Philips 32PF4321/96 Schematic

Published by JH 0664 TV Service Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 16140
©
Copyright 2006 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
Al
l rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retr
ieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechan
ical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
Colour Television Chassis
MQC1.0A
LA
Contents
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
3. Directions for Use
4. Mechanical Instructions
5. Service Modes, Faultfinding
6. Block Diagrams
7. Circuit Diagrams, PCB Layouts
Alignments
8.
9. IC data sheet
10. Space Parts list
. Revision List
11
Page
1
3
4
5
8
15
19
53
54
55
56
EN 1
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
1.
MQC1.OA LA
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
Index of this chapter:
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.2 Connections
1.3 Chassis Overview
Note: Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual
situation, due to the different set executions.
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.1.1 Vision
Display type : LCD (CMO)
Screen size : 32 inches (813.3 mm) diagonal
Resolution : 1366x768
Contrast ratio : 1000:1
Light output (cd/m2) : 550 Cd/m²
Response time (ms) : 12ms
Viewing angle : 85° (L) / 85° (R), 85° (U) / 85° (D)
TV color systems : NTSC
Video playback : NTSC, PAL, SECAM
Supported inputs : 480i
: 576i
: 480p
: 576p
: 1080i
: 720p
1.1.2 Sound
Sound systems : MTS (NTSC), FM-FM
Internal speaker : 10 W x 2 stereo, volume adjustable
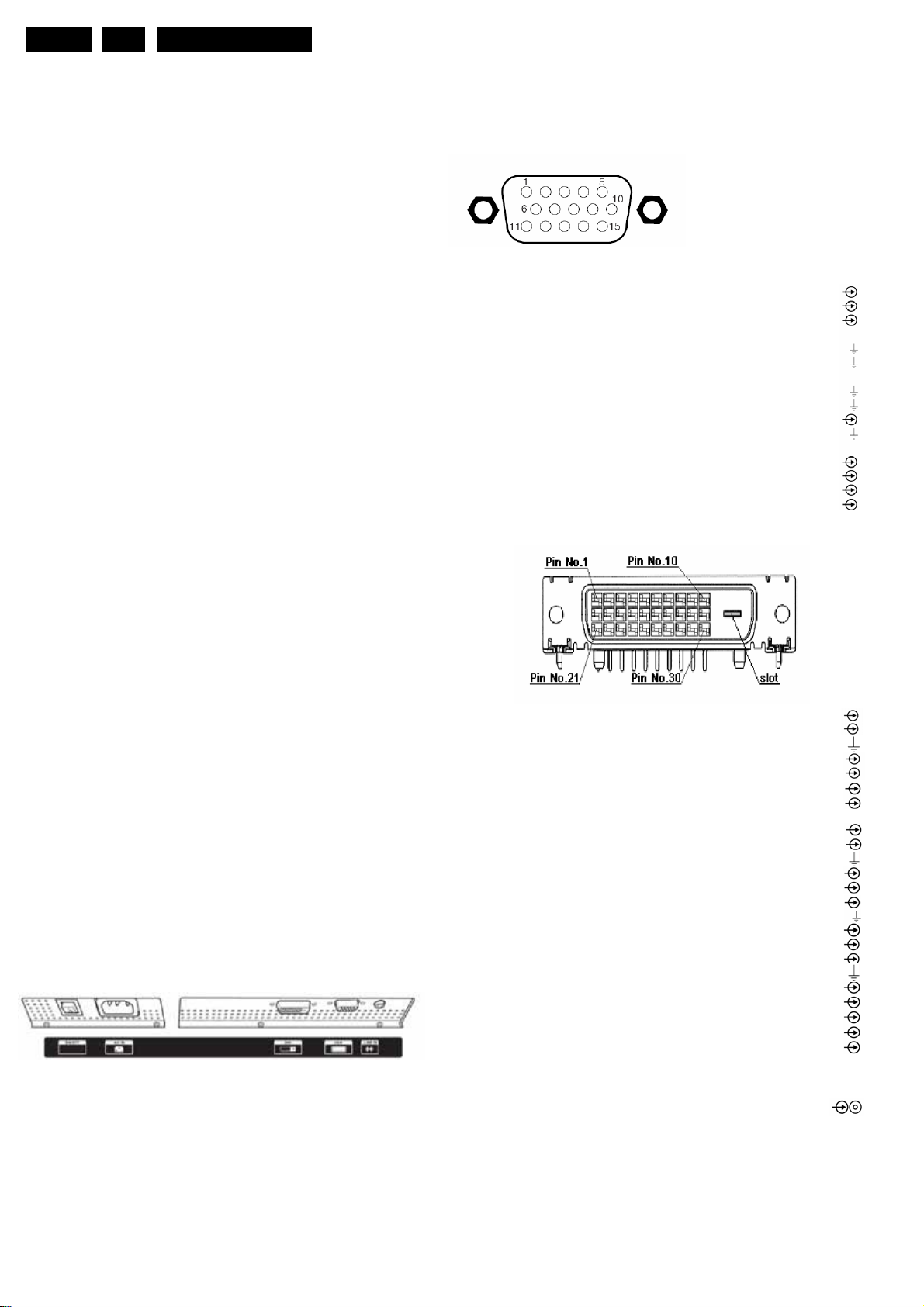
VGA:Video 2fh RGB In
Figure 1-2 VGA Connector
1 - Video Red 0.7 VPP / 75 ohm
2 - Video Green 0.7 V
3 - Video Blue 0.7 V
4 – n.c
5 –Ground Gnd
6 -Ground Red Gnd
7 -Ground
Green Gnd
8 -Ground Blue Gnd
9 - +5V_DC +5V
10 -Gnd Sync Gnd
11 - n.c.
12 - DDC_SDA DDC data
13 - H-sync 0 - 5V
14 - V-sync 0 - 5V
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock
DVI Digital Video-In
PP / 75 ohm
PP / 75 ohm
DC
1.1.3 Miscellaneous
Power supply:
-AC Power voltage (VAC) : 90-264V
-AC Power frequency (Hz) : 47~63Hz
Ambient conditions:
-Temperature range : 0~35°C
- Maximum humidity : 10%~90%
Power consumption
- Normal operation : 210 W
- Stand-by: < 5 W
Dimensions (WxHxD mm) :617.7*1017.4*210.0
Weight (kg) :20.5Kg
1.2 Connections
1.2.1 Rear I/O Connections
Figure 1-1 back connections
1 TMDS Data 2- Data channel
2 TMDS Data 2+ Data channel
3 TMDS Data 2/4 shield GND
4 TMDS Data 4- Data channel
5 TMDS Data 4+ Data channel
6 DDC Clock DDC Clock
7 DDC Data DDC Data
8 N.C
9 TMDS Data 1- Data channel
10 TMDS Data 1+ Data channel
11 TMDS Data 1/3 shield
12 TMDS Data 3- Data channel
13 TMDS Data 3+ Data channel
14 +5V
15 Ground ( For +5V) GND
16 Hot Plug Detect Hot Plug Detect
17 TMDS Data 0- Data channel
18 TMDS Data 0+ Data channel
19 TMDS Data 0/5 shield GND
20 TMDS Data 5- Data channel
21 TMDS Data 5+ Data Channel
22 TMDS Clock shield Data channel
23 TMDS Clock+ Data channel
24 TMDS Clock Data channel
Audio-In
Gn Stereo R/L Channels 500mVrms/22K ohm
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
EN 2
1.
MQC1.OA LA
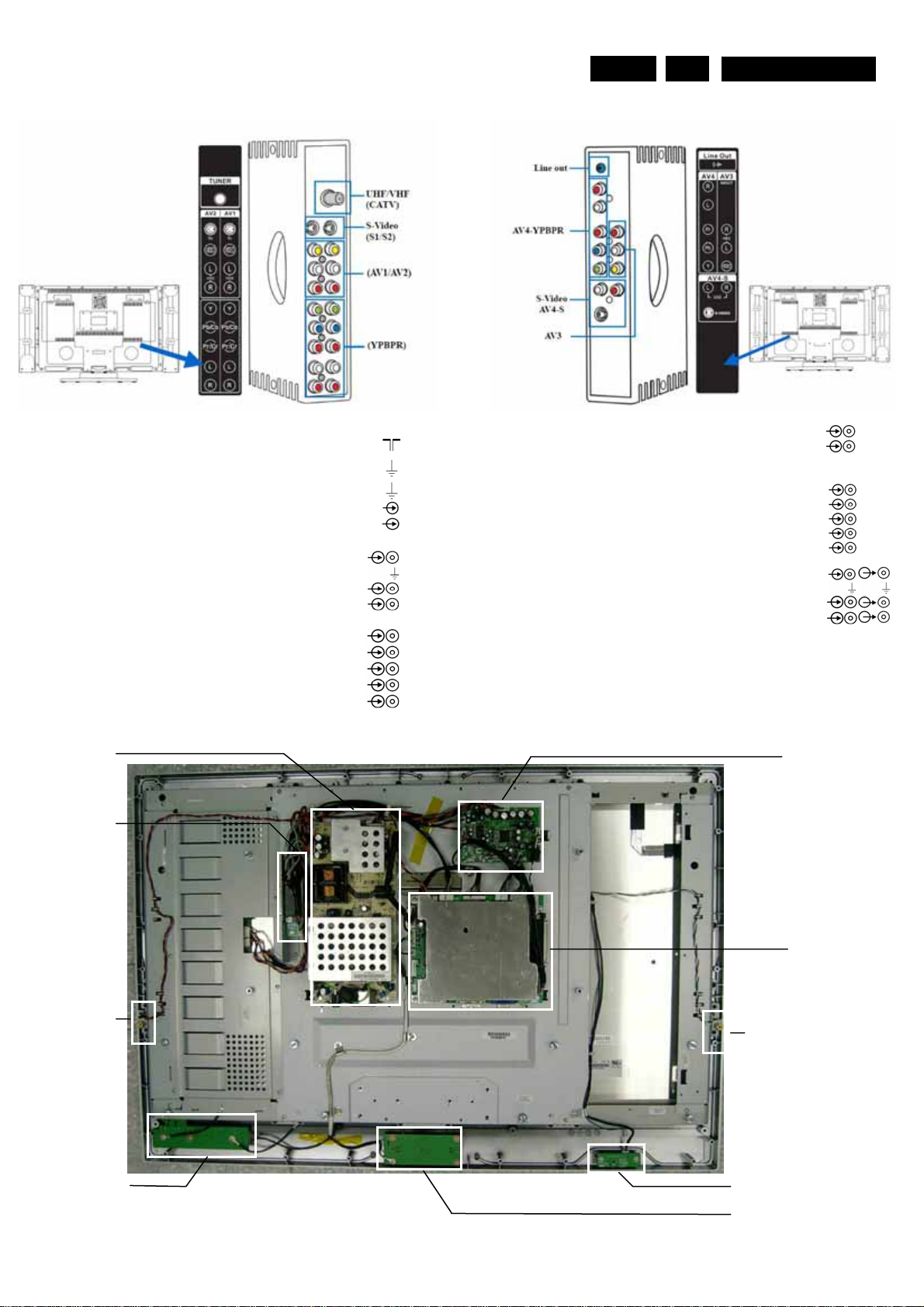
1.2.2 Right I/O Connections
Aerial-In
-F-type 75ohm
AV1-S1/AV2-S2: S-Video 1Fh Y/C-In
1 -Ground Y Gnd
2 -Ground C Gnd
3 -Video Y 1Vpp/75 ohm
4 -Video C 0.3Vpp/75 ohm
AV1/AV2 Video In, Audio In
1 -Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
2 -Gnd CVBS Gnd
3 -Video CVBS 1Vpp/75 ohm
4 -Audio L 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
YPBPR1/YPBPR2
Wh….-Audio L 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
Rd….-Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
Bu Video Pb 0.7 Vpp/75 ohm
Rd Video Pr 0.7 Vpp/75 ohm
Gn Video Y 1Vpp/75 ohm
1.3 Chassis overview
1.2.3 Left I/O Connections
Line-out
1 Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
2 Audio L 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
AV4-YPBPR
AV4-YPBPR
Wh….-Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
Rd….-Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
Bu Video Pb 0.7 Vpp/75 ohm
Rd Video Pr 0.7 Vpp/75 ohm
Gn Video Y 1Vpp/75 ohm
AV3 Video In/out /Audio in/out
1 -Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
2 -Gnd CVBS Gnd
3 -Video CVBS 1Vpp/75 ohm
4 -Audio L 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
AV4 S-Video In/Audio In
1 -Ground Y Gnd
2 -Ground C Gnd
3 -Video Y 1Vpp/75 ohm
4 -Video C 0.3Vpp/75 ohm
Rd….-Audio R 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
Wh….-Audio L 0.5 Vrms/10Kohm
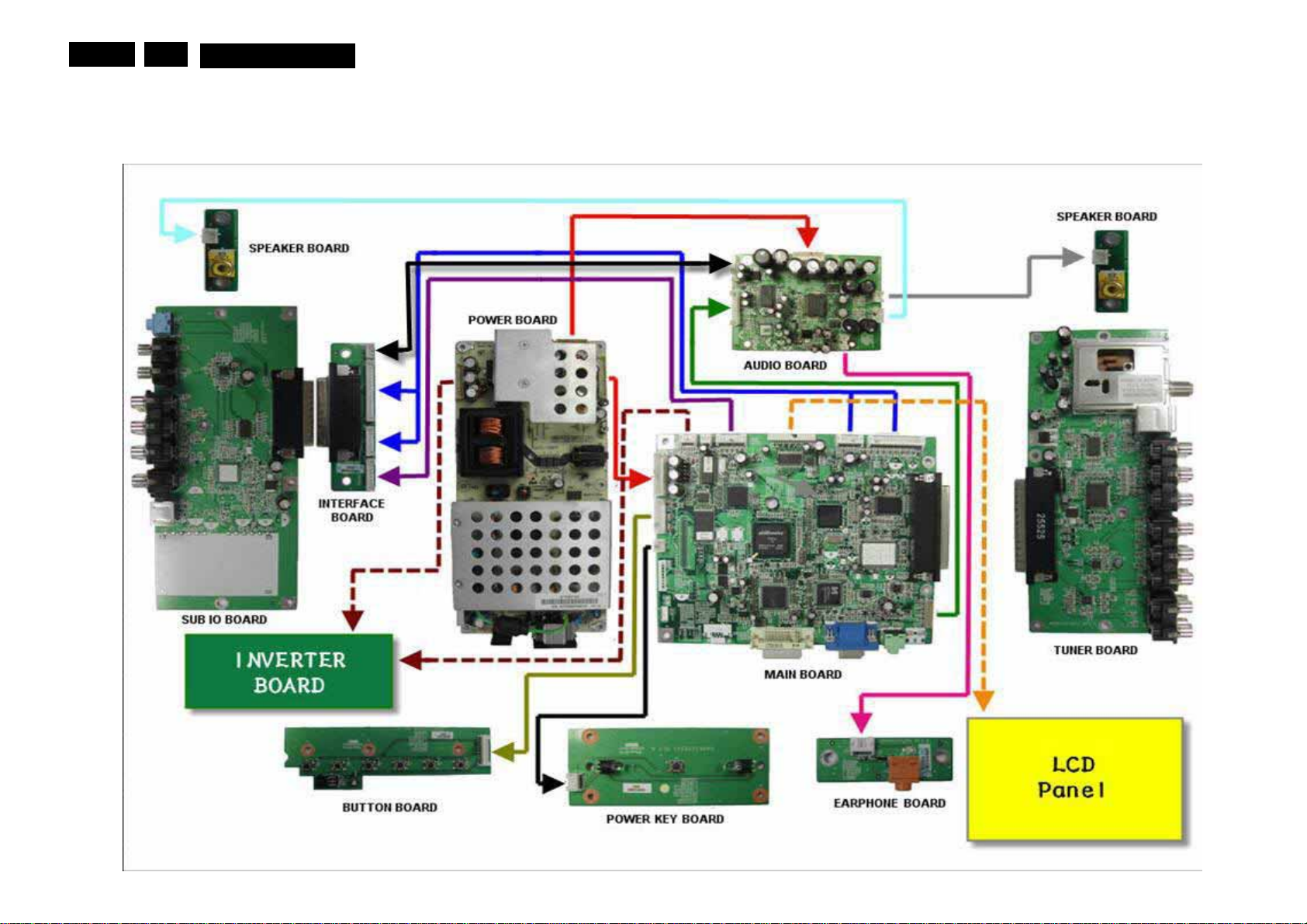
Power Board
Interface Board
Speaker Board
Button Board
Audio Board
Main Board
Speaker Board
Earphone Board
Power Key Board

EN 3
Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2.
MQC1.OA LA
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require that during a repair:
• Connect the set to the AC Power via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the AC Power lead for external
damage.
• Check the strain relief of the AC Power cord for proper
function.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the AC Power
plug and the secondary side (only for sets which have a AC
Power isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the AC Power cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the AC Power plug.
2. Set the AC Power switch to the "on" position (keep the
AC Power cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
AC Power plug and the metal shielding of the tuner or
the aerial connection on the set. The reading should be
between 4.5 Mohm and 12 Mohm.
4. Switch "off" the set, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the AC Power plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to avoid touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
,
2.2 Warnings
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential. Available
ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable) 4822
310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched "on".
• When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
). Careless handling
2.3 Notes
2.3.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground ( ), or hot ground ( ), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode (see chapter 5) with a color bar
signal and stereo sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated
otherwise) and picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or
61.25 MHz for NTSC (channel 3).
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with ( ) and without ( ) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation ( ) and in stand-by ( ). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
• The semiconductors indicated in the circuit diagram and in
the parts lists, are interchangeable per position with the
semiconductors in the unit, irrespective of the type
indication on these semiconductors.
• Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories.
“Dolby” and the “double-D symbol”, are trademarks of
Dolby Laboratories.
2.3.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 Kohm).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an "E" or an "R" (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220
ohm).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (µ= x10
nano-farads (n= x10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An "asterisk" (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed in the Electrical
Replacement Parts List. Therefore, always check this list
when there is any doubt.
2.3.3 Rework on BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
General
Although (LF)BGA assembly yields are very high, there may
still be a requirement for component rework. By rework, we
mean the process of removing the component from the PWB
and replacing it with a new component. If an (LF)BGA is
removed from a PWB, the solder balls of the component are
deformed drastically so the removed (LF)BGA has to be
discarded.
Device Removal
As is the case with any component that, it is essential when
removing an (LF)BGA, the board, tracks, solder lands, or
surrounding components are not damaged. To remove an
(LF)BGA, the board must be uniformly heated to a temperature
close to the reflow soldering temperature. A uniform
temperature reduces the chance of warping the PWB.
To do this, we recommend that the board is heated until it is
certain that all the joints are molten. Then carefully pull the
component off the board with a vacuum nozzle. For the
appropriate temperature profiles, see the IC data sheet.
Area Preparation
When the component has been removed, the vacant IC area
must be cleaned before replacing the (LF)BGA.
Removing an IC often leaves varying amounts of solder on the
mounting lands. This excessive solder can be removed with
either a solder sucker or solder wick. The remaining flux can be
removed with a brush and cleaning agent.
After the board is properly cleaned and inspected, apply flux on
the solder lands and on the connection balls of the (LF)BGA.
Note: Do not apply solder paste, as this has shown to result in
problems during re-soldering.
-9
), or pico-farads (p= x10
-6
-12
),
).
Device Replacement
The last step in the repair process is to solder the new
component on the board. Ideally, the (LF)BGA should be
aligned under a microscope or magnifying glass. If this is not
possible, try to align the (LF)BGA with any board markers.
To reflow the solder, apply a temperature profile according to
the IC data sheet. So as not to damage neighboring
components, it may be necessary to reduce some
temperatures and times.
More Information
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com (needs subscription,
URL:
not available for all regions). After login, select “Magazine”,
then go to “Workshop Information”. Here you will find
Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
2.3.4 Lead Free Solder
Philips CE is going to produce lead-free sets (PBF) from
1.1.2005 onwards.
Lead-free sets will be indicated by the PHILIPS-lead-free logo
on the Printed Wiring Boards (PWB):
Figure 2-1 Lead-free logo
This sign normally has a diameter of 6 mm, but if there is less
space on a board also 3 mm is possible.
In case of doubt wether the board is lead-free or not (or with
mixed technologies), you can use the following method:
• Always use the highest temperature to solder, when using
SAC305 (see also instructions below).
• De-solder thoroughly (clean solder joints to avoid mix of
two alloys).
Caution: For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature
profile,which is coupled to the 12NC. For an overview of these
profiles, visit the website
You will find this and more technical information within the
"Magazine", chapter "Workshop information".
For additional questions please contact your local repair-helpdesk.
http://www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com/
EN 4 Directions for Use MQC1.OA LA
3.
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin Philips SAC305 with order
code 0622 149 00106. If lead-free solder paste is required,
please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able
– To reach at least a solder-tip temperature of 400°C.
– To stabilise the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature around 360°C
-380°C is reached and stabilised at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will rise drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed. To
avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If not to avoid, clean carefully the
solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin.
• Use only original spare-parts listed in the Service-Manuals.
Not listed standard material (commodities) has to be
purchased at external companies.
• Special information for lead-free BGA ICs: these ICs will be
delivered in so-called "dry-packaging" to protect the IC
against moisture. This packaging may only be opened
short before it is used (soldered). Otherwise the body of the
IC gets "wet" inside and during the heating time the
structure of the IC will be destroyed due to high (steam)pressure inside the body. If the packaging was opened
before usage, the IC has to be heated up for some hours
(around 90°C) for drying (think of ESD-protection !).
Do not re-use BGAs at all!
• For sets produced before 1.1.2005, containing leaded
soldering tin and components, all needed spare parts will
be available till the end of the service period. For the repair
of such sets nothing changes.
2.3.5 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions - reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching
into a powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage
insulation. It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
3. Directions for Use
You can download this information from the following websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
http://www.p4c.philips.com
Mechanical Instructions
EN 5
4.
MQC1.OA LA
4. Mechanical Instructions
Index of this chapter:
4.1 Cable Dressing
Service Positions
4.2
4.3 ASSY/PCBA Removal
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.2 Service Positions
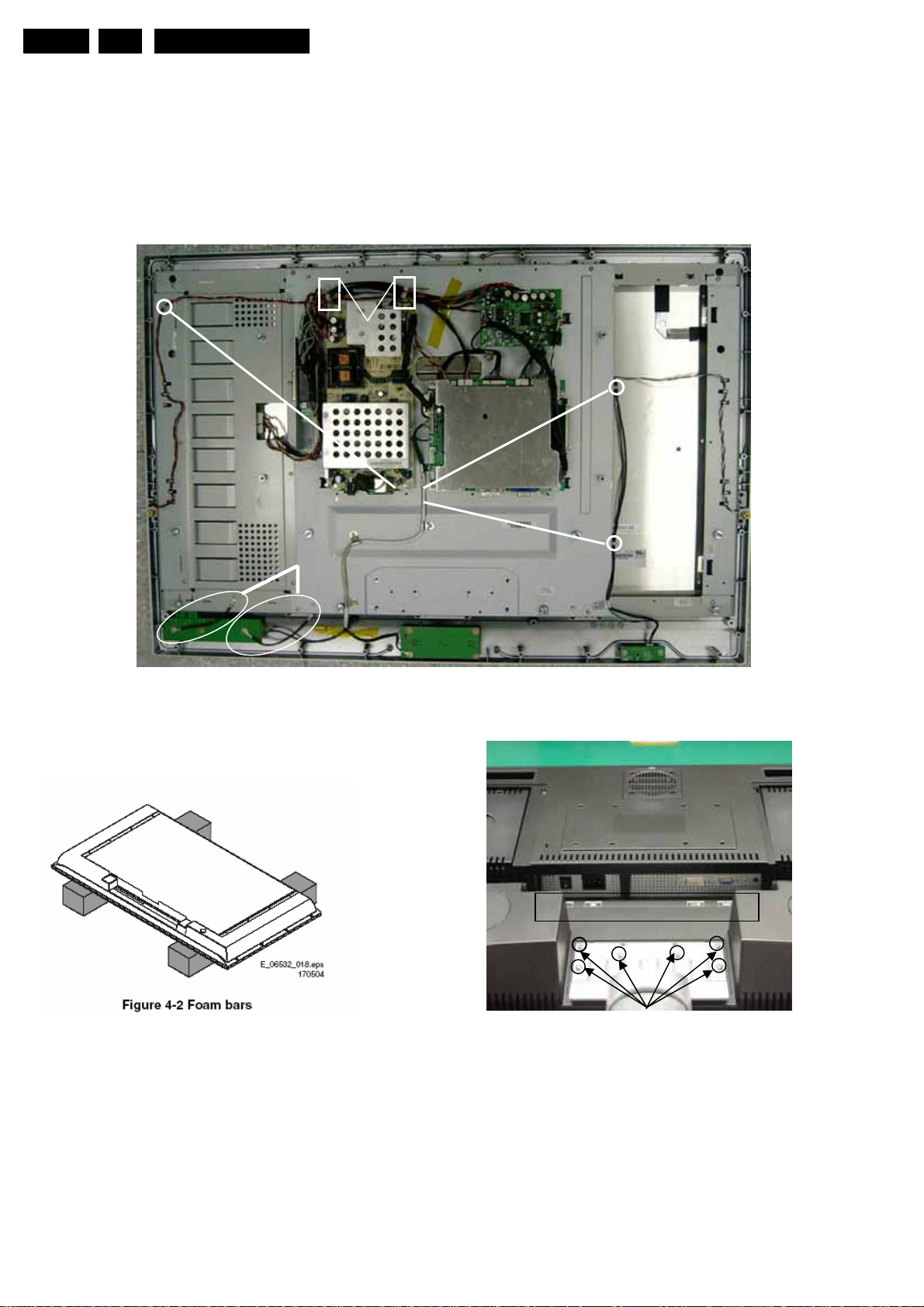
4.2.1 Foam Bars
67
68
69
4.2.2 Stands
The foam bars (order code 3122 785 90580 for two pieces) can
be used for all types and sizes of Flat TVs. By laying the TV
face down on the (ESD protective) foam bars, a stable situation
is created to perform measurements and alignments.
By placing a mirror under the TV, you can monitor the screen.
70
Figure 4-3 Stands
The stands can be mounted with the back cover removed or
still left on. So, the stand can be used to store products or to do
measurements. It is also very suitable to perform duration tests
without taking much space, without having the risk of overheating
,or the risk of products falling. The stands can be mounted and
removed quick and easy with use of the delivered screws that
can be tightened and loosened manually without the use of tools.
See figure above.
Note: Only use the delivered screws to mount the monitor to
the stands

Mechanical Instructions
4.3 Assy/Panel removal
4.3.1 IO/Sub IO
Warning: Disconnect the AC Power cord before you open the
set.
1. Place the TV set upside down on a table top, using the
foam bars (see part "Foam Bars").
Caution: do not put pressure on the display, but let the
monitor lean on the speakers or the Front cover.
2. Remove M3*12(4 pieces) from IO Box and Sub-IO Box
4.3.2 R&L Speaker/Fan cover/Back cover
1. Remove T3*8 (4 pieces) screws from the Fan cover
2. Remove all T4*12(16 pieces) screws from the Back cover.
3. Than, remove the T4*24(6 pieces) from R/L speaker
4. Lift the back cover from the set. Make sure that wires and
flat foils are not damaged during the back cover removal.
4.3.3 Wall mount
1. Remove T3*5(4 pieces) screws from down of wall mount
2. Remove M3*4(4 pieces) screw from top of wall mount
3. Remove Io Nut(4 pieces) screw from down of wall mount
4. Remove 4-40(2 pieces) screw from right side of wall mount
5. Lift the wall mount from chassis. Make sure wires are not
damaged during the back cover removal.
4.3.11 LCD Panel
7
4.3.4 Main Board
1. Disconnect all cable from Base unit
2. Remove the fixation screws
3. Take out Main Board
4.3.5 Audio Board
1. Remove the fixation screws
2. Take out Main Board
4.3.6 Power Board
1. Remove the fixation screws
2. Take out Main Board
4.3.7 Interface Board
1. Remove the fixation screws
2. Take out Main Board
4.3.8 Power-Key Board
1. Remove the fixation screws
2. Take out Main Board
4.3.9 Earphone Board
1. Remove the fixation screws
2. Take out Main Board
4.3.10 Button Board
1. Remove the fixation screws
2. Take out Main Board and Bracket
10
6
11
EN 6
4.
MQC1.OA LA
8
4
9
2
3
11
1
1111
5

EN 7
Mechanical Instructions
4.
MQC1.OA LA
Disassembly
1. Place the TV set down on the foam bars. Place the
bars at the edges of the set, so they will support the
front frame and not only the glass plate!
2. Remove the Earphone cable (1), Button cable (2), Power key cable (3)
Speak L Cable (4), Speaker R cable (5) from all PCBA. Remove
LVDS cable from LCD panel (6)
3. Remove the eight M3*5 screws (7) from Inverter shielding
Lift the shielding and remove inverter cable (8)
4. Remove the two M3*5 screws (9) and two M3*4 screws (10)
Lift the PCB tray from the set. Make sure that wires and
flat foils are not damaged during the PCB tray removal.
5. Remove the sixteen T4*12 screws (11) from front cover
Lift the LCD panel from front cover.
6. Remove the ten M4*10 screws from Chassis-U, Chassis-R
Chassis-D, Chassis-L. Lift the LCD from Chassis.
2. Remove the 5 screws from shielding
3. Remove the 5 screws from shielding
4. Remove the screw from shielding
Assembly
To re-assemble the LCD panel, execute all processes
in reverse order.
Note:
.While re-assemble, make sure that all are placed and
And connected in their original position. See figure
“Cable dressing”
.Pay special attention not to damage the EMC foams at the
SSB shielding. Check that EMC foams are put correctly on
their places.
4.3.12 R,L speaker
Disassembly
1. Remove the four screws from speaker shielding
and lift the shielding
.
4.3.13 IO Assy
Disassembly
1. Remove the three screws form shielding.
2. Remove the eight screws from speaker back cover
and open the mylar then lift the speaker back cover.
2. Remove the 4 screws from shielding
3. Remove the four screws
3. Remove the 2 screws from shielding
4.3.13 Tune r Assy
Disassembly
1. Remove the three screws from shielding
4. Remove the screw from shielding
5 Service mode and Fault Finding
Service mode, Fault Finding
EN 8
5
MQC1.OA LA
Index if this chapter:
5.1Service Modes
5.1Fault Finding
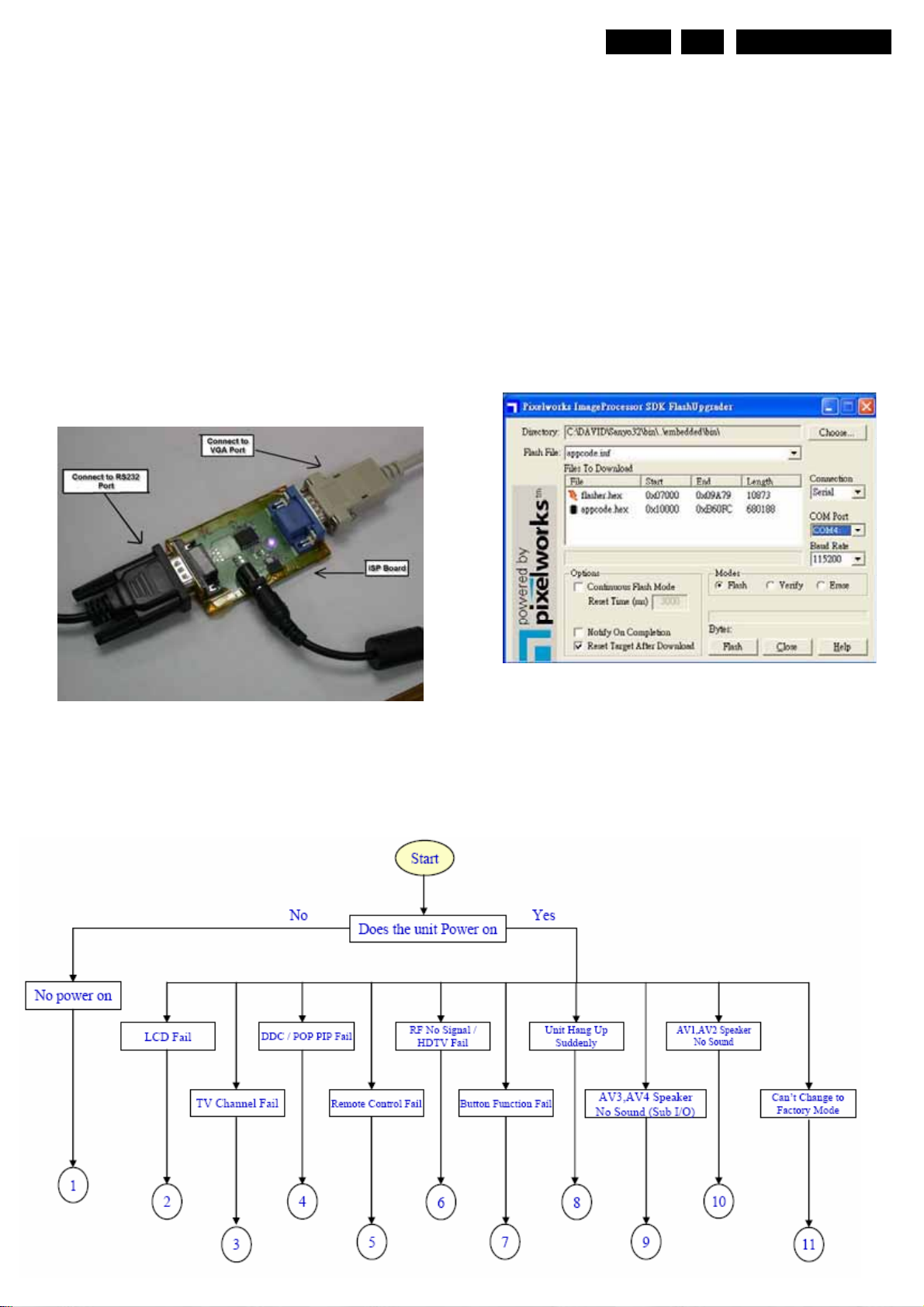
5.1 Service Mode (update BIOS)
Purpose
. To update new version BIOS
Tools
. ISP Board
. RS232 cable
. VGA cable
. Software (Pixlworks)
5.2 Fault Finding
Purpose
.To find the fault
How to find fault
Setup
1. Off TV Pow e r
2. Process Pixlworks program
3. Choose appcode.inf
4. Check connection. Should be in serial
5. Check COM Port of R232
6. Check Baud Rate
7. Click Flash
8. Turn on the TV .The program will automatic
9. After few seconds, then screen will showing flash
completed. TV will power on itself
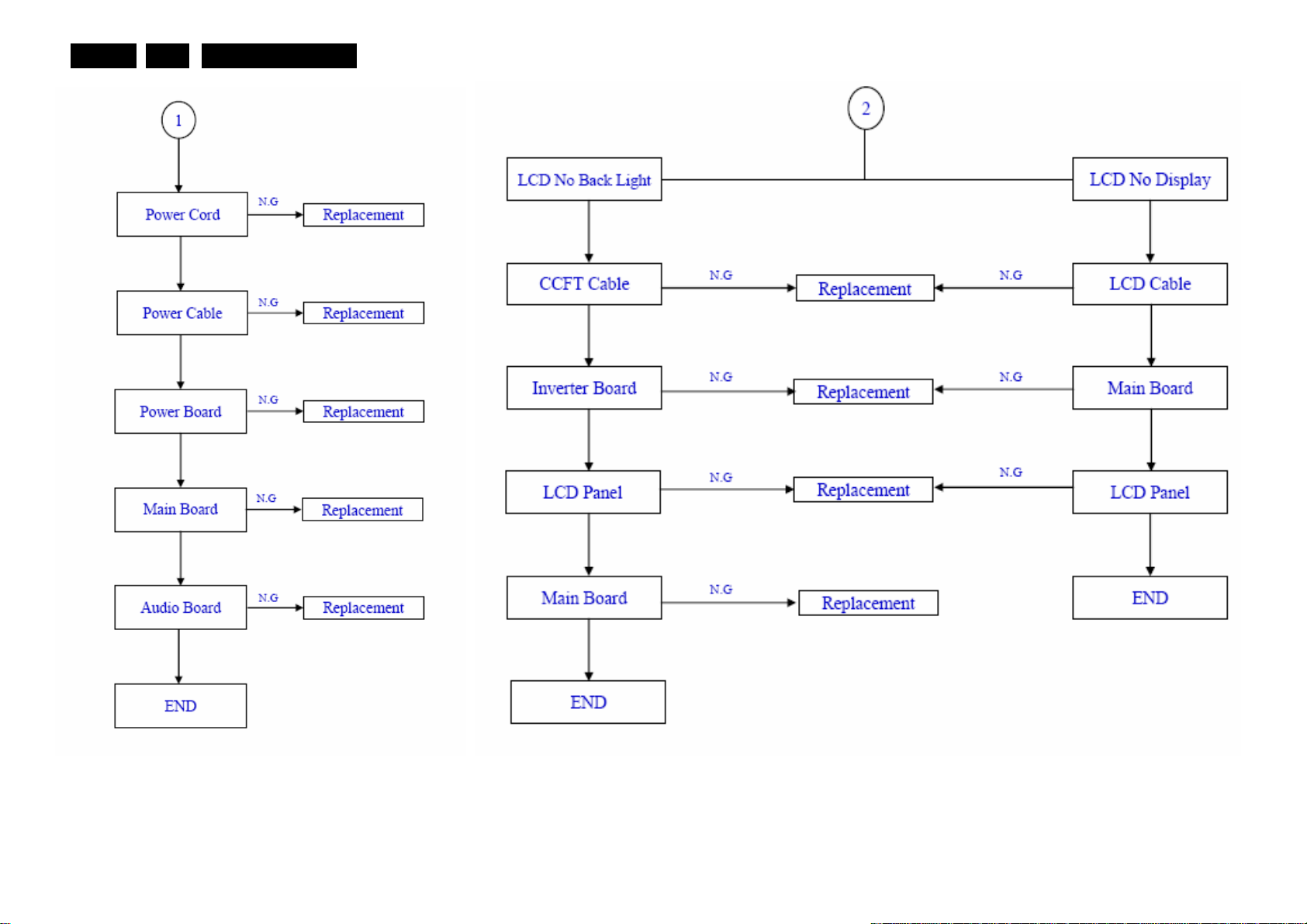
Service mode, Fault Finding
EN 9
5
MQC1.OA LA
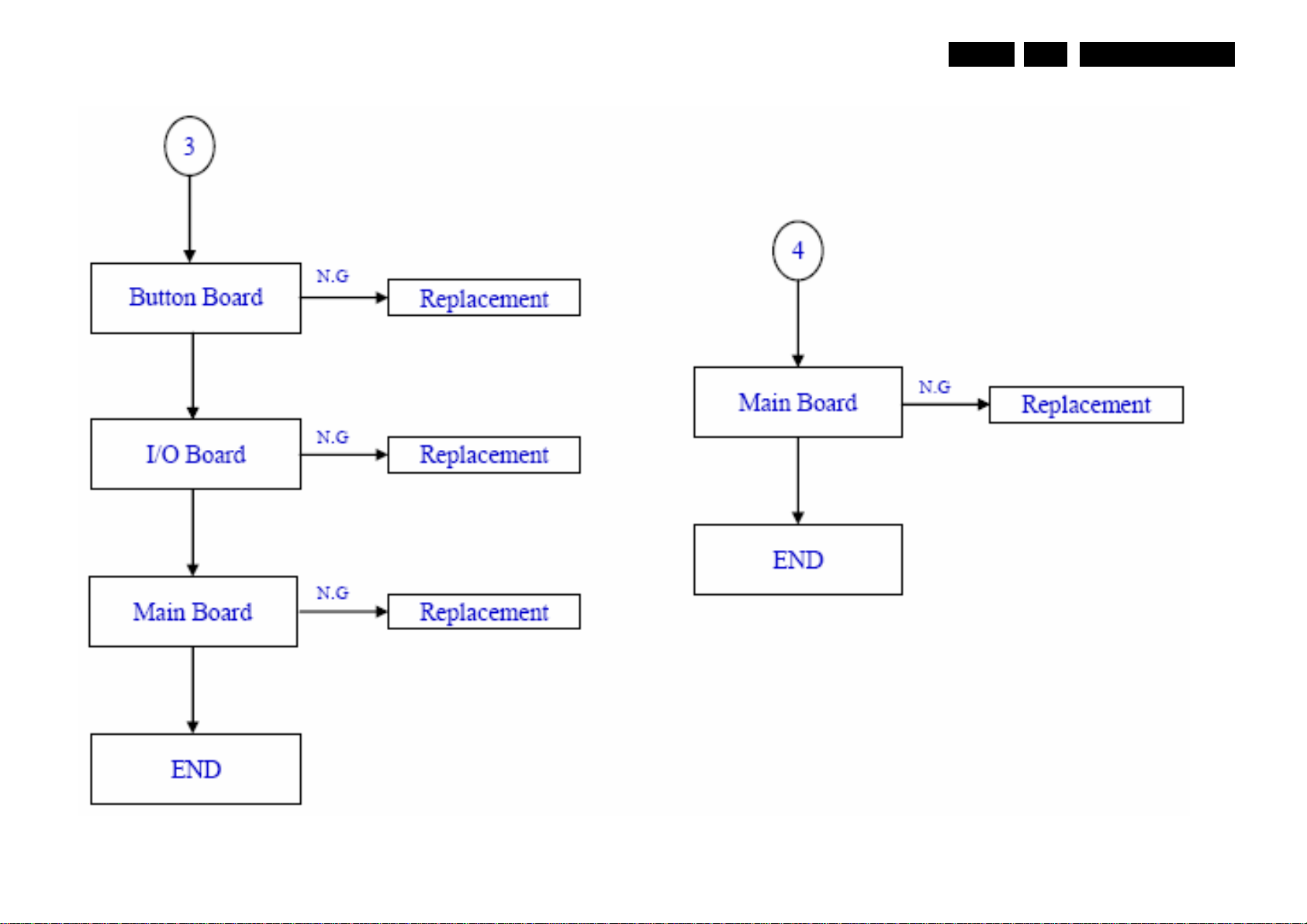
Service mode, Fault Finding
EN 10
5
MQC1.OA LA
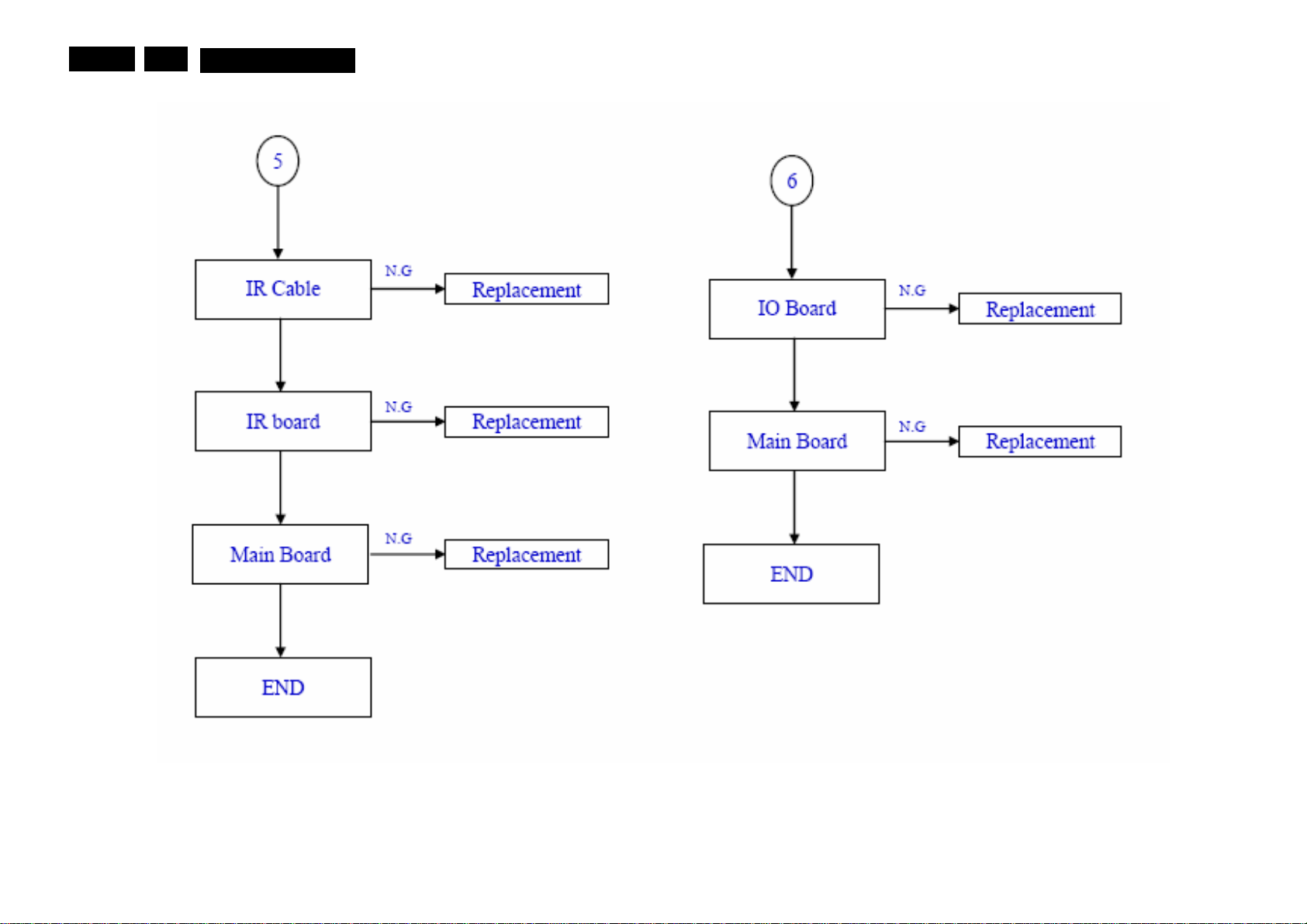
Service mode, Fault Finding
EN 11
5
MQC1.OA LA
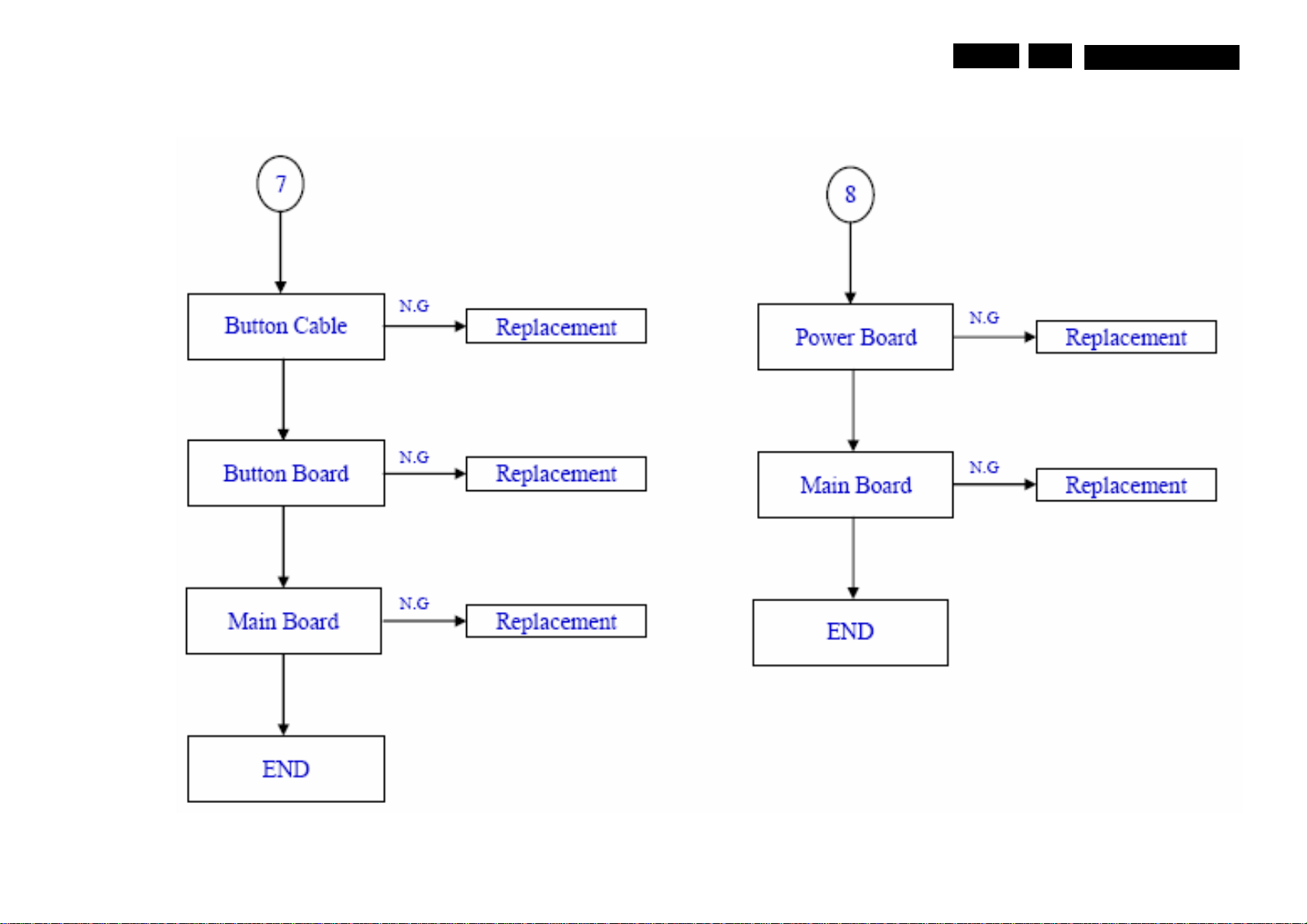
MQC1.OA LA Service mode, Fault Finding 5EN 12
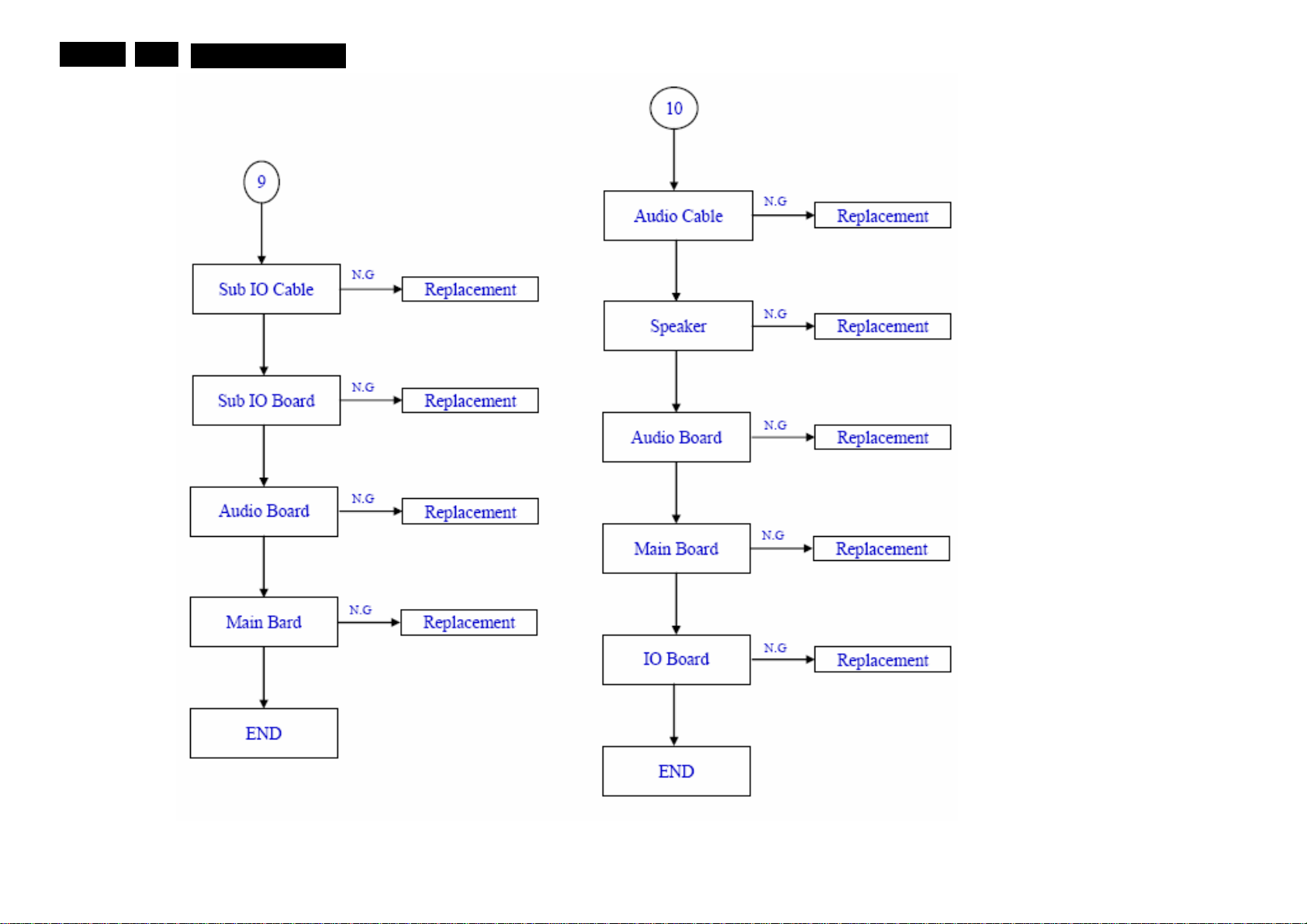
EN 13
5
MQC1.OA LA
Service mode, Fault Finding
Service mode, Fault Finding
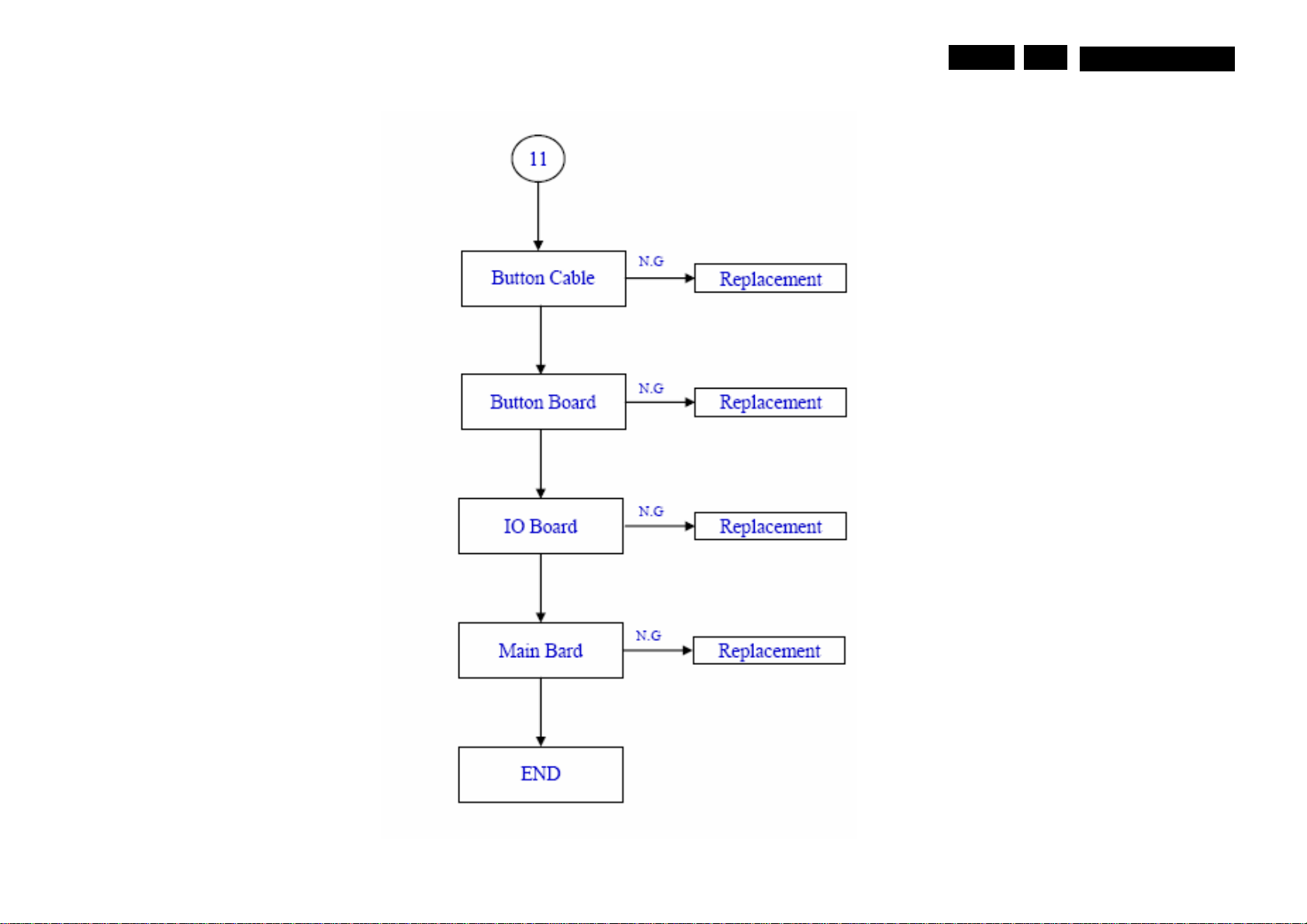
EN 14
5
MQC1.OA LA
EN 15
6
MQC1.OA LA
6. Block Diagrams
Wiring Diagram
Block Diagrams
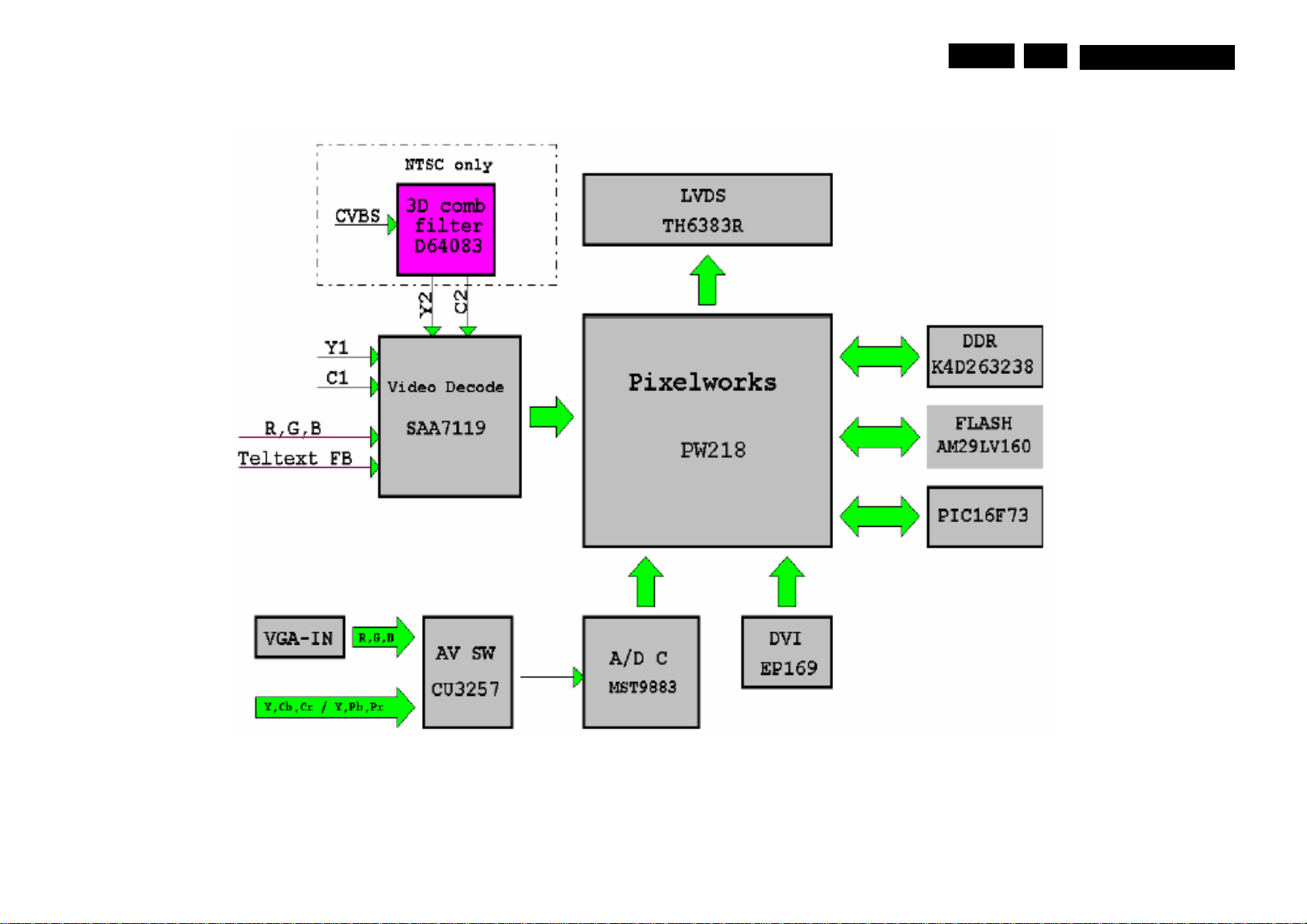
Main Board Block diagrams
MQC1.OA LA Block Diagrams 6EN 16
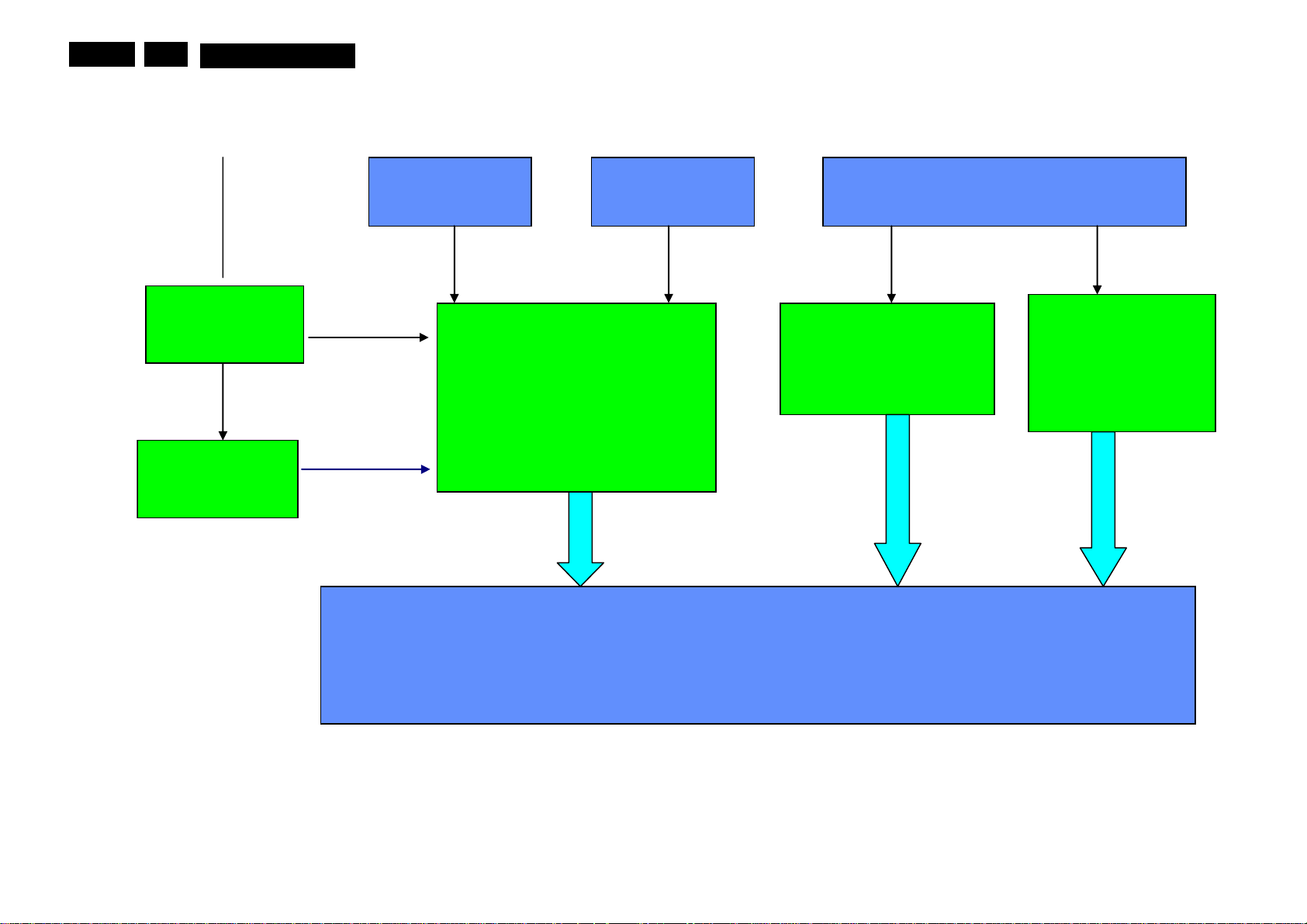
EN 17
Io Board Block diagrams
6
TV
MQC1.OA LA
signal
Block Diagrams
TV Tune r
TMQH6-011A
Audio Decoder
AN5832SA
TV Video
Audio
AV1 /AV2
Video& Audio Video
Video & Audio SW
Video & Audio SW
CVBS & YC
TA1218
TA1218
S1/S2
YUV Video
IO PORT
CU3257
YUV
YUV1/YUV2
SoundVideo
YUV Sound
74HCT4052_0
 Loading...
Loading...