Philips PCA82C252T-N2 Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Mar 07
File under Integrated Circuits, IC18
1997 Oct 28
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
PCA82C252
Fault-tolerant CAN transceiver
1997 Oct 28 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fault-tolerant CAN transceiver PCA82C252
FEATURES
Optimized for in-car low-speed communication
• Baud rate up to 125 kBaud
• Up to 15 nodes can be connected
• Supports unshielded bus wires
• Low RFI due to built-in slope control function
• Fully integrated receiver filters.
Bus failure management
• Supports one-wire transmission modes with ground
offset voltages up to 1.5 V
• Automatic switching to single-wire mode in the event of
bus failure
• Automatic reset to differential mode if bus failure is
removed.
Protection
• Short-circuit proof to battery and ground in 12 V
powered systems
• Thermally protected
• Bus lines protected against transients in an automotive
environment
• An unpowered node does not disturb the bus lines.
Support for low-power modes
• Low current sleep/standby mode with wake-up via the
bus lines
• Power-on reset flag on the output.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCA82C252 is the interface between the CAN
protocol controller and the physical bus. It is primarily
intended for low-speed applications, up to 125 kBaud, in
passenger cars. The device provides differential transmit
capability but will switch in error conditions to a single-wire
transmitter and/or receiver.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MIN. UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage 4.75 − 5.25 V
V
BAT
battery voltage no time limit −0.3 − +27 V
operating 6.0 − 27 V
load dump −−40 V
I
sleep
sleep mode current VCC=0V; V
BAT
=12V − 50 −µA
V
CANH,VCANL
CANH, CANL input voltage VCC= 0 to 5.5 V; V
BAT
≥ 0V;
no time limit
−10 − +27 V
V
CC
= 0 to 5.5 V; V
BAT
≥ 0V;
t < 0.1 ms; load dump
−40 − +40 V
V
DROP(H)
CANH transmitter drop voltage I
CANH
=40mA −−1.4 V
V
DROP(L)
CANL transmitter drop voltage I
CANL
=40mA −−1.4 V
t
PD
propagation delay TXD to RXD − 1 −µs
t
f
bus output fall time 90% to 10% − 0.5 −µs
t
r
bus output rise time 10% to 90% − 0.5 −µs
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −40 − +125 °C
TYPE
NUMBER
P ACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCA82C252T SO14 plastic small outline package; 14 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT108-1
1997 Oct 28 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fault-tolerant CAN transceiver PCA82C252
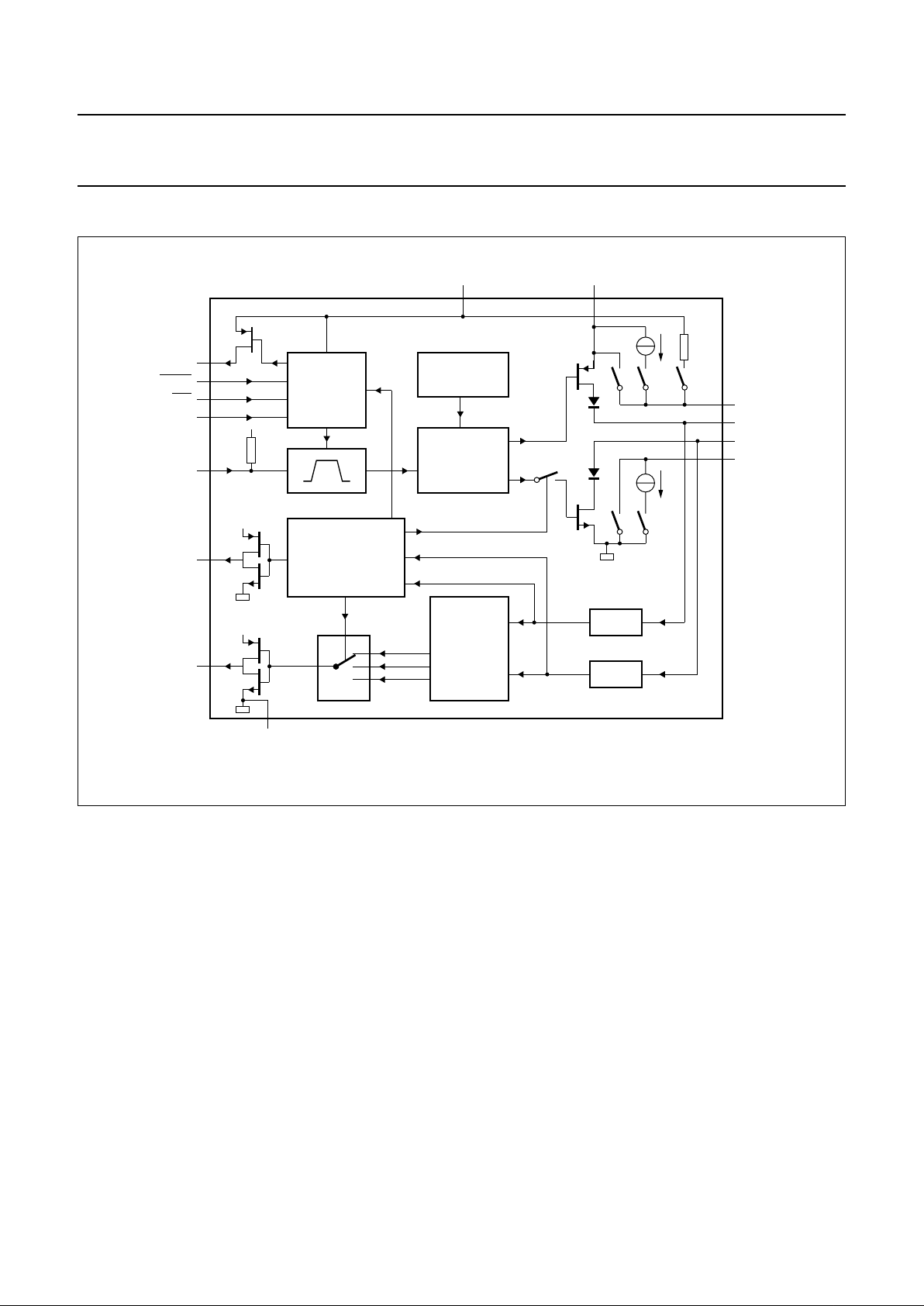
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
MBH548
FAILURE DETECTOR
PLUS WAKE UP
PLUS TIME-OUT
WAKE-UP
STANDBY
CONTROL
INH
1
WAKE
7
STB
5
EN
6
TXD
V
CC
2
NERR
4
RXD
3
TEMPERATURE
PROTECTION
DRIVER
RECEIVER
16
kΩ
BAT
14
V
CC
10
13
GND
FILTER
FILTER
PCA82C252
9
11
12
8
RTL
CANH
CANL
RTH
1997 Oct 28 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fault-tolerant CAN transceiver PCA82C252
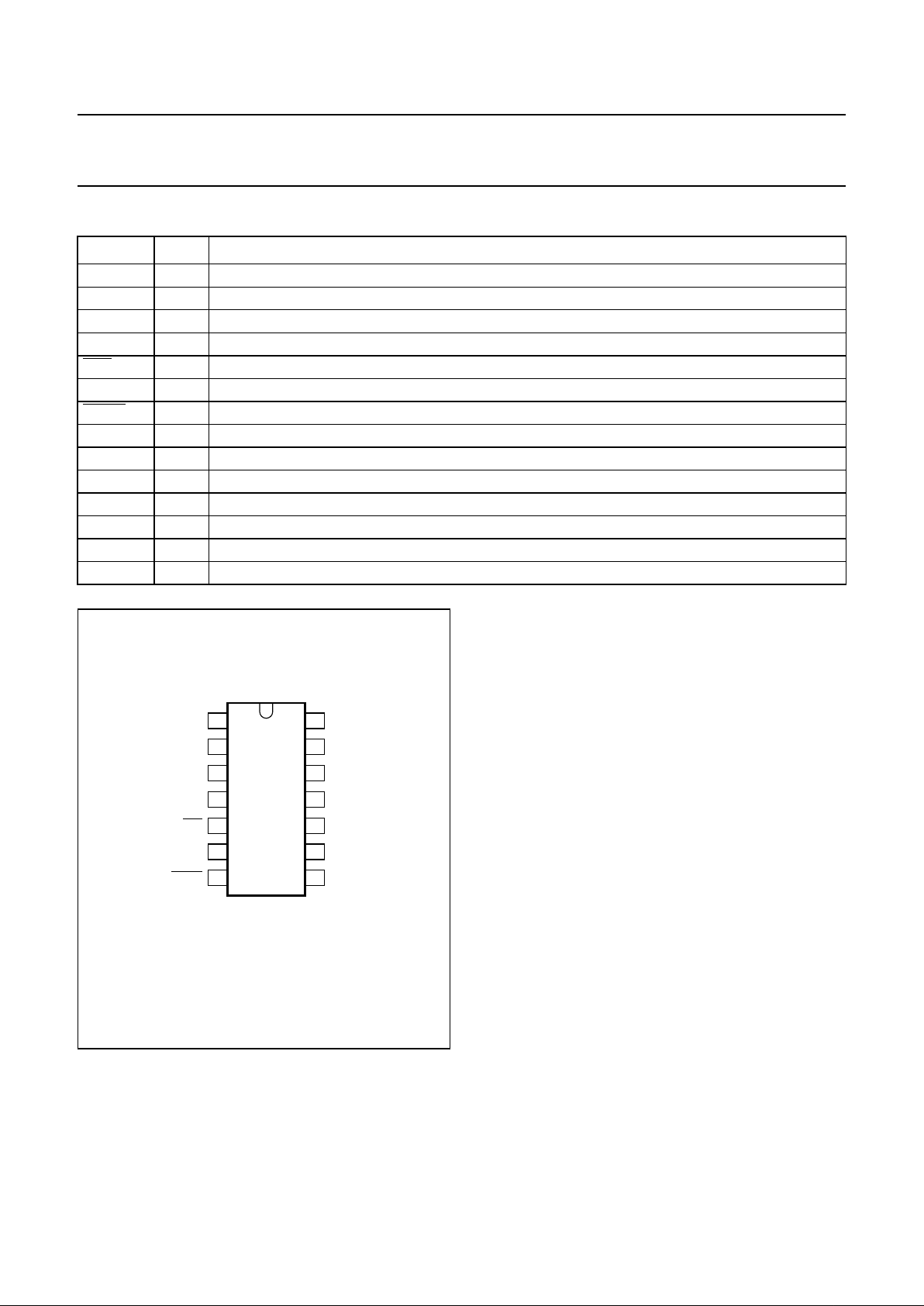
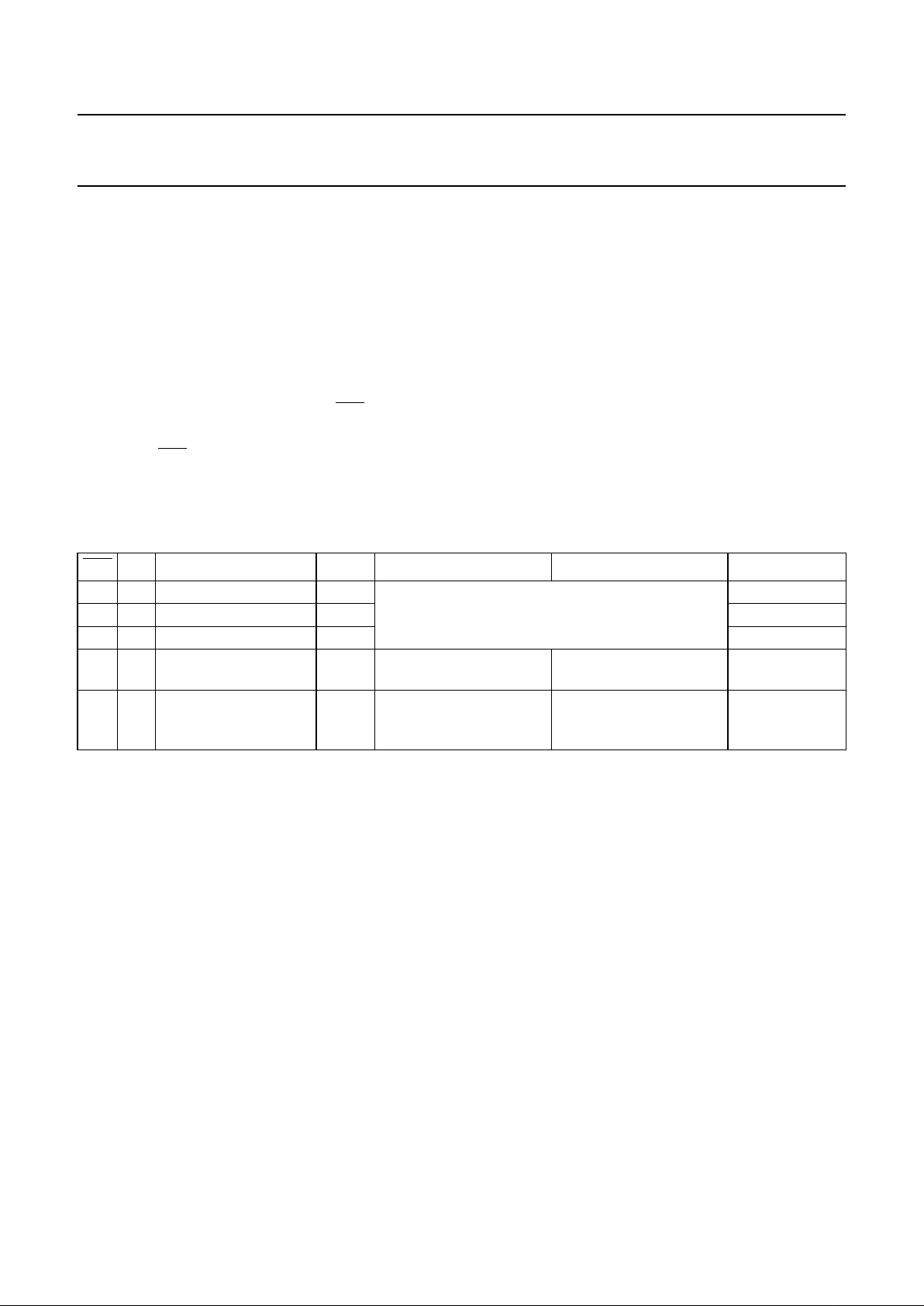
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
INH 1 inhibit output for switching external 5 V regulator
TXD 2 transmit data input, when LOW bus data will be dominant, when HIGH bus data will be recessive
RXD 3 receive data output, when LOW bus data will be dominant
NERR 4 error output pin, when LOW a bus error exists
STB 5 not standby digital control input signal (active LOW)
EN 6 enable digital control input signal
WAKE 7 not wake input signal, when pulled down INH becomes active for wake-up (active LOW)
RTH 8 termination resistor, CANH line will be high-impedance with certain bus errors
RTL 9 termination resistor, CANL line will be high-impedance with certain bus errors
V
CC
10 supply voltage (+5 V)
CANH 11 high voltage bus line, will be HIGH in dominant state
CANL 12 low voltage bus line, will be LOW in dominant state
GND 13 ground
BAT 14 battery voltage
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, halfpage
PCA82C252
MBG621
1INH
2
3
4
5
6
7
14 BAT
TXD GND
RXD CANL
NERR CANH
STB V
CC
EN RTL
WAKE RTH
13
12
11
10
9
8
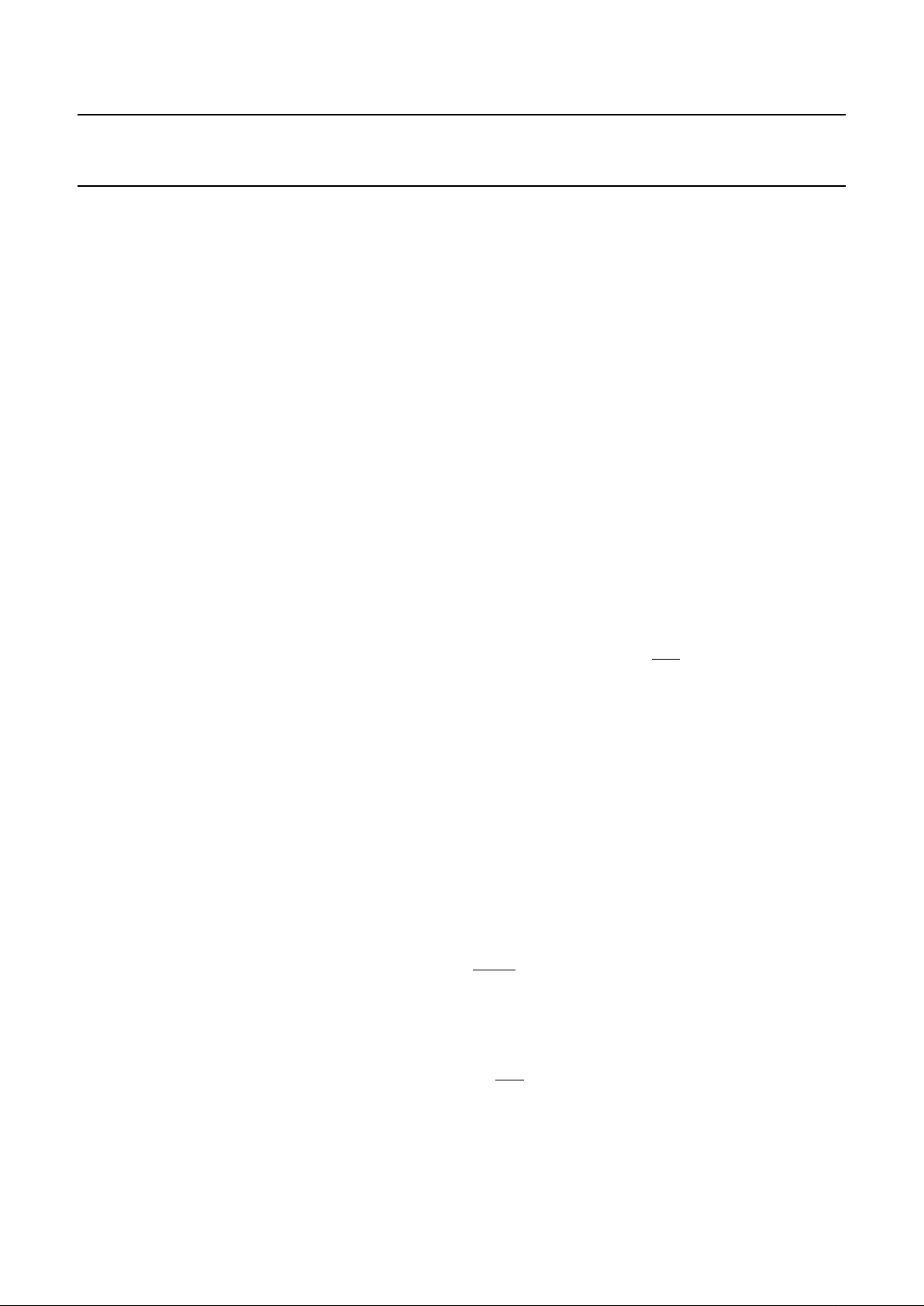
1997 Oct 28 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fault-tolerant CAN transceiver PCA82C252
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The PCA82C252 is the interface between the CAN
protocol controller and the physical bus. It is primarily
intended for low speed applications, up to 125 kbaud, in
passenger cars. The device provides differential transmit
capability to the bus and differential receive capability to
the CAN controller.
To reduce RF interference the rise and fall slope are
limited. This allows the use of an unshielded twisted pair or
a parallel pair of wires for the bus. Moreover, it supports
transmission capability on either bus wire if one of the bus
wires is corrupted. The failure detection logic automatically
selects a suitable transmission mode.
In normal operation (no wiring failures) the differential
receiver is output to RXD. The differential receiver inputs
are connected to CANH and CANL through integrated
filters. The filtered input signals are also used for the single
wire receivers. The CANH and CANL receivers have
threshold voltages that ensure a maximum noise margin in
single-wire modes.
Failure detector
The failure detector is active in the normal operation mode
and detects the following single bus failures and switches
to an appropriate mode:
1. CANH wire interrupted
2. CANL wire interrupted
3. CANH short-circuited to battery
4. CANL short-circuited to ground
5. CANH short-circuited to ground
6. CANL short-circuited to battery
7. CANL mutually shorted to CANH.
The differential receiver threshold is set at −2.9 V.
This ensures correct reception in the normal operating
modes and, in the event of failures 1, 2 and 5 with a noise
margin as high as possible. These failures, or recovery
from them, do not destroy ongoing transmissions.
To ensure speed requirements the differential receiver has
an acceleration function.
Failures 3 and 6 are detected by comparators connected
to CANH and CANL, respectively. If the comparator
threshold is exceeded for a certain period of time, the
reception is switched to the single-wire mode. This time is
needed to avoid false triggering by external RF fields.
Recovery from these failures is detected automatically
after a certain time-out (filtering) and no transmission is
lost.
Failures 4 and 7 initially result in a permanent dominant
level at RXD. After a time-out, the CANL driver and the
RTL pin are switched off. Only a weak pull-up at RTL
remains. Reception continues by switching to the
single-wire mode via CANH. When failures 4 or 7 are
removed, the recessive bus levels are restored. If the
differential voltage remains below the recessive threshold
level for a certain period of time, reception and
transmission switch back to the differential mode.
If any of the seven wiring failures occur, the output NERR
will be made LOW. On error recovery, NERR will be made
HIGH again.
During all single-wire transmissions, the EMC
performance (both immunity and emission) is worse than
in the differential mode. Integrated receiver filters
suppress any HF noise induced into the bus wires.
The cut-off frequency of these filters is a compromise
between propagation delay and HF suppression. In the
single-wire mode, low frequency noise cannot be
distinguished from the required signal.
Low power modes
The transceiver provides 3 low power modes which can be
entered and exited via pins
STB and EN.
The sleep mode is the mode with the lowest power
consumption. The INH pin is switched to high-impedance
for deactivation of external voltage regulators. CANL is
biased to the battery voltage via the RTL output. If the
supply voltage is provided the RXD and NERR will signal
the wake-up interrupt
The V
BAT
standby mode will react the same as the sleep
mode with an active INH output.
The VCC standby mode is the V
BAT
standby with RTL
switched to the VCC voltage. In this mode the NERR output
signals the V
BAT
power-on flag and the RXD output will
show the wake-up interrupt.
Wake-up requests are recognized by the transceiver when
a dominant signal is detected on either bus line or if the
WAKE pin is connected to ground. On a wake-up request
the transceiver will set the INH output which can be used
to activate the external VCC voltage regulator. If VCC is
provided the wake-up request can be read on the NERR or
RXD outputs, on which the external microcontroller can
wake up the transceiver (switch to normal operating mode)
via STB and EN.
1997 Oct 28 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fault-tolerant CAN transceiver PCA82C252
To prevent false wake-up due to transients or RF fields,
wake-up voltage threshold levels have to be maintained
for a certain period of time. In the low power modes the
failure detection circuit remains partly active to prevent
increased power consumption should errors 3, 4 and 7
occur.
Power on
After power-on V
BAT
is switched on, the INH pin will
become HIGH and an internal power-on flag will be set.
This flag can be read via the NERR pin (STB = 1, EN = 0)
and will be reset by entering the normal operation mode.
The EN and
STB pins will internally be set to LOW level, if
the VCC voltage is below a certain threshold level, to
provide fail safe functionality.
Protections
A current limiting circuit protects the transmitter output
stages against short-circuit to positive and negative
battery voltage.
If the junction temperature exceeds a maximum value, the
transmitter output stages are disabled. Because the
transmitter is responsible for the major part of the power
dissipation, this will result in a reduced power dissipation
and hence a lower chip temperature. All other parts of the
IC will remain operating.
The CANH and CANL inputs are protected against
electrical transients which may occur in an automotive
environment.
Table 1 Truth table of CAN transceiver
Notes
1. Wake-up interrupts are released when entering normal operating mode.
2. If go to sleep command was used before (EN may turn LOW as V
CC
drops, without affecting internal functions
because of fail safe functionality).
3. V
BAT
power-on flag will be reset when entering normal operation mode.
STB EN MODE INH NERR RXD RTL
00V
BAT
standby
(1)
HIGH LOW active wake-up interrupt signal if VCC is present switched to V
BAT
0 0 sleep
(2)
floating switched to V
BAT
0 1 go to sleep command floating switched to V
BAT
10VCC standby
(3)
HIGH LOW active V
BAT
power-on flag
LOW active wake-up
interrupt
switched to V
CC
1 1 normal operation mode HIGH LOW active error flag HIGH = receive;
LOW = dominant
received data
switched to V
CC
 Loading...
Loading...