
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 User manual
Document information
Info Content
Keywords P89LPC933/934/935/936
Abstract Technical information for the P89LPC933/934/935/936 devices.

Philips Semiconductors
Revision history
Rev Date Description
01 20050304 Initial version
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 2 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
1. Introduction
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 are single-chip microcontrollers designed for applications
demanding high-integration, low cost solutions over a wide range of performance
requirements. The P89LPC933/934/935/936 are based on a high performance processor
architecture that executes instructions in two to four clocks, six times the rate of standard
80C51 devices. Many system-level functions have been incorporated into the
P89LPC933/934/935/936 in order to reduce component count, board space, and system
cost.
1.1 Product comparison overview
Ta bl e 1 highlights the differences between the four devices.
Table 1: Product comparison overview
Device Flash memory Sector size ADC1 ADC0 CCU Data EEPROM
P89LPC933 4 kB 1 kB X - - -
P89LPC934 8 kB 1 kB X - - -
P89LPC935 8 kB 1 kB X X X X
P89LPC936 16 kB 2 kB X X X X
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
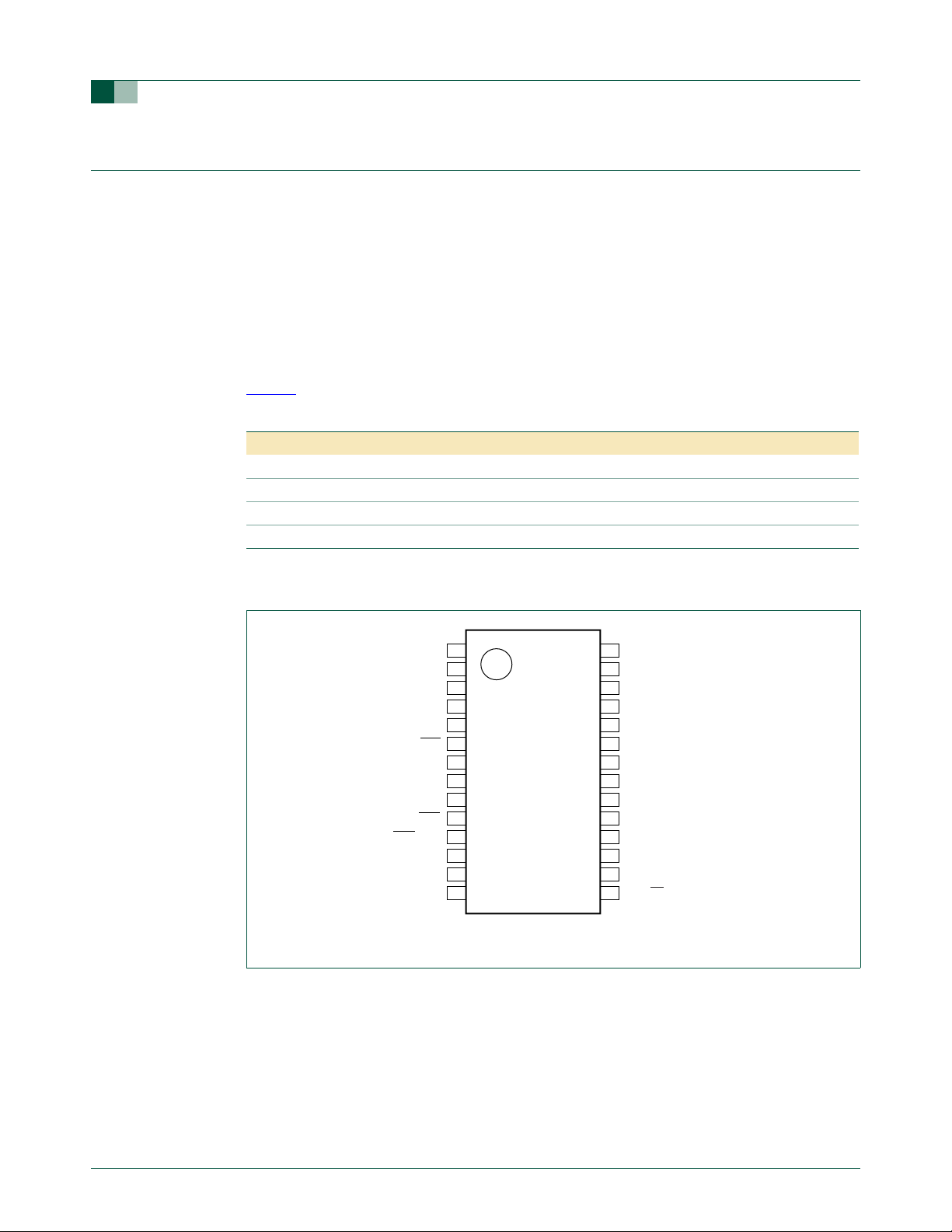
1.2 Pin configuration
P2.0/DAC0
P0.0/CMP2/KBI0
P3.1/XTAL1
P3.0/XTAL2/CLKOUT
P1.3/INT0/SDA
P1.2/T0/SCL
Fig 1. P89LPC933/934 TSSOP28 pin configuration.
P2.1
P1.7
P1.6
P1.5/RST
V
SS
P1.4/INT1
P2.2/MOSI
P2.3/MISO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P89LPC933FDH
8
P89LPC934FDH
9
10
11
12
13
14
002aab071
28
P2.7
27
P2.6
26
P0.1/CIN2B/KBI1/AD10
25
P0.2/CIN2A/KBI2/AD11
24
P0.3/CIN1B/KBI3/AD12
23
P0.4/CIN1A/KBI4/DAC1/AD13
22
P0.5/CMPREF/KBI5
21
V
DD
20
P0.6/CMP1/KBI6
19
P0.7/T1/KBI7
18
P1.0/TXD
17
P1.1/RXD
16
P2.5/SPICLK
15
P2.4/SS
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 3 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
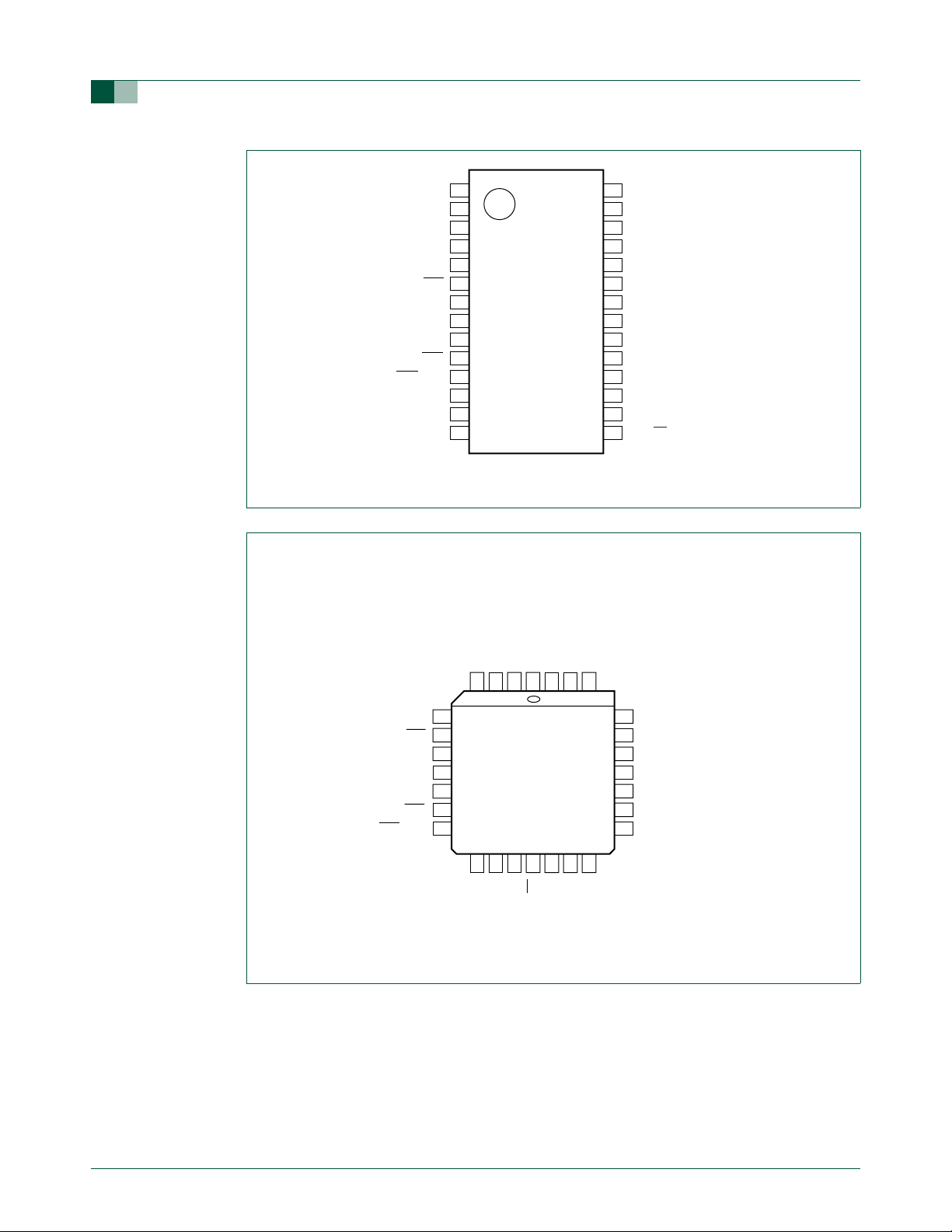
P2.0/ICB/DAC0/AD03
P2.1/OCD/AD02
P0.0/CMP2/KBI0/AD01
P1.7/OCC/AD00
P1.6/OCB
P1.5/RST
P3.1/XTAL1
P3.0/XTAL2/CLKOUT
P1.4/INT1
P1.3/INT0/SDA
P1.2/T0/SCL
P2.2/MOSI
P2.3/MISO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
V
SS
P89LPC935FDH
8
P89LPC936FDH
9
10
11
12
13
14
002aab072
Fig 2. P89LPC935/936 TSSOP28 pin configuration.
28
P2.7/ICA
27
P2.6/OCA
26
P0.1/CIN2B/KBI1/AD10
25
P0.2/CIN2A/KBI2/AD11
24
P0.3/CIN1B/KBI3/AD12
23
P0.4/CIN1A/KBI4/DAC1/AD13
22
P0.5/CMPREF/KBI5
21
V
DD
20
P0.6/CMP1/KBI6
19
P0.7/T1/KBI7
18
P1.0/TXD
17
P1.1/RXD
16
P2.5/SPICLK
15
P2.4/SS
P1.7/OCC/AD00
P0.0/CMP2/KBI0/AD01
P2.1/OCD/AD02
P2.0/ICB/DAC0/AD03
1
2
4
3
P1.6/OCB
P1.5/RST
P3.1/XTAL1
P3.0/XTAL2/CLKOUT
P1.4/INT1
P1.3/INT0/SDA
5
6
7
V
SS
8
9
10
11
P89LPC935FA
121314
P1.2/T0/SCL
15
P2.4/SS
P2.2/MOSI
P2.3/MISO
Fig 3. P89LPC935 PLCC28 pin configuration.
P2.7/ICA
P2.6/OCA
P0.1/CIN2B/KBI1/AD10
26
27
28
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
161718
P2.5/SPICLK
P1.0/TXD
P1.1/RXD
002aab074
P0.2/CIN2A/KBI2/AD11
P0.3/CIN1B/KBI3/AD12
P0.4/CIN1A/KBI4/DAC1/AD13
P0.5/CMPREF/KBI5
V
DD
P0.6/CMP1/KBI6
P0.7/T1/KBI7
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 4 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
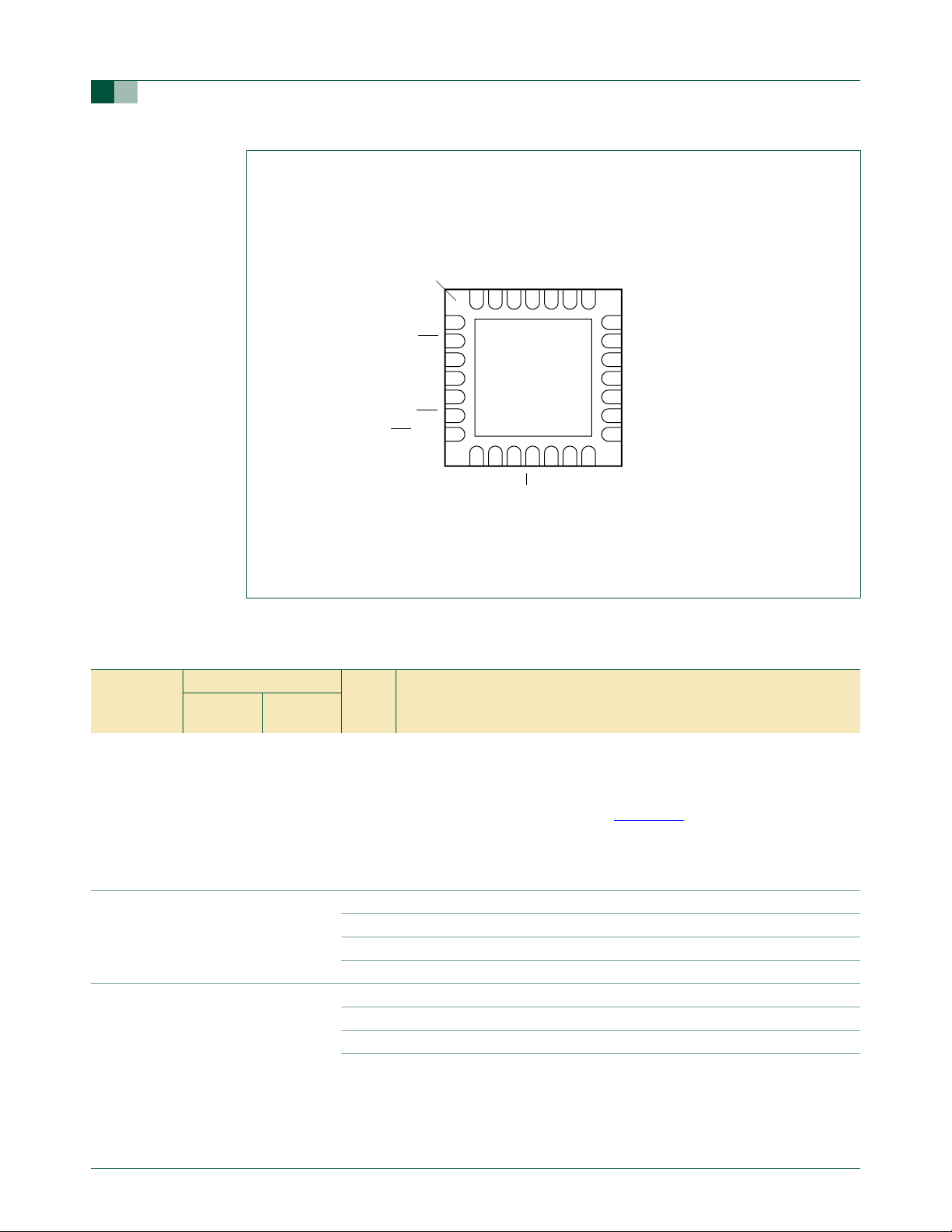
terminal 1
index area
P1.6/OCB
P1.5/RST
V
P3.1/XTAL1
P3.0/XTAL2/CLKOUT
P1.4/INT1
P1.3/INT0/SDA
SS
P1.7/OCC/AD00
P0.0/CMP2/KBI0/AD01
28272625242322
1 21
2 20
3
4 18
P89LPC935FHN
5 17
6 16
7 15
8
9
P2.2/MOSI
P1.2/T0/SCL
Transparent top view
P2.7/ICA
P2.1/OCD/AD02
P2.0/ICB/DAC0/AD03
P2.6/OCA
P0.1/CIN2B/KBI1/AD10
1011121314
P2.4/SS
P2.3/MISO
P1.0/TXD
P1.1/RXD
P2.5/SPICLK
P0.2/CIN2A/KBI2/AD11
P0.3/CIN1B/KBI3/AD12
19
P0.4/CIN1A/KBI4/DAC1/AD13
P0.5/CMPREF/KBI5
V
DD
P0.6/CMP1/KBI6
P0.7/T1/KBI7
002aab076
Fig 4. P89LPC935/936 HVQFN28 pin configuration.
1.2.1
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol Pin Typ e Description
TSSOP28,
HVQFN28
PLCC28
P0.0 to P0.7 I/O Port 0: Port 0 is an 8-bit I/O port with a user-configurable output type.
During reset Port 0 latches are configured in the input only mode with the
internal pull-up disabled. The operation of Port 0 pins as inputs and
outputs depends upon the port configuration selected. Each port pin is
configured independently. Refer to Section 5.1
for details.
The Keypad Interrupt feature operates with Port 0 pins.
All pins have Schmitt trigger inputs.
Port 0 also provides various special functions as described below:
P0.0/CMP2/
KBI0/AD01
327I/OP0.0 — Port 0 bit 0.
O CMP2 — Comparator 2 output.
I KBI0 — Keyboard input 0.
I AD01 — ADC0 channel 1 analog input. (P89LPC935/936)
P0.1/CIN2B/
KBI1/AD10
26 22 I/O P0.1 — Port 0 bit 1.
I CIN2B — Comparator 2 positive input B.
I KBI1 — Keyboard input 1.
I AD10 — ADC1 channel 0 analog input.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 5 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol Pin Typ e Description
TSSOP28,
PLCC28
P0.2/CIN2A/
KBI2/AD11
P0.3/CIN1B/
KBI3/AD12
P0.4/CIN1A/
KBI4/DAC1
P0.5/
CMPREF/
KBI5
P0.6/CMP1/
KBI6
P0.7/T1/
KBI7
P1.0 to P1.7 I/O, I
P1.0/TXD 18 14 I/O P1.0 — Port 1 bit 0.
P1.1/RXD 17 13 I/O P1.1 — Port 1 bit 1.
P1.2/T0/SCL 12 8 I/O P1.2 — Port 1 bit 2 (open-drain when used as output).
25 21 I/O P0.2 — Port 0 bit 2.
24 20 I/O P0.3 — Port 0 bit 3.
23 19 I/O P0.4 — Port 0 bit 4.
22 18 I/O P0.5 — Port 0 bit 5.
20 16 I/O P0.6 — Port 0 bit 6.
19 15 I/O P0.7 — Port 0 bit 7.
…continued
HVQFN28
I CIN2A — Comparator 2 positive input A.
I KBI2 — Keyboard input 2.
I AD11 — ADC1 channel 1 analog input.
I CIN1B — Comparator 1 positive input B.
I KBI3 — Keyboard input 3.
I AD12 — ADC1 channel 2 analog input.
I CIN1A — Comparator 1 positive input A.
I KBI4 — Keyboard input 4.
O DAC1 — Digital-to-analog converter output 1.
I AD13 — ADC1 channel 3 analog input.
I CMPREF — Comparator reference (negative) input.
I KBI5 — Keyboard input 5.
O CMP1 — Comparator 1 output.
I KBI6 — Keyboard input 6.
I/O T1 — Timer/counter 1 external count input or overflow output.
I KBI7 — Keyboard input 7.
[1]
Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit I/O port with a user-configurable output type,
except for three pins as noted below. During reset Port 1 latches are
configured in the input only mode with the internal pull-up disabled. The
operation of the configurable Port 1 pins as inputs and outputs depends
upon the port configuration selected. Each of the configurable port pins
are programmed independently. Refer to Section 5.1
P1.3 are open drain when used as outputs. P1.5 is input only.
All pins have Schmitt trigger inputs.
Port 1 also provides various special functions as described below:
O TXD — Transmitter output for the serial port.
I RXD — Receiver input for the serial port.
I/O T0 — Timer/counter 0 external count input or overflow output (open-drain
when used as output).
I/O SCL — I
2
C serial clock input/output.
for details. P1.2 and
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 6 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol Pin Typ e Description
TSSOP28,
PLCC28
P1.3/INT0/
SDA
P1.4/INT1
P1.5/RST
P1.6/OCB 5 1 I/O P1.6 — Port 1 bit 6.
P1.7/OCC/
AD00
11 7 I/O P1.3 — Port 1 bit 3 (open-drain when used as output).
10 6 I P1.4 — Port 1 bit 4.
62IP1.5 — Port 1 bit 5 (input only).
428I/OP1.7 — Port 1 bit 7.
…continued
HVQFN28
I INT0
I/O SDA — I
I INT1
I RST
O OCB — Output Compare B. (P89LPC935/936)
O OCC — Output Compare C. (P89LPC935/936)
I AD00 — ADC0 channel 0 analog input. (P89LPC935/936)
— External interrupt 0 input.
2
C serial data input/output.
— External interrupt 1 input.t
— External Reset input during power-on or if selected via UCFG1.
When functioning as a reset input, a LOW on this pin resets the
microcontroller, causing I/O ports and peripherals to take on their default
states, and the processor begins execution at address 0. Also used during
a power-on sequence to force ISP mode. When using an oscillator
frequency above 12 MHz, the reset input function of P1.5 must be
enabled. An external circuit is required to hold the device in reset at
power-up until V
power is removed VDD will fall below the minimum specified
operating voltage. When using an oscillator frequency above
12 MHz, in some applications, an external brownout detect circuit
may be required to hold the device in reset when V
minimum specified operating voltage.
has reached its specified level. When system
DD
falls below the
DD
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 7 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol Pin Typ e Description
TSSOP28,
PLCC28
P2.0 to P2.7 I/O Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit I/O port with a user-configurable output type.
P2.0/ICB/
DAC0/AD03
P2.1/OCD/
AD02
P2.2/MOSI 13 9 I/O P2.2 — Port 2 bit 2.
P2.3/MISO 14 10 I/O P2.3 — Port 2 bit 3.
P2.4/SS
P2.5/SPICLK 16 12 I/O P2.5 — Port 2 bit 5.
P2.6/OCA 27 23 I/O P2.6 — Port 2 bit 6.
P2.7/ICA 28 24 I/O P2.7 — Port 2 bit 7.
125I/OP2.0 — Port 2 bit 0.
226I/OP2.1 — Port 2 bit 1.
15 11 I/O P2.4 — Port 2 bit 4.
…continued
HVQFN28
During reset Port 2 latches are configured in the input only mode with the
internal pull-up disabled. The operation of Port 2 pins as inputs and
outputs depends upon the port configuration selected. Each port pin is
configured independently. Refer to Section 5.1
All pins have Schmitt trigger inputs.
Port 2 also provides various special functions as described below:
I ICB — Input Capture B. (P89LPC935/936)
I DAC0 — Digital-to-analog converter output.
I AD03 — ADC0 channel 3 analog input. (P89LPC935/936)
O OCD — Output Compare D. (P89LPC935/936)
I AD02 — ADC0 channel 2 analog input. (P89LPC935/936)
I/O MOSI — SPI master out slave in. When configured as master, this pin is
output; when configured as slave, this pin is input.
I/O MISO — When configured as master, this pin is input, when configured as
slave, this pin is output.
I SS
I/O SPICLK — SPI clock. When configured as master, this pin is output; when
configured as slave, this pin is input.
O OCA — Output Compare A. (P89LPC935/936)
I ICA — Input Capture A. (P89LPC935/936)
— SPI Slave select.
for details.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 8 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol Pin Typ e Description
TSSOP28,
PLCC28
P3.0 to P3.1 I/O Port 3: Port 3 is a 2-bit I/O port with a user-configurable output type.
P3.0/XTAL2/
CLKOUT
P3.1/XTAL 8 4 I/O P3.1 — Port 3 bit 1.
V
SS
V
DD
95I/OP3.0 — Port 3 bit 0.
73IGround: 0 V reference.
21 17 I Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal operation as
…continued
HVQFN28
During reset Port 3 latches are configured in the input only mode with the
internal pull-up disabled. The operation of Port 3 pins as inputs and
outputs depends upon the port configuration selected. Each port pin is
configured independently. Refer to Section 5.1
All pins have Schmitt trigger inputs.
Port 3 also provides various special functions as described below:
O XTAL2 — Output from the oscillator amplifier (when a crystal oscillator
option is selected via the FLASH configuration.
O CLKOUT — CPU clock divided by 2 when enabled via SFR bit (ENCLK -
TRIM.6). It can be used if the CPU clock is the internal RC oscillator,
watchdog oscillator or external clock input, except when XTAL1/XTAL2 are
used to generate clock source for the RTC/system timer.
I XTAL1 — Input to the oscillator circuit and internal clock generator circuits
(when selected via the FLASH configuration). It can be a port pin if
internal RC oscillator or watchdog oscillator is used as the CPU clock
source, and if XTAL1/XTAL2 are not used to generate the clock for the
RTC/system timer.
for details.
well as Idle and Power-down modes.
[1] Input/Output for P1.0 to P1.4, P1.6, P1.7. Input for P1.5.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 9 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
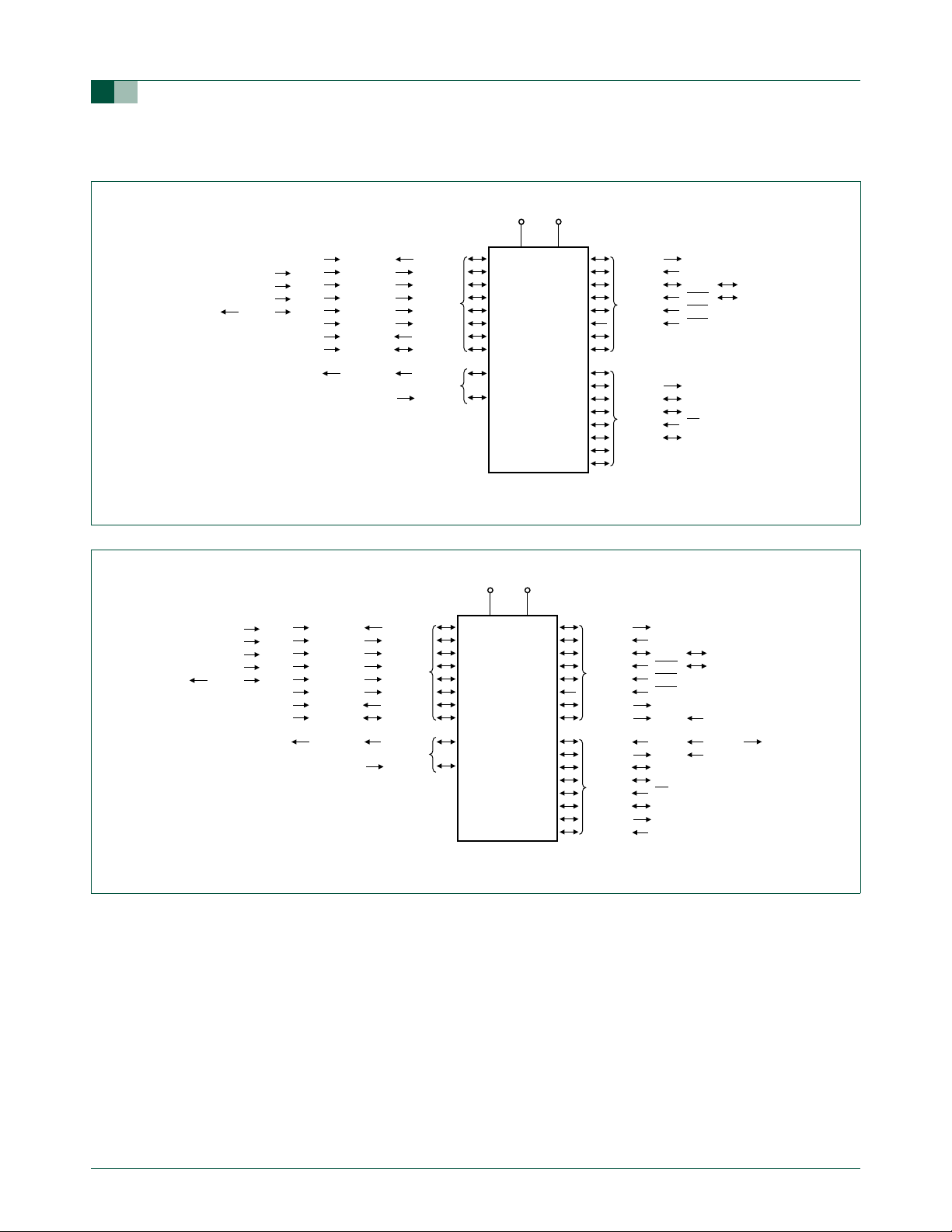
1.2.2 Logic symbols
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
V
V
DD
SS
KBI0
KBI1
KBI2
KBI3
KBI4
KBI5
KBI6
KBI7
CLKOUT
DAC1
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
Fig 5. P89LPC933/934 logic symbol.
CMP2
CIN2B
CIN2A
CIN1B
CIN1A
CMPREF
CMP1
XTAL2
XTAL1
DAC1
AD01
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
KBI0
KBI1
KBI2
KBI3
KBI4
KBI5
KBI6
KBI7
CLKOUT
CMP2
CIN2B
CIN2A
CIN1B
CIN1A
CMPREF
CMP1
T1
XTAL2
XTAL1
T1
PORT 0
PORT 3
PORT 0
PORT 3
V
DD
P89LPC935
P89LPC936
P89LPC933
P89LPC934
002aab077
V
SS
002aab078
PORT 1
PORT 2
PORT 1
PORT 2
TXD
RXD
T0
INT0
INT1
RST
OCB
OCC
ICB
OCD
MOSI
MISO
SS
SPICLK
OCA
ICA
TXD
RXD
T0
INT0
INT1
RST
DAC0
MOSI
MISO
SS
SPICLK
SCL
SDA
AD00
AD03
AD02
SCL
SDA
DAC0
Fig 6. P89LPC935/936 logic symbol.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 10 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
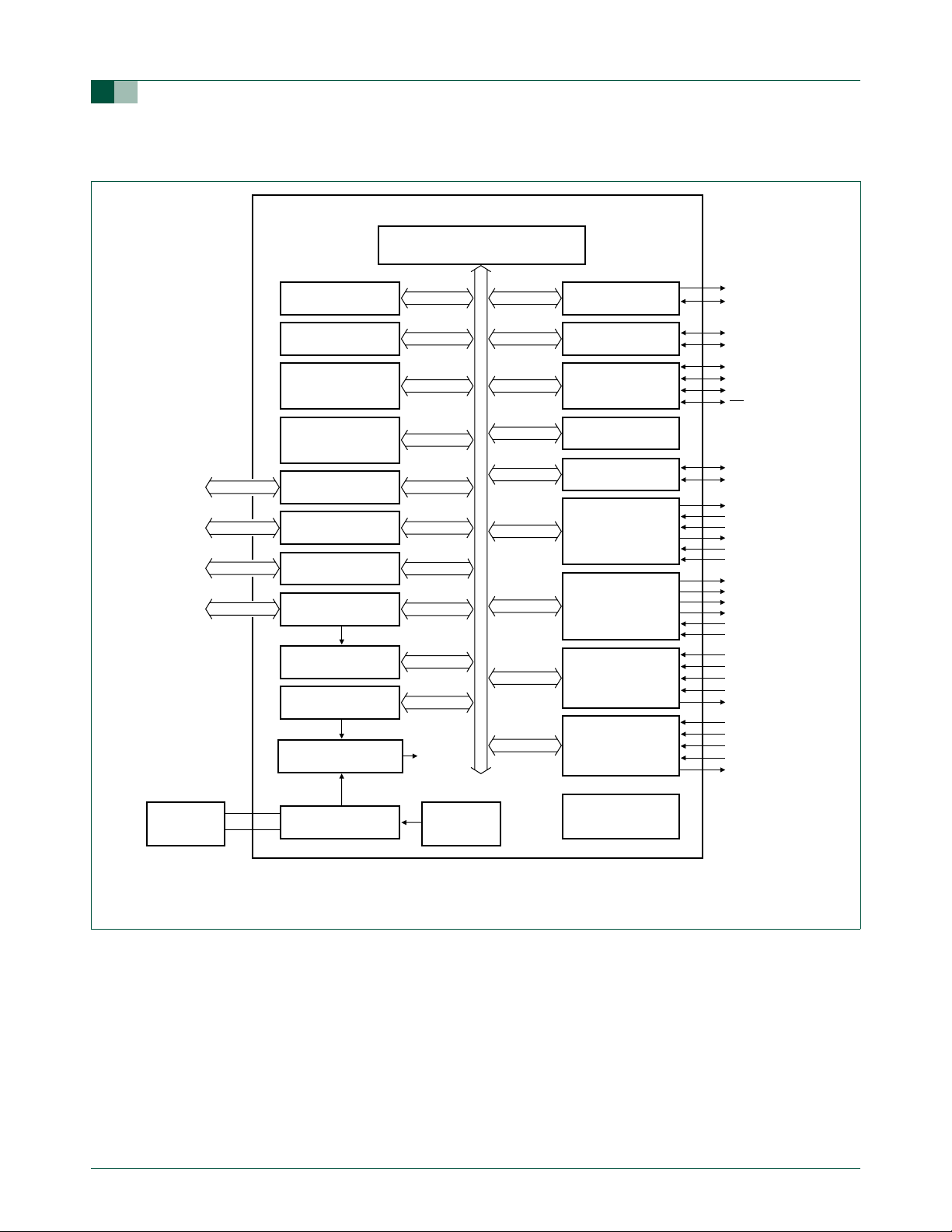
1.2.3 Block diagram
P89LPC933/934/935/936
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
ACCELERATED 2-CLOCK 80C51 CPU
P3[1:0]
P2[7:0]
P1[7:0]
P0[7:0]
4 kb/8 kB/16 kB
CODE FLASH
256-BYTE
DATA RAM
512-BYTE
AUXILIARY RAM
512-BYTE
DATA EEPROM
(P89LPC935/936)
PORT 3
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
PORT 2
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
PORT 1
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
PORT 0
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
KEYPAD
INTERRUPT
WATCHDOG TIMER
AND OSCILLATOR
PROGRAMMABLE
OSCILLATOR DIVIDER
internal bus
CPU
clock
UART
I2C-BUS
SPI
REAL-TIME CLOCK/
SYSTEM TIMER
TIMER 0
TIMER 1
ANALOG
COMPARATORS
CCU (CAPTURE/
COMPARE UNIT)
(P89LPC935/936)
ADC1/DAC1
ADC0/DAC0
(P89LPC935/936)
TXD
RXD
SCL
SDA
SPICLK
MOSI
MISO
SS
T0
T1
CMP2
CIN2B
CIN2A
CMP1
CIN1A
CIN1B
OCA
OCB
OCC
OCD
ICA
ICB
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
DAC1
AD00
AD01
AD02
AD03
DAC1
CRYSTAL
OR
RESONATOR
X1
X2
CONFIGURABLE
OSCILLATOR
ON-CHIP
RC
OSCILLATOR
POWER MONITOR
(POWER-ON RESET,
BROWNOUT RESET)
002aab070
Fig 7. Block diagram.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 11 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
1.3 Special function registers
Remark: SFR accesses are restricted in the following ways:
• User must not attempt to access any SFR locations not defined.
• Accesses to any defined SFR locations must be strictly for the functions for the SFRs.
• SFR bits labeled ‘-’, logic 0 or logic 1 can only be written and read as follows:
– ‘-’ Unless otherwise specified, must be written with logic 0, but can return any
– Logic 0 must be written with logic 0, and will return a logic 0 when read.
– Logic 1 must be written with logic 1, and will return a logic 1 when read.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
value when read (even if it was written with logic 0). It is a reserved bit and may be
used in future derivatives.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 12 of 147
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 13 of 147
Table 3: Special function registers - P89LPC933/934
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
ACC* Accumulator E0H 00 00000000
ADCON0A/D control register0 8EH-----ENADC0--0000000000
ADCON1 A/D control register 1 97H ENBI1 ENADCI1TMM1 EDGE1 ADCI1 ENADC1 ADCS11 ADCS10 00 00000000
ADINSA/D input select A3HADI13ADI12ADI11ADI10----0000000000
ADMODA A/D mode register A C0H BNDI1 BURST1 SCC1 SCAN1 ----0000000000
ADMODB A/D mode register B A1H CLK2 CLK1 CLK0 - ENDAC1 ENDAC0 BSA1 - 00 000x0000
AD0DAT3 A/D_0 data register 3 F4H 00 00000000
AD1BH A/D_1 boundary high register C4H FF 11111111
AD1BL A/D_1 boundary low register BCH 00 00000000
AD1DAT0 A/D_1 data register 0 D5H 00 00000000
AD1DAT1 A/D_1 data register 1 D6H 00 00000000
AD1DAT2 A/D_1 data register 2 D7H 00 00000000
AD1DAT3 A/D_1 data register 3 F5H 00 00000000
AUXR1 Auxiliary function register A2H CLKLP EBRR ENT1 ENT0 SRST 0 - DPS 00 000000x0
B* B register F0H 00 00000000
BRGR0
BRGR1
BRGCONBaud rate generator controlBDH------SBRGSBRGEN00
CMP1 Comparator 1 control register ACH - - CE1 CP1 CN1 OE1 CO1 CMF1 00
CMP2 Comparator 2 control register ADH - - CE2 CP2 CN2 OE2 CO2 CMF2 00
DIVM CPU clock divide-by-M control 95H 00 00000000
DPTR Data pointer (2 bytes)
DPH Data pointer high 83H 00 00000000
DPL Data pointer low 82H 00 00000000
FMADRH Program Flash address high E7H 00 00000000
FMADRL Program Flash address low E6H 00 00000000
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
Bit address E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0
MSB LSB Hex Binary
Bit address F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0
[2]
Baud rate generator rate low BEH 00 00000000
[2]
Baud rate generator rate high BFH 00 00000000
[2]
[1]
[1]
xxxxxx00
xx000000
xx000000
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116

xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 14 of 147
Table 3: Special function registers - P89LPC933/934
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
FMCON Program Flash control (Read) E4H BUSY - - - HVA HVE SV OI 70 01110000
FMDATA Program Flash data E5H 00 00000000
I2ADR I
I2CON* I
I2DAT I
I2SCLH Serial clock generator/SCL
I2SCLL Serial clock generator/SCL
I2STAT I
ICRAH Input capture A register high ABH 00 00000000
ICRAL Input capture A register low AAH 00 00000000
ICRBH Input capture B register high AFH 00 00000000
ICRBL Input capture B register low AEH 00 00000000
IEN0* Interrupt enable 0 A8H EA EWDRT EBO ES/ESR ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 00 00000000
IEN1* Interrupt enable 1 E8H EAD EST - - ESPI EC EKBI EI2C 00
IP0* Interrupt priority 0 B8H - PWDRT PBO PS/PSR PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0 00
IP0H Interrupt priority 0 high B7H - PWDRTHPBOH PSH/
IP1* Interrupt priority 1 F8H PAD PST - - PSPI PC PKBI PI2C 00
IP1H Interrupt priority 1 high F7H PADH PSTH - - PSPIH PCH PKBIH PI2CH 00
KBCON Keypad control register 94H ------PATN
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
…continued
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
Program Flash control (Write) E4H FMCMD.7FMCMD.6FMCMD.5FMCMD.4FMCMD.3FMCMD.2FMCMD.1FMCMD.
2
C slave address register DBH I2ADR.6 I2ADR.5 I2ADR.4 I2ADR.3 I2ADR.2 I2ADR.1 I2ADR.0 GC 00 00000000
Bit address DF DE DD DC DB DA D9 D8
2
C control register D8H - I2EN STA STO SI AA - CRSEL 00 x00000x0
2
C data register DAH
DDH 00 00000000
duty cycle register high
DCH 00 00000000
duty cycle register low
2
C status register D9H STA.4 STA.3 STA.2 STA.1 STA.0 0 0 0 F8 11111000
Bit address AF AE AD AC AB AA A9 A8
Bit address EF EE ED EC EB EA E9 E8
Bit address BF BE BD BC BB BA B9 B8
Bit address FF FE FD FC FB FA F9 F8
MSB LSB Hex Binary
0
[1]
[1]
PT1H PX1H PT0H PX0H 00
PSRH
KBIF 00
_SEL
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
00x00000
x0000000
x0000000
UM10116
00x00000
00x00000
xxxxxx00
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 15 of 147
Table 3: Special function registers - P89LPC933/934 …continued
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
KBMASK Keypad interrupt mask
KBPATN Keypad pattern register 93H FF 11111111
P0* Port 0 80H T1/KB7 CMP1
P1* Port 1 90H - - RST
P2* Port 2 A0H - - SPICLK SS
P3*Port3 B0H------XTAL1XTAL2
P0M1 Port 0 output mode 1 84H (P0M1.7) (P0M1.6) (P0M1.5) (P0M1.4) (P0M1.3) (P0M1.2) (P0M1.1) (P0M1.0) FF
P0M2 Port 0 output mode 2 85H (P0M2.7) (P0M2.6) (P0M2.5) (P0M2.4) (P0M2.3) (P0M2.2) (P0M2.1) (P0M2.0) 00
P1M1 Port 1 output mode 1 91H (P1M1.7) (P1M1.6) - (P1M1.4) (P1M1.3) (P1M1.2) (P1M1.1) (P1M1.0) D3
P1M2 Port 1 output mode 2 92H (P1M2.7) (P1M2.6) - (P1M2.4) (P1M2.3) (P1M2.2) (P1M2.1) (P1M2.0) 00
P2M1 Port 2 output mode 1 A4H (P2M1.7) (P2M1.6) (P2M1.5) (P2M1.4) (P2M1.3) (P2M1.2) (P2M1.1) (P2M1.0) FF
P2M2 Port 2 output mode 2 A5H (P2M2.7) (P2M2.6) (P2M2.5) (P2M2.4) (P2M2.3) (P2M2.2) (P2M2.1) (P2M2.0) 00
P3M1Port3 output mode1 B1H------(P3M1.1)(P3M1.0)03
P3M2Port3 output mode2 B2H------(P3M2.1)(P3M2.0)00
PCON Power control register 87H SMOD1 SMOD0 BOPD BOI GF1 GF0 PMOD1 PMOD0 00 00000000
PCONA Power control register A B5H RTCPD - VCPD ADPD I2PD SPPD SPD - 00
PSW* Program status word D0H CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P 00 00000000
PT0AD Port 0 digital input disable F6H - - PT0AD.5 PT0AD.4 PT0AD.3 PT0AD.2 PT0AD.1 - 00 xx00000x
RSTSRC Reset source register DFH - - BOF POF R_BK R_WD R_SF R_EX
RTCCON Real-time clock control D1H RTCF RTCS1 RTCS0 - - - ERTC RTCEN 60
RTCH Real-time clock register high D2H 00
RTCL Real-time clock register low D3H 00
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
86H 00 00000000
register
Bit address 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
Bit address 97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90
Bit address A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Bit address B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Bit address D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
MSB LSB Hex Binary
/KB6
CMPREF
/KB5
CIN1A
/KB4
INT1 INT0/
CIN1B
/KB3
SDA
MISO MOSI - -
CIN2A
/KB2
T0/SCL RXD TXD
CIN2B
/KB1
CMP2
/KB0
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1][6]
[6]
[6]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
11111111
00000000
11x1xx11
00x0xx00
11111111
00000000
xxxxxx11
xxxxxx00
00000000
[3]
011xxx00
00000000
00000000
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116

xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 16 of 147
Table 3: Special function registers - P89LPC933/934 …continued
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
SADDR Serial port address register A9H 00 00000000
SADEN Serial port address enable B9H 00 00000000
SBUF Serial Port data buffer register 99H xx xxxxxxxx
SCON* Serial port control 98H SM0/FE SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI 00 00000000
SSTAT Serial port extended status
SP Stack pointer 81H 07 00000111
SPCTL SPI control register E2H SSIG SPEN DORD MSTR CPOL CPHA SPR1 SPR0 04 00000100
SPSTAT SPI status register E1H SPIF WCOL ------0000xxxxxx
SPDAT SPI data register E3H 00 00000000
TAMOD Timer 0 and 1 auxiliary mode 8FH - - - T1M2 - - - T0M2 00 xxx0xxx0
TCON* Timer 0 and 1 control 88H TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 00 00000000
TH0 Timer 0 high 8CH 00 00000000
TH1 Timer 1 high 8DH 00 00000000
TL0 Timer 0 low 8AH 00 00000000
TL1 Timer 1 low 8BH 00 00000000
TMOD Timer 0 and 1 mode 89H T1GATE T1C/T T1M1 T1M0 T0GATE T0C/T T0M1 T0M0 00 00000000
TRIM Internal oscillator trim register 96H RCCLK ENCLK TRIM.5 TRIM.4 TRIM.3 TRIM.2 TRIM.1 TRIM.0
WDCON Watchdog control register A7H PRE2 PRE1 PRE0 - - WDRUN WDTOF WDCLK
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
Bit address 9F 9E 9D 9C 9B 9A 99 98
BAH DBMOD INTLO CIDIS DBISEL FE BR OE STINT 00 00000000
register
Bit address 8F 8E 8D 8C 8B 8A 89 88
MSB LSB Hex Binary
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
[5] [6]
[4] [6]
UM10116

xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 17 of 147
Table 3: Special function registers - P89LPC933/934
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
WDL Watchdog load C1H FF 11111111
WFEED1 Watchdog feed 1 C2H
WFEED2 Watchdog feed 2 C3H
[1] All ports are in input only (high-impedance) state after power-up.
[2] BRGR1 and BRGR0 must only be written if BRGEN in BRGCON SFR is logic 0. If any are written while BRGEN = 1, the result is unpredictable.
[3] The RSTSRC register reflects the cause of the UM10116 reset. Upon a power-up reset, all reset source flags are cleared except POF and BOF; the power-on reset value is
[4] After reset, the value is 111001x1, i.e., PRE2 to PRE0 are all logic 1, WDRUN = 1 and WDCLK = 1. WDTOF bit is logic 1 after watchdog reset and is logic 0 after power-on reset.
[5] On power-on reset, the TRIM SFR is initialized with a factory preprogrammed value. Other resets will not cause initialization of the TRIM register.
[6] The only reset source that affects these SFRs is power-on reset.
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
xx110000.
Other resets will not affect WDTOF.
MSB LSB Hex Binary
…continued
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 18 of 147
Table 4: Special function registers - P89LPC935/936
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
ACC* Accumulator E0H 00 00000000
ADCON0 A/D control register 0 8EH ENBI0 ENADCI0TMM0 EDGE0 ADCI0 ENADC0 ADCS01 ADCS00 00 00000000
ADCON1 A/D control register 1 97H ENBI1 ENADCI1TMM1 EDGE1 ADCI1 ENADC1 ADCS11 ADCS10 00 00000000
ADINS A/D input select A3H ADI13 ADI12 ADI11 ADI10 ADI03 ADI02 ADI01 ADI00 00 00000000
ADMODA A/D mode register A C0H BNDI1 BURST1 SCC1 SCAN1 BNDI0 BURST0 SCC0 SCAN0 00 00000000
ADMODB A/D mode register B A1H CLK2 CLK1 CLK0 - ENDAC1 ENDAC0 BSA1 BSA0 00 000x0000
AD0BH A/D_0 boundary high register BBH FF 11111111
AD0BL A/D_0 boundary low register A6H 00 00000000
AD0DAT0 A/D_0 data register 0 C5H 00 00000000
AD0DAT1 A/D_0 data register 1 C6H 00 00000000
AD0DAT2 A/D_0 data register 2 C7H 00 00000000
AD0DAT3 A/D_0 data register 3 F4H 00 00000000
AD1BH A/D_1 boundary high register C4H FF 11111111
AD1BL A/D_1 boundary low register BCH 00 00000000
AD1DAT0 A/D_1 data register 0 D5H 00 00000000
AD1DAT1 A/D_1 data register 1 D6H 00 00000000
AD1DAT2 A/D_1 data register 2 D7H 00 00000000
AD1DAT3 A/D_1 data register 3 F5H 00 00000000
AUXR1 Auxiliary function register A2H CLKLP EBRR ENT1 ENT0 SRST 0 - DPS 00 000000x0
B* B register F0H 00 00000000
BRGR0
BRGR1
BRGCONBaud rate generator controlBDH------SBRGSBRGEN00
CCCRA Capture compare A control
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
Bit address E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0
MSB LSB Hex Binary
Bit address F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0
[2]
Baud rate generator rate low BEH 00 00000000
[2]
Baud rate generator rate high BFH 00 00000000
[2]
EAH ICECA2 ICECA1 ICECA0 ICESA ICNFA FCOA OCMA1 OCMA0 00 00000000
register
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116
xxxxxx00
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 19 of 147
Table 4: Special function registers - P89LPC935/936
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
CCCRB Capture compare B control
CCCRC Capture compare C control
CCCRD Capture compare D control
CMP1 Comparator 1 control register ACH - - CE1 CP1 CN1 OE1 CO1 CMF1 00
CMP2 Comparator 2 control register ADH - - CE2 CP2 CN2 OE2 CO2 CMF2 00
DEECON Data EEPROM control
DEEDAT Data EEPROM data register F2H 00 00000000
DEEADR Data EEPROM address
DIVM CPU clock divide-by-M control 95H 00 00000000
DPTR Data pointer (2 bytes)
DPH Data pointer high 83H 00 00000000
DPL Data pointer low 82H 00 00000000
FMADRH Program Flash address high E7H 00 00000000
FMADRL Program Flash address low E6H 00 00000000
FMCON Program Flash control (Read) E4H BUSY - - - HVA HVE SV OI 70 01110000
FMDATA Program Flash data E5H 00 00000000
I2ADR I
I2CON* I
I2DAT I
I2SCLH Serial clock generator/SCL
I2SCLL Serial clock generator/SCL
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
…continued
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
EBH ICECB2 ICECB1 ICECB0 ICESB ICNFB FCOB OCMB1 OCMB0 00 00000000
register
ECH-----FCOCOCMC1OCMC000xxxxx000
register
EDH-----FCODOCMD1OCMD000xxxxx000
register
F1H EEIF HVERR ECTL1 ECTL0 - - - EADR8 0E 00001110
register
F3H 00 00000000
register
MSB LSB Hex Binary
[1]
[1]
Program Flash control (Write) E4H FMCMD.7FMCMD.6FMCMD.5FMCMD.4FMCMD.3FMCMD.2FMCMD.1FMCMD.
0
2
C slave address register DBH I2ADR.6 I2ADR.5 I2ADR.4 I2ADR.3 I2ADR.2 I2ADR.1 I2ADR.0 GC 00 00000000
Bit address DF DE DD DC DB DA D9 D8
2
C control register D8H - I2EN STA STO SI AA - CRSEL 00 x00000x0
2
C data register DAH
DDH 00 00000000
duty cycle register high
DCH 00 00000000
duty cycle register low
Philips Semiconductors
xx000000
xx000000
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 20 of 147
Table 4: Special function registers - P89LPC935/936
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
I2STAT I2C status register D9H STA.4 STA.3 STA.2 STA.1 STA.0 0 0 0 F8 11111000
ICRAH Input capture A register high ABH 00 00000000
ICRAL Input capture A register low AAH 00 00000000
ICRBH Input capture B register high AFH 00 00000000
ICRBL Input capture B register low AEH 00 00000000
IEN0* Interrupt enable 0 A8H EA EWDRT EBO ES/ESR ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 00 00000000
IEN1* Interrupt enable 1 E8H EADEE EST - ECCU ESPI EC EKBI EI2C 00
IP0* Interrupt priority 0 B8H - PWDRT PBO PS/PSR PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0 00
IP0H Interrupt priority 0 high B7H - PWDRTHPBOH PSH/
IP1* Interrupt priority 1 F8H PADEE PST - PCCU PSPI PC PKBI PI2C 00
IP1H Interrupt priority 1 high F7H PAEEH PSTH - PCCUH PSPIH PCH PKBIH PI2CH 00
KBCON Keypad control register 94H ------PATN
KBMASK Keypad interrupt mask
KBPATN Keypad pattern register 93H FF 11111111
OCRAH Output compare A register
OCRAL Output compare A register
OCRBH Output compare B register
OCRBL Output compare B register
OCRCH Output compare C register
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
…continued
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
Bit address AF AE AD AC AB AA A9 A8
Bit address EF EE ED EC EB EA E9 E8
Bit address BF BE BD BC BB BA B9 B8
Bit address FF FE FD FC FB FA F9 F8
86H 00 00000000
register
EFH 00 00000000
high
EEH 00 00000000
low
FBH 00 00000000
high
FAH 00 00000000
low
FDH 00 00000000
high
MSB LSB Hex Binary
PSRH
PT1H PX1H PT0H PX0H 00
KBIF 00
_SEL
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Philips Semiconductors
00x00000
x0000000
x0000000
00x00000
00x00000
xxxxxx00
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 21 of 147
Table 4: Special function registers - P89LPC935/936 …continued
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
OCRCL Output compare C register
OCRDH Output compare D register
OCRDL Output compare D register
P0* Port 0 80H T1/KB7 CMP1
P1* Port 1 90H OCC OCB RST
P2* Port 2 A0H ICA OCA SPICLK SS
P3*Port3 B0H------XTAL1XTAL2
P0M1 Port 0 output mode 1 84H (P0M1.7) (P0M1.6) (P0M1.5) (P0M1.4) (P0M1.3) (P0M1.2) (P0M1.1) (P0M1.0) FF
P0M2 Port 0 output mode 2 85H (P0M2.7) (P0M2.6) (P0M2.5) (P0M2.4) (P0M2.3) (P0M2.2) (P0M2.1) (P0M2.0) 00
P1M1 Port 1 output mode 1 91H (P1M1.7) (P1M1.6) - (P1M1.4) (P1M1.3) (P1M1.2) (P1M1.1) (P1M1.0) D3
P1M2 Port 1 output mode 2 92H (P1M2.7) (P1M2.6) - (P1M2.4) (P1M2.3) (P1M2.2) (P1M2.1) (P1M2.0) 00
P2M1 Port 2 output mode 1 A4H (P2M1.7) (P2M1.6) (P2M1.5) (P2M1.4) (P2M1.3) (P2M1.2) (P2M1.1) (P2M1.0) FF
P2M2 Port 2 output mode 2 A5H (P2M2.7) (P2M2.6) (P2M2.5) (P2M2.4) (P2M2.3) (P2M2.2) (P2M2.1) (P2M2.0) 00
P3M1Port3 output mode1 B1H------(P3M1.1)(P3M1.0)03
P3M2Port3 output mode2 B2H------(P3M2.1)(P3M2.0)00
PCON Power control register 87H SMOD1 SMOD0 BOPD BOI GF1 GF0 PMOD1 PMOD0 00 00000000
PCONA Power control register A B5H RTCPD DEEPD VCPD ADPD I2PD SPPD SPD CCUPD 00
PSW* Program status word D0H CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P 00 00000000
PT0AD Port 0 digital input disable F6H - - PT0AD.5 PT0AD.4 PT0AD.3 PT0AD.2 PT0AD.1 - 00 xx00000x
RSTSRC Reset source register DFH - - BOF POF R_BK R_WD R_SF R_EX
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
FCH 00 00000000
low
FFH 00 00000000
high
FEH 00 00000000
low
Bit address 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
Bit address 97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90
Bit address A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Bit address B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Bit address D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
MSB LSB Hex Binary
/KB6
CMPREF
/KB5
CIN1A
/KB4
INT1 INT0/
CIN1B
/KB3
SDA
MISO MOSI OCD ICB
CIN2A
/KB2
T0/SCL RXD TXD
CIN2B
/KB1
CMP2
/KB0
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
11111111
00000000
11x1xx11
00x0xx00
11111111
00000000
xxxxxx11
xxxxxx00
00000000
[3]
Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116

xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 22 of 147
Table 4: Special function registers - P89LPC935/936
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
RTCCON Real-time clock control D1H RTCF RTCS1 RTCS0 - - - ERTC RTCEN 60
RTCH Real-time clock register high D2H 00
RTCL Real-time clock register low D3H 00
SADDR Serial port address register A9H 00 00000000
SADEN Serial port address enable B9H 00 00000000
SBUF Serial Port data buffer register 99H xx xxxxxxxx
SCON* Serial port control 98H SM0/FE SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI 00 00000000
SSTAT Serial port extended status
SP Stack pointer 81H 07 00000111
SPCTL SPI control register E2H SSIG SPEN DORD MSTR CPOL CPHA SPR1 SPR0 04 00000100
SPSTAT SPI status register E1H SPIF WCOL ------0000xxxxxx
SPDAT SPI data register E3H 00 00000000
TAMOD Timer 0 and 1 auxiliary mode 8FH - - - T1M2 - - - T0M2 00 xxx0xxx0
TCON* Timer 0 and 1 control 88H TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 00 00000000
TCR20* CCU control register 0 C8H PLEEN HLTRN HLTEN ALTCD ALTAB TDIR2 TMOD21 TMOD20 00 00000000
TCR21 CCU control register 1 F9H TCOU2 - - - PLLDV.3 PLLDV.2 PLLDV.1 PLLDV.0 00 0xxx0000
TH0 Timer 0 high 8CH 00 00000000
TH1 Timer 1 high 8DH 00 00000000
TH2 CCU timer high CDH 00 00000000
TICR2 CCU interrupt control register C9H TOIE2 TOCIE2DTOCIE2CTOCIE2B TOCIE2A - TICIE2B TICIE2A 00 00000x00
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
…continued
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
addr.
Bit address 9F 9E 9D 9C 9B 9A 99 98
BAH DBMOD INTLO CIDIS DBISEL FE BR OE STINT 00 00000000
register
Bit address 8F 8E 8D 8C 8B 8A 89 88
MSB LSB Hex Binary
[1][6]
[6]
[6]
Philips Semiconductors
011xxx00
00000000
00000000
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
TIFR2 CCU interrupt flag register E9H TOIF2 TOCF2D TOCF2C TOCF2B TOCF2A - TICF2B TICF2A 00 00000x00
TISE2 CCU interrupt status encode
register
TL0 Timer 0 low 8AH 00 00000000
TL1 Timer 1 low 8BH 00 00000000
TL2 CCU timer low CCH 00 00000000
DEH-----ENCINT.
ENCINT.1ENCINT.000 xxxxx000
2
UM10116
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 23 of 147
Table 4: Special function registers - P89LPC935/936
* indicates SFRs that are bit addressable.
Name Description SFR
TMOD Timer 0 and 1 mode 89H T1GATE T1C/T T1M1 T1M0 T0GATE T0C/T T0M1 T0M0 00 00000000
TOR2H CCU reload register high CFH 00 00000000
TOR2L CCU reload register low CEH 00 00000000
TPCR2HPrescaler control register highCBH------TPCR2H.
TPCR2L Prescaler control register low CAH TPCR2L.7TPCR2L.6TPCR2L.5TPCR2L.4TPCR2L.3TPCR2L.2TPCR2L.1TPCR2L.000 00000000
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
addr.
…continued
Bit functions and addresses Reset value
MSB LSB Hex Binary
TPCR2H.000 xxxxxx00
1
Philips Semiconductors
TRIM Internal oscillator trim register 96H RCCLK ENCLK TRIM.5 TRIM.4 TRIM.3 TRIM.2 TRIM.1 TRIM.0
WDCON Watchdog control register A7H PRE2 PRE1 PRE0 - - WDRUN WDTOF WDCLK
WDL Watchdog load C1H FF 11111111
WFEED1 Watchdog feed 1 C2H
WFEED2 Watchdog feed 2 C3H
[1] All ports are in input only (high-impedance) state after power-up.
[2] BRGR1 and BRGR0 must only be written if BRGEN in BRGCON SFR is logic 0. If any are written while BRGEN = 1, the result is unpredictable.
[3] The RSTSRC register reflects the cause of the UM10116 reset. Upon a power-up reset, all reset source flags are cleared except POF and BOF; the power-on reset value is
xx110000.
[4] After reset, the value is 111001x1, i.e., PRE2 to PRE0 are all logic 1, WDRUN = 1 and WDCLK = 1. WDTOF bit is logic 1 after watchdog reset and is logic 0 after power-on reset.
Other resets will not affect WDTOF.
[5] On power-on reset, the TRIM SFR is initialized with a factory preprogrammed value. Other resets will not cause initialization of the TRIM register.
[6] The only reset source that affects these SFRs is power-on reset.
[5] [6]
[4] [6]
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
UM10116
Philips Semiconductors
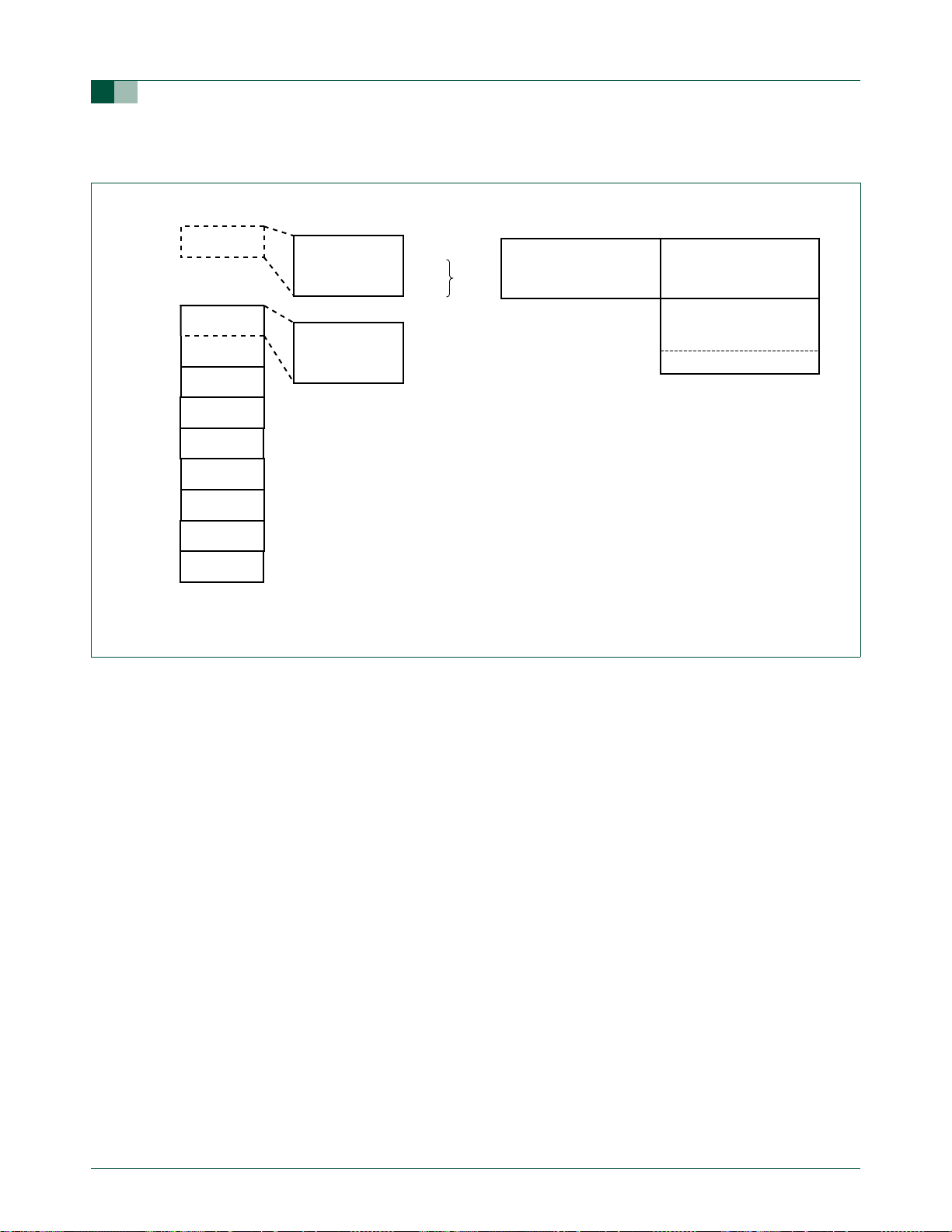
1.4 Memory organization
FF00h
FFEFh
1FFFh
1E00h
1C00h
1BFFh
1800h
17FFh
1400h
13FFh
1000h
0FFFh
0C00h
0BFFh
0800h
07FFh
0400h
03FFh
0000h
IAP entry-
points
ISP CODE
(1)
(512B)
SECTOR 7
SECTOR 6
SECTOR 5
SECTOR 4
SECTOR 3
SECTOR 2
SECTOR 1
SECTOR 0
read-protected
IAP calls only
IDATA routines
entry points for:
-51 ASM. code
-C code
ISP serial loader
entry points for:
-UART (auto-baud)
-I2C, SPI, etc.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
FFEFh
FF1Fh
FF00h
1FFFh
(1)
1E00h
entry
points
SPECIAL FUNCTION
REGISTERS
(DIRECTLY ADDRESSABLE)
IDATA (incl. DATA)
128 BYTES ON-CHIP
DATA MEMORY (STACK
AND INDIR. ADDR.)
DATA
128 BYTES ON-CHIP
DATA MEMORY (STACK,
DIRECT AND INDIR. ADDR.)
4 REG. BANKS R[7:0]
data memory
(DATA, IDATA)
002aab228
(1) ISP code located in Sector 3 for the P89LPC933 device.
Fig 8. P89LPC933/934/935/936 memory map.
1.5 Memory organization
The various P89LPC933/934/935/936 memory spaces are as follows:
• DATA
128 bytes of internal data memory space (00H:7FH) accessed via direct or indirect
addressing, using instructions other than MOVX and MOVC. All or part of the Stack
may be in this area.
• IDATA
Indirect Data. 256 bytes of internal data memory space (00H:FFH) accessed via
indirect addressing using instructions other than MOVX and MOVC. All or part of the
Stack may be in this area. This area includes the DATA area and the 128 bytes
immediately above it.
• SFR
Selected CPU registers and peripheral control and status registers, accessible only
via direct addressing.
• XDATA (P89LPC935/936)
‘External’ Data or Auxiliary RAM. Duplicates the classic 80C51 64 kB memory space
addressed via the MOVX instruction using the SPTR, R0, or R1. All or part of this
space could be implemented on-chip. The P89LPC935/936 has 512 bytes of on-chip
XDATA memory.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 24 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
• CODE
64 kB of Code memory space, accessed as part of program execution and via the
MOVC instruction. The UM10116 have 4 KB/8 kB/16 kB of on-chip Code memory.
The P89LPC935/936 also has 512 bytes of on-chip Data EEPROM that is accessed via
SFRs (see Section 18 “
2. Clocks
2.1 Enhanced CPU
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 uses an enhanced 80C51 CPU which runs at six times the
speed of standard 80C51 devices. A machine cycle consists of two CPU clock cycles, and
most instructions execute in one or two machine cycles.
2.2 Clock definitions
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 device has several internal clocks as defined below:
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Data EEPROM (P89LPC935/936)”).
OSCCLK — Input to the DIVM clock divider. OSCCLK is selected from one of four clock
sources and can also be optionally divided to a slower frequency (see Figure 10
Section 2.8 “
OSCCLK frequency.
CCLK — CPU clock; output of the DIVM clock divider. There are two CCLK cycles per
machine cycle, and most instructions are executed in one to two machine cycles (two or
four CCLK cycles).
RCCLK — The internal 7.373 MHz RC oscillator output.
PCLK — Clock for the various peripheral devices and is
2.2.1 Oscillator Clock (OSCCLK)
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 provides several user-selectable oscillator options. This
allows optimization for a range of needs from high precision to lowest possible cost. These
options are configured when the FLASH is programmed and include an on-chip watchdog
oscillator, an on-chip RC oscillator, an oscillator using an external crystal, or an external
clock source. The crystal oscillator can be optimized for low, medium, or high frequency
crystals covering a range from 20 kHz to 18 MHz.
2.2.2 Low speed oscillator option
This option supports an external crystal in the range of 20 kHz to 100 kHz. Ceramic
resonators are also supported in this configuration.
CPU Clock (CCLK) modification: DIVM register”). Note: f
CCLK
⁄2.
and
is defined as the
osc
2.2.3 Medium speed oscillator option
This option supports an external crystal in the range of 100 kHz to 4 MHz. Ceramic
resonators are also supported in this configuration.
2.2.4 High speed oscillator option
This option supports an external crystal in the range of 4 MHz to 18 MHz. Ceramic
resonators are also supported in this configuration. When using an oscillator frequency
above 12 MHz, the reset input function of P1.5 must be enabled. An external circuit
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 25 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
is required to hold the device in reset at power-up until VDD has reached its
specified level. When system power is removed V
specified operating voltage. When using an oscillator frequency above 12 MHz, in
some applications, an external brownout detect circuit may be required to hold the
device in reset when V
2.3 Clock output
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 supports a user-selectable clock output function on the
XTAL2 / CLKOUT pin when the crystal oscillator is not being used. This condition occurs if
a different clock source has been selected (on-chip RC oscillator, watchdog oscillator,
external clock input on X1) and if the Real-time Clock is not using the crystal oscillator as
its clock source. This allows external devices to synchronize to the
P89LPC933/934/935/936. This output is enabled by the ENCLK bit in the TRIM register
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
will fall below the minimum
DD
falls below the minimum specified operating voltage.
DD
The frequency of this clock output is
in Idle mode, it may be turned off prior to entering Idle, saving additional power. Note: on
reset, the TRIM SFR is initialized with a factory preprogrammed value. Therefore when
setting or clearing the ENCLK bit, the user should retain the contents of other bits of the
TRIM register. This can be done by reading the contents of the TRIM register (into the
ACC for example), modifying bit 6, and writing this result back into the TRIM register.
Alternatively, the ‘ANL direct’ or ‘ORL direct’ instructions can be used to clear or set bit 6
of the TRIM register.
1
⁄2 that of the CCLK. If the clock output is not needed
2.4 On-chip RC oscillator option
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has a TRIM register that can be used to tune the frequency
of the RC oscillator. During reset, the TRIM value is initialized to a factory
pre-programmed value to adjust the oscillator frequency to 7.373 MHz, ± 1 %. (Note: the
initial value is better than 1 %; please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet for
behavior over temperature). End user applications can write to the TRIM register to adjust
the on-chip RC oscillator to other frequencies. Increasing the TRIM value will decrease
the oscillator frequency.
Table 5: On-chip RC oscillator trim register (TRIM - address 96h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol RCCLK ENCLK TRIM.5 TRIM.4 TRIM.3 TRIM.2 TRIM.1 TRIM.0
Reset 0 0 Bits 5:0 loaded with factory stored value during reset.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 26 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
9
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 6: On-chip RC oscillator trim register (TRIM - address 96h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 TRIM.0 Trim value. Determines the frequency of the internal RC oscillator. During reset,
1TRIM.1
2TRIM.2
3TRIM.3
4TRIM.4
5TRIM.5
6 ENCLK when = 1,
7 RCCLK when = 1, selects the RC Oscillator output as the CPU clock (CCLK). This allows for
these bits are loaded with a stored factory calibration value. When writing to either
bit 6 or bit 7 of this register, care should be taken to preserve the current TRIM value
by reading this register, modifying bits 6 or 7 as required, and writing the result to
this register.
CCLK
⁄2 is output on the XTAL2 pin provided the crystal oscillator is not
being used.
fast switching between any clock source and the internal RC oscillator without
needing to go through a reset cycle.
2.5 Watchdog oscillator option
The watchdog has a separate oscillator which has a frequency of 400 kHz. This oscillator
can be used to save power when a high clock frequency is not needed.
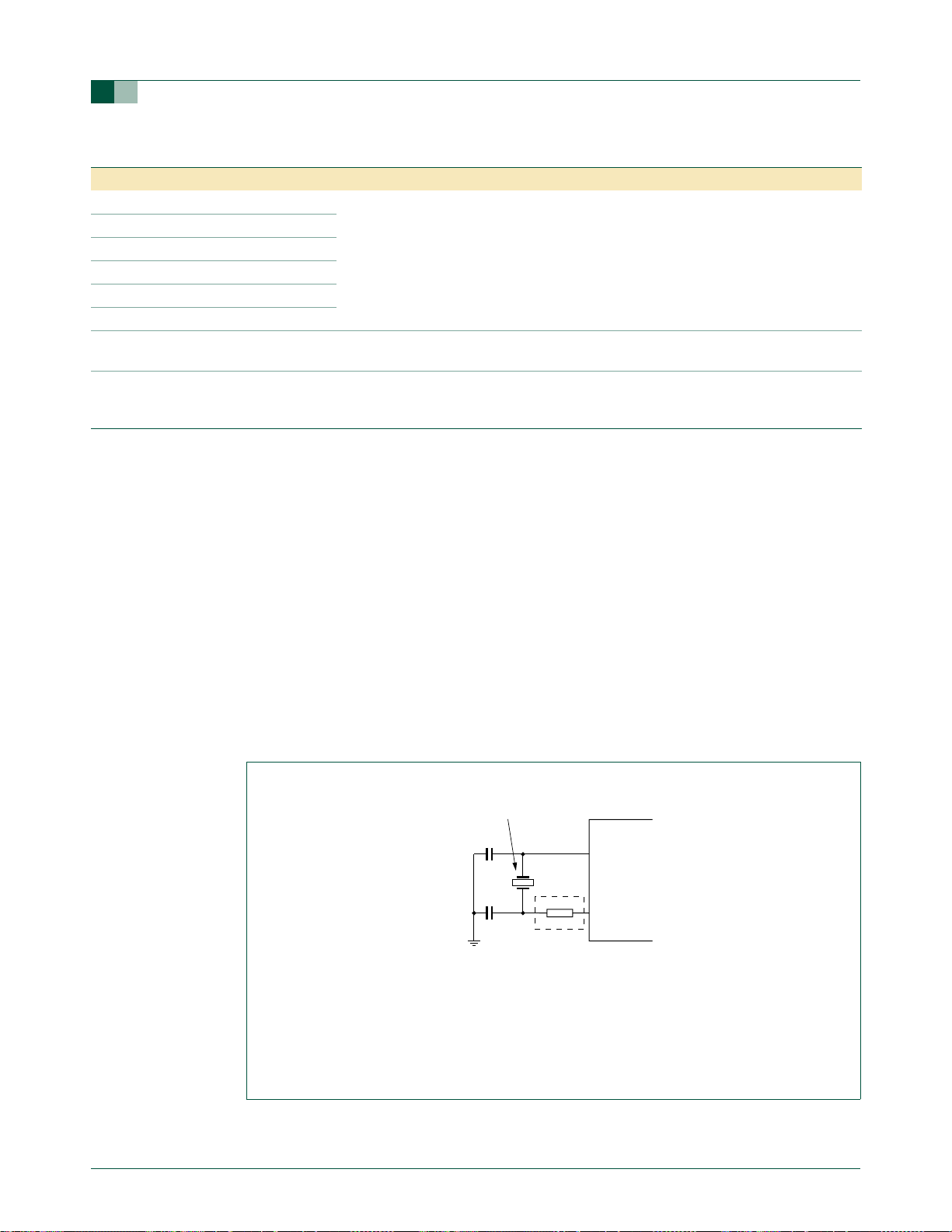
2.6 External clock input option
In this configuration, the processor clock is derived from an external source driving the
XTAL1 / P3.1 pin. The rate may be from 0 Hz up to 18 MHz. The XTAL2 / P3.0 pin may be
used as a standard port pin or a clock output. When using an oscillator frequency
above 12 MHz, the reset input function of P1.5 must be enabled. An external circuit
is required to hold the device in reset at power-up until V
specified level. When system power is removed V
specified operating voltage. When using an oscillator frequency above 12 MHz, in
some applications, an external brownout detect circuit may be required to hold the
device in reset when V
has reached its
DD
will fall below the minimum
DD
falls below the minimum specified operating voltage.
DD
quartz crystal or
ceramic resonator
P89LPC93x
XTAL1
(1)
XTAL2
002aab22
Note: The oscillator must be configured in one of the following modes: Low frequency crystal,
medium frequency crystal, or high frequency crystal.
(1) A series resistor may be required to limit crystal drive levels. This is especially important for low
frequency crystals.
Fig 9. Using the crystal oscillator.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 27 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
XTAL1
XTAL2
(7.3728 MHz ±1 %)
(400 kHz +30 % −20 %)
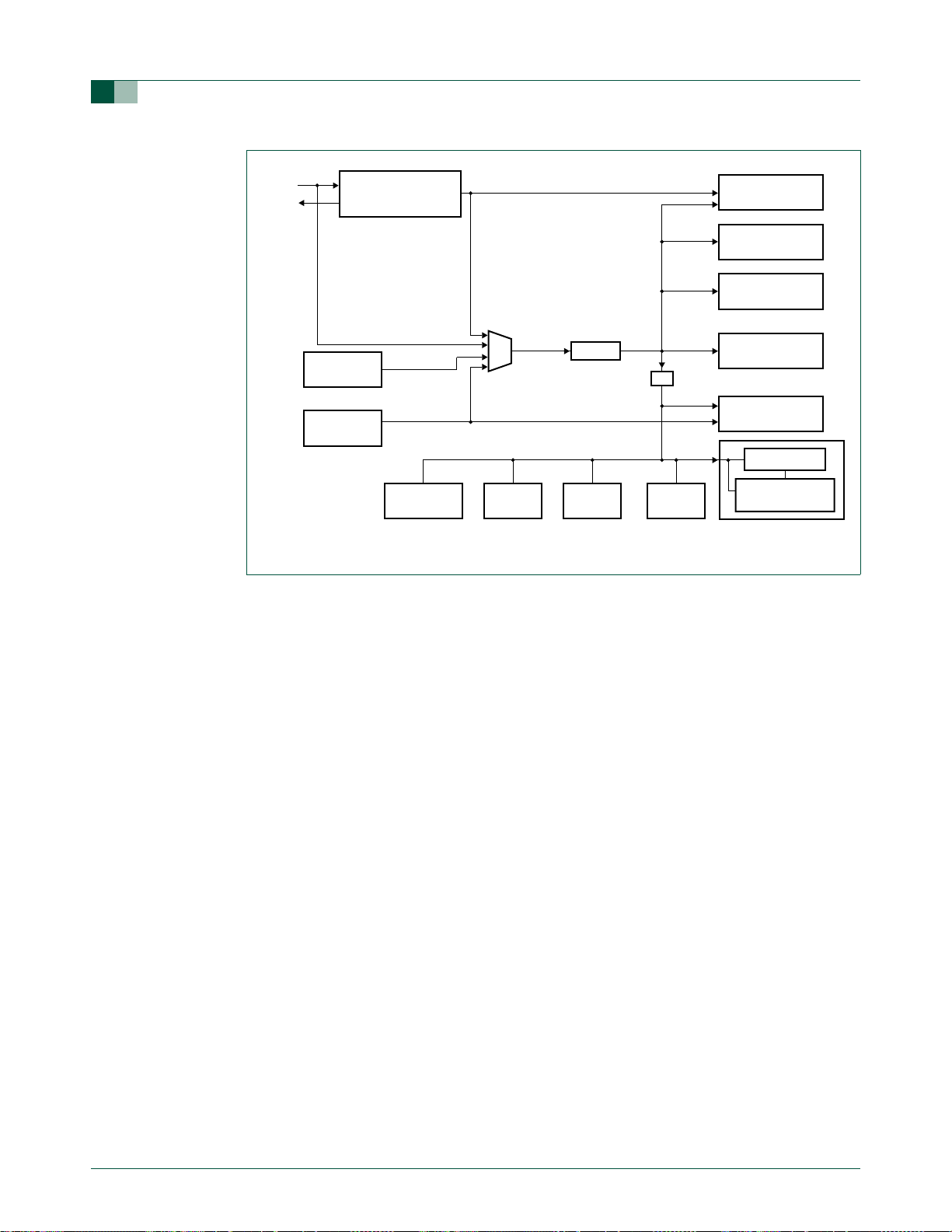
Fig 10. Block diagram of oscillator control.
HIGH FREQUENCY
MEDIUM FREQUENCY
LOW FREQUENCY
RC
OSCILLATOR
WATCHDOG
OSCILLATOR
RCCLK
TIMER 0 AND
TIMER 1
OSCCLK
I2C-BUS
PCLK
DIVM
SPI
CCLK
PCLK
÷2
UART
ADC1
ADC0
(P89LPC935/936)
(P89LPC935/936)
2.7 Oscillator Clock (OSCCLK) wake-up delay
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has an internal wake-up timer that delays the clock until it
stabilizes depending to the clock source used. If the clock source is any of the three
crystal selections, the delay is 992 OSCCLK cycles plus 60 µs to 100 µs. If the clock
source is either the internal RC oscillator or the Watchdog oscillator, the delay is 224
OSCCLK cycles plus 60 µs to 100 µs.
RTC
CPU
WDT
32 × PLL
CCU
002aab079
2.8 CPU Clock (CCLK) modification: DIVM register
The OSCCLK frequency can be divided down, by an integer, up to 510 times by
configuring a dividing register, DIVM, to provide CCLK. This produces the CCLK
frequency using the following formula:
CCLK frequency = f
Where: f
is the frequency of OSCCLK, N is the value of DIVM.
osc
Since N ranges from 0 to 255, the CCLK frequency can be in the range of f
(for N = 0, CCLK = f
This feature makes it possible to temporarily run the CPU at a lower rate, reducing power
consumption. By dividing the clock, the CPU can retain the ability to respond to events
other than those that can cause interrupts (i.e. events that allow exiting the Idle mode) by
executing its normal program at a lower rate. This can often result in lower power
consumption than in Idle mode. This can allow bypassing the oscillator start-up time in
cases where Power-down mode would otherwise be used. The value of DIVM may be
changed by the program at any time without interrupting code execution.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 28 of 147
osc
osc
).
/ (2N)
osc
to f
osc
/510.

Philips Semiconductors
2.9 Low power select
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 is designed to run at 12 MHz (CCLK) maximum. However,
if CCLK is 8 MHz or slower, the CLKLP SFR bit (AUXR1.7) can be set to a logic 1 to lower
the power consumption further. On any reset, CLKLP is logic 0 allowing highest
performance. This bit can then be set in software if CCLK is running at 8 MHz or slower.
3. A/D converter
3.1
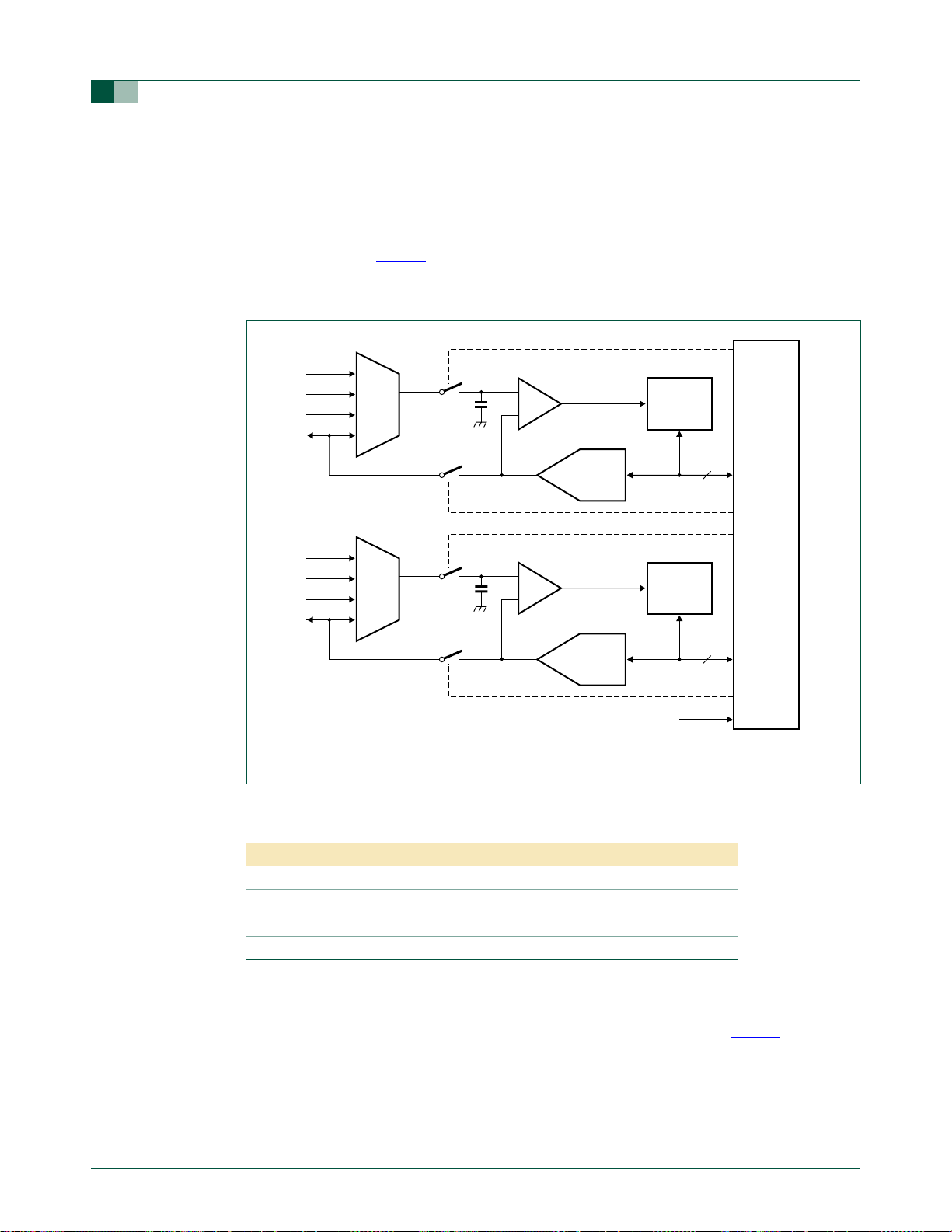
The P89LPC935/936 have two 8-bit, 4-channel multiplexed successive approximation
analog-to-digital converter modules sharing common control logic. The P89LPC933/934
have a single 8-bit, 4-channel multiplexed analog-to-digital converter (ADC1) and an
additional DAC module (DAC0). A block diagram of the A/D converter is shown in
Figure 11
circuit providing an input signal to one of two comparator inputs. The control logic in
combination with the SAR drives a digital-to-analog converter which provides the other
input to the comparator. The output of the comparator is fed to the SAR.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
. Each A/D consists of a 4-input multiplexer which feeds a sample-and-hold
3.2 A/D features
• Two (P89LPC935/936) 8-bit, 4-channel multiplexed input, successive approximation
A/D converters with common control logic (one A/D on the P89LPC933/934).
• Four result registers for each A/D.
• Six operating modes
– Fixed channel, single conversion mode
– Fixed channel, continuous conversion mode
– Auto scan, single conversion mode
– Auto scan, continuous conversion mode
– Dual channel, continuous conversion mode
– Single step mode
• Four conversion start modes
– Timer triggered start
– Start immediately
– Edge triggered
– Dual start immediately (P89LPC935/936)
• 8-bit conversion time of ≥3.9 µs at an A/D clock of 3.3 MHz
• Interrupt or polled operation
• Boundary limits interrupt
• DAC output to a port pin with high output impedance
• Clock divider
• Power down mode
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 29 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
0
3.2.1 A/D operating modes
3.2.1.1 Fixed channel, single conversion mode
A single input channel can be selected for conversion. A single conversion will be
performed and the result placed in the result register which corresponds to the selected
input channel (see Ta bl e 7
completes. The input channel is selected in the ADINS register. This mode is selected by
setting the SCANx bit in the ADMODA register.
INPUT
MUX
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
). An interrupt, if enabled, will be generated after the conversion
comp
+
–
SAR
INPUT
MUX
DAC1
comp
+
–
SAR
8
CONTROL
LOGIC
DAC0
CCLK
Fig 11. ADC block diagram.
Table 7: Input channels and result registers for fixed channel single, auto scan single, and
auto scan continuous conversion modes
Result register Input channel Result register Input channel
AD0DAT0 AD00 AD1DAT0 AD10
AD0DAT1 AD01 AD1DAT1 AD11
AD0DAT2 AD02 AD1DAT2 AD12
AD0DAT3 AD03 AD1DAT3 AD13
8
002aab08
3.2.1.2 Fixed channel, continuous conversion mode
A single input channel can be selected for continuous conversion. The results of the
conversions will be sequentially placed in the four result registers (see Tab le 8
). An
interrupt, if enabled, will be generated after every four conversions. Additional conversion
results will again cycle through the four result registers, overwriting the previous results.
Continuous conversions continue until terminated by the user. This mode is selected by
setting the SCCx bit in the ADMODA register.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 30 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 8: Result registers and conversion results for fixed channel, continuous conversion
Result register Contains
ADxDAT0 Selected channel, first conversion result
ADxDAT1 Selected channel, second conversion result
ADxDAT2 Selected channel, third conversion result
ADxDAT3 Selected channel, fourth conversion result
3.2.1.3 Auto scan, single conversion mode
Any combination of the four input channels can be selected for conversion by setting a
channel’s respective bit in the ADINS register. The channels are converted from LSB to
MSB order (in ADINS). A single conversion of each selected input will be performed and
the result placed in the result register which corresponds to the selected input channel
(See Ta bl e 7
been converted. If only a single channel is selected this is equivalent to single channel,
single conversion mode.This mode is selected by setting the SCANx bit in the ADMODA
register.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
mode
). An interrupt, if enabled, will be generated after all selected channels have
3.2.1.4 Auto scan, continuous conversion mode
Any combination of the four input channels can be selected for conversion by setting a
channel’s respective bit in the ADINS register. The channels are converted from LSB to
MSB order (in ADINS). A conversion of each selected input will be performed and the
result placed in the result register which corresponds to the selected input channel (See
Ta bl e 7
converted. The process will repeat starting with the first selected channel. Additional
conversion results will again cycle through the result registers of the selected channels,
overwriting the previous results.Continuous conversions continue until terminated by the
user.This mode is selected by setting the BURSTx bit in the ADMODA register.
3.2.1.5 Dual channel, continuous conversion mode
The co.Any combination of two of the four input channels can be selected for conversion.
The result of the conversion of the first channel is placed in the first result register. The
result of the conversion of the second channel is placed in the second result register.The
first channel is again converted and its result stored in the third result register. The second
channel is again converted and its result placed in the fourth result register (See Ta bl e 9
An interrupt is generated, if enabled, after every set of four conversions (two conversions
per channel).This mode is selected by setting the SCCx bit in the ADMODA register.
Table 9: Result registers and conversion results for dual channel, continuous conversion
). An interrupt, if enabled, will be generated after all selected channels have been
mode
Result register Contains
ADxDAT0 First channel, first conversion result
ADxDAT1 Second channel, first conversion result
ADxDAT2 First channel, second conversion result
ADxDAT3 Second channel, second conversion result
).
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 31 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
3.2.1.6 Single step mode
This special mode allows “single-stepping” in an auto scan conversion mode. Any
combination of the four input channels can be selected for conversion. After each channel
is converted, an interrupt is generated, if enabled, and the A/D waits for the next start
condition. The result of each channel is placed in the result register which corresponds to
the selected input channel (See Tab l e 7
mode is selected by clearing the BURSTx, SCCx, and SCANx bits in the ADMODA
register which correspond to the ADC in use.
3.2.2 Conversion mode selection bits
Each A/D uses three bits in ADMODA to select the conversion mode for that A/D. These
mode bits are summarized in Ta bl e 1 0
the combinations shown, are undefined.
Table 10: Conversion mode bits
Burst1 SCC1 Scan1 ADC1 conversion
0 0 0 Single step 0 0 0 Single step
0 0 1 Fixed channel,
0 1 0 Fixed channel,
011Auto scan,
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
). May be used with any of the start modes. This
,below. Combinations of the three bits, other than
Burst0 SCC0 Scan0 ADC0 conversion
mode
0 0 1 Fixed channel,
single
Auto scan, single Auto scan, single
0 1 0 Fixed channel,
continuous
Dual channel,
continuous
0 1 1 Auto scan,
continuous
mode
single
continuous
Dual channel,
continuous
continuous
3.2.3 Conversion start modes
3.2.3.1 Timer triggered start
An A/D conversion is started by the overflow of Timer 0. Once a conversion has started,
additional Timer 0 triggers are ignored until the conversion has completed. The Timer
triggered start mode is available in all A/D operating modes.This mode is selected by the
TMMx bit and the ADCSx1 and ADCSx0 bits (See Tab le 1 2
3.2.3.2 Start immediately
Programming this mode immediately starts a conversion.This start mode is available in all
A/D operating modes.This mode is selected by setting the ADCSx1 and ADCSx0 bits in
the ADCONx register (See Tab le 1 2
3.2.3.3 Edge triggered
An A/D conversion is started by rising or falling edge of P1.4. Once a conversion has
started, additional edge triggers are ignored until the conversion has completed. The edge
triggered start mode is available in all A/D operating modes.This mode is selected by
setting the ADCSx1 and ADCSx0 bits in the ADCONx register (See Tab le 1 2
Ta bl e 1 4
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 32 of 147
).
and Ta bl e 1 4).
and Ta bl e 1 4).
and

Philips Semiconductors
3.2.3.4 Dual start immediately (P89LPC935/936)
Programming this mode starts a synchronized conversion of both A/D converters.This
start mode is available in all A/D operating modes. Both A/D converters must be in the
same operating mode. In the autoscan single conversion modes, both A/D converters
must select an identical number of channels. Writing a 11 to the ADCSx1, ADCSx0 bits in
either ADCONx register will start a simultaneous conversion of both A/Ds. Both A/Ds must
be enabled.
3.2.4 Boundary limits interrupt
Each of the A/D converters has both a high and low boundary limit register. After the four
MSBs have been converted, these four bits are compared with the four MSBs of the
boundary high and low registers. If the four MSBs of the conversion are outside the limit
an interrupt will be generated, if enabled. If the conversion result is within the limits, the
boundary limits will again be compared after all 8 bits have been converted. An interrupt
will be generated, if enabled, if the result is outside the boundary limits. The boundary limit
may be disabled by clearing the boundary limit interrupt enable.
3.2.5 DAC output to a port pin with high output impedance
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Each A/D converter’s DAC block can be output to a port pin. In this mode, the ADxDAT3
register is used to hold the value fed to the DAC. After a value has been written to the DAC
(written to ADxDAT3), the DAC output will appear on the channel 3 pin. The DAC output is
enabled by the ENDAC1 and ENDAC0 bits in the ADMODB register (See Tab l e 1 8
3.2.6 Clock divider
The A/D converter requires that its internal clock source be in the range of 500kHz to
3.3MHz to maintain accuracy. A programmable clock divider that divides the clock from 1
to 8 is provided for this purpose (See Tab l e 1 8
3.2.7 I/O pins used with ADC functions
The analog input pins maybe be used as either digital I/O or as inputs to A/D and thus
have a digital input and output function. In order to give the best analog performance, pins
that are being used with the ADC should have their digital outputs and inputs disabled and
have the 5V tolerance disconnected. Digital outputs are disabled by putting the port pins
into the input-only mode as described in the Port Configurations section (see Ta bl e 2 4
Digital inputs will be disconnected automatically from these pins when the pin has been
selected by setting its corresponding bit in the ADINS register and its corresponding A/D
has been enabled
When used as digital I/O these pins are 5 V tolerant. If selected as input signals in ADINS,
these pins will be 3V tolerant if the corresponding A/D is enabled and the device is not in
power down. Otherwise the pin will remain 5V tolerant. Please refer to the
P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet for specifications.
).
).
).
3.2.8 Power-down and Idle mode
In Idle mode the A/C converter, if enabled, will continue to function and can cause the
device to exit Idle mode when the conversion is completed if the A/D interrupt is enabled.
In Power-down mode or Total Power-down mode, the A/D does not function. If the A/D is
enabled, it will consume power. Power can be reduced by disabling the A/D.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 33 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 11: A/D Control register 0 (ADCON0 - address 8Eh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol ENBI0 ENADCI0 TMM0 EDGE0 ADCI0 ENADC0 ADCS01 ADCS00
Reset00000000
Table 12: A/D Control register 0 (ADCON0 - address 8Eh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
1:0 ADCS01,ADCS00 A/D start mode bits, see below.(P89LPC935/936)
00 — Timer Trigger Mode when TMM0 = 1. Conversions starts on overflow of Timer
0. When TMM0 =0, no start occurs (stop mode).
01 — Immediate Start Mode. Conversion starts immediately.
10 — Edge Trigger Mode. Conversion starts when edge condition defined by bit
EDGE0 occurs.
11 — Dual Immediate Start Mode. Both ADC’s start a conversion immediately.
2 ENADC0 Enable A/D channel 0. When set = 1, enables ADC0. Must also be set for D/A
operation of this channel.
3 ADCI0 A/D Conversion complete Interrupt 0. Set when any conversion or set of multiple
conversions has completed. Cleared by software.(P89LPC935/936)
4 EDGE0 When = 0, an Edge conversion start is triggered by a falling edge on P1.4 When = 1,
an Edge conversion start is triggered by a rising edge on P1.4. (P89LPC935/936)
5 TMM0 Timer Trigger Mode 0. Selects either stop mode (TMM0 = 0) or timer trigger mode
(TMM0 = 1) when the ADCS01 and ADCS00 bits = 00. (P89LPC935/936)
6 ENADCI0 Enable A/D Conversion complete Interrupt 0. When set, will cause an interrupt if the
ADCI0 flag is set and the A/D interrupt is enabled. (P89LPC935/936)
7 ENBI0 Enable A/D boundary interrupt 0. When set, will cause and interrupt if the boundary
interrupt 0 flag, BNDI0, is set and the A/D interrupt is enabled. (P89LPC935/936)
UM10116
Table 13: A/D Control register 1(ADCON1 - address 97h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol ENBI1 ENADCI1 TMM1 EDGE1 ADCI1 ENADC1 ADCS11 ADCS10
Reset00000000
Table 14: A/D Control register 1(ADCON1 - address 97h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
1:0 ADCS11,ADCS10 A/D start mode bits, see below.
00 — Timer Trigger Mode when TMM1 = 1. Conversions starts on overflow of Timer
0. When TMM1 =0, no start occurs (stop mode).
01 — Immediate Start Mode. Conversion starts immediately.
10 — Edge Trigger Mode. Conversion starts when edge condition defined by bit
EDGE1 occurs.
11 — Dual Immediate Start Mode. Both ADC’s start a conversion immediately
(P89LPC935/936).
2 ENADC1 Enable A/D channel 1. When set = 1, enables ADC1. Must also be set for D/A
operation of this channel.
3 ADCI1 A/D Conversion complete Interrupt 1. Set when any conversion or set of multiple
conversions has completed. Cleared by software.(P89LPC935/936)
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 34 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 14: A/D Control register 1(ADCON1 - address 97h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
4 EDGE1 When = 0, an Edge conversion start is triggered by a falling edge on P1.4 When = 1,
an Edge conversion start is triggered by a rising edge on P1.4. (P89LPC935/936)
5 TMM1 Timer Trigger Mode 1. Selects either stop mode (TMM1 = 0) or timer trigger mode
(TMM1 = 1) when the ADCS11 and ADCS10 bits = 00. (P89LPC935/936)
6 ENADCI1 Enable A/D Conversion complete Interrupt 1. When set, will cause an interrupt if the
ADCI1 flag is set and the A/D interrupt is enabled. (P89LPC935/936)
7 ENBI1 Enable A/D boundary interrupt 1. When set, will cause and interrupt if the boundary
interrupt 1flag, BNDI1, is set and the A/D interrupt is enabled. (P89LPC935/936)
Table 15: A/D Mode register A (ADMODA - address 0C0h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol BNDI1 BURST1 SCC1 SCAN1 BNDI0 BURST0 SCC0 SCAN0
Reset00000000
Table 16: A/D Mode register A (ADMODA - address 0C0h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 SCAN0 When = 1, selects single conversion mode (auto scan or fixed channel) for ADC0
(P89LPC935/936).
1 SCC0 When = 1, selects fixed channel, continuous conversion mode for ADC0
(P89LPC935/936).
2 BURST0 When = 1, selects auto scan, continuous conversion mode for ADC0
(P89LPC935/936).
3 BNDI0 ADC0 boundary interrupt flag. When set, indicates that the converted result is
outside of the range defined by the ADC0 boundary registers (P89LPC935/936).
4 SCAN1 When = 1, selects single conversion mode (auto scan or fixed channel) for ADC1.
5 SCC1 When = 1, selects fixed channel, continuous conversion mode for ADC1.
6 BURST1 When = 1, selects auto scan, continuous conversion mode for ADC1.
7 BNDI1 ADC1 boundary interrupt flag. When set, indicates that the converted result is
outside of the range defined by the ADC1 boundary registers.
…continued
Table 17: A/D Mode register B (ADMODB - address A1h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol CLK2 CLK1 CLK0 - ENDAC1 ENDAC0 BSA1 BSA0
Reset00000000
Table 18: A/D Mode register B (ADMODB - address A1h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 BSA0 ADC0 Boundary Select All. When =1, BNDI0 will be set if any ADC0 input exceeds
the boundary limits. When = 0, BNDI0 will be set only if the AD00 input exceeded
the boundary limits.(P89LPC935)
1 BSA1 ADC1 Boundary Select All. When =1, BNDI1 will be set if any ADC1 input exceeds
the boundary limits. When = 0, BNDI1 will be set only if the AD10 input exceeded
the boundary limits.
2 ENDAC0 When =1 selects DAC mode for ADC0; when = 0 selects ADC mode. (Note: This bit
must
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 35 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 18: A/D Mode register B (ADMODB - address A1h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
3 ENDAC1 When =1 selects DAC mode for ADC1; when = 0 selects ADC mode.
4- reserved
7:5 CLK2,CLK1,CLK0 Clock divider to produce the ADC clock. Divides CCLK by the value indicated below.
The resulting ADC clock should be 3.3MHz or less. A minimum of 0.5MHz is
required to maintain A/D accuracy.
CLK2:0 — Divisor
000 — 1
001 — 2
010 — 3
011 — 4
011 — 5
011 — 6
011 — 7
011 — 8
Table 19: A/D Input select (ADINS - address A3h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol AIN13 AIN12 AIN11 AIN10 AIN03 AIN02 AIN01 AIN00
Reset00000000
…continued
Table 20: A/D Input select (ADINS - address A3h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 AIN00 When set, enables the AD00 pin for sampling and conversion (P89LPC935/936).
1 AIN01 When set, enables the AD01 pin for sampling and conversion (P89LPC935/936).
2 AIN02 When set, enables the AD02 pin for sampling and conversion (P89LPC935/936).
3 AIN03 When set, enables the AD03 pin for sampling and conversion (P89LPC935/936).
4 AIN10 When set, enables the AD10 pin for sampling and conversion.
5 AIN11 When set, enables the AD11 pin for sampling and conversion.
6 AIN12 When set, enables the AD12 pin for sampling and conversion.
7 AIN13 When set, enables the AD13 pin for sampling and conversion.
4. Interrupts
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 uses a four priority level interrupt structure. This allows
great flexibility in controlling the handling of the P89LPC933/934/935/936’s 15 interrupt
sources.
Each interrupt source can be individually enabled or disabled by setting or clearing a bit in
the interrupt enable registers IEN0 or IEN1. The IEN0 register also contains a global
enable bit, EA, which enables all interrupts.
Each interrupt source can be individually programmed to one of four priority levels by
setting or clearing bits in the interrupt priority registers IP0, IP0H, IP1, and IP1H. An
interrupt service routine in progress can be interrupted by a higher priority interrupt, but
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 36 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
not by another interrupt of the same or lower priority. The highest priority interrupt service
cannot be interrupted by any other interrupt source. If two requests of different priority
levels are received simultaneously, the request of higher priority level is serviced.
If requests of the same priority level are pending at the start of an instruction cycle, an
internal polling sequence determines which request is serviced. This is called the
arbitration ranking. Note that the arbitration ranking is only used for pending requests of
the same priority level. Ta bl e 2 2
addresses, enable bits, priority bits, arbitration ranking, and whether each interrupt may
wake-up the CPU from a Power-down mode.
4.1 Interrupt priority structure
Table 21: Interrupt priority level
Priority bits
IPxH IPx Interrupt priority level
0 0 Level 0 (lowest priority)
01Level 1
10Level 2
11Level 3
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
summarizes the interrupt sources, flag bits, vector
There are four SFRs associated with the four interrupt levels: IP0, IP0H, IP1, IP1H. Every
interrupt has two bits in IPx and IPxH (x = 0, 1) and can therefore be assigned to one of
four levels, as shown in Ta bl e 2 2
.
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has two external interrupt inputs in addition to the Keypad
Interrupt function. The two interrupt inputs are identical to those present on the standard
80C51 microcontrollers.
These external interrupts can be programmed to be level-triggered or edge-triggered by
clearing or setting bit IT1 or IT0 in Register TCON. If ITn = 0, external interrupt n is
triggered by a low level detected at the INTn
triggered. In this mode if consecutive samples of the INTn
cycle and a low level in the next cycle, interrupt request flag IEn in TCON is set, causing
an interrupt request.
Since the external interrupt pins are sampled once each machine cycle, an input high or
low level should be held for at least one machine cycle to ensure proper sampling. If the
external interrupt is edge-triggered, the external source has to hold the request pin high
for at least one machine cycle, and then hold it low for at least one machine cycle. This is
to ensure that the transition is detected and that interrupt request flag IEn is set. IEn is
automatically cleared by the CPU when the service routine is called.
If the external interrupt is level-triggered, the external source must hold the request active
until the requested interrupt is generated. If the external interrupt is still asserted when the
interrupt service routine is completed, another interrupt will be generated. It is not
necessary to clear the interrupt flag IEn when the interrupt is level sensitive, it simply
tracks the input pin level.
pin. If ITn = 1, external interrupt n is edge
pin show a high level in one
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 37 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
If an external interrupt has been programmed as level-triggered and is enabled when the
P89LPC933/934/935/936 is put into Power-down mode or Idle mode, the interrupt
occurrence will cause the processor to wake-up and resume operation. Refer to Section
6.3 “Power reduction modes” for details. Note: the external interrupt must be programmed
as level-triggered to wake-up from Power-down mode.
UM10116
4.2 External Interrupt pin glitch suppression
Most of the P89LPC933/934/935/936 pins have glitch suppression circuits to reject short
glitches (please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet, Dynamic characteristics
for glitch filter specifications). However, pins SDA/INT0
the glitch suppression circuits. Therefore, INT1
not.
Table 22: Summary of interrupts
Description Interrupt flag
bit(s)
External interrupt 0 IE0 0003h EX0 (IEN0.0) IP0H.0, IP0.0 1 (highest) Yes
Timer 0 interrupt TF0 000Bh ET0 (IEN0.1) IP0H.1, IP0.1 4 No
External interrupt 1 IE1 0013h EX1 (IEN0.2) IP0H.2, IP0.2 7 Yes
Timer 1 interrupt TF1 001Bh ET1 (IEN0.3) IP0H.3, IP0.3 10 No
Serial port Tx and Rx TI and RI 0023h ES/ESR (IEN0.4) IP0H.4, IP0.4 13 No
Serial port Rx RI
Brownout detect BOF 002Bh EBO (IEN0.5) IP0H.5, IP0.5 2 Yes
Watchdog timer/Real-time
clock
2
C interrupt SI 0033h EI2C (IEN1.0) IP0H.0, IP0.0 5 No
I
KBI interrupt KBIF 003Bh EKBI (IEN1.1) IP0H.0, IP0.0 8 Yes
Comparators 1 and 2
interrupts
SPI interrupt SPIF 004Bh ESPI (IEN1.3) IP1H.3, IP1.3 14 No
Capture/Compare Unit 005Bh ECCU(IEN1.4) IP1H.4, IP1.4 6 No
Serial port Tx TI 006Bh EST (IEN1.6) IP0H.0, IP0.0 12 No
ADC, Data EEPROMwrite
complete (P89LPC935/936)
WDOVF/RTCF 0053h EWDRT (IEN0.6) IP0H.6, IP0.6 3 Yes
CMF1/CMF2 0043h EC (IEN1.2) IP0H.0, IP0.0 11 Yes
ADCI1, BNDI1 0073h EAD (IEN1.7) IP1H.7, IP1.7 15 (lowest) No
Vector
address
Interrupt enable
bit(s)
has glitch suppression while INT0 does
/P1.3 and SCL/T0/P1.2 do not have
Interrupt
priority
Arbitration
ranking
Powerdown
wake-up
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 38 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
RTCF
ERTC
(RTCCON.1)
WDOVF
any CCU interrupt
(2)
EEIF
ADCI0
ENADCI1
ADCI1
ENBI0
BNDI0
ENBI1
BNDI1
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
ENADCI0
EADEE (P89LPC935)
EAD (P89LPC933/934)
IE0
EX0
IE1
EX1
BOF
EBO
KBIF
EKBI
EWDRT
CMF2
CMF1
EC
EA (IE0.7)
TF0
ET0
TF1
ET1
TI & RI/RI
ES/ESR
EST
EI2C
SPIF
ESPI
ECCU
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
wake-up
(if in power-down)
TI
SI
(1)
interrupt
to CPU
002aab081
(1) See Section 10 “Capture/Compare Unit (CCU)”
(2) P89LPC935/936
Fig 12. Interrupt sources, interrupt enables, and power-down wake-up sources.
5. I/O ports
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has four I/O ports: Port 0, Port 1, Port 2, and Port 3. Ports
0, 1, and 2 are 8-bit ports and Port 3 is a 2-bit port. The exact number of I/O pins available
depends upon the clock and reset options chosen (see Ta bl e 2 3
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 39 of 147
).

Philips Semiconductors
Table 23: Number of I/O pins available
Clock source Reset option Number of I/O
On-chip oscillator or watchdog
oscillator
External clock input No external reset (except during power up) 25
Low/medium/high speed oscillator
(external crystal or resonator)
[1] required for operation above 12 MHz.
5.1 Port configurations
All but three I/O port pins on the P89LPC933/934/935/936 may be configured by software
to one of four types on a pin-by-pin basis, as shown in Tab le 2 4
quasi-bidirectional (standard 80C51 port outputs), push-pull, open drain, and input-only.
Two configuration registers for each port select the output type for each port pin.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
pins
No external reset (except during power up) 26
External RST pin supported 25
External RST
No external reset (except during power up) 24
External RST
pin supported
pin supported
[1]
[1]
. These are:
24
23
P1.5 (RST
P1.2 (SCL/T0) and P1.3 (SDA/INT0
open drain.
Table 24: Port output configuration settings
PxM1.y PxM2.y Port output mode
0 0 Quasi-bidirectional
0 1 Push-pull
1 0 Input only (high-impedance)
1 1 Open drain
) can only be an input and cannot be configured.
) may only be configured to be either input-only or
5.2 Quasi-bidirectional output configuration
Quasi-bidirectional outputs can be used both as an input and output without the need to
reconfigure the port. This is possible because when the port outputs a logic high, it is
weakly driven, allowing an external device to pull the pin low. When the pin is driven low, it
is driven strongly and able to sink a large current. There are three pull-up transistors in the
quasi-bidirectional output that serve different purposes.
One of these pull-ups, called the ‘very weak’ pull-up, is turned on whenever the port latch
for the pin contains a logic 1. This very weak pull-up sources a very small current that will
pull the pin high if it is left floating.
A second pull-up, called the ‘weak’ pull-up, is turned on when the port latch for the pin
contains a logic 1 and the pin itself is also at a logic 1 level. This pull-up provides the
primary source current for a quasi-bidirectional pin that is outputting a 1. If this pin is
pulled low by an external device, the weak pull-up turns off, and only the very weak pull-up
remains on. In order to pull the pin low under these conditions, the external device has to
sink enough current to overpower the weak pull-up and pull the port pin below its input
threshold voltage.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 40 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
The third pull-up is referred to as the ‘strong’ pull-up. This pull-up is used to speed up
low-to-high transitions on a quasi-bidirectional port pin when the port latch changes from a
logic 0 to a logic 1. When this occurs, the strong pull-up turns on for two CPU clocks
quickly pulling the port pin high.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
port latch
data
The quasi-bidirectional port configuration is shown in Figure 13
.
Although the P89LPC933/934/935/936 is a 3 V device most of the pins are 5 V-tolerant. If
5 V is applied to a pin configured in quasi-bidirectional mode, there will be a current
flowing from the pin to V
causing extra power consumption. Therefore, applying 5 V to
DD
pins configured in quasi-bidirectional mode is discouraged.
A quasi-bidirectional port pin has a Schmitt-triggered input that also has a glitch
suppression circuit
(Please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet, Dynamic characteristics for
glitch filter specifications).
V
DD
2 CPU
CLOCK DELAY
PP P
very
weak
weakstrong
PORT
PIN
input
data
glitch rejection
002aaa914
Fig 13. Quasi-bidirectional output.
5.3 Open drain output configuration
The open drain output configuration turns off all pull-ups and only drives the pull-down
transistor of the port pin when the port latch contains a logic 0. To be used as a logic
output, a port configured in this manner must have an external pull-up, typically a resistor
tied to V
The open drain port configuration is shown in Figure 14
An open drain port pin has a Schmitt-triggered input that also has a glitch suppression
circuit.
Please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet, Dynamic characteristics for glitch
filter specifications.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 41 of 147
. The pull-down for this mode is the same as for the quasi-bidirectional mode.
DD
.

Philips Semiconductors
Fig 14. Open drain output.
5.4 Input-only configuration
The input port configuration is shown in Figure 15. It is a Schmitt-triggered input that also
has a glitch suppression circuit.
port latch
data
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
PORT
PIN
input
data
glitch rejection
002aaa915
(Please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet, Dynamic characteristics for
glitch filter specifications).
Fig 15. Input only.
input
data
glitch rejection
PORT
PIN
002aaa916
5.5 Push-pull output configuration
The push-pull output configuration has the same pull-down structure as both the open
drain and the quasi-bidirectional output modes, but provides a continuous strong pull-up
when the port latch contains a logic 1. The push-pull mode may be used when more
source current is needed from a port output.
The push-pull port configuration is shown in Figure 16
A push-pull port pin has a Schmitt-triggered input that also has a glitch suppression
circuit.
(Please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet, Dynamic characteristics for
glitch filter specifications).
.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 42 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Fig 16. Push-pull output.
port latch
data
input
data
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
V
DD
P
strong
PORT
N
glitch rejection
PIN
002aaa917
5.6 Port 0 and Analog Comparator functions
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 incorporates two Analog Comparators. In order to give the
best analog performance and minimize power consumption, pins that are being used for
analog functions must have both the digital outputs and digital inputs disabled.
Digital outputs are disabled by putting the port pins into the input-only mode as described
in the Port Configurations section (see Figure 15
Digital inputs on Port 0 may be disabled through the use of the PT0AD register. Bits 1
through 5 in this register correspond to pins P0.1 through P0.5 of Port 0, respectively.
Setting the corresponding bit in PT0AD disables that pin’s digital input. Port bits that have
their digital inputs disabled will be read as 0 by any instruction that accesses the port.
On any reset, PT0AD bits 1 through 5 default to logic 0s to enable the digital functions.
).
5.7 Additional port features
After power-up, all pins are in Input-only mode. Please note that this is different from
the LPC76x series of devices.
• After power-up, all I/O pins except P1.5, may be configured by software.
• Pin P1.5 is input only. Pins P1.2 and P1.3 are configurable for either input-only or
open drain.
Every output on the P89LPC933/934/935/936 has been designed to sink typical LED drive
current. However, there is a maximum total output current for all ports which must not be
exceeded. Please refer to the P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet for detailed
specifications.
All ports pins that can function as an output have slew rate controlled outputs to limit noise
generated by quickly switching output signals. The slew rate is factory-set to
approximately 10 ns rise and fall times.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 43 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 25: Port output configuration
Port pin Configuration SFR bits
P0.0 P0M1.0 P0M2.0 KBIO, CMP2, AD01
P0.1 P0M1.1 P0M2.1 KBI1, CIN2B, AD10 Refer to Section 5.6 “
P0.2 P0M1.2 P0M2.2 KBI2, CIN2A, AD11
P0.3 P0M1.3 P0M2.3 KBI3, CIN1B, AD12
P0.4 P0M1.4 P0M2.4 KBI4, CIN1A, AD13,
P0.5 P0M1.5 P0M2.5 KBI5, CMPREF
P0.6 P0M1.6 P0M2.6 KBI6, CMP1
P0.7 P0M1.7 P0M2.7 KBI7, T1
P1.0 P1M1.0 P1M2.0 TxD
P1.1 P1M1.1 P1M2.1 RxD
P1.2 P1M1.2 P1M2.2 T0, SCL Input-only or open-drain
P1.3 P1M1.3 P1M2.3 INTO
P1.4 P1M1.4 P1M2.4 INT1
P1.5 P1M1.5 P1M2.5 RST
P1.6 P1M1.6 P1M2.6 OCB
P1.7 P1M1.7 P1M2.7 OCC, AD00
P2.0 P2M1.0 P1M2.0 ICB, AD03, DAC0
P2.1 P2M1.1 P1M2.1 OCD, AD02
P2.2 P2M1.2 P1M2.2 MOSI
P2.3 P2M1.3 P1M2.3 MISO
P2.4 P2M1.4 P1M2.4 SS
P2.5 P2M1.5 P1M2.5 SPICLK
P2.6 P2M1.6 P1M2.6 OCA
P2.7 P2M1.7 P1M2.7 ICA
P3.0 P3M1.0 P3M2.0 CLKOUT, XTAL2
P3.1 P3M1.1 P3M2.1 XTAL1
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
PxM1.y PxM2.y Alternate usage Notes
Port 0 and
Analog Comparator functions” for
usage as analog inputs.
DAC1
, SDA input-only or open-drain
6. Power monitoring functions
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 incorporates power monitoring functions designed to
prevent incorrect operation during initial power-on and power loss or reduction during
operation. This is accomplished with two hardware functions: Power-on Detect and
Brownout Detect.
6.1 Brownout detection
The Brownout Detect function determines if the power supply voltage drops below a
certain level. The default operation for a Brownout Detection is to cause a processor reset.
However, it may alternatively be configured to generate an interrupt by setting the BOI
(PCON.4) bit and the EBO (IEN0.5) bit.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 44 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Enabling and disabling of Brownout Detection is done via the BOPD (PCON.5) bit, bit field
PMOD1/PMOD0 (PCON[1:0]) and user configuration bit BOE (UCFG1.5). If BOE is in an
unprogrammed state, brownout is disabled regardless of PMOD1/PMOD0 and BOPD. If
BOE is in a programmed state, PMOD1/PMOD0 and BOPD will be used to determine
whether Brownout Detect will be disabled or enabled. PMOD1/PMOD0 is used to select
the power reduction mode. If PMOD1/PMOD0 = ‘11’, the circuitry for the Brownout
Detection is disabled for lowest power consumption. BOPD defaults to logic 0, indicating
brownout detection is enabled on power-on if BOE is programmed.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
If Brownout Detection is enabled the brownout condition occurs when V
Brownout trip voltage, VBO (see P89LPC933/934/935/936 data sheet, Static
characteristics), and is negated when V
P89LPC933/934/935/936 device is to operate with a power supply that can be below
2.7 V, BOE should be left in the unprogrammed state so that the device can operate at
2.4 V, otherwise continuous brownout reset may prevent the device from operating.
If Brownout Detect is enabled (BOE programmed, PMOD1/PMOD0 ≠ ‘11’, BOPD = 0),
BOF (RSTSRC.5) will be set when a brownout is detected, regardless of whether a reset
or an interrupt is enabled. BOF will stay set until it is cleared in software by writing a
logic 0 to the bit. Note that if BOE is unprogrammed, BOF is meaningless. If BOE is
programmed, and a initial power-on occurs, BOF will be set in addition to the power-on
flag (POF - RSTSRC.4).
For correct activation of Brownout Detect, certain V
observed. Please see the data sheet for specifications.
rises above VBO. If the
DD
rise and fall times must be
DD
falls below the
DD
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 45 of 147
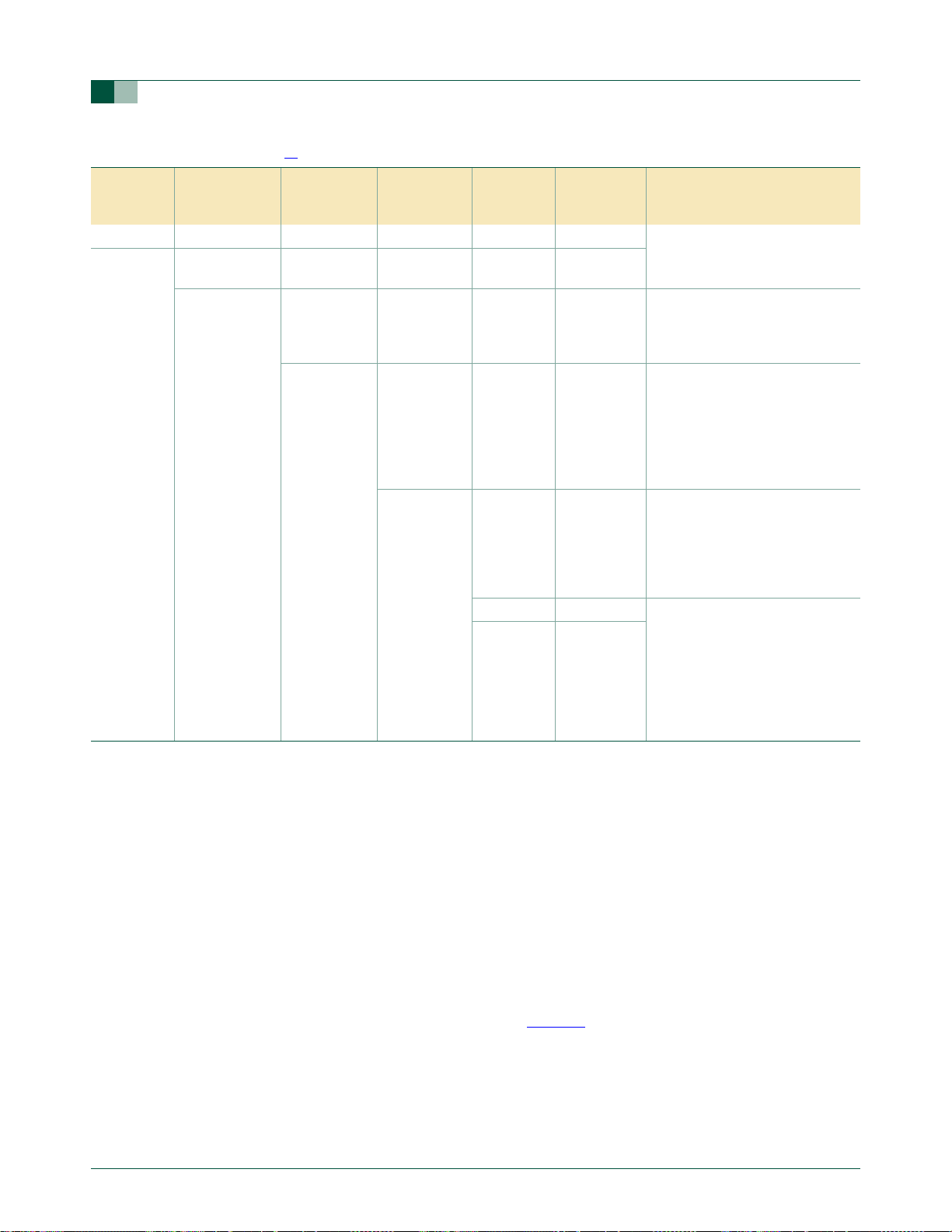
Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 26: Brownout options
BOE
(UCFG1.5)
0 (erased) XX X X X X Brownout disabled. V
1(program
med)
PMOD1/
PMOD0
(PCON[1:0])
11 (total
power-down)
≠ 11 (any mode
other than total
power-down)
[1]
BOPD
(PCON.5)
XXXX
1 (brownout
detect
power-down)
0 (brownout
detect active)
BOI
(PCON.4)
X X X Brownout disabled. V
0 (brownout
detect
generates
reset)
1 (brownout
detect
generates an
interrupt)
EBO
(IEN0.5)
X X Brownout reset enabled. V
1 (enable
brownout
interrupt)
0 X Both brownout reset and
X0
EA (IEN0.7) Description
1 (global
interrupt
enable)
operating range is 2.4 V to 3.6 V.
operating range is 2.4 V to 3.6 V.
However, BOPD is default to
logic 0 upon power-up.
operating range is 2.7 V to 3.6 V.
Upon a brownout reset, BOF
(RSTSRC.5) will be set to
indicate the reset source. BOF
can be cleared by writing a
logic 0 to the bit.
Brownout interrupt enabled. V
operating range is 2.7 V to 3.6 V.
Upon a brownout interrupt, BOF
(RSTSRC.5) will be set. BOF can
be cleared by writing a logic 0 to
the bit.
interrupt disabled. V
range is 2.4 V to 3.6 V. However,
BOF (RSTSRC.5) will be set
when V
Detection trip point. BOF can be
cleared by writing a logic 0 to the
bit.
falls to the Brownout
DD
DD
DD
operating
DD
DD
DD
[1] Cannot be used with operation above 12 MHz as this requires VDD of 3.0 V or above.
6.2 Power-on detection
The Power-On Detect has a function similar to the Brownout Detect, but is designed to
work as power initially comes up, before the power supply voltage reaches a level where
the Brownout Detect can function. The POF flag (RSTSRC.4) is set to indicate an initial
power-on condition. The POF flag will remain set until cleared by software by writing a
logic 0 to the bit. Note that if BOE (UCFG1.5) is programmed, BOF (RSTSRC.5) will be
set when POF is set. If BOE is unprogrammed, BOF is meaningless.
6.3 Power reduction modes
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 supports three different power reduction modes as
determined by SFR bits PCON[1:0] (see Ta bl e 2 7
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 46 of 147
).

Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 27: Power reduction modes
PMOD1
(PCON.1)
0 0 Normal mode (default) - no power reduction.
0 1 Idle mode. The Idle mode leaves peripherals running in order to allow them to activate the
1 0 Power-down mode:
PMOD0
(PCON.0)
Description
processor when an interrupt is generated. Any enabled interrupt source or reset may terminate Idle
mode.
The Power-down mode stops the oscillator in order to minimize power consumption.
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 exits Power-down mode via any reset, or certain interrupts - external
pins INT0/INT1, brownout Interrupt, keyboard, Real-time Clock/System Timer), watchdog, and
comparator trips. Waking up by reset is only enabled if the corresponding reset is enabled, and
waking up by interrupt is only enabled if the corresponding interrupt is enabled and the EA SFR bit
(IEN0.7) is set. External interrupts should be programmed to level-triggered mode to be used to exit
Power-down mode.
In Power-down mode the internal RC oscillator is disabled unless both the RC oscillator has been
selected as the system clock AND the RTC is enabled.
In Power-down mode, the power supply voltage may be reduced to the RAM keep-alive voltage
VRAM. This retains the RAM contents at the point where Power-down mode was entered. SFR
contents are not guaranteed after V
wake-up the processor via Reset in this situation. V
before the Power-down mode is exited.
When the processor wakes up from Power-down mode, it will start the oscillator immediately and
begin execution when the oscillator is stable. Oscillator stability is determined by counting 1024
CPU clocks after start-up when one of the crystal oscillator configurations is used, or 256 clocks
after start-up for the internal RC or external clock input configurations.
Some chip functions continue to operate and draw power during Power-down mode, increasing the
total power used during power-down. These include:
has been lowered to VRAM, therefore it is recommended to
DD
must be raised to within the operating range
DD
UM10116
• Brownout Detect
• Watchdog Timer if WDCLK (WDCON.0) is logic 1.
• Comparators (Note: Comparators can be powered down separately with PCONA.5 set to
logic 1 and comparators disabled);
• Real-time Clock/System Timer (and the crystal oscillator circuitry if this block is using it, unless
RTCPD, i.e., PCONA.7 is logic 1).
1 1 Total Power-down mode: This is the same as Power-down mode except that the Brownout
Detection circuitry and the voltage comparators are also disabled to conserve additional power.
Note that a brownout reset or interrupt will not occur. Voltage comparator interrupts and Brownout
interrupt cannot be used as a wake-up source. The internal RC oscillator is disabled unless both
the RC oscillator has been selected as the system clock AND the RTC is enabled.
The following are the wake-up options supported:
• Watchdog Timer if WDCLK (WDCON.0) is logic 1. Could generate Interrupt or Reset, either
one can wake up the device
• External interrupts INTO/INT1 (when programmed to level-triggered mode).
• Keyboard Interrupt
• Real-time Clock/System Timer (and the crystal oscillator circuitry if this block is using it, unless
RTCPD, i.e., PCONA.7 is logic 1).
Note: Using the internal RC-oscillator to clock the RTC during power-down may result in relatively
high power consumption. Lower power consumption can be achieved by using an external low
frequency clock when the Real-time Clock is running during power-down.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 47 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 28: Power Control register (PCON - address 87h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol SMOD1 SMOD0 BOPD BOI GF1 GF0 PMOD1 PMOD0
Reset00000000
Table 29: Power Control register (PCON - address 87h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 PMOD0 Power Reduction Mode (see Section 6.3
1PMOD1
2 GF0 General Purpose Flag 0. May be read or written by user software, but has no effect
on operation
3 GF1 General Purpose Flag 1. May be read or written by user software, but has no effect
on operation
4 BOI Brownout Detect Interrupt Enable. When logic 1, Brownout Detection will generate a
interrupt. When logic 0, Brownout Detection will cause a reset
5 BOPD Brownout Detect power-down. When logic 1, Brownout Detect is powered down and
therefore disabled. When logic 0, Brownout Detect is enabled. (Note: BOPD must
be logic 0 before any programming or erasing commands can be issued. Otherwise
these commands will be aborted.)
6 SMOD0 Framing Error Location:
)
• When logic 0, bit 7 of SCON is accessed as SM0 for the UART.
• When logic 1, bit 7 of SCON is accessed as the framing error status (FE) for the
UART
7 SMOD1 Double Baud Rate bit for the serial port (UART) when Timer 1 is used as the baud
rate source. When logic 1, the Timer 1 overflow rate is supplied to the UART. When
logic 0, the Timer 1 overflow rate is divided by two before being supplied to the
UART. (See Section 11
)
Table 30: Power Control register A (PCONA - address B5h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol RTCPD DEEPD VCPD ADPD I2PD SPPD SPD CCUPD
Reset00000000
Table 31: Power Control register A (PCONA - address B5h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 CCUPD Compare/Capture Unit (CCU) power-down: When logic 1, the internal clock to the
CCU is disabled. Note that in either Power-down mode or Total Power-down mode,
the CCU clock will be disabled regardless of this bit. (Note: This bit is overridden by
the CCUDIS bit in FCFG1. If CCUDIS = 1, CCU is powered down.)
1 SPD Serial Port (UART) power-down: When logic 1, the internal clock to the UART is
disabled. Note that in either Power-down mode or Total Power-down mode, the
UART clock will be disabled regardless of this bit.
2 SPPD SPI power-down: When logic 1, the internal clock to the SPI is disabled. Note that in
either Power-down mode or Total Power-down mode, the SPI clock will be disabled
regardless of this bit.
2
3I2PDI
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 48 of 147
C power-down: When logic 1, the internal clock to the I2C-bus is disabled. Note
that in either Power-down mode or Total Power-down mode, the I
disabled regardless of this bit.
2
C clock will be

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 31: Power Control register A (PCONA - address B5h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
4 ADPD A/D Converter Power down: When ‘1’, turns off the clock to the ADC. To fully
power-down the ADC, the user should also set the ENADC1 and ENADC0 bits in
registers ADCON1 and ADCON0.
5 VCPD Analog Voltage Comparators power-down: When logic 1, the voltage comparators
are powered down. User must disable the voltage comparators prior to setting this
bit.
6 DEEPD Data EEPROM power-down: When logic 1, the Data EEPROM is powered down.
Note that in either Power-down mode or Total Power-down mode, the Data
EEPROM will be powered down regardless of this bit.
7 RTCPD Real-time Clock power-down: When logic 1, the internal clock to the Real-time
Clock is disabled.
…continued
7. Reset
The P1.5/RST pin can function as either an active low reset input or as a digital input,
P1.5. The RPE (Reset Pin Enable) bit in UCFG1, when set to 1, enables the external reset
input function on P1.5. When cleared, P1.5 may be used as an input pin.
Note: During a power-on sequence, The RPE selection is overridden and this pin will
always functions as a reset input. An external circuit connected to this pin should not hold
this pin low during a Power-on sequence as this will keep the device in reset. After
power-on this input will function either as an external reset input or as a digital input as
defined by the RPE bit. Only a power-on reset will temporarily override the selection
defined by RPE bit. Other sources of reset will not override the RPE bit.
Note: During a power cycle, V
sheet, Static characteristics) before power is reapplied, in order to ensure a power-on
reset.
Note: When using an oscillator frequency above 12 MHz, the reset input function of P1.5
must be enabled. An external circuit is required to hold the device in reset at power-up
until V
below the minimum specified operating voltage. When using an oscillator frequency above
12 MHz, in some applications, an external brownout detect circuit may be required to hold
the device in reset when V
Reset can be triggered from the following sources (see Figure 17
has reached its specified level. When system power is removed VDD will fall
DD
must fall below V
DD
falls below the minimum specified operating voltage.
DD
(see P89LPC933/934/935/936 data
POR
):
• External reset pin (during power-on or if user configured via UCFG1);
• Power-on Detect;
• Brownout Detect;
• Watchdog Timer;
• Software reset;
• UART break detect reset.
For every reset source, there is a flag in the Reset Register, RSTSRC. The user can read
this register to determine the most recent reset source. These flag bits can be cleared in
software by writing a logic 0 to the corresponding bit. More than one flag bit may be set:
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 49 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
8
• During a power-on reset, both POF and BOF are set but the other flag bits are
cleared.
• For any other reset, any previously set flag bits that have not been cleared will remain
set.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
RPE (UCFG1.6)
RST pin
WDTE (UCFG1.7)
watchdog timer reset
software reset SRST (AUXR1.3)
power-on detect
UART break detect
EBRR (AUXR1.6)
brownout detect reset
BOPD (PCON.5)
Fig 17. Block diagram of reset.
Table 32: Reset Sources register (RSTSRC - address DFh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol - - BOF POF R_BK R_WD R_SF R_EX
[1]
Reset
[1] The value shown is for a power-on reset. Other reset sources will set their corresponding bits.
Table 33: Reset Sources register (RSTSRC - address DFh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 R_EX external reset Flag. When this bit is logic 1, it indicates external pin reset. Cleared by software by writing a
1 R_SF software reset Flag. Cleared by software by writing a logic 0 to the bit or a Power-on reset
2 R_WD Watchdog Timer reset flag. Cleared by software by writing a logic 0 to the bit or a Power-on reset.(NOTE:
3 R_BK break detect reset. If a break detect occurs and EBRR (AUXR1.6) is set to logic 1, a system reset will occur.
4 POF Power-on Detect Flag. When Power-on Detect is activated, the POF flag is set to indicate an initial power-up
5 BOF Brownout Detect Flag. When Brownout Detect is activated, this bit is set. It will remain set until cleared by
6:7 - reserved
xx110000
logic 0 to the bit or a Power-on reset. If RST
UCFG1.7 must be = 1)
This bit is set to indicate that the system reset is caused by a break detect. Cleared by software by writing a
logic 0 to the bit or on a Power-on reset.
condition. The POF flag will remain set until cleared by software by writing a logic 0 to the bit. (Note: On a
Power-on reset, both BOF and this bit will be set while the other flag bits are cleared.)
software by writing a logic 0 to the bit. (Note: On a Power-on reset, both POF and this bit will be set while the
other flag bits are cleared.)
is still asserted after the Power-on reset is over, R_EX will be set.
chip reset
002aaa91
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 50 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
7.1 Reset vector
Following reset, the P89LPC933/934/935/936 will fetch instructions from either address
0000h or the Boot address. The Boot address is formed by using the Boot Vector as the
high byte of the address and the low byte of the address = 00h. The Boot address will be
used if a UART break reset occurs or the non-volatile Boot Status bit (BOOTSTAT.0) = 1,
or the device has been forced into ISP mode. Otherwise, instructions will be fetched from
address 0000H.
8. Timers 0 and 1
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has two general-purpose counter/timers which are upward
compatible with the 80C51 Timer 0 and Timer 1. Both can be configured to operate either
as timers or event counters (see Ta bl e 35
upon timer overflow has been added.
In the ‘Timer’ function, the timer is incremented every PCLK.
In the ‘Counter’ function, the register is incremented in response to a 1-to-0 transition on
its corresponding external input pin (T0 or T1). The external input is sampled once during
every machine cycle. When the pin is high during one cycle and low in the next cycle, the
count is incremented. The new count value appears in the register during the cycle
following the one in which the transition was detected. Since it takes two machine cycles
(four CPU clocks) to recognize a 1-to-0 transition, the maximum count rate is
CPU clock frequency. There are no restrictions on the duty cycle of the external input
signal, but to ensure that a given level is sampled at least once before it changes, it should
be held for at least one full machine cycle.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
). An option to automatically toggle the Tx pin
1
⁄4 of the
The ‘Timer’ or ‘Counter’ function is selected by control bits TnC/T
and 1 respectively) in the Special Function Register TMOD. Timer 0 and Timer 1 have five
operating modes (modes 0, 1, 2, 3 and 6), which are selected by bit-pairs (TnM1, TnM0)
in TMOD and TnM2 in TAMOD. Modes 0, 1, 2 and 6 are the same for both
Timers/Counters. Mode 3 is different. The operating modes are described later in this
section.
Table 34: Timer/Counter Mode register (TMOD - address 89h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol T1GATE T1C/T
Reset00000000
Table 35: Timer/Counter Mode register (TMOD - address 89h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 T0M0 Mode Select for Timer 0. These bits are used with the T0M2 bit in the TAMOD register to determine the
1T0M1
2T0C/T
3 T0GATE Gating control for Timer 0. When set, Timer/Counter is enabled only while the INT0
Timer 0 mode (see Ta b le 3 7
Timer or Counter selector for Timer 0. Cleared for Timer operation (input from CCLK). Set for Counter
operation (input from T0 input pin).
control pin is set. When cleared, Timer 0 is enabled when the TR0 control bit is set.
T1M1 T1M0 T0GATE T0C/T T0M1 T0M0
).
(x = 0 and 1 for Timers 0
pin is high and the TR0
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 51 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 35: Timer/Counter Mode register (TMOD - address 89h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
4 T1M0 Mode Select for Timer 1. These bits are used with the T1M2 bit in the TAMOD register to determine the
5T1M1
6T1C/T
7 T1GATE Gating control for Timer 1. When set, Timer/Counter is enabled only while the INT1
Table 36: Timer/Counter Auxiliary Mode register (TAMOD - address 8Fh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol----T1M2---T0M2
Resetxxx0xxx0
Table 37: Timer/Counter Auxiliary Mode register (TAMOD - address 8Fh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 T0M2 Mode Select for Timer 0. These bits are used with the T0M2 bit in the TAMOD register to determine the
1:3 - reserved
4 T1M2 Mode Select for Timer 1. These bits are used with the T1M2 bit in the TAMOD register to determine the
5:7 - reserved
Timer 1 mode (see Ta b le 3 7 ).
Timer or Counter Selector for Timer 1. Cleared for Timer operation (input from CCLK). Set for Counter
operation (input from T1 input pin).
control pin is set. When cleared, Timer 1 is enabled when the TR1 control bit is set.
Timer 0 mode (see Ta b le 3 7
Timer 1 mode (see Ta b le 3 7
The following timer modes are selected by timer mode bits TnM[2:0]:
000 — 8048 Timer ‘TLn’ serves as 5-bit prescaler. (Mode 0)
001 — 16-bit Timer/Counter ‘THn’ and ‘TLn’ are cascaded; there is no prescaler.(Mode 1)
010 — 8-bit auto-reload Timer/Counter. THn holds a value which is loaded into TLn when it overflows.
(Mode 2)
011 — Timer 0 is a dual 8-bit Timer/Counter in this mode. TL0 is an 8-bit Timer/Counter controlled by the
standard Timer 0 control bits. TH0 is an 8-bit timer only, controlled by the Timer 1 control bits (see text).
Timer 1 in this mode is stopped. (Mode 3)
100 — Reserved. User must not configure to this mode.
101 — Reserved. User must not configure to this mode.
110 — PWM mode (see Section 8.5
111 — Reserved. User must not configure to this mode.
).
).
).
…continued
pin is high and the TR1
8.1 Mode 0
Putting either Timer into Mode 0 makes it look like an 8048 Timer, which is an 8-bit
Counter with a divide-by-32 prescaler. Figure 18
In this mode, the Timer register is configured as a 13-bit register. As the count rolls over
from all 1s to all 0s, it sets the Timer interrupt flag TFn. The count input is enabled to the
Timer when TRn = 1 and either TnGATE = 0 or INTn
Timer to be controlled by external input INTn
TRn is a control bit in the Special Function Register TCON (Tab le 3 9
in the TMOD register.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 52 of 147
shows Mode 0 operation.
= 1. (Setting TnGATE = 1 allows the
, to facilitate pulse width measurements).
). The TnGATE bit is

Philips Semiconductors
The 13-bit register consists of all 8 bits of THn and the lower 5 bits of TLn. The upper 3
bits of TLn are indeterminate and should be ignored. Setting the run flag (TRn) does not
clear the registers.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Mode 0 operation is the same for Timer 0 and Timer 1. See Figure 18
different GATE bits, one for Timer 1 (TMOD.7) and one for Timer 0 (TMOD.3).
. There are two
8.2 Mode 1
Mode 1 is the same as Mode 0, except that all 16 bits of the timer register (THn and TLn)
are used. See Figure 19
.
8.3 Mode 2
Mode 2 configures the Timer register as an 8-bit Counter (TLn) with automatic reload, as
shown in Figure 20
contents of THn, which must be preset by software. The reload leaves THn unchanged.
Mode 2 operation is the same for Timer 0 and Timer 1.
. Overflow from TLn not only sets TFn, but also reloads TLn with the
8.4 Mode 3
When Timer 1 is in Mode 3 it is stopped. The effect is the same as setting TR1 = 0.
Timer 0 in Mode 3 establishes TL0 and TH0 as two separate 8-bit counters. The logic for
Mode 3 on Timer 0 is shown in Figure 21
T0GATE, TR0, INT0
cycles) and takes over the use of TR1 and TF1 from Timer 1. Thus, TH0 now controls the
‘Timer 1’ interrupt.
, and TF0. TH0 is locked into a timer function (counting machine
. TL0 uses the Timer 0 control bits: T0C/T,
Mode 3 is provided for applications that require an extra 8-bit timer. With Timer 0 in Mode
3, an P89LPC933/934/935/936 device can look like it has three Timer/Counters.
Note: When Timer 0 is in Mode 3, Timer 1 can be turned on and off by switching it into and
out of its own Mode 3. It can still be used by the serial port as a baud rate generator, or in
any application not requiring an interrupt.
8.5 Mode 6
In this mode, the corresponding timer can be changed to a PWM with a full period of 256
timer clocks (see Figure 22
). Its structure is similar to mode 2, except that:
• TFn (n = 0 and 1 for Timers 0 and 1 respectively) is set and cleared in hardware;
• The low period of the TFn is in THn, and should be between 1 and 254, and;
• The high period of the TFn is always 256−THn.
• Loading THn with 00h will force the Tx pin high, loading THn with FFh will force the Tx
pin low.
Note that interrupt can still be enabled on the low to high transition of TFn, and that TFn
can still be cleared in software like in any other modes.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 53 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 38: Timer/Counter Control register (TCON) - address 88h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
Reset00000000
Table 39: Timer/Counter Control register (TCON - address 88h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 IT0 Interrupt 0 Type control bit. Set/cleared by software to specify falling edge/low level triggered external
interrupts.
1 IE0 Interrupt 0 Edge flag. Set by hardware when external interrupt 0 edge is detected. Cleared by hardware
when the interrupt is processed, or by software.
2 IT1 Interrupt 1 Type control bit. Set/cleared by software to specify falling edge/low level triggered external
interrupts.
3 IE1 Interrupt 1 Edge flag. Set by hardware when external interrupt 1 edge is detected. Cleared by hardware
when the interrupt is processed, or by software.
4 TR0 Timer 0 Run control bit. Set/cleared by software to turn Timer/Counter 0 on/off.
5 TF0 Timer 0 overflow flag. Set by hardware on Timer/Counter overflow. Cleared by hardware when the processor
vectors to the interrupt routine, or by software. (except in mode 6, where it is cleared in hardware)
6 TR1 Timer 1 Run control bit. Set/cleared by software to turn Timer/Counter 1 on/off
7 TF1 Timer 1 overflow flag. Set by hardware on Timer/Counter overflow. Cleared by hardware when the interrupt
is processed, or by software (except in mode 6, see above, when it is cleared in hardware).
PCLK
Tn pin
TRn
gate
INTn pin
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
control
Fig 18. Timer/counter 0 or 1 in Mode 0 (13-bit counter).
PCLK
Tn pin
TRn
gate
INTn pin
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
control
TLn
(5-bits)
TLn
(8-bits)
THn
(8-bits)
THn
(8-bits)
toggle
overflow
toggle
overflow
TFn
ENTn
002aaa919
TFn
ENTn
002aaa920
interrupt
Tn pin
interrupt
Tn pin
Fig 19. Timer/counter 0 or 1 in mode 1 (16-bit counter).
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 54 of 147
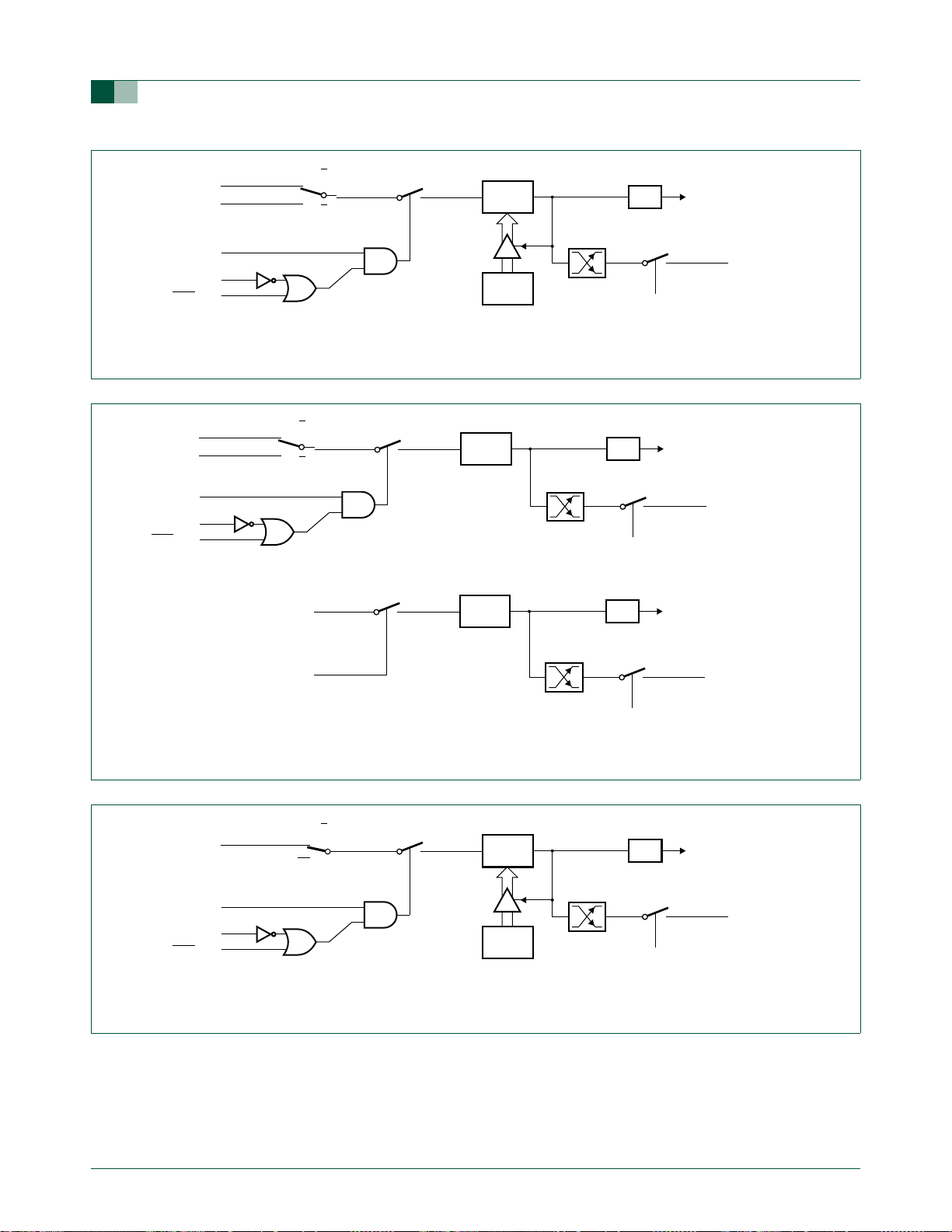
Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
PCLK
Tn pin
TRn
gate
INTn pin
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
control
Fig 20. Timer/counter 0 or 1 in Mode 2 (8-bit auto-reload).
PCLK
T0 pin
TR0
gate
INT0 pin
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
osc/2
TR1
control
control
TL0
(8-bits)
TH0
(8-bits)
TLn
(8-bits)
THn
(8-bits)
reload
overflow
overflow
toggle
overflow
toggle
toggle
TFn
ENTn
002aaa921
TF0
ENT0
(AUXR1.4)
TF1
interrupt
Tn pin
interrupt
T0 pin
(P1.2 open drain)
interrupt
T1 pin
(P0.7)
ENT1
(AUXR1.5)
002aaa922
Fig 21. Timer/counter 0 Mode 3 (two 8-bit counters).
PCLK
TRn
gate
INTn pin
C/T = 0
control
TLn
(8-bits)
THn
(8-bits)
overflow
reload THn on falling transition
and (256 − THn) on rising transition
toggle
TFn
ENTn
002aaa923
interrupt
Tn pin
Fig 22. Timer/counter 0 or 1 in mode 6 (PWM auto-reload).
8.6 Timer overflow toggle output
Timers 0 and 1 can be configured to automatically toggle a port output whenever a timer
overflow occurs. The same device pins that are used for the T0 and T1 count inputs and
PWM outputs are also used for the timer toggle outputs. This function is enabled by
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 55 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
control bits ENT0 and ENT1 in the AUXR1 register, and apply to Timer 0 and Timer 1
respectively. The port outputs will be a logic 1 prior to the first timer overflow when this
mode is turned on. In order for this mode to function, the C/T bit must be cleared selecting
PCLK as the clock source for the timer.
9. Real-time clock system timer
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has a simple Real-time Clock/System Timer that allows a
user to continue running an accurate timer while the rest of the device is powered down.
The Real-time Clock can be an interrupt or a wake-up source (see Figure 23
The Real-time Clock is a 23-bit down counter. The clock source for this counter can be
either the CPU clock (CCLK) or the XTAL1-2 oscillator, provided that the XTAL1-2
oscillator is not being used as the CPU clock. If the XTAL1-2 oscillator is used as the CPU
clock, then the RTC will use CCLK as its clock source regardless of the state of the
RTCS1:0 in the RTCCON register. There are three SFRs used for the RTC:
RTCCON — Real-time Clock control.
RTCH — Real-time Clock counter reload high (bits 22 to 15).
RTCL — Real-time Clock counter reload low (bits 14 to 7).
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
).
The Real-time clock system timer can be enabled by setting the RTCEN (RTCCON.0) bit.
The Real-time Clock is a 23-bit down counter (initialized to all 0’s when RTCEN = 0) that is
comprised of a 7-bit prescaler and a 16-bit loadable down counter. When RTCEN is
written with logic 1, the counter is first loaded with (RTCH, RTCL, ‘1111111’) and will
count down. When it reaches all 0’s, the counter will be reloaded again with (RTCH,
RTCL, ‘1111111’) and a flag - RTCF (RTCCON.7) - will be set.
RTCH RTCL RTC RESET
RELOAD ON UNDERFLOW
MSB LSB
23-BIT DOWN COUNTER
wake-up from power-down
Interrupt if enabled
(shared with WDT)
ERTC
RTCF
RTC underflow flag
power-on
reset
7-BIT PRESCALER
÷128
RTCEN
RTC enable
XTAL2 XTAL1
LOW FREQUENCY
MEDIUM FREQUENCY
HIGH FREQUENCY
CCLK
internal
oscillators
RTCS1 RTCS2
RTC clk select
002aaa924
Fig 23. Real-time clock/system timer block diagram.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 56 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
9.1 Real-time clock source
RTCS1/RTCS0 (RTCCON[6:5]) are used to select the clock source for the RTC if either
the Internal RC oscillator or the internal WD oscillator is used as the CPU clock. If the
internal crystal oscillator or the external clock input on XTAL1 is used as the CPU clock,
then the RTC will use CCLK as its clock source.
9.2 Changing RTCS1/RTCS0
RTCS1/RTCS0 cannot be changed if the RTC is currently enabled (RTCCON.0 = 1).
Setting RTCEN and updating RTCS1/RTCS0 may be done in a single write to RTCCON.
However, if RTCEN = 1, this bit must first be cleared before updating RTCS1/RTCS0.
9.3 Real-time clock interrupt/wake-up
If ERTC (RTCCON.1), EWDRT (IEN1.0.6) and EA (IEN0.7) are set to logic 1, RTCF can
be used as an interrupt source. This interrupt vector is shared with the watchdog timer. It
can also be a source to wake-up the device.
9.4 Reset sources affecting the Real-time clock
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Only power-on reset will reset the Real-time Clock and its associated SFRs to their default
state.
Table 40: Real-time Clock/System Timer clock sources
FOSC2:0 RCCLK RTCS1:0 RTC clock source CPU clock source
000 0 00 High frequency crystal High frequency crystal
1 00 High frequency crystal Internal RC oscillator
001 0 00 Medium frequency crystal Medium frequency crystal
1 00 Medium frequency crystal Internal RC oscillator
01
10
11 High frequency crystal
/DIVM
01
10
11 Internal RC oscillator
01
10
11 Medium frequency crystal
/DIVM
01
10
11 Internal RC oscillator
/DIVM
/DIVM
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 57 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 40: Real-time Clock/System Timer clock sources
FOSC2:0 RCCLK RTCS1:0 RTC clock source CPU clock source
010 0 00 Low frequency crystal Low frequency crystal
01
10
11 Low frequency crystal
/DIV
1 00 Low frequency crystal Internal RC oscillator
01
10
11 Internal RC oscillator
011 0 00 High frequency crystal Internal RC oscillator
01 Medium frequency crystal
10 Low frequency crystal
11 Internal RC oscillator
/DIVM
1 00 High frequency crystal Internal RC oscillator
01 Medium frequency crystal
10 Low frequency crystal
11 Internal RC oscillator
100 0 00 High frequency crystal Watchdog oscillator
01 Medium frequency crystal
10 Low frequency crystal
11 Watchdog oscillator /DIVM
1 00 High frequency crystal Internal RC oscillator
01 Medium frequency crystal
10 Low frequency crystal
11 Internal RC oscillator
101 x xx undefined undefined
110 x xx undefined undefined
111 0 00 External clock input External clock input
01
10
11 External clock input /DIVM
1 00 External clock input Internal RC oscillator
01
10
11 Internal RC oscillator
…continued
/DIVM
/DIVM
/DIVM
/DIVM
Table 41: Real-time Clock Control register (RTCCON - address D1h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol RTCF RTCS1 RTCS0 - - - ERTC RTCEN
Reset011xxx00
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 58 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 42: Real-time Clock Control register (RTCCON - address D1h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 RTCEN Real-time Clock enable. The Real-time Clock will be enabled if this bit is logic 1.
Note that this bit will not power-down the Real-time Clock. The RTCPD bit
(PCONA.7) if set, will power-down and disable this block regardless of RTCEN.
1 ERTC Real-time Clock interrupt enable. The Real-time Clock shares the same interrupt
as the watchdog timer. Note that if the user configuration bit WDTE (UCFG1.7)
is logic 0, the watchdog timer can be enabled to generate an interrupt. Users
can read the RTCF (RTCCON.7) bit to determine whether the Real-time Clock
caused the interrupt.
2:4 - reserved
5 RTCS0 Real-time Clock source select (see Ta bl e 4 0
6RTCS1
7 RTCF Real-time Clock Flag. This bit is set to logic 1 when the 23-bit Real-time Clock
reaches a count of logic 0. It can be cleared in software.
10. Capture/Compare Unit (CCU)
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
).
This unit features:
• A 16-bit timer with 16-bit reload on overflow
• Selectable clock (CCUCLK), with a prescaler to divide the clock source by any integer
between 1 and 1024.
• Four Compare / PWM outputs with selectable polarity
• Symmetrical / Asymmetrical PWM selection
• Seven interrupts with common interrupt vector (one Overflow, 2xCapture,
4xCompare), safe 16-bit read/write via shadow registers.
• Two Capture inputs with event counter and digital noise rejection filter
10.1 CCU Clock (CCUCLK)
The CCU runs on the CCUCLK, which can be either PCLK in basic timer mode or the
output of a PLL (see Figure 24
0.5 MHz to 1 MHz that is multiplied by 32 to produce a CCUCLK between 16 MHz and
32 MHz in PWM mode (asymmetrical or symmetrical). The PLL contains a 4-bit divider
(PLLDV3:0 bits in the TCR21 register) to help divide PCLK into a frequency between
0.5 MHz and 1 MHz
10.2 CCU Clock prescaling
This CCUCLK can further be divided down by a prescaler. The prescaler is implemented
as a 10-bit free-running counter with programmable reload at overflow. Writing a value to
the prescaler will cause the prescaler to restart.
). The PLL is designed to use a clock source between
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 59 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
16-BIT SHADOW REGISTER
TOR2H TO TOR2L
16-BIT TIMER RELOAD
REGISTER
16-BIT SHADOW REGISTER
OCRxH TO OCRxL
TIMER > COMPARE
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
16-BIT COMPARE
VALUE
OCD
OCC
OCB
OCA
OVERFLOW/
UNDERFLOW
16-BIT UP/DOWN TIMER
WITH RELOAD
10-BIT DIVIDER
4-BIT
DIVIDER
Fig 24. Capture Compare Unit block diagram.
32 × PLL
10.3 Basic timer operation
The Timer is a free-running up/down counter counting at the pace determined by the
prescaler. The timer is started by setting the CCU Mode Select bits TMOD21 and
TMOD20 in the CCU Control Register 0 (TCR20) as shown in the table in the TCR20
register description (Ta bl e 4 7
The CCU direction control bit, TDIR2, determines the direction of the count. TDIR2 = 0:
Count up, TDIR2 = 1: Count down. If the timer counting direction is changed while the
counter is running, the count sequence will be reversed in the CCUCLK cycle following the
write of TDIR2. The timer can be written or read at any time and newly-written values will
take effect when the prescaler overflows. The timer is accessible through two SFRs,
TL2(low byte) and TH2(high byte). A third 16-bit SFR, TOR2H:TOR2L, determines the
overflow reload value. TL2, TH2 and TOR2H, TOR2L will be 0 after a reset
COMPARE CHANNELS A TO D
16-BIT CAPTURE
REGISTER ICRxH, L
COUNTER
INTERRUPT FLAG
TICF2x SET
).
FCOx
ICNFx
EVENT
CAPTURE CHANNELS A, B
NOISE
FILTER
ICESx
EDGE
SELECT
002aab009
ICB
ICA
Up-counting: When the timer contents are FFFFH, the next CCUCLK cycle will set the
counter value to the contents of TOR2H:TOR2L.
Down-counting: When the timer contents are 0000H, the next CCUCLK cycle will set the
counter value to the contents of TOR2H:TOR2L. During the CCUCLK cycle when the
reload is performed, the CCU Timer Overflow Interrupt Flag (TOIF2) in the CCU Interrupt
Flag Register (TIFR2) will be set, and, if the EA bit in the IEN0 register and ECCU bit in
the IEN1 register (IEN1.4) are set, program execution will vector to the overflow interrupt.
The user has to clear the interrupt flag in software by writing a logic 0 to it.
When writing to the reload registers, TOR2H and TOR2L, the values written are stored in
two 8-bit shadow registers. In order to latch the contents of the shadow registers into
TOR2H and TOR2L, the user must write a logic 1 to the CCU Timer Compare/Overflow
Update bit TCOU2, in CCU Timer Control Register 1 (TCR21). The function of this bit
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 60 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
depends on whether the timer is running in PWM mode or in basic timer mode. In basic
timer mode, writing a one to TCOU2 will cause the values to be latched immediately and
the value of TCOU2 will always read as zero. In PWM mode, writing a one to TCOU2 will
cause the contents of the shadow registers to be updated on the next CCU Timer
overflow. As long as the latch is pending, TCOU2 will read as one and will return to zero
when the latching takes place. TCOU2 also controls the latching of the Output Compare
registers OCR2A, OCR2B and OCR2C.
When writing to timer high byte, TH2, the value written is stored in a shadow register.
When TL2 is written, the contents of TH2’s shadow register is transferred to TH2 at the
same time that TL2 gets updated. Thus, TH2 should be written prior to writing to TL2. If a
write to TL2 is followed by another write to TL2, without TH2 being written in between, the
value of TH2 will be transferred directly to the high byte of the timer.
If the 16-bit CCU Timer is to be used as an 8-bit timer, the user can write FFh (for
upcounting) or 00h (for downcounting) to TH2. When TL2 is written, FFh:TH2 (for
upcounting) and 00h (for downcounting) will be loaded to CCU Timer. The user will not
need to rewrite TH2 again for an 8-bit timer operation unless there is a change in count
direction
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
When reading the timer, TL2 must be read first. When TL2 is read, the contents of the
timer high byte are transferred to a shadow register in the same PCLK cycle as the read is
performed. When TH2 is read, the contents of the shadow register are read instead. If a
read from TL2 is followed by another read from TL2 without TH2 being read in between,
the high byte of the timer will be transferred directly to TH2.
Table 43: CCU prescaler control register, high byte (TPCR2H - address CBh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol------TPCR2H.1TPCR2H.0
Resetxxxxxx00
Table 44: CCU prescaler control register, high byte (TPCR2H - address CBh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 TPCR2H.0 Prescaler bit 8
1 TPCR2H.1 Prescaler bit 9
Table 45: CCU prescaler control register, low byte (TPCR2L - address CAh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol TPCR2L.7 TPCR2L.6 TPCR2L.5 TPCR2L.4 TPCR2L.3 TPCR2L.2 TPCR2L.1 TPCR2L.0
Reset00000000
Table 46: CCU prescaler control register, low byte (TPCR2L - address CAh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 TPCR2L.0 Prescaler bit 0
1 TPCR2L.1 Prescaler bit 1
2 TPCR2L.2 Prescaler bit 2
3 TPCR2L.3 Prescaler bit 3
4 TPCR2L.4 Prescaler bit 4
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 61 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 46: CCU prescaler control register, low byte (TPCR2L - address CAh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
5 TPCR2L.5 Prescaler bit 5
6 TPCR2L.6 Prescaler bit 6
7 TPCR2L.7 Prescaler bit 7
Table 47: CCU control register 0 (TCR20 - address C8h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol PLLEN HLTRN HLTEN ALTCD ALTAB TDIR2 TMOD21 TMOD20
Reset00000000
Table 48: CCU control register 0 (TCR20 - address C8h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
1:2 TMOD20/21 CCU Timer mode (TMOD21, TMOD20):
00 — Timer is stopped
01 — Basic timer function
10 — Asymmetrical PWM (uses PLL as clock source)
11 — Symmetrical PWM (uses PLL as clock source)
2 TDIR2 Count direction of the CCU Timer. When logic 0, count up, When logic 1, count down.
3 ALTAB PWM channel A/B alternately output enable. When this bit is set, the output of PWM channel A and B
are alternately gated on every counter cycle.
4 ALTCD PWM channel C/D alternately output enable. When this bit is set, the output of PWM channel C and D
are alternately gated on every counter cycle.
5 HLTEN PWM Halt Enable. When logic 1, a capture event as enabled for Input Capture A pin will immediately
stop all activity on the PWM pins and set them to a predetermined state.
6 HLTRN PWM Halt. When set indicates a halt took place. In order to re-activate the PWM, the user must clear
the HLTRN bit.
7 PLLEN Phase Locked Loop Enable. When set to logic 1, starts PLL operation. After the PLL is in lock this bit it
will read back a one.
10.4 Output compare
The four output compare channels A, B, C and D are controlled through four 16-bit SFRs,
OCRAH:OCRAL, OCRBH:OCRBL, OCRCH:OCRCL, OCRDH: OCRDL. Each output
compare channel needs to be enabled in order to operate. The channel is enabled by
selecting a Compare Output Action by setting the OCMx1:0 bits in the Capture Compare x
Control Register – CCCRx (x = A, B, C, D). When a compare channel is enabled, the user
will have to set the associated I/O pin to the desired output mode to connect the pin.
(Note: The SFR bits for port pins P2.6, P1.6, P1.7, P2.1 must be set to logic 1 in order for
the compare channel outputs to be visible at the port pins.) When the contents of TH2:TL2
match that of OCRxH:OCRxL, the Timer Output Compare Interrupt Flag - TOCFx is set in
TIFR2. This happens in the CCUCLK cycle after the compare takes place. If EA and the
Timer Output Compare Interrupt Enable bit – TOCIE2x (in TICR2 register), as well as
ECCU bit in IEN1 are all set, the program counter will be vectored to the corresponding
interrupt. The user must manually clear the bit by writing a logic 0 to it.
Two bits in OCCRx, the Output Compare x Mode bits OCMx1 and OCMx0 select what
action is taken when a compare match occurs. Enabled compare actions take place even
if the interrupt is disabled.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 62 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
In order for a Compare Output Action to occur, the compare values must be within the
counting range of the CCU timer.
When the compare channel is enabled, the I/O pin (which must be configured as an
output) will be connected to an internal latch controlled by the compare logic. The value of
this latch is zero from reset and can be changed by invoking a forced compare. A forced
compare is generated by writing a logic 1 to the Force Compare x Output bit – FCOx bit in
OCCRx. Writing a one to this bit generates a transition on the corresponding I/O pin as set
up by OCMx1/OCMx0 without causing an interrupt. In basic timer operating mode the
FCOx bits always read zero. (Note: This bit has a different function in PWM mode.) When
an output compare pin is enabled and connected to the compare latch, the state of the
compare pin remains unchanged until a compare event or forced compare occurs.
Table 49: Capture compare control register (CCRx - address Exh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol ICECx2 ICECx1 ICECx0 ICESx ICNFx FCOx OCMx1 OCMx0
Reset00000000
Table 50: Capture compare control register (CCRx - address Exh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 OCMx0 Output Compare x Mode. See
1OCMx1
2 FCOx Force Compare X Output Bit. When set, invoke a force compare.
3 ICNFx Input Capture x Noise Filter Enable Bit. When logic 1, the capture logic needs to see four consecutive
samples of the same value in order to recognize an edge as a capture event. The inputs are sampled
every two CCLK periods regardless of the speed of the timer.
4 ICESx Input Capture x Edge Select Bit. When logic 0: Negative edge triggers a capture, When logic 1: Positive
edge triggers a capture.
5 ICECx0 Capture Delay Setting Bit 0. See Ta bl e 5 1
6 ICECx1 Capture Delay Setting Bit 1. See Ta bl e 5 1
7 ICECx2 Capture Delay Setting Bit 2. See Ta bl e 5 1
for details.
for details.
for details.
UM10116
When the user writes to change the output compare value, the values written to OCRH2x
and OCRL2x are transferred to two 8-bit shadow registers. In order to latch the contents of
the shadow registers into the capture compare register, the user must write a logic 1 to the
CCU Timer Compare/Overflow Update bit TCOU2, in the CCU Control Register 1 TCR21. The function of this bit depends on whether the timer is running in PWM mode or
in basic timer mode. In basic timer mode, writing a one to TCOU2 will cause the values to
be latched immediately and the value of TCOU2 will always read as zero. In PWM mode,
writing a one to TCOU2 will cause the contents of the shadow registers to be updated on
the next CCU Timer overflow. As long as the latch is pending, TCOU2 will read as one and
will return to zero when the latch takes place. TCOU2 also controls the latching of all the
Output Compare registers as well as the Timer Overflow Reload registers - TOR2.
10.5 Input capture
Input capture is always enabled. Each time a capture event occurs on one of the two input
capture pins, the contents of the timer is transferred to the corresponding 16-bit input
capture register ICRAH:ICRAL or ICRBH:ICRBL. The capture event is defined by the
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 63 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Input Capture Edge Select – ICESx bit (x being A or B) in the CCCRx register. The user
will have to configure the associated I/O pin as an input in order for an external event to
trigger a capture.
A simple noise filter can be enabled on the input capture input. When the Input Capture
Noise Filter ICNFx bit is set, the capture logic needs to see four consecutive samples of
the same value in order to recognize an edge as a capture event. The inputs are sampled
every two CCLK periods regardless of the speed of the timer.
An event counter can be set to delay a capture by a number of capture events. The three
bits ICECx2, ICECx1 and ICECx0 in the CCCRx register determine the number of edges
the capture logic has to see before an input capture occurs.
When a capture event is detected, the Timer Input Capture x (x is A or B) Interrupt Flag –
TICF2x (TIFR2.1 or TIFR2.0) is set. If EA and the Timer Input Capture x Enable bit –
TICIE2x (TICR2.1 or TICR2.0) is set as well as the ECCU (IEN1.4) bit is set, the program
counter will be vectored to the corresponding interrupt. The interrupt flag must be cleared
manually by writing a logic 0 to it.
When reading the input capture register, ICRxL must be read first. When ICRxL is read,
the contents of the capture register high byte are transferred to a shadow register. When
ICRxH is read, the contents of the shadow register are read instead. (If a read from ICRxL
is followed by another read from ICRxL without ICRxH being read in between, the new
value of the capture register high byte (from the last ICRxL read) will be in the shadow
register).
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 51: Event delay counter for input capture
ICECx2 ICECx1 ICECx0 Delay (numbers of edges)
0000
0011
0102
0113
1004
1015
1107
11115
10.6 PWM operation
PWM Operation has two main modes, asymmetrical and symmetrical. These modes of
timer operation are selected by writing 10H or 11H to TMOD21:TMOD20 as shown in
Section 10.3 “
In asymmetrical PWM operation, the CCU Timer operates in downcounting mode
regardless of the setting of TDIR2. In this case, TDIR2 will always read 1.
In symmetrical mode, the timer counts up/down alternately and the value of TDIR2 has no
effect. The main difference from basic timer operation is the operation of the compare
module, which in PWM mode is used for PWM waveform generation. Ta bl e 5 2
behavior of the compare pins in PWM mode.
Basic timer operation”.
shows the
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 64 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
3
The user will have to configure the output compare pins as outputs in order to enable the
PWM output. As with basic timer operation, when the PWM (compare) pins are connected
to the compare logic, their logic state remains unchanged. However, since the bit FCO is
used to hold the halt value, only a compare event can change the state of the pin.
Fig 25. Asymmetrical PWM, downcounting.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
TOR2
compare value
timer value
0x0000
non-inverted
inverted
002aaa89
TOR2
compare value
timer value
non-inverted
inverted
Fig 26. Symmetrical PWM.
The CCU Timer Overflow interrupt flag is set when the counter changes direction at the
top. For example, if TOR contains 01FFH, CCU Timer will count: …01FEH, 01FFH,
01FEH,… The flag is set in the counter cycle after the change from TOR to TOR-1.
When the timer changes direction at the bottom, in this example, it counts …,0001H,
0000H, 0001H,… The CCU Timer overflow interrupt flag is set in the counter CCUCLK
cycle after the transition from 0001H to 0000H.
The status of the TDIR2 bit in TCR20 reflects the current counting direction. Writing to this
bit while operating in symmetrical mode has no effect.
0
002aaa894
10.7 Alternating output mode
In asymmetrical mode, the user can program PWM channels A/B and C/D as alternating
pairs for bridge drive control. By setting ALTAB or ALTCD bits in TCR20, the output of
these PWM channels are alternately gated on every counter cycle. This is shown in the
following figure:
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 65 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
TOR2
compare value A (or C)
compare value B (or D)
PWM output A (or C) (P2.6)
PWM output B (or D) (P1.6)
Fig 27. Alternate output mode.
Table 52: Output compare pin behavior
OCMx1
0 0 Output compare disabled. On power-on, this is the default state, and pins
0 1 Set when compare in
1 0 Inverted PWM. Cleared
1 1 Toggles on compare
[1]
OCMx0
timer value
0
002aaa895
[1]
Output Compare pin behavior
Basic timer mode Asymmetrical PWM Symmetrical PWM
are configured as inputs.
operation. Cleared on
compare match.
[2]
[2]
match
Non-Inverted PWM. Set
on compare match.
Cleared on CCU Timer
underflow.
on compare match. Set
on CCU Timer
underflow.
[2]
Non-Inverted PWM.
Cleared on compare
match, upcounting. Set
on compare match,
downcounting.
Inverted PWM. Set on
compare match,
upcounting. Cleared on
compare match,
downcounting.
[2]
[1] x = A, B, C, D
[2] ‘ON’ means in the CCUCLK cycle after the event takes place.
10.8 Synchronized PWM register update
When the OCRx registers are written, a built in mechanism ensures that the value is not
updated in the middle of a PWM pulse. This could result in an odd-length pulse. When the
registers are written, the values are placed in two shadow registers, as is the case in basic
timer operation mode. Writing to TCOU2 will cause the contents of the shadow registers
to be updated on the next CCU Timer overflow. If OCRxH and/or OCRxL are read before
the value is updated, the most currently written value is read.
10.9 HALT
Setting the HLTEN bit in TCR20 enables the PWM Halt Function. When halt function is
enabled, a capture event as enabled for the Input Capture A pin will immediately stop all
activity on the PWM pins and set them to a predetermined state defined by FCOx bit. In
PWM Mode, the FCOx bits in the CCCRx register hold the value the pin is forced to during
halt. The value of the setting can be read back. The capture function and the interrupt will
still operate as normal even if it has this added functionality enabled. When the PWM unit
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 66 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
is halted, the timer will still run as normal. The HLTRN bit in TCR20 will be set to indicate
that a halt took place. In order to re-activate the PWM, the user must clear the HLTRN bit.
The user can force the PWM unit into halt by writing a logic 1 to HLTRN bit.
10.10 PLL operation
The PWM module features a Phase Locked Loop that can be used to generate a
CCUCLK frequency between 16 MHz and 32 MHz. At this frequency the PWM module
provides ultrasonic PWM frequency with 10-bit resolution provided that the crystal
frequency is 1 MHz or higher (The PWM resolution is programmable up to 16 bits by
writing to TOR2H:TOR2L). The PLL is fed an input signal of 0.5 MHz to 1 MHz and
generates an output signal of 32 times the input frequency. This signal is used to clock the
timer. The user will have to set a divider that scales PCLK by a factor of 1 to 16. This
divider is found in the SFR register TCR21. The PLL frequency can be expressed as
follows:
PLL frequency = PCLK / (N+1)
Where: N is the value of PLLDV3:0.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Since N ranges in 0 to 15, the CCLK frequency can be in the range of PCLK to
Table 53: CCU control register 1 (TCR21 - address F9h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SymbolTCOU2---PLLDV.3PLLDV.2PLLDV.1PLLDV.0
Reset0xxx0000
Table 54: CCU control register 1 (TCR21 - address F9h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0:3 PLLDV.3:0 PLL frequency divider.
4:6 - Reserved.
7 TCOU2 In basic timer mode, writing a logic 1 to TCOU2 will cause the values to be latched immediately and the
value of TCOU2 will always read as logic 0. In PWM mode, writing a logic 1 to TCOU2 will cause the
contents of the shadow registers to be updated on the next CCU Timer overflow. As long as the latch is
pending, TCOU2 will read as logic 1 and will return to logic 0 when the latching takes place. TCOU2 also
controls the latching of the Output Compare registers OCRAx, OCRBx and OCRCx.
Setting the PLLEN bit in TCR20 starts the PLL. When PLLEN is set, it will not read back a
one until the PLL is in lock. At this time, the PWM unit is ready to operate and the timer
can be enabled. The following start-up sequence is recommended:
1. Set up the PWM module without starting the timer.
2. Calculate the right division factor so that the PLL receives an input clock signal of
500 kHz - 1 MHz. Write this value to PLLDV.
3. Set PLLEN. Wait until the bit reads one
4. Start the timer by writing a value to bits TMOD21, TMOD20
PCLK
⁄16.
When the timer runs from the PLL, the timer operates asynchronously to the rest of the
microcontroller. Some restrictions apply:
• The user is discouraged from writing or reading the timer in asynchronous mode. The
results may be unpredictable
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 67 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
• Interrupts and flags are asynchronous. There will be delay as the event may not
actually be recognized until some CCLK cycles later (for interrupts and reads)
10.11 CCU interrupt structure
There are seven independent sources of interrupts in the CCU: timer overflow, captured
input events on Input Capture blocks A/B, and compare match events on Output Compare
blocks A through D. One common interrupt vector is used for the CCU service routine and
interrupts can occur simultaneously in system usage. To resolve this situation, a priority
encode function of the seven interrupt bits in TIFR2 SFR is implemented (after each bit is
AND-ed with the corresponding interrupt enable bit in the TICR2 register). The order of
priority is fixed as follows, from highest to lowest:
• TOIF2
• TICF2A
• TICF2B
• TOCF2A
• TOCF2B
• TOCF2C
• TOCF2D
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
An interrupt service routine for the CCU can be as follows:
1. Read the priority-encoded value from the TISE2 register to determine the interrupt
source to be handled.
2. After the current (highest priority) event is serviced, write a logic 0 to the
corresponding interrupt flag bit in the TIFR2 register to clear the flag.
3. Read the TISE2 register. If the priority-encoded interrupt source is ‘000’, all CCU
interrupts are serviced and a return from interrupt can occur. Otherwise, return to step
2
for the next interrupt.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 68 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
EA (IEN0.7)
ECCU (IEN1.4)
TOIE2 (TICR2.7)
TOIF2 (TIFR2.7)
TICIE2A (TICR2.0)
TICF2A (TIFR2.0)
TICIE2B (TICR2.1)
TICF2B (TIFR2.1)
TOCIE2A (TICR2.3)
TOCF2A (TIFR2.3)
TOCIE2B (TICR2.4)
TOCF2B (TIFR2.4)
TOCIE2C (TICR2.5)
TOCF2C (TIFR2.5)
TOCIE2D (TICR2.6)
TOCF2D (TIFR2.6)
interrupt
sources
PRIORITY
ENCODER
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
interrupt to
other
CPU
ENCINT.0
ENCINT.1
ENCINT.2
002aaa896
Fig 28. Capture/compare unit interrupts.
Table 55: CCU interrupt status encode register (TISE2 - address DEh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol-----ENCINT.2ENCINT.1ENCINT.0
Resetxxxxx000
Table 56: CCU interrupt status encode register (TISE2 - address DEh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
2:0 ENCINT.2:0 CCU Interrupt Encode output. When multiple interrupts happen, more than one interrupt flag is set in
CCU Interrupt Flag Register (TIFR2). The encoder output can be read to determine which interrupt is
to be serviced. The user must write a logic 0 to clear the corresponding interrupt flag bit in the TIFR2
register after the corresponding interrupt has been serviced. Refer to Ta b le 5 8
000 — No interrupt pending.
001 — Output Compare Event D interrupt (lowest priority)
010 — Output Compare Event C interrupt.
011 — Output Compare Event B interrupt.
100 — Output Compare Event A interrupt.
101 — Input Capture Event B interrupt.
110 — Input Capture Event A interrupt.
111 — CCU Timer Overflow interrupt (highest priority).
3:7 - Reserved.
for TIFR2 description.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 69 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 57: CCU interrupt flag register (TIFR2 - address E9h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol TOIF2 TOCF2D TOCF2C TOCF2B TOCF2A - TICF2B TICF2A
Reset00000x00
Table 58: CCU interrupt flag register (TIFR2 - address E9h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 TICF2A Input Capture Channel A Interrupt Flag Bit. Set by hardware when an input capture event is detected.
Cleared by software.
1 TICF2B Input Capture Channel B Interrupt Flag Bit. Set by hardware when an input capture event is detected.
Cleared by software.
2 - Reserved for future use. Should not be set to logic 1 by user program.
3 TOCF2A Output Compare Channel A Interrupt Flag Bit. Set by hardware when the contents of TH2:TL2 match that
of OCRHA:OCRLA. Compare channel A must be enabled in order to generate this interrupt. If EA bit in
IEN0, ECCU bit in IEN1 and TOCIE2A bit are all set, the program counter will vectored to the
corresponding interrupt. Cleared by software.
4 TOCF2B Output Compare Channel B Interrupt Flag Bit. Set by hardware when the contents of TH2:TL2 match that
of OCRHB:OCRLB. Compare channel B must be enabled in order to generate this interrupt. If EA bit in
IEN0, ECCU bit in IEN1 and TOCIE2B bit are set, the program counter will vectored to the corresponding
interrupt. Cleared by software.
5 TOCF2C Output Compare Channel C Interrupt Flag Bit. Set by hardware when the contents of TH2:TL2 match that
of OCRHC:OCRLC. Compare channel C must be enabled in order to generate this interrupt. If EA bit in
IEN0, ECCU bit in IEN1 and TOCIE2C bit are all set, the program counter will vectored to the
corresponding interrupt. Cleared by software.
6 TOCF2D Output Compare Channel D Interrupt Flag Bit. Set by hardware when the contents of TH2:TL2 match that
of OCRHD:OCRLD. Compare channel D must be enabled in order to generate this interrupt. If EA bit in
IEN0, ECCU bit in IEN1 and TOCIE2D bit are all set, the program counter will vectored to the
corresponding interrupt. Cleared by software.
7 TOIF2 CCU Timer Overflow Interrupt Flag bit. Set by hardware on CCU Timer overflow. Cleared by software.
UM10116
Table 59: CCU interrupt control register (TICR2 - address C9h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol TOIE2 TOCIE2D TOCIE2C TOCIE2B TOCIE2A - TICIE2B TICIE2A
Reset00000x00
Table 60: CCU interrupt control register (TICR2 - address C9h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 TICIE2A Input Capture Channel A Interrupt Enable Bit. If EA bit and this bit all be set, when a capture event is
detected, the program counter will vectored to the corresponding interrupt.
1 TICIE2B Input Capture Channel B Interrupt Enable Bit. If EA bit and this bit all be set, when a capture event is
detected, the program counter will vectored to the corresponding interrupt.
2 - Reserved for future use. Should not be set to logic 1 by user program.
3 TOCIE2A Output Compare Channel A Interrupt Enable Bit. If EA bit and this bit are set to 1, when compare channel
is enabled and the contents of TH2:TL2 match that of OCRHA:OCRLA, the program counter will vectored
to the corresponding interrupt.
4 TOCIE2B Output Compare Channel B Interrupt Enable Bit. If EA bit and this bit are set to 1, when compare channel
B is enabled and the contents of TH2:TL2 match that of OCRHB:OCRLB, the program counter will
vectored to the corresponding interrupt.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 70 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 60: CCU interrupt control register (TICR2 - address C9h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
5 TOCIE2C Output Compare Channel C Interrupt Enable Bit. If EA bit and this bit are set to 1, when compare channel
C is enabled and the contents of TH2:TL2 match that of OCRHC:OCRLC, the program counter will
vectored to the corresponding interrupt.
6 TOCIE2D Output Compare Channel D Interrupt Enable Bit. If EA bit and this bit are set to 1, when compare channel
D is enabled and the contents of TH2:TL2 match that of OCRHD:OCRLD, the program counter will
vectored to the corresponding interrupt.
7 TOIE2 CCU Timer Overflow Interrupt Enable bit.
…continued
11. UART
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 has an enhanced UART that is compatible with the
conventional 80C51 UART except that Timer 2 overflow cannot be used as a baud rate
source. The P89LPC933/934/935/936 does include an independent Baud Rate
Generator. The baud rate can be selected from the oscillator (divided by a constant),
Timer 1 overflow, or the independent Baud Rate Generator. In addition to the baud rate
generation, enhancements over the standard 80C51 UART include Framing Error
detection, break detect, automatic address recognition, selectable double buffering and
several interrupt options.
The UART can be operated in 4 modes, as described in the following sections.
11.1 Mode 0
Serial data enters and exits through RxD. TxD outputs the shift clock. 8 bits are
transmitted or received, LSB first. The baud rate is fixed at
11.2 Mode 1
10 bits are transmitted (through TxD) or received (through RxD): a start bit (logic 0), 8
data bits (LSB first), and a stop bit (logic 1). When data is received, the stop bit is stored in
RB8 in Special Function Register SCON. The baud rate is variable and is determined by
the Timer 1 overflow rate or the Baud Rate Generator (see Section 11.6 “
generator and selection” on page 72).
11.3 Mode 2
11 bits are transmitted (through TxD) or received (through RxD): start bit (logic 0), 8 data
bits (LSB first), a programmable 9th data bit, and a stop bit (logic 1). When data is
transmitted, the 9th data bit (TB8 in SCON) can be assigned the value of 0 or 1. Or, for
example, the parity bit (P, in the PSW) could be moved into TB8. When data is received,
the 9th data bit goes into RB8 in Special Function Register SCON and the stop bit is not
saved. The baud rate is programmable to either
determined by the SMOD1 bit in PCON.
1
⁄16 of the CPU clock frequency.
Baud Rate
1
⁄16 or 1⁄32 of the CCLK frequency, as
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 71 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
11.4 Mode 3
11 bits are transmitted (through TxD) or received (through RxD): a start bit (logic 0), 8
data bits (LSB first), a programmable 9th data bit, and a stop bit (logic 1). Mode 3 is the
same as Mode 2 in all respects except baud rate. The baud rate in Mode 3 is variable and
is determined by the Timer 1 overflow rate or the Baud Rate Generator (see Section 11.6
“Baud Rate generator and selection” on page 72).
In all four modes, transmission is initiated by any instruction that uses SBUF as a
destination register. Reception is initiated in Mode 0 by the condition RI = 0 and REN = 1.
Reception is initiated in the other modes by the incoming start bit if REN = 1.
11.5 SFR space
The UART SFRs are at the following locations:
Table 61: UART SFR addresses
Register Description SFR location
PCON Power Control 87H
SCON Serial Port (UART) Control 98H
SBUF Serial Port (UART) Data Buffer 99H
SADDR Serial Port (UART) Address A9H
SADEN Serial Port (UART) Address Enable B9H
SSTAT Serial Port (UART) Status BAH
BRGR1 Baud Rate Generator Rate High Byte BFH
BRGR0 Baud Rate Generator Rate Low Byte BEH
BRGCON Baud Rate Generator Control BDH
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
11.6 Baud Rate generator and selection
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 enhanced UART has an independent Baud Rate
Generator. The baud rate is determined by a value programmed into the BRGR1 and
BRGR0 SFRs. The UART can use either Timer 1 or the baud rate generator output as
determined by BRGCON[2:1] (see Figure 29
the SMOD1 bit (PCON.7) is set. The independent Baud Rate Generator uses CCLK.
). Note that Timer T1 is further divided by 2 if
11.7 Updating the BRGR1 and BRGR0 SFRs
The baud rate SFRs, BRGR1 and BRGR0 must only be loaded when the Baud Rate
Generator is disabled (the BRGEN bit in the BRGCON register is logic 0). This avoids the
loading of an interim value to the baud rate generator. (CAUTION: If either BRGR0 or
BRGR1 is written when BRGEN = 1, the result is unpredictable.)
Table 62: UART baud rate generation
SCON.7
(SM0)
00XX
0100
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 72 of 147
SCON.6
(SM1)
PCON.7
(SMOD1)
10
X1
BRGCON.1
(SBRGS)
Receive/transmit baud rate for UART
CCLK
⁄
16
CCLK
⁄
(256−TH1)64
CCLK
⁄
(256−TH1)32
CCLK
⁄
((BRGR1, BRGR0)+16)

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 62: UART baud rate generation
SCON.7
(SM0)
100X
1100
Table 63: Baud Rate Generator Control register (BRGCON - address BDh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol-------SBRGSBRGEN
Resetxxxxxx0 0
Table 64: Baud Rate Generator Control register (BRGCON - address BDh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 BRGEN Baud Rate Generator Enable. Enables the baud rate generator. BRGR1 and
1 SBRGS Select Baud Rate Generator as the source for baud rates to UART in modes 1 and
2:7 - reserved
SCON.6
(SM1)
BRGR0 can only be written when BRGEN = 0.
3 (see Ta bl e 6 2
PCON.7
(SMOD1)
1X
10
X1
for details)
…continued
BRGCON.1
(SBRGS)
Receive/transmit baud rate for UART
CCLK
⁄
32
CCLK
⁄
16
CCLK
⁄
(256−TH1)64
CCLK
⁄
(256−TH1)32
CCLK
⁄
((BRGR1, BRGR0)+16)
timer 1 overflow
(PCLK-based)
baud rate generator
(CCLK-based)
Fig 29. Baud rate generation for UART (Modes 1, 3).
11.8 Framing error
A Framing error occurs when the stop bit is sensed as a logic 0. A Framing error is
reported in the status register (SSTAT). In addition, if SMOD0 (PCON.6) is 1, framing
errors can be made available in SCON.7. If SMOD0 is 0, SCON.7 is SM0. It is
recommended that SM0 and SM1 (SCON[7:6]) are programmed when SMOD0 is logic 0.
11.9 Break detect
A break detect is reported in the status register (SSTAT). A break is detected when any 11
consecutive bits are sensed low. Since a break condition also satisfies the requirements
for a framing error, a break condition will also result in reporting a framing error. Once a
break condition has been detected, the UART will go into an idle state and remain in this
idle state until a stop bit has been received. The break detect can be used to reset the
device and force the device into ISP mode by setting the EBRR bit (AUXR1.6)
÷2
SMOD1 = 1
SMOD1 = 0
SBRGS = 0
SBRGS = 1
baud rate modes 1 and 3
002aaa897
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 73 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 65: Serial Port Control register (SCON - address 98h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol SM0/FE SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
Resetxxxxxx00
Table 66: Serial Port Control register (SCON - address 98h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 RI Receive interrupt flag. Set by hardware at the end of the 8th bit time in Mode 0, or
1 TI Transmit interrupt flag. Set by hardware at the end of the 8th bit time in Mode 0, or
2 RB8 The 9th data bit that was received in Modes 2 and 3. In Mode 1 (SM2 must be 0),
3 TB8 The 9th data bit that will be transmitted in Modes 2 and 3. Set or clear by software
4 REN Enables serial reception. Set by software to enable reception. Clear by software to
5 SM2 Enables the multiprocessor communication feature in Modes 2 and 3. In Mode 2 or
6 SM1 With SM0 defines the serial port mode, see Ta bl e 6 7
7 SM0/FE The use of this bit is determined by SMOD0 in the PCON register. If SMOD0 = 0,
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
approximately halfway through the stop bit time in Mode 1. For Mode 2 or Mode 3,
if SMOD0, it is set near the middle of the 9th data bit (bit 8). If SMOD0 = 1, it is set
near the middle of the stop bit (see SM2 - SCON.5 - for exceptions). Must be
cleared by software.
at the stop bit (see description of INTLO bit in SSTAT register) in the other modes.
Must be cleared by software.
RB8 is the stop bit that was received. In Mode 0, RB8 is undefined.
as desired.
disable reception.
3, if SM2 is set to 1, then Rl will not be activated if the received 9th data bit (RB8)
is 0. In Mode 0, SM2 should be 0. In Mode 1, SM2 must be 0.
this bit is read and written as SM0, which with SM1, defines the serial port mode. If
SMOD0 = 1, this bit is read and written as FE (Framing Error). FE is set by the
receiver when an invalid stop bit is detected. Once set, this bit cannot be cleared
by valid frames but is cleared by software. (Note: UART mode bits SM0 and SM1
should be programmed when SMOD0 is logic 0 - default mode on any reset.)
.
Table 67: Serial Port modes
SM0, SM1 UART mode UART baud rate
CCLK
00 Mode 0: shift register
01 Mode 1: 8-bit UART Variable (see Ta bl e 6 2
10 Mode 2: 9-bit UART
11 Mode 3: 9-bit UART Variable (see Tab l e 6 2 )
Table 68: Serial Port Status register (SSTAT - address BAh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DBMOD INTLO CIDISDBISELFE BR OE STINT
Resetxxxxxx00
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 74 of 147
⁄16 (default mode on any reset)
)
CCLK
⁄32 or
CCLK
⁄
16

Philips Semiconductors
Table 69: Serial Port Status register (SSTAT - address BAh) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 STINT Status Interrupt Enable. When set = 1, FE, BR, or OE can cause an interrupt. The
1 OE Overrun Error flag is set if a new character is received in the receiver buffer while it
2 BR Break Detect flag. A break is detected when any 11 consecutive bits are sensed
3 FE Framing error flag is set when the receiver fails to see a valid STOP bit at the end
4 DBISEL Double buffering transmit interrupt select. Used only if double buffering is enabled.
5 CIDIS Combined Interrupt Disable. When set = 1, Rx and Tx interrupts are separate.
6 INTLO Transmit interrupt position. When cleared = 0, the Tx interrupt is issued at the
7 DBMOD Double buffering mode. When set = 1 enables double buffering. Must be logic 0 for
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
interrupt used (vector address 0023h) is shared with RI (CIDIS = 1) or the
combined TI/RI (CIDIS = 0). When cleared = 0, FE, BR, OE cannot cause an
interrupt. (Note: FE, BR, or OE is often accompanied by a RI, which will generate
an interrupt regardless of the state of STINT). Note that BR can cause a break
detect reset if EBRR (AUXR1.6) is set to logic 1.
is still full (before the software has read the previous character from the buffer), i.e.,
when bit 8 of a new byte is received while RI in SCON is still set. Cleared by
software.
low. Cleared by software.
of the frame. Cleared by software.
This bit controls the number of interrupts that can occur when double buffering is
enabled. When set, one transmit interrupt is generated after each character written
to SBUF, and there is also one more transmit interrupt generated at the beginning
(INTLO = 0) or the end (INTLO = 1) of the STOP bit of the last character sent (i.e.,
no more data in buffer). This last interrupt can be used to indicate that all transmit
operations are over. When cleared = 0, only one transmit interrupt is generated per
character written to SBUF. Must be logic 0 when double buffering is disabled. Note
that except for the first character written (when buffer is empty), the location of the
transmit interrupt is determined by INTLO. When the first character is written, the
transmit interrupt is generated immediately after SBUF is written.
When cleared = 0, the UART uses a combined Tx/Rx interrupt (like a conventional
80C51 UART). This bit is reset to logic 0 to select combined interrupts.
beginning of the stop bit. When set = 1, the Tx interrupt is issued at end of the stop
bit. Must be logic 0 for mode 0. Note that in the case of single buffering, if the Tx
interrupt occurs at the end of a STOP bit, a gap may exist before the next start bit.
UART mode 0. In order to be compatible with existing 80C51 devices, this bit is
reset to logic 0 to disable double buffering.
11.10 More about UART Mode 0
In Mode 0, a write to SBUF will initiate a transmission. At the end of the transmission, TI
(SCON.1) is set, which must be cleared in software. Double buffering must be disabled in
this mode.
Reception is initiated by clearing RI (SCON.0). Synchronous serial transfer occurs and RI
will be set again at the end of the transfer. When RI is cleared, the reception of the next
character will begin. Refer to Figure 30
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 75 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
write to
SBUF
shift
RXD (data out)
TXD (shift clock)
TI
WRITE to SCON
(clear RI)
RI
shift
RXD
(data in)
TxD (shift clock)
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16S1 ... S16S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16S1 ... S16S1 ... S16 S1 ... S16
transmit
D0 D1 D5D2 D6D3 D4 D7
receive
D0 D1 D5D2 D6D3 D4 D7
002aaa925
Fig 30. Serial Port Mode 0 (double buffering must be disabled).
11.11 More about UART Mode 1
Reception is initiated by detecting a 1-to-0 transition on RxD. RxD is sampled at a rate 16
times the programmed baud rate. When a transition is detected, the divide-by-16 counter
is immediately reset. Each bit time is thus divided into 16 counter states. At the 7th, 8th,
and 9th counter states, the bit detector samples the value of RxD. The value accepted is
the value that was seen in at least 2 of the 3 samples. This is done for noise rejection. If
the value accepted during the first bit time is not 0, the receive circuits are reset and the
receiver goes back to looking for another 1-to-0 transition. This provides rejection of false
start bits. If the start bit proves valid, it is shifted into the input shift register, and reception
of the rest of the frame will proceed.
The signal to load SBUF and RB8, and to set RI, will be generated if, and only if, the
following conditions are met at the time the final shift pulse is generated: RI = 0 and either
SM2 = 0 or the received stop bit = 1. If either of these two conditions is not met, the
received frame is lost. If both conditions are met, the stop bit goes into RB8, the 8 data
bits go into SBUF, and RI is activated.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 76 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
6
7
TX clock
write to
SBUF
shift
TxD
TI
RX
clock
RxD
shift
RI
÷16 reset
Fig 31. Serial Port Mode 1 (only single transmit buffering case is shown).
start
bit
D0 D1 D5D2 D6D3 D4 D7
start
D0 D1 D5D2 D6D3 D4 D7
bit
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
transmit
stop bit
INTLO = 0
INTLO = 1
stop bit
receive
002aaa92
TX clock
write to
SBUF
shift
TxD
RX
clock
RxD
shift
11.12 More about UART Modes 2 and 3
Reception is the same as in Mode 1.
The signal to load SBUF and RB8, and to set RI, will be generated if, and only if, the
following conditions are met at the time the final shift pulse is generated. (a) RI = 0, and
(b) Either SM2 = 0, or the received 9th data bit = 1. If either of these conditions is not met,
the received frame is lost, and RI is not set. If both conditions are met, the received 9th
data bit goes into RB8, and the first 8 data bits go into SBUF.
start
TI
÷16 reset
RI
D0 D1 D5D2 D6D3 D4 D7
bit
start
D0 D1 D5D2 D6D3 D4 D7
bit
TB8
stop bit
INTLO = 0 INTLO = 1
RB8
stop bit
SMOD0 = 0 SMOD0 = 1
transmit
receive
002aaa92
Fig 32. Serial Port Mode 2 or 3 (only single transmit buffering case is shown).
11.13 Framing error and RI in Modes 2 and 3 with SM2 = 1
If SM2 = 1 in modes 2 and 3, RI and FE behaves as in the following table.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 77 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 70: FE and RI when SM2= 1 in Modes 2 and 3
Mode PCON.6
2 0 0 No RI when RB8 = 0 Occurs during STOP
3 1 0 No RI when RB8 = 0 Will NOT occur
11.14 Break detect
A break is detected when 11 consecutive bits are sensed low and is reported in the status
register (SSTAT). For Mode 1, this consists of the start bit, 8 data bits, and two stop bit
times. For Modes 2 and 3, this consists of the start bit, 9 data bits, and one stop bit. The
break detect bit is cleared in software or by a reset. The break detect can be used to reset
the device and force the device into ISP mode. This occurs if the UART is enabled and the
the EBRR bit (AUXR1.6) is set and a break occurs.
(SMOD0)
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
RB8 RI FE
bit
1 Similar to Figure 32
occurs during RB8, one bit before FE
[32]
1 Similar to
during STOP bit
, with SMOD0 = 1, RI occurs
, with SMOD0 = 0, RI
Occurs during STOP
bit
Occurs during STOP
bit
UM10116
11.15 Double buffering
The UART has a transmit double buffer that allows buffering of the next character to be
written to SBUF while the first character is being transmitted. Double buffering allows
transmission of a string of characters with only one stop bit between any two characters,
provided the next character is written between the start bit and the stop bit of the previous
character.
Double buffering can be disabled. If disabled (DBMOD, i.e. SSTAT.7 = 0), the UART is
compatible with the conventional 80C51 UART. If enabled, the UART allows writing to
SnBUF while the previous data is being shifted out.
11.16 Double buffering in different modes
Double buffering is only allowed in Modes 1, 2 and 3. When operated in Mode 0, double
buffering must be disabled (DBMOD = 0).
11.17 Transmit interrupts with double buffering enabled (Modes 1, 2, and 3)
Unlike the conventional UART, when double buffering is enabled, the Tx interrupt is
generated when the double buffer is ready to receive new data. The following occurs
during a transmission (assuming eight data bits):
1. The double buffer is empty initially.
2. The CPU writes to SBUF.
3. The SBUF data is loaded to the shift register and a Tx interrupt is generated
immediately.
4. If there is more data, go to 6, else continue.
5. If there is no more data, then:
– If DBISEL is logic 0, no more interrupts will occur.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 78 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
8
– If DBISEL is logic 1 and INTLO is logic 0, a Tx interrupt will occur at the beginning
– If DBISEL is logic 1 and INTLO is logic 1, a Tx interrupt will occur at the end of the
– Note that if DBISEL is logic 1 and the CPU is writing to SBUF when the STOP bit of
6. If there is more data, the CPU writes to SBUF again. Then:
– If INTLO is logic 0, the new data will be loaded and a Tx interrupt will occur at the
– If INTLO is logic 1, the new data will be loaded and a Tx interrupt will occur at the
– Go to 3.
TxD
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
of the STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter (which is also the last data).
STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter (which is also the last data).
the last data is shifted out, there can be an uncertainty of whether a Tx interrupt is
generated already with the UART not knowing whether there is any more data
following.
beginning of the STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter.
end of the STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter.
write to
SBUF
Tx interrupt
single buffering (DBMOD/SSTAT.7 = 0), early interrupt (INTLO/SSTAT.6 = 0) is shown
TxD
write to
SBUF
Tx interrupt
double buffering (DBMOD/SSTAT.7 = 1), early interrupt (INTLO/SSTAT.6 = 0) is shown,
no ending Tx interrupt (DBISEL/SSTAT.4 = 0)
TxD
write to
SBUF
Tx interrupt
double buffering (DBMOD/SSTAT.7 = 1), early interrupt (INTLO/SSTAT.6 = 0) is shown,
with ending Tx interrupt (DBISEL/SSTAT.4 = 1)
Fig 33. Transmission with and without double buffering.
002aaa92
11.18 The 9th bit (bit 8) in double buffering (Modes 1, 2, and 3)
If double buffering is disabled (DBMOD, i.e. SSTAT.7 = 0), TB8 can be written before or
after SBUF is written, provided TB8 is updated before that TB8 is shifted out. TB8 must
not be changed again until after TB8 shifting has been completed, as indicated by the Tx
interrupt.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 79 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
If double buffering is enabled, TB8 MUST be updated before SBUF is written, as TB8 will
be double-buffered together with SBUF data. The operation described in the Section
11.17 “Transmit interrupts with double buffering enabled (Modes 1, 2, and 3)” on page 78
becomes as follows:
1. The double buffer is empty initially.
2. The CPU writes to TB8.
3. The CPU writes to SBUF.
4. The SBUF/TB8 data is loaded to the shift register and a Tx interrupt is generated
immediately.
5. If there is more data, go to 7, else continue on 6.
6. If there is no more data, then:
– If DBISEL is logic 0, no more interrupt will occur.
– If DBISEL is logic 1 and INTLO is logic 0, a Tx interrupt will occur at the beginning
– If DBISEL is logic 1 and INTLO is logic 1, a Tx interrupt will occur at the end of the
7. If there is more data, the CPU writes to TB8 again.
8. The CPU writes to SBUF again. Then:
– If INTLO is logic 0, the new data will be loaded and a Tx interrupt will occur at the
– If INTLO is logic 1, the new data will be loaded and a Tx interrupt will occur at the
9. Go to 4.
10.Note that if DBISEL is logic 1 and the CPU is writing to SBUF when the STOP bit of
the last data is shifted out, there can be an uncertainty of whether a Tx interrupt is
generated already with the UART not knowing whether there is any more data
following.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
of the STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter (which is also the last data).
STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter (which is also the last data).
beginning of the STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter.
end of the STOP bit of the data currently in the shifter.
11.19 Multiprocessor communications
UART modes 2 and 3 have a special provision for multiprocessor communications. In
these modes, 9 data bits are received or transmitted. When data is received, the 9th bit is
stored in RB8. The UART can be programmed such that when the stop bit is received, the
serial port interrupt will be activated only if RB8 = 1. This feature is enabled by setting bit
SM2 in SCON. One way to use this feature in multiprocessor systems is as follows:
When the master processor wants to transmit a block of data to one of several slaves, it
first sends out an address byte which identifies the target slave. An address byte differs
from a data byte in that the 9th bit is 1 in an address byte and 0 in a data byte. With
SM2 = 1, no slave will be interrupted by a data byte. An address byte, however, will
interrupt all slaves, so that each slave can examine the received byte and see if it is being
addressed. The addressed slave will clear its SM2 bit and prepare to receive the data
bytes that follow. The slaves that weren’t being addressed leave their SM2 bits set and go
on about their business, ignoring the subsequent data bytes.
Note that SM2 has no effect in Mode 0, and must be logic 0 in Mode 1.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 80 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
11.20 Automatic address recognition
Automatic address recognition is a feature which allows the UART to recognize certain
addresses in the serial bit stream by using hardware to make the comparisons. This
feature saves a great deal of software overhead by eliminating the need for the software to
examine every serial address which passes by the serial port. This feature is enabled by
setting the SM2 bit in SCON. In the 9 bit UART modes (mode 2 and mode 3), the Receive
Interrupt flag (RI) will be automatically set when the received byte contains either the
‘Given’ address or the ‘Broadcast’ address. The 9 bit mode requires that the 9th
information bit is a 1 to indicate that the received information is an address and not data.
Using the Automatic Address Recognition feature allows a master to selectively
communicate with one or more slaves by invoking the Given slave address or addresses.
All of the slaves may be contacted by using the Broadcast address. Two special Function
Registers are used to define the slave’s address, SADDR, and the address mask,
SADEN. SADEN is used to define which bits in the SADDR are to be used and which bits
are ‘don’t care’. The SADEN mask can be logically ANDed with the SADDR to create the
‘Given’ address which the master will use for addressing each of the slaves. Use of the
Given address allows multiple slaves to be recognized while excluding others. The
following examples will help to show the versatility of this scheme:
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 71: Slave 0/1 examples
Example 1 Example 2
Slave 0 SADDR = 1100 0000 Slave 1 SADDR = 1100 0000
SADEN = 1111 1101 SADEN = 1111 1110
Given = 1100 00X0 Given = 1100 000X
In the above example SADDR is the same and the SADEN data is used to differentiate
between the two slaves. Slave 0 requires a 0 in bit 0 and it ignores bit 1. Slave 1 requires
a 0 in bit 1 and bit 0 is ignored. A unique address for Slave 0 would be 1100 0010 since
slave 1 requires a 0 in bit 1. A unique address for slave 1 would be 1100 0001 since a 1 in
bit 0 will exclude slave 0. Both slaves can be selected at the same time by an address
which has bit 0 = 0 (for slave 0) and bit 1 = 0 (for slave 1). Thus, both could be addressed
with 1100 0000.
In a more complex system the following could be used to select slaves 1 and 2 while
excluding slave 0:
Table 72: Slave 0/1/2 examples
Example 1 Example 2 Example 3
Slave 0 SADDR = 1100 0000 Slave 1 SADDR = 1110 0000 Slave 2 SADDR = 1100 0000
SADEN = 1111 1001 SADEN = 1111 1010 SADEN = 1111 1100
Given = 1100
0XX0
Given = 1110 0X0X Given = 1110 00XX
In the above example the differentiation among the 3 slaves is in the lower 3 address bits.
Slave 0 requires that bit 0 = 0 and it can be uniquely addressed by 1110 0110. Slave 1
requires that bit 1 = 0 and it can be uniquely addressed by 1110 and 0101. Slave 2
requires that bit 2 = 0 and its unique address is 1110 0011. To select Slaves 0 and 1 and
exclude Slave 2 use address 1110 0100, since it is necessary to make bit 2 = 1 to exclude
slave 2. The Broadcast Address for each slave is created by taking the logical OR of
SADDR and SADEN. Zeros in this result are treated as don’t-cares. In most cases,
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 81 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
interpreting the don’t-cares as ones, the broadcast address will be FF hexadecimal. Upon
reset SADDR and SADEN are loaded with 0s. This produces a given address of all ‘don’t
cares’ as well as a Broadcast address of all ‘don’t cares’. This effectively disables the
Automatic Addressing mode and allows the microcontroller to use standard UART drivers
which do not make use of this feature.
12. I2C interface
The I2C-bus uses two wires, serial clock (SCL) and serial data (SDA) to transfer
information between devices connected to the bus, and has the following features:
• Bidirectional data transfer between masters and slaves
• Multimaster bus (no central master)
• Arbitration between simultaneously transmitting masters without corruption of serial
data on the bus
• Serial clock synchronization allows devices with different bit rates to communicate via
one serial bus
• Serial clock synchronization can be used as a handshake mechanism to suspend and
resume serial transfer
• The I
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
2
C-bus may be used for test and diagnostic purposes
UM10116
A typical I
direction bit (R/W), two types of data transfers are possible on the I
2
C-bus configuration is shown in Figure 34. Depending on the state of the
2
C-bus:
• Data transfer from a master transmitter to a slave receiver. The first byte transmitted
by the master is the slave address. Next follows a number of data bytes. The slave
returns an acknowledge bit after each received byte.
• Data transfer from a slave transmitter to a master receiver. The first byte (the slave
address) is transmitted by the master. The slave then returns an acknowledge bit.
Next follows the data bytes transmitted by the slave to the master. The master returns
an acknowledge bit after all received bytes other than the last byte. At the end of the
last received byte, a ‘not acknowledge’ is returned. The master device generates all of
the serial clock pulses and the START and STOP conditions. A transfer is ended with
a STOP condition or with a repeated START condition. Since a repeated START
condition is also the beginning of the next serial transfer, the I
released.
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 device provides a byte-oriented I
operation modes: Master Transmitter Mode, Master Receiver Mode, Slave Transmitter
Mode and Slave Receiver Mode
2
C-bus will not be
2
C interface. It has four
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 82 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
2
C-bus
I
Fig 34. I2C-bus configuration.
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 CPU interfaces with the I2C-bus through six Special
Function Registers (SFRs): I2CON (I
I2STAT (I
2
C Status Register), I2ADR (I2C Slave Address Register), I2SCLH (SCL Duty
Cycle Register High Byte), and I2SCLL (SCL Duty Cycle Register Low Byte).
12.1 I2C data register
I2DAT register contains the data to be transmitted or the data received. The CPU can read
and write to this 8-bit register while it is not in the process of shifting a byte. Thus this
register should only be accessed when the SI bit is set. Data in I2DAT remains stable as
long as the SI bit is set. Data in I2DAT is always shifted from right to left: the first bit to be
transmitted is the MSB (bit 7), and after a byte has been received, the first bit of received
data is located at the MSB of I2DAT.
P1.3/SDA P1.2/SCL
P89LPC932A1
R
OTHER DEVICE
WITH I
INTERFACE
2
C Control Register), I2DAT (I2C Data Register),
R
2
C-BUS
P
SDA
SCL
OTHER DEVICE
2
C-BUS
WITH I
INTERFACE
002aaa898
P
Table 73: I2C data register (I2DAT - address DAh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol I2DAT.7 I2DAT.6 I2DAT.5 I2DAT.4 I2DAT.3 I2DAT.2 I2DAT.1 I2DAT.0
Reset00000000
12.2 I2C slave address register
I2ADR register is readable and writable, and is only used when the I2C interface is set to
slave mode. In master mode, this register has no effect. The LSB of I2ADR is general call
bit. When this bit is set, the general call address (00h) is recognized.
Table 74: I2C slave address register (I2ADR - address DBh) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol I2ADR.6 I2ADR.5 I2ADR.4 I2ADR.3 I2ADR.2 I2ADR.1 I2ADR.0 GC
Reset00000000
2
Table 75: I
Bit Symbol Description
0 GC General call bit. When set, the general call address (00H) is recognized,
1:7 I2ADR1:7 7 bit own slave address. When in master mode, the contents of this register has
C slave address register (I2ADR - address DBh) bit description
otherwise it is ignored.
no effect.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 83 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
12.3 I2C control register
The CPU can read and write this register. There are two bits are affected by hardware: the
SI bit and the STO bit. The SI bit is set by hardware and the STO bit is cleared by
hardware.
CRSEL determines the SCL source when the I
this bit is ignored and the bus will automatically synchronize with any clock frequency up
to 400 kHz from the master I
Timer 1 overflow rate divided by 2 for the I
by the user in 8 bit auto-reload mode (Mode 2).
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
2
C-bus is in master mode. In slave mode
2
C device. When CRSEL = 1, the I2C interface uses the
2
C clock rate. Timer 1 should be programmed
Data rate of I
If f
= 12 MHz, reload value is 0 to 255, so I2C data rate range is 11.72 Kbit/sec to
osc
2
C-bus = Timer overflow rate / 2 = PCLK / (2*(256-reload value)).
3000 Kbit/sec.
When CRSEL = 0, the I
2
C interface uses the internal clock generator based on the value
of I2SCLL and I2CSCLH register. The duty cycle does not need to be 50 %.
The STA bit is START flag. Setting this bit causes the I
2
C interface to enter master mode
and attempt transmitting a START condition or transmitting a repeated START condition
when it is already in master mode.
The STO bit is STOP flag. Setting this bit causes the I
2
C interface to transmit a STOP
condition in master mode, or recovering from an error condition in slave mode.
If the STA and STO are both set, then a STOP condition is transmitted to the I
2
C-bus if it is
in master mode, and transmits a START condition afterwards. If it is in slave mode, an
internal STOP condition will be generated, but it is not transmitted to the bus.
Table 76: I2C Control register (I2CON - address D8h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol - I2EN STA STO SI AA - CRSEL
Resetx00000x0
2
Table 77: I
Bit Symbol Description
0 CRSEL SCL clock selection. When set = 1, Timer 1 overflow generates SCL, when cleared
1- reserved
2 AA The Assert Acknowledge Flag. When set to 1, an acknowledge (low level to SDA)
C Control register (I2CON - address D8h) bit description
= 0, the internal SCL generator is used base on values of I2SCLH and I2SCLL.
will be returned during the acknowledge clock pulse on the SCL line on the
following situations:
(1)The ‘own slave address’ has been received. (2)The general call address has
been received while the general call bit (GC) in I2ADR is set. (3) A data byte has
been received while the I
byte has been received while the I
Mode. When cleared to 0, an not acknowledge (high level to SDA) will be returned
during the acknowledge clock pulse on the SCL line on the following situations: (1)
A data byte has been received while the I
Mode. (2) A data byte has been received while the I
Slave Receiver Mode.
2
C interface is in the Master Receiver Mode. (4)A data
2
C interface is in the addressed Slave Receiver
2
C interface is in the Master Receiver
2
C interface is in the addressed
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 84 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 77: I
Bit Symbol Description
3SI I2C Interrupt Flag. This bit is set when one of the 25 possible I2C states is entered.
4 STO STOP Flag. STO = 1: In master mode, a STOP condition is transmitted to the
5 STA Start Flag. STA = 1: I
6I2EN I
7- reserved
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
2
C Control register (I2CON - address D8h) bit description …continued
When EA bit and EI2C (IEN1.0) bit are both set, an interrupt is requested when SI
is set. Must be cleared by software by writing 0 to this bit.
2
C-bus. When the bus detects the STOP condition, it will clear STO bit
I
automatically. In slave mode, setting this bit can recover from an error condition. In
this case, no STOP condition is transmitted to the bus. The hardware behaves as if
a STOP condition has been received and it switches to ‘not addressed’ Slave
Receiver Mode. The STO flag is cleared by hardware automatically.
2
C-bus enters master mode, checks the bus and generates a
START condition if the bus is free. If the bus is not free, it waits for a STOP
condition (which will free the bus) and generates a START condition after a delay
of a half clock period of the internal clock generator. When the I
already in master mode and some data is transmitted or received, it transmits a
repeated START condition. STA may be set at any time, it may also be set when
2
C interface is in an addressed slave mode. STA = 0: no START condition or
the I
repeated START condition will be generated.
2
C Interface Enable. When set, enables the I2C interface. When clear, the I2C
function is disabled.
2
C interface is
12.4 I2C Status register
This is a read-only register. It contains the status code of the I2C interface. The least three
bits are always 0. There are 26 possible status codes. When the code is F8H, there is no
relevant information available and SI bit is not set. All other 25 status codes correspond to
defined I
Ta bl e 8 3
Table 78: I2C Status register (I2STAT - address D9h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol STA.4 STA.3 STA.2 STA.1 STA.0 0 0 0
Reset00000000
Table 79: I
Bit Symbol Description
0:2 - Reserved, are always set to 0.
3:7 STA[0:4] I
2
C states. When any of these states entered, the SI bit will be set. Refer to
to Ta bl e 8 6 for details.
2
C Status register (I2STAT - address D9h) bit description
2
C Status code.
12.5 I2C SCL duty cycle registers I2SCLH and I2SCLL
When the internal SCL generator is selected for the I2C interface by setting CRSEL = 0 in
the I2CON register, the user must set values for registers I2SCLL and I2SCLH to select
the data rate. I2SCLH defines the number of PCLK cycles for SCL = high, I2SCLL defines
the number of PCLK cycles for SCL = low. The frequency is determined by the following
formula:
Bit Frequency = f
Where f
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 85 of 147
is the frequency of PCLK.
PCLK
/ (2*(I2SCLH + I2SCLL))
PCLK

Philips Semiconductors
The values for I2SCLL and I2SCLH do not have to be the same; the user can give different
duty cycles for SCL by setting these two registers. However, the value of the register must
ensure that the data rate is in the I
I2SCLL and I2SCLH have some restrictions and values for both registers greater than
three PCLKs are recommended.
Table 80: I2C clock rates selection
I2SCLL+
I2SCLH
6 0 - 307 154 - -
7 0 - 263 132 - -
8 0 - 230 115 - 375
9 0 - 205 102 - 333
10 0 369 184 92 - 300
15 0 246 123 61 400 200
25 0 147 74 37 240 120
30 0 123 61 31 200 100
50 0 74 37 18 120 60
60 0 61 31 15 100 50
100 0 37 18 9 60 30
150 0 25 12 6 40 20
200 0 18 9 5 30 15
- 1 3.6 Kbps to
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
2
C data rate range of 0 to 400 kHz. Thus the values of
Bit data rate (Kbit/sec) at f
CRSEL 7.373 MHz 3.6865 MHz 1.8433 MHz 12 MHz 6 MHz
osc
922 Kbps
Timer 1 in
mode 2
1.8 Kbps to
461 Kbps
Timer 1 in
mode 2
0.9 Kbps to
230 Kbps
Timer 1 in
mode 2
5.86 Kbps to
1500 Kbps
Timer 1 in
mode 2
2.93 Kbps to
750 Kbps
Timer 1 in
mode 2
12.6 I2C operation modes
12.6.1 Master Transmitter mode
In this mode data is transmitted from master to slave. Before the Master Transmitter mode
can be entered, I2CON must be initialized as follows:
Table 81: I2C Control register (I2CON - address D8h)
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- I2EN STA STO SI AA - CRSEL
value- 1000x- bit rate
CRSEL defines the bit rate. I2EN must be set to 1 to enable the I
is 0, it will not acknowledge its own slave address or the general call address in the event
of another device becoming master of the bus and it can not enter slave mode. STA, STO,
and SI bits must be cleared to 0.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 86 of 147
2
C function. If the AA bit

Philips Semiconductors
The first byte transmitted contains the slave address of the receiving device (7 bits) and
the data direction bit. In this case, the data direction bit (R/W) will be logic 0 indicating a
write. Data is transmitted 8 bits at a time. After each byte is transmitted, an acknowledge
bit is received. START and STOP conditions are output to indicate the beginning and the
end of a serial transfer.
2
The I
C-bus will enter Master Transmitter Mode by setting the STA bit. The I2C logic will
send the START condition as soon as the bus is free. After the START condition is
transmitted, the SI bit is set, and the status code in I2STAT should be 08h. This status
code must be used to vector to an interrupt service routine where the user should load the
slave address to I2DAT (Data Register) and data direction bit (SLA+W). The SI bit must be
cleared before the data transfer can continue.
When the slave address and R/W bit have been transmitted and an acknowledgment bit
has been received, the SI bit is set again, and the possible status codes are 18h, 20h, or
38h for the master mode or 68h, 78h, or 0B0h if the slave mode was enabled (setting
AA = Logic 1). The appropriate action to be taken for each of these status codes is shown
in Ta bl e 8 3
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
.
S R/W A DATA DATA
from master to slave
from slave to master
Fig 35. Format in the Master Transmitter mode.
12.6.2 Master Receiver mode
In the Master Receiver Mode, data is received from a slave transmitter. The transfer
started in the same manner as in the Master Transmitter Mode. When the START
condition has been transmitted, the interrupt service routine must load the slave address
and the data direction bit to I
the data transfer can continue.
When the slave address and data direction bit have been transmitted and an acknowledge
bit has been received, the SI bit is set, and the Status Register will show the status code.
For master mode, the possible status codes are 40H, 48H, or 38H. For slave mode, the
possible status codes are 68H, 78H, or B0H. Refer to Ta b le 8 5
A A/A Pslave address
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
2
C Data Register (I2DAT). The SI bit must be cleared before
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
P = STOP condition
002aaa929
for details.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 87 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
0
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
S R Aslave address
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
from master to slave
from slave to master
Fig 36. Format of Master Receiver mode.
DATA DATA
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
A A P
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
After a repeated START condition, I2C-bus may switch to the Master Transmitter Mode.
S R ASLA
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
from master to slave
from slave to master
Fig 37. A Master Receiver switches to Master Transmitter after sending Repeated Start.
DATA DATA
A W ASLA DATA A PA RS
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
P = STOP condition
SLA = slave address
RS = repeat START condition
002aaa93
002aaa931
12.6.3 Slave Receiver mode
In the Slave Receiver Mode, data bytes are received from a master transmitter. To
initialize the Slave Receiver Mode, the user should write the slave address to the Slave
Address Register (I2ADR) and the I
follows:
Table 82: I2C Control register (I2CON - address D8h)
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- I2EN STA STO SI AA - CRSEL
value- 10001- -
CRSEL is not used for slave mode. I2EN must be set = 1 to enable I
must be set = 1 to acknowledge its own slave address or the general call address. STA,
STO and SI are cleared to 0.
After I2ADR and I2CON are initialized, the interface waits until it is addressed by its own
address or general address followed by the data direction bit which is 0(W). If the direction
bit is 1(R), it will enter Slave Transmitter Mode. After the address and the direction bit have
been received, the SI bit is set and a valid status code can be read from the Status
Register(I2STAT). Refer to Ta bl e 8 6
2
C Control Register (I2CON) should be configured as
2
C function. AA bit
for the status codes and actions.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 88 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
S W Aslave address
from master to slave
from slave to master
Fig 38. Format of Slave Receiver mode.
12.6.4 Slave Transmitter mode
The first byte is received and handled as in the Slave Receiver Mode. However, in this
mode, the direction bit will indicate that the transfer direction is reversed. Serial data is
transmitted via P1.3/SDA while the serial clock is input through P1.2/SCL. START and
STOP conditions are recognized as the beginning and end of a serial transfer. In a given
application, the I
2
I
C hardware looks for its own slave address and the general call address. If one of these
addresses is detected, an interrupt is requested. When the microcontrollers wishes to
become the bus master, the hardware waits until the bus is free before the master mode is
entered so that a possible slave action is not interrupted. If bus arbitration is lost in the
master mode, the I
slave address in the same serial transfer.
2
C-bus may operate as a master and as a slave. In the slave mode, the
2
C-bus switches to the slave mode immediately and can detect its own
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
DATA DATA
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
P = STOP condition
RS = repeated START condition
A A/A P/RS
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
002aaa932
S R Aslave address
logic 0 = write
logic 1 = read
from master to slave
from slave to master
Fig 39. Format of Slave Transmitter mode.
DATA DATA
A = acknowledge (SDA LOW)
A = not acknowledge (SDA HIGH)
S = START condition
P = STOP condition
A A P
data transferred
(n Bytes + acknowledge)
002aaa933
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 89 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
8
P1.3/SDA
P1.2/SCL
P1.3
INPUT
FILTER
OUTPUT
STAGE
INPUT
FILTER
OUTPUT
STAGE
P1.2
timer 1
overflow
I2CON
I2SCLH
I2SCLL
ADDRESS REGISTER
COMPARATOR
SHIFT REGISTER
8
BIT COUNTER /
ARBITRATION
AND SYNC LOGIC
CONTROL
SERIAL CLOCK
GENERATOR
CONTROL REGISTERS AND
SCL DUTY CYCLE REGISTERS
I2DAT
TIMING
AND
LOGIC
I2ADR
ACK
8
CCLK
interrupt
INTERNAL BUS
status bus
I2STAT
STATUS
DECODER
STATUS REGISTER
8
002aaa899
Fig 40. I2C serial interface block diagram.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 90 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
Table 83: Master Transmitter mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
08H A START
10H A repeat START
18h SLA+W has been
20h SLA+W has been
28h Data byte in I2DAT
Status of the I2C
hardware
condition has
been transmitted
condition has
been transmitted
transmitted; ACK
has been received
transmitted;
NOT-ACK has
been received
has been
transmitted; ACK
has been received
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Application software response Next action taken by I2C
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI AA
Load SLA+W x 0 0 x SLA+W will be transmitted;
Load SLA+W or
Load SLA+R
Load data byte or000xData byte will be transmitted;
no I2DAT action or100xRepeated START will be
no I2DAT action or010xSTOP condition will be
no I2DAT action 110xSTOP condition followed by a
Load data byte or000x Data byte will be transmitted;
no I2DAT action or100xRepeated START will be
no I2DAT action or010xSTOP condition will be
no I2DAT action 110xSTOP condition followed by a
Load data byte or000x Data byte will be transmitted;
no I2DAT action or100xRepeated START will be
no I2DAT action or010xSTOP condition will be
no I2DAT action 110xSTOP condition followed by a
x 0 0 x As above; SLA+W will be
hardware
ACK bit will be received
2
transmitted; I
to Master Receiver Mode
ACK bit will be received
transmitted;
transmitted;
STO flag will be reset
START condition will be
transmitted; STO flag will be
reset.
ACK bit will be received
transmitted;
transmitted; STO flag will be
reset
START condition will be
transmitted; STO flag will be
reset
ACK bit will be received
transmitted;
transmitted; STO flag will be
reset
START condition will be
transmitted; STO flag will be
reset
C-bus switches
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 91 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 83: Master Transmitter mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
30h Data byte in I2DAT
38H Arbitration lost in
Table 84: Master Receiver mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
08H A START
10H A repeat START
38H Arbitration lost in
40h SLA+R has been
48h SLA+R has been
Status of the I2C
hardware
has been
transmitted, NOT
ACK has been
received
SLA+R/W or data
bytes
Status of the I2C
hardware
condition has
been transmitted
condition has
been transmitted
NOT ACK bit
transmitted; ACK
has been received
transmitted; NOT
ACK has been
received
…continued
Application software response Next action taken by I2C
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI AA
Load data byte or000x Data byte will be transmitted;
no I2DAT action or100xRepeated START will be
no I2DAT action or010xSTOP condition will be
no I2DAT action110x STOP condition followed by a
No I2DAT action or000xI
No I2DAT action 100xA START condition will be
Application software response Next action taken by I2C hardware
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
Load SLA+R x 0 0 x SLA+R will be transmitted; ACK bit
Load SLA+R or x 0 0 x As above
Load SLA+W SLA+W will be transmitted; I
no I2DAT action or 0 0 0 x I
no I2DAT action 1 0 0 x A START condition will be
no I2DAT action or 0 0 0 0 Data byte will be received; NOT ACK
no I2DAT action or 0 0 0 1 Data byte will be received; ACK bit
No I2DAT action or1 0 0 x Repeated START will be transmitted
no I2DAT action or 0 1 0 x STOP condition will be transmitted;
no I2DAT action or 1 1 0 x STOP condition followed by a START
STA STO SI STA
hardware
ACK bit will be received
transmitted;
transmitted; STO flag will be
reset
START condition will be
transmitted. STO flag will be
reset.
2
C-bus will be released; not
addressed slave will be entered
transmitted when the bus
becomes free.
will be received
2
C-bus
will be switched to Master Transmitter
Mode
2
C-bus will be released; it will enter a
slave mode
transmitted when the bus becomes
free
bit will be returned
will be returned
STO flag will be reset
condition will be transmitted; STO
flag will be reset
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 92 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 84: Master Receiver mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
50h Data byte has
58h Data byte has
Table 85: Slave Receiver mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
60H Own SLA+W has
68H Arbitration lost in
70H General call
78H Arbitration lost in
80H Previously
Status of the I2C
hardware
been received;
ACK has been
returned
been received;
NACK has been
returned
Status of the I2C
hardware
been received;
ACK has been
received
SLA+R/Was
master; Own
SLA+W has been
received, ACK
returned
address(00H) has
been received,
ACK has been
returned
SLA+R/W as
master; General
call address has
been received,
ACK bit has been
returned
addressed with
own SLA address;
Data has been
received; ACK
has been returned
…continued
Application software response Next action taken by I2C hardware
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI STA
Read data byte 0 0 0 0 Data byte will be received; NOT ACK
bit will be returned
read data byte 0 0 0 1 Data byte will be received; ACK bit
will be returned
Read data byte or 1 0 0 x Repeated START will be transmitted;
read data byte or 0 1 0 x STOP condition will be transmitted;
STO flag will be reset
read data byte 1 1 0 x STOP condition followed by a START
condition will be transmitted; STO
flag will be reset
Application software response Next action taken by I2C hardware
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI AA
no I2DAT action orx000Data byte will be received and NOT
ACK will be returned
no I2DAT action x001Data byte will be received and ACK
No I2DAT action orx000Data byte will be received and NOT
no I2DAT action x001Data byte will be received and ACK
No I2DAT action orx000Data byte will be received and NOT
no I2DAT action x001Data byte will be received and ACK
no I2DAT action orx000Data byte will be received and NOT
no I2DAT action x001Data byte will be received and ACK
Read data byte orx000Data byte will be received and NOT
read data bytex001Data byte will be received; ACK bit
will be returned
ACK will be returned
will be returned
ACK will be returned
will be returned
ACK will be returned
will be returned
ACK will be returned
will be returned
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 93 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 85: Slave Receiver mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
88H Previously
90H Previously
98H Previously
Status of the I2C
hardware
addressed with
own SLA address;
Data has been
received; NACK
has been returned
addressed with
General call; Data
has been
received; ACK
has been returned
addressed with
General call; Data
has been
received; NACK
has been returned
…continued
Application software response Next action taken by I2C hardware
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI AA
Read data byte or0000Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
general address
read data byte
or
read data byte
or
read data byte1001Switched to not addressed SLA
Read data byte orx000Data byte will be received and NOT
read data bytex001Data byte will be received and ACK
Read data byte0000Switched to not addressed SLA
read data byte0001Switched to not addressed SLA
read data byte1000Switched to not addressed SLA
read data byte1001Switched to not addressed SLA
0001Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; Own SLA will be recognized;
general call address will be
recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1
1000Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address. A START
condition will be transmitted when
the bus becomes free
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1. A
START condition will be transmitted
when the bus becomes free.
ACK will be returned
will be returned
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1.
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address. A START
condition will be transmitted when
the bus becomes free.
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1. A
START condition will be transmitted
when the bus becomes free.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 94 of 147
Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 85: Slave Receiver mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
A0H A STOP condition
Table 86: Slave Transmitter mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
A8h Own SLA+R has
B0h Arbitration lost in
B8H Data byte in
Status of the I2C
hardware
or repeated
START condition
has been received
while still
addressed as
SLA/REC or
SLA/TRX
Status of the I2C
hardware
been received;
ACK has been
returned
SLA+R/W as
master; Own
SLA+R has been
received, ACK
has been returned
I2DAT has been
transmitted; ACK
has been received
…continued
Application software response Next action taken by I2C hardware
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI AA
No I2DAT action0000Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address
no I2DAT action0001Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1.
no I2DAT action1000Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address. A START
condition will be transmitted when
the bus becomes free.
no I2DAT action1001Switched to not addressed SLA
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1. A
START condition will be transmitted
when the bus becomes free.
Application software response Next action taken by I2C
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
Load data byte orx000Last data byte will be transmitted
load data bytex001Data byte will be transmitted; ACK
Load data byte orx000Last data byte will be transmitted
load data bytex001Data byte will be transmitted; ACK
Load data byte orx000Last data byte will be transmitted
load data bytex001Data byte will be transmitted; ACK
STA STO SI AA
hardware
and ACK bit will be received
will be received
and ACK bit will be received
bit will be received
and ACK bit will be received
will be received
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 95 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
Table 86: Slave Transmitter mode
Status code
(I2STAT)
C0H Data byte in
C8H Last data byte in
Status of the I2C
hardware
I2DAT has been
transmitted;
NACK has been
received
I2DAT has been
transmitted
(AA = 0); ACK has
been received
…continued
Application software response Next action taken by I2C
to/from I2DAT to I2CON
STA STO SI AA
No I2DAT action or0000Switched to not addressed SLA
no I2DAT action or0001Switched to not addressed SLA
no I2DAT action or1000Switched to not addressed SLA
no I2DAT action 1001Switched to not addressed SLA
No I2DAT action or0000Switched to not addressed SLA
no I2DAT action or0001Switched to not addressed SLA
no I2DAT action or1000Switched to not addressed SLA
no I2DAT action 1001Switched to not addressed SLA
hardware
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address.
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1.
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address. A START
condition will be transmitted when
the bus becomes free.
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1. A
START condition will be transmitted
when the bus becomes free.
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address.
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1.
mode; no recognition of own SLA or
General call address. A START
condition will be transmitted when
the bus becomes free.
mode; Own slave address will be
recognized; General call address
will be recognized if I2ADR.0 = 1. A
START condition will be transmitted
when the bus becomes free.
13. Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
The P89LPC933/934/935/936 provides another high-speed serial communication
interface, the SPI interface. SPI is a full-duplex, high-speed, synchronous communication
bus with two operation modes: Master mode and Slave mode. Up to 3 Mbit/s can be
supported in either Master or Slave mode. It has a Transfer Completion Flag and Write
Collision Flag Protection.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 96 of 147
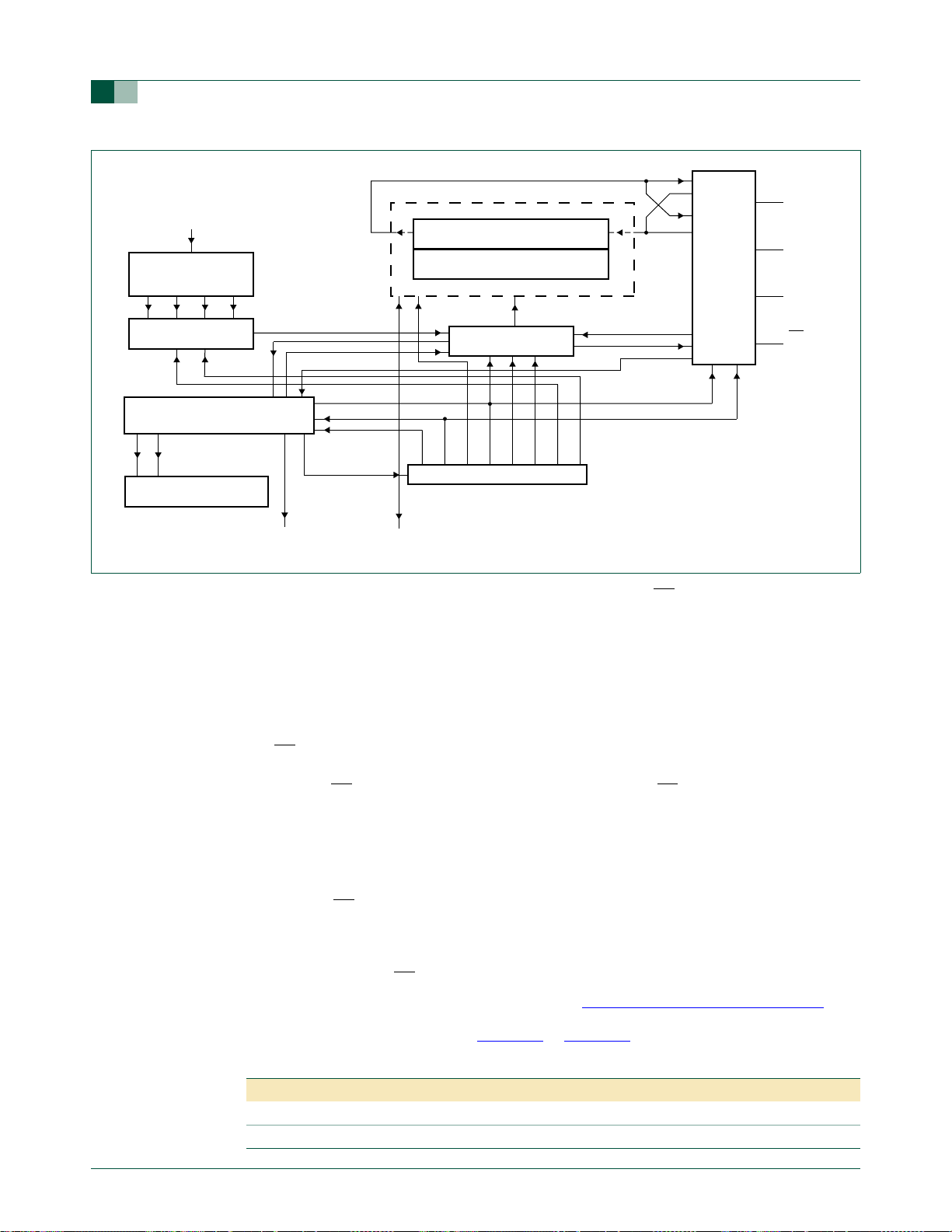
Philips Semiconductors
CPU clock
DIVIDER
BY 4, 16, 64, 128
SELECT
SPR1
SPR0
SPI CONTROL
SPIF
WCOL
SPI STATUS REGISTER
SPI clock (master)
MSTR
SPEN
SPI
interrupt
request
8-BIT SHIFT REGISTER
READ DATA BUFFER
CLOCK LOGIC
SSIG
SPEN
DORD
MSTR
SPI CONTROL REGISTER
internal
data
bus
clock
CPHA
CPOL
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
S
M
M
S
PIN
CONTROL
LOGIC
S
M
SPEN
MSTR
SPR1
SPR0
002aaa900
MISO
P2.3
MOSI
P2.2
SPICLK
P2.5
SS
P2.4
Fig 41. SPI block diagram.
The SPI interface has four pins: SPICLK, MOSI, MISO and SS:
• SPICLK, MOSI and MISO are typically tied together between two or more SPI
• SS is the optional slave select pin. In a typical configuration, an SPI master asserts
Note that even if the SPI is configured as a master (MSTR = 1), it can still be converted to
a slave by driving the SS
happen, the SPIF bit (SPSTAT.7) will be set (see Section 13.4 “
devices. Data flows from master to slave on the MOSI (Master Out Slave In) pin and
flows from slave to master on the MISO (Master In Slave Out) pin. The SPICLK signal
is output in the master mode and is input in the slave mode. If the SPI system is
disabled, i.e. SPEN (SPCTL.6) = 0 (reset value), these pins are configured for port
functions.
one of its port pins to select one SPI device as the current slave. An SPI slave device
uses its SS
following conditions are true:
– If the SPI system is disabled, i.e. SPEN (SPCTL.6) = 0 (reset value)
– If the SPI is configured as a master, i.e., MSTR (SPCTL.4) = 1, and P2.4 is
configured as an output (via the P2M1.4 and P2M2.4 SFR bits);
– If the SS
functions.
pin to determine whether it is selected. The SS is ignored if any of the
pin is ignored, i.e. SSIG (SPCTL.7) bit = 1, this pin is configured for port
pin low (if P2.4 is configured as input and SSIG = 0). Should this
Mode change on SS”)
Typical connections are shown in Figure 42
to Figure 44.
Table 87: SPI Control register (SPCTL - address E2h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol SSIG SPEN DORD MSTR CPOL CPHA SPR1 SPR0
Reset00000100
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 97 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
Table 88: SPI Control register (SPCTL - address E2h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0 SPR0 SPI Clock Rate Select
1 SPR1
2 CPHA SPI Clock PHAse select (see Figure 45 to Figure 48):
3 CPOL SPI Clock POLarity (see Figure 45
4 MSTR Master/Slave mode Select (see Ta bl e 9 2 ).
5 DORD SPI Data ORDer.
6 SPEN SPI Enable.
7 SSIG SS IGnore.
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
SPR1, SPR0:
CCLK
00 —
01 —
10 —
11 —
1 — Data is driven on the leading edge of SPICLK, and is sampled on the trailing
edge.
0 — Data is driven when SS
SPICLK, and is sampled on the leading edge. (Note: If SSIG = 1, the operation is
not defined.
1 — SPICLK is high when idle. The leading edge of SPICLK is the falling edge and
the trailing edge is the rising edge.
0 — SPICLK is low when idle. The leading edge of SPICLK is the rising edge and
the trailing edge is the falling edge.
1 — The LSB of the data word is transmitted first.
0 — The MSB of the data word is transmitted first.
1 — The SPI is enabled.
0 — The SPI is disabled and all SPI pins will be port pins.
1 — MSTR (bit 4) decides whether the device is a master or slave.
0 — The SS
used as a port pin (see Tab l e 9 2
⁄
4
CCLK
⁄
16
CCLK
⁄
64
CCLK
⁄
128
is low (SSIG = 0) and changes on the trailing edge of
to Figure 48):
pin decides whether the device is master or slave. The SS pin can be
).
Table 89: SPI Status register (SPSTAT - address E1h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SymbolSPIFWCOL------
Reset00xxxxxx
Table 90: SPI Status register (SPSTAT - address E1h) bit description
Bit Symbol Description
0:5 - reserved
6 WCOL SPI Write Collision Flag. The WCOL bit is set if the SPI data register, SPDAT, is
written during a data transfer (see Section 13.5 “
is cleared in software by writing a logic 1 to this bit.
7 SPIF SPI Transfer Completion Flag. When a serial transfer finishes, the SPIF bit is set
and an interrupt is generated if both the ESPI (IEN1.3) bit and the EA bit are set. If
is an input and is driven low when SPI is in master mode, and SSIG = 0, this bit
SS
will also be set (see Section 13.4 “
in software by writing a logic 1 to this bit.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 98 of 147
Mode change on SS”). The SPIF flag is cleared
Write collision”). The WCOL flag

Philips Semiconductors
2
Table 91: SPI Data register (SPDAT - address E3h) bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol MSB LSB
Reset00000000
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
master slave
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
SPI CLOCK
GENERATOR
MISO
MOSI
SPICLK
PORT
MISO
MOSI
SPICLK
SS
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
002aaa901
Fig 42. SPI single master single slave configuration.
In Figure 42, SSIG (SPCTL.7) for the slave is logic 0, and SS is used to select the slave.
The SPI master can use any port pin (including P2.4/SS
master slave
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
MISO
MOSI
) to drive the SS pin.
MISO
MOSI
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
SPI CLOCK
GENERATOR
SPICLK
SS
SPICLK
SS
SPI CLOCK
GENERATOR
002aaa90
Fig 43. SPI dual device configuration, where either can be a master or a slave.
Figure 43
shows a case where two devices are connected to each other and either device
can be a master or a slave. When no SPI operation is occurring, both can be configured
as masters (MSTR = 1) with SSIG cleared to 0 and P2.4 (SS
) configured in
quasi-bidirectional mode. When a device initiates a transfer, it can configure P2.4 as an
output and drive it low, forcing a mode change in the other device (see Section 13.4 “
Mode
change on SS”) to slave.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 99 of 147

Philips Semiconductors
UM10116
P89LPC933/934/935/936 User manual
master slave
MISO
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
SPI CLOCK
GENERATOR
Fig 44. SPI single master multiple slaves configuration.
In Figure 44, SSIG (SPCTL.7) bits for the slaves are logic 0, and the slaves are selected
by the corresponding SS
P2.4/SS
) to drive the SS pins.
MOSI
SPICLK
port
port
signals. The SPI master can use any port pin (including
MISO
MOSI
SPICLK
SS
MISO
MOSI
SPICLK
SS
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
slave
8-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
002aaa903
13.1 Configuring the SPI
Ta bl e 9 2 shows configuration for the master/slave modes as well as usages and directions
for the modes.
Table 92: SPI master and slave selection
SPEN SSIG SS Pin MSTR Master
or Slave
Mode
[1]
0xP2.4
1 0 0 0 Slave output input input Selected as slave.
1 0 1 0 Slave Hi-Z input input Not selected. MISO is high-impedance to avoid
1001 (->
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 01 — 4 March 2005 100 of 147
xSPI
Disabled
[2]
0)
Slave output input input P2.4/SS is configured as an input or
MISO MOSI SPICLK Remarks
P2.3
[1]
P2.2
[1]
P2.5
[1]
SPI disabled. P2.2, P2.3, P2.4, P2.5 are used
as port pins.
bus contention.
quasi-bidirectional pin. SSIG is 0. Selected
externally as slave if SS
driven low. The MSTR bit will be cleared to
logic 0 when SS
is selected and is
becomes low.
 Loading...
Loading...