Philips Heartstart HSI Service manual

HeartStart HS1 Defibrillators
TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

Introductory Note
Heartstream, Inc., was founded in 1992. Its mission was to design and produce an automated external
defibrillator (AED) that could be successfully used by a layperson responding to sudden cardiac arrest and
that was:
•small
• light-weight
•low-cost
• rugged
•reliable
•safe
• easy-to-use, and
• maintenance-free.
Heartstream introduced its first AED, the ForeRunner, in 1996. The Heartstream ForeRunner AED
marked the first widespread commercial use of a biphasic waveform in an external defibrillator.
Hewlett-Packard (HP) purchased Heartstream in 1997. Heartstream then added a relabeled version of
the ForeRunner for Laerdal Medical Corporation called the Heartstart FR.
In 1999, Hewlett-Packard spun off its Medical Products Group, including the Heartstream Operation, into
Agilent Technologies. While part of Agilent, Heartstream introduced a new AED, the Agilent
Heartstream FR2. Laerdal Medical marketed this device as the Laerdal Heartstart FR2. The FR2 evolved
into the FR2+, with the addition of an enhanced feature set, in 2001.
Heartstream became part of Philips Medical Systems in 2001, when Philips purchased the entire
Medical Group from Agilent Technologies. The following year, all Philips defibrillators were rebranded as
HeartStart Defibrillators, and Philips introduced the HeartStart HS1 family of AEDs, including the Philips
and Laerdal HeartStart, and Philips HeartStart Home, and Philips HeartStart OnSite defibrillators.
The Philips HeartStart FRx AED was brought onto the market in 2005, along with a Laerdal version.
This manual is intended to provide technical and product information that generally applies to the Philips
HeartStart OnSite, the Laerdal HeartStart HS1, and the Philips HeartStart Home Defibrillators, models
M5066A, M5067A, and M5068A, respectively. To simplify the discussion, these defibrillators will be
referred to as the HeartStart HS1 in this manual.
Philips Medical Systems
October 2007
CONTENTS
1 The HeartStart HS1 Defibrillator
Sudden cardiac arrest and the automated external defibrillator ......... 1-1
Design philosophy for the HS1 Defibrillators .......................................... 1-1
Design features of the HS1 Defibrillators ................................................. 1-2
Reliability and Safety ................................................................................ 1-2
Ease of Use ................................................................................................ 1-3
No Maintenance ....................................................................................... 1-5
2 Defibrillation and Electricity
The Heart’s Electrical System ....................................................................... 2-1
Simplifying Electricity ...................................................................................... 2-4
3 SMART Biphasic Waveform
A Brief History of Defibrillation .................................................................. 3-1
SMART Biphasic ............................................................................................... 3-4
Understanding Fixed Energy .................................................................. 3-5
Evidence-Based Support for the SMART Biphasic Waveform ...... 3-6
SMART Biphasic Superior to Monophasic ......................................... 3-6
Key Studies ................................................................................................ 3-7
Philips Medical Systems
Frequently Asked Questions ........................................................................ 3-8
Are all biphasic waveforms alike? ......................................................... 3-8
How can the SMART Biphasic waveform be more effective at
lower energy? ........................................................................................... 3-9
Is escalating energy required? ............................................................... 3-10
Is there a relationship between waveform, energy level,
and post-shock dysfunction? ................................................................. 3-13
How does SMART Biphasic compare to other
biphasic waveforms? ................................................................................ 3-14
Is there a standard for biphasic energy levels? .................................. 3-14
Commitment to SMART Biphasic ........................................................ 3-15
References ........................................................................................................ 3-16
4 SMART Analysis
Pad Contact Quality ....................................................................................... 4-1
Artifact Detection ........................................................................................... 4-1
Overview ................................................................................................... 4-1
CPR at High Rates of Compression .................................................... 4-2
Pacemaker Detection ............................................................................. 4-2
I

ii
Arrhythmia Detection .................................................................................... 4-4
Rate ............................................................................................................. 4-5
Conduction ............................................................................................... 4-5
Stability ....................................................................................................... 4-6
Amplitude .............................................................................................................. 4-7
Specific Analysis Examples ..................................................................... 4-7
Sensitivity and Specificity ........................................................................ 4-10
Shockable Rhythms ......................................................................................... 4-11
Validation of Algorithm .................................................................................. 4-14
Specific Concerns for Advanced Users of HeartStart AEDs ................ 4-16
HeartStart AED vs. HeartStart ALS Defibrillator Algorithms ....... 4-16
Simulator Issues with SMART Analysis ............................................... 4-16
Use of External Pacemakers with Internal Leads ............................. 4-17
5 Other Features of the HeartStart HS1 Defibrillator
Overview ........................................................................................................... 5-1
Self-Tests ........................................................................................................... 5-1
Battery Insertion Test ............................................................................. 5-1
Ready Light ................................................................................................ 5-1
Periodic Self-Tests ................................................................................... 5-2
“Power On” and “In Use” Self-Tests .................................................. 5-4
Cumulative Device Record ........................................................................... 5-5
Supplemental Maintenance Information for Technical Professionals .. 5-5
Background ................................................................................................ 5-5
Calibration requirements and intervals .............................................. 5-5
Maintenance testing ................................................................................. 5-5
Verification of energy discharge ........................................................... 5-6
Service/Maintenance and Repair Manual ............................................ 5-6
CPR Coaching .................................................................................................. 5-6
Quick Shock ..................................................................................................... 5-6
Pediatric Defibrillation ................................................................................... 5-7
HeartStart Trainer .......................................................................................... 5-8
Training Scenarios .................................................................................... 5-8
Philips Medical S ystems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

iii
6 Theory of Operation
Overview ........................................................................................................... 6-1
User interface ................................................................................................... 6-3
Operation .................................................................................................. 6-3
Maintenance .............................................................................................. 6-3
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................... 6-3
Control Board .................................................................................................. 6-3
Battery ........................................................................................................ 6-4
Power Supply ............................................................................................ 6-4
ECG Front End ......................................................................................... 6-4
Patient Circuit ........................................................................................... 6-4
Data Recording ......................................................................................... 6-5
Temperature Sensor ............................................................................... 6-5
Real-Time Clock ...................................................................................... 6-6
IR Port ........................................................................................................ 6-6
7 HeartStart Data Management Software
Overview ........................................................................................................... 7-1
System Requirements ..................................................................................... 7-3
Comparison of Event Review and Event Review Pro ............................. 7-3
Data Management Software Versions ........................................................ 7-5
System Annotations ........................................................................................ 7-6
Philips Medical Systems
Technical Support for Data Management Software ................................ 7-6
Configuration Software .................................................................................. 7-8
CONTENTS

iv
APPENDICES
A Technical Specifications
Standards Applied ............................................................................................ A-1
HS1 AED Specifications ................................................................................. A-2
Electromagnetic Conformity ........................................................................ A-6
Accessories Specifications ............................................................................. A-9
Environmental considerations ...................................................................... A-11
B Troubleshooting Information
Troubleshooting the Heartstart HS1 Defibrillator ................................. B-1
Verification of Energy Delivery .................................................................... B-3
C Pads and Battery
Defibrillator Pads for the HeartStart HS1 AED ....................................... C-1
Defibrillator Pads Placement with HS1 AED ............................................ C-2
Batteries for HS1 AED ................................................................................... C-3
D Use Environment
Defibrillation in the Presence of Oxygen .................................................. D-1
Defibrillation on a Wet or Metal Surface .................................................. D-1
Protection against Water and Particles ..................................................... D-4
Effects of Extreme Environments ................................................................ D-6
Self-Test Aborts Due to Temperature Extremes .................................... D-8
Philips Medical S ystems
E Guidelines 2005
F Literature Summary for HeartStart AEDs
Introduction ...................................................................................................... F-1
References ........................................................................................................ F-2
Selected Study Summaries ............................................................................. F-15
HeartStart Low-Energy, High-Current Design ................................. F-15
HeartStart Quick Shock Feature .......................................................... F-17
HeartStart’s Human Factors Design .................................................... F-20
HeartStart Defibrillation Therapy Testing in Adult
Victims of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest ....................................... F-23
HeartStart Patient Analysis System Testing with
Pediatric Rhythms .................................................................................... F-25
HeartStart Defibrillation Therapy Testing in a Pediatric
Animal Model ............................................................................................ F-28
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

1 The HeartStart HS1 Defibrillators
Sudden cardiac arrest and the automated external defibrillator
Each year in the United States alone, approximately 340,000 people suffer
1
sudden cardiac arrest (SCA).
Fewer than 5% of them survive. SCA is most
often caused by an irregular heart rhythm called ventricular fibrillation (VF),
for which the only effective treatment is defibrillation, an electrical shock.
Often, a victim of SCA does not survive because of the time it takes to
deliver the defibrillation shock; or every minute of VF with cardiopulmonary
resuscitation (CPR), the chances of survival decrease by 7% to 10%.
2
Traditionally, only trained medical personnel were allowed to use a
defibrillator because of the high level of knowledge and training involved.
Initially, this meant that the victim of SCA would have to be transported to a
medical facility in order to be defibrillated. In 1969, paramedic programs
were developed in several communities in the U.S. to act as an extension of
the hospital emergency room. Paramedics went through extensive training to
learn how to deliver emergency medical care outside the hospital, including
training in defibrillation. In the early 1980s, some Emergency Medical
Technicians (EMTs) were also being trained to use defibrillators to treat
victims of SCA. However, even with these advances, in 1990 fewer than half
of the ambulances in the United States carried a defibrillator, so the chances
of surviving SCA outside the hospital or in communities without highly
developed Emergency Medical Systems were still very small.
Philips Medical Systems
The development of the automated external defibrillator (AED) made it
possible for the first responders (typically lay persons) at the scene to treat
SCA with defibrillation. People trained to perform CPR can now use a
defibrillator to defibrillate a victim of SCA. The result: victims of sudden
cardiac arrest can be defibrillated more rapidly than ever before, and they
have a better chance of surviving until more highly trained medical personnel
arrive who can treat the underlying causes.
Design philosophy for the HS1 Defibrillators
The Philips HeartStart HS1 family of automated external defibrillators
(AEDs) include the HeartStart HS1, the HeartStart OnSite, and the
HeartStart Home.
The Philips HeartStart HS1 automated external defibrillator (AEDs) are
designed specifically for use by the first people responding to an emergency.
They are reliable, easy to use, and virtually maintenance free. The design
allows these AEDs to be used by people with no medical training in places
1 American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2005 Update. Dallas,
TX.:American Heart Association;2005.
2 2005 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and
Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2005;112 Supplement IV
1-1

1-2
where defibrillators have not traditionally been used. In fact, the HeartStart
Home was the first AED cleared by the United States Food and Drug
Administration for sale without a prescription.
Factors that had to be considered in their design included the fact that an
AED might not be used very often, might be subjected to harsh
environments, and probably would not have personnel available to perform
regular maintenance.
The HS1 AEDs were not designed to replace the manual defibrillators used
by more highly trained individuals. Instead, they are intended to complement
the efforts of medical personnel by allowing the initial shock to be delivered
by the first person to arrive at the scene.
Design features of the HS1 AEDs
Reliability and Safety
• FAIL-SAFE DESIGN — The HS1 AEDs are intended to detect a
shockable rhythm and instruct the user to deliver a shock if needed. They
will not allow a shock if one is not required.
• DAILY AUTOMATIC SELF-TEST — The HS1 AEDs perform daily as well
as weekly and monthly self-tests to help ensure they are ready to use
when needed. An active LED Ready light serves as a status indicator and
demonstrates at a glance that the unit has passed its last self-test and is
therefore ready to use.
• ENVIRONMENTAL PARAMETERS — Environmental tests were
conducted to prove the HS1 AEDs’ reliability and ability to operate in
conditions relevant to expected use.
• NON-RECHARGEABLE LITHIUM BATTERY — The HS1 long-life
battery pack M5070A was designed for use in an emergency environment
and is therefore small, lightweight, and safe to use. The battery pack
contains multiple 2/3A size, standard lithium camera batteries. These
same batteries can be purchased at local drug stores for use in other
consumer products. These batteries have been proven to be reliable and
safe over many years of operation. The HS1 battery pack uses lithium
manganese dioxide (Li/MnO
) technology and does not contain
2
pressurized sulfur dioxide. The battery pack meets the U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency's Toxicity Characteristic Leaching
Procedure. All battery cells contain chemicals and should be recycled at
an appropriate recycling facility in accordance with local regulations.
Philips Medical Systems
• QUICK SHOCK — The HS1 can deliver a defibrillation shock very
quickly – typically within 8 seconds – after the end of a patient care
pause.
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

Ease of Use
• SMALL AND LIGHT — The biphasic waveform technology used in the
HS1 AEDs has allowed them to be small and light. They can easily be
carried and operated by one person.
1-3
• SELF-CONTAINED —
Both the standard and hard-shell carry cases for
the HS1 have room for an extra defibrillator Pads Cartridge and an extra
battery.
• VOICE PROMPTS — The HS1 AEDs provide clear, calm, audible
prompts that guide the user through the process of using the device.
• CPR COACHING — In its default configuration, the HS1 AEDs provide
basic verbal instructions for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation,
including hand placement, rescue breathing, compression depth and
timing, provided by the HS1 when the flashing blue i-button is pressed
during the first 30 seconds of a patient care pause. If the Infant/Child
Pads Cartridge is inserted in the HS1, the CPR Coaching provided will be
for infant/child CPR.
• PRE-CONNECTED PADS — The HS1 uses a pre-installed HeartStart
SMART Pads Cartridge. The HeartStart Infant/Child Pads Cartridge is
designed for use in the event defibrillation is required for an infant or
child under 55 pounds and 8 years old. The AED can be turned on by
pulling the green Pads Cartridge handle, as well as by using the green
On/Off button.
Philips Medical Systems
• CAUTION LIGHT — When the HS1 is in use and is
analyzing the patient’s heart rhythm, a triangular Caution
light on the front of the HS1 flashes to alert the user not to
touch the patient. When the HS1 advises a shock, the
Caution light stops flashing and stays on as a reminder not to touch the
patient during shock delivery.
• I-BUTTON — The HS1 has a blue information button
(i-button) on the front. When it is on solid (without
flashing), it is an indicator that it is safe to touch the patient.
When the button flashes the user can press it to get
information such as summary data about the last use or (default) CPR
Coaching.
• SHOCK BUTTON — The orange Shock button on the
front of the HS1 bears a lightning bolt symbol to identify it.
It flashes when the unit has charged for a shock and directs
the user to press the button to deliver a shock by pressing
the Shock button.
INTRODUCTION TO THE HEARTSTART HS1 AED

1-4
• CLEAR LABELING AND GRAPHICS — The
HS1 AEDs are designed to enable fast response
by the user. The 1-2-3 operation guides the user
to: 1) turn the unit on, 2) follow the prompts,
and 3) deliver a shock if instructed. A Quick
Reference Card stored inside the carry case
reinforces these instructions. The pads
placement icon on the pads cartridge indicates
clearly where pads should be placed, and the
pads themselves are labeled to specify where
each one should be placed. The polarity of the
pads does not affect the operation of the AED,
but user testing has shown that people apply the pads more quickly and
accurately if a specific position is shown on each pad.
• PROVEN ANALYSIS SYSTEM — The SMART rhythm analysis system
used in the HS1 AEDs analyzes the patient’s ECG rhythm and determines
whether or not a shock should be administered. The algorithm’s decision
criteria allow the user to be confident that the HS1 will advise a shock
only when it is appropriate treatment for the patient.
• ARTIFACT DETECTION SYSTEM — An artifact detection system in the
HS1 AEDs senses if the ECG is being corrupted by some form of artifact
from electrical “noise” in the surrounding environment, patient handling,
or the activity of an implanted pacemaker. Because such artifact might
inhibit or delay a shock decision, the HS1 filters out the noise from the
ECG, prompting the user to stop patient handling, or determining that
the level of artifact does not pose a problem for the algorithm.
• PADS DETECTION SYSTEM — The HS1 AEDs’ pads detection system
provides a voice prompt to alert the user if the pads are not making
proper contact with the patient's skin.
No Maintenance
• AUTOMATIC DAILY/WEEKLY/MONTHLY SELF-TESTS — There is no
need for calibration, energy verification, or manual testing with the HS1
AEDs. Calibration and energy verification are automatically performed
once a month as part of the HS1 self-test routine.
• ACTIVE STATUS INDICATOR — The green LED Ready light in the
upper right-hand corner of the HS1 AED shows whether or not the
device has passed its last self-test. When the Ready light is blinking, you
can confident that the device has passed its last self-test and is ready for
use. A solid Ready light means the defibrillator is being used
Philips Medical Systems
• BATTERY LEVEL INDICATOR — The HS1 AEDs prompt the user with
an audible alarm when the battery needs to be replaced.
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
2 Defibrillation and Electricity
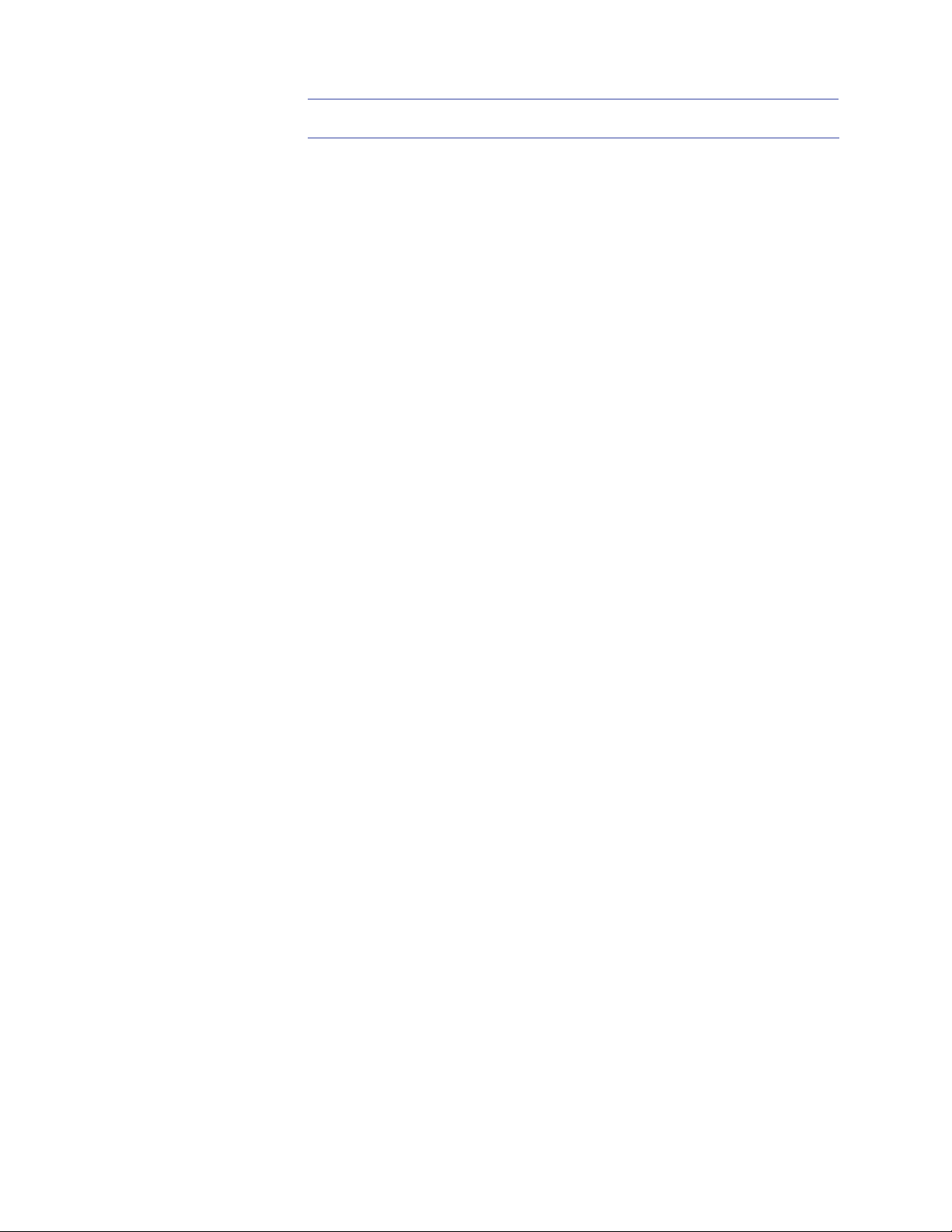
Relation of an ECG to the anatomy of the cardiac conduction system
The Hear t’s Electrical System
The heart muscle, or myocardium, is a mass of muscle cells. Some of these
cells (“working” cells) are specialized for contracting, which causes the
pumping action of the heart. Other cells (“electrical system” cells) are
specialized for conduction. They conduct the electrical impulses throughout
the heart and allow it to pump in an organized and productive manner. All of
the electrical activity in the heart is initiated in specialized muscle cells called
“pacemaker” cells, which spontaneously initiate electrical impulses that are
conducted through pathways in the heart made up of electrical system cells.
Although autonomic nerves surround the heart and can influence the rate or
strength of the heart’s contractions, it is the pacemaker cells, and not the
autonomic nerves, that initiate the electrical impulses that cause the heart
to contract.
Philips Medical Systems
The heart is made up of four chambers, two smaller, upper chambers called
the atria, and two larger, lower chambers called the ventricles. The right
atrium collects blood returning from the body and pumps it into the right
ventricle. The right ventricle then pumps that blood into the lungs to be
oxygenated. The left atrium collects the blood coming back from the lungs
and pumps it into the left ventricle. Finally, the left ventricle pumps the
oxygenated blood to the body, and the cycle starts over again.
2-1

2-2
Normal sinus rhythm
The electrocardiogram (ECG) measures the heart's electrical activity by
monitoring the small signals from the heart that are conducted to the surface
of the patient’s chest. The ECG indicates whether or not the heart is
conducting the electrical impulses properly, which results in pumping blood
throughout the body. In a healthy heart, the electrical impulse begins at the
sinus node, travels down (propagates) to the A-V node, causing the atria to
contract, and then travels down the left and right bundle branches before
spreading out across the ventricles, causing them to contract in unison.
The “normal sinus rhythm” or NSR (so called because the impulse starts at
the sinus node and follows the normal conduction path) shown below is an
example of what the ECG for a healthy heart looks like.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) occurs when the heart stops beating in an
organized manner and is unable to pump blood throughout the body. A
person stricken with SCA will lose consciousness and stop breathing within a
matter of seconds. SCA is a disorder of the heart’s electrical conduction
pathway that prevents the heart from contracting in a manner that will
effectively pump the blood.
Although the terms “heart attack” and “sudden cardiac arrest” are
sometimes used interchangeably, they are actually two distinct and different
conditions. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction (MI), refers to a physical
disorder where blood flow is restricted to a certain area of the heart. This
can be caused by a coronary artery that is obstructed with plaque and results
in an area of tissue that doesn't receive any oxygen. This will eventually cause
those cells to die if nothing is done. A heart attack is typically accompanied
by pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms, and is usually treated with
drugs or angioplasty. Although sudden death is possible, it does not always
occur. Many times, a heart attack will lead to SCA, which does lead to sudden
death if no action is taken.
Philips Medical Systems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
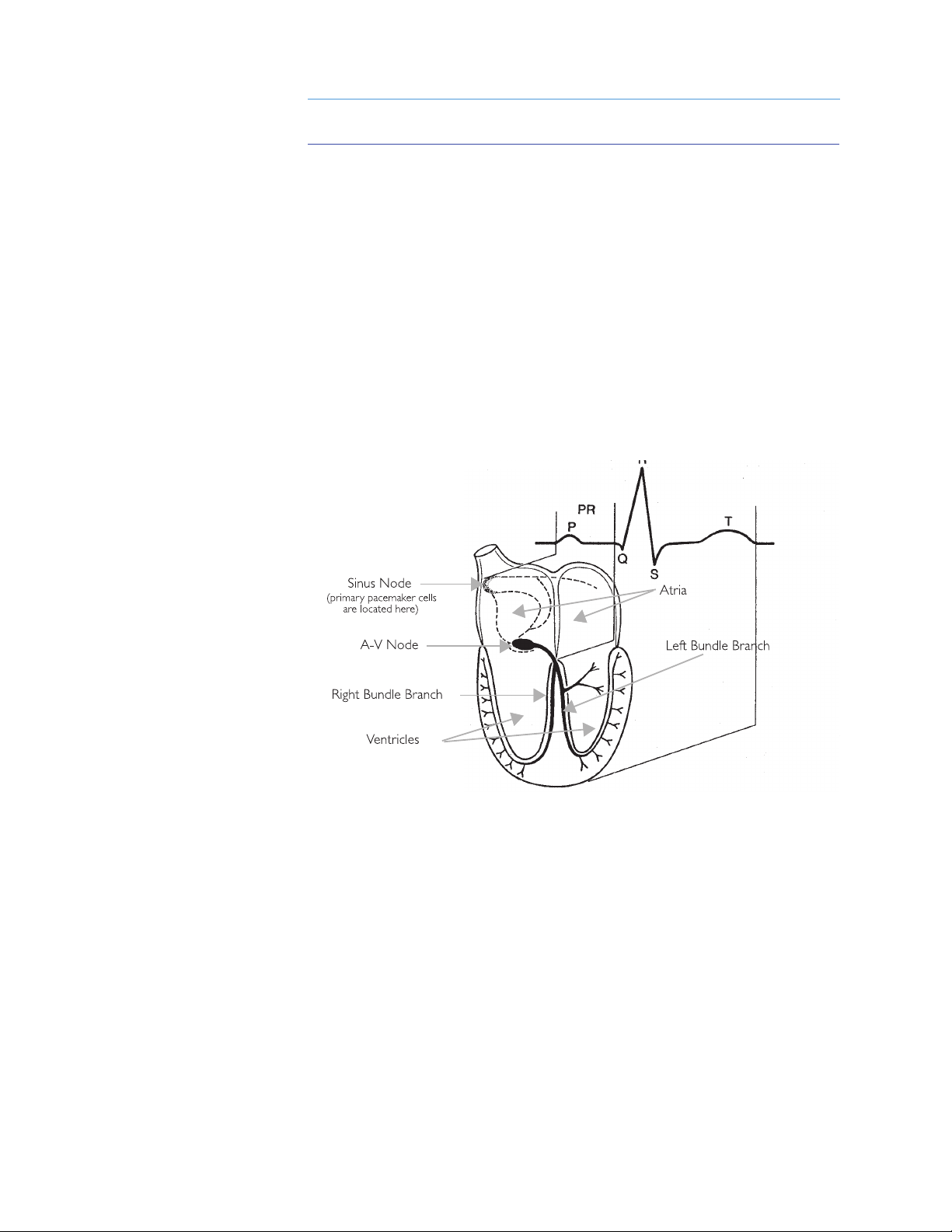
2-3
Ventricular fibrillation
The most common heart rhythm in SCA is ventricular fibrillation (VF). VF
refers to a condition that can develop when the working cells stop
responding to the electrical system in the heart and start contracting
randomly on their own. When this occurs, the heart becomes a quivering
mass of muscle and loses its ability to pump blood through the body. The
heart “stops beating”, and the person will lose consciousness and stop
breathing within seconds. If defibrillation is not successfully performed to
return the heart to a productive rhythm, the person will die within minutes.
The ECG below depicts ventricular fibrillation.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR, allows some oxygen to be delivered
to the various body organs (including the heart), but at a much-reduced rate.
CPR will not stop fibrillation. However, because it allows some oxygen to be
supplied to the heart tissue, CPR extends the length of time during which
defibrillation is still possible. Even with CPR, a fibrillating heart rhythm will
Philips Medical Systems
eventually degenerate into asystole, or “flatline,” which is the absence of any
electrical activity. If this happens, the patient has almost no chance of survival.
Defibrillation is the use of an electrical shock to stop fibrillation and allow the
heart to return to a regular, productive rhythm that leads to pumping action.
The shock is intended to cause the majority of the working cells to contract
(or “depolarize”) simultaneously. This allows them to start responding to the
natural electrical system in the heart and begin beating in an organized
manner again. The chance of survival decreases by about 10% for every
minute the heart remains in fibrillation, so defibrillating someone as quickly
as possible is vital to survival.
An electrical shock is delivered by a defibrillator, and involves placing two
electrodes on a person's chest in such a way that an electrical current travels
from one pad to the other, passing through the heart muscle along the way.
Since the electrodes typically are placed on the patient's chest, the current
must pass through the skin, chest muscles, ribs, and organs in the area of the
chest cavity, in addition to the heart. A person will sometimes “jump” when a
shock is delivered, because the same current that causes all the working cells
in the heart to contract can also cause the muscles in the chest to contract.
DEFIBRILLATION AND ELECTRICITY

2-4
Simplifying Electricity
Energy is defined as the capacity to do work, and electrical energy can be
used for many purposes. It can drive motors used in many common
household appliances, it can heat a home, or it can restart a heart. The
electrical energy used in any of these situations depends on the level of the
voltage applied, how much current is flowing, and for what period of time
that current flows. The voltage level and the amount of current that flows are
related by impedance, which is basically defined as the resistance to the flow
of current.
If you think of voltage as water pressure and current as the flow of water out
of a hose, then impedance is determined by the size of the hose. If you have a
small garden hose, the impedance would be relatively large and would not
allow much water to flow through the hose. If, on the other hand, you have a
fire hose, the impedance would be lower, and much more water could flow
through the hose given the same pressure. The volume of water that comes
out of the hose depends on the pressure, the size of the hose, and the
amount of time the water flows. A garden hose at a certain pressure for a
short period of time works well for watering your garden, but if you used a
fire hose with the same pressure and time, you could easily wash your garden
away.
1
Philips Medical Systems
Electrical energy is similar. The amount of energy delivered depends on the
voltage, the current, and the duration of its application. If a certain voltage is
present across the defibrillator pads attached to a patient's chest, the amount
of current that will flow through the patient's chest is determined by the
impedance of the body tissue. The amount of energy delivered to the patient
is determined by how long that current flows at that level of voltage.
In the case of the biphasic waveforms shown in the following pages, energy
E) is the power (P) delivered over a specified time (t), or E = P x t.
(
1 Voltage is measured in volts, current is measured in amperes (amps), and impedance is
measured in ohms. Large amounts of electrical energy are measured in kilowatt-hours, as
seen on your electric bill. Small amounts can be measured in joules (J), which are
watt-seconds.
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

Electrical power is defined as the
SMART Biphasic waveform
voltage (V) times the current (volts=
joules/coulomb, amps = coulombs/sec):
2-5
P = V x I
From Ohm's law, voltage and
current are related by resistance (R)
(impedance):
Power is therefore related to voltage
and resistance by:
Substituting this back into the equation
for energy means that the energy
delivered by the biphasic waveform is
V = I x R or
I = V/R
2
/R or
P = V
2
P = I
2
/R x t or
E = V
2
R x t
E = I
R
represented by:
In determining how effective the energy is at converting a heart in fibrillation,
how the energy is delivered -- or the shape of the waveform (the value of the
voltage over time) -- is actually more important than the amount of energy
delivered.
For the SMART Biphasic waveform, the design strategy involved starting with
a set peak voltage stored on the capacitor that will decay exponentially as
current is delivered to the patient. The SMART Biphasic waveform shown
here is displayed with the voltage plotted versus time, for a patient with an
impedance of 75 ohms. By changing the time duration of the positive and
negative pulses, the energy delivered to the patient can be controlled.
Philips Medical Systems
Although the relationship of voltage and energy is of interest in designing the
defibrillator, it is actually the current that is responsible for defibrillating the
heart.
DEFIBRILLATION AND ELECTRICITY
2-6
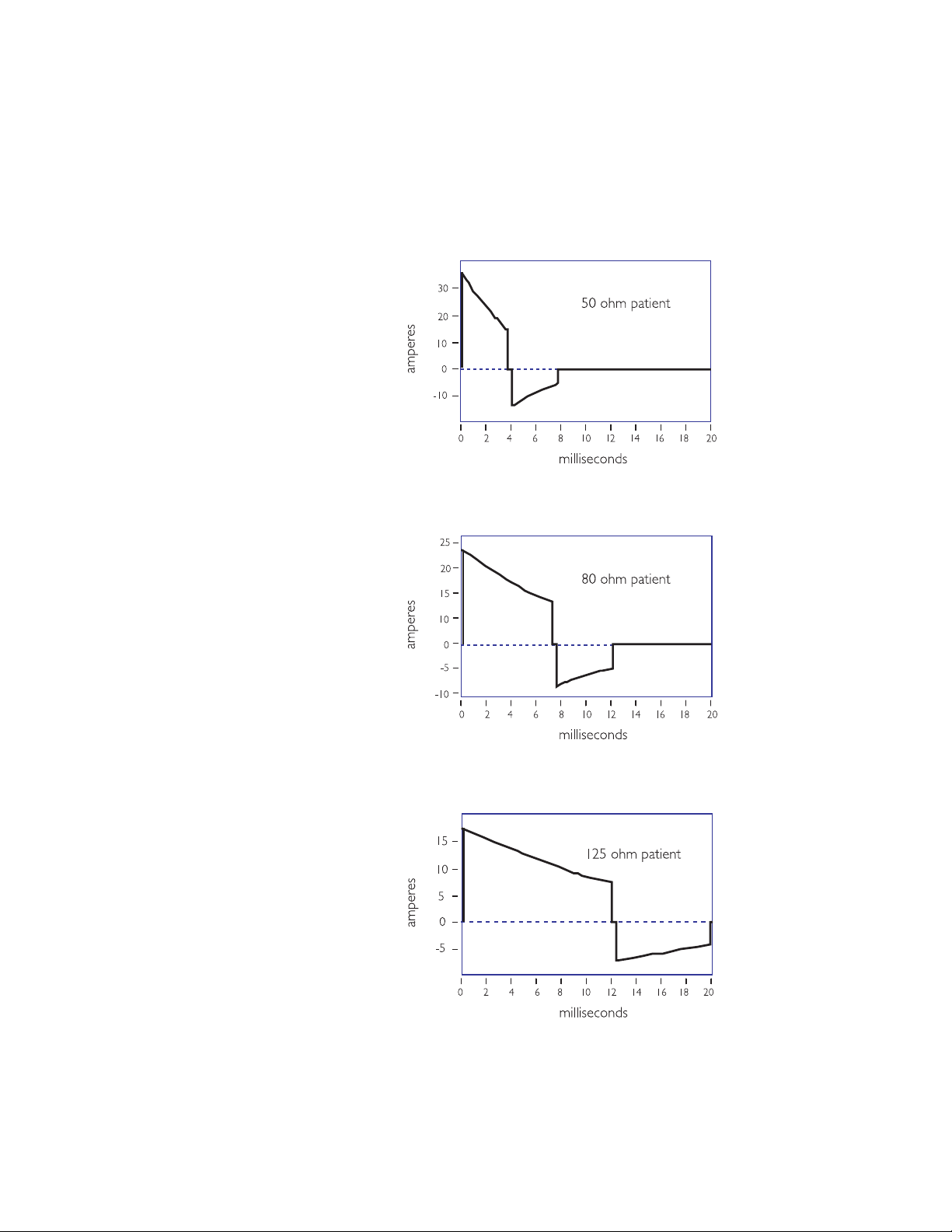
The following three graphs demonstrate how the shape of the current
waveform changes with different patient impedances. Once again, the SMART
Biphasic waveform delivers the same amount of energy (150 J) to every
patient, but the shape of the waveform changes to provide the highest level of
effectiveness for defibrillating the patient at each impedance value.
Philips Medical Systems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

2-7
With the SMART Biphasic waveform, the shape of the waveform is optimized
for each patient. The initial voltage remains the same, but the peak current
will depend on the patient’s impedance. The tilt (slope) and the time duration
are adjusted for different patient impedances to maintain approximately 150 J
for each shock. The phase ratio, or the relative amount of time the waveform
spends in the positive pulse versus the negative pulse, is also adjusted
depending upon the patient impedance to insure the waveform remains
effective for all patients. Adjusting these parameters makes it easier to
control the accuracy of the energy delivered since they are proportionally
related to energy, whereas voltage is exponentially related to energy.
The HeartStart Defibrillator measures the patient's impedance during each
shock. The delivered energy is controlled by using the impedance value to
determine what tilt and time period are required to deliver 150 J.
The average impedance in adults is 75 ohms, but it can vary from 25 to 180
ohms. Because a HeartStart Defibrillator measures the impedance and
adjusts the shape of the waveform accordingly, it delivers 150 J of energy to
the patient every time the shock button is pressed. Controlling the amount
of energy delivered allows the defibrillator to deliver enough energy to
defibrillate the heart, but not more. Numerous studies have demonstrated
that the waveform used by HeartStart Defibrillator is more effective in
defibrillating out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients than the waveforms used
by conventional defibrillators. Moreover, the lower energy delivered results
in less post-shock dysfunction of the heart, resulting in better outcomes for
Philips Medical Systems
survivors.
DEFIBRILLATION AND ELECTRICITY

Notes
Philips Medical Systems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
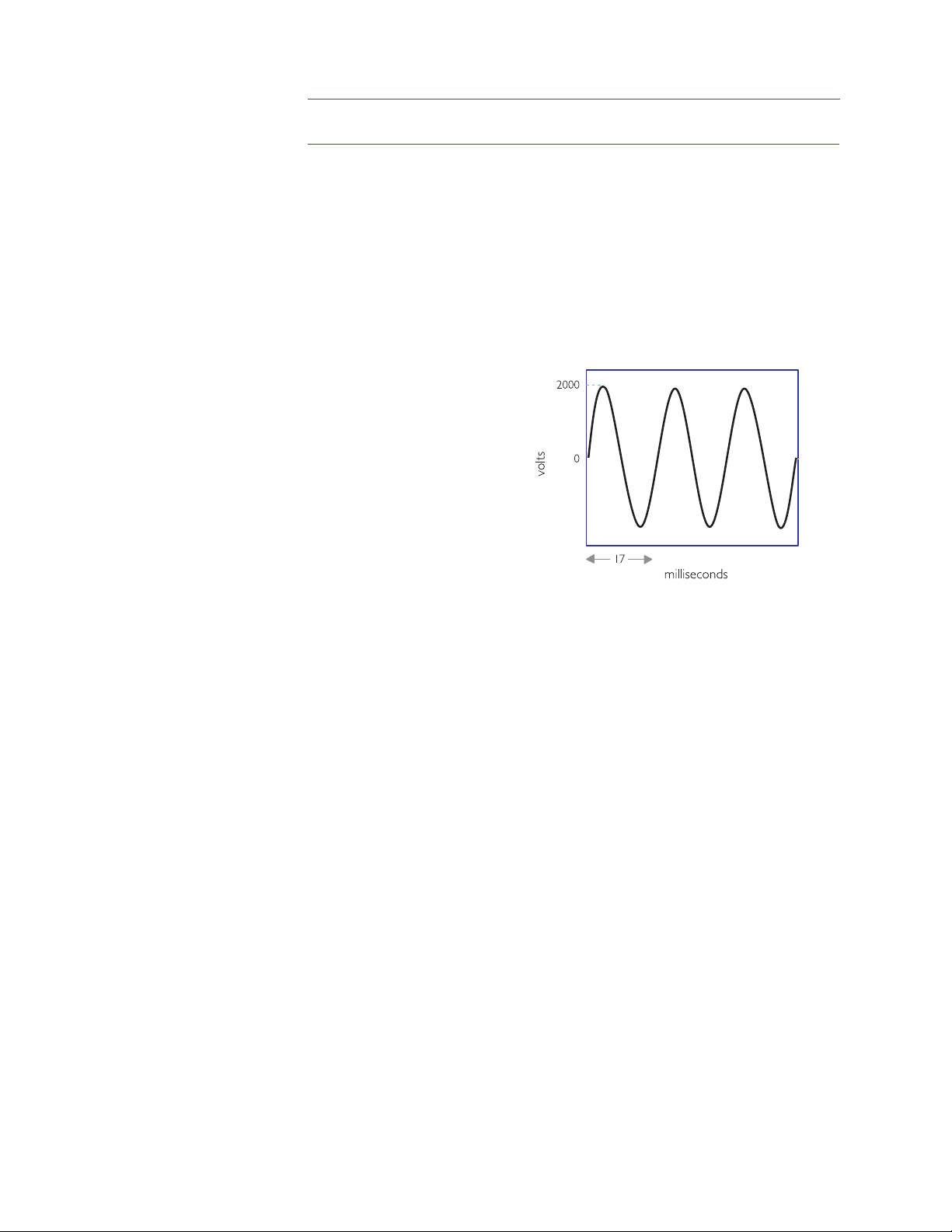
3 SMART Biphasic Waveform
alternating current (AC) waveform
Defibrillation is the only effective treatment for ventricular fibrillation, the
most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). The defibrillation
waveform used by a defibrillator determines how energy is delivered to a
patient and defines the relationship between the voltage, current, and patient
impedance over time. The defibrillator waveform used is critical for
defibrillation efficacy and patient outcome.
A Brief History of Defibrillation
The concept of electrical
defibrillation was introduced
over a century ago. Early
experimental defibrillators
used 60 cycle alternating
current (AC) household
power with step-up
transformers to increase the
voltage. The shock was
delivered directly to the
heart muscle. Transthoracic
(through the chest wall)
defibrillation was first used in
Philips Medical Systems
the 1950s.
The desire for portability led to the development of battery-powered direct
current (DC) defibrillators in the 1950s. At that time it was also discovered
that DC shocks were more effective than AC shocks. The first “portable”
defibrillator was developed at Johns Hopkins University. It used a biphasic
waveform to deliver 100 joules (J) over 14 milliseconds. The unit weighed 50
pounds with accessories (at a time when standard defibrillators typically
weighed more than 250 pounds) and was briefly commercialized for use in
the electric utility industry.
Defibrillation therapy gradually gained acceptance over the next two decades.
An automated external defibrillator (AED) was introduced in the mid-1970s,
shortly before the first automatic internal cardioverterdefibrillator (AICD) was implanted in a human.
Historically, defibrillators used one of two types of monophasic waveforms:
monophasic damped sine (MDS) or monophasic truncated exponential
(MTE). With monophasic waveforms, the heart receives a single burst of
electrical current that travels from one pad or paddle to the other.
3-1
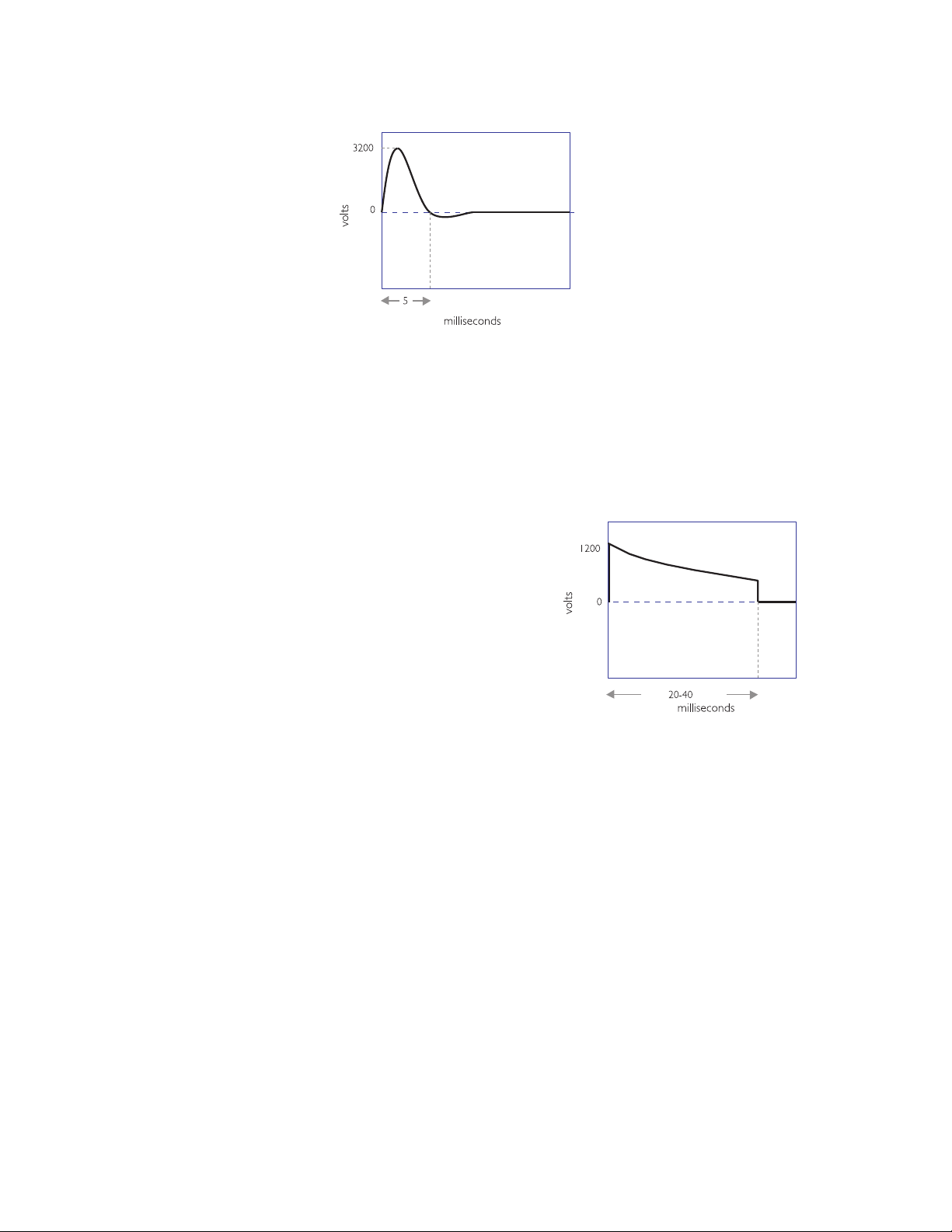
3-2
biphasic damped sine (MDS) waveform
monophasic truncated exponential (MTE) waveform
The M DS waveform
requires high energy levels,
up to 360 J, to defibrillate
effectively. MDS waveforms
are not designed to
compensate for differences
in impedance — the
resistance of the body to
the flow of current —
encountered in different
patients. As a result, the
effectiveness of the shock
can vary greatly with the
patient impedance.
Traditional MDS waveform defibrillators assume a patient impedance of 50
ohms, but the average impedance of adult humans is between 70 and 80
ohms. As a result, the actual energy delivered by MDS waveforms is usually
higher than the selected energy.
The monophasic truncated
exponential (MTE) waveform
also uses energy settings of
up to 360 J. Because it uses a
lower voltage than the MDS
waveform, the MTE waveform
requires a longer duration to
deliver the full energy to
patients with higher
impedances. This form of
impedance compensation
does not improve the efficacy
of defibrillation, but simply
allows extra time to deliver the selected energy. Long-duration shocks
(> 20 msec) have been associated with refibrillation.
1
Philips Medical Systems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
Despite the phenomenal advances in the medical and electronics fields during
the last half of the 20th century, the waveform technology used for external
defibrillation remained the same until just recently. In 1992, research
scientists and engineers at Heartstream (now part of Philips Medical Systems)
began work on what was to become a significant advancement in external
defibrillation waveform technology. Extensive studies for implantable
defibrillators had shown biphasic waveforms to be superior to monophasic
2,3,4
waveforms.
In fact, a biphasic waveform has been the standard waveform
for implantable defibrillators for over a decade. Studies have demonstrated
that biphasic waveforms defibrillate at lower energies and thus require
smaller components that result in smaller and lighter devices.
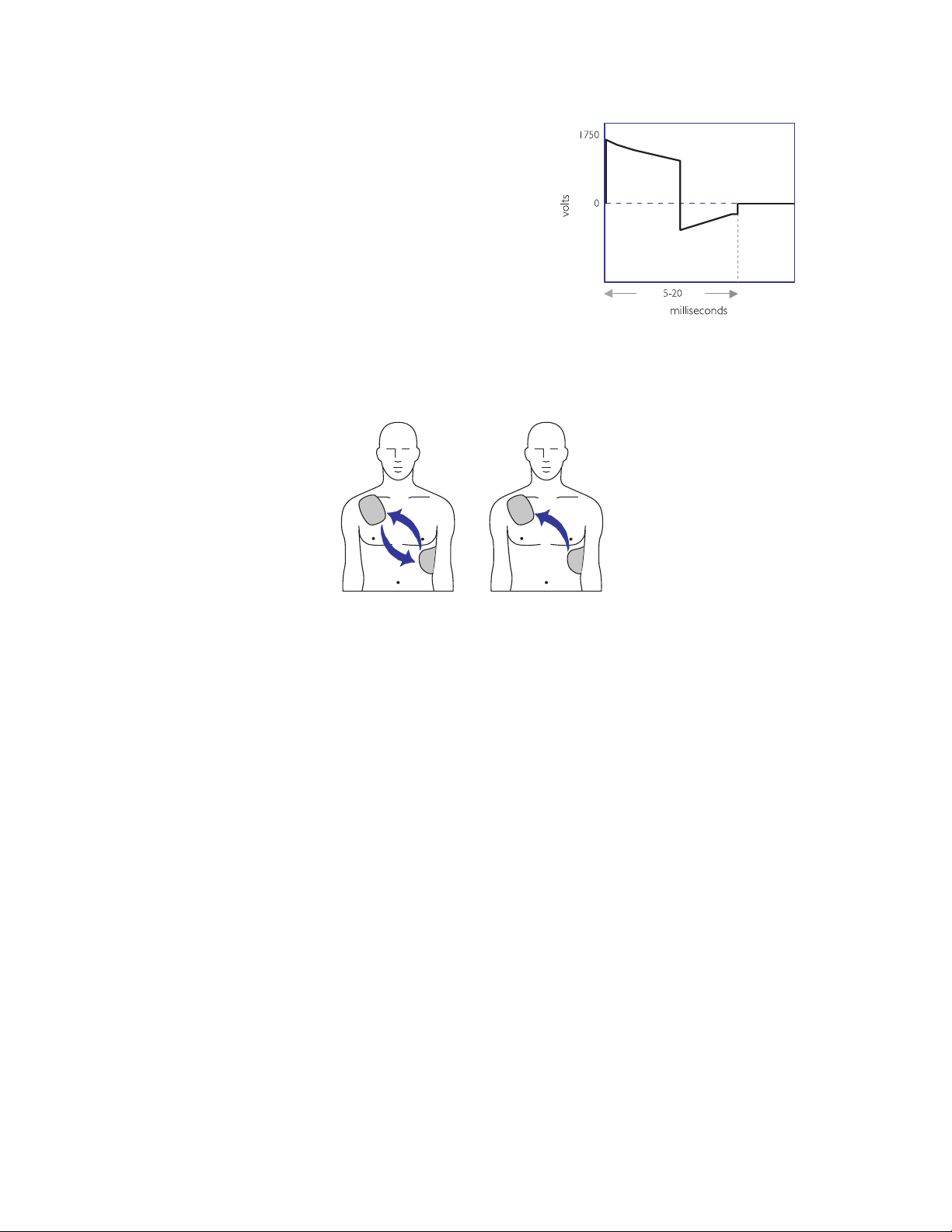
3-3
biphasic truncated exponential (BTE) waveform
/QPQRJCUKE9CXGHQTO$KRJCUKE9CXGHQTO
defibrillation current flow
Heartstream pursued the use
of the biphasic waveform in
AEDs for similar reasons; use
of the biphasic waveform
allows for smaller and lighter
AEDs. The SMART Biphasic
waveform has been proven
effective at an energy level of
150 joules and has been used
in HeartStart AEDs since
they were introduced in
1996.
The basic difference
between monophasic and
biphasic waveforms is the
direction of current flow
between the defibrillation
pads. With a monophasic
waveform, the current
flows in only one direction.
With a biphasic waveform,
the current flows in one
direction and then reverses
Philips Medical Systems
and flows in the opposite
direction. Looking at the
waveforms, a monophasic waveform has one positive pulse, whereas a
biphasic starts with a positive pulse that is followed by a negative one.
In the process of developing the biphasic truncated exponential waveform for
use in AEDs, valuable lessons have been learned:
1. Not all waveforms are equally effective. How the energy is delivered (the
waveform used) is actually more important than how much energy is
delivered.
2. Compensation is needed in the waveform to adjust for differing patient
impedances because the effectiveness of the waveform may be affected
by patient impedance. The patient impedance can vary due to the energy
delivered, electrode size, quality of contact between the electrodes and
the skin, number and time interval between previous shocks, phase of
ventilation, and the size of the chest.
3. Lower energy is better for the patient because it reduces post-shock
dysfunction. While this is not a new idea, it has become increasingly clear
as more studies have been published.
SMART BIPHASIC WAVEFORM
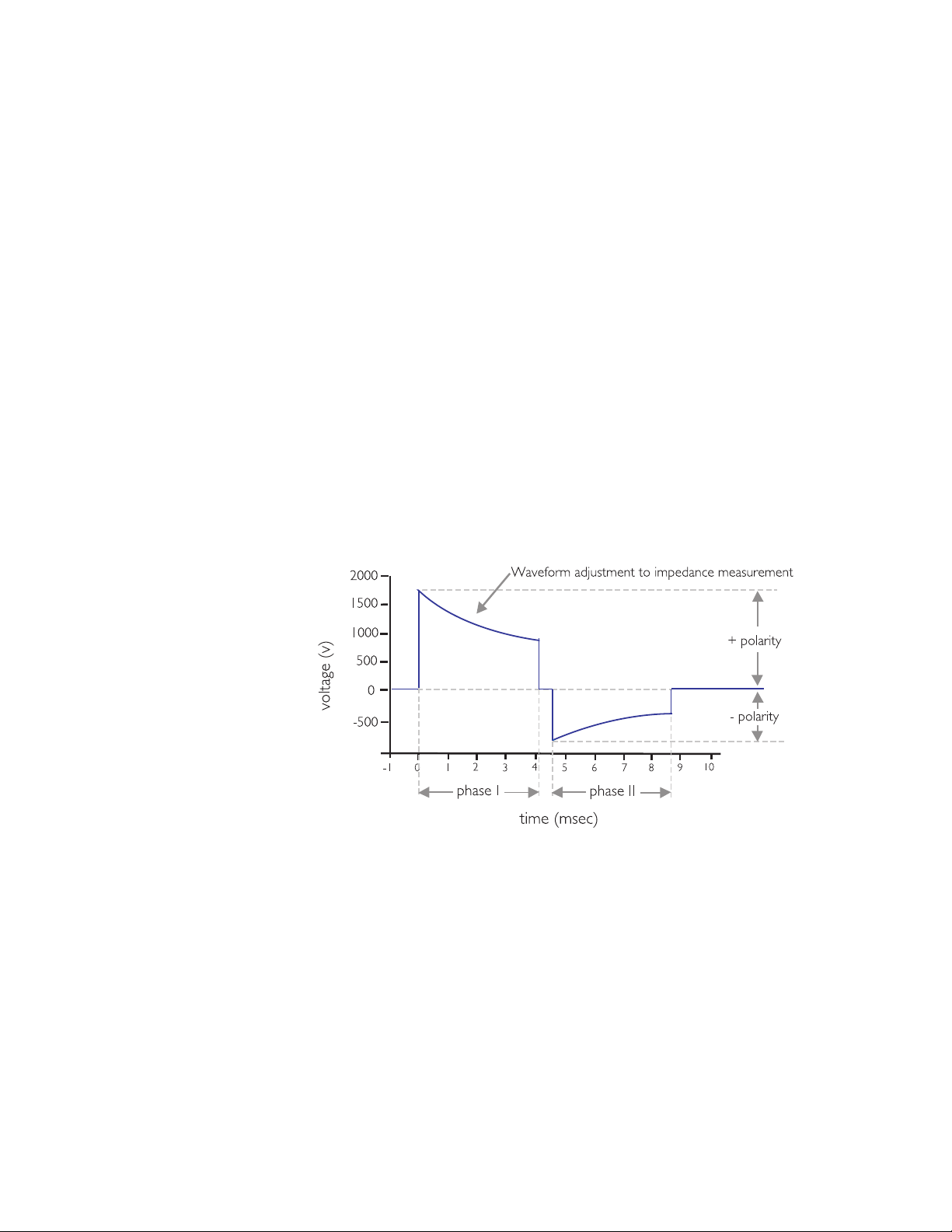
3-4
SMART Biphasic waveform
The characteristics for the monophasic damped sine and monophasic
truncated exponential waveforms are specified in the AAMI standard
DF80:2003; the result is that these waveforms are very similar from one
manufacturer to the next.
There is no standard for biphasic waveforms, each manufacturer has designed
their own. This has resulted in various wave-shapes depending on the design
approach used. While it is generally agreed that biphasic waveforms are
better than the traditional monophasic waveforms, it is also true that
different levels of energy are required by different biphasic waveforms in
order to be effective.
SMART Biphasic
SMART Biphasic is the patented waveform used by all HeartStart AEDs. It is
an impedance-compensating, low energy (<200 J), low capacitance (100 µF),
biphasic truncated exponential (BTE) waveform that delivers a fixed energy
of 150 J for defibrillation. Heartstream was the first company to develop a
biphasic waveform for use in AEDs.
The SMART Biphasic waveform developed by Heartstream compensates for
different impedances by measuring the patient impedance during the
discharge and using that value to adjust the duration of the waveform to
deliver the desired 150 joules. Since the starting voltage is sufficiently large,
the delivered energy of 150 joules can be accomplished without the duration
ever exceeding 20 milliseconds. The distribution of the energy between the
positive and negative pulses was fine tuned in animal studies to optimize
defibrillation efficacy and validated in studies conducted in and out of the
hospital environment.
Philips Medical Systems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
3-5
Different waveforms have different dosage requirements, similar to a dosage
associated with a medication. “If energy and current are too low, the shock
will not terminate the arrhythmia; if energy and current are too high,
5
myocardial damage may result.” (I-63)
The impedance compensation used in
the SMART Biphasic waveform results in an effective waveform for all
patients. The SMART Biphasic waveform has been demonstrated to be just as
effective or superior for defibrillating VF when compared to other
waveforms and escalating higher energy protocols.
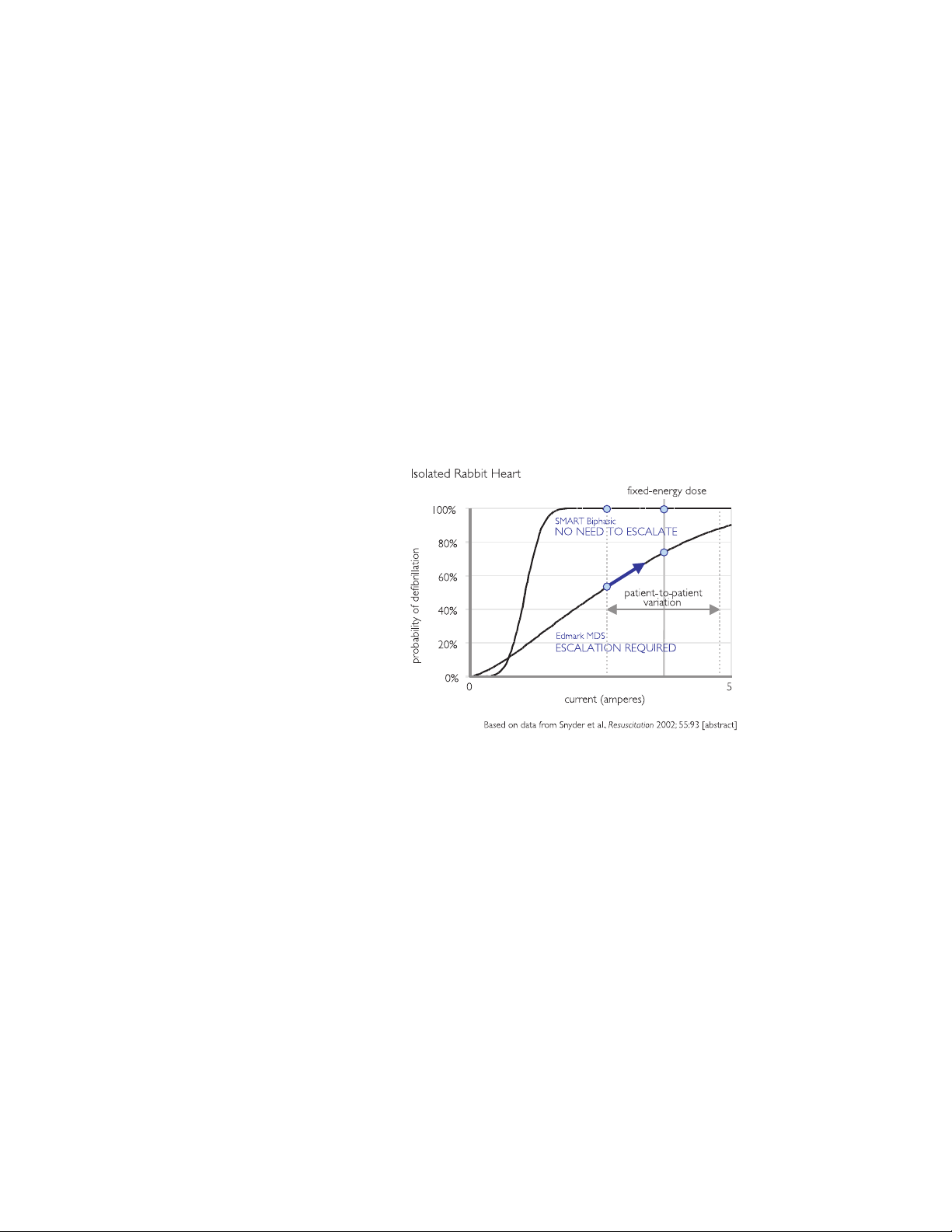
Understanding Fixed Energy
The BTE waveform has an advantage over the monophasic waveforms related
to the shape of the defibrillation response curve. The following graph, based
on Snyder et al., demonstrates the difference between the defibrillation
response curves for the BTE and the MDS waveform.
Philips Medical Systems
With the gradual slope of the MDS waveform, it is apparent that as current
increases, the defibrillation efficacy also increases. This characteristic of the
MDS response curve explains why escalating energy is needed with the MDS
waveform; the probability of defibrillation increases with an increase in peak
current, which is directly related to increasing the energy.
For a given amount of energy the resulting current level can vary greatly
depending on the impedance of the patient. A higher-impedance patient
receives less current, so escalating the energy is required to increase the
probability of defibrillation.
The steeper slope of the BTE waveform, however, results in a response curve
where the efficacy changes very little with an increase in current, past a
certain current level. This means that if the energy (current) level is chosen
appropriately, escalating energy is not required to increase the efficacy. This
SMART BIPHASIC WAVEFORM

3-6
fact, combined with the lower energy requirements of BTE waveforms,
16,18
means that it is possible to choose one fixed energy that allows any patient to
be effectively and safely defibrillated.
Evidence-Based Support for the SMART Biphasic Waveform
Using a process outlined by the American Heart Association (AHA) in 1997,6
the Heartstream team put the SMART Biphasic waveform through a rigorous
sequence of validation studies. First, animal studies were used to test and
fine-tune the waveform parameters to achieve optimal efficacy. Electrophysiology laboratory studies were then used to validate the waveform on
humans in a controlled hospital setting. Finally, after receiving FDA clearance
for the Heartstream AED, post-market studies were used to prove the
efficacy of the SMART Biphasic waveform in the out-of-hospital,
emergency-resuscitation environment.
Even when comparing different energies delivered with a single monophasic
waveform, it has been demonstrated that lower-energy shocks result in fewer
post shock arrhythmias.
waveform has several clinical advantages. It has equivalent efficacy to higher
energy monophasic waveforms but shows no significant ST segment change
from the baseline.
when the biphasic waveform is used.
biphasic waveform has improved performance when anti-arrhythmic drugs
12,13
are present,
and with long duration VF.
demonstrated improved neurological outcomes for survivors defibrillated
with SMART Biphasic when compared to patients defibrillated with
monophasic waveforms.
7
Other studies have demonstrated that the biphasic
8
There is also evidence of less post shock dysfunction
15
9,10,11,29
14,20
There is evidence that the
A more recent study has also
Philips Medical Systems
The bottom line is that the SMART Biphasic waveform has been
demonstrated to be just as effective or superior to monophasic waveforms at
defibrillating patients in VF. In addition, there are indications that patients
defibrillated with the SMART Biphasic waveform suffer less dysfunction than
those defibrillated with conventional escalating-energy monophasic
waveforms. SMART Biphasic has been used in AEDs for over a decade, and
there are numerous studies to support the benefits of this waveform,
including out-of-hospital data with long-down-time VF.
SMART Biphasic Superior to Monophasic
Researchers have produced over 20 peer-reviewed manuscripts to prove the
efficacy and safety of the SMART Biphasic waveform. Thirteen of these are
out-of-hospital studies that demonstrated high efficacy of the SMART
Biphasic waveform on long-down-time patients in emergency environments.
No other waveform is supported by this level of research.
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL

3-7
Using criteria established by the AHA in its 1997 Scientific Statement,27 the
data from the ORCA study
15,34
demonstrate that the 150J SMART Biphasic
waveform is superior to the 200J - 360J escalating energy monophasic
waveform in the treatment of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This is true for
one-shock, two-shock, and three-shock efficacy and return of spontaneous
circulation.
Key Studies
year waveforms studied results
1992 low-energy vs.
high-energy damped sine
monophasic
1994
biphasic vs. damped sine
1995 171 patients (electrophysiology laboratory). First-shock efficacy of
monophasic
1995 low-energy truncated
biphasic vs. high-energy
damped sine monophasic
249 patients (emergency resuscitation). Low-energy and high-energy
damped sine monophasic are equally effective. Higher energy is
associated with increased incidence of A-V block with repeated shocks.
19 swine. Biphasic shocks defibrillate at lower energies, and with less
post-shock arrhythmia, than monophasic shocks.
biphasic damped sine is superior to high-energy monophasic damped
17
sine.
16
30 patients (electrophysiology laboratory). Low-energy truncated
biphasic and high-energy damped sine monophasic equally
effectiveness.
18
7
1996 115 J and 130 J truncated
biphasic vs. 200 J and 360
J damped sine
Philips Medical Systems
monophasic
294 patients (electrophysiology laboratory). Low-energy truncated
biphasic and high-energy damped sine monophasic are equally effective.
High-energy monophasic is associated with significantly more
post-shock ST-segment changes on ECG.
8
This study of a 115 J and 130
J waveform contributed to the development of the 150 J, nominal,
therapy that ships with Philips AEDs.
1997
18 patients (10 VF, emergency resuscitation). SMART Biphasic
terminated VF at higher rates than reported damped sine or truncated
exponential monophasic.
19
1998 30 patients (electrophysiology laboratory). High-energy monophasic
showed significantly greater post-shock ECG ST-segment changes than
SMART Biphasic vs.
1999 286 patients (100 VF, emergency resuscitation). First-shock efficacy of
standard high-energy
monophasic
SMART Biphasic.
SMART Biphasic was 86% (compared to pooled reported 63% for
damped sine monophasic); three or fewer shocks, 97%; 65% of patients
had organized rhythm at hand-off to ALS or emergency personnel.
9
20
116 patients (emergency resuscitation). At all post-shock assessment
1999 low-energy (150 J) vs.
high-energy (200 J)
biphasic
times (3 - 60 seconds) SMART Biphasic patients had lower rates of VF.
Refibrillation rates were independent of waveform.
20 swine. Low-energy biphasic shocks increased likelihood of
successful defibrillation and minimized post-shock myocardial
dysfunction after prolonged arrest.
21
10
SMART BIPHASIC WAVEFORM

3-8
year waveforms studied results
1999 low-capacitance biphasic
vs. high-capacitance
biphasic
10 swine. Five of five low-capacitance shock animals were resuscitated,
compared to two of five high-capacitance at 200 J. More cumulative
energy and longer CPR were required for high-capacitance shock
animals that survived.
22
10 swine. Stroke volume and ejection fraction progressively and
1999
significantly reduced at 2, 3, and 4 hours post-shock for monophasic
animals but improved for biphasic animals.
11
338 patients (115 VF, emergency resuscitation). Demonstrated
superior defibrillation performance in comparison with escalating,
2000
SMART Biphasic vs.
escalating high-energy
monophasic
high-energy monophasic shocks in out-of hospital cardiac arrest
(average time from call to first shock was 8.9 minutes). SMART Biphasic
defibrillated at higher rates than MTE and MDS (96% first-shock efficacy
vs. 59%), with more patients achieving ROSC. Survivors of SMART
Biphasic resuscitation were more likely to have good cerebral
performance at discharge, and none had coma (vs. 21% for monophasic
survivors).
15
2001 338 patients (115 VF, emergency resuscitation). Use of a low-energy
impedance-compensating biphasic waveform device resulted in superior
first-shock efficacy, in the first set of two or three shocks, time to
shock, and first successful shock compared to traditional defibrillators
2004
using escalating energy monophasic truncated exponential and
monophasic damped sine waveforms.
62 patients (shockable rhythms; 41% of patients were classified as
34
overweight, 24% as obese, and 4% as extremely obese). Overweight
patients were successfully defibrillated by the 150 J SMART Biphasic
waveform, without energy escalation.
35
SMART Biphasic
2005 102 patients (all presenting with shockable rhythms). SMART Biphasic
successfully defibrillated high-impedance patients without energy
escalation. Rapid defibrillation rather than differences in patient
impedance accounted for resuscitation success.
36
Philips Medical Systems
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all biphasic waveforms alike?
No. Different waveforms perform differently, depending on their shape,
duration, capacitance, voltage, current, and response to impedance. Different
biphasic waveforms are designed to work at different energies. As a result, an
appropriate energy dose for one biphasic waveform may be inappropriate for
a different waveform.
There is evidence to suggest that a biphasic waveform designed for lowenergy defibrillation may result in overdose if applied at high energies (the
Tang AHA abstract from 1999 showed good resuscitation performance for
the SMART Biphasic waveform, but more shocks were required at 200 J than
at 150 J
defibrillation may not defibrillate effectively at lower energies. (The Tang
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
21
). Conversely, a biphasic waveform designed for high-energy

3-9
Peak Current Levels
AHA abstract from 1999 showed poor resuscitation performance for the
200 µF capacitance biphasic waveform at 200 J compared to the 100 µF
22
capacitance biphasic waveform [SMART Biphasic] at 200 J.
The Higgins
manuscript from 2000 showed that the 200 µF capacitance biphasic
23
waveform performed better at 200 J than at 130 J.
)
It is consequently necessary to refer to the manufacturer's recommendations
and the clinical literature to determine the proper dosing for a given biphasic
waveform. The recommendations for one biphasic waveform should not be
arbitrarily applied to a different biphasic waveform. “It is likely that the
optimal energy level for biphasic defibrillators will vary with the units'
waveform characteristics. An appropriate energy dose for one biphasic
24
waveform may be inappropriate for another.”
SMART Biphasic was designed for low-energy defibrillation, while some
other biphasic waveforms were not. It would be irresponsible to use a
waveform designed for high energy with a low-energy protocol.
How can the SMART Biphasic waveform be more effective at
lower energy?
The way the energy is delivered makes a significant difference in the efficacy
of the waveform. Electric current has been demonstrated to be the variable
most highly correlated with defibrillation efficacy. The SMART Biphasic
Philips Medical Systems
waveform uses a 100 µF capacitor to store the energy inside the AED; other
biphasic waveforms use a 200 µF capacitor to store the energy. The energy
(E) stored on the capacitor is given by the equation:
E = ½ C V
2
The voltage (V) and the current (I) involved with defibrillating a patient are
related to the patient impedance (R) by the equation:
V = I R
SMART BIPHASIC WAVEFORM
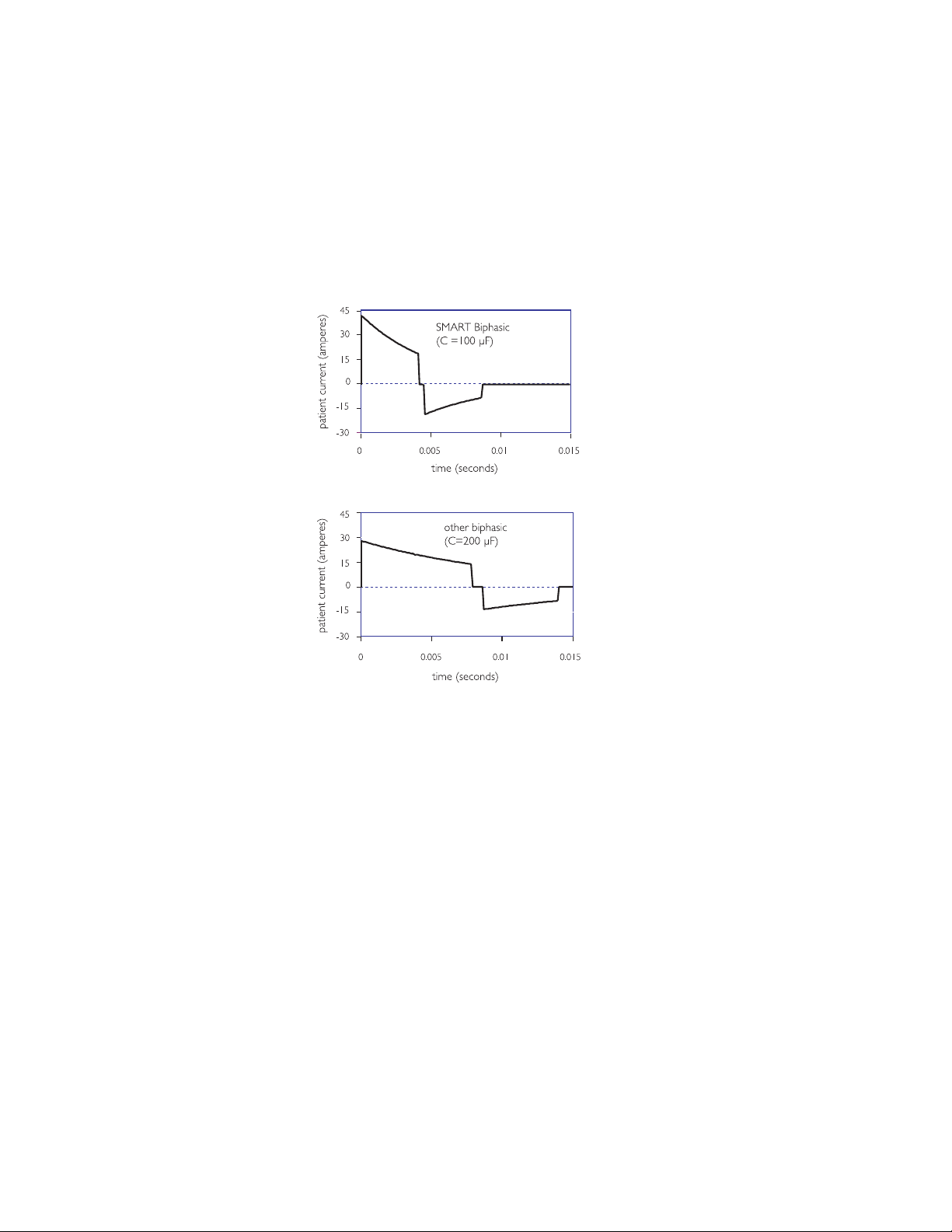
3-10
For the 200 µF capacitance biphasic waveform to attain similar levels of
current to the SMART Biphasic (100 µF) waveform, it must apply the same
voltage across the patient's chest. This means that to attain similar current
levels, the 200 µF biphasic waveform must store twice as much energy on the
capacitor and deliver much more energy to the patient; the graph at right
demonstrates this relationship. This is the main reason why some biphasic
waveforms require higher energy doses than the SMART Biphasic waveform
to attain similar efficacy.
The illustrations to the left show
the SMART Biphasic waveform
and another biphasic waveform
with a higher capacitance, similar
to that used by another AED
manufacturer. The low
capacitance used by the patented
SMART Biphasic waveform
delivers energy more efficiently. In
an animal study using these two
waveforms, the SMART Biphasic
waveform successfully
resuscitated all animals and
required less cumulative energy
and shorter CPR time than the
other biphasic waveform, which
resuscitated only 40% of the
animals.
22
Philips Medical Systems
The amount of energy needed depends on the waveform that is used. SMART
Biphasic has been demonstrated to effectively defibrillate at 150 J in
15
out-of-hospital studies.
Animal studies have indicated that the SMART
Biphasic waveform would not be more effective at higher energies
seems to be supported with observed out-of-hospital defibrillation efficacy of
96% at 150 J.
15
Is escalating energy required?
Not with SMART Biphasic technology. In the “Guidelines 2005,”5 the AHA
states, “Energy levels vary by type of device.” (IV-37) The SMART Biphasic
waveform has been optimized for ventricular defibrillation efficacy at 150 J.
Referring to studies involving the SMART Biphasic waveform, it states,
Overall this research indicates that lower-energy biphasic waveform shocks have
“
equivalent or higher success for termination of VF than either damped sinusoidal or
truncated exponential monophasic waveform shocks delivering escalating energy
(200 J, 300 J, 360 J) with successive shocks
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
.” (I V- 37)
21
and this

3-11
All HeartStart AEDs use the 150 J SMART Biphasic waveform. Two ALS
defibrillator products, the HeartStart XL and MRx, provide an AED mode as
well as ALS features such as manual defibrillation, synchronized cardioversion, etc. Selectable energy settings (from 2 to 200 J for the XL or
1 to 200 J for the MRx) are available in the XL and MRx only in the manual
mode. A wider range of energy settings is appropriate in a device designed
for use by advanced life support (ALS) responders who may perform
manual pediatric defibrillation or synchronized cardioversion, as energy
requirements may vary depending on the type of cardioversion rhythm.
25,26
For treating VF in patients over eight years of age in the AED mode, however,
the energy is preset to 150 J.
Some have suggested that a patient may need more than 150 J with a BTE
waveform when conditions like heart attacks, high-impedance, delays before
the first shock, and inaccurate electrode pad placement are present. This is
not true for the SMART Biphasic waveform, as the evidence presented in the
following sections clearly indicates. On the other hand, the evidence
indicates that other BTE waveforms may require more than 150 J for
defibrillating patients in VF.
Heart Attacks
One manufacturer references only animal studies using their waveform to
support their claim that a patient may require more than 200 J for cardiac
arrests caused by heart attacks (myocardial infarction) when using their
waveform. The SMART Biphasic waveform has been tested in the real world
Philips Medical Systems
with real heart attack victims and has proven its effectiveness at terminating
ventricular fibrillation (VF). In a prospective, randomized, out-of-hospital
study, the SMART Biphasic waveform demonstrated a first shock efficacy of
96% versus 59% for monophasic waveforms, and 98% efficacy with 3 shocks
15
as opposed to 69% for monophasic waveforms.
Fifty-one percent of the
victims treated with the SMART Biphasic waveform were diagnosed with
acute myocardial infarction. The published evidence clearly indicates that the
SMART Biphasic waveform does not require more than 150 J for heart attack
victims.
High-Impedance or Large Patients
High impedance patients do not pose a problem with the low energy SMART
Biphasic waveform. Using a patented method, SMART Biphasic technology
automatically measures the patient's impedance and adjusts the waveform
dynamically during each shock to optimize the waveform for each shock on
each patient. As demonstrated in published, peer-reviewed clinical literature,
the SMART Biphasic waveform is as effective at defibrillating patients with
high impedance (greater than 100 ohms) as it is with low-impedance
19
patients.
The bottom line is that the SMART Biphasic waveform does not
require more than 150 J for high-impedance patients.
SMART BIPHASIC WAVEFORM
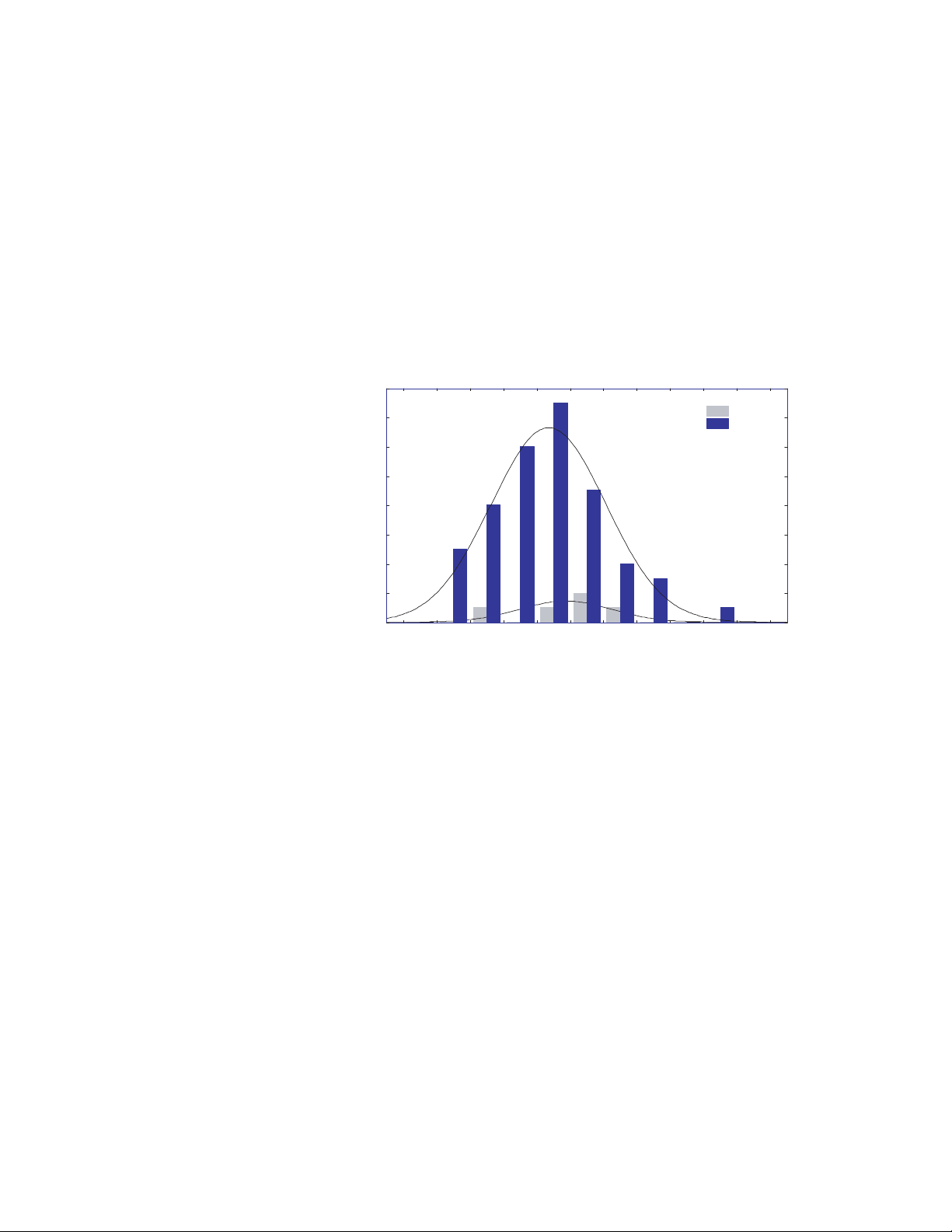
3-12
0ATIENTS
&IRST3HOCK
0ATIENT7EIGHTLBS
P
&AIL
3UCCEED
Data collected from a group of patients defibrillated by the Rochester,
Minnesota, EMS organization during actual resuscitation attempts was
examined to determine if patient weight affected the defibrillation
effectiveness of the 150 J non-escalating SMART biphasic shock that was
used. Of the patients for whom both weight and height data were available,
41% were overweight, 24% were obese, and 4% were extremely obese by
BMI (Body Mass Index) standards. As shown in the graph below, the success
and failure distributions were identical for the three groups. Thus,
defibrillation effectiveness on the first shock was in no way related to the
weight of the patient. The cumulative two-shock success rate was 99%, and
all patients were defibrillated by the third shock.
Delays before the First Shock
The SMART Biphasic waveform is the only biphasic waveform to have
extensive, peer-reviewed and published emergency resuscitation data for
long-duration VF. In a randomized out-of-hospital study comparing the
low-energy SMART Biphasic waveform to high-energy escalating monophasic
waveforms, the average collapse-to-first-shock time was 12.3 minutes. Of the
54 patients treated with the SMART Biphasic waveform, 100% were
successfully defibrillated, 96% on the first shock and 98% with three or fewer
shocks. With the monophasic waveforms, only 59% were defibrillated on the
first shock and only 69% with three or fewer shocks. Seventy-six percent of
the patients defibrillated with the SMART Biphasic waveform experienced a
return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), versus only 55% of the patients
treated with high-energy monophasic waveforms.
15
In a post-market,
out-of-hospital study of 100 VF patients defibrillated with the SMART
Biphasic waveform, the authors concluded, “Higher energy is not clinically
20
warranted with this waveform.”
SMART Biphasic does not require more
than 150 J when there are delays before the first shock.
Philips Medical Systems
HEARTSTART HS1 DEFIBRILLATORS TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
 Loading...
Loading...