Page 1

Colour Television Chassis
L04E
AA
E_14480_142.eps
260504
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Technical Specifications, Connections,
and Chassis Overview 2
2. Safety and Maintenance Instructions,
Warnings, and Notes 4
3. Directions for Use 6
4. Mechanical Instructions 7
5. Service Modes, Error C
6. Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews,
and Waveforms
Wiring Diagram 19
Block Diagram Supply and Deflection 20
Testpoint Overview Mono Carrier 21
Block Diagram Video 22
Testpoint Overview CRT, LTI & PIP Panel 23
Block Diagram Audio/Control 24
I2C and Supply Voltage Overview 25
7. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts Diagram PWB
Power Supply (Diagram A1) 26 38-43
Diversity Table for A1 (Power Supply) 27 38-43
Deflection (Diagram A2) 28 38-43
Diversity Table for A2 (Deflection) 29 38-43
Tuner IF (Diagram A3) 30 38-43
Hercules (Diagram A4) 31 38-43
Features & Connectivities (Diagram A5) 32 38-43
Class D - Audio Amplifier (Diagram A6) 33 38-43
Audio Amplifier (Diagram A7) 34 38-43
Rear I/O Scart (Diagram A8) 35 38-43
Front Control (Diagram A9) 36 38-43
DVD Power Supply (Diagram A10)37 38-43
CRT Panel (Diagram B1) 44 46-47
ECO Scavem Panel (Diagram B2) 45 46-47
Side AV + HP Panel (PV2) (Diagram D) 48 49
Side AV + HP Panel (FL-13) (Diagram D) 50 51
Top Control Panel (PV2) (Diagram E) 52 52
©
Copyright 2004 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
odes, and Fa
ultfinding 9
Top Control Panel (FL-13) (Diagram E) 53 53
Power Supply PIP Panel (Diagram F1) 54 56-57
Tuner IF and Demodulator PIP (Diagram F2) 55 56-57
Linearity & Panorama Panel (Diagram G) 58 58
LTI/CTI Interface Panel (Diagram H) 59 60
Front Interface Panel (FL-13) (Diagram J) 61 61
Front Interface Panel (PV2) (Diagram J) 62 62
Front Interface and Keyb. Panel (Diagram J) 63 64
8. Alignments 65
9. Circuit Descriptions 73
Abbreviation List 82
IC Data Sheets 84
10 Spare Parts List 86
11 Revision List 90
Published by BB 0466 Service PaCE Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 14480
Page 2
EN 2 L04E AA1.
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
Notes:
• Described specifications ar
e valid for the whole product
range.
• Figures below
can deviate slightly from the actual situation,
due to different set executions.
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.1.1 Vision
Display type : DV-CRT-RF
Scree
n size : 21” (55 cm), 4:3
Tuning system : PLL
TV Colour systems : PAL B/G
Video playback : NTSC
Channel selections : 100 presets
Aerial input : 75 ohm, Co
1.1.2 Sound
: DV-CRT-FSQ
: DV-CRT-SF
: 24” (61 cm), 16:9
: 25” (63 cm), 4:3
: 28” (70 cm), 4:3
: 29” (72 cm), 4:3
: 32” (82 cm), 16:9
, B/H, D/K, I
: SECAM
: SECAM B/G, D/K, L/L
: UVSH
ax
: IEC-type
'
onn
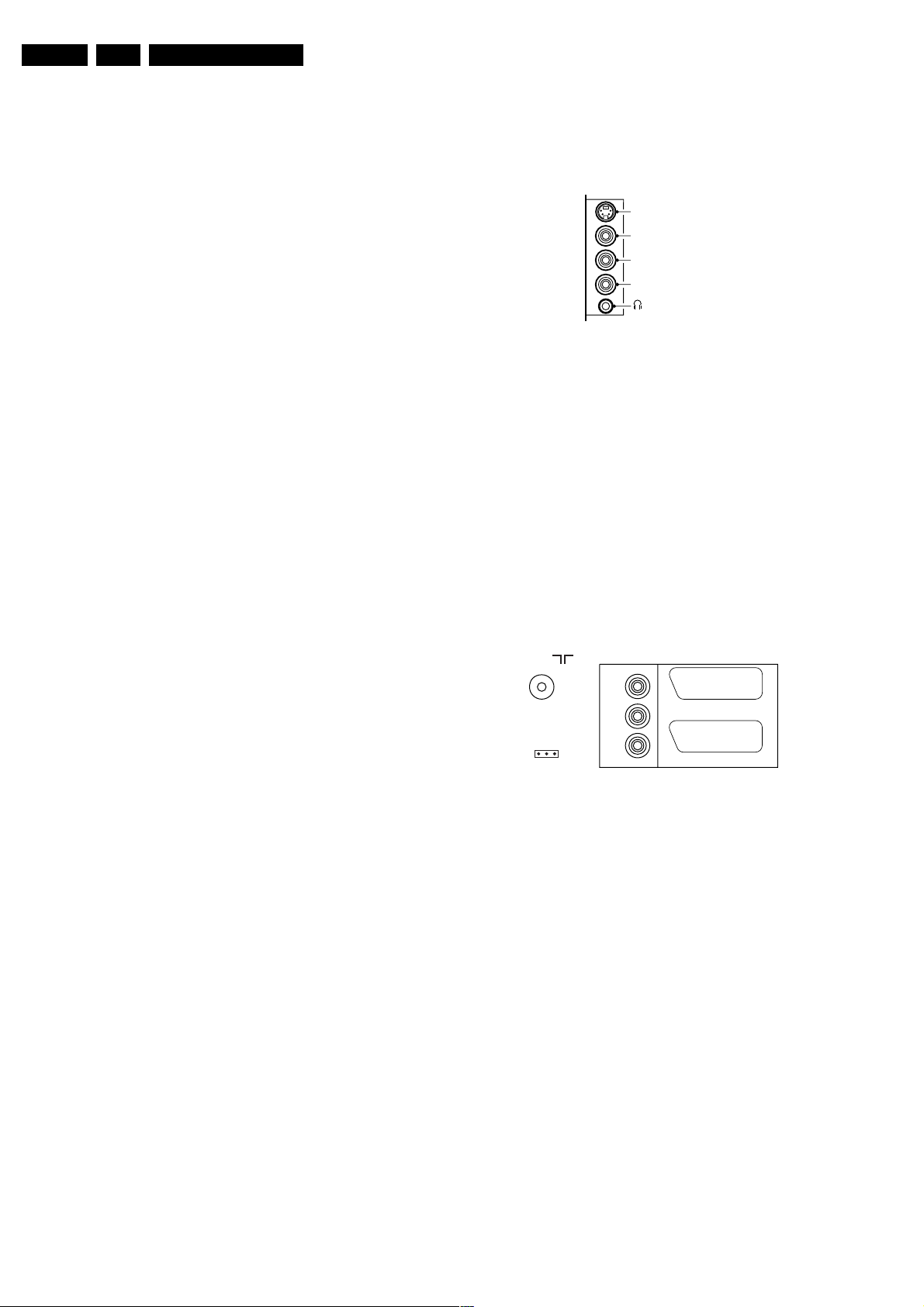
1.2.1 Side C
ections
SIDE I/O
S-Video (optional)
Video
L
Audio
R
E_14480_111.eps
060504
Figure 1-1 Side I/O
SVHS: Y/C - In (Hosiden) (optional)
1-Ground Gnd H
2- Ground Gnd H
3-Y 1 V_pp / 75 ohm j
4-C 0.3 V_pp / 75 ohm j
Audio / Video In
Ye -Video (CVBS) 1 V_pp / 75 ohm jq
Wh -Audio - L 0.5 V_rms / 10 kohm jq
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V_rms / 10 kohm jq
Bk -Headphone 8 - 600 Ohm / 4 mW ot
ections
1.2.2 Rear Co
nn
Sou
nd systems : NICAM Ster
ximum power : 2x10/ 2x5 W_rms
Ma
(int.)
1.1.3 Mis
cellaneo
us
Power supply:
- Mains voltage : 220 -
- Mains frequency : 50/60 Hz
Ambient conditio
ns:
- Temperature range : +5 to +40 deg. C
- Maximum humidity : 90 % R.H.
er consumption
Pow
- Normal operation : from 60
: to 91 W (32”
- Standby : < 1 W
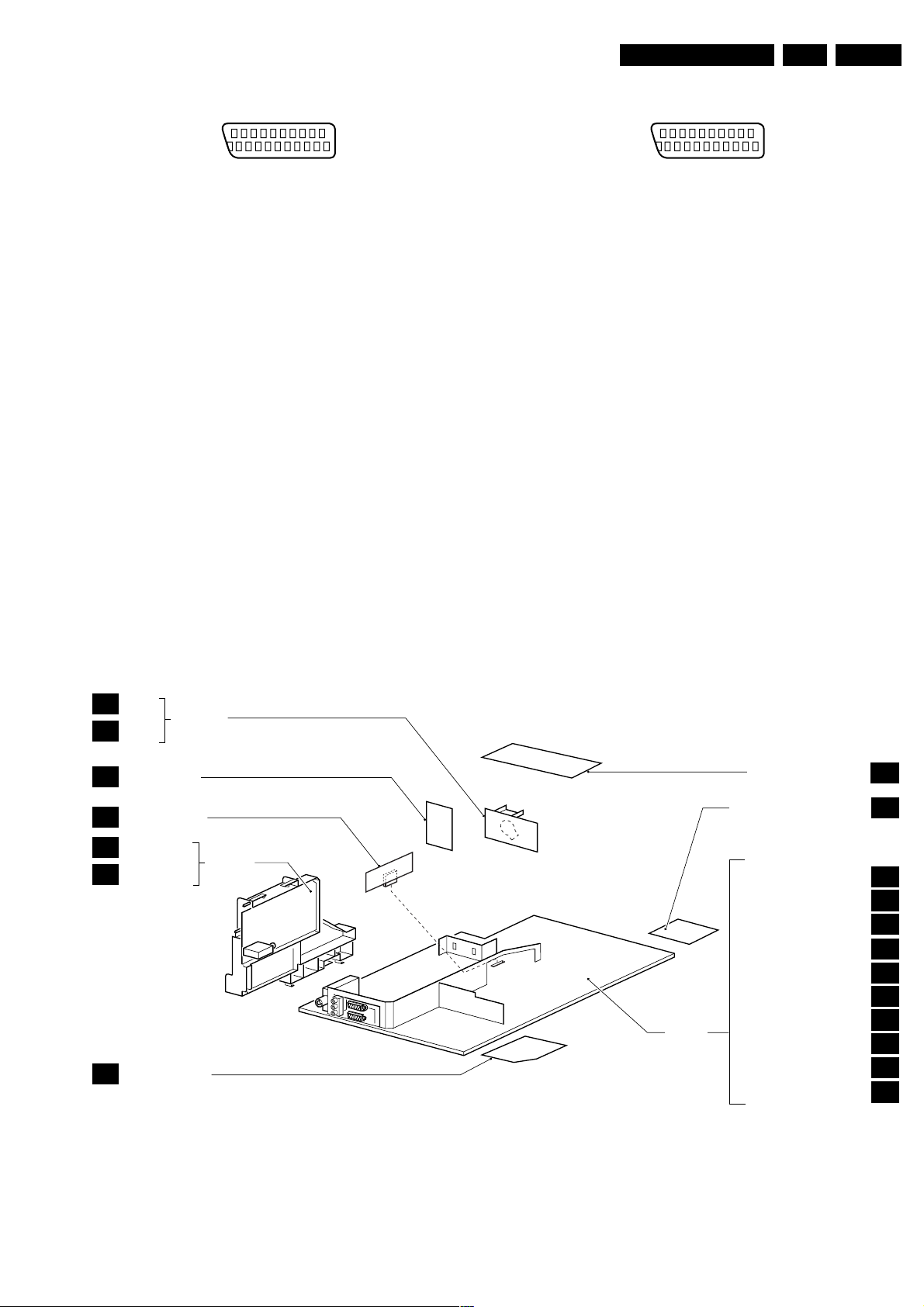
1.2 Connections
Note: The following connector colour abbreviations are used
(acc. to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green, Gy=
Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, Ye= Yellow.
eo
240 V_ac
W (21”)
)
AUDIO
75 Ohm
OUT
S
L
EXTERNAL 2
R
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
EXTERNAL 1
CL 36532058_080.eps
101003
Figure 1-2 Rear connections
Aerial In
-F-type Coax, 75 ohm D
Audio Out
1-Subwoofer Var. level (optional) kq
Wh -Audio - L 0.5 V_rms / 1 kohm kq
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V_rms / 1 kohm kq
Page 3
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
EN 3L04E AA 1.
External 1: RGB/YUV - In and CVBS - In/Out
20
21
2
E_06532_001.eps
050404
1
Figure 1-3 SCART connector
1-Audio - R 0.5 V_rms / 1 kohm k
2-Audio - R 0.5 V_rms / 10 kohm j
3-Audio - L 0.5 V_rms / 1 kohm k
4-Audio - gnd Ground H
5-Blue - gnd Ground H
6-Audio - L 0.5 V_rms / 10 kohm j
7-Blue/U - in 0.7 V_pp / 75 ohm j
8-CVBS - status 0 - 2 V: INT
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3
9-Green - gnd Ground H
10 - n.c.
11 - Green/Y - in 0.7 V_pp / 75 ohm j
12 - n.c.
13 - Red - gnd Ground H
14 - FBL - gnd Ground H
15 - Red/V - in 0.7 V_pp / 75 ohm j
16 - Status/FBL 0 - 0.4 V: INT
1 - 3 V: EXT / 75 ohm j
17 - Video Ground H
18 - Video Ground H
19 - CVBS - out 1 V_pp / 75 ohm k
20 - CVBS - in 1 V_pp / 75 ohm j
21 - Shielding Ground H
External 2: CVBS- In and SVHS - In
20
21
2
E_06532_001.eps
050404
1
Figure 1-4 SCART connector
1-Audio - R 0.5 V_rms / 1 kohm k
2-Audio - R 0.5 V_rms / 10 kohm j
3-Audio - L 0.5 V_rms / 1 kohm k
4-Audio - gnd Ground H
5-Blue - gnd Ground H
6-Audio - L 0.5 V_rms / 10 kohm j
7-n.c.
8-CVBS - status 0 - 2 V: INT
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3
9-Green - gnd Ground H
10 - n.c.
11 - n.c.
12 - n.c.
Red - gnd Ground H
13 14 - FBL - gnd Ground H
15 - YC-C - in 0.7 V_pp / 75 ohm j
16 - n.c.
17 - Video Ground H
18 - Video Ground H
19 - CVBS - out 1 V_pp / 75 ohm k
20 - Y/CVBS - in 1 V_pp / 75 ohm j
21 - Shielding Ground H
1.3 Chassis Overview
B1
CRT
ECO
B2
SCAVEM
SIDE AV PANEL +
D
HEADPHONE
LTI/CTI INTERFACE
H
PANEL
F1
POWER SUPPLY
TUNER IF &
F2
DEMODULATION
LINEARITY &
G
PANORAMA PANEL
CRT PANEL
PIP PANEL
MONO
CARRIER
TOP CONTROL PANEL
FRONT INTERFACE PANEL
POWER SUPPLY
LINE DEFLECTION
TUNER IF
HERCULES
FEATURES & CONNECTIVITIES
CLASS D AUDIO AMPLIFIER
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
REAR I/O CINCH
FRONT CONTROL
DVD POWER SUPPLY
E_14480_138.eps
E
J
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
260504
Figure 1-5 PWB location
Page 4
EN 4 L04E AA2.
Safety and Maintenance Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2. Safety and Maintenance Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require that during a repair:
• Due to the chassis concept, a very large
(incl. deflection) is 'hot'. Therefore, connect the set to the
mains via an isolation transformer.
• Replace
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
• Wear safety goggles when you replace the CRT.
Safe
e set
th
the following points:
• Gen
you to
horizontal deflection current is flowing. In particular this is
valid for the:
1. Pins of the line output
2. Fly-back capacitor(s).
3. S-correction capacito
4. Line output transistor.
5. Pins of the conn
6. Other components through which the deflection
Note: This re-solderin
due to metal fatigue in solder connections, and is therefore only
necessary for television sets more than two years old.
• Route the
them with the mounted cable clamps.
• Check th
damage.
• Check the strain
to prevent the cord from touching the CRT, hot
components, or heat sinks.
• Check the elect
and the secondary side (only for sets that have an isolated
power supply). Do this as follows:
1. Unplug the ma
2. Turn on the main pow
3. Measure the resistance va
4. Switch the TV 'off' and
• Check th
the customer touching any internal parts.
safety components, indicated
ty regulations require that after a repair, you must return
in its original condition. Pay, in particular, attention to
eral repair instruction: as a strict precaution, we advise
re-solder the solder connections through which the
transformer (LOT).
r(s).
ector with wires to the deflection coil.
flows.
g is advised to prevent bad connections
wire trees and
e insulation
relief of the mains cord for proper function,
r
ical DC resistance between the mains plug
two pins of the mains plug.
unplugged!).
mains plug and the metal shielding of the tuner or the
aerial connection of the set. The reading should be
between 4.5 MΩ and 12 MΩ.
two pins of the mains plug.
e cab
inet for defects, to prevent the possibility of
EHT cable correctly and secure
of the mains cord for external
ins cord and
connect a wire between the
er switch (keep the mains cord
lue betwe
remove the wire between the
part of the circuitry
by the symbol h,
current
en the pins of the
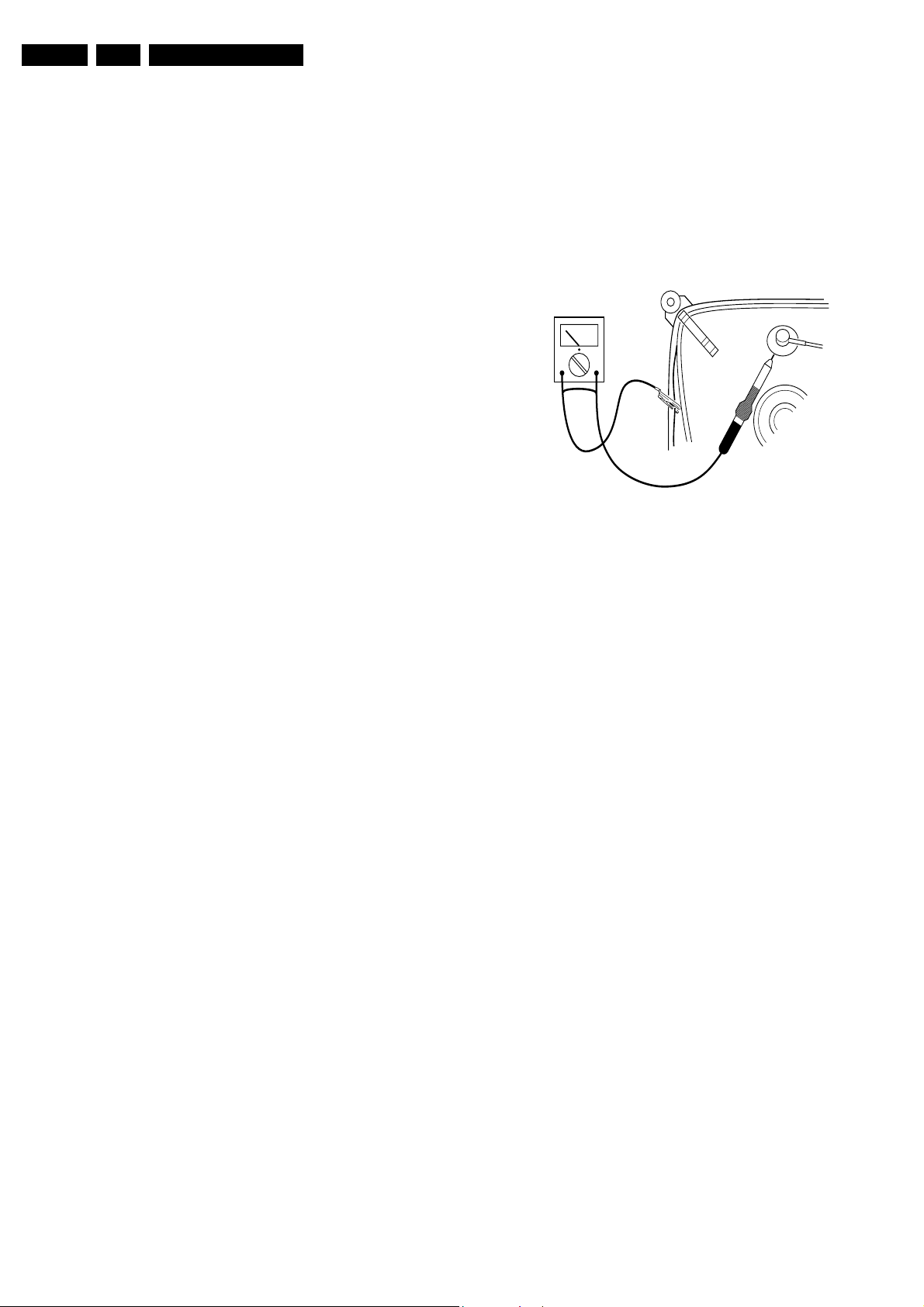
2.3 Warnings
• In order to prevent damage to ICs and transistors, avoid all
high voltage flashovers. In order to prevent damage to the
picture tube, use the method shown in Fig. 2-1, to
discharge the picture tube. Use a high voltage probe and a
multi-meter (position V_dc). Discharge until the meter
reading is 0 V (after approx. 30 s).
V
Figure 2-1 Discharge picture tube
ot
• All ICs and many
electrostatic discharges (ESD, w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this potential. Available ESD
protection equipment:
omplete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
– C
connection box, extension cable and ground cable
4822 310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13
• Together with the deflection unit and any multi-pole unit,
flat square p
deflection and the multi-pole units are set optimally at the
factory. We do not recommend adjusting this unit during
repair.
• Be carefu
section and on the picture tube.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is 'on’.
• When yo
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
l during
u
align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
her semiconductors are susceptible to
999.
icture tubes form an integrated unit. The
measurements in the high voltage
2.4 Notes
E_06532_007.eps
250304
)
2.2 Maintenance Instructions
We recommend a maintenance inspection carried out by
qualified service personnel. The interval depends on the usage
conditions:
en a customer uses the set under normal
• Wh
circumstances, for example
recommended interval is three to five years.
en a customer uses the set in an environment with
• Wh
high
er dust, grease, or moisture levels, for example in a
kitchen, the recommended interval is one year.
intena
• The ma
1. Perform the 'general repair instru
2. Clean the power supply and deflection circuitry on the
chassis.
3. Clean the pictu
tube.
nce inspection includes the following actions:
r
in a living room, the
ction' noted above.
e tube panel and the neck of the picture
2.4.1 General
• Measure the voltage
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry.
he voltages and waveforms shown in the diagrams are
• T
indicative. Measure them in the Service Default Mode (see
chapter 5) with a color bar signal and stereo
(L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated otherwise) and picture
carrier at 475.25
(channel 3).
• Where nece
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in standby (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
s and waveforms with regard to the
sound
MHz fo
r PAL, or 61.25 MHz for NTSC
s
sary, measure the waveforms and voltages
Page 5

Safety and Maintenance Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
EN 5L04E AA 2.
• The picture tube panel has printed spark gaps. Each spark
gap is connected between an electrode of the picture tube
and the Aquadag coating.
he semiconductors indicated in
• T
the parts lists, are interchangeable per position with the
semiconductors in the unit, irrespective of the type
indication on these semiconductors.
tic Notes
2.4.2 Schem
2.4.3 Practic
a
• All resistor values are in ohms and the value multiplier is
of
ten used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 kohm).
esistor values with no multiplier may b
• R
either an "E" or an "R" (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220
ohm).
• All capacitor valu
(µ= x 10^-6), nano-farads (n= x 10^-9),
(p= x 10^-12).
apacitor values may also use the value mult
• C
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An "asterisk" (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
the diversity tables for the correct values.
to
• The correct component values are listed in the Electrical
eplacement Parts List. Therefore, always check this list
R
when there is any doubt.
al Service Precaution
es are expressed in
the circuit diagram and in
e indicated with
micro-farads
or pico-farads
s
iplier as the
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature around
217 - 220 deg. C
• Do not mix lead-free soldering tin with lead
this will lead to un
• Use only original spare parts listed
are lead-free parts!
• On the website
find more information on:
– Aspects of lead-free technology.
– BGA (de-)soldering
Philips sets, and others
is reached at the solder joint.
reliable solder joints!
www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com you can
,
heating-profiles of BGAs used in
ed soldering tin;
in this manual. These
• It makes sense
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
lways respect voltages. While some may not be
• A
da
ngerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions - reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching
into a powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage
insulation. It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
efore powering up the TV set with the back cover off
• B
(or on a
ground and to a screwdriver blade that has a well insulated
handle. After the TV is powered "on" and high voltage has
developed, probe the anode lead with the blade, starting at
the case of the High Voltage Transformer (flyback - IFT).
Move the blade to within two inches of the connector of the
CRT. If there is an arc, you found it the easy way,
without getting a shock! If there is an arc to the
screwdriver blade, replace the part that is causing the
problem: the High Voltage Transformer or the lead (if it is
removable).
2.4.4 L
ead Free Solder
T
his set is manufactured with lead-free
This is also indicated on the PWB by the PHILIPS lead-free
logo (either by a service-printing or by a sticker).
to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
test fixture), attach a clip lead to the CRT DAG
production technology.
P
b
Figure 2-2 Lead-free logo
This set is produced with lead-free solder
lead-free sub-parts. It can be considered as lead-free.
Due to this fact, some rules have to be respected by the
workshop during a rep
• Use only lead-free soldering tin
code 0622 149 00106. If lead-free solder paste is required,
please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment.
se only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
• U
soldering tin.
air:
alloy as well as with
Philips SAC305 with order
Page 6
EN 6 L04E AA3.
3. Directions for Use
You can download this information from the following website:
http://www.philips.com/support
1. Click on “Dow
2. Fill in the T
Type?” [2] and click on “Search” [3].
Note: The correct model/typenumber can be found on the
rear cover
model/typenumber, just fill in e.g. “32PW95” or “PW95” (do
not use wildcards).
en results are returned, click o
3. Wh
typenumber under “Model” [4].
4. Now, click on the “Owner's manual” [5]
language. To read/open the PDF files you can download
and install the free Acrobat Reader
http://www.adobe.com/products/acrobat/readstep2.html
1
nloads and Troubleshooting” [1].
V model/type number in the field “Which Model/
of the set. If you do not have the complete
n the desired model/
in the desired
Directions for Use
2
4
Figure 3-1 Screenshot DFU website (1)
E_06532_015.eps
050404
3
5
Figure 3-2 Screenshot DFU website (2)
E_06532_016.eps
050404
Page 7
4. Mechanical Instructions
Mechanical Instructions
EN 7L04E AA 4.
Index of this chapter:
1. Set Disassembly
2. Service Position
3. Assies/Panels Removal
4. Set Re-a
Note: Figures below can deviate slightly fro
ssembly
m the actual
situation, due to different set executions.
4.1 Set Disassembly
Warning: Be sure to disconnect the AC power from the set
before opening it.
4.1.1 Rea
Cover
r
1. Remove all fixation screws of the rear cover (do not forget
th
e screws that hold the rear connection panel).
2. Pull the rear cover backwards to remove it.
4.2 Service Position
Before placing the Mono Carrier in its service position, remove
the Front Interface assy/panel (see paragraph “Front Interface
Assy/Panel removal”), the Side AV assy/panel (see paragraph
“Side AV Assy/Panel removal”) and the PIP assy/panel (if
exists) (see paragraph “PIP Assy/Panel removal”).
1. Disconnect the de
gaussing coil [1].
2. Release the two fixation clamps (at the
right side of the bracket), and remove the bracket from the
bottom tray, by pulling it backwards [2].
3. Turn the chassis
tray 90 degrees counte
4. Move the panel bracket somewhat to the le
degrees [3], with the components towards the CRT.
5. Turn the pane
6. Place the hook of the tray in t
l bracket with the rear I
he fixation hole of the cabinet
bottom [4] and secure it.
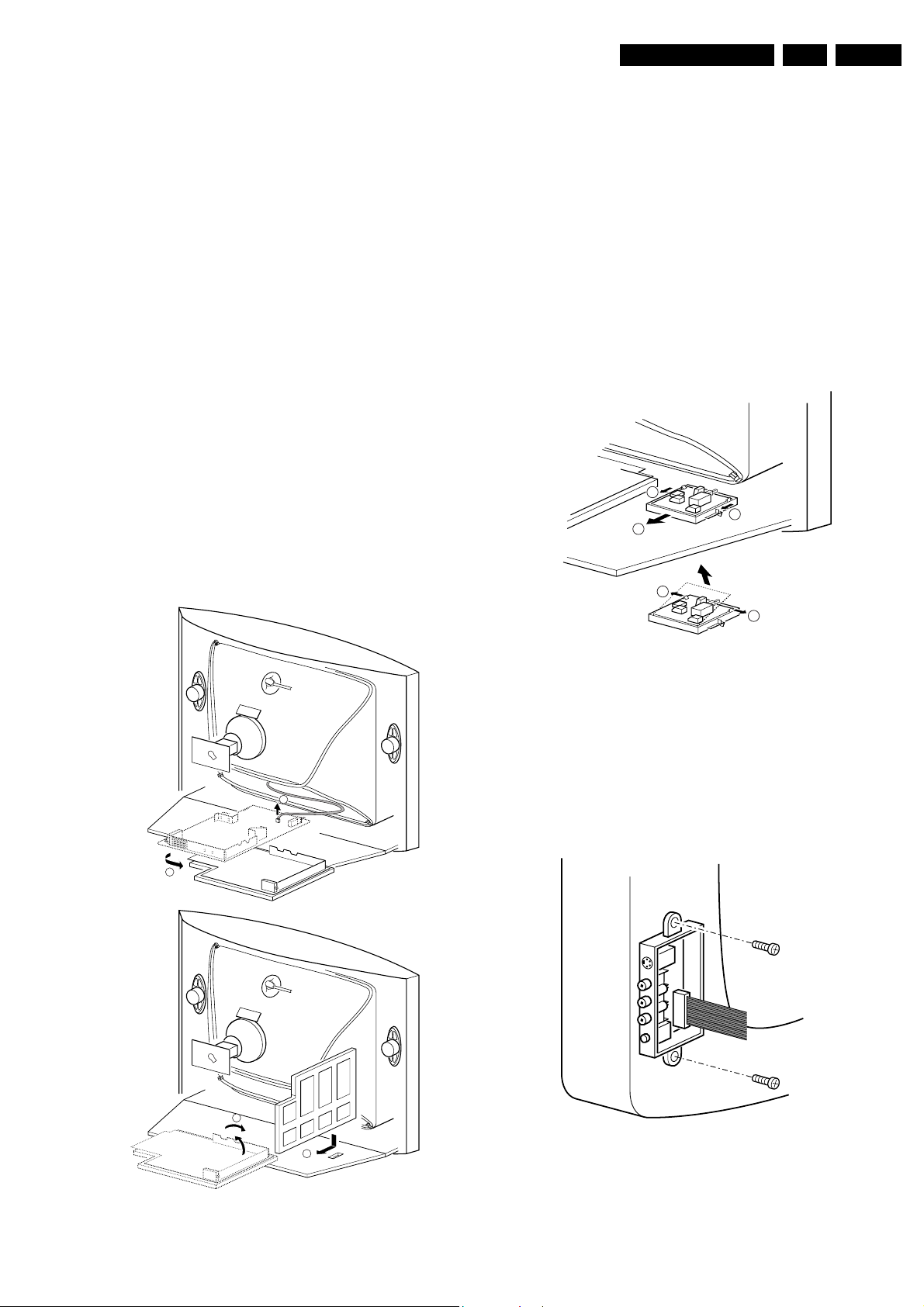
4.3 Assies/ Panels Removal
4.3.1 Front Interface Assy/Panel Removal
1
2
3
1
3
mid left and mid
r clockwise.
ft and flip it 90
/O toward the CRT.
E_14480_049.eps
110204
Figure 4-2 Front interface assy/panel removal
1. Remove the complete module from
the bottom plate, by
pulling the two fixation clamps upward [1], while sliding the
module away from the CRT [2].
i
Note: these clamps are diff
cult to access.
2. Release the two fixation clamps [3] at the side of the
bracket, and lift
1
one side).
4.3.2 Side AV Assy/Panel R
2
A
the panel out of the bracket (it hinges at
emoval
3
4
B
E_14480_048.eps
Figure 4-1 Service position Mono Carrier
110204
E_14480_050.eps
Figure 4-3 Side AV assy/panel removal
1. Remove the two fixation screws,
Side AV assembly.
2. Release the two fixation cla
mps, and lift the panel out of the
bracket.
170204
and remove the complete
Page 8
EN 8 L04E AA4.
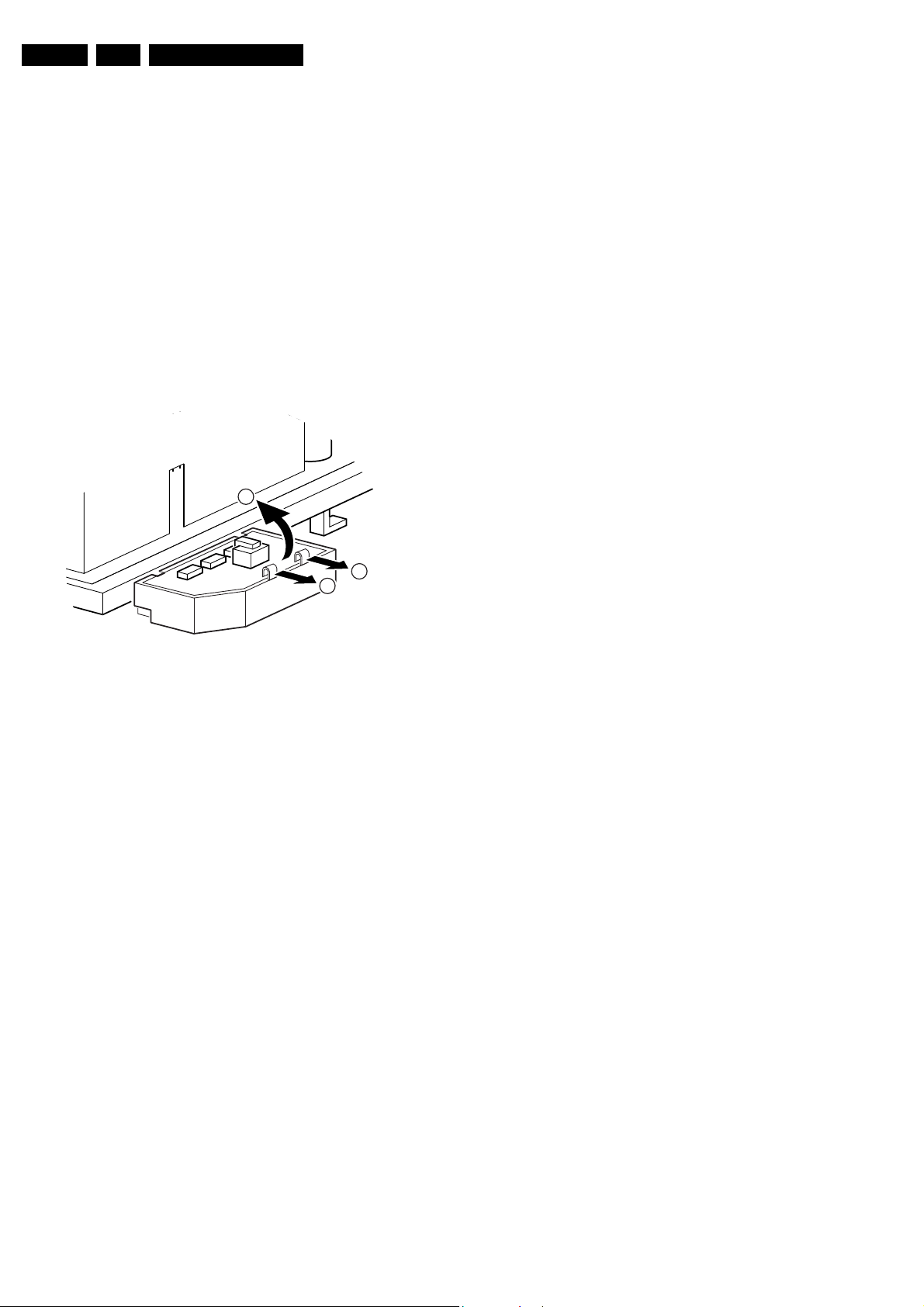
4.3.3 LTI/CTI Interface Panel Removal
Remove the LTI/CTI Interface panel from the Mono Carrier, by
di
sconnecting it from connector 1212.
4.3.4 Top Control Assy/Panel Removal
tes:
No
• PV02 styling: assy is mounted in the front cabinet;
• FL13B styling: assy is mounted in the rea
1. Remove the two
2. Push the assy a little bit upwards, an
backwards to release it from the front hinge.
he panel from its bracket, while rele
3. Lift t
fixation clamps.
fixation scre
ws.
d then pull it
Mechanical Instructions
r cover.
asing the four
4.3.5 L
4.3.6 PIP A
inearity Assy/Panel Removal
Fig
1. Release the two fixa
the bracket [2].
ssy/Panel R
1. Release the two fixa
bracket.
2
E_14480_051.eps
ure 4-4 Linearity assy/panel removal
tion clamps [1] to lift the panel out of
emoval
tion clamps to lift the panel out of the
1
1
270204
4.4 Set Re-assembly
To re-assemble the whole set, do all processes in reverse
order.
Note: before you mount the rear cover, pe
checks:
1. Check wh
its guiding brackets.
2. Check whether a
position
ether the AC
power cord is mounted correctly in
ll cables are replaced in their original
rform the following
Page 9
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 9L04E AA 5.
Index:
1. Test Points.
2. Service Modes.
3. Problems and
Solving Tips (related to CSM).
4. ComPair.
5. Error Codes.
6. The Blinking LED Procedure.
7. Protections.
8. Repair Tips.
5.1 Test Points
The chassis is equipped with test points printed on the circuit
board assemblies. These test points refer to the functional
blocks:
Table 5-1 Test point overview
Test point Circuit Diagram
F508, F535, F536, F537, F552, F561, F563,
F
573, F664,I513, I518, I519, I524, I5 31, I533,
I546
F401, F412, F413, F414, F418, F452, F453,
455, F456, F458, F459, F460, F461, I408,
F
I416, I417, I420, I462, I468
F003, F004, I001, I002 Tuner IF A3
F201, F203, F205, F206 Hercules A4
F240, F241, F242 Features &
F952, F955, I951, I952 Audio Amplifier A7
F692 Front Control A9
F331, F332, F333, F338, F339, F341, F351,
F353, F354
F361, F362, F381, F382 ECO Scavem B2
Power supply A1
Line + Frame
Deflection
Co
nnectivities
CRT Panel B1
Perform measurements under the following conditions:
• Television set in Service Def
ault Alignment Mode.
• Video input: Colour bar signal.
• Audio input: 3 kHz left cha
nnel, 1 kHz right channel.
5.2 Service Modes
Service Default mode (SDM) & Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
offers several features for the service technician, while the
Customer Service Mode (CSM) is used for communication
between the call centre and the customer.
tion o
This chassis also offers the op
hardware interface between a computer and the TV chassis. It
offers the abilities of structured troubleshooting, error code
reading, and software version readout for all these chassis.
Minimum requirements for ComPair: a Pentium processor, a
Windows OS, an
d a CD-ROM drive (se
f using ComPair, a
e "ComPair" section).
Table 5-2 Software cluster overview
SW Clusters SW Version First Mask Remarks
L4LEF1 L04EF11.0
L4LEF2 L04EF21.0
L4LEF3 L04EF31.0
L4LEF4 L04EF41.0
L4LEF5 L04EF51.0
L4LEF6 L04EF61.0
L4LEF7 L04EF71.0 TDA12020H1/N1B11 ICON UI
A2
5.2.1 Service
Default Mode (SDM)
TDA12020H1/N1B11 Western Europe
TDA12021H1/N1B11 Radio 4:3 set only.
TDA12020H1/N1B11 Eastern Europe
TDA12021H1/N1B11 Radio 4:3 set only.
TDA12020H1/N1B11 Western Europe
TDA12021H1/N1B11 PIP
TDA12020H1/N1B11 Eastern Europe
TDA12021H1/N1B11 PIP
TDA12020H1/N1B11 Western Europe
TDA12021H1/N1B11 Radio & PIP.
TDA12020H1/N1B11 Eastern Europe
TDA12021H1/N1B11 Radio & PIP.
Purpose
A5
• To create a predefined setting for measurements to be
made.
• To override software protections.
• To start the blinking LED proc
edure.
Specifications
• Tuning frequency:
• Colour system: P
• All picture settings at 50
475.25 MHz.
AL/SECAM.
%
(brightness, colour contrast, hue).
• Bass, treble and balance
• All service-unfriendly modes (if present)
at 50 %; volume at 25 %.
are disabled. The
service unfriendly modes are:
– Timer / Sleep timer.
– Child / parental lock.
– Blue mute.
– Hotel / hospital mode.
– Auto shut o
ff (when no 'IDENT' video signal is received
for 15 minutes).
– Skipping of non-favourite preset
s / channels.
– Auto-storage of personal presets.
– Auto user menu time
-out.
– Auto Volume Levelling (AVL).
How to enter
To enter SDM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: '0 6 2
5 9 6' directly followed by the 'MENU'
button (do not allow the display to time out between entries
while keying the sequence).
925
• Short jumper wires
2 and 9275 on the family board (see
Fig. 8-1) and apply mains. Then press the power button
(remove the short after start-up).
y
Caution: Entering SDM b
shorting wires 9252 and 9275
will override the +8V-protection. Do this only for a short
period. When doing this, the service-technician must know
exactly what he is doing, as it could damage the television
set.
• Or via C
omPair (with the C
omPair ‘Tools’, it should be
possible to enter SDM via the ComPair interface).
After entering SDM, the following screen
is visible,
with SDM in
the upper right corner of the screen to indicate that the
television is in Service Default Alignment Mode.
Page 10
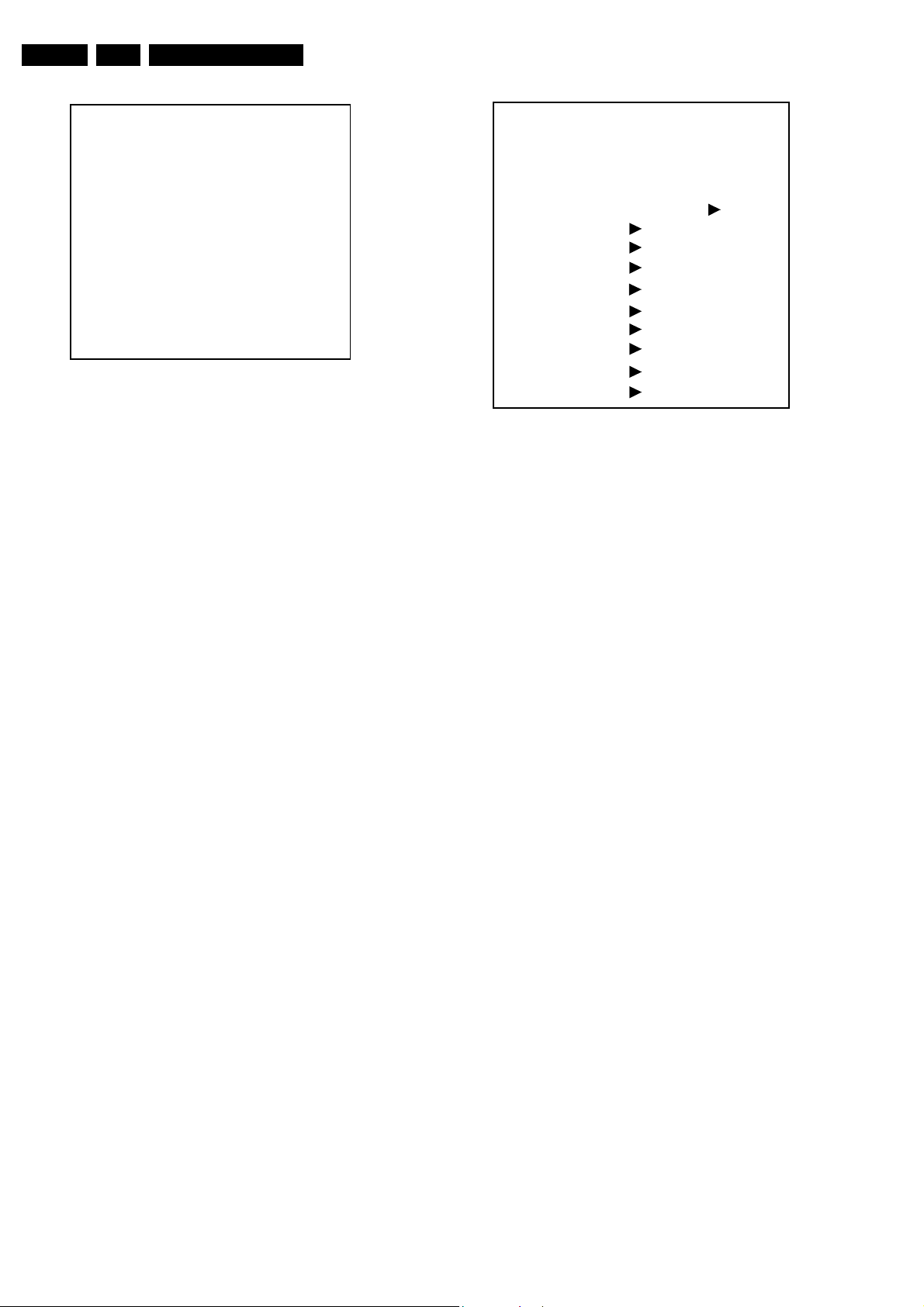
EN 10 L04E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
00028 L04EF30.10 SDM
ERR 0 0 0 0 0
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
E_14480_139.eps
Figure 5-1 SDM menu
How to navigate
Use one of the following methods:
• When you press the MENU button on the remote control,
the set will sw
mode.
the TV, press and hold the 'VOLUME down' and press
• On
the 'C
SDM to SAM and reverse.
How to exit
Switch the set to STANDBY by pressing the POWER button on
e remote control t
th
If you turn the television set off by removing the Mains (i.e.,
nplug
ging the television) without using the POWER button,
u
the television set will remain in SDM when mains is re-applied,
and the error buffer is not cleared.
5.2.2 Servic
e Align
Purpose
• To change option settings.
• To display / clear the error code
• To perform alignments.
Specifications
• Run timer (maximum five digits displayed
• Software version, Error & Option Byt
• Clear error buffer.
• Option settings
• AKB switching
• Software alignments (T
Geometry & Audio)
• NVM Editor
• ComPair Mode switching
w to enter
Ho
To enter SAM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the
transmitter: '0 6 2 5 9 6' directly followed by the “On Screen
Display icon “i +” button (do not allow the display to time out
between entries while keying the sequence).
• Or via ComPair.
After entering SAM, the following scr
the upper right corner of the screen to indicate that the
television is in Service Alignment Mode.
itch on the normal user menu in the SDM
HANNEL down' for a few seconds, to switch from
ransmitter or the television set.
ment Mode (SAM)
buffer.
es display
uner, 2 Tuner PIP, White Tone,
following key seque
nce on the remote control
en is visible, with SAM in
e
)
250504
00028 L04EF30.10 SAM
ERR 0 0 0 0 0
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
. Clear Clear ?
. Options
. AKB On
. Tuner
. 2 Tuner PIP*
. White Tone
. Geometry
. Audio
. NVM Editor
. ComPair on
optional
*
Figure 5-2 SAM menu
Menu explanation
LLLL. T
1. L
normal operation hours, but does not count standby hours
(maximum four digits displayed).
2. AA
main microprocessor:
– A = the project name (L04).
– B = the region: E= Europe, A= Asia Pacific, U= NAFTA,
– C = the software diversity:
– D = the language cluster number.
– X = the main software version number (updated with a
– Y = the sub software version
3. SAM. In
4. Error Buffer. Shows all errors
the buffer was erased. Five errors possible.
5. Option Bytes. U
in the Alignments section for a detailed description. Seven
codes are possible.
6. Cle
CLEAR
content of the error buffer is cleared.
7. Op
Alignme
8. AK
current loop' (AK
9. Tuner. U
Alignments section for a detailed description.
10. 2
11. White Tone. Used to
in the Alignments section for a detailed description.
12. Geo
televisio
detailed description.
13. Au
set.
his represents the run timer. The run timer counts
ABCD-X.Y. This
AM.
L= LAT
• Europe: T =
control.
• LATAM and NAFTA: N = Stere
Stereo dBx.
• Asian P
NTSC.
• ALL regions:
major chan
versions).
minor change that is compatible with previous
versions).
dication of the Service Alignment Mode
ar. Erases the contents of the error buffer. Select the
menu item and press the MENU RIGHT key. The
tions. Used to set the option bits. See 'Options' in the
nts section for a detailed description.
B. Used to disable (Off) or enable (On) the 'black
sed to align the tuner. See 'Tuner' in the
Tuner PIP. Used to align the tuner PIP (optional)
metry. Used to align the geometry settings of the
n. See 'Geometry' in the Alignments section for a
dio. No audio alignme
is the software identification of the
1 page TXT, F = Full TXT, V = Voice
a
cific: F = Full TXT, N = non TXT, C =
M = mono, D = DVD, Q = Mk2.
ge that is incompatible with previous
sed to set the option bytes. See 'Options'
B = Auto Kine Bias).
align the white tone. See 'White Tone'
nt is necessary for this television
E_14480_140.eps
260504
o non-dBx, S =
number (updated w
detected since the last time
ith a
.
Page 11

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
14. NVM Editor. Used to change the NVM data in the
television set.
mPair Mode. Used to switch on the television to ISP
15. Co
mod
e (for uploading software)
How to navigate
• In SAM, select menu items with the MENU UP/DOWN keys
on
the remote control transmitter. The selected item will be
highlighted. When not all menu items fit on the screen, use
the MENU UP/DOWN keys to display the next / previous
menu items.
LEFT/R
• With the MENU
– Activate the selected menu item.
– Change the value of th
– Activate the selected submenu.
• In SAM, when you press the MENU button twice, the set
ill switch to the normal user menus (with the SAM mode
w
still active in the background). To return to the SAM menu
press the MENU or STATUS/EXIT button.
• When you press the ME
submenu, you will return to the previous menu.
IGHT keys, it is possible to:
e selected menu item.
NU key in while in an SDAM
1 00028 L04EF30.10 CSM
2 CODES 0 0 0 0 0
3 OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
4 nnXXnnnn/nnX
5 P3C-1
6 NOT TUNED
7 PAL
8 STEREO
9 CO 50 CL 50 BR 50 HU 0
0 AVL Off BS 50
E_14480_141.eps
igure 5-3 CSM menu
F
EN 11L04E AA 5.
250504
How to store SAM settings
To store settings changed in SAM leave the top level SAM
menu by
transmitter or the television set.
How to exit
Switch the set to STANDBY by pressing the POWER button on
the remote contro
If you turn the television set off by removing the mains (i.e.,
unplugging the television) without
the television set will remain in SAM when mains is re-applied,
and the error buffer is not cleared.
5.2.3 Cu
Purpose
T
information on the TV operation se
instruct the customer to enter CSM by telephone and read off
the information displayed. This helps the call centre to
diagnose problems and failures in the TV set before making a
service call.
The CSM is a read-only mode; therefore, modifications are not
possible in this mode.
How to enter
To enter CSM, press the following key sequence on the remote
control tra
out between entries while keying the sequence).
Upon entering the Customer Service Mode, the following
screen will appear:
using the POWER button on the remote control
l transmitter or the te
stomer Service Mode (CSM)
he Customer Service Mode shows error codes and
nsmitter: '
1 2 3 6 5 4' (do not allow the display to time
levision set.
using the POWER button,
ttings. The call centre can
Menu explanation
1. Indication of the service mode (CSM = Customer Service
Mode).
2. Reserved item.
3. Software ide
'Service Default Alignment Mode' for an explanation)
4. Reserved item for P3C c
Advanced Knowledge Base System).
5. Indicates the
television is receiving an 'IDENT' signal on the selected
source. If no 'IDENT' signal is detected, the display will
read 'NOT TUNED'
6. Displays th
buffer.
How to exit
To exit CSM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the MENU, STATU
remote control transmitter.
• Press the POWER button on the television set.
ntification o
type of TV system or whether or not the
e last five e
f the main microprocessor (see
all centres (AKBS stands for
rrors detected in the error code
/EXIT, or POWER button on the
S
5.3 Problems and Solving Tips Related to CSM
5.3.1 Picture Problems
Note: The pr
settings. The procedures used to change the value (or status)
of the different settings are described.
Picture too dark or too bright
If:
• The
PICTU
• The picture improves when you enter the Customer
Service Mode
oblems described below are all related to the TV
picture improves when you have press the AUTO
RE button on the remote control transmitter, or
Then:
1. Press
2. Press the
3. In the normal user menu, use the MEN
4. Press
5. Use the MENU UP/DOWN
6. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to increase or
7. Use the MENU
the AUTO PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter repeatedly (if nece
PERSONAL picture mode.
MENU button on the remote control transmitter.
This brings up the normal user menu.
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu (if necessary).
the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to enter the PICT
sub menu.
BRIGHTNESS.
decrease the BRIGHTNESS v
UP/DOWN
ssary) to choose
U UP/DOWN keys
keys (if necessary) to select
alue.
keys to select PICTURE.
URE
Page 12

EN 12 L04E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
8. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to increase or
decrease the PICTURE value.
9. Press the
twice to exit the user menu.
10. The new PERSONAL preference values are automa
stored.
White line around picture elements and text
If:
The picture improves after you have pressed the
PICTURE button on the remote control transmitter
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTU
transmitter repeatedly (if necessary) to choose
PERSONAL picture mode.
2. Press the MENU butt
This brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal u
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu (if necessary).
4. Press the MENU LEF
sub menu.
5. Use the MENU UP
6. Press the MENU LEFT key to decrease the SHARPNESS
value.
7. Press the MENU button
twice to exit the user menu.
8. The ne
stored.
Sn
owy picture
To enter CSM, press the following key sequence on the remote
control transmitter: '123654' (do no
out between entries while keying the sequence).
Check CSM line 5. If this line reads 'Not Tuned,' check the
llowing:
fo
• Antenna not connected. Connect the antenn
• No antenna signa
antenna signal.
• The tuner is faulty (in this
will contain error number 10). Check the tuner and replace/
repair the tuner if necessary.
Black and white picture
If:
• The picture improves after you have p
PICTURE button on the remote control transmitter
MENU button
s
w PERSONAL preference value is automatically
on the remote control transmitter
tically
UTO
A
RE button on the remote control
on on
the remote control transmitter.
er menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
T/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
/DOWN keys to select SHARPNESS.
on the remote control transmitter
t allow the display to time
a.
l or bad antenna signal. Connect a proper
case line 6, the Error Buffer line,
ressed the AUTO
text not sharp enough
Menu
If:
he picture improves after you have pressed the AUT
• T
PICTURE button on the remote control transmitter.
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter repeate
PERSONAL picture mode.
ss the MENU button on the remote control transmitter.
2. Pre
T
his brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal user menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
to highligh
4. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
sub menu.
5. Use the MEN
6. Press the MENU LEFT key to decrease the PICTURE
val
7. Pre
twice to exit th
8. The new PERSONAL preference valu
stored.
t the PICTURE sub menu (if necessary).
ue.
ss the MENU button on the remote control transmitter
dly (if necessary) to choose
U
UP/DOWN keys to select PICTURE.
e user menu.
e is automatically
5.4 ComPair
5.4.1 Introduction
ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a service tool for Philips
Consumer E
development on the European DST (service remote control),
which allows faster and more accurate diagnostics. ComPair
has three big advantages:
• ComPair helps you
to repair the chassis in a short time by guiding you
systematically through the repair procedures.
• ComPair a
and is therefore capable of accurately indicating problem
areas. You do not have to know anything about I2C
commands yourself because ComPair takes care of this.
• ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
autom
microprocessor is working) and all repair information is
directly available. When ComPair is installed together with
the SearchMan electronic manual of the defective chassis,
schematics and PWBs are only a mouse click away.
5.4.2 Specificati
lectronics products. ComPair is a further
to quickly get
lows very detailed diagnostics (on I2C level)
l
atically communicate with the chassis (when the
ons
an understanding on how
O
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTU
transmitter repeatedly (if necessary) to choose
PERSONAL picture mode.
2. Press the MENU butt
This brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal u
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu (if necessary).
4. Press the MENU LEF
sub menu.
5. Use the MENU UP
6. Press the MENU RIGHT key to increase the COLOR value.
7. Press the MENU button
twice to exit the user menu.
8. The new PERSONAL preference value is automatically
stored.
s
RE button on the remote control
on on
the remote control transmitter.
er menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
T/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
/DOWN keys to select COLOR.
on the remote control transmitter
ComPair consists of a Wind
and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product.
The ComPair interface box is connected to the PC via a serial
or RS232 cable.
In this chassis, the ComPair interface box and the TV
communicate via a bi-direction
connector.
The ComPair faultfinding program
problem of the defective television. ComPair can gather
diagnostic information in two ways:
tomatic (by communication with the television):
• Au
ComPair can au
entire error buffer. Diagnosis is done on I2C level. ComPair
can access the I2C bus of the television. ComPair can
send and receive I2C commands to the micro controller of
the television. In this way, it is possible for ComPair to
communicate (read and write) to devices on the I2C
busses of the TV-set.
ually (by asking questions to you): Automatic
• Man
diagnosis is on
television is working correctly and only to a certain extend.
When this is not the case, ComPair will guide you through
the faultfinding tree by asking you questions (e.g. Does the
screen give a picture? Click on the correct answer: YES /
ly possible if the micro controller of the
ows based faultf
al service cable via the
is able to determine the
tomatically read out the contents of the
inding program
service
Page 13
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 13L04E AA 5.
NO) and showing you examples (e.g. Measure test-point I7
and click on the correct waveform you see on the
oscilloscope). You can answer by clicking on a link (e.g.
text or a waveform picture) that will bring you to the next
step in the faultfinding process.
By a combination of automatic diagnostics and an interactive
ComPair will enable you to find
question / answer procedure
,
most problems in a fast and effective way.
Beside fault finding, ComPair provides some additio
features like:
p- or downloading of pre-sets.
• U
• Managing of pre-set lists.
• Emulation of the Dealer Service T
ool (DST).
• If both ComPair and SearchMan (Electronic Service
ual) are installed, all the schematics and the PWBs of
Man
the set are available by clicking on the appropriate
hyperlink. Example: Measure the DC-voltage on capacitor
C2568 (Schematic/Panel) at the Mono-carrier.
– Click on the
'Panel' hype
rlink to automatically show the
PWB with a highlighted capacitor C2568.
– Click on the 'Schematic' hy
perlink to automatically
show the position of the highlighted capacitor.
5.4.3 How To Connect ComPair
1. First, install the ComPair Browser software (see the Quick
eference Card for installation instructions).
R
onnect the RS232 interface cable between a free serial
2. C
(COM) port of you
r PC and the PC connector (marked with
'PC') of the ComPair interface.
onnect the mains adapter to the supply connector
3. C
(marked with 'P
OWER 9V DC') of the ComPair interface.
4. Switch the ComPair interface “off”.
5. Switch the television set “
off” with the mains switch.
6. Connect the ComPair interface cable between the
connector on the re
ar side of the ComPair interface
(marked with 'I2C') and the ComPair (or Service) connector
at the rear side of the TV (for its location see figure 8-1 in
chapter “Alignments”).
7. Plug the mains adapter in
a mains outlet, and
interface “on”. The green and red LEDs light up together.
The red LED extinguishes after approx. 1 second while the
green LED remains lit.
r
8. Start the ComPair p
ogram and read the 'Introduction'
chapter.
nal
switch the
• SearchMan32 CD
(update): 3122 785 60080 (year 2002),
3122 785 60120 (year 2003).
c
• ComPair interfa
e cable: 3122 785 90004.
• Transformer (non-UK): 4822 727 21632.
• Transformer UK: 4822 727 21633.
e: If you encounter any problems, contact
Not
support desk.
5.5 Error Codes
The error code buffer contains all errors detected since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right. When an error occurs that is not yet in the error code
buffer, it is displayed at the left side and all other errors shift one
position to the right.
The Error Buffer
5.5.1 How To
5.5.2 How To Clear T
Read
You can read the error buffer in 3 ways:
• On scree
Examp
– ERROR: 0
n via the SDAM (if you have a picture).
les:
0 0 0 0 : No
errors detected
– ERROR: 6 0 0 0 0 : Error code 6 is the last a
detected error
– ERROR: 9 6 0 0 0 : Error
code 6 w
as detected first and
error code 9 is the last detected (newest) error
• Via the blinking LED procedure (when you have no
picture). See 'The Blinking LED Proced
ure'.
• Via ComPair.
he Error Buffer
The error code buffer is cleared in the following cases:
• By using the CLEAR command in the SDAM menu:
– To enter SAM, press the following key sequence on the
re
mote control transmitter: '062596' directly followed
by the “OSD" icon button (do not allow the display to
time out between entries while keying the sequence).
enu ite
– Make sure the m
m CLEAR is highlighted. Use
the MENU UP/DOWN buttons, if necessary.
– Press the MENU RIGH
T button to clear the error
buffer. The text on the right side of the 'CLEAR' line will
change from 'CLEAR?' to 'CLEARED'
• If the contents of the
hours, the
error buffer resets automatically.
error buffer have not changed for 50
your local
nd only
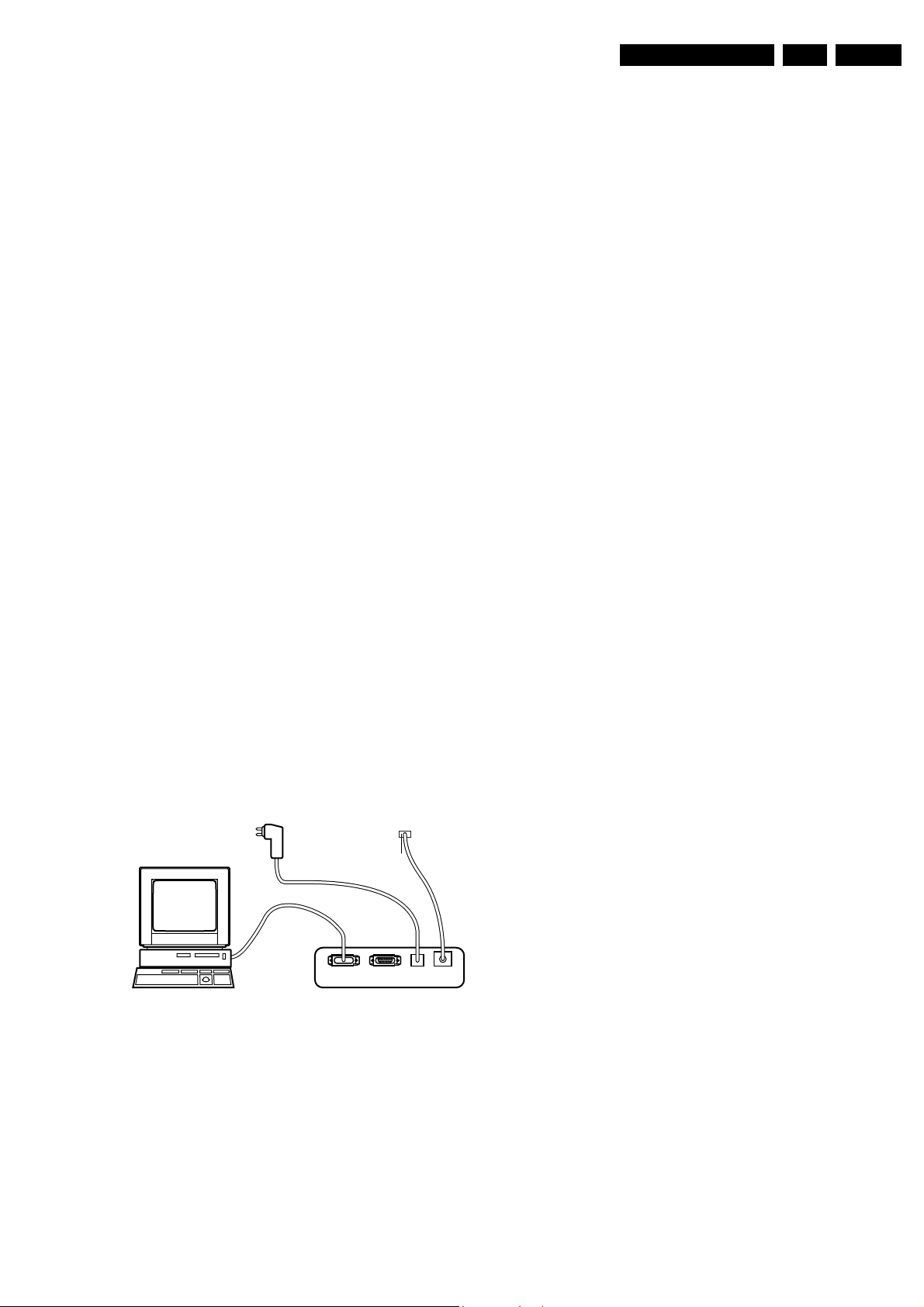
Figure 5-4 ComPair connection
5.4.4 Ho
w To Order
ComPair o
rder codes:
• Starter kit ComPair32/SearchMan
ComPair interface (excl. transformer): 3122 785 90450.
omPair interface (excluding transformer): 4822 727
• C
21
631.
• Starter kit ComPair32 softw
are (registration version): 3122
785 60040.
• Starter kit SearchMan32 software: 3122 785 60050.
• ComPair32 CD (update): 3122 785 6
3122 785 60110 (year 2003).
TO SERVICE
CONNECTOR
PC VCR I2CPower
32 so
9V DC
E_06532_008.eps
ftware and
0070 (year 2002,
190204
Note: If you exit S
AM by disconnecting the Mains from the
television set, the error buffer is not reset.
5.5.3 Er
ror Codes
In case of non-inte
rmittent faults, write
down the errors present
in the error buffer and clear the error buffer before you begin
the repair. This ensures that old error codes are no longer
present.
If possible, check the entire contents of the error buffer. In
some situation
s, an error code is only the result of another error
and not the actual cause of the problem (for example, a fault in
the protection detection circuitry can also lead to a protection).
Page 14
EN 14 L04E AA5.
Table 5-3 Error codes overview
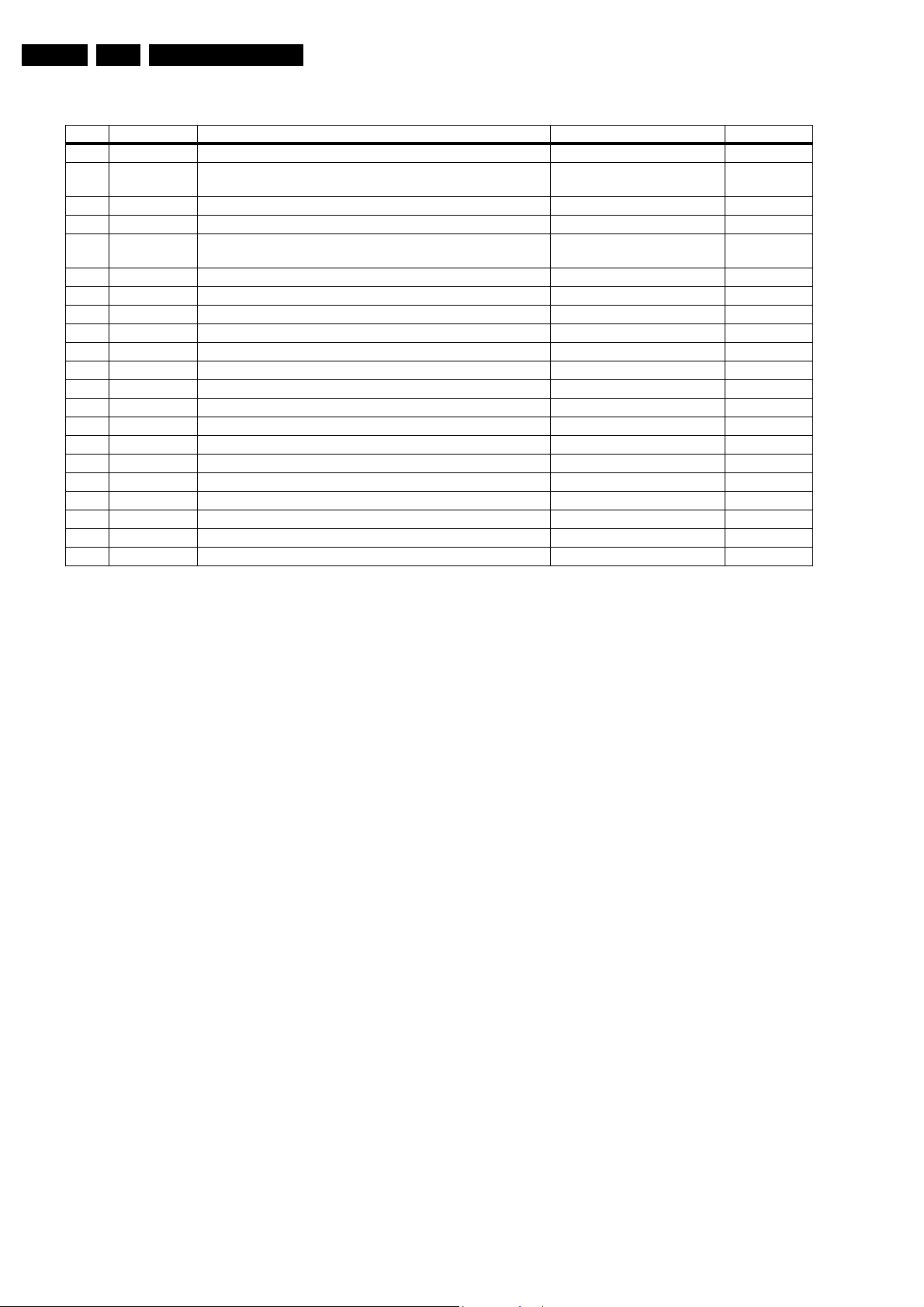
Error Device Error description Check item Diagram
0 Not applicable No Error
1 Not applicable X-Ray / over-voltage protection (US only) 2411, 2412, 2413, 6404, 6411,
2 Not applicable High beam (BCI) protection 3404, 7405 A2
3 Not applicable Vertical guard protection 3466, 7451, 7452, 7453, 7454 A2
4 Tuner
UA1316/A
5 Not applicable +5v protection 7604, 7605 A5
6 I2C bus General I2C error 7200, 3207, 3214 A4
7 Not applicable - - 8 Not applicable - - 9 24C16 I2C error while communicating with the EEPROM 7601, 3604, 3605 A5
10 Tuner = I2C error while communicating with the PLL tuner 1000, 5001 A3
11 TDA6107/A Black current loop instability protection 7330, 3351, CRT B1
12 SDA9488X I2C error while communicating with the PIP processor 7242 (PIP Module) F1
13 Not applicable - - 14 DVD Loader I2C error while communicating with the DVD Interface module DVD Interface module DVD Loader
15 TDA9178T/N1 I2C error while communicating with LTI module 7610 H
16 TDA9887 I2C error while communicating with PIP_Demodulator 7201 F2
17 Not applicable - - 18 Not applicable - - 19 TDA1200 I2C error while communicating with SSD stereo sound decoder 7200 A4
TDA1200 I2C error while communicating with video cosmic in Hercules IC 7200 A4
20
I2C error while communicating with 2nd tuner 1000, 5010 (PIP Module) F2
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
6412.
A2
Note: Errors 7, 8, 13, 17, 18 are
not applicable.
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
Using this procedure, you can make the contents of the error
buffer visible via the front LED. This is especially useful when
there is no picture.
When the SDM is entered, the LED will blink the contents of the
-buffer:
error
en all the error-codes are displayed, the sequence
• Wh
finishes w
• The sequence starts again.
Example of error buffer: 12 9
After entering SDM, the following occurs:
• 1 long 'on' blink of 5 seconds to start the sequence,
• 12 short blinks follow
• 9 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 6 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 1 long 'on' blink of 1.5 seconds to finish the sequence,
• The sequence starts again at 12 short blinks.
ith an 'on' LED blink of 1.5 seconds,
6 0 0
ed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
5.7 Protections
If a fault situation is detected, an error code will be generated;
and, if necessary, the television set will go into protection
mode. Blinking of the red LED at a frequency of 3 Hz indicates
the protection mode. In some error cases, the microprocessor
does not put the set in protection mode. The error codes of the
error buffer and the blinking LED procedure can be read via the
Service Default Menu (SDM), or via ComPair.
t
To get a quick diagnosis the chassis has
implemented:
• The Customer Service Mode (CSM).
• The Service Default Mode (SDM).
• The Service Alignment Mode (SAM).
or a detailed description, see the "Customer Service Mode,
F
Service Default mode" and "Service
hree service modes
Alig
nment Mode" sections.
5.8 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
Notes:
• It is assumed that
with correct values and no bad solder joints.
• Before any fault finding actions, check if the correct options
t.
are se
5.8.1 NVM Editor
In some cases, it ca
NVM conte
mode. In the next table, the default NVM values are given.
nts. This can be done with the “NVM Editor” in SAM
the components are mounted correctly
n be handy if one directly can change the
Page 15
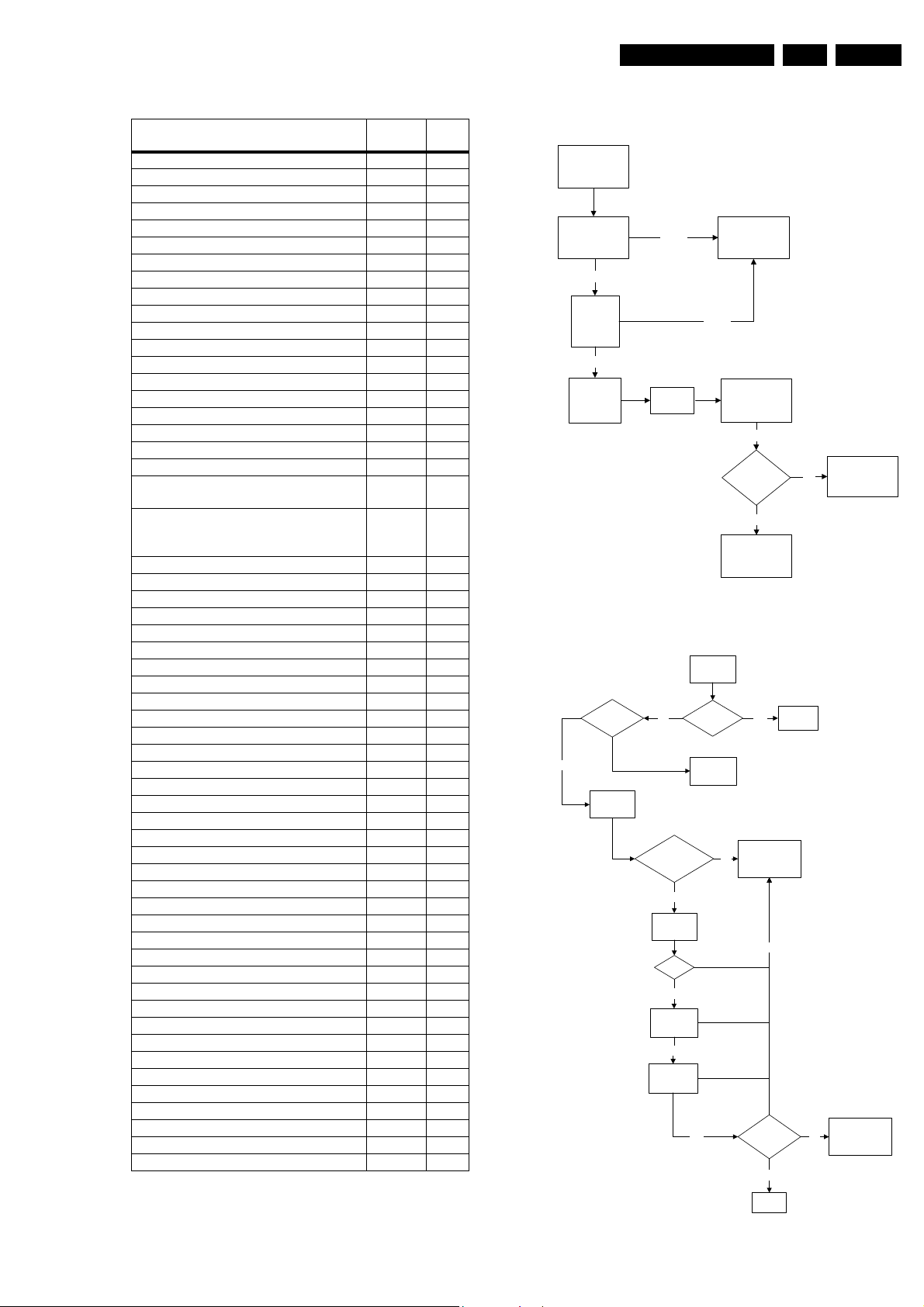
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Table 5-4 NVM default values 5.8.2 Power Supply
EN 15L04E AA 5.
Address
(dec)
Value
(hex)
EW (EW width) 19 25
PW (EW parabola width) 20 0A
HS (Horizontal shift) 21 1A
HP (Horizontal parallelogram) 22 1F
HB (Horizontal Bow) 23 1F
UCP (EW upper corner parabola) 24 1E
LCP (EW lower corner parabola) 25 28
TC (EW trapezium) 26 1A
VS (Vertical slope) 27 25
VA (Vertical amplitude) 28 1E
SC (S-Correction) 29 1C
VSH (Vertical Shift) 30 1A
VX (Vertical Zoom) 31 19
VSL (Vertical scroll) 32 20
VL (Vertical linearity) 33 20
AGC (AGC Takeover) 36 1E
OIF (IF-PLL Offset) 37 20
AGC10 (AGC 10) 38 1
H60 (60 Hz Horizontal Shift) 39 9
PF_SC_PWL (Peaking Frequency,
40 0A
Soft Clipper, Peak White Limit)
COR (Phase 1 time constant,
41 0F
Video Dependant Coring,
Ratio & White stretch)
60 Hz Vertical amplitude 42 40
YD & CL 43 2
RGB amplitude for full teletext mode 46 0C
NVM_TABLE_VERSION 60 26
OPTION_TABLE_VERSION 61 11
CVI_BLOR 62 1E
CVI_BLOG 63 1C
TXT Brightness 64 0F
V60 offset (60Hz Vertical Amplitude) 66 FE
FOAB, CHSE 139 3
SPR, WS 140 0
VMA, SVM 141 31
NVM_SOC_SMD 142 33
CCC_Preset_Gain_Red 143 1F
CCC_Preset_Gain_Green 144 1F
CCC_Preset_Gain_Blue 145 1F
NVM_FMWS 149 2
NVM_ASD_SC1_THR 150 10
NVM_CRYSTAL_ALIGN
208 4F
Last Brightness (VID PP others) 264 34
Last Color (VID PP others) 265 2C
Last Contrast (VID PP others) 266 4B
Last Sharpness (VID PP others) 267 37
Last Hue (VID PP others) 268 32
Last Colour Temperature (VID PP others) 269 0D
White-D Cool Red 294 FD
White-D Cool Blue 296 8
White-D Normal Red 297 22
White-D Normal Green 298 20
White-D Normal Blue 299 1B
White-D Warm Red 300 2
White-D Warm Blue 302 FA
Last Volume 343 19
Last Balance 344 32
Last Treble (AUD PP others) 345 32
Last Bass (AUD PP others) 346 32
Set Not Working
Check Power
Supply Mains
Switch
Bridge Rectifier
circuit 6500
Ok
Check DC
voltage at
2505/2507
Ok
Check
fusible
resistor 3532
Not Ok
Check
7512
Not Ok
Check fusible
resistor 3510 &
circuit before it
Check IC7511 &
IC7531
Ok
Set able to
start-up
Yes
End
No
Check other
fusible resistor
and capacitor in
the circuit
E_14480_057.eps
190204
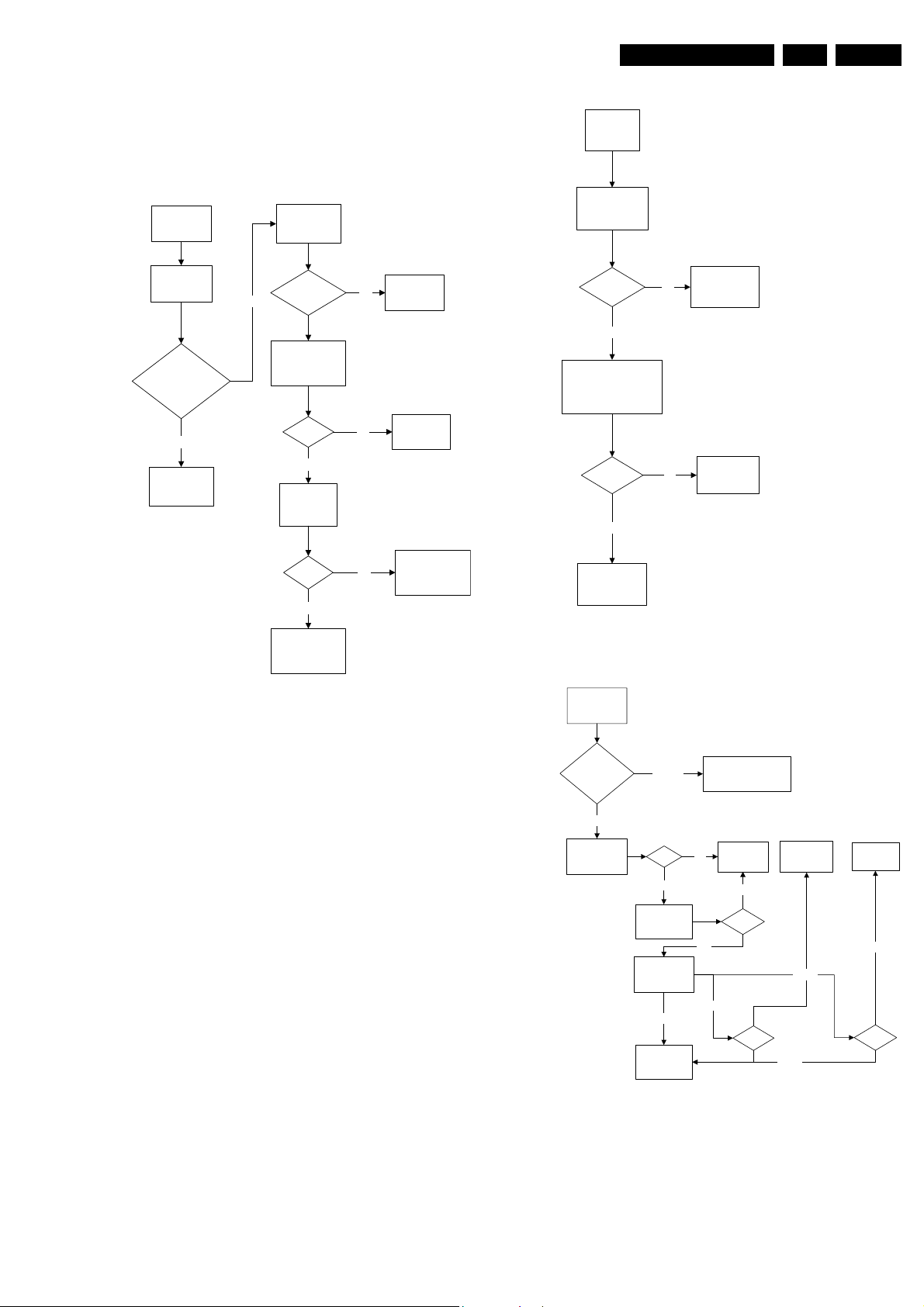
Figure 5-5 Fault finding tree “Set not working”
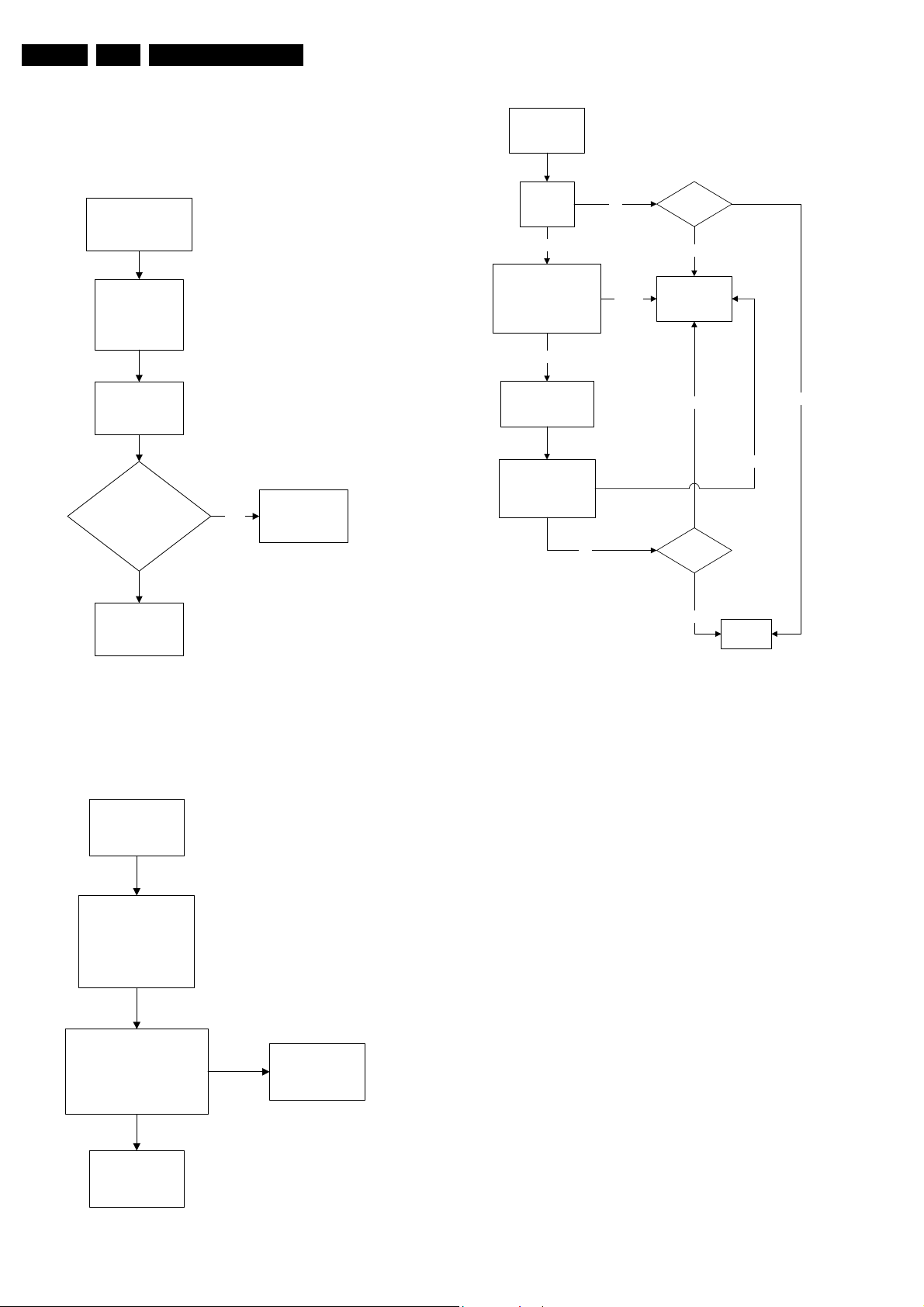
Set Does Not Start Up
Set Unable
to Start
Software
loaded?
Yes
Check
voltage
across 2552
No
Is Vbatt
approximately
140V
Yes
Check
voltage 2562
&2563
16V
Yes
Check 3V
across 2535
Yes
Check 6V
across 2535
Fuse Blown?
Load
Software
Yes
No
Yes
Check Power
Supply circuit
No
Set able to
Start
Yes
Change
Fuse
No
Check Line
Transistor 7405
Figure 5-6 Fault finding tree “Set do
End
es no
E_14480_058.eps
t start up”
170204
Page 16
EN 16 L04E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.8.3 Deflection
One Thin Vertical Line
Quick check:
• Set in pr
• LED blinking with error “3
One Thin Vertical Line
LED Blinking
Check all
connection and
peripheral at
Deflection Circuit in
place
Check
Line Transistor
7405
Is VBE between
200mV to 30mV & V
approximately 500mV
otection mode.
CB
”.
Yes
Check Horizontal
Deflection
Circuitry
Blank Screen
Blank Screen
Check Vg2
(fine tune)
Not Ok
Check Beam Current Limit
(voltage is 1.8V-2V when
brightness and contrast is
set to the maximum
Ok
Check heater voltage
(measure pin 9&10
at the CRT socket)
Check video supply
(2457) is approximately
180V
Ok
Not Ok
Ok
Picture
appears?
Picture not appearing
Check deflection
circuit
Picture not appearing
Picture
appears?
Ok
Not Ok
Replace transistor
E_14480_059.eps
170204
Figure 5-7 Fault finding tree “One thin vertical line”
One Thin Horizontal Line
Quick check:
• Set in pr
• LED blinking with error “2
Check all connection
(7451, 7523, 7543) at
Vertical Deflection Circuitry
otection mode.
One Horizontal
Thin Line
LED Blinking
and peripheral at
Deflection Circuit
in place
Check transistor
Check Vertical
Deflection Circuit
”.
Replace transistor
E_14480_060.eps
170204
Ok
Figure 5-9 Fault finding tree “Blank screen”
5.8.4 Sour
ce Selection
Set is not able to go into AV or any missing AV is
tered
encoun
E.g. AV1 is available but not able to enter to AV1: Check if the
option setting
Set is
is correct.
able to go to AV, but no audio is heard.
1. Check that continuity of signal is there from the SCART/
Cinch in
put to the input of the Hercules.
2. If continuity is there and
still no audio, check that option
settings are correct.
3. If logic setting is correct
and still no audio, proceed to Audio
Decoder/Processor troubleshooting section.
Set is able to go into AV but no video is available:
1. Check continuity from AV input to HERCULES depending
on th
e input.
2. If continuity is available and yet no video, proceed to Video
Pro
cessor troubleshooting section.
5.8.5 Tu
ner and IF
Picture
No
1. Che
ck that the Option settings are correct.
2. If correct, check that s
3. If supply voltages are p
upply voltages are there.
r
esent, check whether picture is
present in AV.
4. If picture is present in AV, check with the scope the T
IF output signal by manual storage to a known channel.
End
E_14480_061.eps
170204
uner
Figure 5-8 Fault finding tree “One thin horizontal line”
Page 17
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 17L04E AA 5.
5. If IF output is present, Tuner is working fine. If no IF output,
I2C data lines may be open, check continuity of I2C lines.
If I2C lines are ok, Tuner may be defect, replaced Tuner.
uner IF is present and yet still no picture in RF mode, go
6. If T
to
Video Processing troubleshooting section.
No Picture, No Sound
Yes
Check tuning
supply voltage,
pin 9 of tuner
>30V & <35V
Check supply
voltage, pin 7 of
tuner
5V
Yes
Check Tuner
pin 4 & 5
I2C Bus
Check
V
Supply
No
T
Section
Check Power
No
Supply
No Picture,
No Sound,
Raster Ok
Check AGC
Voltage, pin 1
of tuner
AGC voltage
changes with
different signal
strength
No
Check AGC
circuit section
Picture Ok, No Sound
Picture Ok,
No Sound
Check IF output of
tuner, pin 11
CVBS
present?
Yes
Check SAW filter output
(pin 4&5)
EU/AP/CH (QSS)- 1001
NA/LA/AP INT - 1002
Output Ok?
Yes
No
No
Refer to fig.
"Power Supply:
Set not working"
Replace SAW
filter
Ok
Yes
Replace Tuner
No
Check other
functional area
E_14480_062.eps
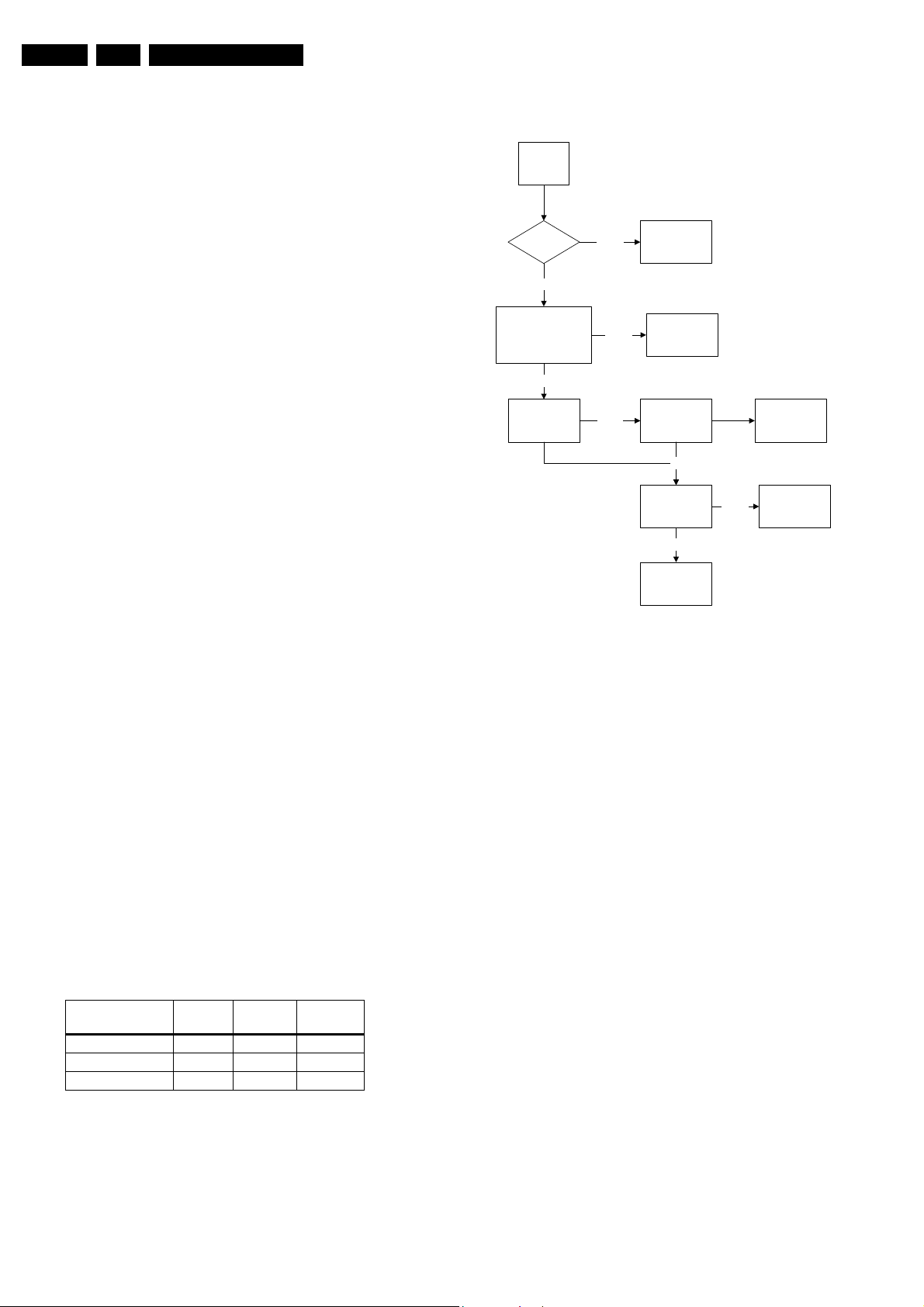
Figure 5-10 Fault finding tree “No picture, no sound”
170204
Check other
functional area
E_14480_063.eps
170204
Figure 5-11 Fault finding tree “Picture ok, no sound”
Unable To Perform Tuning
Unable to
perform tuning
Enter SDM
check optionbyte 1
Correct
Check if tuner
Supply Voltage
pin 7
Incorrect
5V
Yes
Check Tuner
Supply Voltage
Check I2C at pin
4 & 5 and tuner
Ok
Check other
functional area
Enter SDM and change
to the appropriate byte
Check Power
No
Supply
No
33V
Yes
Not Ok
Check I2C
circuit
Not Ok
I2C
Not Ok
E_14480_064.eps
Replace
Tuner
Not Ok
Tuner
170204
Figure 5-12 Fault finding tree “Unable to perform tuning”
5.8.6 Con
t
roller
Below are some guidelines for troubleshooting of the Micro
Controller function. Normal
ly Micro Controller should be
checked when there is a problem of startup.
V
1. Check that both +3.3 V_dc and +1.8
_dc are present.
2. Check that crystal oscillator is working.
Page 18
EN 18 L04E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
3. Check that Power Good signal is at “high” logic, normal
operation.
4. Check th
at HERCUL
ES is not in standby mode. Pin 15 of
HERCULES should be 0 V_dc.
5. Make sure H-drive pulse is there. This can
resistor R3239. If H-drive does not exist, remove resistor
R3239 to check if there is loading.
Note: When the set shuts down after a few second after power
“on”, t
he main cause is that Vg2 not aligned properly, try
adjusting Vg2 during the few seconds of power “on”.
5.8.7 Video Pro
cessing
No Picture
When “no picture in RF”, first c
eck if the microprocessor is
h
functioning ok in section “Controller”. If that is ok, follow the
next steps.
When “no picture in AV”, first check if the video
select
ion is functioning ok in section “Source Selection”. If that
is ok, follow the next steps.
1. Check th
at normal operatin
2. Check that there is video signal a
g conditions are met.
t pin 81. If no video,
demodulator part of the HERCULES is faulty, replace with
new HERCULES.
3. If video
signal is available at
pin 81, check pin 56, 57, and
58 for the RGB signal.
4. If signal is not available, try checking the BRIGHTNESS
and/or CONTR
5. If still wi
AST control, and make sure it is not at zero.
th the correct settings and no video is available,
proceed to the CRT/RGB amplifier diagram.
For sets with TDA9178, follow steps below:
Option Byte 2 bit 4 to “0”; if video
1. Put
signal is not available,
then check fault finding section “Controller”, Section
“Source Selection”, and steps above.
but n
2. If video is available
ot correct, put Option Byte 2 bit 4
to “1”, then check if LTI panel is present. If not, put LTI
panel in the main chassis (connector 1221).
3. If LTI p
anel is in main chassis, check cable between LTI
panel and main ch
assis (position is 1206). If it is
connected, then the LTI panel is faulty, replace it.
For sets with Scavem, and Scavem does not work, follo
below:
1. Check Scavem coil con
nector (position is 1361) if
connected; if not, connect it.
2. If conne
cted, check NVM “bit sto
rage” byte 1 bit 7; if it is not
“1”, set it to “1”.
3. If it is “1”, then check the data of the NVM addresses as in
the next table. If the da
ta is not correct, then set these
addresses to diagram values.
4. If it still not wo
rks, track Scavem
output from pin64 of
HERCULES to CRT panel.
Table 5-5 NVM default values for Scavem
be checked at
source
w
steps
5.8.8 Au
dio Processing
No
Sound
Picture Ok,
No Sound
Tuner IF Ok Check T uner/IFNot Ok
Ok
Check AUDOUTLSL &
AUDOUTLSR pin at
Hercules
Ok
Check Audio
Amplifier
Not Ok
Not Ok
Check Hercules IC
Check Audio
Power Supply
Ok
Check Audio
Amplifier Circuit
and loud speaker
Ok
Check NVM
Not Ok
Figure 5-13 Fault finding tree “No sound”
No RF audio for QSS/Inter-Carrier stereo sets.
1. Check pin 99 and 100 for SIF signal (for QSS) or pin 104
and 1
05 for video with SIF (for Inter-Carrier)
signal is not present, check for the
2. If
QSS/FMI bit settings.
Check also the NVM data.
3. If signals are present and still no aud
io, check the audio
supply voltage +8V are present.
4. If still no aud
io signal at Hercules output, Hercules is faulty.
No AV audio.
1. Check troubleshooting methods in section “Source
Select
ion”.
2. Check the output of the Hercules to see if there is signal
available. If no,
check the normal operating condition and
also the NVM data.
aud
3. If still no
io signal at Hercules output, Hercules is faulty.
Note: If there is audio signal at Hercules output and no audio
at loudspeaker, procee
d to Audio Amplifier troubleshooting
methods.
Check Power
Supply
Replace Audio
Amplifier
E_14480_065.eps
170204
Description Address
)
(dec
Address
(hex)
Value
(hex)
SPR, WS 140 8C 00
VMA, SVM 141 8D 31
NVM_SOC_SMD 142 8E 33
5.8.9 Audio Amplifier
No
RF as well as AV audio at the loudspeaker:
1. Check that the normal operation condition of the amplifier
t.
is me
2. If normal operation
conditions are met, check the continuity
from Hercules output to input of the amplifier.
y
3. If continuit
is there and still no audio, check speaker wire
connections. If still no audio, amplifier IC might be faulty.
Page 19
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
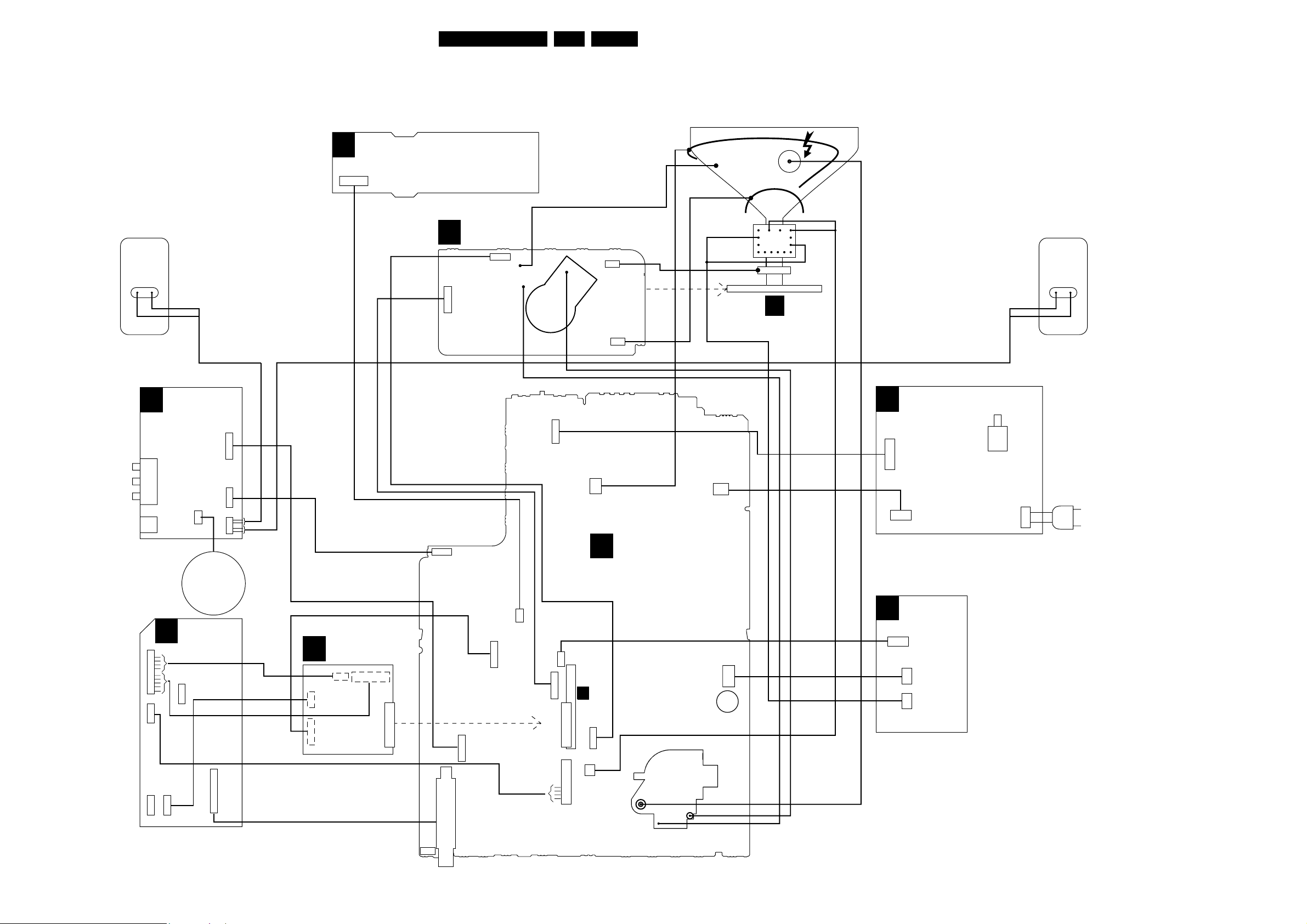
6. Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Wiring Diagram
19L04E AA 6.
CVBS (YELLOW)
LEFT (WHITE)
RIGHT (RED)
HEADPHONE
RIGHT
SPEAKER
D
91
9P
1212
4P
1219
NC
4P
1206
RED
BLACK
SIDE
A/V PANEL +
HEADPHONE
1279
3P
to
SUB
WOOFER
(OPTIONAL)
PIP
F
NC
5P
1220
4P
1214
1252
1254
1278
TUNER
AQUADAG
DEGAUSSING COIL
CRT
16:9
ROTATION
BLUE
RED
FRAME
COIL
B
YELLOW
ORANGE
SCAVEM
COIL
EHT
CRT
BLACK
RED
LEFT
SPEAKER
TOP CONTROL PANEL
E
1010
3P
(component view)
CRT PANEL
B
5P
1351
7P
1352
1332
CRT
SOCKET
1361
3P
CRT PANEL
1381
3P
FRONT INTERFACE
1693
6P
7P
1504
2P
5P
4P
MONO
A
CARRIER
3P
LTI/
H
CTI
1401
12P
5P
1451
2P
9P91
LOT
(track view)
LTI/CTI
H
INTERFACE
1216
1206
7P 4P
4P 5P 15
1215
1214
1212
12P
5P
1280
1207
TUNER
1682
3P
1206
7P
7P
1221
1204
7P
1212
1219
1505
2P
1404
2P
5401
J
1693
6P
1212
2P
LINEARITY&
G
PANORAMA
1462
3P
1464
2P
1461
2P
MAINS
SWITCH
1211
MAINS
CORD
2P
1005
3P
COMPAIR
CONNECTOR
E_14480_080.eps
170504
Page 20
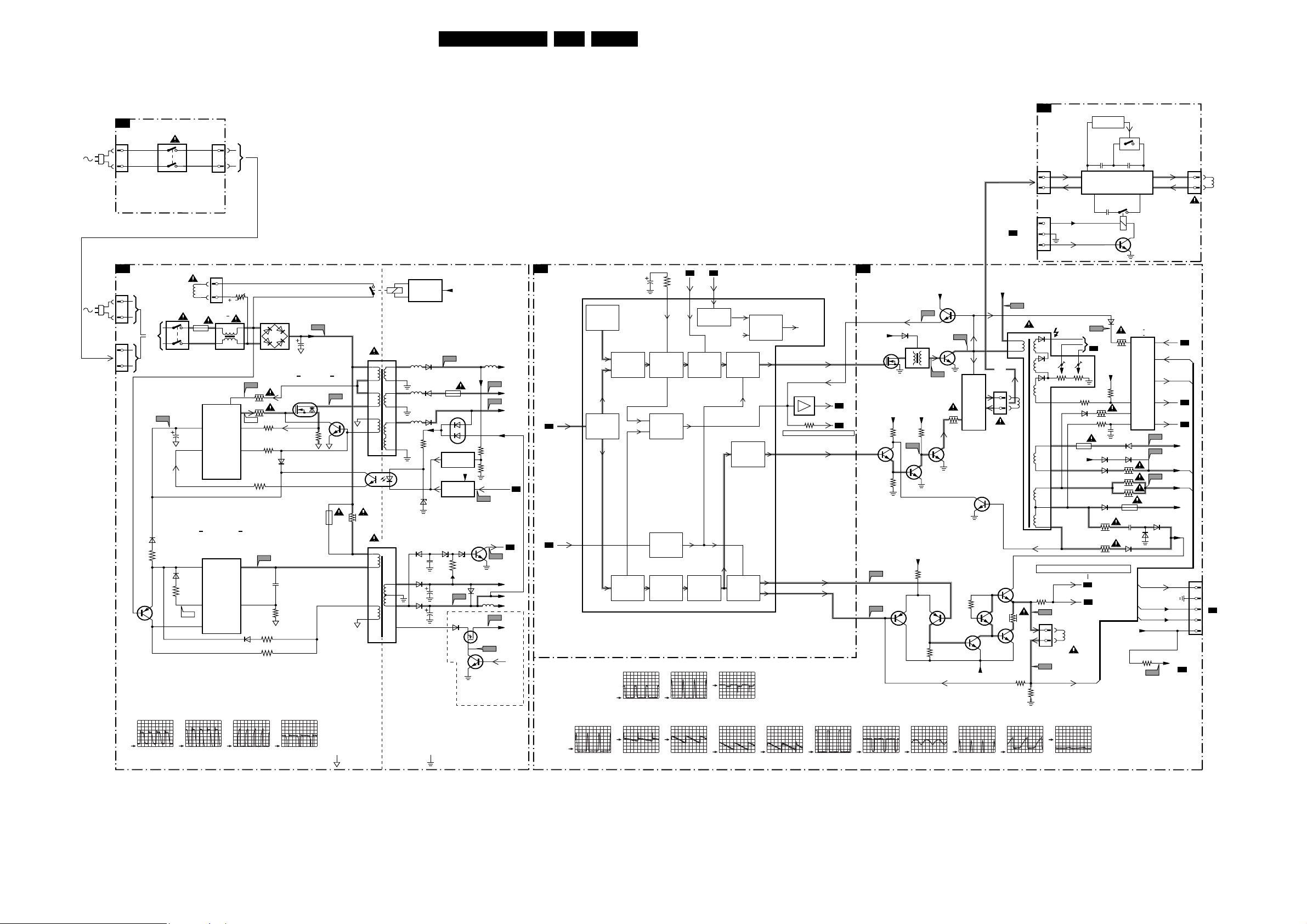
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Supply and Deflection
20L04E AA 6.
SUPPLY AND DEFLECTION
SUPPLY
FRONT INTERFACE
J
1211
A1
1505
1505
1
2
1231
MAINS
SWITCH
(not USA)
POWER SUPPLY
Degaussing
1506
OR
MAINS
SWITCH
(not USA)
I511
6512
3519
7532
F508 268V
/ div DC
F511 15V5 / div DC
F531 2V7 / div DC
F537 0V (N.A.)
Coil
2511
6533
3530
I531
1212
1504
1500
T4E
7511
TEA1506T
2
Vcc
CONTROL
6
CTRL
STANDBY
SUPPLY
7531
TEA1620
3
Vcc
CONTROL
6
REG
11
AUX
F552 130V
F561 15V9
F564 9V4 / div DC
F573 0V (N.A.)
1
2
5500 :
5502
DRAIN
IC
IC
SOURCE
DRIVER
SENSE
DEMAG
DRAIN
3507
t
14
/ div DC
/ div DC
I513 I516 I519 I533
11
9
7
14
12
6532
LINEARITY & PANORAMA
TO 1221
A5
CONNECTIONS
G
ONLY FOR:
28"WSRF LA/NA
32" WSRF LA/NA
28" WS-SF LA
1404
4
1
1462
1
2
3
+9V
I2SD/1
7460
ACTIVATING
CIRCUIT
2466
LINEARITY AND
PANORAMA
CORRECTION
2474
2475
7462
7463
2464
2467
1463
1461
4
1
HOR.
DEFL.
COIL
DEFLECTION
HERCULES
Vbatt
-Vaudio
+Vaudio
+6VA
A4
A4
+3V
+6VA
+6VA
+6V
Vaux
2x
A4
INTF_Y GREEN_IN
A5
EHTinfo
A2
F401 130V
F402 32V8
56
97
7200-H
(SYNC)
VIDEO
IDENT
MAIN
SYNC
SEPARATOR
EHTo
/ div DC
/ div DC
2240
PHI 1
DETECTOR
VERTICAL
SEPARATOR
HORIZONTAL
GENERATOR
PROTECTION
SYNC
F412 F414
2V
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
7541
1503
43
ENERGIZING
2
6500
AC
I513
3513
3514
I519
3532
3517
3518
I533
2534
3538
3534
3531
F508
2505
DC
5520
I516
7514
9
8
4
5
3
2
4
3
35321532
1A
5531
4
5
1
2
6511
G
7512
MAIN
SUPPLY
D
S
3516
CIRCUIT
1
(optional)
5551 5552
17
18
5562
13
14
5561
10
11
1
7515
TCET1103
2
6564
6535
10
9
6536
8
6
6551
6563
6562
3571
6573
F552
1543
7571
REFERENCE
7573
6565 6566
2564
2535
2536
V_DG
6571
CIRCUIT
+3V3
STANDBY
CIRCUIT
3565
F536
6537
S
G
7536
7561
D
I573
6676
7535
For IDTV only
F563
F561
3575
3576
Stdby_Con
POWER-DOWN
F564
5537
F537
I548
F455 F458 F459
3232
112
OSC.
SAND-
CASTLE
X-RAY
VERTICAL
DIVIDER
200V
20µs
A2 A2
EHTinfo
113 116
VERTICAL
GUARD
DETECTOR
PHI 2
DETECTOR
VERTICAL
SAW-
THOOTH
/ div DC
/ div
Vguard
HORIZONTAL
OUTPUT
E/W
+
GEOMETRY
VERTICAL
OUTPUT
+
GEOMETRY
F418
5V
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
F460 F461
R.G.B.
BLANKING
F452 -13V4
F453 190V8
62
63
108
106
107
TO RGB
PROC.
HDRIVE
HD
7207
SANDCASTLE
A5
HD_PIP
3291
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM VIDEO
/ div DC
/ div DC
A5
EW_DRIVE
VDRA
VDRB
I416 I417 I468I423 I433 I462
LINE + FRAME DEFLECTION
A2
LINE
HD
6486
-9V
5402
7404
E/W
+8V
+8V
3420 3440
7410
I417
7484
3498
FRAME
+9V
F460
F461
7455 7456
3462
F412
+6VA
BU4508DX
F418
7406
3463
7408
7405
3497
F414
LINE
OUTPUT
CIRCUIT
+
E/W
CORR.
7452
3465
-12V
7411
7454
1404
1
2
Vbatt
OR
7451
7453
F402
6401
5445
3
1
FOCUS
10
HOR.
DEFL.
COIL
6
5
7
8
9
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM VIDEO
3474
F458
3466
1491
1
2
VER.
DEFL.
COIL
F459
3461
FRAME_FB
3471
EHT
VD
Vguard
VG2
1454
3442
6481
Vbatt
A5
A4
CRT
I433
TO
B1
3481
3410
3411
+Vbatt
3451
2403
6452
6483 6484
3458
6453
3484
3485
6456
1452
3457
2456
3455
6459
7401 : 7403
7480 : 7483
EHTb
EHTinfo
PROC.
Vbatt
+
+
BCL
F452
F453
F455
6454
6455
FILAMENT
VIDEO/SUPPLY
3401
F401
POWER-DOWN
FRAME_FB
EHTb
EHTinfo
BCL
VIDEO/SUPPLY
FILAMENT
EHTb
VT_SUPPLY
A4
A1
A4
A4
-12V
+9V
1401
5
4
TO 1351
3
B1
2
CRT
1
100V
5µs
/ div DC
/ div
100V
5µs
/ div DC
/ div
2V
5µs
/ div DC
/ div
100V
5µs
/ div DC
/ div
HOT GROUND COLD GROUND
5V
20µs
/ div DC
/ div
20 V
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
1V
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
500mV
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
500mV
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
500mV
20V
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
20µs
/ div DC
/ div
10V
20µs
/ div DC
/ div
10V
20µs
/ div DC
/ div
10V
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
5V
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
E_14480_081.eps
060504
Page 21
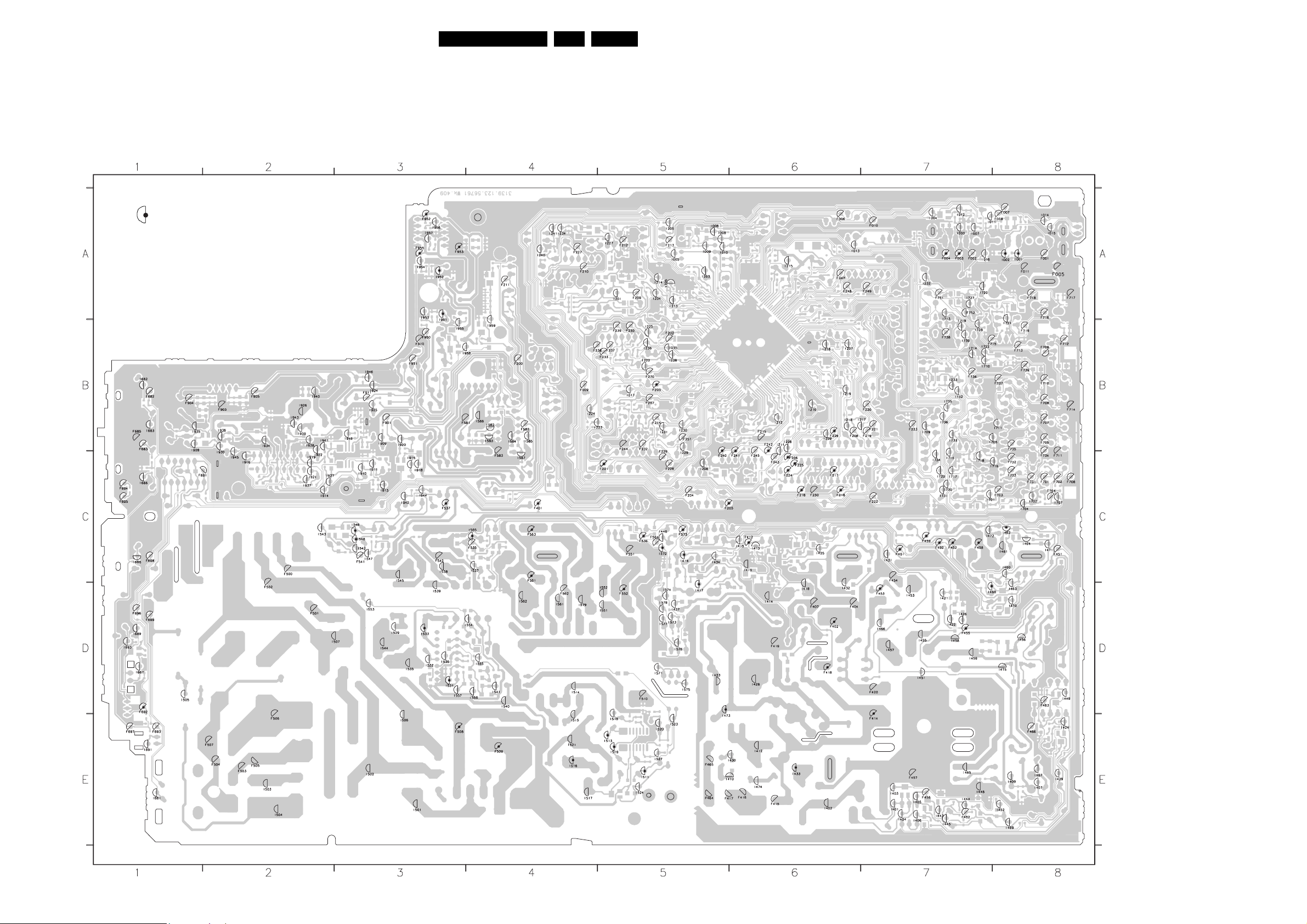
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Testpoint Overview Mono Carrier
F001 A8
F002 A7
F003 A7
F004 A7
F005 A8
F006 A6
F007 A8
F008 A8
F009 B4
F010 A7
F011 A8
F200 B4
F201 C5
F202 B5
F203 B5
F204 C5
F205 C5
F206 C6
F207 B5
F208 B6
F209 A5
F210 A4
F211 A4
F212 A5
F213 A5
F214 B5
F215 B6
SERVICE
TESTPOINT
F216 C6
F217 C6
F218 C6
F219 B7
F220 B7
F221 B7
F222 C7
F223 B7
F224 C6
F225 C6
F226 B6
F227 A4
F228 C5
F229 C5
F230 B5
F232 B5
F233 B5
F237 B5
3139 123 5676.1
F238 B4
F239 B5
F240 C5
F241 C6
F242 B6
F243 C6
F244 B5
F245 C6
F247 A6
F248 A6
F249 A7
F250 C6
F251 B5
F270 B5
F401 C4
F402 D6
F404 D6
F407 D6
F412 C6
F414 E7
F415 E6
F416 E6
F417 E5
F418 D6
F419 D6
F420 D7
F451 C8
F452 C7
F453 D7
F454 C7
F455 D7
F456 E7
F457 E7
F458 C7
F459 C7
F460 C7
F461 C7
F462 E7
F463 D8
F464 E5
F465 E5
F466 E8
F500 C2
F501 D2
F502 D2
F503 E2
F504 E2
F505 E2
F506 E2
F507 E2
F508 E3
F509 E4
F510 D5
F535 C4
F536 C5
F537 C3
F541 C3
F542 C3
F551 C5
F552 D5
F561 C4
F562 D4
F563 C4
F564 C5
F573 C5
F581 B3
F582 B4
F583 C4
F682 B1
F683 B1
F685 B1
F691 C1
21L04E AA 6.
F692 D1
F693 E1
F694 C1
F695 C1
F696 D1
F697 E1
F698 C1
F699 D1
F701 C8
F702 C8
F703 C8
F704 C8
F705 B8
F706 C8
F707 B8
F708 B8
F709 B8
F710 B8
F711 C8
F712 B8
F713 B8
F714 B8
F715 B7
F716 A8
F717 A8
F718 A8
F719 B8
F731 C8
F732 C8
F733 C8
F734 C8
F735 B8
F736 B7
F737 B8
F738 B7
F739 B8
F751 A7
F752 A7
F901 B3
F903 B2
F904 B1
F905 B2
F910 B3
F911 B3
F950 B3
F951 B3
F952 A3
F953 A3
F955 A3
I001 A8
I002 A8
I003 A7
I004 A7
I005 A5
I006 A5
I007 A7
I008 A5
I009 A5
I010 A5
I011 A7
I012 A7
I013 A6
I014 A8
I015 A8
I016 A7
I017 B5
I201 A5
I203 A5
I204 A5
I205 A5
I206 A5
I207 B6
I208 C5
I209 B6
I210 B6
I211 B6
I212 B6
I213 A5
I214 A5
I215 A6
I216 B6
I217 B7
I218 B6
I219 B6
I222 B5
I223 B5
I224 B4
I225 B5
I226 B6
I227 A5
I228 B5
I229 C5
I230 B5
I231 B5
I232 A7
I233 B7
I234 A4
I235 B5
I236 B5
I240 A4
I241 A4
I401 E7
I402 E6
I403 E7
I404 E7
I405 E7
I406 E7
I407 E8
I409 E8
I410 E6
I412 E6
I413 C6
I414 D6
I415 C6
I416 C5
I417 D5
I418 D6
E_14480_095.eps
270504
I419 C6
I421 D7
I422 D7
I423 D5
I424 E8
I425 C6
I426 D7
I427 D5
I428 D6
I429 E8
I430 E6
I431 C7
I432 D6
I433 E6
I434 C5
I443 E7
I444 E7
I445 E7
I446 C5
I448 E7
I449 D8
I451 D7
I452 E8
I453 D7
I455 D7
I456 D8
I457 D7
I458 D7
I459 D7
I460 C8
I461 C8
I462 C8
I463 D8
I464 C8
I465 E7
I466 D7
I467 E8
I468 D7
I469 E8
I470 D8
I471 C8
I472 C7
I473 E5
I474 E6
I475 D8
I501 E3
I502 E3
I503 E2
I504 E2
I505 D1
I506 E3
I507 D3
I511 E5
I513 E5
I514 D4
I515 E4
I516 E4
I517 E4
I518 E5
I519 E5
I520 E5
I521 E4
I523 E5
I524 E5
I527 E5
I529 D3
I531 D3
I532 D3
I533 D3
I535 D3
I536 D3
I537 C4
I538 C3
I539 D3
I540 D4
I541 D4
I542 C3
I543 C2
I544 D3
I545 C3
I546 C3
I547 C3
I548 C3
I551 D5
I552 D5
I553 D3
I554 D4
I555 D4
I556 D4
I557 D3
I561 D4
I562 D4
I565 C4
I571 D5
I572 C5
I573 D5
I574 D5
I575 D5
I576 D5
I577 D5
I578 D5
I579 D4
I582 B4
I583 B4
I584 B4
I585 B4
I587 C4
I588 B4
I681 E1
I682 B1
I683 B1
I686 C1
I687 D1
I688 C1
I689 D1
I691 E1
I693 D1
I701 C7
I702 C8
I704 C8
I705 B8
I707 C8
I709 B7
I710 B7
I711 B8
I713 A7
I714 B7
I715 C7
I716 C8
I717 C7
I718 C7
I719 B7
I720 A7
I721 B8
I722 B7
I727 A7
I728 B7
I729 C7
I730 C7
I731 C7
I732 B7
I733 B7
I734 C7
I735 B7
I736 B7
I739 B7
I909 B3
I910 C3
I911 C3
I913 C3
I914 C2
I915 C3
I916 C2
I918 C3
I919 C2
I920 B3
I921 C2
I922 C2
I924 B3
I925 B3
I926 B2
I927 C2
I928 B1
I930 C2
I934 B2
I935 B1
I936 B2
I937 C2
I938 B2
I939 B2
I940 B2
I941 B2
I942 C3
I943 B2
I944 C3
I945 C2
I946 B3
I948 B3
I951 B3
I952 A3
I953 A3
I954 A3
I955 B3
I956 A3
I957 A3
I958 B4
I959 B4
Page 22
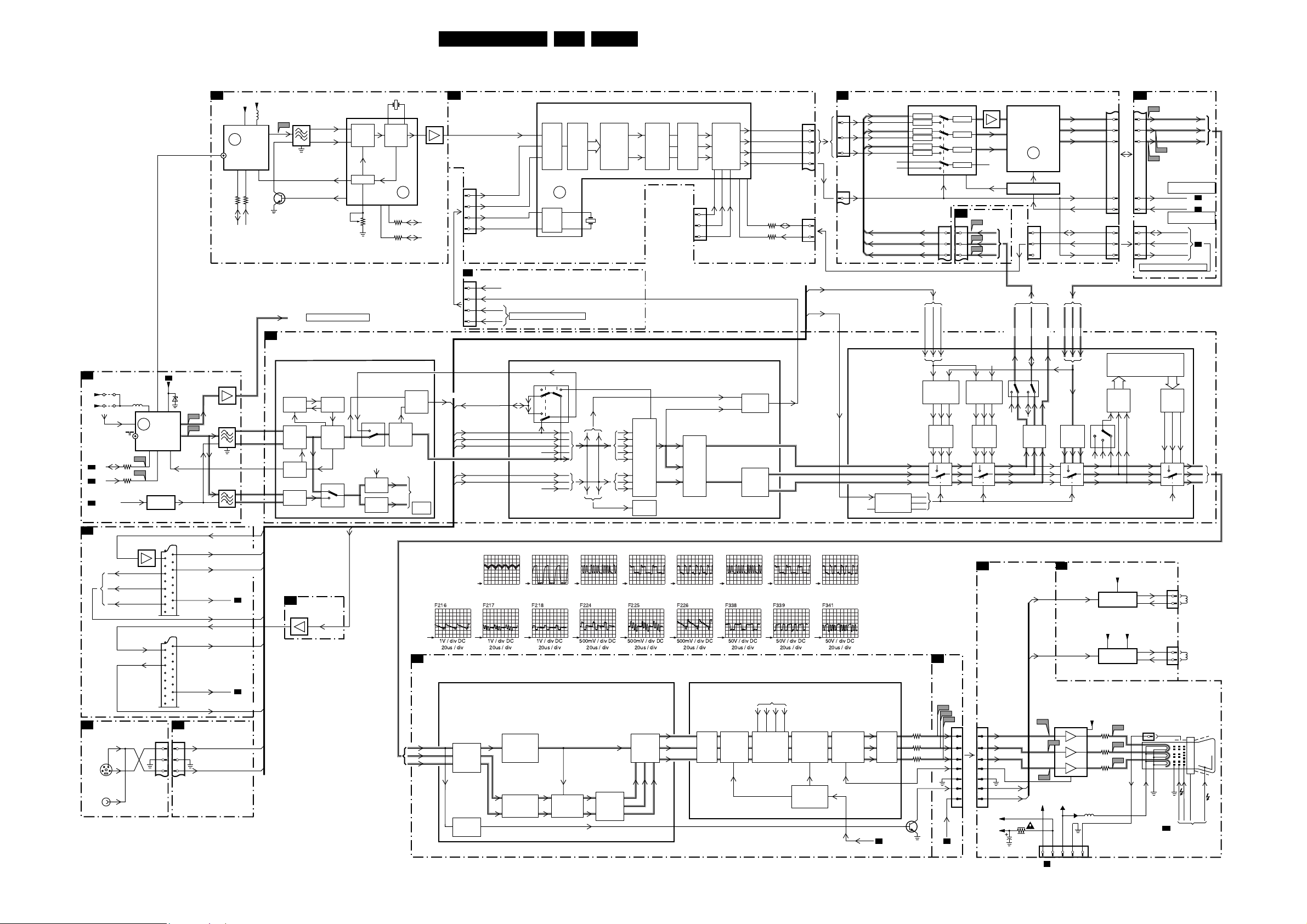
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Video
VIDEO
TUNER IF
A4
+5VS
+5V
A4
A4
A4
9002
FM
SDA
SCL
SEL-LLPIM
3001
3000
50019003
1000
ERR
TV
I002
I001
6 7
10
5
7001
SELECTION
FM-RADIO
TUNER
+
TV TUNER
4
FILTER
A2
98
VT
AGC
VT_SUPPLY
FM
IF
1
6001
BZX79-C33
F002
10
F004
11
PIP
PIP TUNER IF MULTISTANDARD VIDEO DEMODULATION
F2
+5VA
1000
UV1316/A
TV
3002 3001
7003
1002
1003
1004
ERR
4
79
PIP
+
TV TUNER
5
4
SDA
SDL
SSIF
VIF_1
VIF_2
RF_AGC
SIF1
SIF2
5001
VST
AGC
1
IF
SSIF
A4
105
104
100
11
7001
7200-A (IF)
98
99
F002
TO
AUDIO
PART
HERCULES
PHASE
DISC
VIDEO
TUNER IF
AGC
AUDIO IF
QSS/AM
1002
1003
IF
VIF_1
VIF_2
TUNER_AGC
SEL_P_N
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM AUDIO
VCO
VIDEO
DEMOD
7201
TDA9887
1
2
14
3
PLL
1201
15 19
VIDEO
VIDEO
PLL
IF
DEM.
AGC
910
11
3207
AGC
ADJ.
3206
SOUND
PLL
FM/QSS
SOUND
MIXER
AM
SOUND
DET.
TRAP
22L04E AA 6.
CONN.
A5
1212
F216
INTF_Y/GREEN_IN
4
INTF_Pb/BLUE_IN
6
INTF_Pr/RED_IN
8
F217
F218
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM
DEFLECTION
INTF_FBL
9
SANDCASTLE
10
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM
1206
1
3
6
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM CONTROL
DEFLECTION
E
D
INTF_BBL
DAC
DINT
A4
A4
A4
Y
Pr
Pb
SC1_FBL
H
1214
1216
LTI/CTI
1
3
5
1
7200-C
INSSW352
INTF_Y_OUT
INTF_Y
INTF_U_OUT
INTF_Pb
INTF_V_OUT
INTF_Pr
INTF_FBL
INTF_Y_OUT
INTF_U_OUT
INTF_V_OUT
(RGB/YPrPb/YUV
INPUT SWITCHING)
Yint
Uint
Vint
SELECTION
LOGIC
2
6
3
7
4
8
15
14
7611
TDA8601T
CLAMP
CLAMP
CLAMP
CLAMP
CLAMP
CLAMP
YUV
RGB
DVD
1212
1
2
3
SC1_RED_IN
SC1_GREEN_IN
SC1_BLUE_IN
49
50
51
YPrPb2/
YPrPb3
SELECTION
DVD
TO
DVD
DVD
3-STATE
3-STATE
3-STATE
3-STATE
A5
1212
165
1
2
3
7630
7635
12
11
10
13
F224
F225
F226
RGB2/
RGB3
SELECTION
RGB
TO
DVD
NC
RGB
7610
TDA9178T
6
YIN
8
UIN
9
VIN
INTF_V-OUT
YOUT
LTI/C+I
UOUT
PROC.
VOUT
ERR
15
SC
1
PULSE FORMER
1
SDA
SCL
3
INTF_Y_OUT
INTF_U-OUT58INTF_Pb/BLUE_IN
54
53
DVD
TO
YUV
55
19
17
16
INTF_FBL
SANDCASTLE
INTF_BBL
INTF_Pr/RED_IN
INTF_Y/GREE_IN
57
59
YUV
TO
DVD
YUV
1212
Y_2
4
Pb_2
6
Pr_2
8
9
10
12061215
1
SDA
SCL
3
6
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROC.
- 4:3 LINEAR/NON-LINEAR SCALING
- DOUBLE WINDOW PROC.
ADC
PIP-PROC.
F1
7202
17
ERR
16
SDA
SCL
SC1_CVBS_OUT
86
SWITCH
TO
AUDIO
PART
AM
See block
diagram
AUDIO
CVBS1_PIP
1219
INTF_CVBS_IN
1
INTF_CVBS_OUT
4
VD
2
HD_PIP
3
CONN.
A5
1219
INTF_CVBS_IN (NC)
5
INTF_CVBS_OUT
9
VD
7
HD-PIP
8
SW_SC2_CVBS
SC1_CVBS_IN
SC2_Y/CVBS_IN
SIDE_Y/CVBS_IN
CVBS1
SC2_CHROMA_IN
SIDE_CHROMA_IN
81
74
71
78
70
77
7242
SDA9488X
28
INPUT
24
26
4
3
SEE BLOCK DIAGRAM DEFLECTION
7200-B (CVBS I/O + FILTERS + COLOUR DECODING)
SWITCH
SYNC.
PROC.
ADC
STANDARD
DECODING
ERR
12
1
1241
2
MULTI
Y
UV
INPUT
SWITCH
VIDEO
IDENT
RGB
MATRIX
R
G
B
CVBS/Y
C
DAC
NC
COMB
FILTER
&TRAP
SWITCH
1220
R
G
B
1
2
3
FAST
RGB
SWITCH
11 12 13 6 5
CHROMA/CVBS
18
INTF_Y/GREEN_OUT
17
16
15
OUTPUT
SWITCH
PAL, NTSC
SECAM
DECODER
INTF_PrRED_OUT
INTF_PbBLUE_OUT
INTF_FBL
3244
SDA
3243
SCL
65
INTF_CVBS_OUT
YintYint
Uint
Vint
1212
1214
5
1
3
6
1
3
SC1_R/G/B
SC1_FBL
REAR I/O SCART (VIDEO PART)
A8
SC1-RED-IN
SC1-GREEN-IN
SC1-BLUE-IN
SC2-CVBS-OUT
SC2-CHROMA-IN
SIDE AV
D
32
SVHS
154
VIDEO
IN
A5
7606
7607
SW_SC2_CVBS
SW_SC2_CVBS
F201 2V / div DC
F203 2V / div DC
HERCULES
A4
7200-D (YUV PROCESSING)
Y
Pr
PEAKING
Pb
SCAVEM
PROC.
F205
500mV
10ms
/ div DC
/ div
WHITE/BLACK
STRETCH
GAMMA COR.
TINT CONTROL
SKINTONE
F206
1V
20µs
/ div DC
/ div
F240 F241 F242
500mV
/ div DC
500mV
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
20µs
/ div
500mV
MATRIXSATURATION
RGB
ADDER
R_Y
G_Y
B_Y
R
G
B
64
F331 F332 F333
/ div DC
500mV
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
20µs
/ div
500mV
CLAMP
MUTE
BLUE
STRETCH
+
&
CONTRAST
7200-E (RGB PROCESSING + CATHODE CALIBRATION)
FROM µP PART
R_OSD
G_OSD
B_OSD
OSD
INSERTION
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
FBL
BRIGHTNESS
+
PEAK WHITE
LIM.
BEAM
CURRENT
LIM.
500mV
/ div DC
20µs
CATHODE
CALIBRATION
/ div
OUTPUT
STAGE
46
BCL
A2 A4
CRT
B1
A5
F240
F241
F242
ROT
13311204
B
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
G
2
R
3
4
5
6
7
+200V
+200VA
BC_INFO
SVM
ROT
2351
3351
1351
3226
BOUT
42
3227
43
GOUT
3228
44
ROUT
IBLACK
45
SVM
7308
SCAVEM
B2
ROT
SVM
F331
7330
3
F332
1
2
F333
VSVM
FILAMENT
1351
12345
to 1401
A2
DEFLECTION
FILAMENT
1381
1
ROTATION
OUTPUT
FILAMENT
VSVM
SCAVEM
OUTPUT
+200VA
F341
3332
7
B
3334
9
G
3336
8
R
5
5352
EHT-b
1332
11
F338
F339
B
6
G
8
R
10 9 5 7 1
ROTATION
COIL
2
(OPTIONAL)
1361
1
SCAVEM
COIL
2
(OPTIONAL)
AQUADAG
DEFLECTION
FOCUS
VG2
A2
FROM DEFLECTION
E_14480_085.eps
280504
CRT
25kV
EHT
7701
SCART 1
21
19
15
20
16
SC1-CVBS-OUT
SC1-CVBS-IN
SC1-FBL
11
7
SCART 2
21
19
15
8
20
16
SC1-STATUS
SC1-R/G/B
SC2-CVBS-OUT
SC2-Y/CVBS-IN
A4
11
A5
1207
7
6
5
CONNECTION
SIDE_CHROMA_IN
SIDE_Y/CVBS_IN
SC2-STATUS/ITV_MSG
A4
SC2-CHROMA-IN
8
7
1252
Y
7
6
C
5
Page 23
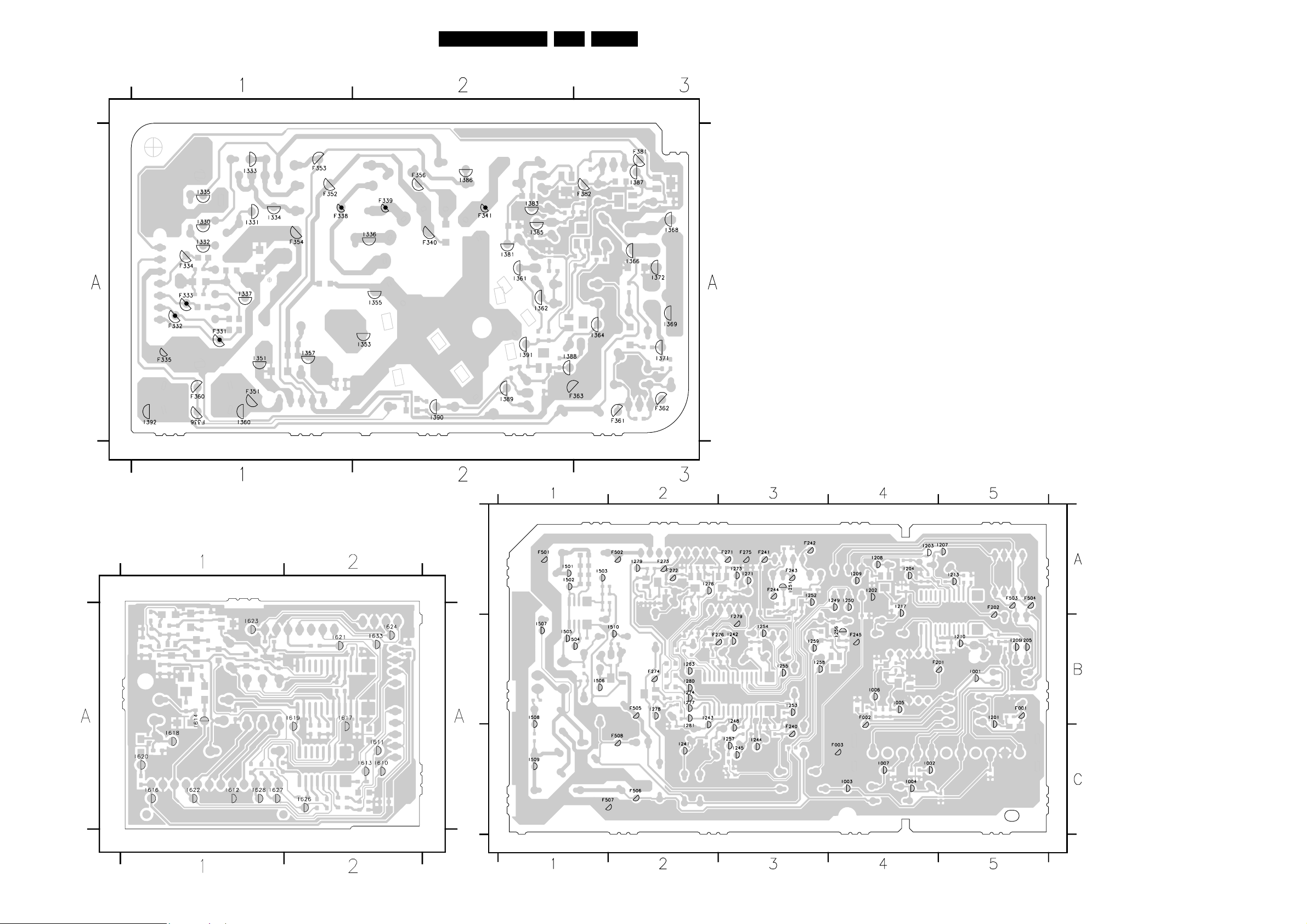
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Testpoint Overview CRT, LTI & PIP Panel
CRT
3139 123 5889.1
23L04E AA 6.
F331 A1
F332 A1
F333 A1
F334 A1
F335 A1
F336 A1
F338 A1
F339 A2
F340 A2
F341 A2
F351 A1
F352 A1
F353 A1
F354 A1
F356 A2
F360 A1
F361 A3
F362 A3
F363 A3
F381 A3
F382 A3
I330 A1
I331 A1
I332 A1
I333 A1
I334 A1
I335 A1
I336 A2
I337 A1
I351 A1
I353 A2
I355 A2
I357 A1
I360 A1
I361 A2
I362 A2
I364 A3
I366 A3
I368 A3
I369 A3
I371 A3
I372 A3
I381 A2
I383 A2
I385 A2
I386 A2
I387 A3
I388 A2
I389 A2
I390 A2
I391 A2
I392 A1
1610 A2
1611 A2
1612 A1
1613 A2
1616 A1
1617 A2
1618 A1
1620 A1
1621 A2
1622 A1
1619 A2
1614 A1
LTI INTERFACE
3139 123 5740.1
1623 A1
1624 A2
1626 A2
1627 A1
1628 A1
1633 A2
PIP
3139 123 5821.1
E_14480_091.eps
020404
F001 B5
F002 B4
F003 C4
F201 B4
F202 A5
F240 C3
F241 A3
F242 A3
F243 A3
F244 A3
F245 B4
F271 A3
F272 A2
F273 A2
F274 B2
F275 A3
F276 B2
F279 B3
F501 A1
F502 A2
F503 A5
F504 A5
F505 B2
F506 C2
F507 C1
F508 C2
I001 B5
I002 C4
I003 C4
I004 C4
I005 B4
I006 B4
I007 C4
I201 B5
I202 A4
I203 A4
I204 A4
I205 B5
I206 B5
I207 A5
I208 A4
I209 A4
I210 B5
I213 A5
I217 A4
I241 C2
I242 B3
I243 B2
I244 C3
I245 C3
I248 B3
I249 A4
I250 A4
I251 A3
I252 A3
I253 B3
I254 B3
I255 B3
I256 B4
I257 C3
I258 B3
I259 B3
I263 B2
I271 A3
I273 A3
I274 B2
I276 A2
I277 B2
I278 B2
I279 A2
I280 B2
I281 C2
I501 A1
I502 A1
I503 A1
I504 B1
I505 B1
I506 B1
I507 B1
I508 B1
Page 24
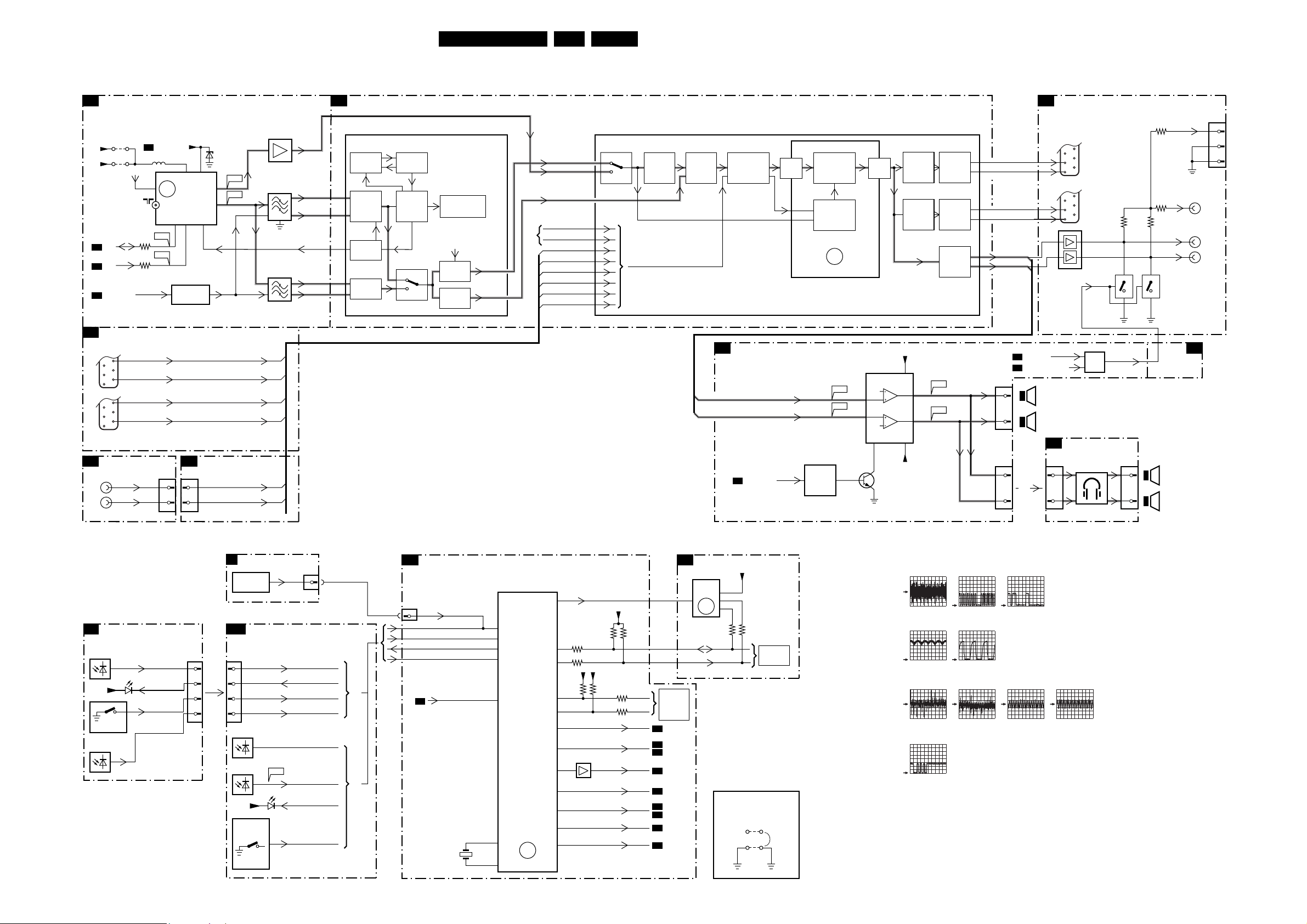
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Audio/Control
AUDIO
TUNER IF
A3
+5V
+5VS
SDA
A4
SCL
A4
SEL-LLPIM
A4
REAR I/O SCART
A8
SCART 1
SCART 2
SIDE AV
D
L
R
9002
6
3
2
1
6
3
2
1
FM
3001
3000
VT_SUPPLY
A2
50019003
1000 6, 7 9
2
ERR
10
TV
I002
I001
1252
3
1
FM-RADIO
TUNER
+
TV TUNER
5
4
7001
FILTER
SELECTION
A5
1207
3
1
6001
BZX79-C33
VT
F002
10
FM
F004
11
IF
AGC
1
CONNECTIVITIES
SIDE_L_IN
SIDE_R_IN
SC1_L_IN
SC1_R_IN
SC2_L_IN
SC2_R_IN
7003
1002
1003
1004
SSIF
VIF_1
VIF_2
RF
SIF1
SIF2
A4
24
25
31
29
30
HERCULES
7200-A (IF)
PHASE
DISC
VIDEO
IF
TUNER IF
AGC
AUDIO IF
QSS/AM
VCO
VIDEO
DEMOD
PLL
To VIDEO PART
see block diagram
VIDEO
PLL
SOUND
MIXER
AM
SOUND
DET.
FM/QSS
24L04E AA 6.
REAR I/O SCART
A8
3764 3761
12781254
1
2
3762
3757
L 8 Ohm/15W
R 8 Ohm/15W
7200-F (AUDIO)
DIGITAL PART
SC1_L_OUT
FM/QSS
SSIF
96
AM
INTF_R_IN 75
N.C.
INTF_L_IN 76
SC2_R_IN 72
SC2_L_IN 73
SIDE_R_IN 79
SIDE_L_IN 80
AM
SC1_R_IN 94
SC1_L_IN 95
FM
DEM.
AMPLI
+
MUTE
MAIN_OUTL
MAIN_OUTR
AUDIO
SOURCE
SELECTION
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
A7
A4
VOL_MUTE
PROCESSING
DECODER
7991
7992
VOLUME
+
MUTE
DIGITAL
SOUND
DIGITAL
STEREO
SOUND
ERR
19
I951
I952
7990
TDA2616Q
1
9
2
7991
ADC DAC
AUDIO
SELECT
AUDIO
SELECT
V AUDIO+1
7
5
-V AUDIO
SCART
CINCH
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
F952
4
F955
6
93
SC1_R_OUT
92
SC2_L_OUT
67
HP
LS
66
68
69
SC2_R_OUT
MAIN_OUTR
MAIN_OUTL
A4
A4
1281
5
2
1280
1
2
Stby_Con
POWER_DOWN
OR
SCART 1
6
3
2
1
SCART 2
6
3
2
1
7705
5
2
L 8 Ohm/15W
R 8 Ohm/15W
SIDE AV
D
5
2
4
1
MUTING
7993, 7994
MUTE
7703 7702
MUTING
SPDIF
(optional)
1228
SUBWOOFER
(optional)
MONITOR
OUT
L
R
A5
1
2
3
CONTROL
FRONT INTERFACE
J1
(PARTLY)
6692
TSOP1836
+3.3V
ON/OFF
USA only
6693
6691
KEYBOARD
LIGHT_SENSOR
LED
TOP CONTROL
E
LOCAL
KEYBOARD
FRONT CONTROL
A9
1693
3
IR
4
5
6
1693
3
4
5
6
6693
6692
TSOP1836
+3.3V
LOCAL
KEYBOARD
(USA only)
F692
+
ON/OFF
6691
1010
2
LED
KEYBOARD
LIGHT_SENSOR
LIGHT_SENSOR
LED
KEYBOARD
IR
OR
IR1
OR
HERCULES (CONTROL)
A4
1682
2
KEY_PROTN 9
IR 32
LED 30
LIGHT-SENSOR 14
POWER_DOWN 31
A1
1205
24MHz
7200-G (Control)
TDA12001H1
I/O PORTS
IIC BUS
TRANSCEIVER
PWM
OUTPUTS
TELETEXT
(close caption)
ROM
119
118
+
+
+
CPU
+
+
RAM
ERR
20
22
3207
20
3214
21
2
1
18
15
17
16
23
24
25
SEL_SC2_INTF
+3.3V
VOL_MUTE
Stdby_Con
7205
SEL_LLPIM
Reset__5V
WRITE_PROTECT
+3.3V
32043202
32803279
3266
3265
ROT
I2SD/1
SDA
SCL
E
D
DIAGRAM
A7
A1
A7
B2
A3
A5
G
A5
A5
see
IIC
(FOR LTI
AND PIP)
A5
FEATURES
EEPROM
(NVM)
7
ERR
8
6
5
9
+3.3V
36043605
see
IIC
DIAGRAM
SERVICE JUMPER
9275
SDM
9252
F003 0V (N.A.)
F201 2V / div DC
F203 2V / div DC
F004 I001 I002
/ div AC
200mV
10ms / div
F205
500mV
/ div DC
10ms / div
50mV / div AC
2ms / div
F692
2V / div DC
2ms / div
1V / div DC
20µs / div
F206
1V / div DC
20µs / div
I952I951 F952 F955
50mV / div AC
2ms / div
500mV / div AC
1V / div DC
20µs / div
2ms / div
500mV / div AC
2ms / div
E_14480_087.eps
280504
Page 25
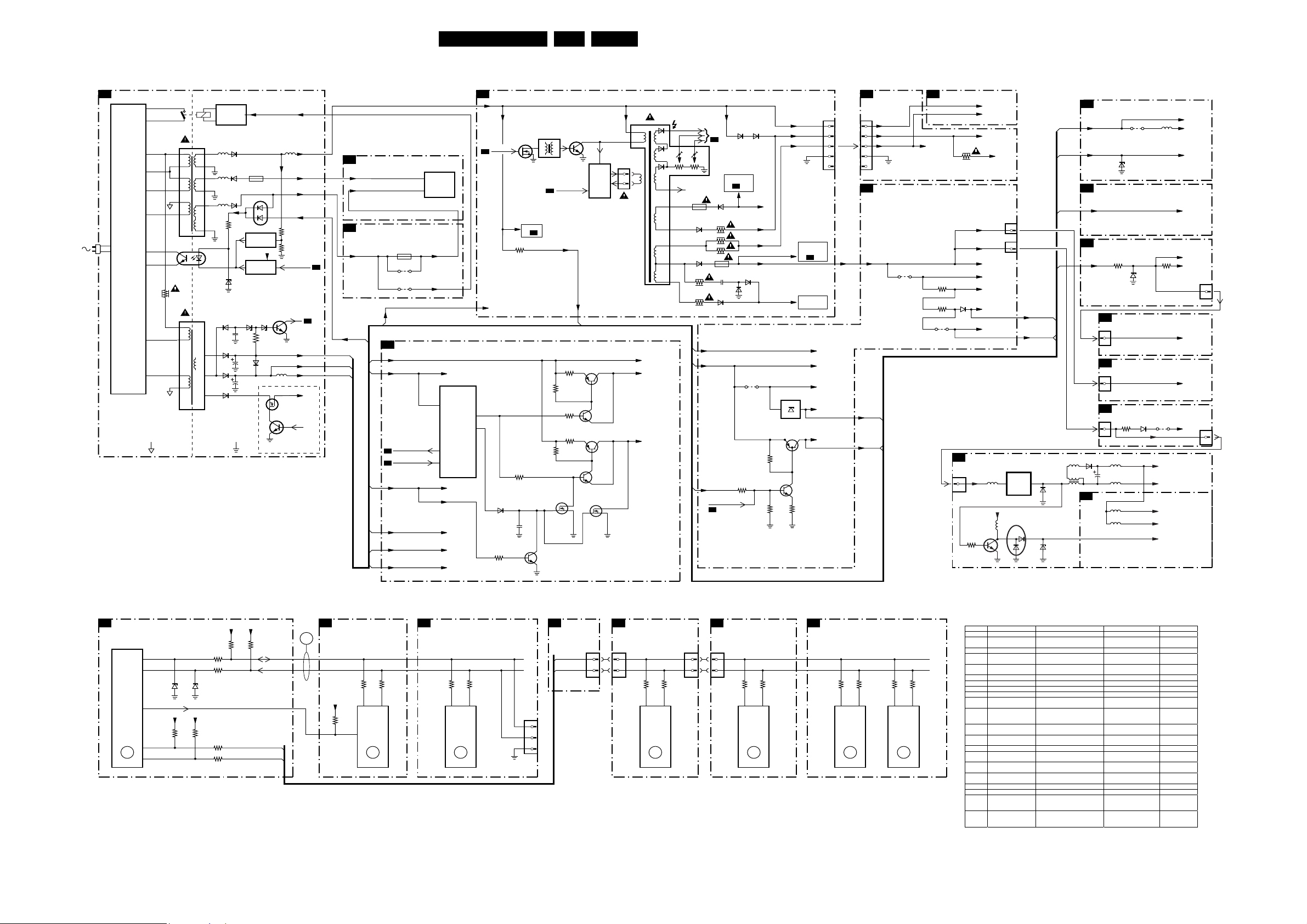
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
I2C and Supply Voltage Overview
SUPPLY LINES DIAGRAM
POWER SUPPLY
A1
SUPPLY
PRIMARY
SIDE
5520
9
8
4
5
3
2
3
4
3532
5531
4
5
1
2
HOT GROUND COLD GROUND
7541
1503
43
ENERGIZING
1
2
5551 5552
17
18
5562
14
13
5561
10
12
1
7515
TCET1103
2
10
8
6
CIRCUIT
(optional)
6551
6563
6562
6564
6535
6536
6537
3571
6573
2564
2535 6676
2536
1543
6571
7571
REFERENCE
CIRCUIT
7573
STANDBY
CIRCUIT
6565 6566
V_DG V_DG
3575
3576
+3V3
STDBY_CON
POWER-DOWN
7561
3565
5537
D
S
7535
G
7536
only used in sets with DVD
Vbatt
-Vaudio -Vaudio
+Vaudio
+6VA
AUDIO_AMPLIFIER
A7
Vaudio+1
CLASS D
A6
AUDIO AMP
(RESERVED)
+Vaudio
A4
A4
+6VA
+3V
+6VA
+6V
Vaux
2X
2X
2X
1903
see diversity table
*
+6VA
HERCULES
A4
+3V
+3.3V
Stdby_Con
A1
POWER_DOWN
A1
+5V
+Vbutter
+6V
+8V
9911
9910
25L04E AA 6.
LINE + FRAME DEFLECTION
A2
+Vbatt
FILAMENT
To 6403, 3480,
3420, b-7401,
c-7403
on
To
VERTICAL
DEFLECTION
7605
7604
3609
A2
Vbatt
1401
1
2
3
4
5
+3V (N.C.)
+6V
+6VS
+3.3V
+5V
5445
3
1
1404
1
2
+
E/W
HOR.
DEFL.
COIL
7990
TDA2616Q
5
OUTPUT
7
AUDIO
Vaudio+1
5402
A4
EW_DRIVE
7405
LINE
OUTPUT
CIRCUIT
CORR.
7404
HDRIVE
A4
To 6407
on
A2
3401
VT_SUPPLY
*
V_DG
7200
HERCULES
19
35
125
15
31
+3.3V
+5V
+Vbutter
+6V
+8V
PWM1
115
16
+6VA (To 3445)
DECDIG
6207
3217
3295
2204
7202
VT_SUPPLY
2X
3210
3211
3206
3209
3208
7210
G
7204
7201-2
7203
7201-1
7209
D
S
D
G
S
+3V
+1.8V_A
+1.8V_B
EHT
FOCUS VG2
10
BCL
6
5
7
8
9
1454
6453
6456
3457 2456
3455
TO
CRT
B1
6452
3458
3484
3485
1452
6459
+3V
+6V
VT_SUPPLY
RESET +5V
A4
Vbatt
6483 6484
To 3405, 3463,
3475
on
A2
VIDEO SUPPLY
6455
3606
6454
4604
FILAMENT
VIDEO SUPPLY
-12V
+9V
7603
L78L33ACZ
13
3608
3607
CRT
B1
1351
A5
+9V
VSVM
1
+200V
2
FILAMENT
3
4
5
FEATURES & CONNECTIVITIES
+9V
+3.3V
1X
2X
+5V
1X
4611
B2
FILAMENT
3639
3610 6610
9605
SCAVEM
VSVM
FILAMENT
+200V
3351
F1
1212
962
+200A
1221
1
+9V
1212
12
+9V
+9V
+9VA
+9VA_1
+8V
Vbuffer
PIP POWER SUPPLY
+9V
3505
7502
5501
+3V3
5502
7501
MC34063AD
SUPPLY
6502
IC
+8V
Vbuffer
6509
6503
-/B33
TUNER IF
A3
+5V
5001
+5V
VT_SUPPLY
REAR I/O CINCH
A8
Vbutter
FRONT CONTROL
A9
+5V
1X
1X
1X
6504
5507
????
PIP TUNER IF
F2
9002
6001
-/C33
3690 3693
6694
-/C5V1
FRONT INTERFACE
J
1693
LINEARITY & PANORAMA
G
1462
1
LTI/CTI
H
1212
3610
5504
5506
5220
5010
6610
9V
12
2507
9613
+5V
+3V3
+5VS
+5VA
+33V
To TUNER
Pin 6.7
To TUNER
Pin 9
Vbutter
To LED
To 3-6692
(IR_REC)
+6V
+9V
+8V
1693
1216
1
4
I2C BUS INTERCONNECTION DIAGRAM PIP MODULE
A4
HERCULES
7200
SET
PROCESSOR
PART OF
VIDEO-
PROCESSER
(HERCULES)
ERR
19,20
+3.3V
+3.3V
3202
20
21
22
+3.3V
3279 3280
2
1
3207
3214
62116210
+3.3V
3266
3265
3204
SDA
SCL
WRITE_PROTECT
E
D
A5
ERR
6
FEATURES & CONNECTIONS
+3.3V
3601
56
7601
PCF8511
EEPROM
7
(NVM)
ERR
9
TUNER IF
A3
1206 1206
E
1
D
3
36043605
30003001
54
1000
TUNER
ERR
10
COMPAIR
1005
1
2
3
For
only
LTI/CTI INTERFACE
H
1
3
14 11
7610
TDA9178T
LTI/CTI
PROC.
ERR
15
SDA
SCL
36173616
F1
1215 1214
1
3
PIP POWER SUPPLY TUNER IF
32433244
56
7242
SDA9488X
PIP
PROC.
ERR
12
SDA
SCL
1
3
F2A5
30013002
54
1000
UV1316
TUNER
PIP
ERR
4
10 11
7201
TDA9887
PIP
IF
DEMO.
ERR
16
32063207
ERROR CODE LIST
ERROR Device Error description Check item Diagram
0 Not applicable No Error
1 Not applicable X-Ray / over-voltage protection
2 Not applicable High beam (BCI) protection 3404, 7405 A2
3 Not applicable Vertical guard protection 3466, 7451, 7452, 7453,
4 Tuner UA1316/A I2C error while communicating
5 Not applicable +5v protection 7604, 7605 A5
6 I2C bus General I2C error 7200, 3207, 3214 A4
7 Not applicable - - 8 Not applicable - - 9 24C16 I2C error while communicating
10 Tuner = I2C error while
11 TDA6107/A Black current loop instability
12 SDA9488X I2C error while communicating
13 Not applicable - - -
14 DVD Loader I2C error while communicating
15 TDA9178T/N1 I2C error while communicating
16 TDA9887 I2C error while communicating
17 Not applicable - - -
18 Not applicable - - 19 TDA1200 I2C error while communicating
20 TDA1200 I2C error while communicating
(US only)
with 2nd tuner
with the EEPROM
communicating with the PLL
tuner
protection
with the PIP processor
with the DVD Interface module
with LTI module
with PIP_Demodulator
with SSD stereo sound
decoder
with video cosmic in Hercules
IC
2411, 2412, 2413, 6404,
6411, 6412.
7454
1000, 5010
(PIP Module)
A2
A2
F2
7601, 3604, 3605 A5
1000, 5001 A3
7330, 3351, CRT B1
7242 (PIP Module) F1
DVD Interface module DVD Loader
7610 H
7201 F2
7200 A4
7200 A4
E_14480_084.eps
060504
Page 26
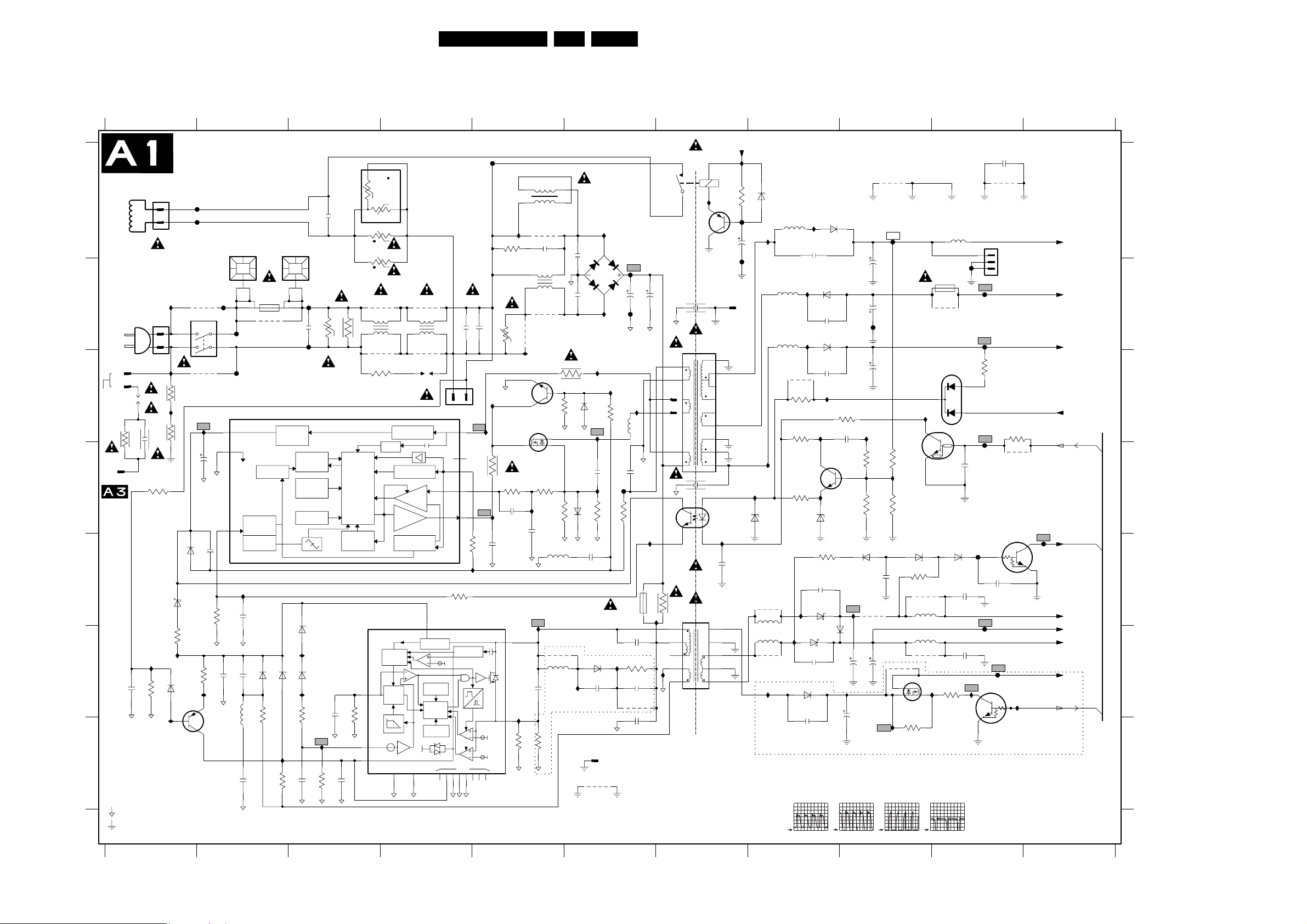
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
7. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Mono Carrier: Power Supply
1234567891011
POWER SUPPLY
3
DEGAUSSING COIL
A
B
1508
1509
For
C
Lightning
Protection
3506
1510
TO 1013 OF
D
(For
Lightning
Protection)
E
F
2528
G
"$"
FOR MAINS 120V AC 170V (177V)
..V.. Normal Operation
(..V..) Standy Mode
HOT GROUND
COLD GROUND
3139 123 5676.1
1504
1505
1n5
3M3
2509
3529
*
I553
3528
**
F500
2
F501
1
9507
*
1506
*
2
1
MAINS SWITCH
9508
*
I511
2511
6511
RGP10D
BAT54 COL
15K
3527
I555
13V
0V3
56
50V22u
2517
3512
*
7532
BC857B
F503
4
3
15V5
2532
I503
3500
3501
6538
I554
2
1
I504
3M3
I505
3M3
6512
3519
I541
*
3V8
220V AC 309V (317V)
1501
PFC5000
F505
F504
7511
TEA1506T/N1
2
Vcc
3
Gnd
6
Ctrl
0V
1n0
I527
1K2
2512
10u
2530
5533
2544
*
T4E.250V
for ITV only
FREQUENCY
INPUT
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
BURST
DETECTOR
100n
6532
330p
33u
3534
10n
1500
9500
CONTROL
BAV21WS
100R
I536
1502
PFC5000
SUPPLY
MANAGEMENT
TEMPERATURE
PROTECTIOM
6533
I556
6531
6534
BZX384-C15
I557
3530
3531
2533
100K
F506
2500
F507
VOLTAGE
CONTRLLED
OSCILLATOR
OVER
POWER-ON
RESET
BZX384-B6V8
220R BZX384-B3V9
4n7
470n
I531
3537
2501
3505
*
2531
2K2
RES
V
3504
CONTROL
MAXIMUM
ON-TIME
PROTECTION
470p
2549
3523
2
1M5
LOGIC
CIRCUIT
3533
2V7
0V3
100p
+t
Rs
Rp
*
3507
+t
*
3509
+t
RES
9501
RES
5501
4
1
23
DMF-2405
9503
RES
3502
*
CURRENT SOURCE
VALLEY
*
TEA1620 (Basic)
7531
TEA1623 (IDTV)
LOGIC
STOP
5
RC
OSC
1V
LOW FREQ
8K2
F
1.8 U
2.5V
6
REG
+
-
11
AUX
GND SGND NC
4
1
9502
*
5500
1
*
23
9504
*
3503
*
DSP
START-UP
START-UP
CURRENT SOURCE
CURRENT
SENSING
OUTPUT
DRIVER
OVER
POWER
PROTECTION
3
SUPPLY
PWM
POWER-UP
10X
4
2
1507
For 70W Subwoofer
Drain
HVS
Demag
Sense
Driver
3518
3K3
VCC
VALLEY
+
THERMAL
SHTDWN
PROT
LOGIC
RESET
110
789
RES
2502
14
297V
7
0V
9
0V
11
2V2
1
3517
I520
131415162
2508
I513
F502
I519
330K
BLANK
+
+
100n
I517
3514
2513
DRAIN
SOURCE
26L04E AA 7.
I513 C5
3575 D9
1500 B2
1501 A2
1502 A3
1503 A7
1504 A1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1505 B1
1506 B1
1507 C4
1508 C1
1509 C1
1510 D1
1532 E6
1535 A10
1542 B8
1543 B10
1545 G6
2500 B3
2501 A3
2502 B4
2503 A6
2504 B6
2505 B6
2506 A5
2507 B6
2508 B5
2509 C1
2511 D2
2512 E2
2513 E5
2514 D6
2515 D6
2516 D5
2517 E2
2518 E6
2519 D5
2528 F1
2530 F2
2531 F3
2532 F2
2533 G3
2534 F5
2535 F9
2536 F9
2537 F9
2538 E8
2539 F8
2540 G8
2541 A7
2542 B7
2543 F6
2544 G2
2545 F6
2546 F6
2547 E10
2548 F10
2549 G3
2550 F6
2551 A8
2552 B9
2553 A10
2561 C8
2562 C9
2563 B9
2564 E9
2565 B8
2566 E10
2570 D7
2571 C9
2572 D10
2573 E7
3500 C1
3501 C1
3502 C4
3503 C4
3504 B3
3505 B3
3506 C1
3507 A4
3508 A5
3509 A4
3510 B5
3511 D6
3512 E2
3513 C6
3514 D5
3515 D5
3516 D5
3517 E4
3518 E4
3519 F1
3520 D6
3521 C6
3522 D5
3523 A3
3524 C5
3527 F2
3528 F1
3529 D1
3530 F3
3531 G2
3532 E6
3533 F3
3534 F2
3535 G9
3536 F10
3537 G3
3538 G5
3539 G5
3541 A7
3542 F6
3563 E8
3565 E9
3571 C8
3572 C10
3573 D9
3574 D9
1503
LKS1AF
81
"$"
7541
BC857B
23
Vaux_GND
I506
3508
470R
45
5502
*
9506
*
2506
33n
2503
5503
23
I501
2
2n2
4
6500
F508
1
*
14
DMF-2810
9505
RES
4R7
RES
9511
3510
-T
I507
3513
7514
BC847B
2V3
2V3
7512
*
G
2K2
0V
3524
295V
D
S
0V
*
3515
3522
I532
3538
1K0
I518
100p
2519
I533
68P
2534
2R2 (IDTV)
1R8 (Basic)
0R1
3516
5513
1u0
9532
5532
I529
For IDTV Only
3R3
3539
Vaux_GND
470p
47K
2516
100n
-8V3
12
0V
2504
47K
6575
6514
3
2n2
I502
I514
I524
BAS316
3521
I516
1n5
2514
I521
3520
*
1N5062
2518
10n
6540
2546
470p
1545
Provision For
Lightning Protection
4538
Vaux_GND
I544
2505
3K3
F510
4K7
3511
For IDTV
5511
2515
Only
I515
1532
2550
33P
3542
68K
2545
10n
9512
2543
2n2
*
F509
470p
T315MA
2507
RES
*
*
2
3
4
5
8
9
15V6
4
1
5V
I523
I535
32
7513
TCET1103(G)
4R7
3532
5531
56
4
3
I540
2
110
SS22220-03
HOT
COLD
F508 268V / div DC
F511 15V5 / div DC
F531 2V7 / div DC
F537 0V (N.A.)
I543
14
I542
16V4
F542
Vaux_GND
2542
For Heatsink
5512
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
AUDIO_GND1
11
AUDIO_GND2
10
2570
470P
9V3
8V2
I575
220n
2573
Vaux_GND
7
8
Vaux_GND
9
F552 130V / div DC
F561 15V9 / div DC
F564 9V4 / div DC
F573 0V (N.A.)
V_DG
3541
2541
1542
47K
16V4
F541
47u 25V
I571
6573
6541
BZX384-C12
I551
I561
BZX79-C9V1
4534
RES
5534
1u0
5535
1u0
4535
RES
I539
For IDTV Only
9510
Audio_Gnd
I552
I579
2551
1n
6551
*
6563
5551
5562
*
2565
AUDIO_GND1
3579
2K2
2571
15n
7571
BC547B
6V8
BZX384-B6V2
6576
2537
Vaux_GND
100V / div DC
5µs / div
F562
AUDIO_GND2
I576
3573
3574
6564
BAS316
Vaux_GND
I565
BAS316
2535
1m0 6.3V
Vaux_GND
16V2m2
1n
I562
5561
I538
6562
*
2561
9513
1n
RES
3571
*
I572
I573
3578
470R
7V6
6V2
3577
I577
1K5
6572
3563
220R
2538
470P
6535
SB160
I537
6536
SB180
2539
470P
6537
STPS10L60D
2540
1n
I513 I516 I519 I533
100V / div DC
5µs / div
AUDIO_GND2
F552
160V
2552
100u
2563
*
2562
**
7573
PDTC114ET
82K
15K
3575
I578
4K7
3576
*
2564
100n
4537
10V
4536
2536
2m2
SI2307DS
I545
2V / div DC
5µs / div
*
*
7535
3535
1K0
6565
3565
I574
9536
RES
5536
RES
5537
RES
9537
RES
8V2
I547
AUDIO_GND1
1543
*
9514
*
6571
BAV70
K
BAS316
3536
*
100V / div DC
5µs / div
5552
27u
F551
6566
A1
A2
2572
2547
1u0
Vaux_GND
2548
1u0
Vaux_GND
I548
Vaux_GND
10n
F535
3
2
1
F563
F561
3572
F573
F536
1535
0V
2566
100n
F537
PDTC143ZT
2553
180P
9509
Vaux_GND
for DVD
3589
100R
9589
7561
PDTC143ZT
I546
7536
F564
3V3
Vaux_GND
Vbatt
140V
-Vaudio
-16V
+Vaudio
+16V
+6VA
Stdby_Con
POWER_DOWN
+3V
+6VA
+6V
Vaux
B
E_14480_116.eps
A4
A2
A4(3x)
A4
260504
3576 D9
3577 D8
3578 C8
3579 C9
3589 C10
4534 E8
4535 F8
4536 F9
4537 E9
4538 G6
5500 B4
5501 B4
5502 A5
5503 B5
5511 C6
5512 C7
5513 E5
5531 E7
5532 F5
5533 F2
5534 E8
5535 F8
5536 E9
5537 F9
5551 A8
5552 A10
5561 B8
5562 B8
6500 B6
6511 E1
6512 E1
6514 C6
6531 F2
6532 F2
6533 F3
6534 F3
6535 E8
6536 F8
6537 F8
6538 F1
6540 F6
6541 A8
6551 A8
6562 B8
6563 B8
6564 E9
6565 E9
6566 E10
6571 C10
6572 D8
6573 D8
6575 D6
6576 F8
7511 C2
7512 C5
7513 E7
7514 C5
7531 E3
7532 F2
7535 F9
7536 G10
7541 A7
7561 E10
7571 D9
7573 C9
9500 B2
9501 B4
9502 B4
9503 C4
9504 C4
9505 B5
9506 A5
9507 B2
9508 C2
9509 A10
9510 A9
9511 B5
9512 F6
9513 C8
9514 B10
9532 F5
9536 E9
9537 F9
9589 D10
F500 A2
F501 A2
F502 A5
F503 B2
F504 C2
F505 B2
F506 B3
F507 C3
F508 B6
F509 B6
F510 D6
F535 E10
F536 E10
F537 F10
F541 A8
F542 B7
F551 B10
F552 A9
F561 B10
F562 B9
F563 B10
F564 E11
F573 C10
I501 A6
I502 B6
I503 B1
I504 C1
I505 C1
I506 A5
I507 B5
I511 C2
I514 C6
I515 C6
I516 C6
I517 C5
I518 D5
I519 D5
I520 E5
I521 D6
I523 E6
I524 C6
I527 E2
I529 F6
I531 G3
I532 F5
I533 E5
I535 E6
I536 G2
I537 E8
I538 F8
I539 F8
I540 F7
I541 F1
I542 A7
I543 A7
I544 F6
I545 G9
I546 F10
I547 F10
I548 F10
I551 A8
I552 A8
I553 F1
I554 G1
I555 F1
I556 F3
I557 F3
I561 D8
I562 B8
I565 E9
I571 D8
I572 C8
I573 C8
I574 C9
I575 E7
I576 C9
I577 D8
I578 D9
I579 B8
123
4567891011
Page 27

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Mono Carrier: Diversity Table for A1 (Power Supply)
12345678910
27L04E AA 7.
DIVERSITY TABLE FOR
REGION
MAIN RANGE
A
B
C
D
SET
VBATT
AUDIO
OUTPUT
1508
1510
2505
2506
2508
2509
2528 --- --- --2542
2570
3505
3506
3507
3508
3514
3520
3527
3528
3529
3523
3565
3574
5500
5502
5512
6500
6538 --6551
6565
7512
7532 --- --9502
9504
9506
AUDIO
OUTPUT
1543
25V 1000uF
2562
25V 1000uF 25V 2200uF 25V 2200uF
2563
3571
3572
6562
6563
9514
27RF
27FSQ 32RF
130V 130V
2X5W
2X10W
--- ---
200V 470U 200V 470U 200V 470U 400V 330U
--- ---
--- --- ---
--- --- ---
250V 1N5 250V 1N5
--- --- ---
1MA/423V 1MA/423V 1MA/423V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V
---
---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --100R 100R 100R 47R 47R 47R
0R18 0R18 0R18 0R33
---
---
---
145V 1R5
15K 15K 15K 18K
150K 150K
--- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
GBU4JL GBU6JL GBU6JL GBU4JL
STTH8L06D BYV29X-500
UDZS9.1B UDZS9.1B UDZS9.1B UDZS7.5B
FQPF9N50 FQPF9N50
2X5W 2X10W 2X10+20W 2X15W
---
220R 220R 680R
220R 220R 470R
SB360 SB360 SB380
SB360 SB360
JMP
SS40310-01SS40310-01 SS40312-01 SS42315-01 SS42315-01 SS42315-01
JMP
JMP
JMP
--- ---
--25V 2200uF
25V 2200uF
220R
220R
SB360
SB360
JMP
LR
26WSRF
30WSRF
32FSQ
143V 130V 130V 130V
2X5W
2X10W
---
144V 3R
---
---
---
---
--- ---
JMP
JMP
JMP
25V 2200uF 25V 2200uF
2X5W
2X10W
---------
---
---
250V 1N5 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N
---
144V 3R
---
---
---
---
33K 150K 150K 150K
BYV29X-500STTH8L06D STTH8L06D STTH8L06D STTH8L06D STTH8L06D BYV29X-500 STTH8L06D
FQPF9N50 FQPF7N80 STP10NK8OZFP STP10NK8OZFP
JMP
JMP
JMP
2A 250V 2A250V
--- ---
POWER SUPPLY
LATAM / APNAFTA
FR
21RF
2X10W 2X5W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
---
275V 100N 275V 100N
250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5
470N 470N 470N 470N 470N 470N 470N 470N
250V 470P
3M3
--- --- --- --- --- --- ---
47K
1M
2M2
276V 4R5 276V 4R5 276V4R5 276V 4R5 276V 4R5 276V 4R5 276V 4R5
10MH 2A 10MH 2A 10MH 2A 10MH 2A 10MH 2A
BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316
---
--- --- --- ---
JMP
SB380
25RF
29FSQ 29RF 29RF 28WSSF
130V 143V 143V 130V 130V 130V 130V 130V
2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
400V 330U 400V 330U 400V 330U 400V 330U
--- --- --- ---
250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P
3M3 3M3 3M3 3M3
0R33 0R33 0R22 0R33 0R22 0R33 0R33 0R33
47K
1M
2M2
18K 18K 18K 18K
GBU4JL GBU6JL GBU6JL GBU6JL GBU6JL GBU4JL GBU4JL
UDZS7.5B UDZS7.5B UDZS7.5B UDZS7.5B
--- ---
JMP
2X5W 2X10W 2X5W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
275V 100N 275V 100N 275V 100N 275V 100N
47K
1M
2M2
JMP JMP JMP
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N
1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V
47R 47R 47R 47R 47R 47R 47R 47R
47K
1M
2M2
150K 33K 33K 150K 150K 150K 150K 150K
SS49309-01 SS42316-01 SS49308-01 SS42315-01 SS42315-01 SS42315-01 SS42315-01 SS42317-01
STP10NK8OZFP STP10NK8OZFP STP10NK8OZFP FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80
------
--- ---
JMP JMP JMP JMP
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
47K
1M
2M2
---
---
28WSRF
32WSRF 21/25RF 29RF 34RF
2X10W 2X10W 2X5W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
400V 330U 450V 220U 450V 220U 450V 220U 450V 220U 450V 220U
--- ---
250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5 250V 1N5
3M3 3M3 3M3 3M3 3M3 3M3
--- ---------
47K
1M
2M2
18K 15K 15K 15K 15K 15K
10MH 2A 20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5
--- ---
UDZS7.5B UDZS10B UDZS10B UDZS10B UDZS10B UDZS10B
--- --- JMP
---
------
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
275V 100N 275V 100N 275V 100N
47K
1M
2M2
---
HR HR
2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
400V 33N 400V 33N
1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V
--- --- --- ---
47K
1M
2M2
276V 4R5 276V 4R5 276V 4R5 276V 4R5
65MH 65MH
STTH8L06D
BC857B BC857BBC857BBC857B BC857BBC857B BC857BBC857B BC857B
---
--- ---
2X10W 2X5W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
470N
470R470R
47K
1M
2M2
BYV29X-500
BAS316 BAS316 BAS316 BAS316
GBU4JL
2X10+20W
250V 470P 250V 470P
STTH8L06D STTH8L06D
---
------
INDIACHINA
21/29RF
21/29RF
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
--- ---
--- ---
470N 470N 470N 470N 470N 470N 470N
0R33 0R33
47K
1M
2M2
--- ---
--- ---
GBU4JL GBU4JL
JMP JMP
29FSQ
2X15W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
47K
1M
2M2
JMP
21RF
130V 130V 130V 143V
2X5W
2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
400V 220U 400V 220U 400V 220U 400V 220U
--- ---
250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N 250V 1N
1MA/612V
3M3 3M3 3M3
--- --- --- ---
--- ---
47R 47R
0R33 0R33 0R33 0R33
47K
1M
2M2
276V 4R5 276V 4R5
15K 15K 15K 15K 15K 15K
150K 150K 150K 33K 33K 33K
20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5 20MH 1A5
--- ---
GBU4JL GBU4JL
STTH8L06D BYV29X-500STTH8L06D STTH8L06DSTTH8L06D
UDZS10B UDZS10B UDZS10B
FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80 FQPF7N80
---
---
JMP
29RF
2X5W 2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
250V 1N5250V 1N5
1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V 1MA/612V
--- ---
47K
1M
2M2
276V 4R5 276V 4R5
SS42315-01SS42315-01 SS42315-01 SS42316-01 SS42316-01 SS42316-01
---
---
JMP
EUROPE
HR
29RF
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
400V 33N
275V 100N275V 100N275V 100N
250V 1N5
250V 470P250V 470P250V 470P
470R
47R 47R 47R 47R
47K
1M
2M2
65MH
GBU4JL GBU4JL GBU4JL GBU4JL
STTH8L06D
---
---
---
24WR
25/28BLD28WSSF
2X5W
2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
---
275V 100N 275V 100N 275V 100N
250V 1N5
250V 470P 250V 470P 250V 470P
3M3 3M3 3M3
---
47K
1M
2M2
---
UDZS10B UDZS10B UDZS10B
--- --- ---
--- --- ---
JMP
28WSRF 32WSRF
143V 143V
2X5W
2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
400V 220U 400V 220U
400V 33N 400V 33N
250V 1N5 250V 1N5
470R 470R
0R33 0R33
47K
1M
2M2
276V 4R5 276V 4R5
65MH 38MH
FQPF7N80
--- ---
2X5W
2X10W
WIRE SIN
180 SIN
18ST BK
WIRE SIN
400 SIN
18ST BK
470N
47K
1M
2M2
FQPF7N80
BC857B--- BC857B BC857B BC857B BC857B BC857B BC857B BC857B
A
B
C
D
E
REGION NAFTA ROW
1506
9507
9508
3139 123 5676.1
---
Main Switch
JMP
JMP
---
---
1234567
E
E_14480_126.eps
100504
8910
Page 28

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
28L04E AA 7.
Mono Carrier: Deflection
12345678910
LINE & FRAME DEFLECTION
F402
VT_Supply
VideoSupply
Filament
A2
A4
Frame_FB
A2
A4
+9V
HDRIVE
A4
EW_DRIVE
A4
EW DRIVE
Vbatt
EHTb
EHTinfo
-12V
+6VA
HD
6486
BAV21
6403
RGP10D
Vbatt
F401
F412
I419
3499
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
3139 123 5676.1
3445
820K
BC847B
3489
47R
3414
*
2420
*
2414
1u0
7408
3418
100R
3495
3401
68K
1V
3402
1K0
3419
3K3
6V
2409
100n
2410
100n
6407
BAV21WS
3V6
1453
RES
F404
6490
BAS316
6443
BZX384-C12
-2V2
I413
2408
7410
BC857B
To 1351 of
CRT PANEL
1
2
3
4
5
I401
3441
680K
3415
1K0
7404
SI2306DS
1
0V7
1n
I427
+9V
3420
I425
0V2
I434
4K7
3498
+9V +9V
7401
BUH2M20AP
1401
7485
BC847B
I404
50V4u7
2493
100p2486
6441
68V
I418
10n
2489
I414
3
4V5
2
F407
6408
BAV21WS
10n
3446
2482
3440
470R
820K
3V3
I417
1V3
7484
BC847B
I403
3447
I406
6442
1
3
PSD10-204B
2488
100p
0V6
7406
KTC2800
470R
BC857B
I402
390R
7411
1402
I405
3407
5402
3497
I416
27V6
I431
2V8
From LOT 5450
(For A80ERF042X14
Tube Only)
3411
I433
680K
2405
7403
BC847B
I407
68R
3409
1K8
33n
2402
3430
7405
680K
BU4508DX
F418
3416
0V
33R
5
6
K
6404
A
*
2411
5403
5405
35m
1R0
3425
100K
I415
RES
2425
6401
BYD33V
2KV
1n
0V
AK
I421
2404
I409
33n
2403
126V
F419
6412
*
DMV1500M
6411
*
I423
1n0
2487
3431
100K
2428
47u
F414
*
2412
BYV29X-500
*
2413
BYV29X-500
3436
*
56n
*
2427
I432
15n
HORIZONTAL
DEFLECTION
COIL
OR
To 1404 of
I430
6491
BY228-1500
6410 RGP10D
I473
*
*
2492
2416
3427
1K5
5410
27u
9410
I410
3404
6406
I422
I426
3432
22R
I474
3412
4R7
3417
RGP10D
I412
9401
I428
*
2419
5406
*
3428 2R2
6488
BAS316
6489
BZX384-C33
F420
3433
220R
3434
F415
220R
2406
680p
1K0
*
1404
2415
100V2u2
15K
2417
*
5408
12
4
CI-15
3
SC21329
VDRA
A4
-12V
VDRB
A4
FRAME DEFLECTION
3488
10K
5401
3451
*
LOT
5450
*
L.LIN
F416
3
F417
1
4
1
F464
10
3452
*
EHT
TO PICTURE TUBE
FOCUS
VG2
6
F465
5
9417
2418
*
11
7
12
9402
8
9
9452
5452
2
9407
*
1
2461
1n
3462
2K2
I470
1V4
0V8
3460
F460
2K2
7455
BC857B
-12V4
3463
-12V4
I468
1K0
F461
F401 130V
/ div DC
F402 32V8
/ div DC
F452 -13V4
/ div DC
F453 190V8
/ div DC
I416 I417 I468I423 I433
/ div
500mV
20µs
20V
20µs
/ div DC
F412 F414 F460 F461
2V
20µs
/ div DC
/ div
10V
20µs
I443
I451
BC857B
/ div DC
/ div
/ div DC
/ div
I465
I455
I457
I458
I475
I459
2462
0V8
3469
1K0
+9V
7480
BC857B
0V
To
3456 1R0
7456
I444
1R03422
2459 470p
6456
RGP15G
I460
1n
6457
I463
-11V8
3461
2K2
200V
/ div DC
20µs
10V
/ div DC
20µs
3480
0V5
2K2
3487
33R
I445
3491
56K
3477
3454
2481
3473
680K
22K
3490
7483
50V10u
BC857B
6V2
I424
2491
RESRES
I469
8K2
*
3453
2451
I448
of CRT PANEL
3442
6K8
1454
1R
MRT
6453
RGP10D
3484
*
3485
*
I467
3464
330R
50V 100u2463
*
TO 1382 of
I453
I466
3459 4R7
1452
MRT
330R3465
6451
1470
3443
6K8
6452
RGP10D
3458
4R7
6481
1N4148
4R73423
RGP10D
1R
I461
2453
BZX384-C4V7
I452
3493
6459
2460
F457
16V1u0
2454
16V 470u
2457
16V470u
-0V6
RES
F454
7451
BD135
BAS316
7454
6458
BC847B
BAS316
I471
2464
470p
-1V9
7452
BF422
-12V4
F418 F455 F458 F459
5V
I462
10V
/ div DC
20µs
/ div DC
5ms
/ div
/ div
/ div
/ div
I464
0V5
2468
220p
3470
22R
2469
220n
5V
20µs
5V
5ms
/ div DC
/ div
/ div DC
/ div
-1V6
3476
2K2
6450
BAS316
3478
6K8
3486
6K8
4u7
2458
2490
-0V8
7453
BD136
2V6
*
24V
20 V
3n3
47n2456
3466
5ms
7482
PDTA114ET
0V
17V1
I449
16V 470u
2484
5404
6454
I462
2465
1R
-1V1
I472
-12V4
/ div DC
/ div
1V7
I429
F451
F462
1V7
6480
BZX79-B5V1
F463
2455
*
RES
2480
I456
220u
RGP10D
2470
22u 100V
3467
220R
3468
220R
3R3
3471
2483
4492
3492
7481
BC857B
18V1
100n
3481
9404
2467
1V
5ms
I446
7V9
47n
56K
3K3
3482
F466
F455
6455
RGP10D
1u0
F458
15n
3472
/ div DC
/ div
6482
BZX384-C6V8
RES
3494
F452
F453
6483
*
BAV21WS
BAV21WS
F456
3437
2K0
4437
1451
1
2
F459
3R3
500mV
3483
*
5ms
6484
5451
9451
3474
/ div DC
10K
/ div
3475
8K2
15K
VERTICAL
DEFLECTION COIL
500mV
/ div DC
5ms
POWER_DOWN
EHTinfo
BCL
EHTb
-12V
VideoSupply
Vbatt
Filament
+9V
-12V
Vguard
Frame_FB
/ div
E_14480_117.eps
200V
A1
A4
A4
A2
A4
A2
280504
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1401 A2
1402 A3
1404 B5
1451 F9
1452 D8
1453 G2
1454 C7
1470 B8
2402 C3
2403 C4
2404 A4
2405 A4
2406 A5
2408 D2
2409 C2
2410 D2
2411 D3
2412 D4
2413 D4
2414 D1
2415 C5
2416 D4
2417 C5
2418 C6
2419 D5
2420 D1
2425 G3
2427 A5
2428 G4
2451 B7
2453 B8
2454 C8
2455 C9
2456 D8
2457 C8
2458 C8
2459 D7
2460 D8
2461 E6
2462 E7
2463 E7
2464 F7
2465 E9
2467 F9
2468 E8
2469 F8
2470 E9
2480 C9
2481 A8
2482 F2
2483 A9
2484 C9
2486 C2
2487 E4
2488 E3
2489 C2
2490 D9
2491 A8
2492 D5
2493 B2
3401 A2
3402 B2
3404 C5
3407 B3
3409 B4
3411 A3
3412 B5
3414 C1
3415 C2
3416 C3
3417 C5
3418 F1
3419 B2
3420 G2
3422 D7
3423 D8
3425 E3
3427 G5
3428 F5
3430 C3
3431 F4
3432 A5
3433 A5
3434 A5
3436 E4
3437 E9
3440 G2
3441 C2
3442 B7
3443 B8
3445 C1
3446 F3
3447 B3
3451 A6
3452 A7
3453 B7
3454 A8
3456 D7
3458 C8
3459 D8
3460 F6
3461 F7
3462 E6
3463 F6
3464 E7
3465 E7
3466 E9
3467 E9
3468 F9
3469 F7
3470 F8
3471 F9
3472 F9
3473 A8
3474 E10
3475 D10
3476 A8
3477 A8
3478 B8
3480 A7
3481 C9
3482 B9
3483 B9
3484 C7
3485 C7
3486 B8
3487 A8
3488 A6
3489 C1
3490 A8
3491 A8
3492 A9
3493 B8
3494 B9
3495 G1
3497 E3
3498 G2
3499 E1
4437 E9
4492 A9
5401 B5
5402 C3
5403 E4
5404 D9
5405 E4
5406 E5
5408 D5
5410 A5
5450 B6
5451 D10
5452 D7
6401 A4
6403 C1
6404 D4
6406 C5
6407 E2
6408 E3
6410 D4
6411 D4
6412 D4
6441 C3
6442 C3
6443 C2
6450 B8
6451 B8
6452 C8
6453 C7
6454 D9
6455 D9
6456 D7
6457 E7
6458 E7
6459 D8
6480 B9
6481 C8
6482 A9
6483 C9
6484 C10
6486 C1
6488 G5
6489 G5
6490 B2
6491 D4
7401 A3
7403 B3
7404 D2
7405 C4
7406 F3
7408 C1
7410 G2
7411 G3
7451 E8
7452 F8
7453 F8
7454 E8
7455 E6
7456 E7
7480 A7
7481 B9
7482 A9
7483 A8
7484 G2
7485 B3
9401 D5
9402 D5
9404 D9
9407 E6
9410 A5
9417 C5
9451 D10
9452 D7
F401 A1
F402 A1
F404 B2
F407 D2
F412 C1
F414 A4
F415 A5
F416 B6
F417 B6
F418 C3
F419 C4
F420 A5
F451 A9
F452 C9
F453 C9
F454 C8
F455 D9
F456 D9
F457 E8
F458 F9
F459 F9
F460 E6
F461 F6
F462 A9
F463 C9
F464 C6
F465 C6
F466 C9
I401 B2
I402 A3
I403 B3
I404 B3
I405 B3
I406 C3
I407 B4
I409 B4
I410 C5
I412 D5
I413 D2
I414 C3
I415 F3
I416 E3
I417 G2
I418 C3
I419 C1
I421 G4
I422 F5
I423 E4
I424 A8
I425 G2
I426 G5
I427 E2
I428 D5
I429 A9
I430 C5
I431 G3
I432 A5
I433 A4
I434 G2
I443 A7
I444 A7
I445 A8
I446 A9
I448 B7
I449 B9
I451 A7
I452 B8
I453 C8
I455 C7
I456 D9
I457 C7
I458 C7
I459 D7
I460 E7
I461 E8
I462 E9
I463 E7
I464 F8
I465 B7
I466 C8
I467 D7
I468 F7
I469 A8
I470 E6
I471 E7
I472 F9
I473 D4
I474 A5
I475 D7
12345678910
Page 29

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Mono Carrier: Diversity Table for A2 (Deflection)
12345678910
DIVERSITY TABLE FOR DEFLECTION
29L04E AA 7.
Region NAFTA
A
B
C
Tube
Size
2411
2412
2413
2416
2418
2419
2425
2451
2457 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7
2487
2490 47n - - - - - 47n - - - - 3224
3295
3414
3431
3451
3452
3453
3467
3468
3471
3472
3473
3474
3481
3482
3483
3491
3494
3499
5401
5408
5450
5451
6404
6411
6412
7405
9407
9417
LPD
27 V
470pF
12nF
120nF
-
390nF
-
-
150nF
-
680K 5%
8K2 5%
1R 1W 5%
82K 1%
68K 1%
18K 5%
33K 5%
120R 5%
220R 5%
-
3R3 1%
390K 5%
15K 5%
5R6 5%
22K 1%
56K 1%
100K 5%
180K 5%
-680K 5%
50uH
-
JF0501-21835B
27uH 10%
DVM1500M
-
-
BU4508DX
-
-
LPD LPD LPD LPD LPD SMGK LPD
28 WR 29 RF 32 V 32 V RF 32 WR 25 RF
1.2nF
13nF
15nF
3n3
-
390nF
33nF
150nF
1n5
680K 5%
10K 5%
2R2 1W 5%
82K 1%
82K 1%
15K 5%
22K 5%
120R 5%
150R 5%
2R7 1%
2R4 1%
680K 5%
12K 5%
5R6 5%
22K 1%
56K 1%
100K 5%
-
-680K 5%
42uH
SC2132 9-00B
JF0501-85021B
JMP
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
JMP
1.5nF
15nF
39nF
330nF
2u2
33nF
180nF
1n5
680K 5%
8K2 5%
1R 1W 5%
82K 1%
68K 1%
15K 5%
33K 5%
120R 5%
150R 5%
2R4 1%
2R4 1%
820K 5%
15K 5%
10R 5%
2K4 1%
5K6 1%
100K 5%
100K 5%
33uH
CU15
JF0501-21836B
33uH 10%
DVM1500M
BU4508DX
JMP
D
Region EUROPE
Tube
Size
2411
2412
2413
2416
2418
2419
E
F
G
2425
2451
2457 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7
2487
2490 47n - - - - - - 3224
3295
3414
3431
3451
3452
3453
3467
3468
3471
3472
3473
3474
3481
3482
3483
3491
3494
3499
5401
5408
5450
5451
6404
6411
6412
7405
9407
9417
3139 123 5676.1
LPD
21RF
470pF
8n2
33nF
-
470nF
2u2
33nF
220nF
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
4R7 1W
82K 1%
68K 1%
18K 5%
22K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
3R3 1%
3R3 1%
470K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-680K 5%
82uH
CU15
1342.0033CY
22uH 10%
DVM1500M
-
-
BU4508DX
JMP
-
LPD LPD LPD LPD
24 WR 25 I 28 I 29 RF 28 WR 28 WS
1n2
13nF
15nF
2n2
-
470nF
33nF
220nF
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
4R7 1W
82K 1%
56K 1%
18K 5%
22K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
3R3 5%
3R3 1%
470K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-680K 5%
37uH
SC21329-00B
1342.0048B
22uH 10%
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
JMP
470pF
9n1
18nF
390nF
470nF
33nF
220nF
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
10R 1W 5%
82K 1%
120K 5%
18K 5%
33K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
1R5 1%
2R2 1%
680K 5%
15K 5%
56K 5%
56K 5%
50uH
SC21329-00B
1342.0048B
27uH 10%
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
-680K 5%
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-680K 5%
-
-
-
2.2nF
15nF
33nF
-
470nF
2u2
33nF
180nF
1n5
680K 5%
8K2 5%
0R33 1W 5%
82K 1%
75K 1%
15K 5%
22K 5%
220R 5%
150R 5%
2R4 1%
2R7 1%
820K 5%
15K 5%
2R7 5%
22K 1%
56K 1%
82K 5%
150K 5%
-330K 5%
33uH
CU15
JF0501-21140B
27uH 10%
DVM1500M
-
-
BU2725DX
JMP
-
470pF
9n1
18nF
-
390nF
470nF
33nF
220nF
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
10R 1W 5%
82K 1%
120K 5%
18K 5%
33K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
1R5 1%
2R2 1%
680K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-680K 5%
50uH
SC21329-00B
1342.0048B
27uH 10%
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
-
680pF
12nF
33nF
4n7
270nF
2u2
10nF
150nF
2n2
560K 5%
8K2 5%
1R 1W 5%
10K 1%
68K 1%
6K8 5%
33K 5%
150R 5%
150R 5%
2R2 1%
2R2 1%
820K 5%
15K 5%
5R6 5%
22K 1%
56K 1%
68K 5%
680K 5%
-680K 5%
25uH
CU15
JF0101-85020B
JMP
DVM1500M
-
-
BU4508DX
JMP
-
1nF
13nF
33nF
-
360nF
2u2
33nF
220nF
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
2R2 1W
82K 1%
68K 1%
18K 5%
33K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
2R2 1%
2R2 1%
680K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-680K 5%
25uH
CU15
1362.0016AB
39uH 10%
DVM1500M
-
-
BU4508DX
JMP
-
330pF
13nF
18nF
-
-
430nF
33nF
180nF
1n5
680K 5%
8K2 5%
6R8 1W 5%
82K 1%
82K 1%
6K8 5%
22K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
1R8 1%
3R3 1%
820K 5%
15K 5%
4R7 5%
22K 1%
56K 1%
82K 5%
680K 5%
-680K 5%
42uH
SC2132 9-00B
JF0101-85021B
JMP
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
JMP
LPD LPD
680pF
11nF
15nF
4n7
-
430nF
33nF
220nF
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
3R3 1W
82K 1%
68K 1%
18K 5%
22K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
1R5 1%
6R8 1%
470K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-680K 5%
50uH
SC21329-00B
1362-0015AB
0.588 COL
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
JMP
LATAM AP
LPD
25 RF
1.2nF
15nF
33nF
-
390nF
2u2
33nF
100nF
1n5
680K 5%
8K2 5%
3R3 1W 5%
82K 1%
68K 1%
18K 5%
33K 5%
120R 5%
150R 5%
2R2 1%
2R 1%
680K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
-
100K 5%
-
-680K 5%
33uH
CU15
JF0501-21835B
33uH 10%
DVM1500M
-
-
BU4508DX
JMP
- - - JMP JMP JMP -
680nF 470pF 1.2nF 1.2nF 330pF 1.5nF
15nF 12nF 15nF 13nF 13nF 15nF
33nF 120nF 18nF 15nF 18nF 39nF
-- --
360nF 390nF 330nF
2u2 470nF 390nF 430nF 2u2
33nF 33nF 33nF 33nF 33nF
100nF 150nF 120nF 150nF 180nF 100nF
1n5 1n5 1n5 1n5 3n3
680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 560K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5%
8K2 5% 8K2 5% 8K2 5% 10K 5% 8K2 5% 8K2 5%
1R 1W 5% 1R 1W 5% 4R7 1W 5% 2R2 1W 5%
82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1%
68K 1% 68K 1% 120K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 68K 1%
18K 5% 18K 5% 27K 5% 15K 5% 6K8 5% 15K 5%
33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5% 22K 5% 22K 5% 33K 5%
120R 5% 120R 5% 220R 5% 120R 5% 220R 5% 120R 5%
150R 5% 220R 5% 220R 5% 150R 5% 220R 5% 150R 5%
2R4 1% 2R2 1% 2R7 1% 1R8 1% 1R8 1%
2R4 1% 3R3 1% 3R3 1% 2R4 1% 3R3 1% 2R2 1%
820K 5% 390K 5% 1M 5% 680K 5% 820K 5% 1M 5%
15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 12K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5%
-
-
-
100K 5% 100K 5% 82K 5% 100K 5% 82K 5% 82K 5%
--
-680K 5% -680K 5% -680K 5% -680K 5% -680K 5%-680K 5%
37uH 50uH 16uH 42uH 42uH 25uH
CU15 SC2132 9-00B SC2132 9-00B SC2132 9-00B CU15
JF0501-2153B JF0501-21835B JF0501-21133B JF0501-85021B JF0101-85021B JF0501-2136B
27uH 10% 27uH 10% 39uH 10% JMP JMP 27uH 10%
DVM1500M - - - DMV1500M
- - BY229X-80 BY229X-80 BY229X-800 -
- - BY359X-1500
BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU2725DX BU2725DX BU4508DX
JMP - - - - JMP - JMPJMP JMP - JMP
27V
-
-
4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7
-
47n
-
180K 5% 680K 5%
-
DVM1500M
LPD
28WS
2n2 3n3
-
-
-
LPD
28WR
---
5R6 5% 4R7 5%5R6 5%
22K 1% 22K 1%22K 1%
56K 1% 56K 1%56K 1%
-
BY359X-1500 BY359X-1500 -
LPD
32WR
6R8 1W 5% 0R33 1W 5%
LPD
32 WR
680pF
11nF
15nF
2n2
-
470nF
33nF
220nF
4u7
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
4R7 1W
82K 1%
68K 1%
18K 5%
22K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
3R3 1%
3R3 1%
470K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-680K 5%
25uH
SC21329-00B
1342.0042CY
22uH 10%
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU4508DX
-
JMP JMP
680pF
11nF
15nF
4n7
-
430nF
33nF
220nF
4u7
1nF
1M 5%
8K2 5%
3R3 1W
68K 1%
18K 5%
220R 5%
220R 5%
1R5 1%
6R8 1%
470K 5%
15K 5%
-
-
56K 5%
56K 5%
-
680K 5%
680K 5%
25uH
SC21329-00B
1362-0015AB
33uH 10%
-
BY229X-800
BY359X-1500
BU2725DX
-
SMGK
29RF
-
--
-
--
CHINA INDIA
CPT LPD LPD LPD LPD LPD
21RF
220pF 680nF 1.2nF 330pF
8n2 15nF 15nF 13nF 12nF 15nF 8n2 15nF 12nF 8n2 15nF 13nF
68nF 33nF 33nF 18nF 33nF 33nF 68nF 33nF 33nF 68nF 33nF 39nF
220nF 360nF 330nF - 300nF 360nF 270nF 330nF 300nF 220nF 330nF 390nF
120nF 120nF 220nF 180nF 270nF 120nF 220nF 220nF 270nF 120nF 220nF 220nF
4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7
1nF 1n5 1nF 1n5 3n3 1n5 1nF 1nF 3n3 1nF 1nF 1nF
1M 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 1M 5% 680K 5% 1M 5% 680K 5% 1M 5% 1M 5% 680K 5% 1M 5%
2K7 5% 8K2 5% 10K 5% 8K2 5% 7K5 1% 8K2 5% 8K2 5% 10K 5% 7K5 1% 2K7 5% 10K 5% 8K2 5%
10R 1W 5%
82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 10K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1% 10K 1%
82K 1% 68K 1% 68K 1% 82K 1% 68K 1% 68K 1% 68K 1% 68K 1% 68K 1% 82K 1% 68K 1% 56K 1%
18K 5% 18K 5% 15K 5% 6K8 5% 18K 5% 18K 5% 18K 5% 15K 5% 18K 5% 18K 5% 15K 5% 18K 5%
33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5% 22K 5% 33K 5%
220R 5% 120R 5% 120R 5% 220R 5% 150R 5% 120R 5% 220R 5% 120R 5% 150R 5% 220R 5% 120R 5% 220R 5%
220R 5% 150R 5% 150R 5% 220R 5% 150R 5% 150R 5% 220R 5% 150R 5% 150R 5% 220R 5% 150R 5% 220R 5%
2R2 1%
3R9 1% 2R4 1% 2R4 1% 3R3 1% 2R2 1% 2R4 1% 4R7 1% 2R4 1% 2R2 1% 3R9 1% 2R4 1% 2R2 1%
390K 5% 820K 5% 680K 5% 820K 5% 430K 5% 820K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 430K 5%
15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5% 15K 5%
82K 5% 100K 5% 82K 5% 82K 5% 82K 5% 100K 5% 56K 5% 82K 5% 82K 5% 82K 5% 82K 5%
680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5% 56K 5% 56K 5% 56K 5%
82uH 37uH 33uH 42uH 42uH
JF0501-2135B
68uH 5% 27uH 10% 27uH 10% 0.58mm COL
DVM1500M DVM1500M DVM1500M - DVM1500M DVM1500M
BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU2725DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX BU4508DX
25RF 29RF 32WR 34RF 25RF 21RF 29RF 34RF 21RF 29RF 29FSQ
1nF 680nF 220pF 1.2nF 1nF 220pF 1.2nF 680pF
-
- 2u2 2u2 430nF 2u2 2u2 - 2u2
- 33nF 33nF 33nF 33nF10nF - 33nF 10nF - 33nF 33nF
--- - - ---- - --
---
---
---
- CU15 CU15 SC2132 9-00B CU15 CU15
- -
- - - BY359X-1500 - -
- - - JMP - -
- 3n3 - - - - 3n3 3n3-- -
4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7 4u7
1R 1W 5% 1R 1W 5% 6R8 1W 5% 6R8 1W 5% 1R 1W 5% 4R7 1W 5% 1R 1W 5% 6R8 1W 5% 10R 1W 5% 1R 1W 5% 4R7 1W 5%
33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5% 33K 5%
2R4 1% 2R4 1% 1R8 1% 2R2 1% 2R4 1% 3R9 1% 2R4 1% 2R2 1%
4R7 5%
22K 1%
56K 1%
--
JF0501-2135B JF0501-2136B JF0101-85021B JF0501-2601B JF0501-2135B JF0501-2135B JF0501-2136B JF0501-2601B JF0501-2135B JF0501-2136B JF0501-2133B
- - BY229X-800 - -
680K 1%
-
-
-
-
22uH 27uH 10% 68uH 5% 27uH 10% 22uH 68uH 5% 27uH 10% 22uH 10%
37uH
-
-
-
-
LPD LPD LPD CPD LPD SMGK
2u2 - 2u2 2u2
82K 1% 82K 1% 82K 1%
-
-
-
--
-
2R4 1% 2R2 1%
56K 5%
56K 5% 56K 5%
DVM1500M
JMP
DVM1500M
-
-
-
-
E_14480_127.eps
JMP
2R2 1%
390K 5% 680K 5% 680K 5%
-- --- -
-- --- -
-- --- -
-- --- --
82uH
-
DVM1500M
-
-
-
--
-
33uH 42uH 82uH 33uH 33uH
CU15 CU15 - CU15 CU15
DVM1500M
JMP
DVM1500M
-
-
-
-
JMP
DVM1500M
-
-
-
-
A
B
C
-
-
-
-
D
E
F
G
100504
12345678910
Page 30

Mono Carrier: Tuner IF
12345678910
A
B
C
D
E
ITEM EU Normal
1000
UV1316E/A I-4
2002
2008
2009
2013
2014
2016
3010
3014
3016
3018
5002
7003
50V 22P
68u
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
EU FM Radio
UR1316/A I-3
16V 100N
F
ITEM NA/LA/AP INT
EU-QSS
1001
K9656M
1002
1003
2003
3002
3006
3007
3008
3009
G
4002
4003
4004
4006
4011
4012
6002
6004
7001
3139 123 5676.1
K3953M
---
50V 10N
10K
10K
2K2 2K2
6K8
2K2
JMP
---
---
---
JMP
--BAS316
1SS356 1SS356
PDTC124ET PDTC124ET
M1971M
TUNER IF
EU Splitter
TEDE9-703A
50V 22P 50V 22P
68u
25V 1N
25V 1N
25V 1N
330R
820R
100K
560R
150K
0U470U47
BFS20
---
---
---
---
---
---
--JMP
JMP
--JMP
---
---
---
---
---
68u
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
0U47
AP QSS CH QSS
K9362M
K7257M
50V 10N
K9352M
---
K6274M
50V 10N
---
10K
6K8 6K8
2K2
---
--JMP
JMP
--JMP
---
PDTC124ET
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
FOR ITV ONLY
1010
TEDH9-305A
---
100u
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---3019
0U39
---------
---
---
10K---
2K2
2K2
JMP
---
---
JMP
---
JMP
---
1SS356
TO 0282
POWER SUPPLY
UV1356A/A I G-3
FOR EMC ONLY
OF
A4
A4
SEL_LLP|M
A4
AP LNANA/LA/AP NTSC
100u
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
0U39 0U47
1011
SCL
SDA
1005
1
2
3
For Compair only
AP Splitter
50V 22P50V 22P
68u
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
------
F011
I014
I015
I017
UV1356A/A I G-3TEDE9-703A
F007
F008
F009
CH LNA
50V 22P
100u
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
0U39
---
4000
3000
RES
4001
3001
RES
F005
3006
30L04E AA 7.
1000 A4
1001 E8
1002 D8
1003 D8
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1004 A10
1005 C3
1010 A3
1011 B3
1012 C10
1013 D10
2001 C4
2002 C4
2003 B5
2004 B6
2005 A6
2006 A6
2007 A7
2008 B6
2009 C9
2013 C9
2014 C8
2016 C9
3000 B4
3001 B4
3002 B7
3003 A7
3004 B7
3005 B8
3006 D4
3007 D7
3008 C7
3009 C5
3010 C8
3014 C9
3016 C9
3018 C9
3019 C9
3020 A9
4000 B4
4001 B4
4002 E8
4003 B6
4004 E8
4005 A8
4006 B7
4010 C8
4011 E8
4012 F8
4013 E9
5001 A8
5002 B6
5003 E9
6001 B6
6002 B7
6003 B7
6004 C5
6006 A9
7001 D4
7003 C9
9002 A9
F001 A5
F002 A5
F003 A5
F004 B5
F005 A4
F006 B9
F007 B3
F008 B3
F009 D3
F010 C10
F011 C3
I001 B4
I002 B4
I003 C8
I004 C9
I005 D4
I006 D6
I007 C9
I008 D7
I009 D8
I010 E8
I011 B7
I012 C9
I013 A9
I014 B3
I015 B3
I016 A6
I017 D3
+5VS+5V
Vbuffer
1000
*
12
13
14
15
*
TV TUNER
MT
SCL5SDA7+5 ADC
AS
4
4.3V
4.3V
I001
I002
RES
2002
2001
7001
PDTC124ET
I005
0V
F003 0V (N.A.)
4.9V
*
5V
0V
IFGND
1
2
6
NC
9
10
11
83
+5V
3009
F004 I001 I002
200mV
10ms / div
34V5
F003
*
/ div AC
2003
F001
F002
F004
*
6004
I016
4003
*
*
I006
1V / div DC
20µs / div
5002
2004
VT_Supply
2005
47n
6001
1V / div DC
20µs / div
10u 50V
2006
BZX79-C33
2008
*
470u
6002
BAS316
6003
3002
4006
*
2007
*
*
100n
3003
3004
I011
1K5
RES
3008
3007
*
*
IFGND
I008
3005
100R
9002
5001
4005
RES
2009
** *
4010
RES
3010
4004
*
4011
*
*
IFGND
I009
4002
*
I010
4012
*
IFGND
I003
1002
*
1
2
GND_28
1003
*
10
SWI
1
IN
2
ING
GND_28
1001
*
1
2
2014
I007
*
3
O1
O2
GND
38
GND_28
3
GND_28
4
5
4
5
4
5
6006
3016
1V1
3019
3020
220R
BZX79-B8V2
*
1u8
5003
5V
F006
3014
3018
I004
7003
*
0V3
*
for EMC
4013
1
I013
2
3
for ATSC
2016
*
I012
2013
*
1013
(For Lightning Protection)
GND_28
1004
1012
F010
TO 1510 OF
FOR DVD
ONLY
SIF2
SIF1
RF_AGC
SSIF
VIF1
VIF2
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
E_14480_118.eps
280504
12*345678910
Page 31

Mono Carrier: Hercules
1234567891011
HERCULES
A
B
3273
GND68
C
(+8V)
6204
5211
2273
GND2
To 1729 Of
Rear I/O Scart
1684
Vbuffer
SS14
D
E
F
Vguard
A2
Vguard
A4
POWER_DOWN
A1
G
requested by Leong
4209
IFGND
requested by Gozali
4212
H
3139 123 5676.1
A5
SANDCASTLE
7207
0v6
BC847B
0v7
1K0
3254
10V100u
2272
GND3
123
+5V
3272
820R
I218
GND2
GND68
GND68
+1.8V_B
GND125
+3.3V
120R
+3.3V
100n
GND89
3220
180R
I226
3221
390R
5295
TO 1282 OF
1683
2207
Vaux_GND
I219
+5V
BAS316
+1.8V_B
5201
2206
+6V+3V
220n
2208
A5
HD_PIP
GND1
6203
220n
GND121
220n
1K0
3291
1K0
3250
5212
2276
100n
2265
10V100u
+5V
5210
2250
100u 25V
2249
100n
5203
2210
220n
5215
2212
220n
5216
2211
220n
F203
2203
HD
3240
16V
100u
3288
A2
A2
HDRIVE
F208
+5V
F206
3238
22K
3239
100R
+5V
GND3
5209
2224
10V100u
+1.8V_A
F207
GND92
+1.8V_A
3229
1K0
2264
GND3
3276
100R
Iblack
BCL
C
A5
A5
A2
requested by Rama Rao
9205
Vaux_GND
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
A3
A8A8A8
A8
A8
1208
2K2
for ITV only
5208
2234
100u
25V
2233
100n
GND1
F201
220n
+3.3V
GND95
GND92
560p
100n
2231
9266
100R
*
3277
SC1_BLUE_IN
SC1_GREEN_IN
A8
9202
2288
1n0
5207
2205
5205
220n
2232
A8
2238
220n
5206
2216
220n
2225
220n
100R
1
2
3
I210
3V3
2215
2213
220n
100n
9265
GND_1
A8
SC2_L_OUT
100R
3258
5202
2209
220n
3V3
5V1
5V1
5V1
5V0
2V0
2V0
2V0
2V0
3V3
3V3
2V0
7V0
100n
2237
2286
GND2
3278
9261
100R
*
*
SC1_RED_IN
A8
requested by Hock Aun
A8
SC2_R_OUT
MAIN_OUTL
3257
3249
100R
2253
10n
+3.3V+5V
GND121
47
VP3
82
VP2
114
VP1
19
VDDP_3.3
60
VDDCOMB
126
VDDC4
5
VDDC3
29
VDDC2
12
VDDC1
2V0
33
VDDADC_1.8
125
VDDA3_3.3
35
VDDA2_3.3
41
VDDA1
36
VDDA_1.8
84
VCC8V
2267
GND2
2284
100p
10n
2262
3270
9257
100R
SC2_CHROMA_IN
A8
4210
MAIN_OUTR
100R
3248
2u2
100p
GND2
2255
*
SIDE_CHROMA_IN
GND95
RF_AGC
2289
100R
4V5
3V8
98
67
AGCOUT
AUDOUTHPL
AGC2SIF
AUDIOIN2L
76757372807995
83
1V9
2V2
10n
INTF_L_IN
A5
A5
SC1_R_OUT
SC1_L_OUT
3255
100R
3256
1n0
3V3
3V3
3V6
6669689392
AUDOUTLSL
AUDOUTLSR
AUDOUTHPR
Φ
VIDEO
SIGNAL
AUDIOIN2R
AUDIOIN3L
AUDIOIN3R
2V2
2V2
2V2
2V2
INTF_R_IN
SC2_L_IN
SC2_R_IN
SIDE_L_IN
A5
A8A8A5
9203
for EMC
A3
SSIF
100R
3V6A53V6
0V0
96
AVL
AUDOUTSL
AUDOUTSR
PROCESSOR
AUDIOIN4L
AUDIOIN4R
AUDIOIN5L
2V2
2V2
SC1_L_IN
SIDE_R_IN
A5
GND2
31L04E AA 7.
A5
A5
A5
A5
Rout
Gout
Bout
3222
680R
INTF_CVBS_OUT
100R
100R
3226
3228
100n
2271
100R
100n
2270
3227
GND2
GND2
3289
2V4
0V0
2V3
2V4
43
65
42
44
BO
RO
GO
SSIF
SWO
REFO
REFIN
G
AUDIOIN5RBBCLIN
PBIN3
YIN3
PRIN3
50
46
51
49
94
1V3
2V2
1V3
1V3
3V4
I211
2230
GND3
100n
2261
2283
100p
2287
GND2
GND2
3274
9215
3275
100R
*
SC1_R_IN
SC1_CVBS_IN
SC2_Y|CVBS_IN
A8
A8
c201
GND2
GND1
A5
A5
INTCO
ITV_V1OUT
9260
3268
for ITV only
100R
9201
3267
4V4
85
86
PIP
DVBO
FMRO
CVBSO
C2C4CVBS2
BLKIN
C3
45
70
3V2A81V4
1V6
1V6
50V
4u7
2256
100n
2260
100p
9262
100R
*
SIDE_Y|CVBS_IN
A8
A5
c205
c202
GND3
A2
SC1_CVBS_OUT
4u7
5217
*
100R
3236
100R
3V5
3V8
108
EWD
IFVO
DVBO
FMRO
CVBS3
Y2Y3Y4
777471
1V5
2244
+5V
100n
2285
100p
GND2
+8V
c210
GND12
EW_DRIVE
33n
2221
GND1
F205
3223
GND_1
100R
0V8
63
AVL
FBISO
CVBS4
78
2V3
1V4
2u2
2241
GND1
2254
1n0
3243 33K
3251
c203
GND_28
A5
A5
A5
A5
I2SD|1
Reset_+5V
SEL_SC2_INTF
SW_SC2_CVBS
100R
5K6
3260
9204
3253
100R
1V4
1V3
62
81
CSY
SVO
IFVO
HOUT
*
DECBG
DECDIG
DECSDEM
11
91
115
109
2V0
2V3
2V8
I215
50V
2275
10u
22n
2274
GND2
3244
33K3297
I205
10K
3295
EHTinfo
A2
c204
+5V
3261
3269
0V0
0V0
2425262732
23
O
CVBSI
I2SDI1
7200
TDA12001H1
DECV1V8
EHTO
INSSW3
52
102
97
2V0
1V7
0V0
3231
100n
2235
3232
100R
I206
2240
15K
SC1_FBL
A8
c206
GND89
A5
I2SCLK
4K7
100R
0V0
I2SDO2
I2SDO1
IREF
PH1LF
112
2V3
100R
I213
6n8
GND1
12K
3224
1u5
GND1
GND92
A9
A9
A5
+3.3V
IR
4K7
I2SWS
POWER_DOWN
3215
1u0
100p
2280
2279
10R
3216
100R
3218
0V0
5V5
3V3
0V0
3V9
3032221212018171615
31
T0
INT1
INT0
I2SWS
I2SCLK
P0<0:5>
DVBAGC
SIFAGC
PH2LF
PLLIFRSECPLL
SIFIN1
11087100
113
88
0V3
1V5
2V3
4V0
2V0
2u2
2266
390R
3247
GND2
100n
2239 220n
2263
GND1
GND2
I214
SIF1
1M0
10n
2236
A3
GND1
c211
c207
GND95
GND121GND68
LED
A5
0V0
INT2
DVBIN1
0V3
SIF2
A3
c208
A3,A5
SCL
WRITE_PROTECT
3204
3214
3V3
T1
SIFIN2
99
3241
GND1
3230
F204
c200
VD
A5
GND125
3K3
3202 3K3
10R
6211
3V3
3V3
RX
DVBIN2
116
0V5
39K
Vguard
A2
c209
+3.3V
7208
A2
A2
*
1V4
3271220R
I207
+5V
3292
56K
3293
*
GND2
SC2_STATUS|ITV_MSG
2252
3n3
1230
for ITV only
2257
3V3
2V5
2V0
9
90
ADC3
QSSO
AMOUT
P3<0:3>
AUDEEM
UIN
VIN
XTALOUT
YIN
YSYNC
59
575556
118
1V5
2V0
1V6
1V5
1V5
1u0
2246
100n
2247
100n
INTF_Pr|RED_IN
INTF_Pb|BLUE_IN
A5
TDA12001H1/N1B50
TDA12021H1/N1B10
13V
+3.3V
4213
*
VDRB
VDRA
3246
100R
I208
3235
3237
100R
3259
1n0
5n6
10n
2245 1n0
2248
2222
GND1
3242
I216
645854
2243
INTF_Y|GREEN_IN
A5
1K0
0V3
1V2
1V2
5V0
1V7
53
107
106
SVM
YOUT
VOUT
VDRB
VDRA
UOUT
VSSP2
VSSCOMB
VSSC4
VSSC3
VSSC2
VSSC1|P
VSSADC
VSSA1
GNDA
GND3
GND2
GND1
GNDIF
2242
100n
100n
2258
2268
100n
3225
100R
INTF_Y_OUT
A5
LATA M EU
39K 22K
---
22K
22K
2259
128
0V0
61
0V0
127
4
28
8
34
117
37
48
89
111
101
1205
HC49U
24MHZ576
39p
GND12
TDA12020H1/N1B11
TDA12021H1/N1B11
A8
A3
A6
A3,A5
6209
SDA
POWER_DOWN
VOL_MUTE
SEL_LLP|M
BAS316
100R3219
4219
*
BZX384-C5V6
10R
6210
GND121
BZX384-C5V6
GND121
3207
2V1
3V4
2V2
3V2
0V0
TX
SCL
SDA
PWM1
PWM0
TPWM
P1<0:7>
VGUARD
VIFIN1
VIFIN2
VREF_NEG_HPL+HPR
VREF_NEG_LSL+HPL
VREF_POS_HPR
SWIO
120
121
123
105
104
3V3
0V0
0V0
0V0
2V0
I212
2223
2218
47u 25V
GND92
100R
BAS3166208
VIF2
VIF1
GND89
A3
A3
3217 10K 10K
3293 39K
4213
7200 TDA12001H1/N1B50
7202
7208
A8
A5
A1,A3
+3.3V
Stdby_Con
3252 10K
SC1_STATUS
LIGHT_SENSOR
4K7
3284
3212
100R
for ITV only
1234
3298 100R
0V0
0V0
0V5
0V0
0V0
0V0
13
7
6
10
14
ADC2
ADC1
ADC0
PWM4
PWM3
PWM2
P2<0:5>
VREF_POS_LSL
VREF_POS_LSR+HPR
VREFAD
VREFAD_NEG
VREFAD_POS
VSC
XTALIN
38
40
39
124
3V3
2229
119
122
103
3V3
1V6
4V0
3V3
0V0
1V6
I203
GND89
100n
2278
150n
2251
GND1
220n
5213
+3.3V
NAFTAITEM NO
--- ---
---
TDA12001H1/N1B51
--- ---
BC847B BC847B BC847B
ROT
1V7
GND1
JUMP
---
A5
BC847B
220n
3287
F202
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
0V0
39p2269
GND12
3294
100R
13V
1V
7205
3245
100R
2282
GND68
GND125
GND121
GND95
GND12
GND92
GND3
GND2
GND1
GND_28
2214
220n
2226
TDA12060H1/N1B11
TDA12020H1/N1B11
TDA12021H1/N1B11
TDA12020H1/N1B10
TDA12021H1/N1B10
I217
62051n0
220R
1K0
GND121
3285
100n
3206
5K6
3296
5K6
2290
GND12
PDTC114ETPDTC114ET
4214
*
BZX384-C27
3201
+5V
1K0
GND_1
+3.3V
5214
2217
4u7
AP
39K
---
A5
INTF_FBL
SVM
3290
100R
4211
*
KEY_protn
+3.3V
3205
15K
6207
100u 10V
GND_1
I204
2227
GND_1
A5
6202
I209
I228
I236
I222
F270
I235
3263
100R
3265
100R
3217
*
BAS316
3203 150K
7209
BSH103
10V4u7
A5
A5
INTF_V_OUT
INTF_U_OUT
3234
100R
BAS316
3233
3280
4K7
3283
4K7
3262
100R
3264
100R
3266
100R
5V
-1V
2204
GND_1
22n
GND_1
7201-1
2V
IMX1
5
2V6
F201 2V / div DC
F203 2V / div DC
100R
3281
4K7
3282
4K7
3279
4K7
A9
KEY_protn
2277
7202
*
3208
I201
3
2V
2V
4
2V6
7210
BSH103
GND_1
1682
1
2
3
1u0
27K
7203
BC327-25
To 1010 or 1682 of
TOP CONTROL PANEL
OR
To 1280 of
SIDE AV PANEL+HP PANEL(FL13)
+3.3V
A5
A
A1,A5
B
A5
C
D
A5
A5
E
+3V
+3.3V
for ITV only
6201
BAS316
F200
1R0
3211
3209
2V9
7201-2
IMX1
6
2V
2
2V
2V6
F205
500mV
1
/ div DC
10ms / div
2V
for
ITV
only
LTI
PIP
27K
1R0
3210
7204
2V8
BC327-25
2V
I224
I225
F209
SERVICE JUMPER
SDM
9252
F206
1V / div DC
20µs / div
E_14480_119.eps
+1.8V_A
+1.8V_B
260504
4567891011
G
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
1205 E8
1208 B2
1230 B7
1234 B7
1682 B10
1683 G1
1684 F1
2203 F2
2204 E9
2205 D2
2206 F1
2207 H1
2208 H1
2209 C3
2210 D2
2211 E2
2212 E2
2213 E2
2214 E9
2215 D2
2216 E2
2217 E9
2218 F7
2221 A5
2222 B8
2223 F7
2224 C2
2225 E2
2226 F9
2227 F9
2229 F7
2230 F4
2231 F2
2232 F2
2233 C2
2234 C2
2235 F5
2236 G6
2237 F3
2238 C2
2239 F6
2240 G5
2241 F5
2242 E8
2243 F8
2244 F5
2245 B8
2246 F7
2247 F7
2248 B8
2249 D2
2250 D2
2251 F7
2252 B8
2253 B3
2254 F5
2255 G3
2256 F4
2257 B7
2258 F8
2259 B8
2260 F4
2261 F4
2262 F3
2263 F6
2264 F2
2265 C2
2266 F6
2267 E3
2268 F8
2269 F8
2270 B4
2271 B4
2272 E1
2273 E1
2274 F5
2275 F5
2276 C2
2277 D10
2278 F7
2279 B6
2280 B6
2282 C9
2283 F4
2284 F3
2285 G5
2286 F3
2287 F4
2288 A2
2289 B3
2290 F9
3201 B9
3202 B6
3203 E9
3204 B6
3205 D9
3206 F9
3207 B6
3208 E10
3209 E10
3210 E11
3211 E11
3212 B7
3214 B6
3215 B6
3216 B6
3217 D9
3218 B6
3219 B7
3220 E1
3221 F1
3222 A4
3223 B5
3224 G6
3225 F8
3226 B4
3227 C4
3228 B4
3229 E2
3230 F6
3231 F5
3232 F5
3233 B10
3234 A9
3235 A8
3236 B5
3237 A8
3238 B2
3239 B2
3240 B2
3241 F6
3242 B8
3243 G5
3244 F5
3245 B9
3246 A8
3247 F6
3248 B3
3249 B3
3250 B2
3251 G5
3252 B7
3253 C5
3254 E1
3255 A3
3256 B4
3257 B3
3258 B2
3259 B8
3260 B5
3261 B5
3262 C9
3263 C9
3264 C9
3265 D9
3266 D9
3267 B5
3268 B4
3269 B5
3270 G3
3271 A7
3272 B1
3273 B1
3274 G4
3275 G4
3276 G2
3277 G2
3278 G2
3279 C10
3280 C10
3281 B10
3282 C10
3283 C10
3284 B7
3285 D9
3287 B8
3288 G2
3289 C4
3290 A9
3291 B2
3292 A7
3293 A7
3294 A9
3295 G5
3296 F9
3297 G5
3298 B7
4209 G1
4210 H3
4211 B9
4212 H1
4213 A8
4214 A9
4219 B6
5201 F1
5202 C3
5203 D2
5205 D2
5206 E2
5207 D2
5208 C2
5209 C2
5210 D2
5211 E1
5212 C2
5213 F7
5214 E9
5215 E2
5216 E2
5217 B5
5295 F1
6201 E10
6202 B9
6203 E1
6204 D1
6205 B9
6207 E9
6208 G6
6209 A7
6210 B7
6211 B6
7200 D5
7201-1 E10
7201-2 E10
7202 D10
7203 E10
7204 E11
7205 B9
7207 B1
7208 A8
7209 F9
7210 F10
9201 B4
9202 H2
9203 H4
9204 B5
9205 H2
9215 G4
9257 G3
9260 B5
9261 G3
9262 G4
9265 G2
9266 G2
F200 E10
F201 D2
F202 C8
F203 F2
F204 F6
F205 B5
F206 B2
F207 D2
F208 B2
F209 F11
F270 C9
I201 E10
I203 E7
I204 F9
I205 G5
I206 G5
I207 A8
I208 A8
I209 B9
I210 C2
I211 E4
I212 E7
I213 F6
I214 F6
I215 E5
I216 B8
I217 A9
I218 C1
I219 B1
I222 C9
I224 F11
I225 F11
I226 E1
I228 B9
I235 C9
I236 B9
c200 F6
c201 H4
c202 H4
c203 H5
c204 H5
c205 H5
c206 H5
c207 H6
c208 H6
c209 H6
c210 H5
c211 H6
Page 32

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Mono Carrier: Features & Connectivities
32L04E AA 7.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
3139 123 5676.1
12345678 9
FEATURES & CONNECTIVITIES
F210
+6VS
F211
+6V
+9V
+9VA
VT_Supply
2u2
2625
GND_1
GND_1
1213
MTV
1
2 ITV DATAIN
I2SCLK
I2SDI1
3
GND Rx
4
Light sensor
5
6
7
C
Stdby-con
1234567
4604
4611
3606
150K
5V
I241
27K
3607
9603
ITV
ITV DATA OUT/SDAI2SWS
ITV CLOCK Bus Request
GND
ITV SCL
ITV POR 1
Stdby-con
4610
RES
3610
100R
6602
BAV99
A
9639
RES
3639
22R
3608
I227
1
IN
I240
27K
BC327-25
5V4
7604
BC847B
0V5
AK
7603
L78L33ACZ
OUTIN
COM
GND
2
GND_1
4612
6610
BAS316
7605
K
3
OUT
2620
GND_1
6V
5V
F213
3609
GND_1
5601
2630
1n0
4630
100n
GND_1
I234
GND_1
470R
2611
47u 16V
F212
2621
2623
1206
A
B
C
D
E
I230
GND_1
9605
10V100u
+6V
10V
2624
100n
100u
GND_1
Power On
Bus Request
+5V
DVD
Rx
Tx
I232
-
+3.3V
+9VA_1
+8V
Vbuffer
Reset_+5V
iDTV
Power On
Bus Request
A4
-
-
-
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
WRITE_PROTECT
A4
INTF_CVBS_IN
A4
SEL_SC2_INTF
A4
SW_SC2_CVBS
A8
SC2_CVBS_OUT
A4
A7
INTF_V_OUT
INTF_U_OUT
INTF_Y_OUT
INTF_Y|GREEN_IN
INTF_Pb|BLUE_IN
INTF_Pr|RED_IN
MUTING
USB
-
Power On
Bus Request
Rx
Tx
2631
22u
50V
2615
4u7
PCMCIA
-
Power On
Tx
+3.3V
4K7
3601
F214
1n0
2601
F215
3614
100R
1240
(FOR CINCH)
3V3
TO 1138
OF
7601
PCF85116
8
7
4
3
2
2614
4u7
9235
RES
5602
4u7
6
5
EEPROM
1
7602
PDTC124ET
I223
3635
I233
2622
TO 1763 & 1764
/
(FOR SCART)
3604
100R
47K
7606
BC847B
33p
OF
3605
100R
Vbuffer
68K
3636
3637
7V
3V3
3634
SCL
SDA
47R
2617
BC847B
1K0
3616
100R
3618
100R
100n
3V2
7607
3631
3617
100R
A4
A4
A4
22K
F217
F218
75R
3619
3620
GND3
INTF_FBL
A4
A4
SANDCASTLE
INTF_R_IN
A4
A4
INTF_L_IN
INTF_CVBS_IN
A2
VD
A4
HD_PIP
A4
INTF_CVBS_OUT
A4
ITV_V1OUT
A4
Stdby_Con
+9VA_1
For ITV
Only
I2SD|1
A4
F224
F225
F226
F216
F250
75R
3621
75R
4602
9604
RES
3603
100R
for EMC
F219
F221
4605
RES
F222
F223
9612
GND_1
3622
F227
1242
100K
3623 100K
+3.3V
+3V
GND_1
+5V
For ITV
Only
1243
+9V
9280
1241
for ITV only
+9V
9607
4606
+6VS
+6V
4601
4607
F220
1212
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14
15 16
For ITV
Only
1245
1219
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1221
1
2
3
To 1212 of
1220
1
2
3
4
5
6
LT1/CT1 INTERFACE PANEL
FOR ITV
E
A4
D
A4
C
A4
B
A4
A
A4
SEL_SC2_INTF
A4
Bout
A4
Gout
A4
Rout
A4
Iblack
A4
SVM
A4
ROT
A4
2626
27p
2627
2613
100n
F239
F233
F238
F237
27p
F230
F240
F241
F242
F243
F244
F245
2628
27p
2629
27p
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1206
To 1206 of
1204
To 1331 of
To 1219 of
F249
1207
1
2
3
4
5
6
To 1252 of
7
1213
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
E_14480_120.eps
I2S
SIDE_R_IN
A4
SIDE_L_IN
A4
SIDE_Y|CVBS_IN
A4
SIDE_CHROMA_IN
A4
FOR ITV ONLY
I229
I2SWS
A4
I2SCLK
F251
A4
I231
I2SD|1
A4
LIGHT_SENSOR
A4
To 1462 of
C
A4
Stdby_Con
A4
F240 F241 F242
500mV / div DC
20µs / div
500mV / div DC
20µs / div
3625
10R
3626
10R
3628
10R
F247
4609
F248
F228
F229
F232
500mV / div DC
20µs / div
89
LT1/CT1 INTERFACE PANEL
CRT PANEL
AV PANEL
RES
280504
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1204 B9
1206 A9
1207 D9
1212 A7
1213 E9
1219 C8
1220 E8
1221 F8
1240 F4
1241 F7
1242 E6
1243 F7
1245 C8
2601 C4
2611 B2
2613 B9
2614 D5
2615 E4
2617 D6
2620 C2
2621 C2
2622 E5
2623 E2
2624 E3
2625 E1
2626 D8
2627 D9
2628 D9
2629 D9
2630 F2
2631 E4
3601 B4
3603 B7
3604 C5
3605 C5
3606 D1
3607 E1
3608 D2
3609 E2
3610 C1
3614 E4
3616 B6
3617 B6
3618 B6
3619 B6
3620 B6
3621 B6
3622 E7
3623 E7
3625 E9
3626 E9
3628 E9
3631 E6
3634 E5
3635 D5
3636 D5
3637 D5
3639 C2
4601 E7
4602 C6
4604 B1
4605 D7
4606 D7
4607 E7
4609 D9
4610 C1
4611 B1
4612 C2
4630 F2
5601 F2
5602 E5
6602 E2
6610 C2
7601 B5
7602 D5
7603 A2
7604 E2
7605 D2
7606 E5
7607 E6
9235 E5
9280 F7
9603 F1
9604 B7
9605 C3
9607 D7
9612 E7
9639 B2
F210 A1
F211 B1
F212 C2
F213 D2
F214 C4
F215 C4
F216 B6
F217 B6
F218 B6
F219 C7
F220 D7
F221 C7
F222 D7
F223 D7
F224 A6
F225 A6
F226 A6
F227 E7
F228 E9
F229 E9
F230 A9
F232 E9
F233 B9
F237 B9
F238 B9
F239 A9
F240 B9
F241 B9
F242 C9
F243 C9
F244 C9
F245 C9
F247 D9
F248 E9
F249 E9
F250 B7
F251 E8
I223 D5
I227 D2
I229 E8
I230 B3
I231 E8
I232 C3
I233 E5
I234 E2
I240 C2
I241 E1
Page 33

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Mono Carrier: Class D - Audio Amplifier
33L04E AA 7.
A
B
C
D
E
And
F
For SUB Woofer
3975
100R, 2W
AMP-ST-5W-GL
1903
9911
3139 123 5676.1
For ITV
Europe
1222
JMP
---
123456789
CLASS D - AUDIO AMP
3975
33u
680p
*
9911
*
1903
VALUE
9910
5910
RES
4913
9915
I935
I940
2981
Audio_Gnd
MRT
Vaudio-
Vaudio+
Vaudio-
Vaudio+
2972
220n
7906
BC327-25
2978
2984
220n
2980
220n
5907
33u
220n
I926
I927
22u
2979
50V
Audio_Gnd
2958
Audio_Gnd
5908
33u
4914
4915
9913
5913
RES
47n
Audio_Gnd
Audio_Gnd
220n
2957
2973
220n
Audio_Gnd
I942
3964
Vaux_GND
2982
220n
Audio_Gnd
2974
220n
4916
4917
Audio_Gnd
3965
10K
22K
15n
3956
15n
2983
Audio_Gnd
I944
4910
Audio_Gnd
Audio_Gnd
10K
Audio_Gnd
10K
3972
6903
BAS316
F904
2931
560p
3931
150K
Audio_Gnd
2928
I909
2934
220p
I913
I920
3946
Audio_Gnd
I925
2939
220p
---
1V5
47K
1n0
3930
10K
2932
1u0
3933
2K7
7904
BC857B
3948
47K
2936
560p
3937
150K
2929
1n0
3936
10K
2937
1u0
3939
2K7
I910
I911
3934
I914
+Vaudio
1V6
-15V6
I918
3940
I948
MAIN_OUTL
A4
VOL_MUTE
A4
MAIN_OUTR
A4
1
2
3
4
5
6
Audio_Gnd
150R, 2W
F910
F911
Vaudio+
ROW
AMP-ST-10W+20W-GL AMP-ST-15W/20W-GL AMP-ST-5W-NO.SAV-EU
FUSE RAD LT 2A 250V IEC
---
2930
100n
3932
4K7
2933
120p
Audio_Gnd
3962
F901
4K7
6901
BAS316
-Vaudio
2935
100n
3938
4K7
2938
120p
Audio_Gnd
FUSE RAD LT 2A 250V IEC
Vaudio+
10K
3973
3
2
47K
-V
3935
100K
3K9
3959
I915
3961
470R
Audio_Gnd
5
6
47K
-V
3941
100K
JMP
--- ---
8
-9V1
1
7901-1
LM393N
4
3947
39K
7903
BC847B
-15V6
6904
BZX384-C27
8
7
7901-2
LM393N
4
AMP-ST-10W-GL
I941
Vaudio-
I919
-9V1
---
3949
-V
-2V8
22K
2977
1u0
2960
22u
2942
100n
3943
Audio_Gnd
I916
3942
2K2
3974
2K2
4K7
I921
I922
Vaudio-
Audio_Gnd
Vaudio-
I945
TDA8925J
-9V1
-2V7
-2V8
-8V8
-9V1
-2V8
Audio_Gnd
AMP-ST-5W-ITV-GLAMP-ST-5W-NO.SAV-ITV-EU
7902
1
2
4
9
15
17
16
14
2951
2950
2949
2948
2947
2945
2946
JMP
Vaudio+
47n
47n
35V470u
22u
47n
VDD1
AMPLIFIER
SW1
REL1
EN1
STAB
POWERUP
SW2
REL2
EN2
470u35V
47n
---
I928
3958
I924
5
Φ
CLASS-D
VSS1
8
AMP-ST-5W-EU
2K2
6905
1
13
VDD2
BOOT1
BOOT2
VSS2
10
JMPJMPJMP
---
2961
47u25V
3960
100K
P0102DA
OUT1
DIAG
OUT2
Vaudio-
6906
2
3
2963
6
10V7
7
-2V8
3
I937
10V5
12
11
3953
Vaudio+
AMP-ST-10W-EU
JMP
---
BAV99
I930
10p
Vaudio+
39K
3952
2952
1u0
2953
1u0
39K
AMP-ST-5W-ITV-EU
I934
I938
JMP
---
-Vaudio
4911
5911
3955
4R7
3971
4R7
4912
5912
Vaudio-
+Vaudio
I936
I939
5914
RES
9914
I943
5901
2971
Vaux_GND
33u
2955
680p
2954
680p
2970
680p
5902
123456789
3945
I946
10K
F903
F905
+9VB
Vaudio+
Vaudio+1
V_DG
VT_Supply
Vaudio-
-V
1902
5
4
3
2
1
3957
39K
Vaudio+
E_14480_121.eps
100504
A
B
C
D
E
F
1222 F1
1902 C9
1903 A7
2928 A2
2929 E2
2930 A2
2931 A2
2932 B2
2933 B2
2934 B2
2935 E2
2936 D2
2937 E2
2938 F2
2939 E2
2942 C4
2945 D5
2946 D5
2947 B5
2948 B5
2949 A5
2950 A5
2951 A5
2952 C6
2953 C6
2954 D7
2955 C7
2957 C8
2958 C8
2960 B4
2961 A5
2963 B6
2970 D7
2971 D7
2972 E7
2973 E8
2974 E8
2977 A4
2978 B7
2979 B8
2980 C8
2981 E7
2982 C8
2983 E8
2984 C8
3930 A2
3931 A2
3932 B2
3933 B2
3934 B3
3935 B3
3936 E2
3937 D2
3938 E2
3939 F2
3940 E3
3941 F3
3942 B4
3943 C4
3945 E9
3946 D2
3947 C3
3948 D2
3949 C3
3952 C6
3953 D6
3955 C7
3956 C8
3957 D9
3958 A5
3959 C3
3960 A5
3961 C3
3962 C2
3964 A8
3965 A8
3971 D7
3972 E8
3973 A3
3974 C4
3975 A7
4910 B9
4911 C7
4912 D7
4913 B7
4914 F8
4915 F8
4916 F8
4917 F8
5901 C7
5902 D7
5907 C8
5908 D8
5910 B7
5911 C7
5912 D7
5913 A8
5914 B7
6901 D1
6903 A9
6904 D3
6905 B5
6906 A6
7901-1 B3
7901-2 E3
7902 B5
7903 D3
7904 C2
7906 A8
9910 A7
9911 A7
9913 A8
9914 B7
9915 B7
F901 C2
F903 D9
F904 C9
F905 D9
F910 F1
F911 F1
I909 A2
I910 A3
I911 B2
I913 B2
I914 B3
I915 C3
I916 A4
I918 D2
I919 C3
I920 C2
I921 C4
I922 D4
I924 A5
I925 E2
I926 B8
I927 B8
I928 A5
I930 A6
I934 C6
I935 C7
I936 C7
I937 C6
I938 D6
I939 D7
I940 D7
I941 A3
I942 A8
I943 D7
I944 A9
I945 D4
I946 D9
I948 F3
Page 34

Mono Carrier: Audio Amplifier
123456789
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
A
MAIN_OUTL
A4
B
MAIN_OUTR
A4
C
VOL_MUTE
A4
D
Stdby_Con
E
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
TO 1683 OF
POWER_DOWN
1282
3998
10K
6990
BAS316
2911
7994
BC847B
4u7
2912
4u7
F950
F951
I958
I959
2913
4u7
2914
2985
RES
3985
1K0
2991
RES
3991
1K0
Vaudio+1
4u7
2915
4u7
3997
3999
3994
68K
820K
120K
7992
BC847B
0V7
7993
BC847B
I953
3988
I954
3992
4K7
4K7
2989
220n
2992
220n
2990
2993
3996
34L04E AA 7.
1n0
I952
1n0
7991
BC847B
68K
I951
I955
16V
3995
2916
47K
4u7
+16V
7990
TDA2616Q
INV1-
1
MUTE
2
V|GND
3
INV2-
9
INV12
8
+16V
-16V
2988
7
VP+
VP-
5
2987
100n
100n
OUT1
OUT2
4
6
50mV / div AC
2ms / div
Vaudio+1
2986
100n
I956
2994
22n
I957
2995
22n
-Vaudio
I952I951 F952 F955
50mV / div AC
2ms / div
500mV / div AC
2ms / div
3989
10R
3993
10R
AmpOutL
2996
Audio_Gnd
AmpOutR
2997
Audio_Gnd
500mV / div AC
2ms / div
47n
47n
F952
F955
F953
Audio_Gnd
1280 B9
1281 B9
1282 D2
2911 D3
2912 D3
2913 D3
2914 D3
2915 D3
2916 C5
2985 A4
A
2986 A7
2987 A6
2988 C6
2989 B4
2990 B5
2991 B4
2992 B4
2993 C5
2994 B7
B
2995 C7
2996 B8
2997 C8
3985 B4
3988 B4
3989 B8
1280
1281
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
8 ohm / 15W
8 ohm / 15W
3991 B4
3992 C4
3993 C8
3994 C4
3995 C5
3996 C5
3997 D4
3998 E2
3999 D4
C
6990 D2
7990 A6
7991 C5
7992 C4
7993 D4
7994 E2
F950 B3
F951 B3
F952 B9
F953 B9
F955 B9
D
I951 B5
I952 B5
I953 B4
I954 B4
I955 C5
I956 B8
I957 C8
I958 C3
I959 D3
E
MUTING
A5
3139 123 5676.1
E_14480_122.eps
280504
123456789
Page 35

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Mono Carrier: Rear I/O Scart
35L04E AA 7.
A
Audio-R_out
Audio-R_in
Audio-L_out
Audio-L_in
B
RGB-B_in
Function_Sw
RGB-G_in
C
RGB-R_in
RGB-BL_in
Terr_CVBS_out
Video_in
D
SINGLE
ITEM SCART
IN-DVD
2731
2732
2733
2734
2735
2736
2737
2738
E
2739
2740
2741
2742
2743
2744
2745
2747
3721
3731
3732
3733
3734
3735
F
3736
3738
3739
3740
3742
3743
3744
3746
JMP
4705
WITH MON.
ITEM
OUT
330pF
2731
G
3139 123 5676.1
2752
2753
2754
3751
3752
3753
3754
7731
4u7
330pF
4u7
150R
220K
150R
220K
BC847B
1234567891011
SCART 1
DUAL
SCART
---
390pF
---
390pF
---
---
390pF
---
390pF
---
---
390pF
---
390pF
---
---
390pF
---
390pF
--330pF
---
---
330pF
---
22pF
---
22pF
75R
---
150R
220K
--150R
---
--150R
---
220K
---
---
---
---
---
---
100R
---
---
---
REAR I/O SCART
1735-1
1A
2A
3A
F711
4A
5A
6A
7A
8A
9A
10A
IN
4u7
4u7
4u7
4u7
---
47K
47K
27K
6K8
75R3741
68R
1K
JMP
---
WITHOUT
MON.OUT
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
11A
12A
13A
14A
15A
16A
17A
18A
19A
20A
21A
1109
F714
1107
1101
11021113
1103
1104
1105
1106
1108
1110
1111
1112
F701
F702
F704
F705
F706
F707
F708
F709
F710
F712
4701
6706
3719
68R
RES
4702
3701
150R
3703
22K
3705
150R
RES
3707
22K
RES
FOR ITV ONLY
1769
3711
I710
3722
75R
3721
FOR ITV ONLY
TO 1684 OF
33K
9722
RES
2702
2705
2708
2711
3709
3712
3713
3715
3717
1770
330p
330p
330p
330p
75R
6K8
75R
75R
75R
3702
3704
3706
3708
3
2
3720
220K
47K
220K
47K
3710
330R
9710
RES
3714
330R
9714
RES
3716
330R
9716
RES
3718
330R
7701
BC847B
1K0
1
I701
I702
F703
I704
FOR ITV ONLY
1765
I705
I707
FOR ITV ONLY
I709
FOR ITV ONLY
I711
FOR ITV ONLY
I713
I722
3758
47R
2760
16V
I714
2759
33p
F713
1762
6
7
7706
BC847B
2703
50V
10u
2706
2u2
2709
10u
50V
2712
2u2
1766
1767
1768
Vbuffer
100n
FOR ITV ONLY
1
2
SC2_STATUS|ITV_MSG
3
SC1_FBL
4
5
TO 1240 OF
I729
SC1_R_OUT
I730
SC1_R_IN
I731
SC1_L_OUT
SC1_L_IN
I732
SC1_BLUE_IN
SC1_STATUS
SC1_GREEN_IN
SC1_RED_IN
SC1_FBL
SC1_CVBS_OUT
SC1_CVBS_IN
1764
7707
BC847B
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4, A8
A4
A4
A5
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
A4
FOR ITV ONLY
1727
SC2_R_OUT
SC2_R_IN
SC2_L_OUT
SC2_L_IN
SC2_STATUS|ITV_MSG
SC2_CHROMA_IN
SC2_CVBS_OUT
SC2_Y|CVBS_IN
Vbuffer
MAIN_OUTR
MAIN_OUTL
1
4706
F751
F752
2
3
I736
I735
I734
I733
I719
I739
2733
50V
10u
2736
100n
2739
50V
10u
2742
100n
3742
330R
9742
*
9746
*
3746
330R
1729
FOR ITV ONLY
123
7705-1
IMT1A
Vbuffer
7705-2
IMT1A
I715
I716
I717
I718
F738
150R
22K
150R
22K
33K
68R
6733
3745
7709
BC847B
RES
4707
RES
4708
75R
3741
BZX384-C5V6
75R
RES
6732
7702
BC847B
7703
BC847B
1131
1132
1133
1134
1136
1139
1141
1142
I721
3764
F731
F732
F733
F734
F735
F736
F737
F739
100K
3752
3754
I720
220K
220K
3761
2751
2753
1135
100K
330p
330p
3751
1K2
3753
1K2
3757
3756
1K0
47K
1137
2763
1153
1151
1152
F718
F719
1138
1140
3762
22R
47p
F716
2755
2756
SCART 2
1735-2
1B
2B
3B
4B
5B
6B
7B
8B
9B
10B
11B
12B
13B
14B
15B
16B
17B
18B
19B
20B
21B
F715
100n
2757
RES
3770
RES
3771
1728
1
2
3
4
3
2
820R
1
LPR6520-M920F
BLACK-WHITE-RED
F717
820R
Audio-R_out
Audio-R_in
Audio-L_out
Audio-L_in
Function_Sw
YC-C_in
CVBS_out
Video/YC-Y_in
SPDIF
1734
Woofer
LEFT
RIGHT
A
B
C
D
E
F
MONITOR OUTPUT
7708
BC847B
3731
3732
3734
3736
3738
3740
3769
1K2
4
5
3
I728
3767
1K2
1
2
6
2732
220K
47K
2735
2738
220K
47K
2741
6K8
TO 1240 OF
A5
I727
1K0
3768
1K0
3766
50V
50V
330p
330p
330p
330p
1763
2752
2754
3733
3735
3737
3739
3743
MUTING
10u
10u
G
E_14480_123.eps
260504
1234567891011
1101 A3
1102 B3
1103 B3
1104 C3
1105 C3
1106 D3
1107 C2
1108 D3
1109 C2
1110 E3
1111 E3
1112 F3
1113 F3
1131 A9
1132 B9
1133 B9
1134 C9
1135 B10
1136 C9
1137 C10
1138 C10
1139 D9
1140 C10
1141 D9
1142 E9
1151 F10
1152 F10
1153 E10
1727 A7
1728 D11
1729 E7
1734 E11
1735-1 A1
1735-2 A11
1762 G5
1763 E9
1764 A6
1765 C5
1766 D5
1767 D5
1768 E5
1769 C4
1770 G4
2702 A4
2703 A5
2705 B4
2706 B5
2708 B4
2709 B5
2711 C4
2712 C5
2732 A8
2733 A7
2735 B8
2736 B7
2738 B8
2739 B7
2741 C8
2742 C7
2751 F10
2752 F9
2753 F10
2754 F9
2755 F10
2756 F10
2757 E10
2759 F5
2760 E5
2763 E10
3701 A4
3702 A4
3703 B4
3704 B4
3705 B4
3706 B4
3707 C4
3708 C4
3709 C4
3710 C5
3711 D4
3712 D4
3713 D4
3714 D5
3715 E4
3716 E5
3717 E4
3718 E5
3719 F3
3720 F4
3721 F4
3722 F4
3731 A9
3732 A8
3733 B9
3734 B8
3735 B9
3736 B8
3737 C9
3738 C8
3739 C9
3740 C8
3741 D9
3742 D7
3743 D9
3745 E9
3746 E7
3751 F10
3752 F9
3753 F10
3754 F9
3756 E10
3757 E10
3758 E5
3761 E10
3762 D10
3764 E9
3766 G8
3767 F8
3768 F8
3769 E8
3770 F11
3771 F11
4701 A3
4702 B3
4706 B7
4707 A9
4708 B9
6706 F3
6732 E9
6733 D9
7701 F5
7702 F9
7703 G9
7705-1 F8
7705-2 F8
7706 A6
7707 A6
7708 A8
7709 A9
9710 C5
9714 D5
9716 E5
9722 F4
9742 D7
9746 D7
F701 A3
F702 B3
F703 B5
F704 C3
F705 C3
F706 D3
F707 D3
F708 E3
F709 E3
F710 F3
F711 A2
F712 F3
F713 F5
F714 C2
F715 D11
F716 E10
F717 F11
F718 F10
F719 F10
F731 A9
F732 B9
F733 B9
F734 C9
F735 C9
F736 D9
F737 D10
F738 C8
F739 E9
F751 F7
F752 F7
I701 A5
I702 B5
I704 C5
I705 C5
I707 D5
I709 D5
I710 E4
I711 E5
I713 E5
I714 F5
I715 A8
I716 B8
I717 B8
I718 B8
I719 D7
I720 F10
I721 F9
I722 E5
I727 F8
I728 F8
I729 A5
I730 A5
I731 B5
I732 B5
I733 B7
I734 B7
I735 A7
I736 A7
I739 E7
Page 36

Mono Carrier: Front Control
12
FRONT CONTROL
A
B
C
D
E
A4,A9
KEY_PROTN
F692
2V / div DC
2ms / div
A4
A4
LED
IR
For Engg Purpose Only
F694
4694
LIGHT_SENSOR
A4
KEY_PROTN
A9
F696
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
F682
1K2
3689
F695
RES
3695
RES
4692
3683
POWER
TS
LED_OUT
I687
2692
RES
I681
1606
USA
F693
3692
6693
47n
9683
STANDBY LED
6691
*
4691
IR
BPW46
3696
680K
3684
DVD Eject
*
4693
*
3697
10K
I688
1604
I691
21
F692F691
7691
BC847B
channel+
4695
RES
3691
330R
IR_OUT
F698
34
A
3685
150R
I682
1603
3686
390R
I683
1602
channel-
3687
F683
1601
volume+
1K8
3681
volume-
820R
I686
1600
B
F685
+6V
3690
220R
I689
C
3693
3694
I693
4K7
F699
for ITV only
6692
TSOP1836
3
VS
1
OUT
2
GND
IR RECEIVER
1692
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
F697
2691
1
2
3
4
5
6
220R
100u
1693
6694
BZX384-C5V1
To
1693
of
D
E
36L04E AA 7.
1600 B4
1601 B4
1602 B4
1603 B3
1604 B3
1606 B2
1692 D4
1693 D4
2691 D4
2692 E2
3681 A4
3683 A2
3684 A2
3685 A3
3686 A3
3687 A4
3689 A2
3690 C4
3691 C3
3692 C2
3693 C4
3694 D3
3695 C2
3696 E2
3697 E3
4691 D2
4692 C2
4693 E3
4694 E1
4695 C3
6691 C3
6692 C4
6693 E2
6694 D4
7691 D3
9683 A2
F682 A2
F683 A4
F685 B4
F691 D2
F692 D3
F693 C2
F694 D1
F695 D2
F696 C2
F697 D4
F698 E3
F699 D3
I681 A2
I682 A3
I683 A4
I686 A4
I687 E2
I688 A3
I689 C4
I691 C3
I693 C3
ITEM NO. EU
F
6691
3139 123 5676.1
NAFTA
LTL-10234WHCR
(GREEN)
LATAM
LTL-10234WHCR
(GREEN)
LTL-10224WHCR
(RED)
AP
LTL-10224WHCR
(RED)
SETS WITH LIGHT_SENSOR
JMP4693
E_14480_124.eps
260504
1234
F
E_06532_012.eps
130204
Page 37

Mono Carrier: DVD Power Supply
123456
DVD POWER SUPPLY
A
ITV only
Vaux
3585
B
Vaux_GND
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
25V100u
3581
220n
100R
2581
Vaux_GND
2582
I582
Vaux_GND
2583
22K
2n2
I583
2584
37L04E AA 7.
7581
L4978
5
VCC
34
OSC
2
SS_INH
COMP GND BOOT
1
I584
Vaux_GND
8K2
100n
3582
I585
FB
OUT
67
8
100n
2586
I587
I588
6581
SB340
Vaux_GND
2587
1n0
5581
47u
2588
Vaux_GND
16V
1m0
3583
Vaux_GND
4K7
3584
2K7
F581
F582
F583
Vaux_GND
+5V
Vaux
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
1582
1581
ITV only
DVD/IDTV
A
B
1581 A6
1582 A6
2581 B2
2582 B2
2583 C2
2584 C2
2585 C3
2586 B4
2587 B4
2588 B5
2589 C1
2590 C2
3581 B2
3582 C3
3583 B5
3584 B5
3585 B1
4581 C2
5581 B5
6581 B4
7581 A3
7582 C2
F581 B6
F582 B6
F583 B6
I582 B2
I583 B3
I584 B3
I585 C3
I587 B4
I588 B4
C
+9VA
+9VB
3139 123 5676.1
13
2u2
2589
MainSupplyGnd
4581
7582
L78L08ACZ
OUTIN
COM
2
MainSupplyGnd
Vaux_GND
2590
MainSupplyGnd
2u2
Vaux_GND
2585
Vaux_GND
22n
E_14480_125.eps
100504
C
123456
Page 38

Layout Mono Carrier: (Top Side)
1000 E8
1001 E6
1002 E5
1003 E5
1004 E7
1005 E8
1010 E7
1011 E7
1012 E6
1013 E8
1204 C6
1205 D5
1206 D5
1207 E7
1208 D7
1212 C6
1213 C5
1219 C7
1220 E4
1221 C5
1222 D3
1230 D5
1234 D5
1240 D4
1241 D5
1242 E4
1243 C6
1245 D6
1280 E3
1281 E3
1282 D3
1401 C7
1402 A6
1404 A5
1451 C7
1452 A8
1453 B5
1454 B7
1470 A8
3139 123 5676.1
1500 A2
1501 A2
1502 B2
1503 C3
1504 C2
1505 A2
1506 A2
1507 C2
1508 A2
1509 C2
1510 B1
1532 B3
1535 C5
1542 C4
1543 C4
1545 C4
1581 D4
1582 C3
1600 C1
1601 C1
1602 D1
1603 D1
1604 C1
1606 A1
1682 D4
1683 C5
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
1684 D6
1692 C1
1693 C1
1727 C7
1728 D8
1729 D7
1734 D8
1735 D8
1762 D7
1763 E8
1764 C7
1765 C7
1766 D7
1767 D7
1768 E7
1769 D8
1770 D8
1902 D2
1903 D3
2005 E5
2006 E7
2008 E8
2203 D5
2217 E5
2218 D6
2224 E5
2230 D6
2234 D6
2240 E5
2250 D6
2251 E5
2265 E6
2273 E6
2275 E6
2404 B6
2405 A6
2406 A6
2411 B6
2412 A6
2413 B6
2415 A5
2416 B6
2417 A6
2418 A5
2419 B6
2427 B6
2451 A8
2454 A8
2455 A8
2457 C7
2458 C7
2459 A8
2460 A7
2463 C8
2465 C8
2467 C7
2481 A7
2484 A8
2486 B6
2492 B6
2493 A7
2500 A2
2501 C2
2502 C2
2503 A4
2504 A4
2505 A4
2506 A3
2507 A3
2508 C2
2509 C1
2511 A5
2514 A4
2528 B4
2534 B3
2535 C3
2536 C3
2537 C3
2539 C3
2540 C3
2541 C3
2542 B4
2543 B3
2545 B3
2546 B3
2551 B5
2552 C5
2561 C4
2562 B4
2563 C4
2565 C4
2570 B4
2581 C4
2588 C4
2611 E4
2621 E5
2624 E5
2631 D7
2691 B1
2703 C7
2709 C7
2733 C7
2739 C7
2752 E7
2754 E8
2945 D2
2948 D2
2949 D2
2960 D2
2961 D1
2978 C3
3020 E7
3201 D5
3215 D5
3224 E5
3230 D4
3231 D6
38L04E AA 7.
3234 C6
3239 C7
3241 E5
3246 D5
3249 D7
3252 D5
3258 D7
3260 D5
3270 D7
3274 D7
3275 E7
3276 C7
3277 C7
3278 D7
3291 D7
3401 C6
3402 A7
3407 A7
3411 A6
3412 A6
3414 C6
3415 B6
3417 A6
3418 C5
3425 C5
3430 B6
3431 C6
3432 B7
3433 B6
3434 B6
3440 C5
3441 B6
3442 A7
3443 A7
3447 A7
3451 B6
3454 A8
3458 B7
3460 B7
3461 C7
3466 C7
3467 C7
3468 C7
3470 C8
3471 C7
3472 C7
3482 B8
3483 B8
3484 B8
3485 B8
3497 C5
3500 B1
3501 B1
3502 A1
3503 B1
3504 B2
3505 A2
3506 B1
3507 B3
3508 A3
3509 B2
3510 B2
3511 B5
3513 A5
3514 A5
3515 A5
3516 A4
3519 B4
3520 A4
3521 A5
3523 B2
3529 B3
3531 B4
3532 B3
3534 B4
3542 B3
3563 C4
3571 B5
3574 B5
3575 B5
3577 B5
3584 C4
3585 D4
3589 C5
3603 C6
3606 E4
3616 C6
3617 C6
3618 C6
3639 E4
3683 B1
3701 C8
3703 C8
3705 C8
3707 C8
3709 D8
3710 D8
3713 D8
3714 D8
3715 D8
3716 D8
3717 D8
3718 D8
3721 D8
3722 D8
3731 C8
3733 C8
3735 C8
3737 C8
3739 D8
3741 D8
3742 D7
3743 D7
3745 D8
3746 D7
3751 E8
3753 E8
3757 D8
3758 D7
3943 C2
3945 D3
3961 C3
3962 D3
3975 D3
5201 D5
5208 D6
5216 D6
5217 D7
5295 C5
5401 A6
5402 B6
5403 B5
5404 B8
5405 B5
5406 B6
5408 B6
5410 B6
5450 B7
5451 B7
5452 A8
5500 B2
5501 B2
5502 A3
5503 A3
5511 A4
5512 B4
5512C B4
5512D B4
5531 B4
5532 B3
5536 C4
5537 C4
5551 B5
5552 B5
5561 B4
5562 B4
5581 D4
5602 D7
5901 D2
5902 D2
5907 D1
5908 D2
5913 D3
5914 D3
6001 E8
6006 E7
6401 A6
6403 C6
6404 A6
E_14480_093.eps
6406 A6
6410 A6
6411 A6
6412 A6
6452 C7
6453 B7
6454 B8
6455 B8
6456 A8
6459 B8
6480 B8
6481 B8
6486 C6
130404
6491 A6
6500 A4
6511 A5
6535 C4
6536 C3
6537 C3
6540 B3
6551 C5
6562 B4
6563 C4
6573 B5
6575 A4
6581 D4
6691 A1
6692 B1
6693 B1
6905 D1
7203 E5
7204 E5
7401 A6
7405 B6
7406 C5
7451 C8
7452 C8
7453 C7
7512 A4
7513 B5
7531 B3
7571 B5
7581 D4
7582 D4
7601 D5
7603 E4
7605 E5
7902 C2
7906 C3
7990 E3
9002 E7
9201 E6
9202 E4
9203 E6
9204 E7
9205 D4
9206 D4
9207 D4
9208 D4
9209 C5
9210 E7
9211 D7
9212 E7
9213 D7
9214 D4
9215 E7
9216 D4
9217 D6
9218 E6
9219 D6
9220 D5
9221 D5
9222 E5
9223 E6
9224 D5
9225 D4
9226 D4
9227 D5
9228 D4
9229 D5
9230 D5
9231 E6
9232 E5
9233 E6
9234 E7
9235 D7
9236 C5
9237 D6
9238 D7
9239 E6
9240 E5
9241 C6
9242 D4
9243 C4
9244 E6
9245 E4
9246 E6
9247 E4
9248 E6
9249 D4
9250 E6
9251 E5
9252 C5
9253 D5
9254 C7
9255 C7
9257 D7
9258 C7
9259 D7
9260 D7
9261 D7
9262 D7
9263 E7
9264 C7
9265 C7
9266 C7
9267 D7
9268 D7
9269 C4
9271 E5
9272 D4
9273 D4
9274 D4
9275 C5
9276 D5
9277 C6
9278 D4
9279 D4
9280 D5
9290 E6
9294 C6
9296 C5
9297 C4
9298 C5
9299 C5
9401 B5
9402 B6
9404 B8
9407 B6
9410 B6
9417 A5
9451 B7
9452 A8
9460 B6
9466 B5
9467 B6
9469 C5
9470 C6
9473 C5
9474 C5
9475 C5
9476 C5
9477 C6
9478 C6
9479 C6
9480 C6
9481 C6
9482 C7
9483 C8
9484 C7
9485 C7
9486 B7
9487 B8
9488 A8
9489 B8
9490 A8
9491 A6
9492 C6
9500 A2
9501 B2
9502 B2
9503 B2
9504 B2
9505 B3
9506 A3
9507 A2
9508 A2
9509 C4
9510 C4
9511 B2
9512 B3
9513 B5
9514 C4
9532 B3
9536 C4
9537 C4
9570 A3
9573 C2
9574 B4
9575 C3
9576 A4
9577 B5
9578 B3
9579 C3
9582 C4
9583 C4
9584 B4
9585 A4
9586 C4
9587 B4
9589 C5
9590 C5
9591 C3
9592 C3
9593 C4
9603 C7
9604 C6
9605 E6
9607 D7
9612 E4
9631 C6
9633 C7
9637 E7
9639 E4
9642 D7
9643 D5
9653 D4
9660 C1
9661 C1
9662 B1
9663 C1
9664 C1
9665 B1
9666 C1
9683 B1
9688 E4
9689 E4
9690 E4
9694 E6
9695 E4
9696 D4
9710 D8
9714 D8
9716 D8
9720 D7
9721 D7
9722 D8
9723 D8
9724 D7
9728 D7
9729 D7
9742 D7
9746 D7
9910 C3
9911 D3
9913 D3
9914 D3
9915 C3
9920 D3
9921 D3
9924 D2
9926 D3
9927 D2
9933 D3
9935 D3
9936 C3
9937 C3
9939 D3
9940 C3
9941 D3
9942 D3
9943 D3
9944 D3
9946 C2
Page 39

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Mono Carrier (Overview Bottom Side)
2001 A8
2002 A8
2003 A7
2004 A7
2007 A7
2009 A7
2013 A7
2014 A7
2016 A7
2204 A5
2205 B5
2206 B5
2207 A4
2208 A4
2209 B5
2210 B5
2211 B6
2212 B5
2213 B5
2214 A5
2215 B6
2216 B6
2221 A5
2222 A5
2223 B6
2225 B6
2226 A5
2227 A5
2229 B6
2231 B6
2232 B6
2233 B6
2235 A5
2236 A5
2237 B6
2238 A5
2239 A5
2241 A5
2242 B6
2243 B6
2244 A5
2245 A5
2246 B6
2247 B6
2248 A5
2249 B6
2252 B6
2253 A6
2254 A6
2255 A7
2256 A6
2257 A6
2258 B6
2259 B5
2260 A6
2261 A6
2262 B6
2263 A6
2264 B6
2266 A6
2267 A6
2268 A5
2269 A5
2270 A6
2271 A6
2272 A6
2274 A6
2276 A6
2277 B5
2278 A5
2279 B5
2280 B5
2282 B5
2283 A6
2284 A6
2285 A6
2286 B6
2287 B6
2288 B4
2289 B4
2290 A5
2402 E8
2403 E8
2408 C6
2409 D6
2410 C6
2414 C6
2420 C6
2425 C6
2428 D7
2453 E8
2456 D8
2461 D7
2462 D7
2464 C8
2468 C8
Part 1
E_14480_094a.eps
Part 3
E_14480_094c.eps
3139 123 5676.1
2469 D7
2470 C8
2480 E8
2482 C5
2483 E8
2487 D6
2488 C5
2489 D6
2490 D8
2491 E8
2512 E5
2513 E5
2515 D5
2516 E5
2517 E5
2518 E5
2519 E5
2530 D4
2531 D4
2532 D4
2533 D3
2538 C4
2544 D4
2547 C4
2548 C4
2549 D3
2550 D3
2553 D4
2564 C4
2566 C4
2571 D5
2572 C5
2573 D5
2582 C4
2583 B4
2584 B4
2585 B4
2586 B4
2587 B4
2589 B4
2590 B4
2601 B5
2613 B5
2614 B7
2615 B7
2617 B7
2620 A5
2622 B7
2623 A5
2625 A4
2626 C6
2627 B6
2628 B6
2629 B6
2630 C7
2692 D1
2702 C8
2705 C8
2706 C8
2708 C7
2711 C8
2712 C8
2732 C7
2735 C7
2736 B7
2738 C7
2741 B7
2742 B7
2751 A8
2753 A8
2755 A8
2756 B8
2757 B8
2759 B7
2760 B8
2763 A8
2911 A4
2912 A4
2913 A4
2914 A4
2915 A4
2916 B3
2928 C3
2929 B3
39L04E AA 7.
2930 B3
2931 C3
2932 C3
2933 C3
2934 C3
2935 B3
2936 B3
2937 B3
2938 B3
2939 B3
2942 C2
2946 B2
2947 C2
2950 B2
2951 C2
2952 C2
2953 C2
2954 B2
2955 B2
2957 B1
2958 B2
2963 B2
2970 B2
2971 B2
2972 B2
2973 B2
2974 B2
2977 C2
2979 C3
2980 B1
2981 B2
2982 B2
2983 B2
2984 B2
2985 B3
2986 A3
2987 A3
2988 A3
2989 B3
2990 A3
2991 A3
2992 A3
2993 A3
2994 A3
2995 A3
2996 A3
2997 A3
3000 A8
3001 A8
3002 A8
3003 A7
3004 A8
3005 A7
3006 A5
3007 A5
3008 A7
3009 A5
3010 A7
3014 A7
3016 A7
3018 A7
3019 A7
3202 B5
3203 A5
3204 B5
3205 A5
3206 A5
3207 B5
3208 A4
3209 A4
3210 A4
3211 A4
3212 B5
3214 B5
3216 B6
3217 A5
3218 B5
3219 B5
3220 B6
3221 B6
3222 A6
3223 A4
3225 B6
3226 B6
3227 B6
3228 B6
3229 B6
3232 A5
3233 C6
3235 A5
3236 A5
3237 A5
3238 B6
3240 B6
3242 B6
3243 A5
3244 A6
3245 C5
3247 A6
3248 B7
3250 B7
3251 A6
3253 A6
3254 A6
3255 A6
3256 A6
3257 B7
3259 B5
Part 2
E_14480_094b.eps
Part 4
E_14480_094d.eps
3261 B4
3262 B5
3263 B5
3264 B5
3265 B5
3266 B5
3267 A6
3268 B7
3269 B5
3271 B6
3272 B6
3273 B6
3279 B5
3280 B5
3281 B5
3282 B5
3283 B5
3284 B5
3285 A4
3287 B5
3288 B5
3289 B6
3290 C6
3292 B6
3293 B6
3294 C6
3295 A5
3296 A5
3297 A6
3298 B5
3404 E6
3409 E8
3416 D6
3419 E7
3420 C6
3422 D8
3423 D7
3427 D7
3428 D7
3436 D5
3437 C7
3445 C5
3446 C5
3452 D7
3453 E7
3456 D8
3459 D7
3462 D8
3463 D8
3486 D8
3464 C8
3487 E7
3465 C8
3488 E7
3469 C8
3489 C6
3473 E8
3490 E8
3474 C7
3491 E8
3475 C7
3492 E8
3476 E7
3493 E8
3477 E8
3494 E8
3478 D8
3495 C6
3480 E7
3498 C6
3481 D8
3499 C6
E_14480_094.eps
130404
3512 E5
3517 E5
3518 E5
3522 E5
3524 E5
3527 D4
3528 D4
3530 D3
3533 D3
3535 C3
3536 C3
3537 D3
3538 D3
3539 D3
3541 C3
3565 C4
3572 C5
3573 D5
3576 D5
3578 D5
3579 D5
3581 B4
3582 B4
3583 B4
3601 B5
3604 B5
3605 B5
3607 A4
3608 A5
3609 A4
3610 A4
3614 B7
3619 C6
3620 C6
3621 C6
3622 A4
3623 A4
3625 B5
3626 B5
3628 B5
3631 B7
3634 B7
3635 B7
3636 B7
3637 B7
3681 C1
3684 C1
3685 B1
3686 B1
3687 C1
3689 C1
3690 C2
3691 E1
3692 E1
3693 D1
3694 E1
3695 D1
3696 D1
3697 D1
3702 C7
3704 C8
3706 C7
3708 C8
3711 C8
3712 C8
3719 B8
3720 B8
3732 C7
3734 C7
3736 C7
3738 C8
3740 B8
3752 A7
3754 B8
3756 B8
3761 A8
3762 B8
3764 A7
3766 B7
3767 A7
3768 A7
3769 A7
3770 A8
3771 B8
3930 C3
3931 C3
3932 C3
3933 C3
3934 C3
3935 C2
3936 B3
3937 B3
3938 B3
3939 B3
3940 B3
3941 B2
3942 C2
3946 B3
3947 C2
3948 C3
3949 C2
3952 C2
3953 C2
3955 B2
3956 B2
3957 B3
3958 B1
3959 C3
3960 B1
3964 C3
3965 C3
3971 B2
3972 B2
3973 B2
3974 C2
3985 B3
3988 A3
3989 A3
3991 A3
3992 A3
3993 A3
3994 B3
3995 A3
3996 B4
3997 B4
3998 A4
3999 A4
4000 A8
4001 A8
4002 A5
4003 A7
4004 A5
4005 A7
4006 A8
4010 A7
4011 A6
4012 A6
4013 A6
4015 A8
4209 A6
4210 B6
4211 B6
4212 B5
4213 B6
4214 C6
4219 B5
4221 B5
4222 A5
4223 A6
4224 A5
4226 A5
4227 A6
4240 C4
4241 C4
4437 C7
4470 E8
4471 E8
4472 E7
4473 E8
4474 C6
4492 E8
4533 E5
4534 C4
4535 C4
4536 C3
4537 C4
4538 C3
4581 B4
4601 A4
4602 C6
4604 A4
4605 C7
4606 C7
4607 A4
4609 A6
4610 A4
4611 B4
4612 A5
4620 C7
4630 C7
4631 B4
4635 C7
4637 B6
4642 A7
4644 A7
4645 B6
4646 B5
4648 B7
4649 A4
4650 B4
4651 B4
4691 C1
4692 D1
4693 D1
4694 C1
4695 E1
4696 C1
4701 C8
4702 C8
4706 B7
4707 C8
4708 C8
4730 C7
4910 B3
4911 B2
4912 B2
4913 C2
4914 A4
4915 A4
4916 A4
4917 A4
4921 C2
5001 A7
5002 A7
5003 A5
5202 B5
5203 B5
5205 B6
5206 B5
5207 B5
5209 A5
5210 B6
5211 A6
5212 A6
5213 B6
5214 A5
5215 B5
5513 D5
5533 D4
5534 C4
5535 C4
5601 C7
5910 C2
5911 B2
5912 B2
6002 A8
6003 A8
6004 A5
6201 A4
6202 B6
6203 B6
6204 A6
6205 C6
6207 A5
6208 C5
6209 C4
6210 B5
6211 B5
6407 D5
6408 D5
6441 D6
6442 D6
6443 C5
6450 E7
6451 E7
6457 C7
6458 C8
6482 C5
6483 C7
6484 D6
6488 D7
6489 D7
6490 E7
6512 D5
6514 E5
6531 D3
6532 D4
6533 D4
6534 D4
6538 D4
6541 C3
6564 C4
6565 C4
6566 C4
6571 C5
6572 D5
6576 C3
6602 A4
6610 A5
6694 C1
6706 B8
6732 B8
6733 B8
6901 B3
6903 C3
6904 C2
6906 B2
6990 B4
7001 A5
7003 A7
7200 B6
7201 A5
7202 A5
7205 C5
7207 B6
7208 B6
7209 A5
7210 A5
7403 E7
7404 C6
7408 C6
7410 C6
7411 C6
7454 C8
7455 D8
7456 D8
7480 E7
7481 D8
7482 C5
7483 E8
7484 C5
7485 E7
7511 E5
7514 E5
7532 D4
7535 C3
7536 C3
7541 C2
7561 C4
7573 C5
7602 B7
7604 A4
7606 B7
7607 B7
7691 D1
7701 B8
7702 A7
7703 A8
7705 A7
7706 C7
7707 C7
7708 C7
7709 C7
7901 C3
7903 C3
7904 C3
7991 B3
7992 B3
7993 B4
7994 A4
Page 40

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Mono Carrier (Part 1 Bottom Side)
40L04E AA 7.
Part 1
E_14480_094a.eps
130404
Page 41

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Mono Carrier (Part 2 Bottom Side)
41L04E AA 7.
Part 2
E_14480_094b.eps
130404
Page 42

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Mono Carrier (Part 3 Bottom Side)
42L04E AA 7.
Part 3
E_14480_094c.eps
130404
Page 43

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Mono Carrier (Part 4 Bottom Side)
43L04E AA 7.
Part 4
E_14480_094d.eps
130404
Page 44

A
B
C
D
E
F
G
CRT Panel
1234567891011
1331
From 1204 of
Features &
Connectivities
B2
B2
B2
From 1401 of
Line + Frame
Deflection
CRT PANEL
0330
MECHPART
3329
4329
100R3328
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ROT
SVM
VSVM
4328
F331
B
F332
G
F333
R
F334
F335
F336
1351
4330
BC_INFO
1
F351
I351
2
3
F352
4
5
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
+200VA
Vdd
Vdd
100n
BC1
BC2
2334
10n
OUT1 9
OUT2 8
I330
140V
I331
140V
100R
2V5
2V5
7330
IN11
IN22
3k77
3k75
3k77
3k75
Vdd
Vref
Vref
6
2330
188k7
A1
188k7
A2
188k7
3k77
3330 100R
2V5
IN33
3k75
Vref
2.5V
I337
Vref
THERMAL
PROTECTION
GND
4
6338
*
A3
2336
Vdd
*
BC3
*
4336
OUT3 7
BCI 5
7V
*
I332
140V
6V
4337
3337
*
9351
5351
*
+200V
10n
2335
3351
EHTb
100R
F354
2351
10u
F353
+200VA
Filament
3333
100R
3335
100R
3331
100R
2333
6333
I333
1n
BAV21
6331
I335
5330
6332
I334
BAV21
3332
1K
5352
27u
BAV21
3334
1K
3336
1K
F341
F356
F338
F339
2332
1n5
44L04E AA 7.
EHTb
1255
1
4
5
6
G
I336
F340
3354
I353
7
8
R
9
10
11
B
12
2331
GND_CRT
1K5
F331 F332 F333
500mV
/ div DC
20µs
/ div
ITEM
RGB+DISPL-21RF.28WS-EU &
RGB+DISPL-24WR.25.28BLD-EU
3328
3329
3330
3337
4328
4329
4330
4337
5351
9351
3356
10R
CRT Sockets
1256-A
1
G3
5
G1
6
CG
7
G2
8
CR
9
H1
10
H2
11
CB
12
GND
V
10n
500mV
20µs
3357
/ div DC
/ div
2354
I355
500mV
1254-A
1
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
10n
3358
20µs
EUROPE
---
---
---
--JMP
JMP
JMP
---
--JMP
1332
I357
G3
G1
CG
G2
CR
H1
H2
CB
GND
T0 CRT SOCKET
V
3n3
680p
2352
2353
/ div DC
/ div
RGB+DISPL-29RF-EU &
RGB+DISPL-24WR.28.32WR-EU
IND FXD LAL04 A 22U PM10
JMP
JMP
JMP
---
---
---
---
---
---
AQUADAG
WIRE
Blue
Green
Red
5
T0 CRT SOCKET
1352
VG2
1
7
NOT USED
FOCUS
FROM LOT, MAIN CHASSIS
CRT
EHT
LINE + FRAME DEFLECTION
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
0330 B1
1254-A B7
1255 B6
1256-A B6
1331 D1
1332 B7
1351 G2
1352 F9
2330 B3
2331 D6
2332 C5
2333 D4
2334 B3
2335 G2
2336 E3
2351 G3
2352 F7
2353 F7
2354 D6
3328 D2
3329 C2
3330 D2
3331 D4
3332 C4
3333 C4
3334 C5
3335 C4
3336 C5
3337 E4
3351 G3
3354 F5
3356 B6
3357 D6
3358 D6
4328 D2
4329 C2
4330 D2
4336 E3
4337 E4
5330 G4
5351 F3
5352 F4
6331 C4
6332 B4
6333 B4
6338 E3
7330 C2
9351 F3
F331 D2
F332 E2
F333 E2
F334 E2
F335 E2
F336 E2
F338 C5
F339 C5
F340 C5
F341 C5
F351 G2
F352 G2
F353 G3
F354 G3
F356 F5
I330 C4
I331 C4
I332 D4
I333 C4
I334 C4
I335 D4
I336 C5
I337 D3
I351 G2
I353 F5
I355 E6
I357 B7
3139 123 5889.1
1234567891011
E_14620_144.eps
280504
Page 45

CRT Panel: Eco Scavem
12
A
B
C
D
Filament
E
F
G
3139 123 5889.1
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
ECO SCAVEM
VSVM
SVM
ROT
F360
I386
9365
3365
1K0
6383
RGP10D
I381
2381
25V
100u
I390
2392
2387
4362
2391
3396
100n
3390
2386
3397
RES
I388
RES RES
45L04E AA 7.
345678910
3388
10R
3391
2389
3373
4K7
220R
100n
3389
10R
2382
2383
100n
1u0
2364
22n
2365
22n
2367
I366
100V
100nF
F381
F382
I392
3363
3366
3367
3368
820R
56K
I371
56K
820R
3
2
1
1381
2363
22u 100V
2368
100V
22n
1382
To 1470 of
7363
2SA1358
3364
3372
*
I368
I369
7364
2SC3421
I372
1361
1
2
3
TO
SCAVEM COIL
5361
RES
9361
3371
150R
2388
F361
F363
330p
F362
*
E_14620_145.eps
1K0
100n
4K7
3395
7365
BC547B
I389
I387
6363 BAV99
270R
7331
BC847B
7332
BC857B
2390
100N
K
A
6361 BAV99
K
I360
A
BAV996362
AK
AK
K
4361
RES
AK
A
3394
220R
7362
BC557B
3361
I391
2K7
I364
3398
220R
7361
BC547B
I361
I362
*
9362
3362
*
1K2
3383
7381
BC337-40
7382
BC337-40
3374
*
7366
BC857B
3381
100R
3384
10K
I383
I385
3385
3386
82K
1K0
280504
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1361 C10
1381 F7
1382 B8
2363 A7
2364 C6
2365 D6
2367 D6
2368 A7
2381 E2
2382 F6
2383 G6
2386 G2
2387 C2
2388 D9
2389 E5
2390 B3
2391 D2
2392 E2
3361 B4
3362 D4
3363 B7
3364 B8
3365 C2
3366 C7
3367 D7
3368 E7
3371 D9
3372 E8
3373 A5
3374 G4
3381 F3
3383 E4
3384 G4
3385 G4
3386 G4
3388 C5
3389 D6
3390 E3
3391 D5
3394 C3
3395 D3
3396 D2
3397 B3
3398 C4
4361 C3
4362 C2
5361 D9
6361 C3
6362 B3
6363 B3
6383 E2
7331 F3
7332 F3
7361 C4
7362 D4
7363 C8
7364 D8
7365 C3
7366 F5
7381 F4
7382 G4
9361 D9
9362 D4
9365 C2
F360 C1
F361 C9
F362 D9
F363 C9
F381 F6
F382 F6
I360 A4
I361 C4
I362 C5
I364 C4
I366 C7
I368 C8
I369 C8
I371 D7
I372 D8
I381 E2
I383 F4
I385 G4
I386 E1
I387 F3
I388 C3
I389 D3
I390 C2
I391 B4
I392 A7
1234567
8910
Page 46

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout CRT Panel (Top Side)
3139 123 5889.1
46L04E AA 7.
0330 A1
1254 A2
1255 A2
1256 A2
1331 A1
1332 A1
1351 A1
1352 A1
1361 A3
1381 A3
1382 A2
2330 A1
2351 A1
2352 A2
2353 A2
2363 A2
2364 A3
2367 A3
2368 A3
2381 A2
3331 A1
3332 A2
3333 A1
3334 A1
3335 A1
3336 A1
3351 A1
3354 A2
3356 A1
3362 A3
3364 A3
3365 A2
3366 A3
3371 A3
3373 A1
3381 A3
3390 A3
5330 A1
5351 A1
5352 A2
5361 A3
6331 A1
6332 A1
6333 A1
6383 A2
7330 A1
7361 A2
7362 A3
7363 A3
7364 A3
7365 A2
7381 A2
7382 A2
9351 A1
9361 A3
9362 A3
9365 A2
9390 A3
9391 A3
E_14480_088.eps
020404
Page 47

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout CRT Panel (Bottom Side)
47L04E AA 7.
2331 A1
2332 A2
2333 A1
2334 A1
2335 A1
2336 A1
2354 A1
2365 A3
2382 A3
2383 A3
2386 A3
2387 A2
2388 A3
2389 A2
2390 A3
2391 A2
2392 A2
3328 A1
3329 A1
3330 A1
3337 A1
3357 A1
3358 A1
3361 A2
3363 A3
3367 A3
3368 A3
3372 A3
3374 A2
3383 A2
3384 A3
3385 A3
3386 A2
3388 A3
3389 A3
3391 A2
3394 A2
3395 A2
3396 A2
3397 A3
3398 A2
4310 A1
4328 A1
4329 A1
4330 A1
4336 A1
4337 A1
4361 A2
4362 A2
6338 A1
6361 A2
6362 A3
6363 A3
7331 A3
7332 A3
7366 A2
3139 123 5889.1
E_14480_089.eps
020404
Page 48

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Side AV + Headphone Panel (PV-2)
1 2345678910
SIDE AV PANEL + HP PANEL
A
B
1277-A
*
C
D
1277-B
*
3139 123 5718.1
VIDEO IN
1250-C
*
1250-A
*
1250-B
*
2
3
1
Video_Gnd
RIGHT
8
9
7
LEFT
5
6
4
1251
LAP5100-1411F
Video_Gnd
6
1
2
3
4
5
3154
4180
75R
3155
9152
Video_Gnd
75R
9181
*
SG02
Video_Gnd
I155
SG04
RES
I152
SG03
SG01
Video_Gnd
I157
6161
Video_Gnd
RES
2173
RES
2174
BZX79-C6V8
3153
*
3151
150R
75R
3158
Video_Gnd
3152
*
47K
3150
3159
100R
3160
100R
2172
2171
SG08
*
F151
330p
SG09
*
2180
2u2 50
*
2175
9180
2u2
9175
SG10
SG11
F153
F152
F150
48L04E AA 7.
1252
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
From Main Chassis 1207
for 2X5W from 1280
for 2X10W from 1902
Features & Connectivities
from Main Chassis
1254
1232 A9
1250-A C1
1250-B D1
1250-C C1
1251 A2
1252 B5
1254 B6
1277-A C1
1277-B D1
1278 A10
1279 B10
2171 D4
2172 C4
A
B
C
D
2173 C3
2174 D3
2175 C4
2176 B8
2178 B8
2180 D4
2181 C8
3150 D3
3151 D3
3152 C3
3153 C3
3154 B2
3155 A2
3156 B8
3157 B8
3158 A3
3159 A4
3160 B4
3161 C8
4180 A2
6161 B3
9152 D3
9175 C4
9180 D4
9181 A3
F150 D4
F151 D4
F152 C4
F153 B4
F154 B7
I152 D3
I155 C3
I157 B3
I162 B7
I163 C8
I166 B7
I168 B8
I169 C8
I170 B10
I171 B10
SG01 A3
SG02 B3
SG03 D3
SG04 C3
SG08 B4
HEADPHONE
1
I166
5
4
3
F154
2
1
I162
3156
*
3157
*
2176 2178
3161
2181
I168
470pF
470pF
I163
I169
39K
1u
1232
6
5
4
2
3
7
8
9
I170
I171
1278
4
3
2
1
1279
3
2
1
E_14480_037.eps
TO
SPEAKER
TO
ECO SUB
190204
SG09 B4
SG10 B4
SG11 B4
1 2345678910
Page 49

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Side AV + Headphone Panel (PV-2) (Top Side)
49L04E AA 7.
1232 A4
1250 A3
1251 A2
1252 A1
1254 A3
1277 A2
1278 A4
1279 A4
2171 A1
2172 A2
2173 A3
2174 A2
2175 A2
2180 A1
3150 A2
3151 A2
3152 A3
3153 A3
3154 A1
3155 A1
3156 A4
3157 A4
3158 A1
3159 A1
3160 A1
6161 A1
9152 A3
9175 A2
9180 A1
9181 A1
3139 123 5718.1
Layout Side AV + Headphone Panel (PV-2) (Bottom Side)
2176 A1 2178 A1 2181 A2 3161 A2 4180 A3
2181
E_14480_038.eps
100204
3139 123 5718.1
E_14480_039.eps
100204
Page 50

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Side AV + Headphone Panel (FL-13)
1 2345678910
SIDE AV PANEL + HP PANEL (FL13)
A
B
C
1277-A
*
D
E
1277-B
*
3139 123 5823.1
1251
YKF51-5304
576
VIDEO IN
*
*
*
1
3
4
2
1250-C
1250-A
1250-B
Video_Gnd
2
3
1
Video_Gnd
RIGHT
8
9
7
LEFT
5
6
4
4180
Video_Gnd
9152
RES
3154
75R
Video_Gnd
SG04
SG03
SG01
Video_Gnd
I157
SG02
Video_Gnd
I155
2173
I152
2174
3158
6161
330p
330p
75R
BZX79-C6V8
3153
22K
3151
22K
Video_Gnd
47K
3152
47K
3150
3159
100R
3160
100R
2172
2171
SG08
F151
330p
330p
SG09
2175
2180
9180
RES
2u2
9175
RES
SG10
502u2
SG11
F153
F152
F150
50L04E AA 7.
1252
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
from Main Chassis 1207
for 2X5W from 1280
for 2X10W from 1902
from Main Chassis
Features & Connectivities
1254
1232 B9
1250-A D1
1250-B E1
1250-C C1
1251 A1
1252 C5
1254 B6
1277-A C1
A
1277-B E1
1278 B10
1279 B10
B
C
D
E
1280 D10
1281 E10
2171 E4
2172 D4
2173 D3
2174 E3
2175 C4
2176 C8
2178 B8
2180 E4
2181 D8
3150 E3
3151 E3
3152 D3
3153 D3
3154 B2
3156 B8
3157 C8
3158 A3
3159 A4
3160 C4
3161 C8
4180 B2
6161 C3
9152 D2
9175 C4
9180 E4
F150 E4
F151 E4
F152 C4
F153 C4
F154 B7
I152 E3
I155 D3
I157 B3
I162 C7
I163 C8
I166 B7
I168 B8
I169 C8
I170 B10
I171 C10
SG01 A3
SG02 C3
SG03 E3
SG04 D3
SG08 C4
SG09 C4
SG10 C4
SG11 C4
HEADPHONE
1
I166
5
4
3
F154
2
1
I162
3156
820R
3157
820R
2178
2176
3161
2181
I168
470p
100n
I163
I169
39K
1u
1232
6
5
4
2
3
7
8
9
I170
I171
1280
1
2
3
1281
1
2
3
Top Control (FL13)
Main Chassis 1682
From 1010 of
1278
4
3
2
1
1279
3
2
1
To
E_14480_132.eps
TO
SPEAKER
TO
ECO SUB
180504
1 2345678910
Page 51
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
51L04E AA 7.
Layout Side AV + Headphone Panel (FL-13) (Top Side)
Layout Side AV + Headphone Panel (FL-13) (Bottom Side)
1232 B2
1250 D2
1251 E2
1252 E1
1254 B2
1277 D2
1278 A1
1279 A2
1280 A1
1281 A2
2171 D1
2172 C1
2173 C1
2174 D2
2175 C1
2180 D1
3150 D1
3151 D1
3152 C1
3153 C1
3154 E2
3156 B2
3157 C2
3158 E1
3159 E1
3160 E1
6161 E1
9152 C1
9175 D1
9180 D1
3139 123 5823.1
E_14480_133.eps
180504
3139 123 5823.1
E_14480_134.eps
180504
Page 52

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
52L04E AA 7.
Top Control Panel (PV2)
1010 A1
1011 B3
1012 B3
1013 B2
123
E
FROM 1682
TOP CONTROL (PV2)
1010
OF
A
1014 B2
3010 A2
1
KEY_PROTN
2
3
3011 A2
3012 A2
F011
3010
3013 A3
3014 B3
RES
3011
3015 A3
3016 B3
*
F011 A2
F012 A3
3012
I013
*
I011 A2
I013 A3
3013
F012
3014
I017 B3
I018 A3
A
*
3015
I018I011
**
3016
*
Layout Top Control Panel (PV2) (Bottom Side)
3010 A1
3011 A1
3012 A1
3013 B1
3014 B1
3015 B1
3016 C1
ITEM
L03SS
L04
B
3011
3012
3013
3014
3015
3016
3139 123 5714.1
200R
430R
2K2
200R
820R
120R
150R
390R
1K8
JMP
820R
JMP
123
Layout Top Control Panel (PV2) (Top Side)
1010 A1
1011 B1
1012 C1
1013 A1
1014 A1
1013
SKQNAB
channel+
1014
SKQNAB
channel-
1011
SKQNAB
volume+
I017
1012
SKQNAB
volume-
E_14480_031.eps
190204
B
3139 123 5714.1
E_14480_032.eps
190204
3139 123 5714.1
E_14480_033.eps
100204
Page 53

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
53L04E AA 7.
Top Control Panel (FL-13)
12 3
TOP CONTROL (FL-13)
FROM 1682
OF
1010
A
B
3139 123 5825.1
OR
FROM 1281
OF
Layout Top Control Panel (FL-13)
Top
1010 A1
1011 B3
1012 B3
1013 B2
A
B
1014 B3
1015 B2
3010 A1
3011 A2
3012 A3
3013 A3
3015 A3
3017 A2
3018 A2
F011 A2
F012 A3
I011 A3
I012 A2
I013 A3
I017 B3
I018 A3
1
F011
2
3
RES
3010
3017
1K8
1015
3018
KEY_PROTN
820R
I012
1013
menu
SKQNAB
3011
150R
I011
SKQNAB
channel+
3012
1014
390R
I013
SKQNAB
channel-
3013
1011
1K8
F012
1012
SKQNAB
volume+
I017
E_14480_135.eps
3015
180504
820R
I018
SKQNAB
volume-
Bottom
12 3
3139 123 5825.1
1010 B9 1011 B3 1012 B1 1013 B8 1014 B7 1015 B5
3139 123 5825.1
3010 B6 3011 B3 3012 B4 3013 B8 3015 B10 3017 B6 3018 B6
E_14480_137.eps
180504
Page 54

SYNC
PROC.
eDRAM
512KB
RGB
MATRIX
MEM
CTRL
DISPLAY
TRIPLE
DAC
3X7BIT
FAST
RGB/YUV
I2C
PEAKING
FRAME
INSERTION
MUX
CTRL
SWITCH
PARANT
SYNC
PROC.
FRAME
GEN
CLK
SYNTH
VDDA
VSSA
ADC
8-BIT
INP
SEL
CLAMP
GAIN
CONTR
DATA
SLICER
Y/C &
SYNC
SEP.
SKEWCOMP
MUX
COLOR
DEC.
INSERT
H/V SCALER
DECIMATION
3V3
2V1
1V2
1V9
1V7
2V1
3V2
3V2
1V5
1V7
1V7
1V
-0V3
0V5
0V5
0V5
0V5
1V
0V6
1V
1V
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
9V
9V
9V
1V3
9V
3V5
0V7
3V
0V4
33V
3V
POWER SUPPLY PIP
C
D
E
F
G
1206 D4
1212 E1
1214 D4
1219 E4
1220 B11
1241 E8
2007 B10
2241 D6
2242 D7
2243 B7
2244 B7
2245 B8
2246 B8
2247 B9
2248 B9
2249 B10
2250 B10
2251 C7
2252 C7
2253 C7
2254 C7
2255 E7
2256 E7
2257 E8
2258 E8
RES
1234567891011
1234567891011
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
A
B
1R2
2259 E10
2261 E6
2262 B10
2263 C10
2264 D5
2265 E5
2271 E2
2272 E2
2273 E5
2274 E4
2275 F5
2276 F3
2277 G5
2278 G4
2279 C6
2280 C6
2501 B1
2502 B1
2503 C2
2504 B3
2505 A4
2506 A5
2507 B5
2508 B5
2509 C5
2510 C5
2511 A5
2512 B4
3010 B11
3241 D6
3243 D6
2K
3244 D7
3245 E6
3246 E7
3247 E7
3248 E7
3249 E9
3250 E9
3251 E6
3252 C10
3253 C10
3254 D11
3255 C11
3271 E3
3272 E3
3273 F4
3274 E4
3275 G3
3276 F3
3277 G4
3278 G3
3279 G5
3280 E3
3281 F4
3282 C6
3283 C6
3284 C6
3285 C6
3286 C7
3287 B6
3500 B1
3501 B1
3502 B1
3503 B1
1K0
3506
3504 B2
3505 A3
3506 A4
3507 B1
4270 E3
4271 F4
4272 G3
RES
4273 G4
4274 E6
4275 E4
4276 F5
4278 F5
4279 G5
5241 B7
5242 B7
5243 B10
5244 D6
5245 B6
5271 D2
5501 B1
5502 A4
5503 A4
5504 B5
5505 B5
5506 B3
5507 A4
6501 B3
6502 A5
6503 A5
6504 B5
7241 E7
7242 C8
7243 C6
7271 E3
7272 F4
7273 G3
7274 G4
7501 A2
1R2
7502 A4
F240 D6
F241 E6
F242 C5
F243 F6
F244 F6
F245 C5
F271 E2
F272 F2
F273 F2
F274 F2
F275 F1
F276 B11
F279 B11
F501 C1
F502 A1
F503 D6
F504 D6
F505 A5
F506 B5
F507 B5
F508 B5
I241 B7
I242 B8
I243 B9
I244 B7
I245 C7
I248 D7
I249 D7
I250 D7
I251 D7
*
I252 E7
I253 E7
I254 E9
I255 E9
I256 B6
I257 C7
I258 C6
I259 C6
I263 C10
I271 D2
I273 E4
I274 E5
I276 F4
I277 F5
I278 G4
I279 F3
I280 F5
I281 G5
I501 B1
I502 A1
I503 B1
I504 B3
I505 A3
I506 A4
I507 C4
I508 A5
I509 A5
I510 A3
HD_PIP
INTF_CVBS_IN
INTF_CVBS_OUT
2507
470u 16V
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
1n0
2505
27p
2257
27p
2258
I242
15K
3274
AT-49
20M
SB140
6504
1241
I255
1220
1
2
3
4
5
2262
3245
15K
I249
2254
10n
3247
75R
5242
10u
2273
10n
2274
I271
I252
5505
10u
I244
50V1u0
2248
75R
3010
2
3
4
F275
1214
1
2u2
3K3
3504
2272
10n
2261
16V
2501
470u
10n
2241
10n
2276
I273
I509
F507
10u
5241
2251
1u0 50V
F503
15K
3272
I250
2504
470p
10u
5243
5502
1m
50V100u
2506
100n
2255
5507
3505
2K2
I248
F243
F240
I257
3243
100R
390R
3271
10n
2247
7272
1K0
3277
3275
390R
3252
15K
3276
2u2
2279
1
2
3
4
1206
1
2
3
4
1219
4276
2280
75R
3287
F502
5506
7241
F245
4272
I508
2275
10n
2244
I507
I501
6503
BZX79-B33
3501
3502
F504
5u6
5244
I251
16V470u
2508
820p
2264
2265
100p
2259
100p
4275
I263
I278
I259
I510
I256
3244
100R
F508
3250
5K6
I503
2007
7271
2263
I504
2503
4n7
5271
1n0
5u6
3279
2511
3500
1R0
I277
2510
470u 16V
50V1u0
2253
3249 8K2
3255
3254
F501
5K6
3281
3253
2242
16V470u
I274
2509
50V10u
2271
F276
I281
I502
F244
4274
I276
10n
2256
3284
XIN1XQ
2
O2 17
O3 16
SCL6
SDA5
15SEL
VDD
72219
VREFH21
VREFL25
VREFM27
VSP
4
VSS
82320
7242
CVBS128
CVBS226
CVBS324
FSW 14
HSP
3
I2C9
IN1 11
IN2 12
IN3 13
INT10
O1 18
SDA9488X
3285
3273
390R
7243
3248
75R
1
3
2
6502
BAV99
I241
I279
10n
2252
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
3283
1212
EH-B
BC337-25
7502
I245
5K6
3278
1
3
5
6
I506
PSD10-204B
5503
I280
2502
1n0
F242
2250
50V1u0
10n
2249
4270
I254
VCC
F279
CIN_NEG
8
DCOL
4
GND
7
IS
1
SWC
2
SWE
3
TIMC
6
7501
MC34063AD
SRQ
IPK
OSC
REFERENCE
REGULATOR
5
3282
I258
2278
10n
7274
50V10u
2245
390R
3246
3507
SB140
6501
3286
1R5
3241
10u
5504
I253
5245
4271
3503
5501
10u
10n
2246
7273
2512
1n0
3251
5K6
4273
5K6
3280
4278
2277
4279
I243
F241
50V1u0
2243
CVBS1_PIP
+5V
VD
+5V
SDA
SCL
IRQ
RVOUT
BUOUT
+33V
INTF_Pb|BLUE_OUT
+5VD
GYOUT
+9V
+9V
SEL
+3.3V
+3.3V
+5VD
+5VD
+5VD
INTF_FBL
+5V
+3.3V
+5VD
INTF_Pr|RED_OUT
INTF_Y|GREEN_OUT
+5VD
+5V
+3.3V
+3.3V
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
54L04E AA 7.
Power Supply PIP Panel
ITEM PIP-EU PIP-RD+DVD-EU PIP-AP PIP+DVD-AP
1206
F505
I505
F2
TO 1219 OF
FEATURES &
CONNECTIVITIES
TO 1214 of
From 1216 of
LTI/CTI
LTI/CTI
F274
F271
F272
F273
3139 123 5821.1
To 1215 of
LTI/CTI
F506
1220
2007
2242
2262
2263
2280
3010
3252
3253
3254
3255
3282
3283
3284
3285
3286
5245
7243
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
CON BM V 4P M 2.50
CON BM V 5P M 2.5
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N
CER2 0603 X7R 10V 220N
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N
CER2 0603 X7R 10V 2U2
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
---
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5
RST CRB 1/6W A 2K2 PM5
RST SM 0603 15K PM5
RST SM 0603 5K6 PM5
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
RST SM 0603 390R PM5
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
FXDIND SM 0805 5U6 PM10
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
CON BM V 4P M 2.50
CON BM V 5P M 2.5
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N
CER2 0603 X7R 10V 220N
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N
CER2 0603 X7R 10V 2U2
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
---
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5
RST CRB 1/6W A 2K2 PM5
RST SM 0603 15K PM5
RST SM 0603 5K6 PM5
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
RST SM 0603 390R PM5
RST SM 0603 75R PM5
FXDIND SM 0805 5U6 PM10
E_14480_107.eps
NC
150404
Page 55

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Tuner IF and Demodulator PIP Panel
55L04E AA 7.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1000 D3
1002 D5
1003 D5
1004 D3
1201 C7
2001 C1
2002 C2
2003 C2
2004 C3
2005 D4
2006 D4
2010 B4
2011 B4
2201 E7
2202 C7
2203 C7
2204 C7
2205 C8
2206 C8
2207 C8
2208 C9
2209 F7
2210 F8
2211 F8
2220 B7
2221 B7
3001 C2
3002 C2
3003 B3
3004 C3
3005 E2
3006 E2
3007 D4
3008 D4
3009 E4
3201 E7
3202 E6
3203 E6
3204 C7
3205 D7
3206 C8
3207 C8
3208 D9
3210 D9
3211 D9
3212 F9
3215 F7
3216 D10
4001 E5
4002 E5
4004 C3
4208 D9
5001 C2
5002 E3
5010 A4
5220 A7
6001 C3
6002 D4
7001 E5
7201 E8
7202 C9
F001 C3
F002 D4
F003 E4
F201 E6
F202 E7
I001 C2
I002 C2
I003 C2
I004 A4
I005 D5
I006 E4
I007 E2
I201 E6
I202 C7
I203 C7
I204 D7
I205 C8
I206 C8
I207 D9
I208 D8
I209 D9
I210 F7
I213 F7
I217 A7
12345678910
TUNER IF & DEMODULATOR PIP
TUNER / IF
+5VA
+5VA
3K3
3003
3001
3002
100R
100R
I001
I002
RES
RES
2002
2001
4
SCL5SDA
VT
AS
NC
68
2
3
3006
I007
1K0
0R
3005
ITEM
1000
1003
2005
3004 --3007
3008
3009
3203
4001
4002
4004
6001
6002
7001
PIP-EU PIP-RD+DVD-EU PIP-AP PIP+DVD-AP
TUNER UV1316E/A I-4
FIL SAW 38MHZ9 OFWK3953
---
RST SM 0603 10K PM5
---
---
---
---
---
RST SM 0603 JUMP OR05
---
DIO SIG SM 1SS356 (RH)
---
---
+33V
5u6
5001
*
I003
47n
2003
9
1
VST
AGC
1000
*
VSPLL
7
+5VA
TUNER UV1316T/A I X-3
FIL SAW 38MHZ9 OFWK3953
---
RST SM 0603 10K PM5
---
---
---
---
---
RST SM 0603 JUMP 0R05
---
DIO SIG SM 1SS356 (RH)
---
---
4004
F001
3004
12
*
*
6001
100u
2004
13 14 15
GND
IF2|GND
IF1
TUNER UV1316T/A I-4
FIL SAW 38MHZ9 OFWK7257
CER2 0603 X7R 50V 10N
RST SM 0603 6K8 PM5
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5
RST CRB 1/6W A 4K7 PM5
RST SM 0603 JUMP 0R05
RST SM 0603 JUMP 0R05
DIO SIG SM 1SS356 (RH)
TRA SIG SM PDTC124ET (C)
1004
10
11
TUNER_AGC
5002
F003
---
---
I004
2010
100n
2011
+5VA
2005
*
F002
2006
10n
820n
TUNER UV1316T/A I-4
FIL SAW 38MHZ9 OFWK7257
CER2 0603 X7R 50V 10N
RST SM 0603 6K8 PM5
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5
RST CRB 1/6W A 4K7 PM5
RST SM 0603 JUMP 0R05
RST SM 0603 JUMP 0R05
DIO SIG SM 1SS356 (RH)
TRA SIG SM PDTC124ET (C)
100u
3007
I006
5010
5u6
3008
6002
3009
+5V
1
*
**
2
I005
1002
OFWK6274K
10
*
*
4001
4002
1
2
SWI
IN
ING
38
1003
3
NCGND
67
4
5
4
O1
5
O2
**
3
1
SEL_P-N
7001
*
2
---
---
---
DEMODULATOR
I201
3202
VIF1
VIF2
15K
3201
220R
I217
2220
100n
F202
2201
2221
I202
3204
3205
22n
AGC
ADJ
F201
+5VS
3203
+5VS
*
5V2
0V4
330R
1M0
1
2
2V
23
24
14
3
220u
3215
5220
5u6
2202
2203
19
VIF1
VIF2
SIF1
SIF2
TAGC
OP1
I210
1n5
I203
470n
I204
1V6
VPLL
10K
1201
2204
15
9
REF
TOP16VAGC
+5V
+5VS
4MHZ02797
22p
2205
18
2V5
AGND
7201
TDA9887
3V
3V5
I213
2209
470n
7
10n
+5VS
20
DGND
3V
F1
SCL
SDA
68R
7202
RES
4208
3212
5K6
+5VS
2208
I209
3211
100n
220R
3210
68R
CVBS1_PIP
75R
3216
3207
RES
21
3V2
SDA
CVBS
SIOMAD
AUD
FMIN
OP2
FMPLL
4
2V1
I206
AFC
47R
2207
17
3V2V
12
8
13
22
2210
10n
2211
390p
RES
I208
3208
I207
47R
3206
I205
2206
11
10
3V2
Vp
SCL
AFD
DEEM
5
6
3139 123 5821.1
12345678910
E_14480_108.eps
280504
Page 56

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PIP Panel (Top Side)
56L04E AA 7.
1000 D2
1002 C2
1003 C2
1004 D1
1201 A1
1206 A1
1212 A5
1214 B1
1219 A3
1220 B4
1241 C4
2004 C1
2011 D2
2221 B2
2243 D4
2245 B4
2248 D4
2250 C4
2251 D3
2253 D4
2271 B5
2501 B6
2506 C5
2507 D6
2508 D5
2509 C6
2510 D5
3001 C1
3002 C1
3003 C1
3006 D2
3201 B1
3203 B2
3206 B1
3207 B1
3208 B2
3210 B3
3215 C1
3243 B3
3244 B3
3247 C3
3249 B4
3250 B3
3255 B4
3505 B5
5001 D3
5010 D2
5220 B3
5241 D4
5242 B4
5243 D4
5244 B3
5271 D5
5501 A6
5502 C5
5503 C6
5504 D6
5505 C5
6501 C6
6503 D5
6504 C6
7502 B5
9280 D5
9281 C3
9282 B3
9283 B1
9284 C4
9285 B4
9286 C3
9287 C1
9288 C1
9289 B5
9290 D3
9550 B6
3139 123 5821.1
E_14480_055.eps
160204
Page 57

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PIP Panel (Bottom Side)
57L04E AA 7.
2001 D5
2002 D5
2003 D6
2005 C5
2006 C5
2007 C3
2010 D5
2201 B6
2202 B5
2203 B5
2204 B6
2205 B5
2206 B6
2207 B6
2208 B5
2209 B5
2210 B5
2211 B5
2220 B5
2241 C4
2242 C3
2244 C3
2246 C3
2247 C3
2249 C2
2252 C3
2254 C3
2255 B4
2256 C4
2257 B3
2258 B3
2259 C2
2261 B3
2262 B2
2263 C3
2264 A4
2265 B3
2272 B3
2273 C2
2274 B3
2275 C2
2276 B2
2277 C2
2278 C2
2279 B4
2280 B4
2502 B2
2503 B2
2504 B1
2505 C2
2511 C1
2512 C1
3004 C6
3005 D5
3007 C5
3008 C5
3009 C5
3010 B3
3202 B6
3204 B5
3205 B5
3211 B5
3212 B5
3216 B4
3241 C4
3245 B4
3246 B4
3248 C4
3251 B4
3252 B3
3253 B3
3254 B3
3271 B3
3272 B3
3273 B2
3274 B3
3275 B2
3276 B2
3277 C2
3278 B2
3279 C2
3280 B3
3281 B3
3282 B4
3283 B4
3284 D3
3285 D3
3286 C3
3287 B4
3500 A1
3501 B1
3502 B1
3503 B2
3504 B2
3506 B2
3507 B1
4001 C5
4002 C5
4004 C6
4050 C6
4208 A5
4250 D3
4251 B2
4252 D4
4270 B3
4271 B3
4272 B2
4273 C2
4274 B4
4275 C2
4276 C2
4278 C2
4279 C2
5002 C4
5245 B4
5506 C1
5507 C1
6001 C6
6002 C5
6502 C2
7001 C5
7201 B5
7202 B5
7241 B4
7242 C3
7243 C4
7271 B3
7272 B3
7273 B2
7274 C2
7501 B1
3139 123 5821.1
E_14480_056.eps
160204
Page 58
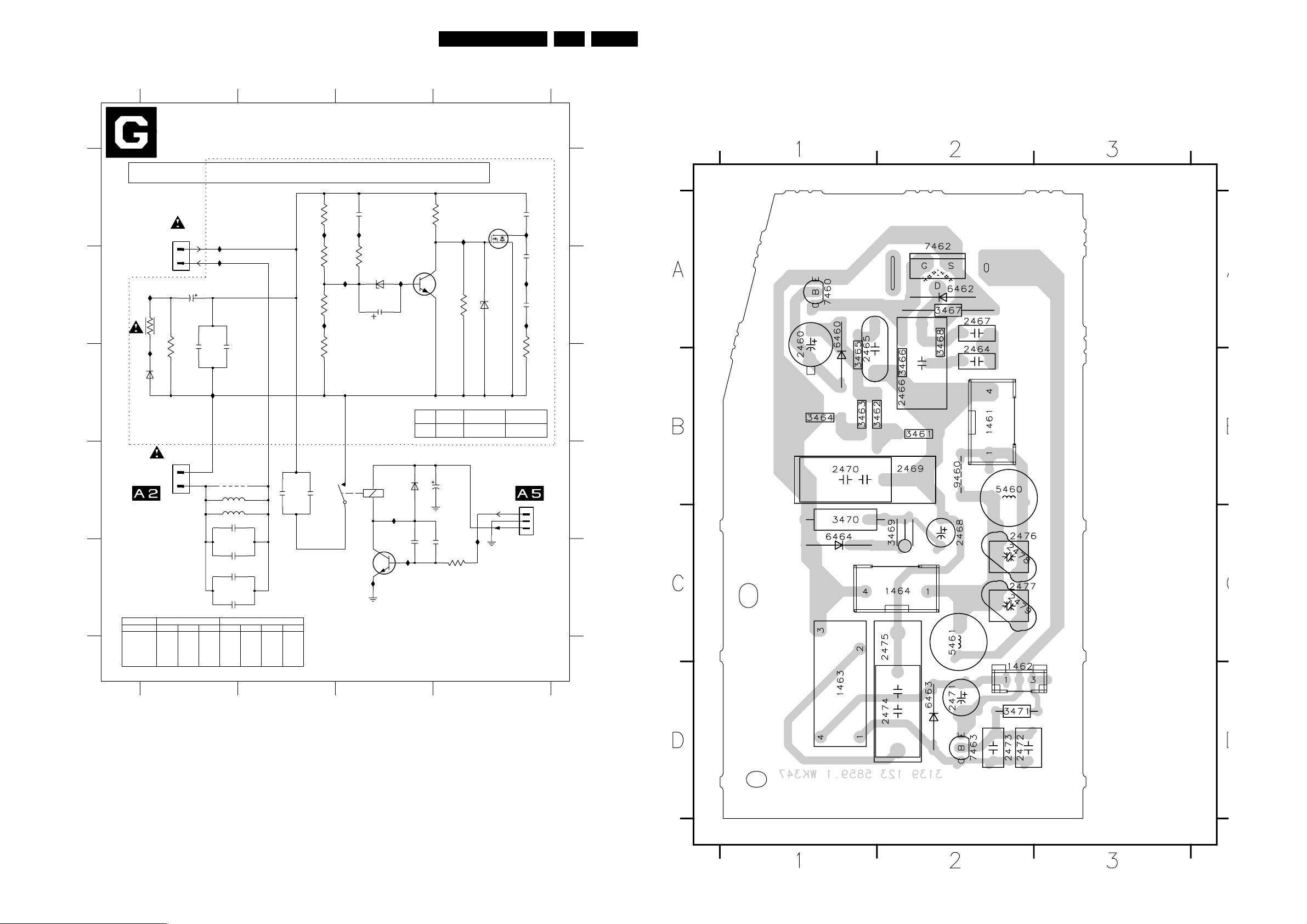
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
58L04E AA 7.
Linearity & Panorama Panel
123 4
LINEARITY & PANORAMA PANEL
INNER PIN CUSHION CORRECTION
A
TO HORIZONTAL
DEFLECTION COIL
B
C
TO 1404 OF
LINE DEFLECTION
D
E
Regions
Screen Size
2469
2470
2474
2475
9460
3139 123 5859.1
1461
I412
4R7
3469
15K
3470
I413
6464
RGP10D
1464
NA / LA /AP
28WR
28WS
680nF
560nF
---
330nF
---
560nF
--- --- --- JMP JMP JMP JMP
2468
---
---
4
1
100V2u2
2469
4
1
I415
32WR
470nF
330nF
I407
I417
*
---
---
2470
*
5460
5461
24WR
680nF
470nF
---
---
9460
2476
470n
2478
470n
2477
1u
2479
1u
Layout Linearity & Panorama Panel (Top Side)
1461 A1
1462 D4
1463 D3
1464 D1
2460 B3
2464 B4
2465 A3
2466 A4
2467 B4
2468 B1
2469 C1
2470 C1
2471 D3
2472 E3
A
2473 E3
B
C
D
E
2474 D2
2475 D2
2476 D1
2477 E1
2478 E1
2479 E1
3461 A2
3462 B2
3463 B2
3464 C2
3465 B3
3466 A3
3467 B4
3468 C4
3469 B1
3470 C1
3471 E4
5460 D1
5461 D1
6460 B3
6462 B4
6463 D3
6464 C1
7460 B3
7462 A4
7463 E3
9460 D1
I402 A3
I403 A2
I404 A4
I405 A4
I406 B3
I407 A1
I408 B3
I409 B2
I410 B4
I412 B1
I413 C1
I415 C1
I416 B4
I417 B1
I418 E3
I419 D3
I420 E4
I421 E3
3461
I403
3462
3463
I409
32WR
--470nF
330nF
---
3464
*
2474
*
22u
22u
28WS
560nF
330nF
2475
EU
28WR
---
470nF
--330nF
---
---
2465
100K
I402
6K8
3465
I406
2K7
2K2
*
23
100n
470K
6460
BZX79-C4V7
2460
10u
1463
14
I421
I408
I419
7463
BC547B
7460
BC547B
6463
2473
I418
47K
3466
3467
2K7
DIVERSITY TABLE
*
34 BMCC
470N
2466
10u
2471
1N4148
1u
10n
2472
3471
3K9
I404
29 RF PDCC
I420
7462
IRF640
6462
BZX79-C12
220N
From 1221 of
I2SD/1
2466
*
2467
I416
2464
I410
3468
34 RF PDCC
120N
3
2
1
+9V
1462
E_14480_043.eps
I405
2n2
2n2
100R
270504
1461 B2
1462 D2
1463 D1
1464 C2
2460 A1
2464 B2
2465 B1
2466 B2
2467 A2
2468 C2
2469 B2
2470 B1
2471 D2
2472 D2
2473 D2
2474 D2
2475 C2
2476 C2
2477 C2
2478 C2
2479 C2
3461 B2
3462 B1
3463 B1
3464 B1
3465 B1
3466 B2
3467 A2
3468 A2
3469 C2
3470 C1
3471 D2
5460 B2
5461 C2
6460 A1
6461 A2
6462 D2
6463 C1
7460 A1
7461 A2
7462 D2
9460 B2
123 4
3139 123 5859.1
E_14480_044.eps
100204
Page 59

LTI/CTI Interface Panel
12345678 9
LTI/CTI INTERFACE PANEL
A
B
C
D
75R
3619
3620
75R
75R
3621
E
F
3139 123 5740.1
INTF_Y|GREEN_IN
INTF_Pb|BLUE_IN
INTF_Pr|RED_IN
2613
2
2V4
100n
2614
6
2V2
100n
2615
3
2V1
100n
2616
7
2V1
100n
2617
4
2V1
100n
2618
8
2V1
100n
5
0V
15
14
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
To 1212 of
7611
TDA8601T
VIDIa1
VIDIa2
VIDIb1
VIDIb2
VIDIc1
VIDIc2
SEL
FBI1
FBI2
1214
from PIP panel
12345
for DVD/IDTV panels
I610
I612
SELECTABLE
CLAMP
SELECTABLE
CLAMP
SELECTABLE
CLAMP
SELECTABLE
CLAMP
SELECTABLE
CLAMP
SELECTABLE
CLAMP
I611
I613
B5B-EH-A
GND
INTF_FBL
1216
123
4
+9V
DECODING
3-STATE
3-STATE
3-STATE
3-STATE
B4B-EH-A
+9V
SANDCASTLE
IOCNTR
VIDOa
VIDOb
VIDOc
FBO
GND
59L04E AA 7.
1206 E8
1212 B9
1214 A2
1215 E8
1216 A3
2605 C5
2606 F4
2610 E9
2611 E9
2612 C5
2613 C1
3627
3626
1K0
4633
4634
2K2
2628
1215
I633
6625
6611
BZX384-C6V8
I619
4612
4611
4613
3V9
4636
2605
100n
2612
100n
3614
100K
9V
3632
10K
+8V
7630
BC847BW
3633
270R
6633
1K2
2633
BAS316
20
15
1
3
4
4614
3634
1K0
2634
680p
5
6
7
18
100K3615
680p
16
0V6
12
2V1
3613
100K
11
2V1
4631
10
2V1
2630
4V5
5610
2606
9612
100n
1u0
RES
3631
10K
2631 6636
BAS3161u0
*
3630
+8V
+8V
13
1
Vp
9V2
9
I614
3612
1K0
7610
TDA9178T/N1
PICTURE
IMPROVEMENT
9V2
VCC
5V1
DECDIG
0V6
SC
0V3
ADEXT1
0V2
ADEXT2
0V2
ADEXT3
0V5
YIN
0V
ADR
0V
VEE
3V9
3635
560R
6635
BAS316
Φ
4V5
3636
470R
7635
BC857BW
BZX384-C2V7
UIN
VIN
SCL
SDA
VOUT
UOUT
YOUT
SOUT
CF
2636
0V
2V
2V
3V2
3V2
2V7
2V7
2V9
470p
3637
2
10
12
13
23
24
8
9
11
14
16
17
19
21
22
2M2
3628
1K0
4632
+8V
from DVD/IDTV/PIP panels
From 1214 of
3638
330K
2638
1u0
0V
4n7
SDA
1
GND
2
SCL
3
4
From 1206 of
2626
1206
0V5
INTF_V_OUT
INTF_U_OUT
INTF_Y_OUT
INTF_FBL
SANDCASTLE
3616
RES
I623
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
7627
PMBT2369
Y_2
Pb_2
Pr_2
I621
100R
3617
100R
I624
4625
3625
2627
RES
RES
I626
I627
I628
I622
*
*
GND
I616
4610
I620
4630
I618
+9V
3610
6610
5613
+8V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1212
100R
BAS316
RES
25V
2610
100n
2611
9613
From 1212 of
I617
10u
A
B
C
D
E
F
2614 D1
2615 D1
2616 D1
2617 D1
2618 E1
2626 E8
2627 E9
2628 A8
2630 E4
2631 F4
2633 E5
2634 E6
2636 E7
2638 F7
3610 D9
3612 B6
3613 D5
3614 D5
3615 D5
3616 E8
3617 E8
3619 E1
3620 E1
3621 E1
3625 F9
3626 A8
3627 A8
3628 A7
3630 F5
3631 F4
3632 E5
3633 E5
3634 E6
3635 E6
3636 E6
3637 E7
3638 F7
4610 D9
4611 B6
4612 B6
4613 B6
4614 F6
4625 F9
4630 E9
4631 D5
4632 D7
4633 C8
4634 C8
4636 E5
5610 E4
5613 F9
6610 E9
6611 A6
6625 A7
6633 F5
6635 F6
6636 E4
7610 C6
7611 C2
7627 A8
7630 E5
7635 E6
9612 E4
9613 F9
I610 B2
I611 B2
E_14480_040.eps
200204
I612 B2
I613 B3
I614 B6
I616 D9
I617 E9
I618 F9
I619 B6
I620 E9
I621 C8
I622 C9
I623 E8
I624 F8
I626 B9
I627 B9
I628 B9
I633 F8
12345678 9
Page 60

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
60L04E AA 7.
Layout LTI/CTI Interface Panel (Top Side)
1206 A1
1212 A2
1214 A1
1215 A1
1216 A1
2611 A2
2636 A2
5610 A2
5613 A2
9612 A2
9613 A2
9614 A2
9615 A2
9616 A2
9617 A2
9618 A2
Layout LTI/CTI Interface Panel (Bottom Side)
2605 A1
2606 A1
2610 A1
2612 A2
2613 A2
2614 A2
2615 A2
2616 A2
2617 A2
2618 A2
2626 A1
2627 A2
2628 A1
2630 A1
2631 A1
2633 A1
2634 A1
2638 A1
3610 A1
3612 A1
3613 A2
3614 A2
3615 A2
3616 A1
3617 A2
3619 A2
3620 A2
3621 A2
3625 A2
3626 A1
3627 A1
3628 A1
3630 A1
3631 A1
3632 A1
3633 A1
3634 A1
3635 A1
3636 A1
3637 A1
3638 A1
4610 A1
4611 A1
4612 A1
4613 A1
4614 A2
4617 A2
4625 A2
4630 A1
4631 A1
4632 A1
4633 A2
4634 A2
4635 A1
4636 A1
4637 A1
6610 A1
6611 A1
6625 A1
6633 A1
6635 A1
6636 A1
7610 A2
7611 A2
7627 A1
7630 A1
7635 A1
3139 123 5740.1
E_14480_041.eps
100204
3139 123 5740.1
E_14480_042.eps
100204
Page 61

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
61L04E AA 7.
Front Interface Panel (FL-13)
123 4
FRONT INTERFACE PANEL (FL13)
LATAM 100V - 250V
NAFTA 110V
EUROPE 220V - 240V
AC MAINS
A
B
C
INPUT
110V/220V
FROM 1693
OF
FRONT
CONTROL
1108
1693
1
2
1
I108
2
3
4
5
6
I107
I109
I110
I120
I101
3M3
3100
*
I002
3M3
3101
*
I003
6101
**
12
LTL-10224WHCR
*
2
1
SDKVE30100
*
3113
3111
I111
9101
1110
9102
9120
RES
1K2
65
T4.0AE
4
3
FOR
ITV
9111
ONLY
I105I104
I106
3112
*
220R
1505
1
2
I112
100n
2103
2101
10u 50V
**
FROM 1505 OF
POWER SUPPLY
6102
*
TSOP1836
3
VS
1
OUT
2
GND
A
B
C
1108 A1
1110 A3
1505 A4
1693 C1
2101 C4
2102 D2
2103 C4
3100 B2
3101 B2
3111 C3
3112 C4
3113 C3
3114 D2
3115 D2
6101 C3
6102 B4
6103 D2
7101 D2
9101 A3
9102 B3
9111 C3
9112 D2
9120 B3
I002 B3
I003 B3
I101 A2
I104 A2
I105 A4
I106 A4
I107 C2
I108 C1
I109 C2
I110 C2
I111 C3
I112 C4
I119 D2
I120 D2
Layout Front Interface Panel (FL-13) (Top Side)
1108 B2
1110 B1
1505 C2
1693 A2
2101 A1
2102 A2
2103 A1
3100 B2
3101 B2
3111 A1
3112 A1
3113 A1
3114 A2
3115 A2
6101 A1
6102 A1
6103 A1
7101 A1
9101 B2
9102 B2
9111 A1
9112 A1
9120 A2
9161 C1
9162 A1
D
3139 123 5827.1
6103
7101
BC547B
9112
3115
10K
3114
BPW46
I119
2102
180K
1u
123
E_14480_131.eps
4
180504
D
3139 123 5827.1
E_14480_130.eps
270504
Page 62

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
62L04E AA 7.
Front Interface Panel (PV-2)
1234
FRONT INTERFACE PANEL
A
LATAM 100V - 250V
NAFTA 110V
EUROPE 220V - 240V
AC MAINS
B
C
D
INPUT
110V/220V
FROM 1693
OF
FRONT
CONTROL
A9
1211
1693
1
2
1
I006
2
3
4
5
6
I005
I004
I008
I010
I015
Layout Front Interface Panel (PV-2) (Top Side)
1211 D1
1231 C3
1505 A1
1606 D4
1693 A3
2691 A4
2698 A3
3500 B2
3501 B3
3691 B3
3693 B3
3694 B3
6691 B4
6692 B4
6693 A4
9001 C1
9002 D2
9685 B3
1211 B1
1231 A3
1505 B4
1606 D3
1693 D1
2691 D4
2692 E2
A
2698 D4
B
3500 B2
3501 B2
3691 D3
3693 D3
3694 C4
3696 E2
3697 E2
4001 C3
4601 E2
6691 D3
6692 C4
6693 E2
7691 E2
9001 A3
9002 B3
9695 D3
I001 B2
I002 B3
I003 C3
I004 D1
I001
I012
3500
3501
I002
I003
3M3
3M3
9001
RES
1231
T4.0AE
56
2
1
SDKVE30100
9002
RES
4001
4
3
I013
I014
1505
1
2
From 1505 OF
POWER SUPPLY
I005 D1
I006 D1
C
D
I007 D3
I008 D1
I009 D4
I010 D1
I011 D3
I012 B2
I013 B4
I014 B4
I015 D1
I016 E2
3139 123 5722.1
Layout Front Interface Panel (PV-2) (Bottom Side)
6692
TSOP1836
RES
50V10u
2698
100n
3
VS
1
OUT
2
GND
3694
3693
+6
FOR
ITV
9695
3691
330R
ONLY
I011
POWER
7691
RES
LTL-10224WHCR
6693
LTR-301
I016
6691
I007
21
L01 USA ONLY
I009
220R
2691
1606
9695 B3
9696 A3
E_14480_035.eps
100204
E
3139 123 5722.1
4601
3697
10K
3696
680K
2692
47n
123
E_14480_034.eps
4
200204
E
3139 123 5722.1
E_14480_036.eps
100204
Page 63

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Front Interface and Keyboard Panel
63L04E AA 7.
A
B
C
D
E
1234 5
FRONT INTERFACE + KEYBOARD
9101
RES
only
for ITV
F101
47n
BPW46
1110
56
T4.0AE
9102
RES
I109
RES
3113
3111
330R
RES
3110
3112
220R
3104
POWER
TS
C6
0R
I113
1106
USA
2101
9104
I105
I106
10u
2103
DVD Eject
3
4
AC MAINS
110V/220V AC
FROM 1693
OF
FRONT
CONTROL
INPUT
1693
I107
1
I108
2
3
I110
4
KEY_PROTN
5
6
LIGHT_SENSOR
F103
1108
7101
RES
1
2
3115
10K
9112
3100
3M3
3101
3M3
6101
I104
I102
I103
I111
3114
I101
680K
6103
1
2
9111
2102
I119
1
2
3
I112
100n
3105
1505
FROM 1505 OF
POWER SUPPLY
6102
TSOP1836
VS
1
OUT
2
GND
1K2
I114
1104
3106
150R
1103
channel+
3107
390R
I116I115
1102
channel-
3108
F102
1101
volume+
I120
1K8
3102
I118
volume-
820R
1100
A
B
C
D
E
1100 E5
1101 E5
1102 E5
1103 E4
1104 E4
1106 E3
1108 A2
1110 A3
1505 A4
1693 C1
2101 D3
2102 D3
2103 D4
3100 B2
3101 B2
3102 D5
3104 D3
3105 D4
3106 D4
3107 D5
3108 D5
3110 D3
3111 D3
3112 C3
3113 C3
3114 D2
3115 D2
6101 D2
6102 C4
6103 E3
7101 E2
9101 A3
9102 B3
9104 D4
9111 D3
9112 D2
F101 D3
F102 D5
F103 D2
I101 A3
I102 B3
I103 B3
I104 A2
I105 A4
I106 A4
I107 C2
I108 D2
I109 C3
I110 D2
I111 D3
I112 C4
I113 E3
I114 E4
I115 E4
I116 E5
I118 E5
I119 E3
I120 E5
3139 123 5756.1
1234 5
E_14620_146.eps
270504
Page 64

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Front Interface and Keyboard Panel (Top Side)
64L04E AA 7.
1100 D5
1101 D6
1102 D6
1103 D7
1104 D4
1106 D2
1108 B1
1110 B2
1505 B3
1693 B5
2101 D4
2102 C5
2103 D3
3100 C2
3101 C3
3102 C5
3104 D3
3105 C5
3106 C5
3107 C5
3108 C5
3110 C5
3111 D3
3112 D3
3113 D3
3114 D4
3115 D5
6101 D3
6102 D3
6103 D4
7101 C4
9101 B2
9102 B2
9103 C4
9104 D3
9111 D3
9112 C4
3139 123 5756.1
E_14620_147.eps
270504
Page 65

8. Alignments
Alignments
EN 65L04E AA 8.
Index of this chapter:
1. General Alignment Conditions
2. Hardware Alignments
3. Software Alignments and Settings
te:
No
he Service Default Mode (SDM) and Service Alignment
• T
Mod
e (SAM) are described in chapter 5 “Service Modes,
...”.
u navigation is done with the CURSOR UP, DOWN,
• Men
LEF
T, or RIGHT keys of the remote control transmitter.
8.1 General Alignment Conditions
Perform all electrical adjustments under the following
conditions:
e
• AC voltag
and frequency: 120 V_ac / 60 Hz or 240 V_ac /
50 Hz (region dependent).
• Connect the set to the Mains voltage via an isolation
transformer wit
h a low internal resistance.
• Allow the set to warm up for approximately 20 minutes.
• Measure the voltages and waveforms in relation to chassis
ground (with
the exception of the voltages on the primary
side of the power supply). Never use the cooling fins /
plates as ground.
est probe: Ri > 10 Mohm; Ci < 2.5 pF.
• T
• Use an isolated trimmer / screwdriver to perform the
alignments.
8.2 Hardware Alignments
5. SATURATION/COLOR
6. CONTRA
7. BRIGHTNE
ST to “0”.
SS to minimum (OSD just visible).
to “0”.
8. Return to the SAM via the MENU key.
9. Connect the RF
output of a pattern generator to the
antenna input. Test pattern is a 'black' picture (blank
screen on CRT without any OSD info) with a signal
strength of 1 V_pp.
10. Set the channel of the oscillos
cope to 50 V/div and the time
base to 0.2 ms (external triggering on the vertical pulse).
Ground the scope at the CRT panel and connect a 10:1
probe to one of the cathodes of the picture tube socket (see
diagram B).
11. Measure the cut off pulse during first full line after
blanking (see
figure “V_cutoff waveform”). You will see two
pulses, one being the “cut off” pulse and the other being the
“white drive” pulse. Choose the one with the lowest value;
this is the “cut off” pulse.
12. Sele
ct the cathode with the highest V_dc value for the
alignmen
t. Adjust the V_cutoff of this gun with the
SCREEN potentiometer (see figure “Top view family
board”) on the LOT to 160 V_dc, except for the 25/28BLD
picture tube (Black Line Display, for EU only); this tube
must be aligned to 140 V_dc.
13. Restore BRIGHTNESS and
CONTRAST t
o normal (= 31).
max.
V
CUTOFF
[VDC]
the frame
D
1005
ComPair
7990
1000 (TUNER)
7601
1204
9252
SDM
9275
1221
0V Ref.
E_06532_011.eps
110204
Figure 8-2 V_cutoff waveform
1504
C
1506
8.2.2 Focusin
g
1. Tune the set to a circle or crosshatch test pattern (use an
external video p
2. Choose pictur
attern generator).
e mode NATURAL (or MOVIES) with the
SMART PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter.
3. Adju
Focus
Screen
5512
B
LOT
VG2
E_14480_030.eps
130204
A
st the FOCUS potentiometer (see figure “Top view
family board”) u
ntil the vertical lines at 2/3 from east and
west, at the height of the centreline, are of minimum width
without visible haze.
Figure 8-1 Top view family board
8.2.1 Vg2 Adjustment
1. Activate the SA
2. Go to the WH
M.
ITE TONE sub menu.
3. Set the values of NORMAL RED, GREEN and BLUE to
“32”.
4. Go, via the MENU key, to the normal user menu and set
Page 66

EN 66 L04E AA8.
8.3 Software Alignments and Settings
Alignments
00028 L04EF 30.10 SDM
ERR00000
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
00028 L04EF 30.10 SAM
ERR00000
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
. Clear Clear? . AGC 30
. Options
. AKB On
. Tuner
. 2 Tuner PIP
. White Tone
. Geometry
. Audio
. NVM Editor
. ComPair on
1 00028 L04EF 30.10 CSM
2 CODES00000
3 OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
4 nnXXnnnn/nnX
5 P3C-1
6 NOT TUNED
7 PAL
8 STEREO
9CO50CL50BR50HU0
0 AVL Off BS 50
. OP1 0
. OP2 57
. OP3 140
. OP4 32
. OP5 120
. OP6 128
. OP7 0
. IFPLL 32
.CL 10
. PIP AGC 0
SAM
SAM
SAM
. Delta Cool Red -3
. Delta Cool Green -1
. Delta Cool Blue 5
. Normal Red 32
. Normal Green 35
. Normal Blue 41
SAM
SAM
SAM SAM
. Cool . Delta Warm Red 2
. Normal . Delta Warm Green -3
. Warm . Delta Warm Blue -13
SAM SAM
. Horizontal .HP 37
. Vertical .HB 31
SAM SAM
. QSS Off
. FMI On
. NICAM Alignment 63
SAM
.HSH 34
.EWW 45
.EWP 14
.EWT 27
.UCP 42
.LCP 53
.SBL OFF
.VS 37
.VSH 29
.VAM 30
.VSC 25
.ADR 0x0000 0
.VAL 0x0000 0
.Store Store ?
Figure 8-3 Service Mode overview
E_14480_143.eps
260504
Page 67

Alignments
EN 67L04E AA 8.
Enter the Service Alignment Mode (see also chapter 5 “Service
Modes, ....”). The SAM menu will now appear on the screen.
Select one of the following alignments:
• Options
uner
• T
• White Tone
• Geometry
• Audio
8.3.1 Options
Options a
featur
re used to control the presence/absence of certain
es and hardware.
How to change an Option Byte
An Option Byte represents a number of different options.
Changing
these bytes directly, makes it possible to set all
options very fast. All options are controlled via seven option
bytes. Select the option byte (OP1.. OP7) with the MENU UP/
DOWN keys, and enter the new value.
Leaving the OPTION submenu saves the changes in the
Option Byte settings. Some changes will only take effect after
the set has been
switched “of
f” and “on” with the AC power
switch (cold start).
How to calculate the value of an Option Byte
• Calculate an Option Byte value (OP
1 .. OP7) in the
following way:
• Check the status o
f the single option bits (OB): are they
enabled (1) or disabled (0).
abled
• When an option bit is en
(1) it represents a certain
value (see column “Bit value” in table below). When an
option bit is disabled, its value is 0.
l value
• The tota
of an Option Byte (decimal) is formed by the
sum of its eight option bits. The factory values are printed
on a sticker on the CRT.
Table 8-1 Option Byte calculation
Bit (value) OP1 OP2 OP3 OP4 OP5 OP6 OP7
0 (1) OB10 OB20 OB30 OB40 OB50 OB60 OB70
1 (2) OB11 OB21 OB31 OB41 OB51 OB61 OB71
2 (4) OB12 OB22 OB32 OB42 OB52 OB62 OB72
3 (8) OB13 OB23 OB33 OB43 OB53 OB63 OB73
4 (16) OB14 OB24 OB34 OB44 OB54 OB64 OB74
5 (32) OB15 OB25 OB35 OB45 OB55 OB65 OB75
6 (64) OB16 OB26 OB36 OB46 OB56 OB66 OB76
7 (128) OB17 OB27 OB37 OB47 OB57 OB67 OB77
Total: Sum Sum Sum Sum Sum Sum Sum
Option Bit Assignment
Following are the option bit assignmen
cl
usters.
ts for all software
Table 8-2 Option code overview per model
Bit Byte_0 Description
21PT5458/01
21PT5509/01
21PT5518/01
21PT5518/05
21PT5518/58
21PT5618/01
21PT5618/05
21PT5618/58
25PT4458/01
25PT4458/05
28PT4458/01
28PT4458/05
28PT5008/01
28PT5008/05
28PT4408/01
28PT4418/01
29PT5408/01
29PT5408/58
29PT5458/01
29PT5509/01
29PT5518/01
29PT5518/05
29PT5518/58
29PT5618/01
29PT5618/05
29PT5618/58
24PW6518/01
24PW6518/05
28PW5408/01
28PW6008/01
28PW6008/05
28PW6008/58
28PW6408/01
28PW6408/05
28PW6408/58
28PW6508/01
28PW6518/01
28PW6518/05
28PW6518/58
28PW6558/01
28PW6618/01
28PW6618/05
28PW6618/58
32PW6408/01
32PW6408/05
32PW6518/01
7 MVK 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 OSVE Black current measuring in
5 TFR DC transfer ratio of luminance
4 FSL Forced slicing level for vertical
3 HP2 Synchronization of OSD/Text
2 HCO EHT tracking mode 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 FMI Connection of output of QSS
0
QSS Mode of quasi split sound
Decimal 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
Hex 0505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050505050
Bit Byte_1 Description
7 SVMA Scavem On / Off 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 SAM Mode Service Align mode on/off 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 SDM Mode Service default mode on/off 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 White Pattern OnLast colour pattern status in
3 Continuous
Factory
2 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Decimal 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Hex 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Bit Byte_2 Description
7 PSNS For PAL colour enhancement in
6 Factory Mode Factory mode on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 Surf Mode Surf mode on/off 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 Child Lock
Mode
3 Last Power
Mode
2 Cable Mode Cable/Antenna mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
overscan
signal
sync
display
amplifier
amplifier
factory mode
Continuous factory mode
ES4
Child lock enabled 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Last power status of the set 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
32PW6518/05
32PW6618/01
32PW6618/05
5
0
Page 68

EN 68 L04E AA8.
Bit Byte_0 Description
1 Tuner Auto
Mode
0
Mute Status Mute status
Decimal 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
Hex 0808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080808080
Bit Byte_3 Description
7 CFA0 Comb filter On/Off
6 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 BLS Blue stretch mode
4 LNA Last
Status
3 Hotel KBD
Lock
2 Hotel Mode TV in Hotel mode
1 Wake Up
Mode
0
Radio/TV
Mode
Decimal 1
Hex 8080808080000000808080808080808080808000000000000000000080808080808080000000000000000080800000000
Bit Byte_4 Description
7 PIP QSS PIP QSS 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
6 CRA0 Coring on SVM 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 BSD Black Stretch Depth 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 BKS Black Stretch Mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 SCRSAVER
Mode
2 DVD Tray
Lock
1 LPG 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
Signal
Strength
Decimal 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Hex 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000808080000000000000000000000000000080808000000000808
Bit Byte_5 Description
7 DSK Dynamic Skin Control 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 DSA Dynamic skin tone angle 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 LLB Low level of beam current limiter 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 CBS Control sequence of beam
3 GAM Gamma control 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 MUS NTSC matrix 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 NRR No red reduction during blue
0
FFI Fast Filter
Decimal 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
Hex 0
Bit Byte_6 Description
7 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
LTI Status LTI last status
Decimal 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Hex 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Auto mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Keyboard locked 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Radio mode or TV mode
Screen saver mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Lock/Unlock DVD tray
Signal Strength Switch in MK2
current limiting
etch
str
Alignments
21PT5458/01
21PT5509/01
21PT5518/01
21PT5518/05
21PT5518/58
21PT5618/01
21PT5618/05
21PT5618/58
25PT4458/01
25PT4458/05
28PT4458/01
28PT4458/05
28PT5008/01
28PT5008/05
28PT4408/01
28PT4418/01
29PT5408/01
29PT5408/58
29PT5458/01
29PT5509/01
29PT5518/01
29PT5518/05
29PT5518/58
29PT5618/01
29PT5618/05
29PT5618/58
24PW6518/01
24PW6518/05
28PW5408/01
28PW6008/01
28PW6008/05
28PW6008/58
28PW6408/01
28PW6408/05
28PW6408/58
28PW6508/01
28PW6518/01
28PW6518/05
28PW6518/58
28PW6558/01
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1
1
1
1
0 0 0 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
06060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060606060
6
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2
8
8
8
8
8
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
2
2
2
2
8
8
8
8
1
2
2
8
8
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
8
8
8
8
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
2
2
2
8
8
8
1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
2
8
2
8
28PW6618/01
1
2
8
28PW6618/05
28PW6618/58
2
8
1
0 0 0 0 1
2
8
32PW6408/01
1
2
8
32PW6408/05
32PW6518/01
0 0 0 0
32PW6518/05
32PW6618/01
32PW6618/05
8
0
1
2
2
8
8
0
6
0
Page 69

Alignments
EN 69L04E AA 8.
• Option Byte 1 (OP1)
– OB17: PHILIPS TUNER
– OB16: FM
– OB15: LNA
– OB14: ATS (EU)
– OB13: ACI
– OB12: UK
– OB11: VIRG
– OB10: CHINA
• Option Byte 2 (OP2)
– OB27: SC
– OB26: GREEN U
– OB25: CH
– OB24: LT
– OB23: TILT
– OB22: FINE TU
– OB21: PIP PHILIPS TUNER
– OB20: HUE
• Option Byte 3 (OP3)
– OB37: EW FUNCT
– OB36: 2 TUNER
– OB35: PIP SPLITTER
– OB34: SPLITTER
– OB33: VIRT
– OB32: WIDE SCREEN
– OB31: WSSB (EU)
– OB30: ECO SUBWOOFER
• Option Byte 4 (OP4)
– OB47: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB46: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB45: ULTRA BASS
– OB44: DE
– OB43: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB42: VOLUME LIMITE
– OB41: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB40: STEREO NICAM 2CS
• Option Byte 5 (OP5)
– OB57: AV1
– OB56: AV2
– OB55: AV3
– OB54: C
– OB53: SVHS2
– OB52: SVHS3
– OB51: HO
– OB50: Reserved (value= 0)
• Option Byte 6 (OP6)
– OB67: PERSONAL ZAPPING
– OB66: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB65: FM
– OB64: CO
– OB63: ACTIVE CONTROL
– OB62: VIDE
– OB61: LIGHT SENSOR
– OB60: DUAL TEXT
• Option Byte 7 (OP7)
– OB77: TIME WIN1
– OB76: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB75: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB74: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB73: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB72: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB71: Reserved (value= 0)
– OB70: Reserved (value= 0)
ption bit definition
O
Option Byte 1 (OP1)
• OB17: PHILIP
– 0 : ALPS / MASCO compatible tuner is in use.
– 1 : Philips compatible tuner is in us
• OB16: FM
– 0 : FM radio feature
– 1 : FM radio feature
• OB15: LNA
RADIO
PNP
IN MODE
I
ANNEL NAMING
I
NING
PIP
UAL DOLBY
LTA VOLUME
I
V
TEL MODE
TRAP
MB FILTER
O TEXT
S TUNER
RADIO
ION
R
e.
is disabled or not applicable.
is enabled.
– 0 : Auto Picture Booster is not available or not
applicable.
– 1 : Auto Picture Booster
• OB14: ATS
– 0 : Automatic Tuning System (ATS
or not applicable.
– 1 : ATS feature is enabled. When ATS is enabled, it
sorts the program in an ascending order starting from
program “1”.
13: ACI
• OB
– 0 : Automatic Channe
disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : ACI feature is enabled.
• OB12: UK PNP
– 0 : UK's default Plug
not applicable.
– 1 : UK's default Plug and Play setting
– When UK PNP and V
initial setup and after exiting from menu, VIRGIN
MODE will be set automatically to “0” while UK PNP
remains “1”.
• OB11: VIRGIN MODE
– 0 : Virgin mode is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Virgin mode is enabled. Plug and Play menu item
will be displayed to p
startup of the TV when VIRGIN MODE is set to “1”.
After installation is finished, this option bit will be
automatically set to “0”.
10: CHINA
• OB
– 0 : Tuning is not for China set, or th
applicable.
– 1 : Tuning is for China set.
Option Byte 2 (OP2)
• OB
27: SC
– 0 : Soft clipping is disabled.
– 1 : Soft clipping is enable
• OB26: GREEN UI
– 0 : Green UI is disabled
– 1 : Green UI is ena
– Note: only for NAFTA region.
• OB25: CHANNEL NAMING
– 0 : Name FM Channel is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Name FM Channel is enabled.
– Note : Name FM channel can be enabled only when
M RADIO= “1”.
F
24: LTI
• OB
– 0 : Luminance Transient Improveme
or not applicable.
– 1 : LT
• OB23: TILT
– 0 : Rotate Picture is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Rotate Picture is enabled.
• OB22: FINE TUNING
– 0 : Fine Tuning for Channel Offset
– 1 : Fine Tuning for Channel Offset is enabled.
• OB21: PIP PHILIPS TUNER
– 0 : ALPS / MASCO compatible tuner is in use for
– 1 : Philips compatible tune
• OB20: HUE
– 0 : Hue/Tint Level is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Hue/Tint Level is enabled.
Option Byte 3 (OP3)
• OB
– 0 : EW function is disabl
– 1 : EW function is enabled. In this case, b
• OB
– 0 : Software selection no PIP
– 1 : Software selection with PIP
I is enabled.
applicable.
module.
37: EW FUNCTION
4:3 is allowed, Compress 16:9 is not applicable.
4:3 and Compress 16:9 are applicable.
36: 2 TUNER PIP
is available.
) feature is disabled
l Installation (ACI) feature is
and Play setting is not available or
is available.
IRGIN MODE are set to “1” at the
erform installation at the initial
is option bit is not
d.
(for Philips brand).
bled (for Magnavox brand).
nt (LTI) is disabled
is disabled or not
r is in use for PIP module.
ed. In this case, only Expand
oth Expand
PIP
Page 70

EN 70 L04E AA8.
Alignments
– Note: Only for EU/AP region for sets with PIP.
• OB35: PIP SPLITTER
– 0 : Normal Tuner in PIP
– 1 : Splitter in
– Note: Only for EU/AP region. For PIP sets and build in
with Splitter
• OB34: SP
– 0 : Normal Tuner for main chassis
– 1 : Splitter
– Note: Only for EU/AP re
• OB33: VIR
– 0 : Virtual Dolby is not applicable.
– 1 : Virtual Dolby is applicable.
• OB32: WIDE
– 0 : Softwar
– 1 : Softwar
• OB31: WSSB (EU)
– 0 : WSSB is
– 1 : WSSB is
– Note : This option bit can
SCREEN= “1”.
• OB30: ECO SUBWOOFER
– 0 : Feature is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Feature is enabled.
Option Byte 4 (OP4)
• OB47: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB46: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB45: ULTRA BASS
– 0 : Ultra B
– 1 : Ultra B
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB44: DELTA VOLUME
– 0 : Delta Volume Level is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Delta Volume Level is enabled.
• OB43: Rese
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB42: VO
– 0 : Volume Limiter Level is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Toggle Volume Limiter Level is enabled.
• OB41: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB40: STEREO NICAM 2CS
– 0 : For AV Stereo.
– 1 : For NICAM Stereo 2CS.
Option Byte 5 (OP5)
• OB57: AV
– 0 : AV1 source is not present.
– 1 : AV1 source is present.
• OB56: AV
– 0 : AV2 source is not present.
– 1 : AV2 source is present.
– Note : For EU, when AV2=“1”, both EXT2 and SVHS2
should
• OB55: AV
– 0 : Side/Front AV3 source is not present.
– 1 : Side/Front AV3 source is present
• OB54: CVI
– 0 : CVI source is not available.
– 1 : CVI source is available.
• OB53: SV
– 0 : SVHS2 source is not ava
– 1 : SVHS2 source is av
– Note : This option bit is not applicable for EU.
• OB52: SV
– 0 : SVHS3 source is not ava
– 1 : SVHS3 source is av
– Note : This option bit is not applicable for EU.
• OB51: HOTE
– 0 : Hotel mode is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Hotel mode is enabled.
PIP
in PIP tuner.
LITTER
Tun
er for main chassis
TUAL DOLBY
SCREEN
e is used for 4:3 sets or not applicable.
e is used for 16:9 sets.
disabled or not applicable.
enabled.
ass is disabled or not applicable.
ass is enabled.
rved
LUME LIMITER
1
2
be included in the OSD loop.
3
HS2
HS3
L MODE
gion.
be set to “1” only when WIDE
.
ilable.
ailable.
ilable.
ailable.
• OB50: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
Byte 6 (OP6)
Option
• OB67: PERSONAL ZAPPING
– 0 : Personal Zapping feature is disabled or not
ap
plicable.
– 1 : Personal Zapping feature is enabled.
• OB66: Reserved
efault setting is “0”.
– D
• OB65: FM TR
– 0 : FM Trap is not present.
– 1 : FM Trap is present.
– Note: Only for LATAM region.
• OB64: COMBFILTER
– 0 : 3D-combfilter is not present.
– 1 : 3D-combfilter is present.
• OB63: ACTIVE CONTROL
– 0 : Active Control feature is disabled
– 1 : Active Control feature is enabled.
• OB62: VIDEO TEXT
– 0
ap
– 1 : Video Text (DW with TXT) is enabled.
– Note: For EU only.
• OB61: LIGHT
– 0 : Light sensor feature is disabled or not applicable.
– 1 : Light sensor feature is enabled.
• OB60: DUAL TEXT
– 0 : Dual Text and Text Dual
applicable.
– 1: Dual Text and Text Dual Screen are enabled.
Byte 7 (OP7)
Option
• OB77: TIME WIN1
– 00 : The time window is set to 1.2 s.
– 01 : The time window is set to 2 s.
– Note :The time-out for all digit entries depends on this
setting.
• OB76: Reserved
– D
• OB75: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB74: Reserved
– D
• OB73: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB72 Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
• OB71 Reserved
– D
• OB70: Reserved
– Default setting is “0”.
3.2 Tuner
8.
No
te: Described alignments are only necessary when
(item 7601) is replaced.
IF PLL
This adjustment is auto-aligned. Therefo
required.
AGC (AGC take over point)
1. Set the external pattern g
signal and connect the RF output to aerial input. Set
amplitude to 10 mV and set frequency to 475 MHz.
nect a DC multimeter to pin 1 of the tuner (item 1000
2. Con
on th
e main panel).
3. Activate the
4. Go to the TUNER sub men
5. Select AGC with the UP/DOWN cursor keys.
AP
: Video Text (DW with TXT) is disabled or not
plicable.
SENSOR
efault setting is “0”.
efault setting is “0”.
efault setting is “0”.
enerator to a colour bar video
S
AM.
or not applicable.
Screen are disabled or not
the NVM
re, no action is
u.
Page 71

Alignments
EN 71L04E AA 8.
6. Adjust the AGC-value with the LEFT/ RIGHT cursor keys
until the voltage at pin 1 of the tuner lies between 3.8 and
2.3 V (default value is “20”).
7. Switch the set to STAN
DBY, in o
rder to store the
alignments.
CL (Cathode drive level)
Always set to “5”.
8.3.3 W
hite Tone
In the WHITE TONE sub
menu, the values of the black cut off
level can be adjusted. Normally, no align
ment is needed, and
you can use the given default values.
The colour temperature mode (NORMAL, COOL and WARM)
he colour (R, G, and B) ca
and t
n be selected with the UP/
DOWN RIGHT/LEFT cursor keys. The value can be changed
with the LEFT/RIGHT cursor keys. First, select the values for
the NORMAL colour temperature. Then select the values for
the COOL and WARM mode. After alignment, switch the set to
STANDBY, in order to store the alignments.
Default settings:
RMAL:
• NO
– NORMAL R= “26”
– NORMAL G= “32”
– NORMAL B= “27”
• COOL:
– DELTA COOL R= “-3”
– DELTA COOL G= “0”
– DELTA COOL B= “5”
• WARM:
”
– DELTA WARM R= “
2
– DELTA WARM G= “0”
– DELTA WARM B= “-6”
8.3.4 Geom
etry
The geometry alignments menu contains several items to align
the set, in order to obt
ain correct picture geometry.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VERT. SLOPE
VERT. SHIFT
VERT. AMPLITUDE
V.S-CORRECTION
HOR. SHIFT
HOR. AMPLITUDE
E/W PARABOLE
UPPER E/W CORNER
1. Connect an ex
ternal video pattern generator to the aerial
input of the TV-set and input a crosshatch test pattern. Set
the generator amplitude to at least 1 mV and set frequency
to 475 MHz.
Smart Picture' to NATURAL (or MOVIES).
2. Set '
3. Activate the SAM menu (see chap
ter 5 “Service Modes,
...”).
4. Go to the GEOMETRY sub menu.
5. Choose HORIZO
NTAL or VERTICAL alignment.
Now the following alignments can be p
erformed:
Horizontal
• Horizon
al Parallelogram (HP). Align straight vertical
t
lines in the top and the bottom; vertical rotation around the
centre.
t
• Horizon
al Bow (HB). Align straight horizontal lines in the
top and the bottom; horizontal rotation around the centre.
• Horizontal Shift (HSH). Align the ho
rizontal centre o
picture to the horizontal centre of the CRT.
• East West Width (EWW). Align the picture w
idth until the
complete test pattern is visible.
• East West Parabola
(EWP). Align straight vertical lines at
the sides of the screen.
o
• Upper C
rner Parabola (UCP). Align straight vertical lines
in the upper corners of the screen.
• Lower Corner Parabola (LCP). Align
straight vertical lines
in the lower corners of the screen.
• East West Trapeziu
m (EWT). Align straight vertical lines
in the middle of the screen.
HSH fo
• H60 (Delta
r 60Hz, if present). Align straight
horizontal lines if NTSC system is used (60 Hz) i.s.o. PAL
(50 Hz). Default value is “9”.
Vertical
• Service blanking
(SBL). Switch the blanking of the lower
half of the screen “on” or “off” (to be used in combination
with the vertical slope alignment).
h
• Vertical S
ift (VSH). Align the vertical centring so that the
test pattern is located vertically in the middle. Repeat the
'vertical amplitude' alignment if necessary.
e
• Vertical slop
(VS). Align the vertical centre of the picture
to the vertical centre of the CRT. This is the first of the
vertical alignments to perform. For an easy alignment, set
SBL to “on”.
• Vertical Am
plitude (VAM). Align the vertical amplitude so
that the complete test pattern is visible.
• Vertical S-Correction (VSC). Align
meaning that vertical intervals of a grid patte
the vertical linearity,
rn must be
equal over the entire screen height.
o
• Vertical Z
om (VX, if present). The vertical zoom is
added in for the purpose of development. It helps the
designer to set proper values for the movie expand or
movie (16x9) compress. Default value is “25”.
• V60 (Delta VAM for 60Hz, if present). A
lign straight
vertical lines if NTSC system (60 Hz) is used i.s.o. PAL (50
Hz). Default value is “-2”.
In the next table, you will find the GEOMET
for the d
ifferent sets.
RY default values
f the
9
10
11
12
LOWER E/W CORNER
E/W TRAPEZIUM
HOR. PARALLELOGRAM
HOR. BOW
E_06532_010.eps
110204
Figure 8-4 Geometry alignments
Page 72

EN 72 L04E AA8.
Table 8-3 Default geometry values
Alignments
Default
nment
Alig
HP (Horizontal parallelogram) 1F 31
HB (Horizontal Bow) 1F 31
HS (Horizontal shift) 1A 26
EWW (EW width) 25 37
EWP (EW parabola width) 0A 10
EWT (EW trapezium) 1A 26
UCP (EW upper corner parabola) 1E 30
LCP (EW lower corner parabola) 28 40
VSH (Vertical Shift) 1A 26
VS (Vertical slope) 25 37
VAM (Vertical amplitude) 1E 30
VSC (Vertical S-Correction) 19 25
8.3.5 Audio
N
o alignments are needed for the audio sub menu. Use the
ven default values.
gi
QSS (Quasi Split Sound)
• For NICAM/2CS sound system (EU/AP, except for
AP
NTSC), set to “On”.
• For A
• For all other sets (NAFTA/LATAM/AP-NTSC), set to “Off”.
V-Stereo sound system (sets without NICAM), set to
“O
n”.
values
ex)
(h
Default
values
(dec)
MI (Freq. Modulation Intercarrier)
F
• For NICAM/2CS sound system (EU/AP, except for
AP
NTSC), set to “On”.
• For AV-Stereo sound system (sets without NICAM), set to
“Off”.
• For dBx/non-dBx soun
NICAM Alignment
• For sets with NICAM/2CS (EU/AP, except for AP-NTSC)
soun
d system, set to “79”.
• For all other sets (NAFTA/LATAM/AP-NTSC), set to “63” (=
don’t care).
d systems, set to “On”.
Page 73

Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
EN 73L04E AA 9.
9. Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
Index of this chapter:
1. Introduction
2. Power Supply
3. Deflection
4. Control
5. Tuner and IF
6. Source Selection
7. Video Proc
8. Audio Proc
essing
essing
9. Picture in Picture (PIP)
10. Abbreviations
11. IC Data Sheets
tes:
No
• Only
new (not recently published) circuits are described in
th
is chapter. For the other circuit descriptions, see the
L01.1/M8 Service Manual.
he descriptions below are a co
• T
py from the L04U manual,
therefore sometimes a reference is made to region specific
terminology or chassis (like the M8). Only the PIP
description is new.
igures can deviate slightly from the a
• F
ctual situation, due
to different set executions.
• For a good understanding of the following circuit
scriptions, please use the diagrams in sections “Block
de
Diagrams, ...”, and/or “Electrical Diagrams”. Where
necessary, you will find a separate drawing for clarification.
9.1 Introduction
The "L04" chassis is a global TV chassis for the model year
2004 and is used for TV sets with large screen sizes (from 21
to 36 inch), in Super Flat and Real Flat executions (both in 4:3
and 16:9 variants).
There are three types of CRT namely the 100 degrees, 110
degrees and Wide
Screen CRT
• The 100 deg. 4:3 CRT is
not need East/West Correction (except when used in AP
regions), therefore the corrections needed are Horizontal
Shift, Vertical Slope, Vertical Amplitude, Vertical SCorrection, Vertical Shift, and Vertical Zoom for geometry
corrections.
he 110 deg. 4:3 CRT comes with East/West Cor
• T
In addition to the parameter mentioned above, it also
needs the Horizontal Parallelogram, Horizontal Bow,
Horizontal Shift, East/West Width, East/West Parabola,
East/West Upper and Lower Corners, and East/West
Trapezium correction.
he Wide Screen TV sets ha
• T
110 deg. 4:3 CRTs and also have additional picture format
like the 4:3 format, 16:9, 14:9, 16:9 zoom, subtitle zoom,
and the Super-Wide picture format.
In comparison to its predecessor (the L01.1/M8
has the following (new
• Audio:
The sound processor is part of the UOC processor
) features:
(called “Hercules”).
• Video: Enhanced video features, video
Control.
ontrol:
• C
Comparable to L01.1/M8 (e.g. Dual clock, I/O
mapping, I/O switching).
• Power Supply: Adapted to supply the
enable 0.5 W Standby power dissipation. Also provisions
are made for future extensions like DVD and iDTV.
The standard architecture consists of a Main pane
"family board"), a Picture Tube panel, a Side I/O panel, and a
Top Control panel. The Main panel consists primarily of
conventional components with some surface mounted devices
in the audio and video processing part.
.
raster-correction-free and does
ve all the correction of the
drivers, and Active
Hercules IC, and to
rection.
), this chassis is
l (calle
d
The functions for video/audio processing, microprocessor (P),
and CC/T
eletext (TXT) decoder are all combined in one IC
(TDA1200x, item 7200), the so-called third generation Ultimate
One Chip (UOC-III) or “Hercules”. This chip is mounted on the
“solder” side of the main panel, and has the following features:
• Control, small signal, mono/stereo, an
d exte
Video switching in one IC.
• Upgrade with digital sound & vide
• Alignment free IF, including
• FM sound 4.5/5.5/6.0/6.5,
o processing.
SECAM-L/L1 and AM.
no traps/bandpass filters.
• Full multi-standard color decoder.
• One Xtal referenc
e for all functions (microprocessor, RCP,
TXT/CC, RDS, color decoder, and stereo sound
processor).
The tuning system features 181 channels wit
display. T
he main tuning system uses a tuner, a
microcomputer, and a memory IC mounted on the main panel.
The microcomputer communicates with the memory IC, the
oard,
customer keyb
remote receiver, tuner, signal processor IC
and the audio output IC via the I2C bus. The memory IC retains
the settings for favorite stations, customer-preferred settings,
and service / factory data.
s
The on-screen graphics and clo
ed caption decoding are done
within the microprocessor where they are added to the main
signal.
P
The chassis uses a Switching Mode
ower Supply (SMPS) for
the main voltage source. The chassis has a 'hot' ground
reference on the primary side and a cold ground reference on
the secondary side of the power supply and the rest of the
chassis.
9.2 Power Supply
9.2.1 Block Diagram
Vbatt (to deflection & DVD interface board)
FILTER &
SWITCH
Degaussing Supply (V_DG)
Derived from =Vaudio
MH COIL
RELAY
DEGAUSS
RECTIFIER
MAIN SMPS
AUX SMPS
Figure 9-1 Block diagram power supply
Stdby_con signal
The Hercules generates this signal. This line is
under normal operation and in semi-Standby of the TV, and is
“high” (3.3 V) during Standby.
Power_down signal
The AUX SMPS generates this signal. It is logic “h
under normal operation of the TV and goes “low” (0 V) when the
AC power (or Mains) input voltage supply goes below 70 V_ac.
B (Hercules port)
This port is used to switch the AUX SMPS output V_aux “On/
Off”. This is required for DVD and iDT
-Vaudio
+Vaudio
+6V (from AUX SMPS for Stdby feedback)
Stdby_Con (from HERCULES)
Power_Down (to HERCULES)
+3V (to derive HERCULES supply 1.8V)
+6V (to derive HERCULES & TUNER)
supply +5V & +3.3V)
Vaux (for IDTV)
B (connected to HERCULES port B to
switch ON/OFF Vaux)
(for future extensions).
V
nsive Audio/
h on-screen
E_14480_072.eps
logic “low” (0 V)
igh” (3 .3 V)
120504
Page 74

EN 74 L04E AA9.
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
9.2.2 Timing Diagrams
Power ON - To Standby - Out of
Power ON
3, 3.3, 6V
POWER_DOWN
STDBY
+1V8 EXT.
Stdby_con
Vbat, Vaudio
STB bit
VT_supply
PIP Supplies
Relay status
Normal
+5V
10mS
B
Closed
2s(ref)
200ms 100ms(ref)
1s(ref)
To Standby
Standby - Power OFF
Out of Standby
Standby mode
Open
800ms
200ms
Normal
2s(ref)
Figure 9-2 Timing diagram Standby
Power ON - To Semi Standby - Out of Semi Stand
Power OFF
Power ON
3, 3.3,6V
STDBY
+1V8 ext
Stdby_con
Vbat, Vaudio
STB bit
VT_supply
+5V
PIP Supplies
B
Relay status
Normal
10mS
Closed
200ms 20ms (ref) 10ms(ref)
1s(ref)
2s(ref)
To Semi Standby Out of Semi Standby
Semi Standby Normal
Open
800ms
Figure 9-3 Timing diagram Semi Standby
9.2.3 Startup Sequ
ence
When the set is connected to the AC power, the rectified line
voltage (via winding 4-5 of
L5531 connected to pin 14 of
IC7531) will start the internal voltage source to charge the V_cc
capacitor (C2532). The IC starts to switch as soon as the V_cc
reaches the V_cc start level of 9.5 V. This supply is
automatically taken over by winding 1-2, as soon as the V_cc
is high enough, and the internal supply source will stop (for high
efficiency switching).
Power off
20ms(ref)
Power OFF
Perform hard-reset
10ms(ref
10ms(ref)
E_14480_073.eps
by -
under start_up
Perform
sequence for details.
Hard-reset
10ms(ref)
E_14480_074.eps
Pin Symbol Description
12 Sense This pin contains three different functions.: 1) Dectection of soft
14 Drain This pin is connected to the drain of the switch or center tap of
start, protection levels of 2) OCP, and 3) SWP.
the transformer. It contains three functions: 1) M-level (mainsdependent operation-enabling level), 2) Supply for star t- up
current, and 3) Valley detection.
As C2532 of IC7531 is charged, it will also start to charge the
(C2511) of IC7511. Via resistor R3519 and
V_cc capacito
r
C2511, the TEA1506 starts to switch as soon as the V_cc
voltage reaches the V_cc start level of is about 11 V. The V_cc
voltage is automatically taken over by the main transformer
L5512 (winding 2-3) when the V_cc is high enough (when this
voltage is even higher than the voltage on C2511, there is no
current flow from C2532 to C2511 due to diode D6512).
Table 9-2 Pinning overview TEA1506
200204
9.2.4 Stan
200204
Pin Symbol Description
2 Vcc This pin is connected to the supply voltage. When this voltage
is high (Vcc_start level, about 11 V), the IC will start switching.
When the voltage is lower than Vcc_uvlo (about 8.7 V), the IC
will stop switching.Note: This pin is not self supplied by internal
source like in TEA1507
3 Gnd This pin is Ground of the IC.
6 Ctrl This pin is connected to the feedback loop. The pin will control
7 Demag This pin is connected to the Vcc winding of 5512. It co ntains
the "on" time between 1 V to 1.5 V.
three functions: 1) During magnetisation, the input voltage is
sensed to compensate OCP level for OPP, 2) During
demagnetisation, the output voltage is sensed for OVP and 3)
a comparator is used to prevent continuous conduction when
the output is overloaded.
9 Sense This pin contains three different functions: 1) dectection of soft
start, protection levels of 2) OCP, and 3) SWP.
11 Driver This pin will drive the (MOSFET) switch.
12 HVS This is High Volt Spacer (n.a.)
14 Drain Connected to the Drain of the external MOSFET switch, th i s i s
db
In this mode, IC7511 (TEA1506) will be totally disable
the input for valley sensing and initial internal supply.
y Mode
d. So
there is no voltage on the main transformer output. But IC7531
(TEA1523) will still work and will provide the necessary output
voltages (6V -> 5V, 3.3V, 3V -> 1.8V) to the Hercules (IC7200).
Table 9-3 PSU voltage overview
Voltage Normal operation Stdby mode
V_batt 130 - 143 V 0 V
V_audio +/- 15.5 V 0 V
+6V 6 V 6 V
+3V 3 V 3 V
Stdby_con 0 V 3.3 V
Table 9-1 Pinning overview TEA1523
Pin Symbol Description
2 Gnd This pin is Ground of the IC.
3 V_cc This pin is connected to the supply voltage. An internal current
5 RC Frequency setting
6 REG This pin is connected to the feedback loop. The pin contains two
11 Demag This pin is connected to the V_cc winding of 5531. It has three
charges the V_cc capacitor (2532), and the start-up sequence
is initiated when this voltage reaches a level of 9.5 V. Note: The
output power is disabled when the voltage gets below 9 V
(UVLO). Operating range is between 0 to 40 V.
ns: 1) Between 1 to 1.425 V it controls the "on" time. 2)
functio
Above the threshold of 3.5 V, it is possible to initiate "burst
mode" standby.
functi
ons: 1) During Magnetisation, the input voltage is sensed
to compensate OCP level for OP P. 2) During demagn etisation,
the output voltage is sensed for OVP and 3) A comparator is
used to prevent continuous conduction when output is
overloaded.
9.3 Deflection
9.3.1 Synchronization
Before the Hercules (IC7200) can generate horizontal drive
pulses, the +3.3
start up command of the microprocessor (via I2C), the
Hercules outputs the horizontal pulses. These horizontal
pulses begin “initially” with double line frequency and then
change “gradually” to line frequency in order to limit the current
in the line stage (slow-start).
The VDRA and VDRB signals are the bala
(sawtoot
the Hercules). These output signals are balanced, so they are
less sensitive to disturbances.
V supply voltages must be present. After the
nced output currents
h shaped) of the frame oscillator (pins 106 and 107 of
Page 75

Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
EN 75L04E AA 9.
There is a current source inside the UOC at pin 102. This
pumps energy in the capacitor connected to this pin producing
a pure saw tooth. The vertical drive signals and the E/W
correction signal are derived.
Pin 108 is the East-West drive (or AVL), and it is a single ended
current output. T
EHT” from this pin is available by setting the HCO bit to “1”.
The Phase-2 Compensation available at pin 113 gives frame
correction for high beam curr
signal is used to correct the phase of the picture from the
horizontal drive signal.
Pin 63 is the SANDCASTLE output (contains all sync info) and
HORIZONTAL FLYBACK (HFB) input.
o
als
Pin 97 is the EHT tracking/over-voltage protection pin. T
HCO bit can switch on the tracking on EW. If the voltage at pin
97 exceeds 3.9 V, the over-voltage protection will be activated
and the horizontal drive is switched “off” via a slow stop.
9.3.2 Ho
rizontal Deflection
here are several executions (depending on the CRT):
T
• Sets with no
horizontal deflection is based on the quasi-diode
modulation circuit. This horizontal deflection circuit
supplies the deflection current and auxiliary voltages from
the LOT.
• Sets with Eas
horizontal deflection is based on a diode modulator with
east-west correction. This horizontal deflection circuit
supplies the deflection current and auxiliary voltages from
the LOT.
• Sets with d
of the horizontal deflection is based on a diode modulator
with dynamic east-west correction for picture tubes with
inner pincushion. This horizontal deflection circuit supplies
the deflection current and auxiliary voltages from the LOT.
Basic Principle
During a scan period, either the Line T
conduct to ensure a constant voltage over the deflection coil
(that results in a linear current). During the flyback period, the
Line Transistor stops conducting, and the flyback capacitor(s)
together with the inductance of the deflection coil creates
oscillation.
First Part of Scan
Pin 62 of the UOC delivers the horizontal drive signal for the
Line Output stage. T
frequency. L5402 is the flyback drive transformer. This
transformer de-couples the line output stage from the UOC. It
has a direct polarization. The flyback drive circuit works with
the start-up supply taken from +6V of the Aux supply (and
subsequently taking from VlotAux+9V). When the H-drive is
high, TS7404 conducts, and transformer L5402 starts to store
energy. The base of the line transistor TS7405 is low and
therefore blocks. The current in the deflection coil returns from
diode D6404.
Second Part of Scan
When the H-drive is low, T
energy that is stored in the transformer will transfer to the
secondary, making the base of the Line Transistor high. Then
the Line Transistor starts to conduct. The current in the
deflection coil returns from the transistor in another direction.
Flyback
At the moment the H-drive becomes high, the base of the Line
ansistor becomes low. Both the Line Transistor and the
r
T
Flyback Diode will block. There is an oscillation between the
flyback capacitor C2412 and the deflection coil. Because of the
inductance of the LOT, the Line Transistor cannot stop
he correction for “horizon
ents. The phase compensation
East-West correction. The principle of the
t-West correcti
ic East-West correction. The principle
ynam
his signal is a square pulse of line
S
7404 does not conduct, and the
tal width for changed
on. The principle of the
ansistor or diode(s)
r
he
conducting immediately. After the Line Transistor is out of
conduction, the flyback pulse is created. The flyback capacitor
charges until the current in the deflection coil reduce to zero.
Then it discharges through the deflection coil and the deflection
current increases from the other direction. The flyback diode
conducts and is back to the first part of the scan.
Linearity Correction
Because the deflection coil has a certain resistance, a picture
out any linearity issues cann
with
linearity coil to compensate for this resistance. It is a coil with a
pre-magnetized core. This correction is called linearity
correction.
Horizontal S-Correction
Because the electronic beam needs to
to both sides of the screen than the center, the middle of the
screen would become narrower than both sides. To prevent
this, a parabolic voltage is applied across the deflection coil
during scan. To create this parabolic voltage, a capacitor called
S-cap (C2417/C2418) is used as a voltage source during scan.
The sawtooth current of the deflection through this capacitor
creates the required parabolic voltage. This correction is called
S-Correction.
Mannheim-Circuit
When the EHT is heavily loaded with a bright line, the flyback
time can be
scan delays a bit causing a DC-shift to the right in the next line,
which would create a small spike on the S-cap. This spike
oscillates with the inductance of the deflection coil and the
primary of LOT. The result is visible in vertical lines under
horizontal white line. This is called the Mannheim-effect.
To prevent this from happening, a circu
circuit is added. This consists of C2415, R3404, R3417 and
D6406. During the scan, C2415 is charged via R3417. During
the flyback, the S-correction parabola across the S-Cap
C2417/C2418 is in its most negative, and D6406 conducts.
Thus, C2415 is switched in parallel to C2417/C2418 during
flyback. As C2415 is much larger than C2417/C2418, the
voltage across C2415 reduces the Mannheim-effect oscillation.
Class D East-West Driver
To reduce the power loss of the
amplifier, a class-D East-West circuit is used. To achieve this,
the East-West parabola waveform EW_DRIVE from the
Hercules (frame frequency) is sampled with a saw tooth (line
frequency) taken from the line aux output. Then a series of
width-modulated pulses is formed via two inverted phase
amplifiers, filtered by an inductor, which then directly drive the
diode modulated line circuit.
East-West Correction
To achieve a good geometry, dyn
The design is such that the tube/yoke needs East-West
correction. Besides that, an inner pincushion is present after
East-West correction. The line deflection is modulated with a
parabolic voltage (frame frequency). In this way it is not so
much at top and bottom, and much more in the middle.
Upon entering the picture geometry menu in the SAM mode,
the follow
• EWW: East West Width.
• EWP: East West Parabola.
• UCP: Upper Co
• LCP: Lower Corner Parabola.
• EWT: East West Tr
The East-West drive circuit realizes
be changed by a remote control. All changed data will be
stored into the NVM after the geometry alignment.
increased a b
ing corrections will be displayed.
rner Parabola.
apezium.
ot be expected. L5401 is the
a longer distance
travel
it in this situation. As a result, the
t called Mannheim-
i
normal used linear East-West
mic S-correction is needed.
a
them all. The settings can
Page 76

EN 76 L04E AA9.
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
Panorama
For Wide Screen sets, the S-correction of the picture has to
dapt between the different picture modes. In particular,
a
between 16:9 Wide Screen and 4:3 picture modes. This is
achieved with the (separate) Panorama circuit (see diagram
“G”). A signal (I2SDI1) from the UOC controls the state of
TS7463. When in the normal 16:9 Wide Screen mode, the
signal is “low” and therefore TS7463 is switched “off”.
When the 4:3 mode is selected, this signal from the UOC is
ulled “h
p
Panorama panel is subsequently turned “on” and, in effect,
paralleling capacitor C2475/C2474 to the S-Cap C2469/
C2470. This changes the overall effective S-correction. The
relay is switched “on” in 4:3 and Superwide picture modes.
9.3.3 A
T
d
the LOT:
• +
• +11V: This supplies the frame amplifier.
• -12V: This supplies the frame amplifier.
• 50V: This supplies t
• Filament: This supplies th
• VideoSupply (+200V from primary side
Notes:
• The V_T
• The EHT voltage
9.3.4 B
T
components R
EHT_info characteristic. The voltage across C2412 varies
when the beam current changes. This EHT_info is used to
compensate the picture geometry via pin 97 of the Hercules
when the picture changes rapidly, and compensate the phase
2 loop via pin 113 of the Hercules. Also from the EHT_info line,
a BCL signal is derived and sent to the Hercules for controlling
the picture’s contrast and brightness.
When the picture content becomes brighter,
• Geometry distortion due to the impedance of the LOT
• Picture bl
Because of the above mentioned, we will need a circuit for
Beam
(EHT_info). These two circuits derive the signal from the
picture tube current info through LOT pin 10.
BCL
• Wh
• When it reaches 1.7 V, then the BRIGHTNESS gain limit
• Wh
Components TS7483, R3490, R3491, R3492, and C2483 are
fo
pattern).
Components R3454, D6451, D6450, C2453, R3493, and
C2230 are for avera
R3493 also control the timing where average beam current
limiting is more active or less active.
igh”, switching TS7463 “on”. The relay 1463 on the
uxiliary Voltages
he horizontal deflection provides various auxiliary voltages
erived either directly or indirectly from the secondary pins of
9V: This supplies the Hercules’s fly
he frame amplifier.
e heater pins of the picture tube.
supplies the RGB amplifier and Scavem circuit at the CRT
panel.
vo
ltage (to tuner) is drawn from V_batt.
Transformer (LOT). The Focus and Vg2 voltages are
created with two potentiometers integrated in the
transformer.
eam Current
he beam current is adjusted with R3451 and R3452. The
causing the EHT
Current Limiter (BCL) and EHT compensation
en the BCL pin voltage goes to 2.8 V, the Hercules will
t to limit CONTRAST gain.
star
t to react.
will star
en BCL pin voltage goes to 0.8 V, the RGB will be
blan
ked.
r fast beam current limiting
is generated by the Line Output
3473, R3453 and C2451 determine the
to drop.
ooming due to the picture characteristics
(e.g. with a Black-to-White
ge beam current limiting. C2453 and
back driver.
of LOT): This
it will introd
uce:
EHT_info
The “PHI2 correction” is to correct the
the Line Output Transistor, which is causing geometry
distortion due to brightness change.
Line EHT_info is to correct the geometry distortion due to EHT
deviation.
Both of them feedback through the EHTO and PH2LF pin, and
ct the
corre
Power Down
The power down connection is for EHT discharge during AC
Power
trigger the X-ray protection circuit via a 2fH soft stop sequence.
The Hercules bits OSO (Switch Off in Vertical Over scan) and
FBC (Fixed Beam Current Switch Off) will discharge the EHT
with 1mA cathode current at over-scan position.
During switch-off, the H_out fre
and the duty cycle is set to 25% fixed, during 43 ms. The RGB
outputs are driven “high” to get a controlled discharge of the
picture tube with 1 mA during 38 ms. This will decrease the
EHT to about half the nominal value (= safety requirement).
When bit OSO is set, the white spot/flash during switch-off will
be written in overscan and thus will not be visible on the screen.
Careful application must guarantee that the vertical deflection
stays operational until the end of the discharge period.
9.3.5 DAF
The Dynamic Astigmatic Focus (DAF)
34RF sets only. It provides vertical DAF and horizontal DAF.
Both of the parabola signals are derived through integration by
using chassis available signals:
• T
• T
Both of the parabolas are added on the output stage through
adder TS7402 and TS7403
drives TS7401 and is amplified by pull up resistor R3411.
D6401 and C2405 provide the rectified supply voltage.
9.3.6 X-ray Protectio
The
uses it to trigger TS7481 w
biased at “off” condition by D6480, R3482, and R3483 during
normal operation. When the EHT goes too high, the voltage
across R3482 will tend to increase as well, while the voltage
across D6481 is fixed. Up to certain level (triggering point),
TS7481 will be “on” and will force the EHT_info > 3.9 V. The
chassis will be shut down through a soft stop sequence.
9.3.7 Vertical D
The
has the advantage f
was used.
The Frame differential drive signal from the Hercules comes
from
them into a voltage, and feed them into the differential amplifier
TS7455 and TS7456. The output of TS7456 is input to the next
amplification stage of TS7452. Finally, TS7451 and TS7453
deliver the Vertical yoke current to the coil and feedback
through the sensing resistors R3471 and R3472.
D6458 and TS7454 are used to bias TS7451 and TS7453, to
get rid
the screen center.
The negative supply is from -12V and the
supply is from +12V through D6459. The flyback supply is
derived from D6455, D6456 and C2456. This circuit is a voltage
doubler, which stores energy in C2456 during the Line flyback
geometry through the East-West circuit.
“Off” state. In the Hercules, if EHT_info > 3.9 V, it will
he vertical parabola is using RC integration (via R3403
and C
2401) on the Frame sensing resistor saw tooth
(Frame_FB).
he horizontal parabola is obtained by 2 RC integration
(R3409, R3
X-ray protection circuit rectifies the filament voltage and
Frame stage consists fully of discrete components. This
a current source. Resistors R3460 and R3461 convert
o
410, C2402, C2403) on the +9V LOT output.
. The collector of TS7402 emitter-
n
hen the EHT is too high. TS7481 is
eflection
or better flash behavior than when an IC
f zero crossovers, which can cause horizontal lines at
storage time deviation
quency is doubled imme
ci
rcuit is required by
positive scannin
of
diately
g
Page 77

Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
EN 77L04E AA 9.
period and delivers the energy to C2465 during the Line
scanning period. Throughout the Frame period, the charging
and discharging of C2456 works alternatively. However, at the
first half of the Frame scanning, TS7451 is “on” and consumes
all the charge from C2456. When entering 2nd half Frame
period, TS7451 is “off”, so C2456 will gradually charge up to the
required flyback supply.
C2463, R3464 and D6457 are for boosting the base voltage of
S
7451 during the flyback period and the 1st half Frame period
T
as well. C2463 is charged by D6457 during the 2nd half
scanning. R3467 and R3468 are for oscillation damping.
the
The V_guard protection is to protect
Frame stage if a fault
condition happens. The V_guard will sense the pulse with
voltage > 3.8 V and period < 900 us. Any signal out of this
range will be considered as fault, and the chassis will be shut
down.
9.3.8 T
ilt and Rotation
he rotation control signal is a PWM output from th
T
filtered by R3252, R3246, R3259 and C2259. The DC voltage
after filtering at C2259 will be amplified by R3245 (Main Board)
and R3390 (CRT panel).
The output stage functions similarly as in L01.1/M8 with
IC TD
rotation
A8941P. TS7331/TS7382 and TS7332/TS7381
will function alternatively corresponding to the rotation setting.
9.3.9 CRT panel
T
he RGB amplifier stage is exactly the same as in L01.1/M8.
ver, the RGB amplifier IC has been changed to
Howe
TDA6107AJF or TDA6108AJF. The “A” indication is with gain
of “80” rather than “50” in L01.1/M8. The diode D6332 used in
the former chassis, to solve the bright screen during start up, is
not required because this IC has the error correction
implemented.
Scavem
ed to enhance the
In certain versions, the Scavem feature is u
s
sharpness of the picture. The RGB signals are first
differentiated and subsequently amplified before feeding to an
auxiliary coil known as the SVM coil. The current, flowing
through the SVM coil during the picture intensity transients,
modulates the deflection field and thus the scan velocity.
During the first half of the intensity in
crease,
is increased (thus decreasing the current density by spreading
it on a wider area). During the second half of the intensity
increase, the scan velocity is decreased (increasing the current
density by concentrating it on a smaller area). The increasing
current density transition is sharpened. A decreasing current
density transition is processed in a similar way and is also
sharpened.
In this chassis the SCAVEM signal is different from its
predecessor b
ecause the H
ercules generates the differential
SCAVEM signal inside the IC.
The supply of the SCAVEM is taken from V_bat through a 1k5
ared w
/ 5 W resistor. Comp
ith the L01.1/M8, this has the
advantage of getting better performance for the pattern with
tremendous SCAVEM current (like V_sweep). In this former
chassis, because the supply was taken from the 200 V through
a 8k2 / 5 W resistor, the supply dropped significantly during a
large SCAVEM current. In this chassis, the drop due to the
pattern will be less because of the lower supply voltage
impedance.
In the Main Board, 1st stage amplification is taken care by 7208
7) lo
with the pull up resistors (3361, 338
cated in the CRT panel.
TS7361 and TS7362 is the current buffer delivering the current
output stage. T
to the
he diode D6361 is to lightly bias these
transistors, to get rid of the zero crossover of the stage.
e UOC. It is
the scan velocity
After that, the signal is ac-coupled to TS7363 and TS7364
where the emitter resistors (R3364
and R3370) will determine
the final SCAVEM current. TS7363 and TS7364 are biased by
R3363, R3366, R3367 and R3368.
C2387, R3388, R3389, R3365, R3369, C2384, and C2385 are
used
for suppre
ssing unwanted oscillations.
The function of TS7376 is to limit the SCAVEM current from
going too
high. It basically senses the voltage after R3373 and
clamps the SCAVEM signal through D6367 and C2376.
9.4 Control
The Micro Controller is integrated with the Video Processor,
and is called the Hercules. For dynamic data storage, such as
SMART PICTURE and SMART SOUND settings, an external
NVM IC is being used.
Another feature includes an optional Teletext/Closed Caption
der with the possibility of diff
deco
on the Hercules type number.
The Micro Controller ranges in ROM
decoder to 128 kB with a 10 page Teletext or with Closed
Caption.
9.4.1 Block Diagram
The block diagram of the Micro Controller ap
below.
# !$$%
KEYBOARD/
PROTECTION
CIRCUIT
VOLUME/MUTE/TREBBLE /BASS/PANORAMA
STBY_CON
POWER GOOD
KEYBOARD/PROTECTION
INPUT
OUTPUT
LIGHT SENSOR
LED
IR
Figure 9-4 Micro Controller block diagram
9.4.2 Basic Sp
The
ecification
Micro Controller operates at
• +3.3 V_dc at pins 33, 125, and 19
• +1.8 V_dc at pins 126, 36, and 33
• I2C pull up supply: +3.3V_dc.
9.4.3 Pin Co
guration and Functionality
nfi
The ports of the Micro Controller can be configured as follows:
• A normal input port.
• An input ADC port.
• An output Open Dr
ain port.
• An output Push-Pull port.
• An output PWM port.
• Input/Output Port
The following table shows the ports used for the L04 control:
erent page storage depending
from 128
WRITE
PROTECT
"
!
the following supply voltages:
.
.
kB with no TXT-
plication is shown
E_14480_070.eps
120504
Page 78

EN 78 L04E AA9.
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
Table 9-4 Micro Controller ports overview
Pin Name Description Configuration
32 INT0/ P0.5 IR INT0
31 P1.0/ INT1 PWRDOWN INT1
30 P1.1/ T0 LED P1.1
27 P0.4/ I2SWS (for future use) 26 P0.3/ I2SCLK (for future use) 25 P0.2/ I2SDO2 SEL_SC2_INTERF
ACE/ SDM
24 P0.1/ I2SDO1 (for future use) P0.1
23 P0.0/ I2SDI/O Panorama P0.0
22 P1.3/ T1 Write Protect P1.3
21 P1.6/ SCL SCL SCL
20 P1.7/ SDA SDA SDA
18 P2.0/ TPWM VOL_MUTE P2.0
17 P2.1/ PWM0 ROTATION PWM0
16 P2.2/ PWM1 SEL_LL'/M P2.2
15 P2.3/ PWM2 STANDBY_CON P2.3
14 P3.0/ ADC0 Light Sensor ADC0
13 P3.1/ ADC1 (for future use) 10 P3.2/ ADC2 (for future use) -
9 P3.3/ ADC3 KEYBOARD ADC3
7 P2.4/ PWM3 A (for future use) P2.4
6 P2.5/ PWM4 B (for future use) P2.5
3 P1.2/ INT2 C (for future use) INT2
2 P1.4/ RX E (for future use) 1 P1.5/ TX D (for future use) -
The description of each functional pin is explained below
P0.2
:
• LED. This signal is used as an indication for the Standby,
Remote and
– During p
Error Indicator. Region diversity:
r
otection mode, the LED blinks and the set is
in standby mode.
– During error co
– After receiving a va
nditions it blinks at a predefined rate.
lid RC-5 or local keyboard
command it flashes once.
– For sets with error message indication,
the LED blinks
when message is active and the set is in standby
mode.
Table 9-5 LED signal diversity
LED Europe AP/ LATAM NAFTA
0 LED bright er Standby LED lighted Standby LED lighted Normal
1 LED dimmer Normal LED "off" Normal LED "off" Standby
is the clock wire of the two-wire single master bi-
• SCL. Thi
s
directional I2C bus.
• SDA. Th
is is the da
ta wire of the two-wire single master bi-
directional I2C bus.
• STDBY_CON
. The Hercules generates this signal. This
can enable the MAIN SMPS in normal operation and
disable it during Standby. It is of logic “low” (0 V) under
normal operation and “high” (3.3 V) during Standby.
• IR. Th
is input pin is connected to an RC5 remote control
rec
eiver.
• SEL-IF-LL’/ M-TRAP. For AP: All L04 AP sets are Multi
System QSS set.
This is an output pin to switch the Video
SAW filter between M system and other systems.
– 0: NT
SC M (default)
– 1: PAL B/G, DK, I, L
• Write Protect.
The global pro
tection line is used to enable
and disable write protection to the NVM. When write to the
NVM is required, pin 7 of the NVM must be pulled to logic
‘0’ first (via Write_Protect of the micro-controller pin) before
a write is performed. Otherwise pin 7 of NVM must always
be at logic “1”
– 0: Disabled
efault
– 1: Enabled (d
• Mute. This p
in is use to MUTE the audio amplifier. It is
)
configured as push pull.
• Rotation. T
his pin is configured as PWM for the Rotation
feature. The output of the PWM is proportional to the
feature control.
ight Sensor. This pin is conf
• L
igured as ADC input for the
Light Sensor.
Inte
• Sel_SC2_
rface. This pin is use to switch between the
SC2_CVBS_OUT and the INTF_CVBS_OUT for the
SCART_2_CVBS_OUT/ MONITOR_OUT signal.
Hercules CVBS Output (default)
– 0:
– 1: Interface CVBS Output
• PWRDOWN. The AUX SMPS generates this sig
“high” (3.3 V) under normal operation of the TV and goes
“low” (0 V) when the Mains input voltage supply goes below
70 V_ac.
• Key
board. Followin
g are the Keyboard functions and the
step values (8 bit) for it.
Table 9-6 Local keyboard values
Function Voltage (V_dc) Step values (8 bit)
NAFTA Standby 0 0 - 6
Ch + 0.43 7 - 3 3
Exit Factory (Ch- and Vol-) 0.69 34 - 53
Ch - 0.93 54 - 73
Menu (Vol - and Vol +) 1.19 74 - 96
Vol - 1.49 97 - 121
DVD Eject 1.8 122 - 147
Vol + 2.12 148 - 169
• SDM. This
pin is conf
igured as Open Drain during the cold
start only. If this pin is shorted to ground during cold start,
it will enter the SDM mode (for Service use).
• ISP. T
his pin is configured as Open Drain d
start only. If this pin is shorted to ground during cold start,
it will enter the ISP mode (for Service use).
• PANEL
. This pin is con
figured as Open Drain during the
cold start only. If this pin is shorted to ground during that,
then it will enter to the PANEL mode.
• Res
etEnabled.
This is an output pin to switch the control
transistor (pos. TS7202) “high” or “low” for the reset of 1.8
V in case there is a corruption in the Hercules.
9.5 Tuner and IF
The tuner used in this chassis comes from two sources, from
Philips and from Alps. Both tuner sources have the same pin
configuration so they are 1 to 1 compatible except for the
software, which will be selected by means of Option Settings.
Some features:
• Multi-Standard alignment free PLL-IF
L’.
• Integ
rated IF-AGC time constant.
• Integrated sound band-passes and traps (4.5 / 5.5 / 6.0 /
6.5 MH
z).
• Group
delay compensation (for NTSC and for PAL).
• QSS versions with digital Second-Sound-IF SSIF
demodulator for free).
M mono operation possible:
• F
9.5.1 Diversity
The following Tuners can be present (depending on the region
and the set execution):
• Normal tuner wi
thout PIP.
• FM radio tuner without PIP.
• Normal tuner wi
th PIP (main tuner with splitter).
• FM radio set with PIP (PIP tuner with splitter).
The
SAW filter used, depends on the application concept
hether it is a QSS conce
(w
• OFWM3953M for QSS V
• OFWK9656M for QSS
pt or an Intercarrier):
ideo.
Audio.
• OFWM1971M for Intercarrier.
, including
Inter-Carrier or QSS.
nal. Logic
uring the cold
SECAM L/
(AM
Page 79

Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
EN 79L04E AA 9.
9.5.2 Pin Assignments and Functionality
Pin assignment of the Tuner:
Table 9-7 Pinning Tuner
Pin Pin Description DC Voltages
1 RF-AGC 4V for Maximum Gain < 4V for Stro ng Signal
2 FM Radio Input or N.C 3 NC (Address Pin) 4 SCL 0 to 3.3 V_dc
5 SDA 0 to 3.3 V_dc
6/7 Supply Voltage 5 V_dc +/- 0.25 V
8 N.C -
9 Tuning Supply Voltage 30 to 35 V_dc
10 FM Radio IF Output/Ground 11 TV IF Output -
Pin assignment of the several S
Condition
A
W filters (depends on region/
execution):
Table 9-8 Pinning SAW filters
QSS Video
Pin
(item 1002)
1 Input Input Input Input
2 Input Ground Input Ground Switching Input Input Ground
3 Ground Ground Ground Ground
4 Output Output Output Output
5 Output Output Output Output
6 - n.c. - -
7 - n.c. - -
8 - Ground - -
9 - Free - 10 - Switching input - -
QSS Video
(item 1003)
QSS Audio
(item 1001)
Intercarrier
(item 1002)
The table below shows the switching behavior of SAW filter.
Table 9-9 Switching behavior SAW filter
Condition
High Low
System M BG/DK/I/L
Note: The logic level is measured at th
7001
.
e base of transistor
9.5.3 Option Settings
T
he option settings for the Tuner type can be found in Option
setting 1 of the
SAM mode. The Option settings for Option 1 are
as follows:
• Option Byte 1
it 7: OP_PHILIPS_TUNER
– B
– Bit 6: OP_FM_RADIO
– Bit 5: OP_LNA
– Bit 4: OP_ATS
– Bit 3: OP_ACI
– Bit 2: OP_UK_PNP
– Bit 1: OP_VIRGIN_MODE
– Bit 0: OP_CHINA
or more details on the option settings, please refer to the
F
chapter 8 “Alignments”.
9.6 Source Select
For this chassis, the audio/video source selection is controlled
via the Hercules.
The Audio/Video Source Select is one of the more complex
i
ons due to its diversity and complex switching. The Audio/
funct
Video Source Select comprises of the following components:
• The
• The
9.6.1 Op
The opt
Option settings of the SAM mode. T
Hercules itself for Mono Audio and Video Source
Sele
ction.
HEF switch for Stereo Audio as well as Video
Sele
ction.
tions
ion settings for the Source Selection can be found in
he Option settings for
Option 5 are as follows:
• Option Byte 5
– Bit 7: AV1
– Bit 6: AV2
– Bit 5: AV3
– Bit 4: CVI
– Bit 3: SVHS2
– Bit 2: SVHS3
– Bit 1: HOTEL MODE
– Bit 0:
For more detail on the option settings, please refer to the
ter 8 “Alignments”.
chap
9.6.2 Diversity
The basic diversity of the
between the Mono and th
Audio/Video Source Select is
e Stereo sets and the number of
Cinch/SCART’s as specified in the product specification. The
table below shows the Audio/Video Source Select diversity for
all regions:
Table 9-10 AV Source Select diversity
Pin Symbol Remark
51 R/Pr IN3 AV1 (CVI)
50 G/Y IN3
49 B/Pb IN3
52 INSSW3
74 CVBS2/Y2
95 AUDIO IN5 L
94 AUDIO IN5 R
73 AUDIO IN3 L AV2 (SVHS)
72 AUDIO IN3 R
71 CVBS3/Y3
70 C2/C3
80 AUDIO IN4 L Side (SHVS)
79 AUDIO IN4 R
78 CVBS4/Y4
77 C4
81 IFVO/SVO/CVBSI Monitor Out
67 AUD OUT HP L
66 AUD OUT HP R
69 AUD OUT LS L (AUD OUT/AM OUT) HP/ LS Out
68 AUD OUT LS R
59 V IN (R/Pr IN2/CX) Interface
58 U IN (B/Pb IN2)
57 Y IN (G/Y IN2/CVBS-Yx)
54 U OUT (INSSW2)
76 AUDIO IN2 L
75 AUDIO IN2 R
86 DVBO/IFVO/FMRO N.C.
65 CVBSO/PIP PIP application
56 Y SYNC 100 nF
55 Y OUT 100 nF
53 V OUT (SWO) N.C.
93 AUD OUT S L N.C.
92 AUD OUT S R N.C.
Page 80

EN 80 L04E AA9.
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
Table 9-11 SCART Source Select diversity
Pin Symbol Remark
51 R/Pr IN3 SCART 1
50 G/Y IN3
49 B/Pb IN3
52 INSSW3
74 CVBS2/Y2
86 DVBO/IFVO/FMRO
95 AUDIO IN5 L
94 AUDIO IN5 R
93 AUD OUT S L
92 AUD OUT S R
71 CVBS3/Y3 SCART 2
70 C2/C3
81 IFVO/SVO/CVBSI
73 AUDIO IN3 L
72 AUDIO IN3 R
67 AUD OUT HP L
66 AUD OUT HP R
80 AUDIO IN4 L Side I/O
79 AUDIO IN4 R
78 CVBS4/Y4
77 C4
69 AUD OUT LS L (AUD OUT/AM OUT) LS/ HP/ MON OUT
68 AUD OUT LS R
59 V IN (R/Pr IN2/CX) Interface
58 U IN (B/Pb IN2)
57 Y IN (G/Y IN2/CVBS-Yx)
54 U OUT(INSSW2)
76 AUDIO IN2 L
75 AUDIO IN2 R
65 CVBSO/PIP for PIP
56 YSYNC 100 nF
55 YOUT 100 nF
53 VOUT(SWO) N.C.
9.6.3 Audio Source Selection
T
he signals coming out of the DEMDEC (internal demodulator/
decode
r block of the Hercules) are selectable and consist of
the following (depending on the transmission):
• DEC L/R (Can be
• Mono (Refers to fallb
NICAM, FM 2
ack/forced Mono in Stereo
Transmission).
• SAP.
or L04, the assigned I/O with respec
F
follows:
r
• SCART1 o
• SCART2 or
AV1 Input assigned to Audio In 5.
AV2 Input assigned to Audio In 3.
• Side AV Input assigned to Au
• External Interface Input
assigned to Audio In 2.
• SCART1 Output assigned to SCAR
• SCART2 Output (EU) o
r Monitor Output (LA/NA/AP)
assigned to Headphone Output.
• Constant Level Output assigned to L
9.6.4 Video Source Selection
CS, or BTSC Stereo).
t to the Hercules is as
dio In 4.
T Output.
oudspeaker Output.
9.7 Video Processing
The Video Processor is basically the Hercules and the
TDA9178 (CTI/LTI). Video processing is done in these two
chips such as the Brightness Control, Contrast Control and so
on.
Some features:
ull YUV-loop interface (alternative functions: DVD, RGB
• F
or Y/C).
• Internal OSD insertion (not Saturation or Contrast
• Double window implementation.
• Linear / non linear scaling for 16:9
• Tint (hue) on UV signals (including DVD).
• Peaking, Coring, Black \ Blue \ White-stretch.
• Transfer-Ratio and Scavem
9.7.1 Feat
The features included in the Hercules are as follows:
• Brightness Control.
• Contrast Control.
• Saturation Control.
• Sharpness Control.
• Peak White Limiter.
• Beam Curren
• Black Stretch (Contrast Plus).
For sets w
• Luminance Transient Improvement (LTI).
• Color Transient Improveme
9.7.2 Block Diag
Following diagram is the block diagram of
part:
TUNER
VIDEO
SAW
AUDIO
SAW
lled).
contro
sets.
(also on TXT).
ures
t Limiter.
ith the TDA9178, there are two extra features:
nt (CTI).
ram
the video processing
NVM
68,69
2021
MONITOR
OUT
6586,81,
AUDIO
AMP
2425
29,30
95,94,80,79,
78,77,76,75,
74,73,72,71,70
67,66
CVBS/AUDIO
REAR/SIDE
INPUT/OUTPUT
HERCULES
42,4344
49,50,51
53,54,55
57,5859
SW
CRT
RGB/CVI
INPUT
LTI/CTI
PIP/
DVD
E_14480_071.eps
200204
Video source selection is done inside the
ercules. Therefore
H
it provides a video switch with 3 external CVBS inputs and a
CVBS output. All CVBS inputs can be used as Y-input for Y/C
signals. However, only 2 Y/C sources can be selected because
the circuit has 2 chroma inputs.
All input signals are converted to YUV, and looped through an
x
ternal interface. This to enable picture improvement features
e
(like LTI/CTI) or PIP.
Figure 9-5 Video processing block diagram
9.7.3 LTI/CTI
The
TDA9178 is an I2C-bus controlled IC (INCREDIBLE chip)
with YUV interface. This IC can do mainly histogram
processing, color transient improvement
transient improvement (LTI).
• Luminance Vector Processing
involve
which provides scene dependent contrast improvement,
adaptive black and white point stretching.
e
• Color V
ctor Processing involves skin tone correction,
green enhancement and blue stretch.
(CTI) and line
s histogram function,
Page 81

Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
EN 81L04E AA 9.
• Spectral Processor involves step improvement processing,
contour processing, smart sharpness control, color
dependant sharpness and Color Transient Improvement.
oise detector, feature mode detector and cue flash
• N
fu
nctions.
emonstration mode shows all the
• D
improvement features
in one picture.
Table 9-12 Pinning overview TDA9178
Pin Symbol Description
1 SC Sandcastle input pin
2 n.c. Not connected pin
3 ADEXT1 External AD-conversion #1 input pin
4 ADEXT2 External AD-conversion #2 input pin
5 ADEXT3 External AD-conversion #3 input pin
6 Y in Luminance input pin
7 ADR Address selection input pin
8 U in -(B-Y) signal input pin
9 V in -(R-Y) signal input pin
10 TP Testpin, connected to ground
11 SCL I2C-bus: clock input pin
12 n.c. Not connected pin
13 n.c. Not connected pin
14 SDA I2C-bus: data input pin
15 DECDIG Decoupling digital supply
16 V out -(R-Y) signal output pin
17 U out -(B-Y) signal output pin
18 V ee Ground pin
19 Y out Luminance output pin
20 V cc Supply-voltage pin
21 S out Luminance output fo r SCAVEM
22 CF Cue-flash output pin
23 n.c. Not connected pin
24 n.c. Not connected pin
9.7.4 Op
tions
he option settings allow for process of the video as per set
T
specification. T
he option settings can be found in “Option 2”
and “Option 6” in the SAM mode. The option settings are as
follows:
• Option Byte 2
t 7:
– Bi
– Bit 6 :OP_GREEN_UI
– Bit 5: OP_CHANNEL_NAMING,
– Bit 4: OP_LTI,
– Bit 3: OP_TILT,
– Bit 2: OP_FINE_TUNING
– Bit 1: OP_PIP_PHILIPS_TUNER,
– Bit 0: OP_HUE,
• Option Byte 6
– Bit 7: OP_PERSONAL_ZAPPING,
– Bit 6:
– Bit 5: OP_FMTRAP
– Bit 4: OP_COMBFILTER
– Bit 3: OP_ACTIVE_CONTROL
– Bit 2: OP_VIDEO_TEXT
– Bit 1 :OP_LIGHT_SENSOR,
– Bit 0: OP_DUAL_TEXT
or more details on the option settings, please refer to the
F
chapter 8 “Alignments”.
9.8 Audio Processing
The audio decoding is done entirely via the Hercules. The IF
output from the Tuner is fed directly to either the Video-IF or the
Sound-IF input depending on the type of concept chosen.
There are mainly two types of decoder in the Hercules, an
analog decoder that decodes only Mono, regardless of any
standards, and a digital decoder (or DEMDEC) that can decode
both Mono as well as Stereo, again regardless of any
standards.
In this chassis, the analog decoder is used in
• It is used for AM Sound demodulation in the Euro
SECAM LL’ transmission.
• It is used for all FM
demodulation in AP AV-Stereo sets.
9.8.1 Diversity
The diversity for the Audio decoding can be broken up into two
main concepts:
• The Quasi Split So
und concept used in Europe and some
AP sets.
• The Inter Carrier concept, used in NAFTA and LATAM.
The UOC-III family makes n
o difference anymore be
QSS- and Intercarrier IF, nearly all types are softwareswitchable between the two SAW-filter constructions.
Simple data settings are required for the set to determine
whether it is us
ing the Inter Carrier or the QSS concept. These
settings are done via the “QSS” and “FMI” bit found in SAM
mode. Due to the diversity involved, the data for the 2 bits are
being placed in the NVM location and it is required to write once
during startup.
On top of that, it can be further broken down into various
systems de
pending on the regio
n. The systems or region
chosen, will in turn affect the type of sound standard that is/are
allowed to be decoded.
or the case of Europe, the standa
• F
rd consists of BG/DK/I/
LL’ for a Multi-System set. There are also versions of
Eastern Europe and Western Europe set and the standard
for decoding will be BG/DK and I/DK respectively. FM
Radio is a feature diversity for the Europe sets. The same
version can have either FM Radio or not, independent of
the system (e.g. sets with BG/DK/I/LL’ can have or not
have FM radio).
NAFTA and LATAM, there is only one
• For the case
of
transmission standard, which is the M standard. The
diversity then will be based on whether it has a dBx noise
reduction or a Non-dBx (no dBx noise reduction).
or the case of AP, the stan
• F
dard consists of BG/DK/I/M for
a Multi-System set. The diversity here will then depends on
the region. AP China can have a Multi-System and I/DK
version. For India, it might only be BG standard.
nality
9.8.2 Fun
ctio
The features available in the Hercules are as follow
• Treble and Bass Control.
• Surround Sound Effect that includes:
– Incredible Stereo.
– Incredible Mono.
– 3D Sou
nd (not fo
r AV Stereo).
– TruSurround (not for AV Stereo).
– Virtual Dolby Surround, VDS422 (no
– Virtual Dolby Surround, VDS423 (no
– Dolby Pro-Logic (n
ot for AV Stereo).
• Bass Feature that includes:
– Dynamic Ul
tra-Bass.
– Dynamic Bass Enhancement.
– BBE (not for AV Stereo).
• Auto-Volume Leveler.
• 5 Band Equalizer.
• Loudness Control.
All the fea
tures stated are available for the F
ull Stere
and limited features for the AV Stereo
9.8.3 Aud
o Amplifier
i
The audio amplifier part is very straightforward. It uses the
integr
ated power amplifier TDA2616Q, and delivers a
maximum output of 2 x 10 W_rms.
The maximum operating condition for this amplifier is 21 V
ded. Normal op
unloa
erating supply is from 7.5 V to 16 V.
two cases:
pe
tween
s:
t for AV Stereo).
t for AV Stereo).
o versions
Page 82

EN 82 L04E AA9.
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
Muting is done via the VOLUME_MUTE line connected to pin
2 of the amplifier-IC and coming from the UOC.
The following table shows pin functionality of the Audio
e
r:
Amplifi
Table 9-13 Pinning overview TDA2616
Pin Pin Name Normal Operation
1 Input Left Input AC signal
2 Mute 16 V_dc
3 Ground 0 V
4 Output L Channel AC waveform
5 Supply Voltage (negative) -16 V_dc
6 Output R Channel AC waveform
7 Supply Volta ge (positive) + 16 V_dc
8 Inverting inputs L and R 0 V
9 Input Right Input AC signal
9.9 Picture in Picture (PIP)
The PIP application has two tuners, one with a splitter on the
main chassis and another with "phono" input on the PIP panel.
The same signal is injected to both tuners, so that it does not
need separate auto tuning for the PIP tuner.
The TDA9887TS (item 7201) is an alignment free multistanda
positive and negative modulation, including sound AM and FM
processing.
The SDA9489 (item 7242) is a multi system color decoder with
ny f
ma
YPbPr, 16:9 application, WSS detection, Closed Caption, and
OSD display for PIP window etc.
The PIP power supply is based o
principle. The +9V input voltage is converted to +5V and +3.3V
via the regulator (item 7501).
n and sound IF signal PLL demodulator for
rd visio
eatures such as: half screen size PIP, selectable YUV or
the step down converter
n
9.10 Abbreviation list
2CS 2 Carrier (or Channel) Stereo
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV sets dir
from cable network by means of a
predefined TXT page
ADC Analogue to Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control: control
s
signal u
frequency
AFT Automatic Fine Tuning
AGC Automatic Gain Control: algorithm that
controls the vid
box
AM Amplitude Modulation
AP Asia Pacific region
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ATS Automatic Tuning System
AV External Audio Video
AVL Automatic Volume Leveler
BCL Beam Current Limitation
B/G Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 5
BTSC Broadcast Television Standard
Committee
system, originating from the USA and
used e.g. in LATAM and AP-NTSC
countries
CC Closed Caption
CCC Continuous Cathode Calibration
ComPair Computer aided rePair
CRT Cathode Ray Tube or picture tube
CSM Customer Service Mode
CTI Color Transient Improvement:
man
transients
CVBS Composite Video Blanking and
Synchroniza
CVI C
DAC Digital to Analogue Converter
DBX Dynamic Bass Expander or noise
reduction syste
D/K Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.
DFU Direction For Use: description for the
end user
DNR D
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool: special remote
control designed for dealers to enter
e.g
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Rea
EHT Extra High Tension
EHT-INFO Extra High Tension information
EPG Electronic Programming Guide
EU Europe
EW East West, related to horizontal
def
EXT External (source), entering the set via
SCART or
FBL Fast Blanking: DC signal
accompanying RGB signals
FILAMENT F
FM Field Memory or Frequency
Mod
H Horizontal sync signal
HP Headphone
I Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6
I2C Integrated IC bus
IF Intermediate Frequency
ed to tune to the correct
eo inp
.
. Multiplex FM stereo sound
pulates steepness of chroma
i
tion
omponent Video Input
m in BT
ynamic Noise Reduction
.
service mode
d On
n of the set
lectio
Cinch
ilament of CRT
u
lation
.
ectly
ut of the feature
5 MHz
SC
5 MHz
ly Memory
0 MHz
Page 83

Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
IIC Integrated IC bus
ITV Institutional TV
LATAM Latin American countries like Brazil,
LED Light Emitting Diode
L/L' Monochrome TV system. Sound
LS Large Screen or Loudspeaker
M/N Monochrome TV system. Sound
NC Not Connected
NICAM Near Instantaneous Compounded
NTSC National Television Standard
NVM Non Volatile Memory: IC containing
OB Option Bit
OC Open Circuit
OP Option Byte
OSD On Screen Display
PAL Phase Alternating Line. Color system
PCB Printed Circuit board
PLL Phase Locked Loop. Used for e.g.
POR Power-On Reset
PTP Picture Tube Panel (or CRT-panel)
RAM Random Access Memory
RC Remote Control handset
RGB Red, Green, and Blue video signals
ROM Read Only Memory
SDAM Service Default / Alignment Mode
SAP Second Audio Program
SC Sandcastle: pulse derived from sync
S/C Short Circuit
SCL Serial Clock
SDA Serial Data
SECAM SEequence Couleur Avec Memoire.
SIF Sound Intermediate Frequency
SS Small Screen
STBY Standby
SVHS Super Video Home System
SW Software
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
TXT Teletext
uP Microprocessor
UOC Ultimate One Chip
V Vertical sync signal
V_BAT Main supply voltage for the deflection
V-chip V
VCR Video Cassette Recorder
WYSIWYR What You See Is What You Record:
XTAL Quartz crystal
YC Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C)
r
gentina, etc.
A
carrier distance is 6.5 MH
I, L is all ba
carr
ud
A
sound system, mainly used in Europe.
Committ
in North America and Japan. Color
carrier NTSC M/N = 3.579545 MHz,
NTSC 4.43 = 4.433619 MHz (this is a
VCR norm, it is not transmitted off-air)
TV related da
mainly used
carrier = 4.433619 MHz) and South
America (color carrier PAL M =
3.575612 MHz and PAL N = 3.582056
MHz)
FST tun
can give directly the desired frequency
signals
Colo
and East
4.406250 MHz and 4.250000 MHz
stage
iolence Chip
record selection that f
picture and sound
signal
nds except for Band I
ier distance is 4.5 MHz
io Multiplexing. This is a digital
ee. C
olor system mainly used
ta e.g. alignme
in West Europe
i
ng systems. The customer
r system mainly used in France
Europe. Color carriers =
(mostly 141 V)
z. L' is Band
nts
(color
ollows main
EN 83L04E AA 9.
Page 84

EN 84 L04E AA9.
9.11 IC Data Sheets
This section shows the internal block diagrams and pin layouts
of ICs that are drawn as "black boxes" in the electrical diagrams
(with the exception of "memory" and "logic" ICs).
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
9.11.1 D
iagram F, TDA9887 (IC7201)
BLOCK DIA
VIF2
2
1
VIF1
SIF2
24
23
SIF1
GRAM
C
VAGC(pos)
TAGC
14
C
AGC(neg)
TUNER AGC
SUPPLY SIF AGC
VIF-AGC
VIF-PLL
filter
VAGCTOP
C
SINGLE REFERENCE QSS MIXER
C
VPLL
19916 1521
BL
RC VCO
VIF-PLL
INTERCARRIER MIXER
AND AM DEMODULATOR
AGC
OUTPUT
PORTS
I2C-BUS TRANSCEIVER
external reference signal
or 4 MHz crystal
DIGITAL VCO CONTROL AFC DETECTOR
TDA9887TS
MAD
REF AFC
SOUND TRAPS
4.5 to 6.5 MHz
AUDIO PROCESSING
NARROW-BAND
FM-PLL DEMODULATOR
AND SWITCHES
17
CVBS
video output: 2 V (p-p)
[1.1 V (p-p) without trap]
AUD
8
5
6
DEEM
AFD
audio output
de-emphasis
network
C
AF
AGND
V
P
PIN CONFIGURATION
113
22
OP1 OP2 FMPLLFMIN
sound intercarrier output
VIF1
1
VIF2
2
3
OP1
FMPLL
4
DEEM
5
AFD
6
DGND
AUD
TOP
SDA
SCL
SIOMAD
TDA9887TS
7
8
9
10
11
12
MHC144
121820
7
SIOMADSDASCL
DGND
and MAD select
SIF2
24
SIF1
23
OP2
22
AFC
21
V
20
P
19
VPLL
AGND
18
17
CVBS
VAGC
16
REF
15
TAGC
14
FMIN
13
41310
MHC143
FM-PLL
filter
E_14480_129.eps
120504
Fig
ure 9-6 Internal Block Diagram and Pin Configuration
Page 85
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
9.11.2 Diagram H, TDA9178 (IC7610)
BLOCK DIAGRAM
EN 85L04E AA 9.
Sout
Yin
Uin
Vin
DEC
DIG
Vcc
ground
Sandcastle
inputstage
supply
window
generation
calibrate
Y
U,V
Luminance vector processing
luminance
processing
saturation
correction
skin tone correction
green enhancement
blue stretch
noise
measuring
featuremode
detection
black stretch
histogram processing
gamma control
colour vector processing
"cue flash"
spectral processing
smart peaking
LTI
VDC
delay
control
colour
processing
CDS
CTI
+
ADC
output
stage
ADext1 (low frequencies)
ADext2 (low frequencies)
ADext3 (low frequencies)
Yout
Uout
Vout
CF
I2C
PIN CONFIGURATION
2
C-control
I
Sc
Nc
ADEXT1
ADEXT2
ADEXT3
Yin
1
2
3
4
5
6
24
23
22
21
20
19
TDA9178
ADR
Uin
Vin
TP
SCL
Nc Nc
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
18
17
16
15
14
Nc
Nc
CF
Sout
Vcc
Yout
Vee
Uout
Vout
DEC
SDA
DIG
E_14480_075.eps
270204
Figure 9-7 Internal Block Diagram and Pin Configuration
 Loading...
Loading...