Philips PCF8575CTS-F1 Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC12
1999 Aug 05
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
PCF8575C
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for
I
2
C-bus

1999 Aug 05 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
PCF8575C
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 Quasi-bidirectional I/Os
6.2 Addressing
6.3 Reading from a port (input mode)
6.4 Writing to the port (output mode)
6.5 Interrupt
7 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I2C-BUS
7.1 Bit transfer
7.2 START and STOP conditions
7.3 System configuration
7.4 Acknowledge
8 LIMITING VALUES
9 HANDLING
10 CHARACTERISTICS
11 I2C-BUS TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
12 DEVICE PROTECTION
13 PACKAGE OUTLINE
14 SOLDERING
14.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
14.2 Reflow soldering
14.3 Wave soldering
14.4 Manual soldering
14.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
wave and reflow soldering methods
15 DEFINITIONS
16 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
17 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1999 Aug 05 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
PCF8575C
1 FEATURES
• Operating supply voltage from 4.5 to 5.5 V
• Low standby current consumption of 10 µA maximum
• I2C-bus to parallel port expander
• 400 kbits/s FAST I2C-bus
• Open-drain interrupt output
• 16-bit remote I/O port for the I2C-bus
• Compatible with most microcontrollers
• Latched outputs with high current drive capability for
directly driving LEDs
• Address by 3 hardware address pins for use of up to
8 devices
• SSOP24 package.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The device is a silicon CMOS circuit. It provides general
purpose remote I/O expansion for most microcontroller
families via the two-line bidirectional bus (I2C-bus).
The deviceconsists of a 16-bit quasi-bidirectional port and
an I2C-bus interface. The PCF8575C has a low current
consumption and includes latched outputs with high
current drive capability for directly driving LEDs. It also
possesses an interruptline (INT) which can beconnected
to the interrupt logic of the microcontroller. By sending an
interrupt signal on this line, the remote I/O can inform the
microcontrollerif thereis incoming dataon itsportswithout
having to communicate via the I2C-bus. This means that
the device is an I2C-bus slave transmitter/receiver.
Every data transmission fromthe PCF8575Cmust consist
of an even number of bytes, the first byte will be referred
to as P07 to P00 and the second byteas P17 to P10. The
third will be referred to as P07 to P00 and so on.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCF8575CTS SSOP24 plastic shrink small outline package; 24 leads; body width 5.3 mm SOT340-1
1999 Aug 05 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
PCF8575C
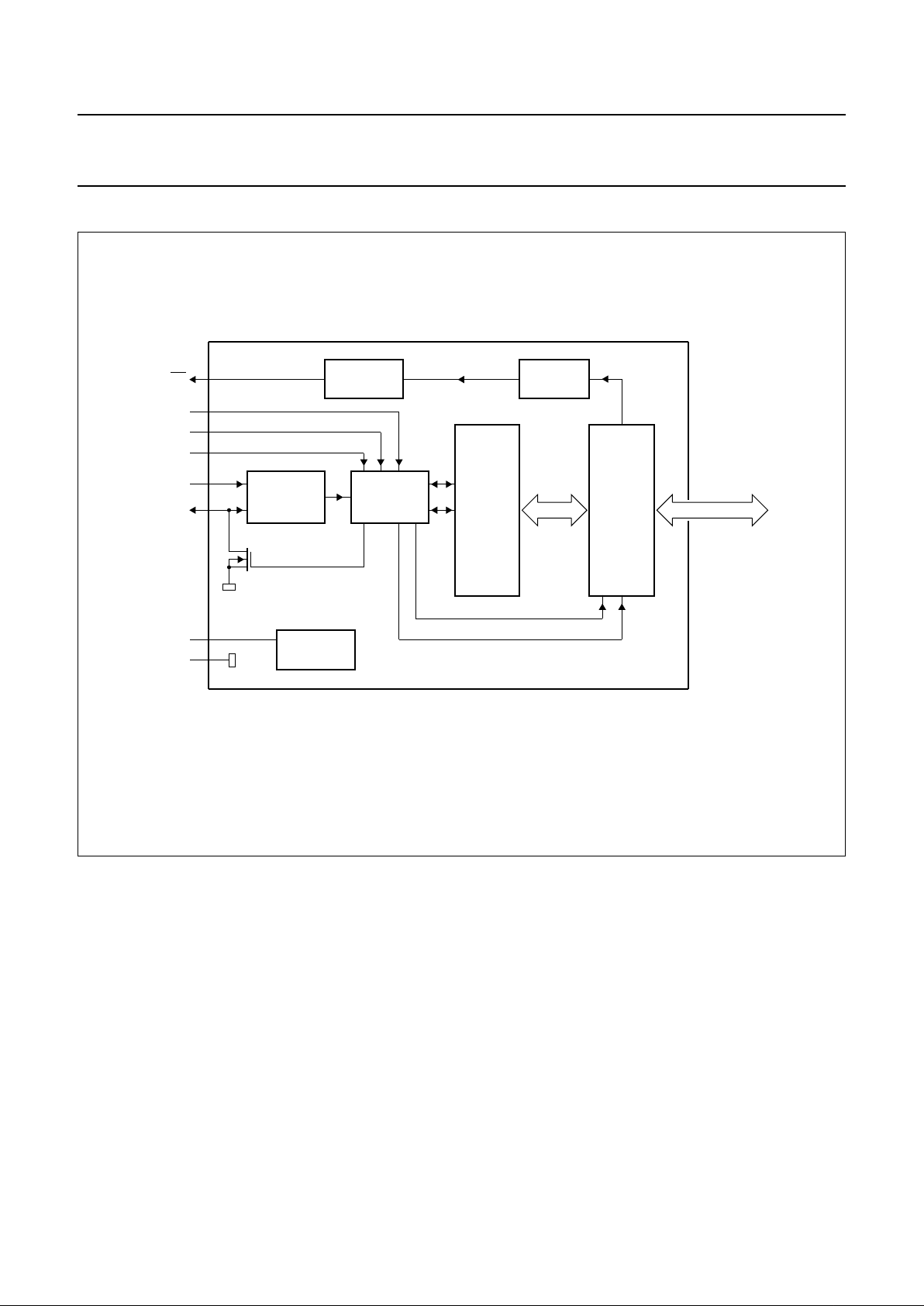
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
MGS630
I2C-BUS
CONTROL
INPUT
FILTER
1
2
3
22
23
21
INTERRUPT
LOGIC
16 BITS
P00 to P07
4 to 11
P10 to P17
13 to 20
I/O
PORT
SHIFT
REGISTER
LP FILTER
WRITE pulse
READ pulse
POWER-ON
RESET
24
12
V
DD
V
SS
SDA
SCL
A2
A1
A0
INT
PCF8575C
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1999 Aug 05 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
PCF8575C
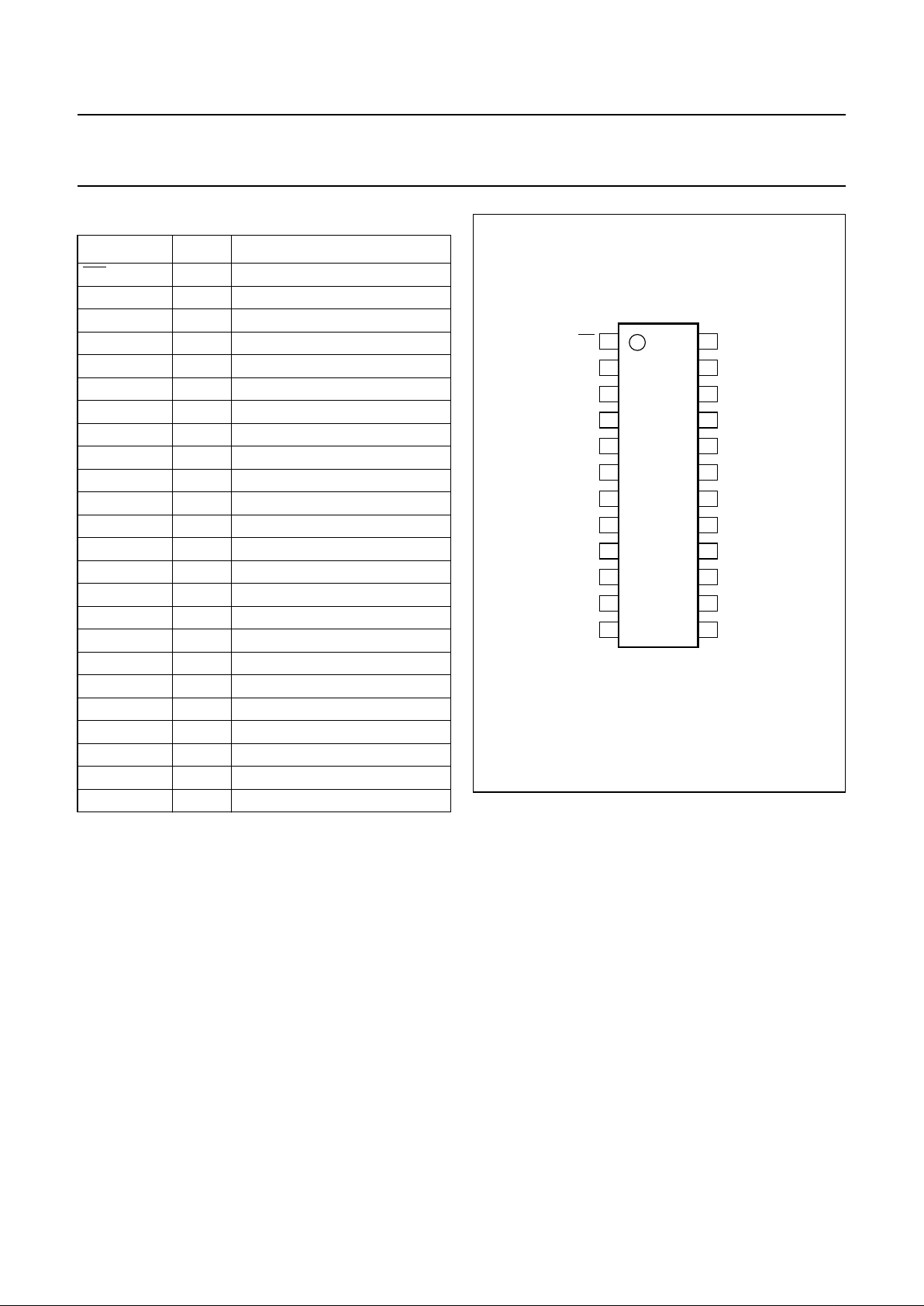
5 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
INT 1 interrupt output (active LOW)
A1 2 address input 1
A2 3 address input 2
P00 4 quasi-bidirectional I/O 00
P01 5 quasi-bidirectional I/O 01
P02 6 quasi-bidirectional I/O 02
P03 7 quasi-bidirectional I/O 03
P04 8 quasi-bidirectional I/O 04
P05 9 quasi-bidirectional I/O 05
P06 10 quasi-bidirectional I/O 06
P07 11 quasi-bidirectional I/O 07
V
SS
12 supply ground
P10 13 quasi-bidirectional I/O 10
P11 14 quasi-bidirectional I/O 11
P12 15 quasi-bidirectional I/O 12
P13 16 quasi-bidirectional I/O 13
P14 17 quasi-bidirectional I/O 14
P15 18 quasi-bidirectional I/O 15
P16 19 quasi-bidirectional I/O 16
P17 20 quasi-bidirectional I/O 17
A0 21 address input 0
SCL 22 serial clock line input
SDA 23 serial data line input/output
V
DD
24 supply voltage
handbook, halfpage
PCF8575C
MGS631
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
INT
A1
A2
P00
P01
P02
P03
P04
P05
P06
P07
V
SS
V
DD
SDA
SCL
A0
P17
P16
P15
P14
P13
P12
P11
P10
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1999 Aug 05 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
PCF8575C
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
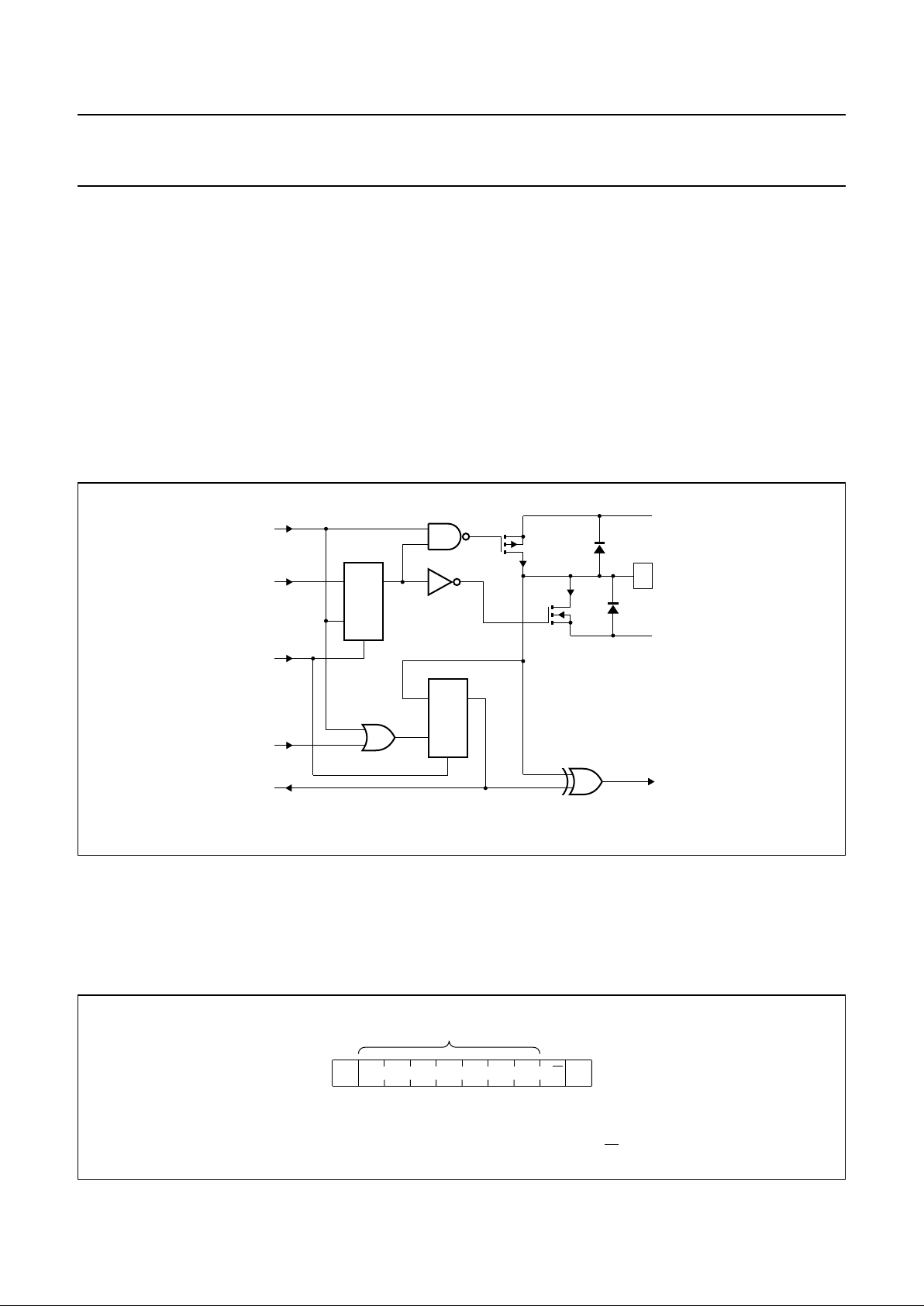
6.1 Quasi-bidirectional I/Os
The16 ports (seeFig.3) areentirely independent andcan beused eitheras input oroutput ports.Input dataistransferred
from the ports to the microcontroller in the READ mode (see Fig.6). Output data istransmitted to the portsin the WRITE
mode (see Fig.5).
This quasi-bidirectional I/O can be used as an input or output without the use of a control signal for data direction.
At power-on all the I/Os are in 3-state mode. The strong pull-up to VDD (I
OHt
) allows a fast rising edge into a heavily
loaded output. This strong pull-up turns on when the output is written HIGH, and is switched off by the negative edge of
SCL. Afterthis short periodthe output isin 3-state mode.The I/O should bewritten HIGH beforebeing used asan input.
After power-on as all the I/Os are set to 3-state all of them can be used as inputs. Any change in setting of the I/Os as
either inputs or outputs can be donewith the write mode.Warning: If a HIGH is applied to an I/O whichhas been written
earlier to LOW, a large current (IOL) will flow to VSS (see Chapter 10; note 3).
6.2 Addressing
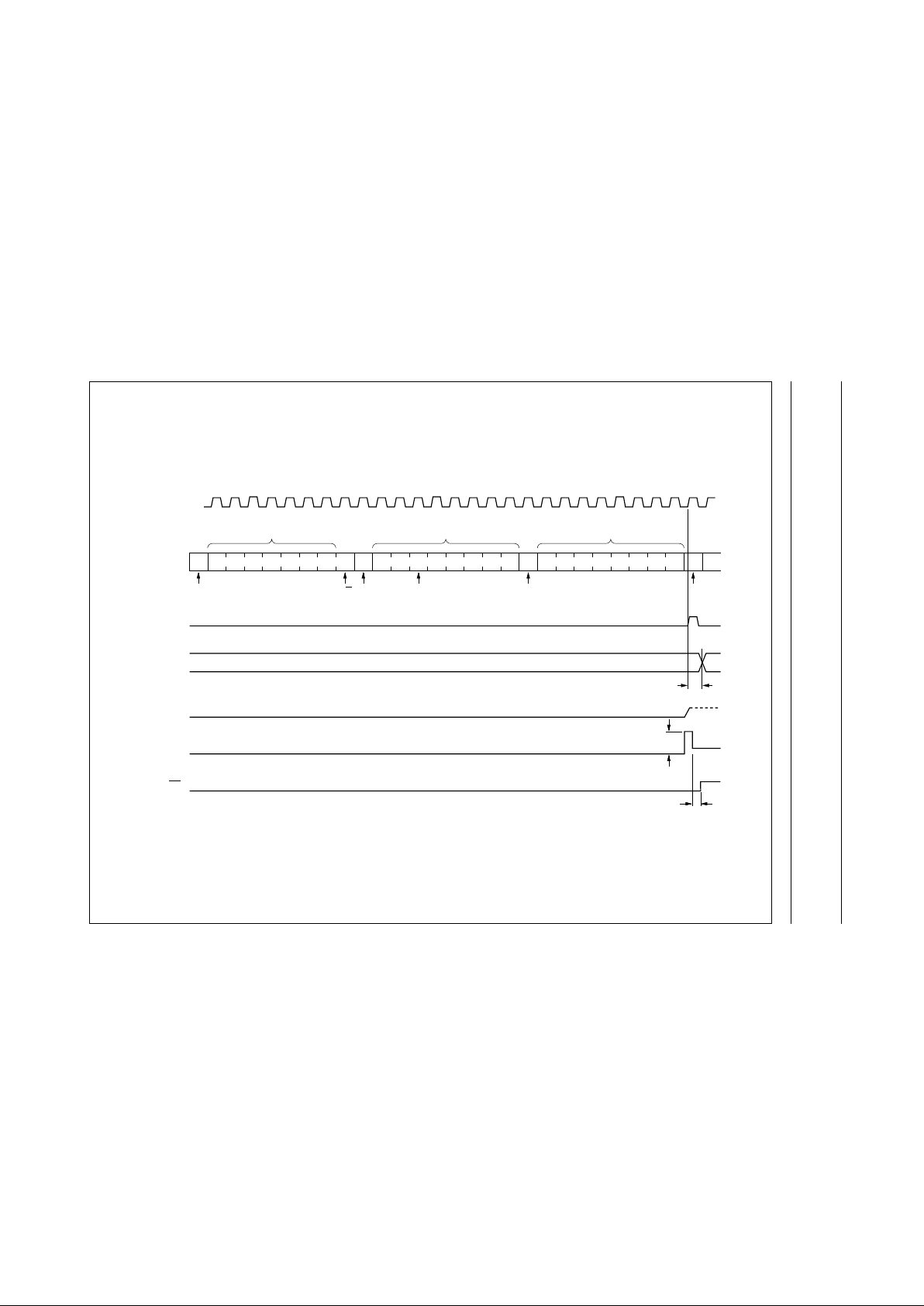
Figures 4, 5 and 6 show the address and timing diagrams. Before any data is transmitted or received the master must
sendthe addressof thereceivervia theSDA line.Thefirst bytetransmitted aftertheSTART conditioncarries theaddress
of theslave deviceand theread/write bit. Theaddress ofthe slavedevice must notbe changedbetween theSTART and
the STOP conditions. The PCF8575C acts as a slave receiver or a slave transmitter.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGS632
DQ
C
I
C
I
S
FF
D
I
OL
I
OHt
Q
S
FF
to interrupt
logic
V
SS
V
DD
P00 to P07
P10 to 17
write pulse
data from
shift register
power-on
reset
read pulse
data to
shift register
Fig.3 Simplified schematic diagram of each I/O.
MGL541
handbook, halfpage
S 0 1 0 0 A2 A1 A0 R/W A
slave address
Fig.4 Byte containing the slave address and the R/W bits.
1999 Aug 05 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I
2
C-bus
PCF8575C
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to forcelandscape pages tobe rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pagesto be rotated correctly whenbrowsingthrough the pdf in theAcrobat reader. white to forcelandscapepages to be ...
n
dbook, full pagewidth
MGS633
S 0 1 0 0 A2 A1 A0 0 A P07 P06 P00 P17 P101
start condition R/W P05acknowledge
from slave
A ASDA
SCL
Integral multiples of two bytes
WRITE TO
PORT
t
pv
I
OHt
DATA OUTPUT
FROM PORT
05 OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
05 PULL-UP
OUTPUT CURRENT
INT
slave address (PCF8575C)
data to port 0 data to port 1
12345678
acknowledge
from slave
acknowledge
from slave
t
ir
Data A0 and
B0 valid
Fig.5 WRITE mode (output).
1999 Aug 05 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 16-bit I/O expander for I
2
C-bus
PCF8575C
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to forcelandscape pages tobe rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pagesto be rotated correctly whenbrowsingthrough the pdf in theAcrobat reader. white to forcelandscapepages to be ...
b
ook, full pagewidth
MGL543
S 0 1 0 0 A2 A1 A0 1 A P07 P06 P05 P04
P07 to P00 P17 to P10P07 to P00 P17 to P10 P07 to P00 P17 to P10
P03 P02 P01 P00 P17 P10
R/W acknowledge
from slave
A A P07 P00 A P17 P10 1P
SDA
SCL
READ FROM PORT
t
h
DATA INTO PORT
INT
acknowledge
from receiver
acknowledge
from receiver
acknowledge
from receiver
non acknowledge
from receiver
t
su
t
ir
t
ir
t
iv
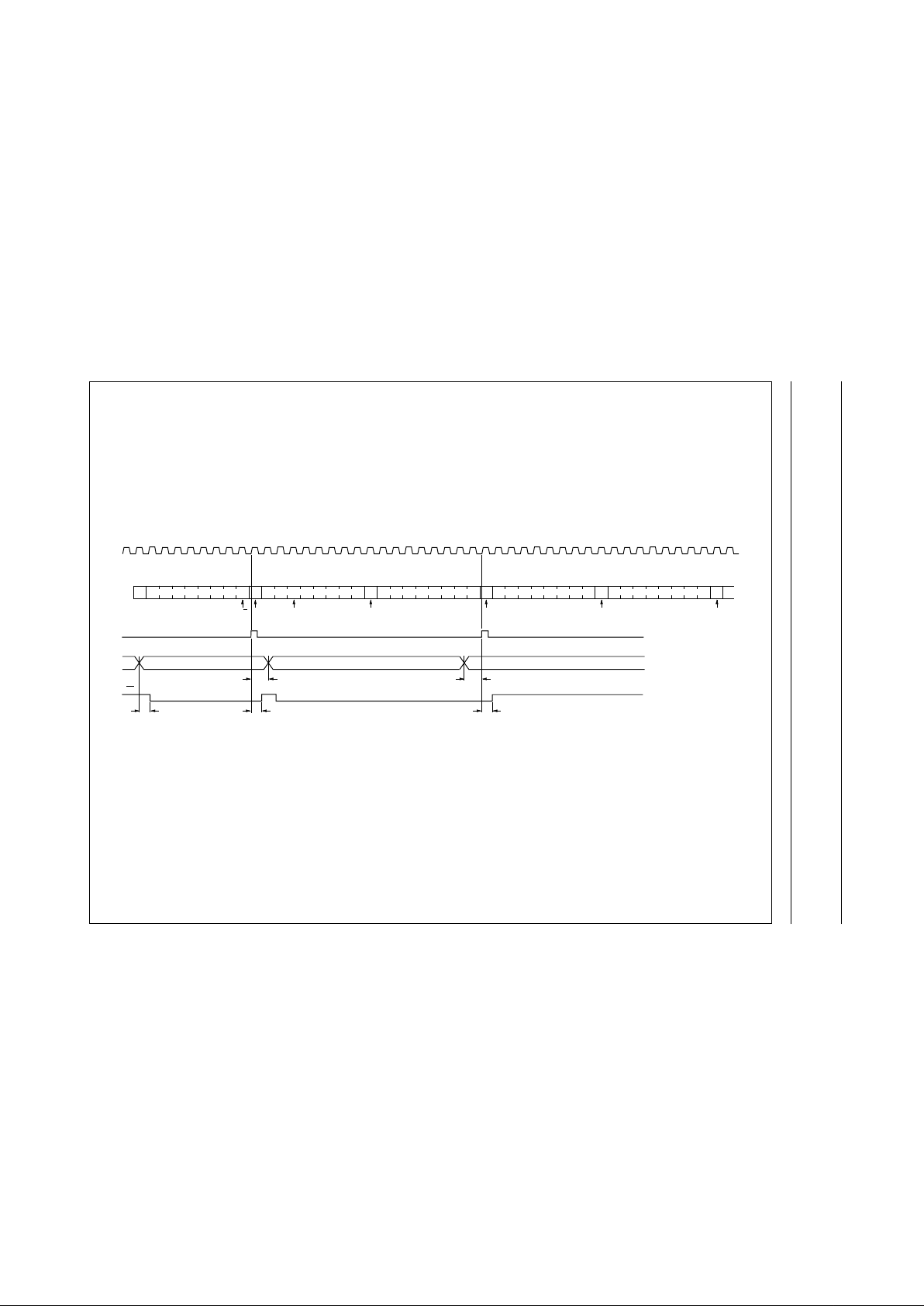
Fig.6 READ mode (input).
A LOW-to-HIGHtransition of SDA, while SCL is HIGH is defined as the STOP condition (P). Transfer of data can be stopped at any moment by a STOP condition. When this occurs, data present
at the latest acknowledge phase is valid (output mode). Input data is lost.
 Loading...
Loading...