Page 1

Parallels® H-Sphere
Parallels H-Sphere 3.4 Control Panel
Installation Guide
Revision 1.0
Page 2

Legal and Copyright Notice
Parallels Holdings, Ltd.
c/o Parallels International GMbH.
Parallels International GmbH
Vordergasse 49
CH8200 Schaffhausen
Switzerland
Tel: + 49 (6151) 42996 - 0
Fax: + 49 (6151) 42996 - 255
www.parallels.com
© 1999-2010 Parallels Holdings, Ltd. and its affiliates. All rights reserved.product is
protected by United States and international copyright laws. The product’s underlying
technology, patents, and trademarks are listed at http://www.parallels.com/trademarks.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows NT, Windows Vista, and MS-DOS are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Mac is a registered trademark of Apple, Inc.
All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Preface 5
Typographical Conventions ........................................................................................................... 5
Feedback ....................................................................................................................................... 6
Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation 7
Supported Operating Systems ...................................................................................................... 7
Single-Server and Multi-Server Installation ................................................................................... 9
Required Components and Configuration ................................................................................... 13
Open SSH ......................................................................................................................... 13
Kernel ................................................................................................................................ 14
Locale ................................................................................................................................ 14
Disk Quota ......................................................................................................................... 14
Quotacheck ....................................................................................................................... 15
Ports .................................................................................................................................. 15
DNS Server Notes ............................................................................................................. 20
Perl .................................................................................................................................... 20
Make .................................................................................................................................. 20
Command-Line URL Download Utility (wget or fetch)....................................................... 21
Compat3x Package ........................................................................................................... 21
SELinux Must Be Off ......................................................................................................... 21
Libmap Content ................................................................................................................. 21
ifconfig ............................................................................................................................... 22
Installing Parallels H-Sphere 23
Step 1. Running the Parallels H-Sphere Installation Script ......................................................... 24
Step 2. Installing the Parallels H-Sphere via Control Panel ........................................................ 24
Step 3. Completing Parallels H-Sphere Installation Wizard ........................................................ 29
Installing Parallels SiteStudio with Parallels H-Sphere ............................................................... 30
Performing Post-Installation Tasks 31
Appendix A. Installing with Prepared Parallels H-Sphere Configuration 33
Appendix B. Installation Script Options 35
Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 37
Control Panel Apache .................................................................................................................. 39
Extra Control Panel Apache Configuration Files ......................................................................... 39
Apache ......................................................................................................................................... 40
Extra Apache Configuration Files ................................................................................................ 41
PHP 4 .......................................................................................................................................... 43
PHP 5 .......................................................................................................................................... 44
FTP .............................................................................................................................................. 45
Page 4

Preface 4
MySQL ......................................................................................................................................... 46
PostgreSQL ................................................................................................................................. 47
DNS ............................................................................................................................................. 47
Other Files Included into Parallels H-Sphere Packages ............................................................. 48
Appendix D. Download Locations 50
Mirror Server for Updating Parallels H-Sphere ............................................................................ 52
Appendix E. Miscellaneous 53
Restarting Parallels H-Sphere ..................................................................................................... 53
Network Address Translation (NAT) ............................................................................................ 54
Page 5
C HAPTER 1
Preface
In this chapter:
Typographical Conventions ................................................................................. 5
Feedback ............................................................................................................ 6
Typographical Conventions
Before you start using this guide, it is important to understand the documentation
conventions used in it.
The following kinds of formatting in the text identify special information.
Formatting convention Type of Information Example
Special Bold
Italics
Monospace
Items you must select,
such as menu options,
command buttons, or
items in a list.
Titles of chapters,
sections, and
subsections.
Used to emphasize the
importance of a point, to
introduce a term or to
designate a command
line placeholder, which is
to be replaced with a real
name or value.
The names of
commands, files,
directories, and domain
names.
Go to the System tab.
Read the Basic
Administration chapter.
The system supports the
so called wildcard
character search.
The license file is located
in the
http://docs/common/
licenses directory.
Page 6

6 Preface
#
–
a
#
Preformatted
Preformatted
Bold
CAPITALS Names of keys on the
KEY+KEY Key combinations for
On-screen computer
output in your commandline sessions; source
code in XML, C++, or
other programming
languages.
What you type,
contrasted with on-screen
computer output.
keyboard.
which the user must
press and hold down one
key and then press
another.
ls
total 14470
cd /root/rpms/php
SHIFT, CTRL, ALT
CTRL+P, ALT+F4
l /files
Feedback
If you have found a mistake in this guide, or if you have suggestions or ideas on how to
improve this guide, please send your feedback using the online form at
http://www.parallels.com/en/support/usersdoc/
guide's title, chapter and section titles, and the fragment of text in which you have found
an error.
. Please include in your report the
Page 7
C HAPTER 2
Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation
This chapter provides comprehensive information on how to prepare Linux and Unix
servers for the installation of Parallels H-Sphere components.
Note: configuration files for Apache, FTP, PHP, DNS, MySQL, and PostgreSQL should
be customized indirectly via respective template files. Otherwise, all custom changes in
major default configuration files are removed with each H-Sphere update! If you need
those files customized, please carefully follow the configuration file templates
customization instruction in Appendix C (on page 37).
In this chapter:
Supported Operating Systems ............................................................................ 7
Single-Server and Multi-Server Installation ......................................................... 9
Required Components and Configuration ........................................................... 13
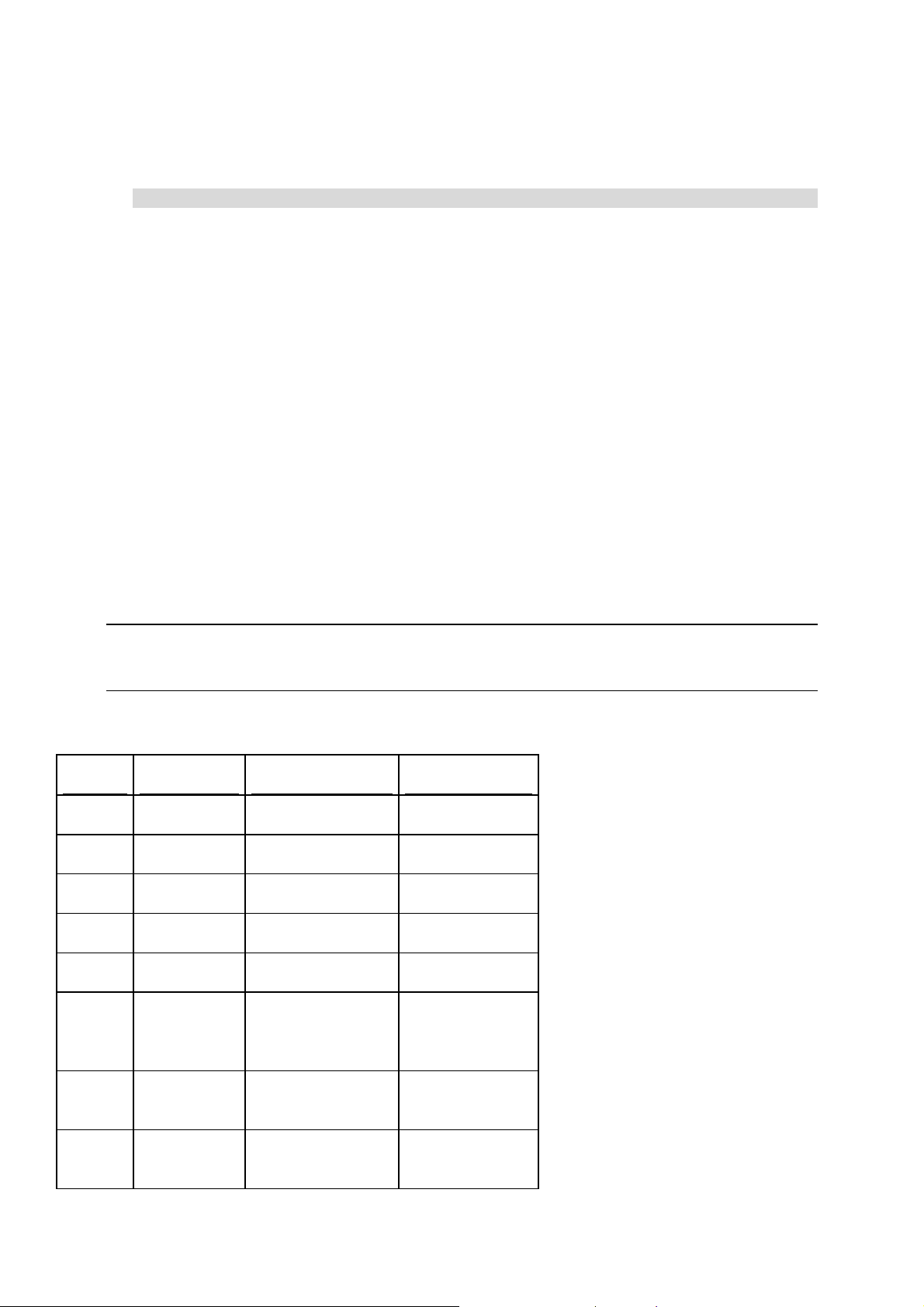
Supported Operating Systems
Before requesting Parallels H-Sphere installation, make sure to install one of the
following operating systems:
Operating System Supported OS Version
RedHat Enterprise Linux
CentOS
3.x
4.x; 4.x (x86_64)
5.x; 5.x (x86_64)
3.x
4.x; 4.x (x86_64)
5.x; 5.x (x86_64)
Page 8

8 Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation
CloudLinux
White Box Enterprise
Linux
FreeBSD
5.5
3.x
4.x; 4.x (x86_64)
6.1
6.2
6.3
6.4
7.0; 7.0 (amd64)
7.1; 7.1 (amd64)
7.2; 7.2 (amd64)
7.3; 7.3 (amd64)
Important:
1. By Supported Operating System we assume a 32-bit system if not specified
otherwise.
2. We claim Parallels H-Sphere support on WhiteBox OS, assuming it is a RedHat
Enterprise Linux clone. However, we do not test Parallels H-Sphere on WhiteBox
servers.
3. FreeBSD: Control Panel installed on a server with 64-bit operating system requires
glibc 32-bit compatibility library.
4. CloudLinux 5.5 is supported as a RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x clone. The
customizations allowed by it are not propagated to UI, and should be performed
manually according to instructions published on the CloudLinux site, if needed.
Page 9

Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation 9
Single-Server and Multi-Server Installation
General Considerations
Parallels H-Sphere can be installed on one or more servers. The required number of
servers and their hardware configuration will largely depend on the number of accounts
you are planning to host, Web and mail quotas, traffic load and other related factors.
Here are some general considerations common to Parallels H-Sphere server
environment:
We recommend installing Control Panel to a separate server. It is also acceptable
to install one DNS server to the Control Panel server box, for example, if you are
planning 2-server installation.
You must not install PostgreSQL hosting service on the same box with Control
Panel, as the latter requires a separate PostgreSQL server for its system database.
You can have several DNS servers on one box. However, for multiserver Parallels
H-Sphere installation, you should install each DNS server on a separate box. The
best solution is to have two DNS servers on separate boxes.
We advise installing mail server on the same box with MySQL server, as mail
server requires its own MySQL database.
It is reasonable to allocate separate physical servers for the most resource-
consuming services. Usually, these are Web and mail servers, but sometimes it
may be MySQL and PostgreSQL.
According to these recommendations, the following 4-server installation may be an
optimal solution:
Server 1: Control Panel (with the system PostgreSQL database);
Server 2: Web1 + DNS1;
Server 3: Mail + MySQL1 (user DB) + DNS2;
Server 4: PostgreSQL (user DB) + MySQL2 (user DB).
Later on, you may add more boxes to your system, as your needs grow:
Server 5: Web2;
Server 6: Mail2 (with its own MySQL DB);
Hardware Requirements
If you are going to install Parallels H-Sphere to only one computer, make sure it is at
least Pentium III, 500MHz CPU and 512MB RAM. This will allow to host only a small
number of customers. Adding Parallels SiteStudio will require at least 1000MHz CPU
and 1GB RAM.
Page 10

10 Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation
Sample 1/2/3-Server Configurations
Below are sample 1/2/3-server H-Sphere installations with preferable partitioning
schemes outlined.
One Server Installation Two Server Installation Three Server Installation
Single-server installation
includes Control Panel,
DNS, Web, mail, and
MySQL services. The
PostgreSQL hosting service
isn't included because of the
Parallels H-Sphere system
PostgreSQL database.
Make sure you have at least
two IPs available, because
some features (like
OpenSRS) require at least
two DNS servers.
Examples:
40GB HDD:
/root partition (/etc, /tmp,
/root) - 1-3 GB
/usr - 3-5 GB
/var - 5-7 GB for mail and
MySQL files
/hsphere (or /home) - the
remaining disk space for
Parallels H-Sphere
installation and Web hosting.
80GB HDD:
Consider the following
partitioning scheme for the
two-server configuration:
1) Control Panel + DNS2:
The partitioning
requirements are similar to
those for one server
installation. This box will
have the Parallels H-Sphere
control panel, the system
database, DNS server, and
Parallels SiteStudio
(optional).
2) Web + Mail + MySQL +
PostgreSQL + DNS1:
/ - 1-3 GB
/usr -3-5 GB
/var - 5-7 GB for mail and
MySQL files.
/hsphere - takes the rest of
the space for Web content
and is the biggest partition.
Consider the following
partitioning scheme for a threeserver configuration:
1) Control Panel
The partitioning requirements
are the similar to those for the
one server installation. This box
will have the Parallels H-Sphere
control panel, the system
database, and Parallels
SiteStudio (optional).
2) Web + DNS2:
/ - 1-3 GB
/usr - 3-5 GB
/var -3-5 GB
/hsphere - takes the rest of the
space and is the biggest
partition.
3) Mail + DNS1 + MySQL +
PostgreSQL:
/ - 1-3 GB
/usr - 3-5 GB
/var - takes the rest of the space
for mail and MySQL files.
/ root partition (/etc, /tmp,
/root) - 2-6 GB
/usr - 6-10 GB
/var - 10-15 GB for mail and
MySQL files
/hsphere (or /home) - the
remaining disk space for
Parallels H-Sphere
installation and Web hosting.
120+ GB HDD:
/ root partition (/etc, /tmp,
/root) - 3-10 GB
/usr - 10-20 GB
Page 11

Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation 11
/var - 15-30 GB for mail and
MySQL files
/hsphere (or /home) - the
remaining disk space for
Parallels H-Sphere
installation and Web hosting.
The more users you are
planning to have, the more
disk space is required. If you
want to have Parallels
SiteStudio, it will also be
installed onto this partition.
However, this will require at
least 512 RAM and a
500MHz processor.
In addition, you can create a
separate mail partition for
the Parallels H-Sphere mail
system. Its size will depend
on your mail quotas for users
and the number of
mailboxes.
Page 12

12 Preparing for Parallels H-Sphere Installation
HDD Partitioning
Parallels H-Sphere is installed to the /hsphere directory.
We recommend dedicating a separate partition for the Parallels H-Sphere installation
directory and mount it as /hsphere.
# mkdir -p /hsphere
# chmod 755 /hsphere
Parallels H-Sphere directory can be located on any other partition as well. However, we
do not recommend installing Parallels H-Sphere to the root / partition. Having Parallels
H-Sphere on the root partition may cause certain problems. For instance, if disk quota
gets damaged, you cannot repair it without server reboot and fsck check in the single
user mode.
If your Parallels H-Sphere installation directory is to be located on another partition, for
example, /usr/hsphere on the /usr partition, the /hsphere symlink to this
directory must be anyway created:
# mkdir -p /usr/hsphere
# ln -s /usr/hsphere /hsphere
# chmod 755 /usr/hsphere
Important: Do not create /hsphere as a symlink to another partition on servers with
FreeBSD 5.3 and up! Allocate the separate /hsphere partition instead! If this is
impossible, use nullfs partitioning for this purpose.
There are no more requirements to partitioning the servers, just make sure there is
enough disk space to store user and other Parallels H-Sphere data.
Page 13

Required Components and Configuration
Prior to the installation, make sure your server is configured properly and has all necessary
components.
In this section:
Open SSH ........................................................................................................... 13
Kernel .................................................................................................................. 14
Locale .................................................................................................................. 14
Disk Quota ........................................................................................................... 14
Quotacheck ......................................................................................................... 15
Ports .................................................................................................................... 15
DNS Server Notes ............................................................................................... 20
Perl ...................................................................................................................... 20
Make .................................................................................................................... 20
Command-Line URL Download Utility (wget or fetch) ......................................... 21
Compat3x Package ............................................................................................. 21
SELinux Must Be Off ........................................................................................... 21
Libmap Content ................................................................................................... 21
ifconfig ................................................................................................................. 22
Open SSH
1 Install OpenSSH package on each Parallels H-Sphere box. You can use
standard RPMs under Linux or packages under FreeBSD. Usually, the
standard Linux and FreeBSD installations contain the OpenSSH package,
you can use it without any restrictions. However, we recommend updating
the package to the latest version. SSH keys need to be configured under
the cpanel user.
2 To enable Permit Root Login, open file /etc/ssh/sshd_config and
uncomment the line:
PermitRootLogin yes
Make sure PermitRootLogin is set to yes. Then restart SSH:
for Linux:
/etc/init.d/sshd restart
for FreeBSD:
/etc/rc.d/sshd restart
3 Enable the OpenSSH daemon start at server startup.
4 Start the OpenSSH daemon
Page 14

Kernel
We strongly recommend using typical Linux/FreeBSD kernel (i.e., coming with official OS
distributives or updates). In particular, in case of FreeBSD we insist on GENERIC kernel with
basic configuration. We do not guarantee correct Parallels H-Sphere work on a server with
customized kernel! Please carefully test Parallels H-Sphere functionality on such a server
before it becomes a production server!
Warning: If you are on RHEL 4 operating system, use kernel 2.6.9-55.0.9.EL and higher to
work correctly with Java 1.6.
Locale
Please make sure that the Control Panel server's default locale is set to en_US.UTF-8.
Disk Quota
Enable the disk quota feature on each Parallels H-Sphere Web server. There is no need to
enable it on other servers.
¾ To enable disk quota:
1 Log in as root.
2 Insert the usrquota directive (userquota for FreeBSD) into the /etc/fstab file
for the corresponding partition.
On Linux, it must look similar to this:
LABEL=/hsphere /hsphere ext2 defaults,usrquota 1 1
On FreeBSD, it must look similar to this:
LABEL=/hsphere /hsphere ufs rw,userquota 2 2
3 Execute the following commands:
quotaoff /partition_with_userquota_enabled
mount -o remount /partition_with_userquota_enabled (Linux only,
skip this line with FreeBSD)
rm -rf /partition_with_userquota_enabled/aquota.user
/partition_with_userquota_enabled/quota.user
quotacheck -mufv /partition_with_userquota_enabled(Linux)
quotacheck -guv /partition_with_userquota_enabled(FreeBSD)
quotaon /partition_with_userquota_enabled
4 Perform the following steps:
1. # touch
/partition_with_userquota_enabled/aquota.user
2. # quotacheck -m /partition_with_userquota_enabled
and ignore the message:
"quotacheck: WARNING - Quotafile
/partition_with_userquota_enabled/aquota.user was probably
truncated. Can't save quota settings..."
Page 15
# quotaon /partition_with_userquota_enabled
5 FreeBSD Web server installations: Enable disk quota in the kernel
configuration. Also, in /etc/default/rc.conf set:
enable_quotas="YES"
Root Partitions
We don't recommend enabling the disk quota feature on root partitions. Use other partitions
for this! Therefore, we advise not to place Parallels H-Sphere files on the root partition.
Quotacheck
Quota versions can have some differences on different operating systems. You may need to
execute the quotacheck command with some additional parameters. Please read the
command manual before performing this action.
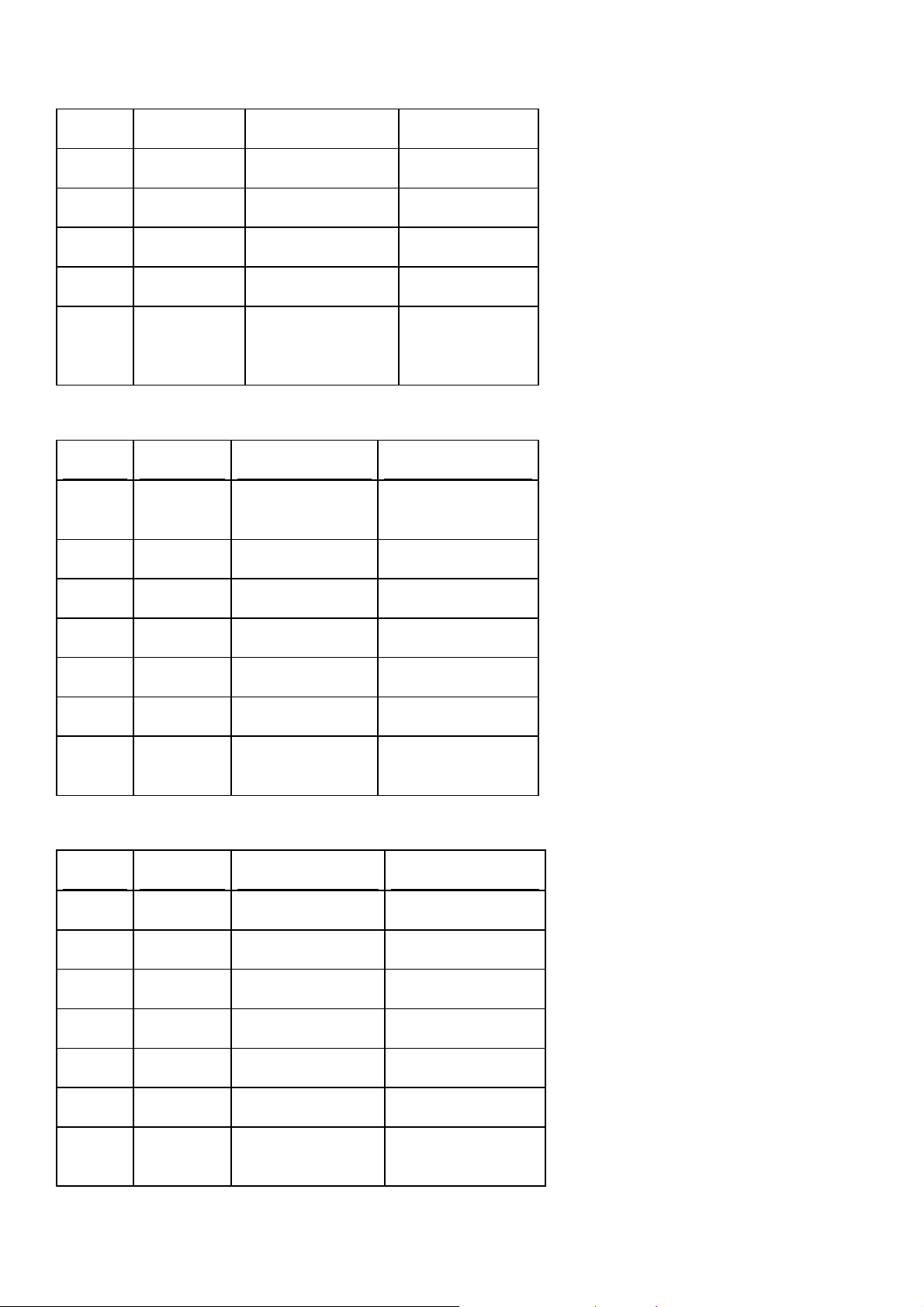
Ports
In your firewall settings, open the following ports in both directions and specify the connection
type - tcp or udp or both.
We need that firewall be configured by our customers.
Note: Pix firewall doesn't work correctly with Parallels H-Sphere and Parallels SiteStudio,
because it doesn't allow servers within one Parallels H-Sphere cluster to communicate by
external IPs, which is critical for both products.
Control Panel Server
Port Usage Connection Type Note
20 FTP-DATA tcp
21 FTP tcp
22 SSH tcp
53 DNS udp
443 HTTPS tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between
Parallels HSphere servers
1922 IMAGEMAK
ER
3306 MySQL tcp to all MySQL
tcp localhost only
servers
Page 16
5432 Postgres tcp CP only
8009 Tomcat tcp CP only
8080 HTTP tcp
8443 SSL tcp
55000 OpenSRS tcp if used
10125 SOAP tcp between
Parallels HSphere servers
Web Server
Port Usage Connection Type Note
20 FTP-
DATA
21 FTP tcp
22 SSH tcp
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
443 HTTPS tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
tcp
H-Sphere servers
Mail Server
Port Usage Connection Type Note
22 SSH tcp
25 SMTP tcp
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
110 POP tcp
143 IMAP tcp
144 IMAP
proxy
tcp localhost only
Page 17
465 Mail SSL tcp open this port only
if you want to use
Mail SSL
587 submission tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
993 Mail SSL tcp open this port only
if you want to use
Mail SSL
995 Mail SSL tcp open this port only
if you want to use
Mail SSL
DNS Server
Port Usage Connection Type Note
22 SSH tcp
53 DNS tcp and udp For highest
security, open:
udp
permanently
tcp worldwide
during Parallels
H-Sphere
installation and
post-installation
tests
tcp between
Parallels HSphere DNS
servers
permanently.
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
953 RNDC tcp and udp For highest
security, open:
udp
permanently
tcp worldwide
during Parallels
H-Sphere
installation and
Page 18

post-installation
tests
tcp between
Parallels HSphere DNS
servers
permanently.
MySQL Server
Port Usage Connection Type Note
22 SSH tcp
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
PgSQL
Ports Usage Connection Type Note
22 SSH tcp
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
5432 Postgres tcp
RealServer
Ports Usage Connection Type Note
22 SSH tcp
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
Page 19

Windows Server
Ports Usage Connection Type Note
20 FTP-DATA tcp
21 FTP tcp
25 SMTP tcp
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
443 HTTPS tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
1433 MS SQL tcp
3306 MySQL tcp
3389 Terminal
Service
5432 Postgres tcp
5631 pcAnywhere tcp optional
10125 SOAP tcp
tcp
MS SQL Server
Ports Usage Connection Type Note
53 DNS udp
80 HTTP tcp
873 RSYNC tcp between Parallels
H-Sphere servers
1433 MS SQL tcp
3389 Terminal
Service
5631 pcAnywhere tcp optional
10125 SOAP tcp
tcp
Page 20

MPS Server
Ports Usage Connection Type Note
80 HTTP tcp
MRTG Server
Ports Usage Connection Tye Note
80 HTTP
443 HTTPS
Note: all ports should be opened for external connections unless specified otherwise (for
example, "tcp between Parallels H-Sphere servers").
DNS Server Notes
1 Port 953 (rndc) should be open for localhost only if your DNS server is
using BIND 9.x.
2 If your DNS server is using BIND 8.x, it can be upgraded to run with
Parallels H-Sphere, but old domains would still have to be managed by
hand. Please agree your DNS server upgrade with our installation team.
Please mind that we don't provide support for Reverse DNS configuration.
Perl
Parallels H-Sphere installation script is written in Perl, therefore Perl is required on each box.
To check if Perl is installed, run:
perl -V
Caution: Do not update or change any configuration to your system Perl, as it will most likely
damage your Parallels H-Sphere installation.
Make
Make sure the make utility is installed on every box. To check if make is installed, run:
make -v
Page 21

Command-Line URL Download Utility (wget or fetch)
Parallels H-Sphere installation script requires the command-line URL download utility, wget
for Linux, fetch for FreeBSD.
Compat3x Package
On FreeBSD 4.X servers, make sure to have the compat3x package installed for compatibility
with 3.x. To diagnose if your compat3x is missing, run:
/stand/sysinstall
and then go to Configure -> Distributions
SELinux Must Be Off
(RedHat Enterprise Linux 4, CentOS 4 and up, and White Box Enterprise Linux 4 only)
Before Parallels H-Sphere installation, make sure SELinux is off on your Linux servers.
To check SELinux status, run:
selinuxenabled && echo $?
If as a result of this command you receive 0, SELinux is enabled. No result means that
SELinux is off.
To disable SELinux, set the following option in /etc/selinux/config:
SELINUX=disabled
This will turn off SELinux after reboot. To disable SELinux immediately, type:
setenforce 0
Libmap Content
If you are to install Control Panel on a FreeBSD box, especially in case of multiprocessor
architecture, please make sure you have the /etc/libmap.conf file on the Control Panel
box with the following content:
[java]
libpthread.so libc_r.so
libpthread.so.2 libc_r.so.6
[javac]
libpthread.so libc_r.so
libpthread.so.2 libc_r.so.6
[/hsphere/shared/java/diablo-jdk1.5.0/bin/java]
libpthread.so libc_r.so
libpthread.so.2 libc_r.so.6
[/hsphere/shared/java/diablo-jdk1.5.0/bin/javac]
libpthread.so libc_r.so
Page 22

libpthread.so.2 libc_r.so.6
ifconfig
Make sure the ifconfig utility on the Control Panel box has '755' permissions by running:
#which ifconfig
/path/to/ifconfig
#chmod 755 /path/to/ifconfig
Page 23

C HAPTER 3
Installing Parallels H-Sphere
To install Parallels H-Sphere from scratch, please carefully follow the instructions
provided below in this chapter. If you want to install Parallels H-Sphere by importing a
specially formatted config.xml file, refer to Appendix A. Installing with prepared
Parallels H-Sphere configuration (on page 33).
In this chapter:
Step 1. Running the Parallels H-Sphere Installation Script ................................. 24
Step 2. Installing the Parallels H-Sphere via Control Panel ................................ 24
Step 3. Completing Parallels H-Sphere Installation Wizard ................................ 29
Installing Parallels SiteStudio with Parallels H-Sphere ....................................... 30
Page 24

24 Installing Parallels H-Sphere
Step 1. Running the Parallels H-Sphere Installation Script
1 Log into the server where you install Parallels H-Sphere as root:
$ su -l
2 Download the Parallels H-Sphere install script:
Linux:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
FreeBSD:
# fetch
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
3 Run the install script with the install option:
# sh ./U34.0 install
4 Choose the cpinstall mode to install basic Parallels H-Sphere
packages on the Control Panel server to be able to run Parallels HSphere Control Panel. In the installer's command line type in the
following command:
cpinstall zone=SERVICE_ZONE ip=SERVICE_IP
where SERVICE_ZONE is the service domain name (for example,
samplehosting.com), and SERVICE_IP is the service domain IP.
This will start the Control Panel installation process.
You can find more info on Parallels H-Sphere installation script options in Appendix B
(on page 35).
Step 2. Installing the Parallels H-Sphere via Control Panel
1 Upon successful installation, run Parallels H-Sphere Contr ol Panel at
http://SERVICE_IP:8080/ in your favorite browser.
Note: If you have problems with running Control Panel, please try to When restarting
the Control Panel, make sure that you are logged into the Control Panel server as root.
For Linux:
Page 25

Installing Parallels H-Sphere 25
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpdcp stop
killall -9 java
sleep 10
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpdcp start
For FreeBSD:
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/apachecp.sh stop
killall -9 java
sleep 10
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/apachecp.sh start.
1 Log into Parallels H-Sphere Control Panel as admin with pass word
admin. Later on you will be able to change the administrator password.
After you log in, you must enter your valid Parallels H-Sphere license purchased
from the Buy Parallels Support and Services for Parallels H-Sphere page.
Otherwise, you won't be able to proceed with the installation. H-Sphere 3.2 and up
introduces licensing through a unified Parallels licensing system.
2 Run Parallels H-Sphere Installation Wizard which allows shaping your
Parallels H-Sphere cluster by adding boxes and hosting services and
configuring basic Parallels H-Sphere settings.
Running Parallels H-Sphere Installation Wizard
Now that you ran the Parallels H-Sphere updater in the installation mode with the
cpinstall option, you need to:
Step 1. Manage configuration file
Installation Wizard writes the Parallels H-Sphere cluster configuration into the specially
formatted config.xml file (see sample config.xml). The Configuration File section on the
main page enables you to:
Page 26

26 Installing Parallels H-Sphere
Import: You upload the prepared XML file from a local machine to Parallels H-
Sphere and later reconfigure Parallels H-Sphere in the wizard. Read more on
Parallels H-Sphere installation from prepared config.xml file;
Export: export config.xml with your Parallels H-Sphere cluster configuration to your
local machine.
Restore to Default: choose this option to recreate config.xml and to restart configuring
Parallels H-Sphere cluster in the wizard.
Step 2. Edit general settings
1 Click the Edit General Settings icon on the right corner of the General
Settings caption and proceed to the following page:
System Domain: Specify the service domain name here.
One Server Installation: check this box if you need a single server installation. You
can't add more than one physical server by checking this options.
Use NAT IP mapping: Check this box if you implement NAT (on page 54) on your
Parallels H-Sphere.
2 Press Submit and return to the main page of the wizard.
Page 27

Installing Parallels H-Sphere 27
Step 3. Add physical servers
1 Click the Add Physical Server icon on the right corner of the Physical Servers
caption.
2 Fill in the form for adding new physical servers and services:
3 Set physical server Name, IP, root password, and choose which
logical servers (Control Panel, Web, mail, DNS, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
will be installed there. They will be installed with default settings which
can be changed if necessary.
4 Click Submit.
After you have added physical servers into Parallels H-Sphere cluster, you will see
them on the main page of the wizard:
Page 28

28 Installing Parallels H-Sphere
Here you may also configure physical server profiles, setting update rules for each
physical server or groups of servers. Click Manage install/update profiles below the
Physical Servers form to configure the profiles:
Step 4. Add logical servers
Once physical server is added, you can add logical servers:
1 Select the type of logical server you want to add and click Submit.
Choosing Use defaults for this server will apply default names for Parallels H-Sphere
logical servers on this server. By default, they are named webN, mailN, nsN,
mailN, mysqlN, respectively.
You can edit logical server parameters, if necessary.
Step 5. Choose between full and reduced installation
Now that you're done with Parallels H-Sphere configuration:
1 Click Proceed With Installation Wizard.
Note: If you choose to Skip Installation Wizard, you will be taken directly to
Administrator Control Panel and all your pre-configuration will be lost.
2 Choose the installation mode: full or reduced installation.
Aborted Installation
If at any point of your installation process, you:
Go to your wizard Home in the middle of installation
Loose connection with your browser
Skip installation (as on Step 5)
you will have a choice of further actions:
Proceed with Installation Wizard will take you to the point of interrupted installation
process
Go to Admin CP will take you to your administrator panel without completing
installation
Page 29

Installing Parallels H-Sphere 29
Clear Installed Data will cancel all settings and you can start installation from scratch
Step 3. Completing Parallels H-Sphere Installation Wizard
There are two alternative ways to complete full installation: via Control Panel web
interface or running Parallels H-Sphere install/update script with postinstall option.
Option One: completing installation via Control Panel web interface
1 On the page that appears check the servers you want to be
updated/installed and click Start. To see the update log, click the
server name link.
On multiserver installations, you can see the update process simultaneously on
each server. To do it, click the logical server links to switch between the server logs.
Update process indicator
Yellow: ready for update
Blue: update is running
Green: update successfully finished
Red: update finished with error. If update fails, you will see an error message
with details.
Important: You don't need to restart the whole update process if the update fails
only on a certain server. Just log into this server manually, fix possible issues
and resume this step on this particular server.
2 When update is finished and the light turns green, click Proceed to
complete installation.
3 On the page that appears, click Return to Admin CP.
You will be taken to administrator Control Panel.
legend:
Option Two: Completing installation with postinstall option
Return to the Parallels H-Sphere installation script (on page 24) and choose the
postinstall option there:
postinstall
This will complete Parallels H-Sphere installation according to the configuration you
built. You can find more info on Parallels H-Sphere install script options in Appendix B
(on page 35).
Page 30

30 Installing Parallels H-Sphere
Installing Parallels SiteStudio with Parallels H-Sphere
To install Parallels SiteStudio with Parallels H-Sphere, run after the Parallels H-Sphere
installation:
# sh U34.0 install postinstall sitestudio
Page 31

C HAPTER 4
Performing Post-Installation Tasks
Built-in Accounts
Standard Parallels H-Sphere installation would include two accounts, neither of which
may be deleted:
1 the admin account (login: admin, password: admin) to configure system
settings. It is extremely recommended to change the password of the
admin account after the installation and testing have been completed.
2 the wwwuser account (login: wwwuser, password: userwwww) to
manage the control panel domain.
Control Panel URL
After the installation, the control panel becomes accessible at the address:
http://your_ip_address:8080
http://cp.your_domain_name:8080
If your Parallels H-Sphere has been configured with SSL protection, use the addresses:
https://your_ip_address:8443
https://cp.your_domain_name:8443
See also Customize your Control Panel URL documentation in System Administrator
Guide.
or
or
DNS Configuration
Some Parallels H-Sphere features (like webmail, WebShell, phpMyAdmin) will work
only after you add a DNS zone and an instant alias template. To check these features
immediately, specify in the DNS configuration of your local workstation (not Parallels HSphere server) that Parallels H-Sphere primary DNS server is your primary
nameserver. For example, if your workstation is Linux, add a corresponding line in
/etc/resolv.conf.
If you are running a one box installation, you can have two DNS IPs for ns1 and ns2. At
least two DNS servers are required to offer domian registration services with OpenSRS
or Enom. If you need more than two DNS servers, you need to set up one more box,
and your DNS services need to be fully reconfigured.
Page 32

32 Performing Post-Installation Tasks
PostgreSQL
The Parallels H-Sphere Control Panel requires the postgresql daemon running. Don't
start Parallels H-Sphere Control Panel without it. To find out if PostgreSQL is running,
type:
Linux:
/etc/init.d/postgresql status
FreeBSD:
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/010.pgsql.sh
Page 33

C HAPTER 5
Appendix A. Installing with Prepared Parallels H-Sphere Configuration
It is possible to perform Parallels H-Sphere installation by importing a specially
formatted config.xml file with all Parallels H-Sphere physical and logical servers'
configuration.
Run the install script with the install option. In the installer's command line, enter:
install xml=CONFIG_XML_LOCATION [ skip-sitestudio ]
Creating config.xml file
Parallels H-Sphere includes the hsphere-info package installed on each Parallels
H-Sphere Unix server. The package installs the /hsphere/shared/bin/hsinfo
script on each server, and the script collects information about this server into the
/hsphere/shared/etc/config.xml file.
The hsinfo has the following syntax:
Usage:
hsinfo [ -ame ] [ -p box IP ] [ -g group ] [ -t type ] [ -f xmlfile ] [
-s delimiter ]
hsinfo -l [ -p box IP ] [ -g group ] [ -s delimiter ] [ -f xmlfile ]
hsinfo -i [ -ame ] [ -g group ] [ -f xmlfile ] [ -s delimiter ]
hsinfo -n [ -p box IP ] [ -g group ] [ -f xmlfile ]
hsinfo -o a[ddress]|i[nterface]|n[umber] [ -f xmlfile ]
hsinfo -d [ -f xmlfile ]
hsinfo -v [ -f xmlfile ]
hsinfo -G
hsinfo -T
hsinfo -h -l list of logical server names
-i list of physical server IPs -n domain name of the logical
server
-d servise zone name -p phisical box IP (default: local physical
box)
-v hspere version
-a show IP address -m show mask
-e show external IP addreyyss
-o show network interface name of the physical IP
-G list of possible logical server groups
-T list of possible IP types
-h help
by default show only IP addresses
group: cp, mail, unix_hosting, windows_hosting, mysql, pgsql, mssql,
dns, mrtg, system (default: all)
type: system, service, shared, dedicated, resellerSSL, resellerDNS, all
(default: service)
xmlfile: XML file location (default: /hsphere/shared/etc/config.xml)
Page 34

34 Appendix A. Installing with Prepared Parallels H-Sphere Configuration
The /hsphere/shared/etc/config.xml XML file contains information about
physical and logical server names, ids, IPs; system zones; current Parallels H-Sphere
version, etc.
Sample config.xml
The /hsphere/local/config/customs/customs utility returns the files
customized by user according to the customization conf_file. It has the following
syntax:
Usage:
customs [ -hmv ] [ -c conf_file ] { package_name1 }
[ package_name2 ... ]
-h : to see this help message;
-m : to return the masks of the given packages (names only);
-v : verbose, package mask output before the list of its
customized files;
-c conf_file : path to the user customization configuration file,
default:
/hsphere/local/config/customs/customs.conf;
package_nameN : name of the package to list the customized files for.
Page 35

C HAPTER 6
Appendix B. Installation Script Options
Parallels H-Sphere installation is performed by a script that brings about more flexibility
in the process of installation and introduces a variety of advanced features and
improvements.
¾ Before running Parallels H-Sphere installer:
1 Download the install script. For example, for Parallels H-Sphere 3.4
run under root on Linux box:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U34.0/U34.
0
2 Run script the script in the install mode:
# sh U34.0 install
You will get the list of installation modes, each having its own options.
(1) install -- Full installation mode. Requires prepared config.xml with Parallels
H-Sphere cluster configuration.
(2) cpinstall -- Control Panel installation mode. Afterwards, log into Parallels HSphere Control Panel Web interface, go through Pre-Configuration wizard, and then
complete installation in mode (3).
(3) postinstall -- post-installation Parallels H-Sphere cluster configuration, to
be run after mode (2).
(4) sitestudio -- install Parallels SiteStudio on the Control Panel box.
(5) sitebuilder -- install Parallels Sitebuilder on the Control Panel box (for
Parallels H-Sphere 3.3 and up).
If you want more information on every mode, simply type its number in the command
line.
Install Modes:
install - Parallels H-Sphere installation from the prepared config.xml file with
configuration of Parallels H-Sphere cluster to be installed. config.xml contains
information about Parallels H- Sphere physical and logical servers, with root
passwords to physical server where Parallels H-Sphere is to be installed (see
sample config.xml at
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/HSdocumentation/xmls/config.xml
the installation this file is temporarily stored in the ~cpanel/.settings directory.
You can also use the cpinstall mode and run Parallels H-Sphere Pre-Configuration
Wizard in administrator Control Panel to create and import/export config.xml.
). During
install xml=CONFIG_XML [ skip-sitestudio ] [ url=Link ] [
mirror=mirror_number ]
Page 36

36 Appendix B. Installation Script Options
cpinstall - install only system PostgreSQL and packages to be able to run Control
Panel. Later on, you need to log into administrator Control Panel and go through
Parallels H-Sphere Pre-Configuration Wizard to shape your Parallels H-Sphere
cluster, and finally, run the installer in the postinstall mode.
cpinstall zone=SERVICE_ZONE ip=IP1 [ ip2=IP2 ] [ natip=NAT_IP
] [ mask=MASK ] [ url=Link ] [ mirror=mirror_number ]
postinstall - run this mode to complete Parallels H-Sphere installation after
cpinstall and after adding servers and services in the Parallels H-Sphere PreConfiguration mode in administrator Control Panel.
postinstall
sitestudio - install Parallels SiteStudio on the Control Panel box.
sitestudio [ url=Link ] [ mirror=mirror_number ]
sitebuilder - install Parallels Sitebuilder on the Control Panel box.
sitebuilder [ url=Link ] [ mirror=mirror_number ]
Where:
Obligatory Parameters:
xml - the path to config.xml file. This path should not be
/hsphere/shared/etc/config.xml
zone - service domain name (e.g., samplehosting.com).
ip - service zone IP - IP of Control Panel box.
Optional parameters:
ip2 - the IP of the second DNS logical server (ns2). If ip2 is not set, the ns2 logical
server will not be created.
natip - the external server IP for NAT mapping.
mask - the network mask. If mask is not set, the default value (255.255.255.0) is
used.
skip-sitestudio - install Parallels H-Sphere without Parallels SiteStudio.
group - comma-separated list of logical servers to be installed. Possible groups:
mail, web, dns, mysql, pgsql, cp, vps (using common ips and group tags is allowed).
url - alternative path to package download, this option differs from 'mirror', which
includes predefined list of the maintained HS mirrors. Package lists are downloaded
from default location or mirror, pointed via mirror option. (Default path is
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS
)
mirror - allows setting another mirror instead of the default one. At this moment
available the following HS servers: [0] - download.hsphere.parallels.com
(default) and [1] - download2.hsphere.parallels.com (mirror).
Page 37

C HAPTER 7
Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
You cannot customize some major service configuration files (for Web, mail, DNS,
databases) directly, as your changes in these files will be overwritten with a
consequent Parallels H- Sphere update! Instead, you need to create configuration file
templates by means of the hsphere-update wrapper and customize these templates
instead of default configuration files.
You can customize configuration file templates by means of Parallels H-Sphere
updater, provided you have not customized your templates already. For this purpose
two new options are added to the hspackages wrapper of the Parallels H-Sphere
update script:
hspackages ctemplates=[OPTIONS] - Place custom templates for comma-
separated list of services into predefined locations if custom templates are not there
already.
hspackages edit=IP:/path/to/custom/template - Edit custom template
on a specified server in a specified location.
Important:
If you run the hspackages ctemplates command without options, it will create custom
templates on all related servers of the Parallels H-Sphere cluster! To specify
particular servers where custom configuration templates should be created, please
use the extended syntax of the hspackages command. For example, to create PHP
custom configuration templates only on the physical boxes 192.168.1.10 and
192.168.1.11, run:
hspackages ctemplates=php ips=192.168.1.10,192.168.1.11
The hspackages ctemplates command should be run only once, in order to create
custom configuration templates! Then you customize these files according to your
needs. Next time you run it, it will prompt re-creating your custom configuration
templates, thus you may lose your customization!
The only exclusion when you need to run hspackages ctemplates again is when a
coming version of the hsphere-update package contains updates of default
configuration templates. You will be specially notified of this in the respective update
notes.
In this chapter:
Control Panel Apache ......................................................................................... 39
Extra Control Panel Apache Configuration Files ................................................. 39
Apache ................................................................................................................ 40
Extra Apache Configuration Files ........................................................................ 41
PHP 4 .................................................................................................................. 42
Page 38

38 Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
PHP 5 .................................................................................................................. 43
FTP ..................................................................................................................... 44
MySQL ................................................................................................................ 46
PostgreSQL ......................................................................................................... 46
DNS ..................................................................................................................... 47
Other Files Included into Parallels H-Sphere Packages ..................................... 48
Page 39

Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 39
Control Panel Apache
Default Control Panel Apache httpd.conf template is included into the hsphereupdate and installed here:
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/cpapache/httpd.conf.tmpl.default
¾ To customize the template:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=httpdcp option:
hspackages ctemplates=httpdcp [OPTIONS]
Custom template will be placed into the following location:
/hsphere/local/home/cpanel/apache/etc/httpd.conf.tmpl.custo
m
1 Edit the
/hsphere/local/home/cpanel/apache/etc/httpd.conf.tmpl
.custom file according to your needs.
2 To immediately apply changes, run the conf file generating script
which is as a rule executed in the postinstall section of the
package:
/hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-restart
Extra Control Panel Apache Configuration Files
Parallels H-Sphere allows to customize some extra Apache configuration files for
Control Panel. They are located in the
/hsphere/local/home/cpanel/apache/conf/extra/ directory:
httpd-autoindex.conf - directives controlling the display of server-generated
directory listings
httpd-cache.conf - directives providing HTTP content cache configuration
httpd-info.conf - Apache status-related directive blocks
Page 40

40 Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
httpd-languages.conf - directives which provide the mod_mime and
mod_negotiation modules global configuration
vh-ssl-default.conf - Global SSL default VirtualHost configuration
These extra configuration files are provided for easier configuration of Apache modules,
such as mod_cache, mod_security, etc.
After the configuration file customization, the correspondent *.tmpl.custom files will
be created in the same directory:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=httpdcp_extra
option:
hspackages ctemplates=httpdcp_extra [OPTIONS]
After that, custom templates
/hsphere/local/home/cpanel/apache/conf/extra/*.tmpl.custom will
be created.
2 Edit the
/hsphere/local/home/cpanel/apache/conf/extra/*.tmpl.c
ustom files according to your needs.
3 To immediately apply changes, restart Apache:
/hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-restart
Apache
Default configuration Apache templates are included into the hsphere-update
package and installed in the following locations:
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/hs31/apache/httpd.conf.tmpl.default
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/hs31/apache/httpd2.conf.tmpl.default
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/hs31apache/lsrv.conf.tmpl.default
¾ To customize them, perform:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
Page 41

Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 41
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=httpd option for Apache
1.3 and/or ctemplates=httpd2 option for Apache 2.2:
hspackages ctemplates=httpd [OPTIONS]
Custom templates will be placed into the following locations:
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/lsrv.conf.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/httpd.conf.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/local/config/httpd2/lsrv.conf.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/local/config/httpd2/httpd.conf.tmpl.custom
2 Edit the .custom files according to your needs:
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/lsrv.conf.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/httpd.conf.tmpl.custom
3 To immediately apply changes, run the conf file generating script
which is as a rule executed in the postinstall section of the package:
/hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-restart
Customizing /hsphere/shared/apache/htdocs/index.html
If you need to leave /hsphere/shared/apache/htdocs/index.html unchanged
after the update, create the following file:
touch /hsphere/local/config/httpd/index.html.custom
If the latter file exists, then you can customize your index.html file without the risk of
its being overwritten.
Extra Apache Configuration Files
Parallels H-Sphere allows to customize some extra Apache configuration files, such as:
httpd-autoindex.conf - directives controlling the display of server-generated
directory listings
httpd-cache.conf - directives providing HTTP content cache configuration
(Apache 2.2 only)
httpd-gzip.conf - directives for global settings provided by the mod_gzip
module (Apache 1.3 only)
httpd-info.conf - Apache status-related directives
httpd-languages.conf - directives which provide the mod_mime and
mod_negotiation modules global configuration
httpd-security.conf - ModSecurity configuration options
Page 42

42 Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
httpd-security2.conf - ModSecurity v.2 configuration options (Apache 2.2
only)
vh-ssl-default.conf - global SSL default VirtualHost configuration
Default templates *.tmpl.defaiult for these configuration files are installed with
hsphere-updater to the following directories:
Apache 1.3: /hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/hs-
31/apache/extra.default/
Apache 2.2: /hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/hs-
31/apache/extra2.default/
After Parallels H-Sphere 3.2 update, the respective custom .tmpl.custom files will be
created in the following directories:
Apache 1.3: /hsphere/local/config/httpd/extra/
Apache 2.2: /hsphere/local/config/httpd2/extra/
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=httpd_extra
option:
hspackages ctemplates=httpd_extra [OPTIONS]
After that, custom templates *.tmpl.custom will be created in respective
directories.
2 Edit the *.tmpl.custom files according to your needs:
Apache 1.3: /hsphere/local/config/httpd/extra/*.tmpl.custom
Apache 2.2: /hsphere/local/config/httpd2/extra/*.tmpl.custom
3 To immediately apply changes, restart Apache:
/hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-restart
Page 43

Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 43
PHP 4
PHP 4 configuration files are located:
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/php4/php.ini.tmpl.custom (when PHP4
uses fastcgi, for all Apache versions)
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/php4/php.ini.tmpl.custom (when libphp4
is used, for Apache 1.x)
/hsphere/local/config/httpd2/php4/php.ini.tmpl.custom (when libphp4
is used, for Apache 2.x)
¾ To customize PHP 4 configuration files:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=php option:
hspackages ctemplates=php [OPTIONS]
Custom templates will be placed into the following location:
/hsphere/local/config/httpd2/php4/php.ini.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/php4/php.ini.tmpl.custom
2 Edit the above mentioned tmpl.custom files according to your
needs.
3 To immediately apply changes, restart Apache service:
/hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-restart
Page 44

44 Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
PHP 5
PHP 5 configuration files are located:
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/php5/php.ini.tmpl.custom (when
PHP5 uses fastcgi, for all Apache versions)
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/php5/php.ini.tmpl.custom (when
libphp5 is used, for Apache 1.x)
/hsphere/local/config/httpd2/php5/php.ini.tmpl.custom (when
libphp5 is used, for Apache 2.x)
¾ To customize PHP 5 configuration files:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=php option:
hspackages ctemplates=php [OPTIONS]
Custom templates will be placed into the following location:
/hsphere/local/config/httpd/php5/php.ini.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/local/config/httpd2/php5/php.ini.tmpl.custom
2 Edit the above mentioned tmpl.custom files according to your
needs.
3 To immediately apply changes, restart Apache service:
/hsphere/shared/scripts/apache-restart
Page 45

Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 45
FTP
FTP configuration file templates are included into the hsphere-update package and
installed in the following locations:
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/proftpd/shared.proftpd.conf.tmpl.d
efault
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/proftpd/local.proftpd.conf.tmpl.d
efault
¾ To customize these templates, perform:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=ftpd option:
hspackages ctemplates=ftpd [OPTIONS]
Custom templates will be placed into the following locations:
/hsphere/local/config/ftpd/proftpd.conf.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/shared/config/ftpd/proftpd.conf.tmpl.custom
2 Edit the .custom files according to your needs:
/hsphere/local/config/ftpd/proftpd.conf.tmpl.custom
/hsphere/shared/config/ftpd/proftpd.conf.tmpl.custom
3 To immediately apply changes, run:
/hsphere/shared/config/ftpd/configure-proftpd.sh
4 Restart FTP service.
Page 46

46 Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
MySQL
MySQL configuration file templates are included into the hsphere-update package and
installed in the following locations:
Linux: /hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/FreeBSD/my.cnf_tmpl.default
FreeBSD: /hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/Linux/my.cnf_tmpl.default
¾ To customize these templates, perform:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=mysql option:
hspackages ctemplates=mysql [OPTIONS]
Custom templates will be placed into the following location:
/hsphere/local/config/mysql/my.cnf_tmpl.custom
2 Edit the /hsphere/local/config/mysql/my.cnf_tmpl.custom
file according to your needs.
3 To immediately apply changes, run the conf file generating script
which is as a rule executed in the package postinstall section:
/hsphere/local/config/mysql/scripts/config_mysql
Page 47

Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 47
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL configuration file templates are included into the hsphere-update package
and installed in the following locations:
Linux:
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/FreeBSD/postgresql.conf_tmpl.defa
ult
FreeBSD:
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/Linux/postgresql.conf_tmpl.defaul
t
¾ To customize these templates, perform:
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=pgsql option:
hspackages ctemplates=pgsql [OPTIONS]
Custom templates will be placed into the following location:
/hsphere/local/config/pgsql/postgresql.conf_tmpl.custom
2 Edit the
/hsphere/local/config/pgsql/postgresql.conf_tmpl.cust
om file according to your needs.
Important: By default, PostgreSQL listens on localhost (parameter
virtual_host=127.0.0.1 in configuration file). Change this parameter if required.
3 To immediately apply changes, run the conf file generating script
which is as a rule executed in the package postinstall section:
/hsphere/local/config/pgsql/scripts/config_pgsql
DNS
/etc/named.conf
Default template is located at
/hsphere/pkg/scripts/templates/named/named.conf.tmpl.default
Page 48

48 Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates
1 Create custom configuration template if required. Otherwise, skip this
step.
1. Download H-Sphere updater:
# wget
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/U
34.0/U34.0
2. Run the update script:
# sh ./<script_filename>
3. Execute the hspackages wrapper with the ctemplates=named option:
hspackages ctemplates=named [OPTIONS]
Custom template will be placed into the following location:
/etc/named.conf.tmpl.custom
2 Edit the /etc/named.conf.tmpl.custom file according to your
needs.
3 To immediately apply changes, run the configuration file generating
script which is as a rule executed in the postinstall section of the
package:
/hsphere/local/config/bind/scripts/config_bind
/etc/resolv.conf
To leave /etc/resolv.conf unchanged during the update (e.g., when MyDNS is
used), perform:
touch /etc/resolv.conf.custom
If the latter file exists, then you can customize your /etc/resolv.conf file without
the risk of its being overwritten.
Other Files Included into Parallels HSphere Packages
Warning: It is not recommended that you customize the files included into Parallels HSphere packages by yourself. Any alterations made to them are at your own risk!
Besides customization of some major service configuration files (for Web, mail, DNS,
databases, etc.), we have implemented for your convenience a possibility to customize
other files included into Parallels H-Sphere packages. For this, we have created a
configuration file /hsphere/local/config/customs/customs.conf and a
special template /hsphere/local/config/customs/customs.conf.tmpl that
will help you to save customized Parallels H-Sphere packages files during future
updates.
¾ To customize a file included into Parallels H-Sphere Package and save the changes:
Page 49

Appendix C. Customizing Server Configuration Files by Means of Templates 49
1 Make necessary changes to the file you want to customize.
2 Copy a template of custom files to a configuration file:
cp -p /hsphere/local/config/customs/customs.conf.tmpl
/hsphere/local/config/customs/customs.conf
3 Go to the customs.conf file
4 Add the full path to the customized file(-s) under the mask of the
relevant package, e.g.:
[hsphere-imap-h2.5]
/etc/rc.d/init.d/courier-imapd
/etc/rc.d/init.d/courier-imapd-ssl
/hsphere/local/config/mail/imap/etc/imapd
/hsphere/local/config/mail/imap/etc/imapd-ssl
Please note that during the package updates all custom files will be saved in the
/hsphere/local/config/customs/$package_mask/ directory. The default files
of Parallels H-Sphere packages, in their turn, will be stored at
/hsphere/local/config/customs/default/$package_mask/. The above
mentioned locations store the latest versions of both custom and default files, no matter
custom or default file is being used.
Page 50

C HAPTER 8
Appendix D. Download Locations
This table contains codes for all Linux/FreeBSD operating systems supported by
Parallels H-Sphere and links to the directories on the
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com
required by Parallels H-Sphere.
Operating System OSCODE Download Location
website where you can download packages
RedHat EL 3,
CentOS 3.x, White
Box EL 3.x
RedHat EL 4,
CentOS 4.x, White
Box EL 4.x
RedHat EL 4,
CentOS 4.x, White
Box EL 4.x (x86_64)
RedHat EL 5,
CentOS 5.x,
CloudLinux 5.5
RedHat EL 5,
CentOS 5.x (x86_64)
FreeBSD 6.1 FBSD61
FreeBSD 6.2 FBSD62
RHES3
RHES4
RHES4_64
RHES5
RHES5_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/RHES3
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/RHES4
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/RHES4_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/RHES5
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/RHES5_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD61
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD62
FreeBSD 6.3 FBSD63
FreeBSD 6.4 FBSD64
FreeBSD 7.0 FBSD70
FreeBSD 7.0
(amd64)
FBSD70_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD63
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD70
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD70_64
Page 51

Appendix D. Download Locations 51
FreeBSD 7.1 FBSD71
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD71
FreeBSD 7.1
FBSD71_64
(amd64)
FreeBSD 7.2 FBSD72
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD71_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD72
FreeBSD 7.2
FBSD72_64
(amd64)
FreeBSD 7.3 FBSD73
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD72_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD73
FreeBSD 7.3
(amd64)
FBSD73_64
http://download.hsphere.parallels.c
om/shiv/HS/FBSD73_64
In this chapter:
Mirror Server for Updating Parallels H-Sphere ................................................... 52
Page 52

52 Appendix D. Download Locations
Mirror Server for Updating Parallels HSphere
If you have 2 and more boxes with the same operating system and you want to speed
up package downloads, you can create a mirror server and in the updater set an
alternative URL for package downloads.
¾ To create a mirror:
1 Set up a web server (or just an IP-based virtual host in existing web
server).
2 In the web server's (or appropriate virtual host's) document root
directory, create directory shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/, e.g.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/
3 Download all contents of
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/ into
your shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/ directory.
4 Download the script
http://download.hsphere.parallels.com/shiv/HS/sync34.
sh, adjust it for your paths, and run:
sh sync34.sh
5 This will download you H-Sphere packages according to the package
lists in shiv/HS/releases/U34.0/.
Now you can specify this mirror server to be used by the Parallels H-Sphere
install/update script by setting the mirror parameter.
Page 53

C HAPTER 9
Appendix E. Miscellaneous
In this chapter:
Restarting Parallels H-Sphere ............................................................................. 53
Network Address Translation (NAT) ................................................................... 54
Restarting Parallels H-Sphere
When restarting the Control Panel, make sure that you are logged into the Control
Panel server as root.
For Linux:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpdcp stop
killall -9 java
sleep 10
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpdcp start
For FreeBSD:
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/apachecp.sh stop
killall -9 java
sleep 10
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/apachecp.sh start
Page 54

C HAPTER 10
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Parallels H-Sphere supports NAT (Network Address Translation) which allows you to
use internal IPs in your local area network. When configuring Parallels H-Sphere, use
internal IPs in all instances, and Parallels H-Sphere will convert them into external IPs
for the DNS settings and control panel web interface.
¾ To enable NAT support in Parallels H-Sphere:
1 Log into Control Panel server as cpanel user:
1. Log in as root first:
$ su -
2. Log in as the cpanel user:
# su -l cpanel
2 Create the ips-map.xml file in the
~cpanel/shiva/psoft_config/ directory in the following format:
<ips>
<ip ext="external_ip" int="internal_ip"/>
. . .
</ips>
Example:
<ips>
<ip ext="65.219.197.236" int="192.168.1.27"/>
<ip ext="65.219.197.237" int="192.168.1.28"/>
<ip ext="65.219.197.238" int="192.168.1.29"/>
<ip ext="65.219.197.239" int="192.168.1.30"/>
<ip ext="65.219.197.242" int="192.168.1.31"/>
<ip ext="65.219.197.243" int="192.168.1.32"/>
<ip ext="65.219.197.244" int="192.168.1.33"/>
</ips>
3 Set the following record in
~cpanel/shiva/psoft_config/hsphere.properties:
IPS-XML-FILENAME =
/hsphere/local/home/cpanel/shiva/psoft_config/ips-map.xml
4 Restart Parallels H-Sphere to apply changes. To do this, run under
root:
For Linux:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpdcp stop
killall -9 java
sleep 10
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpdcp start
Page 55

Appendix E. Miscellaneous 55
For FreeBSD:
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/apachecp.sh stop
killall -9 java
sleep 10
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/apachecp.sh start
¾ To disable NAT support
1 Remove the line mentioned in step 3 above from
hsphere.properties.
2 Restart Parallels H-Sphere.
See below for particular cases of configuring NAT in your Parallels H-Sphere cluster.
 Loading...
Loading...