Philips TDA4689 Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA4689
Video processor with automatic
cut-off control
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1997 Jul 01

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
FEATURES
• Operates from an 8 V DC supply
• Black level clamping of the colour difference, luminance
and RGB input signals with coupling-capacitor for DC
level storage
• Two analog RGB inputs, selected either by fast switch
signals or via I2C-bus; brightness and contrast control of
both RGB inputs
• Saturation, contrast, brightness and white adjustment
via I2C-bus
• Same RGB output black levels for Y/CD and RGB input
signals
• Timing pulse generation from either a 2 or 3-level
sandcastle pulse for clamping, vertical synchronization
and cut-off timing pulses
• Automatic cut-off control or clamped output selectable
2
C-bus
via I
• Automatic cut-off control with picture tube leakage
current compensation
• Cut-off measurement pulses after end of the vertical
blanking pulse or end of an extra vertical flyback pulse
• Ultra-black or nominal black blanking selectable via
I2C-bus in clamped output mode
• Two switch-on delays to prevent discolouration before
steady-state operation
• Average beam current and peak drive limiting
• PAL/SECAM or NTSC matrix selection via I2C-bus
• Emitter-follower RGB output stages to drive the video
output stages
• I2C-bus controlled DC output e.g. for hue-adjust of
NTSC (multistandard) decoders
• Positive amplification factor of cut-off control voltage.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA4689 is a monolithic integrated circuit with a
luminance and a colour difference interface for video
processing in TV receivers. Its primary function is to
process the luminance and colour difference signals from
a colour decoder which is equipped e.g. with the
multistandard decoder TDA4655 or TDA9160 plus delay
line TDA4661 and the Picture Signal Improvement (PSI)
IC, TDA467x, or from a feature module.
The required input signals are:
• Luminance and negative colour difference signals
• 2 or 3-level sandcastle pulse for internal timing pulse
generation
2
C-bus data and clock signals for microcontroller
• I
control.
Two sets of analog RGB colour signals can also be
inserted, e.g. one from a peritelevision connector and the
other from an on-screen display generator. The TDA4689
includes full I2C-bus control of all parameters and
functions with automatic cut-off control of the picture tube
cathode currents. It provides RGB output signals for the
video output stages.
The TDA4689 is a simplified, pin compatible (except for
pin 18) version of the TDA4680. The special module
address of the TDA4689 avoids conflicts with other video
processors. A similar software, as used for the TDA4687
or TDA4680 could be used; where a function is not
included in the TDA4689 the I2C-bus command is not
executed. The differences with the TDA4680 are:
• No automatic white level control; the white levels are
determined directly by the I2C-bus data
• RGB reference levels for automatic cut-off control are
not adjustable via I2C-bus
• Clamping delay is fixed
• Only contrast and brightness adjust for the RGB input
signals
• The measurement lines are triggered either by the
trailing edge of the vertical component of the sandcastle
pulse or by the trailing edge of an optional external
vertical flyback pulse (on pin 18), according to which
occurs first.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
TDA4689 DIP28 plastic dual in-line package; 28 leads (600 mil) SOT117-1
1997 Jul 01 2
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
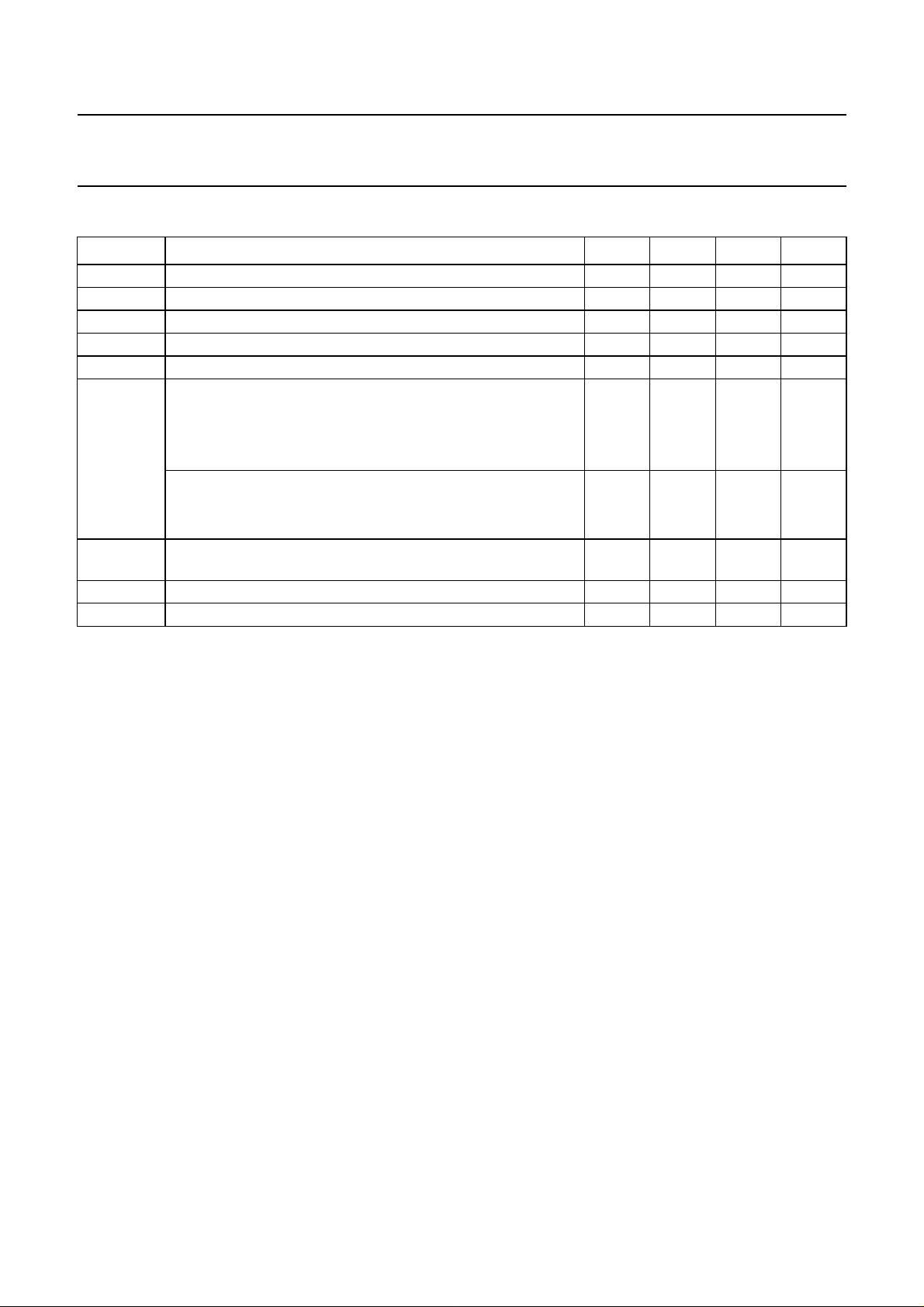
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
P
V
8(p-p)
V
6(p-p)
V
7(p-p)
V
14
V
i(p-p)
V
o(b-w)
T
amb
supply voltage (pin 5) 7.2 8.0 8.8 V
supply current (pin 5) − 60 − mA
luminance input (peak-to-peak value) − 0.45 − V
−(B − Y) input (peak-to-peak value) − 1.33 − V
−(R − Y) input (peak-to-peak value) − 1.05 − V
3-level sandcastle pulse
H+V − 2.5 − V
H − 4.5 − V
BK − 8.0 − V
2-level sandcastle pulse
H+V − 2.5 − V
BK − 4.5 − V
RGB input signals at pins 2, 3, 4, 10, 11and12
− 0.7 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
RGB outputs at pins 24, 22 and 20 (black-to-white value) − 2.0 − V
operating ambient temperature 0 − 70 °C
1997 Jul 01 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
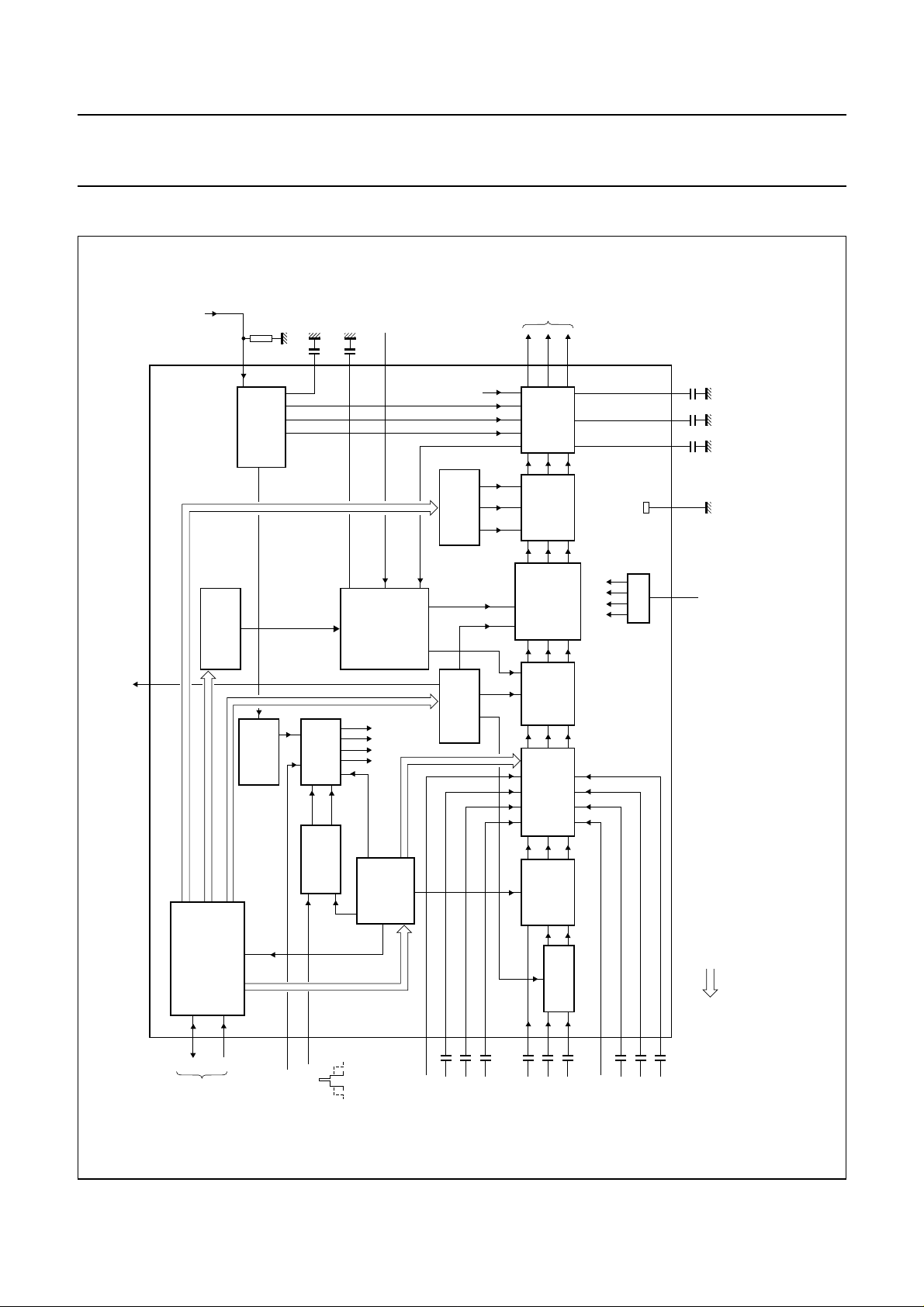
BLOCK DIAGRAM
RGB
outputs
O
O
R
G
242220
OUTPUT
ADJUST,
CUT-OFF
R
G
POINT
WHITE
R
G
O
B
STAGES
B
ADJUST
B
MHA749
21 23 25
9
R
GB
cut-off storage
leakage
and cut-off
current input
cut-off
control
19
C
R
CUT-OFF
COMPARATORS
leakage
storage
17
peak drive
limiting
storage
16
average
15
beam
current
BCOF
3 x 6-BIT D/A
CONVERTERS
6-BIT D/A
hue control voltage
26
A45 to A40, A55 to A50, A65 to A60
AA5 to AA0
C-BUS
2
I
RECEIVER
27
28
SDA
SCL
C-bus
2
I
AND
AVERAGE
TIMING
GENERATOR
(H)
H + V
PULSE
DETECTOR
SC5
PEAK DRIVE
timing
pulses
BCOF
FSDIS2, FSON2,
2 x 8-BIT
CONTROL
CONVERTER
DELAYS
1st AND 2nd
SWITCH-ON
BK
TDA4689
A05 to A00, A15 to A10, A25 to A20, A35 to A30
BREN
18
VFB
14
sandcastle
SANDCASTLE
pulse
LIMITING
BEAM CURRENT
4 x 6-BIT D/A
FSDIS1, FSON1
NMEN
REGISTERS
101112
13
1
1
R
FSW
CONVERTERS
1
1
B
G
ADJUST,
BLANKING 2,
BRIGHTNESS
MEASUREMENT
B
R
G
ADJUST
CONTRAST
B
R
G
BLANKING 1
FAST SIGNAL
SOURCE SWITCH,
B
R
G
NTSC
MATRIX
PAL/SECAM,
SATURATION
8
7
6
Y
−(R − Y)
−(B − Y)
PULSES
ADJUST
1
2
FSW
5
= 8 V
P
SUPPLY
V
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.1 Block diagram.
C-bus data and
2
control signals
I
2
3
4
2
2
2
B
R
G
1997 Jul 01 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
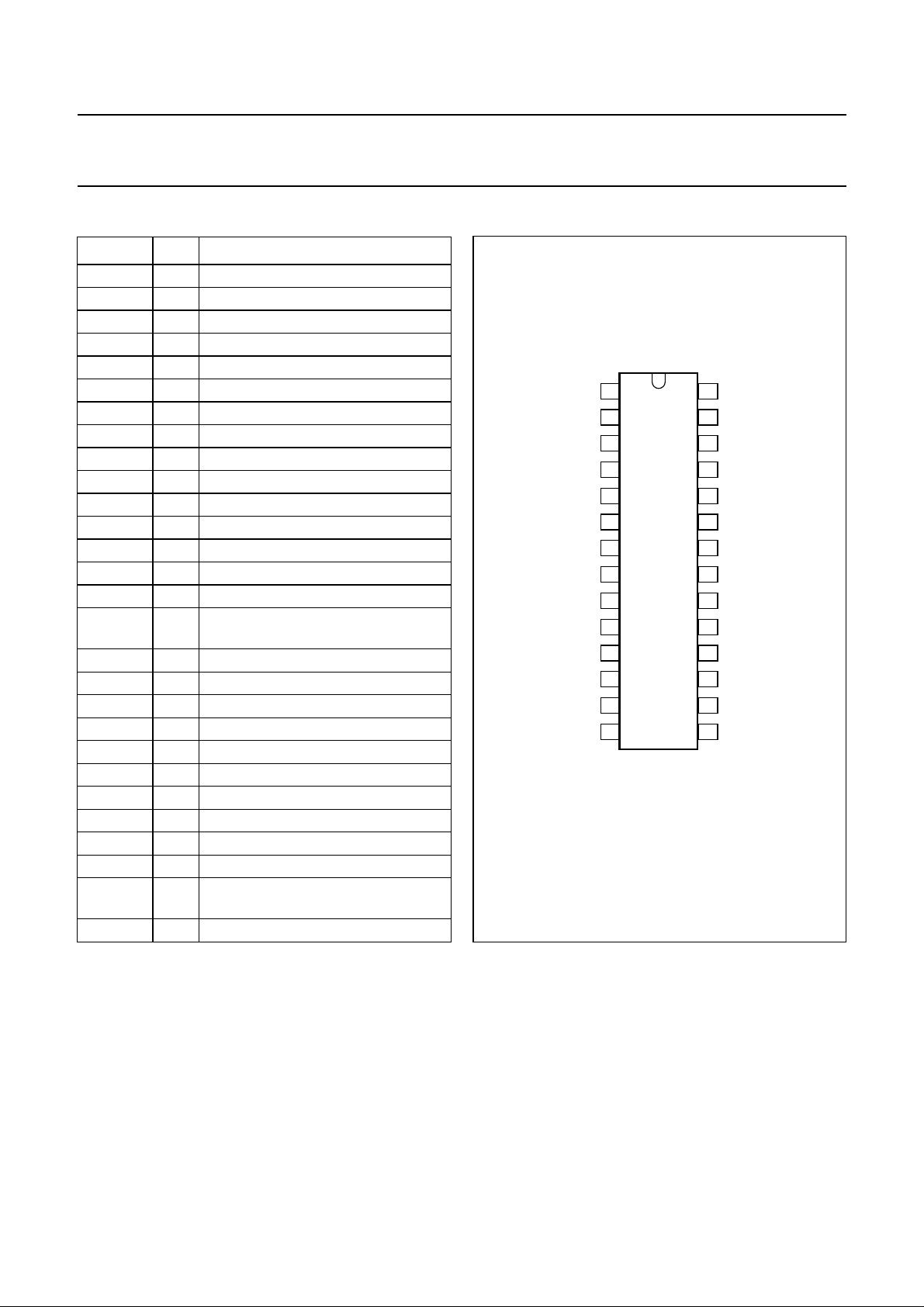
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
FSW
2
R
2
G
2
B
2
V
P
−(B − Y) 6 colour difference input −(B − Y)
−(R − Y) 7 colour difference input −(R − Y)
Y 8 luminance input
GND 9 ground
R
1
G
1
B
1
FSW
1
SC 14 sandcastle pulse input
BCL 15 average beam current limiting input
C
PDL
C
L
VFB 18 vertical flyback pulse input
CI 19 cut-off measurement input
B
O
C
B
G
O
C
G
R
O
C
R
HUE 26 hue control output
SDA 27 I
SCL 28 I
1 fast switch 2 input
2 red input 2
3 green input 2
4 blue input 2
5 supply voltage
10 red input 1
11 green input 1
12 blue input 1
13 fast switch 1 input
16 storage capacitor for peak drive
limiting
17 storage capacitor for leakage current
20 blue output
21 blue cut-off storage capacitor
22 green output
23 green cut-off storage capacitor
24 red output
25 red cut-off storage capacitor
2
C-bus serial data input;
acknowledge output
2
C-bus serial clock input
handbook, halfpage
FSW
1
2
R
2
2
G
3
2
B
4
2
V
5
P
−(B − Y)
−(R − Y)
GND
FSW
R
G
B
SC
6
7
TDA4689
Y
8
9
10
1
11
1
12
1
13
1
14
MHA748
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
28
SCL
27
SDA
26
HUE
C
25
R
R
24
O
C
23
G
G
22
O
C
21
B
B
20
O
CI
19
18
VFB
C
17
L
C
16
PDL
BCL
15
1997 Jul 01 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
I2C-BUS PROTOCOL
Control
2
C-bus transmitter provides the data bytes to select
The I
and adjust the following functions and parameters:
• Brightness adjust
• Saturation adjust
• Contrast adjust
• DC output e.g. for hue control
• RGB gain adjust
• Peak drive limiting level adjust
• Selects either 3-level or 2-level (5 V) sandcastle pulse
• Enables cut-off control; enables output clamping
(2 different modes)
• Selects either PAL/SECAM or NTSC matrix
• Enables/disables synchronization of the execution of
I2C-bus commands with the vertical blanking interval
• Enables Y/CD, RGB1 or RGB2 input.
2
C-bus transmitter and data transfer
I
2
I
C-BUS SPECIFICATION
The I2C-bus is a bidirectional, two-wire, serial data bus for
intercommunication between ICs in an equipment.
The microcontroller transmits data to the I2C-bus receiver
in the TDA4689 over the serial data line SDA (pin 27)
synchronized by the serial clock line SCL (pin 28).
Both lines are normally connected to a positive voltage
supply through pull-up resistors. Data is transferred when
the SCL line is LOW. When SCL is HIGH the serial data
line SDA must be stable. A HIGH-to-LOW transition of the
SDA line when SCL is HIGH is defined as a START bit.
A LOW-to-HIGH transition of the SDA line when SCL is
HIGH is defined as a STOP bit.
Each transmission must start with a START bit and end
with a STOP bit. The bus is busy after a START bit and is
only free again after a STOP bit has been transmitted.
2
I
C-BUS RECEIVER (MICROCONTROLLER WRITE MODE)
Each transmission to the I2C-bus receiver consists of at
least three bytes following the START bit. Each byte is
acknowledged by an acknowledge bit immediately
following each byte. The first byte is the Module Address
(MAD) byte, also called slave address byte. This includes
the module address, 0100001 for the TDA4689.
The TDA4689 is a slave receiver (R/W = 0), therefore the
module address byte is 01000010 (42H; see also Fig.3).
The length of a data transmission is unrestricted, but the
module address and the correct subaddress must be
transmitted before the data byte(s). The order of data
transmission is shown in Figs 4 and 5.
Without auto-increment (BREN = 0 or 1) the module
address (MAD) byte is followed by a SubAddress (SAD)
byte and one data byte only (see Fig.4).
1997 Jul 01 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
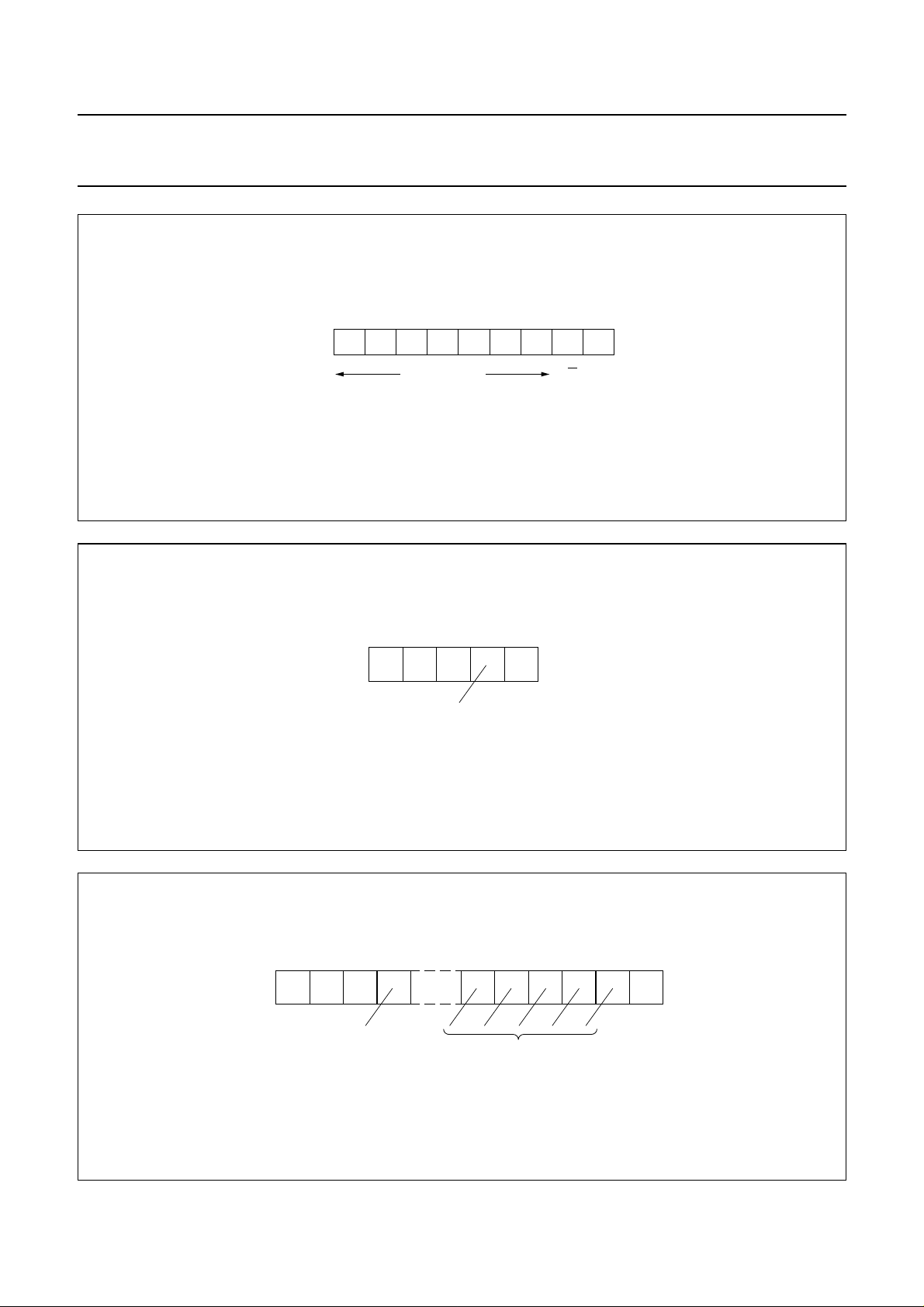
MSB LSB
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 ACK
R/Wmodule address
Fig.3 The module address byte.
STOSAD
STOP
condition
MED697
START
condition
MADSTA
data byte
MED893
Fig.4 Data transmission without auto-increment (BREN = 0 or 1).
handbook, full pagewidth
START
condition
MADSTA
SAD
data byte
Fig.5 Data transmission with auto-increment (BREN = 0).
1997 Jul 01 7
data bytes
STO
STOP
condition
MED698

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video processor with automatic cut-off control TDA4689
AUTO-INCREMENT
The auto-increment format enables quick slave receiver
initialization by one transmission, when the I2C-bus control
bit BREN = 0 (see control register bits of Table 1).
If BREN = 1 auto-increment is not possible.
If the auto-increment format is selected, the MAD byte is
followed by a SAD byte and by the data bytes of
consecutive subaddresses (see Fig.5).
All subaddresses from 00H to 0FH are automatically
incremented, the subaddress counter wraps round from
0FH to 00H. Reserved subaddresses 07H, 08H, 09H,
0BH and 0FH are treated as legal but have no effect.
Subaddresses outside the range 00H and 0FH are not
acknowledged by the device.
Subaddresses are stored in the TDA4689 to address the
following parameters and functions (see Table 1):
• Brightness adjust
• Saturation adjust
• Contrast adjust
• Hue control voltage
• RGB gain adjust
• Peak drive limiting adjust
• Control register functions.
The data bytes D7 to D0 (see Table 1) provide the data of
the parameters and functions for video processing.
C
ONTROL REGISTER 1
NMEN (NTSC Matrix Enable):
0 = PAL/SECAM matrix
1 = NTSC matrix.
BREN (Buffer Register Enable):
0 = new data is executed as soon as it is received
1 = data is stored in buffer registers and is transferred to
the data registers during the next vertical blanking
interval.
The I2C-bus receiver does not accept any new data until
this data is transferred into the data registers.
ONTROL REGISTER 2
C
FSON2 (Fast Switch 2 ON).
FSDIS2 (Fast Switch 2 Disable).
FSON1 (Fast Switch 1 ON).
FSDIS1 (Fast Switch 1 Disable).
The RGB input signals are selected by FSON2 and
FSON1 or FSW2 and FSW1:
• FSON2 has priority over FSON1
• FSW2 has priority over FSW
• FSDIS1 and FSDIS2 disable FSW1 and FSW
1
2
(see Table 2).
BCOF (Black level Control Off):
0 = automatic cut-off control enabled
1 = automatic cut-off control disabled; RGB outputs are
clamped to fixed DC levels.
C
ONTROL REGISTER 3
MOD2 (output clamp MODe2):
0 = inactive
1 = output clamping, but brightness inactive.
When MOD2 = 1 and BCOF = 1 the output clamp is
enabled and brightness adjust is disabled (for clamping
purposes of following RGB receivers).
(BCOF = 0) AND (MOD2 = 1); from the description given
above the influence on the clamping stage is contradictory.
Consequently, there is no purpose to this combination and
it makes no sense to switch this combination.
When the supply voltage has dropped below
approximately 6.0 V (usually occurs when the TV receiver
is switched on or the supply voltage is interrupted) all data
and function bits are set to 01H.
SC5 (SandCastle 5 V):
0 = 3-level sandcastle pulse
1 = 2-level (5 V) sandcastle pulse.
1997 Jul 01 8
 Loading...
Loading...