Philips BC547A, BC546B, BC547C, BC547B Datasheet
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
ook, halfpage
M3D186
BC546; BC547
NPN general purpose transistors
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Mar 04
1999 Apr 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
NPN general purpose transistors BC546; BC547
FEATURES
• Low current (max. 100 mA)
• Low voltage (max. 65 V).
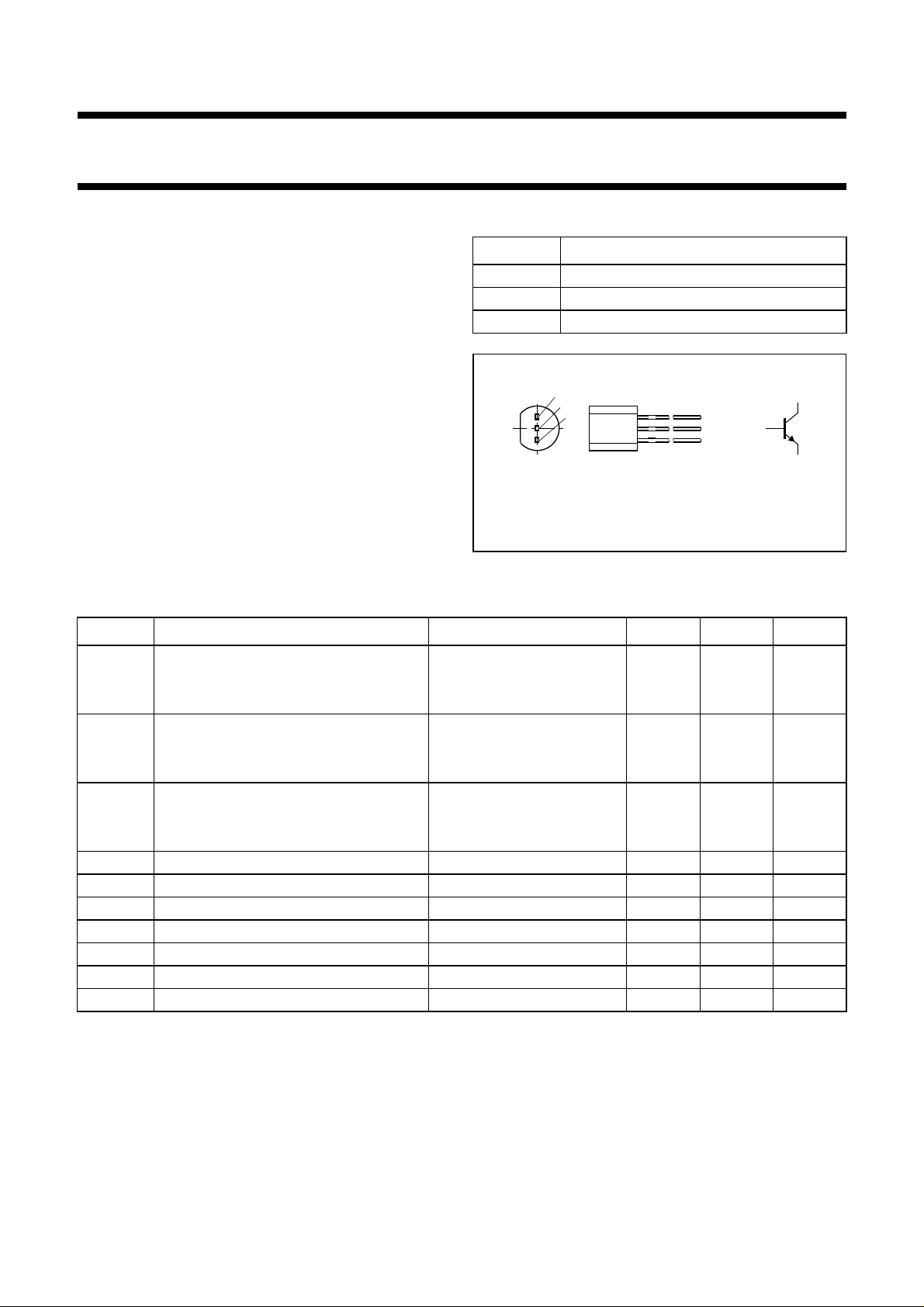
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 emitter
2 base
APPLICATIONS
3 collector
• General purpose switching and amplification.
DESCRIPTION
NPN transistor in a TO-92; SOT54 plastic package.
PNP complements: BC556 and BC557.
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
MAM182
3
2
1
Fig.1 Simplified outline (TO-92; SOT54)
and symbol.
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CBO
collector-base voltage open emitter
BC546 − 80 V
BC547 − 50 V
V
CEO
collector-emitter voltage open base
BC546 − 65 V
BC547 − 45 V
V
EBO
emitter-base voltage open collector
BC546 − 6V
BC547 − 6V
I
C
I
CM
I
BM
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
T
amb
collector current (DC) − 100 mA
peak collector current − 200 mA
peak base current − 200 mA
total power dissipation T
≤ 25 °C; note 1 − 500 mW
amb
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
junction temperature − 150 °C
operating ambient temperature −65 +150 °C
Note
1. Transistor mounted on an FR4 printed-circuit board.
1999 Apr 15 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
NPN general purpose transistors BC546; BC547
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th j-a
Note
1. Transistor mounted on an FR4 printed-circuit board.
CHARACTERISTICS
=25°C unless otherwise specified.
T
j
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
CBO
I
EBO
h
FE
V
CEsat
V
BEsat
V
BE
C
c
C
e
f
T
F noise figure I
thermal resistance from junction to ambient note 1 0.25 K/mW
collector cut-off current IE= 0; VCB=30V −−15 nA
I
= 0; VCB= 30 V; Tj= 150 °C −−5µA
E
emitter cut-off current IC= 0; VEB=5V −−100 nA
DC current gain IC=10µA; VCE=5V;
BC546A − 90 −
see Figs 2, 3 and 4
BC546B; BC547B − 150 −
BC547C − 270 −
DC current gain IC= 2 mA; VCE=5V;
BC546A 110 180 220
see Figs 2, 3 and 4
BC546B; BC547B 200 290 450
BC547C 420 520 800
BC547 110 − 800
BC546 110 − 450
collector-emitter saturation
voltage
IC= 10 mA; IB= 0.5 mA − 90 250 mV
I
= 100 mA; IB=5mA − 200 600 mV
C
base-emitter saturation voltage IC= 10 mA; IB= 0.5 mA; note 1 − 700 − mV
I
= 100 mA; IB= 5 mA; note 1 − 900 − mV
C
base-emitter voltage IC= 2 mA; VCE= 5 V; note 2 580 660 700 mV
I
= 10 mA; VCE=5V −−770 mV
C
collector capacitance IE=ie= 0; VCB= 10 V; f = 1 MHz − 1.5 − pF
emitter capacitance IC=ic= 0; VEB= 0.5 V; f = 1 MHz − 11 − pF
transition frequency IC= 10mA; VCE= 5 V; f = 100 MHz 100 −−MHz
= 200 µA; VCE=5V;
C
− 210dB
RS=2kΩ; f = 1 kHz; B = 200 Hz
Notes
1. V
decreases by about 1.7 mV/K with increasing temperature.
BEsat
2. VBE decreases by about 2 mV/K with increasing temperature.
1999 Apr 15 3
 Loading...
Loading...