Panasonic U-72ME2U9, U-120ME2U9, U-96ME2U9, U-144ME2U9, U-72ME2U94 service manual
...
U-72ME2U9
U-96ME2U9
U-120ME2U9
U-144ME2U9
U-72ME2U94
Order No. SBPAC1404012CE
2WAY VRF System
U-96ME2U94
U-120ME2U94
U-144ME2U94
Model No.
Outdoor Unit
Outdoor Unit TypeType
ME2 2WAY VRF System
To be connecting Indoor Units
Indoor Units
Indoor Unit TypeType
U2 4-Way Cassette 36"x36"
4-Way Cassette 24"x24"
Y2
D1
1-Way Cassette
Concealed Duct
F2
-Medium Static
Concealed Duct
M2
-Low Static
Concealed Duct
E1
-High Static
T2
Ceiling
K2
Wall Mounted
P1
Floor Standing
R1
Concealed Floor Standing
S-07MD1U6
S-07MF2U6
S-07MM2U6
S-07MK2U6
S-07MP1U6
S-07MR1U6
Nominal Capacity
72 96 120 144
U-72ME2U9
U-72ME2U94
7 9 12 15 18 24 36 48 54
S-12MU2U6S-09MU2U6S-07MU2U6
S-09MY2U6S-07MY2U6
S-09MD1U6
S-09MF2U6
S-09MM2U6
S-09MK2U6
S-09MP1U6
S-09MR1U6
S-12MY2U6
S-12MD1U6
S-12MF2U6
S-12MM2U6
S-12MT2U6
S-12MK2U6
S-12MP1U6
S-12MR1U6
U-96ME2U9 U-120ME2U9 U-144ME2U9
U-96ME2U94 U-120ME2U94 U-144ME2U94
Nominal Capacity
S-15MF2U6
S-15MM2U6
S-15MP1U6
S-15MR1U6
S-18MY2U6
S-18MF2U6
S-18MM2U6
S-18MT2U6
S-18MK2U6
S-18MP1U6
S-18MR1U6
S-24MU2U6
S-24MF2U6
S-24MT2U6
S-24MK2U6
S-24MP1U6
S-24MR1U6
S-36MU2U6
S-36MF2U6
S-36ME1U6
S-48MF2U6 S-54MF2U6
S-48ME1U6
85464849337007
This air conditioner uses the refrigerant R410A.
REFERENCE NO.
SM830237-07
IMPORTANT!
• Do not leak refrigerant while piping work for an
installation or re-installation, and while repairing
refrigeration parts.
Handle liquid refrigerant carefully as it may cause
frostbite.
When Servicing
• Turn the power OFF at the main power box (mains)
before opening the unit to check or repair electrical
parts and wiring.
• Keep your fingers and clothing away from any moving
parts.
• Clean up the site after you finish, remembering to
check that no metal scraps or bits of wiring have been
left inside the unit.
WARNING
• This product must not be modified or
disassembled under any circumstances.
Modified or disassembled unit may cause fire,
electric shock or injury.
• Do not clean inside the indoor and outdoor
units by users. Engage authorized dealer or
specialist for cleaning.
• In case of malfunction of this appliance, do
not repair by yourself. Contact to the sales
dealer or service dealer for a repair.
CAUTION
• Do not touch the air inlet or the sharp
aluminum fins of the outdoor unit. You
may get injured.
• Ventilate any enclosed areas when installing or
testing the refrigeration system. Leaked
refrigerant gas, on contact with fire or heat, can
produce dangerously toxic gas.
• Confirm after installation that no refrigerant gas
is leaking. If the gas comes in contact with a
burning stove, gas water heater, electric room
heater or other heat source, it can cause the
generation of toxic gas.
Others
CAUTION
• Do not sit or step on the unit, you may
fall down accidentally.
• Do not touch the air inlet or the sharp
aluminum fins of the outdoor unit.
You may get injured.
• Do not stick any object into the FAN
CASE.
You may be injured and the unit may
be damaged.
Check of Density Limit
The room in which the air conditioner is to be
installed requires a design that in the event of
refrigerant gas leaking out, its density will not exceed
a set limit.
The refrigerant (R410A), which is used in the air
conditioner, is safe, without the toxicity or combustibility of
ammonia, and is not restricted by laws imposed to protect
the ozone layer. However, since it contains more than air,
it poses the risk of suffocation if its density should rise
excessively. Suffocation from leakage of refrigerant is
almost non-existent. With the recent increase in the
number of high density buildings, however, the installation
of multi air conditioner systems is on the increase
because of the need for effective use of floor space,
individual control, energy conservation by curtailing heat
and carrying power, etc.
Most importantly, the multi air conditioner system is able
to replenish a large amount of refrigerant compared to
conventional individual air conditioners.
If a single unit of the multi air conditioner system is to be
installed in a
small room, select a suitable model and
installation procedure so that if the refrigerant
accidentally leaks out, its density does not reach the limit
(and in the event of an emergency, measures can be
made before injury can occur).
ASHRAE and the International Mechanical Code of the
ICC as well as CSA provide guidance and define
safeguards related to the use of refrigerants, all of which
define a Refrigerant Concentration Level (RCL) of
refrigerant.
For additional guidance and precautions related to
refrigerant safety, please refer to the following documents:
International Mechanical Code 2012 (IMC-2012)
(or more recently revised)
ASHRAE 15
ASHRAE 34
400 oz (11.3 kg) per 1,000 ft3 (28.3 m3) for R410A
Please Read Before Starting
This air conditioning system meets strict safety and
operating standards. As the installer or service person, it is
an important part of your job to install or service the
system so it operates safely and efficiently.
For safe installation and trouble-free operation, you
must:
● Carefully read this instruction booklet before beginning.
● Follow each installation or repair step exactly as shown.
● This air conditioner shall be installed in accordance with
National Wiring Regulations.
● Pay close attention to all warning and caution notices
given in this manual.
If Necessary, Get Help
These instructions are all you need for most installation
sites and maintenance conditions. If you require help for a
special problem, contact our sales/service outlet or your
certified dealer for additional instructions.
In Case of Improper Installation
The manufacturer shall in no way be responsible for
improper installation or maintenance service, including
failure to follow the instructions in this document.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS
•Do not supply power to the unit until all wiring and tubing
are completed or reconnected and checked.
• Highly dangerous electrical voltages are used in this system.
Carefully refer to the wiring diagram and these instructions
when wiring. Improper connections and inadequate
grounding can cause accidental injury or death.
•Ground the unit following local electrical codes.
•Connect all wiring tightly. Loose wiring may cause over-
heating at connection points and a possible fire hazard.
•To prevent possible hazards from insulation failure,
the unit must be grounded.
•This equipment is strongly recommended to be installed
with Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) or Residual
Current Device (RCD). Otherwise, it may cause electrical
shock and fire in case of equipment breakdown or
insulation breakdown.
WARNING
CAUTION
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK CAN CAUSE
SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
ONLY A QUALIFIED, EXPERIENCED
ELECTRICIAN SHOULD ATTEMPT TO
WIRE THIS SYSTEM.
This symbol refers to a hazard or
unsafe practice which can result
in severe personal injury or death.
This symbol refers to a hazard or
unsafe practice which can result
in personal injury or product or
property damage.
When Wiring
When Transporting
Be careful when picking up and moving the indoor and
outdoor units. Get a partner to help, and bend your knees
when lifting to reduce strain on your back. Sharp edges or
thin aluminum fins on the air conditioner can cut your
fingers.
When Installing…
Select an installation location which is rigid and strong
enough to support or hold the unit, and select a location for
easy maintenance.
…In a Room
Properly insulate any tubing run inside a room to prevent
“sweating” that can cause dripping and water damage to
walls and floors.
…In Moist or Uneven Locations
Use a raised concrete pad or concrete blocks to provide a
solid, level foundation for the outdoor unit. This prevents
water damage and abnormal vibration.
…In an Area with High Winds
Securely anchor the outdoor unit down with bolts and a
metal frame. Provide a suitable air baffle.
…In a Snowy Area (for Heat Pump-type Systems)
Install the outdoor unit on a raised platform that is higher
than drifting snow. Provide snow vents.
When Connecting Refrigerant Tubing
• Pay particular attention to refrigerant leakages.
•Ventilate the room immediately, in the event that is
refrigerant gas leaks during the installation. Be careful not
to allow contact of the refrigerant gas with a flame as this
will cause the generation of toxic gas.
•Keep all tubing runs as short as possible.
•Apply refrigerant lubricant to the matching surfaces of the
flare and union tubes before connecting them, then tighten
the nut with a torque wrench for a leak-free connection.
•Check carefully for leaks before starting the test run.
i
CAUTION
Keep the fire alarm and the air
outlet at least 5 ft. (1.5 m) away
from the unit.
WARNING
•When performing piping work, do not mix air
except for specified refrigerant (R410A) in
refrigeration cycle. It causes capacity down, and
risk of explosion and injury due to high tension
inside the refrigerant cycle.
•If the refrigerant comes in contact with a flame,
it produces a toxic gas.
•Do not add or replace refrigerant other than
specified type. It may cause product damage,
burst and injury, etc.
• Do not leak refrigerant while piping work for an
installation or re-installation, and while repairing
refrigeration parts.
Handle liquid refrigerant carefully as it may cause
frostbite.
When Servicing
• Turn the power OFF at the main power box (mains)
before opening the unit to check or repair electrical
parts and wiring.
• Keep your fingers and clothing away from any moving
parts.
• Clean up the site after you finish, remembering to
check that no metal scraps or bits of wiring have been
left inside the unit.
CAUTION
• Do not touch the air inlet or the sharp
aluminum fins of the outdoor unit. You
may get injured.
• Ventilate any enclosed areas when installing or
testing the refrigeration system. Leaked
refrigerant gas, on contact with fire or heat, can
produce dangerously toxic gas.
• Confirm after installation that no refrigerant gas
is leaking. If the gas comes in contact with a
burning stove, gas water heater, electric room
heater or other heat source, it can cause the
generation of toxic gas.
WARNING
• This product must not be modified or
disassembled under any circumstances.
Modified or disassembled unit may cause fire,
electric shock or injury.
• Do not clean inside the indoor and outdoor
units by users. Engage authorized dealer or
specialist for cleaning.
• In case of malfunction of this appliance, do
not repair by yourself. Contact to the sales
dealer or service dealer for a repair.
Check of Density Limit
The room in which the air conditioner is to be
installed requires a design that in the event of
refrigerant gas leaking out, its density will not exceed
a set limit.
The refrigerant (R410A), which is used in the air
conditioner, is safe, without the toxicity or combustibility of
ammonia, and is not restricted by laws imposed to protect
the ozone layer. However, since it contains more than air,
it poses the risk of suffocation if its density should rise
excessively. Suffocation from leakage of refrigerant is
almost non-existent. With the recent increase in the
number of high density buildings, however, the installation
of multi air conditioner systems is on the increase
because of the need for effective use of floor space,
individual control, energy conservation by curtailing heat
and carrying power, etc.
Most importantly, the multi air conditioner system is able
to replenish a large amount of refrigerant compared to
conventional individual air conditioners.
Others
CAUTION
• Do not sit or step on the unit, you may
fall down accidentally.
• Do not touch the air inlet or the sharp
aluminum fins of the outdoor unit.
You may get injured.
• Do not stick any object into the FAN
CASE.
You may be injured and the unit may
be damaged.
If a single unit of the multi air conditioner system is to be
installed in a
installation procedure so that if the refrigerant
accidentally leaks out, its density does not reach the limit
(and in the event of an emergency, measures can be
made before injury can occur).
ASHRAE and the International Mechanical Code of the
ICC as well as CSA provide guidance and define
safeguards related to the use of refrigerants, all of which
define a Refrigerant Concentration Level (RCL) of
400 oz (11.3 kg) per 1,000 ft3 (28.3 m3) for R410A
For additional guidance and precautions related to
refrigerant safety, please refer to the following documents:
International Mechanical Code 2012 (IMC-2012)
(or more recently revised)
ASHRAE 15
ASHRAE 34
small room, select a suitable model and
refrigerant.
ii
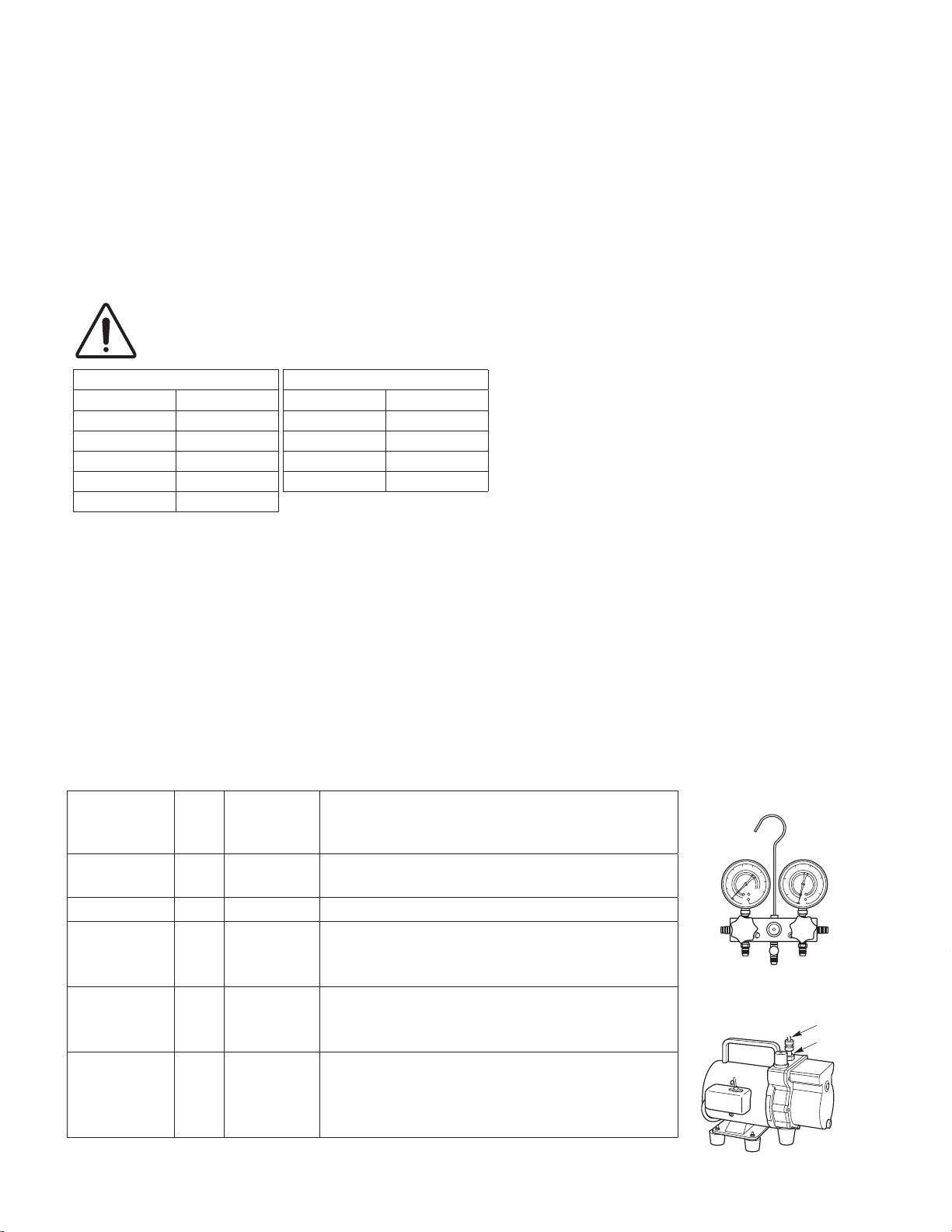
Precautions for Installation Using New Refrigerant
3-2. Use R410A exclusive cylinder only.
Single-outlet valve
(with siphon tube)
Liquid refrigerant should be recharged
with the cylinder standing on end as
shown.
New refrigerant R410A cannot be used for
earlier models
1. Compressor specifications are different.
If recharging a R22 or R407C compressor with
R410A, durability will significantly decrease since
some of the materials used for compressor parts are
different.
2. Existing tubing cannot be used (especially R22).
Completely cleaning out residual refrigerating
machine oil is impossible, even by flushing.
3. Refrigerating machine oil differs (R22).
Since R22 refrigerating machine oil is mineral oil, it
does not dissolve in R410A. Therefore, refrigerating
machine oil discharged from the compressor can
cause compressor damage.
R22 refrigerating machine oil Mineral oil (Suniso oil)
R407C refrigerating machine oil Synthetic fluid (ether oil)
R410A refrigerating machine oil Synthetic fluid (ether oil)
Valve
Liquid
1. Care regarding tubing
1-1. Process tubing
l
Material: Use clean, dry, free of oil, refrigeration grade, seamless, phosphorous deoxidized copper tube rated for
R410A only. Wall thickness shall comply with the applicable legislation. The minimal wall thickness must be in
accordance with the table below.
l
Tubing size: Be sure to use the sizes indicated in the table below.
l
Use a tube cutter when cutting the tubing, and be sure to remove any flash. This also applies to distribution joints
(optional).
l
When bending tubing, use a bending radius that is 4 times the outer diameter of the tubing or larger.
Use sufficient care in handling the tubing. Seal the tubing ends with caps or tape to
CAUTION
prevent dirt, moisture, or other foreign substances from entering.
These substances can result in system malfunction.
Outer diameter Wall thickness Outer diameter Wall thickness
5/8" (15.88) 0.040 (1.016) 1-5/8" (41.28) 0.060 (1.524)
3/4" (19.05) 0.042 (1.0668) Unit: in. (mm)
Material: O Material: O
1/4" (6.35) 0.025 (0.635) 7/8" (22.22) 0.045 (1.143)
3/8" (9.52) 0.030 (0.762) 1-1/8" (28.58) 0.050 (1.27)
1/2" (12.7) 0.035 (0.889) 1-3/8" (34.92) 0.055 (1.397)
1-2. Prevent impurities including water, dust and oxide from entering the tubing. Impurities can cause R410A
refrigerant deterioration and compressor defects. Due to the features of the refrigerant and refrigerating machine
oil, the prevention of water and other impurities becomes more important than ever.
2. Be sure to recharge the refrigerant only in liquid form.
2-1. Since R410A is a non-azeotrope, recharging the refrigerant in gas form can lower performance and cause defects
in the unit.
2-2. Since refrigerant composition changes and performance decreases when gas leaks, collect the remaining
refrigerant and recharge the required total amount of new refrigerant after fixing the leak.
3. Different tools required
3-1. Tool specifications have been changed due to the characteristics of R410A.
Some tools for R22- and R407C-type refrigerant systems cannot be used.
Item
Manifold gauge Yes No
Charge hose Yes No To resist higher pressure, material must be changed.
Vacuum pump Yes Yes
Leak detector Yes No
Flaring oil Yes No
* Using tools for R22 and R407C and new tools for R410A together can cause defects.
tools?
New
R407C tools
compatible
with R410A?
Remarks
Types of refrigerant, refrigerating machine oil, and
pressure gauge are different.
Use a conventional vacuum pump if it is equipped with
a check valve. If it has no check valve, purchase and
attach a vacuum pump adapter.
Leak detectors for CFC and HCFC that react to chlorine
do not function because R410A contains no chlorine.
Leak detector for HFC134a can be used for R410A.
For systems that use R22, apply mineral oil (Suniso
oil) to the flare nuts on the tubing to prevent refrigerant
leakage. For machines that use R407C or R410A, apply
synthetic oil (ether oil) to the flare nuts.
Manifold gauge
Vacuum pump
Outlet
Inlet
iii
3-2. Use R410A exclusive cylinder only.
New refrigerant R410A cannot be used for
earlier models
1. Compressor specifications are different.
If recharging a R22 or R407C compressor with
R410A, durability will significantly decrease since
some of the materials used for compressor parts are
different.
Valve
Single-outlet valve
(with siphon tube)
Liquid refrigerant should be recharged
with the cylinder standing on end as
shown.
Liquid
2. Existing tubing cannot be used (especially R22).
Completely cleaning out residual refrigerating
machine oil is impossible, even by flushing.
3. Refrigerating machine oil differs (R22).
Since R22 refrigerating machine oil is mineral oil, it
does not dissolve in R410A. Therefore, refrigerating
machine oil discharged from the compressor can
cause compressor damage.
R22 refrigerating machine oil Mineral oil (Suniso oil)
R407C refrigerating machine oil Synthetic fluid (ether oil)
R410A refrigerating machine oil Synthetic fluid (ether oil)
iv

—
CONTENTS
—
Section 1: CONTROL FUNCTIONS .......................................... 1-1
1. Introduction .............................................................1-2
2. Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation .......................................... 1-3
3. Compressor Control .......................................................1-5
4. Output of PCB ..........................................................1-12
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control .................................................. 1-18
6. Outdoor Unit CCU (command controller unit) Control ............................1-22
7. Oil Control .............................................................1-27
8. 4-Way Valve Adjustment Control ............................................1-30
9. Defrost Control ..........................................................1-31
10. Upper Current Limitation Mode (Demand control) ............................... 1-34
11. Backup Operation ....................................................... 1-36
12. Other Functions .........................................................1-40
13. Detailed Settings in EEPROM of Outdoor Unit .................................1-42
14. Outdoor Unit Control PCB .................................................1-44
Section 2: OUTDOOR UNIT REPAIR PROCEDURES ........................... 2-1
1. Removing Panels ......................................................... 2-2
2. Discharging Compressor Oil ................................................ 2-4
3. Backup Operation ........................................................ 2-7
4. Recovering Refrigerant .................................................... 2-9
5. Checking for Leakage After Repair .......................................... 2-14
6. Evacuating System ...................................................... 2-15
7. Charging Compressor Oil ................................................. 2-16
8. Pumping Out Refrigerant from Outdoot Unit ................................... 2-22
9. Compressor ........................................................... 2-26
10. Replacing Peripheral Parts of Fusible Plug .................................... 2-36
11. High and Low Pressure Sensors ............................................ 2-37
Section 3: OUTDOOR UNIT MAINTENANCE REMOTE CONTROLLER ............. 3-1
1. Overview ............................................................... 3-2
2. Functions ...............................................................3-3
3. Ordinary Display Controls and Functions ...................................... 3-4
4. Monitoring Operations .....................................................3-9
5. Outdoor Unit Alarm History Monitor .......................................... 3-11
6. Mode Settings ..........................................................3-12
Section 4: REMOTE CONTROLLER FUNCTIONS ............................. 4-1
1. Simple Settings Function ................................................... 4-2
2. Detailed Settings Function .................................................. 4-8
3. Remote Controller Servicing Functions ....................................... 4-28
v

Section 5: TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS .......................................... 5-1
1. Contents of Remote Controller Switch Alarm Display .............................5-2
2. Outdoor Unit Control Panel LED Display .......................................5-4
3. 2WAY Alarm Codes .......................................................5-5
4. Blinking Inspection Display on the Remote Controller ............................5-30
5. Inspection and Characteristics of Parts .......................................5-31
6. Test Pin ...............................................................5-35
7. Symptom: Thermostat in OFF continues or cycles OFF & ON too Frequently .........5-36
Section 6: TEST RUN .................................................... 6-1
1. Preparing for Test Run ..................................................... 6-2
2. Test Run Procedure ....................................................... 6-3
3. Main Outdoor Unit PCB Setting ..............................................6-4
4. Function Switches on P. C. Board ............................................6-7
5. Auto Address Setting ......................................................6-9
6. Setting Test Run Remote Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-17
7. Caution for Pump Down ................................................... 6-18
8. Self-Diagnosis Function Table and Contents of Alarm Display ..................... 6-18
vi

– MEMO –
vii

2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
Contents
Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1. 1-2
Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.
Compressor Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.
Output of PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.
Outdoor Unit Fan Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.
Outdoor Unit CCU (command controller unit) Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.
1. CONTROL FUNCTIONS
Control Functions
1-3
1-5
1-12
1-18
1-22
7. Oil Control
4-Way Valve Adjustment Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8.
Defrost Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9.
Upper Current Limitation Mode (Demand control) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10.
Backup Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11.
Other Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-27
1-30
1-31
1-34
1-36
1-40
1-4213. Detailed Settings in EEPROM of Outdoor Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-4414. Outdoor Unit Control PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
2
3
4
5
1 - 1
6
7
8
9
1
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
1. Introduction
2. Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation
Outdoor Unit Operating Rules
(1) Outdoor Unit Operating Rules
As a result of setting the main outdoor and sub outdoor units due to the O/U.ADD setting, the order of priority for
the outdoor units is determined in small values of O/U.ADD sequence. Because in this system all outdoor units
contain an inverter compressor, ordinarily there is no absolute order of priority for compressor operation.
(2) Delayed Start of Outdoor Units
1. Delayed start of outdoor unit in the same system
If it is necessary to operate the compressors simultaneously at multiple outdoor units, each outdoor unit will
start in order of unit No. every one second, beginning with unit No. 1.
*
Operation starts
Main outdoor unit Sub outdoor unit Sub outdoor unit
O/U.ADD = 1 O/U.ADD = 2 O/U.ADD = 3
Starts after 1 second Starts after 2 seconds Starts after 3 seconds
This is in order to reduce the load on the power supply equipment.
2. Delayed start for each system
When systems are linked with one communication cable and multiple systems are required to operate
simultaneously by the central control device, all main outdoor units will begin operating simultaneously.
In this situation, the load of the power supply equipment increases temporarily.
To prevent the overload, the start timing of each system can be delayed.
In order to enable this delay time, it must be set in the EEPROM for each system (Main outdoor unit).
Those systems (Main outdoor units) where this setting has been made will start after a delay according to
their system addresses.
To activate this delay start function, it is necessary to set it to EEPROM on main outdoor PCB.
EEPROM setting in main outdoor unit
CODE: 3E
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
Delay timeSetting No.
0
(factory preset mode)
No delay start for each system
1 (System address × 1 × 8) seconds delay
2 (System address × 2 × 8) seconds delay
3 (System address × 3 × 8) seconds delay
2
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
1. Introduction
1. Introduction
The ME2U series outdoor units for USA is a system that allows multiple outdoor units to be connected.
All the outdoor units do not utilize the sub units that were used in earlier systems.
The O/U.ADD of outdoor unit PCB where the unit is set to “1” becomes the main unit and activates
as the CCU (command controller unit) functions that controls the entire system.
PCB Setting of Outdoor Unit
In order to determine the outdoor unit to be the main or sub unit, it is necessary to make settings at each PCB.
Main outdoor unit
The outdoor unit where the O/U.ADD is set to “1” activates the CCU (command controller unit) functions that
controls the entire system. This outdoor unit is the main outdoor unit.
* For the main outdoor unit, perform all the settings in the table (PCB setting of outdoor unit) below.
Sub outdoor unit
The outdoor unit where the unit No. is set to other than “1” is a sub outdoor unit.
* The system will not operate if outdoor units have been set other than unit No. “1”.
PCB Setting of Outdoor Unit
Control Functions
3
4
5
6
7
Factory
O/U.ADD [SW5] 11Outdoor units address
R.C.ADD [SW1, SW2] 1 Not necessarySystem 1 ~ 30System address
NO.OF I/U [SW3, SW4] 1 Not necessarySystem 1 ~ 64 unitsNo. of indoor units
NO.OF O/U 1 Not necessarySystem 1 ~ 3 unitsNo. of outdoor units[SW6]
* This system can be exteded to connect a maximum of 3 outdoor units.
preset
mode
Main outdoor unit
On-site setting
Sub outdoor unit
On-site setting
Setting other than 1
(Duplication prohibited)
8
9
1 - 2
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2. Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2. Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation
Outdoor Unit Operating Rules
(1) Outdoor Unit Operating Rules
As a result of setting the main outdoor and sub outdoor units due to the O/U.ADD setting, the order of priority for
the outdoor units is determined in small values of O/U.ADD sequence. Because in this system all outdoor units
contain an inverter compressor, ordinarily there is no absolute order of priority for compressor operation.
(2) Delayed Start of Outdoor Units
1. Delayed start of outdoor unit in the same system
If it is necessary to operate the compressors simultaneously at multiple outdoor units, each outdoor unit will
start in order of unit No. every one second, beginning with unit No. 1.
*
This is in order to reduce the load on the power supply equipment.
Operation starts
Control Functions
1
2
Main outdoor unit Sub outdoor unit Sub outdoor unit
O/U.ADD = 1 O/U.ADD = 2 O/U.ADD = 3
Starts after 1 second Starts after 2 seconds Starts after 3 seconds
2. Delayed start for each system
When systems are linked with one communication cable and multiple systems are required to operate
simultaneously by the central control device, all main outdoor units will begin operating simultaneously.
In this situation, the load of the power supply equipment increases temporarily.
To prevent the overload, the start timing of each system can be delayed.
In order to enable this delay time, it must be set in the EEPROM for each system (Main outdoor unit).
Those systems (Main outdoor units) where this setting has been made will start after a delay according to
their system addresses.
To activate this delay start function, it is necessary to set it to EEPROM on main outdoor PCB.
EEPROM setting in main outdoor unit
CODE: 3E
Delay timeSetting No.
0
(factory preset mode)
No delay start for each system
3
4
5
6
7
1 (System address × 1 × 8) seconds delay
2 (System address × 2 × 8) seconds delay
3 (System address × 3 × 8) seconds delay
1 - 3
8
9
1
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2. Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation
3. Compressor Control
(1) Compressors Mounted in the Outdoor Units
(2) Compressor Selection Rules
Placement of compressor seen from the top
1. Priority order of compressors
A.
A
B
C
D
Decide first priority order of compressor in each outdoor unit.
B. Priority order of compressor trip counter = 0 is higher than that of compressor trip counter = 1.
C. Inverter compressor: Shorter operating time > Longer operating time
D. Compressor that “outdoor unit small address”
installed in outdoor unit
Compressor that “outdoor unit large address”
installed in outdoor unit
First priority order of inverter compressor in each outdoor unit > Other inverter compressor
Compressor trip counter =0 > Compressor trip counter =1
Shorter operating time > Longer operating time
“Outdoor unit small address”
installed in outdoor unit
“Outdoor unit large address”
installed in outdoor unit
>
>
*1
*1 Select first priority order of compressor in each outdoor unit by following method.
The compressor that has no trip counter, shorter operating time and smaller number of compressor will be
taken first priority.
First priority order of inverter compressor in each outdoor unit > Other inverter compressor
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
Type 72, 96 Type 120, 144
Front side
1st compressor
2nd compressor
1st compressor
Front side
Compressor trip counter =0 > Compressor trip counter =1
Shorter operating time > Longer operating time
1st compressor > 2nd compressor
Priority order flow of all compressors
Priority order flow of each outdoor unit
2. Selecting Outdoor Unit for Operation
(3) Outdoor Unit Stop Rules
1. Stopping of all outdoor units
When all outdoor units must stop, all units will stop in order of unit No. every one second.
2. Stopping of individual outdoor units
When it is necessary to reduce the number of operating compressors due to load reduction of indoor units,
the outdoor units will stop in order of priority for the compressors. All outdoor units stop when all compressors
installed in the outdoor units stop.
The outdoor unit which operates continuously until the end installs the highest priority order of compressor in it.
Cooling operation
There are two patterns of operation.
One is that the operation continues to run until the last one outdoor unit runs due to the detected outdoor
temperature and the other is that all outdoor units stop simultaneously.
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2
3
4
5
All outdoor units stop simultaneously in the operating range of all outdoor units.
Outdoor
temperature
118.4°F (48°C)
109.4°F (43°C)
59°F (15°C)
50°F (10°C)
The inverter compressor mounted in the outdoor unit which continues to run until the end is short operating
time. The priority order of this inverter compressor is higher than that of other outdoor unit.
Operating range in
all outdoor units
*1
Operating range in each
inverter compressor
*2
Operating range in
all outdoor units
When starting at 109.4°F (43°C) - 118.4°F (48°C),
*1
operation starts from all outdoor operating
ranges.
*2
When starting at 50°F (10°C) - 59°F (15°C),
operation starts from all outdoor operating
ranges.
6
7
8
9
Heating operation
Operation continues to run until the last outdoor unit remains in the operating mode.
1 - 4
3. Compressor Control
3. Compressor Control
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
(1) Compressors Mounted in the Outdoor Units
Placement of compressor seen from the top
Type 72, 96 Type 120, 144
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
1st compressor
2nd compressor
Front side
(2) Compressor Selection Rules
1. Priority order of compressors
A.
Decide first priority order of compressor in each outdoor unit.
The compressor that has no trip counter, shorter operating time and smaller number of compressor will be
taken first priority.
First priority order of inverter compressor in each outdoor unit > Other inverter compressor
B. Priority order of compressor trip counter = 0 is higher than that of compressor trip counter = 1.
C. Inverter compressor: Shorter operating time > Longer operating time
D. Compressor that “outdoor unit small address”
installed in outdoor unit
Priority order flow of all compressors
A
First priority order of inverter compressor in each outdoor unit > Other inverter compressor
Compressor that “outdoor unit large address”
>
installed in outdoor unit
Front side
1st compressor
1
2
3
*1
B
C
D
*1 Select first priority order of compressor in each outdoor unit by following method.
Compressor trip counter =0 > Compressor trip counter =1
Shorter operating time > Longer operating time
“Outdoor unit small address”
installed in outdoor unit
Priority order flow of each outdoor unit
Compressor trip counter =0 > Compressor trip counter =1
Shorter operating time > Longer operating time
1st compressor > 2nd compressor
“Outdoor unit large address”
>
installed in outdoor unit
4
5
6
7
8
1 - 5
9
1
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
3. Compressor Control
2
3
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
3. Compressor Control
2. Operating compressors
The compressor with higher priority order starts according to the priority orders described on previous page.
3. Stopping compressors
The compressor with lower priority order stops according to the priority orders described on previous page.
(3) Operation When Starting 2 Compressors Mounted in Outdoor Unit
When necessary capacity gradually increases and one more inverter compressor is additionally started under
the present operating compressor, reduce the compressor frequency to 25Hz temporarily and then start an additional
compressor.
The operation noted above is performed when 1st compressor or 2nd compressor is additionally started.
If necessary capacity is initially higher and two compressors are started simultaneously, the operation noted above
is not performed and both of them are regarded as the target frequency.
(4) Operating Frequency Range of Inverter Compressor
The inverter compressor can operate within the range in the table below.
1
When the high pressure is over 435psi (3.0MPa), the upper limit frequency is 90Hz.
If the high pressure is over 450psi (3.1MPa) and the minimum frequency operation is in progress, the system
2
is stopped. (P25: Pre-trip)
If the low pressure is over 213psi (1.47MPa) during operation of the inverter compressor, the system is stopped.
3
(P27: Pre-trip)
If 2 inverter compressors are simultaneously operating in the same outdoor unit, the frequency of 1st
4
compressor becomes 5Hz lower than that of the 2nd compressor.
Control Functions
4
5
6
7
8
Type of outdoor unit
Minimum frequency (Hz)
Maximum frequency (Hz) 80
The frequency range in the table above is subject to change without notice.*
(5) Forced Stopping of Compressor
Once a compressor stops, it will not start for a period of 3 minutes (3-minute forced OFF).
However, this does not apply when the compressor was forced to stop as the result of a special control operation.
(start control, defrost control, refrigerant oil recovery control, etc.)
72 96 120 144
15 15 15
100
15
80
80
9
1 - 6
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
3. Compressor Control
(6) Capacity Control (Roadmap control)
1 The capacity control by the compressors is performed according to the pressure sensor attached to the outdoor
unit and temperature thermistor attached to the indoor / outdoor unit heat exchanger.
* With roadmap control, the pressure detected by the pressure sensor is converted to saturation temperature
before it is used by microcomputer. This converted temperature is called “pressure sensor temperature”.
2 This control is performed every 30 seconds.
3 Required level of each indoor unit
Required level of indoor unit is calculated by difference between preset temperature in remote controller and
intake temperature of indoor unit (TA), difference between preset discharge air temperature in EEPROM on
indoor unit PCB and discharge air temperature of indoor unit (TF).
Required level has “0” to “30” phases. This level becomes “31” at the test run.
The target temperature of indoor unit heat exchanger is decided according to the maximum required level.
* Target temperature of all indoor units heat exchanger is same value because all indoor units are connected
with the same pressure piping.
4 Denition of evaporation temperature and condensation temperature
● Evaporation temperature (Te):
Shows the lowest temperature among the temperature sensors (E1 or E3) when the indoor unit heat exchanger
is functioning as an evaporator.
● Condensation temperature (Tc):
Shows the highest temperature among the high-pressure saturated temperature in the system.
Control Functions
1
2
6-1. Evaporation temperature adjustment by roadmap control
The cooling capacity is adjusted with this control. It prevents freezing of the indoor unit's heat exchanger and the
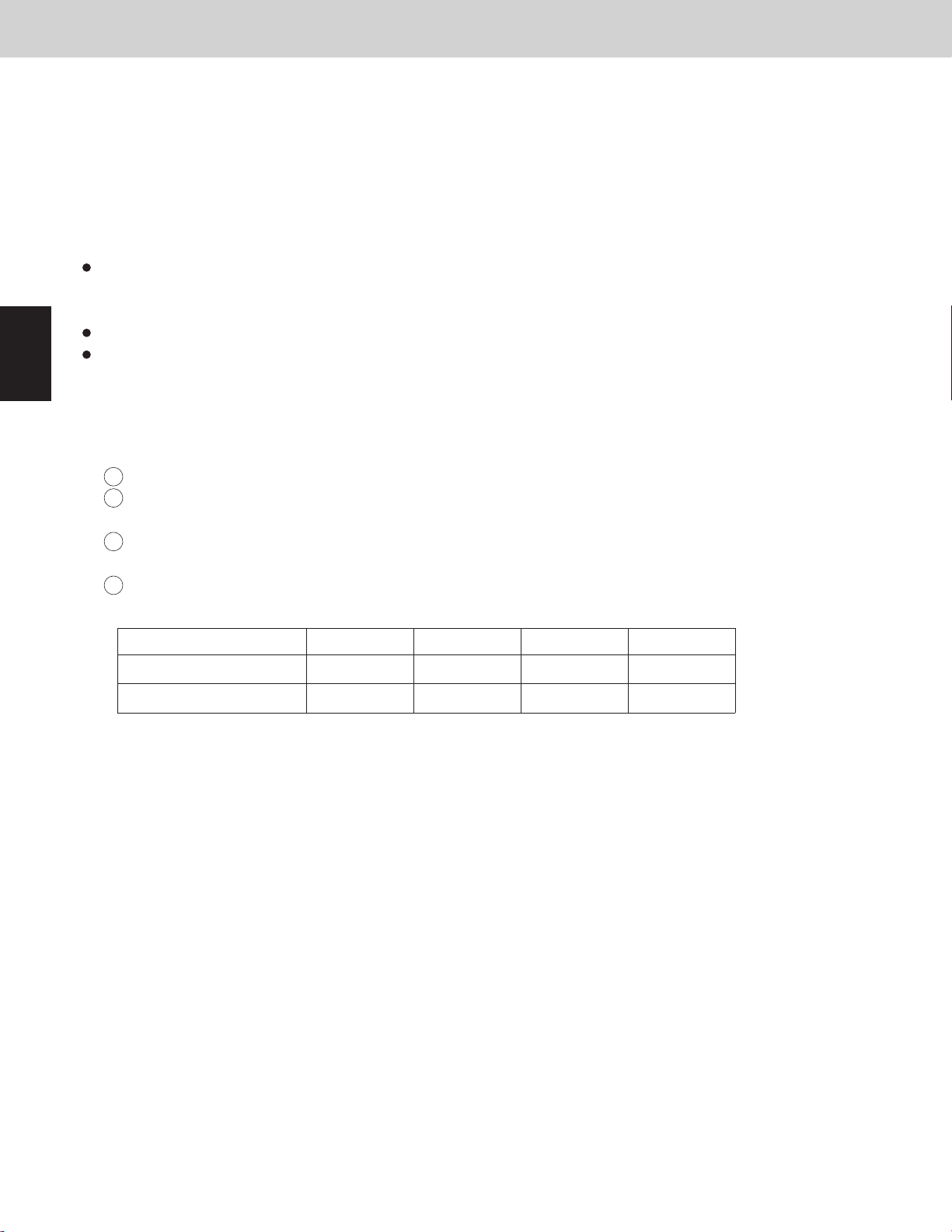
dew to the outside panel of the indoor unit. The capacity is adjusted according to the following gure.
Evaporation temperature area
deg
Compressor capacity increase possible
43.0 (6.1)
42.8 (6.0)
37.4 (3.0)
37.2 (2.9)
* The evaporation temperature area changes depending on the maximum required level of each indoor unit as
shown above.
* Area C is regarded as area B for 6 minutes after compressor starts.
* When the system operates in a minimum capacity, the system will continue operating for at least 6 minutes if the
evaporation temperature area is area C.
* The evaporation temperature is not adjusted while specially controlling defrosting and the oil recovery, etc.
* The evaporation temperature is not adjusted when there are one or more indoor units that select the test run.
If one or more indoor units are selected into test run, the system doesn't stop in all states except alarm appearing.
* The test run will nish automatically in about one hour.
Compressor capacity
increase prohibited
Compressor capacity decrease
60.8 (16.0)
55.4 (13.0)
Area A
Area B
Area C
46.4 (8.0)
0
Max. required level
15
51.8 (11.0)
unit: °F (°C)
42.8 (6.0)
37.4 (3.0)
30
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 - 7
9
1
2
3
4
3. Compressor Control
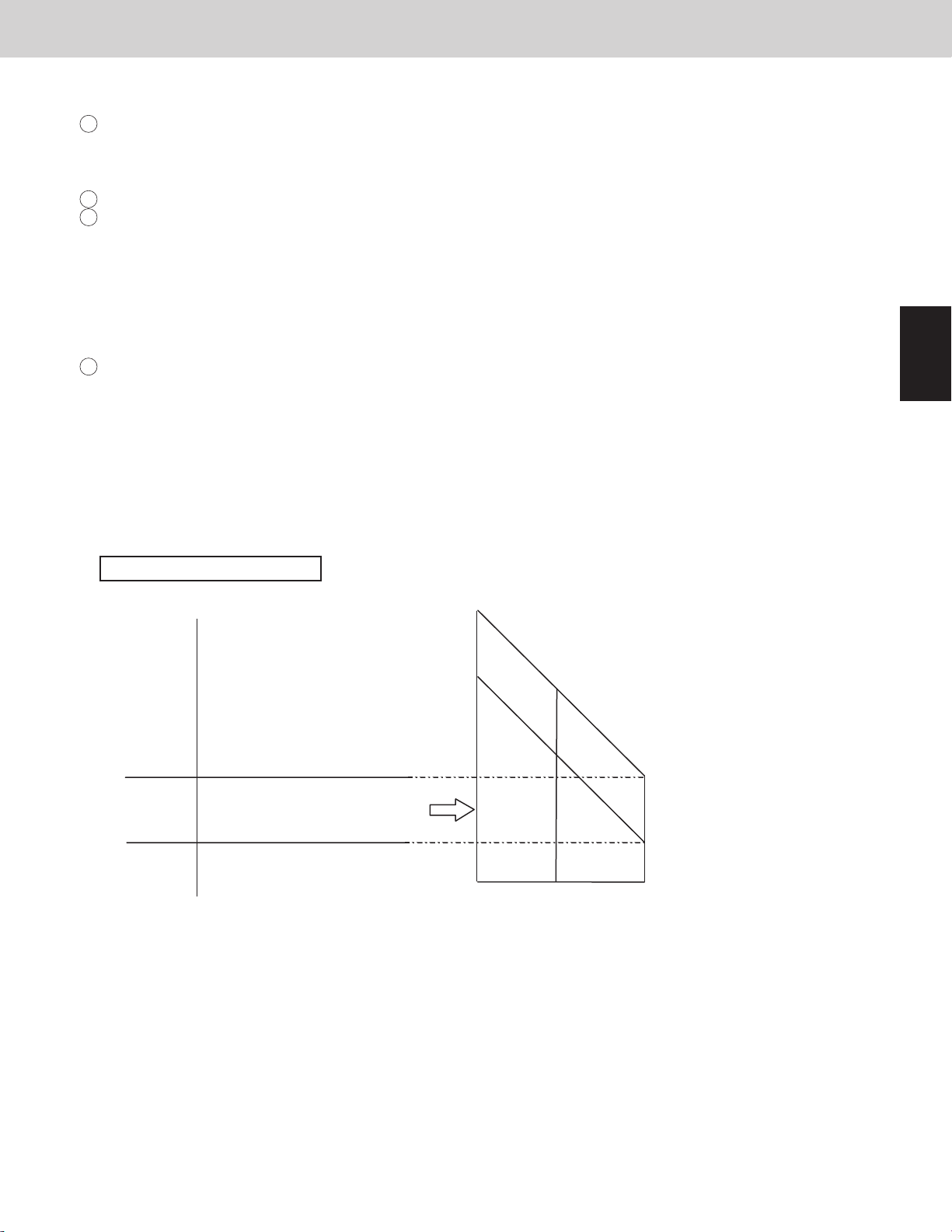
6-2. Condensation temperature adjustment by roadmap control
The area B target temperature is different due to cooling and heating operation.
Target lower temperature
Cooling 127.4°F (53.0°C) 131.0°F (55.0°C)
Heating 118.4°F (48.0°C) 123.8°F (51.0°C)
Cooling mode
1
The purpose of this control at cooling
is to prevent abnormal high-pressure.
・Standard setting (at the shipment)
°F (°C) °F (°C)
PX=136.4
(58.0)
136.2
(57.9)
131.2
(55.1)
131.0
(55.0)
127.4
(53.0)
127.2
(52.9)
Thermostat
OFF
Compressor
capacity
decrease
Compressor
capacity
increase
prohibited
Compressor
capacity
increase
possible
Area D
Area C
Area B
Area A
(Tc_tgt_min)
2
PX=136.4
Heating mode
Heating capacity is adjusted with this control.
It also prevents abnormal high-pressure simultaneously.
The capacity is controlled in the following diagram.
(58.0)
136.2
(57.9)
124.0
(51.1)
123.8
(51.0)
118.4
(48.0)
118.2
(47.9)
Target upper temperature
(Tc_tgt_max)
Thermostat
OFF
Compressor
capacity
decrease
Compressor
capacity
increase
prohibited
Compressor
capacity
increase
possible
Area D
Area C
Area B
Area A
95.0
(35.0)
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
°F (°C)
123.8
(51.0)
118.4
109.4
(43.0)
104.9
(40.5)
(48.0)
5
6
7
8
91.4
(33.0)
15 300
Max. required level
* PX is usually xed to 136.4°F (58°C). If the high pressure goes up rapidly after the compressor starts, the
system experiences urgent stop. The next time the system will start with lower PX.
* In the area B, the compressor capacity changes depending on the refrigerant condition.
* When the system operates in a minimum capacity, the system will continue operating for at least 6 minutes
if the condensation temperature area is area C.
* The condensation temperature is not adjusted when there are one or more indoor units that select the test run.
Limit pressure adjustment function
Operation pressure is able to be adjusted for existing old piping.
If area shift function is set, values below shift.
EEPROM setting in main outdoor unit
CODE : 4B
Setting No. Limited pressure PX °F (°C) Cooling mode Heating mode
Tc_tgt_min Tc_tgt_max Tc_tgt_min Tc_tgt_max
0 478.5psi (3.3MPa) 126.5 (52.5) 116.6 (47.0) 120.2 (49.0) 116.6 (47.0) 118.4 (48.0)
1 No use - - - - 2 551.1psi (3.8MPa) 136.4 (58.0) 127.4 (53.0) 131.0 (55.0) 118.4 (48.0) 123.8 (51.0)
3 No use - - - - -
9
1 - 8

2WAY VRF SYSTEM
3. Compressor Control
6-3. Protection Control
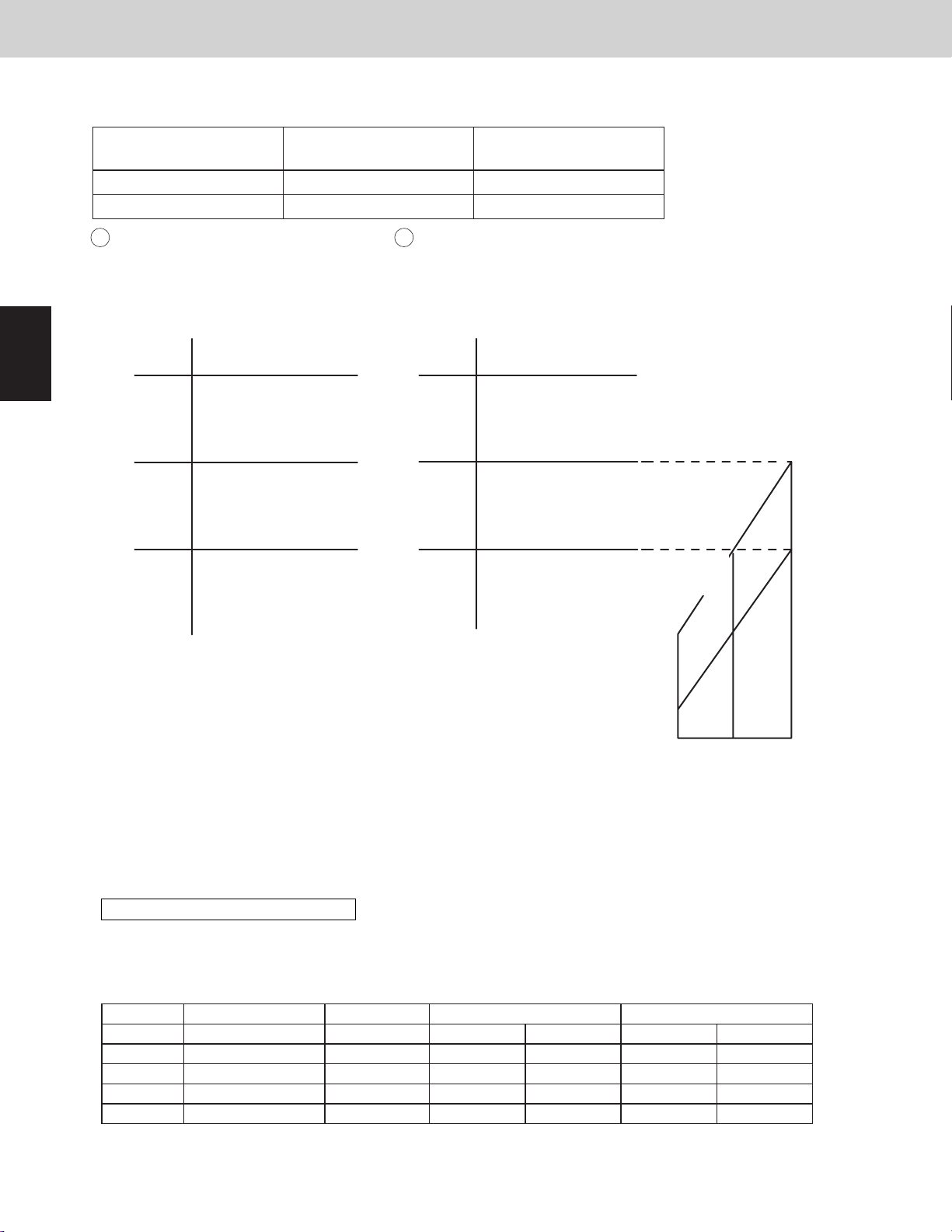
1
Compressor discharge temperature protection
The compressor capacity is controlled according to the table below.
*Discharge temperature that is used for this control is the highest temperature among all compressors.
Discharge temp.
°F (°C)
222.8
(106)
221.0 (105)
219.2 (104)
217.4 (103)
213.8 (101)
2
Abnormal low pressure protection
The compressor capacity is controlled according to the table below.
Low pressure
psi (MPa)
36.3 (0.25)
29.0 (0.20)
24.7 (0.17)
Stop
If this temperature is detected at regular intervals, alarm appears.
Compressor
capacity
decrease
Compressor capacity increase prohibited
Compressor capacity increase possible
No restriction
Capacity goes up slowly
Capacity increase prohibited
Capacity goes down
Capacity goes down 2.0 hp
Capacity goes down 1.0 hp
Capacity goes down 0.5 hp
Control Functions
hp = horsepower
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 - 9
9
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
3. Compressor Control
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
3. Compressor Control
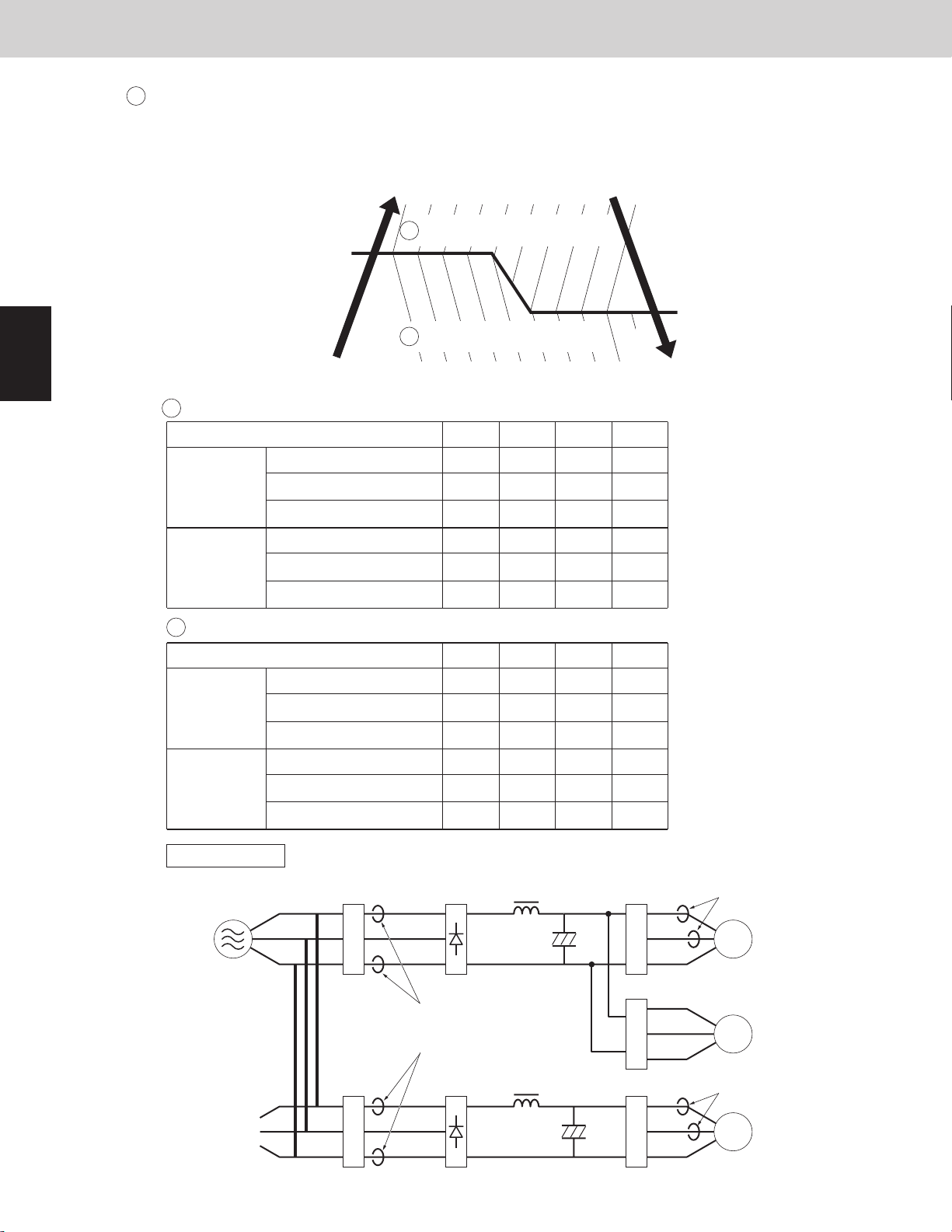
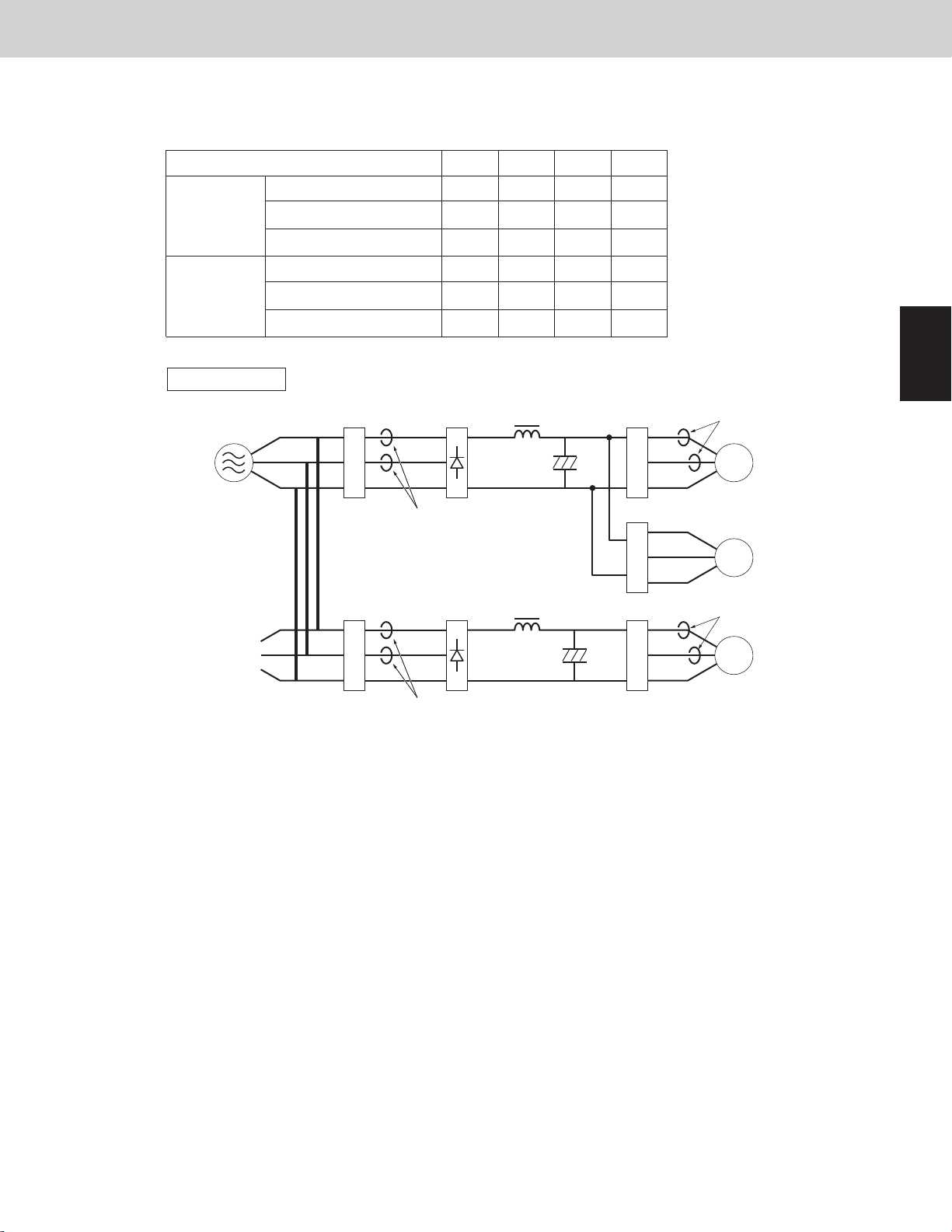
Inverter layout
Noise
filter
R
S
T
U
V
W
U
V
W
U
V
W
R
S
T
Power
supply
Primary CT1
Primary CT2
Secondary CT1
Secondary CT2
Diode
bridge
IPM (CM)
1st compressor
Fan motor
U-72ME2U94 / U-96ME2U94 / U-120ME2U94 / U-144ME2U94
Use the same values of 1st compressor and 2nd compressor.
unit: Ampere
Current limit 1
Maximum current 1 H
Primary
Maximum current 1 L 15.5
19.5 19.5 19.5 19.5
72 96 120 144
15.5
16.5
15.5
16.5 16.5 16.5
15.5
Current limit 2
Maximum current 2 H
Secondary
Maximum current 2 L 13.1
16.6 23.0 16.6 16.6
19.5
14.1
13.1
14.1 20.5 14.1
13.1
Type of outdoor unit
Noise
filter
Diode
bridge
IPM (CM)
IPM (FN)
2nd compressor
3. Compressor Control
3
Current protection
This restriction protects the compressor and controls the compressor electric current simultaneously.
The current limitation value changes to “normal status” and “overload status” according to the outdoor
temperature.
The primary and secondary current values of 1st compressor or 2nd compressor are measured.
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
1
2
3
4
Outdoor temperature
U-72ME2U9 / U-96ME2U9 / U-120ME2U9 / U-144ME2U9
A Normal status: Use the same values of 1st compressor and 2nd compressor.
Primary
Secondary
Overload status: Use the same values of 1st compressor and 2nd compressor.
B
114.8°F (46°C)
Type of outdoor unit
Type of outdoor unit
Current limit 1
Maximum current 1 H
Maximum current 1 L24
Current limit 2
Maximum current 2 H
Maximum current 2 L24
Current limit 1
B
A
Current table <Overload>
Current table <Normal>
72 96 120 144
30 43 30 30
25 38 22.5
30 44 30 30
25 40 25
72 96 120 144
30 43 30 30
37
39
22.5
21.5
25
24
21.5
24
Outdoor temperature
109.4°F (43°C)
unit: Ampere
unit: Ampere
5
6
7
8
Primary
Secondary
Inverter layout
Power
supply
R
S
T
Maximum current 1 H
Maximum current 1 L24
Current limit 2
Maximum current 2 H
Maximum current 2 L24
Noise
R
S
T
Noise
filter
Primary CT1
Primary CT2
filter
25 38 21
30 44 30 30
25 40 23
Diode
bridge
Diode
bridge
37
39
21
20
23
22
20
22
IPM (CM)
U
V
W
IPM (FN)
U
V
W
IPM (CM)
U
V
W
Secondary CT1
1st compressor
Fan motor
Secondary CT2
2nd compressor
9
1 - 10
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
3. Compressor Control
3. Compressor Control
U-72ME2U94 / U-96ME2U94 / U-120ME2U94 / U-144ME2U94
Use the same values of 1st compressor and 2nd compressor.
Type of outdoor unit
Current limit 1
72 96 120 144
19.5 19.5 19.5 19.5
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
unit: Ampere
Primary
Secondary
Inverter layout
Power
supply
R
S
T
Maximum current 1 H
Maximum current 1 L 15.5
Current limit 2
Maximum current 2 H
Maximum current 2 L 13.1
Noise
filter
R
S
T
Primary CT1
Noise
filter
16.5 16.5 16.5
16.6 23.0 16.6 16.6
14.1 20.5 14.1
Diode
bridge
Diode
bridge
15.5
19.5
16.5
15.5
14.1
13.1
15.5
13.1
IPM (CM)
U
V
W
IPM (FN)
U
V
W
IPM (CM)
U
V
W
Secondary CT1
1st compressor
Fan motor
Secondary CT2
2nd compressor
1
2
3
4
Primary CT2
5
6
7
8
1 - 11
9

1
4. Special Control
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
4. Special Control
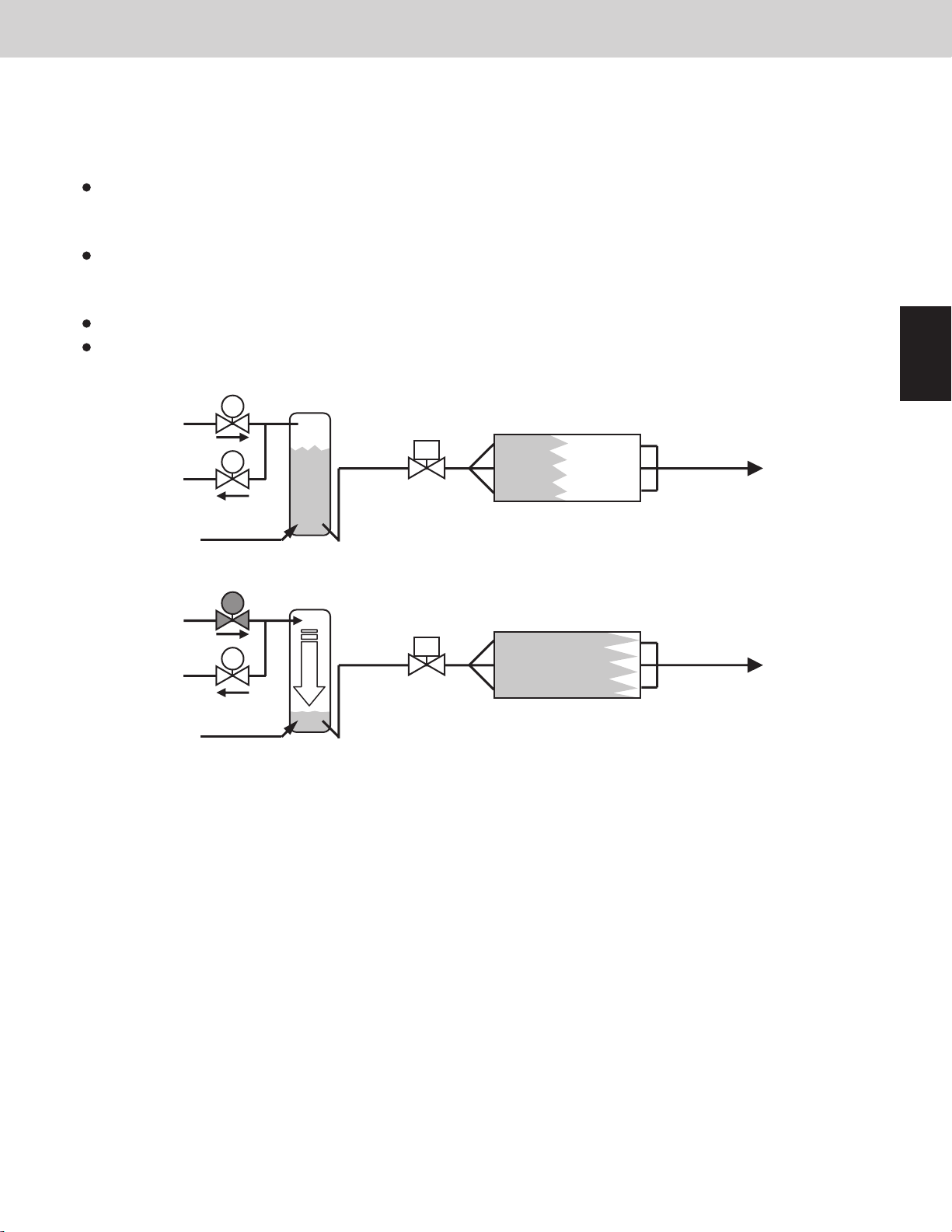
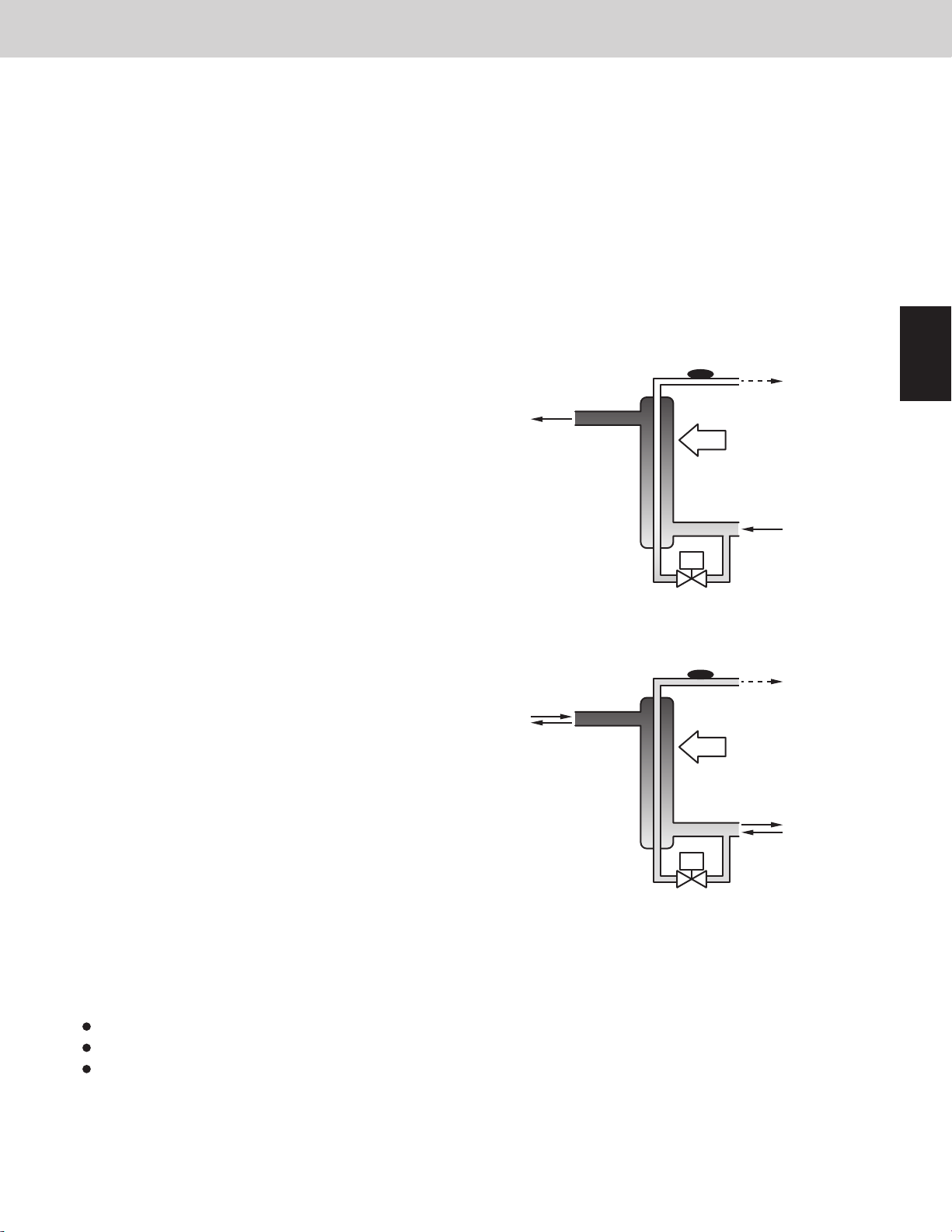
(3) Refrigerant Control Valve [RCV]
The main purpose of this valve is to adjust the flow of refrigerant (refrigerant volume).
When the outdoor unit receives a sign of refrigerant shortage, the valve opens and refrigerant is supplied from the
receiver tank to the system.
This valve turns ON when the evaporator is refrigerant shortage.
The heat exchanger of indoor unit is the evaporator in cooling mode.
The heat exchanger of outdoor unit is the evaporator in heating mode.
This valve turns OFF when the excessive amount of refrigerant is in the condenser.
The heat exchanger of indoor unit is the condenser in heating operation.
The heat exchanger of outdoor unit is the condenser in cooling operation.
This valve turns OFF when the outdoor unit is stopped.
This valve might turn ON when a special control is in progress.
Evaporator
RBV
RCV
LP
HP
Refrigerant shortage in evaporator.
Receiver tank holds refrigerant.
Two-phase
flow
Evaporator
RBV
RCV
LP
HP
Sufficient refrigerant is supplied to evaporator.
High pressure from RCV pushes the liquid refrigerant out of the receiver tank.
ON
Two-phase flow
2
3
4
5
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
4. Output of PCB
Control Functions
Solenoid valve
Expansion valve
Crankcase heater
(1) 4-way Valve [20S]
This valve turns OFF at cooling mode, and turns ON at heating mode.
This valve turns OFF at defrosting control.
* When the outdoor unit stops, the 4-way valve maintains in the same state as before.
(2) SAVE Valve [SAVE]
● This valve turns ON for 5 seconds before the inverter compressor starts.
After the inverter compressor starts, the valve turns ON for 10 seconds. Then it turns OFF.
● This valve turns ON for 30 seconds after the outdoor unit stops. Then it turns OFF.
● This valve turns ON when high pressure sensor detects 496psi (3.42MPa) to prevent abnormal pressure.
This valve turns OFF when the high pressure goes down below 481.5psi (3.32MPa).
● This valve might turn ON when the system capacity is excessive although the inverter compressor operates at
Min. frequency.
● This valve turns ON in the following status :
(Compressor discharge temperature - High pressure saturation temperature) < 9deg F (5deg C)
● Under control of 4-way valve adjustment control
● This valve turns ON when low pressure sensor goes down 24.7psi (0.17MPa) to prevent abnormal pressure.
This valve turns OFF when low pressure sensor increase 29psi (0.20MPa) or over.
Items Remarks Indication on PCB
20S
SAVE
RCV
RBV
ORVR
BPV
ACV
O
2
MOV1
MOV2
MOV4
CH1
CH2
4-way valve
Save valve
Refrigerant control valve
Refrigerant balance valve
Oil recovery valve
By-pass valve
Accumulator valve
O
2 valve
MOV for heat exchanger 1
MOV for heat exchanger 2
SC circuit expansion valve
Crankcase heater for 1st compressor
Crankcase heater for 2nd compressor
6
7
8
9
1 - 12
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
4. Special Control
4. Output of PCB
(3) Refrigerant Control Valve [RCV]
The main purpose of this valve is to adjust the flow of refrigerant (refrigerant volume).
When the outdoor unit receives a sign of refrigerant shortage, the valve opens and refrigerant is supplied from the
receiver tank to the system.
This valve turns ON when the evaporator is refrigerant shortage.
The heat exchanger of indoor unit is the evaporator in cooling mode.
The heat exchanger of outdoor unit is the evaporator in heating mode.
This valve turns OFF when the excessive amount of refrigerant is in the condenser.
The heat exchanger of indoor unit is the condenser in heating operation.
The heat exchanger of outdoor unit is the condenser in cooling operation.
This valve turns OFF when the outdoor unit is stopped.
This valve might turn ON when a special control is in progress.
RCV
HP
Evaporator
Control Functions
1
LP
HP
LP
RBV
RCV
RBV
Two-phase
flow
Refrigerant shortage in evaporator.
Receiver tank holds refrigerant.
ON
Evaporator
Two-phase flow
Sufficient refrigerant is supplied to evaporator.
High pressure from RCV pushes the liquid refrigerant out of the receiver tank.
2
3
4
5
6
1 - 13
7
8
9
1
4. Special Control
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
4. Special Control
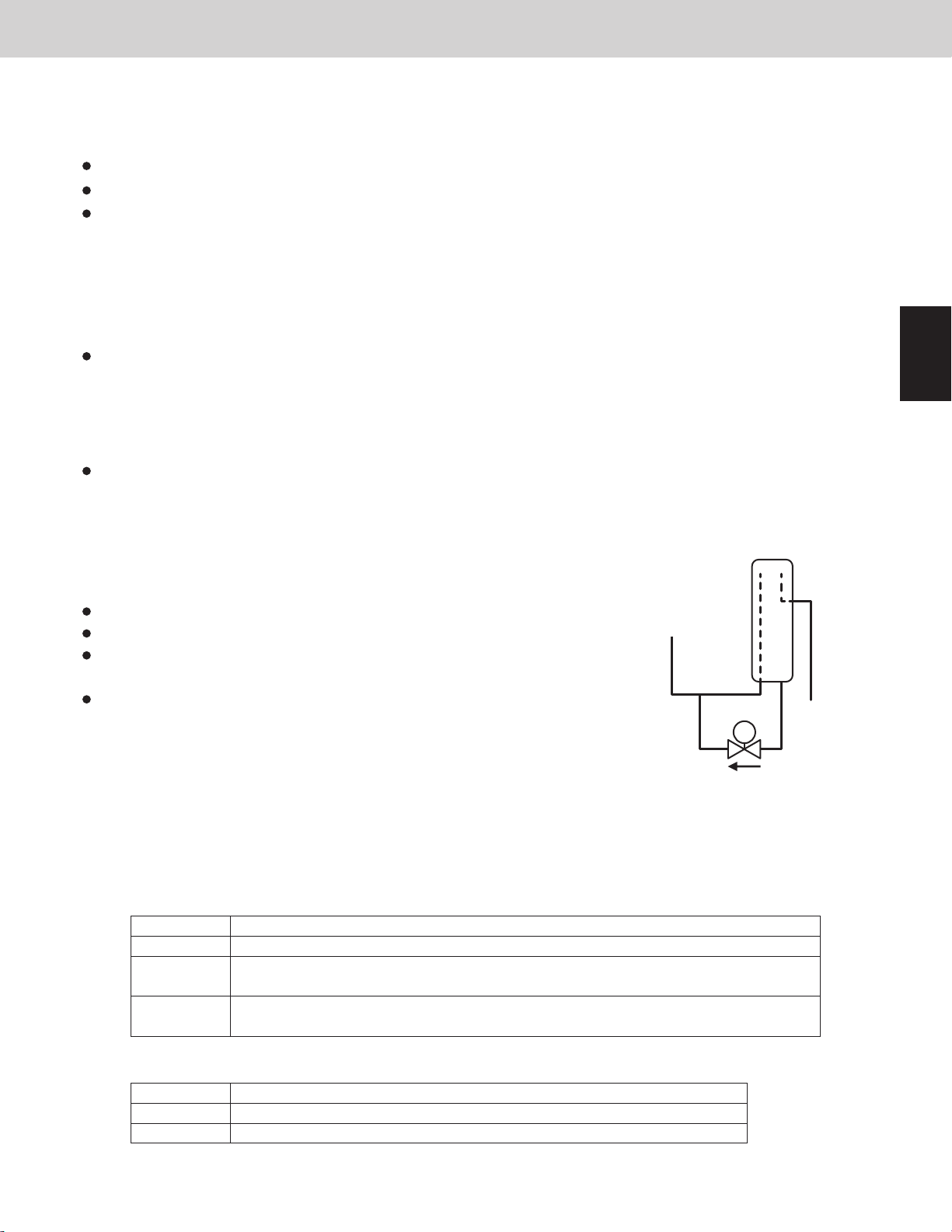
(5) Oil Recovery Valve [ORVR]
The purpose of this valve is to recover oil from the oil separator of its own outdoor unit or balance tube to the
compressor.
This valve turns ON when the oil level of the compressor is “0” or “1”.
This valve turns ON for 2 minutes after the compressor starts.
This valve is always OFF when outdoor unit is stopped.
* For oil level of compressor, see “7. Oil Control”.
This valve turns ON when recovering refrigerant from the stopped outdoor unit.
(6) By-pass Valve [BPV]
This valve is for pushing the oil in the balance piping into other outdoor units.
When the compressor oil level of its own outdoor unit is in the “2” or “1”, this valve turns ON when the oil level “0”
is detected in other outdoor units.
When the compressor itself is stopped with a full of refrigerant, this valve turns ON.
Then the refrigerant is supplied to the other operating outdoor units.
* This valve turns ON for 10 seconds and turns OFF for 20 seconds.
This operation is repeated while oil is supplied to others.
* For more information on oil level of compressor, see “7. Oil Control”.
(7) Accumulator Valve [ACV]
The purpose of this valve is to recover oil and refrigerant from the accumulator
to the compressor.
This valve turns OFF when the compressor operation just started.
This valve turns ON when the compressor is warmed up.
This valve turns ON while the oil recovery among the systems and defrost
control are in progress.
This valve turns ON while the MOV4 is operating.
(8) O2 Valve [O2*]
ACV
Accumulator
This valve works when the outdoor unit receives signal of the refrigerant leakage from the indoor unit.
*O
2
valve is the field supply parts.
The indoor unit that transmits the signal of the refrigerant leakage gives “P14”alarm.
To activate this function, it is necessary to set it to EEPROM on the main outdoor PCB and indoor PCB.
EEPROM setting in main outdoor unit
CODE: C1
Setting No
Setting No
0
0
1
1
2
This function invalid (factory preset mode)
This valve is turned OFF when the system is normal.
This valve is turned ON when the outdoor unit receives signal from the indoor unit
This valve is turned ON when the system is normal.
This valve is turned OFF when the outdoor unit receives signal from the indoor unit
EEPROM setting in indoor unit
CODE: 0B
Function of EXCT plug short-circuit
Indoor unit does thermostat OFF
(factory preset mode)
Indoor unit gives “P14”alarm and transmits the refrigerant leakage signal.
2
3
4
5
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
4. Output of PCB
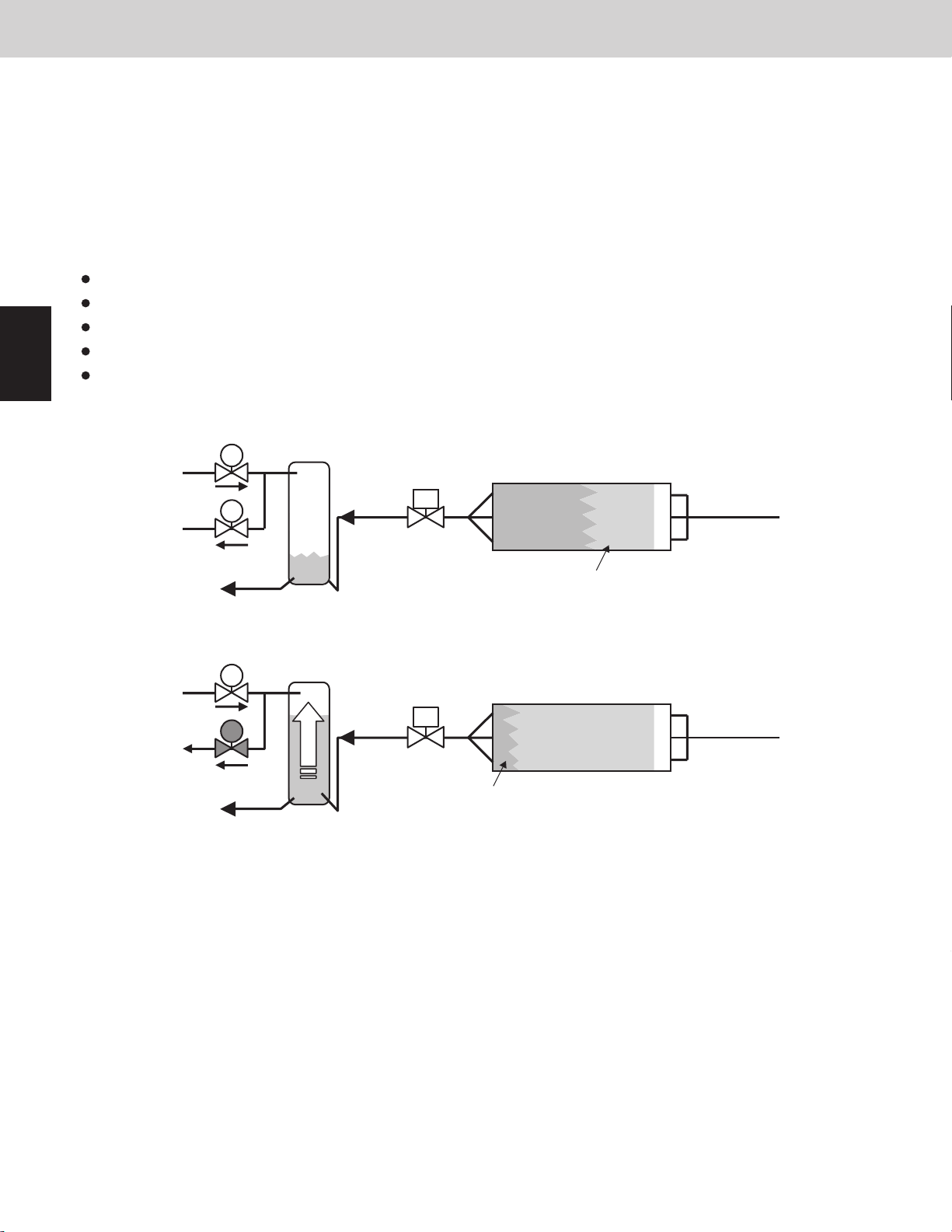
(4) Refrigerant Balance Valve [RBV]
The main purpose of this valve is to adjust the flow of refrigerant (refrigerant volume) in the evaporator.
When the outdoor unit receives a sign of overcharged refrigerant, the valve opens and refrigerant is recovered at the
receiver tank.
This valve also turns ON in order to recover refrigerant at the outdoor unit after heating operation is stopped.
* It is possible to set the RBV to valid or invalid by the outdoor unit EEPROM settings.
Initial setting is invalid.
* This valve is never turned ON with the RCV at the same time.
This valve turns ON for 20 seconds after heating operation is stopped, and then turns OFF.
This valve turns OFF when an abnormal drop in compressor discharge gas temperature is detected.
This valve turns OFF when an abnormal drop in compressor suction gas temperature is detected.
After the valve turns from ON to OFF, it will not turn ON again for 15 minutes.
This valve turns ON when low pressure sensor decreases 24.7psi (0.17MPa) at stopped system.
This valve turns OFF when low pressure sensor increases 29psi (0.20MPa).
RCV
HP
RBV
LP
Receiver tank holds a low refrigerant volume.
RCV
HP
RBV
LP
ON
Condenser
Liquid flow
Two-phase flow
Over charge condition
Condenser
Two-phase flow
Liquid flow
Control Functions
6
7
8
9
Appropriate condition
Refrigerant gas in the top of receiver tank is absorbed into low pressure side.
1 - 14
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
4. Special Control
4. Output of PCB
Control Functions
(5) Oil Recovery Valve [ORVR]
The purpose of this valve is to recover oil from the oil separator of its own outdoor unit or balance tube to the
compressor.
This valve turns ON when the oil level of the compressor is “0” or “1”.
This valve turns ON for 2 minutes after the compressor starts.
This valve is always OFF when outdoor unit is stopped.
* For oil level of compressor, see “7. Oil Control”.
This valve turns ON when recovering refrigerant from the stopped outdoor unit.
(6) By-pass Valve [BPV]
This valve is for pushing the oil in the balance piping into other outdoor units.
When the compressor oil level of its own outdoor unit is in the “2” or “1”, this valve turns ON when the oil level “0”
is detected in other outdoor units.
* This valve turns ON for 10 seconds and turns OFF for 20 seconds.
This operation is repeated while oil is supplied to others.
* For more information on oil level of compressor, see “7. Oil Control”.
When the compressor itself is stopped with a full of refrigerant, this valve turns ON.
Then the refrigerant is supplied to the other operating outdoor units.
1
2
(7) Accumulator Valve [ACV]
The purpose of this valve is to recover oil and refrigerant from the accumulator
to the compressor.
This valve turns OFF when the compressor operation just started.
This valve turns ON when the compressor is warmed up.
This valve turns ON while the oil recovery among the systems and defrost
control are in progress.
This valve turns ON while the MOV4 is operating.
(8) O2 Valve [O2*]
This valve works when the outdoor unit receives signal of the refrigerant leakage from the indoor unit.
The indoor unit that transmits the signal of the refrigerant leakage gives “P14”alarm.
To activate this function, it is necessary to set it to EEPROM on the main outdoor PCB and indoor PCB.
EEPROM setting in main outdoor unit
CODE: C1
Setting No
0
1
2
EEPROM setting in indoor unit
CODE: 0B
Setting No
0
1
This function invalid (factory preset mode)
This valve is turned OFF when the system is normal.
This valve is turned ON when the outdoor unit receives signal from the indoor unit
This valve is turned ON when the system is normal.
This valve is turned OFF when the outdoor unit receives signal from the indoor unit
Function of EXCT plug short-circuit
Indoor unit does thermostat OFF
Indoor unit gives “P14”alarm and transmits the refrigerant leakage signal.
valve is the field supply parts.
*O
2
(factory preset mode)
Accumulator
ACV
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 - 15
9

1
4. Special Control
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
4. Special Control
(10) SC Circuit Expansion Valve [MOV4]
During cooling operation, the liquid refrigerant which condenses at the outdoor unit heat exchanger flows into
the receiver tank, and SC (sub-cooling) approaches 32°F (0°C).
When SC is small and the length of the tubing connecting the indoor and outdoor units is long, the refrigerant
flow in the indoor unit will be reduced significantly.
To prevent this trouble from occurring, MOV4 operates so as to increase super-cooling in the double tube coil.
10-1.
(11) Crankcase Heater Control [CH1, CH2]
When the compressor stops, the crankcase heater of its own compressor is turned ON in the following conditions.
Cooling SC Control
During heating operation, MOV4 operates so as to
improve the refrigerant flow of the outdoor unit heat
exchanger and the system.
MOV4 controls refrigerant flow volume so that it will
not flow back to the compressor in the liquid state.
MOV4 controls the difference of temperature
between the SCG thermistor and low pressure
saturated temperature to 5.4deg F (3deg C).
10-2. Heating SC Control
When the discharge temperature increases to
194°F (90°C) or more, MOV 4 opens to 100 pulses
to cool down the compressor.
Then, the MOV 4 operates according to the state of
the discharge temperature between 20 ~ 480 pulses.
This operation takes priority over SC control.
This operation is continued until discharge
temperature decreases to 176°F (80°C) or less.
10-3. Discharge Temperature Control of Compressor
MOV4 controls the difference of temperature between the SCG thermistor and low pressure saturated temperature
to 5.4deg F ~ 9deg F (3deg C ~ 5deg C).
Thermistor (SCG)
MOV4 (SH control)
Gas refrigerant
returns to accumulator.
Liquid refrigerant
Refrigerant on the inner side
evaporates, cooling the liquid
refrigerant on the outer side.
Liquid refrigerant
Thermistor (SCG)
MOV4 (Discharge temperature control of compressor)
Liquid refrigerant
returns to accumulator.
Liquid refrigerant
Does not fully evaporate,
resulting in liquid back-up.
Liquid refrigerant
When the discharge temperature ≤ the outdoor air temperature + 27deg F (+15deg C)
When the outdoor air temperature ≤ 68°F (20°C)
When the compressor stops and 30 minutes later.
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
4. Output of PCB
(9) MOV for Heat Exchanger [MOV1, MOV2]
9-1. Type of expansion valves
MOV1 : For upper side heat exchanger
MOV2 : For lower side heat exchanger
9-2. Power Initialization
If no indoor units have started (even once) after the power supply to the outdoor unit, the MOV holds the 480
pulses (fully open).
*When the indoor unit receives the signal for operation request from the control equipment, the pulse turns
other than the 480 pulses (regardless of the thermostat ON/OFF or operating ON/OFF).
It is necessary to switch ON the power supply again if the 480 pulses are required.
9-3. Control of expansion valves
Expansion valves for heat exchanger control according to the operation mode.
Control Functions
2
3
4
5
6
Stop
0
0
Cooling HeatingMode of system
Operation
480
480
Stop
0
0
Operation
0 ~ 480
0 ~ 480
Compressor
MOV1 (pulse)
MOV2 (pulse)
* If any one compressor in the outdoor unit is operating at heating mode, expansion valves perform SH
control.
SH control adjusts the difference of temperature between the liquid and gas temperature to
-1.8deg F ~ 9deg F (-1deg C ~ 5deg C).
Stop
Stop
0
0
7
8
9
1 - 16
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
4. Special Control
4. Output of PCB
Control Functions
(10) SC Circuit Expansion Valve [MOV4]
10-1.
Cooling SC Control
During cooling operation, the liquid refrigerant which condenses at the outdoor unit heat exchanger flows into
the receiver tank, and SC (sub-cooling) approaches 32°F (0°C).
When SC is small and the length of the tubing connecting the indoor and outdoor units is long, the refrigerant
flow in the indoor unit will be reduced significantly.
To prevent this trouble from occurring, MOV4 operates so as to increase super-cooling in the double tube coil.
MOV4 controls the difference of temperature between the SCG thermistor and low pressure saturated temperature
to 5.4deg F ~ 9deg F (3deg C ~ 5deg C).
10-2. Heating SC Control
During heating operation, MOV4 operates so as to
improve the refrigerant flow of the outdoor unit heat
exchanger and the system.
MOV4 controls refrigerant flow volume so that it will
not flow back to the compressor in the liquid state.
MOV4 controls the difference of temperature
between the SCG thermistor and low pressure
saturated temperature to 5.4deg F (3deg C).
10-3. Discharge Temperature Control of Compressor
When the discharge temperature increases to
194°F (90°C) or more, MOV 4 opens to 100 pulses
to cool down the compressor.
Then, the MOV 4 operates according to the state of
the discharge temperature between 20 ~ 480 pulses.
This operation takes priority over SC control.
This operation is continued until discharge
temperature decreases to 176°F (80°C) or less.
Liquid refrigerant
Liquid refrigerant
Thermistor (SCG)
Refrigerant on the inner side
evaporates, cooling the liquid
refrigerant on the outer side.
MOV4 (SH control)
Thermistor (SCG)
Does not fully evaporate,
resulting in liquid back-up.
1
Gas refrigerant
returns to accumulator.
2
Liquid refrigerant
3
4
Liquid refrigerant
returns to accumulator.
5
Liquid refrigerant
MOV4 (Discharge temperature control of compressor)
(11) Crankcase Heater Control [CH1, CH2]
When the compressor stops, the crankcase heater of its own compressor is turned ON in the following conditions.
When the discharge temperature ≤ the outdoor air temperature + 27deg F (+15deg C)
When the outdoor air temperature ≤ 68°F (20°C)
When the compressor stops and 30 minutes later.
1 - 17
6
7
8
9
1
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
Independent control of outdoor unit
This control is intended to prevent snow from accumulating on stopped fans.
The fan motor rotates at 500rpm in the below conditions even if the outdoor unit stops.
(1)
Control with snow detection sensor (field supply)
If a snow detection sensor (field supply) is available and this function is set in validity, the fan motor of the outdoor
unit rotates at 600 rpm when the snow detection sensor detects snow.
The judgment of this control performs at 10 minutes interval.
One snow detection sensor can control all outdoor units on the communications wiring.
The snow detection sensor is only possible to connect to the main outdoor unit (unit No.1) and it can control all
outdoor units in communication wiring.
(2)
Fan motor operates for 45 seconds and stops for 2 hours when ambient temperature is 41.18°F (5.1°C) or
more.
Fan motor operates for 45 seconds and stops for 1.5 hours when ambient temperature is 32.2 - 41.0°F
(0.1 - 5.0°C).
Fan motor operates for 45 seconds and stops for 1 hour when ambient temperature is 32.0°F (0.0°C) or less.
EEPROM setting in each main outdoor unit
* All outdoor units are connected with same communication wiring.
To activate this function, it is necessary to set it to the EEPROM on each system’s main outdoor unit PCB.
CODE: 04
System address 1
Snow detection sensor installed
Unit No.1
Unit No.1
Unit No.1
Unit No.2
Unit No.2
Unit No.2
Unit No.3
Unit No.3
Unit No.3
System address 2 System address 3
Function
No snow detection sensor is connected but control is available. (at factory shipment)
Snow detection sensor is connected and control is available.
Setting No.
0
1
No snow detection sensor is connected and control is not available.2
Snow detection sensor is connected but control is not available.3
Setting No.
Fan motor
status during
snowfall
100000222
ON ON ON ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF
1-2. Snow removal control
2
3
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
Control Functions
(1) Fan Mode
These outdoor units utilize a DC fan motor that can be controlled in a maximum of 15 steps (15 modes).
However, fan modes 14 and 15 can only be used if high static pressure mode has been set.
* For information concerning EEPROM settings, refer to the eld application functions.
The following table shows the maximum and minimum fan mode and fan forced mode for each unit.
Maximum value
Minimum value * 1 1 1 1
* For the sake of protecting temperature of the electrical parts, the minimum values of the fan mode may
sometimes increase in accordance with the ambient temperature or the amount of secondary current.
1-1. High static pressure mode
The outdoor unit allows a high static pressure changing the settings.
The maximum permissible static pressure is 0.01psi (80Pa).
Standard
High static
pressure mode
setting
Status of
heat exchanger
Condenser 13 13 12 12
Ambient
Evaporator
Condenser 15 15 12 12
Evaporator
temperature
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
temperature
>
≤
>
≤
50°F
(10°C)
50°F
(10°C)
50°F
(10°C)
50°F
(10°C)
72 96 120 144
13 13 12 12
13 13 13 13
15 15 12 12
15 15 13 13
Type of outdoor unit
4
5
6
7
8
EEPROM setting in each outdoor unit
CODE : 8F
However, maximum fan mode is upper limit.
Setting No.
0 Invalid (factory preset mode)
1 High static pressure mode
2 Never use
3 Never use
4 Never use
5 Never use
6 Never use
9
1 - 18

2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
Control Functions
1-2. Snow removal control
Independent control of outdoor unit
(1)
This control is intended to prevent snow from accumulating on stopped fans.
The fan motor rotates at 500rpm in the below conditions even if the outdoor unit stops.
Fan motor operates for 45 seconds and stops for 2 hours when ambient temperature is 41.18°F (5.1°C) or
more.
Fan motor operates for 45 seconds and stops for 1.5 hours when ambient temperature is 32.2 - 41.0°F
(0.1 - 5.0°C).
Fan motor operates for 45 seconds and stops for 1 hour when ambient temperature is 32.0°F (0.0°C) or less.
Control with snow detection sensor (field supply)
(2)
If a snow detection sensor (field supply) is available and this function is set in validity, the fan motor of the outdoor
unit rotates at 600 rpm when the snow detection sensor detects snow.
The judgment of this control performs at 10 minutes interval.
One snow detection sensor can control all outdoor units on the communications wiring.
The snow detection sensor is only possible to connect to the main outdoor unit (unit No.1) and it can control all
outdoor units in communication wiring.
1
2
To activate this function, it is necessary to set it to the EEPROM on each system’s main outdoor unit PCB.
EEPROM setting in each main outdoor unit
CODE: 04
Setting No.
0
1
No snow detection sensor is connected but control is available. (at factory shipment)
Snow detection sensor is connected and control is available.
No snow detection sensor is connected and control is not available.2
Snow detection sensor is connected but control is not available.3
System address 1
Snow detection sensor installed
Unit No.1
Unit No.2
Unit No.3
Function
System address 2 System address 3
Unit No.1
Unit No.2
Unit No.3
Unit No.1
Unit No.2
3
4
5
6
Unit No.3
Setting No.
Fan motor
status during
snowfall
* All outdoor units are connected with same communication wiring.
100000222
ON ON ON ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF
1 - 19
7
8
9
1
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
(2) Fixed Initial Fan Mode
For the first 30 seconds after operation starts, the mode is fixed at the initial mode which was calculated from the
relationship between the outdoor air temperature and the outdoor unit horsepower.
If the outdoor unit horsepower (compressor capacity) changes dramatically, the initial mode may be recalculated
and may be again fixed for 30 seconds.
(3) Operation after Fixed Initial Fan Mode
After the fixed initial fan mode, the fan mode is increased or decreased according to the operating conditions.
3-1. Cooling operation
* The fan mode is always increased when the detected high pressure sensor temperature is 114.8°F (46°C) or
higher.
Fan mode is increased when the detected high pressure saturated temperature is high, and is decreased when
the high pressure saturated temperature is low.
The fan mode may be decreased when the system detects refrigerant shortage at an indoor unit.
During cooling operation, if the fan mode becomes “0” and this condition maintains for 3 minutes, the fan mode is
changed to “1”.
3-2. When all indoor units are operating in heating mode
If the pressure sensor temperature is low, the fan mode is increased at regular intervals.
If the pressure sensor temperature is high, the fan mode is decreased in order to prevent excessive loads.
The fan mode may be increased when the liquid temperature of outdoor unit heat exchanger drops to
1.8deg F (1deg C) or below.
2
3
4
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
Control Functions
1-3. Silent mode
This unit includes 2 types of silent modes.
See the table under the section “(1) Fan Mode” for maximum fan mode in silent mode.
Selecting the silent mode results in operation that gives priority to reducing noise, because these modes involve
restrictions on outdoor unit fan modes, the capacity will be somewhat reduced. (It may sometimes become a
maximum of -5 hp.)
* Maximum fan mode and frequency in silent mode
Type of outdoor unit 72 96 120 144
Fan mode 9 10 11 11
Frequency (Hz) 48.1 64.4 41.4 54.9
* To activate this function, it is necessary to set it to each outdoor unit.
CODE: 05
Setting No. Mode
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
* When the setting is "external input to PCB necessary", this function works by short circuiting "SILENT" pins.
* When the setting is "external input to PCB unnecessary", this function always works.
* When the setting is "silent priority", max. fan mode is decided in the following formula.
Max. fan mode = 13 - ( 35 – Ambient temperature) / 2
However, minimum fan mode is “6”, maximum is “13”. (When high static pressure mode, max is “15”)
* When the setting is "capacity priority", this function works excluding the following conditions.
Condition that silent mode interrupts
Heat exchanger [condenser] of outdoor unit: Ambient temperature ≥ 100.4°F (38°C)
Heat exchanger [evaporator] of outdoor unit: Ambient temperature ≤ 35.6°F (2°C)
This function will be useful for nighttime in summer.
Invalidity (Factory preset mode) - -
Silent priority
Capacity priority
External input to PCB Silent mode
Necessary
Unnecessary
Necessary
Unnecessary
Silent mode
-
Silent mode
-
Silent mode
-
Silent mode
-
5
6
7
8
9
1 - 20

2WAY VRF SYSTEM
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
5. Outdoor Unit Fan Control
(2) Fixed Initial Fan Mode
For the first 30 seconds after operation starts, the mode is fixed at the initial mode which was calculated from the
relationship between the outdoor air temperature and the outdoor unit horsepower.
If the outdoor unit horsepower (compressor capacity) changes dramatically, the initial mode may be recalculated
and may be again fixed for 30 seconds.
(3) Operation after Fixed Initial Fan Mode
After the fixed initial fan mode, the fan mode is increased or decreased according to the operating conditions.
3-1. Cooling operation
Fan mode is increased when the detected high pressure saturated temperature is high, and is decreased when
the high pressure saturated temperature is low.
* The fan mode is always increased when the detected high pressure sensor temperature is 114.8°F (46°C) or
higher.
The fan mode may be decreased when the system detects refrigerant shortage at an indoor unit.
During cooling operation, if the fan mode becomes “0” and this condition maintains for 3 minutes, the fan mode is
changed to “1”.
Control Functions
1
2
3-2. When all indoor units are operating in heating mode
If the pressure sensor temperature is low, the fan mode is increased at regular intervals.
If the pressure sensor temperature is high, the fan mode is decreased in order to prevent excessive loads.
The fan mode may be increased when the liquid temperature of outdoor unit heat exchanger drops to
1.8deg F (1deg C) or below.
3
4
5
6
1 - 21
7
8
9

6. Outdoor Unit CCU (command controller unit) Control
6. Outdoor Unit CCU (command controller unit) Control
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
6. Outdoor Unit CCU (command controller unit) Control
Operating
mode of
indoor unit
Operating
mode of
outdoor unit
Operating
mode of
compressor
Thermostat
ON/OFF
MOV pulse of indoor unit
Stop
Cooling
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Stop
Stop
Stop
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
Operation
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
60 ~ 480 (SH control*
1
)
65 - 480 pulses (SC control*
3
)
20
Operation
Operation
Fan (only)
Cooling
Heating
Heating
Cooling
Cooling
Heating
Heating
1-2. Indoor unit with RAP valve kit
Go to previous page and see the comments with asterisks *1 and *3.
In the case of special controls, the MOV performs a special operation.
For details, see “4. Output of PCB” under this section.
unit : pulse
Some actuators of indoor unit are controlled by CCU.
(1)
MOV of Indoor Unit
2WAY VRF SYSTEM
Control Functions
1
2
3
4
5
6
1-1. Indoor unit without RAP valve kit
Operating
mode of
indoor unit
Stop
Fan (only)
Cooling
Heating
*1 SH control adjusts the difference between the liquid temperature and gas temperature in indoor unit.
SH = gas temperature (E3) - liquid temperature (E1)
Target SH is 37.4deg F (3deg C) when the load level of indoor unit is “30” or “31 (test run)”.
Target SH will be increased up to 63.5deg F (17.5deg C) when the load level of indoor unit is low.
When the refrigerant amount in the system is adjusted, it is necessary to select test run mode that the
required level becomes “31”.
*2 MOV pulse changes to 55 for 1 minute when the MOV pulse continues to be 55 or more for 10 minutes.
The purpose of this control is to decrease the flow volume of the refrigerant so that room temperature can be
detected with less influence of heat from the refrigerant.
*3 SC control adjusts the difference in temperature between the liquid temperature in indoor unit and
high-pressure saturated temperature in outdoor unit.
SC = high-pressure sensor temperature (HPS) - liquid temperature (E1)
Target SC is 9deg F ~ 27deg F (5deg C ~ 15deg C) according to the operating condition.
Operating
mode of
outdoor unit
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
Operating
mode of
compressor
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Stop
Operation
Thermostat
ON/OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
MOV pulse of indoor unit
20
20
85
65 ~ 80
20
20
85
65 ~ 80
20
20
1
60 ~ 480 (SH control*
85
55 ~ 80 (prevent remaining refrigerant,
suction temperature control*
65 - 480 pulses (SC control*
)
2
)
3
)
unit : pulse
7
8
9
1 - 22
 Loading...
Loading...