Philips P89C51X2, P89C52X2, P89C54X2, P89C58X2 Technical data

查询P89C51X2供应商
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
128B/256B RAM
Preliminary data
Supersedes data of 2002 Feb 28
2002 Jun 05
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
DESCRIPTION
The Philips microcontrollers described in this data sheet are
high-performance static 80C51 designs. They are manufactured in
an advanced CMOS process and contain a non-volatile Flash
program memory . They support both 12-clock and 6-clock operation.
The P89C51X2 and P89C52X2/54X2/58X2 contain 128 byte RAM
and 256 byte RAM respectively, 32 I/O lines, three 16-bit
counter/timers, a six-source, four-priority level nested interrupt
structure, a serial I/O port for either multi-processor
communications, I/O expansion or full duplex UART, and on-chip
oscillator and clock circuits.
modes of power reduction — idle mode and power-down mode —
are available. The idle mode freezes the CPU while allowing the
RAM, timers, serial port, and interrupt system to continue
functioning. The power-down mode saves the RAM contents but
freezes the oscillator, causing all other chip functions to be
inoperative. Since the design is static, the clock can be stopped
without loss of user data. Then the execution can be resumed from
the point the clock was stopped.
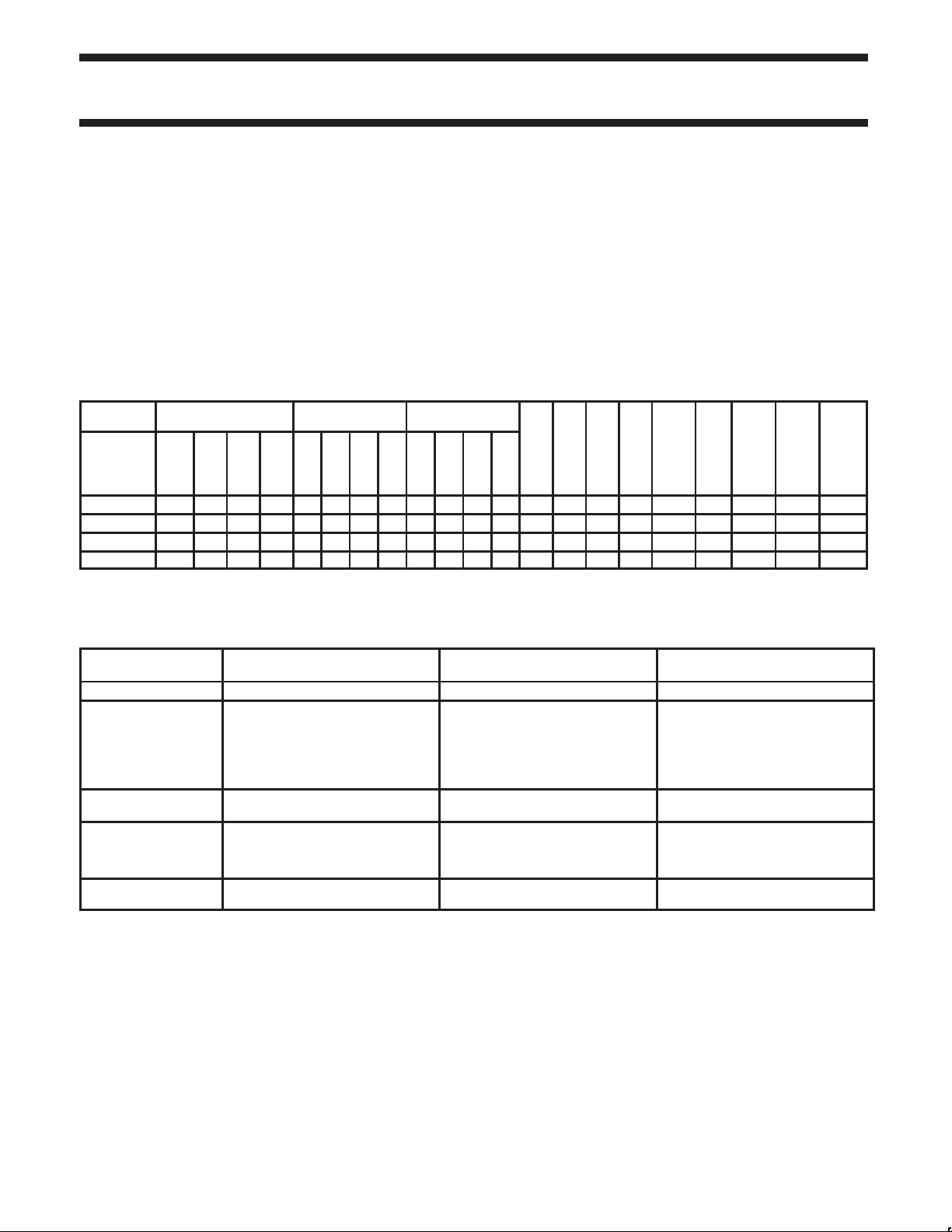
SELECTION TABLE
For applications requiring more Flash and RAM, as well as more
on-chip peripherals, see the P89C66x and P89C51Rx2 data sheets.
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
In addition, the devices are static designs which offer a wide range
of operating frequencies down to zero. Two software selectable
Type Memory Timers Serial Interfaces
Max.
Freq.
Freq.
Range
at 6-clk
at 3V
/ 12-clk
C
RAM
ROM
OTP
P89C58X2
P89C54X2
P89C52X2
P89C51X2
NOTE:
2
C = Inter-Integrated Circuit Bus; CAN = Controller Area Network; SPI = Serial Peripheral Interface; PCA = Programmable Counter Array;
1. I
256B – – 32K 3 – – –
256B – – 16K 3 – – –
256B – – 8K 3 – – –
128B – – 4K 3 – – –
Flash
# of Timers
PWM
PCA
WD
2
UART
I
CAN
– – – – 32 6 (2)
n
– – – – 32 6 (2)
n
– – – – 32 6 (2)
n
– – – – 32 6 (2)
n
SPI
ADC bits/ch.
I/O Pins
Interrupts
(External)
Program
Security
Default Clock
Rate
Optional
12–clk 6-clk 20/33 – 0–20/33
n
12–clk 6-clk 20/33 – 0–20/33
n
12–clk 6-clk 20/33 – 0–20/33
n
12–clk 6-clk 20/33 – 0–20/33
n
Clock Rate
(MHz)
(MHz)
ADC = Analog-to-Digital Converter; PWM = Pulse Width Modulation
DEVICE COMPARISON TABLE
Item P89C5xX2 devices (this data
sheet)
Type Description P89C5xX2Bxx/P89C5xX2Fxx P89C5xBx P89C5xUBxx/P89C5xUFxx
PROGRAMMING
ALGORITHM
When using a parallel programmer,
be sure to select P89C5xX2 devices.
IF DEVICES ARE NOT YET
SELECTABLE ASK YOUR
PROGRAMMER VENDOR FOR A
SOFTWARE UPDATE
Quad Flat Package
LQFP package (P89C5xX2xBD) LQFP package (P89C5xBBD) PQFP package (P89C5xUxBB)
type
Package identifiers PLCC = A
LQFP = BD
PDIP = N
Flash Memory program
10,000 program and erase cycles 10,000 program and erase cycles 100 program and erase cycles
and erase cycles
P89C5xBx devices (separate data
sheet)
When using a parallel programmer,
be sure to select P89C5xBx devices.
IF DEVICES ARE NOT YET
SELECTABLE ASK YOUR
PROGRAMMER VENDOR FOR A
SOFTWARE UPDATE
PLCC = A
LQFP = BD
PDIP = P
P89C5xUxx devices
(discontinued)
When using a parallel programmer,
be sure to select P89C5xUxxx
devices.
PLCC = AA
LQFP = BB
PDIP = PN
Freq.
Range
at 5V
(MHz)
2002 Jun 06
2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
FEATURES
•80C51 Central Processing Unit
– 4 Kbytes Flash (P89C51X2)
– 8 Kbytes Flash (P89C52X2)
– 16 Kbytes Flash (P89C54X2)
– 32 Kbytes Flash (P89C58X2)
– 128 byte RAM (P89C51X2)
– 256 byte RAM (P89C52/54X2/58X2)
– Boolean processor
– Fully static operation
•12-clock operation with selectable 6-clock operation (via software
or via parallel programmer)
•Memory addressing capability
– Up to 64 Kbytes ROM and 64 Kbytes RAM
•Power control modes:
– Clock can be stopped and resumed
– Idle mode
– Power-down mode
•Two speed ranges
– 0 to 20 MHz with 6-clock operation
– 0 to 33 MHz with 12-clock operation
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
•LQFP, PLCC or DIP package
•Extended temperature ranges
•Dual Data Pointers
•Three security bits
•Four interrupt priority levels
•Six interrupt sources
•Four 8-bit I/O ports
•Full-duplex enhanced UART
– Framing error detection
– Automatic address recognition
•Three 16-bit timers/counters T0, T1 (standard 80C51) and
additional T2 (capture and compare)
•Programmable clock-out pin
•Asynchronous port reset
•Low EMI (inhibit ALE, slew rate controlled outputs, and 6-clock
mode)
•Wake-up from Power Down by an external interrupt
2002 Jun 06
3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
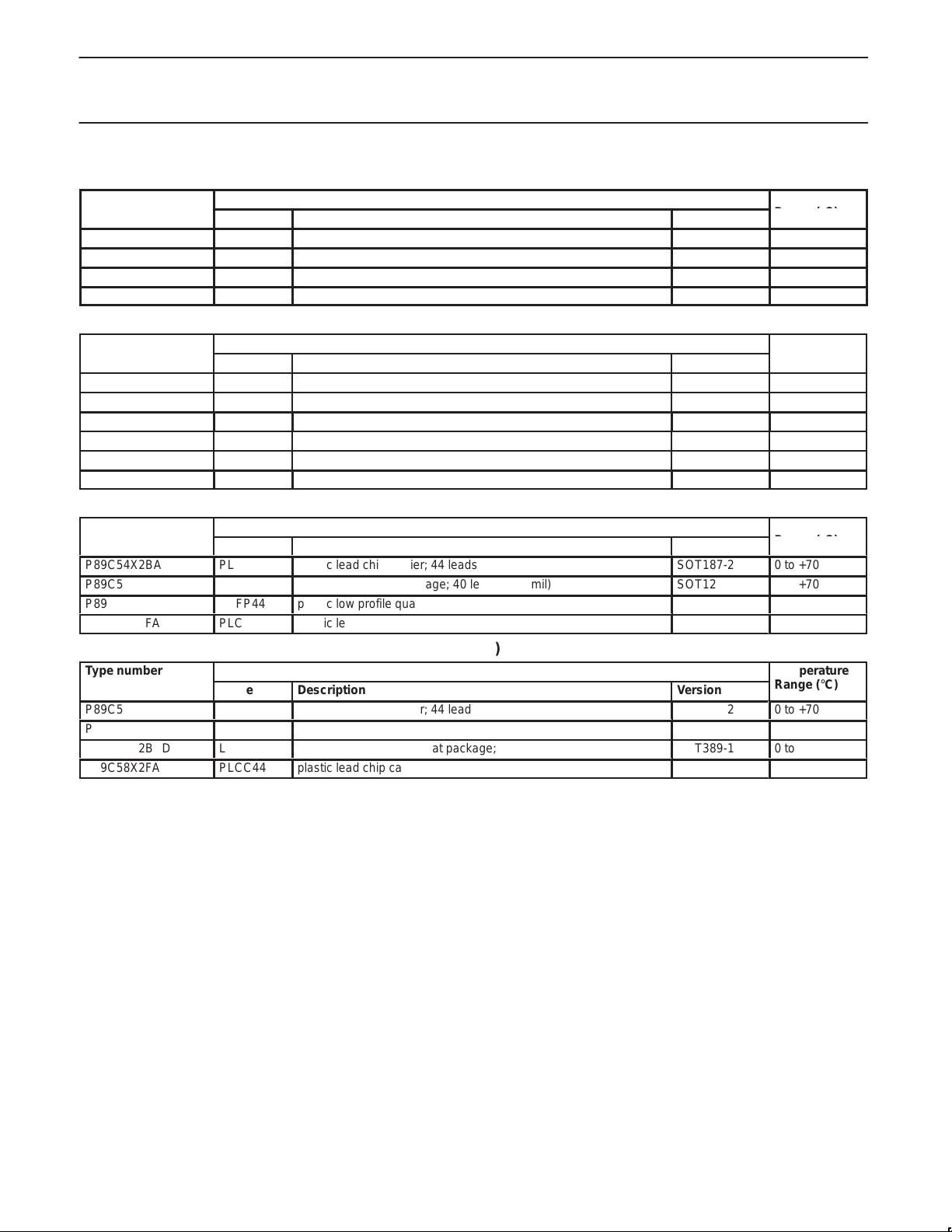
P89C51X2 ORDERING INFORMATION (4 KBYTE FLASH)
Type number Package Temperature
Name Description Version
P89C51X2BA PLCC44 plastic leaded chip carrier; 44 leads SOT187-2 0 to +70
P89C51X2BN DIP40 plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil) SOT129-1 0 to +70
P89C51X2BBD LQFP44 plastic low profile quad flat package; 44 leads SOT389-1 0 to +70
P89C51X2FA PLCC44 plastic leaded chip carrier; 44 leads SOT187-2 –40 to +85
Range (°C)
P89C52X2 ORDERING INFORMATION (8 KBYTE FLASH)
Type number Package Temperature
Name Description Version
P89C52X2BA PLCC44 plastic leaded chip carrier; 44 leads SOT187-2 0 to +70
P89C52X2BN DIP40 plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil) SOT129-1 0 to +70
P89C52X2BBD LQFP44 plastic low profile quad flat package; 44 leads SOT389-1 0 to +70
P89C52X2FA PLCC44 plastic leaded chip carrier; 44 leads SOT187-2 –40 to +85
P89C52X2FN DIP40 plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil) SOT129-1 –40 to +85
P89C52X2FBD LQFP44 plastic low profile quad flat package; 44 leads SOT389-1 –40 to +85
Range (°C)
P89C54X2 ORDERING INFORMATION (16 KBYTE FLASH)
Type number Package Temperature
Name Description Version
P89C54X2BA
P89C54X2BN
P89C54X2BBD LQFP44 plastic low profile quad flat package; 44 leads SOT389-1 0 to +70
P89C54X2FA
PLCC44
DIP40
PLCC44
plastic lead chip carrier; 44 leads
plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil)
plastic lead chip carrier; 44 leads
SOT187-2
SOT129-1
SOT187-2
Range (°C)
0 to +70
0 to +70
–40 to +85
P89C58X2 ORDERING INFORMATION (32 KBYTE FLASH)
Type number Package Temperature
Name Description Version
P89C58X2BA
P89C58X2BN
P89C58X2BBD LQFP44 plastic low profile quad flat package; 44 leads SOT389-1 0 to +70
P89C58X2FA
PLCC44
DIP40
PLCC44
plastic lead chip carrier; 44 leads
plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil)
plastic lead chip carrier; 44 leads
SOT187-2
SOT129-1
SOT187-2
Range (°C)
0 to +70
0 to +70
–40 to +85
2002 Jun 06
4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
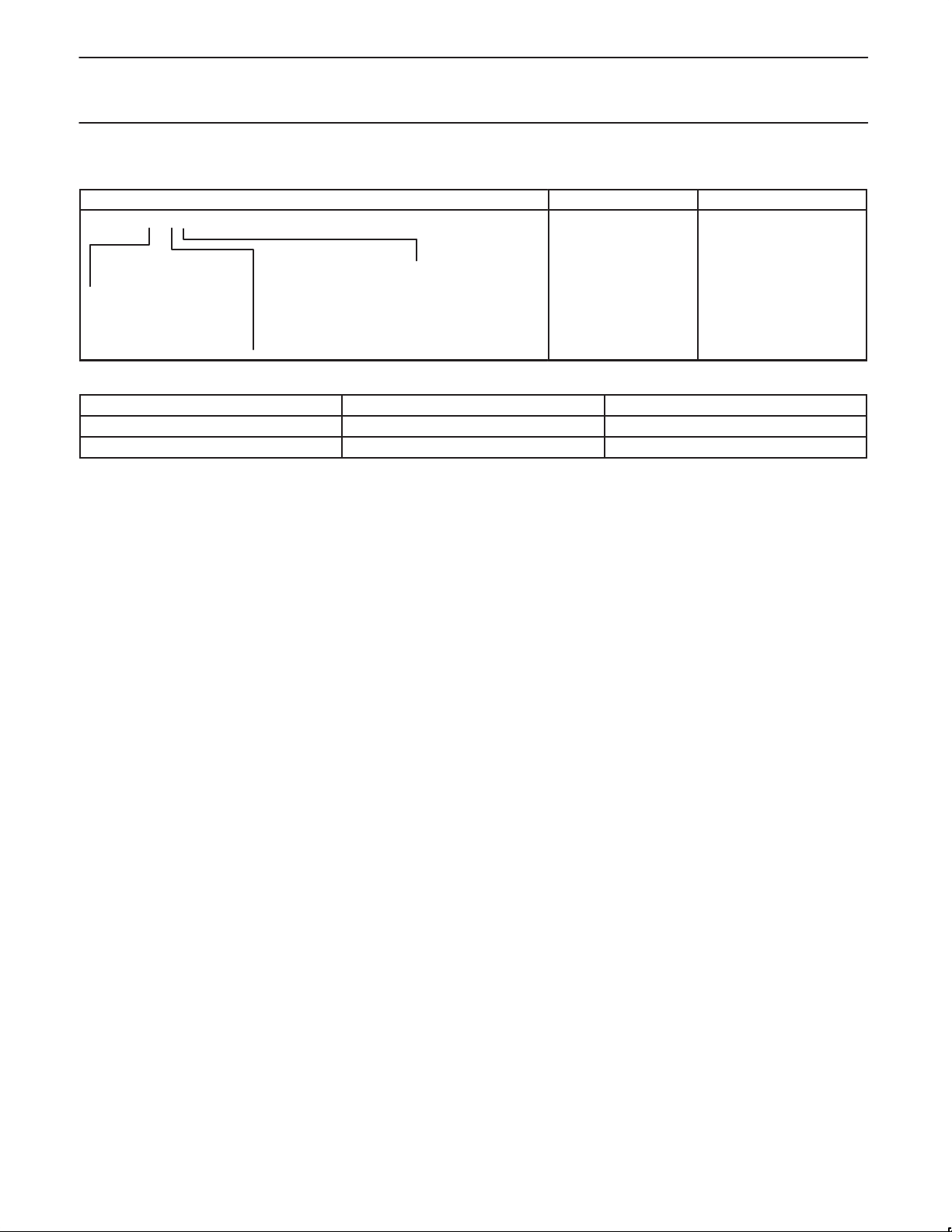
P ART NUMBER DERIVATION
Memory Temperature Range Package
P89C51X2
9 = Flash 1 = 128 BYTES RAM
The following table illustrates the correlation between operating mode, power supply and maximum external clock frequency:
Operating Mode
6-clock 5 V ± 10% 20 MHz
12-clock 5 V ± 10% 33 MHz
4 KBYTES FLASH
2 = 256 BYTES RAM
8 KBYTES FLASH
4 = 256 BYTES RAM
16 KBYTES FLASH
8 = 256 BYTES RAM
32 KBYTES FLASH
Power Supply Maximum Clock Frequency
X2 =6-clock
mode available
B = 0 °C TO +70 °C
F = –40 °C TO +85 °C
A = PLCC
N = DIP
BD = LQFP
2002 Jun 06
5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
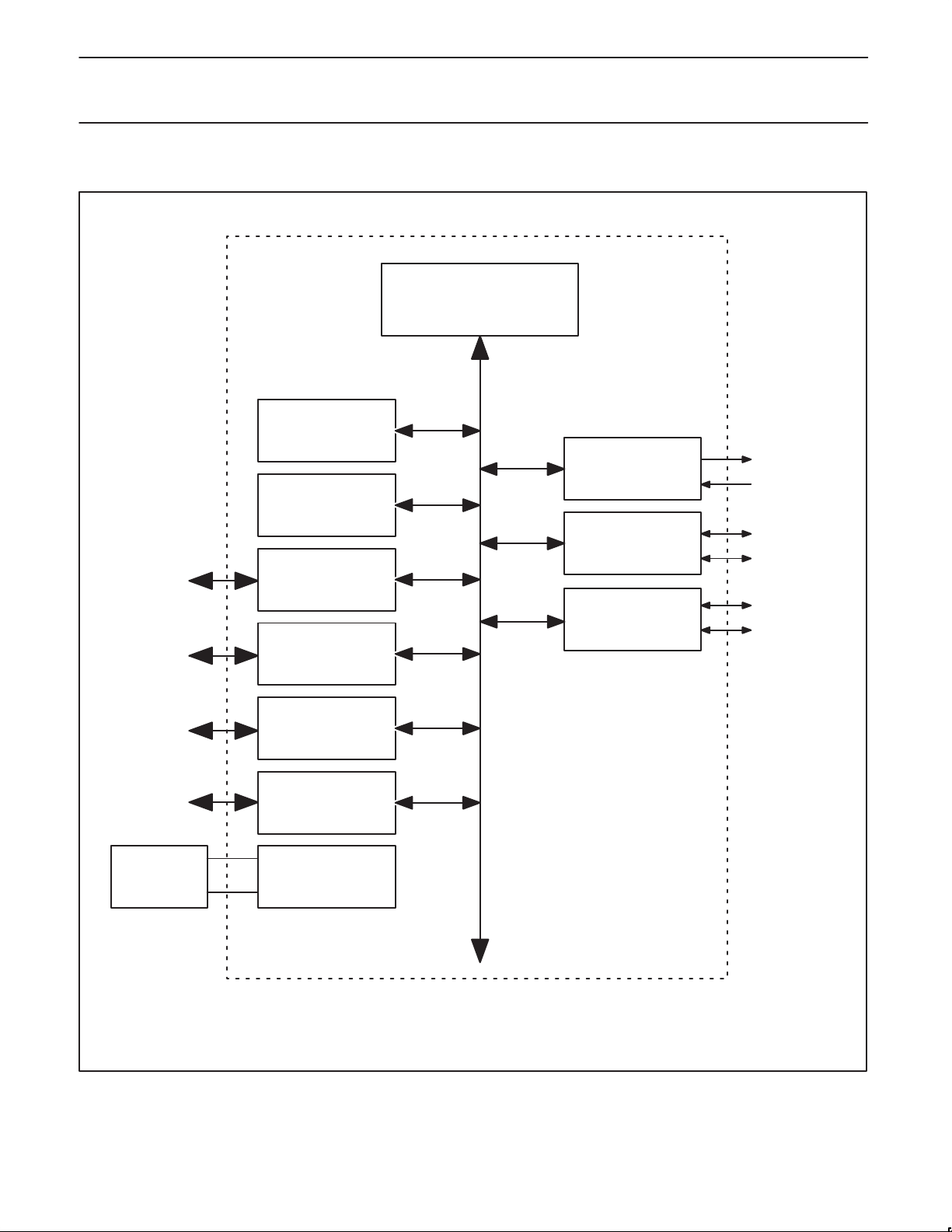
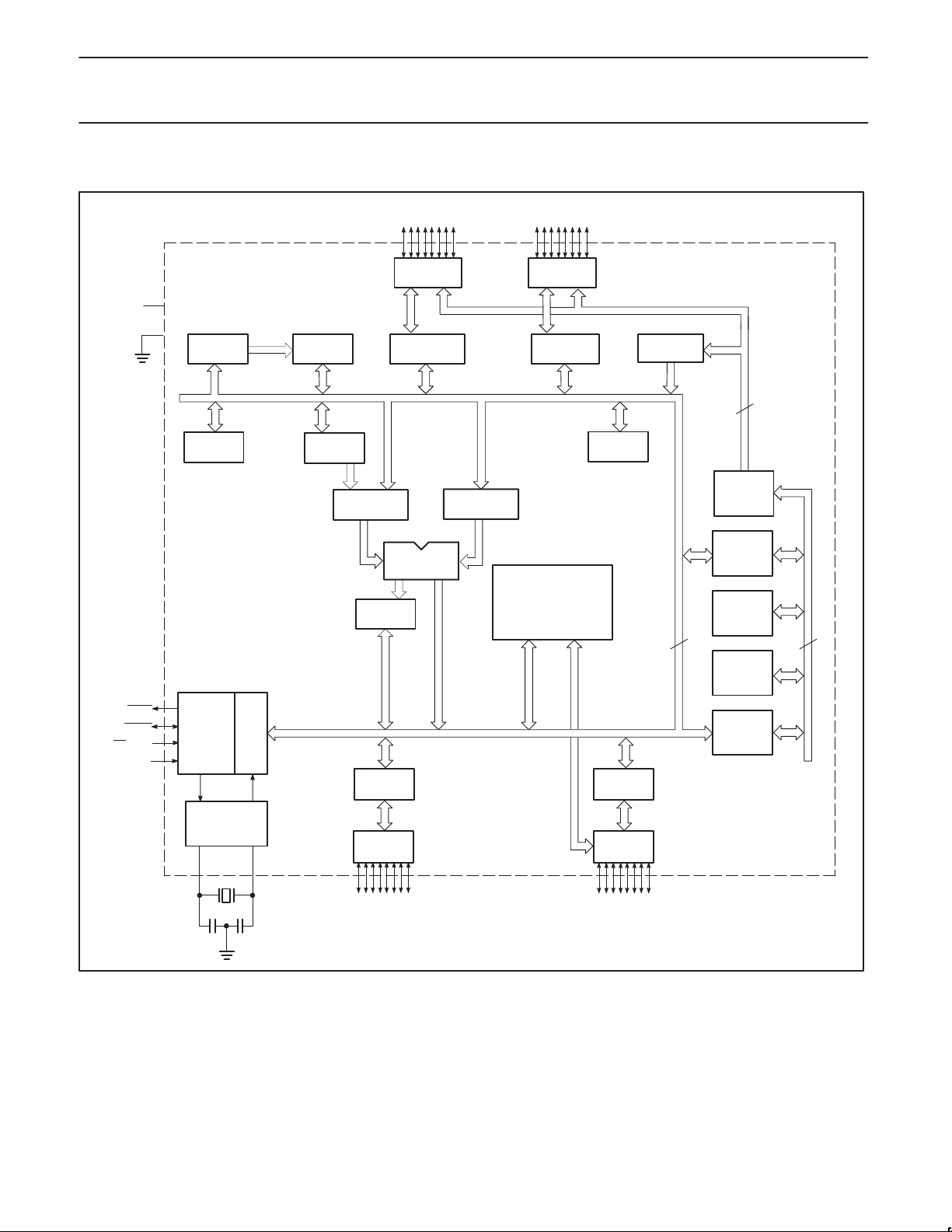
BLOCK DIAGRAM 1
0K / 4K / 8K / 16K /
32 KBYTE
CODE FLASH
128 / 256 BYTE
DATA RAM
PORT 3
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
ACCELERATED 80C51 CPU
(12-CLK MODE, 6-CLK MODE)
FULL-DUPLEX
ENHANCED UART
TIMER 0
TIMER 1
TIMER 2
RESONATOR
PORT 2
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
PORT 1
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
PORT 0
CONFIGURABLE I/Os
OSCILLATORCRYSTAL OR
su01617
2002 Jun 06
6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
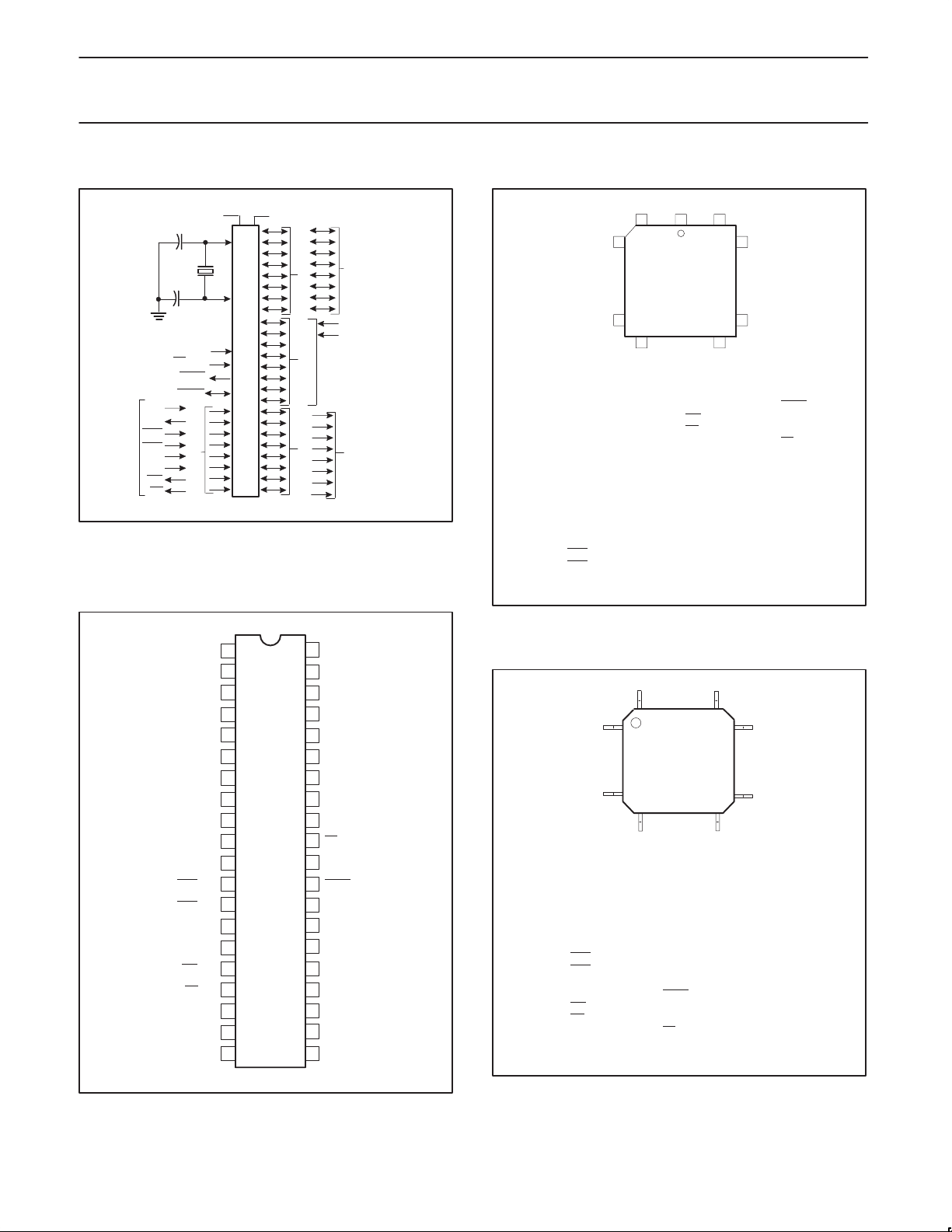
BLOCK DIAGRAM 2 (CPU-ORIENTED)
V
CC
V
SS
RAM ADDR
REGISTER
B
REGISTER
RAM
ACC
TMP2
P0.0–P0.7 P2.0–P2.7
PORT 0
DRIVERS
PORT 0
LATCH
TMP1
PORT 2
DRIVERS
PORT 2
LATCH
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
ROM/EPROM
8
STACK
POINTER
PROGRAM
ADDRESS
REGISTER
PSEN
ALE/PROG
EA / V
PP
RST
TIMING
AND
CONTROL
OSCILLATOR
XTAL1 XTAL2
INSTRUCTION
PD
REGISTER
PSW
PORT 1
LATCH
PORT 1
DRIVERS
P1.0–P1.7
ALU
SFRs
TIMERS
PORT 3
LATCH
PORT 3
DRIVERS
P3.0–P3.7
BUFFER
PC
INCRE-
MENTER
8 16
PROGRAM
COUNTER
DPTR’S
MULTIPLE
SU00845
2002 Jun 06
7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
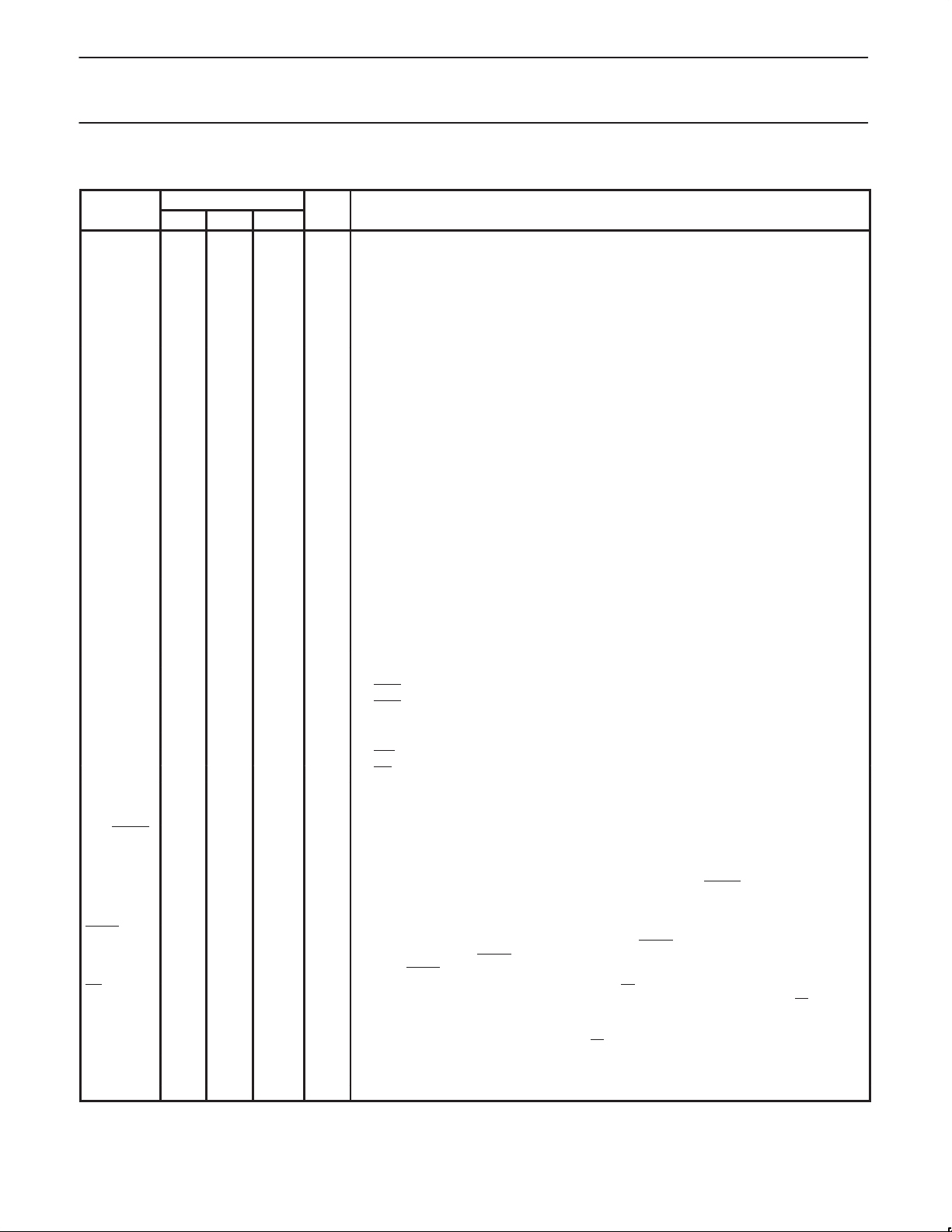
LOGIC SYMBOL
V
V
SS
CC
XTAL1
ADDRESS AND
PORT 0
XTAL2
RST
EA/V
PSEN
ALE/PROG
RxD
TxD
INT0
INT1
T0
T1
WR
RD
SECONDARY FUNCTIONS
PP
PORT 3
PORT 1PORT 2
PLASTIC DUAL IN-LINE P ACKAGE
PIN CONFIGURA TIONS
DATA BUS
T2
T2EX
ADDRESS BUS
SU00830
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
PLASTIC LEADED CHIP CARRIER PIN FUNCTIONS
6140
7
17
Pin Function
1 NIC*
2 P1.0/T2
3 P1.1/T2EX
4 P1.2
5 P1.3
6 P1.4
7 P1.5
8 P1.6
9 P1.7
10 RST
11 P3.0/RxD
12 NIC*
13 P3.1/TxD
14 P3.2/INT0
15 P3.3/INT1
* NO INTERNAL CONNECTION
PLCC
18 28
Pin Function
16 P3.4/T0
17 P3.5/T1
18 P3.6/WR
19 P3.7/RD
20 XTAL2
21 XTAL1
22 V
SS
23 NIC*
24 P2.0/A8
25 P2.1/A9
26 P2.2/A10
27 P2.3/A11
28 P2.4/A12
29 P2.5/A13
30 P2.6/A14
39
29
Pin Function
31 P2.7/A15
32 PSEN
33 ALE
34 NIC*
35 EA/V
36 P0.7/AD7
37 P0.6/AD6
38 P0.5/AD5
39 P0.4/AD4
40 P0.3/AD3
41 P0.2/AD2
42 P0.1/AD1
43 P0.0/AD0
44 V
PP
CC
SU01062
T2/P1.0
T2EX/P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
RST
RxD/P3.0
TxD/P3.1
INT0
/P3.2
/P3.3
INT1
T0/P3.4
T1/P3.5
/P3.6
WR
RD
/P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
SU01063
V
CC
P0.0/AD0
P0.1/AD1
P0.2/AD2
P0.3/AD3
P0.4/AD4
P0.5/AD5
P0.6/AD6
P0.7/AD7
EA
/V
PP
ALE
PSEN
P2.7/A15
P2.6/A14
P2.5/A13
P2.4/A12
P2.3/A11
P2.2/A10
P2.1/A9
P2.0/A8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DUAL
10
IN-LINE
PACKAGE
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
SS
LOW PROFILE QUAD FLAT PACK
PIN FUNCTIONS
44 34
1
LQFP
11
12 22
Pin Function
1 P1.5
2 P1.6
3 P1.7
4 RST
5 P3.0/RxD
6 NIC*
7 P3.1/TxD
8 P3.2/INT0
9 P3.3/INT1
10 P3.4/T0
11 P3.5/T1
12 P3.6/WR
13 P3.7/RD
14 XTAL2
15 XTAL1
* NO INTERNAL CONNECTION
Pin Function
16 V
SS
17 NIC*
18 P2.0/A8
19 P2.1/A9
20 P2.2/A10
21 P2.3/A11
22 P2.4/A12
23 P2.5/A13
24 P2.6/A14
25 P2.7/A15
26 PSEN
27 ALE
28 NIC*
/V
29 EA
30 P0.7/AD7
PP
33
23
Pin Function
31 P0.6/AD6
32 P0.5/AD5
33 P0.4/AD4
34 P0.3/AD3
35 P0.2/AD2
36 P0.1/AD1
37 P0.0/AD0
38 V
CC
39 NIC*
40 P1.0/T2
41 P1.1/T2EX
42 P1.2
43 P1.3
44 P1.4
SU01487
2002 Jun 06
8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN NUMBER
MNEMONIC DIP PLCC LQFP TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
V
SS
V
CC
P0.0-0.7 39–32 43–36 37–30 I/O Port 0: Port 0 is an open-drain, bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to
P1.0–P1.7 1–8 2–9 40–44,
P2.0–P2.7 21–28 24–31 18–25 I/O Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s
P3.0–P3.7 10–17 11,
RST 9 10 4 I Reset: A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running, resets the
ALE/PROG 30 33 27 O Address Latch Enable/Program Pulse: Output pulse for latching the low byte of the
PSEN 29 32 26 O Program Store Enable: The read strobe to external program memory. When the device is
EA/V
PP
XTAL1 19 21 15 I Crystal 1: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock generator
XTAL2 18 20 14 O Crystal 2: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
NOTE:
To avoid “latch-up” effect at power-on, the voltage on any pin at any time must not be higher than V
20 22 16 I Ground: 0 V reference.
40 44 38 I Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power-down operation.
them float and can be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed
low-order address and data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In
this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. Port 0 also outputs the
code bytes during program verification and received code bytes during Flash programming.
External pull-ups are required during program verification.
1–3
1 2 40 I/O T2 (P1.0): Timer/Counter 2 external count input/clockout (see Programmable Clock-Out)
2 3 41 I T2EX (P1.1): Timer/Counter 2 Reload/Capture/Direction control
13–195,7–13
10 11 5 I RxD (P3.0): Serial input port
11 13 7 O TxD (P3.1): Serial output port
12 14 8 I INT0 (P3.2): External interrupt
13 15 9 I INT1 (P3.3): External interrupt
14 16 10 I T0 (P3.4): Timer 0 external input
15 17 11 I T1 (P3.5): Timer 1 external input
16 18 12 O WR (P3.6): External data memory write strobe
17 19 13 O RD (P3.7): External data memory read strobe
31 35 29 I External Access Enable/Programming Supply Voltage: EA must be externally held low to enable the device
I/O Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 1 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 1 pins that are externally pulled low will source current because of the internal pull-ups.
(See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
during program memory verification. Alternate functions for Port 1 include:
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the internal
pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: IIL). Port 2 emits the high-order address byte
during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to external data memory
that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal
pull-ups when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit addresses
(MOV @Ri), port 2 emits the contents of the P2 special function register. Some Port 2 pins
receive the high order address bits during Flash programming and verification.
I/O Port 3: Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the pull-ups.
(See DC Electrical Characteristics: IIL). Port 3 also serves the special features of the 80C51
family, as listed below:
device. An internal diffused resistor to VSS permits a power-on reset using only an external
capacitor to VCC.
address during an access to external memory. In normal operation, ALE is emitted at a
constant rate of 1/6 (12-clk) or 1/3 (6-clk Mode) the oscillator frequency, and can be used for
external timing or clocking. Note that one ALE pulse is skipped during each access to
external data memory. This pin is also the program pulse input (PROG
programming. ALE can be disabled by setting SFR auxiliary.0. With this bit set, ALE will be
active only during a MOVX instruction.
executing code from the external program memory, PSEN is activated twice each machine
cycle, except that two PSEN activations are skipped during each access to external data
memory. PSEN is not activated during fetches from internal program memory.
to fetch code from external program memory locations 0000H to 0FFFH/1FFFH/3FFFH/7FFFH. If EA is held
high, the device executes from internal program memory unless the program counter contains an address
greater than the on-chip Flash. This pin also receives the 5 V / 12 V programming supply voltage (VPP) during
Flash programming. If security bit 1 is programmed, EA will be internally latched on Reset.
circuits.
). Port 1 also receives the low-order address byte
IL
) during Flash
+ 0.5 V or VSS – 0.5 V, respectively.
CC
2002 Jun 06
9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
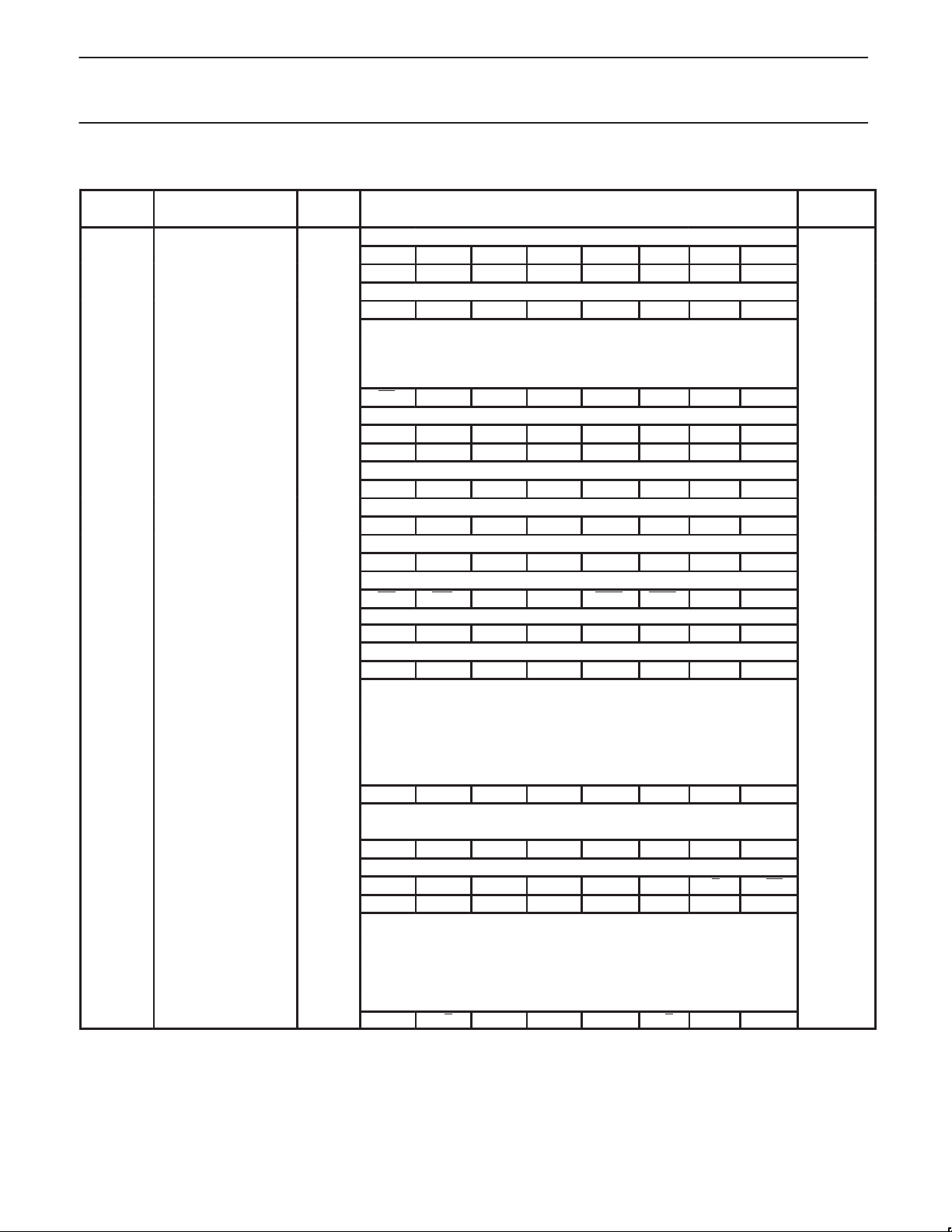
Table 1. Special Function Registers
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
ACC* Accumulator E0H
AUXR# Auxiliary 8EH – – – – – – – AO xxxxxxx0B
AUXR1# Auxiliary 1 A2H – – – – WUPD 0 – DPS xxx000x0B
B* B register F0H
CKCON Clock Control Register 8FH – – – – – – – X2 xxx00000B
DPTR: Data Pointer (2 bytes)
DPH Data Pointer High 83H 00H
DPL Data Pointer Low 82H 00H
IE* Interrupt Enable A8H EA – ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 0x000000B
IP* Interrupt Priority B8H – – PT2 PS PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0 xx000000B
IPH# Interrupt Priority High B7H – – PT2H PSH PT1H PX1H PT0H PX0H xx000000B
P0* Port 0 80H AD7 AD6 AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0 FFH
P1* Port 1 90H – – – – – – T2EX T2 FFH
P2* Port 2 A0H AD15 AD14 AD13 AD12 AD11 AD10 AD9 AD8 FFH
P3* Port 3 B0H RD WR T1 T0 INT1 INT0 TxD RxD FFH
DIRECT
ADDRESS
BIT ADDRESS, SYMBOL, OR ALTERNATIVE PORT FUNCTION
MSB LSB
E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0
F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0
AF AE AD AC AB AA A9 A8
BF BE BD BC BB BA B9 B8
87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
RESET
VALUE
00H
00H
PCON#1Power Control 87H SMOD1 SMOD0 – POF GF1 GF0 PD IDL 00xx0000B
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PSW* Program Status Word D0H CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV – P 000000x0B
RACAP2H# Timer 2 Capture High CBH 00H
RACAP2L# Timer 2 Capture Low CAH 00H
SADDR# Slave Address A9H 00H
SADEN# Slave Address Mask B9H 00H
SBUF Serial Data Buffer 99H xxxxxxxxB
9F 9E 9D 9C 9B 9A 99 98
SCON* Serial Control 98H
SP Stack Pointer 81H 07H
TCON* Timer Control 88H TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 00H
T2CON* Timer 2 Control C8H TF2 EXF2 RCLK TCLK EXEN2 TR2 C/T2 CP/RL2 00H
T2MOD# Timer 2 Mode Control C9H – – – – – – T2OE DCEN xxxxxx00B
TH0 Timer High 0 8CH 00H
TH1 Timer High 1 8DH 00H
TH2# Timer High 2 CDH 00H
TL0 Timer Low 0 8AH 00H
TL1 Timer Low 1 8BH 00H
TL2# Timer Low 2 CCH 00H
TMOD Timer Mode 89H GATE C/T M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0 00H
NOTE:
Unused register bits that are not defined should not be set by the user’s program. If violated, the device could function incorrectly.
* SFRs are bit addressable.
# SFRs are modified from or added to the 80C51 SFRs.
– Reserved bits.
1. Reset value depends on reset source.
SM0/FE
8F 8E 8D 8C 8B 8A 89 88
CF CE CD CC CB CA C9 C8
SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI 00H
2002 Jun 06
10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
FLASH EPROM MEMORY
General Description
The P89C51X2/P89C52X2/P89C54X2/P89C58X2 FLASH reliably
stores memory contents even after 10,000 erase and program
cycles. The cell is designed to optimize the erase and programming
mechanisms. In addition, the combination of advanced tunnel oxide
processing and low internal electric fields for erase and
programming operations produces reliable cycling.
Features
•FLASH EPROM internal program memory with Chip Erase
•Up to 64 kbyte external program memory if the internal program
memory is disabled (EA
= 0)
•Programmable security bits
•10,000 minimum erase/program cycles for each byte
•10 year minimum data retention
•Programming support available from many popular vendors
OSCILLA T OR CHARACTERISTICS
Using the oscillator, XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output,
respectively, of an inverting amplifier. The pins can be configured for
use as an on-chip oscillator, as shown in the logic symbol.
To drive the device from an external clock source, XTAL1 should be
driven while XTAL2 is left unconnected. However, minimum and
maximum high and low times specified in the data sheet must be
observed.
Clock Control Register (CKCON)
This device provides control of the 6-clock/12-clock mode by both
an SFR bit (bit X2 in register CKCON) and a Flash bit (bit FX2,
located in the Security Block). When X2 is 0, 12-clock mode is
activated. By setting this bit to 1, the system is switching to 6-clock
mode. Having this option implemented as SFR bit, it can be
accessed anytime and changed to either value. Changing X2 from 0
to 1 will result in executing user code at twice the speed, since all
system time intervals will be divided by 2. Changing back from
6-clock to 12-clock mode will slow down running code by a factor of
2.
The Flash clock control bit (FX2) activates the 6-clock mode when
programmed using a parallel programmer, superceding the X2 bit
(CKCON.0). Please also see Table 2 below.
Table 2.
FX2 clock mode bit
(can only be set by
parallel programmer)
erased 0 12-clock mode
erased 1 6-clock mode
programmed X 6-clock mode
X2 bit
(CKCON.0)
CPU clock mode
(default)
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
Programmable Clock-Out Pin
A 50% duty cycle clock can be programmed to be output on P1.0.
This pin, besides being a regular I/O pin, has two alternate
functions. It can be programmed:
1. to input the external clock for Timer/Counter 2, or
2. to output a 50% duty cycle clock ranging from 61 Hz to 4 MHz at
a 16 MHz operating frequency in 12-clock mode (122 Hz to
8 MHz in 6-clock mode).
To configure the Timer/Counter 2 as a clock generator, bit C/T
T2CON) must be cleared and bit T20E in T2MOD must be set. Bit
TR2 (T2CON.2) also must be set to start the timer.
The Clock-Out frequency depends on the oscillator frequency and
the reload value of Timer 2 capture registers (RCAP2H, RCAP2L)
as shown in this equation:
Oscillator Frequency
n (65536–RCAP2H,RCAP2L)
Where:
n = 2 in 6-clock mode, 4 in 12-clock mode.
(RCAP2H,RCAP2L) = the content of RCAP2H and RCAP2L
taken as a 16-bit unsigned integer.
In the Clock-Out mode Timer 2 roll-overs will not generate an
interrupt. This is similar to when it is used as a baud-rate generator.
It is possible to use Timer 2 as a baud-rate generator and a clock
generator simultaneously. Note, however, that the baud-rate and the
Clock-Out frequency will be the same.
RESET
A reset is accomplished by holding the RST pin HIGH for at least
two machine cycles (24 oscillator periods in 12-clock and 12
oscillator periods in 6-clock mode), while the oscillator is running. To
insure a reliable power-up reset, the RST pin must be high long
enough to allow the oscillator time to start up (normally a few
milliseconds) plus two machine cycles, unless it has been set to
6-clock operation using a parallel programmer.
LOW POWER MODES
Stop Clock Mode
The static design enables the clock speed to be reduced down to
0 MHz (stopped). When the oscillator is stopped, the RAM and
Special Function Registers retain their values. This mode allows
step-by-step utilization and permits reduced system power
consumption by lowering the clock frequency down to any value. For
lowest power consumption the Power Down mode is suggested.
Idle Mode
In idle mode (see Table 3), the CPU puts itself to sleep while all of
the on-chip peripherals stay active. The instruction to invoke the idle
mode is the last instruction executed in the normal operating mode
before the idle mode is activated. The CPU contents, the on-chip
RAM, and all of the special function registers remain intact during
this mode. The idle mode can be terminated either by any enabled
interrupt (at which time the process is picked up at the interrupt
service routine and continued), or by a hardware reset which starts
the processor in the same manner as a power-on reset.
2 (in
2002 Jun 06
11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
Power-Down Mode
To save even more power, a Power Down mode (see Table 3) can
be invoked by software. In this mode, the oscillator is stopped and
the instruction that invoked Power Down is the last instruction
executed. The on-chip RAM and Special Function Registers retain
their values down to 2.0 V and care must be taken to return V
the minimum specified operating voltages before the Power Down
Mode is terminated.
Either a hardware reset or external interrupt can be used to exit from
Power Down. Reset redefines all the SFRs but does not change the
on-chip RAM. An external interrupt allows both the SFRs and the
on-chip RAM to retain their values. WUPD (AUXR1.3–Wakeup from
Power Down) enables or disables the wakeup from power down with
external interrupt. Where:
WUPD = 0: Disable
WUPD = 1: Enable
To properly terminate Power Down, the reset or external interrupt
should not be executed before V
operating level and must be held active long enough for the
oscillator to restart and stabilize (normally less than 10 ms).
To terminate Power Down with an external interrupt, INT0
must be enabled and configured as level-sensitive. Holding the pin
low restarts the oscillator but bringing the pin back high completes
the exit. Once the interrupt is serviced, the next instruction to be
is restored to its normal
CC
CC
or INT1
to
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
executed after RETI will be the one following the instruction that put
the device into Power Down.
Design Consideration
When the idle mode is terminated by a hardware reset, the device
normally resumes program execution from where it left off, up to two
machine cycles before the internal reset algorithm takes control.
On-chip hardware inhibits access to internal RAM in this event, but
access to the port pins is not inhibited. To eliminate the possibility of
an unexpected write when Idle is terminated by reset, the instruction
following the one that invokes Idle should not be one that writes to a
port pin or to external memory.
ONCE Mode
The ONCE (“On-Circuit Emulation”) Mode facilitates testing and
debugging of systems without the device having to be removed from
the circuit. The ONCE Mode is invoked in the following way:
1. Pull ALE low while the device is in reset and PSEN
2. Hold ALE low as RST is deactivated.
While the device is in ONCE Mode, the Port 0 pins go into a float
state, and the other port pins and ALE and PSEN
high. The oscillator circuit remains active. While the device is in this
mode, an emulator or test CPU can be used to drive the circuit.
Normal operation is restored when a normal reset is applied.
is high;
are weakly pulled
Table 3. External Pin Status During Idle and Power-Down Modes
MODE PROGRAM MEMORY ALE PSEN PORT 0 PORT 1 PORT 2 PORT 3
Idle Internal 1 1 Data Data Data Data
Idle External 1 1 Float Data Address Data
Power-down Internal 0 0 Data Data Data Data
Power-down External 0 0 Float Data Data Data
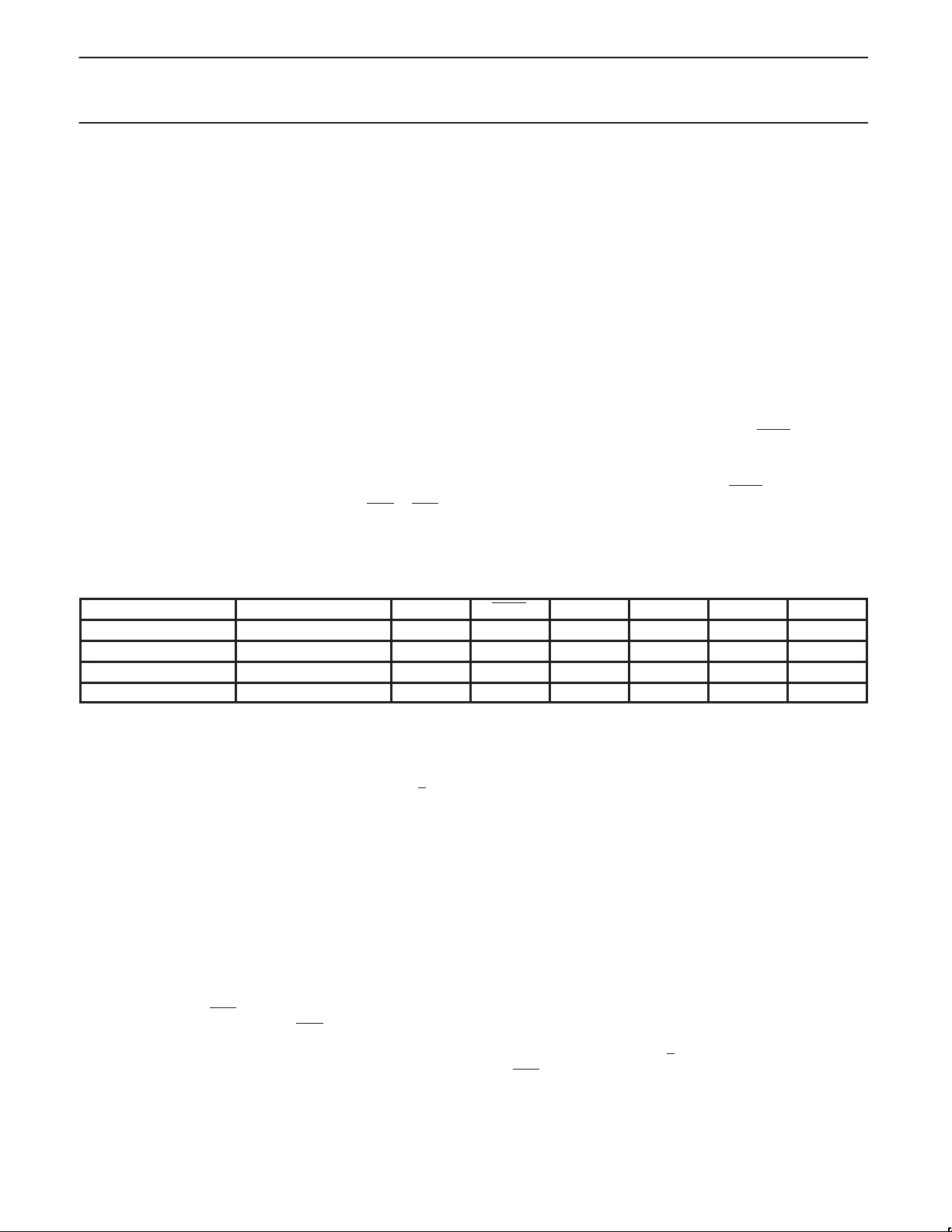
TIMER 0 AND TIMER 1 OPERATION
Timer 0 and Timer 1
The “Timer” or “Counter” function is selected by control bits C/T in
the Special Function Register TMOD. These two Timer/Counters
have four operating modes, which are selected by bit-pairs (M1, M0)
in TMOD. Modes 0, 1, and 2 are the same for both Timers/Counters.
Mode 3 is different. The four operating modes are described in the
following text.
Mode 0
Putting either Timer into Mode 0 makes it look like an 8048 T imer,
which is an 8-bit Counter with a divide-by-32 prescaler. Figure 2
shows the Mode 0 operation.
In this mode, the Timer register is configured as a 13-bit register . As
the count rolls over from all 1s to all 0s, it sets the Timer interrupt
flag TFn. The counted input is enabled to the Timer when TRn = 1
and either GA TE = 0 or INTn
Timer to be controlled by external input INTn
measurements). TRn is a control bit in the Special Function Register
TCON (Figure 3).
The 13-bit register consists of all 8 bits of THn and the lower 5 bits
of TLn. The upper 3 bits of TLn are indeterminate and should be
ignored. Setting the run flag (TRn) does not clear the registers.
= 1. (Setting GATE = 1 allows the
, to facilitate pulse width
Mode 0 operation is the same for Timer 0 as for Timer 1. There are
two different GA TE bits, one for Timer 1 (TMOD.7) and one for Timer
0 (TMOD.3).
Mode 1
Mode 1 is the same as Mode 0, except that the Timer register is
being run with all 16 bits.
Mode 2
Mode 2 configures the Timer register as an 8-bit Counter (TLn) with
automatic reload, as shown in Figure 4. Overflow from TLn not only
sets TFn, but also reloads TLn with the contents of THn, which is
preset by software. The reload leaves THn unchanged.
Mode 2 operation is the same for Timer 0 as for Timer 1.
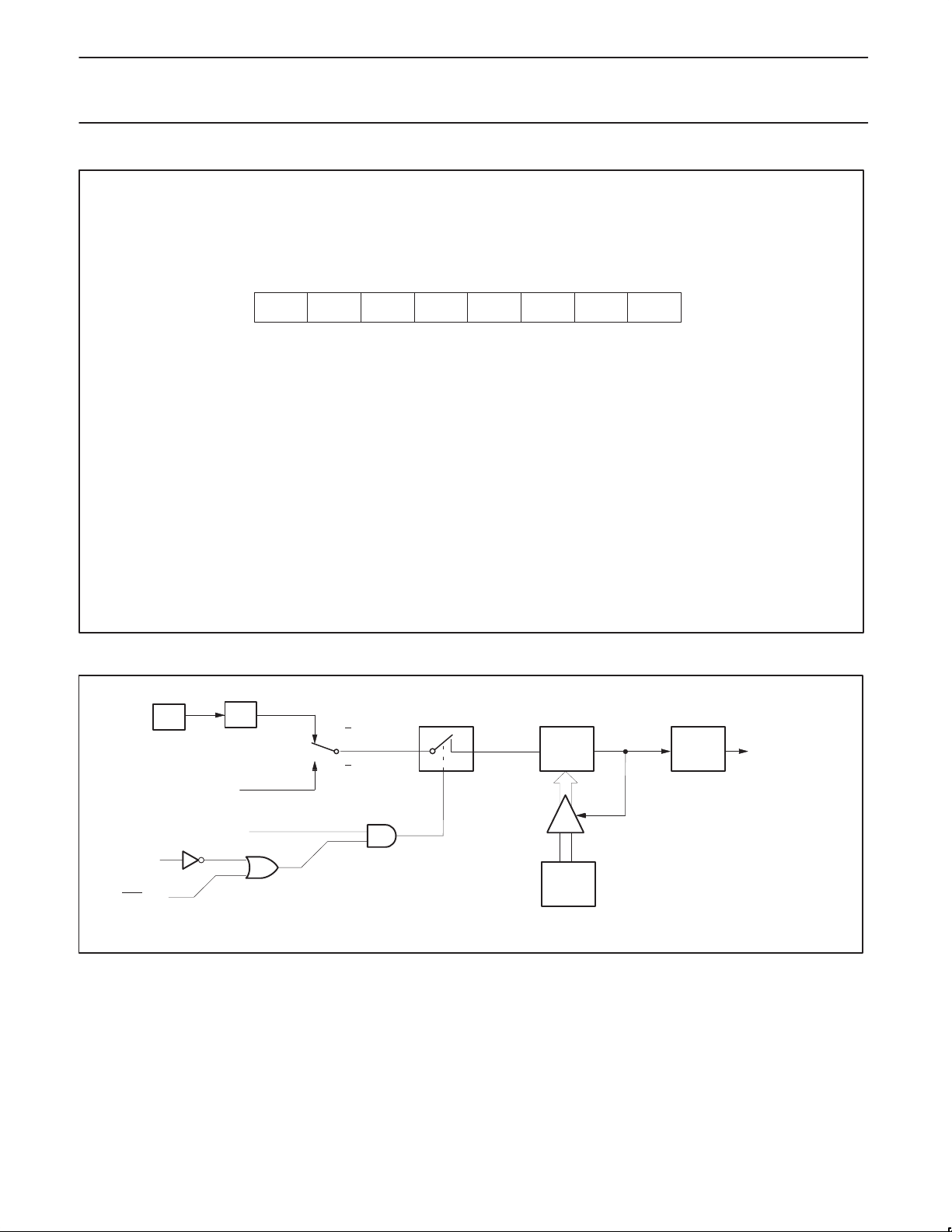
Mode 3
Timer 1 in Mode 3 simply holds its count. The effect is the same as
setting TR1 = 0.
Timer 0 in Mode 3 establishes TL0 and TH0 as two separate
counters. The logic for Mode 3 on Timer 0 is shown in Figure 5. TL0
uses the Timer 0 control bits: C/T
pin INT0
cycles) and takes over the use of TR1 and TF1 from Timer 1. Thus,
TH0 now controls the “Timer 1” interrupt.
. TH0 is locked into a timer function (counting machine
, GATE, TR0, and TF0 as well as
2002 Jun 06
12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
Mode 3 is provided for applications requiring an extra 8-bit timer on
the counter. With Timer 0 in Mode 3, an 80C51 can look like it has
three Timer/Counters. When Timer 0 is in Mode 3, Timer 1 can be
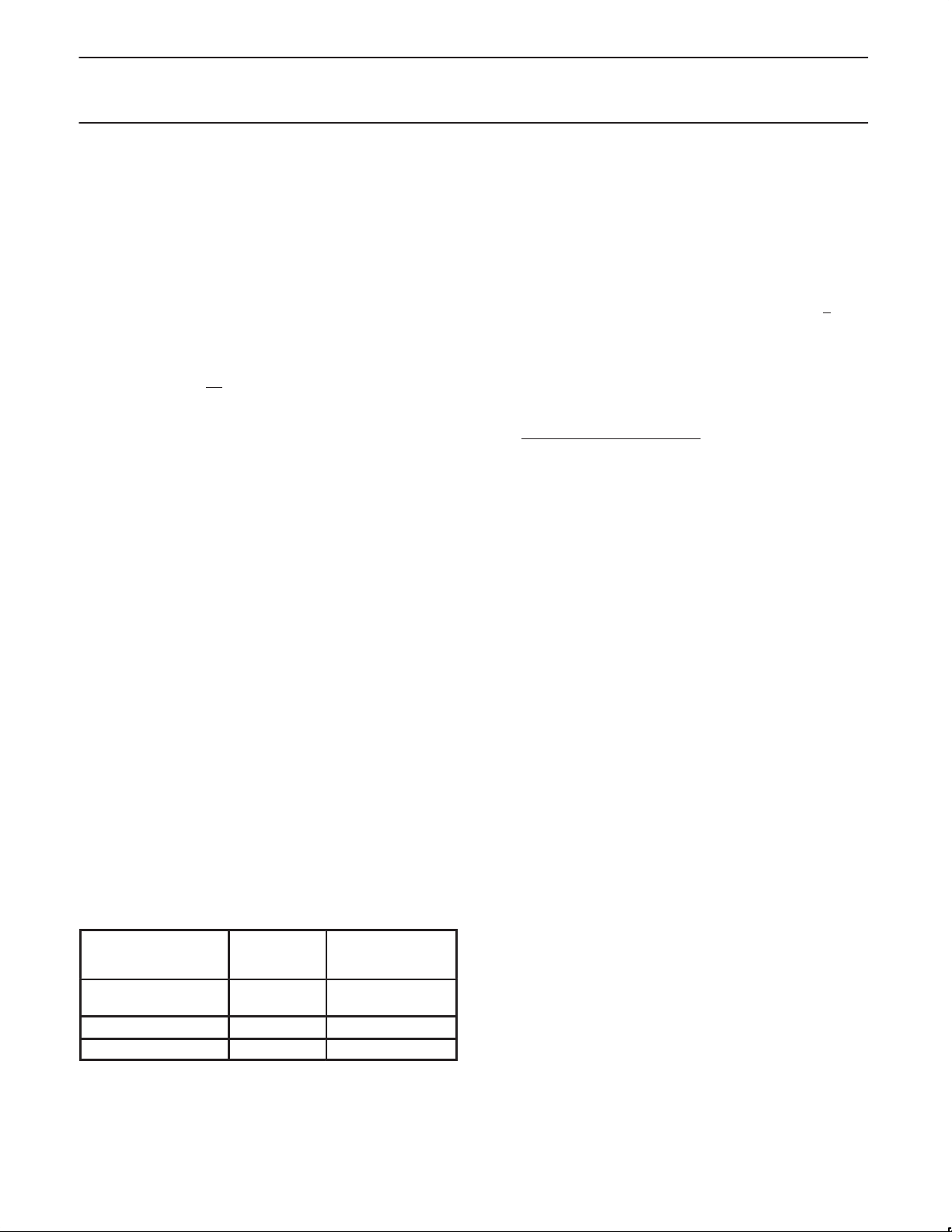
TMOD Address = 89H Reset Value = 00H
Not Bit Addressable
76543 2 1 0
GATE C/T M1
TIMER 1 TIMER 0
BIT SYMBOL FUNCTION
TMOD.3/ GATE Gating control when set. Timer/Counter “n” is enabled only while “INTn” pin is high and
TMOD.7 “TRn” control pin is set. when cleared Timer “n” is enabled whenever “TRn” control bit is set.
TMOD.2/ C/T
Timer or Counter Selector cleared for Timer operation (input from internal system clock.)
TMOD.6 Set for Counter operation (input from “Tn” input pin).
M1 M0 OPERATING
0 0 8048 Timer: “TLn” serves as 5-bit prescaler.
0 1 16-bit Timer/Counter: “THn” and “TLn” are cascaded; there is no prescaler.
1 0 8-bit auto-reload Timer/Counter: “THn” holds a value which is to be reloaded
into “TLn” each time it overflows.
1 1 (Timer 0) TL0 is an 8-bit Timer/Counter controlled by the standard Timer 0 control bits.
TH0 is an 8-bit timer only controlled by Timer 1 control bits.
1 1 (Timer 1) Timer/Counter 1 stopped.
turned on and off by switching it out of and into its own Mode 3, or
can still be used by the serial port as a baud rate generator, or in
fact, in any application not requiring an interrupt.
M0 GATE C/T
M1 M0
SU01580
Figure 1. Timer/Counter 0/1 Mode Control (TMOD) Register
OSC
Timer n
Gate bit
INTn Pin
*d = 6 in 6-clock mode; d = 12 in 12-clock mode.
÷ d*
Tn Pin
TRn
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
Control
TLn
(5 Bits)
THn
(8 Bits)
Figure 2. Timer/Counter 0/1 Mode 0: 13-Bit Timer/Counter
TFn Interrupt
SU01618
2002 Jun 06
13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
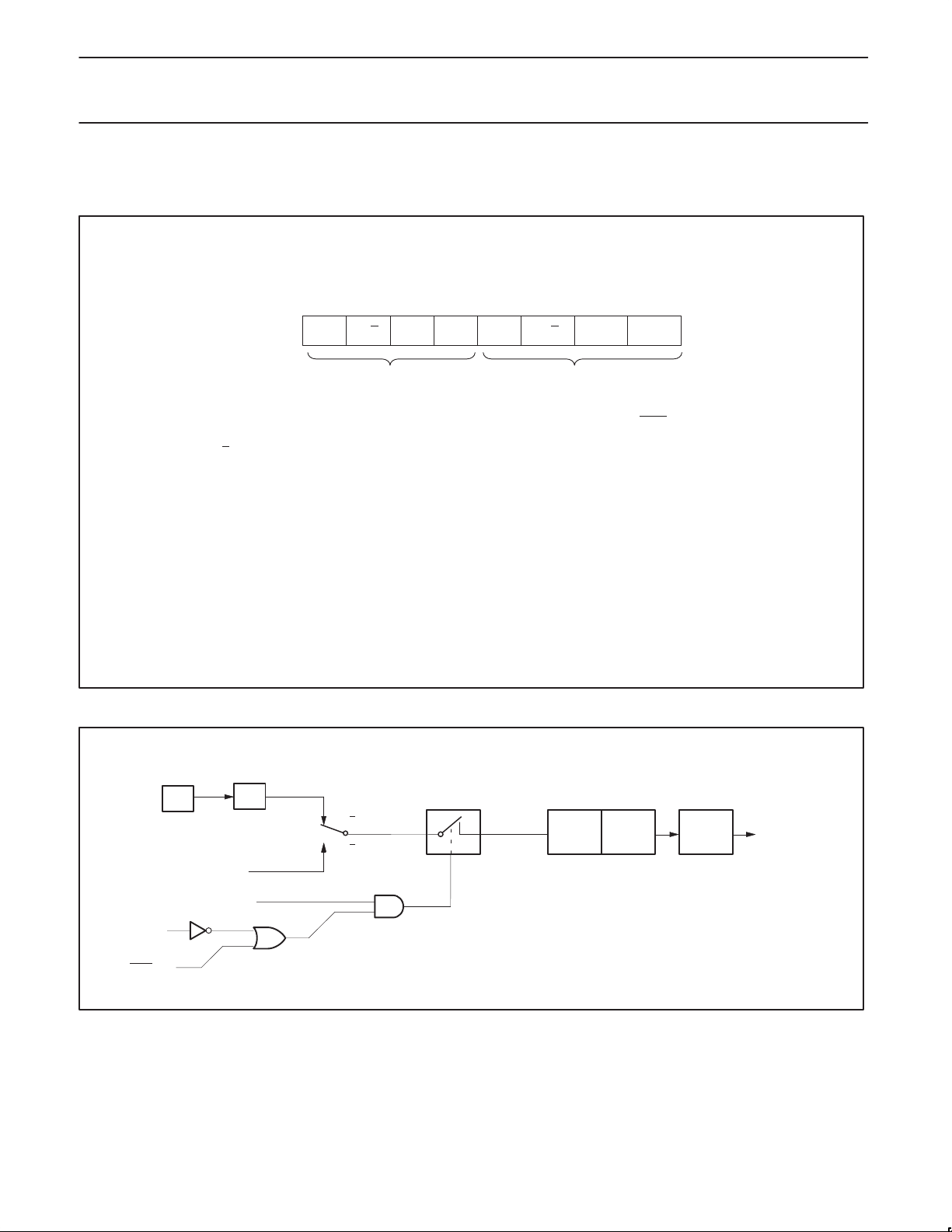
TCON Address = 88H Reset Value = 00H
Bit Addressable
76543210
IE0IT1IE1TR0TF0TR1TF1
BIT SYMBOL FUNCTION
TCON.7 TF1 Timer 1 overflow flag. Set by hardware on Timer/Counter overflow.
Cleared by hardware when processor vectors to interrupt routine, or clearing the bit in software.
TCON.6 TR1 Timer 1 Run control bit. Set/cleared by software to turn Timer/Counter on/of f.
TCON.5 TF0 Timer 0 overflow flag. Set by hardware on Timer/Counter overflow.
Cleared by hardware when processor vectors to interrupt routine, or by clearing the bit in software.
TCON.4 TR0 Timer 0 Run control bit. Set/cleared by software to turn Timer/Counter on/of f.
TCON.3 IE1 Interrupt 1 Edge flag. Set by hardware when external interrupt edge detected.
Cleared when interrupt processed.
TCON.2 IT1 Interrupt 1 type control bit. Set/cleared by software to specify falling edge/low level triggered
external interrupts.
TCON.1 IE0 Interrupt 0 Edge flag. Set by hardware when external interrupt edge detected.
Cleared when interrupt processed.
TCON.0 IT0 Interrupt 0 Type control bit. Set/cleared by software to specify falling edge/low level
triggered external interrupts.
IT0
SU01516
OSC
Timer n
Gate bit
INTn Pin
*d = 6 in 6-clock mode; d = 12 in 12-clock mode.
÷ d*
Tn Pin
TRn
Figure 3. Timer/Counter 0/1 Control (TCON) Register
C/T = 0
= 1
C/T
Control
TLn
(8 Bits)
THn
(8 Bits)
Reload
Figure 4. Timer/Counter 0/1 Mode 2: 8-Bit Auto-Reload
TFn
Interrupt
SU01619
2002 Jun 06
14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
OSC
Timer 0
Gate bit
INT0 Pin
OSC
*d = 6 in 6-clock mode; d = 12 in 12-clock mode.
T0 Pin
÷ d*
TR0
÷ d*
TR1
C/T = 0
= 1
C/T
Control
Control
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
TL0
(8 Bits)
TH0
(8 Bits)
TF0
TF1
Interrupt
Interrupt
SU01620
Figure 5. Timer/Counter 0 Mode 3: Two 8-Bit Counters
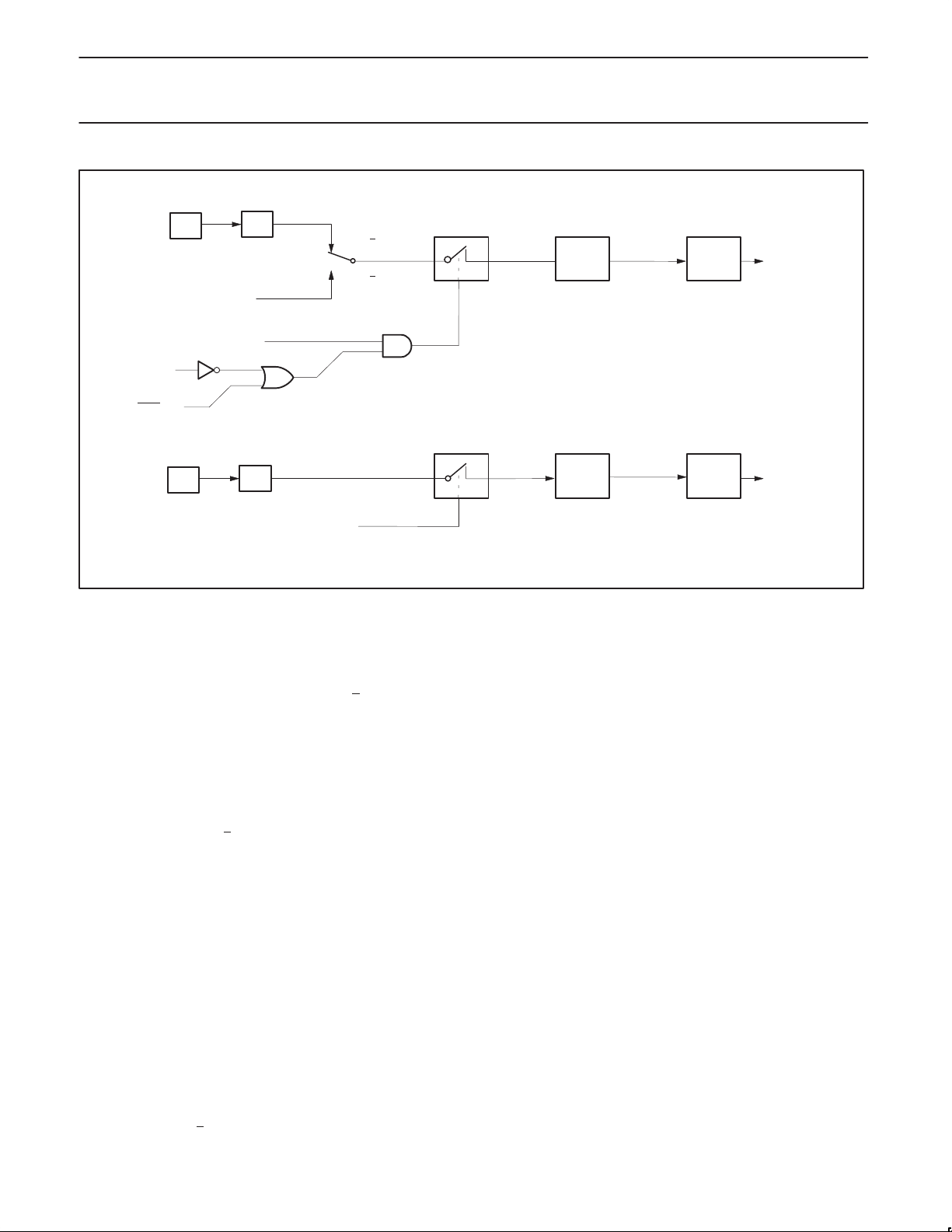
TIMER 2 OPERATION
Timer 2
Timer 2 is a 16-bit Timer/Counter which can operate as either an
event timer or an event counter, as selected by C/T
2 in the special
function register T2CON (see Figure 6). Timer 2 has three operating
modes: Capture, Auto-reload (up or down counting), and Baud Rate
Generator, which are selected by bits in the T2CON as shown in
Table 4.
Capture Mode
In the capture mode there are two options which are selected by bit
EXEN2 in T2CON. If EXEN2=0, then timer 2 is a 16-bit timer or
counter (as selected by C/T
2 in T2CON) which, upon overflowing,
sets bit TF2, the timer 2 overflow bit. This bit can be used to
generate an interrupt (by enabling the Timer 2 interrupt bit in the
IE register). If EXEN2=1, Timer 2 operates as described above, but
with the added feature that a 1-to-0 transition at external input T2EX
causes the current value in the Timer 2 registers, TL2 and TH2, to
be captured into registers RCAP2L and RCAP2H, respectively. In
addition, the transition at T2EX causes bit EXF2 in T2CON to be
set, and EXF2 (like TF2) can generate an interrupt (which vectors to
the same location as Timer 2 overflow interrupt. The Timer 2
interrupt service routine can interrogate TF2 and EXF2 to determine
which event caused the interrupt). The capture mode is illustrated in
Figure 7 (There is no reload value for TL2 and TH2 in this mode.
Even when a capture event occurs from T2EX, the counter keeps on
counting T2EX pin transitions or osc/12 (12-clock Mode) or osc/6
(6-clock Mode) pulses).
Auto-Reload Mode (Up or Down Counter)
In the 16-bit auto-reload mode, Timer 2 can be configured as either
a timer or counter (C/T
or down. The counting direction is determined by bit DCEN (Down
2 in T2CON), then programmed to count up
Counter Enable) which is located in the T2MOD register (see
Figure 8). After reset, DCEN=0 which means Timer 2 will default to
counting up. If DCEN is set, Timer 2 can count up or down
depending on the value of the T2EX pin.
Figure 9 shows Timer 2 which will count up automatically since
DCEN=0. In this mode there are two options selected by bit EXEN2
in T2CON register. If EXEN2=0, then T imer 2 counts up to 0FFFFH
and sets the TF2 (Overflow Flag) bit upon overflow. This causes the
Timer 2 registers to be reloaded with the 16-bit value in RCAP2L
and RCAP2H. The values in RCAP2L and RCAP2H are preset by
software.
If EXEN2=1, then a 16-bit reload can be triggered either by an
overflow or by a 1-to-0 transition at input T2EX. This transition also
sets the EXF2 bit. The Timer 2 interrupt, if enabled, can be
generated when either TF2 or EXF2 are 1.
In Figure 10 DCEN=1 which enables Timer 2 to count up or down.
This mode allows pin T2EX to control the direction of count. When a
logic 1 is applied at pin T2EX, Timer 2 will count up. Timer 2 will
overflow at 0FFFFH and set the TF2 flag, which can then generate
an interrupt, if the interrupt is enabled. This timer overflow also
causes the 16-bit value in RCAP2L and RCAP2H to be reloaded
into the timer registers TL2 and TH2.
A logic 0 applied to pin T2EX causes Timer 2 to count down. The
timer will underflow when TL2 and TH2 become equal to the value
stored in RCAP2L and RCAP2H. A Timer 2 underflow sets the TF2
flag and causes 0FFFFH to be reloaded into the timer registers TL2
and TH2.
The external flag EXF2 toggles when Timer 2 underflows or
overflows. This EXF2 bit can be used as a 17th bit of resolution if
needed. The EXF2 flag does not generate an interrupt in this mode
of operation.
2002 Jun 06
15
 Loading...
Loading...