Page 1

Parallels H-Sphere 3.6.3 Administrator
Guide
Parallels H-Sphere 3.6.3
Revision 1.0
Revision 1.0
Page 2

Legal and Copyright Notice
Parallels IP Holdings GmbH
Vordergasse 59
CH-Schaffhausen
Switzerland
Phone: +41-526320-411
Fax: +41-52672-2010
Copyright © 2012 Parallels IP Holdings GmbH. All rights reserved.
www.parallels.com
This product is protected by United States and international copyright laws. The product‟s
underlying technology, patents, and trademarks are listed at
http://www.parallels.com/trademarks.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows NT, Windows Vista, and MS-DOS are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Mac is a registered trademark of Apple, Inc.
All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3
Contents
Preface 15
Typographical Conventions ......................................................................................................... 15
Feedback ..................................................................................................................................... 16
About This Guide 17
Introduction To Parallels H-Sphere 18
DNS Management ....................................................................................................................... 19
Server Management .................................................................................................................... 20
User Signup ................................................................................................................................. 20
Billing And Plan Management ..................................................................................................... 20
Merchant Gateway Management ................................................................................................ 21
User/Account/Domain Management ........................................................................................... 22
Resellers ...................................................................................................................................... 22
Domain Management .................................................................................................................. 23
SSL .............................................................................................................................................. 24
Support Center ............................................................................................................................ 25
Look and Feel Management ........................................................................................................ 25
Parallels H-Sphere Licensing 26
Purchasing and Leasing Parallels H-Sphere .................................................................... 26
Upgrading to Parallels H-Sphere 3.6.3 or higher .............................................................. 26
Upgrading Parallels H-Sphere Accounts .......................................................................... 27
Getting Started 28
Step1. Disable Global Resources ............................................................................................... 28
Step 2. Set up a Domain Registrar .............................................................................................. 29
Step 3. Configure Mail Notification Addresses ............................................................................ 29
Step 4. Set up Payment Settings ................................................................................................ 30
Step 5. Create Plans ................................................................................................................... 31
Step 6. Create Billing Periods ..................................................................................................... 31
Step 7. Configure Support Center ............................................................................................... 32
Step 8. Configure Look and Feel ................................................................................................. 32
Server Configuration 33
Physical Servers .......................................................................................................................... 33
Adding Physical Servers ................................................................................................... 34
Physical Server Controls ................................................................................................... 35
Deleting a Physical Server ................................................................................................ 36
Logical Servers ............................................................................................................................ 36
Adding Logical Servers ..................................................................................................... 37
Enabling User Signup on Logical Servers ........................................................................ 39
Removing Logical Servers ................................................................................................ 40
Setting Logical Server Additional Options ......................................................................... 40
Adding IPs ................................................................................................................................... 45
DNS Servers ................................................................................................................................ 48
Mail Server Settings .................................................................................................................... 50
Page 4

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 4
SPF and SRS .............................................................................................................................. 51
Enabling SPF and SRS ..................................................................................................... 51
Configuring SPF and SRS ................................................................................................ 52
AntiSpam and AntiVirus .............................................................................................................. 53
Enabling AntiSpam and AntiVirus in Control Panel .......................................................... 54
Configuring AntiSpam and AntiVirus Default Settings ...................................................... 54
System SMTP Relays.................................................................................................................. 55
Advanced Web Server Settings .................................................................................................. 56
Apache Version ................................................................................................................. 56
Apache Modules ............................................................................................................... 57
Using Gotroot.com Modsecurity™ Rules With H-Sphere ................................................. 60
PHP Modes ....................................................................................................................... 62
PHP Plugins ...................................................................................................................... 65
PHP Accelerators .............................................................................................................. 66
Server Groups ............................................................................................................................. 67
Load Balanced Server Clusters ................................................................................................... 69
Platform Change .......................................................................................................................... 71
Updating Physical Boxes From CP Interface .............................................................................. 73
Procedure .......................................................................................................................... 73
Physical Server Installation/Update Profiles ............................................................................... 75
Resource Prerequisites ............................................................................................................... 79
System Service Management ..................................................................................................... 82
DNS and Hosting 85
DNS Manager .............................................................................................................................. 86
Adding DNS Zones ...................................................................................................................... 86
Instant Alias Templates ............................................................................................................... 88
Adding Instant Alias Templates......................................................................................... 88
Editing Instant Alias Templates ......................................................................................... 90
DNS Records ............................................................................................................................... 91
Adding custom A records .................................................................................................. 92
Adding custom MX records ............................................................................................... 93
Adding custom CNAME records ....................................................................................... 93
Re-generating System Custom DNS Records .................................................................. 95
Hosting Your Corporate Site ....................................................................................................... 95
Step 1. Make sure you have a service DNS zone ............................................................ 95
Step 2. Create a service plan ............................................................................................ 96
Step 3. Disallow signups from outside your admin account. ............................................ 97
Step 4. Create a service account ...................................................................................... 97
Adding Domains for Third Level Hosting ..................................................................................... 98
Providing Mail Under Service Domain for Third-Level Hosting ................................................... 98
Control Panel Web Interface 99
Regional Settings ........................................................................................................................ 99
Images and Icons ...................................................................................................................... 101
Logo Images.................................................................................................................... 101
Icons And Control Images ............................................................................................... 103
Interface Texts ........................................................................................................................... 105
Login Texts ...................................................................................................................... 105
Signup Texts ................................................................................................................... 105
Miscellaneous Texts ........................................................................................................ 105
Skins and Colors ....................................................................................................................... 106
Disabling CP Skins .................................................................................................................... 108
Disabling CP Skins globally ............................................................................................ 108
Disabling CP Skins for reseller plans .............................................................................. 108
Setting Interface Language ....................................................................................................... 109
Page 5

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 5
Setting Default System Language .................................................................................. 109
Setting Admin Interface Language .................................................................................. 109
E-Mail Notifications 110
Setting E-Mail Notification Recipients ....................................................................................... 111
Editing E-Mail Notifications ........................................................................................................ 112
Configuring User Notification Rules .......................................................................................... 118
Online Invoices ................................................................................................................ 119
“No Charge” Notifications ................................................................................................ 119
Control Panel Configuration 121
Entering Company Information .................................................................................................. 122
Disabling Global Resources, Hosting Platforms And Reseller CP SSL .................................... 123
Using Background Job Manager ............................................................................................... 126
Supported TLD‟s ........................................................................................................................ 130
Installing Shared SSL Certificates ............................................................................................. 131
Shared SSL installation wizard ....................................................................................... 133
Managing Mail SSL ................................................................................................................... 135
Enabling Mail SSL ........................................................................................................... 136
Editing Mail SSL .............................................................................................................. 138
Reposting Certificates ..................................................................................................... 140
Disabling Mail SSL .......................................................................................................... 141
Using Credit Card Encryption .................................................................................................... 141
Turning On ...................................................................................................................... 141
Loading Private Key ........................................................................................................ 143
Turning Off ...................................................................................................................... 144
If You Lose Your Private Key .......................................................................................... 144
Adding Credit Card Brands ....................................................................................................... 145
Domain Registrars 146
Domain Registrar Manager ....................................................................................................... 146
Configuring Domain Registration Settings ...................................................................... 147
Step 1. Creating Connections with Domain Registrars ................................................... 147
Step 2. Associating Top Level Domains with Domain Registrars ................................... 147
Step 3. Setting Default Domain Registration Prices ....................................................... 148
Step 4. Configuring Registrar Connections for Resellers ............................................... 149
Editing Registrar Connection Settings ............................................................................ 149
Removing TLD Associations ........................................................................................... 149
Deleting Registrar Connections ...................................................................................... 150
Enom Configuration ................................................................................................................... 150
Setting Up Enom Connection .......................................................................................... 150
OpenSRS Configuration ............................................................................................................ 152
Setting Up OpenSRS Connection ................................................................................... 153
Asynchronous Response Management .......................................................................... 155
OnlineNIC Configuration ........................................................................................................... 157
Getting Prepared ............................................................................................................. 157
Setting Up OnlineNIC Connection................................................................................... 157
RRPproxy Configuration ............................................................................................................ 159
Setting Up RRPproxy Connection ................................................................................... 159
Ascionic Configuration ............................................................................................................... 161
Setting Up Ascionic Connection ...................................................................................... 161
TPPInternet Configuration ......................................................................................................... 163
Setting Up TPPInternet Connection ................................................................................ 163
Email Domain Registration ........................................................................................................ 165
Configuring Email Registrar ............................................................................................ 166
Page 6

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 6
Merchant Gateways 169
Merchant Gateway Manager ..................................................................................................... 170
Setting Up Merchant Gateway ........................................................................................ 171
Editing Merchant Gateway Settings ................................................................................ 171
Associating Merchant Gateways with Credit Card Vendors ........................................... 172
Editing Description for User Credit Card Statements...................................................... 172
Handling CC Charge Request Failures ........................................................................... 173
One Step Gateways ........................................................................................................ 174
AssureBuy Configuration ........................................................................................................... 174
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 174
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 174
AuthorizeNet (Sim Protocol) Configuration ............................................................................... 176
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 176
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 177
Bibit Configuration ..................................................................................................................... 179
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 179
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 179
Cardia Services Configuration ................................................................................................... 180
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 180
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 180
ECHO Configuration .................................................................................................................. 181
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 181
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 181
ePDQ Configuration .................................................................................................................. 182
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 182
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 182
eWay Configuration ................................................................................................................... 184
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 184
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 184
HSBC Configuration .................................................................................................................. 185
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 185
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 185
Innovative Gateway Configuration ............................................................................................ 186
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 186
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 186
LinkPoint (API v3.01) Configuration .......................................................................................... 187
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 187
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 189
Moneris Configuration ............................................................................................................... 191
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 191
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 191
NetBilling Configuration ............................................................................................................. 192
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 192
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 192
NTPNow Configuration .............................................................................................................. 194
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 194
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 194
Paradata Configuration ............................................................................................................. 196
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 196
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 196
PayGate Configuration .............................................................................................................. 197
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 197
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 197
PayJunction Configuration ........................................................................................................ 198
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 198
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 198
Plug‟n Pay Configuration ........................................................................................................... 199
Page 7

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 7
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 199
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 199
Pay-Me-Now Configuration ....................................................................................................... 200
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 200
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 200
PosNet Configuration ................................................................................................................ 201
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 201
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 201
Protx (VSP Direct Protocol 2.22) Configuration ........................................................................ 202
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 202
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 202
PSiGate (XML API) Configuration ............................................................................................. 203
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 203
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 203
SecurePay Configuration .......................................................................................................... 205
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 205
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 205
SkipJack Configuration .............................................................................................................. 206
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 206
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 207
SecurePay.com.au Configuration .............................................................................................. 208
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 208
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 208
SecureTrading Configuration .................................................................................................... 209
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 209
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 209
ThePayDesk Configuration ....................................................................................................... 211
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 211
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 212
Tucows Configuration ................................................................................................................ 213
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 213
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 213
VeriSign PayFlow Pro With SSL Support (SDK v. 4) ................................................................ 215
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 215
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 216
Web-based Payments 218
Web Payment Systems Manager .............................................................................................. 219
Work Principles ............................................................................................................... 219
Configuration Procedure ................................................................................................. 219
Setting Web Payment Instant Notification URL .............................................................. 220
2CheckOut Configuration .......................................................................................................... 221
Authorize.Net (Sim Protocol) Configuration .............................................................................. 222
Setting Up Authorize.Net ................................................................................................. 222
ChronoPay Configuration .......................................................................................................... 224
Setting Up ChronoPay .................................................................................................... 224
GestPay Configuration .............................................................................................................. 225
PayNova Configuration ............................................................................................................. 226
PayPal Merchant Gateway Configuration ................................................................................. 227
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 227
Configuration ................................................................................................................... 227
Sentry Configuration .................................................................................................................. 228
Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 228
Setup Procedure ............................................................................................................. 228
Webmoney Configuration .......................................................................................................... 230
1. Set your own purse ..................................................................................................... 230
2. Activate Webmoney payments in your Parallels H-Sphere control panel .................. 230
WorldPay Configuration ............................................................................................................ 231
Setting Up WorldPay ....................................................................................................... 231
Page 8

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 8
Plans 233
Creating and Editing Plans (Plan Wizards) ............................................................................... 234
Starting Plan Creation Wizards ....................................................................................... 234
Starting Plan Edit Wizards .............................................................................................. 234
Simplified Plan Wizards .................................................................................................. 235
A Typical Web Hosting Plan Wizard.......................................................................................... 237
Step 1. Selecting Resources and Configuring Plan Settings .......................................... 238
Subsequent Steps. Setting Prices .................................................................................. 244
MySQL Plan Wizard .................................................................................................................. 245
Windows Plan Wizard................................................................................................................ 245
Windows RealMedia Plan Wizard ............................................................................................. 246
E-mail Plan Wizard .................................................................................................................... 246
Markup Plan Wizard .................................................................................................................. 246
Admin Plans .............................................................................................................................. 247
Creating Admin Plans ..................................................................................................... 247
Editing Admin Plans ........................................................................................................ 248
Demo Plans ............................................................................................................................... 249
Changing Account‟s Plan (Plan Groups) ................................................................................... 251
Understanding Plan Groups ............................................................................................ 252
Grouping Plans................................................................................................................ 252
Access to Plans ......................................................................................................................... 254
Plan Controls ............................................................................................................................. 255
Show ............................................................................................................................... 256
Copy ................................................................................................................................ 257
Delete .............................................................................................................................. 257
Plan Settings ............................................................................................................................. 257
Controlling RAM And CPU Usage ............................................................................................. 260
Enable RLimit in Plans .................................................................................................... 260
Configure RLimit Values ................................................................................................. 261
Limiting Resource Use For Individual Accounts ............................................................. 261
Placing Plans on Particular Boxes ............................................................................................ 262
Resources 265
Users, Accounts, Domains ........................................................................................................ 265
Users ............................................................................................................................... 266
Accounts .......................................................................................................................... 266
Domains .......................................................................................................................... 269
Traffic ......................................................................................................................................... 270
Traffic Calculation ........................................................................................................... 271
Traffic Limit ...................................................................................................................... 271
Traffic Pricing .................................................................................................................. 271
Restricting Traffic Usage and Traffic Limit ...................................................................... 272
Charging for Traffic ......................................................................................................... 273
Traffic Configuration Changes ........................................................................................ 278
Tracking End User Traffic Consumption ......................................................................... 279
Disk Space ................................................................................................................................ 279
Charging Users for Disk Space ....................................................................................... 280
Enabling/Disabling Summary Disk Usage ...................................................................... 281
Recreating Resources ............................................................................................................... 282
Blacklists in Parallels H-Sphere ................................................................................................ 283
Domains in blacklist ........................................................................................................ 283
Emails in blacklist ............................................................................................................ 284
Uploading and Exporting Black Lists .............................................................................. 285
Page 9

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 9
Billing 286
Plans ............................................................................................................................... 286
Billing Types .................................................................................................................... 286
Trial Hosting .................................................................................................................... 286
Billing Profiles .................................................................................................................. 286
Prices .............................................................................................................................. 286
Limiting Resources .......................................................................................................... 287
Billing Periods.................................................................................................................. 287
Crediting Accounts .......................................................................................................... 287
Debiting Accounts ........................................................................................................... 287
Billing Modes ................................................................................................................... 287
Traffic .............................................................................................................................. 287
Disk Space ...................................................................................................................... 288
E-mailing Invoices ........................................................................................................... 288
Taxes ............................................................................................................................... 288
Promotions ...................................................................................................................... 288
Billing Resellers ............................................................................................................... 288
Managing Debtors ........................................................................................................... 288
Money Returns ................................................................................................................ 288
Billing Statements ........................................................................................................... 289
Billing Types .............................................................................................................................. 290
Billing Profiles ............................................................................................................................ 290
Billing Periods and Discounts .................................................................................................... 291
Default and Actual Billing Periods. Base Prices .............................................................. 291
Monthly and Billing Period Resources ............................................................................ 291
Opening a New Billing Period/Month .............................................................................. 291
Creating and Configuring Actual Billing Periods ............................................................. 292
Changing Account‟s Billing Period ............................................................................................ 293
Changing Billing Period Start Date ............................................................................................ 294
Credit Limit ................................................................................................................................ 296
Setting Credit Limit in a Plan ........................................................................................... 297
Increasing Credit Limit for Individual Accounts ............................................................... 297
Resetting Credit Limit For All Users ................................................................................ 297
Fees Collected From Customers ............................................................................................... 298
Plan Fees ........................................................................................................................ 298
Free Units .................................................................................................................................. 299
Setting Prices and Free Units .................................................................................................... 300
Comments on Resources ................................................................................................ 300
Discounts ................................................................................................................................... 305
Billing Consequences of Editing Prices and Free Units ............................................................ 306
Taxes ......................................................................................................................................... 307
Tax Exemption ........................................................................................................................... 309
Enabling Tax Exemption ................................................................................................. 309
Setting Tax Exemption Mode at Signup .......................................................................... 310
Activating User Accounts with Tax Exemption Code Entered ........................................ 310
Money Returns .......................................................................................................................... 311
Events that Trigger Refunds ........................................................................................... 312
Refund Formulas ............................................................................................................. 312
Moneyback Period .......................................................................................................... 313
Reducing Quotas and Limits ........................................................................................... 313
Refund Percentage ......................................................................................................... 313
Managing Debtors ..................................................................................................................... 314
Punitive Measures ........................................................................................................... 314
Punitive Measures Automation ....................................................................................... 314
Start Date of Time in Debt ............................................................................................... 315
Promotions ................................................................................................................................ 316
Promotion Types ............................................................................................................. 316
Calculating Promotion Discounts .................................................................................... 316
Page 10

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 10
Creating Promotions ....................................................................................................... 316
Calculators shipped with H-Sphere ................................................................................. 319
Validators shipped with H-Sphere ................................................................................... 319
Associating Promotions With Plans ................................................................................ 319
Extra Packages ......................................................................................................................... 319
Creating Extra Packs ...................................................................................................... 319
Managing Extra Packs .................................................................................................... 320
Anniversary Based Billing .......................................................................................................... 322
Switching Between Billing Modes .............................................................................................. 322
Sending “No charge” Notifications ............................................................................................. 323
Warning of Immediate Charges in Case of Buying Additional Resources ................................ 323
Charging Accounts Whose Plans Change ................................................................................ 324
Charging End User Accounts .......................................................................................... 324
Charging Reseller Accounts ............................................................................................ 325
Dedicated Servers 326
Enabling Dedicated Servers in Globals ..................................................................................... 327
Adding MRTG Logical Servers and Network Switches ............................................................. 327
Adding MRTG Logical Servers........................................................................................ 328
Adding Network Switches ............................................................................................... 328
Viewing MRTG Server Info ............................................................................................. 330
Creating/Managing Dedicated Server Templates ..................................................................... 331
Custom-built Dedicated Servers ..................................................................................... 332
Dedicated Server Plans ............................................................................................................. 333
User Plans ....................................................................................................................... 333
User‟s Choosing a Server at Signup ............................................................................... 335
Reseller Plans ................................................................................................................. 336
Managing Dedicated Servers .................................................................................................... 338
Adding Dedicated Servers .............................................................................................. 338
Editing Dedicated Servers ............................................................................................... 340
Deleting Dedicated Servers ............................................................................................ 341
Dedicated Server Status ........................................................................................................... 341
Assigning Additional IP Ranges ................................................................................................ 343
1. Set Prices for Extra IPs in Plans ................................................................................. 343
2. Add IP Subnet ............................................................................................................. 343
3. Split IP Subnet to Smaller IP Ranges ......................................................................... 345
4. Create PTR zone for Reverse DNS Records .............................................................. 346
5. Assign IP Range to Dedicated Server ........................................................................ 347
6. Unassign IP Range ..................................................................................................... 348
Billing Dedicated Servers .......................................................................................................... 348
Bandwidth Billing Types .................................................................................................. 349
Bandwidth Billing Types Options..................................................................................... 350
Dedicated Servers‟ Maintenance .............................................................................................. 350
Regular Backups ............................................................................................................. 351
Maintenance Requests ................................................................................................... 351
Automatic Cancellation Settings ..................................................................................... 353
Resellers 354
Plans ............................................................................................................................... 354
Dual Nature of Resellers ................................................................................................. 354
Private Label ................................................................................................................... 354
Look and Feel and Regional Settings ............................................................................. 354
Merchant Gateways ........................................................................................................ 355
Domain Registration ........................................................................................................ 355
Providing Support ............................................................................................................ 355
Control Panel................................................................................................................... 355
Page 11

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 11
Web, Mail, and SQL Resources ...................................................................................... 355
Servers ............................................................................................................................ 355
SSL .................................................................................................................................. 356
Billing ............................................................................................................................... 356
Markup plans ................................................................................................................... 356
Reseller DNS ............................................................................................................................. 357
Step 1. Adding Reseller CP Alias Template ................................................................... 357
Step 2. Configuring Reseller DNS Servers ..................................................................... 359
Creating And Editing Reseller Plans ......................................................................................... 359
Step 1. Configuring The Plan .......................................................................................... 360
Step 2 .............................................................................................................................. 362
Billing Resellers ......................................................................................................................... 366
Fees Collected From Resellers ....................................................................................... 366
Fees for services provided with reseller account ............................................................ 366
Fees for services distributed with user accounts ............................................................ 366
Charging Resellers for Traffic ......................................................................................... 367
Reseller Control Panel SSL ....................................................................................................... 368
Enabling Reseller Control Panel SSL Protection ............................................................ 369
Disabling Reseller Control Panel SSL Protection ........................................................... 373
Reseller Shared SSL ................................................................................................................. 373
Resellers‟ Own Wildcard Certificates .............................................................................. 374
Sharing Your Wildcard Certificates with Resellers .......................................................... 375
Placing Resellers on Separate Boxes ....................................................................................... 377
Allocating Physical Servers to Resellers ................................................................................... 380
Supporting Resellers‟ Customers .............................................................................................. 381
Deleting Resellers ..................................................................................................................... 381
Suspending And Resuming Resellers ....................................................................................... 382
Moving Accounts Between Resellers ........................................................................................ 383
Account Management 384
Finding User Accounts .............................................................................................................. 385
Generic Search ............................................................................................................... 386
Search by Domain Name ................................................................................................ 387
Search by Contact Info .................................................................................................... 387
Search in Resellers ......................................................................................................... 388
Search Suspended Accounts .......................................................................................... 389
Search Deleted Accounts ................................................................................................ 390
Search Dedicated Server Accounts ................................................................................ 390
Search by VPS Hostname .............................................................................................. 391
Search by Account Balance ............................................................................................ 391
Search by Merchant Gateway Transactions ................................................................... 391
Search by Invoice/Balance Entries ................................................................................. 391
Search by Credit Card Charges ...................................................................................... 391
Search by Transfer Traffic ............................................................................................... 392
Search by Disk Usage ..................................................................................................... 393
Search by CC Processing Errors .................................................................................... 393
Search by Logical and Physical Servers ......................................................................... 393
Search by Reseller Traffic ............................................................................................... 394
Search by Resellers Disk Usage..................................................................................... 394
User Details ............................................................................................................................... 394
Admin Notes .............................................................................................................................. 395
Crediting Accounts .................................................................................................................... 396
Debiting Accounts...................................................................................................................... 397
View debits ...................................................................................................................... 400
Deleting Accounts...................................................................................................................... 400
Suspending and Resuming Accounts ....................................................................................... 402
Suspending Accounts ..................................................................................................... 404
Resuming Accounts ........................................................................................................ 404
Restoring Accounts ................................................................................................................... 405
Page 12

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 12
Reports ...................................................................................................................................... 406
Exporting Reports ........................................................................................................... 408
Billing Balance ................................................................................................................. 408
Estimated balance exhaustion date ................................................................................ 410
Daily Report..................................................................................................................... 411
Web Payments Log ......................................................................................................... 412
Charge Log...................................................................................................................... 413
Registrar Log ................................................................................................................... 414
Credit Card Charge ......................................................................................................... 415
Billing Entries................................................................................................................... 415
Signup/Go-away Statistics .............................................................................................. 417
Monthly Revenue ............................................................................................................ 417
Monetary Transactions .................................................................................................... 418
Transfer Traffic Report .................................................................................................... 419
Disk Usage Report .......................................................................................................... 421
Reseller Traffic Report .................................................................................................... 422
In Resellers Disk Usage Report ...................................................................................... 423
IP Addresses Report ....................................................................................................... 424
CC Processing Errors Report .......................................................................................... 425
Account Check ................................................................................................................ 426
Reports Installed in a Package ....................................................................................... 427
Processing Check Payments .................................................................................................... 433
Setting up the Check Mailing Address ............................................................................ 434
Setting E-mail .................................................................................................................. 434
Moderating Accounts ...................................................................................................... 434
Turning Off Check Payments For the Entire System ...................................................... 435
Splitting Multiple Accounts ........................................................................................................ 436
Granting SSH Access To Users ................................................................................................ 437
Customer Signup 439
Signing Up Users ....................................................................................................................... 439
Signing Up Users from Admin Control Panel .................................................................. 439
Signing Up Users from the Street ................................................................................... 441
Moderating User Signups .......................................................................................................... 441
Moderated Signups ......................................................................................................... 441
Email Notifications ........................................................................................................... 442
Activating Or Rejecting Signups...................................................................................... 442
Changing Details of Moderated Accounts ....................................................................... 443
Moderated Credit Card Signup ....................................................................................... 443
Signup Guard Settings .............................................................................................................. 444
Creating moderation rules ............................................................................................... 444
Setting Signup Guard Blacklist........................................................................................ 445
Viewing Signup Info ................................................................................................................... 446
Signup IPs ....................................................................................................................... 446
Signup Statistics .............................................................................................................. 447
Trial Hosting .............................................................................................................................. 448
Introduction to Trial Hosting ............................................................................................ 448
Managing Trial Accounts ................................................................................................. 448
Enabling Trial Registration .............................................................................................. 449
Grouping Trial Plans ....................................................................................................... 450
Managing Trial Accounts ................................................................................................. 451
Enabling Trial Registration .............................................................................................. 452
Grouping Trial Plans ....................................................................................................... 453
Migration 454
Moving Domains Between Accounts ......................................................................................... 454
Page 13
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 13
Domain Move Requirements ........................................................................................... 454
Moving Domains with Domain Mover ............................................................................. 455
Compatibility .................................................................................................................... 456
Manual Domain Move ..................................................................................................... 456
Moving Accounts Between Servers ........................................................................................... 456
Account move implies: .................................................................................................... 456
Cautions .......................................................................................................................... 457
Requirements .................................................................................................................. 457
Procedure ........................................................................................................................ 458
Migrating Individual Cobalt RAQ4 Accounts to Parallels H-Sphere .......................................... 459
Migration Procedure ........................................................................................................ 459
Billing Issues ................................................................................................................... 462
Migrating Individual cPanel Accounts to Parallels H-Sphere .................................................... 463
Preparing for Migration .................................................................................................... 463
Migration Procedure ........................................................................................................ 464
Billing Issues ................................................................................................................... 466
Migrating Individual Ensim Accounts to Parallels H-Sphere ..................................................... 467
Preparing for Migration .................................................................................................... 468
Migration Procedure ........................................................................................................ 469
Migration Notes ............................................................................................................... 472
Billing Issues ................................................................................................................... 473
Migrating Mass Accounts to Parallels H-Sphere ....................................................................... 473
Preparing for Migration .................................................................................................... 473
Migration Procedure ........................................................................................................ 473
Billing Issues ................................................................................................................... 475
Technical Support 476
Client Support Center ................................................................................................................ 477
Configuring Administration Security ................................................................................ 478
Managing Trouble Tickets ............................................................................................... 479
Task System.................................................................................................................... 483
Searching Trouble Tickets .............................................................................................. 484
Exchanging Private Messages ........................................................................................ 485
Managing KnowledgeBase ............................................................................................. 486
Ticket Statistics ............................................................................................................... 486
Ticket Queues ................................................................................................................. 487
Supporting Reseller End Users ....................................................................................... 488
Configuring Support Center ....................................................................................................... 489
Knowledge Base ........................................................................................................................ 492
Creating Knowledge Bases ............................................................................................. 493
Editing and Removing Knowledge Bases ....................................................................... 494
Exporting Knowledge Base ............................................................................................. 494
Importing Knowledge Bases ........................................................................................... 495
Spellcheck ....................................................................................................................... 495
Search ............................................................................................................................. 496
Settings ........................................................................................................................... 496
Custom Jobs .............................................................................................................................. 497
Adding Custom Jobs ....................................................................................................... 498
Adding Tasks to Custom Jobs ........................................................................................ 499
Tracking Custom Job Status ........................................................................................... 500
Mass Mail .................................................................................................................................. 501
Crash Report ............................................................................................................................. 503
Installation ....................................................................................................................... 503
Update ............................................................................................................................. 503
Changing E-Mail Address Where Reports Are Sent ....................................................... 504
Sending Crash Reports ................................................................................................... 504
Extended Physical Server Information ............................................................................ 506
Page 14

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 14
Parallels Virtuozzo Containers 507
Setting Up Parallels Virtuozzo Containers Node Server ........................................................... 508
Creating Virtuozzo Plans ........................................................................................................... 509
Creating Virtuozzo Plan Groups ................................................................................................ 511
Signing Up Users for Virtuozzo Plans ....................................................................................... 511
Configuring Virtuozzo API Socket Read Timeout ..................................................................... 513
Parallels Sitebuilder Integration 514
Setting Up Parallels Sitebuilder ................................................................................................. 515
Licensing Parallels Sitebuilder Accounts................................................................................... 517
Configuring Access to Parallels Sitebuilder Plans from Parallels H-Sphere Plans ................... 517
Migrating from Parallels SiteStudio to Parallels Sitebuilder ...................................................... 518
Third Party Products 519
Urchin ........................................................................................................................................ 520
Miva Kit (intro) ........................................................................................................................... 520
How Does It Work? ......................................................................................................... 521
Adding Miva Merchant Licenses ............................................................................................... 521
Affiliate Programs ...................................................................................................................... 523
How Do Affiliate Programs Work?................................................................................... 524
How Do I Set Up an Affiliate Program? ........................................................................... 524
Kanoodle™ Support .................................................................................................................. 526
AWStats Support ....................................................................................................................... 527
Setup ............................................................................................................................... 528
Configuration on Unix/Linux ............................................................................................ 528
Configuration on Windows .............................................................................................. 528
SpamAssassin Configuration Manager ..................................................................................... 529
Page 15
In this chapter:
Typographical Conventions ............................................................................... 15
Feedback .......................................................................................................... 16
Formatting convention
Type of Information
Example
Special Bold
Items you must select,
such as menu options,
command buttons, or
items in a list.
Go to the System tab.
Titles of chapters,
sections, and subsections.
Read the Basic
Administration chapter.
Italics
Used to emphasize the
importance of a point, to
introduce a term or to
designate a command line
placeholder, which is to be
replaced with a real name
or value.
The system supports the
so called wildcard
character search.
Monospace
The names of commands,
files, directories, and
domain names.
The license file is located
in the
http://docs/common/
licenses directory.
C H A P T E R 1
Preface
Typographical Conventions
Before you start using this guide, it is important to understand the documentation
conventions used in it.
The following kinds of formatting in the text identify special information.
Page 16

16 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Preformatted
On-screen computer
output in your commandline sessions; source code
in XML, C++, or other
programming languages.
# ls –al /files
total 14470
Preformatted
Bold
What you type, contrasted
with on-screen computer
output.
# cd /root/rpms/php
CAPITALS
Names of keys on the
keyboard.
SHIFT, CTRL, ALT
KEY+KEY
Key combinations for
which the user must press
and hold down one key
and then press another.
CTRL+P, ALT+F4
Feedback
If you have found a mistake in this guide, or if you have suggestions or ideas on how to
improve this guide, please send your feedback using the online form at
http://www.parallels.com/en/support/usersdoc/. Please include in your report the
guide‟s title, chapter and section titles, and the fragment of text in which you have
found an error.
Page 17

Parallels H-Sphere Administrator guide aims at hosting providers and explains how to
C H A P T E R 2
About This Guide
configure and administer Parallels H-Sphere control panel.
Page 18

Parallels H-Sphere is a comprehensive hosting automation system that allows you to
In this chapter:
DNS Management ............................................................................................. 19
Server Management .......................................................................................... 20
User Signup ................................ ................................................................ ...... 20
Billing And Plan Management ........................................................................... 20
Merchant Gateway Management ....................................................................... 21
User/Account/Domain Management .................................................................. 22
Resellers ................................................................................................ ........... 22
Domain Management ........................................................................................ 23
SSL ................................................................................................................... 24
Support Center .................................................................................................. 25
Look and Feel Management .............................................................................. 25
C H A P T E R 3
Introduction To Parallels H-Sphere
provide a heterogeneous operating system environment to your customers across
multiple servers. It can manage hosting servers located in various data centers.
Parallels H-Sphere can have a multiple server layout, called a cluster. The main server
in the cluster is the actual Parallels H-Sphere Control Panel, a web application with
graphical interface, which centralizes all hosting management tasks, controls all
hosting servers and services, manages users, domains, events, and processes.
Through Parallels H-Sphere web interface, you can configure and manage these and
other subsystems, other servers (on page 18), user accounts and domains, etc. All
system data, such as billing, domain, and other info, is stored in the Postgres system
database. The Control panel consists of many subsystems, the major of them
described below.
Page 19

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 19
DNS Management
All DNS is managed by Parallels H-Sphere.
A typical Parallels H-Sphere setup requires one service domain name (example.com)
which is used as:
the control panel domain (cp.example.com:8080 or cp.example.com:8443),
web server domain (web1.example.com, web2.example.com),
name server domain (ns1.example.com, ns2.example.com), etc.
It can also be used for third level hosting (on page 98) and instant access domain
aliases (on page 88), as well as to host the corporate (promotional) website. (on page
95)
The most typical configuration is to have two DNS servers, each on a separate box. In
case of one-server installations, you can put two DNS servers on one box (on page
48). By default, Parallels H-Sphere randomly assigns primary and secondary DNS
servers for each domain to balance server load. If you want, you can assign master
and slave roles to DNS logical servers.
Parallels H-Sphere creates a zone file for each domain name on both name servers,
and allows end users to create custom DNS records through a web interface.
You can find more info on DNS Server Configuration in Understanding DNS Server
Configuration documentation in System Administrator Guide.
Page 20
20 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Server Management
We differentiate between physical and logical servers.
Physical servers (on page 33) are actually or virtually separate computers with their
own operating systems (Linux, FreeBSD Unix, or Windows). They can be emulated
with VMWare or other software packages.
Logical servers (on page 36) are programs that run on physical servers and process
client requests. For instance when we talk about web, mail, DNS, mysql and other
servers, we mean logical servers. A physical server can have one or more logical
servers running.
Logical servers of the same nature and purpose make a server group (on page 67). In
case of multiserver installations, logical servers of the same group are located on
different physical servers, and Parallels H-Sphere randomly chooses from them to
create user accounts, which evens server load and disk space usage.
In most instances, Parallels H-Sphere operates with logical servers, not physical
servers. We work with logical servers when we add IPs (on page 45), configure system
SMTP relays (on page 55), assign mail server roles, assign name server roles (on
page 48), etc.
User Signup
To use hosting services, users (site owners and resellers) need to sign up for a hosting
plan.
Parallels H-Sphere offers fully automated user signup (on page 434) through the
signup wizard. Depending on the billing type and signup settings, accounts may not be
created until moderated by administrator (on page 441). For instance, an account may
not be immediately created because it was blacklisted by Signup Guard (on page 444)
or because the user doesn‟t pay with a credit card.
Depending on the plan, access to the signup wizard can be unrestricted (available
“from the street”) or allowed only from the admin control panel. Registration “from the
street” can be performed by anybody without admin‟s interaction. Registration from the
admin control panel goes through exactly the same steps, but can be performed only
by the administrator. The latter is the only way to sign users up for publicly unavailable
plans.
Billing And Plan Management
Parallels H-Sphere comes with a complete billing solution. When users sign up, buy or
use hosting resources, it calculates user charges based on the prices you have
specified and charges them to users‟ credit cards. When credit card charges don‟t
apply, customer payments are added manually in the admin control panel. For more,
see Introduction to Billing and Introduction to Plans.
Page 21

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 21
Merchant Gateway Management
Parallels H-Sphere can work with credit card processors and web based payment
systems to collect payments from customers. To enable a connection with either of
these, you need to configure a connection with the corresponding server.
CREDIT CARD PROCESSORS. Parallels H-Sphere offers complete automation with credit card
processing. To charge an amount to a customer‟s credit card, Parallels H-Sphere
connects to the merchant gateway server and sends an http request. Next, it waits for a
response, and once the success confirmation is received, respective changes are
made to the account balance.
Merchant Gateway Manager allows you to set up different merchant gateway accounts
for different types of credit cards. For instance, you can process VISA cards with
Authorize.Net, and MasterCard, with Verisign PayFlowPro. This way you can maximize
your profits by processing every type of credit card with the gateway that offers the
lowest rate for this type of card. For more, see Merchant Gateway Manager (on page
170).
WEB BASED PAYMENT SYSTEMS. Parallels H-Sphere partially automates payments through
web based payment gateways, including WorldPay (on page 231), PayPal, 2CheckOut
(on page 221), GestPay (on page 225), PaySystems, and PayNova (on page 226).
Once you have registered an account with one of these gateways, you enter the
account details in Parallels H-Sphere. Every time a user chooses to pay, Parallels HSphere passes account ID, amount payable, and possibly other details to the gateway.
The user is then taken to the gateway‟s web interface to enter the credit card number
and complete the transaction. When you receive the payment, you need to credit this
user‟s account (on page 396) through the Parallels H-Sphere admin interface, as in
processing check payments (on page 433). As a result, Parallels H-Sphere doesn‟t
store credit card numbers of customers using web payment systems. For more, see
Web Payment Systems Manager (on page 219).
Page 22

22 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
User/Account/Domain Management
On the user side, Parallels H-Sphere operates with three different tiers: users,
accounts, and domains.
USERS. A user, for the most part, is nothing but a login and password to enter Parallels
H-Sphere control panel. One user can have many accounts (control panels) created
under the same or different plans, and switch between them without having to log in
every time.
ACCOUNTS. Parallels H-Sphere primarily operates with accounts, not users. One account
equals one license and one control panel with its own billing and interface settings.
This means an account has its own balance, billing profiles, invoices, etc. The unique
thing about each account is the numeric account ID. One user can have many
accounts created under different plans and platforms, for instance an account under a
Unix plan for SSH access (on page 437) and an account under a Windows plan for
ODBC or ColdFusion hosting.
DOMAINS. Domains represent the third tier in the end-user side hierarchy. Your
customers can have as many domains as they want under their one control panel
license, unless you limit the domains they can have. In terms of a web server, a
domain is little more than a correspondence to a web-site. Domains within one account
share one control panel (one menu tree with the same look and feel), and, having no
traffic usage or disk quota of their own, are billed in bulk with the same invoices.
Understanding Accounts, Domains, and Users (on page 265)
Resellers
The Reseller feature allows you to sell your hosting services through resellers. Unlike
in other control panels, resellers in Parallels H-Sphere do not resell your plans. Rather,
they sell your hosting resources such as disk space, traffic, mailboxes, etc. at retail
prices, and are charged for them at wholesale prices. In other words, you set wholesale
prices and allow your resellers to group your resources into their own plans and define
their own retail prices for them. More on Billing Resellers (on page 366)
With the reseller admin CP, each reseller gets a private label hosting system, which
leaves you completely invisible to the end customer even at user signup and domain
registration. Resellers can have their own independent control panel URL, DNS server
names, company information, and all other parameters visible from the user‟s control
panel. They will appear to end customers as totally independent hosting companies.
Furthermore, reseller control panels are inaccessible by IP, which excludes the
possibility of accidental or intentional visits to your control panel URL.
Through their admin interface, resellers can customize the default look and feel of their
users‟ control panels. They can change colors, replace all control panel images with
those of their own, edit many texts, change the default control panel language and the
currency of end user payments, etc. in exactly the same manner as it is done by the
master admin.
Page 23

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 23
Domain Management
There are several options to setting up a domain in Parallels H-Sphere:
REGISTER A NEW DOMAIN. Parallels H-Sphere allows automatic registration of standard
second level domains right from the user control panel. It supports the regisrtation
of all TLDs supported by Enom or OpenSRS in real time. You can configure
Parallels H-Sphere to associate different TLDs with different registrars using the
Domain Registrar Manager (on page 146). TLDs with non-automatic registration,
including most regional domains, can be requested by the end user and then
manually registered by the admin through the Email Domain Registrar (on page
165).
TRANSFER an existing domain. Users can transfer domains they have been using
outside Parallels H-Sphere. After the transfer, users will need to update their info on
the root DNS servers.
Set up a THIRD LEVEL DOMAIN. Users can set up domains based on the service domain,
such as userdomain.servicedomain.com.
Set up a WEBSITE WITHOUT A REGULAR DOMAIN NAME. Such websites have all basic
functionalities and are accessible from the web at automatically generated
addresses based on the service domain, such as
123.uNNNN.servicedomain.com.
PARK A DOMAIN. This allows you to use Parallels H-Sphere DNS server for mapping
IPs and domain names serviced and hosted elsewhere.
Create an ACCOUNT WITHOUT ANY DOMAIN. The user will be given disk space on the web
server with FTP access, but no DNS to set up a website.
Page 24

24 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
SSL
Parallels H-Sphere recognizes the following uses and types of SSL certificates:
WEBSITE SSL - users can install SSL certificates one per website right from their user
control panels. For instance, a user can set up a certificate on user.com to have the
user.com website secured with SSL. This can be installed only on websites with
dedicated IPs.
SHARED SSL uses wildcard certificates to secure third level domains. For instance, if
provider.com is a service domain offered for third level hosting, you can set up a
wildcard certificate on provider.com to secure domains like user1.provider.com and
user2.provider.com. More>> (on page 131)
CP SSL - you can secure your control panel with a regular SSL certificate. At this point,
CP SSL is installed from the command line on the CP server.
RESELLER CP SSL - you can configure your Parallels H-Sphere to let resellers secure their
control panels with regular SSL certificates. More>> (on page 368)
RESELLER SHARED SSL - resellers can install wildcard certificates to secure their customers‟
websites. More>> (on page 373)
DELEGATED SHARED SSL - you can allow your resellers to offer their customers your service
domain for third level hosting and wildcard certificate installed on it.
MAIL SSL - you can install SSL on the service DNS zone to secure mail sent and
received by your customers‟ mail clients (such as Outlook Express). Mail SSL is
enabled globally in the system for all end users, including those under resellers. It is
available only to master admin. More>> (on page 135)
Page 25

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 25
Support Center
Parallels H-Sphere Support Center includes Ticket Center, Knowledge Base, and
Custom Jobs modules.
TICKET CENTER. Trouble tickets can be created either from any place in the user control
panel or from email messages. Parallels H-Sphere periodically polls support mailbox,
converts incoming messages into trouble tickets, and puts them in the general queue
where they can be picked up, assigned to other administrators, answered, and closed.
Depending on how they were created, answered tickets are emailed back to the
customers or show up in the ticket center of end users‟ control panels. Support
personnel can exchange notes on tickets - the notes are invisible to customers. More
on Providing Customer Support
KNOWLEDGE BASE. Administrators can add common questions and answers to a
centralized location, group them by categories, and perform search by keywords. The
knowledge base is integrated with the ticket center to suggest answers to typical
questions. More on Knowledge Base (on page 492)
CUSTOM JOBS. Parallels H-Sphere also offers an interface to track additional services
offered to resellers or end users, such as web design and development, installation,
migration, and alike. The list of custom jobs and their status can be viewed from the
customer‟s interface. More on Custom Jobs (on page 497)
Look and Feel Management
Parallels H-Sphere comes with a few skins users can choose from. Different skins offer
different navigation schemes:
XP Reloaded - default left-menu skin since Parallels H-Sphere 3.1.
XPressia - pages are accessible from the horizontal JavaScript navigation bar AND
icons on the home page.
Left Menu - although this skin has a quick access page linking to the most frequently
used pages, the principal navigation is through the left side menu.
No Menu - pages are accessible from clicking navigation icons on the home page.
Each of the skins has a text based variation where navigation icons are replaced with
text links.
As administrator, you can configure interface settings, including images and icons (on
page 101), default skins and colors (on page 106), interface texts (on page 105), and
notification e-mails (on page 112).
The administrator can also allow users to choose preferred skins and languages.
Page 26

Parallels H-Sphere 3.6.3 uses a unified Parallels key administration system for
C H A P T E R 4
Parallels H-Sphere Licensing
licensing.
You will need a new license key if you are going to:
Purchase or lease Parallels H-Sphere 3.6.3 or higher
Upgrade earlier Parallels H-Sphere versions to the latest version
Upgrade the number of accounts
Purchasing and Leasing Parallels H-Sphere
Before installing Parallels H-Sphere, go to http://www.parallels.com/store/hsphere/ to
purchase or lease Parallels H-Sphere.
Every new license purchase includes 12 months of Software Update Service (SUS)
that entitles you to version upgrade licenses throughout the life of your SUS. You will
be required in order to receive further upgrades. All leased license keys (monthly)
include SUS.
After a fresh installation, when you first log into the Parallels H-Sphere control panel,
you will see the prompt to enter the license from the file. Add the purchased license as
described below. After the license has been added successfully, you will see the
license details on the License Info page.
Upgrading to Parallels H-Sphere 3.6.3 or higher
Before upgrading earlier Parallels H-Sphere versions to 3.6.3 or higher, make sure to
upgrade your key at https://www.parallels.com/hsphere/key_upgrade/
Parallels H-Sphere keys can be updated to support newer versions of the software
when they are SUS enabled. When the SUS feature of your key is up-to-date, you can
perform the upgrade of the key without extra costs. In case you run out of this service,
please contact our sales representatives in order to renew/reinstate it.
Warning: Old Parallels H-Sphere licenses are incompatible with Parallels licenses!
Also, no backward compatibility is provided for Parallels licenses on Parallels H-Sphere
3.1 Patch 1 and earlier.
Important: When you upgrade Parallels H-Sphere from 3.1 Patch 1 or earlier, you
would lose your older license and would not be able to enter your control panel unless
you apply a new license. So you must upgrade your license before the upgrade.
To upgrade the license:
1. Click License Info in the Parallels H-Sphere control panel menu.
2. Add the purchased license key. You have two ways of adding the
license key:
Page 27

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 27
Under License Code Activation in the Activate Code field, enter the Key Activation
Code and click Activate.
Under License File in the License Key File field, click Upload, then click Browse
to choose the license key file (you could add the license key either zipped or in
XML format), then click Submit.
After that, you will get the details of the applied key in the page:
Key Number: license key identifier
Key Version: a number which is incremented each time you upgrade your license.
When you add the license for the first time, its value will be 0001.
Auto Update Date: the date when Parallels H-Sphere will try to automatically
update the license.
Expiration Date: 10 days after the Auto Update Date are given to the Parallels H-
Sphere administrator to update the license manually if the automatic update fails
or not possible.
H-Sphere Version: Parallels H-Sphere version the license is applicable to.
Accounts: the number of accounts this license is provided for.
Physical Servers, Resellers, Staff Members: the license may restrict the number of
physical servers, resellers, or administrator accounts in the Control Panel.
Sitebuilder Support: Parallels H-Sphere now comes with Parallels SiteBuilder
integration (reserved for future implementation).
Sharepoint Support, SiteStudio Support, MS Exchange Support, VPS Support: support
for legacy Parallels H-Sphere features.
Upgrading Parallels H-Sphere Accounts
If you want to upgrade the number of accounts that your key holds, you can do that
through our online store at http://www.parallels.com/store/hsphere/upgrades.
Page 28

This document explains what you need to do in order to set up your hosting system
In this chapter:
Step1. Disable Global Resources ...................................................................... 28
Step 2. Set up a Domain Registrar .................................................................... 29
Step 3. Configure Mail Notification Addresses ................................................... 29
Step 4. Set up Payment Settings ....................................................................... 30
Step 5. Create Plans ......................................................................................... 31
Step 6. Create Billing Periods ............................................................................ 31
Step 7. Configure Support Center ..................................................................... 32
Step 8. Configure Look and Feel ....................................................................... 32
C H A P T E R 5
Getting Started
with minimum required configuration, considering the following:
We presume that you have purchased Parallels H-Sphere license, installed
Parallels H-Sphere system, configured and tested it.
A standard Parallels H-Sphere installation sets up a service dns zone (on page 86),
reseller CP alias, and an instant alias template (on page 88), creates a wwwuser
account for hosting your corporate site (on page 95).
Follow the given instructions step by step to configure your control panel.
Step1. Disable Global Resources
Skip this step if you‟re not going to disable any resources, hosting platforms or logical
servers.
You can globally disable resources, hosting platforms, CP designs, dedicated of virtual
private servers, etc. if you don‟t offer them to your customers.
1. Go to Plans - > Globals in your Admin CP.
2. On the page that shows, uncheck the resources and/or hosting platform
you want to be entirely disabled in the system and submit changes. This
will affect all your plans and those of resellers. However, only new singups, but not your current accounts, are subject to such changes.
To disable resources and platforms only for specific plans:
1. Go to Plans - > Manage menu and click to edit the existing plan via Plan
Edit Wizard.
2. Go through Plan Edit Wizard and submit it step by step without changing
prices.
Page 29
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 29
Step 2. Set up a Domain Registrar
Domain registrars need to be added and configured to allow customers to register
second level domains directly from their control panels.
1. Select Domain Registrar in the Settings menu.
2. Select a domain registrar in the Add New Registrar drop down box and
click Add.
3. Enter this domain registrar properties. Check with Domain Registrar
Manager (on page 146) for detailed instructions.
4. In the Set Active drop down box, select this domain registrar.
5. In the TLD drop down box, select the top level domain you would like to
associate with this registrar.
6. Click the Activate button.
7. Click Define Terms/Prices button for the new record that appeared.
Enter prices for each time period and click Submit Query.
Step 3. Configure Mail Notification
Addresses
To subscribe your staff to receive copies of user e-mail notifications:
1. Go to the Settings menu - > Notifications - > Notification Recipients.
2. On the page that appears add subscribers to mailing lists you choose.
Page 30

30 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Step 4. Set up Payment Settings
On this step you can configure Parallels H-Sphere to process credit cards, accept
check payments and perform online web payments for the services you provide.
To configure credit card processing through Merchant Gateway Manager
(on page 170):
1. Go to the Settings menu ->Payment Settings -> CC Brands and add
necessary CC brands.
2. Go to the Settings menu ->Payment Settings -> Merchant Gateway and add
necessary merchant gateway from the drop down menu and click Add.
3. In the Set Active drop down box, select this merchant gateway. You can
have only one active merchant gateway at a time.
4. In the Payment Type drop down box, select the CC brand you would like
to process with this merchant gateway.
5. Click the Activate button.
To configure Web Payment Processor (on page 219), like PayPal or
2CheckOut:
1. Go to the Settings menu ->Payment Settings -> Merchant Gateway.
2. Select the payment system from the drop-down menu and click Edit:
3. Enter your account settings. Once you enter correct settings, the web
payment system will appear in the list as Active
To configure Processing Check Payments (on page 433):
1. Go to the Settings menu ->Payment Settings -> Merchant Gateway.
2. Enable Accept Checks.
Page 31

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 31
Step 5. Create Plans
Now that your control panel is configured, you can create hosting plans.
1. Go to Plans -> Create and click Select next to the plan to start the wizard.
2. Enter the name of the plan at the top of the page.
3. Select the resources (features) you would like to include in the plan.
Make sure to leave Service Domain unchecked.
4. In the last section of the wizard, make sure to enter Credit limit, e.g. 10
and click Next to proceed.
5. Enter prices and free units for each type of resource and click the Create
button at the bottom of the page.
6. Go to Plans -> Manage and turn this plan ON for signups.
Now your control panel is ready for signing up users (on page 434). Please read all
documentation before using Parallels H-Sphere as a production system.
Step 6. Create Billing Periods
Each plan can have several billing periods with different price discounts for each. You
can‟t delete billing periods, but you can change their duration. For instance, if you
create a billing period for 1 year and you find out you don‟t need it, you can change it to
3 months.
To create a billing period for a plan:
1. Go to Plans -> Manage and click Settings in the Advanced section.
2. Scroll down to the Payment Intervals and click Add.
3. Specify the duration of the billing period. For instance, to make it 3
months long, select MONTH and enter 3 in the Size box.
4. Optionally, enter discounts. For instance, if you want to cancel any
setup fee for this billing period, enter 100 in the Setup Discount field.
5. Click Submit. This will add the billing period to the list.
Page 32
32 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Step 7. Configure Support Center
Support Center is the web-based means of providing customer support.
To configure your Support Center:
1. Go to Plans -> Create menu and choose Administrator Plan Wizard.
2. Enter TechSupport Admin as the name of the plan, check to include
TroubleTicket Admin and Allow assignment of trouble tickets and submit.
3. Go to Plans -> Manage and turn this plan ON for signups.
4. Go to Signup menu, click to sign up for Tech Support Admin and create
Tech Support Admin account using the signup wizard.
5. Go to Settings - > Tech Support and configure your Support Center (on
page 489). It is required to collect customers‟ e-mails and convert them
into trouble tickets.
Step 8. Configure Look and Feel
Go to Settings -> Look and Feel menu and enter information to all necessary sections.
These settings will affect all your customers‟ control panels.
Corporate Logos (on page 101): enter Banner HTML Code for the banner to show up
in your users CPs and the location and sizes of the logos. Click the help [ ? ] icon
for details.
Company Info (on page 122): enter the company info that will show in customer e-
mail notifications and the address will be used by customers to send checks.
Default language (on page 109): choose CP interface language. It can be
overridden by individual customers.
Regional options (on page 99): enter preferred currency symbol.The language and
the regional settings will affect all your customers‟ control panels.
Default CP design (on page 106): set designs to be available by users and the
default design for Users CPs.
Page 33
This chapter provides you with the instructions on how you can configure physical and
In this chapter:
Physical Servers ............................................................................................... 33
Logical Servers ................................................................................................. 36
Adding IPs ................................ ................................................................ ......... 45
DNS Servers ..................................................................................................... 48
Mail Server Settings .......................................................................................... 50
SPF and SRS .................................................................................................... 51
AntiSpam and AntiVirus .................................................................................... 53
System SMTP Relays ....................................................................................... 55
Advanced Web Server Settings ......................................................................... 56
Server Groups ................................................................................................... 67
Load Balanced Server Clusters ......................................................................... 69
Platform Change ............................................................................................... 71
Updating Physical Boxes From CP Interface ..................................................... 73
Physical Server Installation/Update Profiles ...................................................... 75
Resource Prerequisites ..................................................................................... 79
System Service Management ............................................................................ 82
In this section:
Adding Physical Servers ....................................................................................34
Physical Server Controls ....................................................................................35
Deleting a Physical Server .................................................................................36
C H A P T E R 6
Server Configuration
logical servers in Parallels H-Sphere.
Physical Servers
Physical servers (also referred to as boxes) are represented by physically or virtually
separate computers with their own operating systems (Linux, FreeBSD Unix, or
Windows). Physical servers can be emulated with VMWare or other software
packages.
Separate physical servers are required for:
Windows web hosting
MS SQL user database hosting
Windows real media hosting
PostgresSQL user database hosting
Page 34
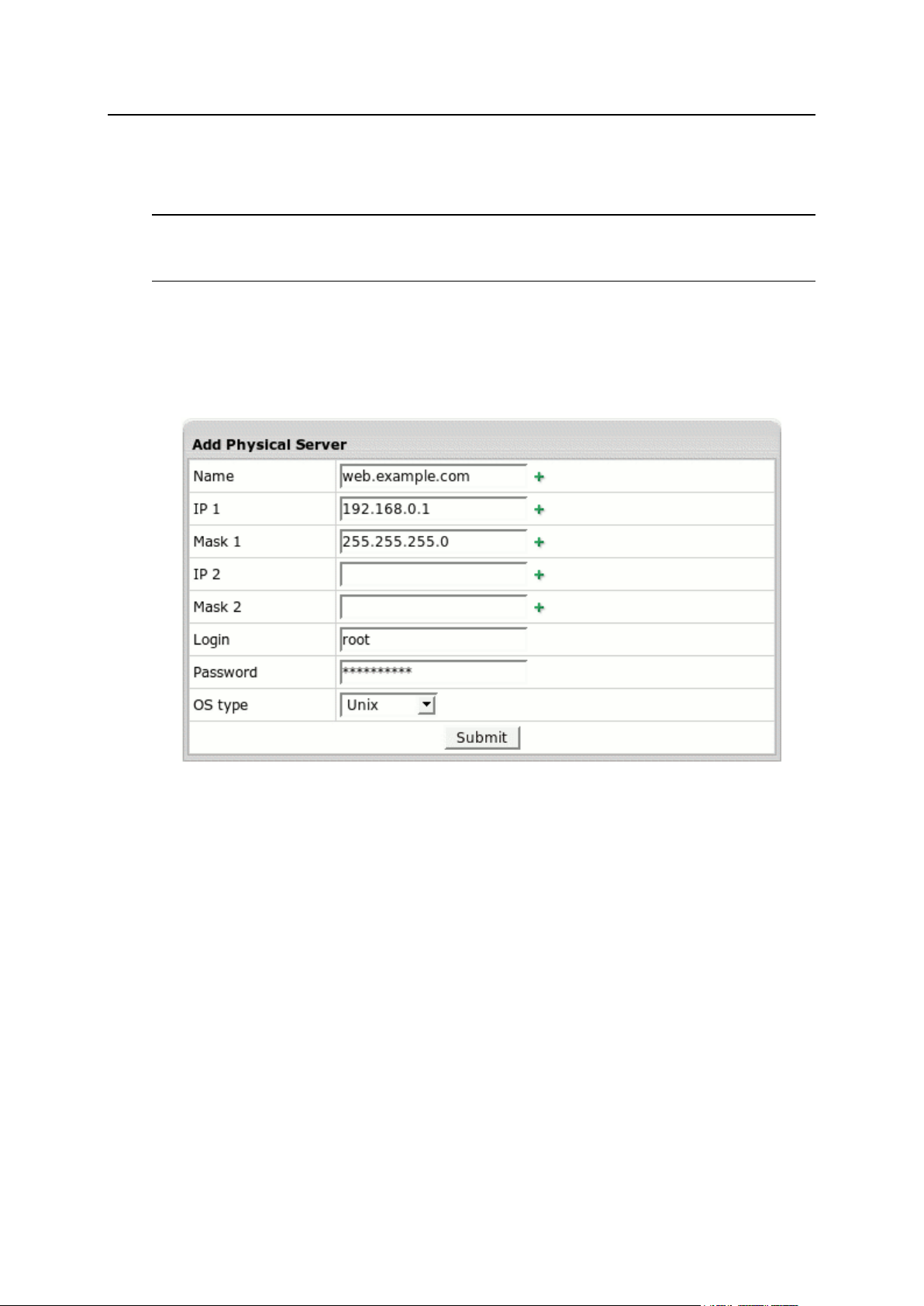
34 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Adding Physical Servers
Important: note that this document provides instructions on how to add physical
servers via the control panel. It is just a step in the procedure of adding servers and
services to the Parallels H-Sphere cluster. You can read about this in a separate guide.
To add a new physical server to Parallels H-Sphere:
1. In your admin control panel, go to E. Manager -> Servers -> Add P.Server.
2. Click Add Physical Server at the bottom of the page that appears.
3. Enter the name of the physical server, its IP and associated net mask:
Specify Login and Password parameters:
For Windows servers, these are login (hsadmin by default) and password
chosen when installing the Winbox.
For Unix servers, enter login: root and root password for this server.
Don‟t enter IP2 and Mask2, they are not implemented for Linux and for Windows.
4. Click Submit.
5. Add server groups (on page 67) (types) of logical servers to be placed
on this physical server.
For example, if you add only web servers and mail servers groups, you
won‟t be able to add any DNS servers to this physical server.
6. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> P.Servers to see the newly added server in
the list of all physical servers in the system.
To finish adding this physical server to Parallels H-Sphere, add to it also logical servers
(on page 36) (services that you plan to place on it). Further steps are described in a
separate guide on Adding servers and services to Parallels H-Sphere.
Page 35
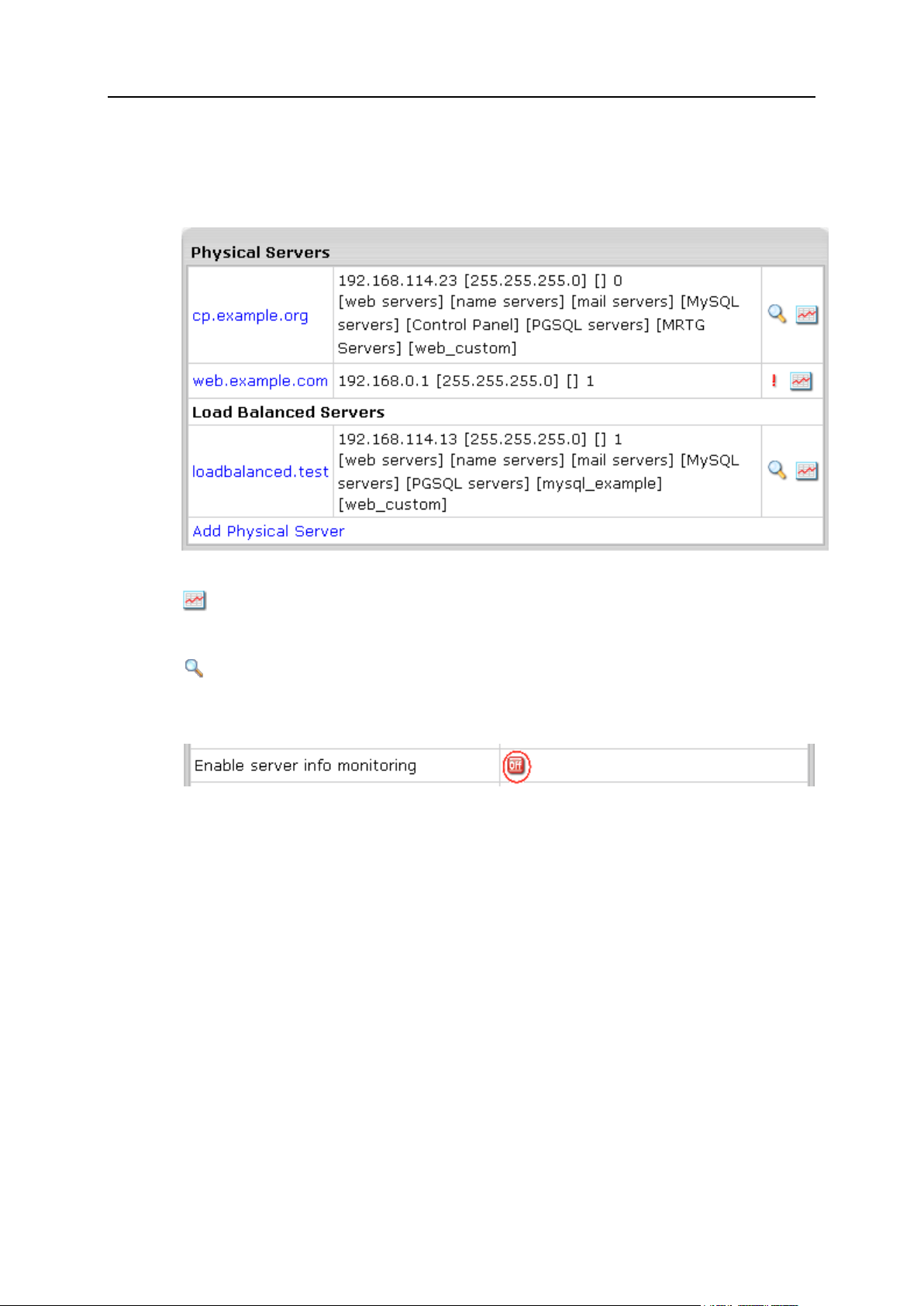
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 35
Physical Server Controls
To see all physical servers in your Parallels H-Sphere cluster, go to E. Manager ->
Servers -> P.Servers:
From this page you can:
- choose Apache version (on page 56) for all Unix boxes and configure settings
for Unix web boxes (on page 56)
! means that this physical server hasn‟t been physically added to the system
- view system information for this server
You can disable monitoring information for this server to preserve resources of the
system. To do this, click the physical server title on the page E. Manager -> Servers ->
P.Servers. Scroll down and click the button against Enable server info monitoring:
When this service is enabled, you can also view, from the System Information page,
which packages and services are installed on the system and perform system
service management (on page 82).
See also:
Load balanced server clusters (on page 69)
Updating physical boxes from the CP interface (on page 73)
Physical server installation/update profiles (on page 75)
Page 36
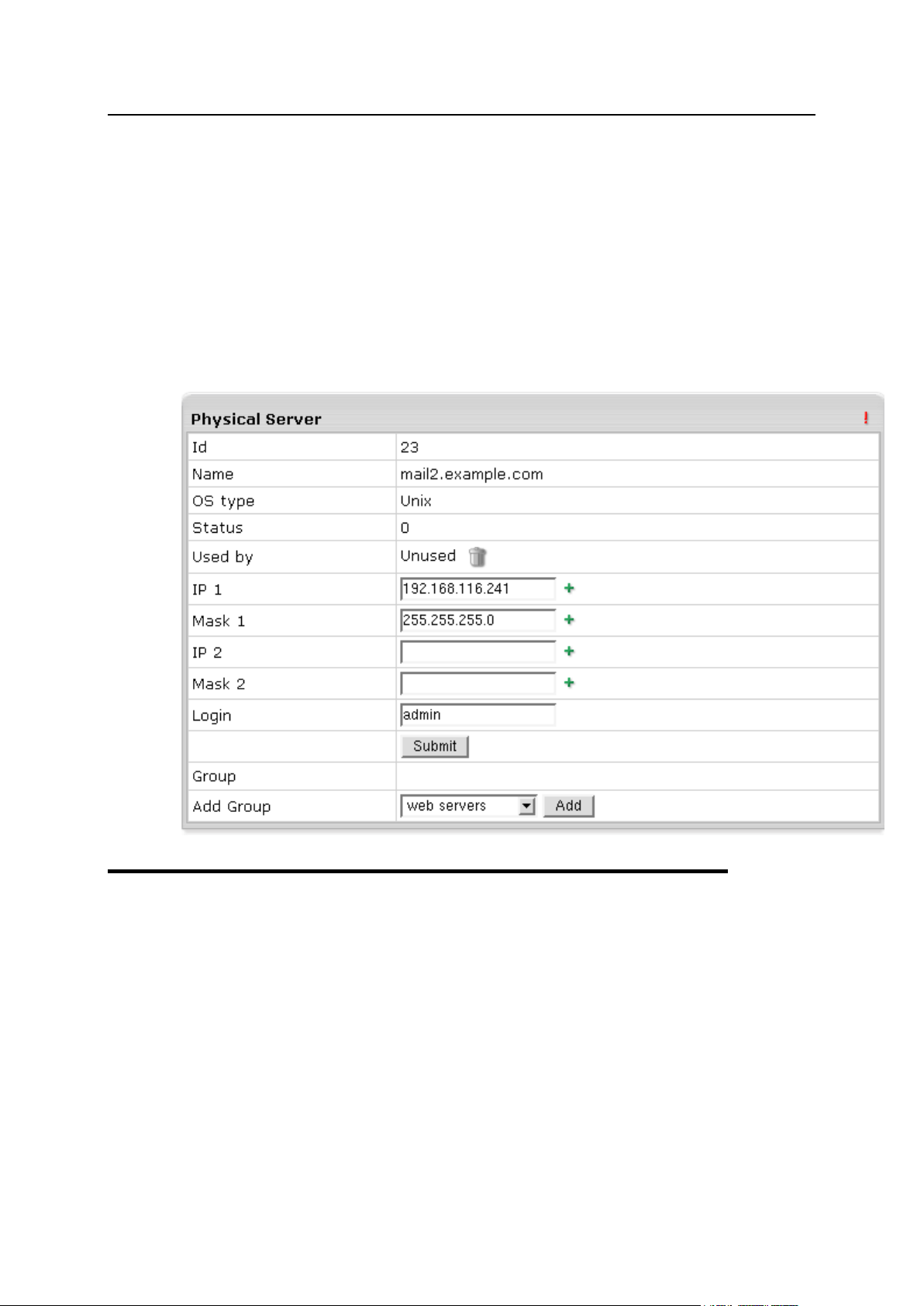
36 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Deleting a Physical Server
In this section:
Adding Logical Servers ..................................................................................... 37
Enabling User Signup on Logical Servers ......................................................... 39
Removing Logical Servers ................................................................................. 40
Setting Logical Server Additional Options .......................................................... 40
A physical server can be deleted only if it‟s free of logical servers.
To delete a physical server:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> P.Servers.
2. Click the name of the physical server you‟ve decided to delete.
3. In the Used by section, find the Delete icon. It appears only if the server
isn‟t used by any services:
Logical Servers
By logical servers we mean the software that runs on physical servers and processes
client requests.
Page 37
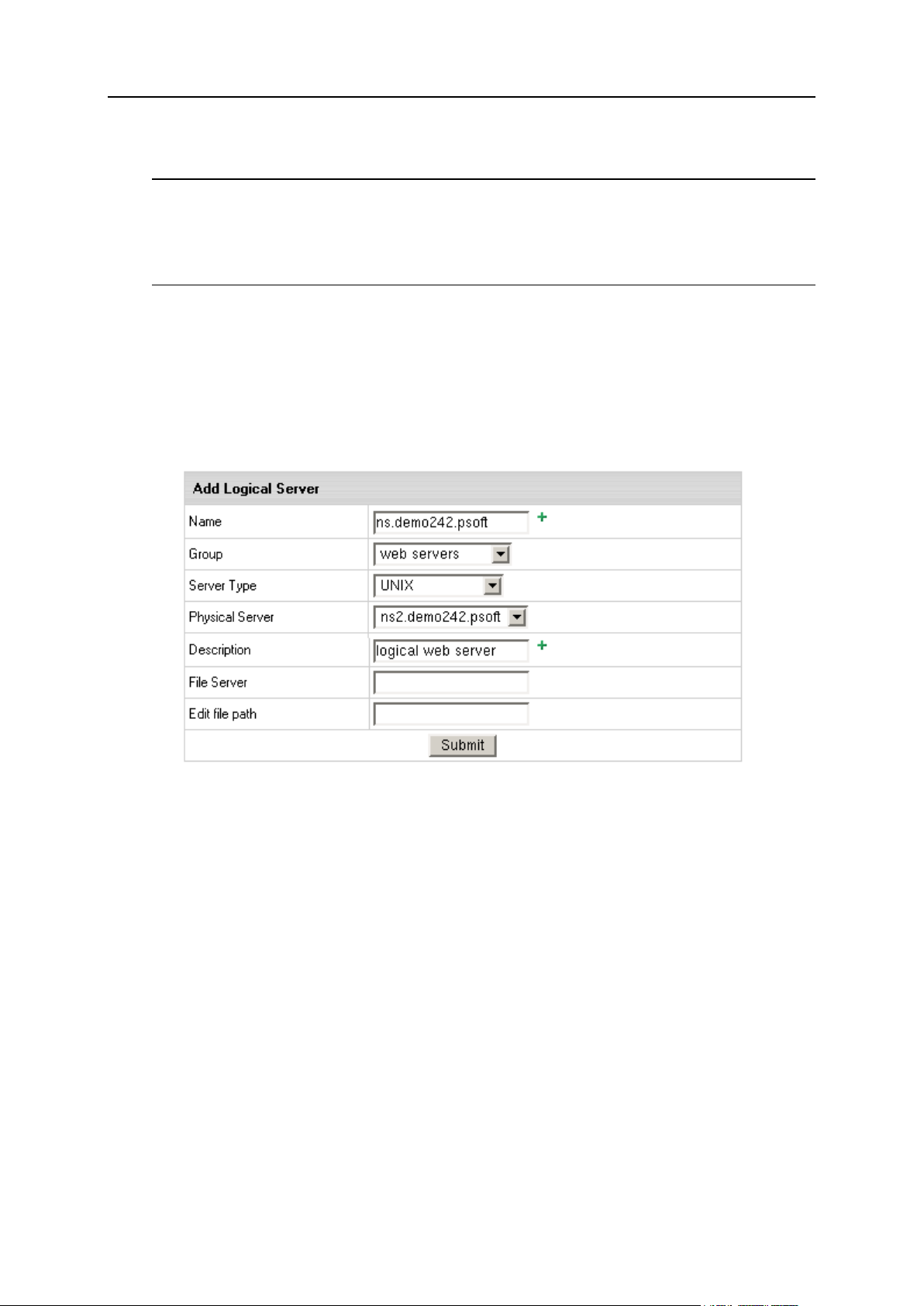
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 37
Adding Logical Servers
Important: for correct system performance, we don‟t recommend that you have more
than one logical server of the same type (web, mail, dns etc.) per each physical box. As
an exception, two logical dns servers are permissible under one- server installation. As
soon as the second box is added to the system, one of the name servers should be
moved to that box.
Before you begin adding a logical server to Parallels H-Sphere, make sure to have the
physical server added to Parallels H-Sphere configuration.
To add a new logical server to Parallels H-Sphere:
1. Go to your admin control panel.
2. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> Add L.Server.
3. On the page that appears, enter the properties of the logical server:
Page 38

38 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Name: The domain name of the logical server;
Group: The group of logical servers you are adding this server to.
Type: The type of the server.
Physical Server: The box where the logical server is installed. If nothing is
available in the dropdown box, add this server group to the physical server (on
page 67) first.
Description: The note that will help you identify this server among others.
File Server: redundant parameter, not in use any longer.
File Path: redundant parameter, not in use any longer.
4. Click Submit to create a logical server. You will proceed to the page
where you can configure other parameters for this logical server:
a Enable user signup (on page 36) on this server
b Automatically generate custom DNS records (on page 91) by clicking Generate in
front of Generate custom DNS records for this logical server
c Add IP range (on page 45) available for hosting on this server
d Configure additional options (on page 36) specific to this logical server type
(Web, mail, DNS, Windows, ...)
5. Add DNS records (on page 91) for this logical server.
6. If you are adding a web server, select Shared SSL Manager in the E.Manager
menu, click the Edit icon next to the domain name and enter the
certificate key and certificate file in the Install completely new certificate
key and file pair boxes. Then click the Upload button. This will update
the shared SSL certificate installation on all servers, including the newly
installed one.
7. For each type of logical servers, configure specific additional options
(on page 36).
Page 39

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 39
Enabling User Signup on Logical Servers
By default, customer signup is disabled on new logical servers. Sometimes you may
want to keep it disabled to provide dedicated servers to individual customers or to
prevent them from getting overloaded. In most cases, however, you would need to turn
it on.
To enable user signup:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> L.Servers.
2. You will be taken to the list of all logical servers in the system. Click the
server you would like to edit:
3. On the page that appears, turn on the Available for signup option.
Page 40

40 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Removing Logical Servers
To remove a logical server:
1. Make sure no accounts, mail domains, web sites or other resources are
run on it.
2. Delete all the IPs designated to it (E.Manager -> L.Servers -> „selected logical
server‟ page)
3. Click the Delete icon which will then appear in the Usage field
Setting Logical Server Additional Options
Once a logical server is added, you can set additional options for it. To set additional
options, click the logical server name in the list of all logical servers and scroll down to
the bottom of the page.
Web server additional options
Page 41

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 41
You can set the following for the webserver:
Miva Merchant version: this option allows setting correct extensions prior to
installation: .mv for v. 4.12 and older and .mvc for v.4.14 and later.
Unix user home directory: enter home directory if necessary.
Webshell (File Manager): this option allows choosing between Webshell4 and
Webshell5 (CGI Mode)
Prohibit users from switching to dedicated IP: disables switching to dedicated IP for all
users
Choose External Horde DB Server: set MySQL logical server for Horde Webmail
Frontend. If you set LOCAL, Parallels H-Sphere will use the default server.
Outgoing rsync connection IP address: Usually, rsync would connect from the Web
server‟s shared IP, but for non-default rsync allow host parameters you can set the
outgoing rsync connection IP(s) (delimited with comma) in the logical server
options.
Make sure to click Set to apply changes.
Windows server additional options
Page 42

42 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 43
Page 43

You can set the following parameters for the Windows server:
FTP Server Type: you can choose between IIS and FTP
Miva Merchant version: this option allows setting correct extensions prior to
installation: .mv for v. 4.12 and older and .mvc for v.4.14 and later.
Maximum number of worker processes by Shared Application Pool: once you set the
restriction, users won‟t be able to exceed it in their User CP.
Maximum number of worker processes by Dedicated Application Pool: once you set the
restriction, users won‟t be able to exceed it in their User CP.
Prohibit users from switching to dedicated IP: disables switching to dedicated IP for all
users, if necessary
DNS server additional options
Additional options in DNS logical server allow assigning master and slave roles to DNS
logical servers and limiting resellers to particular DNS logical servers.
For detailed information, read about DNS Servers (on page 48).
Mail server additional options
Additional options in mailserver allow to choose:
Mail server role at the system level
External Spamassassin DB Server If you set LOCAL, Parallels H-Sphere will use
default server.
Unix Hosting server for Horde If you set LOCAL, Parallels H-Sphere will use default
server.
REMOVING MAIL RELAYS ON A CHOSEN MAIL SERVER
If your mail server has none of mail domains, you can remove all its mail relays in one
click on the Mail Servers Settings page. Firstly, make sure the
CleanMailRelaysForMailServer cron is enabled in Background Job Manager
Page 44

44 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Once you removed all mail relays, you can remove the corresponding logical server.
MySQL server additional options
You can set the following for the MySQL server:
Unix Hosting server for PHPMyAdmin that will host your users‟ built-in phpMyAdmin
control panel. If you set LOCAL, Parallels H-Sphere will use default server.
Remote Access To MySQL Server
PostgreSQL server additional options
Unix Hosting server for PHPPgAdmin that will host your users‟ built-in phpPgAdmin
control panel. If you set LOCAL, Parallels H-Sphere will use local server.
Load Balancer File Server (Filer) Settings
Page 45

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 45
Once the physical server for this logical server (master server only!) is configured in the
load balanced server cluster, the following Load Balancer File Server Settings should be set
in Logical Server options:
File Server Type: file storage OS type, like UNIX for generic Linux NFS;
File Server: file storage volume location, like 10.9.8.7:/vol/vol0;
File Path: (optional) file storage path to Parallels H-Sphere directory, like
/vol/vol0/hsphere.
File server Volume ID: file storage volume ID, like vol0.
See Installation of Load Balanced Web/Mail Clusters in Parallels H-Sphere in Parallels
H-Sphere System Administrator Guide for explanations.
Adding IPs
To add IPs to a logical server:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> L.Servers.
2. Select the logical server from the list:
Page 46

46 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
3. On the page that appears, enter the IP(s):
Page 47

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 47
From: enter the first IP of the range of dedicated IPs. If you are adding only one
IP, enter it here.
To: enter the last IP of the range of dedicated IPs.
Mask: enter the netmask—you should have received it from your Internet Service
Provider. When adding a pool of IPs on FreeBSD servers, add the first IP
separately with the real mask, then add the other IPs as a pool with the mask
255.255.255.255.
Type: select the type of IP you are adding to the system:
Page 48
48 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Dedicated IP - the IP will be dedicated only to one site/service. This means that
Dedicated IP should be unique and cannot be used anywhere else. Choose it
only for Web and Windows servers.
Shared IP - the IP will be used by multiple Web sites under Unix and Windows via
typical Virtual hosting. Choose it only for Web and Windows servers. Make sure
to add shared IPs one by one, NOT as a range of IPs.
Important: We recommend having at least one shared IP (“default” one with
default Shared IP tag 2) on every Web/Windows server. This is in particular
essential for creation of reseller DNS aliases.
Service IP - choose it for logical servers other than Web and Windows. Don‟t
choose it for Web and Windows servers!
Note:
1. For every logical server other than Web/Windows exactly one service IP
must be set!
2. If you add a service IP to a logical server in the “Control Panel” or
“MRTG” group, make sure it is the IP of the physical server.
Mind also, that service IP doesn‟t automatically bind to a physical server.
Instead you have to put it up manually or use physical server‟s primary IP.
DNS Reseller IP - choose it only for resellers‟ name server aliases.
System Management IP - reserved for future use. Don‟t select it.
Outgoing IP - configure separate IP for sending outgoing mail. If this value is
specified, all your mail is sent from the specified IP, not from your actual mail
server IP. Use this control when your mail server IP is added to a spam blacklist,
and mail from your domain is rejected. Important: You can have only one
Outgoing IP per mail server.
Bouncing IP - configure separate IP for sending bounced mail. It allows isolating
bounced message on a different IP address and block them without blocking
other mail. Important: You can have only one Bouncing IP per mail server.
Shared IP Tag: a digital “mark” that helps to separate sites on one logical server. It
allows you to allocate a separate shared IP address to a group of sites of, say,
explicit nature. This may become necessary, because many corporate firewalls
filter sites based on their IP address, not domain name. Note: Make sure to
have one shared IP tag used by one shared IP within one logical server.
IMPORTANT:
1. Make sure the same dedicated or shared IP is not used by more than 1 server.
2. When added to the logical Web server, dedicated IPs are not registered in
ipconfig. They are only added when new accounts are created.
4. Added IPs will show up under IPs in the Logical Server section.
Once added, IPs can be painlessly changed only when no Websites are running on the
system. Changing IPs on production servers implies an IP migration.
DNS Servers
How Do I Put Several DNS Servers On One Box?
Page 49
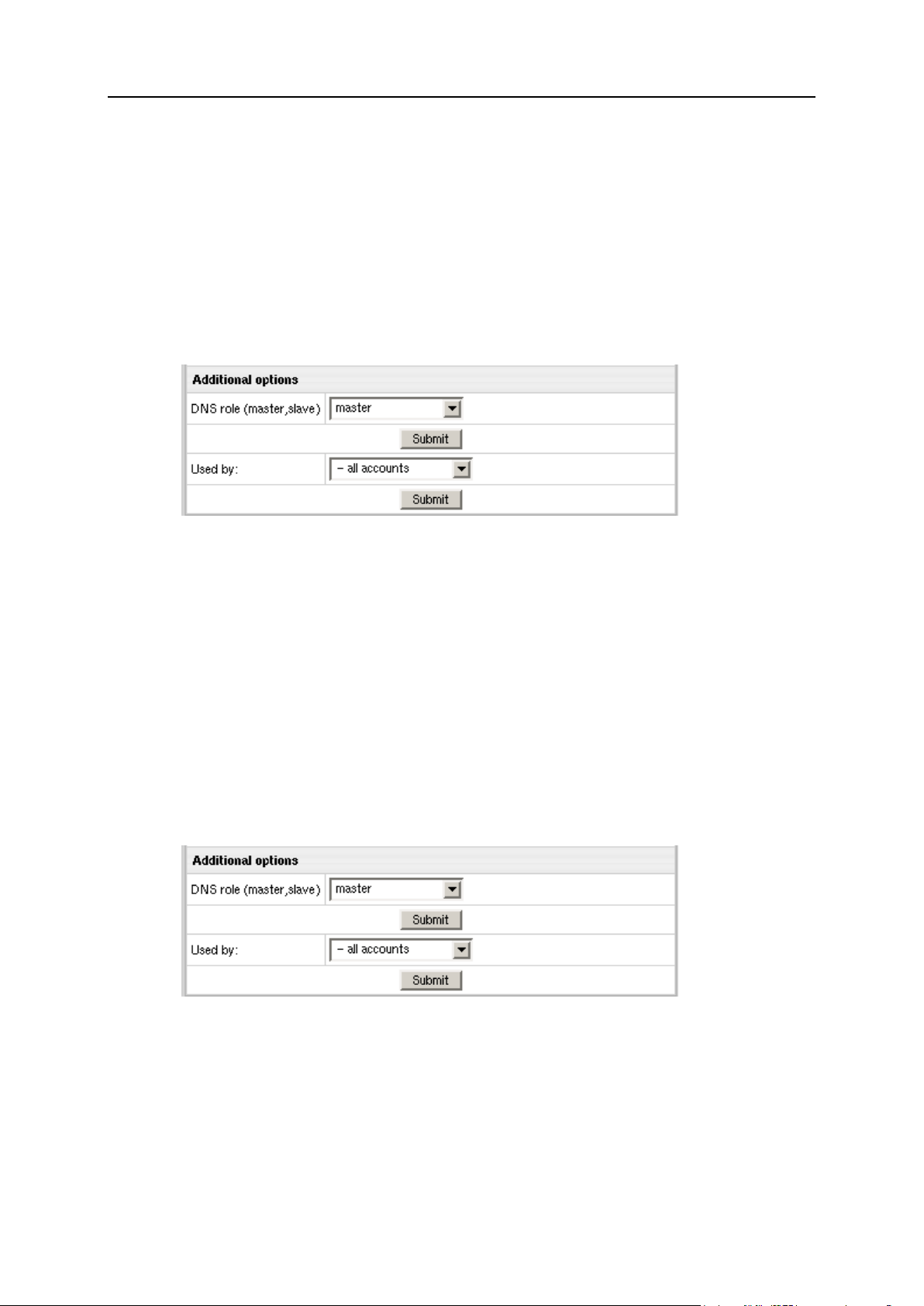
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 49
You can have more than one DNS servers on one box. However, if you‟d like to put
your DNS servers on more than one box, you need to put each of them on a separate
box.
To configure multiple DNS servers on one physical box, see Single DNS Confiruration
in System Administrator Guide.
How do I assign master and slave roles to DNS logical servers?
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> L.Servers.
2. Click DNS logical server name. You‟ll be taken to its configuration page.
At the bottom of the page you‟ll see the Additional options form:
3. From the DNS role drop-down box choose either master or slave1 or
slave2.
4. Repeat steps 1-3 for the rest of your DNS logical servers.
If DNS logical servers are not assigned any roles or more than one DNS logical servers
are assigned the same role (e.g. two master or two slave1 servers), Parallels H-Sphere
will randomly assign “master” to one of them and address another one as “slave”. In
this case it‟s quite likely that the same DNS logical server will have different roles for
different DNS zones.
How do I limit resellers to particular DNS logical servers?
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> L.Servers.
2. Click DNS logical server name. You‟ll be taken to its configuration page.
At the bottom of the page you‟ll see the Additional options form:
Page 50

50 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
3. From the Used by drop-down box choose:
all accounts to allow both regular and reseller customer accounts to use this DNS
logical server;
resellers only to allow only reseller end customer accounts to use this DNS logical
server;
master admin only to allow only your regular customer accounts to use this DNS
logical server.
Important: if all DNS logical servers are used by the same group, signups from under
the other group will fail.
Mail Server Settings
Parallels H-Sphere incorporates the following mail server functionality configured from
CP web interface:
Qmail controls - configuring general and antispam Qmail controls (System
Administrator Guide).
SpamAssassin - configuring mail server SpamAssasin parameters.
SPF and SRS - configuring SPF and SRS on server level.
Blocking IP - fighting spam or ignoring unwanted emails by denying relay to specific
IP.
Adding Qmail Settings To IP/Subnet - adding mail relay and other Qmail settings to
a chosen IP/subnet.
Page 51

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 51
SPF and SRS
In this section:
Enabling SPF and SRS ..................................................................................... 51
Configuring SPF and SRS ................................................................................. 52
SPF or Sender Policy Framework figthts e-mail forgery in SMTP transaction. It
prevents unauthorized people from forging email addresses. When users enable
SPF, a DNS TXT record is created for DNS zone hosting this domain. It defines
what IP‟s can be used to send mail from this domain. On receiving e-mail from
user‟s domain, recipient, providing SPF is enabled on their side, can check if it
indeed was sent from the IP listed in this DNS record.
SRS or Sender Rewriting Scheme is a mechanism to rewrite sender addresses
when a mail is forwarded in such a way that mail forwarding continues to work in an
SPF compliant world. When you add SRS, then srs qmail parameters will be
included on all mail servers, also base64 secret key used in the SRS address
cipher will be generated. You can include mailSRS cron in the Background Job
Manager to regenerate secret key every month.
Enabling SPF and SRS
SPF is included in plans as a regular resources with plan edit wizards.
SRS is enabled for the whole system and doesn‟t require enbaling it in the plans.
To enable SRS, go to Mail Servers (the E.Manager -> Servers menu) and turn it ON,
clicking the OFF button in the SRS entry:
Page 52
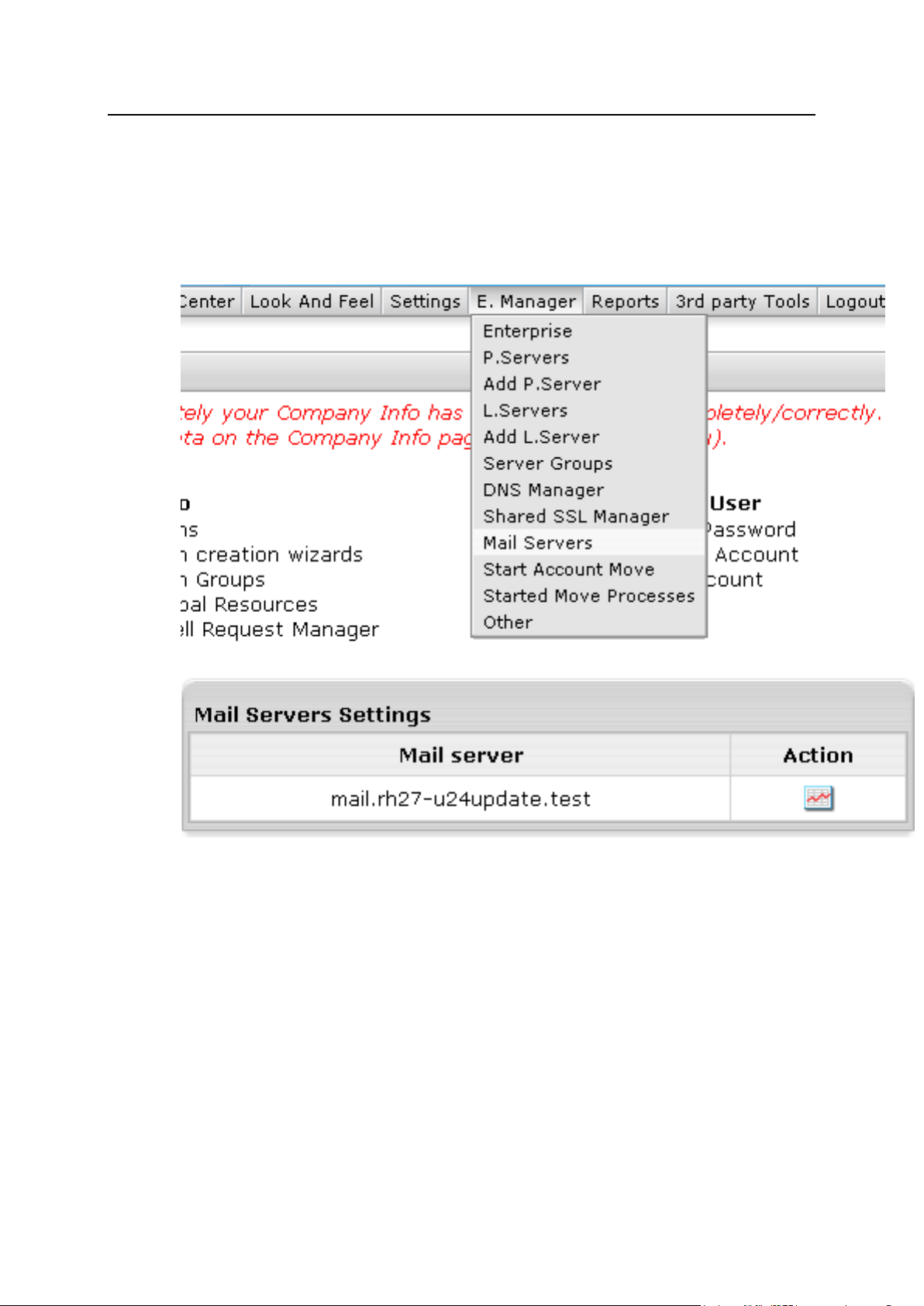
52 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Configuring SPF and SRS
To access SPF/SRS configuration form:
1. Select Mail Servers from the E.Manager -> Servers menu:
2. Click the Action icon in the Mail Server Settings section:
Page 53

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 53
3. At the bottom of the page you will find SPF/SRS configuration form:
In this section:
Enabling AntiSpam and AntiVirus in Control Panel ............................................ 54
Configuring AntiSpam and AntiVirus Default Settings ........................................ 54
For SPF/SRS configuration parameters see details in Configuring SPF/SRS
parameters in System Administrator Guide
AntiSpam and AntiVirus
Parallels H-Sphere incorporates SpamAssassin and ClamAV filters into its mail
servers. They have been added to Parallels H-Sphere as the Antispam and Antivirus
resources globally enabled in the system, and can be configured in Control Panel both
at the server level (on page 50), and for individual plans, accounts, domains and
mailboxes.
Page 54
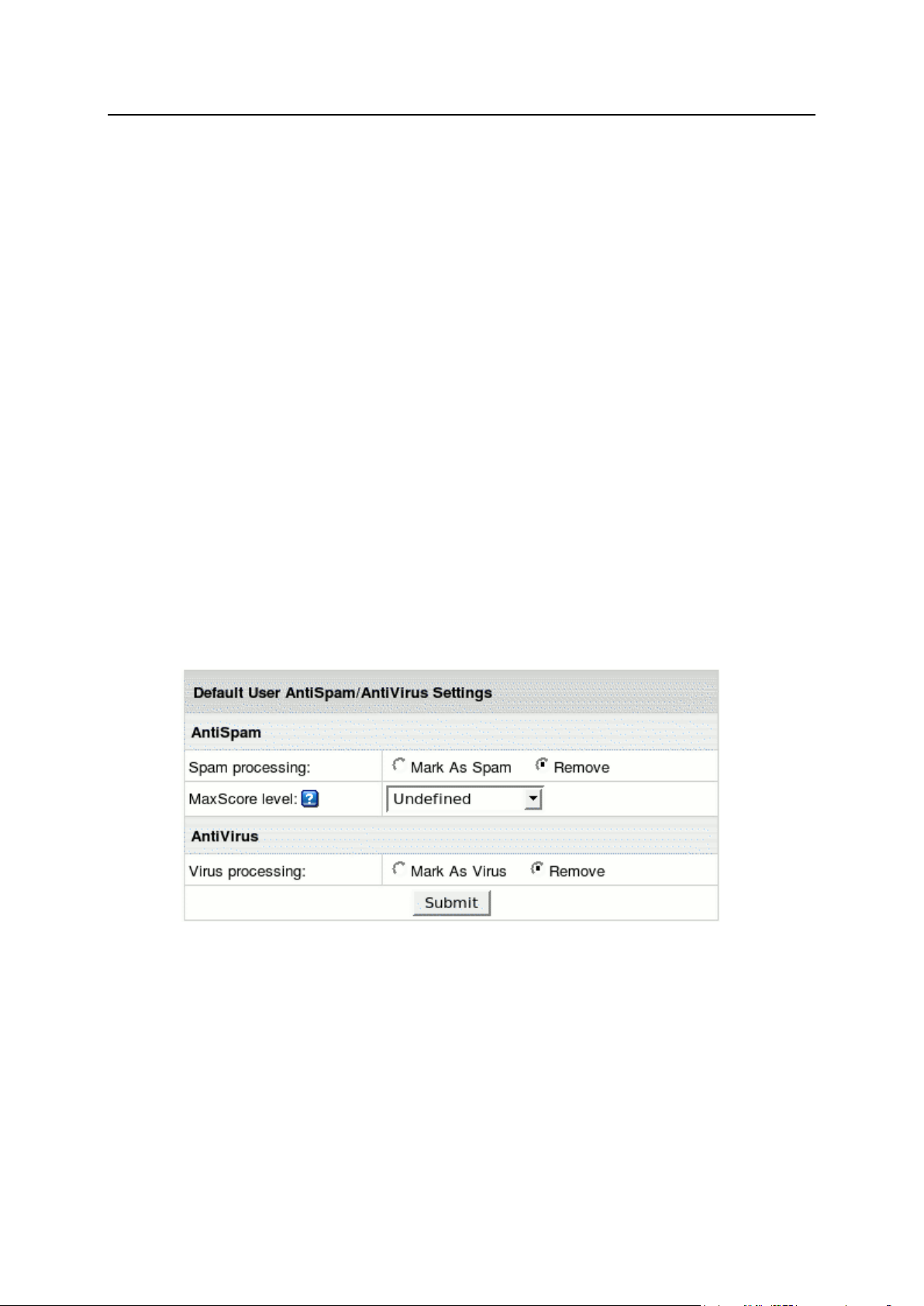
54 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Enabling AntiSpam and AntiVirus in Control Panel
To enable AntiSpam and AntiVirus in Control Panel:
1. GLOBAL SETTINGS: In Info -> Global Resources, check AntiSpam and AntiVirus
and click Submit Query.
2. PLANS: In Info -> Plans select the plans where you would like to enable
spam and virus protection. On the first page of the wizard, enable
Antispam and Antivirus. Optionally, set prices for these resources on the
subsequent steps.
3. Accounts, domains and mailboxes: managing Antispam and Antivirus on this
level is managed via User CP.
Configuring AntiSpam and AntiVirus Default Settings
You can set default AntiSpam and AntiVirus settings for new mail domain. They will be
applied to all new mail domains. Later each user can change it via user CP.
To set defaults in your Admin CP:
1. Go to Settings menu - > AntiSpam and AntiVirus Defaults:
Choose Spam and Virus processing manipulation
Set MaxScore level: this value cannot be chosen with Spam processing Remove
value simultaneously
2. Click Submit
Page 55

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 55
System SMTP Relays
There are two system SMTP relays you can choose for each individual mail server POP before SMTP and SMTP AUTH.
In POP before SMTP, the relay system collects IP addresses of users who successfully
authenticate themselves with a POP server, and then permits SMTP relaying from that
IP address for a short period of time.
If clients do not have known IP addresses, relays use SMTP AUTH, an SMTP based
protocol, in which the client must send a name and password in addition to the normal
SMTP envelope information. Obviously this requires a special client, which has been
configured to use this protocol.
To specify the protocol for a specific server:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> Mail Servers.
2. At the top of the page that appears, click the Action icon next to the mail
server.
3. At the very bottom of the page select the protocol and click Submit.
Page 56

56 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Advanced Web Server Settings
In this section:
Apache Version ................................................................................................. 56
Apache Modules ............................................................................................... 57
Using Gotroot.com Modsecurity™ Rules With H-Sphere ................................... 60
PHP Modes ....................................................................................................... 62
PHP Plugins ...................................................................................................... 65
PHP Accelerators .............................................................................................. 66
Parallels H-Sphere 3.1 branch adds support of Apache 2.2 and adds more flexibility in
configuring the web service for Unix boxes, while many options are available right from
the administrator interface. These settings are available under icon near the server
on E. Manager -> Servers -> P.Servers page. After you‟re done with the settings, don‟t
forget to click Submit.
Apache Version
To choose Apache version for your physical Unix box:
1. Go to E. Manager -> Servers -> P.Servers and click the (Server options)
icon.
2. On the page that appears choose Apache versions:
1 corresponds to Apache 1.3.x, 2 to Apache 2.2.x. If you enable Apache 2.2.x,
choose also MPMs (Multi-Processing Modules): prefork or worker.
3. Click Submit.
Page 57

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 57
Apache Modules
Some Apache modules like apache_ssl consume much of the system resources, some
are obsolete like apache_throttle and apache_frontpage. You can toggle them from the
interface for each Apache version. By default, only apache_ssl of the following is
enabled, the rest are disabled:
Page 58

58 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
apache_ssl - this module provides strong cryptography for the Apache 1.x webserver
via the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL v2/v3) and Transport Layer Security (TLS v1)
protocols by the help of the Open Source SSL/TLS toolkit OpenSSL.
apache_fastcgi - this module provides support for the FastCGI protocol. FastCGI is a
language independent, scalable, open extension to CGI that provides high
performance and persistence without the limitations of server specific APIs.
apache_fcgid - this module replaces mod_fastcgi with the mod_fcgid, a different
FastCGI protocol implementation. This implementation is recommended for
CloudLinux OS physical boxes by its vendor. Note that apache_fastcgi checkbox
should also be enabled.
apache_scgi - the SCGI protocol is a replacement for the Common Gateway
Interface (CGI) protocol. It is a standard for applications to communicate with HTTP
servers. It is similar to FastCGI but is designed to be easier to implement.
apache_throttle - this module limits the bandwidth usage and server load of virtual
hosts, directories, locations, or users according to selected policies.
apache_frontpage - this module adds front page support.
apache_status - this module allows a server administrator to find out how well their
server is performing. The current server statistics is presented in an easily readable
form in an HTML page. If required, this page can be automatically refreshed (given
a compatible browser). Another page gives a simple machine-readable list of the
current server state.
apache_security - an open source Intrusion Detection and Prevention module for
Web applications.
apache_cache - this module enables memory caching scheme with the most common
set of related parameters. If you want to change them, or use disk caching scheme,
or combination of the two, prepare a custom template for corresponding include file.
When enabling apache_security, set also Apache mod_security options.
We also provide a new tool for loading Gotroot rules included into hsphere-apache-
shared-h3.1 package.
If you want to use Gotroot.com rules with Apache mod_security, you should first load
them into H-Sphere. Read about Using Gotroot.com Modsecurity Rules With H-Sphere
(on page 60).
Page 59

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 59
asecurity_rules - Web Application protection. Config file: rules.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
asecurity_jitp - Just in Time Patches for Vulnerable Applications. Config file: jitp.conf.
Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_useragents - Bad UserAgents blocking. Config file: useragents.conf.
Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_blacklist - Comment spam blacklist. Config file: blacklist.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
asecurity_blacklist2 - Compromised/Hacker boxes blacklist. Config file:
blacklist2.conf. Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_apache2-rules - Additional Apache 2.x rules. Effective for apache 2.2 only.
Config file: apache2-rules.conf. Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_rootkits - Known rootkits/worms. Config file: rootkits.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
asecurity_exclude - Rule Exclusions. Config file: exclude.conf. Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_recons - “Google Hacks” signatures. Config file: recons.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
Page 60

60 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Using Gotroot.com Modsecurity™ Rules With H-Sphere
Parallels H-Sphere provides a tool for loading Atomicorp‟s Gotroot Modsecurity rules
included into hsphere-apache-shared-h3.1 package.
At the moment, the following Gotroot rules are supported (the list may differ for Apache
1.x and 2.x, modsecurity 1.9 and 2.0-2.1 versions):
apache2-rules
badips
blacklist2
blacklist
exclude
jitp
proxy
recons
rootkits
rules
useragents
You can download Gotroot rules from https://www.atomicorp.com/.
To be able to use Gotroot rules in Parallels H-Sphere, follow steps below:
Step 1. Download necessary Gotroot rules archives and place
them into the corresponding directories in your web box(es).
Note: Gotroot rules are supported on Apache 2.x only.
1. Enter a temporary directory
2. Download archived Gotroot rules.
http://www6.atomicorp.com/channels/rules/delayed/modsec-
201205051644.tar.gz
Free delayed rules are used in this example. For obtaining rules using a real-time
subscription, please refer to the vendor documentation.
3. Untar it into the temporary directory
# tar zxf modsec-201205051644.tar.gz
4. Copy the configuration *.conf files to the
/hsphere/pkg/config/httpd/gotrootrules directory:
# cp -f ./modsec/*.conf /hsphere/pkg/config/httpd2/gotrootrules2/
Step 2. run apache-load-gotrootrules.sh tool to load Gotroot
rules into H-Sphere from configuration files:
# /hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-load-gotrootrules.sh -h
h|--help option will show usage details:
Page 61

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 61
usage: apache-load-gotrootrules.sh [-f|--force] [<rule> <rule2> <ruleN>] [-h|--help]
f|--force : process rules from gotrootrules configuration files „*.conf‟ by force
even if they were already loaded („*.conf.tmpl‟ exists).
<rule*> : process rules from file ‘<rule*>.conf’ only.
Space separated list allowing to process more then one
gotrootrule configuration file.
h|--help : print this help messagee.
Following gotrootrules are supported:
apache2-rules badips blacklist2 blacklist exclude jitp proxy
recons rootkits rules useragents
Examples:
# apache-load-gotrootrules.sh—force jitp
Process rules from „jitp.conf‟ even if „jitp.conf.tmpl‟ already exists
# apache-load-gotrootrules.sh
That will process only rules from new configuration files (if
‘*.conf’ exista and ‘*.conf.tmpl’ - not).
Step 3. enable Apache mod_security options in Admin CP:
Page 62

62 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
asecurity_rules - Web Application protection. Config file: rules.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
asecurity_jitp - Just in Time Patches for Vulnerable Applications. Config file: jitp.conf.
Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_useragents - Bad UserAgents blocking. Config file: useragents.conf. Default:
0 (disabled).
asecurity_blacklist - Comment spam blacklist. Config file: blacklist.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
asecurity_blacklist2 - Compromised/Hacker boxes blacklist. Config file: blacklist2.conf.
Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_apache2-rules - Additional Apache 2.x rules. Effective for apache 2.2 only.
Config file: apache2-rules.conf. Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_rootkits - Known rootkits/worms. Config file: rootkits.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
asecurity_exclude - Rule Exclusions. Config file: exclude.conf. Default: 0 (disabled).
asecurity_recons - “Google Hacks” signatures. Config file: recons.conf. Default: 0
(disabled).
PHP Modes
For each available Apache version you can choose from libphp (default), cgi, or fastcgi:
libphp - PHP runs as an Apache module. The advantage is that PHP is always in
memory use which results in a higher speed capability and lower server load.
cgi - PHP runs as a CGI script in a separate process which starts with each request
and completes its work upon the script execution. This provides a simpler and more
secure PHP work, but draws excessive memory usage and higher memory load.
fastcgi - PHP also runs as a CGI script, but under a single process which does not
stop when the script is executed. This allows to minimize server load while running
PHP in CGI mode.
To configure advanced PHP mode settings in admin CP, go to E.Manager->Servers-
>P.Servers and click on the Settings icon for a physical server. You will see the following
interface:
Page 63

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 63
This form allows you to choose which PHP 4 and PHP 5 libphp/cgi/fastcgi modes will
be available for end users whose domains are hosted on this physical server, and to
set the default mode for each PHP version.
The fastcgi and cgi modes can be enabled for all PHP versions, but the libphp mode,
only for one of them. Modes checked as Enabled will be available for end users to
choose from in the Advanced PHP configuration interface in Web Options. When users
switch PHP version in the “simplified” PHP configuration interface, they switch between
the default modes of PHP versions (the Default column in the form - choose one default
mode per PHP version). After that, users will be able to choose from the selected
modes for each domain.
If you have enabled fastcgi mode using mod_fastcgi, you can configure its VirtualHost
options in the form below:
Page 64

64 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
fcgi_idle-timeout - the number of seconds of FastCGI application inactivity allowed
before the request is aborted and the event is logged (at the error LogLevel). The
inactivity timer applies only as long as a connection is pending with the FastCGI
application. If a request is queued to an application, but the application doesn‟t
respond (by writing and flushing) within this period, the request will be aborted. If
communication is complete with the application but incomplete with the client (the
response is buffered), the timeout does not apply.
fcgi_killInterval - determines how often the dynamic application instance killing policy
is implemented within the process manager. Smaller numbers result in a more
aggressive policy, larger numbers - in a less aggressive policy.
fcgi_minProcesses - minimum total number of dynamic FastCGI application instances
allowed to run at any time without being killed by the process manager (due to lack
of demand).
fcgi_maxClassProcesses - maximum number of dynamic FastCGI application
instances allowed to run for any FastCGI application. It must be less or equal to
maxProcesses (this condition is not programmatically enforced).
fcgi_maxProcesses - maximum total number of dynamic FastCGI application
instances allowed to run at any time. It must be greater or equal to
maxClassProcesses (this condition is not programmatically enforced).
fcgi_restart - causes the process manager to restart dynamic applications upon
failure (similar to static applications).
fcgi_multiThreshold - an integer between 0 and 100 determining whether any
instance of a FastCGI application should be terminated. If more than one instance
of the application is currently running, this attribute is used to decide whether one of
them should be terminated. If only one instance remains, -singleThreshold is used
instead.
fcgi_singleThreshold - An integer between 0 and 100 determining whether the last
instance of a FastCGI application can be terminated. If the process manager
computed that the load factor for the application is lower than the specified
threshold, the last instance is terminated. In order to make your executables run in
the “idle” mode for a long time, specify a value closer to 1. However, if memory or
CPU time is of primary concern, a value closer to 100 is more appropriate. Setting it
to 0 prevents the last instance of an application from being terminated; this is the
default value, changing it is not recommended (especially if -appConnTimeout is
set).
fcgi_updateInterval - determines how often statistical analysis is performed for
dynamic FastCGI applications.
Page 65

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 65
PHP Plugins
In this form you can disable unwanted PHP plugins (PHP extensions as DSO
modules):
Page 66

66 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
phpext_dbx, phpext_domxml, phpext_filepro, phpext_mcal,
phpext_xslt are implemented only for PHP 4, while phpext_soap and
phpext_mysqli - for PHP 5.
PHP 5.3, 5.4 and 5.5 extensions are not shown in the web interface. The provided
extensions are always enabled, except for the opcache.so module in PHP 5.5, which
should be enabled manually.
To get help on a plugin, click the question mark button near its title.
PHP Accelerators
Parallels H-Sphere 3.3 introduced PHP accelerators. They can be found in settings for
each Web server.
To enable or disable PHP accelerator for a Web server:
1. Go to the E.Manager > P.Servers > [Your Physical Server] menu and click the
icon in the top right corner of the form that appears.
2. In the PHP Accelerators section check or uncheck respective boxes to
enable or disable the following accelerators:
phpacc_apc. Alternative PHP Cache (APC) is a free and open opcode cache for
PHP.
phpacc_eaccelerator. eAccelerator is a free open source PHP accelerator,
optimizer, encoder and dynamic content cache for PHP. It increases
performance of PHP scripts by caching them in compiled state, so that the
overhead of compiling is almost completely eliminated. It also optimises the
script to speed up execution of PHP scripts. eAccelerator typically reduces
server load and increases the speed of your PHP code by 1-10 times.
phpacc_xcache. XCache is a fast, stable PHP opcode cacher that has been
tested and is now running on production servers under high load.
phpacc_ioncube. Loader for ionCube encoded files. ionCube is required for
Parallels Presence Builder.
phpacc_zend. Zend Optimizer is a free runtime application that enables PHP to
run the files encoded by Zend Guard. This can be freely used by anyone looking
to run encoded applications.
3. Click Submit to apply changes.
Page 67
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 67
Server Groups
Consider another example:
Let‟s say you‟ve got:
p.server1 with the following groups on it: Control Panel, Mail, Web, Name and
p.server2 with Mail, Real and MySQL server groups.
In this case logical servers:
cp.net, web.net, name.net can be set up only on ph_server_1 and real.net with mysql.net - on
ph_server_2;
while mail.net can be set up to any of them.
You can also have two logical servers carrying out mail service (e.g.: mail1.net and mail2.net) set up
on different or the same physical server. Several different web, name, etc., logical servers can be
put on one physical server, too. The only requirement is that it has the appropriate server group.
Logical servers are grouped by functionality and purpose. For instance, you can have a
group of name servers, a group of „priority‟ web servers, a group of „basic‟ web servers
etc. Logical server groups allow you to control the distribution of user data across
servers.
Example: You have several customers on a priority hosting plan and you want to
keep their sites on a separate box. To achieve this, you need to create a separate
„priority web‟ server group and add it to this box.
You can add one server group to many physical servers. For instance, if you add
the „priority web‟ server group to p.server1, p.server2, and p.server3, your priority
plan customers will be randomly distributed across these three physical servers.
A physical server may have one or many server groups. For instance, you can add the
„priority web‟ server group to p.server1 and p.server2, whereas all other server groups
can be added to p.server3.
Note: You can‟t add a logical server to a physical server if it doesn‟t have the
respective server group.
To see the server groups available in your system, go to E.Manager-> Servers -> Server
Groups:
Page 68

68 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
How Do I Create a Server Group?
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> Server Groups.
2. At the bottom of the page that appears, enter the name of the server
group and select its type.
3. Click Add.
How Do I Add a Group to a Physical Server?
1. Go to E.Manager-> Servers -> P.Servers.
2. Click the name of the physical server.
3. At the bottom of the page that appears, select a server group and click
Add.
4. Now you can create logical servers in this server group.
How do I delete a server group?
You can delete only custom server groups by clicking the Delete icon next to them.
Page 69
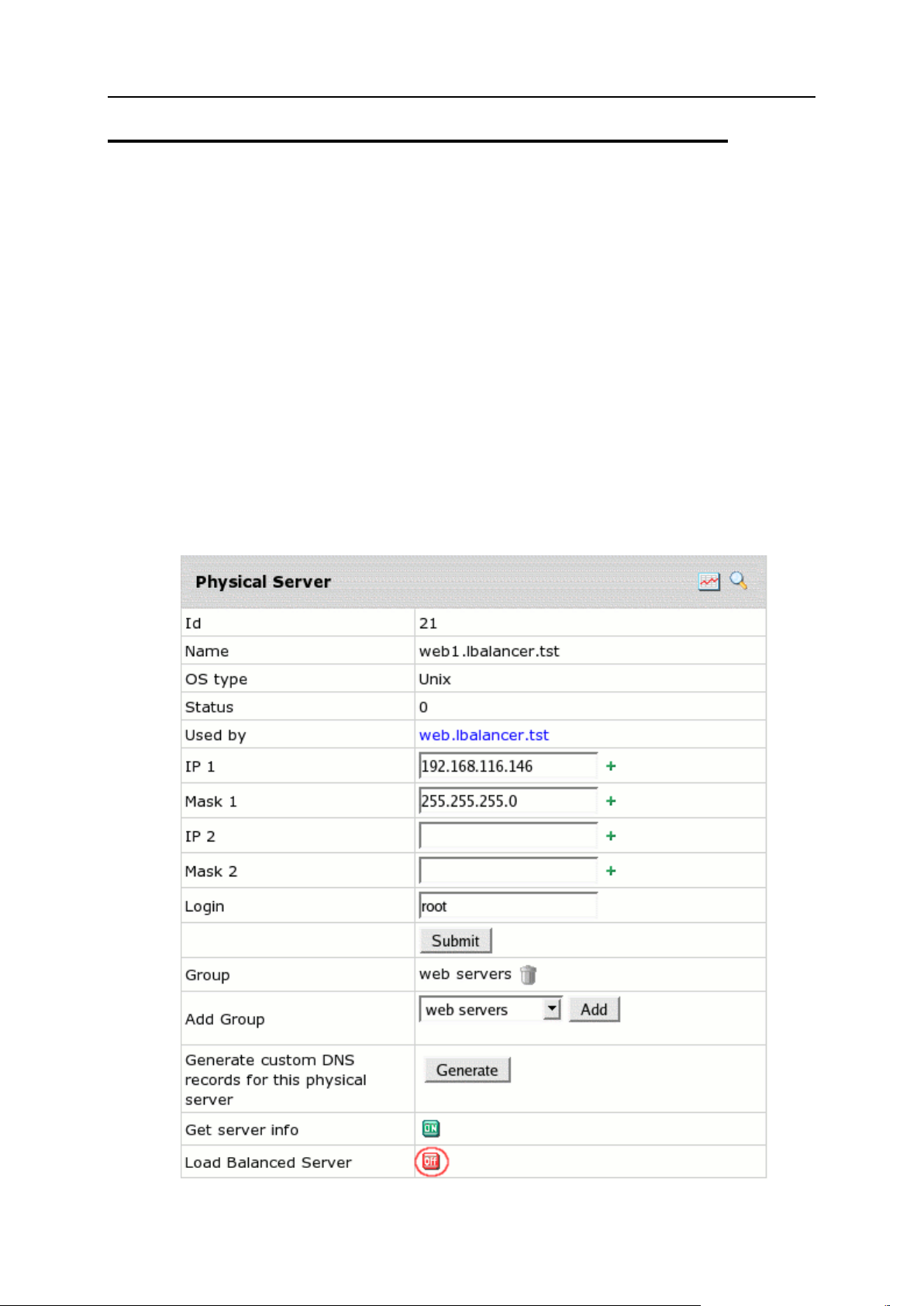
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 69
Load Balanced Server Clusters
Parallels H-Sphere interface allows you to set master-slave relations between servers
in Web and mail clusters. Please refer to the complete procedure of installation and
configuration of load balanced cluster servers in Parallels H-Sphere System
Administrator Guide.
To structure Parallels H-Sphere physical servers in a load balanced
cluster:
1. Add physical servers to Parallels H-Sphere. (on page 33 )
2. Create server groups on these servers (on page 67), depending on their
functionality. Servers that belong to the same cluster must have the
same server group created on them.
3. Create master servers:
1. In the E. Manager -> Servers menu choose P. Servers.
2. On the page which lists physical servers click the needed server name. Turn
Load Balance Server on:
Page 70
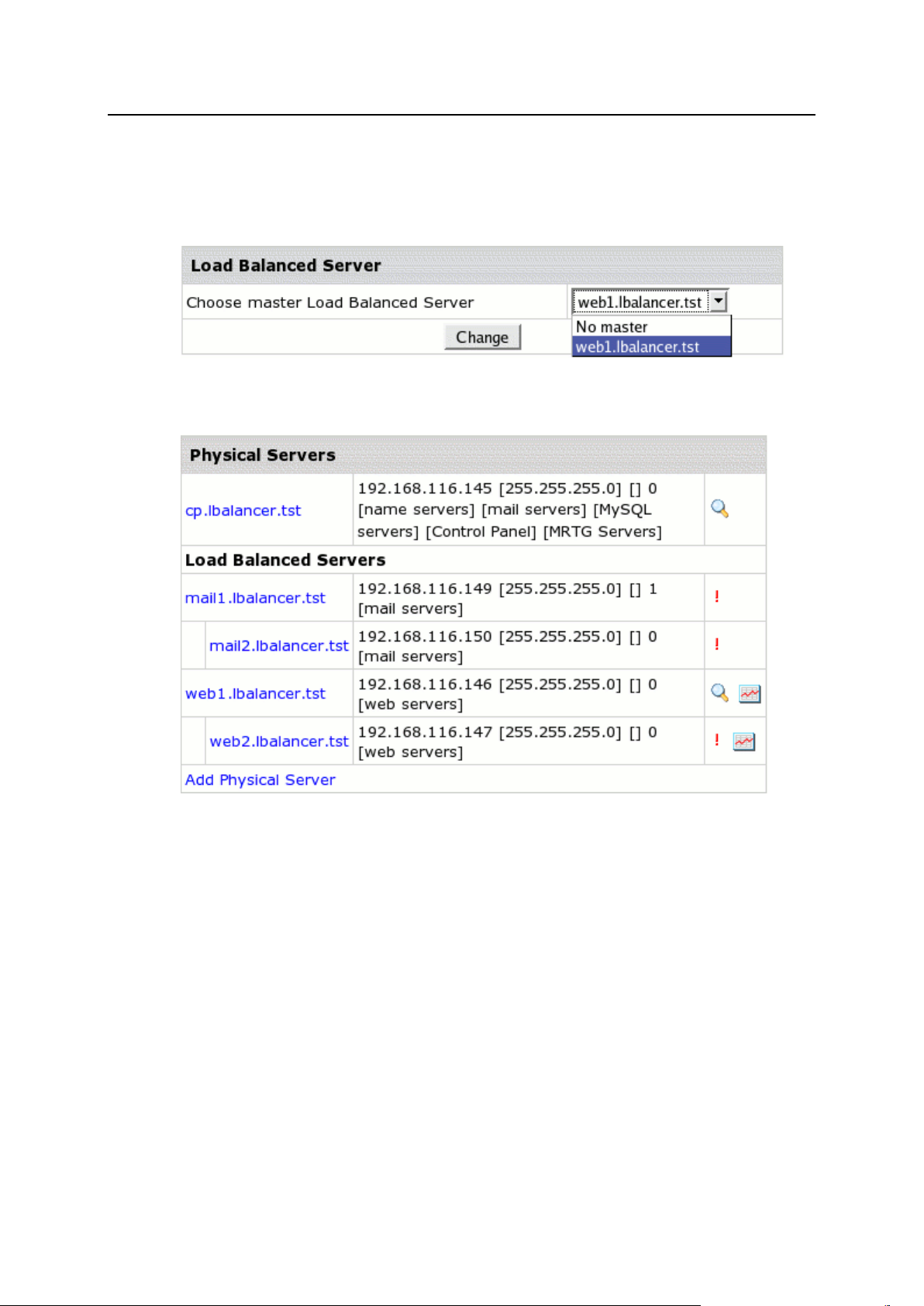
70 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
3. On the Load Balanced Server page chose No master and click change.
4. Add web or mail logical server group to each created physical server.
4. Create slave servers. Enable Load Balanced Server for the rest of the
servers choosing a master server for them:
5. As the result, on the Physical Servers page you should have load
balanced clusters visualized with master and slave servers clearly
distinguished:
Page 71

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 71
Important: Logical servers can‟t be created on slave servers. Any number of slave
servers can be created for master mail and load balanced web servers.
Platform Change
Parallels H-Sphere integrates a hostingPlatformChanger system package that
enables users to change platform from Windows to Unix OS and vice versa.
WARNING:
Currently, hostingPlatformChanger system package is a beta version!
The platform change process with the help of hostingPlatformChanger package
involves:
Hosting plan change
Domains IP change
Deletion of incompatible resources (currently, all resources listed on the Web Options
page)
Manual transfer of a user‟s content
To enable users to change the platform, perform:
Step 1. Install the hostingPlatformChanger system package:
Log into your CP server as To log in as the cpanel user:
1. Log in as root first:
$ su -l
2. Log in as the cpanel user:
1. # su -l cpanel
2. Download
(http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/downloads/index.html#platform_changer
) the latest hostingPlatformChanger package.
3. Install the package. See System Administrator Guide for detailed instructions on
package installation.
Step 2. Define the plans for which platform change is allowed:
1. Go to Plans->Platform Change Groups and click on the Edit icon next to the target
platform.
Page 72
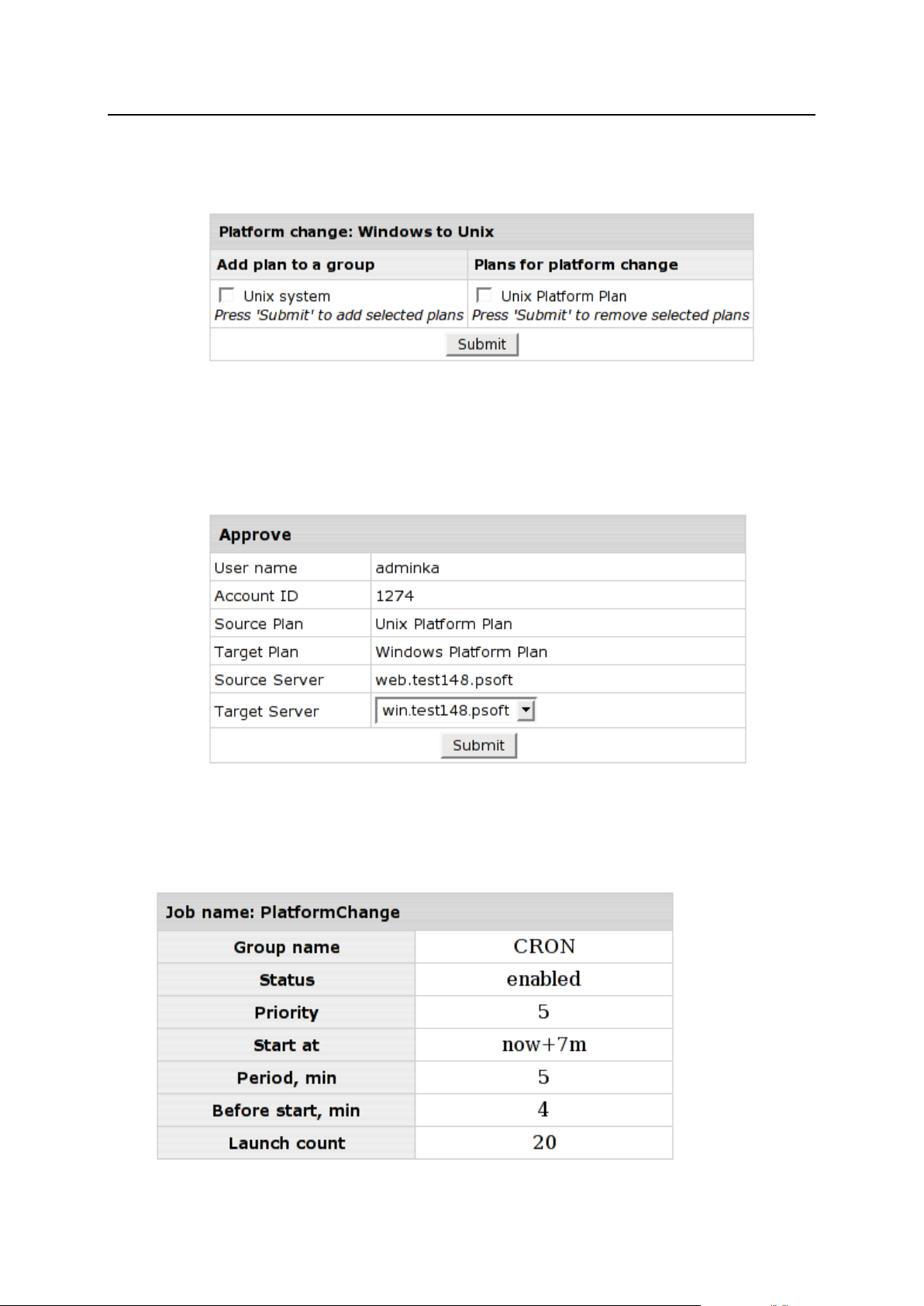
72 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
2. On the page that appears, choose the plans that you are going to allow your
users to switch to. For this, check boxes near the plans in the Add plans to a group
column and Submit the request.
Step 3. After users have requsted platform change from their User CP, you have to
approve the process and choose the target server:
1. Go to E.Manager->Platform Change Processes and find the process to be approved
2. Click on the Approve icon in the Controls column
3. On the page you will be taken to, check with the details of the process, choose
the target box, and approve the process by clicking Submit button
Step 4. Launch the process manually or the process will be handled by a special cron.
To launch manually use the icon in the Controls column of the page you will be taken
to.
You can find the PlatformChange cron details from the Background Job Manager (on
page 126) page:
Page 73

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 73
In general, platform change process takes the following stages:
1. Check if resources to be re-created physically can be created on
selected logical server
2. Physical creation of resources
3. Incompatible resources deletion
4. Plan switch
5. Domains IP and DNS change
6. DNS propagation. In 24hr the content and resources will be removed
from the old server. On this stage, the process can be
suspended/resumed if DNS propagation within 24hr is not acceptable.
To suspend, go to E.Manager->Platform Change Processes and use a
respective icon in the Controls column.
To resume, go to E.Manager->Platform Change Processes and use a respective icon in
the Controls column.
7. Old content on the source server deletion
When the procedure goes fine, the necessary resources are recreated, incompatible
resources removed, DNS and IP changed. If something goes wrong, the process is
rolled back and a trouble ticket created. You can view the TT from the E.Manager-
>Platform Change Processes page.
Updating Physical Boxes From CP
Interface
In Parallels H-Sphere one can perform Parallels H-Sphere software installation and
update on multiple boxes (except for the CP core and Parallels H-Sphere Windows
core services) from the administrative control panel:
Parallels H-Sphere update to the latest version or update of particular services on
selected boxes
Adding Parallels H-Sphere servers and services: physical installation of Parallels H-
Sphere software into the new boxes previously added in admin CP as Parallels H-
Sphere physical (on page 33) and logical (on page 36) servers
Installation and update from admin CP is performed under certain conditions:
Before you run Update Wizard to update the whole cluster to a required Parallels H-
Sphere version, you need first to update Parallels H-Sphere CP core (and Parallels
H-Sphere Winbox core for Windows servers) by downloading and running Parallels
H-Sphere update script with the cpupdate option (HSCore package for Windows
servers) for this version.
Update of particular packages and services on each box is according to physical
server profiles (on page 75) - sets of update rules assigned to a group of physical
servers.
Procedure
Page 74

74 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
To update or install Parallels H-Sphere on selected physical servers:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Update -> Update Boxes:
2. Check the servers you need to update/install.
3. If necessary, you can get info about the box by checking boxes and
clicking the Fetch Boxes Info button.
4. Click Start Update.
Update process indicator legend:
Yellow: ready for update
Blue: update is running
Green: update successfully finished
Red: update finished with error. If update fails, you will see an error message with
details.
Page 75

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 75
Physical Server Installation/Update
Profiles
Parallels H-Sphere allows creating server update profiles to update/install packages on
physical boxes according to the rules set by admin. For this, Parallels H-Sphere uses a
so- called server update profile. By default, Parallels H-Sphere includes the „DEFAULT‟
profile which can‟t be removed or changed. If not set otherwise, the box is updated
according to this DEFAULT profile.
However, you can create your own update profiles and assign them to specific boxes.
In this case, the system will update the server according to the profile it‟s assigned to.
To create a profile:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Update -> Physical server profiles
2. Choose the box (Unix/Windows) and click the Add button:
Page 76

76 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
3. Name and configure your profile in the form that appears:
Adding Unix profile:
Page 77

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 77
Adding Windows profile:
Page 78

78 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Where:
- Update only pointed logical server groups. You can choose between three hosting
modes: Windows hosting only, MsSQL hosting only, or both Windows and MsSQL
hosting modes
- Source URL for packages download redefinition is the link to an alternative server with
MSI packages. If not set, default MSI location is
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/WINDOWS/
- Location of user home directory. If it is not set there, Parallels H-Sphere Winbox
installer will automatically create it on NTFS partition with the largest free space.
- MAC address of network interface to host dedicated IP‟s, etc. If not set there, Parallels
H-Sphere Winbox installer will automatically choose an address based on the free
IPs of a physical server.
- Name of MSSQL server instance. Give a name to a MsSQL server instance if you
want it to differ from a default one generated from a NetBIOS name of a specific
server
4. Click Save to apply. Profile will appear in the list of existing profiles.
5. Click the Assign Profiles to Physical Servers link
You can assign only one profile to a server. But one and the same profile can be
assigned by several servers.
6. Click Apply.
If you want to reassign a profile:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> P. Servers
2. Click the physical server name you want to reassign a profile to
3. Click the Edit icon in the Physical Server Profile field
4. Reassign the profile
From now on, every time you update this physical box from CP interface, it will update
according to the profile.
Page 79

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 79
Resource Prerequisites
Resource Prerequisites implies the following:
1. Some resources can be enabled/disabled for selected logical server
groups despite their availability on physical boxes.
Resources like:
SSL, Throttle, Frontpage and RubyOnRail for Unix web boxes
PHP, Urchin, Miva, Miva Empresa and ColdFusion for Windows web boxes
VPS templates and VPS context RSS limit for VPS boxes
can be enabled or disabled on the level of logical server groups, no matter if they
are installed on physical servers or not.
1. Go E. Manager -> Servers -> Server Groups and click Edit for web server, win server
or vps server group:
2. Enable/disable services for plans under this logical server group:
for web servers group:
for win servers group:
Page 80
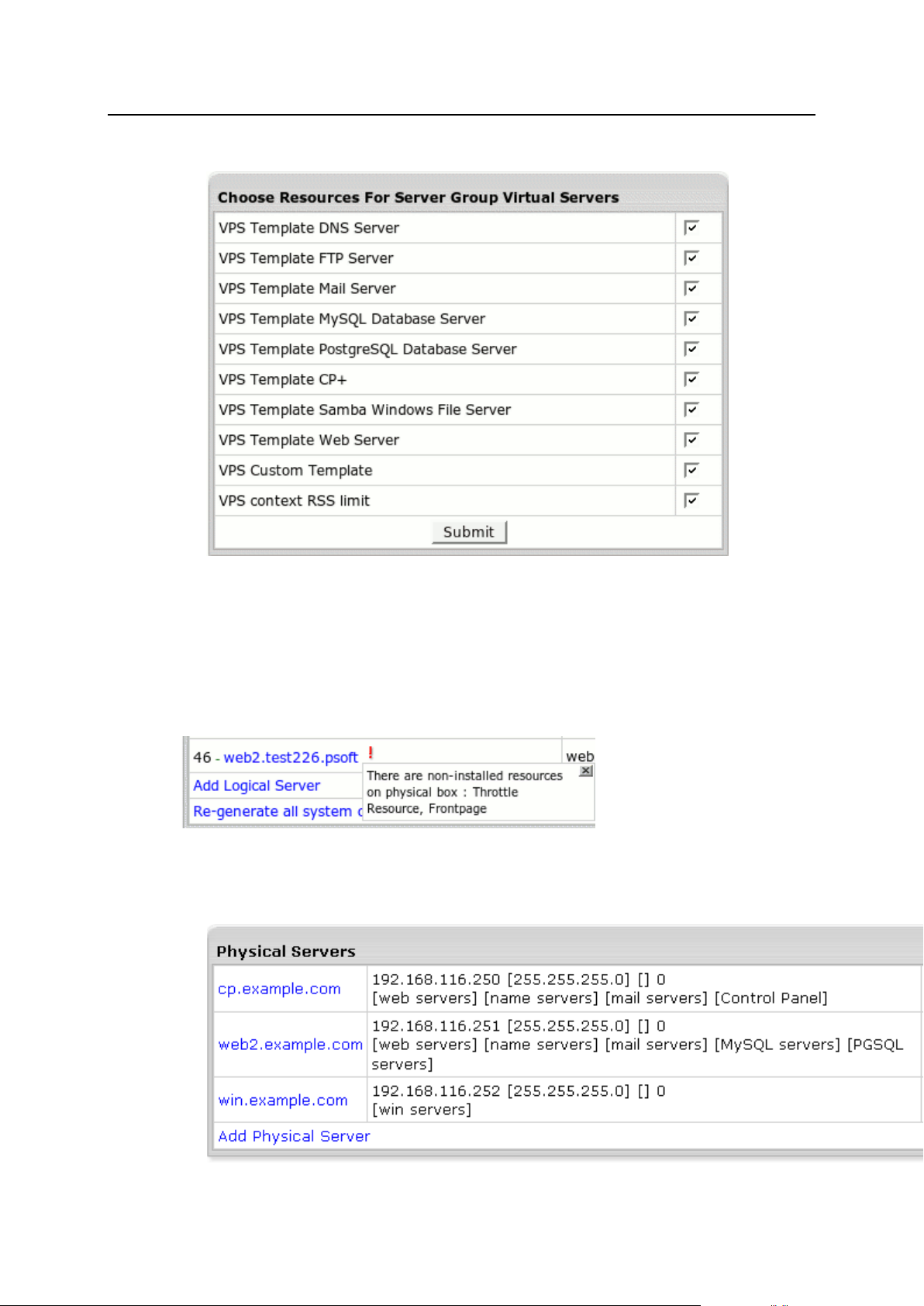
80 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
for virtual servers group:
3. Click Submit. Users who sign up to plans hosted on such server groups will have
these resources enabled or disabled.
2. Periodical availability checks for resources with prerequisites.
A special CP cron periodically polls physical servers to check whether resources
with prerequisites are installed on physical boxes. If some of them are not available,
the ! mark appears near the corresponding logical server name. Go E. Manager ->
Servers -> L.Servers and hover mouse over ! to see which resources are not installed
physically:
Also, it is possible to see which resources with prerequisites are installed on
physical boxes via the Physical Servers menu in administrator interface:
1. Go E. Manager -> Servers -> P.Servers
2. Click the magnifier icon near a physical server:
Page 81
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 81
3. On the page that appears click Installed Services.
Note: For Unix boxes, you will get a page with installed resources with
prerequisites only. For Windows boxes, the page will show all installed
resources.
3. Enabling/disabling of resources automatically affects end users, without
a need of editing respective plans.
You can enable resources with prerequisites when creating or editing a plan, no
matter if these resources are installed or not installed on physical boxes. If a service
is absent on physical box, users will see a red exclamation mark in their control
panels near the service. If they hover mouse over the mark, a note like this
appears:
Then, after you installed missing services later, you don‟t need to go back to Plan
Wizard to enable them in the plan. If they were already enabled in the server group
configuration, users will automatically obtain them in their control panels.
In plan edit wizards, resources which were disabled in server group configuration
have a note like this:
You can choose a different logical server group with a different set of prerequisites
right in plan edit wizards. To do this:
1. Enter a plan edit wizard, scroll to the Web services section and click the control in
blue oval in the Logical Server Group field:
For Virtual Private Server plans, find the Logical Server Group field right below the
plan title:
2. Choose another group and click Apply. Parallels H-Sphere will update this
wizard page with the status of resources with prerequisites for the chosen
group.
Page 82

82 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
System Service Management
System Service Management is a utility that allows managing Parallels H-Sphere
system services from the Admin CP interface.
To manipulate system services via Parallels H-Sphere interface:
1. Go to E.Manager -> Servers -> P.Servers
2. Click the lens icon next to the chosen physical server to get to the
System Information page.
3. Scroll down and click the System Service Management link.
Page 83

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 83
Page 84

84 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
You see the list of all processes involved with this server split by groups; dns, mail,
web, mysql, cp.
Type of the service: supervise - service is managed by supervising process;
standalone - service is independent
Running time: shows how log the service has been running, in seconds
4. Select necessary services and the action to start, restart, stop
processes.
5. Click the Apply button.
Note: You can‟t manipulate httpdcp service for consistency reasons.
Page 85

This chapter discusses the configuration steps required for your DNS.
In this chapter:
DNS Manager ................................................................................................... 86
Adding DNS Zones............................................................................................ 86
Instant Alias Templates ..................................................................................... 88
DNS Records .................................................................................................... 91
Hosting Your Corporate Site .............................................................................. 95
Adding Domains for Third Level Hosting ........................................................... 98
Providing Mail Under Service Domain for Third-Level Hosting .......................... 98
C H A P T E R 7
DNS and Hosting
Page 86
86 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
DNS Manager
DNS Manager in the Admin panel is used to create and manage:
service DNS zones (on page 86) - to host your corporate site and provide third level
domain hosting.
instant alias templates (on page 88) - to provide immediate access to users‟ newly
registered domains until their domain‟s DNS hasn‟t been propagated.
DNS records (on page 91) - to manage servers external to Parallels H-Sphere with
Parallels H-Sphere DNS.
It‟s not intended to work with your user domains‟ dns.
Adding DNS Zones
You must have at least one DNS zone in your system. Before you start adding a DNS
zone, make sure to have added the DNS servers with Service IPs.
To add a DNS zone:
1. Select DNS Manager in the E.Manager menu:
2. Click the Add DNS Zone link:
Page 87

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 87
3. Enter zone name and zone administrator e-mail and choose whether to
allow third level domain hosting in this zone:
Name: the name of the DNS zone you are going to create. If this domain name is
not yet registered, don‟t forget to register it with a domain registration company.
Admin e-mail: the e-mail address of this DNS zone administrator.
Allow third level domain hosting: allow the creation of lower level domains in this
DNS zone.
Master/slave server: available only for service DNS zones - allows you to choose
and appoint a master and a slave server. The information is backed up every
hour.
4. After you submit the form, the new zone appears in the DNS Manager
table:
5. Click the EDIT icon to go to the DNS zone management page. Here you
can add instant alias templates (on page 88 ), custom DNS records (on
page 91) and Reseller CP alias (on page 357) to your DNS zone:
Page 88

88 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Instant Alias Templates
In this section:
Adding Instant Alias Templates ......................................................................... 88
Editing Instant Alias Templates ......................................................................... 90
Instant Alias Templates are used to generate Instant Aliases, temporary addresses
providing immediate access to users‟ domains from the Internet. They are usually
helpful when the DNS servers worldwide are being refreshed and the site is temporarily
unavailable at the regular domain name.
Creating an instant alias template will automatically add one or more A-DNS records to
your service zone. These records resolve all your logical servers.
Adding Instant Alias Templates
To add instant alias, do the following:
1. Select DNS Manager in the E.Manager menu.
Page 89
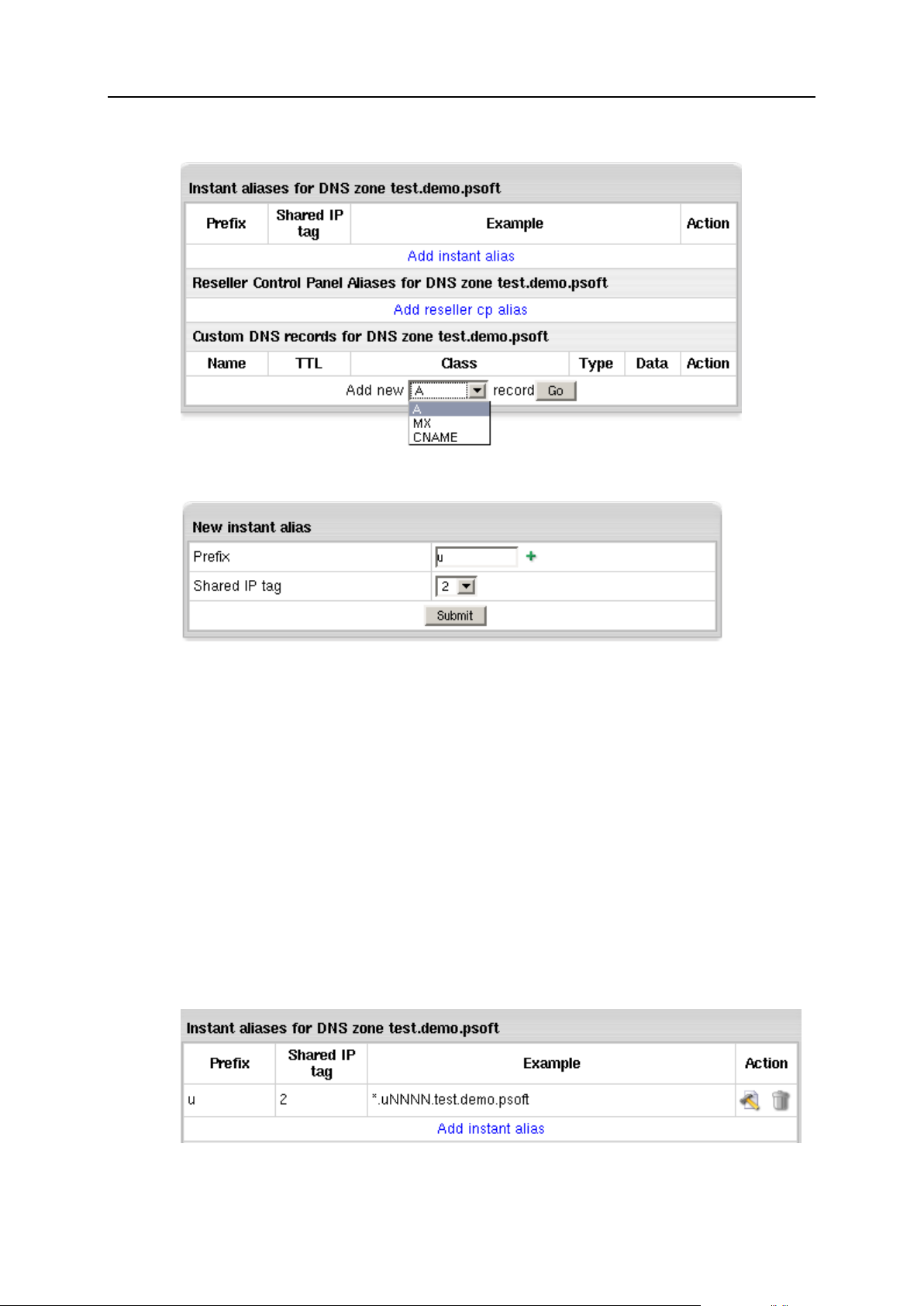
Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 89
2. Click the EDIT icon to go to the DNS zone management page. The
following page appears:
3. To add an instant alias template, click the Add instant alias link. This will
open the following form to fill out:
Prefix: instant alias prefix that will appear on the left to the domain part in user‟s
instant domain alias. Different prefixes should be set if you use different shared
IP tags. Other than that, it is recommended to use one and the same prefix (e.g.
u for all instant alias templates).
Shared IP tag: a digital “mark” that helps separate sites within one plan on one
logical server. All sites located on the same logical host under the same plan
are usually assigned to the same shared IP. This feature allows to give a
different shared IP to a group of sites of, say, explicit nature. This may become
necessary as many corporate firewalls filter sites based on their IP, not the
domain name.
Normally, you are expected to have devoted one IP address for each shared IP
tag. To use a shared IP tag, you need to have it defined for every logical host.
Go to the LServers (on page 36) section for instructions.
Numbers 10 to 99 are acceptable. The default value of 2 is assigned when the
field is submitted being empty.
4. Click Submit. You will be taken back to the list of instant aliases with the
new instant alias template added to the list.
Page 90

90 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Editing Instant Alias Templates
Once an Instant Alias is created, the system adds all necessary A DNS records to this
DNS zone.
To view these DNS records, cilck the Edit button near the necessary Instant Aliases:
The upper part of the table lists the existing DNS A records in the selected DNS zone.
To delete DNS records, click the Trash icon.
The lower part of the table appears only when the DNS zone does not contain A
records for some logical servers. It lists these logical servers with their IP‟s.
To add a logical server to the DNS zone, click the Add button. You can add all these
servers to the DNS zone by clicking the Add records to all listed logical servers link at the
bottom of the table.
If the IP address with the specified shared IP tag doesn‟t exist on one or more logical
servers, you will get the corresponding message on the instant alias properties page. If
you see this message, add a shared IP with this shared IP tag to the listed logical
servers. Go to the LServers (on page 36) section for instructions.
To delete Instant Alias Template, click the Trash icon next to the corresponding alias.
Page 91

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 91
DNS Records
Custom DNS records are required to manage non-HSphere servers with Parallels HSphere DNS zone or to configure new logical servers that are added manually.
Depending on the service, you can add:
A records
MX records
CNAME records
To add new custom DNS records:
1. In your admin control panel go to the E.Manager menu -> DNS Manager.
The following page shows:
2. Click the Edit icon near the chosen DNS zone. A page similar to this will
appear:
Page 92

92 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
3. At the bottom of the page that shows, select a DNS record from the
In this section:
Adding custom A records ................................................................................... 92
Adding custom MX records ................................................................................ 93
Adding custom CNAME records ........................................................................ 93
Re-generating System Custom DNS Records ................................................... 95
drop-down list and click the Go button.
4. On the form that shows enter all necessary data and click Submit to
save.
You can add one of the following types of DNS records:
A records to map domain names and web server IP‟s.
MX records to map domain names and their mail server IP‟s.
5. CNAME records to map aliases with domain names.
Adding custom A records
The Address record (A record) gives you the IP address of a domain. That way, users
that try to go to www.example.com will get to the right IP address.
To add a new DNS A record, you need to provide a set of parameters:
Name: the string appended to the domain name to create a FQDN mapped to the
IP. For example, if your domain name is besthosting.com, entering cp will make
the fully qualified domain name cp.besthosting.com.
TTL (a Time To Live): seconds to elapse before the record is refreshed in the
provider‟s DNS cache.
Data: the IP address that fully qualified domain name will be mapped to. You can
get this IP address with any ping utility.
Page 93

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 93
Adding custom MX records
A host name can have one or more Mail Exchange (MX) records. These records point
to hosts that accept mail messages on behalf of the host. Adding MX records is similar
to adding A records:
Name: your local domain name. If you leave the Name field blank, all mail will be
redirected for the base zone.
Data: the priority of the record and mail domain name (not the IP) mail will be
forwarded to.
Note: The priority of the custom MX record defines whether your external
servers will act as secondary or primary. For instance, if you set the priority of
the custom MX record higher than 10 (e.g. 11), your external mail server will be
used as secondary. If you set the priority of the custom MX record lower than 10
(e.g. 9), your external mail server will be used as primary. In the latter case, your
mail will be sent to your external mail server until it goes down or becomes
otherwise inaccessible. Then the default mail server will take over.
WARNING: Please pay attention to $ORIGIN when you add an MX record.
Adding custom CNAME records
The Canonical Name (CNAME) record allows a machine or host to be referenced by
more than one name. A CNAME can be used to define an alias host name. You can
also use aliases when a host changes its name.
If you have selected CNAME record, the following page appears:
Page 94

94 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
In the case of CNAME records, the values have the same format as in the A record
with the exception of the Data field. In the Data field you have to enter the name of the
server to which you are creating the alias record.
WARNING: Please pay attention to $ORIGIN when you add a CNAME record.
The DNS records you create appear on the zone management page:
You can’t edit DNS records. To remove unnecessary records, click the Trash
icon
Page 95

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 95
Re-generating System Custom DNS Records
When you add a logical server (on page 36), it is necessary to append system DNS
records for it. You can automatically re-generate them.
Prior to re-generating system custom DNS records, make sure that:
the basis of the logical server domain name coincides with the registered system
DNS zones
you have added Shared and Service IPs
To re-generate system custom DNS records for all logical servers:
1. Go to E.Manager->Enterprise.
2. Click on the Re-generate all system custom DNS records link.
To re-generate system custom DNS records for all logical servers
assigned to a particular physical server:
1. Go to P.Servers in the E.Manager menu.
2. You will be taken to the list of all physical servers in the system. Select
the server you would like to generate custom DNS records for.
3. On the page that appears press the Generate button in the Generate custom
DNS records for this physical server field.
To re-generate system custom DNS records for a particular logical server:
1. Go to L.Servers in the E.Manager menu.
2. You will be taken to the list of all logical servers in the system. Select
the server you would like to generate custom DNS records for.
On the page that appears press the Generate button in the Generate custom dns records for
this logical server field.
Hosting Your Corporate Site
This document explains how to host your corporate (promotional) web-site at the
service domain (the domain you are offering for third level hosing). For example, if you
are offering third level domains at example.com, such as thirdlevel.example.com or
userdomain.example.com, you need to have your corporate site available at
www.example.com.
To set up your corporate site:
Step 1. Make sure you have a service DNS zone
1. Select DNS Manager in the E.Manager menu.
2. If the DNS zone is not in the list, click Add DNS Zone.
3. On the page that appears, enter the service domain name and other
values and click Submit.
Page 96
96 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Step 2. Create a service plan
You may already have a service plan in your system. It can also be called „System
plan‟. If you don‟t, do the following:
1. Select Create in the Plans menu:
2. Click the Select icon for Unix plan wizard:
Page 97

Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь отображаться. 97
3. On the fist step of the Unix Plan Creation Wizard, set the plan name to
System or Service.
4. Check the Include boxes next to the resources you would like to use with
your site.
Read more about plan resources in Creating And Editing Plans (Plan
Wizards) (on page 234).
5. Make sure to check Service domain.
6. Scroll down to the the Settings section and set Billing Type to Without billing.
7. Click the Next button to go to Step 2.
8. Complete the wizard.
Step 3. Disallow signups from outside your admin
account.
After you have created the system plan, you need to make sure that it is not used by
your customers:
1. Select Manage in the Plans menu.
2. Click Access for the system plan.
3. Make sure only Admin is checked.
4. Select Manage in the Plans menu.
5. Enable the System plan by clicking the ON/OFF button.
Step 4. Create a service account
Now you can create an account for your service domain:
1. Select the Signup menu.
2. Click Select next to the recently created System plan.
3. Select service plan signup wizard.
4. Create service account using the wizard. When prompted the type of
the domain, select Service domain.
Page 98

98 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Adding Domains for Third Level Hosting
Third level domains are created based on second level domains and have same
features as second level domains. Customers can use your service domain to create
third level domains of their own. For instance, if your second level domain is
example.com, your customers can create domains like
illustrative.example.com.
Third level domains are registered on your DNS server and need no domain
registration company to be registered.
To add a domain for third level hosting, you need to create a DNS zone (on page 86)
and allow third level hosting in the zone settings.
Third level domain registration will be available for your users only if you allow it in the
plans. See Plan Creation Wizard (on page 234) for details.
Providing Mail Under Service Domain for
Third-Level Hosting
In Parallels H-Sphere it is possible to allow third-level domain hosters to create e-mail
resources under their service domains. I.e., users that host third-level domains
user.domain.com under service DNS zone domain.com, will be able to create
mailboxes like anything@domain.com from their user CP.
To allow third-level hosters to create mailboxes under a service domain:
1. Choose Manage in the Plans menu and check the Third level domain (Mail
Under Host Domain) option for a plan:
2. Choose DNS Manager in the Settings menu and click the Off icon to enable
the Allow creating emails under Service Zone option for a particular service
domain:
Then, if you search by domain name in the Search menu, affected third-level domains
will have the domain type Third level domain (Mail Under Host Domain).
Page 99

In this chapter:
Regional Settings .............................................................................................. 99
Images and Icons .............................................................................................. 101
Interface Texts .................................................................................................. 105
Skins and Colors ............................................................................................... 106
Disabling CP Skins ............................................................................................ 108
Setting Interface Language ............................................................................... 109
C H A P T E R 8
Control Panel Web Interface
Regional Settings
This document explains how to change the default currency settings and date
representation. The defaults are set when you change the default language (on page
109). Custom settings are kept until you switch to another default language.
To set custom regional settings:
1. Select Regional Options in Look and Feel under the Settings menu.
2. On the page that appears, enter preferred locale settings:
Page 100
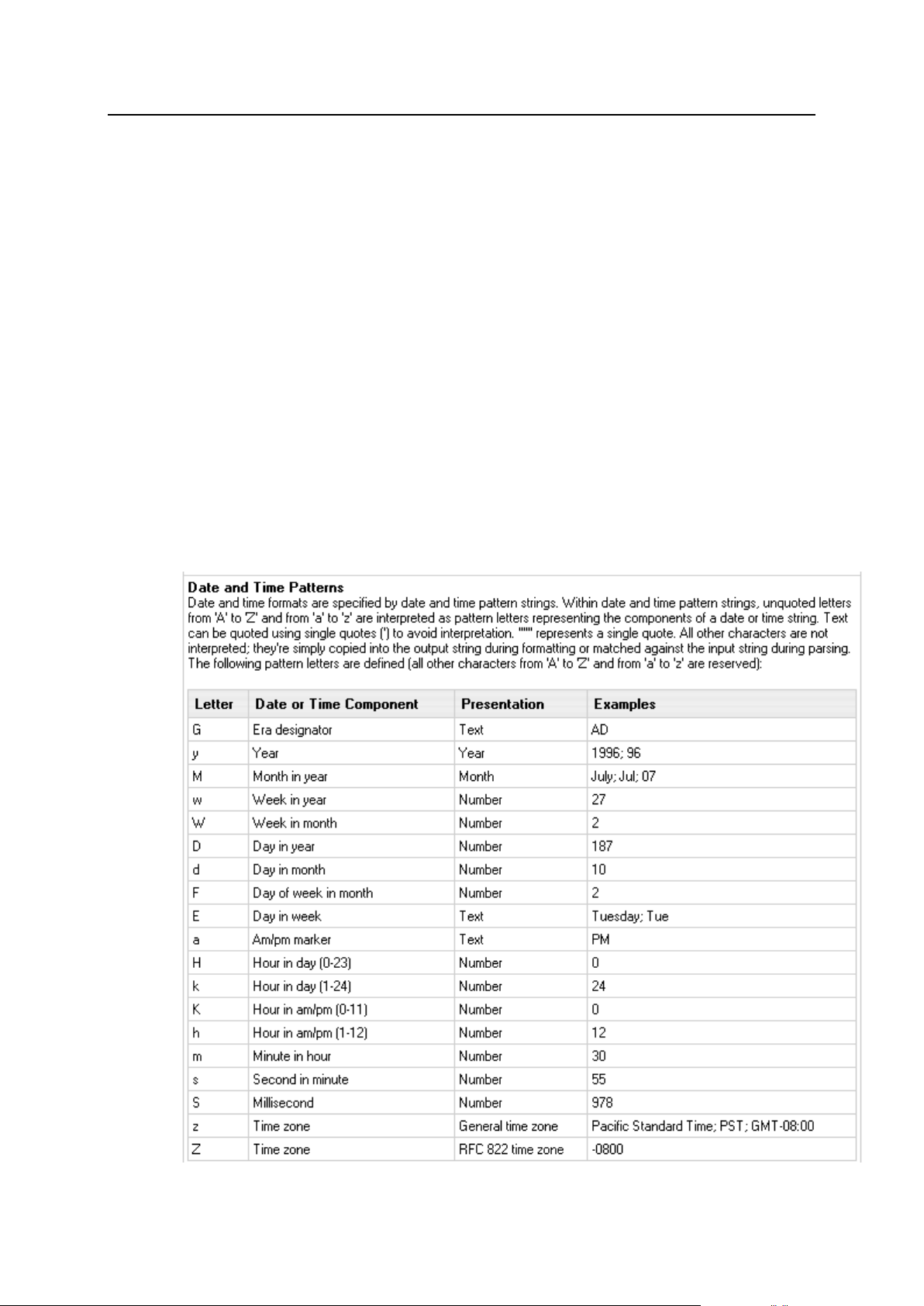
100 Ошибка! Используйте вкладку "Главная" для применения Heading 1 к тексту, который должен здесь
отображаться.
Currency symbol used in your country that you want to show in prices, invoices
etc.
Corresponding International currency symbol which is an international string
denoting the local currency.
Decimal Monetary Separator, a character used to format decimal numbers.
Grouping Separator, a grouping character used to separate thousands, e.g:
100,000,000.
Note: It‟s commonly used for thousands, but in some countries it separates ten-
thousands.
Currency pattern that shows how your monetary amount will look like. Refer to
Comments regarding currency pattern for details. For example, the European
currency pattern will look as follows: # ¤,##0.00;-# ¤,##0.00 (in some countries
negative subpatterns are put into brackets: # ¤,##0.00;(# ¤,##0.00)) Another
example for pattern: #,##0.##: for 3456.00 -> 3,456 although #,0#0.00: for
3,456.00 -> 3,456.00.
Appearance Samples displays monetary amounts the way they will show in the
system after you change the pattern.
Short, medium, long and full date formats represent dates in your control panel.
This feature is not yet implemented, though reserved for future versions.
Regional options page has also information about Day and Time Patterns:
 Loading...
Loading...