Philips TDA8540T-C2, TDA8540-C2 Datasheet

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of April 1993
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1995 Feb 06
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Philips Semiconductors
TDA8540
4 × 4 video switch matrix
1995 Feb 06 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4 × 4 video switch matrix TDA8540
FEATURES
• I2C-bus or non-I2C-bus mode (controlled by
DC voltages)
• S-VHS or CVBS processing
• 3-state switches for all channels
• Selectable gain for the video channels
• sub-address facility
• Slave receiver in the I2C mode
• Auxiliary logic outputs for audio switching
• System expansion possible up to 7 devices
(28 sources)
• Static short-circuit proof outputs
• ESD protection.
APPLICATIONS
• Colour Television (CTV) receivers
• Peritelevision sets
• Satellite receivers.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8540 has been designed for switching between
composite video signals, therefore the minimum of four
input lines are provided as requested for switching
between two S-VHS sources. Each of the four outputs can
be set to a high impedance state, to enable parallel
connection of several devices.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage 7.2 − 8.8 V
I
CC
supply current − 20 30 mA
I
SO
isolation ‘OFF’ state at f = 5 MHz 60 80 − dB
B 3 dB bandwidth 12 −−MHz
α
ct
crosstalk attenuation between
channels
60 70 − dB
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA8540 DIP20 plastic dual in-line package; 20 leads (300 mil) SOT146-1
TDA8540T SO20 plastic small outline package; 20 leads; body width 7.5 mm SOT163-1

1995 Feb 06 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4 × 4 video switch matrix TDA8540
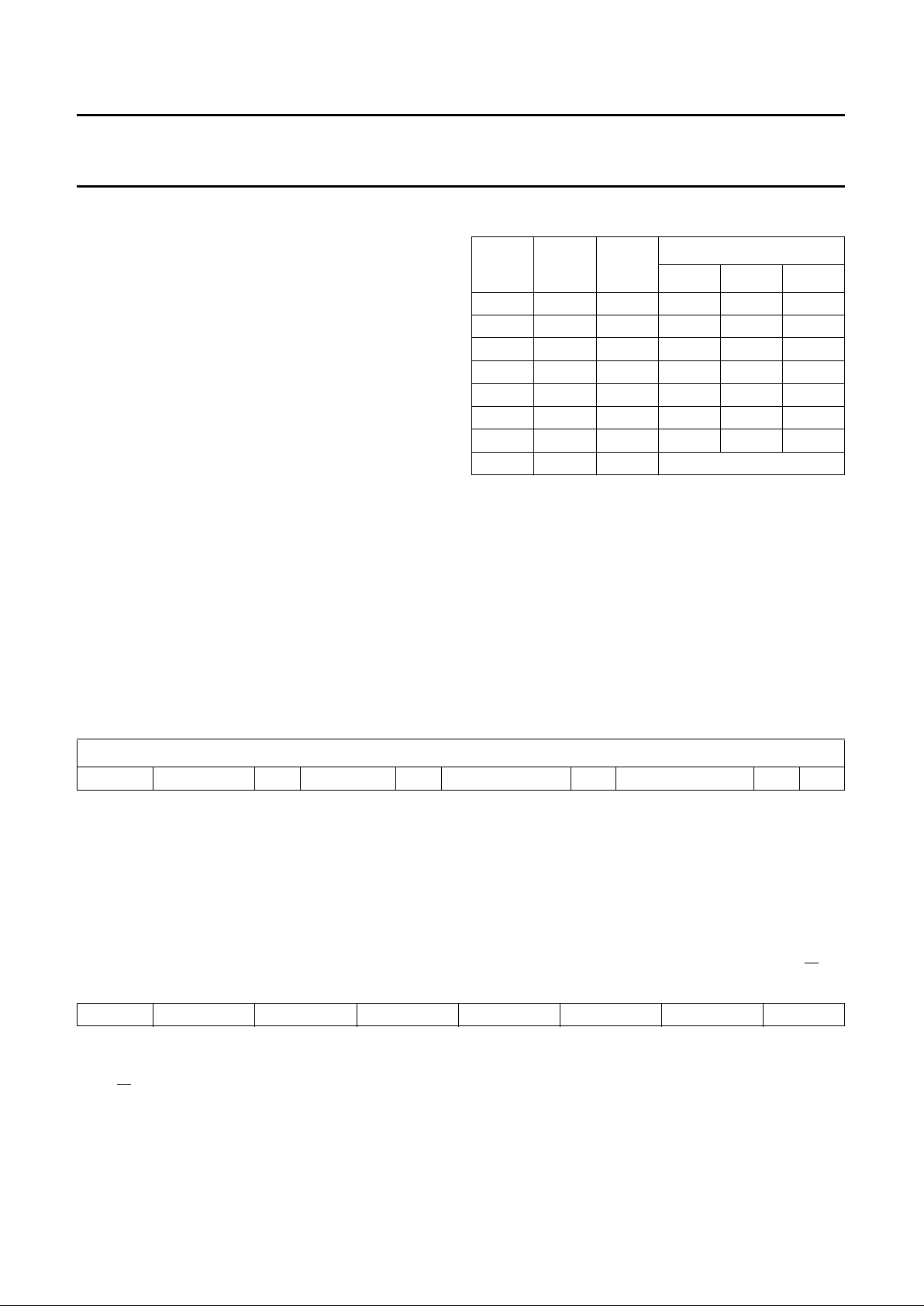
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
PEAK-
CLAMP
PEAK-
CLAMP
PEAK-
CLAMP/
BIAS
SUPPLY
PEAK-
CLAMP/
BIAS
DECODER
1 OF 4
DECODER
1 OF 4
DECODER
1 OF 4
DECODER
1 OF 4
SWITCH MATRIX
DRIVER
3
DRIVER
2
DRIVER
1
DRIVER
0
IN3
IN2
IN1
IN0
V
CC
12
10
8
6
13
20
9
11 7 5 18 19
DGND
AGND
S0 S1 S2 SCL SDA
3
1
14
16
17
2
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
OUT0
D1
D0
V
CC(D0,1)
V
CC(D2,3)
415
I
2
C RECEIVER
MLA279 - 2
TDA8540
EN0 to EN3
4
GAIN
GAIN
GAIN
GAIN
G0 to G3
4
2222
4444
2
CL0 to CL1
power reset
Fig.1 Block diagram.

1995 Feb 06 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4 × 4 video switch matrix TDA8540
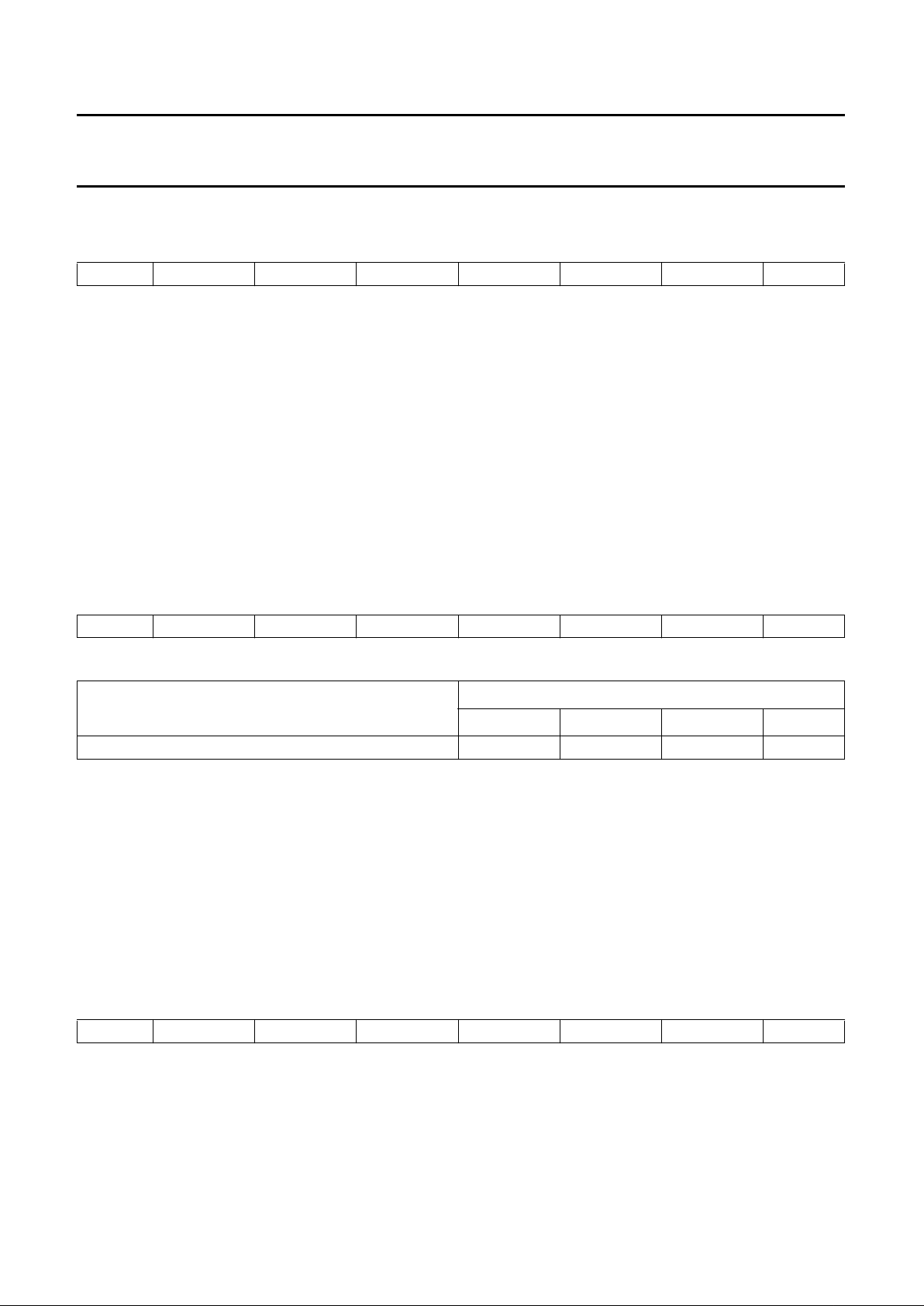
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
OUT2 1 video output 2
D0 2 control output 0
OUT3 3 video output 3
V
CC(D2,3)
4 driver supply voltage; for
drivers 2 and 3
S2 5 sub-address input 2
IN0 6 video input 0 (CVBS or
chrominance signal)
S1 7 sub-address input 1
IN1 8 video input 1 (CVBS or
chrominance signal)
AGND 9 analog ground
IN2 10 video input 2 (CVBS or luminance
signal)
S0 11 sub-address input 0
IN3 12 video input 3 (CVBS or luminance
signal)
V
CC
13 general supply voltage
OUT1 14 video output 1
V
CC(D0,1)
15 driver supply voltage; for
drivers 0 and 1
OUT0 16 video output 0
D1 17 control output 1
SCL 18 serial clock input
SDA 19 serial data input/output
DGND 20 digital ground
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
OUT2
D0
OUT3
V
CC(D2,3)
S2
IN0
S1
IN1
AGND
IN2
DGND
SDA
SCL
D1
OUT0
V
CC(D0,1)
OUT1
V
CC
IN3
S0
TDA8540
MLA277 - 2
Fig.2 Pinning configuration.
1995 Feb 06 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4 × 4 video switch matrix TDA8540
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8540 is controlled via a bidirectional I2C-bus.
3 bits of the I2C address can be selected via the address
pin, thus providing a facility for parallel connection of
7 devices.
Control options via the I2C-bus:
• The input signals can be clamped at their negative peak
(top sync).
• The gain factor of the outputs can be selected between
1× or 2×.
• Each of the four outputs can individually be connected
to one of the four inputs.
• Each output can individually be set in a high impedance
state.
• Two binary output data lines can be controlled for
switching accompanying sound signals.
The SDA and SCL pins (pins 19 and 18) can be connected
to the I
2
C-bus or to DC switching voltage sources. Address
inputs S0 to S2 (pins 11, 7 and 5) are used to select
sub-addresses or switching to the non-I2C mode. Inputs
S0 to S2 can be connected to the supply voltage (HIGH) or
the ground (LOW). In this way no peripheral components
are required for selection.
Table 1 I
2
C-bus sub-addressing
I
2
C-bus control
After power-up the outputs are initialized in the high
impedance state, and D0 and D1 are at a LOW level.
Detailed description of the I2C-bus specification, with
applications, is given in brochure
“The I2C-bus and how to
use it”
. This brochure may be ordered using the code
9398 393 40011.
The TDA8540 is aslave receiver and the protocol is given
in Table 2.
S2 S1 S0
SUB-ADDRESS
A2 A1 A0
LLL000
LLH001
LHL010
LHH011
HLL100
HLH101
HHL110
H H H non I
2
C addressable
Table 2 The TDA8540 protocol
Notes
1. S = START condition.
2. Data transmission to the TDA8540 starts with the slave address (SLV).
3. A = acknowledge bit, generated by TDA8540.
4. P = STOP condition.
Table 3 Data transmission to the TDA8540 begins with SLV
Notes
1. A2 to A0: pin programmable slave address bits.
2. R/
W = 0; write only.
After the SLV, a second byte, SUB, is required for selecting the functions, as shown in Table 4.
SEQUENCE
S
(1)
SLV
(2)
A
(3)
SUB A
(3)
DATA A
(3)
DATA A
(3)
P
(4)
A6
MSB
A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
R/W
LSB
1001A2
(1)
A1
(1)
A0
(1)
0
(2)
1995 Feb 06 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4 × 4 video switch matrix TDA8540
Table 4 The second byte: SUB
Options for SUB:
If SUB = 00H: access to switch control (SW1)
If SUB = 01H: access to gain/clamp/data control (GCO)
If SUB = 02H: access to output enable control (OEN).
Remarks:
If more than one data byte is sent, the SUB byte will be automatically incremented.
If more than 3 data bytes are sent, the internal counter will roll over and the device will then rewrite the first register.
Data Bytes
SWI (SUB = 00H): selects which input is connected to the different outputs, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5 SWI (SUB = 00H) selection of inputs connected to outputs
Table 6 Selection of inputs
Note
1. For j = 0 to 3.
Example: if S21 = 0 and S20 = 1, then OUT2 is connected to IN1.
GCO (SUB = 01H):
• Selects the gain of each output.
• Selects the clamp action or mean value on inputs 0 and 1.
• Determines the value of the auxiliary outputs D1 and D0.
Table 7 GCO byte
Notes
1. For j = 0 to 3: if Gj = 0 (1), then output j has a gain of 2 (1).
2. If CL0 (CL1) = 0, then input signal on IN0 (IN1) is clamped.
3. For j = 0 or 1: if Dj = 0 (1), then logical output j is LOW (HIGH).
7MSB6543210LSB
000000RS1RS0
7MSB6543210LSB
S31 S30 S21 S20 S11 S10 S01 S00
OUTPUT
Sj1 AND Sj0
(1)
00 01 10 11
OUTj IN0 IN1 IN2 IN3
7MSB6543210LSB
G3
(1)
G2
(1)
G1
(1)
G0
(1)
CL1
(2)
CL0
(2)
D1
(3)
D0
(3)
 Loading...
Loading...