Page 1

A
A
CD Stereo System
SA-PM321P
Colour
(S)... Silver Type
ORDER NO. MD0607236CE
A6
Specification
n Amplifier Section
FTC OUTPUT POWER both channel driven simultaneously
10% total harmonic distortion (THD)
60 Hz to 20 kHz 4.3 W per channel (6 Ω)
RMS OUTPUT POWER both channel driven simultaneously
10% total harmonic distortion
(THD)
Output impedance
HEADPHONE 16 to 32 Ω
MUSIC PORT 12 kΩ
Phone jack
Terminal Stereo, 3.5 mm
Music Port jack
Terminal Stereo, 3.5 mm
XM Ready XM Mini-Tuner and Home Dock
n FM Tuner Section
Frequency range 87.90 to 107.90 MHz
Sensitivity 1.50 µV (IHF)
S/N 26 dB 1.20 µV
ntenna terminals 75 Ω (unbalanced)
Preset station FM 15 stations
5 W per channel (6 Ω)
(200 kHz steps)
87.50 to 108.00 MHz
(100 kHz steps)
AM 15 stations
n AM Tuner Section
Frequency range 520 to 1710 kHz
(10 kHz steps)
Sensitivity
S/N 20 dB (at 1000 kHz) 447 µV/m
n CD Section
Disc played [8 cm or 12 cm]
(1) CD-Audio (CD-DA)
(2) CD-R/RW (CD-DA, MP3 formatted disc)
(3) MP3
Sampling frequency
CD 44.1 kHz
MP3 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz
Bit rate
MP3 32 kbps to 384 kbps
Decoding 16/20/24 bit linear
Pickup
Beam source Semiconductor laser
Wavelength 785 nm
Laser power CLASS 1
udio output (Disc)
Number of channels 2 channel
Frequency response 20 Hz to 20 kHz (+1, -2dB)
Wow and flutter Below measurable limit
© 2006 Matsushita Electric Industrial Co. Ltd.. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.
Page 2

SA-PM321P
Digital filter 8fs
D/A converter MASH (1 bit DAC)
n General
Power supply AC 120 V, 60 Hz
Power consumption 30 W
Dimensions (W x H x D) 165 x 227 x 327 mm
(6-1/2” x 8-15/16” x 12-7/8”)
Mass 2.7 kg (6lb.)
Operating temperature range +5 to +35°C (+41°F to +95°F)
Operation humidity range 5 to 90% RH (no condensation)
Power consumption in standby
mode
Notes :
1. Specifications are subject to change without notices. Mass and
dimensions are approximate.
2. Total harmonic distortion is measured by the digital spectrum
analyzer.
n System : SC-PM321P-S
Music center: SA-PM321P-S
Speaker: SB-PM3P-M
CONTENTS
Page Page
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. General Guidelines
1.2. Before Repair and Adjustment
1.3. Protection Circuitry
1.4. Caution For Fuse Replacement
2 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
3 Precaution of Laser Diode
4 Handling Precautions For Traverse Deck
5 Service caution based on legal restrictions
5.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
6 Accessories
7 Operating Instructions Procedures
7.1. Main Unit & Remote Control Operation
7.2. Disc Information
8 Self diagnosis and special mode setting
8.1. Special Mode Table
8.2. Error Code Table
9 Assembling and Disassembling
9.1. Caution
9.2. Disassembly flow chart
9.3. Main Parts Location Diagram
9.4. Disassembly of Side Panel L & R
9.5. Disassembly of Top Cabinet Unit
9.6. Disassembly of Headphone P.C.B
9.7. Disassembly of Front Panel
9.8. Disassembly of Panel P.C.B
9.9. Disassembly of Rear Panel
9.10. Disassembly of XM Ready P.C.B
9.11. Disassembly of Tuner Pack
9.12. Disassembly of Main P.C.B
9.13. Disassembly of Power P.C.B
9.14. Disassembly of Speaker Terminal P.C.B
9.15. Disassembly of Transformer P.C.B
4
4
5
5
5
6
7
8
9
9
10
11
11
12
13
13
14
16
16
17
18
19
19
20
20
21
21
22
22
22
23
24
24
9.16. Disassembly of CD Mechanism
9.17. Disassembly of Traverse Unit, Driving Gear, and Cam
Gear (CD Mechanism Unit)
9.18. Disassembly of Optical Pickup (CD Mechanism Unit)
9.19. Disassembly of Traverse Gear A and Traverse Gear B
(CD Mechanism Unit)
10 Service Fixture and Tools
11 Service Positions
11.1. Checking and Repairing of Headphone P.C.B
11.2. Checking and Repairing of Panel P.C.B
11.3. Checking and Repairing of Transformer P.C.B
11.4. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B
11.5. Checking and Repairing of CD Mechanism P.C.B
11.6. Checking and Repairing of Speaker Terminal P.C.B
11.7. Checking and Repairing of Power P.C.B
11.8. Checking and Repairing of XM Ready P.C.B (Side A)
11.9. Checking and Repairing of XM Ready P.C.B (Side B)
12 Voltage Measurement and Waveform Chart
12.1. Voltage Measurement
12.2. Waveform
13 Wiring Connection Diagram
14 Block Diagram
15 Notes Of Schematic Diagram
16 Schematic Diagram
16.1. CD Servo Circuit
16.2. Main Circuit
16.3. Panel Circuit
16.4. Power Circuit
16.5. Transformer Circuit
16.6. Tuner Extent Circuit, Headphone Circuit and Speaker
Terminal Circuit
16.7. XM Ready Circuit
17 Printed Circuit Board
17.1. CD Servo P.C.B and Panel P.C.B
0.6 W
25
25
28
29
31
31
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
40
44
47
49
53
55
55
56
58
59
60
61
62
63
63
2
Page 3

17.2. Main P.C.B and Tuner Extent P.C.B 64
17.3. Power P.C.B and Speaker Terminal P.C.B
17.4. Transformer P.C.B, Headphone P.C.B and XM Ready
P.C.B
18 Illustration of IC's, Transistors and Diodes
19 Terminal Function of IC's
19.1. IC7001 (MN6627954MA) IC SERVO
PROCESSOR/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR/DIGITA L
FILTER D/A CONVERTER
19.2. IC7002 (BA5948FPE2) IC 4CH Drive
65
19.3. IC803 (MN101CP49KAF) MICROPROCESSOR
20 Troubleshooting Flowchart (CD Section Circuit)
66
21 Exploded Views
67
68
21.1. Cabinet Parts Location
21.2. Traverse Deck Part Location
21.3. Packaging
22 Replacement Parts List
68
SA-PM321P
68
69
71
73
73
74
75
77
3
Page 4

SA-PM321P
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. General Guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, ensure that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly installed.
3. After servicing, check for leakage current checks to prevent from being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1. Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2. Using an ohmmeter measure the resistance value, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabine t part on
the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to the
chassis, the reading should be between 1MΩ and 5.2Ω.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis, the reading must be
.
Figure 1
1.1.2. Leakage Current Hot Check (See Figure 1)
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15µF capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set and a
good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent) may
be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. should the measurement is outside of the limits
specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and re-checked before it is returned
to the customer.
4
Page 5

SA-PM321P
1.2. Before Repair and Adjustment
Disconnect AC power, discharge Power Supply Capacitors C272, C472, C501, C909, C910, C911 & C923 through a 10Ω,1W
resistor to ground.
DO NOT SHORT-CIRCUIT DIRECTLY (with a screwdriver blade, for instance), as this may destroy solid state devices.
After repairs are completed, restore power gradually using a variac, to avoid overcurrent.
· Current consumption at AC 120 V, 60 Hz in NO SIGNAL mode (at volume minimum) should be ~300 mA.
1.3. Protection Circuitry
The protection circuitry may have operated if either of the following conditions are noticed:
· No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
· Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires are
"shorted", or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used.
If this occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3. Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note:
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
1.4. Caution For Fuse Replacement
5
Page 6

SA-PM321P
2 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equiped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equiped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminium
foil, to prevent electrostatic charge build up or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder remover device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)” can
generate electrical charge to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminium foil or
comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installe d.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize body motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the brushing
together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient to
damage an ES device).
6
Page 7

SA-PM321P
3 Precaution of Laser Diode
CAUTION:
This unit utilizes a class 1 laser.
Invisible laser radiation is emitted from the optical pickup lens.
When the unit is turned on:
1. Do not look directly into the pick up lens.
2. Do not use optical instruments to look at the pick up lens.
3. Do not adjust the preset variable resistor on the pickup lens.
4. Do not disassemble the optical pick up unit.
5. If the optical pick up is replaced, use the manufacturer’s specified replacement pick up only.
6. Use of control or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation
exposure.
CAUTION!
THIS PRODUCT UTILIZES A LASER.
USE OF CONTROLS OR ADJUSTMENTS OR PERFORMANCE OF PROCEDURES OTHER THAN THOSE SPECIFIED HEREIN MAY RESULT
IN HAZARDOUS RADIATION EXPOSURE.
7
Page 8
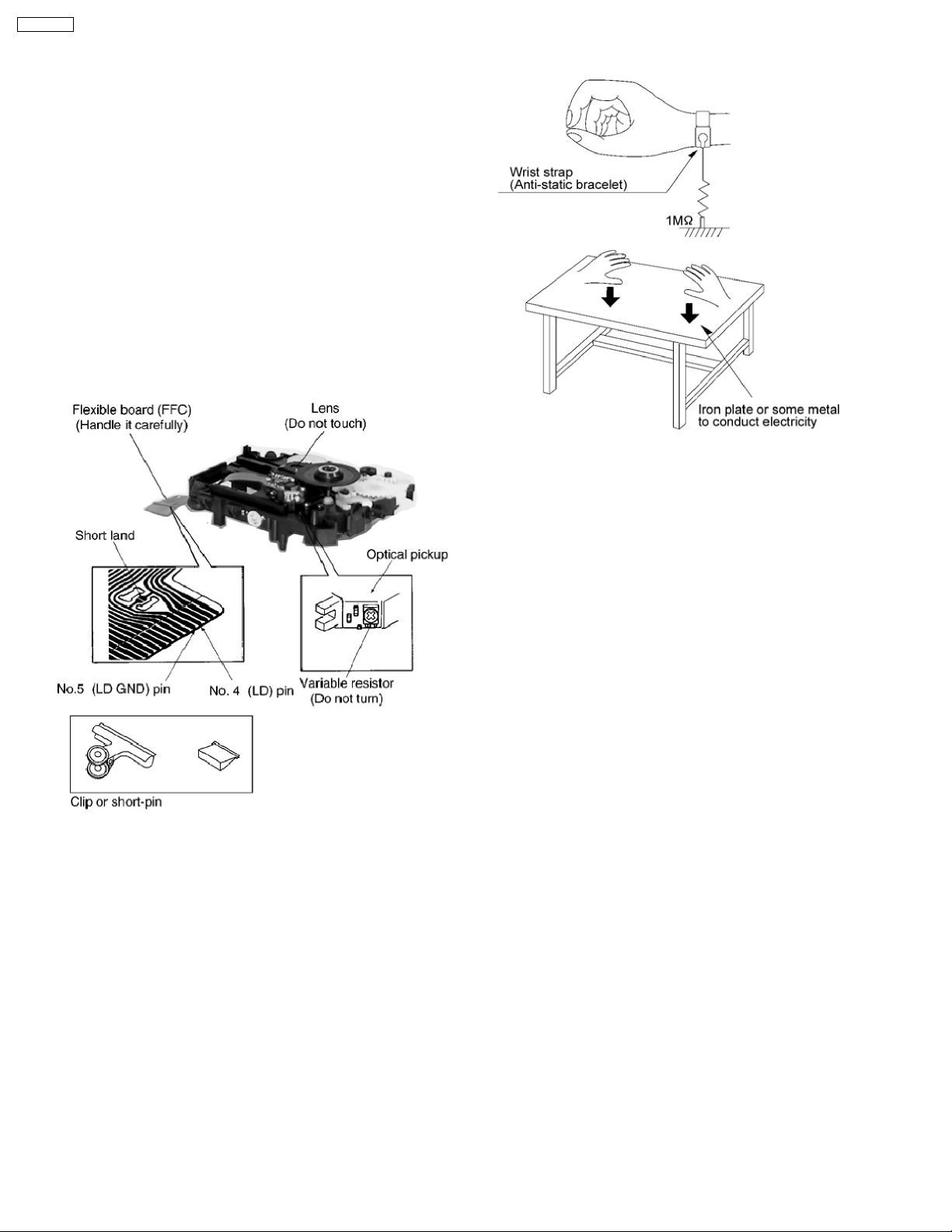
SA-PM321P
4 Handling Precautions For Traverse Deck
The laser diode in the traverse deck (optical pickup) may break
down due to potential differe nce caused by static electricity of
clothes or human body.
So, be careful of electrostatic breakdown during repair of the
traverse deck (optical pickup).
l Handling of CD traverse deck (optical pickup)
1. Do not subject the traverse deck (optical pickup) to
static electricity as it is extremely sensitive to electrical
shock.
2. The short land between the No.4 (LD) and No.5 (GND)
pins on the flexible board (FFC) is shorted with a solder
build-up to prevent damage to the laser diode.
3. Take care not to apply excessive stress to the flexible
board (FFC board) (Fig 4.1).
4. Do not turn the variable resistor (laser power
adjustment). It has already been adjusted.
Fig 4.2
Fig 4.1
l Grounding for electrostatic breakdown prevention
1. Human body grounding (Fig 4.2)
Use the anti-static wrist strap to discharge the static
electricity from your body.
2. Work table grounding (Fig 4.2)
Put a conductive material (sheet) or steel sheet on the
area where the traverse deck (optical pickup) is placed,
and ground the sheet.
Caution :
The static electricity of your clothes will not be grounded
through the wrist strap. So, take care not to let your
clothes touch the traverse deck (optical pickup).
Caution when Replacing the Optical Pickup :
The traverse has a short point shorted with solder to protect
the laser diode against electrostatics breakdown. Be sure to
remove the solder from the short point before making
connections.
8
Page 9

SA-PM321P
5 Service caution based on legal restrictions
5.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
The lead free solder has been used in the mounting process of all electrical components on the printed circuit boards used for this
equipment in considering the globally environmental conservation.
The normal solder is the alloy of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). On the other hand, the lead free solder is the alloy mainly consists of tin
(Sn), silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu), and the melting point of the lead free solder is higher approx.30 degrees C (86°F) more than that
of the normal solder.
Definition of PCB Lead Free Solder being used
The letter of “PbF” is printed either foil side or components side on the PCB using the lead free solder.
(See right figure)
Service caution for repair work using Lead Free Solder (PbF)
· The lead free solder has to be used when repairing the equipment for which the lead free solder is used.
(Definition: The letter of “PbF” is printed on the PCB using the lead free solder.)
· To put lead free solder, it should be well molten and mixed with the original lead free solder.
· Remove the remaining lead free solder on the PCB cleanly for soldering of the new IC.
· Since the melting point of the lead free solder is higher than that of the normal lead solder, it takes the longer time to melt
the lead free solder.
· Use the soldering iron (more than 70W) equipped with the temperature control after setting the temperature at 350±30
degrees C (662±86°F).
Recommended Lead Free Solder (Service Parts Route.)
· The following 3 types of lead free solder are available through the service parts route.
RFKZ03D01K-----------(0.3mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ06D01K-----------(0.6mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ10D01K-----------(1.0mm 100g Reel)
Note
* Ingredient: tin (Sn), 96.5%, silver (Ag) 3.0%, Copper (Cu) 0.5%, Cobalt (Co) / Germanium (Ge) 0.1 to 0.3%
9
Page 10

SA-PM321P
6 Accessories
Note : Refer to Packing Materials & Accessories (Section 22) for part number.
Remote control
AC cord
FM indoor
antenna
AM loop antenna
10
Page 11

7 Operating Instructions Procedures
7.1. Main Unit & Remote Control Operation
SA-PM321P
11
Page 12

SA-PM321P
7.2. Disc Information
12
Page 13
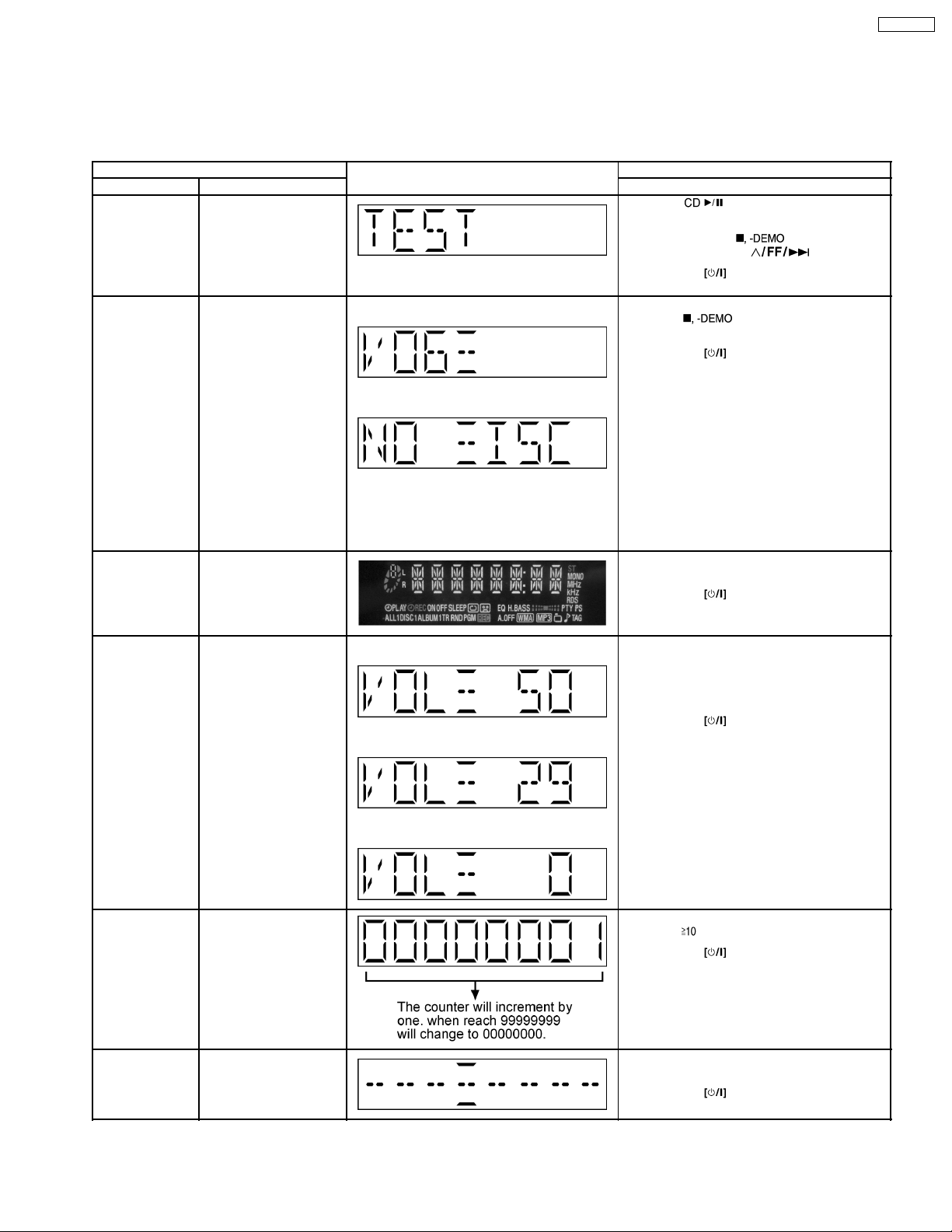
8 Self diagnosis and special mode setting
This unit is equipped with features of self-diagnostic & special mode setting for checking the functions & reliability.
8.1. Special Mode Table
Below is the various special modes for checking:-
Item FL Display Key Operation
Mode Name Description Front Key
Self -Diagnostic
Mode
Doctor Mode To enter into Doctor
To enter into self
diagnostic checking for
main unit.
Mode for checking of
various items and
displaying EEPROM and
firmware version.
(For more information,
refer to section 8.1.2)
Note: The microprocessor version as
shown is an example. It
will be revise when there
is an updates.
1.
2.
The Check Sum of EEPROM and firmware
version will be display for 1 sec.
1. Select [ ] for CD mode (Ensure no
tape or CD inserted).
2. Press and hold [
seconds follow by [
To exit, press
remote control.
In any mode:
1. Press [
by [4] and [7] on remote control.
To exit, press
remote control.
button on main unit or
] button on main unit follow
button on main unit or
]button for 2
].
SA-PM321P
FL Display Test To check the FL
segments display (All
segments will light up)
Volume Setting To Forced Volume
Setting.
Traverse Test To determine the
reliability of CD unit.
* ROM correction
** Firmware version No:
1.
2.
3.
In doctor mode:
1. Press [DIMMER] button on remote control.
To exit, press
remote control.
In doctor mode:
1. Press [7] button on remote control.
2. Press [8] button on remote control.
3. Press [9] button on remote control.
To exit, press
remote control.
In doctor Mode:
1. Press [
To exit, press
remote control.
button on main unit or
button on main unit or
], [1], [2] button on remote control.
button on main unit or
Cold Start To activate cold start ipon
next AC power up.
In doctor mode:
1. Press [SLEEP] button on remote control.
To exit, press
remote control.
8.1.1. EEPROM Checksum (ROM correction)
Purpose : To check for micro-processor firmware version & EEPROM check (ROM correction).
13
button on main unit or
Page 14
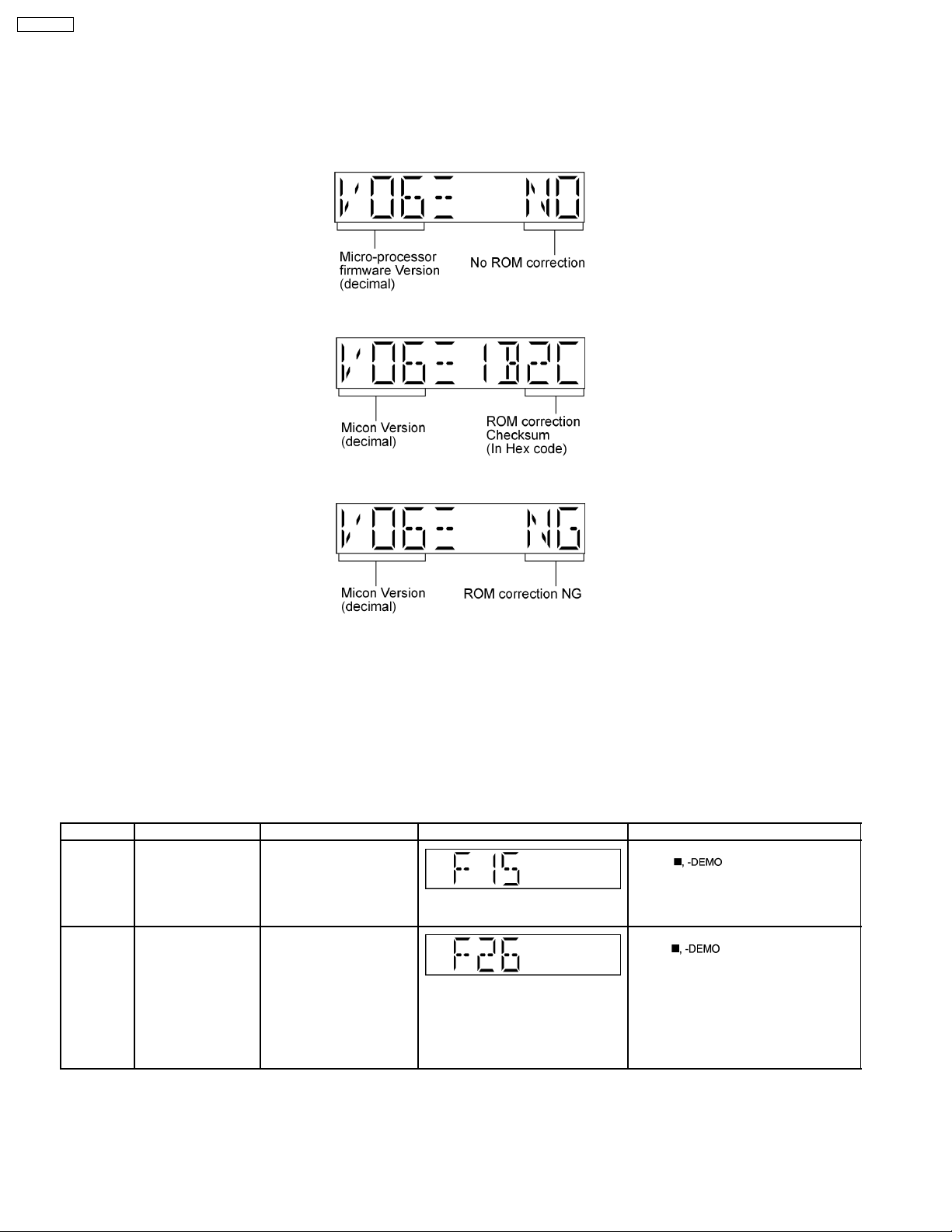
SA-PM321P
Below is the procedures for this mode.
Step 1: Enter into Doctor mode (For more information refer to section 8.1 on key operation to enter into this mode.
Step 2: Check for firmware version & EEPROM checksum.
· W hen entering into DOCTOR MODE the firmware version & checksum of EEPROM (if applica ble) will appear on FL display.
Below is information on the EEPROM IC (Rom correction) under 3 examples:
1. When EEPROM IC is detected and there is no ROM correction:
2. When EEPROM IC is detected and has ROM correction:
3. When EEPROM IC is detected and has ROM correction but working properly.
Note: Micro-processor firmware version refers to version No. (Eg.MS079_12) for micro-processor IC.
It is subject to change which would update accordingly.
· Rom correction checksum refers to the hex code that is display upon key buttons pressed if an EEPROM is loaded in the unit.
(Main P.C.B)
8.2. Error Code Table
Self-Diagnosis Function provides information on any problems occuring for the unit and its respective components by displaying
error codes. Thesed error code such as U**, H** and F** are stored in memory and held unless it is cleared.
The error code is automatically display after entering into self-diagnostic mode.
Error Code Diagnosis Contents Description of error Automatic FL Display Remarks
F15 CD REST SW
Abnormal
F26 Communication
between CD servo
LSI and micro-p
abnormal.
CD traverse position intial
setting operation failsafe
counter (1000 ms) waiting
for REST SW toturn on.
Error No. shall be clear by
force or during cold start.
CD function DTMS
command, after system
setting, If SENSE = ´L´
cannot be detected.
Memory shall contain F26
code. After Power on, CD
function shall continue,
error display shall be "NO
DISC". Error No. shall be
clear by force or cold start.
For CD unit (For Traverse).
Press [
error.
For CD unit (For Traverse).
Press [
error.
] on main unit for next
] on main unit for next
14
Page 15

Error Code Diagnosis Contents Description of error Automatic FL Display Remarks
POWER
AMP output
abnormal
During normal operation, if
DCDET becomes "L",
normal POWER OFF
process shall not be
For Power Supply Related Error
Detection.
Press [
error.
executed, PCONT shall be
switched to "L"
immediately. "GOODBYE"
shall not be display but the
error display F61 is
displayed instead. 2
seconds after the F61
displayed, ECONO shall be
set to "L" and FL display
shall be turned off. The
error content shall be
memorized when the
abnormality occurs and can
be display in the C-mecha
self-diagnostic mode
described later.
SA-PM321P
] on main unit for next
15
Page 16

SA-PM321P
9 Assembling and Disassembling
9.1. Caution
“ATTENTION SERVICER”
Some chassis components may be have sharp edges. Be careful when disassembling and servicing.
1. This section describes procedures for checking the operation of the major printed circuit boards and replacing the main
components.
2. For reassembly after operation checks or replacement, reverse the respective procedures.
Special reassembly procedures are described only when required.
3. Select items from the following index when checks or replacement are required.
Warning:
This product uses a laser diode. Refer to “Precaution of Laser Diode”.
Below is the list of disassembly sections
· Disasse mbly of Side Panel L & R
· Disasse mbly of Top Cabinet Unit
· Disasse mbly of Headphone P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of Front Panel
· Disasse mbly of Panel P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of Rear Panel
· Disasse mbly of XM Ready P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of Tuner Pack
· Disasse mbly of Main P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of Power P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of Speaker Terminal P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of Transformer P.C.B
· Disasse mbly of CD Mechanism
· Disasse mbly of Traverse Unit, Driving Gear, and Cam Gear (CD Mechanism Unit)
· Disasse mbly of Optical Pickup (CD Mechanism Unit)
· Disasse mbly of Traverse Gear A and Traverse Gear B (CD Mechanism Unit)
16
Page 17
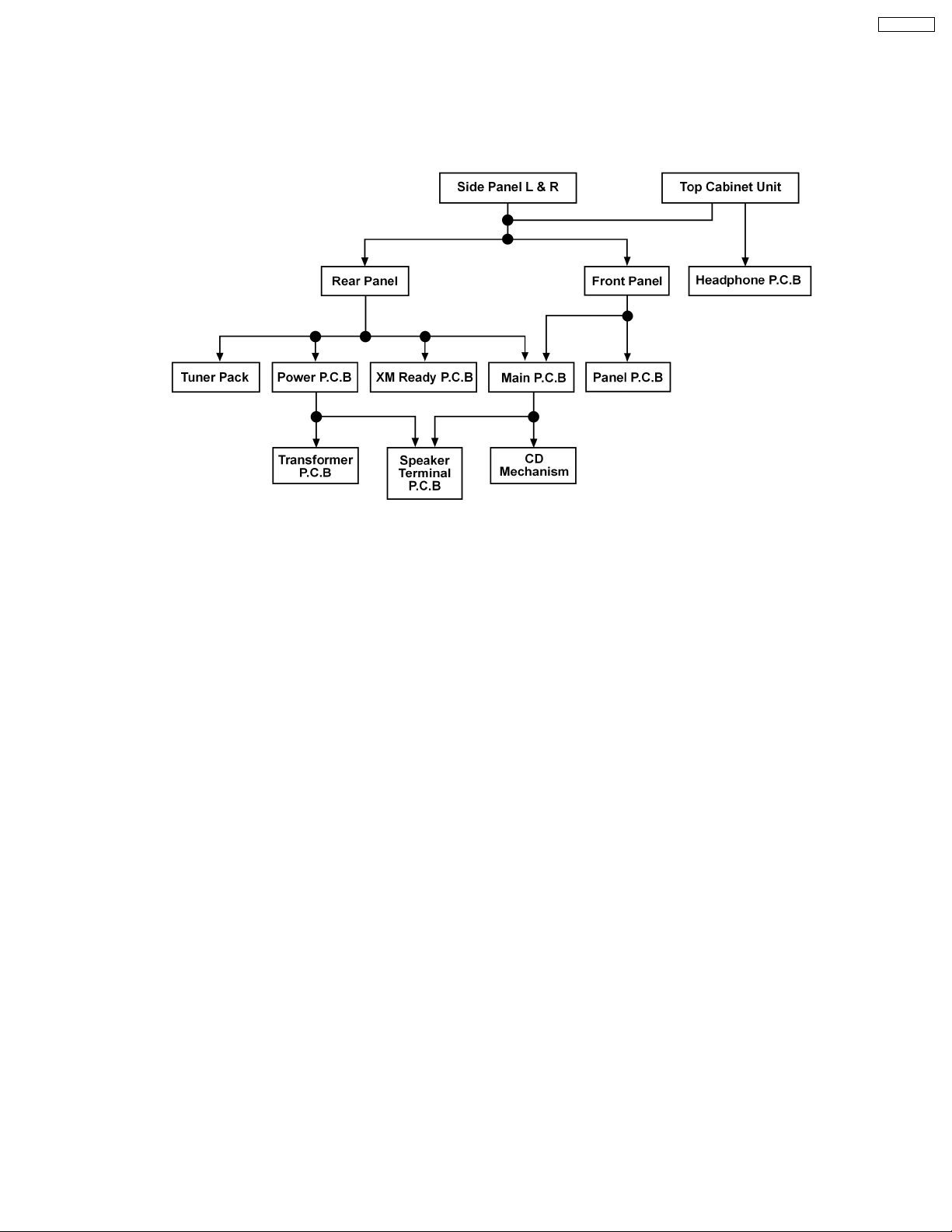
SA-PM321P
9.2. Disassembly flow chart
The following chart is the procedure for disassembling the casing and inside parts for internal inspection when carrying out the
servicing.
To assemble the unit, reverse the steps shown in the chart below.
17
Page 18

SA-PM321P
9.3. Main Parts Location Diagram
18
Page 19
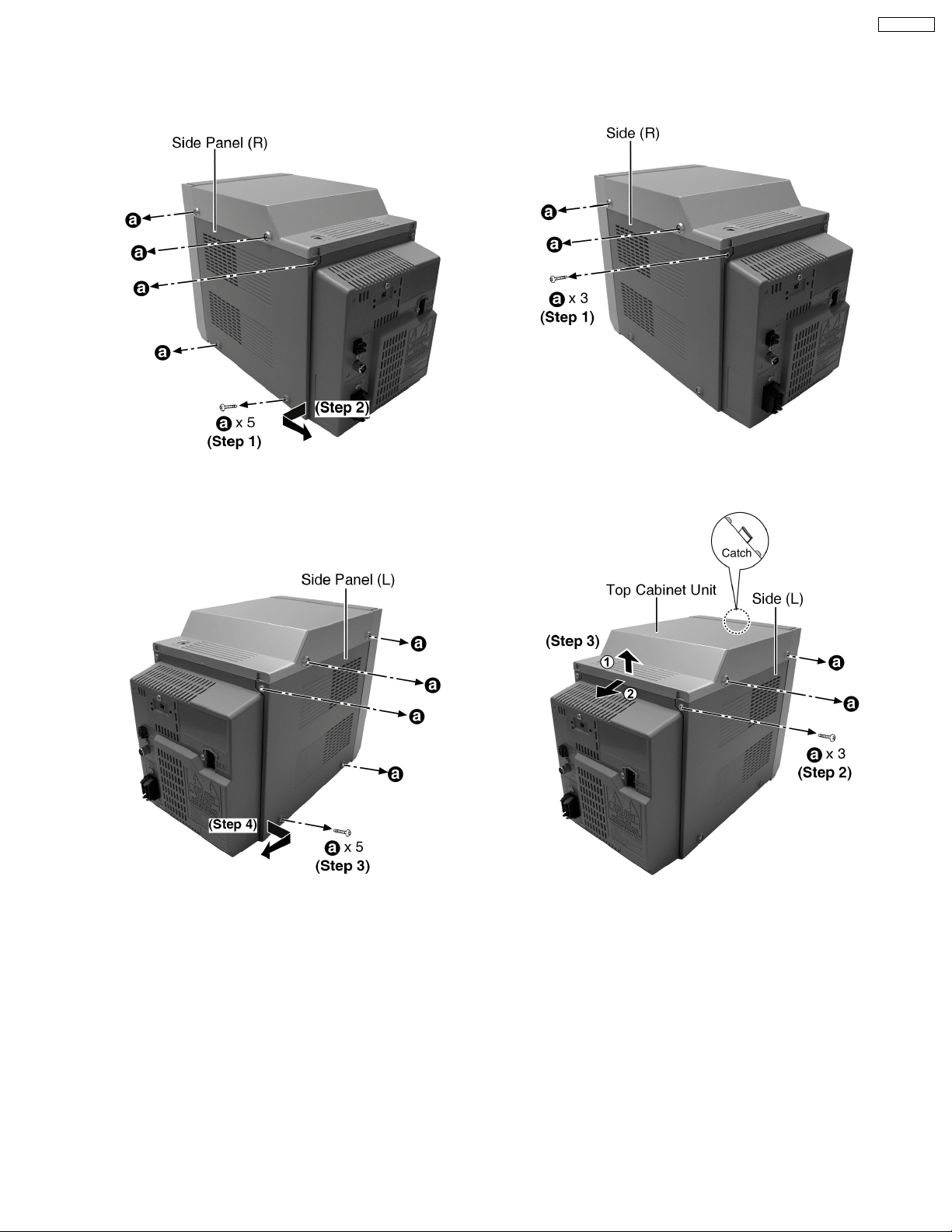
9.4. Disassembly of Side Panel L &
R
· Disasse mbly of Side Panel (R)
Step 1: Remove 5 screws.
Step 2: Remove the side panel (R) as arrow shown.
SA-PM321P
9.5. Disassembly of Top Cabinet
Unit
Step 1: Remove 3 screws.
· Disasse mbly of Side Panel (L)
Step 3: Remove 5 screws.
Step 4: Remove the side panel (L) as arrow shown.
Step 2: Remove 3 screws.
Step 3: Lift up the top cabine t unit, push backward
as arrow shown and flip top cabinet unit sideway.
(Be careful of the catch)
19
Page 20

SA-PM321P
Step 1: Detach connector (CN900B).
Step 4: Detach connector (CN504A).
Step 5: Remove top cabine t unit.
9.6. Disassembly of Headphone
P.C.B
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
Step 1: Remove 1 screw.
Step 2: Release the clutch.
Step 3: Remove the Headp hone P.C.B.
Step 2: Disconnect FFC cable (CN901B).
9.7. Disassembly of Front Panel
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
20
Page 21

Step 1: Remove 10 screws.
Step 2: Remove the Volume Knob.
Step 3: Release 2 catches.
Step 4: Remove the Panel P.C.B.
SA-PM321P
Step 3: Release 3 claws.
Step 4: Remove the Front Panel as arrow shown.
9.8. Disassembly of Panel P.C.B
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.7.
9.9. Disassembly of Rear Panel
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
Step 1: Remove 5 screws.
21
Page 22
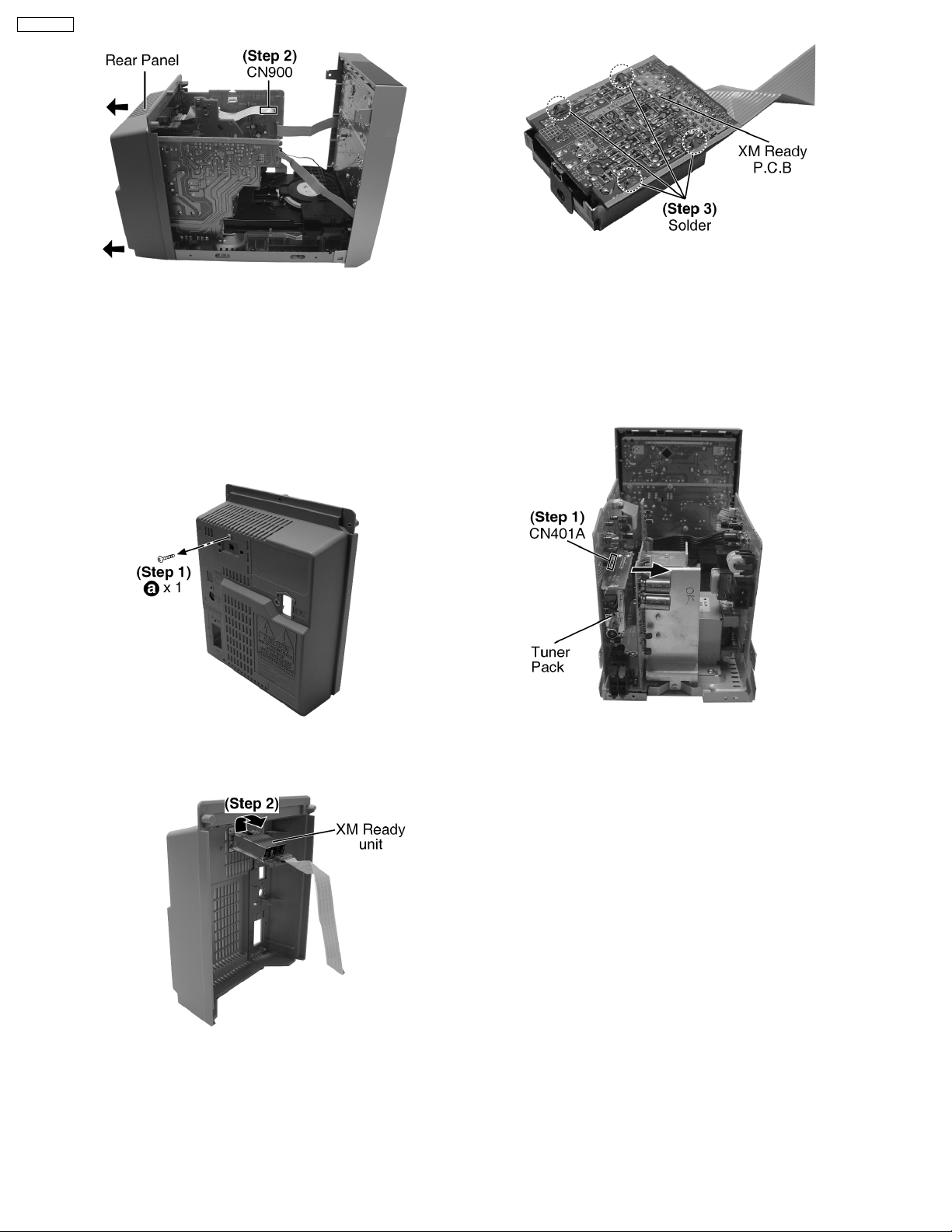
SA-PM321P
Step 2: Detach FFC cable (CN900) and remove the
Rear Panel as arrow shown.
Step 3: Unsolder 4 points to remove XM Ready
P.C.B.
9.11. Disassembly of Tuner Pack
9.10. Disassembly of XM Ready
P.C.B
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9.
Step 1: Remove 1 screw.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9.
Step 1: Detach the connector CN401A and remove
the tuner pack as arrow shown.
9.12. Disassembly of Main P.C.B
Step 2: Remove the XM Ready unit as arrow
shown.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 4) of Item 9.7.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 2) of Item 9.9.
22
Page 23
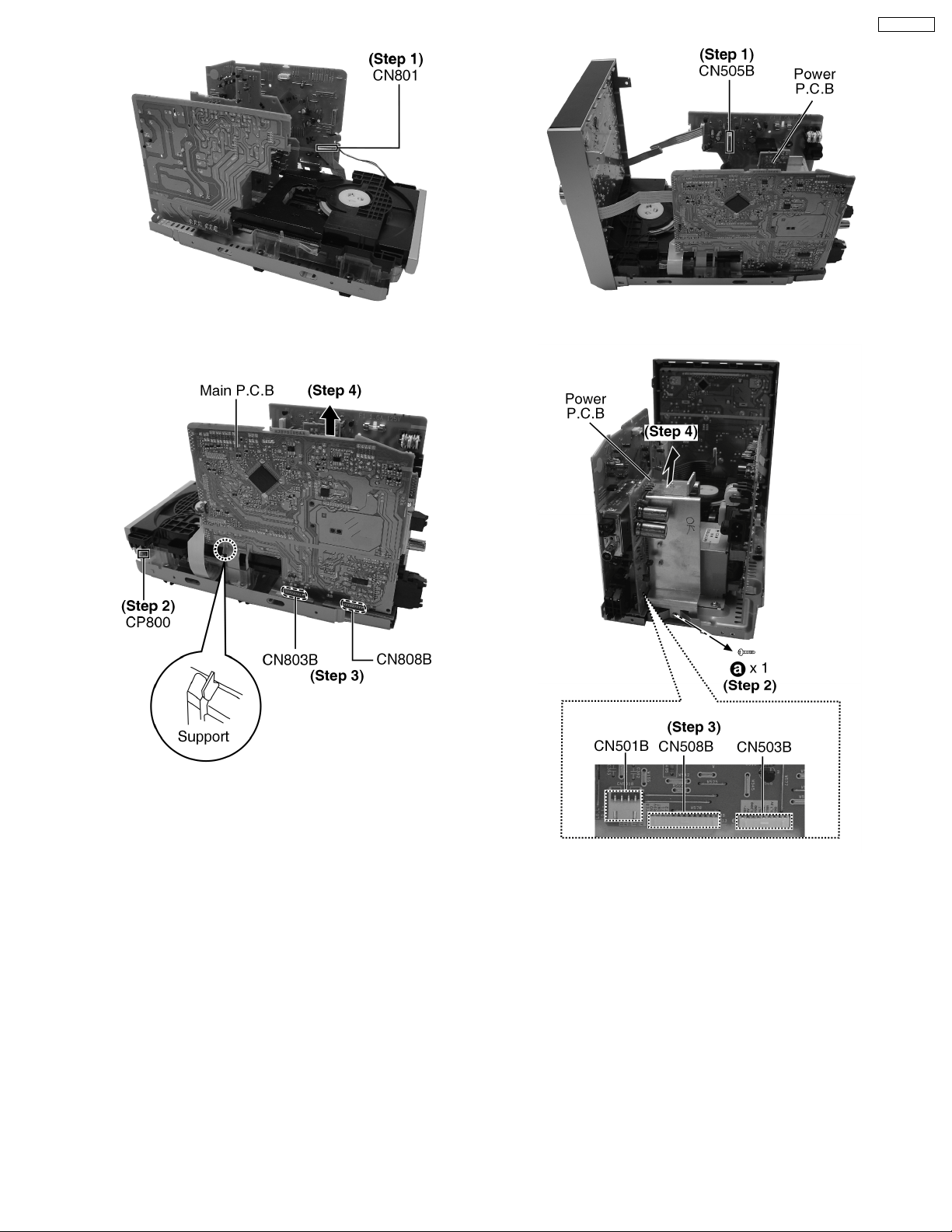
SA-PM321P
Step 1: Detach the FFC CN801.
Step 1: Detach the connector CN505B.
Step 2: Detach connector CP800.
Step 3: Detach connector CN803B and CN808 B.
Step 4: Remove the Main P.C.B as arrow shown.
9.13. Disassembly of Power P.C.B
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9.
Step 2: Remove 1 screw.
Step 3: Detach the connector CN501B, CN508B
and CN503B.
Step 4: Remove the Power P.C.B as arrow shown.
· Replacement of Power Amplifier IC
23
Page 24

SA-PM321P
Step 5: Remove 3 screws.
Step 6: Unsolder the terminal of Power Amp IC
(IC500) and replace the component.
Step 7: Unsolder the terminal of Transistor (Q503)
and replace the component.
9.14. Disassembly of Speaker
Terminal P.C.B
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 2) of Item 9.9.
· Follow the (Step 3) of Item 9.12.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 4) of Item 9.13.
Step 1: Remove 1 screw.
Step 2: Release the clutch.
Step 3: Remove the Speaker Terminal P.C.B as
arrow shown.
9.15. Disassembly of Transformer
P.C.B
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.13.
24
Page 25

Step 1: Remove 4 screws.
Step 2: Remove the Main P.C.B support.
Step 3: Remove CD Mechanism as arrow shown.
SA-PM321P
Step 1: Detach the connector CN900B.
Step 2: Remove 4 screws.
Step 3: Remove the Transformer P.C.B as arrow
shown.
9.16. Disassembly of CD
Mechanism
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 4) of Item 9.7.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 2) of Item 9.9.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (step 4) of Item 9.12.
9.17. Disassembly of Traverse Unit,
Driving Gear, and Cam Gear
(CD Mechanism Unit)
9.17.1. Disassembly of the Traverse Unit
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.7.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9 .
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.12.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 3) of Item 9.16.
25
Page 26

SA-PM321P
· Disasse mbly of gears drive
26
Page 27

SA-PM321P
27
Page 28

SA-PM321P
9.18. Disassembly of Optical Pickup
(CD Mechanism Unit)
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.7.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9 .
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.12.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 3) of Item 9.16.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.17.1.
28
Page 29

SA-PM321P
9.19. Disassembly of Traverse Gear
A and Traverse Gear B (CD
Mechanism Unit)
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.4.
· Follow the (Step 3) - (Step 5) of Item 9.5.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.7.
29
Page 30

SA-PM321P
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.9 .
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 4) of Item 9.12.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 3) of Item 9.16.
· Follow the (Step 1) - (Step 2) of Item 9.17.1.
30
Page 31

10 Service Fixture and Tools
Service Tools
Extension P.C.B.
(A) Main P.C.B. - Speaker Terminal P.C.B. RFKZAPM321PS
11 Service Positions
Note: For description of the disassembly procedures, see the Section 9
11.1. Checking and Repairing of Headphone P.C.B
SA-PM321P
31
Page 32

SA-PM321P
11.2. Checking and Repairing of Panel P.C.B
32
Page 33

11.3. Checking and Repairing of Transformer P.C.B
SA-PM321P
33
Page 34

SA-PM321P
11.4. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B
34
Page 35

11.5. Checking and Repairing of CD Mechanism P.C.B
Note:
Connect AC power cord and switch on the set. Eject tray loading, load in CD and switch off the set .Proceed with checking.
SA-PM321P
35
Page 36

SA-PM321P
11.6. Checking and Repairing of Speaker Terminal P.C.B
36
Page 37

11.7. Checking and Repairing of Power P.C.B
SA-PM321P
37
Page 38

SA-PM321P
11.8. Checking and Repairing of XM Ready P.C.B (Side A)
38
Page 39

11.9. Checking and Repairing of XM Ready P.C.B (Side B)
SA-PM321P
39
Page 40

SA-PM321P
12 Voltage Measurement and Waveform Chart
Note:
· Indicated voltage values are the standard values for the unit measured by the DC electronic circuit tester (high-impedance)
with the chassis taken as standard.
Therefore, there may exist some errors in the voltage values, depending on the internal impedance of the DC circuit tester.
· Circuit voltage and waveform described herein shall be regarded as reference information when probing defect point
because it may differ from actual measuring value due to difference of Measuring instrument and its measuring condition
and product itself.
12.1. Voltage Measurement
12.1.1. CD Servo P.C.B
CD SERVO P.C.B
Ref No.
MODE 1 234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 0 00 00000000 0 0000001.33.3
STANDBY 0 0 00000000 000 0000000.1
Ref No.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 1.6 0 1.6 0 1.8 0 3.3 1.5 3.3 3.3 0 0 1.6 1.6 1.6 2 2 1.4 1.8 1.8
STANDBY 0000000.10000000000000
Ref No.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 0.2 2.4 0 1.8 1.2 1.8 3.3 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.7 1.9 0.8 1.5 1.4 0 0 3 1.5 0
STANDBY 0.100000.10.10.2000000000000
Ref No.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 3.1 3.1 3.1 2.5 0 3.1 0 1.6 0 1.5 3.3 0 3.3 1.6
STANDBY 0 0 00000000 000 0000000
Ref No.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY 1.62.30 00000000 03.30000000
STANDBY 0 0 00000000 000 0000000
Ref No.
MODE 1 234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 1.601.60000007.54.23.53.53.503.303.87.50
STANDBY 0 0 00000000 000 0000000
Ref No.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
CD PLAY 0 7.5 0 0 7.5 0 1.6 0
STANDBY 0 0 000000
Ref No.
MODE E C B
CD PLAY 3.3 2.4 2.4
STANDBY 0.3 0 0.3
Q7601
IC7001
IC7001
IC7001
IC7001
IC7001
IC7002
IC7002
40
Page 41

12.1.2. Main P.C.B
MAIN P.C.B
Ref No.
MODE 1 23 45678
CD PLAY 4.8 4.8 2.4 9.6 0 4.8 4.8 0
STANDBY 0 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0 0 0
Ref No.
MODE 1 23 4567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 0 0 0 9.4 9.4
STANDBY 0.5 0.5 0.1 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.1 0 0 0 0.1 0.1
Ref No.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
CD PLAY 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7
STANDBY 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.2 0.4 0.2 0.3 0 0 0 0.2 0.1
Ref No.
MODE 1 23 45678910111213141516
CD PLAY 0.2 0.3 0.4 0 0 0.1 0 0 0.5 0 0.5 0 0 0 0 1
STANDBY 0 0000000000 00000
Ref No.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 0 3.3 4.9 0 4.9
STANDBY 0 0.2 0 0 0
Ref No.
MODE 1 23 4567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 0 4.8 4.8 2.2 2.2 3.2 1.5 2.2 2.2 4.8 4.8 2.4 2.4 0.5 2 2.4 0 4.8 4.8 4.8
STANDBY 0 4.8 4.8 2.1 2.1 0 1.6 2.1 2.1 4.8 4.9 2.4 2.5 0 2 2.4 0 0 0 0
Ref No.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 4.5 1 4.5 0 4.5 4.8 2.7 4.8 4.8 4.8 1 1 4.8 0 4.6 4.6 0 0 0 2
STANDBY 000004.82.8000004.80000000
Ref No.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 1.1 0.1 0 0.3 0.1 0 0.1 0 4.7 2.4 0 1.3 4.4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
STANDBY 00000.100.1002.40000000000
Ref No.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 0 0 00000003.80.14.84.84.84.80002.20
STANDBY 0 000000004.800 01.500002.30
Ref No.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY 0 0 00000000 04.70.80.80004.704.8
STANDBY 0 00000000004.8000004.804.8
Ref No.
MODE 1 23 45678
CD PLAY 04.8000000
STANDBY 0 0000000
Ref No.
MODE E C B E C B E C B E C B E C B
CD PLAY 0 0 0.3 0 0 0.3 0 0 0.3 0 0 0.3 9.6 0.3 9.7
STANDBY 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.1 0 0.1
Ref No.
MODE E C B E C B E C B E C B E C B
CD PLAY 0 9.7 0 0 4.8 0 0 1 1.2 0 0 4.6 0 4.7 0
STANDBY 0 0.1 0.1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.1 0 0 4.8 0
Ref No.
MODE E C B E C B
CD PLAY 0 9.7 0 0 9.7 0
STANDBY 0 0.1 0 0 0.1 0
Q221 Q222 Q421 Q422
Q751 Q801 Q802 Q803 Q804
Q807 Q801
IC700
IC800
IC800
IC801
IC802
IC803
IC803
IC803
IC803
IC803
IC804
Q750
SA-PM321P
41
Page 42

SA-PM321P
12.1.3. Panel P.C.B
Ref No.
MODE 1 234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 0 0 0 0 2.8 1.6 0.1 0.2 2.8 0 0 0 4.9 -22.7 -22.7 -22.7 -20.6 -22.7 -20.6 -22.7
STANDBY 0 0 00000000 000-21-21-21-21-21-21-21
Ref No.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY -22.7 -22.7 -20.6 -20.6 -22.7 -22.7 -22.7 -22.7 -20.6 -23.2 -20.8 -20.8 -20.8 -20.8 -20.8 -20.9 -20.9 -20.9 -20.9 -20.9
STANDBY -21 -21 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 -20.4 -20.4 -20.4 -20.4 -20.4 -20 -20 -20 -20
Ref No.
MODE 41 42 43 44
CD PLAY -20.9 -20.9 4.9 0
STANDBY -20 -20 0 0
12.1.4. Power P.C.B
Ref No.
MODE 1 23456789101112
CD PLAY
STANDBY
Ref No.
MODE E C B E C B E C B E C B E C B
CD PLAY 23.3 20 23.3 5 15.3 5.6 20.8 9.7 20.3 5 9.6 5.6 4.8 7.5 5.5
STANDBY 4.3 2.4 4.3 2.4 2.5 3.2 2.9 0.2 2.5 2.4 0.2 0.1 0 0 0
Ref No.
MODE E C B E C B
CD PLAY 7.5 9.7 8.2 8.8 9.7 9.5
STANDBY 0 0.1 0.1 0 0.1 0.1
PANEL P.C.B
IC900
IC900
IC900
POWER P.C.B
IC300
0 0 27.2 0 0 0 11.1 0.1 0 10.1 4.7 11
3.200.50000002.700
Q500 Q501 Q503 Q504 Q505
Q507 Q530
12.1.5. Transformer P.C.B
TRANSFORMER P.C.B
Ref No.
MODE E C B E C B E C B E C B
CD PLAY 0 0.2 0.8 5.6 7.4 6.3 0 2.7 1.5 -25.2 -29.1 -25.8
STANDBY 0 5.4 0 5.4 7 6.4 0 2.9 1.6 -0.14 -1.3 -1
Q600 Q601 Q602 Q603
42
Page 43

12.1.6. XM READY P.C.B
Ref No.
MODE 1 234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY
3.1 0 3.1 3.1 3.1 0 0 3.1 0 0 3.1 0
3.1 0 3.2 0 3.2 1.2 1.2 3.2
STANDBY 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.3 0 0 0.4 0.1 0 0.3 0.3 0 0.3 0 0 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.4
Ref No.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY
0 1.2 1.2 0 0 1.3 3.2 1.2 0 0 0 0
3.2 0 3.2 0 0 0 1.6 3.2
STANDBY 0 0.2 0.2 0 0 0.1 0.4 0.1 0 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.2 0.4 0.2 0.1 0 0.4 0.2
Ref No.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48
CD PLAY
1.2 0 1.2 3.2 0 2.5 0 3.2
STANDBY
0.1 0 0.1 0 0 0.4 0 0.1
Ref No.
MODE 1 2345678
CD PLAY
0 0 5.3 0 5.3 5.3 5.3 5.3
STANDBY
0 0 0 0 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6
Ref No.
MODE 1 2345678910111213141516
CD PLAY
1.6 1.6 0 1.6 4.8 0 0 5.3 5.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
STANDBY
0 00 00000000.4
0000.1
IC2
IC3
XM READY P.C.B
IC1
IC1
IC1
SA-PM321P
43
Page 44

SA-PM321P
12.2. Waveform
CN801 PIN 4
CD PLAY
3.4Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN801 PIN 8
CD PLAY
3.36Vp-p (10msec.div)
IC901B PIN 14
CD PLAY
5.28Vp-p (250usec.div)
CN801 PIN 5
CD PLAY
3.32Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN801 PIN 15
CD PLAY
372mVp-p (500usec.div)
IC803 PIN 15
CD PLAY
4.88Vp-p (50msec.div)
CN801 PIN 6
CD PLAY
1.96Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN801 PIN 15
CD PLAY
380mVp-p (500usec.div)
IC7001 PIN 21
CD PLAY
1.82Vp-p (5usec.div)
CN801 PIN 7
CD PLAY
3.72Vp-p (10msec.div)
IC901B PIN 13
CD PLAY
5.28Vp-p (100usec.div)
CN7001 PIN 24
CD PLAY
3.08Vp-p (25usec.div)
CN7001 PIN 25
CD PLAY
3.36Vp-p (10usec.div)
CN7001 PIN 49
CD PLAY
1.14Vp-p (2.5usec.div)
CN7001 PIN 50
CD PLAY
1.14Vp-p (2.5usec.div)
44
CN7001 PIN 56
CD PLAY
528mVp-p (2.5msec.div)
Page 45

SA-PM321P
CN7001 PIN 59
CD PLAY
512mVp-p (1msec.div)
CN7001 PIN 71
CD PLAY
3.28Vp-p (10msec.div)
IC803 PIN 12
CD PLAY
6.08Vp-p (50nsec.div)
CN7001 PIN 68
CD PLAY
3.8Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN7001 PIN 74
CD PLAY
4Vp-p (250nsec.div)
IC803 PIN 13
CD PLAY
2.72Vp-p (50nsec.div)
CN7001 PIN 69
CD PLAY
1.96Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN7001 PIN 80
CD PLAY
4.48Vp-p (50nsec.div)
IC803 PIN 21
CD PLAY
5.18Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN7001 PIN 70
CD PLAY
3.52Vp-p (10msec.div)
CN7001 PIN 81
CD PLAY
2.64Vp-p (50nsec.div)
IC803 PIN 23
CD PLAY
5.28Vp-p (10msec.div)
IC803 PIN 27
CD PLAY
4.72Vp-p (10msec.div)
IC803 PIN 42
CD PLAY
5.28Vp-p (100usec.div)
IC803 PIN 30
CD PLAY
4.96Vp-p (10msec.div)
IC803 PIN 44
CD PLAY
5.28Vp-p (50usec.div)
IC803 PIN 35
CD PLAY
4.88Vp-p (10msec.div)
45
IC803 PIN 40
CD PLAY
5.04Vp-p (50msec.div)
Page 46

SA-PM321P
46
Page 47

13 Wiring Connection Diagram
I
AC IN
120V 60Hz
JK600
SOLDER SIDE
CAUTION
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK
AC VOLTAGE LINE.
PLEASE DO NOT TOUCH THIS P.C.B
TRANSFORMER P.C.B.
T600
(Back Up Transformer)
T601
(Power Transformer)
PbF
CN505B
1
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
8
CN900B
SA-PM321P
G
HEADPHONE P.C.B.
SOLDER SIDE
JK900
4 . . 1
1
.
.
.
5
17 . . . . . . . . . . 1
16 . . . . . . . . . 2
CN900
CN901B
15
.
14
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2
1
B
MAIN P.C.B.
SOLDER SIDE
1..4
CN504A
1 . . . . . . . . . . 10
CN401A
C
TUNER EXTENT P.C.B.
SOLDER SIDE
PbF
HEADPHONE
CN10
To Z401 (Tuner Pack)
1 . . . . . . . . . . 10
WH504
PbF
1 . . . . . . . . . . 10
CD OPEN SW
2 1
CP800
CN801
2 . . . . . . . . 16
1 . . . . . . . . . . 17
CN7002
17
.
16
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2
1
A
CD SERVO P.C.B.
.
.
16
CN7001
2
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
15
1
.
.
.
.
.
SENSOR
Z901
CN901A
15
.
14
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2
1
PbF
VR900
VOLUME
FL900
D
PANEL P.C.B.
SOLDER SIDE
JK303
WH900
CN803B
9 . . . . . . . . . . . 1
CN808B
9 . . . . . . . . . . . 1
PbF
PbF
OPTICAL PICKUP
MUSIC
PORT
1
WH505A
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
8
H
POWER P.C.B.
SOLDER SIDE
9 . . . . . . . . . 1
CN803A
F
SPEAKER TERMINAL P.C.B.
SOLDER SIDE
CN503A
9 . . . . . . . . . 1
CN508A
9 . . . . . . . . . 1
9 . . . . . . . . . 1
CN808A
CN501A
4 . . 1
JK501
SPEAKER
XM READY
E
XM READY P.C.B.
JK1
FP1
16
17
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2
1
PbF
SOLDER SIDE
(SIDE B)
CN508B
CN501B
4 . . 1
PbF
1
.
.
.
5
CN503B
9 . . . . . . . . . 1
9 . . . . . . . . . 1
PbF
47
Page 48

SA-PM321P
48
Page 49

14 Block Diagram
OPTICAL PICKUP
SIGNAL LINES
: MAIN SIGNAL LINE
: FM/AM SIGNAL LINE
( ) Indicates Pin No. of Right Channel
SA-PM321P
CD SIGNAL LINE : XM PLAYBACK SIGNAL LINE
Note : Signal Lines are applicable to the Left Channel only.
PHOTO DETECTOR
EE EE
D C
A B
D C
EFEF
SEMICONDUCTOR
LASER
B
FOCUS
COIL
TRACKING
COIL
35
E
40
A
39
C
38
B
37
D
36
Q7601
SWITCH
LD_SW
F
41
PD
42
LD
OUTL
OUTR
56
59
CD SIGNAL
RCH
TO MAIN BLOCK
A
IC7002
BA5948FPE2
4CH DRIVE
26
VREF
F+
F-
T+
T-
D3-
15
[CH3]
D3+
16
D4-
17
[CH4]
18
D4+
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
IN3
28
27
IN4
B
FOP
TRP
BLKCK
TX
NRST
MLD
MCLK
MDATA
STAT
71
BLKCK
66
TX
72
NRST
69
MLD
67
MCLK
68
MDATA
70
STAT
IC7001
MN6627954MA
LSI IC
SPOUT
TRVP
TRP
FOP
21
22
PC
23
24
25
SPOUT
PC
TRVP
TRP
FOP
M7301
TRAVERSE
MOTOR
M7302
SPINDLE
MOTOR
D2+
14
M
M
[CH2]
13
D2-
D1+
12
[CH1]
D1-
11
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
MUTE
[CH1]
MUTE
[CH2]
IN2
1
3
IN1
PC1
4
PC2
2
TRVP
LOADING
SPOUT
X1
X2
81 80
X7201
PC
S7201
RESET SWITCH
RESTSW
LOADING
49
Page 50

SA-PM321P
IC3
C0FBBK000047
DIGITAL TO ANALOG
CONVERTER IC
AOUTL(AOUTR)
PDN
5
6
MCLK
BICK
SDTI
LRCK
SMUTE
11(10)
1
2
3
4
41
12S_LRCLK
SC_RX_IN
5
37
12S_DA
SC_TX_OUT
3
39 43
12S_CLK
12S_OCLK
18,23
RX_P, TX_P
11
19,22
RST-
RX_M, TX_M
IC1
C1AB00002670
XM DT
9
ANT_REV
OUT
26 28
X1
7(8)
JK303
AUX INPUT JACK
B
1
VCC
3
D+
2
D-
IN
GND
4,5,6,7
LINKACTIVE13I2S_RATE
14
JK1
XM JACK
MUTE
44
A1(A2)
5(6)
LEFT(RIGHT)18S1
C1(C2)
9(10)
22(21)
B1(B2)
IC800
C1BB00000732
ASP
SC
17
IC700
C0ABBB000297
FILTER
FILTER
D1(D2)
11(12)
CD SIGNAL
RCH
JK900
HEADPHONE
OP AMP
D803
D804
98
99
CLOSE_L
OPEN_H
IC805
C0CBCYG00003
5.3V REGULATOR IC
VOL_JOG197VOL_JOG2
96
VR900
VOLUME JOG
D812
Q221,Q222
(Q421,Q422)
MUTING
SWITCH
IC2
C0DBZYG00001
XM_RXD
E_CLK
62
4
E_CLK
POWER SUPPLY
IC803
MN101CP49KAF
MICROPROCESSOR
E_CS
63
3
E_CS
EN
4
76
XM_PCONT
D809
75
XM_RST
QR808
KEY12KEY2
3
S900~S910
KEY SW
SWITCH
74
ANT_REV
73
DAC_RST
QR806
SWITCH
72
LINKACTIVE
QR805
B
SWITCH
71
I2S_RATE
D910
70
D906
STANDBY LED
XM_MUTE
66
TU_ST
OSC212OSC1
X801
8MHz
65
13
Z401
TUNER PACK
47
TU_CL
TU_TUNED
15
45
XI(32KHz)
X802
32KHz
TU_SDA
IC803
MN101CP49KAF
MICROPROCESSOR
XI(32KHz)
16
RMT
26
Z901
REMOTE SENSOR
57
56
ASP_DATA
NRST
33
Q804
RESET
B
SWITCH
ASP_CLK
B
QR807
SWITCH
B
D808
18
XM_TXD
E_DATA
61
5
6
D0
D1
IC804
EEPROM
( NOT SUPPLIED )
Q830
SWITCH
19
50
Page 51

SIGNAL LINES
: MAIN SIGNAL LINE
: FM/AM SIGNAL LINE
( ) Indicates Pin No. of Right Channel
CD SIGNAL LINE : XM PLAYBACK SIGNAL LINE
Note : Signal Lines are applicable to the Left Channel only.
IC500
AN17808B
POWER AMP IC
SA-PM321P
32
GRID1~GRID11
FL_CS
9
40
FL_STB
FL900
FL DISPLAY
42
14
SEG1~SEG17
IC900
C0HBB0000057
FL DISPLAY
FL_DATA8FL_CLK
7
42
FL_DATA
44
FL_CLK
TRANSFORMER
TO CD
BLOCK
29,31
IC803
MN101CP49KAF
MICROPROCESSOR
VCC
1
B
FP352
Q803
MUTING
SWITCH
IN_L(IN_R)
5(2)
Q751
SWITCH
STBY
11
OUT_GND
9
Q750
SWITCH
OUT_L+(OUT_R+)
7(12)
D751
D750
MUTE
9
JK501
SPEAKER L(R)
B
FROM
A
STAT
MDATA
Q802
SWITCH
MCLK
CD
BLKCK
Q801
SWITCH
NRST
MLD
LD_SW/CLDCK
B
5
IC802
C0DBZGC00067
3.3V REGULATOR
2
B
B
Q507
REGULATOR
Q505
REGULATOR
B
Q530
REGULATOR
Q503
STABALIZER
Q501
SWITCH
B
Q600
PCONT
SWITCH
TO FL
DISPLAY
Q603
SWITCH
B
Q500
CURRENT
LIMITTING
D609
D504,D505
D521,D522
T601
POWER
TRANSFORMER
RY600
B
OPEN SW
21
22
CD_MDATA
23
CD_ STAT
CD_MCLK
28
CD_OPEN_SW
30
35
36
BLKCK
CD-RST
CD_MLD
IC803
MN101CP49KAF
MICROPROCESSOR
53
MUTEA
HALT
27
49
PCONT_2
25
PCONT_1
Q602
SWITCH
Q504
SWITCH
B
T600
B
Q601
REGULATOR
SYS6V
D603~D606
Z600
SUB
ZJ01
JK600
L600
F1
AC INLET
TRANSFORMER
D608
51
Page 52

SA-PM321P
52
Page 53

15 Notes Of Schematic Diagram
(All schematic diagrams may be modified at any time with
the development of new technology)
Notes:
S780: CD Open switch.
S900: Stop/-Demo switch (
S901: CD switch (CD
S903: Tuner/Band switch.
S904: FF/Tune Up switch (
S905: REW/Tune Down switch (
S906: Power switch (POWER
S907: CD Open/Close switch (
S908: Bass/Treble switch.
S910: Music Port switch.
S7201: Reset switch.
VR900: VR Volume jog.
· Importance safety notice :
Components identified by
characteristics important for safety.
Furthermore, special parts which have purposes of fireretardant (resistors), high-quality sound (capacitors), lownoise (resistors), etc. are used.
When replacing any of components, be sure to use only
manufacturer´s specified parts shown in the parts list.
-DEMO).
/ ).
/ ).
/ ).
).
).
mark have special
SA-PM321P
· Capacitor values are in microfarad(µF) unless specified
otherwise, F=Farad, pF=Pico-Farad
Resistance values are in ohm(Ω), unless specified
otherwise, 1K=1,000Ω, 1M=1,000KΩ
· Voltage and Signal lines:
: +B Signal line
: -B Signal line
: CD-DA signal line
: CD signal line
: AUX signal line
: FM/AM signal line
: Main signal line
53
Page 54

SA-PM321P
54
Page 55

16 Schematic Diagram
16.1. CD Servo Circuit
SA-PM321P
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 1
CD SERVO CIRCUIT
VCC
1
F
2
E
3
LD
4
LD GND
5
GND
6
A
TO
OPTICAL PICKUP
CIRCUIT (CP701)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 7
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
CN7001
GND
B
VREF
LPD
GND
T-
T+
F-
F+
C7335
0.1
C7334
10V220
W7023 0
W7027
0
39
37
14
D3-
D2+
W7026 0
W7024 0
1615
17
D3+
D2-
1
13
M
M
C7614
6.3V100
C7613 0.1
18
D4-
D4+
D1+
D1-
2
11
W7025
20
19
PVCC2
PGND2
PGND1
PVCC1
10
9
38
M7301
TRV
MOTOR
36
M7302
SRL MOTOR
0
21
GND
NC
IC7002
BA5948FPE2
4 CH DRIVE
GND
NC
8
: +B SIGNAL LINE : CD SIGNAL LINE
R7601
C7601
4.7
6.3V33
R7650
5.6
Q7601
B1ADCF000001
LASER POWER DRIVE
22
NCNCNC
NC
7
23
NC
R7335
25 26 27 28
24
VCC
NC
PC1
100
: CD-DA SIGNAL LINE
C7670
IN3
IN4
VREF
IN1
PC2
IN2
3456
12
C7338
R7323
R7325 330
0.1
W7017 0
W7021 0
0.056
3.3K
C7626
0.1
R7327
1K
R7336
10
R7329
1K
C7352
0.018
C7315
0.47
R7331
22K
W7020 0W7022 0
16
C7203
6.3V220
C7223 50V4.7
C7204 0.1
50
W7016
0
R7328
10K
R7349
18K
C7339
0.018
R7339
1K
R7315
3.3K
W7019
0
W7018
0
C7244 0.015
C7217 0.1
51(RF)
W7014
0
W7015 0
C7102
C7142
C7107
W7012
0
C7154
C7155
R7330 5.6K
C7218
0.082
C7241
1000P
R7211
82K
C7216
680P
C7161
R7 111
10K
W7013
14
0
0
W7010
W7007
0
C7232
6.3V220
0
C7263
S7201
RESET SW
11
8
0.1
13
W7004
0
W7002
0
W7003
0
W7001
0
210
18
7
9
31
LCH OUT
17
A.GND
16
RCH OUT
15
+3.3V
14
D.GND
13
LD SW
12
TX
11
+7.5V
PGND
MCLK
MDATA
MLD
BLKCK
STAT
/RST
REST SW
LOADING
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN801) IN
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 2
CN7002
3
4
C7253
470P
1917
W7011
R7028
W7006
0
0.1
C7233
W7008
W7009
0
0
C7243
0.1
1
C7225
1000P
C7226
1000P
727374
NRST
BLKCK
A6
C7227
C7228
75
SMCK
DQSYTXT
1
234
50V1
50V1
PMCK
IOVDD1
NTEST2
A11
DVDD2
DVSS2
NTEST
D15
D14
DRVDD
D13
D12
D11
D10
SDRCK
D7650
MAZ80560ML
76
77
78
79
80
X2
81
X1
82
83
D2
84
D1
85
D0
86
D3
87
D4
88
D5
89
D6
90
D7
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
D9
99
D8
100
R7253
R7254
C7166
R7220
1M
X7201
H2B169500005
C7264
0.1
C7234 0.1
C7235
16V10
R7332
1K
0.01
R7214
470
10
1K
R7217
1K
R7218
1K
R7212
820
R7221 100
54
53
51
IREF
DSLF
ARFFB
ARFOUT
ARFDC
AVD D2
RFIN
RFOUT
RFENV
CENV
LD
PD
A
C
B
D
F
E
VREF
CTRCRS
OSCIN
AVSS2
SRVMON1
SRVMON0
DVDD1
IOVDD2
DVSS1
ARFIN
FOP
245225
TRP
TRVP
23
0.1
50
49
48
47
0.47
46
45
3300P
44
0.022
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
0
29
0.1
28
0.1
27
26
58
57
55
56
PLLF
OUTL
PLLF0
AVSS1
AVDD1
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR/
DIGITAL FILTER D/A CONVERTER
PRAMVDD15
PRAMVDD33
PC
SPOUT
21
20
19
10
C716510C7164
PRAMVSS33
18
22
59
OUTR
MN6627954MA
BA1
17
C7230 0.1
C7231 6.3V220
W7005
24
60
61
62
63
65
EXT2
EXT1
EXT0
DVSS3
NSRVMONON
IC7001
SERVO PROCESSOR/
BA0
A10
A1A0A2
15
14
126413
16
11
0
A3
66
FLAG
10
676869
TX
MCLK
NRAS
NCAS
70
MLD
MDATA
NWEA8A7A9A5
A4
789
71
STAT
56
SA-PM321P CD SERVO CIRCUIT
1 2345678910111213
55
Page 56

SA-PM321P
16.2. Main Circuit
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 2
MAIN CIRCUIT
QR805, QR806
B1GBCFGG0030
MUTE
17
I2S_RATE
16
LINKACTIVE
15
AOUT_R
14
AGND
13
AOUT_L
12
DAC_RST
11
D3.3V
10
SC_RXD
9
SC_TXD
8
ANT_REV
7
DTIC_RST
6
DGND
5
DGND
4
D5.3V
3
D5.3V
2
PWR_CTRL
1
CD_L
17
A_GND
16
CD_R
15
CD_3.3V
14
CD_DGND
13
LD_SW/CLOCK
12
TX
11
CD_7.5V
10
PWR_GND
9
MCLK
8
MDATA
7
MLD
6
BLKCK
5
STATUS
4
RST
3
REST_SW
2
LOADING
1
GND
2
CD_OPEN_SW
1
SWITCH
R781 100
R782 100 R791 10K
R783 100
R784 100
R785 100
R786 100
R787 100
1000P
WA67
0
Q830
B1ABCF000176
SWITCH
QR807, QR808
B1GBCFGG0030
SWITCH
C812
1000P
WA50 0
R812 100
R813 100
C860 1000P
R792 10K
R793 10K
C861
TO
XM READY
CIRCUIT
(FP1) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 8
TO
CD SERVO
CIRCUIT
(CN7002) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 1
S780
CD
OPEN
CN900
CN801
CP800
QR807
1000P
WA54
0
WA53
0
R790
10K
QR805
C810
R789
4.7K
4.7K
R942
C216
1000P
C416
1000P
R809 100
R810 100
R811 100
R815 10K
R816 10K
R817 100
: +B SIGNAL LINE
R788
4.7K
QR806
D910
B0ACCK000005
R795
4.7K
R794
4.7K
Q830
QR808
L803 J0JKB0000020
Q802
WA68
0
D5V
I2S_RATE
LINKACTIVE
XM_MUTE
XM_R
AGND
XM_L
DAC_RST
CD_3.3V
XM_TXD
XM_RST
XM_PCONT
D5V
XM_RXD
ANT_REV
Q801
WA51
: AUX SIGNAL LINE : MAIN SIGNAL LINE
C0CBCYG00003
5.3V REGULATOR IC
VCTRL
2345
CD_7.5V
0
R805 10K
R806 10K
B0EAKM000117
WA56
0
R804 4.7K
1
D812
C808 16V22
IC802
C0DBZGC00067
3.3V REGULATOR IC
VIN
GND
STBYNCVOUT
2345
1
C805
16V22
WA52 0
Q801, Q802
B1GBCFGG0030
SWITCH
R803 4.7K
: CD SIGNAL LINE : FM/AM SIGNAL LINE
IC805
VIN
CD_GND
VO
R946
8.2K
ADJ
WA70 0
8.2K
R947
1.2K
R948
C804
0.1
CD_OPEN_SW
C809 16V22
D5V
CD_LCH
CD_RCH
CD_3.3V
CD_7.5V
PGND
CD_MCLK
CD_MDATA
CD_MLD
BLKCK
LOADING
CD_RST
REST_SW
STAT
D5V
XM_PCONT
C952 0.1
VOL_JOG1
VOL_JOG2
LOADING
VREF+
D5V
CD_7.5V
B0ACCE000003
C816
16V10
R823 100
R824 100
D803
D804
D803, D804
B0ADCJ000020
1
D802
B0ACCK000005
R821
470K
D889
2
R825 1K
R826 1K
C818 4700P
C817 4700P
3
B0ACCK000005
R940
220
C819 0.1
C820 4700P
C821 4700P
C824 4700P
C825 4700P
D809
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
R827 2.7K
R828 2.7K
R829 10K
R830 10K
R831 10K
R937
XM_PCONT
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
MP1
MP2
CRTIMER
NC
NC
VREF-
VOL_JOG1
VOL_JOG2
CLOSE_L
OPEN_H
VREF+
XM_RST
ANT_REV
220
R936 220
75
XM_RST
ANT_REV
VREF-
KEY1
2
1
R832 100
KEY1
DAC_RST
I2S_RATE
LINKACTIVE
R935 220
R934 220
R933 220
727374
71
DAC_RST
I2S_RATE
LINKACTIVE
KEY2
AN6 (MK_IN1)
AN7 (MK_IN2)
4
3
5
R833 100
KEY2
XM_MUTE
R891 15K
70
NCNCNC
MUTE
PWRDET
REGIONNCNC
6
789
R837 5.6K
A9V
C829 47P
E_CS
TUNED
STEREO
R890 15K
R871 1K
R870 1K
R868 1K
676869
63
65
66
NC
E_CS
TU_ST
TU_TUNED
IC803
MN101CP49KAF
MICROPROCESSOR
VREF+
VDD
OSC2 (8MHZ)
OCS1 (8MHZ)
10
126413
11
X801
R889 100
R840
1M
C833 18P
C834 18P
WA55
0
B0ACCK000005
C832 0.1
C831 0.1
E_CLK
E_DATA
R867 1K
R866 1K
61
62
60
NCNCNC
E_CLK
E_DATA
VSS
XI (32KHZ)
XO (32KHZ)
15
14
16
R842 330K
H4Z8004AA001
X802
C835 18P
C836 22P
R845 10K
R841 10K
D808
ASP_DATA
R865 1K
57
59
58
ASP_DATA
MMOD(GND)NCRDS_DATA
18
17
19
R931 220
R930 220
H0A327200100
XM_TXD
XM_RXD
ASP_CLK
R864 1K
54
55
56
NC
ASP_CLK
RDS_CLK
CD_MDATA
22
20
21
R846 4.7K
CD_MDATA
STAT
MUTEA
53
NC
NC
MUTEA
DEMO SETTING
CD_OPEN_SW
CD_STAT
CD_MCLKNCPCONT_1
245225
23
R848 4.7K
R847 100
CD_MCLK
51
NC
PCONT_2
TU_CL
TU_SDA
FL_CLK
FL_DATA
FL_STB
CD_MLD
CD_RST
NRST
BLKCK
REST_SW
HALT
RMT
R849 1K
PCONT_1
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
WA59
0
50
49
48
R872 1K
47
46
R873 1K
45
R863 100
44
43
R862 100
42
41
R861 100
40
39
38
37
R859 4.7K
36
R858 4.7K
35
34
33
32
31
30
R856 100
29
R855 1K
28
R854 1K
27
R853 1K
26
6.3V1000
PCONT2
C839
C837
6.3V100
R869
1K
R884
100K
WA57
0
C853
C853
100P
100P
G0C3R3JA0027
G0C3R3JA0027
R807 4.7K
R882 1K
L804
C840
6.3V1000
L805
C838
6.3V100
R808 4.7K
C842 1000P
R851 10K
R850 22K
B0ACCE000003
B0ACCE000003
FL_CLK
FL_DATA
FL_STB
CD_MLD
CD_RST
WA58
0
BLKCK
REST_SW
CD_OPEN_SW
R852 10K
SYS6V
D805
D806
SDA
HALT
RMT
R880
4.7K
87216
C851
0.01
E_CS
E_CLK
CL
E_DATA
C843 100P
C844 50V1
Q804
B1GBCFNN0038
RESET SWITCH
VREF+
NC
GND
IC804
EEPROM
(NOT SUPPLIED)
NC
VCCCSCLK
354
R877 22K
R878 22K
C845
0.01
D0
D1
R879 100K
R857
47K
C846
50V1
D807
B0ACCK000005
C852 100P
B1
VDD
TO MAIN
SECTION (2/5)
A
1
/
SA-PM321P MAIN CIRCUIT
2
1 2345678910111213
56
Page 57

SA-PM321P
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 3
MAIN CIRCUIT
AUX_L
AUX_R
XM_L
XM_R
TUNER_LCH
B1
TUNER_RCH
CD_LCH
CD_RCH
ASP_CLK
ASP_DATA
C101
6800P
C102
6800P
R205
4.7K
R207
4.7K
R235
33K
R435
33K
WA60
R203
2.7K
R403
2.7K
0
R201
5.6K
R401
5.6K
R211
8.2K
R411
8.2K
R206
12K
R406
12K
R204
6.8K
R404
6.8K
R202
5.6K
R402
5.6K
C210
220P
C410
220P
C205
220P
C405
220P
C201
220P
C401
220P
C203
220P
C403
220P
: +B SIGNAL LINE
WA69
0
C461
0.12
C462
0.12
C900 50V2.2
C901 50V2.2
C902 50V2.2
C903 50V2.2
C904 50V2.2
C905 50V2.2
C906 50V2.2
C907 50V2.2
C447
25V47
WA61
0
C455
0.12
C456
0.12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
: CD SIGNAL LINE : FM/AM SIGNAL LINE: AUX SIGNAL LINE : MAIN SIGNAL LINE
R446
8.2K
R447
8.2K
IC800
C1BB00000732
ASP IC
VIN1
SEL1OUT
VIN2
SEL2OUT
A1
A2
B1
B2
C1
C2
D1
D2
E1
E2
FILTER
GND
IC800
REC1
REC2
MNF1
MOUT1
MNF2
MOUT2
BNF1
BOUT1
BNF2
BOUT2
LEFT
RIGHT
CAP
VCC
S1
SC
32
31
C440 0.015
30
C449 0.015
29
C441 0.015
28
C442 0.015
27
C443 50V0.1
26
C444 0.082
25
C445 50V0.1
24
C446 0.082
23
C433 50V1
22
C233 50V1
21
C448 50V0.33
20
19
18
17
C465
47P
C464
47P
C463
AGND
16V100
Q750
B1GDCFGG0026
SWITCH
R443
3.3K
R444
3.3K
R442
6.8K
R445
6.8K
R441
33
A9V
FL_CS
MUTEA
R750
4.7K
Q751
Q803
Q803
B1GBCFJJ0044
MUTING SWITCH
C369
100
RIGHT
RMT
FL_CLK
FL_DATA
VOL_JOG1
VOL_JOG2
VREF+
Q750
C361
100
KEY2
KEY1
R7511KR752
D750
B0ACCK000005
50V1
C750
Q751
B1GBCFJJ0044
SWITCH
LEFT
D5V
AUX_R
AUX_L
2.2K
D751
B0ACCK000005
MUTEB
R753
10
R756 4.7K R755 4.7K
C751 6.3V47
C220
50V1
C752 0.01
C420
50V1
C221 330P
R220 100K
C421 330P
R420 100K
R221
15K
GND
H
R222
68K
WA62
C222
C223
100P
100P
5
IC700
364
C422
100P
WA63
0
R421
15K
0
78
+B
12
C423
100P
R422
68K
C0ABBB000297
LEFT
RIGHT
TUNER_9V
A9V
MUTEB
PCONT2
C224
6.3V47
C753 0.01
C424
6.3V47
IC700
OP-AMP
R223
C225
R224 1K
C754 16V220
C425
R424 1K
R423
47
R225
47
Q221 Q222
0.01
0.01
47
Q221, Q222
B1ABGC000001
R226
3.9K
Q421 Q422
R426
3.9K
R425
47
SWITCH
R227
3.9K
R427
3.9K
Q421, Q422
B1ABGC000001
SWITCH
C375
1000P
TUNER_9V
MUTEB
PCONT2
IN_L
AGND
IN_R
TGND
A9V
HP_R
HP_GND
WA64
0
HP_L
HP_SW
WA65
0
CN808B
1
2
3
TO
4
SPEAKER TERMINAL
CIRCUIT (CN808A)
5
ON SCHEMATIC
6
DIAGRAM - 7
7
8
NC
9
TO
1
HEADPHONE
2
CIRCUIT (WH504)
3
ON SCHEMATIC
4
DIAGRAM - 7
CN504A
G
F
E
D
CN803B
VREF-
1
D5V
HALT
PCONT_1
SYS6V
CD_7.5V
PGND
D5V
CD_DGND
9VGND
HALT
PCONT_1
SYS6V
CD_7.5V
PGND
2
3
TO
4
SPEAKER TERMINAL
CIRCUIT (CN803A)
5
ON SCHEMATIC
6
DIAGRAM - 7
7
8
9
C
CN401A
1
CL
SDA
TUNED
TUNER_LCH
STEREO
TUNER_RCH
TUNER_9V
L806 G0A200D00002
SDA
TUNED
TUNER_LCH
STEREO
TUNER_RCH
DET
TUNER_9V
TNR_GND
CL
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TO
TUNER EXTENT
CIRCUIT (CN10)
ON SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 7
B
TO MAIN
SECTION (1/5)
FL_CS
FL_CLK
FL_DATA
RMT
VOL_JOG1
VOL_JOG2
VREF+
KEY2
KEY1
D5V
VREF-
TGND
AUX_RCH
GND
AUX_LCH
14
15
TO
PANEL CIRCUIT (CN901A)
ON SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 4
9
13
12
11
10
4
8
6
7
1
5
2
3
CN901B
A
2
/
SA-PM321P MAIN CIRCUIT
2
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 2614
57
Page 58

SA-PM321P
16.3. Panel Circuit
H
G
F
E
D
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 4
PANEL CIRCUIT
C911
50V22
: +B SIGNAL LINE : AUX SIGNAL LINE: -B SIGNAL LINE
FL1
FL2
FL900
A2BB00000157
FL DISPLAY
56
1
2
89101112 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 43 44
7
151617
SEG14
GRID3
14
SEG15
GRID2
42 43
13
SEG16
GRID1
VDD
VDD
12
VSS
44
FL_CS
FL_CLK
FL_DATA
VSS
DOUT
OSC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
C923
50V22
C912
0.1
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
-VP
SEG17
GRID11
GRID10
19
22
18
20
21
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
IC900
C0HBB0000057
FL DRIVER
GRID9
GRID8
GRID7
GRID6
38
34
36
35
37
SEG12
SEG13
GRID5
GRID4
394041
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C914
0.1
C927
100P
C926
100P
R920
220
C910
50V22
R92268R923
C925
100P
R918
220
B0BC5R600003
R926
82K
R917
220
L901
G0C3R3JA0027
WA90
0
68
D900
C924
10V22
C909
50V22
C913
0.01
-VP
WH900
GND2
1
TO
-VP
2
TRANSFORMER
FL1
3
CIRCUIT (CN900B)
FL2
ON SCHEMATIC
4
SYS6V
FL_CS
FL_CLK
FL_DATA
VOL_JOG1
VOL_JOG2
VREF+
VREF-
TGND
AUX_R
-VP
AUX_L
RMT
KEY2
KEY1
D5V
GND
DIAGRAM - 6
5
CN901A
15
14
13
12
11
10
TO
9
MAIN CIRCUIT
8
(CN901B) ON
7
SCHEMATIC
6
DIAGRAM - 3
5
4
3
2
1
JK303
MUSIC PORT
C
B
3
2
1
R412
1.8K
C411
1000P
C412
4700P
C211
1000P
L203
J0JBC0000019
C212
4700P
G0C3R3JA0027
R212
1.8K
L204
AUX_R
AUX_L
KEY1
KEY2
RMT
VOL_JOG1
VOL_JOG2
VREF+
SYS6V
O
VDD
G
Z901
B3RAD0000125
REMOTE SENSOR
321
C922
6.3V47
R924
100K
R915
VR900
EVEJ1CF3024B
VOLUME JOG
A COM B
1
100K
R925
1K
23
C921
100P
D906
B3AAA0000489
STANDBY LED
C920
100P
FL_CS
S906
FL_CLK
R910
1.2K
POWER
S900
STOP/-DEMO
R901
1.2K
FL_DATA
R911
1.5K
D5V
S908
BASS/TREBLE
R902
CD
S901
R912
2.2K
1.5K
R913
3.3K
R903
2.2K
S910
MUSIC PORT
WA91
0
S903
TUNER/BAND
R914
4.7K
S907
CD OPEN/CLOSE
R904
3.3K
S904
FF/TUNE UP
R905
4.7K
S905
REW/TUNE DWN
A
SA-PM321P PANEL CIRCUIT
1 2345678910111213
58
Page 59

16.4. Power Circuit
SA-PM321P
H
G
F
E
D
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 5
POWER CIRCUIT
CN501B
CN508B
CN503B
OUT_R
1
GND_R
2
GND_L
3
OUT_L
4
IN_L
1
AGND
2
IN_R
3
TUNER_9V
4
TUNER_GND
5
A9V
6
MUTEB
7
PCONT2
8
NC
9
VREF-
1
D5V
2
CD_GND
3
9VGND
4
HALT
5
PCONT_1
6
SYS6V
7
CD_7.5V
8
PGND
9
TO
SPEAKER TERMINAL
CIRCUIT(CN501A)
ON SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 7
TO
SPEAKER TERMINAL
CIRCUIT(CN508A)
ON SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 7
TO
SPEAKER TERMINAL
CIRCUIT(CN503A)
ON SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 7
OUT_R
OUT_L
IN_L
IN_R
TUNER_9V
A9V
MUTEB
PCONT2
HALT
PCONT_1
SYS6V
CD_7.5V
IN_L
IN_R
D5V
: +B SIGNAL LINE
R495
R485
10K
8.2K
C497
1200P
R491
R492
6.8K
8.2K
C493
0.027
AGND
R295
10K
C297
1200P
R291
6.8K
C293
0.027
R251
820
R451
820
R285
8.2K
R292
8.2K
C254
50V1
C454
50V1
: MAIN SIGNAL LINE
R580
5.6K
NC
IN_RRFIN_GND
2
1
R552
56K
AGND
3
45
C580
35V100
R572
IC500
AN17808B
POWER AMP IC
IN_LNCOUT_L
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
R5
2.2K
R6
2.2K
56K
AGND
C586
50V10
R586
47K
R581
10K
C272
25V2200
33
R296
0.33
C298
MUTE
OUTPUT
_GND
FP552
2A
OUT_GND
C581
16V22
VCC
2.2K
2.2K
Q503
R517
470
A9V
C516
0.01
R515
1.5K
C510
25V10
C507
0.01
R505
100K
R501 1.2
C501
35V6800
Q503
D527
D526
D525
R502 1.2
R503 1.2
D530
D529
D528
VCC
SYS6V
D5V
Q505
B1AAJC000019
REGULATOR
C542
25V10
STANDBY
OUT_R
R1
R7
820R8820
C472
25V2200
R2
C582
50V1
R496
C498
33
0.33
INPUT
GND
R3
820
INPUT
GND
INPUT
GND
R4
820
OUT_L
OUT_R
C512
0.1
C521
0.01
C522
0.01
C515
0.01
CD_7.5V
D501, D502, D504, D505
B0EAMM000038
D502
D501
B1AAJC000019
REGULATOR
R518
1K
D508
B0BA5R600016
D504
D505
Q507
C540
16V22
Q501, Q504
B1AACF000063
C502
25V10
C523
0.01
C524
0.01
C514
0.01
D506
SWITCH
R520
470
B0BA8R200005
R514
2.2K
R511
220
R504
220
TUNER_9V
Q530
2SD0592ARA
REGULATOR
C541
16V22
D512
B0BA9R600002
Q504
B1BCCG000023
STABILIZER
Q501
D525 - D530
B0EAKM000117
Q500
Q500
B1GCCFGA0006
CURRENT LIMITING
C
AGND
MUTEB
B
PCONT2
OUTPUT_GND
VCC
AMP_VCC1
AMP_VCC2
AMP_VCC2
AMP_VCC1
A9V
PCONT_1
SYS6V
4
8
5
6
7
TO
TRANSFORMER CIRCUIT
(CN505B) IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 6
GND1
3
GND2
2
HALT
1
WH505A
A
SA-PM321P POWER CIRCUIT
1 2345678910111213
59
Page 60

SA-PM321P
16.5. Transformer Circuit
H
G
F
E
D
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 6
TRANSFORMER CIRCUIT
TO
PANEL CIRCUIT
(WH900) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 4
CN900B
GND2
1
-VP
2
FL1
3
FL2
4
SYS6V
5
Q603
2SB0621AHA
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
Q603
C610
0.01
C611
50V47
B0BA02600017
Q601
C605
25V47
B0AACK000004
Q602
B1GACFJJ0018
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
R611
3.3K
D610
2SC3940ARA
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
C604
R603
0.01
R605
150
D608
R608
50V100
Q601
820
D607
B0BA6R800007
12
C609
R601
C603
R607
10K
22
16V1000
D609
B0EAKM000117
C601
D606
0.01
B0EAKM000117
D605
B0EAKM000117
R606
10K
TO
POWER CIRCUIT (WH505A)
ON SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 5
1
3
2
HALT
GND2
GND1
C612
50V100
D602
B0EAKM000117
D611
B0EAKM000122
D604
B0EAKM000117
D603
B0EAKM000117
: +B SIGNAL LINE: -B SIGNAL LINE
4
5
6
7
8
CN505B
SYS6V
PCONT_1
AMP_VCC1
AMP_VCC2
MOTOR_9V
Q600
B1AACF000063
PCONT SWITCH
R604
4.7K
R600
47K
6
7
T600
G4CYAYY00065
BACKUP
TRANSFORMER
16
15
14
12
11
10
G4CYAYY00102
MAIN TRANSFORMER
D600
329
ERZVA5Z471
T601
342
B0AACK000004
F1
125V 1.25A
FC600 FC601
Z600
1
K6B1AEA00015
2
3
5
6
RL600
3
2
G0B371HA0005
L600
R609
3.3M
JK600
4
1
AC IN
120V 60Hz
C
B
A
SA-PM321P TRANSFORMER CIRCUIT
1 2345678910111213
60
Page 61

16.6. Tuner Extent Circuit, Headphone Circuit and Speaker Terminal Circuit
SA-PM321P
H
G
F
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 7
OPTICAL PICKUP CIRCUIT
LASER DIODE
6
8
11
12
4
9
10
5
2
3
C
C
GND
1
NBOUT
8
2
VCC
C
3
BIN
4
AIN
GND
NAOUT
VREF
7
6
5
C
CP701
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
TO
CD SERVO CIRCUIT
8
(CN7001) ON
9
SCHEMATIC
10
DIAGRAM - 1
11
C
12
13
14
15
16
: -B SIGNAL LINE
: FM/AM SIGNAL LINE: +B SIGNAL LINE
: MAIN SIGNAL LINE: CD-DA SIGNAL LINE
TUNER EXTENT CIRCUIT
TO TUNER PACK
Z401
ENG06816QF
1
CL
2
SDA
3
TUNED
4
TUNER_LCH
5
STEREO
6
TUNER_RCH
7
DET
8
TUNER_9V
9
TNR_GND
10
SDA
TUNED
TUNER_LCH
STEREO
TUNER_RCH
DET
TUNER_9V
TNR_GND
CL
10
1
2
3
TO
4
MAIN CIRCUIT
5
(CN401A) ON
6
SCHEMATIC
7
DIAGRAM - 3
8
9
CN10Z401
E
D
SPEAKER TERMINAL CIRCUIT
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN803B) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 3
C
B
9
PGND
PGND
9
TO
POWER CIRCUIT
(CN503B) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 5
8
7
SYS6V
CD_7.5V
CD_7.5V
SYS6V
8
7
5
6
HALT
PCONT_1
PCONT_1
HALT
5
6
4
1
2
3
CN803A CN808A
D5V
VREF-
9VGND
CD_DNGD
9VGND
CD_DNGD
D5V
VREF-
4
1
2
3
CN503A
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN808B) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 3
9
8
6
5
7
NC
A9V
TGND
MUTEB
PCONT2
A9V
TGND
PCONT2
NC
MUTEB
9
8
6
5
7
TO
POWER CIRCUIT
(CN508B) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 5
2
3
4
IN_R
AGND
TUNER_9V
AGND
IN_R
TUNER_9V
4
3
2
1
IN_L
IN_L
1
CN508A
C371
0.1
LOW_R+
1234
ZJ01
TO
POWER CIRCUIT
(CN501B) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 5
LOW_R-
LOW_L-
L300
L303
L300,303
G0AR76Y00003
LOW_L+
CN501A
C363
100P
C362
100P
4
3
2
1
JK501
SPEAKER
HEADPHONE CIRCUIT
HP_SW
WH504
4
3
2
1
HP_L
HP_GND
HP_R
R230
100K
R430
100K
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN504A) ON
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 3
C230
0.01
C430
0.01
1
7
6
3
2
4
5
JK900
PHONES
A
SA-PM321P OPTICAL PICKUP/TUNER EXTENT/SPEAKER TERMINAL/HEADPHONE CIRCUIT
1 2345678910111213
61
Page 62

SA-PM321P
16.7. XM Ready Circuit
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 8
XM READY CIRCUIT
FP3
Analog OUT
Digital OUT
TO
MAIN
CIRCUIT
(CN900) IN
SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM-2
AOUT_R
AGND
AOUT_L
FP2
12S_OCLK
12S_CLK
12S_DA
12S_LRCLK
DGND
FP1
MUTE
I2S_RATE
LINKACTIVE
AOUT_R
AGND
AOUT_L
DAC_RST
3.3V
SC_RXD
SC_TXD
ANT_REV
DTIC_RST
DGND
DGND
5.3V
5.3V
PWR_CTRL
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
47
R21
LB2
J0JHC0000107
*
C21
100K
R40
100K
*
R39
LB4
J0JGC0000050
R64
1
2
0.1
3
4
47
GND
IN
IN
EN
R16
R17
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
47
47
R19
R20
: +B SIGNAL LINE : FM/AM SIGNAL LINE
LB1
J0JBC0000019
(0)
(0)
*
*
R53
R54
C38
*
10V10
C37
*
10V10
LB3
39P
D1
SAII_EN
LSDP
1
VSS
2
SC_TX_OUT
3
VDD
4
SC_RX_IN
5
RFU(I2C_SCL)
6
RFU(I2C_SDA)
7
VDD
8
ANT_REV
9
VSS
10
RST-
11
12
48
13
0.1
C20
47
SAII_DA
C28
C13
VDD
SLAVE_SEL
I2S_RATE
LINKACTIVE
TX_EN
R11
1K
R12
J0JBC0000014
0.1
D1
45 43 4041 38 3739424446
VSS
MUTE
SAII_CLK
12S_OCLK
IC1
RX_P
RX_M
VDD
VSS
0.1
C4
1K
R9
100
R10 C19
100
12S_LRCLK
VDD
C5
C18
0.1
0.1
C12
0.1
12S_DA
HSDP
VSS
VDD
36
_EN
12S_CLK
DT4_MODE
35
HSDP_CLK
34
VDD
33
HSDP_DA
32
31
VSS
TEST
30
SC_RATE
29
IN
28
VDD
27
OUT
26
VSS
25
VSS
VSS
TX_P
TX_M
23201514 18 1916 17 2221 24
0.1
R13
0
R14
0
R24 100K
R23 100K
100KR2
100KR1
100KR3
47
47
100K
R57
R4
47
R58
47
C22
8
7
6
5
MA2J72800L
C1
0.1
R55
100K
C2
0.1
0.1
C3
IC1
C1AB00002670
MX DT IC
0.1
100K
C9
0.1
100K
R33
R62
C10
0.1
100K
R34
R59
100K
R7
220
R31
R32
1K
1K
C16
C15
10V10
10V22
C17
0.1
16
13 9
R25
3
0
R45
47
VDD
IC3
SDTI
VSS
LRCK
0
R46
47
R26
LB6
10
VCOM
AOUTL
AOUTR
PDN
ACKS
SMUTE
C14
R8
10K
R65
100k
0
R66
VA3
VA1-VA3
EZJZ0V80008B
J0JHC0000107
P/S
DIF0
86117
0.1
VA2
VA1
IC3
C0FBBK000047
DIGITAL TO ANALOG
CONVERTER IC
C43
1000P
4
3
2
1
10V22
C27
LB7
J0JHC0000107
GND
D+
D-
VCC
5
76
JK1
K1FA104B0047
XM READY
14
155412
DZFL
DZFR
BICK
MCLK
21
0
0
R44
R43
47
R22
47
R15
C11
10V22
R6
4.7K
X1
H0A451500001
C7
C6
15P
15P
IC2
C0DBZYG00001
POWER SUPPLY IC
A
SA-PM321P XM READY CIRCUIT
1 2345678910111213
62
Page 63

17 Printed Circuit Board
17.1. CD Servo P.C.B and Panel P.C.B
SA-PM321P
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ABCDEFG
A
CD SERVO P.C.B (REPV0082A)
TP16
TP14
R7028
C7243
CN7002
17
15
13
11
TP31
TP1
C7253
9
7
5
3
1
TP18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
TP3
R7332
TP19
C7226
TP17
R7221
TP13
C7233
C7232
W7004
W7002
W7003
C7235
M7301
(TRV MOTOR)
M
TP7 TP8
TP9
C7231
W7006
W7001
C7227
C7228
W7008
W7011
C7225
W7007
R7254
W7009
W7010
R7218
X7201
C7218
R7217
W7005
TP24
C7166
R7253
C7234
2
TP38
75
76
C7263
R7220
R7214
TP4
31
TP39
TP10
C7241
C7217
C7230
70
80
(RESET SW)
R7211
R7212
65
85
C7264
TP2
S7201
TP37
C7244
60
90
TP11
W7012
C7223
W7013
C7216
51 50
55
IC7001
95
100 1
R7325
R7335
M7302
(SPL MOTOR)
TP36
C7165
R7315
M
C7203
C7315
W7015
C7161
45
5
R7331
R7323
W7014
10
C7338
R7327
28
C7204
C7102
40
R7349
C7352
R7329
2
15
5
C7142
35
R7339
C7339
TP51
(RF)
30
20
R7330
R7328
IC7002
TP50
C7107
26
25
W7026
R7336
W7016
C7155
C7164
C7613
14
16
CN7001
20 15
10 1451
C7154
12
15
C7614
C7670
R7111
W7024
8
10
13
W7017
W7025
6
9
11
D7650
W7023
2
4
5
7
R7650
PbF
7601
C
W7018
W7019
W7022
C7626
1
3
Q7601
B
C7334
W7027
0082A-1
0082A-1
R7601
W7020
W7021
C
E
C7335
D
SENSOR
VOLUME
HI J KL MNO P
PANEL P.C.B (REPV0106A)
30
25
23
22
20
15
FL900
S905
(REW/TUNE DOWN)
R905
R904
(TUNER/BAND)
(STOP/-DEMO)
S903
WA91
S900
W921
R903
R902
C923
(MUSIC PORT)
W922
S901
(CD)
S910
L203
R901
W915
W914
W913
W911
R910
R923
D900
JK303
C211
R922
D906
S906
(POWER)
1
3
2
W917
W912
W910
C411
C910
C909
R915
W916
W920
MUSIC
PORT
C911
C922
W933
C924
CN901A
15
13
11
9
7
5
3
1
1 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 39
34 33
35
40
C913
44
R926
W928
1
C926
5
10
C927
R913
R924
W932
IC900
11 12
C914
C912
S904
(FF/TUNE UP)
W925
W924
W923
W926
Z901
R918
S908
W927
VR900
C921
R917
R911
W931
W930
W929
123
R920
WA90
C925
123
W934
R912
(BASS/TREBLE)
L901
W936
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
C212
R925
R212
W937
R412
C412
W935
L204
C920
8
9
63
R914
S907
(CD OPEN/CLOSE)
W918
PbF
0106A-1
0106A-1
W
W919
H900
1
2
3
4
5
Page 64

SA-PM321P
17.2. Main P.C.B and Tuner Extent P.C.B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ABCDEFG
B
MAIN P.C.B (REPV0106A)
IC804
R877
R879
R880
BCE
R884
Q804
R857
C845
C843
C844
W602
C805
13542
W305
C804
R869
BCE
WA58
W603
CA
R808
R807
R872
R873
A
CA
W307
14
85
C852
R861
D812
C851
R862
D807
C846
D889
WA59
R863
W306
W214
W308
W213
W211
107
W
W311
W118
123456789
W310
W509
W304
R752
Q750
W111
W112
W212
W309
W404
W702
W701
W700
W507
W505
W113
C750
Q751
D751
W114
R222
R750
BCE
423
BCE
R751
C
D750
W312
W219
IC805
3
15
CN401A
12345678910
R235
R435
R201
WA60
R401
R203
R403
85
14
IC700
R422
C422
C809
C101
R206
C205
C405
R406
202
R
C201
401
C
R402
R204
R404
W216
W109
C222C223
W117
C102
C203
C403
W108
R441
R948
C753
R421
C808
R947
R221
C421
R946
R420
WA62
C952
WA61
C221
C420
C904
C905
C447
R220
WA70
C448
C463
W217
C220
WA63
R756
C751
C752
C464
C465
W215
CN808B
222
W218
W
R753
R755
C906
C907
15 5
IC800
20 25 30
C233
C369
W313
W314
W226
W101
W102
QR805
R789
R788
D910
R790
R782
R781
16
W601
BCE
14
12
8
6
4
2
15
13
11
9
7
5
3
1
806
R
WA54
W300
R942
CP800
W200
R816
R813
R817
WA50
J812
R784
R792
BCE BCE
QR808
W600
W500
12
Q802
C812
R793
WA67
BCE
CN801
QR807
Q830
CN901B
10
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
1357911131517
WA53
BCE
W201
WA68
R794
R815
R812
C810
W202
R791
QR806
C860
R786
L803
W203
BCE
R787
CN900
R827
C824
R837
R829
R828
C825
L805
C838
W901
Q801
BCE
C416
W204
L804
W501
C216
C861
R783
13254769811101312151417
R830
R831
W302
R795
WA51
R811
R810
R809
W205
W103
1
30
W
C840
W206
C820
R832
C821
R833
D806
W502
WA52
R805
R804
J801
W207
C839
D805
W208
C833
829
C
C835
R803
D804
R826
W508
C832
C834
D803
R825
C816
R823
R824
C837
X801
R840
X802
785
R
W303
D809
W900
C817
C818
R889
D808
W800
R821
C819
100
1
C831
R842
R930
W801
R940
D802
95
5
C836
R931
10
W802
W104
R935
90
R846
845
R
WA55
W105
R934
85
15
848
R
R847
W803
20
804
W
80
W106
R841
R849
J802
R933
R937
76 75
IC803
25 26
W703
W805
CN504A
1234
WA56
W504
R936
70
65
35
30
R854
R853
R856
R850
C853
R882
W806
W807
R890
R891
60
40
R855
W808
(NOT SUPPLIED)
R871
R870
R868
Q803
55
51
50
45
R852
R851
859
R
R858
C842
WA57
W407
W809
W810
IC802
CN803B
R878
R867
R865
R864
W811
W210
R866
HI J KL MNO P
C
TUNER EXTENT P.C.B (REPV0107A)
CN10
12345678910
TO
Z401(
TUNER PACK)
W223
C754
C433
W224
WA65
L806
361
C
C903
C445
123456789
C424
224
C
C901
116
3217
R423
R424
R223
Q221
C446
C375
Q421
425
C
C225
R224
WA69
R411 R211
R207
C902
C462
C456
C461
C455
R447
R446
C440
C449
C441
C442
443
C
W315
R426
R226
R442
C444
R445
W220
PbF
WA64
W510
W506
W511
C210C410
W115
W116
R443
R444
R425
BCEBCE
R427
R225
BCEBCE
R227
W221
C900
0106A-1
0106A-1
205
R
Q422
Q222
12345678910
PbF
0107A
0107A
9
64
Page 65

17.3. Power P.C.B and Speaker Terminal P.C.B
SA-PM321P
1
2
3
4
5
ABCDEFG
H
POWER P.C.B (REPV0107A)
R514
C521
D502
WH505A
1
2
W94
3
4
5
6
7
8
W57
D530
C512
D527
D529
W56
C501
D526
W95
W68
R511
W66
Q501
C502
R504
D528
W65
Q504
BCE
W69
BCE
R515
C510
D525
W67
W64
W77
W78
HEATSINK
Q503
C541
D512
C586
R586
C581
Q530
B
C
E
C507
R581
W82
R505
R517
C516
R580
BCE
Q500
B
C
E
79
W
FP552
81
W
C582
R2
R1
R501
R502
R503
2A
C472
W87
R4
R3
C272
W93
W88
HI J KL MNO P
F
SPEAKER TERMINAL P.C.B (REPV0107A)
CN803A
CN503A
12
3456789
ZJ01
12
3456789
CN508A
CN808A
W121
C371
CN501A
12
3456789
34
12
3456789
JK501
1
3
C363
2
C362
L300
W122
W123
12
PbF
0107A
0107A
L303
SPEAKER
4
6
7
8
9
D501
C522
D505
D504
W53
W54
W55
C524
C523
D508
D506
W52
C542
R518
C515
Q505
C540
W51
BCE
CN503B
R520
C514
Q507
62
W
123456789
R291
R491
292
R
C493
R451
W84
C254
R251
C293
R572
R552
C580
C454
CN501B
IC500
1234
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
W83
W85
W86
C298
R8
R296
R5
R6
W91
R7
W92
R496
C498
W89
W90
0107A
0107A
PbF
W80
C297
W71
R485
R495
R295
W76
C497
W73
W63
BCE
W59
W60
R285
W74
W75
W70
CN508B
W72
R492
123456789
65
Page 66

SA-PM321P
17.4. Transformer P.C.B, Headphone P.C.B and XM Ready P.C.B
1
2
3
4
5
6
ABCDEFG
I
TRANSFORMER P.C.B (REPV0107A)
AC IN
120V 60Hz
D600
C604
R603
D607
R605
C605
R600
10
W
C603
42
D606
D604
3
D605
C601
W9
65
D603
F1
1.25A 125V
L600
JK600
W5
W6
W7
W4
R609
2
1
W3
FC600
Z600
FC601
T600
(BACK UP TRANSFORMER)
3
2
(MAIN TRANSFORMER)
2
PRIMARY
3
4
1
T601
Q601
RL600
B
C
E
6
7
9
R601
W11
D611
Q600
R607
BCE
604
R
CN505B
R606
D608
Q602
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
BCE
R608
HI J KL MNO P
G
HEADPHONE P.C.B (REPV0106A)
C230
Q603
C610
W12
BCE
CN900B
1
2
3
4
5
D610
R611
611
C
D609
D602
C612
CAUTION
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK
AC VOLTAGE LINE.
PLEASE DO NOT TOUCH THIS P.C.B
W13
609
C
R230
JK900
5
4
3
2
1
6
7
HEADPHONE
E
XM READY P.C.B. (REP4165B)
LB4
C13
R25
R45
LB1
R22
R8
R40
R39
C43
R430
R54
PbF
R2
R1
R33
R53
C430
R24
R26R46
R55
C5
R62
R34
WH504
0106A-1
0106A-1
R4
C3
R23
C4
R10
C9
R6
1234
W951
LB6
LB7
R21
C22
R11
C20
R12
R7
C6
C7
3168A
PbF
3168A
7
8
9
Y
R
A
D
N
O
C
E
S
16 15
14 12
11 10
PbF
0107A
0107A
66
XM READY
(SIDE A)
5
6
IC2
C27
VA1
JK1
5
1
3
6
7
(SIDE B)
FP1
LB2
R57
R3
4
C2
R13
R9
R58
R14
C21
12 5 1
13
15
C18
20
24
C19
C10
R59
X1
IC1
C1
C12
D1
48
45
LB3
40
37
R15
R43
363025
R66
R65
8
IC3
R32
R31
C37
3
2187
VA3
2
4
VA2
C11
1
169
C28
R44
C15
C38
R17
C14
C17
R16
R19
R20
PbF
R64
C16
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
17
15
13
11
9
7
5
3
1
3168A
3168A
Page 67

18 Illustration of IC's, Transistors and Diodes
SA-PM321P
BA5948FPE2 (28P)
1
C0CBCYG00003 (5P)
3
1
5
2SB0621AHA
E
C
B
B0AACK000004
B0ADCJ000020
C0ABBB000297 (8P)
1
4
5
B1AACF000063
B1GACFJJ0018
B
C
E
B1GCCFGA0006
B
C
E
B0EAKM000117
B0EAMM000038
C1BB00000732 (32P)
C0DBZYG00001 (8P)
C0FBBK000047 (16P)
1
8
B1BCCG000023
B
C
E
2SD0592ARA
B1AAJC000019
E
C
B
B0BA6R800007
B0BA02600017
B0BA5R600016
B0BA9R600002
B0BA8R200005
MN6627954MA(100P)
MN101CP49KAF(100P)
C1AB00002670(48P)
C0HBB0000057(44P)
1
2SC3940ARA
B1GDCFGG0026
C
E
B
Ca
Cathode
A
Anode
C0DBZGC00067
5
1
2
3
B1ABGC000001
B1GBCFNN0038
B1GBCFGG0030
B1GBCFJJ0044
B1ADCF000001
B1ABCF000176
B3AAA0000489
Anode
Cathode
A
Ca
MAZ80560ML
Cathode
Ca
Anode
A
AN17808B
4
1
12
C
B
E
B0ACCK000005
B0ACCE000003
MA2J72800L
Cathode
Ca
Anode
A
B0BC5R600003
Anode
A
Cathode
Ca
Cathode
Anode
Cathode
67
Page 68

SA-PM321P
19 Terminal Function of IC's
19.1. IC7001 (MN6627954MA) IC SERVO PROCESSOR/DIGITAL SIGNAL
PROCESSOR/DIGITAL FILTER D/A CONVERTER
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
1 A11 O DRAM address signal O/P 11
2 A9 O DRAM address signal O/P 9
3 A8 O DRAM address signal O/P 8
4 A7 O DRAM address signal O/P 7
5 A6 O DRAM address signal O/P 6
6 A5 O DRAM address signal O/P 5
7 A4 O DRAM address signal O/P 4
8 NWE O Write Enable Signal (DRAM)
9 NCAS O DRAM CAS Control Signal
10 NRAS O DRAM ARS Control Signal
11 A3 O DRAM address Signal O/P 3
12 A2 O DRAM address Signal O/P 2
13 A1 O DRAM address Signal O/P 1
14 A0 O DRAM address Signal O/P 0
15 A10 O DRAM address Signal O/P 10
16 BA0 - No Connection
17 BA1 - No Connection
18 PRAMVSS33 - GND (DRAM)
19 PRAMVDD15 - Power Supply Voltage (DRAM)
20 PRAMVDD33 - Power Supply Voltage (+1.6V)
21 SPOUT O Spindle Drive O/P
22 PC I/O Spindle motor drive O/P signal
serial data/Monitoring I/P
23 TRVP O Traverse Drive O/P (+ve)
24 TRP O Tracking Drive O/P (+ve)
25 FOP O Focusing Drive O/P (+ve)
26 DVSS1 - GND
27 IOVDD2 I/O Digital Power Supply Voltage 2
(I/O)
28 DVDD1 - Digital Power Supply Voltage 1
(Built-In)
29 SRVMON0 - No Connection
30 SRVMON1 - No Connection
31 AVSS2 - GND
32 OSCIN I Oscillating Input
33 CTRCRS - No Connection
34 VREF - +Vref Supply Voltage
35 E I Tracking Input Signal 1
36 F I Tracking Input Signal 2
37 D I Focusing Input Signal 4
38 B I Focusing Input Signal 2
39 C I Focusing Input Signal 3
40 A I Focusing Input Signal 1
41 PD I APC Amp I/P
42 LD O Laser Drive Current O/P
43 CENV I Detection Capacitance
Connection terminal
44 RFENV O RF Envelope O/P
45 RFOUT O RF Summing Amp O/P
46 RFIN I SGC I/P
47 AVDD2 I Analog Power Supply voltage 2
(For DSL/PLL)
48 ARFDC O AGC Capacitive Connection
Terminal
49 ARFOUT O AGC Output
50 ARFFB I ARF Feedback Signal I/P
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
51 ARFIN I Audio RF Signal I/P
52 DSLF I Loop Filter Terminal (For DSL)
53 IREF I Reference I/P
54 PLLF I PLL Loop Filter Terminal (Phase
Compare)
55 PLLF0 O PLL Loop Filter Terminal (Speed
Compare)
56 OUTL\ O Audio O/P (LCH)
57 AVSS1 - GND
58 AVDD1 I Analog Power Supply Voltage 1
59 OUTR O Audio O/P (RCH)
60 DVSS3 - GND3 (Digital Circuit)
61 NSRVMONON - No Connection
62 EXT0 - No Connection
63 EXT1 - No Connection
64 EXT2 - No Connection
65 FLAG - No Connection
66 TX - No Connection
67 MCLK I Micro-Computer Command
Clock I/P
68 MDATA I Micro-Computer Data I/P
69 MLD I Micro-Computer Load I/P
70 STAT O Status Signal O/P
71 BLKCK O Subcode Blk Clock
72 NRST O LSI Reset Signal
73 DQSYTXT - No Connection
74 SMCK - No Connection
75 PMCK - No Connection
76 DVDD2 - Digital Power Supply Voltage 2
(+1.5V)
77 IOVDD1 - Digital Power Supply Voltage 1
(For I/O)
78 DVSS2 - GND2 (For Digital Circuit)
79 NTEST2 I Test Mode Setting (ON:H)
80 X2 O Crystal Oscillating Circuit O/P
81 X1 I Crystal Oscillating Circuit I/P
82 NTEST I Test Mode Setting I/P (ON:H)
83 D2 I/O Data Signal O/P 2
84 D1 I/O Data Signal O/P 1
85 D0 I/O Data Signal O/P 0
86 D3 I/O Data Signal O/P 3
87 D4 I/O Data Signal O/P 4
88 D5 I/O Data Signal O/P 5
89 D6 I/O Data Signal O/P 6
90 D7 I/O Data Signal O/P 7
91 D15 I/O Data Signal O/P 15
92 D14 I/O Data Signal O/P 14
93 DRVDD I/O I/O Power Supply Voltage
(DRAM)
94 D13 I/O Data Signal O/P 13
95 D12 I/O Data Signal O/P 12
96 D11 I/O Data Signal O/P 11
97 D10 I/O Data Signal O/P 10
98 D9 I/O Data Signal O/P 9
99 D8 I/O Data Signal O/P 8
100 SDRCK O Clock Signal O/P
19.2. IC7002 (BA5948FPE2) IC 4CH Drive
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
1 IN2 I Motor Driver 92 Input
68
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
2 PC2 I Turntable Motor Drive Signal
(“L”:ON)
Page 69

Pin No. Mark I/O Function
3 IN1 I Motor Drive (1) Input
4 PC1 - Traverse Motor Drive Signal (“L”:
ON)
5-8 N.C. - No Connection
9 PGND1 - Ground Connection (1) for Drive
10 PVCC1 I Power Supply (1) for Drive
11 D1- O Motor Drive (1) reverse - action
output
12 D1+ O Motor Drive (1) forward - action
output
13 D2- O Motor Drive (2) reverse - action
output
14 D2+ O Motor Drive (2) forward - action
output
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
15 D3- O Motor Drive (3) reverse - action
16 D3+ O Motor Drive (3) forward - action
17 D4- O Motor Drive (4) reverse - action
18 D4+ O Motor Drive (4) forward - action
19 PVCC2 - Power Supply (2) for Driver
20 PGND2 - Ground Connection (2) for Driver
21-24 N.C. - No Connection
25 VCC I Power Supply terminal
26 VREF I Reference Voltage Input
27 IN4 I Motor Driver (4) Input
28 IN3 I Motor Driver (3) Input
19.3. IC803 (MN101CP49KAF) MICROPROCESSOR
SA-PM321P
output
output
output
output
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
1 VREF- - A/D Converter Reference GND
2 KEY1 I Key 1 Input
3 KEY2 I Key 2 Input
4 AN6 (MK_IN1) I Mech Condition Input1 (Mode
5 AN7 (MK_IN2) I Mech Condition Input2 (Half and
6 PWRDET I Power Detect
7 REGION I Destination Setting
8 N.C. - No Connection
9 N.C. - No Connection
10 VREF+ - A/D Converter Reference Volt
11 VDD - Power Input Pin
12 OSC2 (8MHZ) O Main Oscillator Output
13 OSC1 (8MHZ) I Main Oscillator Input
14 VSS - GND
15 XI (32KHZ) I Suboscillator Input
16 XO (32KHZ) O Suboscillator Output
17 MMOD (GND) - Memory Mode Selection
18 N.C. - No Connection
19 RDS_DATA I/O RDS IC CTRL
20 RDS_CLK O RDS CLK IN
21 CD_MDATA O CD LSI Command Data
22 CD_STAT I CD Status Input
23 CD_MCLK O CD LSI Command Clock
24 N.C. - No Connection
25 PCONT_1 O Power Control Output1 (PWR
26 RMT I Remocon Input
27 HALT I AC Failure Detect Signal
28 CD_OPEN
_SW
29 REST_SW I CD Tranverse Limit SW
30 BLKCK I CD Subcode Block Clock Input
31 N.C. - No Connection
32 N.C. - No Connection
33 NRST I Micom Reset (L: Reset)
34 N.C. - No Connection
35 CD_RST O CD Reset Output
36 CD_MLD O CD LSI Command Load
37 N.C. - No Connection
38 N.C. - No Connection
39 N.C. - No Connection
40 FL_STB O FL Strobe Output
41 N.C. - No Connection
42 FL_DATA O FL Data Output
43 N.C. - No Connection
44 FL_CLK O FL Clock Output
45 TU_SDA O IIC Data Line For Tuner
and TPS)
RECINF)
SPLY, Active High)
I CD Open Switch (L: Open, H:
Close)
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
46 N.C. - No Connection
47 TU_CL O IIC Clock Signal For Tuner
48 N.C. - No Connection
49 PCONT_2 O Power Control Output2 (PWR
50 DEMO
SETTING
51 N.C. - No Connection
52 N.C. - No Connection
53 MUTE A O Audio Mute O/P (L: Mute On)
54 N.C. - No Connection
55 N.C. - No Connection
56 ASP_CLK O ASP CLK
57 ASP_DAT O ASP Data
58 N.C. - No Connection
59 N.C. - No Connection
60 N.C. - No Connection
61 E_DATA I/O Eeprom Data In/Out
62 E_CLK O Eeprom Clock Output
63 E_CS O Eeprom CS Output
64 N.C. - No Connection
65 TU_TUNED I/O Tuner Tuned Signal
66 TU_ST I/O Tuner Stereo Signal
67 N.C. - No Connection
68 N.C. - No Connection
69 N.C. - No Connection
70 MUTE O XM Mute
71 I2S_RATE I XM I2s Rate
72 LINKACTIV E I XM Link Active
73 DAC_RST O XM DAC Reset
74 ANT_REV I XM_ANT REV
75 XM_RST O XM_Reset
76 XM_PCONT O XM_PCONT
77 N.C. - No Connection
78 N.C. - No Connection
79 N.C. - No Connection
80 N.C. - No Connection
81 N.C. - No Connection
82 N.C. - No Connection
83 N.C. - No Connection
84 N.C. - No Connection
85 N.C. - No Connection
86 N.C. - No Connection
87 N.C. - No Connection
88 N.C. - No Connection
89 N.C. - No Connection
90 N.C. - No Connection
91 N.C. - No Connection
92 CRTIMER I/O CR Timer
AMP, active H)
I Demo Mode Setting (H: OFF, L:
ON)
69
Page 70

SA-PM321P
Pin No. Mark I/O Function
93 N.C. - No Connection
94 N.C. - No Connection
95 VREF- - D/A Converter Reference GND
96 VOL_JOG1 I Jog Input 1
97 VOL_JOG2 I Jog Input 2
98 CLOSE_L O CD Tray Close Control (Active
L)
99 OPEN_H O CD Tray Open Control (Active
H)
100 VREF+ - D/A Converter Reference
Voltage
70
Page 71

20 Troubleshooting Flowchart (CD Section Circuit)
SA-PM321P
71
Page 72

SA-PM321P
72
Page 73

21 Exploded Views
21.1. Cabinet Parts Location
SA-PM321P
73
Page 74

SA-PM321P
21.2. Traverse Deck Part Location
74
Page 75

21.3. Packaging
SA-PM321P
75
Page 76

SA-PM321P
76
Page 77

SA-PM321P
22 Replacement Parts List
Notes:
· Important safety notice:
Components identified by
Furthermore, special parts which have purposes of fire-retardent (resistors), high-quality sound (capacitors), low noise
(resistors), etc are used.
When replacing any of these components, be sure to use only manufacturer’s specified parts shown in the parts list.
· The parenthesized indications in the Remarks columns specify the areas or colour. (Refer to the cover page for area or colour)
Parts without these indications can be used for all areas.
· Warning: This product uses a laser diode. Refer to “Precaution of Laser Diode”.
· Capacitor values are in microfarads (µF) unless specified otherwise, P= Pico-farads (pF), F= Farads.
· Resistance values are in ohms, unless specified otherwise, 1K=1,000 (OHM).
· The marking (RTL) indicates that the Retention Time is limited for this items. After the discontinuation of this assembly in
production, the item will continue to be available for a specific period of time. The retention period of a availability is dependent
on the type of assembly, and in accordance with the laws governing part and product retention. After the end of this period, the
assembly will no longer be available.
· [M] Indicates in the Remarks columns indicates parts supplied by PAVCSG.
· Reference for O/I book languages are as follows:
Ar: Arabic Du: Dutch It: Italian Sp: Spanish
Cf: Canadian French En: English Ko: Korean Sw: Swedish
Cz: Czech Fr: French Po: Polish Co: Traditional Chinese
Da: Danish Ge: German Ru: Russian Cn: Simplified Chinese
Pe: Persian Ur: Ukraine
mark have special characteristics important for safety.
Ref.
No.
1 REEV0113 15P FFC [M]
2 REEV0114 17P FFC (CD-MAIN) [M]
3 REEV0137 FFC [M]
4 REXV0062 8P WIRE (PWR-TRAN) [M]
5 RGKV0149A-S VOLUME ORN [M]
6 RGLV0061-Q LIGHTING TIP [M]
7 RGUV0134B-S FUNCTION BUTTON [M]
8 RMNV0062 FL HOLDER [M]
9 RGUV0156-S POWER BUTTON [M]
10 RGUV0158-S CD EJECT BUTTON [M]
11 RGUV0159-S CONTROL BUTTON [M]
12 RGWV0039-1S VOLUME KNOB [M]
13 RHD26046-L SCREW [M]
14 RHD30111-3 SCREW [M]
15 RHDV30007 SCREW [M]
16 RHGV0008 LEG CUSHION [M]
17 RKFV0059A-S CD LID [M]
18 RKMV0064A-H SIDE PANEL [M]
19 RKMV0065A-H SIDE PANEL [M]
20 RKMV0067A-S TOP CABINET [M]
21 RMAV0001 MAIN PCB SUPPORT [M]
22 RMYV0053 HEAT SINK [M]
23 RSCV0073 REAR SHIELD [M]
24 RSCV0085 XM REAR SHIELD PLATE [M]
25 SHE187-4J POWER PCB SUPPORT [M]
27 XTB3+20JFJK SCREW [M]
28 XTB3+8FFJ SCREW [M]
29 XTV3+8FFJ SCREW [M]
30 RMKV0051 BOTTOM CHASSIS [M]
31 XTB3+10JFJ SCREW [M]
32 RKSV0035E-H REAR CABINET [M]
33 RFKGAPM321PS FRONT PANEL ASS’Y [M]
34 RSCV0083 XM SHIELD [M]
35 RSCV0084 XM ANGLE [M]
36 RWJ1104150QX 4P WIRE [M]
37 RWJ1105205QX 5P WIRE (PANEL-TRAN) [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
CABINET AND CHASSIS
Ref.
No.
301 RAE0157Z-V TRAVERSE W/O PCB [M]
302 RDG0455 TRAVERSE GEAR (A) [M]
303 RDG0456-1 TRAVERSE GEAR (B) [M]
304 RFKNCT100 TRAVERSE BASE ASS’Y [M]
304-1 RDG0457 LOAD GEAR (A) [M]
304-10 RXQ0632 TRAVERSE MOTOR UNIT [M]
304-2 RDG0458-1 LOAD GEAR (B) [M]
304-3 RDG0459-1 LOAD GEAR (C) [M]
304-4 RME0369-1 PRESS SPRING [M]
304-5 RME0291-1 LOCK SPRING [M]
304-6 RML0551-1 TRIGGER LEVER [M]
304-7 RML0552 LOCK LEVER [M]
304-8 RMM0219-1 STOPPER [M]
304-9 XQN17+C28FJ SCREW [M]
305 RDG0460-2 CAM GEAR [M]
306 RDG0461 DRIVE GEAR [M]
307 RGQ0254-K2 TRAY [M]
308 RHM0001 MAGNET [M]
309 RMB0603 FLOATING SPRING [M]
310 RME0288-1 CENTERING SPRING [M]
311 RFKNXED50-S CLAMPER HOLDER ASS’Y [M]
312 RMG0510-K FLOATING RUBBER (A) [M]
313 RMG0511-K FLOATING RUBBER (B) [M]
314 RMK0422-7 MECHA CHASSIS [M]
315 RMM0218-1 TRAVERSE DRIVE RACK [M]
316 RHD30083-1 CAM. GEAR SCREW [M]
317 RMR1223-K1 CLAMP PLATE [M]
318 RMR1242-X2 FIXTURE [M]
319 XTN2+6GFJ SCREW [M]
320 RXQ0999 OPU UNIT [M]
321 SNSD38-1 SCREW [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
TRAVERSE DECK
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD
REPV0106A MAIN P.C.B / PANEL P.C.B /
HEADPHONE P.C.B
[M]
(RTL)
77
Page 78

SA-PM321P
Ref.
No.
IC1 C1AB00002670 IC XM [M]
IC2 C0DBZYG00001 IC POWER SUPPLY [M]
IC3 C0FBBK000047 IC DAC [M]
IC500 AN17808B IC POWER AMP [M]
IC700 C0ABBB000297 IC DUAL OP-AMP [M]
IC800 C1BB00000732 IC ASP [M]
IC802 C0DBZGC00067 IC 3.3V REGULATOR [M]
IC803 MN101CP49KAF IC MICROPROCESSOR [M]
IC805 C0CBCYG00003 IC 5.3V REGULATOR [M]
IC900 C0HBB0000057 IC FL DRIVER [M]
IC7001 MN6627954MA IC SERVO PROCESSOR/DIGITAL
IC7002 BA5948FPE2 IC 4 CH DRIVE [M]
Q221 B1ABGC000001 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q222 B1ABGC000001 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q421 B1ABGC000001 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q422 B1ABGC000001 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q500 B1GCCFGA0006 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q501 B1AACF000063 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q503 B1BCCG000023 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q504 B1AACF000063 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q505 B1AAJC000019 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q507 B1AAJC000019 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q530 2SD0592ARA TRANSISTOR [M]
Q600 B1AACF000063 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q601 2SC3940ARA TRANSISTOR [M]
Q602 B1GACFJJ0018 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q603 2SB0621AHA TRANSISTOR [M]
Q750 B1GDCFGG0026 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q751 B1GBCFJJ0044 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q801 B1GBCFGG0030 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q802 B1GBCFGG0030 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q803 B1GBCFJJ0044 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q804 B1GBCFNN0038 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q830 B1ABCF000176 TRANSISTOR [M]
Q7601 B1ADCF000001 TRANSISTOR [M]
QR805 B1GBCFGG0030 CHIP TRANSISTOR [M]
QR806 B1GBCFGG0030 CHIP TRANSISTOR [M]
QR807 B1GBCFGG0030 CHIP TRANSISTOR [M]
QR808 B1GBCFGG0030 CHIP TRANSISTOR [M]
D1 MA2J72800L DIODE [M]
D501 B0EAMM000038 DIODE [M]
D502 B0EAMM000038 DIODE [M]
D504 B0EAMM000038 DIODE [M]
D505 B0EAMM000038 DIODE [M]
D506 B0BA8R200005 DIODE [M]
D508 B0BA5R600016 DIODE [M]
D512 B0BA9R600002 DIODE [M]
D525 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D526 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D527 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D528 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D529 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D530 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D600 B0AACK000004 DIODE [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
REPV0107A TUNER EXTENT P.C.B /
REP4165B XM READY P.C.B [M]
REPV0082A CD SERVO P.C.B [M]
TRANSFORMER P.C.B / POWER
P.C.B / SPEAKER TERMINAL
P.C.B
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SIGNAL PROCESSOR/DIGITAL
FILTER D/A CONVERTER
TRANSISTORS
DIODES
[M]
(RTL)
(RTL)
(RTL)
[M]
Ref.
No.
D602 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D603 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D604 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D605 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D606 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D607 B0BA6R800007 DIODE [M]
D608 B0AACK000004 DIODE [M]
D609 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D610 B0BA02600017 DIODE [M]
D611 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D750 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D751 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D802 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D803 B0ACCE000003 DIODE [M]
D804 B0ACCE000003 DIODE [M]
D805 B0ACCE000003 DIODE [M]
D806 B0ACCE000003 DIODE [M]
D807 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D808 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D809 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D812 B0EAKM000117 DIODE [M]
D889 B0ADCJ000020 DIODE [M]
D900 B0BC5R600003 DIODE [M]
D906 B3AAA0000489 DIODE [M]
D910 B0ACCK000005 DIODE [M]
D7650 MAZ80560ML DIODE [M]
VR900 EVEJ1CF3024B VR VOLUME ENCORDER [M]
VA1 EZJZ0V80008B CHIP VARISTOR [M]
VA2 EZJZ0V80008B CHIP VARISTOR [M]
VA3 EZJZ0V80008B CHIP VARISTOR [M]
S780 K0F111E00093 OPEN SWITCH [M]
S900 EVQ21405RJ SW STOP/-DEMO [M]
S901 EVQ21405RJ SW CD [M]
S903 EVQ21405RJ SW TUNER/BAND [M]
S904 EVQ21405RJ SW FF/TUNE UP [M]
S905 EVQ21405RJ SW REW/TUNE DWN [M]
S906 EVQ21405RJ SW POWER [M]
S907 EVQ21405RJ SW CD OPEN/CLOSE [M]
S908 EVQ21405RJ SW BASS/TREBLE [M]
S910 EVQ21405RJ SW MUSIC PORT [M]
S7201 RSH1A048-A SW RESET [M]
CN10 K1KB10B00042 10P CONNECTOR [M]
CN401A K1KA10AA0031 10P CONNECTOR [M]
CN501A K1KB04A00035 4P CONNECTOR [M]
CN501B K1KA04BA0125 4P CONNECTOR [M]
CN503A K1KA09AA0031 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN503B K1KB09B00013 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN504A K1MP04A00003 4P CONNECTOR [M]
CN505B K1KA08AA0319 8P CONNECTOR [M]
CN508A K1KA09AA0031 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN508B K1KB09B00013 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN801 K1MN17AA0004 17P CONNECTOR [M]
CN803A K1KA09AA0031 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN803B K1KB09B00013 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN808A K1KA09AA0031 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN808B K1KB09B00013 9P CONNECTOR [M]
CN900 K1MN17AA0004 17P CONNECTOR [M]
CN900B K1MP05A00004 5P CONNECTOR [M]
CN901A K1MN15A00049 15P FFC CONNECTOR [M]
CN901B K1MN15A00049 15P FFC CONNECTOR [M]
CN7001 K1MN16B00154 16P CONNECTOR [M]
CN7002 K1MN17B00032 17P CONNECTOR [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
VARIABLE RESISTORS
SWITCHES
CONNECTORS
78
Page 79

Ref.
No.
CP800 REXX0230-2 2P WIRE (MAIN-CR120) [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
Ref.
No.
SA-PM321P
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
CHIP JUMPERS
FP1 K1MN17BA0005 17P FFC CONNECTOR [M]
COILS & TRANSFORMERS
L203 J0JBC0000019 CHIP INDUCTOR [M]
L204 G0C3R3JA0027 COIL [M]
L300 G0AR76Y00003 CHOKE COIL [M]
L303 G0AR76Y00003 CHOKE COIL [M]
L600 G0B371HA0005 LINE FILTER [M]
L803 J0JKB0000020 EMI BEAD CORE [M]
L804 G0C3R3JA0027 COIL [M]
L805 G0C3R3JA0027 COIL [M]
L806 G0A200D00002 RF CHOKE COIL [M]
L901 G0C3R3JA0027 COIL [M]
LB1 J0JBC0000019 CHIP INDUCTOR [M]
LB2 J0JHC0000107 INDUCTOR COIL [M]
LB3 J0JBC0000014 CHIP COIL [M]
LB4 J0JGC0000050 EMI FILTER [M]
LB6 J0JHC0000107 INDUCTOR COIL [M]
LB7 J0JHC0000107 INDUCTOR COIL [M]
T600 G4CYAYY00065 SUB TRANSFORMER [M]
T601 G4CYAYY00102 MAIN TRANSFORMER [M]
COMPONENT COMBINATION
Z401 ENG06816QF TUNER PACK [M]
Z600 ERZVA5Z471 ZENER [M]
Z901 B3RAD0000125 REMOTE SENSOR [M]
RELAY
RL600 K6B1AEA00015 POWER RELAY [M]
OSCILLATORS
X1 H0A451500001 CRYSTAL [M]
X801 H4Z8004AA001 CERAMIC RESONATOR [M]
X802 H0A327200100 CRYSTAL [M]
X7201 H2B169500005 CRYSTAL [M]
DISPLAY TUBE
FL900 A2BB00000157 FL DISPLAY [M]
FUSE
F1 K5D122APA009 FUSE [M]
FUSE HOLDERS
FC600 EYF52BCY FUSE CLIP [M]
FC601 EYF52BCY FUSE CLIP [M]
FUSE PROTECTOR
W7001 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7002 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7003 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7004 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7005 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7006 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7007 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7008 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7009 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7010 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7011 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7012 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7013 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7014 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7015 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7016 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7017 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7018 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7019 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7020 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7021 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7022 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7023 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7024 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7025 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7026 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
W7027 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA50 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA51 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA52 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA53 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA54 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA55 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA56 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA57 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA58 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA59 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA60 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA61 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA62 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA63 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA64 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA65 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA67 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA68 ERJ3GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA69 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA70 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA90 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WA91 ERJ6GEY0R00V CHIP JUMPER [M]
WIRE HOLDER
WH504 RMR0313 CABLE HOLDER [M]
WH505A K1YF08000003 8P WIRE HOLDER [M]
WH900 RMR0314 CABLE HOLDER [M]
FP552 K5G202A00044 FUSE PROTECTOR [M]
JACKS
JK1 K1FA104B0047 JK XM CONNECTOR [M]
JK303 K2HC1YYA0003 JK AUX [M]
JK501 K4BC04B00086 JK RED/BLACK SPEAKER [M]
JK600 K2AB2B000007 JK AC INLET [M]
JK900 K2HC103A0024 JK HP [M]
EARTH TERMINAL
ZJ01 SNE1004-3 EARTH TERMINAL [M]
PACKING MATERIALS
P1 RPGV0335 PACKING CASE [M]
P2 RPNV0100 POLYFOAM [M]
P3 RPHV0001-1 MIRAMAT SHEET [M]
ACCESSORIES
A1 N2QAYB000051 REMOTE CONTROL [M]
A1-1 RKK-HTR0283 R/C BATTERY COVER [M]
A2 K2CB2CB00018 AC CORD [M]
A3 RQTV0160-P O/I BOOK (En/Sp) [M]
A4 RSA0007-L FM ANTENNA WIRE [M]
A5 N1DAAAA00001 AM LOOP ANTENNA [M]
79
Page 80

SA-PM321P
Ref.
No.
R1 D0AE222JA048 2.2K 1/4W [M]
R1 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R2 D0AE222JA048 2.2K 1/4W [M]
R2 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R3 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R3 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R4 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R4 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R5 D0AE222JA048 2.2K 1/4W [M]
R6 D0AE222JA048 2.2K 1/4W [M]
R6 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R7 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R7 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R8 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R8 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R9 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R10 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R11 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R12 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R13 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R14 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R15 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R16 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R17 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R19 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R20 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R21 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R22 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R23 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R24 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R25 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R26 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R31 ERJ6GEYJ102V 1K 1/10W [M]
R32 ERJ6GEYJ102V 1K 1/10W [M]
R33 ERJ6GEYJ104V 100K 1/10W [M]
R34 ERJ6GEYJ104V 100K 1/10W [M]
R39 ERJ6GEYJ104V 100K 1/10W [M]
R40 ERJ6GEYJ104V 100K 1/10W [M]
R43 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R44 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R45 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R46 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R53 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R54 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R55 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R57 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R58 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R59 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R62 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R64 D0GB470JA008 47 1/16W [M]
R65 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R66 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R201 ERJ6GEYJ562V 5.6K 1/10W [M]
R202 ERJ6GEYJ562V 5.6K 1/10W [M]
R203 ERJ6GEYJ272V 2.7K 1/10W [M]
R204 ERJ6GEYJ682V 6.8K 1/10W [M]
R205 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R206 ERJ6GEYJ123V 12K 1/10W [M]
R207 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R211 ERJ6GEYJ822V 8.2K 1/10W [M]
R212 D0GB182JA007 1.8K 1/16W [M]
R220 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R221 D0GB153JA007 15K 1/16W [M]
R222 D0GB683JA007 68K 1/16W [M]
R223 ERJ6GEYJ470V 47 1/10W [M]
R224 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R225 ERJ6GEYJ121V 120 1/10W [M]
R226 D0GB392JA007 3.9K 1/16W [M]
R227 D0GB392JA007 3.9K 1/16W [M]
R230 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
RESISTORS
Ref.
No.
R235 D0GB333JA007 33K 1/16W [M]
R251 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R285 ERDS2TJ822T 8.2K 1/4W [M]
R291 ERDS2TJ682T 6.8K 1/4W [M]
R292 ERDS2TJ822T 8.2K 1/4W [M]
R295 D0AE103JA048 10K 1/4W [M]
R296 ERDS2TJ330T 33 1/4W [M]
R401 ERJ6GEYJ562V 5.6K 1/10W [M]
R402 ERJ6GEYJ562V 5.6K 1/10W [M]
R403 ERJ6GEYJ272V 2.7K 1/10W [M]
R404 ERJ6GEYJ682V 6.8K 1/10W [M]
R406 ERJ6GEYJ123V 12K 1/10W [M]
R411 ERJ6GEYJ822V 8.2K 1/10W [M]
R412 D0GB182JA007 1.8K 1/16W [M]
R420 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R421 D0GB153JA007 15K 1/16W [M]
R422 D0GB683JA007 68K 1/16W [M]
R423 ERJ6GEYJ470V 47 1/10W [M]
R424 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R425 ERJ6GEYJ121V 120 1/10W [M]
R426 D0GB392JA007 3.9K 1/16W [M]
R427 D0GB392JA007 3.9K 1/16W [M]
R430 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R435 D0GB333JA007 33K 1/16W [M]
R441 ERD2FCVG330T 33 1/4W [M]
R442 ERJ6GEYJ682V 6.8K 1/10W [M]
R443 D0GB332JA007 3.3K 1/16W [M]
R444 D0GB332JA007 3.3K 1/16W [M]
R445 ERJ6GEYJ682V 6.8K 1/10W [M]
R446 D0GB273JA007 27K 1/16W [M]
R447 D0GB273JA007 27K 1/16W [M]
R451 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R485 ERDS2TJ822T 8.2K 1/4W [M]
R491 ERDS2TJ682T 6.8K 1/4W [M]
R492 ERDS2TJ822T 8.2K 1/4W [M]
R495 D0AE103JA048 10K 1/4W [M]
R496 ERDS2TJ330T 33 1/4W [M]
R501 ERDS2TJ1R2T 1.2 1/4W [M]
R502 ERDS2TJ1R2T 1.2 1/4W [M]
R503 ERDS2TJ1R2T 1.2 1/4W [M]
R504 D0AE221JA048 220 1/4W [M]
R505 D0AE104JA048 100K 1/4W [M]
R511 D0AE221JA048 220 1/4W [M]
R514 D0AE222JA048 2.2K 1/4W [M]
R515 ERDS2TG152T 1.5K 1/4W [M]
R517 D0AE471JA048 470 1/4W [M]
R518 D0AE102JA048 1K 1/4W [M]
R520 D0AE471JA048 470 1/4W [M]
R552 D0AE563JA048 56K 1/4W [M]
R572 D0AE563JA048 56K 1/4W [M]
R580 D0AE562JA048 5.6K 1/4W [M]
R581 D0AE103JA048 10K 1/4W [M]
R586 D0AE473JA048 47K 1/4W [M]
R600 D0AE473JA048 47K 1/4W [M]
R601 D0AE220JA048 22 1/4W [M]
R603 ERDS2TJ821T 820 1/4W [M]
R604 D0AE472JA048 4.7K 1/4W [M]
R605 D0AE151JA048 150 1/4W [M]
R606 D0AE103JA048 10K 1/4W [M]
R607 D0AE103JA048 10K 1/4W [M]
R608 ERD2FCVG120T 12 1/4W [M]
R609 ERC12UGK335D 3.3M 1/2W [M]
R611 D0AE332JA048 3.3K 1/4W [M]
R750 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R751 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R752 D0GB222JA007 2.2K 1/16W [M]
R753 D0AF100JA039 10 1/4W [M]
R755 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R756 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R781 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R782 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R783 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R784 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
80
Page 81

Ref.
No.
R785 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R786 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R787 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R788 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R789 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R790 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R791 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R792 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R793 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R794 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R795 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R803 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R804 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R805 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R806 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R807 ERJ6GEYJ472V 4.7K 1/10W [M]
R808 ERJ6GEYJ472V 4.7K 1/10W [M]
R809 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R810 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R811 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R812 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R813 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R815 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R816 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R817 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R821 D0GB474JA041 470K 1/16W [M]
R823 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R824 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R825 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R826 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R827 D0GB272JA007 2.7K 1/16W [M]
R828 D0GB272JA007 2.7K 1/16W [M]
R829 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R830 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R831 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R832 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R833 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R837 D0GB562JA007 5.6K 1/16W [M]
R840 D0GB105JA007 1M 1/16W [M]
R841 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R842 D0GB334JA007 330K 1/16W [M]
R845 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R846 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R847 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R848 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R849 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R850 D0GB223JA007 22K 1/16W [M]
R851 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R852 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R853 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R854 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R855 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R856 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R857 D0GB473JA007 47K 1/16W [M]
R858 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R859 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R861 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R862 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R863 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R864 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R865 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R866 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R867 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R868 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R869 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R870 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R871 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R872 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R873 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R877 D0GB223JA007 22K 1/16W [M]
R878 D0GB223JA007 22K 1/16W [M]
R879 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R880 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
Ref.
No.
R882 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R884 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R889 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R890 D0GB153JA007 15K 1/16W [M]
R891 D0GB153JA007 15K 1/16W [M]
R901 ERJ3GEYJ122V 1.2K 1/16W [M]
R902 D0GB152JA007 1.5K 1/16W [M]
R903 D0GB222JA007 2.2K 1/16W [M]
R904 D0GB332JA007 3.3K 1/16W [M]
R905 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R910 ERJ3GEYJ122V 1.2K 1/16W [M]
R911 D0GB152JA007 1.5K 1/16W [M]
R912 D0GB222JA007 2.2K 1/16W [M]
R913 D0GB332JA007 3.3K 1/16W [M]
R914 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R915 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R917 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R918 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R920 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R922 D0GB680JA007 68 1/16W [M]
R923 D0GB680JA007 68 1/16W [M]
R924 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R925 D0GB104JA007 100K 1/16W [M]
R926 D0GB823JA007 82K 1/16W [M]
R930 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R931 D0GB221JA007 220 1/16W [M]
R933 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R934 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R935 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R936 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R937 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R940 D0GB221JA041 220 1/16W [M]
R942 D0GB472JA007 4.7K 1/16W [M]
R946 ERJ3GEYF822V 8.2K 1/16W [M]
R947 ERJ3GEYF822V 8.2K 1/16W [M]
R948 ERJ3GEYF122V 1.2K 1/16W [M]
R7028 ERJ3GEY0R00V 0 1/16W [M]
R7111 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R7211 D0GB823JA007 82K 1/16W [M]
R7212 D0GB821JA007 820 1/16W [M]
R7214 D0GB471JA007 470 1/16W [M]
R7217 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7218 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7220 D0GB105JA007 1M 1/16W [M]
R7221 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R7253 D0GB100JA007 10 1/16W [M]
R7254 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7315 D0GB332JA007 3.3K 1/16W [M]
R7323 D0GB332JA007 3.3K 1/16W [M]
R7325 D0GB331JA007 330 1/16W [M]
R7327 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7328 ERJ3GEYJ103V 10K 1/16W [M]
R7329 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7330 D0GB562JA007 5.6K 1/16W [M]
R7331 D0GB223JA007 22K 1/16W [M]
R7332 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7335 D0GB101JA007 100 1/16W [M]
R7336 D0GB100JA007 10 1/16W [M]
R7339 ERJ3GEYJ102V 1K 1/16W [M]
R7349 D0GB183JA007 18K 1/16W [M]
R7601 D0GB4R7JA007 4.7 1/16W [M]
R7650 D0GB5R6JA007 5.6 1/16W [M]
C1 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C2 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C3 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C4 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C5 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C6 ECJ1VC1H150J 15P 50V [M]
C7 ECJ1VC1H150J 15P 50V [M]
C9 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
CAPACITORS
SA-PM321P
81
Page 82

SA-PM321P
Ref.
No.
C10 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C11 F2A1A220A204 22 10V [M]
C12 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C13 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C14 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C15 F3F1A106A046 10 10V [M]
C16 F2A1A220A204 22 10V [M]
C17 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C18 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C19 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C20 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C21 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C22 ECJ1VB1H104K 0.1 50V [M]
C27 F2A1A220A204 22 10V [M]
C28 ECJ1VC1H390J 39 50V [M]
C37 F3F1A106A046 10 10V [M]
C38 F3F1A106A046 10 10V [M]
C43 ECJ1VB1H102K 1000P 50V [M]
C101 ECJ1VB1H682K 6800P 50V [M]
C102 ECJ1VB1H682K 6800P 50V [M]
C201 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C203 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C205 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C210 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C211 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C212 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C216 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C220 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C221 F1H1H331A013 330P 50V [M]
C222 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C223 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C224 ECA0JAK470XB 47 6.3V [M]
C225 F1H1E103A029 0.01 25V [M]
C230 F1H1H103A219 0.01 50V [M]
C233 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C254 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C272 ECA1EAM222XE 2200 25V [M]
C293 ECQB1H273JF3 0.027 50V [M]
C297 F1D1C122A010 1200P 16V [M]
C298 ECQV1H334JL3 0.33 50V [M]
C361 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C362 F1D1H101A012 100P 50V [M]
C363 F1D1H101A012 100P 50V [M]
C369 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C371 F1D1H1040002 0.1 50V [M]
C375 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C401 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C403 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C405 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C410 F1H1H221A748 220P 50V [M]
C411 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C412 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C416 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C420 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C421 F1H1H331A013 330P 50V [M]
C422 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C423 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C424 ECA0JAK470XB 47 6.3V [M]
C425 F1H1E103A029 0.01 25V [M]
C430 F1H1H103A219 0.01 50V [M]
C433 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C440 F1H1E1530002 0.015 25V [M]
C441 F1H1E1530002 0.015 25V [M]
C442 F1H1E1530002 0.015 25V [M]
C443 ECA1HAK0R1XB 0.1 50V [M]
C444 ECJ1VB1C683K 0.068 16V [M]
C445 ECA1HAK0R1XB 0.1 50V [M]
C446 ECJ1VB1C683K 0.068 16V [M]
C447 ECA1EPX470B 47 25V [M]
C448 ECA1HAKR33XB 0.33 50V [M]
C449 F1H1E1530002 0.015 25V [M]
C454 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C455 ECJ1VB1C563K 0.056 16V [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
Ref.
No.
C456 ECJ1VB1C563K 0.056 16V [M]
C461 ECJ1VB1C393K 0.039 16V [M]
C462 ECJ1VB1C393K 0.039 16V [M]
C463 ECA1CAK101XB 100 16V [M]
C464 F1H1H470A230 47P 50V [M]
C465 F1H1H470A230 47P 50V [M]
C472 ECA1EAM222XE 2200 25V [M]
C493 ECQB1H273JF3 0.027 50V [M]
C497 F1D1C122A010 1200P 16V [M]
C498 ECQV1H334JL3 0.33 50V [M]
C501 ECA1VAM682XE 6800 35V [M]
C502 ECA1EAK100XB 10 25V [M]
C507 F1E1H1030001 0.01 50V [M]
C510 ECA1EAK100XB 10 25V [M]
C512 ECQE2104KF3 0.1 250V [M]
C514 F1E1H1030001 0.01 50V [M]
C515 F1E1H1030001 0.01 50V [M]
C516 F1E1H1030001 0.01 50V [M]
C521 ECQB1H103JF3 0.01 50V [M]
C522 ECQB1H103JF3 0.01 50V [M]
C523 ECQB1H103JF3 0.01 50V [M]
C524 ECQB1H103JF3 0.01 50V [M]
C540 ECA1CAK220XB 22 16V [M]
C541 ECA1CAK220XB 22 16V [M]
C542 ECA1EAK100XB 10 25V [M]
C580 ECA1VAM101XB 100 35V [M]
C581 ECA1CAK220XB 22 16V [M]
C582 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C586 ECA1HAK100XB 10 50V [M]
C601 F1B1H103A007 0.01 50V [M]
C603 ECA1CAM102XB 1000 16V [M]
C604 F1E1H1030001 0.01 50V [M]
C605 ECA1EM470B 47 25V [M]
C609 F2A1H1010039 100 50V [M]
C610 F1E1H1030001 0.01 50V [M]
C611 F2A1H470A147 47 50V [M]
C612 F2A1H1010039 100 50V [M]
C750 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C751 ECA0JAK470XB 47 6.3V [M]
C752 F1H1E103A029 0.01 25V [M]
C753 F1H1E103A029 0.01 25V [M]
C754 ECA1CAM221XB 220 16V [M]
C804 F1H1H104A783 0.1 50V [M]
C805 ECA1CAK220XB 22 16V [M]
C808 ECA1CAK220XB 22 16V [M]
C809 ECA1CAK220XB 22 16V [M]
C810 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C812 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C816 ECA1CAK100XB 10 16V [M]
C817 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C818 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C819 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C820 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C821 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C824 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C825 ECJ1VB1H472K 4700P 50V [M]
C829 F1H1H470A230 47P 50V [M]
C831 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C832 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C833 ECJ1VC1H180J 18P 50V [M]
C834 ECJ1VC1H180J 18P 50V [M]
C835 ECJ1VC1H180J 18P 50V [M]
C836 ECJ1VC1H220J 22P 50V [M]
C837 ECA0JAK101XB 100 6.3V [M]
C838 ECA0JAK101XB 100 6.3V [M]
C839 ECA0JAM102XB 1000 6.3V [M]
C840 ECA0JAM102XB 1000 6.3V [M]
C842 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C843 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C844 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C845 F1H1E103A029 0.01 25V [M]
C846 ECA1HAK010XB 1 50V [M]
C851 F1H1E103A029 0.01 25V [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
82
Page 83

Ref.
No.
C852 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C853 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C860 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C861 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C900 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C901 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C902 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C903 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C904 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C905 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C906 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C907 ECA1HAK2R2XB 2.2 50V [M]
C909 ECA1HAK220XB 22 50V [M]
C910 ECA1HAK220XB 22 50V [M]
C911 ECA1HAK220XB 22 50V [M]
C912 F1H1H104A783 0.1 50V [M]
C913 F1H1H103A219 0.01 50V [M]
C914 F1H1H104A783 0.1 50V [M]
C920 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C921 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C922 ECA0JAK470XB 47 6.3V [M]
C923 ECA1HAK220XB 22 50V [M]
C924 ECA1AAK220XB 22 10V [M]
C925 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C926 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C927 F1H1H101A230 100P 50V [M]
C952 F1H1H104A783 0.1 50V [M]
C7102 ECJ1VB1A474K 0.47 10V [M]
C7107 ECJ1VB1H223K 0.022 50V [M]
C7142 F1H1H332A013 3300P 50V [M]
C7154 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7155 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7161 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7164 ECJ2FF1A106Z 10 10V [M]
C7165 ECJ2FF1A106Z 10 10V [M]
C7166 F1H1H103A219 0.01 50V [M]
C7203 F2A0J221A200 220 6.3V [M]
C7204 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7216 ECJ1VB1H681K 680P 50V [M]
C7217 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7218 ECJ1VB1C823K 0.082 16V [M]
C7223 ECEA1HKA4R7I 4.7 50V [M]
C7225 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C7226 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C7227 ECA1HAK010XI 1 50V [M]
C7228 ECA1HAK010XI 1 50V [M]
C7230 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7231 F2A0J221A200 220 6.3V [M]
C7232 F2A0J221A200 220 6.3V [M]
C7233 F1H1C104A008 0.1 16V [M]
C7234 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7235 ECEA1CKA100I 10 16V [M]
C7241 F1H1H102A219 1000P 50V [M]
C7243 F1H1C104A008 0.1 16V [M]
C7244 ECJ1VB1C153K 0.015 16V [M]
C7253 F1H1H471A219 470P 50V [M]
C7263 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7264 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7315 ECJ1VB1A474K 0.47 10V [M]
C7334 ECEA1AKA221I 220 10V [M]
C7335 F1H1C104A008 0.1 16V [M]
C7338 ECJ1VB1C563K 0.056 16V [M]
C7339 ECJ1VB1C183K 0.018 16V [M]
C7352 ECJ1VB1C183K 0.018 16V [M]
C7601 ECEA0JKA330I 33 6.3V [M]
C7613 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7614 F2A0J101A198 100 6.3V [M]
C7626 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
C7670 F1H1C104A041 0.1 16V [M]
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
SA-PM321P
83
FLE0607A/D/M/S/P
 Loading...
Loading...