFH
20kΩ
C
D
E
56
CX-3078
F
7
8
3
1234
1.2 Servo Block (MN35103UB, MN35104UB:IC1501)
Servo block performs focus, tracking, servo control for traverse, spindle motor control and seek control.
A
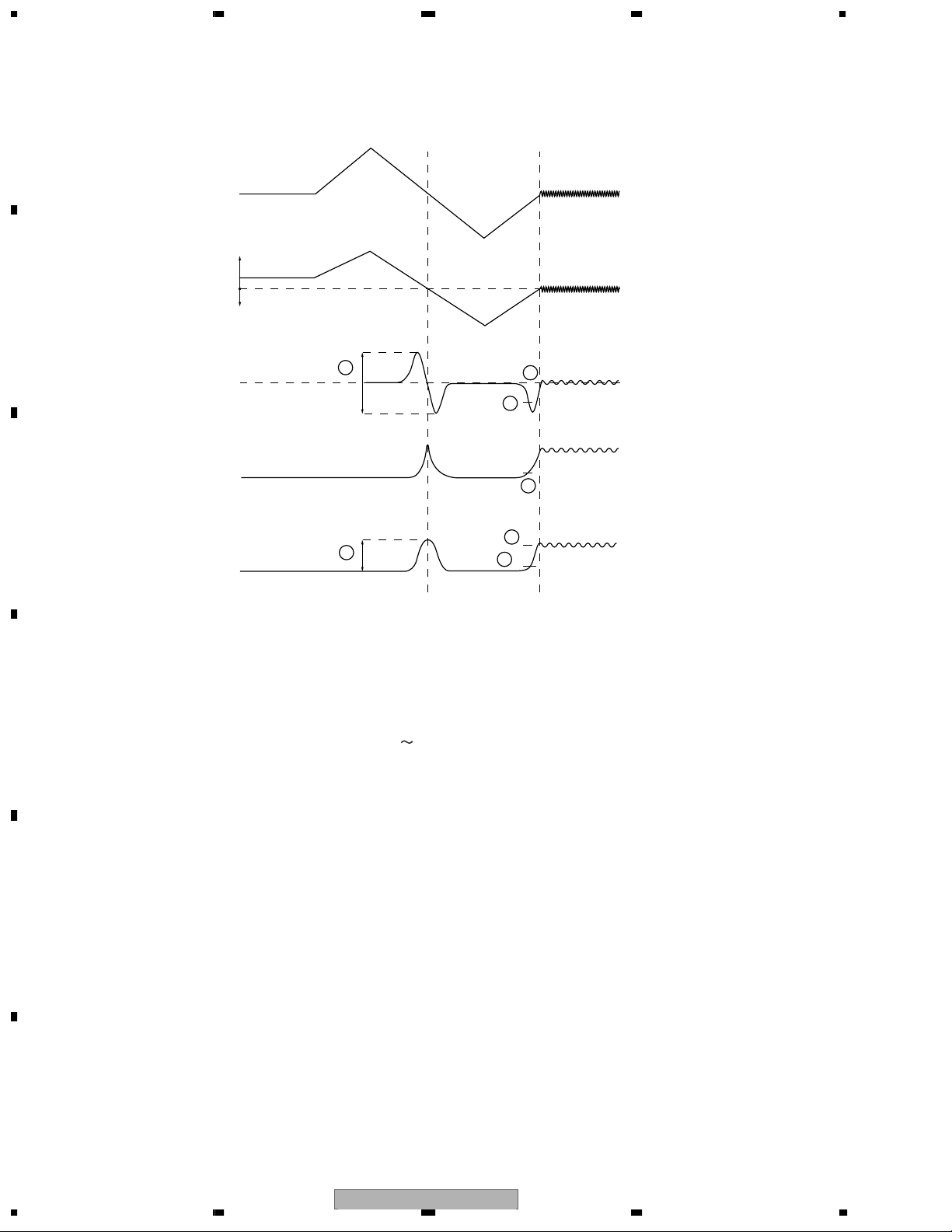
1.2.1 Focus Close
FODRV
Far from disc
Lens
B
C
Close to disc
FE
RFENV
AS
1
2
5
4
7
6
3
VHALF
Focal point
After issuing the focus close command, the following processes are taken for both DVD and CD.
1. Measure and optimize signal levels
First drive PU lens far from the disc and then drive closer to the disc. At the focal point met in the process of
this move, measure signal levels of FE, AS and RFENV respectively, and optimize their levels for FE and AS
(1 & 2 in the above figure).
D
2. Focus closing
Next, drive the lens far from the disc again to detect the closing levels of FE and AS.
Then activate focus loop filter for closing focus (3 6).
3. Check closing
Check the closing with signal levels of AS and RFENV (6 & 7).
Focus search in test mode can check the signal levels and focus drive voltages for FE, AS and RFEV.
1.2.2 Tracking Close
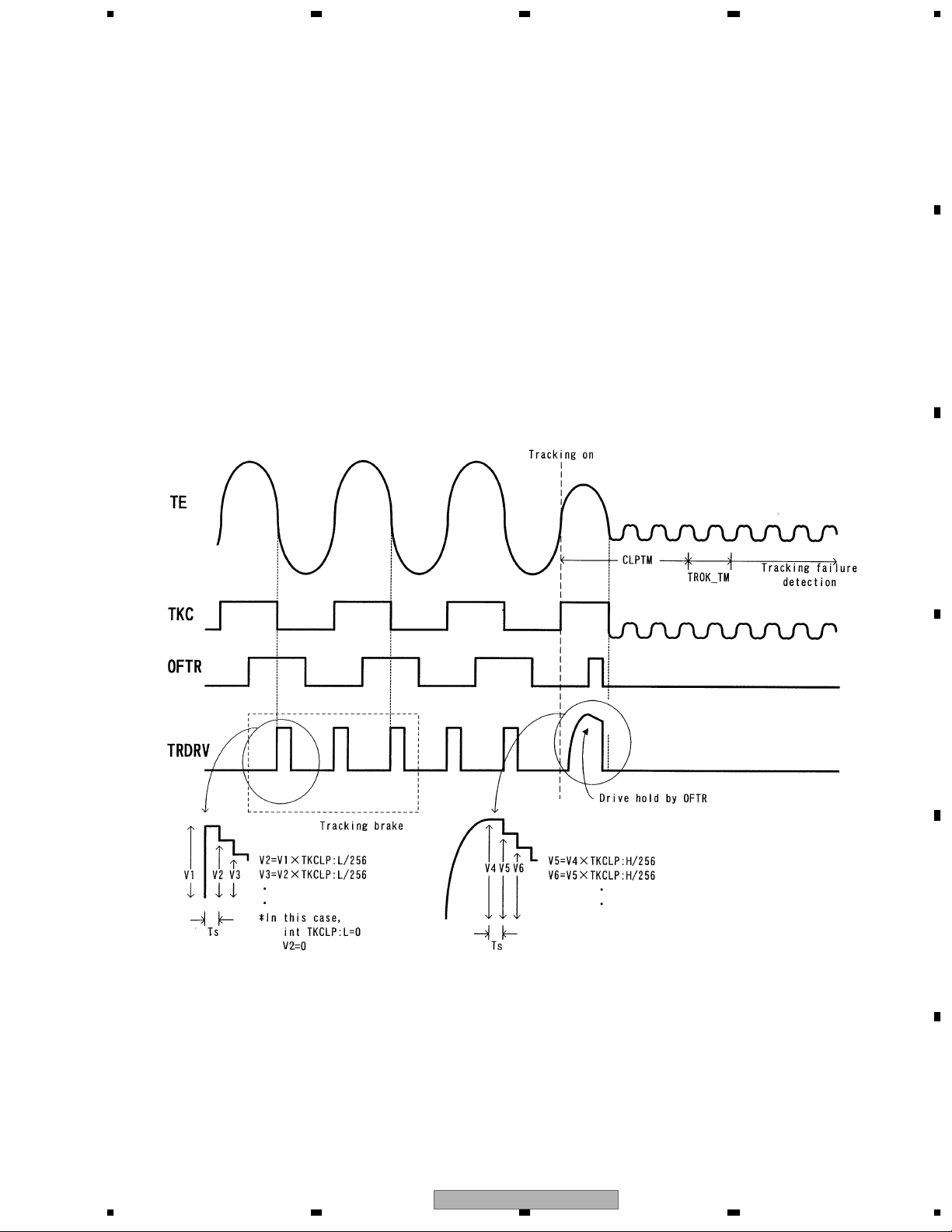
After issuing the tracking close command, the following processes are taken for both DVD and CD
1. Tracking brake
Measure one half cycle of the tracking cross and if the cycle is within the range of designation, output the brake
E
F
pals.
Output direction of brake pals is determined by the phase relations of OFTR and TKC (TE's binarization) signals.
After confirming that the swing of lens against disc is controlled, the brake stops and the closing begins. If the
closing condition is not met within 10msec. after outputting brake, the brake stops and the closing begins.
2. Tracking closing
Process the tracking drive hold with OFTR signal.
3. Check closing
Check whether or not the track jump does not exceed the designated number within the designated term.
Closing check will be time-out at 20msec. Retry using a command from the microcomputer.
1234
CX-30784
5678
1.2.3 Track Jump
The system selects from three types of methods; i.e. interval jump, multi jump and traverse seek,
according to the target number of moving tracks.
1. Interval Jump
The detailed seek is capable due to the execution of repetitive one-track jumps.
It is used when approaching to the target track or seek-operating to an adjacent track.
2. Multi Jump
It counts both edges of the track cross signal TKC and moves for designated number of track counts.
3. Traverse Seek
It controls the movement speed by measuring the time of the track cross signal TKC and manages the
vibration of pickup generated upon movement to the minimum.
Types of target number of moving jumps illustrating the jump switch setting for both DVD and CD
A
DVD
1-10 Interval Jump
11-100 Multi Jump
101-500 Combination of Multi Jump and Interval Jump
Over 501 Traverse Seek
The waveforms of track jumps are shown in the next page.
CD
1-10 Interval Jump
11-32 Multi Jump
33-500 Combination of Multi Jump and Interval Jump
Over 501 Traverse Seek
B
C
D
56
CX-3078
E
F
7
8
5
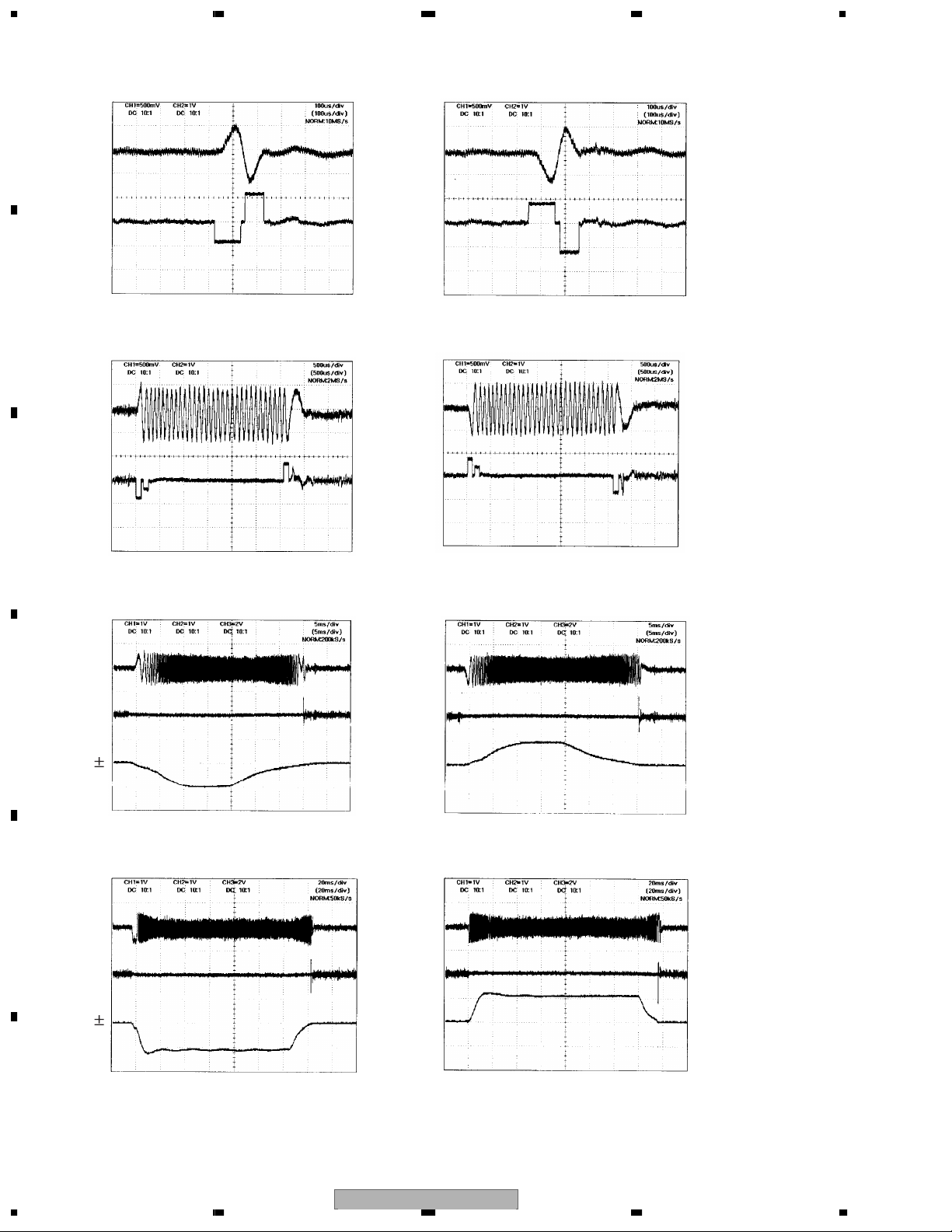
1234
Interval Jump (1 Track)
Outer Jump Inner Jump
A
TE
TD
B
Multi Jump (32 Track)
Outer Jump Inner Jump
TE
TD
C
Traverse Seek (501 Track)
Outer Jump Inner Jump
TE
D
TD
CO
Traverse Seek (5000 Track)
Outer Jump Inner Jump
E
TE
TD
CO
F
CX-30786
1234
5678
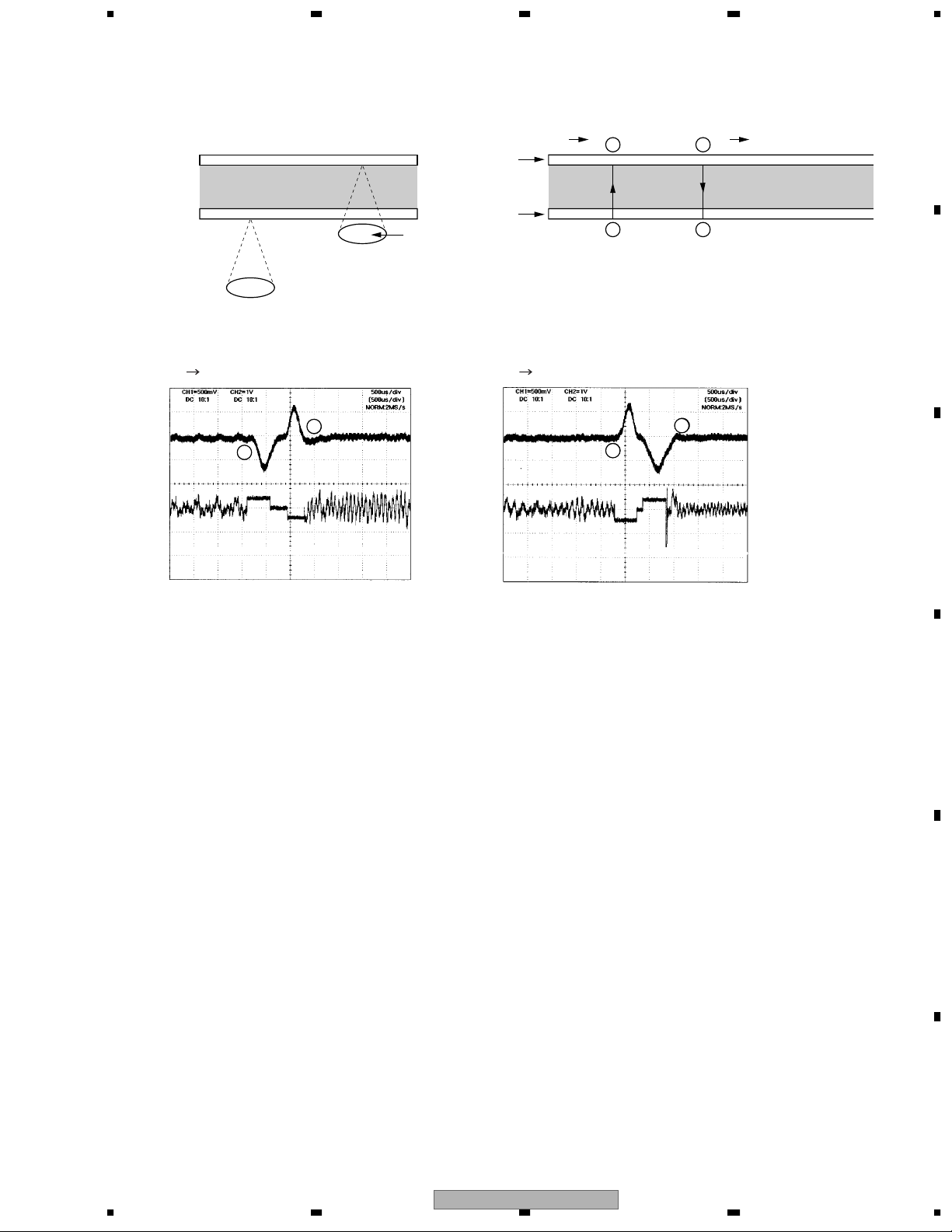
1.2.4 Focus Jump
Focus jump is a function corresponding to the single-sided or both-sided two-layers.
Seen from the object lens, a forward layer is called 0 Layer (L0) and a farther one is called 1 Layer (L1).
A
(1 Layer)
(0 Layer)
L1
L0
object lens
The waveforms of focus jump are shown below.
The waveforms of focus jump
L0 L1
FE
A
B
FD
L1
L0
L1 L0
L0 L1
B C
A D
D
C
L1 L0
B
C
The flow of focus jump is shown below
1. Open tracking at the layer during play.
2. Issue a command to execute jump to the target layer.
3. At the jumped layer, replay by closing the tracking.
Also, the processes when issuing a jump command are as follows
1. Accelerate the lens to the target layer until FE signal detects the acceleration completion level for focus jump.
However, if the time of acceleration time-out reaches before detecting the acceleration completion level,
the acceleration will compulsively stop.
2. Move lens with inertia instead of outputting the drive voltage until FE signal detects the deceleration initiation
level.
3. Decelerate lens for the duration from detection of the deceleration initiation level to the deceleration
completion level.
However, if the time of deceleration time-out reaches before detecting the deceleration completion level,
the deceleration will compulsively stop.
D
E
56
CX-3078
F
7
8
7
1234
1.3 Automatic Adjustment Function
This system totally automates the circuit adjustments.
A
The details of automatic adjustments are explained respectively as follows:
1.3.1 FE, TE, AS and Offset Cancel
Each of analog signals for FE, TE and AS generated at FEP is converted into a digital signal by A/D converter
inside servo block. Offset cancel is a function to cancel the input offset of A/D converter when the power is on.
1.3.2 VCO Gain Adjustment (VARI Adjustment)
It has a function to absorb dispersion of VCO gains among LSI solid by learning and to automatically adjust
VCO gains for the constant allocation. Lock VCO to 186- multiplied frequency against the input clock of crystal
criteria, read Frequency Control Value (FCNT), and then adjust VARI register so that the value becomes
equivalent to the target FCNT value.
B
1.3.3 FE Normalization Adjustment
After A/D-converting FE signal level at servo block which was measured at focus close, adjust it to 190LSB at
the digital equalizer input stage.
1.3.4 Spindle Gain Learning
Measure the duration from the halting state of spindle motor to the point reaching the fixed rotation speed for
Gain adjustment. Then adjust in the way of absorbing torque dispersion on spindle motor.
1.3.5 Tracking Balance (TBAL) Adjustment
C
By applying Newton-Raphson method, search for a balanced point at which DC offset becomes 0 by vibrating
lens toward track direction at the time of the focus close and the tracking open.
1.3.6 Tracking Error Amplitude Learning
After vibrating lens toward track direction at the time of the focus close and the tracking open to A/D-convert
the amplitude level to ADSC, adjust it to 190LSB at the digital equalizer input stage
1.3.7 Focus Balance (FBAL) Adjustment
Adjust the focus position so that RFENV becomes maximum at the tracking close.
1.3.8 Focus Gain Adjustment and Tracking Gain Adjustment
D
Insert disturbance to servo loop at the tracking close and adjust to a target gain intersection.
1.3.9 AS Normalization Adjustment
After measuring AS signal levels for the designated number of samplings at the tracking close to A/D-convert
by ADSC, the precise adjustment is made to set 64LSB at the digital equalizer input stage.
E
F
1234
CX-30788
 Loading...
Loading...