Philips tda8366 DATASHEETS

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8366
2
I
C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
Objective specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
Philips Semiconductors
January 1995

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
FEATURES
• Multistandard vision IF circuit (positive and
negative modulation)
• Video identification circuit in the IF circuit which is
independent of the synchronization for stable On Screen
Display (OSD) under ‘no-signal’ conditions
• Source selection with 2 Colour Video Blanking
Synchronization (CVBS) inputs and a Y/C (or extra
CVBS) input
• Output signals of the video switch circuit for the teletext
decoder and a Picture-In-Picture (PIP) processor
• Integrated chrominance trap and bandpass filters
(automatically calibrated)
• Integrated luminance delay line
• Asymmetrical peaking in the luminance channel with a
(defeatable) noise coring function
• PAL/NTSC colour decoder with automatic search
system
• Easy interfacing with the TDA8395 (SECAM decoder)
for multistandard applications
• RGB control circuit with black-current stabilization and
white point adjustment; to obtain a good grey scale
tracking the black-current ratio of the 3 guns depends on
the white point adjustment
• Linear RGB inputs and fast blanking
• Horizontal synchronization with two control loops and
alignment-free horizontal oscillator
• Vertical count-down circuit
• Geometry correction by means of modulation of the
vertical and EW drive
2
C-bus control of various functions
• I
• Low dissipation (850 mW)
• Small amount of peripheral components compared with
competition ICs
• Only one adjustment (vision IF demodulator)
• Y, U and V inputs and outputs.
TDA8366
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8366 is an I
processor. The circuit has been designed for use with the
baseband chrominance delay line TDA4665 and for
DC-coupled vertical and East-West (EW) output stages.
The device can process both CVBS and Y/C input signals
and has a linear RGB-input with fast blanking.
The peaking circuit generates asymmetrical overshoots
(the amplitude of the ‘black’ overshoots is approximately
2 times higher as the one of the ‘white’ overshoots) and
contains a (defeatable) coring function.
The RGB control circuit contains a black-current stabilizer
circuit with internal clamp capacitors. The white point of the
picture tube is adjusted via the I
The deflection control circuit provides a drive pulse for the
horizontal output stage, a differential sawtooth current for
the vertical output stage and an East-West drive current for
the East-West output stage.These signals can be
manipulated for geometry correction of the picture.
The supply voltage for the IC is 8 V. The IC is available in
an SDIP package with 52 pins and in a QFP package with
64 pins (see Chapter “Ordering information”).
The pin numbers indicated in this document are
referenced to the SDIP52; SOT247-1 package; unless
otherwise indicated.
2
C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
2
C-bus.
January 1995 2
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
TDA8366
processor
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA8366 SDIP52 plastic shrink dual in-line package; 52 leads (600 mil) SOT247-1
(1)
TDA8366H QFP64
plastic quad flat package; 64 leads (lead length 1.95 mm);
body 14 × 20 × 2.8 mm
Note
1. When using IR reflow soldering it is recommended that the Drypack instructions in the
(order number 9398 510 63011) are followed.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
I
P
supply voltage − 8.0 − V
supply current − 100 − mA
Input voltages
V
46,47(rms)
V
15(p-p)
V
9(p-p)
V
8(p-p)
video IF amplifier sensitivity (RMS value) − 70 −µV
external CVBS input (peak-to-peak value) − 1.0 − V
S-VHS luminance input voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 1.0 − V
S-VHS chroma input voltage (burst amplitude)
(peak-to-peak value)
V
21,22,23(p-p)
RGB inputs (peak-to-peak value) − 0.7 − V
Output signals
V
o(p-p)
I
52
V
36(p-p)
V
13(p-p)
V
28(p-p)
V
27(p-p)
V
26
V
19,18,17(p-p)
I
38
I
44,45
I
43
demodulated CVBS output (peak-to-peak value) − 2.5 − V
tuner AGC output current range 0 − 5mA
TXT output voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 1.0 − V
PIP output voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 1.0 − V
−(R−Y) output voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 525 − mV
−(B−Y) output voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 675 − mV
Y output voltage − 450 − mV
RGB output signal amplitudes (peak-to-peak value) − 2.0 − V
horizontal output current 10 −−mA
vertical output current 1 −−mA
EW drive output current 0.5 −−mA
PACKAGE
“Quality Reference Handbook”
− 0.3 − V
SOT319-2
January 1995 3
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
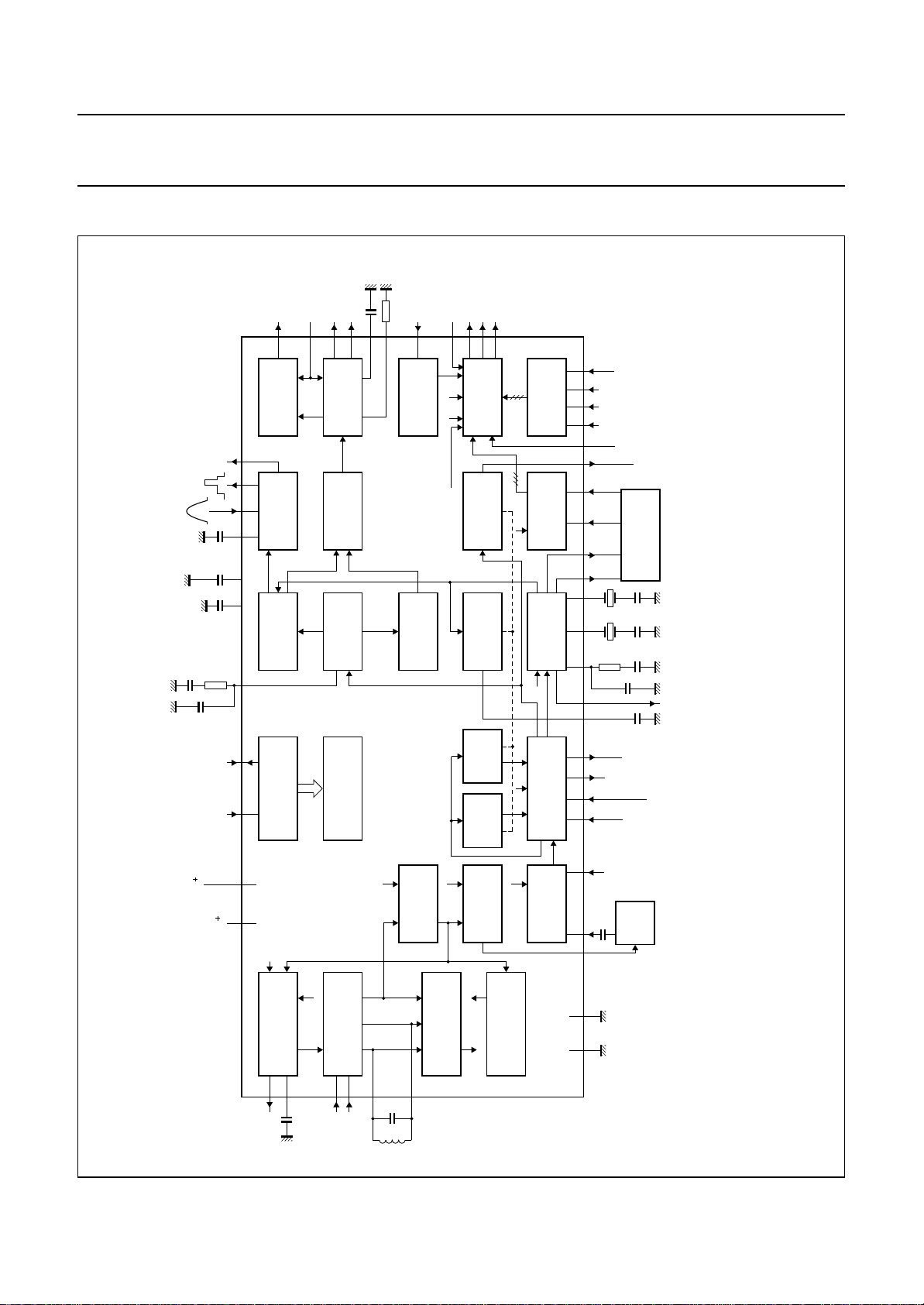
BLOCK DIAGRAM
(pos)
(neg)
VDR
VDR
EHTO
EWD
DIG
DEC
FBI
SCO
PH2LF
BG
DEC
HOUT
43
EW GEOMETRY
HORIZONTAL
2nd LOOP AND
ref
7310 35 40 39 37 38
AND
VCO
48
OUTPUT
CONTROL
49
45
44
VERTICAL
GEOMETRY
DIVIDER
VERTICAL
HORIZONTAL/
SYNC
SEPARATOR
AND 1st LOOP
VSC
50
ref
I
BLKIN
16
BLACK
CURRENT
STABILIZER
WHITE
SYNC
VERTICAL
SEPARATOR
BCLIN
20
191817
BRI CONTR
POINT
ref
BO
RO
GO
AND
OUTPUT
RGB MATRIX
AND
DELAY
PEAKING
FILTER
TUNING
AND
SWITCH
RGB INPUT
AND
G-Y MATRIX
SAT CONTROL
28 27 30 29 26 25 21 22 23 24
PAL/NTSC
DECODER
34 33 32
MLA745 - 1
DET
RYO BYO BYIRYI
RI GI BI
RGBIN
LUMIN
3.6
MHz
4.4
MHz
TDA8366
LUMOUT
TDA4661
XTAL2 XTAL1
PH1LF
SCL SDA
P2
V ( 8 V)
P1
V ( 8 V)
2
I C-BUS
56 41
TRANSCEIVER
TOP
AGC FOR IF
AND TUNER
51
52
(TUNER)
AGCOUT
POL
AGC
DEC
2 x 4 bits
17 x 6 bits
CONTROL DACs
POL
IF AMPLIFIER
AND DEMODULATOR
2
46
47
IFDEM2
IFIN1
IFIN2
TDA8366
VIDEO
AMPLIFIER
1
IFDEM1
BANDPASSTRAP
MUTE
VIDEO MUTE
IDENT
AFC AND
SAMPLE AND HOLD
AFC
HUE
SW SAT
S-VHS - SWITCH
SW
CVBS - SWITCH
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
8 9 13 36 14 31
411 15
4212
FT
DEC
INT
CVBSIFVO
GND2
GND1
PIPO
EXT
CVBS
CVBS/TXT
CVBS/Y
CHROMA
TRAP
SOUND
ref
SEC
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.1 Block diagram (SDIP52; SOT247-1).
January 1995 4
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
PINNING
SYMBOL
SDIP52 QFP64
IFDEM1 1 11 IF demodulator tuned circuit 1
IFDEM2 2 12 IF demodulator tuned circuit 2
DEC
DIG
IFVO 4 14 IF video output
SCL 5 16 serial clock input
SDA 6 17 serial data input/output
DEC
BG
CHROMA 8 20 chrominance input (S-VHS)
CVBS/Y 9 21 external CVBS/Y input
V
P1
CVBS
INT
10 22 main supply voltage 1 (+8 V)
11 29 internal CVBS input
GND1 12 25 ground 1
PIPO 13 27 picture-in-picture output
DEC
CVBS
FT
EXT
14 28 decoupling filter tuning
15 24 external CVBS input
BLKIN 16 30 black-current input
BO 17 31 blue output
GO 18 32 green output
RO 19 33 red output
BCLIN 20 35 beam current limiter input
RI 21 37 red input for insertion
GI 22 38 green input for insertion
BI 23 39 blue input for insertion
RGBIN 24 40 RGB insertion input
LUMIN 25 42 luminance input
LUMOUT 26 43 luminance output
BYO 27 44 (B−Y) signal output
RYO 28 45 (R−Y) signal output
BYI 29 46 (B−Y) signal input
RYI 30 47 (R−Y) signal input
SEC
ref
31 48 SECAM reference output
XTAL1 32 49 3.58 MHz crystal connection
XTAL2 33 50 4.43/3.58 MHz crystal connection
DET 34 52 loop filter phase detector
V
P2
35 54 horizontal oscillator supply voltage (+8 V)
CVBS/TXT 36 55 CVBS/TXT output
SCO 37 56 sandcastle output
HOUT 38 57 horizontal output
PIN
DESCRIPTION
3 13 decoupling digital supply
7 18 bandgap decoupling
TDA8366
January 1995 5
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
SYMBOL
FBI 39 58 flyback input
PH2LF 40 59 phase-2 filter
PH1LF 41 60 phase-1 filter
GND2 42 26 ground 2
EWD 43 63 east-west drive output
VDR
(pos)
VDR
(neg)
IFIN1 46 2 IF input 1
IFIN2 47 3 IF input 2
EHTO 48 4 EHT/overvoltage protection input
VSC 49 5 vertical sawtooth capacitor
I
ref
DEC
AGC
AGCOUT 52 8 tuner AGC output
n.c. − 9 not connected
n.c. − 10 not connected
n.c. − 15 not connected
n.c. − 19 not connected
n.c. − 34 not connected
n.c. − 36 not connected
n.c. − 41 not connected
n.c. − 51 not connected
n.c. − 53 not connected
V
P3
GND3 − 61 ground 3
GND4 − 62 ground 4
SDIP52 QFP64
44 64 vertical drive 1 positive output
45 1 vertical drive 2 negative output
50 6 reference current input
51 7 AGC decoupling capacitor
PIN
DESCRIPTION
− 23 supply voltage 3 (+8 V)
TDA8366
The pin numbers mentioned in the rest of this document are referenced to the SDIP52 (SOT247-1) package.
January 1995 6

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
handbook, halfpage
DEC
CHROMA
CVBS
CVBS
LUMOUT
IFDEM1
IFDEM2
DEC
CVBS/Y
DEC
RGBIN
LUMIN
1
2
3
DIG
4
IFVO
SCL
5
6
SDA
7
BG
8
9
V
10
P1
11
INT
12
GND1
PIPO
13 40
14
FT
15
EXT
16
BLKIN
17
BO
18
GO
19
RO
20
BCLIN
21
RI
22
GI
23
BI
24
25
26
TDA8366
MLA737 - 1
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
AGCOUT
DEC
AGC
I
ref
VSC
EHTO
IFIN2
IFIN1
VDR
(neg)
VDR
(pos)
EWD
GND2
PH1LF
PH2LF
FBI
HOUT
SCO
CVBS/TXT
V
P2
DET
XTAL2
XTAL1
SEC
ref
RYI
BYI
RYO
BYO
TDA8366
Fig.2 Pin configuration (SDIP52).
January 1995 7

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
handbook, full pagewidth
VDR
(neg)
IFIN1
IFIN2
EHTO
VSC
I
DEC
AGC
AGCOUT
n.c.
n.c.
IFDEM1
IFDEM2
DEC
DIG
IFVO
ref
(pos)
VDR
EWD
GND4
64
63
62
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
GND3
61
PH1LF
60
TDA8366H
PH2LF
59
FBI
58
HOUT
57
SCO
56
P2
V
CVBS/TXT
55
54
n.c.
53
DET
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
n.c.
XTAL2
XTAL1
SEC
ref
RYI
BYI
RYO
BYO
LUMOUT
LUMIN
n.c.
RGBIN
BI
GI
TDA8366
n.c.
15
SCL
16
SDA
17
DEC
BG
n.c.
18
19
20
21
CVBS/Y
CHROMA
22
P1
V
24
EXT
CVBS
25
GND1
23
P3
V
Fig.3 Pin configuration (QFP64).
January 1995 8
26
GND2
27
PIPO
28
FT
DEC
29
INT
CVBS
30
BLKIN
31
BO
32
GO
37
36
35
34
33
MLC756
RI
n.c.
BCLIN
n.c.
RO

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Vision IF amplifier
The IF-amplifier contains 3 AC-coupled control stages with
a total gain control range which is in excess of 66 dB. The
sensitivity of the circuit is comparable with that of modern
IF-ICs. The reference carrier for the video demodulator is
obtained by means of passive regeneration of the picture
carrier. The external reference tuned circuit is the only
remaining adjustment of the IC.
The polarity of the demodulator can be switched via the
2
I
C-bus in such a way that the circuit is suitable for both
positive and negative modulated signals.
The AFC-circuit is driven with the same reference signal as
the video demodulator. To avoid that the video content
disturbs the AFC operation a sample-and-hold circuit is
applied for signals with negative modulation. The capacitor
for this function is internal. The AFC information is supplied
to the tuning system via the I2C-bus.
The AGC-detector operates on top-sync or top white-level
depending on the polarity of the demodulator. The
demodulation polarity is switched via the I2C-bus. The
AGC detector time-constant capacitor is connected
externally (this mainly because of the flexibility of the
application). The time-constant of the AGC system during
positive modulation is rather long to avoid visible variations
of the signal amplitude. To obtain an acceptable speed of
the AGC system a circuit has been included which detects
whether the AGC detector is activated every frame period.
When during 3 frame periods no action is detected the
speed of the system is increased.
The circuit contains a video identification circuit which is
independent of the synchronization circuit. Therefore
search tuning is possible when the display section of the
receiver is used as a monitor. The identification output is
supplied to the tuning system via the I2C-bus. The
information of this identification circuit can also be used to
switch the phase-1 (ϕ1) loop to a low gain when no signal
is received so that a stable OSD display is obtained. The
coupling of the video identification circuit with the ϕ1loop
can be switched on and off via the I2C-bus.
TDA8366
Synchronization circuit
The sync separator is preceded by a controlled amplifier
which adjusts the sync pulse amplitude to a fixed level.
These pulses are fed to the slicing stage which is operating
at 50% of the amplitude.
The separated sync pulses are fed to the first phase
detector and to the coincidence detector. This coincidence
detector is only used to detect whether the line oscillator is
synchronized and not for transmitter identification. The first
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) has a very high-statical
steepness so that the phase of the picture is independent
of the line frequency.
The line oscillator is running at twice the line frequency.
The oscillator capacitor is internal. Because of the spreads
of internal components an automatic adjustment circuit
has been added to the IC. It compares the oscillator
frequency with that of the crystal oscillator in the colour
decoder.
To protect the horizontal output transistor the horizontal
drive is switched-off when a power-on-reset is detected.
The frequency of the oscillator is calibrated again when all
subaddress bytes have been sent. When the oscillator has
the right frequency the calibration stops and the horizontal
drive is switched-on again via the soft start procedure
(standby bit in normal mode). When the IC is switched-on
the same procedure is followed.
When the coincidence detector indicates an out-of-lock
situation the calibration procedure is repeated.
The circuit has a second control loop to generate the drive
pulses for the horizontal driver stage. During the start-up
procedure the duty cycle of the horizontal output pulse
increases from 0 to 50% in approximately 100 lines.
The vertical sawtooth generator drives the vertical output
and EW correction drive circuits. The geometry processing
circuits provide control of horizontal shift, EW width, EW
parabola/width ratio, EW corner/parabola ratio, trapezium
correction, vertical shift, vertical slope, vertical amplitude,
and the S-correction. All these controls can be set via the
2
C-bus. The geometry processor has a differential current
I
January 1995 9

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
output for the vertical drive signal and a single-ended
output for the EW drive. Both the vertical drive and the EW
drive outputs can be modulated for EHT compensation.
The EHT compensation pin is also used for overvoltage
protection.
The geometry processor also offers the possibilities for
vertical compression (for display of 16 : 9 pictures on a
4 : 3 screen) and vertical expansion (for display of
4 : 3 pictures on a 16 : 9 screen with full picture width, or
for display of ‘letter-box’ transmissions on a 4 : 3 screen
with full picture height). For the expand mode it is possible
to shift the picture vertically (only one fixed position).
Also the de-interlace of the vertical output can be set via
the I2C-bus.
To avoid damage of the picture tube when the vertical
deflection fails the guard output current of the TDA8350
can be supplied to the sandcastle output. When a failure is
detected the RGB-outputs are blanked and a bit is set
(NDF) in the status byte of the I2C-bus. When no vertical
deflection output stage is connected this guard circuit will
also blank the output signals. This can be overruled by
means of the EVG bit of subaddress 0A (see Table 1).
TDA8366
Video switches
The circuit has two CVBS inputs and an Super-Video
Home System (S-VHS) input. The input can be chosen by
2
the I
C-bus. The input selector also has a position in which
CVBS
S-VHS input. When the input selector is in this position it
switches to the S-VHS input if the S-VHS detector detects
sync pulses on the S-VHS luminance input. The S-VHS
detector output can be read by the I2C-bus. When the
S-VHS option is not used the luminance input can be used
as a second input for external CVBS signals. The choice is
made via the CVS-bit (see Table 1).
The video switch circuit has two outputs which can be
programmed in a different way. The input signal for the
decoder is also available on the TXT output. Therefore this
signal can be used to drive the teletext decoder and the
SECAM add-on decoder. The signal on the PIP output can
be chosen independent of the TXT output. If S-VHS is
selected for one of the outputs the luminance and
chrominance signals are added so that a CVBS signal is
obtained again.
Colour decoder
is processed, unless there is a signal on the
EXT
Integrated video filters
The circuit contains a chrominance bandpass and trap
circuit. The chrominance trap filter in the luminance path is
designed for a symmetrical step response behaviour. The
filters are realized by means of gyrator circuits and they
are automatically tuned by comparing the tuning frequency
with the crystal frequency of the decoder. The luminance
delay line and the delay for the peaking circuit are also
realized by means of gyrator circuits.
It is possible to connect a Colour Transient Improvement
(CTI) or Picture Signal Improvement (PSI) IC to the
TDA8366. Therefore the luminance signal which has
passed the filter and delay line circuit is externally
available. The output signal of the transient improvement
circuit must be supplied to the luminance input circuit.
When the CTI function is not required the two pins must be
AC-coupled.
The colour decoder contains an alignment-free crystal
oscillator, a killer circuit and the colour difference
demodulators. The 90° phase shift for the reference signal
is made internally. The demodulation angle and gain ratio
for the colour difference signals for PAL and NTSC are
adapted to the standard.
The colour decoder is very flexible. Together with the
SECAM decoder TDA8395 an automatic multistandard
decoder can be designed.
Which standard the IC can decode depends on the
external crystals. If a 4.4 MHz and a 3.5 MHz crystal are
used PAL 4.4, NTSC 4.4, NTSC 3.5 and PAL 3.5 can be
decoded. If two 3.5 MHz crystals are used PAL N and M
can be decoded. If one crystal is connected only
PAL/NTSC 4.4 or PAL/NTSC 3.5 can be decoded. The
crystal frequency of the decoder is used to tune the line
oscillator. Therefore the value of the crystal frequency
must be given to the IC via the I
2
C-bus.
January 1995 10

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
RGB output circuit and black-current stabilization
The colour-difference signals are matrixed with the
luminance signal to obtain the RGB-signals. For the
RGB-inputs linear amplifiers have been chosen so that the
circuit is suited for signals coming from the SCART
connector. The contrast and brightness control operate on
internal and external signals.
The output signal has an amplitude of approximately 2 V
black-to-white at nominal input signals and nominal
settings of the controls.
The black current stabilization is realized by means of a
feedback from the video output amplifiers to the RGB
control circuit. The ‘black current’ of the 3 guns of the
picture tube is internally measured and stabilized. The
black level control is active during 4 lines at the end of the
vertical blanking. During the first line the leakage current is
measured and the following 3 lines the 3 guns are
adjusted to the required level. The maximum acceptable
leakage current is ±100 µA. The nominal value of the
‘black current’ is 10 µA. The ratio of the currents for the
various guns automatically tracks with the white point
adjustment so that the back-ground colour is the same as
the adjusted white point.
TDA8366
visible on the screen. As soon as the current supplied to
the measuring input exceeds a value of 190 µA the
stabilization circuit is activated. After a waiting time of
approximately 0.8 s the blanking and the beam current
limiting input pin are released. The remaining switch-on
behaviour of the picture is determined by the external time
constant of the beam current limiting network.
2
C-BUS SPECIFICATION
I
handbook, halfpage
X =don’t care.
Valid subaddresses: 00 to 13; subaddress FE is reserved
for test purposes. Auto-increment mode is available for
subaddresses.
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1000101X
R/W
MLA743
Fig.4 Slave address (8A).
The input impedance of the ‘black-current’ measuring pin
is 15 kΩ. Therefore the beam current during scan will
cause the input voltage to exceed the supply voltage. The
internal protection will start conducting so that the
excessive current is bypassed.
When the TV receiver is switched-on the black current
stabilization circuit is not active, the RGB outputs are
blanked and beam current limiting input pin is
short-circuited. Only during the measuring lines will the
outputs supply a voltage of 5 V to the video output stage
so that it can be detected if the picture tube is warming up.
These pulses are switched-on after a waiting time of
approximately 0.5 s. This ensures that the vertical
deflection is activated so that the measuring pulses are not
Start-up procedure
Read the status bytes until POR = 0 and send all
subaddress bytes. The horizontal output signal is
switched-on when the oscillator is calibrated. It is possible
to have the horizontal output signal available before
calibration. Then the SFM bit must be set to logic 0.
Each time before the data in the IC is refreshed, the status
bytes must be read. If POR = 1, the procedure mentioned
above must be carried out to restart the IC.
When this procedure is not followed the horizontal
frequency may be incorrect after power-up or after a
power dip.
January 1995 11

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
TDA8366
processor
Inputs
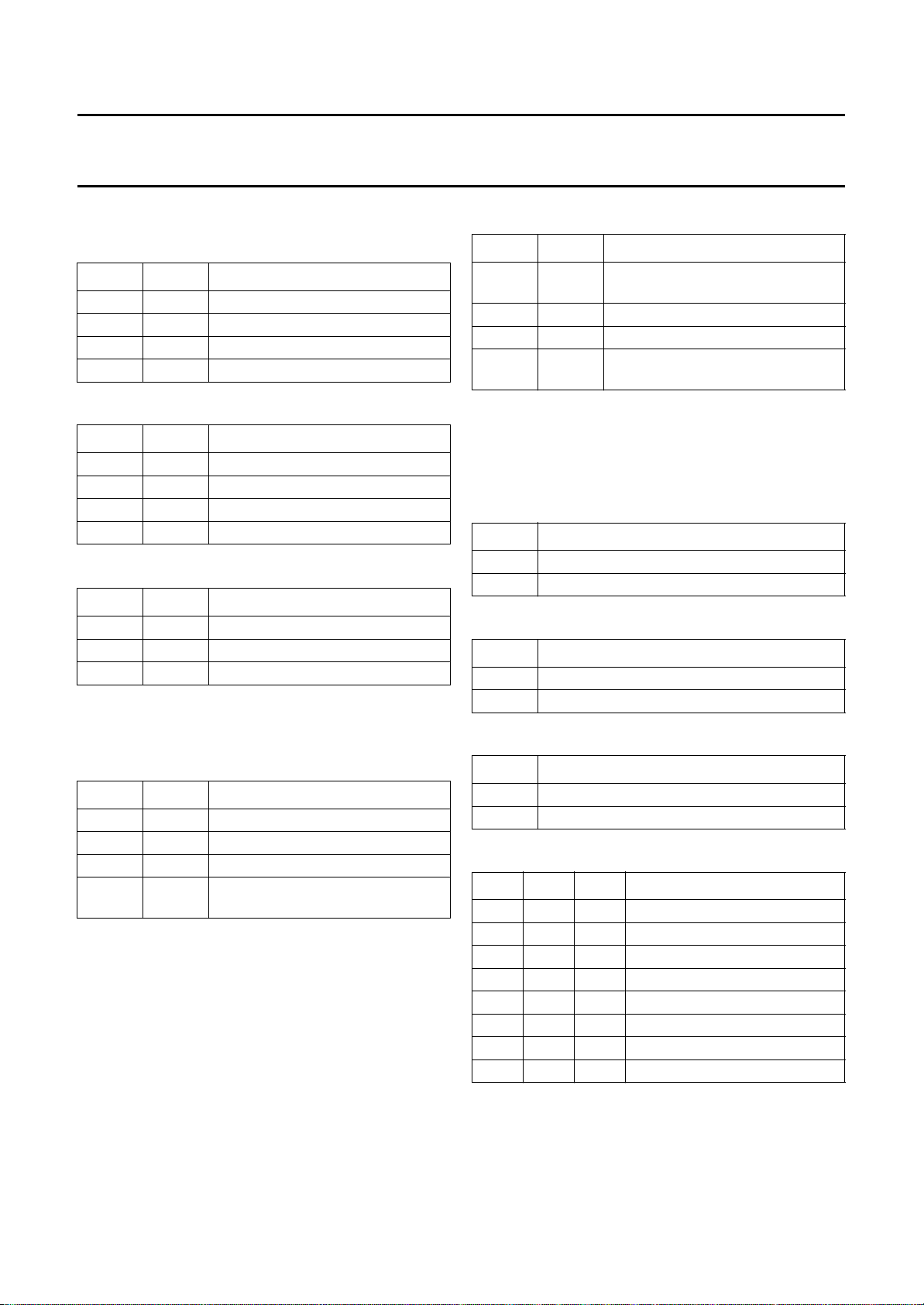
Table 1 Input status bits; note 1
FUNCTION
Source select 00 INA INB INC IND FOA FOB XA XB
Decoder mode 01 FORF FORS DL STB POC CM2 CM1 CM0
Hue 02 X X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal shift (HS) 03 X X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
EW width (EW) 04 X X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
EW parabola/width (PW) 05 X X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
EW corner parabola (CP) 06 X X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
EW trapezium (TC) 07 X X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical slope (VS) 08 NCIN X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical amplitude (VA) 09 VID LBM A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
S-correction (SC) 0A HCO EVG A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical shift (VSH) 0B SBL PRD A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point R 0C EXP CL A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point G 0D SFM CVS A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point B 0E MAT PHL A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Peaking 0F YD3 YD2 YD1 YD0 A3 A2 A1 A0
Brightness 10 RBL COR A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Saturation 11 IE1 X A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Contrast 12 AFW IFS A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
AGC take-over 13 MOD VSW A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
SUBADDRESS
(HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BYTE
Note
1. X = don’t care.
Table 2 Output status bits; note 1
FUNCTION
Output status bytes 00 POR FSI STS SL XPR CD2 CD1 CD0
Note
1. X = don’t care.
January 1995 12
SUBADDRESS
(HEX)
01 NDF IN1 X IFI AFA AFB X X
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BYTE
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
INPUT CONTROL BITS
Table 3 Source select 1
INA INB DECODER AND TXT
0 0 CVBS
0 1 CVBS
1 0 S-VHS
1 1 S-VHS (CVBS
Table 4 Source select 2
INC IND PIP
0 0 CVBS
0 1 CVBS
1 0 S-VHS
1 1 S-VHS (CVBS
Table 5 Phase 1 (ϕ1) time constant
FOA FOB
(1)
0 0 normal
0 1 slow
1 X fast
Note
1. X = don’t care.
Table 6 Crystal indication
XA XB CRYSTAL
0 0 two 3.6 MHz
0 1 one 3.6 MHz (pin 32)
1 0 one 4.4 MHz (pin 33)
1 1 3.6 MHz (pin 32) and 4.4 MHz
(pin 33)
INT
EXT
INT
EXT
)
EXT
)
EXT
MODE
TDA8366
Table 7 Forced field frequency
FORF FORS FIELD FREQUENCY
0 0 auto (60 Hz when line not
synchronized)
0 1 60 Hz; note 1
1 0 50 Hz; note 1
1 1 auto (50 Hz when line not
synchronized)
Note
1. When the forced mode is selected the divider will only
switch to that position when the horizontal oscillator is
not synchronized.
Table 8 Interlace
DL STATUS
0 interlace
1 de-interlace
Table 9 Standby
STB MODE
0 standby
1 normal
Table 10 Synchronization mode
POC MODE
0 active
1 not active
Table 11 Colour decoder mode
CM2 CM1 CM0 DECODER MODE
0 0 0 not forced, own intelligence
0 0 1 forced NTSC 3.6 MHz
0 1 0 forced PAL 4.4 MHz
0 1 1 forced SECAM
1 0 0 forced NTSC 4.4 MHz
1 0 1 forced PAL 3.6 MHz (pin 32)
1 1 0 forced PAL 3.6 MHz (pin 33)
1 1 1 no function
January 1995 13

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
I2C-bus controlled PAL/NTSC TV
processor
Table 12 Vertical divider mode
NCIN VERTICAL DIVIDER MODE
0 normal operation
1 switched to search window
Table 13 Video ident mode
VID VIDEO IDENT MODE
0 ϕ
1 not active
Table 14 Long blanking mode
LBM BLANKING MODE
0 adapted to standard (50 or 60 Hz)
1 fixed in accordance with 50 Hz standard
Table 15 EHT tracking mode
loop switched on and off
1
TDA8366
Table 20 Horizontal frequency during switch-on
SFM START-UP FREQUENCY
0 maximum
1 nominal
Table 21 Condition Y/C input
CVS Y-INPUT MODE
0 switched to Y/C mode
1 switched to CVBS mode
Table 22 PAL/NTSC matrix
MAT MATRIX
0 adapted to standard
1PAL
Table 23 Colour crystal PLL
HCO TRACKING MODE
0 EHT tracking only on vertical
1 EHT tracking on vertical and EW
Table 16 Enable vertical guard (RGB blanking)
EVG VERTICAL GUARD MODE
0 not active
1 active
Table 17 Service blanking
SBL SERVICE BLANKING MODE
0off
1on
Table 18 Overvoltage input mode
PRD OVERVOLTAGE MODE
0 detection mode
1 protection mode
Table 19 Vertical deflection mode
PHL STATE
0 PLL closed
1 oscillator free-running
Table 24 Y-delay adjustment; note 1
YD0 to YD3 Y-DELAY
YD3 YD3 ∗ 160 ns +
YD2 YD2 ∗ 80 ns +
YD1 YD1 ∗ 40 ns +
YD0 YD0 ∗ 40 ns
Note
1. For an equal delay of the luminance and chrominance
signal the delay must be set at a value of 160 ns. This
is only valid for a CVBS signal without group
delay distortions.
Table 25 RGB blanking
RBL RGB BLANKING
0 not active
1 active
EXP CL VERTICAL DEFLECTION MODE
0 0 normal
0 1 compress
1 0 expand
1 1 expand and lift
January 1995 14
Table 26 Noise coring (peaking)
COR NOISE CORING
0off
1on
 Loading...
Loading...