Philips TDA4852 Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA4852
Horizontal and vertical deflection
controller for autosync monitors
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
December 1992
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Horizontal and vertical deflection controller
TDA4852
for autosync monitors
FEATURES
• Low jitter
• All adjustments DC-controllable
• Alignment-free oscillators
• Sync separators for video or horizontal and vertical TTL
sync levels regardless of polarity
• Horizontal oscillator with PLL1 for sync and PLL2 for
flyback
• Constant vertical and E/W amplitude in autosync
operation
• DC-coupling to vertical power amplifier
• Internal supply voltage stabilization with excellent ripple
rejection to ensure stable geometrical adjustments
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
I
P
V
P
i sync
positive supply voltage (pin 1) 9.2 12 16 V
supply current − 40 − mA
AC-coupled composite video signal with negative-going sync
(peak-to-peak value, pin 9)
sync slicing level − 120 − mV
DC-coupled TTL-compatible horizontal sync signal
(peak-to-peak value, pin 9)
slicing level 1.2 1.4 1.6 V
DC-coupled TTL-compatible vertical sync signal
(peak-to-peak value, pin 10)
slicing level 1.2 1.4 1.6 V
I
I
T
oV
oH
amb
vertical differential output current (peak-to-peak value, pins 5 and 6) − 1 − mA
horizontal sink output current on pin 3 −− 60 mA
operating ambient temperature range 0 − +70 °C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA4852 is a monolithic integrated circuit for
economical solutions in autosync monitors. The IC
incorporates the complete horizontal and vertical small
signal processing. In conjunction with TDA4860/61/65, or
TDA8351 (vertical output circuits) the ICs offer an
extremely advanced system solution.
− 1 − V
1.7 −−V
1.7 −−V
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED
TYPE NUMBER
PINS
PIN
POSITION
TDA4852 20 DIL plastic SOT146
Note
1. SOT146-1; 1996 November 27.
December 1992 2
PACKAGE
MATERIAL CODE
(1)
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
December 1992 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Horizontal and vertical deflection controller
for autosync monitors
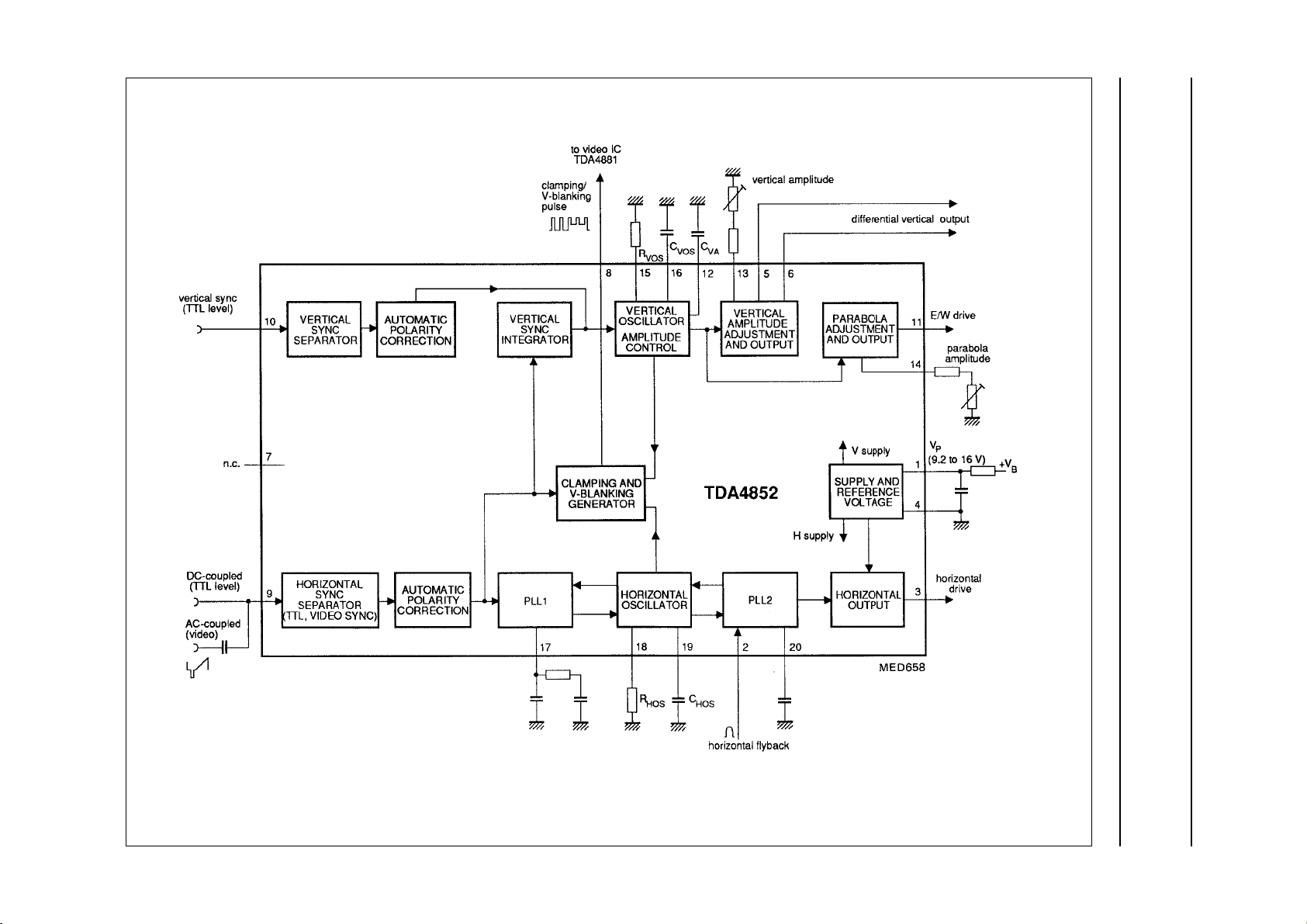
Fig.1 Block diagram.
TDA4852
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Horizontal and vertical deflection controller
for autosync monitors
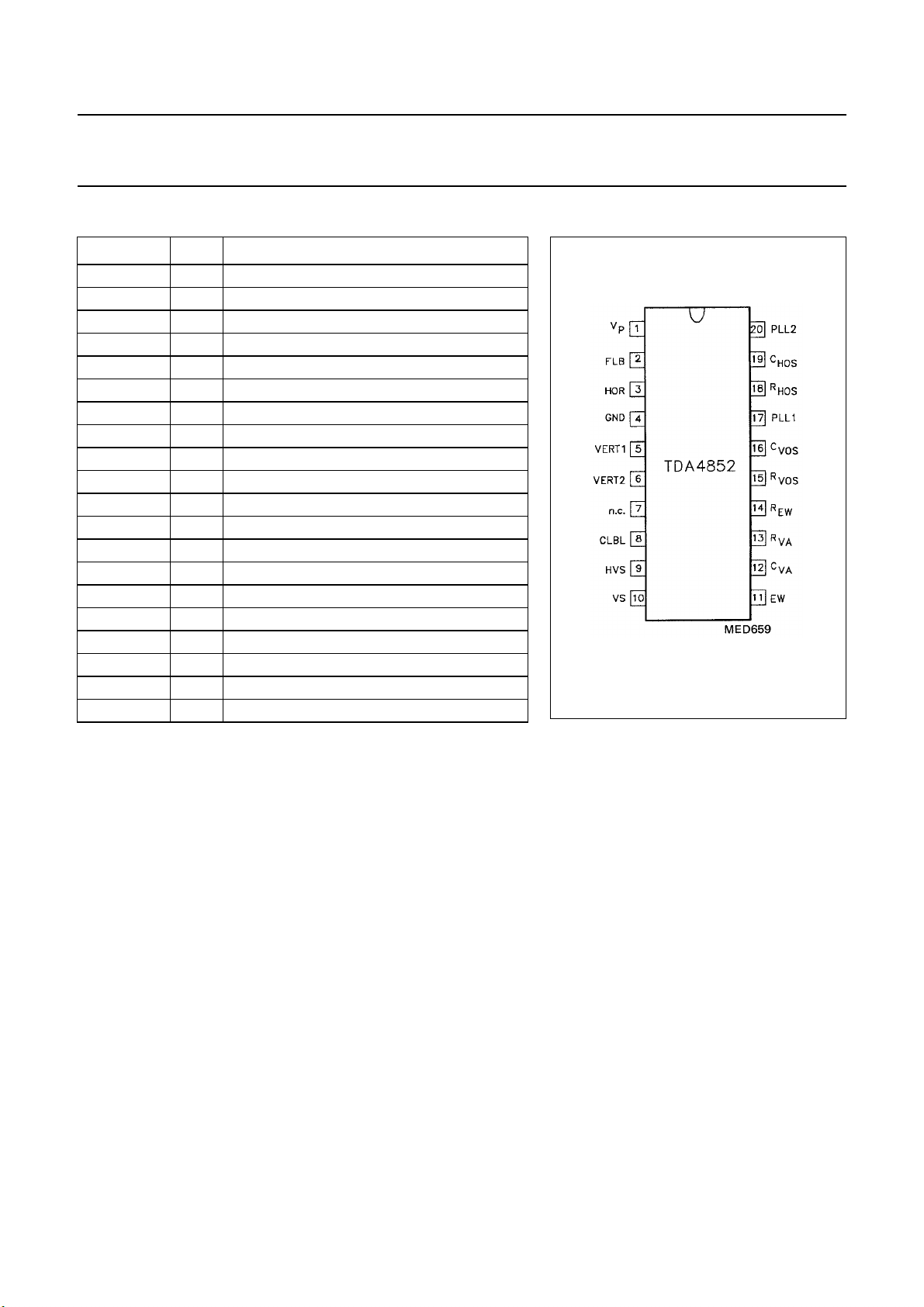
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
V
P
FLB 2 horizontal flyback input
HOR 3 horizontal output
GND 4 ground (0 V)
VERT1 5 vertical output 1; negative-going sawtooth
VERT2 6 vertical output 2; positive-going sawtooth
n.c. 7 not connected
CLBL 8 clamping/blanking pulse output
HVS 9 horizontal sync/video input
VS 10 vertical sync input
EW 11 E/W output (parabola to driver stage)
C
VA
R
VA
R
EW
R
VOS
C
VOS
PLL1 17 PLL1 phase
R
HOS
C
HOS
PLL2 20 PLL2 phase
1 positive supply voltage
12 capacitor for amplitude control
13 vertical amplitude adjustment input
14 E/W amplitude adjustment input (parabola)
15 vertical oscillator resistor
16 vertical oscillator capacitor
18 horizontal oscillator resistor
19 horizontal oscillator capacitor
TDA4852
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
December 1992 4

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Horizontal and vertical deflection controller
for autosync monitors
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Horizontal sync separator and
polarity correction
An AC-coupled video signal or a
DC-coupled TTL sync signal (H only
or composite sync) is input on pin 9.
Video signals are clamped with top
sync on 1.28 V, and are sliced at
1.4 V. This results in a fixed absolute
slicing level of 120 mV related to top
sync. DC-coupled TTL sync signals
are also sliced at 1.4 V, however with
the clamping circuit in current
limitation. The polarity of the
separated sync is detected by internal
integration of the signal, then the
polarity is corrected. The corrected
sync is input signal for the vertical
sync integrator and the PLL1 stage.
Vertical sync separator, polarity
correction and vertical sync
integrator
DC-coupled vertical TTL sync signals
may be applied to pin 10. They are
sliced at 1.4 V. The polarity of the
separated sync is detected by internal
integration, then the polarity is
corrected. If pin 10 is not used, it must
be connected to ground. The
separated V
signal from pin 10, or
i sync
the integrated composite sync signal
from pin 9 (TTL or video) triggers
directly the vertical oscillator.
Clamping and V-blanking
generator
A combined clamping and V-blanking
pulse is available on pin 8 (suitable for
the video pre-amplifier TDA4881).
The lower level of 1.9 V is the
blanking signal derived from the
vertical blanking pulse from the
internal vertical oscillator.
Vertical blanking starts with vertical
sync and stops at the begin of vertical
scan. By this, an optimum blanking is
achieved. The upper level of 5.4 V is
the horizontal clamping pulse with an
internally fixed pulse width of 0.8 µs.
A monoflop, which is triggered by the
trailing edge of the horizontal sync
pulse, generates this pulse. If
composite sync is applied, one
clamping pulse per H-period is
generated during V-sync. The phase
of the clamping pulse may change
during V-sync (see Fig.8).
PLL1 phase detector
The phase detector is a standard type
using switched current sources. The
middle of the sync is compared with a
fixed point of the oscillator sawtooth
voltage. The PLL filter is connected to
pin 17. If composite sync is applied,
the disturbed control voltage is
corrected during V-sync (see Fig.8).
Horizontal oscillator
This oscillator is of the relaxation type
and requires a fixed capacitor of
10 nF at pin 19. By changing the
current into pin 18 the whole
frequency range from 13 to 100 kHz
can be covered. The current can be
generated either by a frequency to
voltage converter or by a resistor.
A frequency adjustment may also be
added if necessary.
The PLL1 control voltage at pin 17
modulates via a buffer stage the
oscillator thresholds. A high DC-loop
gain ensures a stable phase
relationship between horizontal sync
and line flyback pulses.
PLL2 phase detector
This phase detector is similar to the
PLL1 phase detector. Line flyback
signals (pin 2) are compared with a
fixed point of the oscillator sawtooth
voltage. Delays in the horizontal
deflection circuit are compensated by
adjusting the phase relationship
between horizontal sync and
horizontal output pulses. A certain
amount of phase adjustment is
possible by injecting a DC current
from an external source into the PLL2
filter capacitor at pin 20.
TDA4852
Horizontal driver
This open-collector output stage
(pin 3) can directly drive an external
driver transistor. The saturation
voltage is less than 300 mV at 20 mA.
To protect the line deflection
transistor, the horizontal output stage
does not conduct for
V
< 6.4 V (pin 1).
P
Vertical oscillator and amplitude
control
This stage is designed for fast
stabilization of the vertical amplitude
after changes in sync conditions. The
free-running frequency f
determined by the values of R
. The recommended values
C
VOS
should be altered marginally only to
preserve the excellent linearity and
noise performance. The vertical drive
currents I
value of R
and I6are in relation to the
5
. Therefore, the
VOS
oscillator frequency must be
determined only by C
f
=
-----------------------------------------------------
0
10.8 R
1
××
VOSCVOS
To achieve a stabilized amplitude the
free-running frequency f
adjustment) must be lower than the
lowest occurring sync frequency. The
following contributions can be
assumed:
minimum frequency
offset between f0and the
lowest trigger frequency 10%
spread of IC ±3%
spread of R (22 kΩ) ±1%
spread of C (0.1 µF) ±5%
Result: f
50
-----------
0
1.19
(for 50 to 110 Hz application)
VOS
Hz=42Hz=
is
0
VOS
on pin 16.
(without
0
19%
and
December 1992 5
 Loading...
Loading...