Philips TDA4885 Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA4885
150 MHz video controller with
2
I
C-bus
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Mar 19
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1997 Nov 25
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6 PINNING
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Signal input stage
(input clamping, blanking and clipping)
7.2 Electronic potentiometer stages
7.2.1 Contrast control (driven by I2C-bus, 6-bit DAC)
7.2.2 Brightness control (driven by I2C-bus, 6-bit
DAC)
7.2.3 Gain control (driven by I2C-bus, 6-bit DAC) and
grey scale tracking
7.3 Output stage
7.4 Pedestal blanking
7.5 Output clamping, feedback references and
DAC outputs
7.6 Clamping and blanking pulses
7.7 On Screen Display (OSD)
7.8 Limiting by contrast reduction
7.9 Gain modulation
7.10 I2C-bus control
8 LIMITING VALUES
9 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
10 CHARACTERISTICS
11 I2C-BUS PROTOCOL
12 INTERNAL CIRCUITRY
13 TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
13.1 Test application
13.2 Recommendations for building the application
board
14 PACKAGE OUTLINE
15 SOLDERING
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Soldering by dipping or by wave
15.3 Repairing soldered joints
16 DEFINITIONS
17 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
18 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
TDA4885
1997 Nov 25 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
1 FEATURES
• 150 MHz pixel rate
• 2.7 ns rise time
• Gain modulation capability for brightness uniformity
• I2C-bus control
• Grey scale tracking
• On Screen Display (OSD) mixing
• Negative feedback for DC-coupled cathodes
• Positive feedback for AC-coupled cathodes
• DAC outputs for black level restoration with AC-coupled
cathodes
• Integrated black level storage capacitors
• Beam current limiting
• Analog subcontrast setting
• Pedestal blanking
• OSD contrast
• Sync clipping.
TDA4885
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA4885 is a monolithic integrated RGB pre-amplifier
for colour monitor systems (e.g. 15" and 17") with I2C-bus
control and OSD. In addition to bus control beam current
limiting and gain modulation are possible. The signals are
amplified in order to drive commonly used video modules
or discrete solutions. Individual black level control with
negative feedback from the cathode (DC coupling) or fixed
black level control with positive feedback and 3 DAC
outputs for external cut-off control (AC coupling) is
possible.
With special advantages the circuit can be used in
conjunction with the TDA485x monitor deflection IC family.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
TDA4885 SDIP32 plastic shrink dual in-line package; 32 leads (400 mil) SOT232-1
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
1997 Nov 25 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
P
V
P1, 2,3
supply voltage (pin 7) 7.6 8.0 8.8 V
supply current (pin 7) − 20 25 mA
channel supply voltage
7.6 8.0 8.8 V
(pins 29, 24 and 19)
I
P1, 2, 3
channel supply current
− 40 − mA
(pins 29, 24 and 19)
V
i(b-w)
input voltage
− 0.7 1.0 V
(black-to-white value; pins 6, 8 and 10)
V
o(b-w)
nominal output voltage swing
(black-to-white value; pins 30, 25 and 20)
nominal contrast;
maximum gain; pins 12,
2.5 2.8 − V
13 and 14 grounded
V
o(b-w)(max)
maximum output voltage swing
(black-to-white value; pins 30, 25 and 20)
maximum contrast;
maximum gain; pins 12,
− 4.5 − V
13 and 14 grounded
V
o
V
bl
output voltage level (pins 30, 25 and 20) 0.1 − 6.0 V
typical reference black level
0.5 − 2.5 V
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
I
o(sink)
I
o(source)
peak output sink current during fast signal transients −−20 mA
peak output source current during fast signal transients −40 −−mA
B bandwidth −3 dB (small signal) − 150 − MHz
t
r(O)
video rise time at signal outputs
− 2.7 − ns
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
dV
O
over/undershoot at signal outputs
minimum rise/fall time − 5 − %
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
α
ct
crosstalk at signal outputs
f = 80 MHz −−30 − dB
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
C
C
G
C
BC brightness control (typical black level voltage
contrast control related to nominal contrast −28 − +4 dB
gain control related to maximum gain −7 − 0dB
−10 − +30 %
change related to output signal amplitude)
V
o(OSD)(max)
C
OSD
maximum OSD output voltage swing related
to nominal output voltage swing
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
OSD contrast control related to maximum
maximum OSD contrast;
maximum gain; pins 12,
13 and 14 grounded
− 125 − %
−12 − 0dB
OSD contrast
1997 Nov 25 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
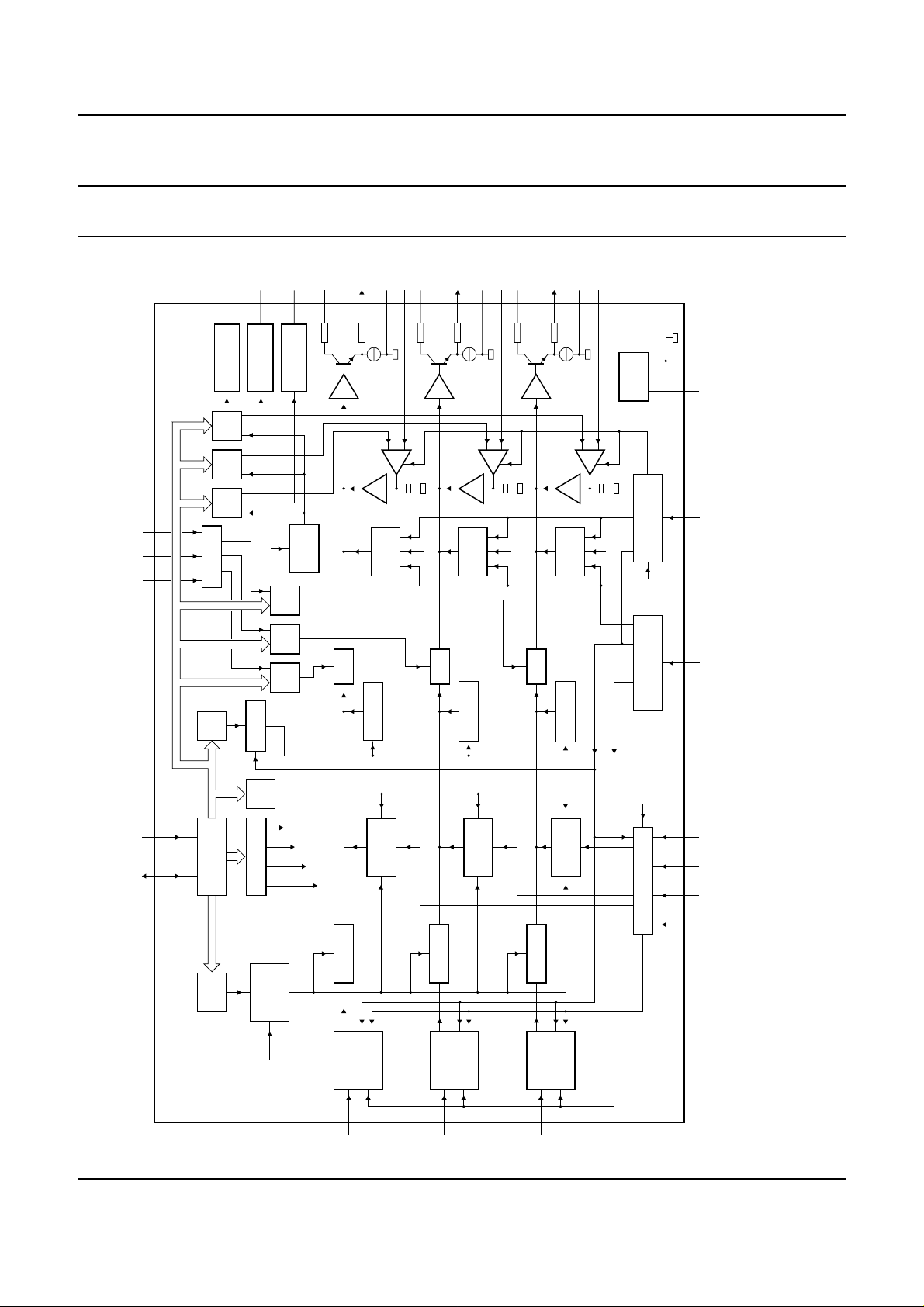
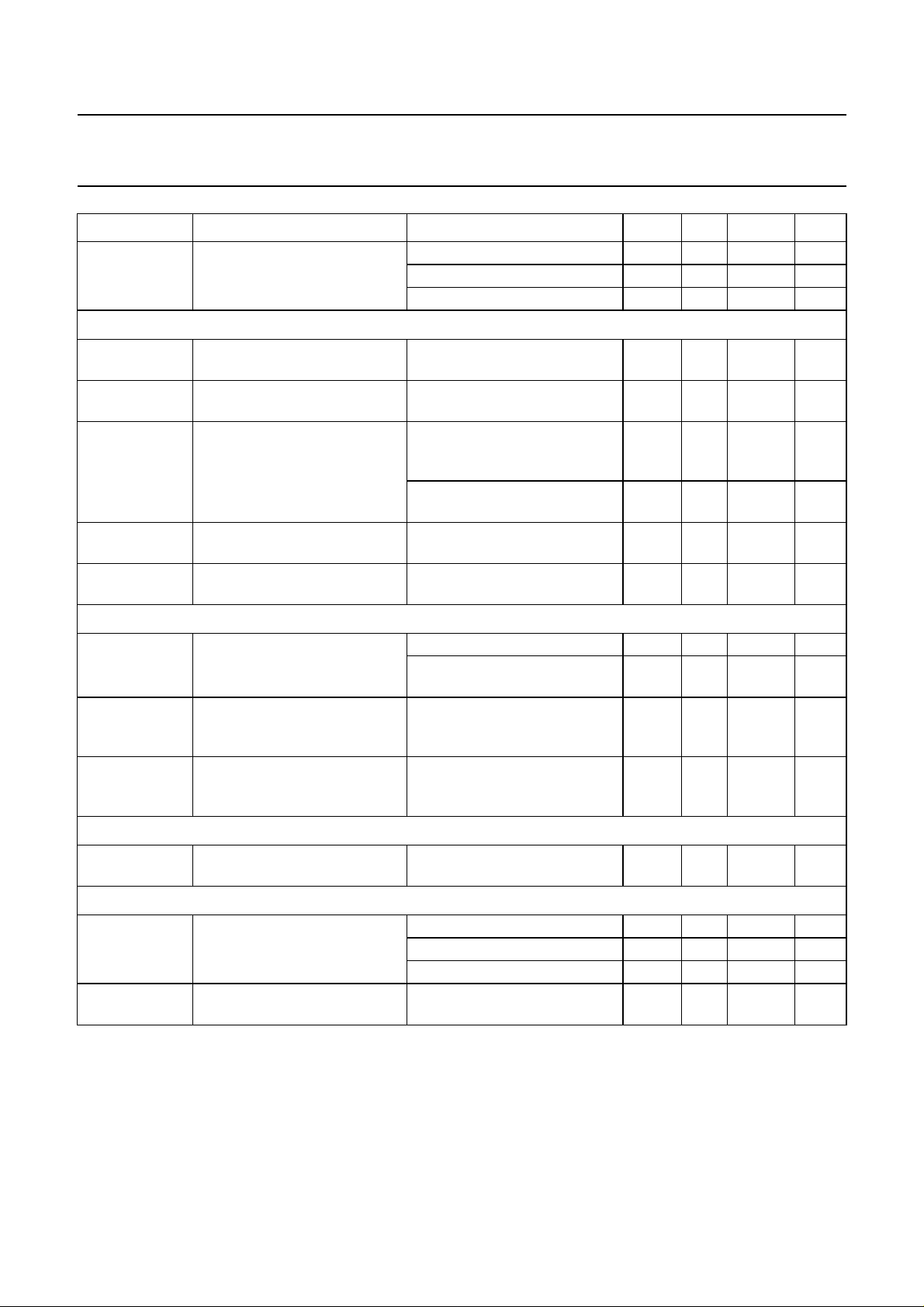
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
32
29
CHANNEL 1
REFERENCE
SWITCH
POLARITY
DAC
P1VO1
30
GND1FB1VP2V
283124
BLANKING
PEDESTAL
GM
GM
GM
REF3REF2REF1V
22
27
CHANNEL 2
CHANNEL 3
REFERENCE
REFERENCE
DAC
8-BIT
DAC
8-BIT
DAC
3
2
13 14
1
12
8-BIT
FPOL
MODULATION
6-BIT
PEDST
O2
25
2
GND
232619
BLANKING
PEDESTAL
FB2V
PEDST
P3VO3
20
3
GND
18
21
BLANKING
PEDESTAL
FB
3
SUPPLY
PEDST
MHA343
79
BLANKING
OUTPUT CLAMPING
DISV
TDA4885
GND
P
V
HFBCLI
k, full pagewidth
LIM SDA SCL
DAC
6-BIT
DISV
DISO
GAIN
signal path 1
PEDST
CONTRAST
INPUT-
BRIGHTNESS
OSD-
CLIPPING
BLANKING
CLAMPING
CONTRAST
DAC
6-BIT
data
DAC
6-BIT
2
6-BIT
17 15 16
C-BUS
I
DAC
BLANKING
DAC
4-BIT
REGISTER
LIMITING
FPOL
GAIN
signal path 2
CONTRAST
INPUT-
BLANKING
CLAMPING
BRIGHTNESS
OSD-
CONTRAST
CLIPPING
GAIN
signal path 3
OSD-
CONTRAST
INPUT-
BLANKING
CLAMPING
BRIGHTNESS
blanking
CONTRAST
CLIPPING
input clamping
511
INPUT CLAMPING
VERTICAL BLANKING
TDA4885
DISO
3
OSD
2
OSD
OSD-INPUT
fast blanking
1
1234
FBL OSD
Fig.1 Block diagram.
6
I1
V
8
I2
V
1997 Nov 25 5
10
I3
V
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
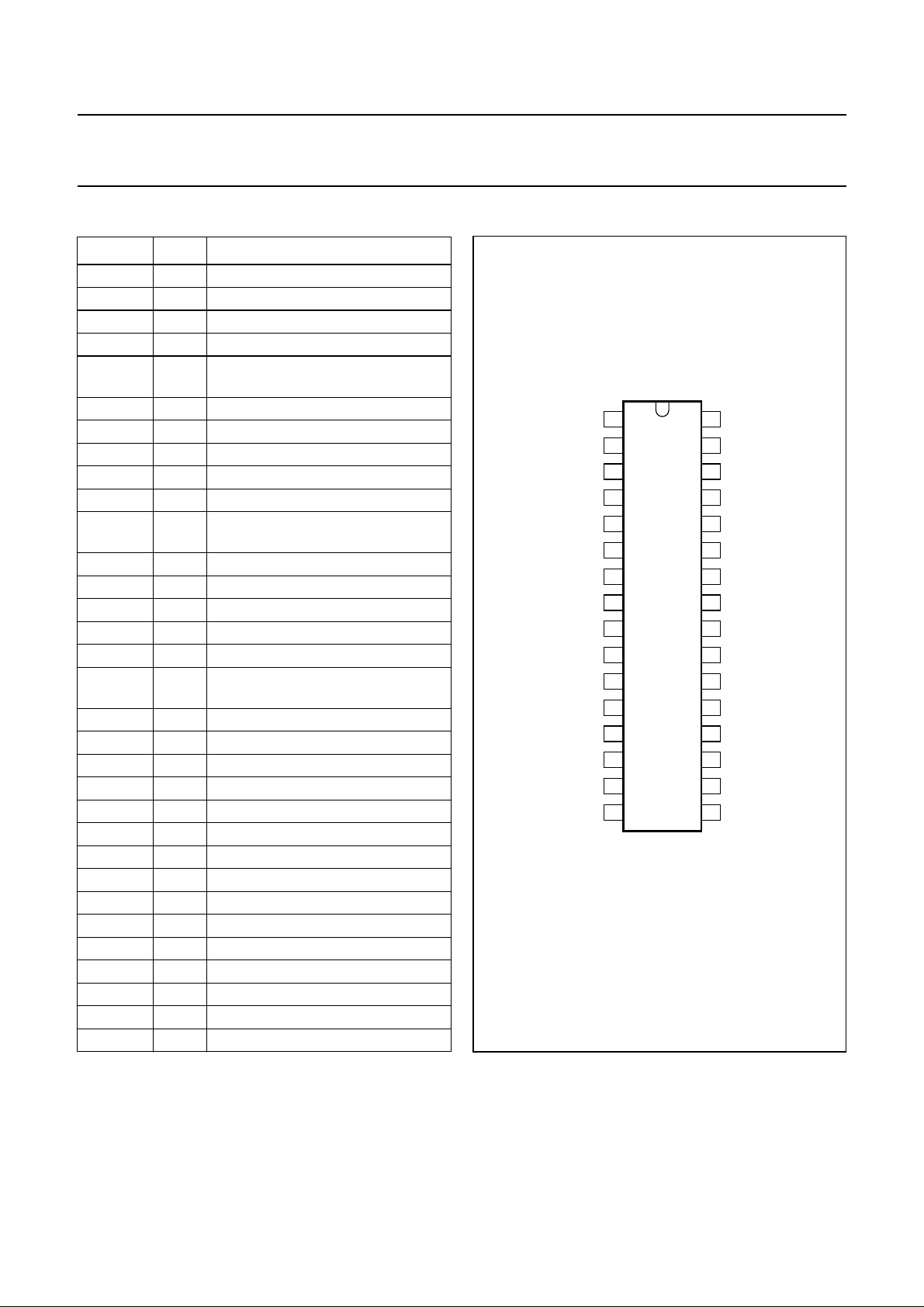
6 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
FBL 1 fast blanking input for OSD insertion
OSD
1
OSD
2
OSD
3
CLI 5 vertical blanking input
V
I1
V
P
V
I2
GND 9 ground
V
I3
HFB 11 horizontal flyback input
GM
1
GM
2
GM
3
SDA 15 I
SCL 16 I
LIM 17 beam current limiting input,
GND
3
V
P3
V
O3
FB
3
REF
3
GND
2
V
P2
V
O2
FB
2
REF
2
GND
1
V
P1
V
O1
FB
1
REF
1
2 OSD input channel 1
3 OSD input channel 2
4 OSD input channel 3
(input clamping)
6 signal input channel 1
7 supply voltage
8 signal input channel 2
10 signal input channel 3
(output clamping, blanking)
12 gain modulation input channel 1
13 gain modulation input channel 2
14 gain modulation input channel 3
2
C-bus serial data input/output
2
C-bus clock input
subcontrast setting
18 ground channel 3
19 supply voltage channel 3
20 signal output channel 3
21 feedback input channel 3
22 reference voltage channel 3
23 ground channel 2
24 supply voltage channel 2
25 signal output channel 2
26 feedback input channel 2
27 reference voltage channel 2
28 ground channel 1
29 supply voltage channel 1
30 signal output channel 1
31 feedback input channel 1
32 reference voltage channel 1
handbook, halfpage
FBL
1
OSD
2
1
OSD
3
2
OSD
4
3
CLI
5
V
6
I1
V
7
P
V
8
I2
GND
V
HFB
GM
GM
GM
SDA
SCL
TDA4885
9
10
I3
11
12
1
13
2
14
3
15
16
MHA342
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
TDA4885
REF
32
1
FB
31
1
V
30
O1
V
29
P1
GND
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
REF
FB
V
O2
V
P2
GND
REF
FB
V
O3
V
P3
GND
LIM
1
2
2
2
3
3
3
1997 Nov 25 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
See block diagram (Fig.1) and definition of levels and
output signals (Chapter “Characteristics” notes 1 to 3;
Figs 3 to 6).
7.1 Signal input stage
(input clamping, blanking and clipping)
The RGB input signals with nominal signal amplitude of
0.7V
low-ohmic source (75 Ω recommended) and actively
clamped to an internal DC voltage during signal black
level. Because of the high-ohmic input impedance of the
TDA4885 the coupling capacitor (which also functions as
storage capacitor during clamping pulses) can be
relatively small (10 nF recommended). The internal
leakage currents will discharge the coupling capacitor
resulting in black output signals for missing input
clamping pulses.
Composite signals will not disturb normal operations
because a clipping circuit cuts all signal parts below
black level.
A fast signal blanking stage belongs to the input stage
which is driven by several blanking pulses (see Section
“Clamping and blanking pulses”) and control bit DISV = 1.
During the off condition the internal reference black level
will be inserted instead of the input signals.
7.2 Electronic potentiometer stages
7.2.1 C
The input signals related to the internal reference black
level can be simultaneously adjusted by contrast control
with a control range of typically 32 dB. The nominal
contrast setting is defined for 26H (4 dB below maximum).
are capacitively coupled into the TDA4885 from a
b-w
ONTRAST CONTROL (DRIVEN BY I
2
C-BUS,6-BIT
DAC)
TDA4885
7.2.3 G
AIN CONTROL (DRIVEN BY I
AND GREY SCALE TRACKING
Gain control is used for white point adjustment (correction
for different voltage to light amplification of the three colour
channels) and therefore individual for the three channels.
The video signals related to the reference black level can
be gain controlled within a range of typical 7 dB.
The nominal setting is maximum gain. The video signal is
the addition of the contrast controlled input signal and the
brightness shift. The gain setting is also valid for OSD
signals, thus the complete ‘grey scale’ is effected by gain
control.
7.3 Output stage
In the output stage the nominal input signal will be
amplified to 2.8V
output colour signal at nominal
b-w
contrast and maximum gain. The maximum input-output
amplification at maximum contrast and gain settings is
16 dB. By output clamping the reference black level can
be adjusted. In order to achieve very fast rise and fall times
of the output signals with minimum crosstalk between the
channels, each output stage has its own supply voltage
and ground pin.
7.4 Pedestal blanking
For the video portion the reference black level should
correspond to the ‘extended cut-off voltage’ at the
cathode. During vertical flyback nevertheless retrace lines
may be visible, though blanking to spot cut-off is useful.
With control bit PEDST = 1 the pedestal black level will be
adjusted by output clamping instead of the reference black
level (see Fig.5). The pedestal black level is more negative
than the video black level at minimum brightness setting
and the voltage difference to reference black level is
independent of any user control.
2
C-BUS,6-BIT DAC)
7.2.2 B
RIGHTNESS CONTROL (DRIVEN BY I
2
C-BUS,6-BIT
DAC)
With brightness control the video black level will be shifted
in relation to the reference black level simultaneously for
all three channels. With a negative setting (maximum 10%
of nominal signal amplitude) dark signal parts will be lost in
ultra black while for positive settings (maximum 30% of
nominal signal amplitude) the background will alter from
black to grey. The nominal brightness setting (10H) is no
shift. The brightness setting is also valid for OSD signals.
During blanking and output clamping the video black level
will be blanked to reference black level (brightness
blanking).
1997 Nov 25 7
7.5 Output clamping, feedback references and
DAC outputs
Aim of the output clamping (pins FB
, FB2 and FB3) is to
1
set the reference black level of the signal outputs to a
value which corresponds to the ‘extended cut-off voltage’
of the CRT cathodes. At lack of output clamping pulses the
integrated storage capacitors will discharge resulting in
output signals going to switch-off voltage. Feedback
references are driven by the I2C-bus.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
1. Control bit FPOL = 0
The cathode voltage (DC-coupled) is divided by a
voltage divider and fed back to the IC. During the
output clamping pulse it is compared with an
adjustable feedback reference voltage with a range of
5.8 to 4.0 V. Any difference will lead to a reference
black level correction (control bit PEDST = 0) or
pedestal black level correction (control bit PEDST = 1)
by charging or discharging the integrated capacitor
which stores the black level information between the
output clamping pulses. The DC voltages of the output
stages should be designed in such a way that the
reference black level/pedestal black level is within the
range of 0.5 to 2.5 V. The reference voltages are also
fed to the DAC output pins (REF1, REF2 and REF3).
For correct operation it is necessary that there is
enough room for ultra black signals (negative
brightness setting, pedestal black level if control bit
PEDST = 1). Any clipping with the video supply
voltage can disturb signal rise/fall times or the black
level stabilization.
2. Control bit FPOL = 1
For applications with AC-coupled cathodes positive
feedback can be taken directly or divided by a voltage
divider from the signal outputs or the emitter of an
external emitter follower. During the output clamping
pulse it is compared with a fixed reference voltage of
0.7 V.
For black level restoration the DAC outputs (REF1,
REF2 and REF3) with a range of 5.8 to 4.0 V can be
used.
The use of pedestal blanking allows a very simple
black level restoration with a DC diode clamp instead
of a complicated pulse restoration circuit because the
pedestal black level is the most negative output signal.
7.6 Clamping and blanking pulses
The pin CLI of TDA4885 can be directly connected to
pin CLBL of e.g. TDA4855 sync processor for input
clamping pulses and vertical blanking pulses.
The threshold for the input clamping pulse (typical 3 V) is
higher than the threshold for the vertical blanking pulse
(typical 1.4 V) but there must be no blanking during input
clamping. Thus vertical blanking only is enabled if no input
clamping is detected. For this reason the input clamping
pulse must have rise/fall times faster than 75 ns/V during
the transition from 1.2 to 3.5 V and opposite. The internal
vertical blanking pulse will be delayed by typical 290 ns.
TDA4885
During the vertical blanking pulse at pin CLI signal
blanking, brightness blanking and with control bit
PEDST = 1 pedestal blanking will be activated. Input
clamping pulses during vertical blanking will not switch off
blanking.
For proper input clamping the input signals have to be at
black level during the input clamping pulse.
An input pulse at pin HFB (e.g. horizontal flyback pulse)
will be scanned with two thresholds. If the input pulse
exceeds the first one (typical 1.4 V) signal blanking,
brightness blanking and if control bit PEDST = 1
pedestal blanking will be activated. If the input pulse
exceeds the second one (typical 3 V) additionally output
clamping will be activated. The vertical blanking pulse can
also be mixed with the horizontal flyback pulse at pin HFB.
7.7 On Screen Display (OSD)
If the fast blanking input signal at pin FBL exceeds the
threshold (typical 1.4 V) the input signals are blanked
(signal blanking) and OSD signals are enabled. Then any
signal at pins OSD
threshold will create an insertion signal with an amplitude
of 125% of the nominal colour signal (approximately 80%
of the maximum colour signal). The amplitude can be
controlled by OSD contrast (driven by I2C-bus) with a
range of 12 dB. The OSD signals are inserted at the same
point as the contrast controlled input signals and will be
treated with brightness and gain control like normal input
signals.
With control bit DISO = 1 OSD, signal insertion and fast
blanking (pin FBL) are disabled.
7.8 Limiting by contrast reduction
Beam current limiting is possible with an external voltage
at pin LIM. The maximum overall voltage gain of contrast
(and OSD contrast) control can be reduced by a voltage
between 4.5 V (start of reduction) and 2.0 V (−26 dB)
without effecting the contrast bit resolution. By setting the
maximum voltage at pin LIM to less than 4.5 V the
maximum gain is reduced for all channels (subcontrast
setting). The open-circuit pin will have a voltage of
approximately 5.0 V but is very high-ohmic and should be
tied to a voltage source of 5.0 V or higher or should be
connected to a capacitance of some nF if not used.
, OSD2 or OSD3 exceeding the same
1
1997 Nov 25 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
7.9 Gain modulation
To achieve brightness uniformity over the screen scan
dependent gain modulation is possible. With open-circuit
pins the gain will be reduced by 20% giving the possibility
of symmetrical gain modulations (±18%) with ±1 V related
to the open-circuit voltage of about 2.0 V at any gain
setting.
If the gain modulation feature will not be used pins GM1,
GM2 and GM3 should be grounded to profit by maximum
voltage gain.
2
7.10 I
The TDA4885 contains an I2C-bus receiver for several
control functions:
1. Contrast control with 6-bit DAC
2. Brightness control with 6-bit DAC
3. OSD contrast control with 4-bit DAC
4. Gain control for each channel with 6-bit DAC
5. Internal feedback reference and external reference
6. Control register with control bits FPOL, DISV, DISO
7. Test register for production tests only.
C-bus control
voltage control for each channel with 8-bit DAC
and PEDST
TDA4885
All registers are set to logic 0 (minimum value for control
registers) after power-up and after internal power-on reset
of the I2C-bus.
1997 Nov 25 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
8 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
V
P1, 2, 3
V
i
V
ext
supply voltage (pin 7) 0 8.8 V
supply voltage channel 1, 2 and 3 (pins 29, 24 and 19) 0 8.8 V
input voltage (pins 6, 8 and 10) −0.1 V
P
external DC voltage applied to the following pins:
pins 1 to 4 −0.1 V
pins 12, 13, 14 and 17 −0.1 V
pins 11 and 5 −0.1 V
pins 15 and 16 −0.1 V
pins 31, 26 and 21 −0.1 V
P
P
+ 0.7 V
P
P
+ 0.7 V
P
pins 30, 25 and 20 note 1 note 1
I
o(av)
I
OM
P
T
T
T
V
tot
stg
amb
j
ESD
pins 32, 27 and 22 −0.1 V
average output current (pins 30, 25 and 20) − 20 mA
peak output current (pins 30, 25 and 20) − 50 mA
total power dissipation − 1300 mW
storage temperature −25 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature −20 +70 °C
junction temperature −25 +150 °C
electrostatic handling for all pins
P
machine model 0.75 µH (note 2) −250 +250 V
human body model (note 3) −3000 +3000 V
V
V
V
V
V
Notes
1. No external voltages.
2. Equivalent to discharging a 200 pF capacitor via a 10 Ω series resistor (
“UZW-B0/FQ-B302”
3. Equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor via a 1500 Ω series resistor (
“UZW-B0/FQ-A302”
).
).
9 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 60 K/W
1997 Nov 25 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
10 CHARACTERISTICS
All voltages and currents are measured in test circuit of Fig.19; all voltages are measured with respect to GND (pins 9,
28, 23 and 18); VP=V
value) at pins 6, 8 and 10]; nominal colour signals at signal outputs (pins 30, 25 and 20); reference black level (V
= 8 V (pins 7, 29, 24 and 19); T
P1, 2, 3
=25°C; nominal input signals [0.7 V (peak-to-peak
amb
)
rbl
approximately 0.7 V; nominal settings for brightness and contrast; maximum settings for OSD contrast and gain; no
limiting of contrast (V17= 5 V); no OSD fast blanking (pin 1 connected to ground); no gain modulation (pins 12, 13
and 14 connected to ground); notes 1 to 3; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
I
P
V
P1, 2, 3
supply voltage (pin 7) 7.6 8.0 8.8 V
supply current (pin 7) note 4 − 20 25 mA
channel supply voltage
7.6 8.0 8.8 V
(pins 29, 24 and 19)
I
P1, 2, 3
V
PSO
channel supply current
(pins 29, 24 and 19)
supply voltage for signal switch
off (threshold at pin 7)
signal outputs (pins 30, 25
and 20) open-circuit;
V
= 0.7 V; note 5
rbl
signal outputs switched to
switch-off voltage; note 1
− 40 45 mA
−−7.2 V
Clamping and blanking pulses (pins 5 and 11)
V
5
input clamping and vertical
blanking input signal
note 6
no blanking, no input
−0.1 − +1.2 V
clamping
blanking, no input clamping 1.6 − 2.6 V
input clamping, no blanking 3.5 − V
I
5
input current V5= 1 V; note 7 −1.5 −0.2 −0.05 µA
P
V
pin 5 grounded; note 7 −80 −60 −30 µA
V
= −0.1 V; note 7 −250 −200 −100 µA
5
t
r/f5
rise/fall time for input clamping
note 6; see Fig.7 −−75 ns/V
pulse, disable for blanking
t
W5
t
dl5
width of input clamping pulse 0.6 −− µs
delay between leading edges
of vertical blanking input pulse
and internal blanking pulse
V11< 0.8 V; input pulse with
50 ns/V; threshold for rising
input pulse V5= 1.4 V;
− 270 − ns
threshold after input clamping
pulse V5= 3 V; see Fig.7
t
dt5
delay between trailing edges of
vertical blanking input pulse
and internal blanking pulse
V
11
output clamping and blanking
input signal
V11< 0.8 V; input pulse with
50 ns/V; threshold V5= 1.4 V;
see Fig.7
note 8
no blanking, no output
− 115 − ns
−0.1 − +0.8 V
clamping
blanking, no output clamping 2.0 − 2.6 V
blanking, output clamping 3.5 − V
P
V
1997 Nov 25 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
11
input current V11= 0.8 V; note 7 −3 −0.4 −0.1 µA
pin 5 grounded; note 7 −80 −60 −30 µA
V
= −0.1 V; note 7 −250 −200 −100 µA
5
Video signal inputs (channel 1: pin 6; channel 2: pin 8; channel 3: pin 10)
V
i(b-w)6, 8, 10
positive input signal referred to
− 0.7 1.0 V
black
V
I(clamp)6, 8, 10
DC voltage during input
note 9 − 4 − V
clamping
I
I6, 8, 10
Z
i6, 8, 10
C
i6, 8, 10
magnitude of signal input
DC input current no input clamping;
V
I6, 8, 10=VI(clamp)6, 8, 10
T
= −20 to +70 °C
amb
during input clamping;
V
I6, 8, 10=VI(clamp)6, 8, 10
f = 100 MHz;
impedance
V
I(DC)6, 8, 10=VI(clamp)6, 8, 10
input capacitance against
0.02 0.20 0.35 µA
;
±110 ±150 ±190 µA
±0.7 V
500 −− Ω
−−3pF
ground
Signal blanking
α
ct(bl)
crosstalk suppression from
input to output during blanking
t
d11(sig)l
delay between blanking input
(leading edge) and output
signal blanking
t
d11(sig)t
delay between blanking input
(trailing edge) and output
signal blanking
Clipping (measured at signal outputs)
∆V
clipp
offset during sync clipping
related to nominal colour signal
Contrast control; see Fig.9 and note 11
d
C
colour signal related to nominal
colour signal
∆G
track
tracking of output colour
signals of channels 1, 2 and 3
control bit DISV = 1; f = 80 MHz 20 30 − dB
control bit DISV = 1;
10 15 − dB
f = 135 MHz
see Fig.8 − 55 − ns
see Fig.8 − 25 − ns
V
I6, 8, 10=VI(clamp)6, 8, 10
;
− 12 %
note 10; see Fig.3
3FH (maximum) − 4 − dB
26H (nominal) − 0 − dB
00H (minimum) −−28 − dB
3FH to 00H; note 12 − 0.0 0.5 dB
1997 Nov 25 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Fast blanking (pin 1) and OSD signal insertion (channel 1: pin 2; channel 2: pin 3; channel 3: pin 4); note 13
V
1
fast blanking input signal no video signal blanking, OSD
0 − 1.1 V
signal insertion disabled
video signal blanking, OSD
1.7 − V
− 1V
P
signal insertion enabled
V
2, 3, 4
OSD input signal V1> 1.7 V
no internal OSD signal
0 − 1.1 V
insertion
t
f(FBL)
fall time of colour signals
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
internal OSD signal insertion 1.7 − V
90 to 10% amplitude; start of
−−10 ns
fast blanking pulse at pin 1 with
− 1V
P
1.2 ns/V; note 14; see Fig.10
t
r(FBL)
rise time of colour signals
(pins 30, 25 and 20)
10 to 90% amplitude; end of
fast blanking pulse at pin 1 with
−−10 ns
1.2 ns/V; note 14; see Fig.10
t
r(OSD)
rise time of OSD colour signals 10 to 90% amplitude; input
−−4ns
pulse with 1.2 ns/V; see Fig.10
t
f(OSD)
fall time of OSD colour signals 90 to 10% amplitude; input
−−7ns
pulse with 1.2 ns/V; see Fig.10
t
g(CO)
width of (negative going) OSD
signal insertion glitch, leading
edge
identical pulses with 1.2 ns/V at
fast blanking input (pin 1) and
OSD signal inputs (pins 2,
−−6ns
3 and 4); note 15; see Fig.10
t
g(OC)
width of (negative going) OSD
signal insertion glitch, trailing
edge
identical pulses with 1.2 ns/V at
fast blanking input (pin 1) and
OSD signal inputs (pins 2,
−−6ns
3 and 4); note 15; see Fig.10
dV
OSD
overshoot/undershoot of OSD
colour signal related to actual
OSD input pulse (pins 2, 3
and 4) with 1.2 ns/V; V1> 1.7 V
− 13 20 %
OSD output pulse amplitude
t
over
V
OSD(max)
time of OSD signal overshoot
exceeding 10%
maximum OSD colour signal
related to nominal colour signal
OSD input pulse (pins 2, 3
and 4) with 1.2 ns/V; V1> 1.7 V
maximum OSD contrast;
maximum gain; pins 12,
−−2ns
100 125 150 %
13 and 14 connected to ground
OSD contrast control; see Fig.11 and note 16
d
OC
OSD colour signal related to
maximum OSD colour signal
00H (minimum) −14 −12 −10 dB
0FH (maximum) − 0 − dB
1997 Nov 25 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Limiting (pin 17); see Fig.9 and note 17
V
17(nom)
V
17(start)
input voltage pin 17 open-circuit 4.7 5.0 5.3 V
starting voltage for contrast
4.2 4.5 4.8 V
and OSD contrast reduction
V
17(stop)
I
17
stop voltage for contrast and
OSD contrast reduction
−32 dB below maximum colour
signal (contrast setting 3FH)
1.5 2.0 2.5 V
maximum input current V17=0V −1.0 −0.5 −0.1 µA
Brightness control; see Fig.12 and notes 18 and 19
∆V
bl
∆V
BT
difference between black level
and reference black level at
signal outputs related to
nominal colour signal
difference of ∆Vbl between any
3FH (maximum) +25 +30 +35 %
10H (nominal) −2 0 +2 %
00H (minimum) −12 −10 −8%
−1.2 0 +1.2 %
two channels related to
nominal colour signal
Brightness blanking
t
d11(br)l
delay between blanking input
see Fig.8 −−60 ns
at pin 11 (leading edge) and
brightness blanking at signal
outputs
t
d11(br)t
delay between blanking input
see Fig.8 −−60 ns
at pin 11 (trailing edge) and
brightness blanking at signal
outputs
Gain control; see Fig.13 and note 20
d
G
video signal related to video
signal at maximum gain
00H (minimum) −8 −7 −6dB
3FH (maximum) − 0 − dB
Gain modulation (channel 1: pin 12; channel 2: pin 13; channel 3: pin 14)
V
12, 13, 14
input voltage symmetrical modulation 1.0 − 3.0 V
modulation feature not in use −−0V
nominal: pins 12, 13 and 14
open-circuit
G
mod1, 2, 3
gain modulation channels 1, 2
and 3
note 21; see Fig.14
pins 12, 13 and 14 grounded
(modulation feature not in
use)
V
12, 13, 14
V
12, 13, 14
V
12, 13, 14
= 1 V (maximum) 112 118 124 %
=2V − 100 − %
= 3 V (minimum) 76 82 88 %
1997 Nov 25 14
1.8 2.0 2.2 V
112 120 130 %
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Pedestal blanking
∆V
30, 25, 20PED
difference of pedestal black
note 22; see Fig.5 −18 −16 −14 %
level to video black level at
nominal brightness at signal
output pins related to nominal
colour signal
∆V
30, 25, 20PED(T)
variation of ∆V
30, 25, 20PED
with
T
= −20 to +70 °C −0.8 0 +0.8 %
amb
temperature related to nominal
colour signal
Signal outputs (channel 1: pin 30; channel 2: pin 25; channel 3: pin 20)
V
30, 25, 20(b-w)
nominal colour signal nominal contrast; maximum
2.5 2.8 3.1 V
gain; pins 12, 13 and 14
grounded; V
I(b-w)
= 0.7 V;
without load
V
30, 25, 20(max)
maximum colour signal maximum contrast; maximum
4.0 4.5 5 V
gain; pins 12, 13 and 14
grounded; V
I(b-w)
= 0.7 V;
without load
V
30, 25, 20(min)
switch-off voltage
− 0.05 0.1 V
(minimum output voltage level)
V
30, 25, 20(max)
maximum output voltage level at arbitrary input signals,
VP− 2 − VP− 1V
contrast, brightness and gain
adjustments; without load
R
30, 25, 20
I
30, 25, 20
I
30, 25, 20M(source)
output resistance − 80 −Ω
maximum source current −15 −− mA
peak source current during fast positive signal
−40 −− mA
transients
I
30, 25, 20M(sink)
peak sink current during fast negative signal
−−20 mA
transients
S/N signal-to-noise ratio note 23 44 50 − dB
D
30, 25, 20(th)
output thermal distortion note 24 −−0.6 %
Frequency response at signal outputs (channel 1: pin 30; channel 2: pin 25; channel 3: pin 20)
∆G
30, 25, 20(f)
amplification decrease by
f = 135 MHz (small signal) − 1.2 3.0 dB
frequency response
t
r(30, 25, 20)
rise time of fast transients 10 to 90% amplitude; nominal
− 2.7 3 ns
colour signal; note 25
t
f(30, 25, 20)
fall time of fast transients 90 to 10% amplitude; nominal
− 3.9 4.3 ns
colour signal; note 25
dV
30, 25, 20
over/undershoot of output
signal pulse related to actual
input rise/fall time = 1 ns;
nominal colour signal
− 510 %
output pulse amplitude
1997 Nov 25 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
SYMBOL P ARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Crosstalk at signal outputs (channel 1: pin 30; channel 2: pin 25; channel 3: pin 20)
α
ct(tr)
transient crosstalk suppression input rise/fall time = 1 ns;
10 25 − dB
note 26
α
ct(f)
crosstalk suppression by
frequency
f = 50 MHz 25 30 − dB
f = 100 MHz 10 20 − dB
Internal feedback reference voltage; see Fig.15 and note 27
V
V
ref(n)
ref(p)
internal reference voltage for
negative feedback polarity
fixed internal reference voltage
FFH; FPOL = 0 3.8 4.0 4.2 V
00H; FPOL = 0 5.6 5.8 6.1 V
FPOL = 1 0.6 0.7 0.8 V
for positive feedback polarity
∆V
/∆T variation of V
ref
ref(n)
and V
ref(p)
in
T
= −20 to +70 °C0−±1.0 %
amb
the temperature range
∆V
/∆V
ref
P
External reference voltages (REF
V
32, 27, 22
variation of V
with supply voltage V
and V
ref(n)
ref(p)
P
: pin 32; REF2: pin 27; REF3: pin 22); see Fig.16 and note 28
1
external reference voltage
(equal to internal reference
7.6 V ≤ VP≤ 8.8 V 0 −±1.0 %
FFH 3.8 4.0 4.2 V
00H 5.6 5.8 6.1 V
voltage with control bit
FPOL = 0 )
∆V
32, 27, 22
/∆T variation of V
32, 27, 22
in the
T
= −20 to +70 °C0−±1.0 %
amb
temperature range
∆V
32, 27, 22
R
32, 27, 22
I
32, 27, 22
I
32, 27, 22
/∆VPvariation of V
supply voltage V
output resistance − 90 −Ω
maximum sink current −−400 µA
maximum source current −−330 −280 µA
32, 27, 22
P
with
7.6 V ≤ VP≤ 8.8 V 0 −±1.0 %
Output clamping, feedback inputs (channel 1: pin 31; channel 2: pin 26; channel 3: pin 21)
I
31, 26, 21(max)
V
30, 25, 20rbl(min)
V
30, 25, 20rbl(max)
∆V
bl(CRT)
∆V
bl(lf)
maximum input current during output clamping;
V11> 3.5 V; V
31, 26, 21
= 0.5 V
−500 −100 −60 nA
minimum reference black level PEDST = 0; V11> 3.5 V 0.01 0.1 0.5 V
minimum pedestal black level PEDST = 1; V
> 3.5 V 0.01 0.1 0.5 V
11
maximum reference black level PEDST = 0; V11> 3.5 V 2.4 2.8 4 V
maximum pedestal black level PEDST = 1; V
> 3.5 V 2.4 2.8 4 V
11
black level variation at CRT note 29 0 40 200 mV
black level variation between
clamping pulses related to
line frequency 60 kHz;
10% duty cycle
− 0.1 0.5 %
nominal colour signal
t
W11
width of clamping pulse measured at V11=3V;
1 −− µs
see Fig.8
t
d11(clamp)l
delay between clamping input
see Fig.8 −−300 ns
at pin 11 (leading edge) and
start of internal output clamping
pulse
1997 Nov 25 16
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
150 MHz video controller with I2C-bus
TDA4885
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
t
d11(clamp)t
delay between clamping input
see Fig.8 −−60 ns
at pin 11 (trailing edge) and
end of internal output clamping
pulse
2
C-bus inputs (pins 15 and 16)
I
f
SCL
V
V
I
IL
I
IH
V
I
ack
IL
IH
OL
SCL clock frequency −−100 kHz
LOW-level input voltage 0.0 − 1.5 V
HIGH-level input voltage 3.0 − 5.0 V
LOW-level input current VIL=0V −−−10 µA
HIGH-level input current VIH=5V −−−10 µA
LOW-level output voltage during acknowledge 0.0 − 0.4 V
output current at pin 15 during
VOL= 0.4 V 3.0 − 5.0 mA
acknowledge
V
th(POR)(r)
threshold for power-on reset on rising supply voltage − 1.5 2.0 V
falling supply voltage − 3.5 − V
V
th(POR)(f)
threshold for power-on reset off rising supply voltage −−7.0 V
falling supply voltage − 1.5 − V
Notes to the characteristics
1. Definition of levels (see Figs 3 to 5):
Reference black level:this is the level to which the input level is clamped during the input clamping pulse
(V5> 3.5 V). It is used internally as a reference for the gain settings. It can be observed on the outputs:
a) when the input is at black and the brightness setting is nominal (subaddress 01H = 10H)
b) during output blanking/clamping (V11> 3.5 V) if control bit PEDST = 0.
Video black level:this is the black level of the actual video. On the input it is still equal to the reference black level.
On the output it may deviate from it according to the brightness setting. Contrast setting leaves the video black level
unaltered.
Pedestal black level:this is an ultra black level which deviates from reference black level by a fixed amount. It can
be observed on the output during output blanking/clamping (V11> 3.5 V) if control bit PEDST = 1.
Switch-off voltage: this is the lowest signal voltage at outputs. The signals will be switched off by discharging the
internal black level storage capacitors if the supply voltage is less than V
PSO
.
Blanking level: this level equals reference black (control bit PEDST = 0) or pedestal black (control bit PEDST = 1).
2. Explanation to black level adjustment:
The actual blanking level on the output depends on the external feedback application. The loop will only function
correctly if it is within the control range of V
30, 25, 20rbl(min)
to V
30, 25, 20rbl(max)
. Note: changing control bit PEDST in a
given application will not affect the blanking level, but instead shifts the video (and needs re-alignment of the three
black levels).
The three reference black levels are aligned correctly when they are made equal to the ‘extended cut-off levels’ of
the three cathodes. Full raster and spot cut-off can only be achieved by enabling the pedestal blanking or by applying
a negative pulse to grid 1.
1997 Nov 25 17
 Loading...
Loading...