Philips TDA4780-V4 Datasheet

DATA SHEET
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of May 1994
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1997 Feb 06
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA4780
RGB video processor with
automatic cut-off control and
gamma adjust

1997 Feb 06 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
FEATURES
• Gamma adjust
• Dynamic black control (adaptive black)
• All input signals clamped on black-levels
• Automatic cut-off control, alternative: output clamping
on fixed levels
• Three adjustable reference voltage levels via I2C-bus for
automatic cut-off control
• Luminance/colour difference interface
• Two luminance input levels allowed
• Two RGB interfaces controlled by either fast switches or
by I
2
C-bus
• Two peak drive limiters, selection via I2C-bus
• Blue stretch, selection via I2C-bus
• Luminance output for scan velocity modulation
(SCAVEM)
• Extra luminance output; same pin can be used as hue
control output e.g. for the TDA4650 and TDA4655
• Non standard operations like 50 Hz/32 kHz are also
possible
• Either 2 or 3 level sandcastle pulse applicable
• High bandwidth for 32 kHz application
• White point adjusts via I2C-bus
• Average beam current and improved peak drive limiting
• Two switch-on delays to prevent discoloration during
start-up
• All functions and features programmable via I2C-bus
• PAL/SECAM or NTSC matrix selection.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA4780 is a monolithic integrated circuit with a
luminance and a colour difference interface for video
processing in TV receivers. Its primary function is to
process the luminance and colour difference signals from
a colour decoder which is equipped e.g. with the
multistandard decoder TDA4655 or TDA9160 plus delay
line TDA4661 or TDA4665 and the Picture Signal
Improvement (PSI) IC TDA467X or from a feature module.
The required input signals are:
• Luminance and negative colour difference signals
• 2 or 3-level sandcastle pulse for internal timing pulse
generation
• I
2
C-bus data and clock signals.
Two sets of analog RGB colour signals can also be
inserted, e.g. one from a peritelevision connector
(SCART plug) and the other one from an On-Screen
Display (OSD) generator. The TDA4780 has I2C-bus
control of all parameters and functions with automatic
cut-off control of the picture tube cathode currents.
It provides RGB output signals for the video output stages.
In clamped output mode it can also be used as an RGB
source.
The main differences with the sister type TDA4680 are:
• Additional features, namely gamma adjust, adaptive
black, blue stretch and two different peak drive limiters
• The measurement lines are triggered by the trailing
edge of the vertical component of the sandcastle pulse
• I2C-bus receiver only. Automatic white level control is
not provided; the white levels are determined directly by
the I2C-bus data.
• The TDA4780 is pin compatible (except pin 18) with the
TDA4680. The I2C-bus slave address can be used for
both ICs. When a function of the TDA4780 is not
included in the TDA4680, the I2C-bus command is not
executed. Special commands (except control bit FSWL)
for the TDA4680 will be ignored by the TDA4780.
1997 Feb 06 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
supply voltage (pin 5) 7.2 8.0 8.8 V
I
P
supply current (pin 5) 80 100 120 mA
V
8(p-p)
luminance input (peak-to-peak value) (C)VBS − 0.45/1.43 − V
V
6(p-p)
−(B − Y) input (peak-to-peak value) − 1.33 − V
V
7(p-p)
−(R − Y) input (peak-to-peak value) − 1.05 − V
V
14
three-level sandcastle pulse
H+V − 2.5 − V
H − 4.5 − V
BK − 8.0 − V
two-level sandcastle pulse
H+V − 2.5 − V
BK − 4.5 − V
V
i
RGB input signals at pins 2, 3, 4, 10, 11 and 12 (black-to-white value) − 0.7 − V
V
o(p-p)
RGB output at pins 24, 22 and 20 (black-to-white value) − 2.0 − V
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −20 − +70 °C
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA4780 DIP28 plastic dual in-line package; 28 leads (600 mil) SOT117-1
1997 Feb 06 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
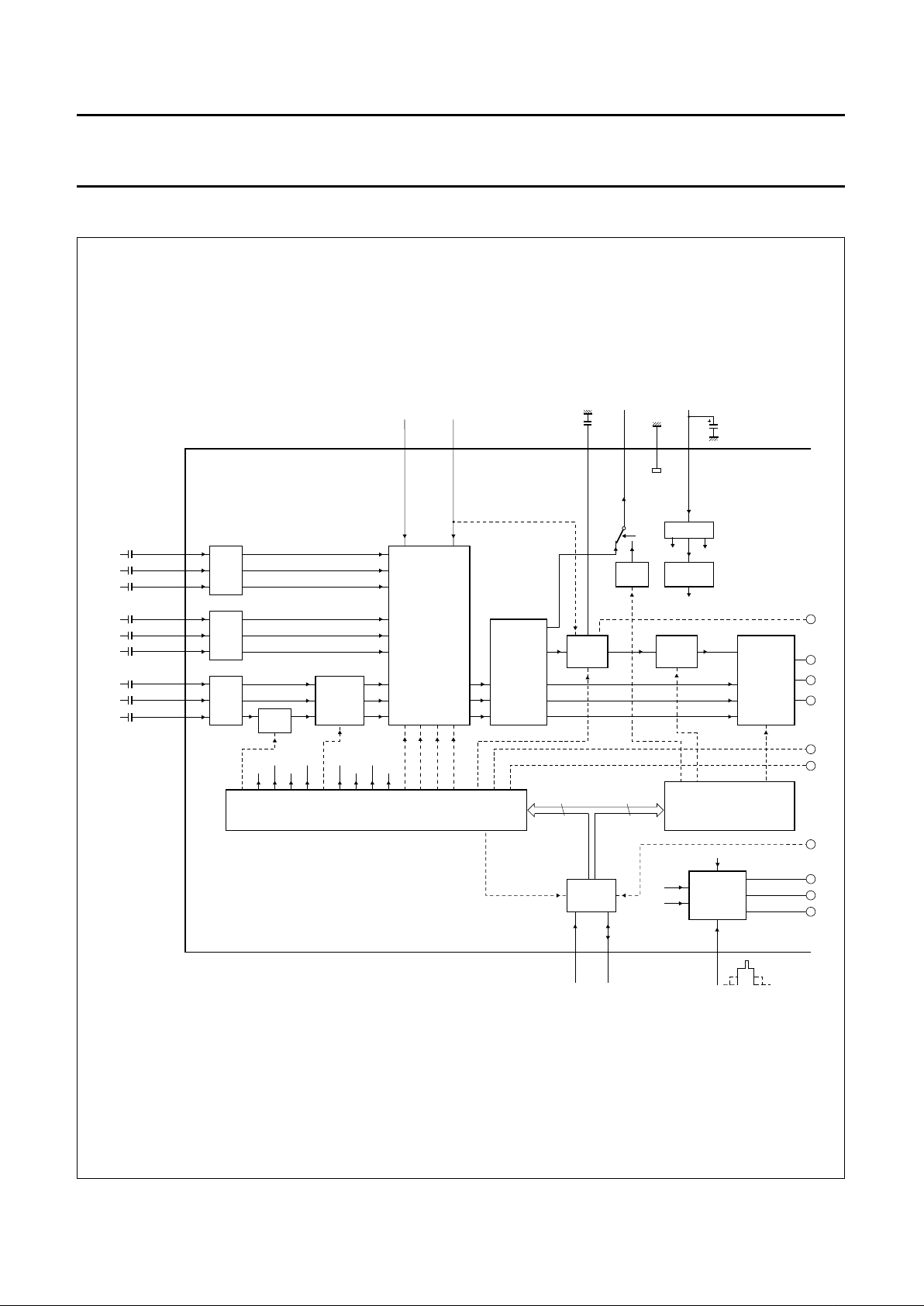
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram (continued in Fig.2).
handbook, full pagewidth
j
i
h
g
e
f
d
c
b
a
MGE875
200 µF
1 µF
CLAMP
TDA4780
CLAMP
CLAMP
0.45 V
1.43 V
PAL / SECAM
NTSC
MATRIX
INPUT
SELECTOR
FSON1
FSON2
FSDIS1
FSDIS2
Y - MATRIX
COLOUR
DIFFERENCE
MATRIX
ADAPTIVE
BLACK
Y
Y
Y
BL
GAMMA
Y
gamma
BL
SATURATION
ADJUST
HUE
ADJUST
BANDGAP
REFERENCE
SUPPLY
CONTROL REGISTERS
TCPL
RELC
BCOF
YEXHHDTV
FSBL
DELOF
SC5
YHI
REGISTERS
DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS
I2C-BUS
RECEIVER
SANDCASTLE
DETECTOR
8 DATA
BREN
V
SC5
DELOF
B
G
R
CL
HV
(H)
NMEN
10
11
12
R
1
G
1
B
1
R
2
G
2
B
2
2
3
4
6
7
8
−(B − Y)
−(B − Y)
−(R − Y)
−(R − Y)
Y
Y
47 nF
10 nF
10 nF
10 nF
10 nF
10 nF
10 nF
10 nF
10 nF
13
FSW
1
FSW
2
FSW
1
FSW
2
1
18 26
C
PDST
YHUE
GND
9
5
V
P
U
GAP
14
SC
27
28
SCL
SDA
R
1
G
1
B
1
R
2
G
2
B
2
ADBL
R − Y
G − Y
B − Y
R
G
B
R
G
B
Y
YEXH
U
GAP
sandcastle input
I
2
C-bus
VP = 8 V
Y - output /
hue adjust
output
peak dark
storage
6 DATA
1997 Feb 06 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
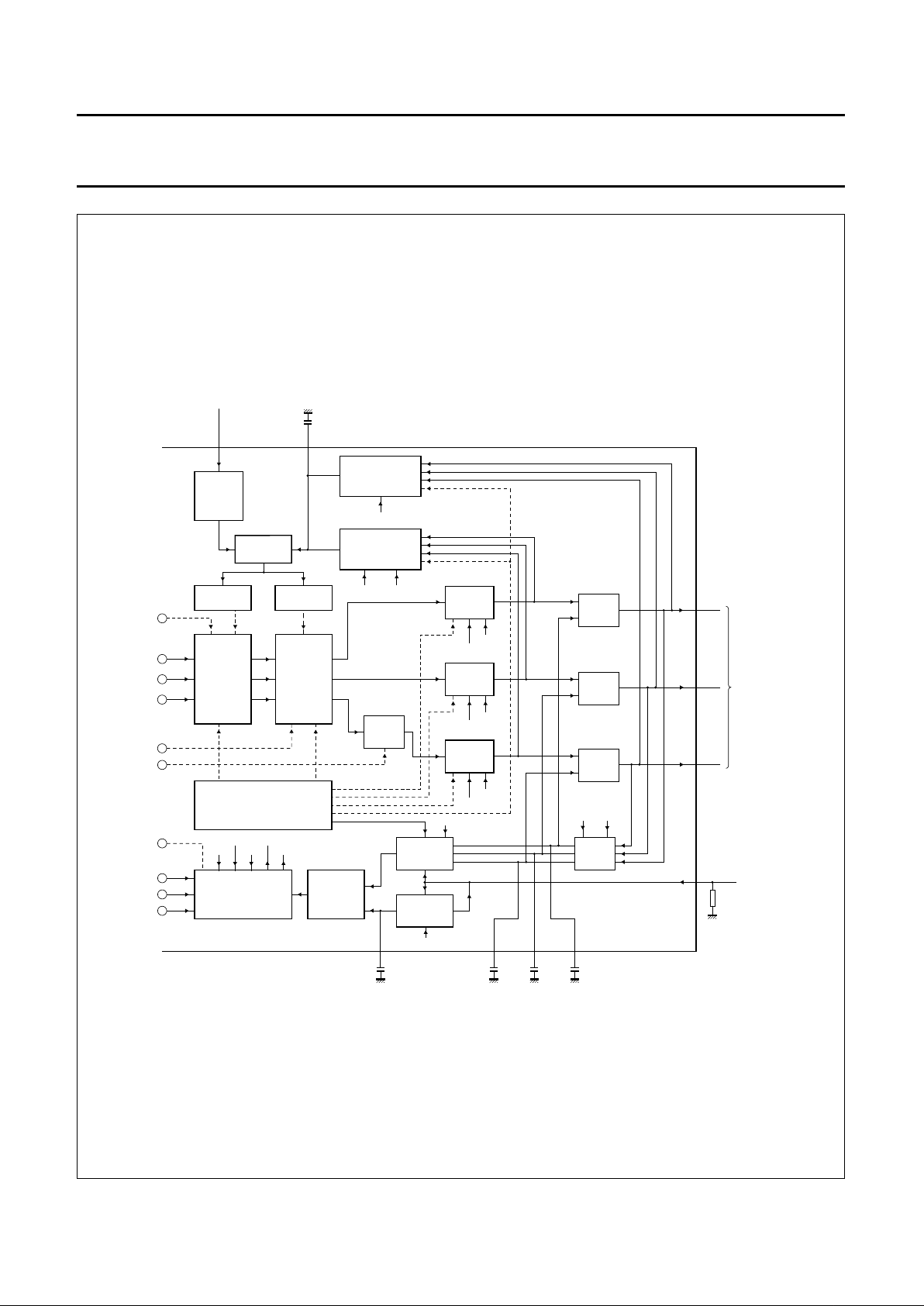
Fig.2 Block diagram (continued from Fig.1).
handbook, full pagewidth
j
i
h
g
e
f
d
c
b
a
MGE876
82 kΩ
1 µF
TDA4780
CONTRAST
ADJUST
BRIGHTNESS
ADJUST
REGISTERS
DIGITAL ANALOG CONVERTERS
TIMING
GENERATOR
B
G
R
B
B
B
G
R
FSBL
NMEN
HDTV
BLANK
MP
CL
HV
(H)
WHITE
POINT
ADJUST
MP
BLANK
WHITE
POINT
ADJUST
MP
BLANK
WHITE
POINT
ADJUST
MP
BLANK
BLUE
STRETCH
VOLTAGE
COMPARATOR
VOLTAGE
COMPARATOR
MINIMUM
DETECTOR
PEAK DRIVE
LIMITER
CUT-OFF RELATED
PEAK DRIVE
LIMITER
ABSOLUTE LEVEL
TCPL RELC
RELC
AVERAGE
BEAM
CURRENT
LIMITING
R
G
B
OUTPUT
BUFFER
OUTPUT
BUFFER
OUTPUT
BUFFER
1st AND 2nd
SWITCH-ON
DELAY
CUT-OFF
CONTROL
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
COMPARATOR
OUTPUT
CLAMP
BCL
15 16
C
PDL
24
22
20
R
O
G
O
B
O
19
CI
U
GAP
U
GAP
BCOF
BCOF
25
23
21
C
R
C
G
C
B
17
C
L
MOD2
220 nF
330 nF
220 nF 220 nF
cut-off storageleakage storage
leakage and
cut - off
current input
RGB
outputs
to
video
amplifiers
peak drive
limiting storage
average beam
current limiting
input
1997 Feb 06 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
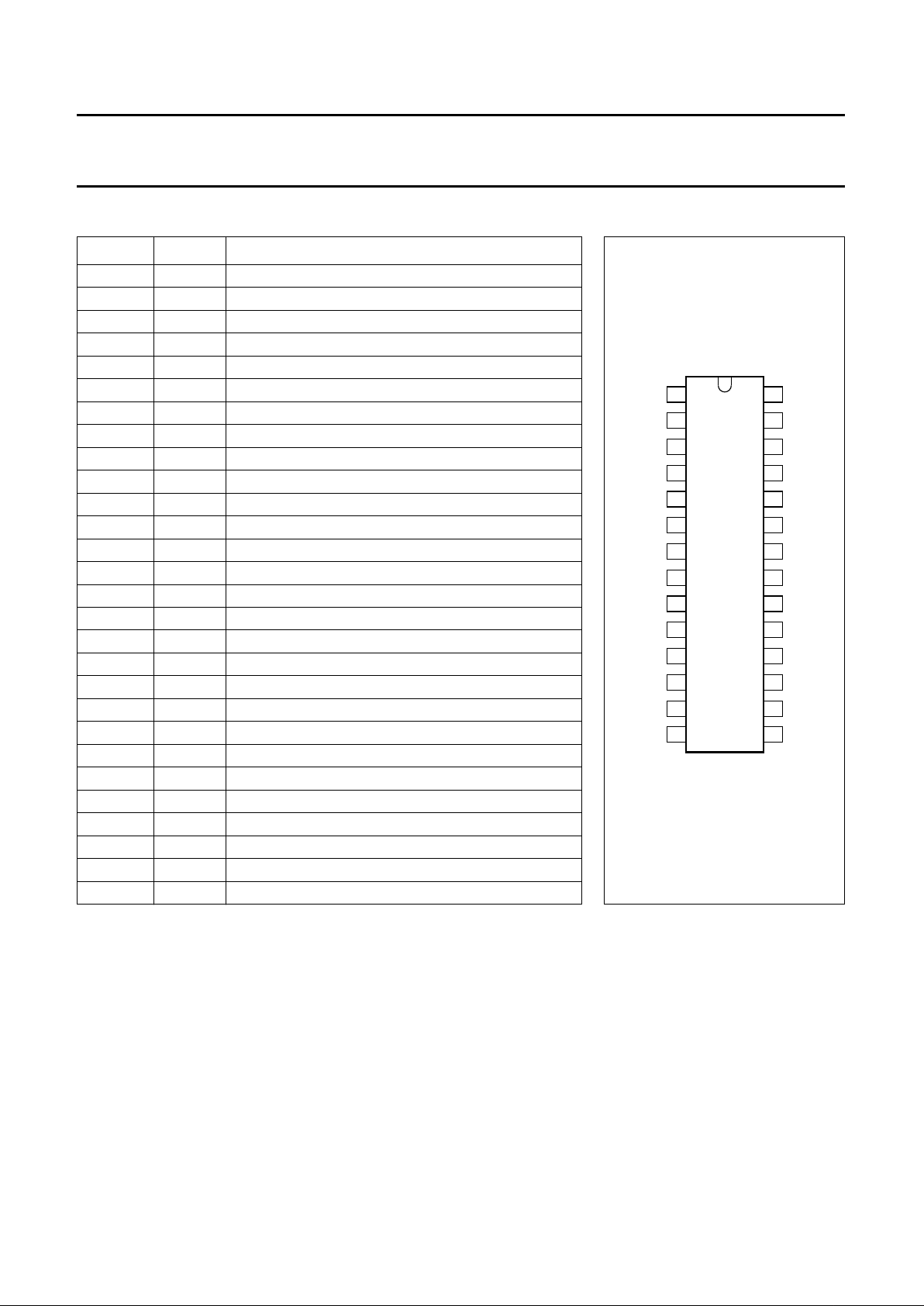
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
FSW
2
1 fast switch 2 input
R
2
2 red input 2
G
2
3 green input 2
B
2
4 blue input 2
V
P
5 supply voltage
−(B − Y) 6 colour difference input −(B − Y)
−(R − Y) 7 colour difference input −(R − Y)
Y 8 luminance input
GND 9 ground
R
1
10 red input 1
G
1
11 green input 1
B
1
12 blue input 1
FSW
1
13 fast switch 1 input
SC 14 sandcastle pulse input
BCL 15 average beam current limiting input
C
PDL
16 storage capacitor for peak limiting
C
L
17 storage capacitor for leakage current compensation
C
PDST
18 storage capacitor for peak dark
CI 19 cut-off measurement input
B
O
20 blue output
C
B
21 blue cut-off storage capacitor
G
O
22 green output
C
G
23 green cut-off storage capacitor
R
O
24 red output
C
R
25 red cut-off storage capacitor
YHUE 26 Y-output/hue adjust output
SDA 27 I
2
C-bus serial data input/acknowledge output
SCL 28 I
2
C-bus serial clock input
Fig.3 Pin configuration.
page
FSW
2
R
2
G
2
B
2
V
P
−(B − Y)
−(R − Y)
Y
GND
R
1
G
1
B
1
FSW
1
SC
SCL
SDA
YHUE
C
R
C
G
G
O
R
O
C
B
B
O
CI
C
PDST
C
L
C
PDL
BCL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
1514
TDA4780
MGE874

1997 Feb 06 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Signal input stages
The TDA4780 contains 3 sets of input signal stages for:
1. Luminance/colour-difference signals:
a) Y: 0.45 V (p-p) VBS or 1.43 V (p-p) VBS,
selectable via I
2
C-bus.
b) −(R − Y): 1.05 V (p-p).
c) −(B − Y): 1.33 V (p-p).
The capacitively coupled signals are matrixed to
RGB signals by either a PAL/SECAM or NTSC matrix
(selected via I2C-bus).
2. (RGB)1signals (0.7 V (p-p) VB), capacitively coupled
(e.g. from external source).
3. (RGB)2signals (0.7 V (p-p) VB), capacitively coupled
(e.g. videotext, OSD).
All input signals are clamped in order to have the same
black levels at the signal switch input. Displayed signals
must be synchronous with the sandcastle pulse.
Signal switches
Both fast signal switches can be operated by switching
pins (e.g. SCART facilities) or set via the I
2
C-bus. With the
pin FSW1 the Y-CD signals or the (RGB)1signals can be
selected, with pin FSW2 the above selected signals or the
(RGB)2signals are enabled. During the vertical and
horizontal blanking time an artificial black level equal to the
clamped black level is inserted in order to clip off the sync
pulse of the luminance signal and to suppress hum during
the cut-off measurement time and eliminate noise during
these intervals.
Saturation, contrast and brightness adjust
Saturation, contrast and brightness adjusts are controlled
via the I
2
C-bus and act on Y, CD as well as on RGB input
signals. Gamma acts on the luminance content of the input
signals.
Gamma adjust
The gamma adjust stage has a non-linear transmission
characteristic according to the formula y = x
gamma
, where x
represents the input and y the output signal. If gamma is
smaller than unity, the lower parts of the signal are
amplified with higher gain.
Adaptive black (ADBL)
The adaptive black stage detects the lowest voltage of the
luminance component of the internal RGB signals during
the scanning time and shifts it to the nominal black level.
In order to keep the nominal white level the contrast is
increased simultaneously.
Blue stretch (BLST)
The blue stretch channel gets additional amplification if the
blue signal is greater than 80% of the nominal signal
amplitude. In the event the white point is shifted towards
higher colour temperature so that white parts of a picture
seem to be brighter.
Measurement pulse and blanking stage
During the vertical and horizontal blanking time and the
measurement period the signals are blanked to an ultra
black level, so the leakage current of the picture tube can
be measured and automatically compensated for.
During the cut-off measurement lines (one line period for
each R, G or B) the output signal levels are at cut-off
measurement level.
The vertical blanking period is timed by the sandcastle
pulse. The measurement pulses (leakage, R, G and B) are
triggered by the negative going edge of the vertical pulse
of the sandcastle pulse and start after the following
horizontal pulse.
The IC is prepared for 2f
H
(32 kHz) application.
Output amplifier and white adjust potentiometer
The RGB signals are amplified to nominal 2 V (p-p), the
DC-levels are shifted according to cut-off control.
The nominal signal amplitude can be varied by ±50% by
the white point adjustment via the I
2
C-bus (individually for
RGB respect).

1997 Feb 06 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
Automatic cut-off control
During leakage measurement time the leakage current is
compensated in order to get a reference voltage at the
cut-off measurement info pin. This compensation value is
stored in an external capacitor. During cut-off current
measurement times for the R, G and B channels, the
voltage at this pin is compared with the reference voltage,
which is individually adjustable via I2C-bus for each colour
channel. The control voltages that are derived in this way
are stored in the external feedback capacitors. Shift stages
add these voltages to the corresponding output signals.
The automatic cut-off control may be disabled via the
I
2
C-bus. In this mode the output voltage is clamped to
2.5 V. Clamping periods are the same as the cut-off
measurement periods.
Signal limiting
The TDA4780 provides two kinds of signal limiting.
First, an average beam limiting, that reduces signal level if
a certain average is exceeded. Second, a peak drive
limiting, that is activated if one of the RGB signals even
shortly exceeds a via I
2
C-bus adjusted threshold.
The latter can be either referred to the cut-off
measurement level of the outputs or to ground.
When signal limiting occurs, contrast is reduced, and at
minimum contrast brightness is reduced additionally.
Sandcastle decoder and timer
A 3-level detector separates the sandcastle pulse into
combined line and field pulses, line pulses, and clamping
pulses. The timer contains a line counter and controls the
cut-off control measurement.
Application with a 2-level 5 V sandcastle pulse is possible.
Switch on delay circuit
After switch on all signals are blanked and a warm up test
pulse is fed to the outputs during the cut-off measurement
lines. If the voltage at the cut-off measurement input
exceeds an internal level the cut-off control is enabled but
the signal remains still blanked. In the event of output
clamping, the cut-off control is disabled and the switch on
procedure will be skipped.
Y output and hue adjust
The TDA4780 contains a D/A converter for hue adjust.
The analog information can be fed, e.g. to the
multistandard decoder TDA4650 or TDA4655. This output
pin may be switched to a Y output signal, which can be
used for scan velocity modulation (SCAVEM). The Y
output is the Y input signal or the matrixed (RGB) input
signal according to the switch position of the fast switch.
I
2
C-bus
The TDA4780 contains an I2C-bus receiver for control
function.
ESD protection
The Pins are provided with protection diodes against
ground and supply voltage (see Chapter “Internal pin
configurations”). I
2
C-bus input pins do not shunt the
I2C-bus signals in the event of missing supply voltage.
EMC
The pins are protected against electromagnetic radiation.
1997 Feb 06 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
I2C-BUS RECEIVER
Table 1 Slave address; note 1
Note
1. Explanation for the cell contents of the table:
a) W means write.
Table 2 Slave receiver format (write mode; BREN = 0); note 1
Notes
1. Explanation for the cell contents of the table:
a) S means START condition.
b) P means STOP condition.
c) A means acknowledge.
2. All subaddresses within the range 00H to 0FH are automatically incremented. The subaddress counter wraps around
from 0FH to 00H. Only in this event 0FH will be acknowledged.
Subaddresses outside the range 00H to 0EH are not acknowledged by the device and neither auto-increment nor
any other internal operation takes place.
All eight bits of the subaddress have to be decoded by the device.
Table 3 Slave receiver format (write mode; BREN = 1); note 1
Notes
1. Explanation for the cell contents of the table:
a) S means START condition.
b) P means STOP condition.
c) A means acknowledge.
2. Auto-increment is not possible.
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
W
10001000
S SLAVE ADDRESS A SUBADDRESS
(2)
A DATA BYTE
n data bytes with auto-increment of subaddresses
AP
S SLAVE ADDRESS A SUBADDRESS A DATA BYTE
(2)
AP
1997 Feb 06 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
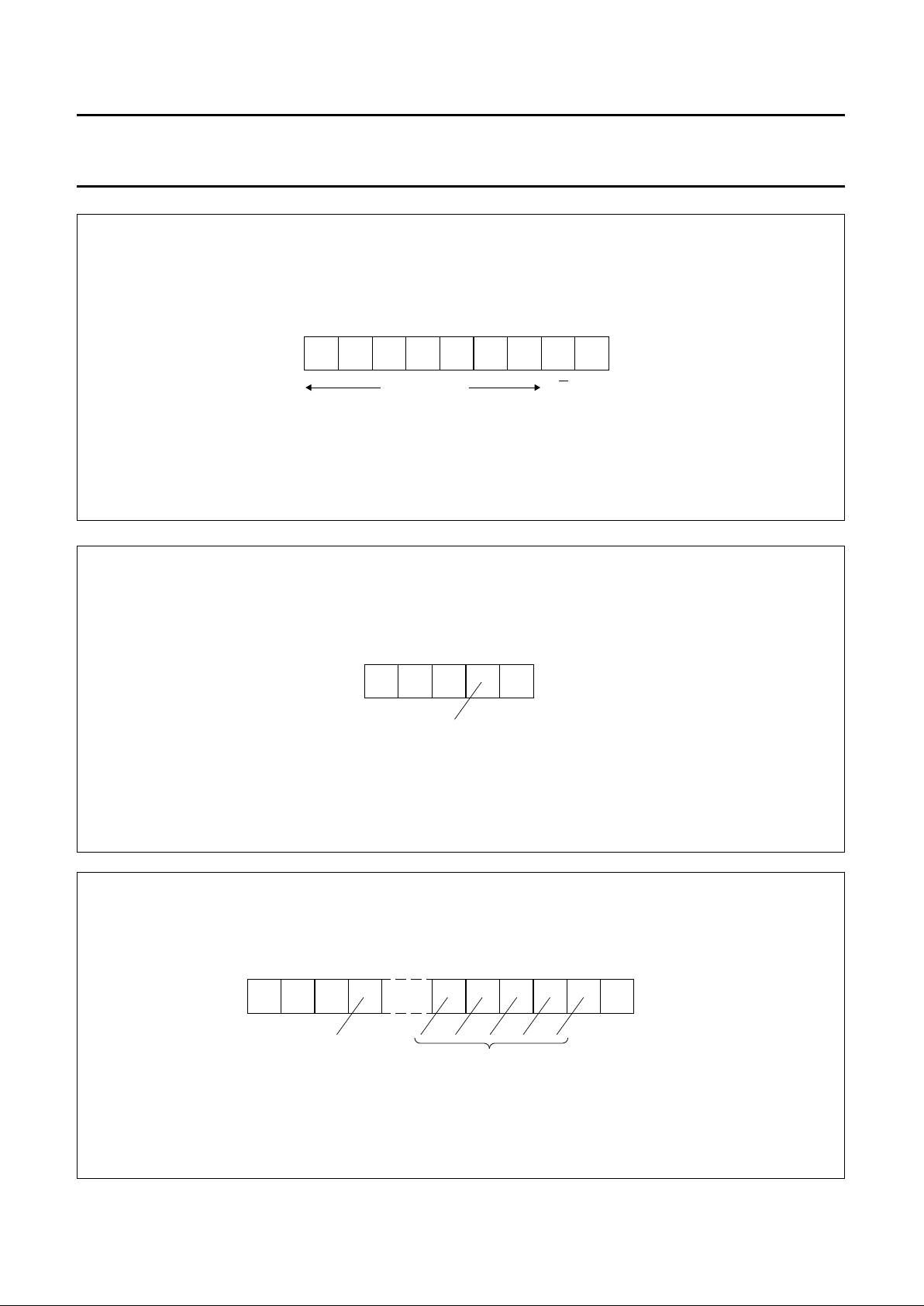
Fig.4 The module address byte.
handbook, full pagewidth
ACKX
R/W
00100
module address
01
MSB LSB
MED696
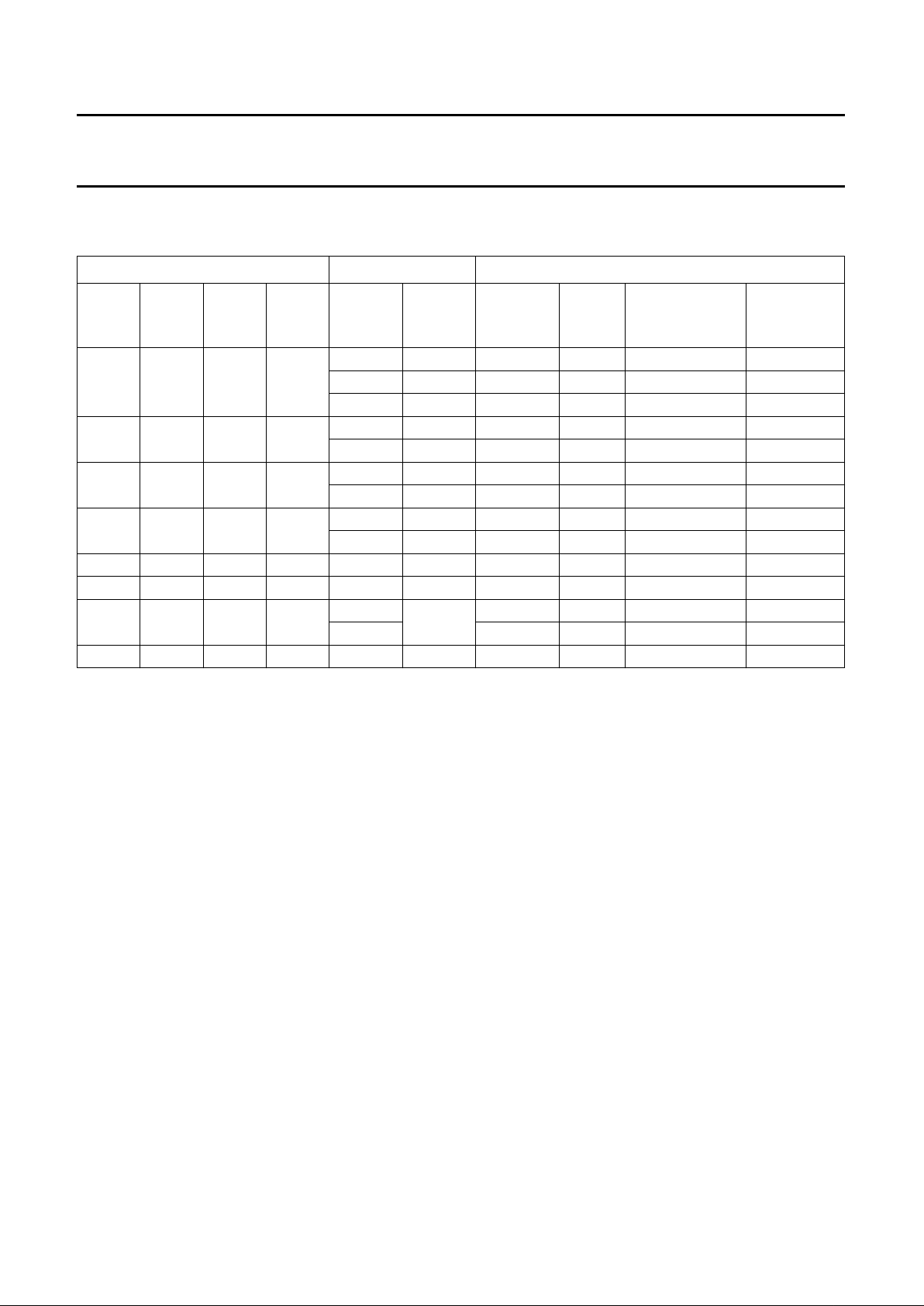
handbook, full pagewidth
STOSAD
START
condition
data byte
STOP
condition
MADSTA
MED697
Fig.5 Data transmission without auto-increment (BREN = 0 or 1).
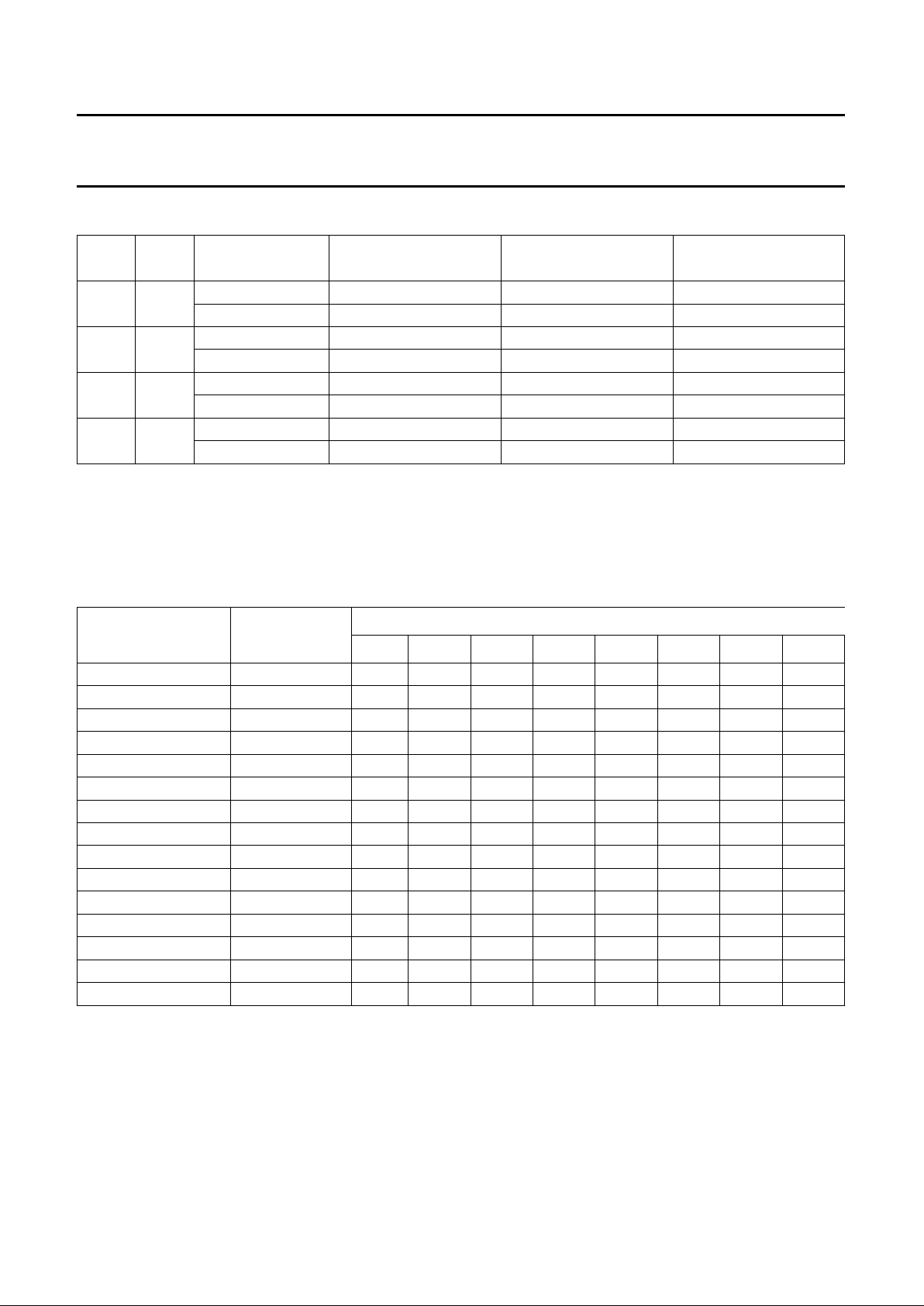
handbook, full pagewidth
SAD
START
condition
data byte
STOP
condition
MADSTA
MED698
STO
data bytes
Fig.6 Data transmission with auto-increment (BREN = 0)
1997 Feb 06 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
Table 4 Signal input selection and effect on adaptive black measurements by fast source switches and I2C-bus;
note 1
Note
1. Explanation for the cell contents of the table:
a) H = set to logic 1 or analog switch (pins 1 and 13) to >0.9 V.
b) L = set to logic 0 or analog switch (pins 1 and 13) to <0.4 V.
c) X = don’t care.
d) ON = this signal is selected.
I
2
C-BUS CONTROLLED BITS ANALOG SWITCH SELECTED SIGNALS
FSON2 FSDIS2 FSON1 FSDIS1
FSW2
(pin 1)
FSW1
(pin 13)
RGB
2
(pins 2, 3
and 4)
ADBL
RGB1 (pins 10,
11 and 12)
TV (pins 6,
7 and 8)
LLLLL L active ON
L H active ON
H X ON inactive
LLLHL X active ON
H X ON inactive
L L H X L X active ON
H X ON inactive
L H L L X L active ON
X H active ON
L H L H X X active ON
L H H X X X active ON
H L X X L X ON active
H ON inactive
H H X X X X ON active
1997 Feb 06 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
Table 5 Crosstalk; note 1
Note
1. Explanation for the cell contents of the table:
a) H = set to logic 1.
b) L = set to logic 0.
Table 6 Subaddress byte and data byte format; notes 1 and 2
Notes
1. Explanation for the cell contents of the table:
a) L = set to logic 0.
b) X means don’t care but for software compatibility with further video ICs with the same slave address, it is
recommended to set all these bits to logic 0.
2. After power on reset all alignment registers are set to 01H.
3. The least significant bit of the analog alignment register.
FSW1 FSW2 CROSSTALK
AT 4 MHz MAXIMUM
VALUE (dB)
AT 8 MHz MAXIMUM
VALUE (dB)
AT 13 MHz MAXIMUM
VALUE (dB)
L L RGB
1
→ Y, CD −58 −55 −50
RGB
2
→ Y, CD −58 −55 −50
L H Y, CD → RGB
1
−51 −50 −47
RGB
2
→ RGB
1
−58 −55 −50
L H Y, CD → RGB
2
−51 −50 −47
RGB
1
→ RGB
2
−58 −55 −50
H H Y, CD → RGB
2
−51 −50 −47
RGB
1
→ RGB
2
−58 −55 −50
FUNCTION SUBADDRESS
DATA BYTE
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
(3)
Brightness 00H L L A05 A04 A03 A02 A01 A00
Saturation 01H L L A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10
Contrast 02H L L A25 A24 A23 A22 A21 A20
Hue 03H L L A35 A34 A33 A32 A31 A30
Red gain 04H L L A45 A44 A43 A42 A41 A40
Green gain 05H L L A55 A54 A53 A52 A51 A50
Blue gain 06H L L A65 A64 A63 A62 A61 A60
Red level reference 07H L L A75 A74 A73 A72 A71 A70
Green level reference 08H L L A85 A84 A83 A82 A81 A80
Blue level reference 09H L L A95 A94 A93 A92 A91 A90
Peak drive limit 0AH L L AA5 AA4 AA3 AA2 AA1 AA0
Gamma 0BH L L AB5 AB4 AB3 AB2 AB1 AB0
Control register 1 0CH SC5 DELOF BREN X NMEN X X X
Control register 2 0DH X HDTV FSBL BCOF FSDIS2 FSON2 FSDIS1 FSON1
Control register 3 0EH ADBL YHI MOD2 BLST YEXH RELC TCPL L
1997 Feb 06 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
Table 7 RGB processor mode bits control register
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
Control register 1
SC5 sandcastle 5 V 0 = 3-level sandcastle pulse
1 = 2-level sandcastle pulse
DELOF delay of leading edge of
clamping pulse switched off
0 = delay
1 = no delay
BREN buffer register enable 0 = new data are executed just after reception
1 = data is held in a latch (buffer register) and will be transferred to their
destination register within the next vertical blanking interval; the device
does not acknowledge any new data transfer until the internal transfer to
the destination register has been completed
NMEN NTSC matrix enable; note 1 0 = PAL matrix
1 = NTSC matrix; hue position set on −2 degrees
Control register 2
HDTV HDTV / progressive scan for
ADBL line counter
0 = 272 (PAL), 224 (NTSC) lines
1 = 544 (PAL), 448 (NTSC) lines
FSBL full screen black level, e.g. for
optical measurement
0 = normal mode
1 = cut-off measurement level during full field, brightness inactive
BCOF internal black level control off 0 = automatic cut-off control active
1 = RGB outputs clamped to fixed DC levels
FSON2 fast switch 2 on see Table 4
FSDIS1 fast switch 1 disable
FSDIS2 fast switch 2 disable
FSON1 fast switch 1 on
Control register 3
ADBL adaptive black 0 = off
1=on
YHI Y high level 0 = input = 0.315 V (p-p) (black-white)
1 = input = 1.0 V (p-p) (black-white)
MOD2 modus 2 0 = inactive;
(BCOF = 0) AND (MOD2 = 1) is senseless, no output stabilization
1 = output clamp without brightness adjust, brightness remains active
e.g. for blue stretch
BLST blue stretch 0 = off
1=on
YEXH Y exclusive hue 0 = pin 26 is switched to hue adjust output
1 = pin 26 is switched to Y output
RELC relative to cut-off 0 = peak drive limit to absolute output
1 = peak drive limit relative to cut-off
TCPL time constant peak drive limiter 0 = 2f
H
1=1f
H
1997 Feb 06 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
RGB video processor with automatic
cut-off control and gamma adjust
TDA4780
Note
1. Matrix coefficients should be tested by comparing RGB output signals with a reference RGB colour bar, which is fed
in at (RGB)1 or (RGB)2 inputs. In the event of NMEN = 1 (NTSC) at minimum saturation the Y output and RGB output
signals are not identical to the Y input signal. PAL/SECAM signals are matrixed by the equation:
V
G −Y
= −0.51V
R − Y
− 0.19V
B − Y
NTSC signals are matrixed by the equations (hue phase shift of −2 degrees):
V
R − Y*
= 1.39V
R − Y
− 0.07V
B − Y
; V
G − Y*
= −0.46V
R − Y
− 0.15V
B − Y
; V
B − Y*=VB−Y
For demodulation axis see Fig.11.
In the matrix equations: V
R − Y
and V
B − Y
are conventional PAL demodulation axes and amplitudes at the output of
the demodulator. V
R − Y*
, V
G − Y*
and V
B − Y*
are the NTSC-modified colour-difference signals.
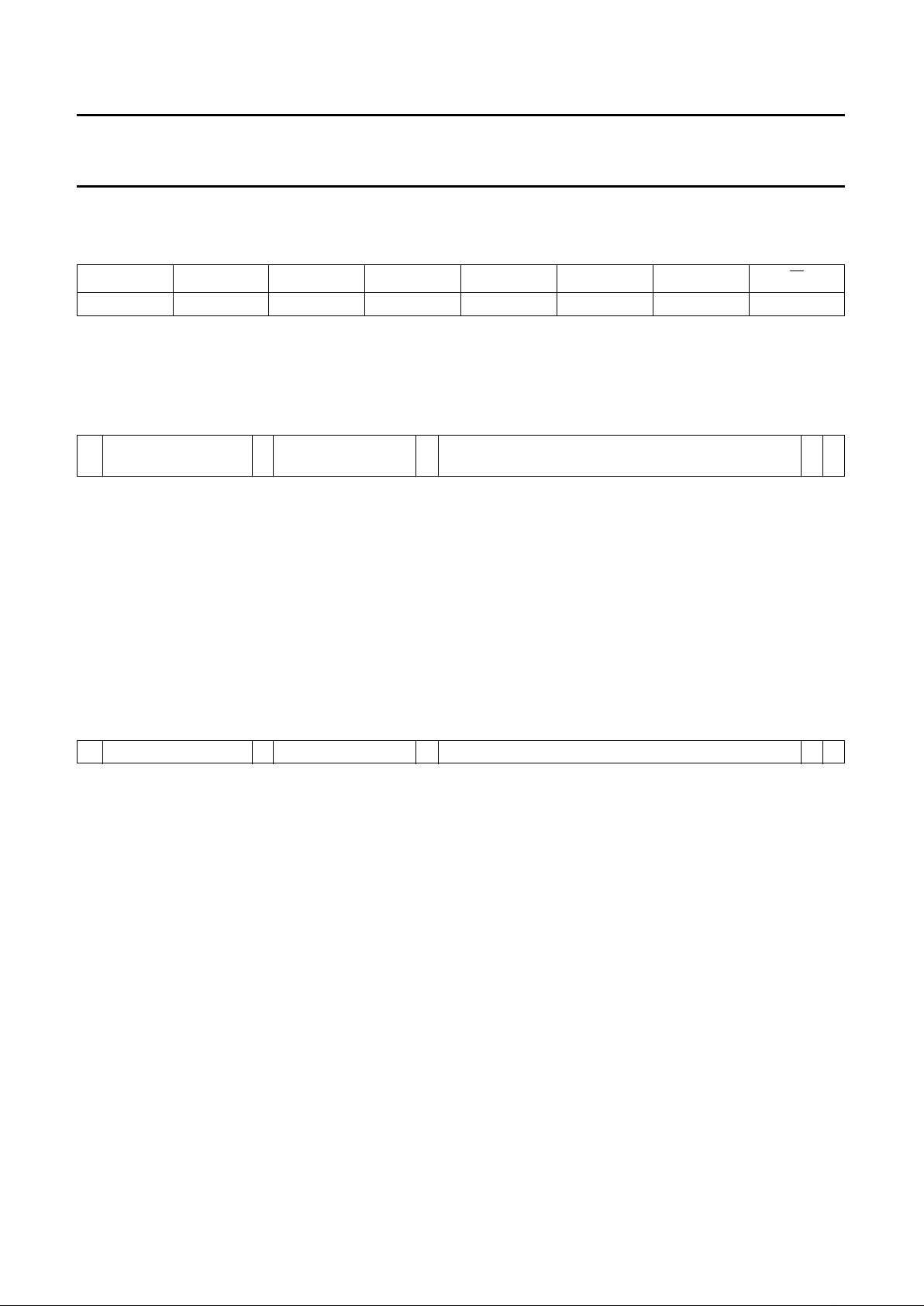
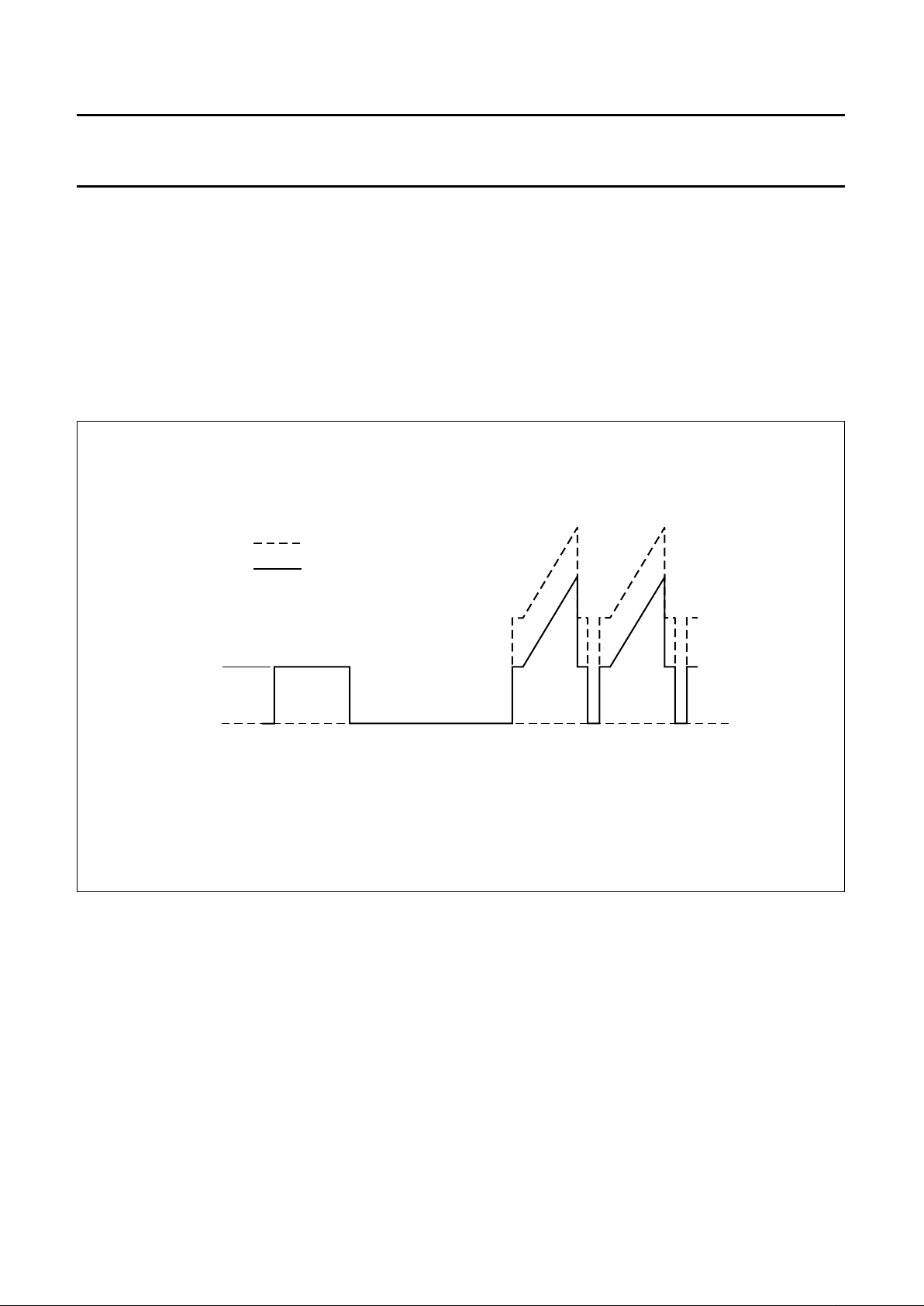
Fig.7 Cut-off measurement pulses.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGE878
maximum brightness
nominal brightness
ultra-black
cut-off measurement line
for green signal
 Loading...
Loading...