Philips UCB1100HL-X3C, UCB1100BE Datasheet

UCB1100
Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1996 Apr 09
1998 May 08
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Version 1.2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
Version 1.2
2
1998 May 08
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The UCB1100 is a single chip, integrated mixed signal audio and
telecom codec. The single channel audio codec is designed for
direct connection of a microphone and speaker. The built-in telecom
codec can directly be connected to a DAA and supports high speed
modem protocols. The incorporated 10 bit analogue to digital
converter and the touch screen interface provides complete control
and readout of a connected 4 wire resistive touch screen. The 10
additional general purpose I/O pins provides programmable inputs
and/or outputs to the system.
The UCB1100 has a serial interface bus (SIB) intended to
communicate to the system controller. Both the codec input and
output data and the control register data is multiplexed on this SIB
interface.
APPLICATIONS
•Personal Intelligent Communicators
•Personal Digital Assistants (PDA)
•Screen phones
•Smart Phone and smart Fax
•Intelligent Communicators
KEY FEATURES
•48-pin LQFP (SOT313-2) small body SMD package and low
external component count result in minimal PCB space
requirement.
•A 12-bit sigma delta audio codec with programmable sample rate,
input and output voltage levels, capable of connecting directly to
speaker and microphone, including digitally controlled mute,
loopback and clip detection functions
•A 14-bit sigma delta telecom codec with programmable sample
rate, including digitally controlled input voltage level, mute,
loopback and clip detection functions. The telecom codec is
intended for direct connection to a DAA (digital access
arrangement) and includes a built-in sidetone suppression circuit.
•A complete 4 wire resistive touch screen interface circuit
supporting position, pressure and plate resistance measurements.
•A 10-bit successive approximation ADC with internal track and
hold circuit and analogue multiplier for touch screen readout and
monitoring of four external high voltage (7.5V) analogue voltages.
•A high speed, 4 wire serial interface data bus (SIB) for
communication to system controller.
•A 3.3V supply voltage and built in power saving modes make the
UCB1100 optimal for portable and battery powered applications.
T ABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
APPLICATIONS 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
KEY FEATURES 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TABLE OF CONTENTS 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.0 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.0 ORDERING INFORMATION 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.0 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.0 DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.0 PINOUT 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 PINLIST 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1 AUDIO CODEC 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1.1 AUDIO INPUT SPECIFICATIONS 10. . . . . . . .
6.1.2 AUDIO OUTPUT SPECIFICATIONS 11. . . . . . .
6.2 TELECOM CODEC 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.2.1 TELECOM INPUT SPECIFICATIONS 14. . . . .
6.2.2 TELECOM OUTPUT SPECIFICATIONS 15. . .
6.3 TOUCH SCREEN MEASUREMENT MODES 16. . . .
6.3.1 POSITION MEASUREMENT 16. . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.2 PRESSURE MEASUREMENT 16. . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.3 PLATE RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT 16. . .
6.4 TOUCH SCREEN INTERFACE 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.4.1 TOUCH SCREEN SPECIFICATIONS 18. . . . .
6.5 10 BIT ADC. 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.5.1 SPECIFICATION OVERVIEW 21. . . . . . . . . . . .
6.6 ON CHIP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.6.1 SPECIFICATION OVERVIEW 21. . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7 SERIAL INTERFACE BUS 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7.1 SIB DATA FORMAT 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7.2 CODEC DATA TRANSFER 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7.3 CONTROL REGISTER DATA TRANSFER 26.
6.7.4 AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 27. . .
6.8 GENERAL PURPOSE I/Os 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.9 INTERRUPT GENERATION 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.10 RESET CIRCUITRY 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7.0 MISCELLANEOUS 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7.1 POWER ROUTING STRATEGY 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8.0 CONTROL REGISTER OVERVIEW 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9.0 PACKAGE OUTLINES 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9.1 PACKAGE OUTLINE LQFP48 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10.0 DEFINITIONS 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
3
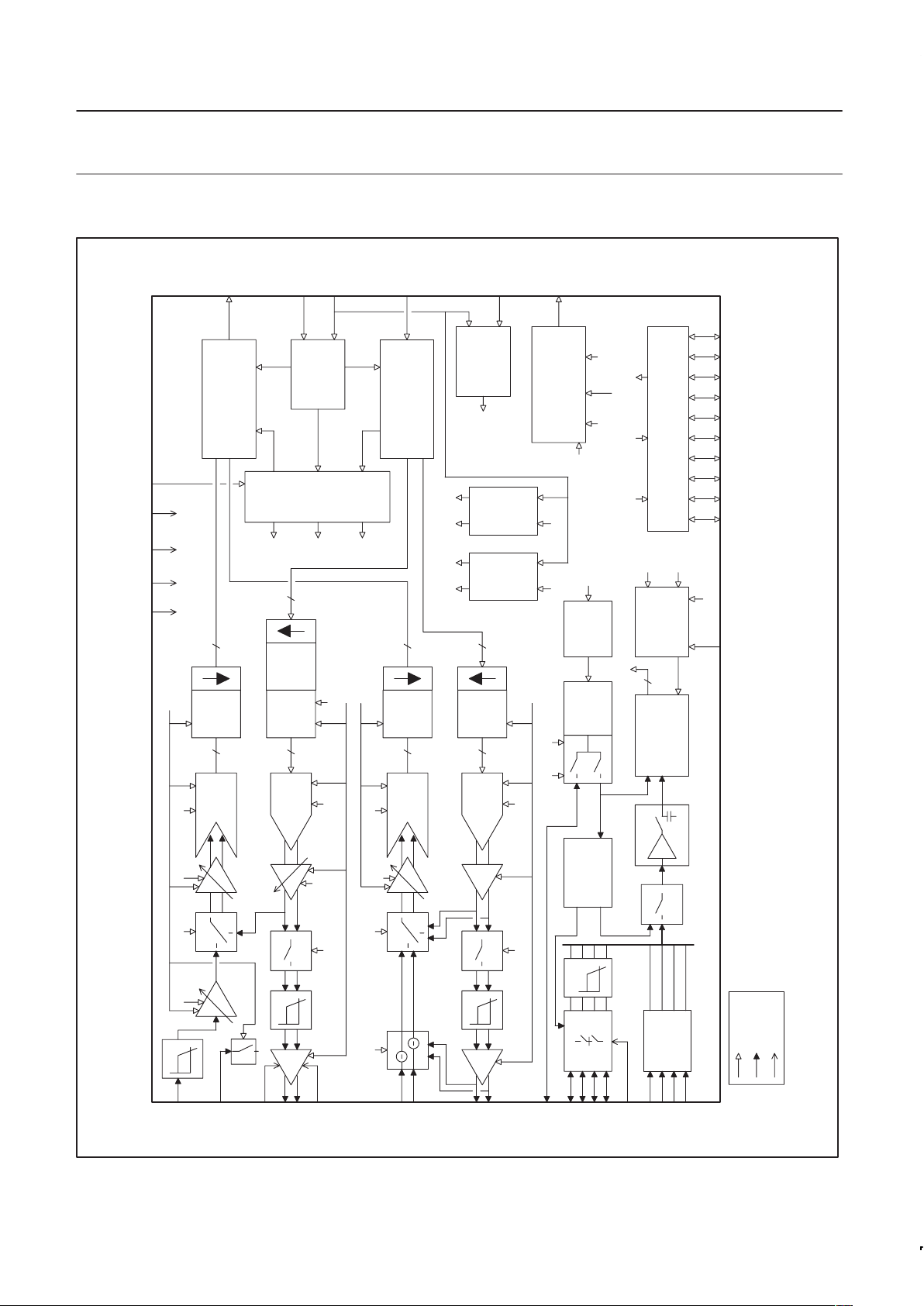
1.0 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
vdda2
vssa2
tinp
tinn
tsmx
tspy
tsmy
vssa3
ad0
ad1
ad2
ad3
switched
voltage
dividers
touch screen
switch matrix
vrefbyp
toutp
toutn
mux
9 to 1
touch screen
bias voltage
mute
echo on loopback
mux
attenuation
1 bit ADC
effect
4 bit DAC
effect
4
64fs
digital
noise
shaper
telecom output enable
4
64fs
digital
decimation
filter
14
fs
14
fs
supply pin
analog pin
digital pin
sample
frequency
divider
divaud[0:6]
fsa 64fsa
sample
frequency
divider
divtel0:6]
fst 64fst
track & hold
reference
voltage
10 bit ADC
TELECOM CODEC
10
to external register 11
side tone suppression
ADC start
stop logic
adcsync
adc_sync_ena
power
control
eanble data
for all
analog blocks
adc
start
sync
enable
io0 io1 io2 io3 io4 io5 io6 io7 io8 io9
Programmable IO pin block
IOmode[0:9] IOwdat[0:9] IOrdat[0:9]
interrupt data
from other blocks
rising_edge_ena[0:15]
clear_interrupt[0:15]
falling_edge_ena[0:15]
Interrupt
controller
irqout
reset
stretcher
internal
reset
nreset
serial bus
decoder
sibdin
serial bus
controller
sibclk
sibsync
serial bus
encoder
sibdout
external
reference
external
filter
control data registers
to all other analog and digital blocks
test
spkrp
spkrn
mute
4 bit DAC
64fsa
4
64fs
digital
volume
control
audio_output_enable
12
fs
telecom input enable
digital
noise
shaper
attn[4,5]
attn[0,3]
loopback
mux
gain[0,2]
1 bit ADC
64fsa
1
64fs
digital
decimation
filter
12
fs
AUDIO CODEC
audio_input_enable
gain[3,4]
vssa1
micgnd
micp
2xVddd2xVssdVdda1Vssa1
SN00126
Figure 1. Block Diagram of the UCB1100

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
4
2.0 ORDERING INFORMATION
ÁÁÁÁ
Á
DESCRIPTION
БББББ
Á
ORDERING
CODE
ÁÁÁ
Á
PACKAGE
DRAWING
ÁÁÁÁ
Á
Plastic low profile
quad flat package;
48 leads
БББББ
Á
UCB1100LP/X3
ÁÁÁ
Á
SOT313-2
3.0 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN MAX UNIT
V
DDMAX
Supply voltage –0.5 5.0 V
V
IMAX
DC input voltage, except AD0–3 inputs –0.5 VDD+0.5 V
V
ADMAX
DC input voltage AD0–3 inputs –0.5 8.5 V
V
OMAX
DC output voltage –0.5 VDD+0.5 V
I
IKMAX
DC diode input current, all inputs 10 mA
I
OKMAX
DC diode output current 10 mA
I
OLMAX
Continuous output current, digital outputs 4 mA
T
stg
Storage temperature –55 150 °C
NOTES:
1. Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and
functional operation of the device at these or any conditions other than those described in the Absolute Maximum Rating section of this
specification is not implied.
2. This product includes circuitry specially designed for the protection of its internal devices from damaging ef fects of excessive static charge.
Nonetheless, it is suggested that conventional precautions be taken to avoid submitting the UCB1100 to conditions exceeding the maximum
ratings.
3. Parameters are valid over the operating ambient temperature unless otherwise specified. All voltages are with respect to the V
SSD
pin,
unless otherwise noted.
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
5
4.0 DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
T
amb
= 0°C to 70°C, V
SSD
= V
SSA1
= V
SSA2
= V
SSA3
= 0V , sibclk = 10MHz, audio_divisor = 12, telecom_divisor = 40.
Voltage with respect to the V
SSD
pin, unless otherwise specified.
LIMITS
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
NOTES
MIN TYP MAX
UNIT
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
V
DDA1
analogue supply voltage (excl.speaker driver) 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
V
DDA2
analogue supply voltage (speaker driver only) 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
V
SSA2
analogue ground voltage wrt. V
SSD
–0.4 0 0.4 V
V
SSA3
analogue ground voltage wrt V
SSD
–0.4 0 0.4 V
I
DDD
digital supply current,
Note 1
full functionality 19 mA
only audio codec activated 17 mA
only telecom codec activated 19 mA
only touch screen activated 15 mA
only adc activated 15 mA
no functions activated, sibclk stopped 10 µA
I
DDA1
analogue supply current,
Note 1, Note 2
full functionality 3.8 mA
only audio codec activated 1.5 mA
only telecom codec activated 1.7 mA
only touch screen activated 0.4 mA
only adc activated 0.5 mA
no analogue functions activated <10 µA
I
DDA2
total speaker driver supply current
Note 1, Note 2
full functionality 0.2 mA
only audio codec activated 0.2 mA
only telecom codec activated 10 µA
only touch screen activated 10 µA
only adc activated 10 µA
no analogue functions activated 10 µA
V
TSCB
touch screen bias voltage 1.8 V
I
TSCB
maximum touch screen bias current 10 mA
V
ADFS
full scale voltage ad0–ad3 inputs 7.5 V
V
TSFS
full scale input touch screen inputs 7.5 V
V
IL
input low voltage –0.5 0.3*V
DDD
V
V
IH
input high voltage 0.7*V
DDD
V
DDD
+0.5 V
V
OL
output low voltage IOL=2mA 0.2*V
DDD
V
V
OH
output high voltage IOH=2mA 0.8*V
DDD
V
f
SIBCLK
clock frequency 0 10 15 MHz
T
amb
Operating Ambient Temperature 0 70 °C
NOTES:
1. Indicative value only. Value will be frozen following silicon measurements.
2. Excluding connected touch screen and speaker load currents.

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
6
5.0 PINOUT
io3
io2
io1
io0
vddd
not used
tspx
tsmy
tsmx
tspy
vssa3
ad0
vddd
io6
io5
io4
not used
irqout
sibdin
sibclk
sibdout
sibsync
nreset
vssd
io7
io8
io9
adcsync
vssd
not used
vssa2
spkrn
sprkp
vdda2
toutp
toutn
test
tinn
tinp
vrefbyp
vdda1
vssa1
not used
micgnd
micp
ad3
ad2
ad1
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
4847464544434241403938
37
1314151617181920212223
24
UCB1100
LQFP48
TOP VIEW
SN00127
Figure 2. LQFP48 (SOT313-2)
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
7
5.1 Pinlist
PINNING
RESET
SYMBOL
LQFP48
PIN TYPE
STATE
DESCRIPTION
NOTE
vddd 32, 48 supply digital supply
vssd 5, 37 ground digital ground 1
vdda1 17 supply analogue supply
vssa1 18 ground analogue ground 1
vdda2 10 supply analogue speaker driver supply
vssa2 7 ground analogue speaker driver ground
vssa3 26 ground touch screen switch matrix ground
sibclk 41 CMOS input SIB serial interface master clock
sibdin 42 CMOS input SIB data input
sibdout 40 CMOS output ‘0’ / Hi-Z SIB data output 2
sibsync 39 CMOS input SIB synchronization
irqout 43 CMOS output
active-High
‘0’ interrupt output
micp 21 analogue input Hi-Z microphone signal input
micgnd 20 analogue input Hi-Z microphone ground switch input
sprkp 9 analogue output Hi-Z positive speaker output 3
spkrn 8 analogue output Hi-Z negative speaker output 3
tinp 15 analogue input Hi-Z positive telecom codec input 3
tinn 14 analogue input Hi-Z negative telecom codec input 3
toutp 11 analogue output Hi-Z positive telecom codec output 3
toutn 12 analogue output Hi-Z negative telecom codec output 3
ad0–3 25–22 analogue input Hi-Z analogue high voltage inputs
tspx 30 analogue IO Hi-Z positive X-plate touch screen
tsmx 28 analogue IO Hi-Z negative X-plate touch screen
tspy 27 analogue IO Hi-Z positive Y-plate touch screen
tsmy 29 analogue IO Hi-Z negative Y-plate touch screen
adcsync 4 digital input adc synchronization pulse input
vrefbyp 16 analogue IO Hi-Z external reference voltage input, external filter connection
io0–9 33–36,
45–47,
1–3
CMOS IO input general purpose IO pins
nreset 38 CMOS input
active-Low
asynchronous reset input
test 13 CMOS input ‘0’ test mode protection 4
not used 6, 19,
31, 44
not connected pins
NOTES:
1. The vssd and vssa1 pins are connected to each other within the UCB1100.
2. The first 64 bits of the sib frame will be ‘0’, the remaining bits in the sib frame will be Hi-Z.
3. The spkrp/spkrn, tinp/tiln and toup/toutn are dif ferential pairs.
4. The test pin contains a internal pull down. This pin should be connected to vssd in normal mode of the UCB1100.

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
8
6.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The UCB1100 consists of several analogue and digital sub circuits
which can be programmed via the Serial Interface Bus (SIB). This
enables the user to set the UCB1100 functionality according actual
application requirements.
6.1 Audio codec
The audio codec contains an input channel, built up from a 64 times
oversampling sigma delta analogue to digital converter (ADC) with
digital decimation filters and a programmable gain microphone
preamp. The output path consists of a digital up sample filter, a 64
time oversampling 4 bit digital to analogue converter (DAC) circuit
followed by a speaker driver, capable of driving directly a low
impedance bridge tied (BTL) speaker. The output path features
digitally programmable attenuation and a mute function. The audio
codec also incorporates a loopback mode, in which codec output
path and the input path are connected in series.
The audio sample rate is derived from the SIB interface clock pin
(SIBclk) and is programmable through the SIB interface. The audio
sample rate is given by the following equation:
Fsa
(2 *
Fsibclk
)
(64 *
audio_divisor
)
(5
audio_divisor
128)
For example, a serial clock of 10 MHz, with a divisor of 14, results in
an audio sample rate of 22.321kHz. Both the rising and the falling
edges of the sibclk are used in case an odd audio_divisor is set.
Thus a 50% duty cycle of the sibclk signal is mandatory to obtain
time equidistant sampling with odd divisors.
The frequency response of the audio codec depends mainly on the
selected sample rate, since the bandwidth is limited in the down and
up sampling filters. These digital filters both contain several FIR and
IIR low pass filters and a DC removal filter (high pass filter). A 1st
order analogue anti aliasing filter is implemented at the input of the
microphone input to prevent aliasing in the adc path. A 3rd order
smoothing filter is implemented between dac and speaker driver
stage to reduce the spurious frequencies at the speaker outputs.
The audio codec input (=ADC) and output (= DAC) paths can be
enabled individually by setting the audio_adc and/or audio_dac bits
in the audio control register B. These enable bits operate both on
the associated analogue and digital functions, for optimal power
control of both the analogue and the digital parts.
vdda2
vssa2
spkrp
spkrn
mute
4 bit DAC
64fsa
4
64fs
digital
volume
control
audio_output_enable
attn[4,5]
attn[0,3]
loopback
mux
gain[0,2]
1 bit ADC
64fsa
1
64fs
audio_input_enable
gain[3,4]
vssa1
micgnd
micp
loop input
Sinc4
FIR
16
DC
removal
half band
WDF
2
half band
WDF
2
+3dB
round
up
12
fs
half band
FIR
2
round
up
half band
WDF
2
+3dB
2
DC
removal
12
fs
low pass
FIR
2
interpolator
loop input
noise
shaper
4
SN00128
Figure 3. Detailed Block Diagram Audio codec
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
9
micp
micgnd
vssa1
vdda1
micp
micgnd
vssa1
vdda1
UCB1100 UCB1100
‘Passive’ Microphone ‘Active’ Microphone
SN00129
Figure 4. Possible Microphone Connections
The UCB1100 audio codec input path accepts microphone signals
directly, only a DC blocking capacitor is needed, since the micp input
is biased around 1.4V . The ‘ground’ side of the microphone is either
connected to the analogue ground (vssa1) or to the micgnd pin of
the UCB1100. The latter will decrease the current consumption of
active microphones, since the micgnd pin is made Hi-Z when the
audio codec input path is disabled.
The full scale input voltage of the audio input path is programmable
in 1.5dB steps by setting the appropriate data in the
audio-input-gain
bits in the audio control register A.
A clip detection circuit will inform the user whenever the input
voltage exceeds the maximum input voltage. In that case the
clip
detect status
bit in audio control register B is set. An interrupt is
generated on the irqout pin of the UCB1100 whenever the
enable
audio
clip detect rising interrupt
or the
enable audio detect falling
edge interrupt
bit is set in the rising edge interrupt enable or falling
edge interrupt control register B is set.
analog attenuation
digital attenuation
0dB
24dB
48dB
0dB
21dB
24dB 48dB 69dB
programmed attenuation
SN00130
Figure 5. Analogue and Digital Attenuation Settings
Audio Output Path
The output level can be attenuated in 3dB steps down to -69dB. The
8 highest attenuation steps are implemented in the analogue
circuitry, while the two 24dB steps are implemented in the digital
domain. This preserves the ‘audio quality’ of the output signal at
lowest attenuation settings. The speaker driver is muted when the
audio-mute
bit in the audio control register B is set. The speaker
driver will remain activated in that case, however no signal is
produced by the speaker driver circuitry.
UCB1100 UCB1100 UCB1100
spkrp
spkrn
spkrp spkrp
spkrn spkrn
Bridge Tied
Speaker
Load
Single Ended Speaker Connections
SN00131
Figure 6. Possible Speaker Connections
The speaker driver is designed to directly drive a bridge tied load
(BTL). This yields the highest output power and it does not require
external DC blocking capacitors. The speaker driver also accepts
single ended connection of a speaker, in which case the maximum
output power is reduced to a quarter of the BTL situation.
Consequently this way of connecting the speaker to the speaker
driver reduces the power consumption of the speaker driver in the
UCB1100 by a factor of 2. Figure 6 shows possible ways to connect
a speaker to the UCB1100.
The audio input and output path are activated independently; the
input path is enabled when the
audio-input-enable
bit is set, the
output path is enabled when the
audio-output-enable
bit is set in the
audio control register B. This provides the user the means to reduce
the current consumption of the UCB1100 if one part of the audio
codec is not used in the application.
The audio codec has a loopback mode for system test purposes,
which is activated when the
audio_loopback enable
bit in the audio
control register B is set. This is an analogue loopback which
internally connects the output of the audio output path to the input of
the audio input path, (see Figure 3). In this mode the normal
microphone input is ignored, but the speaker driver can be operated
normally .
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
10
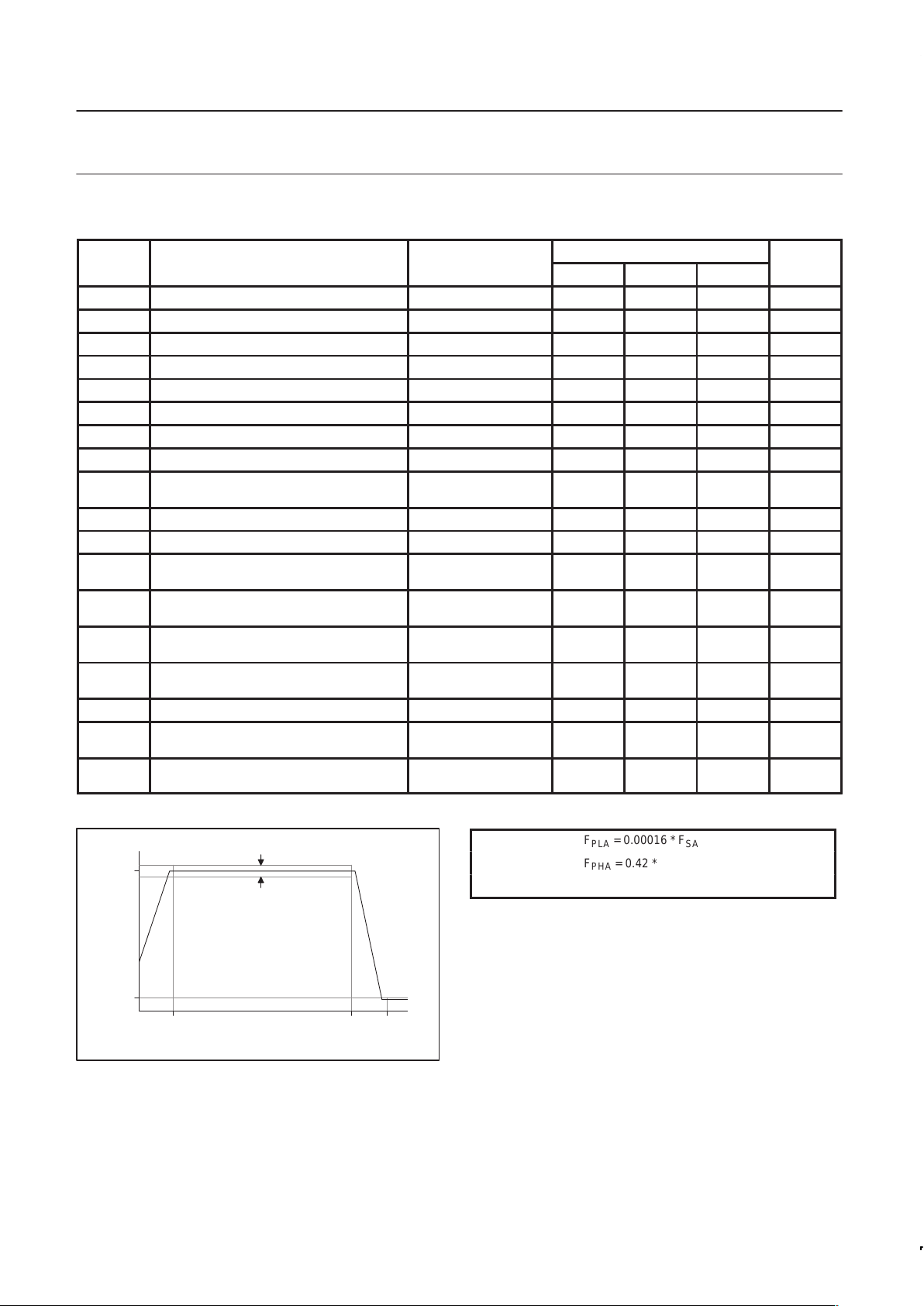
6.1.1 Audio Input Specifications
LIMITS
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNIT
F
SA
audio sample frequency 26 kHz
V
INAM
full scale input voltage 0 dB gain setting 0.28 V
pp
V
MICP
DC bias voltage micp input audio input path enabled 1.4 V
R
INPAI
input impedance audio input path enabled 25 kΩ
R
HINE
impedance micgnd to vssa1 audio input path enabled 100 Ω
G
SA
gain step size 1.3 1.5 1.7 dB
N
AGS
number of gain steps 32
G
mA
maximum gain 46.5 dB
G
EAR
gain error (accuracy of gain setting)
0 dB gain setting,
full scale input voltage
–1 0 1 dB
ROES
AI
resolution audio input 12 bit
DNA
AI
differential non linearity audio input ADC 0.9 LSB
THUD
AI
total harmonic distortion
0db input gain selected
0.28Vpp, 1kHz to micp
0.03 %
THD
MGAI
total harmonic distortion
46.5dB gain setting,
1mVpp, 1kHz to micp
0.1 %
SNR
AI
signal to noise ratio
audio input
0dB input gain selected
0.28Vpp, 1kHz to micp
65 dB
SNR
MGAI
signal to noise ratio
46.5dB gain selected
1mVpp, 1kHz to micp
50 dB
RIP
IA
pass band ripple F
PLAI
<Fsig < F
PHAI
0.5 dB
SBR
IA
stop band rejection
audio input
F
SHAI
<Fsig.<20kHz 70 dB
E
IA
out of band rejection
audio input
F > 20kHz t.b.f. mVrms
NOTE: Coding scheme for ADC output data is 2’s complement.
F
SHA
F
PHA
FREQUENCY (Hz)
F
PLA
RIP
IA
0dB
SBR
IA
SN00132
Figure 7. Audio Input Path Frequency Response
F
PLA
= 0.00016 * F
SA
F
PHA
= 0.42 * F
SA
F
SHA
= 0.6 * F
SA
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
UCB1 100Advanced modem/audio analog front-end
1998 May 08
11
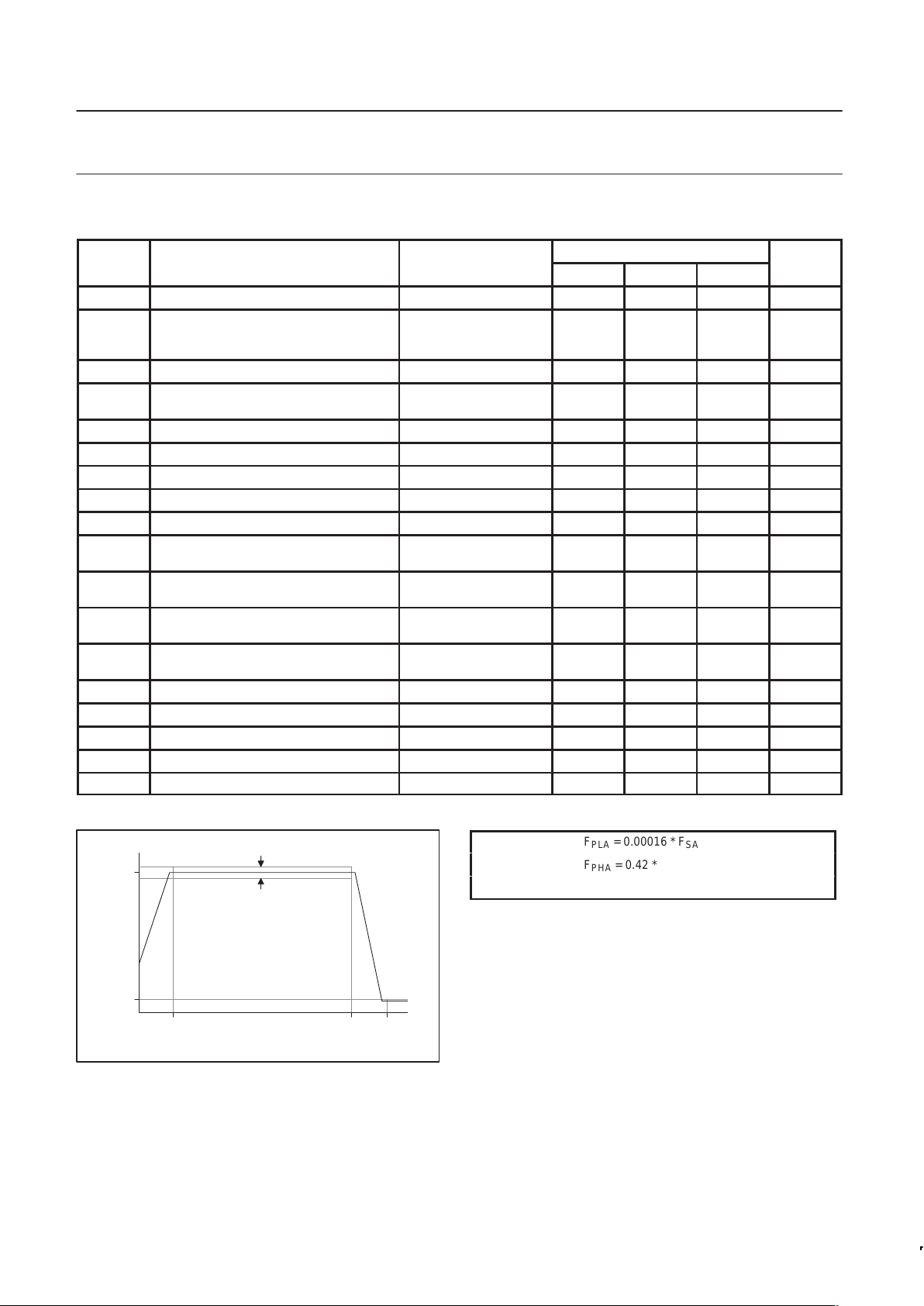
6.1.2 Audio Output Specifications
LIMITS
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNIT
V
OFFIA
offset error No signal applied to micp 0 LSB
V
OOA
full scale output voltage
0dB attenuation,
16ohm speaker
differential Spkrp–Spkrn
3.2 V
pp
V
OFFOA
offset error 16ohm speaker 50 mV
pp
V
SPK
DC bias voltage
spkrp and spkrn pin
Audio output path enabled 1.4 V
A
SOA
attenuation step size 2.8 3.0 3.2 dB
NSOA number of attenuation steps 24
A
MOA
maximum attenuation 69 dB
ROES
OA
resolution 12 bit
DNA
OA
differential non linearity DAC 0.9 LSB
THUD
OAS
total harmonic distortion
16Ω speaker
0dB attenuation
20Hz to 20kHz
0.5 2 %
THUD
OAH
total harmonic distortion
1kΩ headphone
0dB attenuation
20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth
0.03 %
SNR
OAS
signal to noise ratio
16Ω speaker
0dB attenuation
20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth
40 80 dB
SNR
OAH
signal to noise ratio,
1kHΩ headphone
0dB attenuation
20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth
65 80 dB
RIP
OA
pass band ripple F
PLAO
< Fsig <– F
PHAO
0.5 dB
F
SUOA
cut off frequency upper stop band 0.6 F
SA
SBR
OA
stop band rejection F
SHAO
<Fsig.<20kHz 70 dB
E
IOA
integrated out of band energy F > 20kHz 30 mVrms
Z
SPKR
speaker impedance 8 16 Ω
NOTE: Coding scheme for DAC input data is 2’s complement.
F
SHA
F
PHA
FREQUENCY (Hz)
F
PLA
RIP
OA
0dB
SBR
OA
SN00133
Figure 8. Audio Output Filter Frequency Response
F
PLA
= 0.00016 * F
SA
F
PHA
= 0.42 * F
SA
F
SHA
= 0.6 * F
SA
 Loading...
Loading...