INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8541
1 W BTL audio amplifier
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Feb 19
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
1998 Apr 01
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
1 W BTL audio amplifier TDA8541
FEATURES
• Flexibility in use
• Few external components
• Low saturation voltage of output stage
• Gain can be fixed with external resistors
• Standby mode controlled by CMOS compatible levels
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8541(T) is a one channel audio power amplifier
for an output power of 1 W with an 8 Ω load at a 5 V
supply. The circuit contains a BTL amplifier with a
complementary PNP-NPN output stage and standby/mute
logic. The TDA8541T comes in an 8 pin SO package and
the TDA8541 in an 8 pin DIP package.
• Low standby current
• No switch-on/switch-off plops
• High supply voltage ripple rejection
• Protected against electrostatic discharge
• Outputs short-circuit safe to ground, V
CC
and across the
APPLICATIONS
• Portable consumer products
• Personal computers
• Telephony.
load
• Thermally protected.
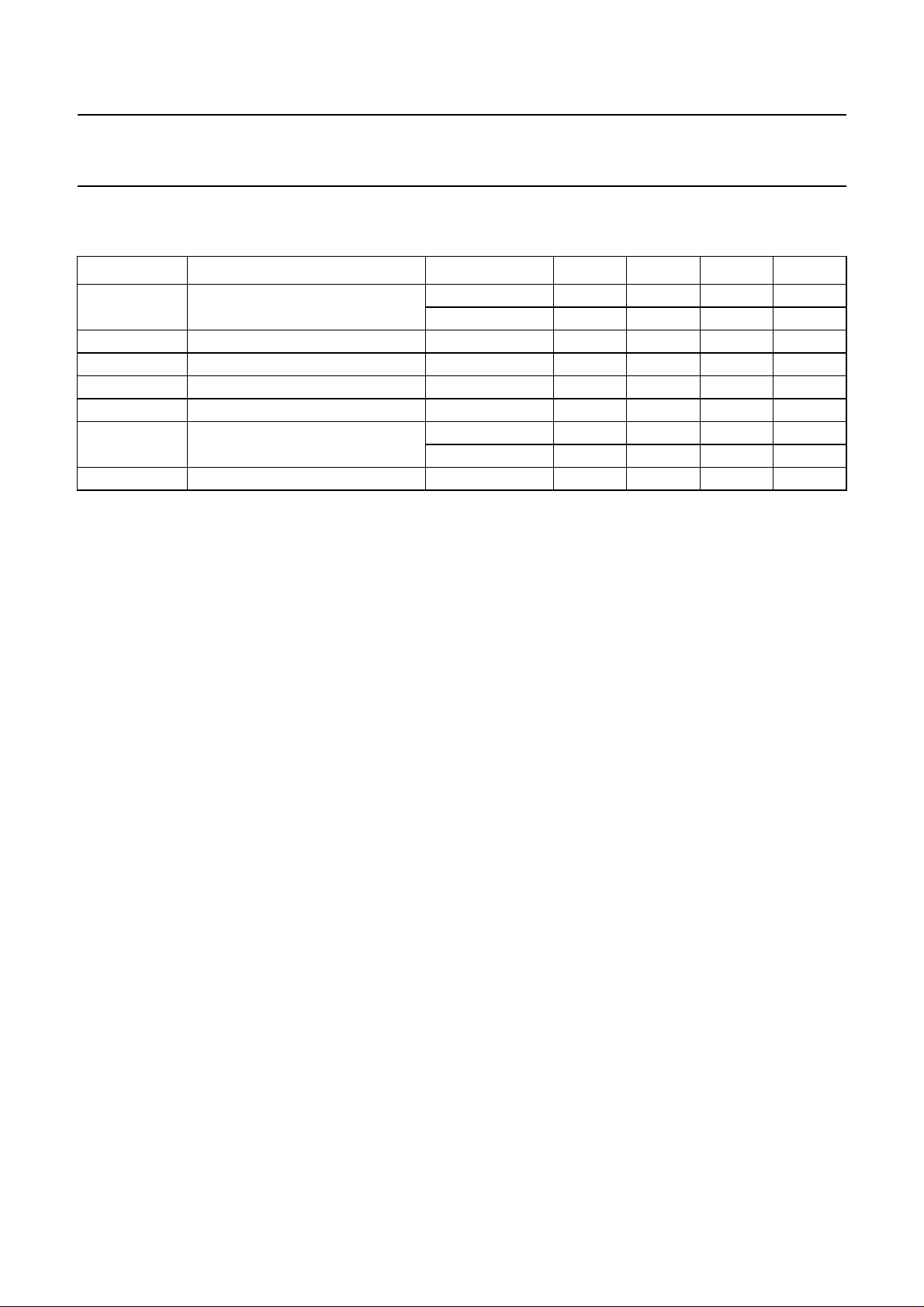
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
I
q
I
stb
P
o
THD total harmonic distortion P
supply voltage 2.2 5 18 V
quiescent current VCC=5V − 812mA
standby current −−10 µA
output power THD = 10%; RL=8Ω; VCC=5V 1 1.2 − W
= 0.5 W − 0.15 − %
o
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection 50 −−dB
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
TDA8541T SO8 plastic small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT96-1
TDA8541 DIP8 plastic dual in-line package; 8 leads (300 mil) SOT97-1
1998 Apr 01 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
1 W BTL audio amplifier TDA8541
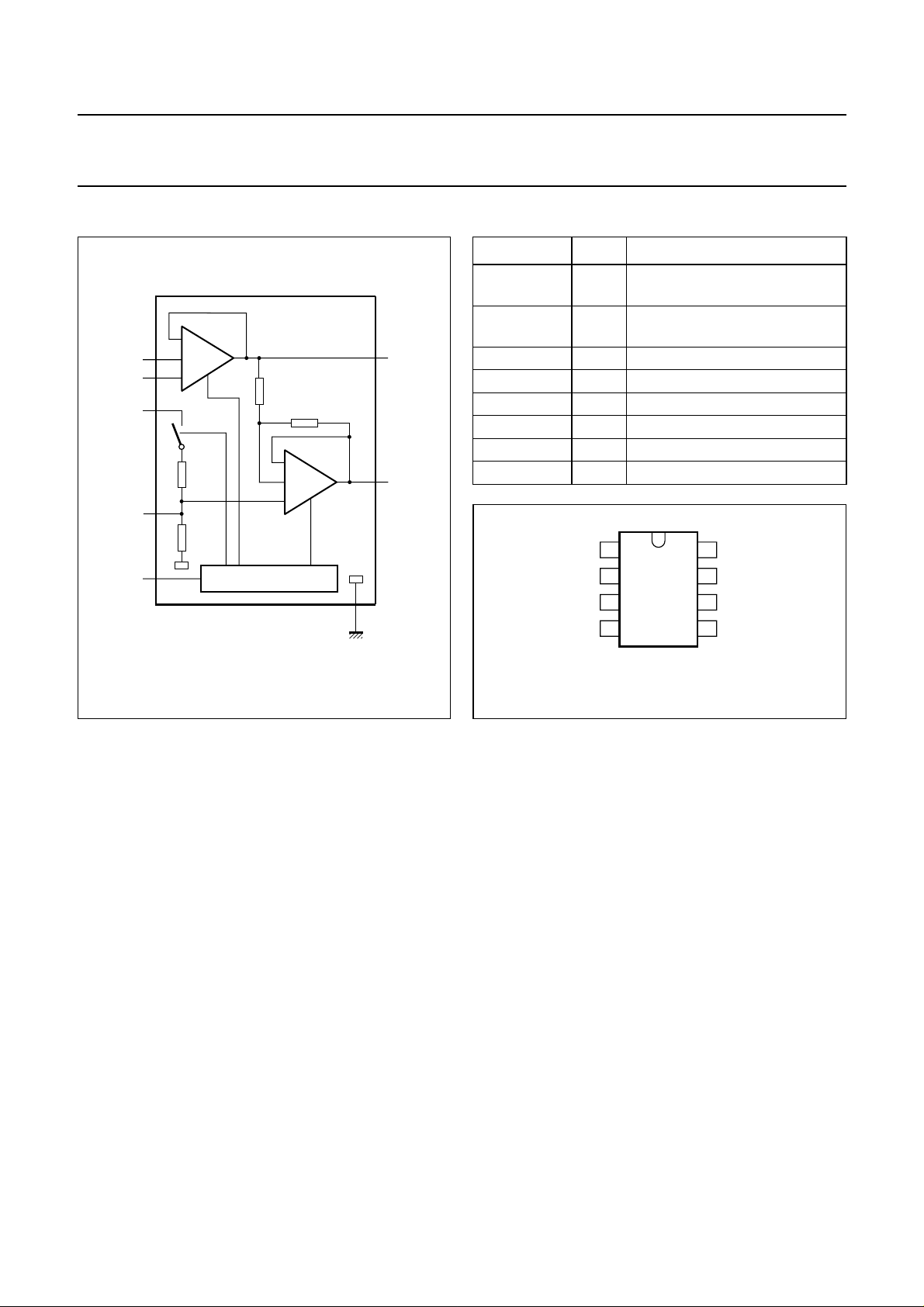
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, halfpage
−
4
IN−
IN+
V
CC
SVR
MODE
−
3
+
6
20 kΩ
2
20 kΩ
1
TDA8541
R
R
−
−
+
STANDBY/MUTE LOGIC
5
8
7
GND
OUT−
OUT+
MGB972
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
MODE 1 operating mode select
(standby, mute, operating)
SVR 2 half supply voltage, decoupling
ripple rejection
IN+ 3 positive input
IN− 4 negative input
OUT− 5 negative loudspeaker terminal
V
CC
6 supply voltage
GND 7 ground
OUT+ 8 positive loudspeaker terminal
handbook, halfpage
MODE
IN+
IN−
1
2
3
4
TDA8541
MGB971
OUT+
8
GNDSVR
7
V
6
CC
OUT−
5
Fig.1 Block diagram.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8541(T) is a BTL audio power amplifier capable
of delivering 1 W output power to an 8 Ω load at
THD = 10% using a 5 V power supply. Using the MODE
pin the device can be switched to standby and mute
condition. The device is protected by an internal thermal
shutdown protection mechanism. The gain can be set
within a range from 6 dB to 30 dB by external feedback
resistors.
Power amplifier
The power amplifier is a Bridge Tied Load (BTL) amplifier
with a complementary PNP-NPN output stage.
The voltage loss on the positive supply line is the
saturation voltage of a PNP power transistor, on the
negative side the saturation voltage of an NPN power
transistor. The total voltage loss is <1 V and with a 5 V
supply voltage and an 8 Ω loudspeaker an output power of
1 W can be delivered.
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
Mode select pin
The device is in standby mode (with a very low current
consumption) if the voltage at the MODE pin is
>(VCC− 0.5 V), or if this pin is floating. At a MODE voltage
level of less than 0.5 V the amplifier is fully operational.
In the range between 1.5 V and VCC− 1.5 V the amplifier
is in mute condition. The mute condition is useful to
suppress plop noise at the output, caused by charging of
the input capacitor.
1998 Apr 01 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
1 W BTL audio amplifier TDA8541
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
V
I
I
ORM
T
stg
T
amb
V
psc
P
tot
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
supply voltage operating −0.3 +18 V
input voltage −0.3 VCC+ 0.3 V
repetitive peak output current − 1A
storage temperature non-operating −55 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature −40 +85 °C
AC and DC short-circuit safe voltage − 10 V
total power dissipation SO8 − 0.8 W
DIP8 − 1.2 W
In accordance with
Handbook”
. The handbook can be ordered using the code 9397 750 00192.
“SNW-FQ-611-E”
. The number of the quality specification can be found in the
“Quality Reference
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th j-a
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air
TDA8541T (SO8) 160 K/W
TDA8541 (DIP8) 100 K/W
DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
CC
=5V; T
=25°C; RL=8Ω; V
amb
= 0 V; measured in test circuit Fig.3; unless otherwise specified.
MODE
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
I
q
I
stb
V
O
V
I
V
I
OUT+
, I
IN+
MODE
MODE
− V
IN−
OUT−
supply voltage operating 2.2 5 18 V
quiescent current RL= ∞; note 1 − 812mA
standby current V
MODE=VCC
−−10 µA
DC output voltage note 2 − 2.2 − V
differential output voltage offset −−50 mV
input bias current −−500 nA
input voltage mode select operating 0 − 0.5 V
mute 1.5 − V
standby V
input current mode select 0 < V
MODE<VCC
− 0.5 − V
CC
−−20 µA
− 1.5 V
CC
CC
V
Notes
1. With a load connected at the outputs the quiescent current will increase, the maximum of this increase being equal
to the DC output offset voltage divided by R
.
L
2. The DC output voltage with respect to ground is approximately 0.5 × VCC.
1998 Apr 01 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
1 W BTL audio amplifier TDA8541
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
=5V; T
CC
SYMBOL P ARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP . MAX. UNIT
P
o
THD total harmonic distortion P
G
v
Z
i
V
no
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection note 3 50 −−dB
V
o
Notes
1. Gain of the amplifier is 2 × R2/R1 in test circuit of Fig.3.
2. The noise output voltage is measured at the output in a frequency range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz (unweighted), with a
source impedance of R
3. Supply voltage ripple rejection is measured at the output, with a source impedance of RS=0Ω at the input.
The ripple voltage is a sine wave with a frequency of 1 kHz and an amplitude of 100 mV (RMS), which is applied to
the positive supply rail.
4. Supply voltage ripple rejection is measured at the output, with a source impedance of RS=0Ω at the input.
The ripple voltage is a sine wave with a frequency between 100 Hz and 20 kHz and an amplitude of 100 mV (RMS),
which is applied to the positive supply rail.
5. Output voltage in mute position is measured with an input voltage of 1 V (RMS) in a bandwidth of 20 kHz, so including
noise.
=25°C; RL=8Ω; f = 1 kHz; V
amb
= 0 V; measured in test circuit Fig.3; unless otherwise specified.
MODE
output power THD = 10% 1 1.2 − W
THD = 0.5% 0.6 0.9 − W
= 0.5 W − 0.15 0.3 %
o
closed loop voltage gain note 1 6 − 30 dB
differential input impedance − 100 − kΩ
noise output voltage note 2 −−100 µV
note 4 40 −−dB
output voltage in mute condition note 5 −−200 µV
=0Ω at the input.
S
1998 Apr 01 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
1 W BTL audio amplifier TDA8541
TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
Test conditions
Because the application can be either Bridge-Tied Load
(BTL) or Single-Ended (SE), the curves of each application
are shown separately.
The thermal resistance = 100 K/W for the DIP8 envelope;
the maximum sine wave power dissipation for
T
=25°C is:
amb
150 25–
---------------------100
For T
amb
150 60–
---------------------100
1.25 W=
=60°C the maximum total power dissipation is:
0.9 W=
.
.
BTL application
=25°C if not specially mentioned, VCC=5V,
T
amb
f = 1 kHz, RL=8Ω, Gv= 20 dB, audio band-pass
22 Hz to 22 kHz.
The BTL application diagram is shown in Fig.3.
The quiescent current has been measured without any
load impedance. The total harmonic distortion as a
function of frequency was measured with a low-pass filter
of 80 kHz. The value of capacitor C2 influences the
behaviour of the SVRR at low frequencies, increasing the
value of C2 increases the performance of the SVRR.
The figure of the mode select voltage (Vms) as a function
of the supply voltage shows three areas; operating, mute
and standby. It shows, that the DC-switching levels of the
mute and standby respectively depends on the supply
voltage level.
SE application
=25°C if not specially mentioned, VCC= 7.5 V,
T
amb
f = 1 kHz, RL=4Ω, Gv= 20 dB, audio band-pass
22 Hz to 22 kHz.
The SE application diagram is shown in Fig.13.
The capacitor value of C3 in combination with the load
impedance determines the low frequency behaviour.
The total harmonic distortion as a function of frequency
was measured with low-pass filter of 80 kHz. The value of
capacitor C2 influences the behaviour of the SVRR at low
frequencies, increasing the value of C2 increases the
performance of the SVRR.
General remark
The frequency characteristic can be adapted by
connecting a small capacitor across the feedback resistor.
To improve the immunity of HF radiation in radio circuit
applications, a small capacitor can be connected in
parallel with the feedback resistor (56 kΩ); this creates a
low-pass filter.
1998 Apr 01 6
 Loading...
Loading...