Page 1

For speed control of 3-phase induction motor
Low-Noise Inverter M1S Series
Operating Instructions
Be sure to provide the customer with a copy of this manual.
● Thank you for purchasing a Panasonic Inverter.
● Be sure to read the instructions thoroughly before attempting to operate the
inverter. After reading, be sure to keep in a safe place for future reference.
Industrial and Appliance Motor Division, Motor Company
Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd
Page 2

CONTENTS
Before use
Preparation and
adjustment
Safety Precautions
Introduction
● When unpacking・・・・・・・・・・・・・8
● Inverter model check ・・・・・・・・・8
・・・・・・・・・・・・8
System Configuratio n
・・・・・・4
・・
12
12
1212
and Wiring
●Wiring general view・・・・・・・・・ 12
●Applicable peripheral ・・・・・・・ 13
If necessary
Application and
equipment
●Wiring ・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・ 14
●Terminal function ・・・・・・・・・・・ 14
●Precautions when wiring ・・・・ 16
Protective Functions
●Protective functions・・・・・・・・・ 26
●Method of resetting trip・・・・・・ 28
Detalied Explanation
・・・26
・・・
31
of Parameters
Specifications
Specifications
‑2‑
・・・・・・・・・・・・
45
Page 3
CONTENTS
Parts Identification
●
Inverter
Precautions
●
Note the following
precautions in order to use
the inverter properly.
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・9
・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・10
Parameter Setting
●
Parameter overview
●
Parameter configuration
and list of parameters
・・・・・・・・17 ●
・・・・・・9
10
・・・・・・
17
・・・・・17
Operation Method
Selection of operation
commands
●
How to change operation
Before use
・・・・・20
・・・・・・20
・・・・ 20
●
Setting
Test Operation
●
Pre-operation inspections
●
Test operation
Maintenance/
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・17
・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・19
・・・・・・・・・・・
Inspection
Troubleshooting
・・・・・・・・
Outer Dimensions
19
・・・19
29
30
・・・・46
command
●
Operation function
Servicing
・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・ 20
Backcover
If necessary Preparation and Adjustment
Parameter Setting
・・・・47
‑3‑
and Spec.
Application
Page 4

Safety Precautions
!
!!
!
!
!!
!
!
!!
!
!!!!
Precautions that must be heeded in order to protect the user and others from harm and
prevent property loss or damage are as follows:
■■■■
The extent of injury or damage that could be suffered by improper
use contrary to directions is ranked as follows:
DANGER
CAUTION
Items labeled as CAUTION could be connected with core serious consequences,
depending upon the circumstances. In any case, these instr uctions are ex tremely import ant
and should be observed in all cases.
■■■■
Installation
Situation involving danger which could result in death or serious
injury if equipment is handled incorrectly.
Situation involving danger which could result in medium to light
injury, or property damage if equipment is handled incorrectly.
CAUTION
● Install on non-combustible material such as metal.
Failure to do so could result in fire.
● Do not locate near combustibles.
Doing so could result in fire.
● Do not carry by the front case when moving the inverter.
Doing so is dangerous and could result in injury if dropped.
● Do not allow foreign material such as metal chips to get inside the inverter.
Doing so could result in fire.
● Be sure to install on a base capable of supporting the inverter’s weight in
accordance with the directions giving in the instruction manual.
Failure to do so could result in the inverter dropping or falling.
‑4‑
Page 5

■■■■
!
!!
!
!
!!
!
Wiring
DANGER
●
Make sure the power is cut off before handling wiring.
Failure to do so could result in electrical shock or fire.
● Be sure to install a no-fuse breaker (NFB).
Failure to do so could result in fire.
● Be sure to ground the GND terminal.
Failure to do so could result in electrical shock or fire.
● Have wiring work done a licensed electrician.
Failure to do so could result in electrical shock or fire.
● Be sure to install the inverter before wiring.
Failure to do so could result in electrical shock or fire.
CAUTION
● Do not ground the AC power source with the output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, W/T3).
Doing so could result in injury or fire.
● Make sure the voltage of the AC power source agrees with the rated voltage of the
inverter.
If not, it could result in injury or fire.
‑5‑
Page 6

Safety Precautions
!
!!
!
!
!!
!
■■■■
Operation
DANGER
● Be sure to mount the case and cover before turning the power on. Never remove
the case or cover while the inverter is receiving power.
Failure to mount or removing the case/cover could result in electric shock.
● The operator should secure the area before turning the power on or off.
Failure to do so could result in injury.
● Never operate the switches with wet hands.
Doing so could result in electric shock.
● Never touch the terminals of the inverter when it is charged with power, even when
it is not running. Doing so could result in electric shock.
● If the retry function is selected, the inverter could unexpectedly start operating
again if tripped. Do not approach the inverter in the condition.
Doing so could result in injury.
● If trip reset is carried out with the operate signal ON, the inverter could
unexpectedly start operating again. Do not approach the inverter in the condition.
Doing so could result in injury.
CAUTION
● The radiator and regenerative resistor become very hot.
Touching these parts could result in skin burning injury.
● The inverter can be easily set to operate at speeds ranging from low to high. Set
the operating speed so that it the motor and machine tolerance is not exceeded.
Failure to do so could result in injury.
‑6‑
Page 7

■■■■
!
!!
!
!
!!
!
Maintenance/inspection
DANGER
● Wait for at least 5 minutes after turning off the power to perform inspections.
Failure to do so could result in electric shock.
● Maintenance and inspection should not be performed by anyone except a qualified
repairman.
The repairman should remove all metallic objects (watch, rings, etc.) before
performing maintenance or inspection.
Use only insulated tools when performing maintenance or inspection.
Failure to do so could result in electric shock or injury.
■■■■
Other
DANGER
● Absolutely DO NOT modify the inverter in any way.
Doing so could result in electric shock, injury or fire.
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
The diagrams given in this instruction manual may show the cases, covers or safety
breakers removed in order to show details.
When operating, be sure to return the cases, covers or safety breakers and operate
as specified in the manual.
When disposing of the inverte r, treat it as industrial waste.
‑7‑
Page 8
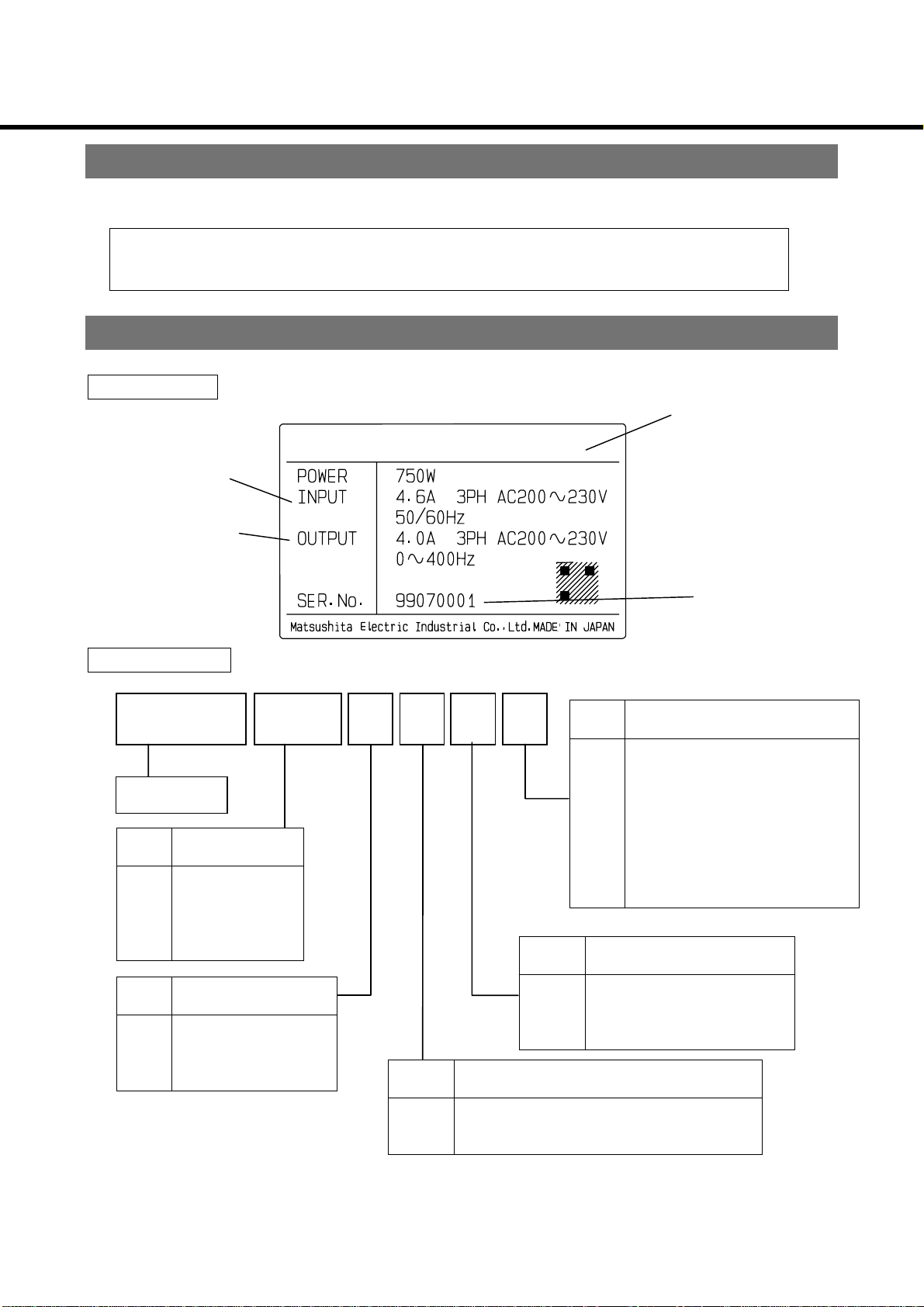
Introduction
ModelNo
When unpacking
・Is the model correct?
・Was the equipment damaged in transport?
If there is anything wrong with the equipment, contact your Panasonic
dealer.
Inverter model check
Nameplate
Model number
Panasonic
Panasonic
PanasonicPanasonic
Rated input
Rated output
M1S083CSA
Product No.
Series name
Code Motor capacity
01
02
04
08
Code Volt age class
1
2
3
0.1 kW
0.2 kW
0.4 kW
0.75 kW
Single-phase 100 V
Single-phase 200 V
3-phase 200 V
Code Interface specs.
A
Without communicatio n functi on/
standard type (NPN logic)
B
Without communicatio n functi on/
standard type (PNP logic)
C
With communication fun ction/
standard type (NPN logic)
D
With communication fun ction/
standard type (NPN logic)
Code Operation panel specs.
S
V
N
Code Regenerative brake specs.
Without volume (standard)
Wit h volum e
Blank cover
Production number
(serial number)
A
Without regenerative brake circuit
C
With regenerative brake circuit (bui lt -in)
Consult your Panasonic de aler regarding products with communicat i on f unctions.
‑8‑
Page 9

Parts Identification
Outer appearance
・
You can remove the
operation panel using the
operation panel fixing
screws.
・ You can remove the case by
removing the case fixing
screw and pulling the lower
claw outward.
Panasonic
Panasonic
PanasonicPanasonic
GND terminal
Operation panel
・ Volume is mounted for
the products with volume.
Operation panel
fixing screws
Case
In case of M1S083CSA
GND terminal
With operation panel removed With case removed
DC reactor terminal Power terminals
Case fixing
screw
Charge
lamp
Operation panel
connector
Control terminals
Communication
connector
Factory-installed
option
Regenerative brake resistor t erminals Motor terminals
Be very careful of static electricity when wiring.
・・・・
After wiring, always replace the case and the operation panel to their
・・・・
original positions.
‑9‑
Page 10

Precautions
Note the following precautions in order to use the inverter properly.
1. Arrange for the power source capacity to be between 1.5 to 500kVA the inverter's
capacity. An excessively high peak current may flow to the power input circuit, and
damage the converter section if the wiring length between the power source and the
inverter is shorter than 100 m with a power source exceeding 500kVA, or the phaseadvancing capacitor is switched on the power source side. In this case, provide
individual power factor-enhancing AC reactors that match the inverter's capacity on
the inverter input side.
2. Do not connect the phase-advancing capacitor to the o utput sid e of th e inv erter. Doing
so could result in damage to the phase-advancing capacitor.
3. Do not provide a magnetic contactor between the inverter and motor. To turn the
motor on/off, use the RUN switch on the control panel or the control input terminal.
Avoid frequently turning the magnetic contactor, provided on the power source, on
and off.
4. Operating the motor by the inverter could increase leakage current and trip the earth
leakage breaker. In this case, use earth leakage breaker s desi gned for hig h freq uency
for this system and other systems.
5. Take the following precautions if using a built-in electronic thermal relay contained in
the inverter:
Check the rated current of your 3-phase ind ucti on m otor, and set the appropr i ate
・
electronic thermal value.
Use one motor for each inverter.
・
6. If operating the inverter w ith multi ple motors connected in parallel, selec t an inv erter of
a capacity that does not exceed the total rated current of the inverter. When
calculating by total output of the motor, the inverter’s rated current may be exceeded,
depending on the type of motor.
7. The total wiring length betw een inv ert er a nd mo tor sh ould not ex ceed 30 me ters. I f th e
wiring is to be longer than this, you should provide a reactor, etc., between inverter
and motor.
8. Install the inverter securely to avoid injuries in the case of an earthquake.
9. Before running the inverter following an earthquake, check installation of the inverter
and motor and make sure they are safe to operate.
‑10‑
Page 11

Installation
Install the inverter properly to prevent equipment failure or accidents.
Inverter
Installation location
Install the inverter indoors in a place not exposed to rain or direct sunlight. The inverter
①
is not waterproof.
Install in a place not ex posed to cor rosiv e/flammabl e gases, g ri nding fl ui d, oil mi st, metal
②
powder or chips.
Place with adequate ventilation, which i s not exposed to ex cessi v e hu mi di ty, dirt or dust.
③
Place not subject to vibration.
④
Environmental conditions
Item Conditions
10 〜 50℃ (Must not freeze)
Ambient temperature
Single-phase input specifications: −10 to 40
Ambient humidity
−
Max. 90%RH(Must be no condensation
)
℃
Storage temperature
Storage humidity
Max. 90 %RH(Must be no condensation
Protection structure IP40(Built-in the panel
Vibration Max. 5.9 m/s
Elevation Max. 1000 m
* Short-term temperature during transport
Mounting direction and clearance
Provide sufficient clearance for effective cooling.
・
30 mm
×
Min.
50 mm
Inverter
Inverter Inverter
Min.
10 mm
−20℃ 〜
Min.
10 mm
65℃ (Must not freeze)
)
2
10 〜 60Hz
(
Min. 100 mm
30 mm
Min.
50 mm
)
×
)
Min.
× 30 mm
50 mm
Make sure ambient tem per atur e d oesn’t exceed al low able te mperat ure at p ositi on in dicat ed
by X in the figure above.
‑11‑
Page 12

System Configuration and Wiring
A
Wiring general view
Main circuit
No-fuse breaker (NFB)
or Earth leakage breaker
Used to protect the power line.
Interrupts the circuit in the case of excessive
current.
* Use an anti-harmonic earth leakage
breaker for the inverter.
Noise filter (NF)
Blocks noise from the power line.
lso reduces effect of noise from the servomotor.
Magnetic contactor (MC)
Turn main power to servomotor on/off.
Used with surge absorber mounted.
Inverter
Motor
GND
AC reactor (AC-L)
Reduces harmonic current of the power source.
Refer to “Option.”
DC reactor (DC-L)
Reduces harmonic current of the power
source.
Refer to “Option.”
Regenerative resistor
Improves regenerative control capacity.
For the regenerative brake circuit built-in type only.
Refer to “Option.”
‑12‑
Page 13

Applicable peripheral equipment
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
Wiring apparatus selection
(1) Selection of no-fuse breaker, magnetic contactor, thermal relay, (Matsushita Electric
Works No.) and wiring
Inverter No.
MIS011*** 0.1
MIS021*** 0.2
MIS041*** 0.4
MIS01
MIS02
MIS04
MIS08
2
3
2
3
2
3
2
3
***
***
***
***
Applicabl
e motor
(kW)
0.1
0.2
0.4
0.75
No-fuse
breaker
(Rated current)
BBP25
(5A)
BBP35
(5A)
BBP310
(10A)
BBP35
(5A)
BBP35
(5A)
BBP35
(5A)
BBP310
(10A)
Magnetic
contactor
(Contact configuration)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
BMFT61842N
(3P+1a)
Thermal
relay
(Current adjustment range)
BMF902E
(0.95〜1.45A)
BMF904E
(1.7〜2.6A)
BMF907E
(2.8〜4.2A)
BMF901E
(0.5〜0.75A)
BMF902E
(0.95〜1.45A)
BMF904E
(1.7〜2.6A)
BMF907E
(2.8〜4.2A)
Use the same size of wire for GND terminal ( ) as the wire for main circuit.
Wiring (mm2)
Main
circuit
2.0
AWG14
2.0
AWG14
2.0
AWG14
2.0
AWG14
2.0
AWG14
2.0
AWG14
2.0
AWG14
Control
circuit
0.75
AWG18
0.75
AWG18
0.75
AWG18
0.75
AWG18
0.75
AWG18
0.75
AWG18
0.75
AWG18
*1
(2) Relay selection
For relays used in control circuits such as the control input terminal, you should use a
small signal relay (min. guaranteed current of 1mA or less) in order to prevent poor
contact.
Examples
<
Matsushita Electric Works: DS type, NK type, HC type
>
Omron: G2A type
(3) Control circuit switch selection
If using a switch instead of a relay, use a switch for extremely small current in order to
prevent poor contact.
<Example> Nihon Kaiheiki: M-2012J-G
*1
Motor cable is used if the distance between inverter and motor is 20 meters or less. If more than 20 meters,
use a larger cable.
‑13‑
Page 14

System Configuration and Wiring
Wiring
Standard wiring diagram
Power source
●Connect to R/L1, S/L2 for single-phase
External frequency setting volume
1/4W, 5kΩ, B characteristic
Frequency meter*
1mA (full scale)
Forward/stop switch
Reverse/stop switch
Frequency setting selection (1)
Frequency setting selection (2)
Trip reset*
Be sure to provide proper treatment
for the shielded wire terminals.
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
5V
FIN1
FOUT
12V
I1
I2
I3
I4
I5
G
Short (direct current reactor connection terminal)
P
PD
Main circuit
G
Control circuit
(Frame ground)
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
Brake resistor
PB
connection terminal
(Collector)
O1
trip output*
C1
(Emitter)
max.=DC24V
V
CE
max.=50mA
I
C
NC
Trip signal
C2
Contact capacity
NO
DC30V 1A
Not built-in to
products without
regenerative
brake circuit.
Motor
GND terminal
Be sure to ground (max. 100Ω)
Asterisk (*) indicates factory-set function.
In case of M1S083CSA
Terminal functi on
(1) Main circuit terminal
Upper PD P R/L1 S/L2 T/L3 E◎ Lower P PB
Terminal
No.
R,S,T
L1,L2,L3
U,V,W
T1,T2,T3
Power source input terminal
Output terminal
E GND terminal
PD, P Reactor terminal DC reactor connection terminal
P, PB
Regenerative resistor
terminal
Terminal name Function description
Connects to 3-phase or singl ephase commercial power sourc e
Connects to 3-phase in duct i on
motor
Terminal for grounding inverter
base
Regenerative resistor conn ect i on
terminal
U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
Terminal
screw size
M3.5 0.8 ~ 1.0
M3.5 0.8 ~ 1.0
M4 1.0 ~ 0.2
M2.5 0.3 ~ 0.5
M2.5 0.3 ~ 0.5
E◎
Tightening
torque N·m
‑14‑
Page 15

(2) Control terminal
NO NC 01 FI FO I1 I3 I5
C2 C1 5V G 12V I2 I4 G
<Terminal screw size: M2, Tightening torque 0.25 ~ 0.3 N·m>
Terminal No. Terminal name Function description
Power source
5V
12V
terminal for frequency setting
Power source
terminal for
input terminal
+ 5VDC applied. I max. = 20 mA
+ 12VDC applied. I max. = 20 mA
FI
G
FOUT
I1
I2
I3
Input terminal
I4
I5
Input terminal
for frequency
setting
Ground for
control
Frequency
meter terminal
Forward/stop
command
terminal
Reverse /stop
command
terminal
Frequency
setting
selection
terminal
Frequency can be set when 0 ~ +5VDC (or 0 - +10VDC) is input
between “FIN1” and “G.”
If using these terminals, change “
−
or
−
.
frequency command” to
Common ground terminal for cont act i nput .
Outputs voltage proportional to output frequency between “FOUT” and
“G.” Connect full-scale 1 mA DC ammeter. You can output pulses
synchronized with output fr equency by altering “
FOUT switch”.
Forward by shorting between “I1” and “G”; stop by release
Reverse by shorting between “I2” and “G”; st op by release
You can change “I1” to run/stop command and “I2” t o forward/reverse
command by altering“
You can select the following functions by "
Operation mode I3 I4 I5
2-speed
operation mode
4-speed
operation mode
8-speed
operation mode
Forward
jogging
I1.12” function selection.
operation mode selection."
Reverse
jogging
G
Ground for
control
Contact input common ground terminal.
Open-collector output termina l. (Not maintained when power is OFF.)
output signal (1) selection.”
O1
C1
Output signal
terminal
You can select contents by “
Factory setting: “01” is trip signa l (transist or ON when tripped)
“O1” (collector) IC max. = 50mA
“C1” (emitter) VCE max. = 24VDC
NC
Output terminal
NO
Output signal
terminal
C2
Relay output termina l. 30VDC 1A (max.)
(Not maintained when power is O FF. )
You can select output contents by “
relay output polarity selection.”
Not built-in to products without regenerative brake circuit.
‑15‑
Page 16
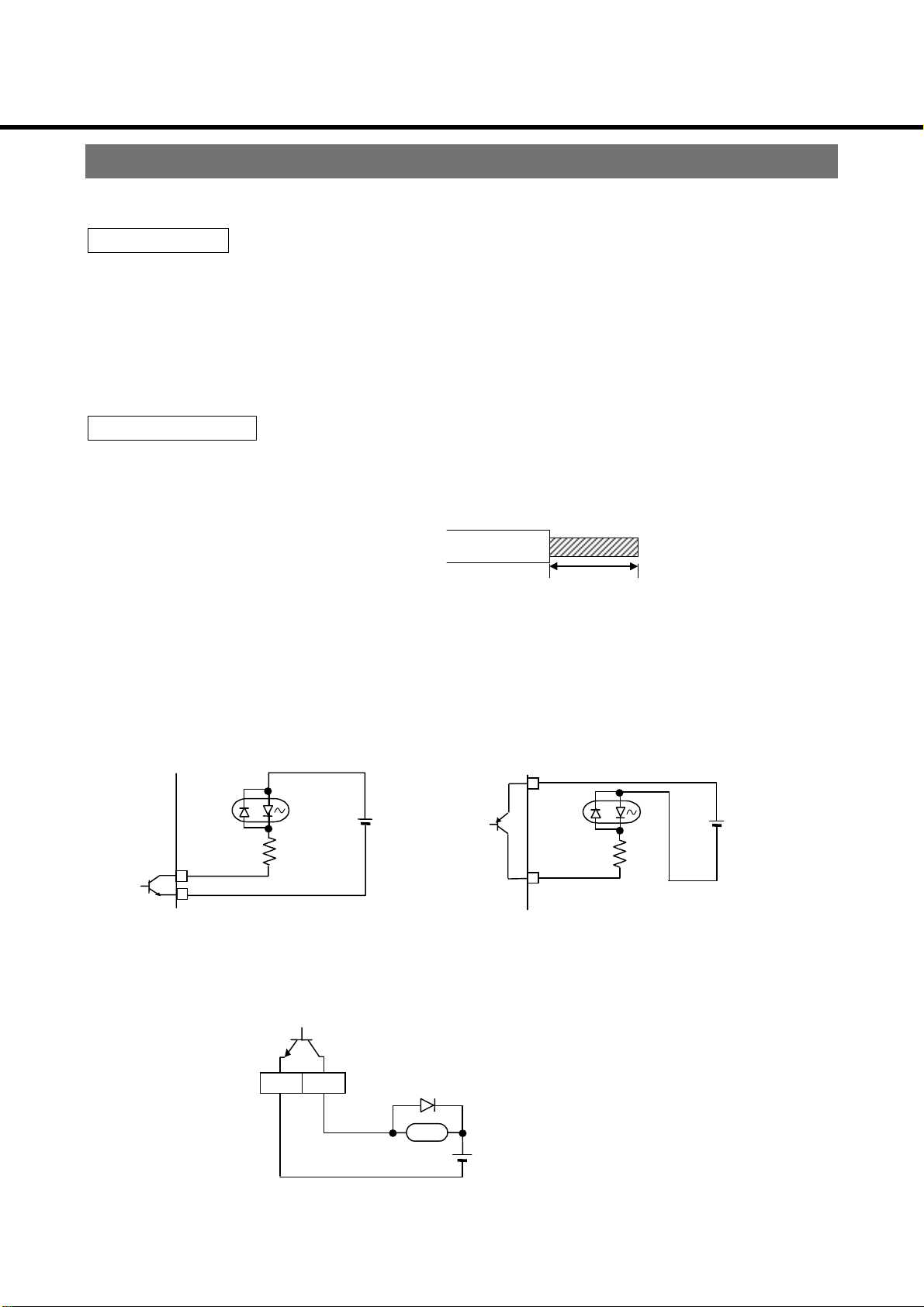
System Configuration and Wiring
Precautions when wiring
The inner circuit is still energized with a high voltage after the input power is turned off. Do
not touch the inverter for at least 5 minutes after turning off the power.
Main circuit
(1) The inverter will be damaged if you invert the conn ections of the power input terminal
and motor output terminal (U/L1, V/L2, W/L3). Absolutely do not invert connections.
(2) Do not ground the main circuit terminal.
(3) Do not short motor output terminals (U/L1, V/L2, W/L3) together.
(4) The GND terminal (E) is the frame ground (FG) for the inverter.
(5) Be sure to use insulated crimp terminals for connecting to the main circuit terminals.
Control circuit
(1) Use the wires with the insulation removed, as shown below, to wire the control circuit.
If the exposed area is too long, there is the possibility of a short occurring with the
adjacent wire. If it is too short, the wire could be pulled. Twist the bare wires when
wiring, so that they will not get loose.
5.5 mm ± 1 mm
(2) Use a wire which diameter is less than 0.9 mm when wiring using a bar terminal or single
wire. If it is larger than 0.9 mm, the screw thread may be damaged when tightened.
(3) Do not apply more than 24VDC, 50mA to the output terminals (O1, C1), or apply
voltage to terminal in reverse.
(4) Input terminal configuration is internally pulled up from approx. +12V by approx. 3.3kΩ.
You can control by contact or by open collector output. Do not apply external voltage.
Internal circuits of I1 – I5 are as follows:
Photo coupler
G
I
1 ~ I5
+12V
power
source
Internal circuits of I1 – I5 are as follows:
+12V
I
1 ~ I5
+12V
power
source
NPN logic PNP logic
(5) Do not short the frequency setting power source terminal (5V) and ground for control
terminal (G).
(6) To directly drive the relay by the output terminals ( O1, C 1), mount a fly w heel di ode (F D ) .
C1 O1
FD(100V 1A)
Y
R
<Examples> Fuji Electric ERA15-01
ERB12-01
Pay attention to polarity of diode.
(7) Use shielded wires for the cable to be connected to the control circuit.
‑16‑
Page 17

Parameter Setting
Setting
Operation Panel
r/min
Hz
STOP
DATA
SET
RUN
MODE
2-digit LED
Frequency Hz is displayed when in the normal monito r mode.
You can display synchronized rotations for the parameter "
A
V
^
^
5-digit LED
display power."
5-digit LED
2-digit LED
MODE
switch
DATA SET
switch
Displays output freque ncy, set frequency or display power , cause of error , or
parameter.
Displays parameter No. Direction of rotation is displayed in the monitor mode.
Switch for changing monitor mo de. Pressing the switch change s t he mode in the
cycle of:
Output frequency
Switch for selecting parameter No. mode and parameter value mode, setting
parameter value.
●
Mode description
Monitor
mode
Parameter
No. mode
Displays output frequency, converter voltage or motor current.
Mode when the power is turned on.
When in the parameter No. mode or parameter value mode,
pressing the MODE
Displays parameter No.
When in the monitor mode, pressing the DATA SET
changes to the parameter No. mode.
Converter voltage
switch changes to the monitor mode.
(
〜
Motor current
)
by flashing.
switch
△ ▽
switch
RUN switch
STOP
switch
Parameter
value mode
Enable you to select parameters, and set/change contents.
Commands the inverter to run.
Commands the inverter to stop.
Displays parameter content s (set t ing value) by flashing.
You can change the setting value with the △ ▽ switches.
After changing the setting, press the DATA SET
enter the setting in the memory.
‑17‑
switch to
Page 18

Power ON Monitor mode Hz
y
Output frequency
↓
MODE
↓
Current
A MODE
↓
MODE
↓
Converter voltage
V
△
▽
Can set directly No. 0
speed setting with UP and
DOWN ke
s.
MODE
MODE
Storage Storage
DATA SET
DATA SET
Parameter No.
mode
DATA SET
Parameter
value mode
frequency command
.
Note) Available when "
selection" is set to
●
Parameter No. display LED will flash.
△
▽
Change (select) parameter numbers
with UP and DOWN keys.
●
Parameter value display LED will flash.
△
▽
Data will be stored every time UP key or
DATA SET key is pressed in the parameter
value mode.
‑18‑
△
▽
Change (select) parameter values with UP
and DOWN keys.
△
▽
Page 19

Test Operation
Pre-operation inspections
After installing and wiring, inspect the following before running the inverter.
(1) Is the wiring connected correctly? (Especially power input terminals R/L1, S/L2 and
T/L3, output terminals U/T1, V/T2 and W/T3, load side short or ground)
(2) Does input power comply with the rating?
(3) Are there any places that could be shorted by wire cuttings, etc?
(4) Are any screws or terminals loose?
Test operation
(1) Conduct the following for safe operation.
Set the motor so that the motor can be operated independently.
①
Set all of the input of the control terminal base to "OFF" (Open)
②
(2) Turn ON the power and run a test operation by following the procedures shown below.
Operation
①
Turn on the
power
Switch LED display
Operation panel
Remarks
・
Turn ON the power in t he monitor
mode. (Output frequency is
displayed.)
When setting with the volume on the operation panel, set " frequency command selection" to
Volume. (See page 21.)
Operation
② Frequency
setting
③ Return to the
monitor mo d e
④ Run command
(forward
rotation)
⑤ Stop
command
Switch LED display
△
Press
△
Press
frequency.
Press MODE
Press RUN
Press STOP
Operation panel
.
to set
.
.
.
Remarks
・
No. 0 speed frequency is
displayed. (Output set tin g: 0.0 Hz )
・
Set No. 0 speed frequency to 60
Hz.
・
Frequency is gradually changed.
・
Rotating direction is displ ayed.
・
Frequency is gradually changed.
<Points to check when running a test operation>
(1) Is the motor running smoothly? Are there any abnormal sounds or vibrations?
(2) Are acceleration and deceleration smooth?
(3) Is the direction of rotating of the motor correct?
‑19‑
Page 20

Operation Method
Selection of operation commands
You can perform the following six kinds of operation using the frequency command and run
command on the operation panel or using the terminal block with the MIS series inverters.
Frequency command Run command Parameter setting
Operation
panel or
volume
1
2 ○○
3 ○○
4 ○○
5 ○○
6 ○○
" frequency command selection " and " run command selection " are
factory-set values.
○○
How to change operation command
Terminal
block
"FIN1"
Operation
panel
*1
*1
Terminal
block
*1
○
*1
○
Frequency command
selection
or (both)
or (both)
or (panel)
or (panel)
or (terminal block)
or (terminal block)
Run command
selection
(Ex.) Change " frequency command selection" to " " from " ".
Operation
① Turn on the
power
② Parameter No.
mode
③ Parameter value
mode
Switch LED display
Press DATA SET
Press △
the parameter No.
Press DATA SET
Store the setting with
MODE
DATA SET
or
Operation panel
.
, and select
.
.
Press △, and select the parameter No.
Press △, and select the parameter No.
*1
When the operation command is set for the operation panel and you are using the terminal block, the
terminal block has priority.
RUN switch on the operation panel is valid only when both the forward/stop switch "I1" and the
reverse/stop switch "12" on the terminal block are "OFF." When either or both of "I1" and "I2" on the
terminal block is turned "ON," the previously set of the RUN switch will be cancelled.
‑20‑
Page 21

Operation Function
Inverters of this series provide the following operation functions. You can issue
commands using the switches on the operation panel or on the terminal block.
Operation function Explanation
Normal operation
JOG (Jogging)
operation
Free-run stop
DC brake
Positioning DC brake
Sudden stop
(all regions) DC brake
■
Operation function with acceleration/deceleration time setting.
You can set acceleration time and deceleration time individually
within the range of 0 to 3600 seconds.
■ Operation function with z ero acceleration/decelerat ion t ime. This function
is useful for positioning.
When the "operation mode" is set t o JO G (jogging) mode, the JOG
(jogging) operation beco mes valid.
When a forward or reverse operation command is given after making the
control terminals between "I 3" and "G " short , it becomes available to
change to normal operation from JOG (jogging) operation.
JOG (jogging) frequency can be set within the range of 0 to 30 Hz .
However, please note that w hen it is too high, a trip caused by an overcurrent may occur.
■ This function trips the app lied voltage to the motor, and sets the motor to a
free-run.
This is useful when braking mechanically. However, be very careful not to
touch the output terminals of the motor (U, V, W) even if the motor is freerunning, because you can receive a serious electric shock.
■ This brakes the motor by applying direct current to the motor when the
inverter stops from the operating status. When a forward, reverse, or JOG
(jogging) operation command is given while the D C bra ke is activated, the
DC brake is stopped, and the spe ci fied operation is started.
■ If a stop command is given durin g normal operation, soft-stop and braking
are activated when output frequ ency reaches 3 Hz (can be changed by t he
parameter setting.)
■ If the setting frequency is set to zero, braking is activated when output
frequency becomes 1 Hz or low er.
■ Braking strength (torque) and time can be set by the parameters.
■ If a stop command is given durin g normal operation, braking is activated
immediately without soft-stop.
■ Braking strength (torque) and time can be set by the parameters.
■ Braking time will be twic e t he t ime of "positioning DC brake mode".
*1
*1
Time that changes in 50 Hz
‑21‑
Page 22

Operation Function
q
<DC brake operation pattern example>
Positioning DC brake
RUN command
Setting deceleration time
Time set in " DC brake time"
Output frequency
Time determined by load GD2, loaded
tor
ue and " DC brake volume"
Motor speed
and brake
RUN command
Output frequency
Regenerative brake DC brake
Sudden stop DC brake
Time set in "
DC brake time"
Time determined by load GD2, loaded
torque and "
DC brake volume"
Motor speed
and brake
DC brake
‑22‑
Page 23

Inverters of this series provide the following kinds of operation mode.
Select an operation mode in the parameter " operation mode selection".
Function of terminal block
"Value on
Operation
mode
I1
I2 I3 I4 I5
*1
operation
mode
selection"
2-speed
operation
mode
4-speed
operation
mode
Forward Reverse
Forward Reverse
Forward
jogging
Reverse
jogging
Frequency setting
selection
Free-run
External forced trip
No. 2 acceleration/deceleration time
Trip reset
Free-run
External forced trip
No. 2 acceleration/deceleration time
Trip reset
[Factory setting]
8-speed
operation
Forward Reverse
Frequency setting selection
mode
You can perform multi-speed operation shown on the next page by conducting
"Short"/"Open" settings in frequency setting selection terminals for operation modes with 4speed or higher. No. 0 speed frequency is selected and the s etting by the param eter "
setting frequency (0 speed)" or by the exter nal fr eq uency setting dial is possible when all o f
the terminals are set to "Open."
(In " frequency command selection", select whether 0 speed frequency is set by the
parameter setting or by the external setting.)
■ Explanation of input terminal function
(1) Priority for the function of input terminals is as follows:
DC brake < Normal operation < Jogging operation < Free-run stop < External forced trip
Ex.) ① The inverter goes into the operation immediately when a run command is
given while the DC brake is activated.
② Free-run stop is performed when a free-run stop command is given during
jogging operation.
③ The operation does not start even if a run command is given while free-run
stop is performed.
A stop command is activated if a contradicting command is given (for example,
command of forward and reverse operations are given at the same time).
(2) The trip status can be released when forward and reverse operation commands are
both given while tripping. Release the trip after removing the causes of the trip.
*1
Select using “14 Function Selection”
‑23‑
Page 24

Operation Function
■ Selection method of the type of frequency setting for multi-speed operation
(1) When " Multi-speed input selection" is set to
You can select 1 type of multi-speed frequency for 1 terminal of the "Frequency
setting selection terminals" using this setting. This runs the inverter in 3 speeds in
4-speed operation mode and 4 speeds in 8-speed operation mode.
Ex.) With 8-speed mode oper a t ion
Input terminals
I3 I4 I5
OFF OFF OFF No. 0 speed frequency
ON × × No. 1 speed frequency
OFF ON × No. 2 speed frequency
OFF OFF ON No. 3 speed frequency
・
"ON" and "OFF" are related to "G" terminal
・
"×" means that either of "ON" or "OFF" is selectable.
(2) When " multi-speed input selection" is set to
You can select the frequency by setting "Frequency setting selection terminals" in
binary using this setting.
Frequency setting
(1 bit): 1 bit input
(Binary): Binary input
<With 4-speed operation mode>
“I3” “I4” Frequency setting
OFF OFF No. 0 speed frequency
ON OFF No. 1 speed frequency
OFF ON No. 2 speed frequency
ON ON No. 3 speed frequency
<With 8-speed operation mode>
“I3” “I4” “I5” Frequency setting
OFF OFF OFF No. 0 speed frequency
ON OFF OFF No. 1 speed frequency
OFF ON OFF No. 2 speed frequency
ON ON OFF No. 3 speed frequency
OFF OFF ON No. 4 speed frequency
ON OFF ON No. 5 speed frequency
OFF ON ON No. 6 speed frequency
ON ON ON No. 7 speed frequency
‑24‑
Page 25

■ Operation pattern example in the 2-speed operation mode
(I3)
(I4)
(I3)
(I4)
When " I5 function selection" is set to −
acceleration/deceleration time
No. 1 acceleration time
Jogging frequency
Positioning DC brake
Forward
Reverse
Forward/stop switch
(I1)
Reverse/stop switch
(I2)
Forward jogging
Reverse jogging
No. 2
acceleration/deceleration time
(I5)
0-speed
No. 1
deceleration time
Positioning DC brake
0-speed
No. 2
deceleration time
■ Operation pattern example in the 4-speed operation mode (factory setting)
No. 0 speed frequency
Forward
Reverse
Deceleration time
Forward/stop switch
(I1)
Reverse/stop switch
(I2)
Frequency setting selection (1)
Acceleration time
No. 1 speed
No. 2 speed
No. 3 speed
Positioning DC brake
No. 3 speed
: 2-speed
Frequency setting selection (2)
‑25‑
Page 26

Protective Function
Protective functions
The protective functions classified as shown below are built-in the inverters of this series.
① Functions that display a warning.
② Functions that do not display a warning, but act to avoid a tripping of the system.
③ Functions that display a warning and shut off inverter output.
④ Functions that trip the inverter. (Trip signal cannot be retained when the power is
turned off.)
Classification
①
②
5-digit LED display Description of protection Countermeasures, etc.
Electronic thermal
relay operation
Monitor display flashes when output
current reaches the electronic thermal
relay level and the timer operat es.
Electronic thermal relay trip.
Be careful of the size of the
load when using.
(Monitor)
(Flashes)
Acceleration/
deceleration stall
prevention
Prevents tripping when acceleration/
deceleration time becomes too long in
the following situ ations:
Increase acceleration/
deceleration time or
decrease inertia load.
(no display)
・
DC voltage of the converter
exceeds approx. 375V.
・
Motor current exceeds inverter’s
current limit operation po int.
Insufficient voltage
warning
If DC voltage of the converter drops
below approx. 170V, it is regarded as
Investigate the wiring and
power source informatio n.
“instantaneous power failure,” and
Instantaneous
power failure
protection
inverter output is shut off.
below approx. 100V, the control circuit
is reset. If voltage is restored by the
*1
If it drops
time the control circuit is reset,
operation can be restarted
automatically.
*2
③
Reverse prevention
*3
Selecting the reverse prevention
function prevents reverse operation if
Check if the reverse
command has been given.
the inverter receives a reverse sign al.
Restart prevention
when power is
restored
*2
Prevents the inverter from restarting
automatically if already given the run
command when power is turned,
After commanding the
inverter to stop, command it
to run again.
restored following power failure or
reset.
*1
The inverter will operate correctly if power failure does not exceed approx. 15ms.
*2
Prevents the inverter from restarting automatically if “ restart prevention when power is restored” is selected for
.
*3
Effective only when “ reverse prev ent ion” is se lecte d fo r .
‑26‑
Page 27

Protective Function
Classification
5-digit LED display Description of protection Countermeasures, etc.
Over-current trip
Regenerative overvoltage trip
Trips if inverter output current
exceeds the rated current approx.
by 200%.
Trips if DC voltage of the
converter rises above approx.
400V.
Possible causes in cl ude drop in
power source voltage, excessive
2
load, acceleratio n/
GD
deceleration time is set too short ,
load short, or grounding. Take the
proper measures to determine
the cause.
If it trips while the inverter is
running, deceleration time could
be too short. Try setting
deceleration time longer. If it trips
when the power is turned on, the
inductance of the power-boosting
AC reactor provided on the input
side of the inverter may be too
high. Select an AC reactor that
matches the inverter capacit y.
④
Over-voltage trip
retry when power is
turned on
Over-load trip
(Electronic thermal
relay)
CPU
error
If over-voltage trip occurs when
the power is turned on because
the inductance of the powerboosting AC reactor provided on
the input side of the invert er is t oo
high, etc.,
and output is shut off.
The trip is automatically reset
when DC voltage of the converter
drops below approx. 400V,
enabling normal operat ion.
If motor current continues to
exceed the electronic thermal
relay setting value, load is
regarded as being to high
causing the function to t r ip.
Trips if a control microcomputer
error is detected.
is displayed
*1
The capacity of the powerboosting AC reactor provided on
the input side of the inverter may
be too large. Select a reactor that
matches the inverter capacit y.
Try reducing load, modifying
operating pattern, or raising
capacity of inverter.
A malfunction caused by outside
noise could have occurred.
Check the area for noise and
remove the source of noise.
*1
Effective only when “ over-voltage trip retry when power is turned on” is selected for .
‑27‑
Page 28

Classification
④
5-digit LED display Description of protection Countermeasures, etc.
Self-diagno sis t rip
External forced trip
Trips if parameter such as “
operation mode selection” is
changed.
Trips when “ I5 function
selection” is set by external
forced trip and I5 – G becomes
open.
Cancel by trip after shorting.
There is nothing wrong with the
equipment. The results of the
change become effective when
the trip is reset.
Investigate the cause of overlo ad.
Try reducing the load, changing
the operation pattern, or raising
the capacity of the inverter and
motor.
Method of resetting trip
In the event of a trip, remove the cause and cancel by one of the following methods.
[1] Turn off the inverter’s power. When the trip display disappears, turn the power
back on.
[2] Short between both I1 – G and I2 – G for at least 0.1 seconds while the cause of
the current trip is being displayed.
*1
[3] Press both △ ▽ switches on the operation panel simultaneously for at
least 1 second while the cause of the current trip is being displayed.
[4] Input the trip reset command while the cause of the current trip is being
displayed.
*2
※ A CPU error cannot be reset by methods 2, 3 or 4. Reset by method 1
given above.
*1
Cannot be reset if “ I1.I2 function selection” is set to I1: Run/stop or I2: Forward/reverse.
*2
Effective only when “ I5 function selection” is selected for .
‑28‑
Page 29

Maintenance/Inspection
You should perform maintenance/inspection on a regular basis in order to ensure safety
and keep the inverter in good running order.
Precautions when performing maintenance/inspections
(1) The power should be turned on/off only by the person performing the task.
(2) The internal circuits of the inverter remain charged with high voltage for a short while
after power is turned off. To perform inspection, first turn off the power and then wait for
the LED display on the front panel to go off (min. 5 minutes).
(3) Do not perform insulation resistance measurement on the inverter. Doing so will
damage the inverter.
Inspection items and environment
● Ordinary/normal usag e condi tions
Ambient conditions: Annual mean temperature 30°C, min. 20 hrs/day at max. load rate 80%
● Perform daily and periodic inspections in accordance with the following items:
Classification Inspection cycle Inspection items
・
Ambient temperatur e, humidit y , dirt, dust, foreign o bjects, etc.
・
Is there abnormal vibration/noise?
・
Is main circuit volt age normal?
・
Daily
inspection
Periodic
inspections
Daily
1 year
Is there strange odor?
・
Is there lint in the air holes?
・
Cleanliness of control unit
・
Is wiring damaged?
・
Are equipment connections loose or off cent er?
・
Are foreign objects lodged in at the load side?
・
Are fastened sections loose?
・
Is there evidence of overhe ating?
・
Are terminal blocks da ma ged?
<Caution>
Inspection cycle for periodic inspections may vary if usage conditions differ from those
given above.
Approximate period for part replacement
Period for part replacement varies according to how the inverter is used. Parts must be
replaced or repaired when something is wrong with them. Under the ordinary/normal
usage conditions.
Product
name
Inverter
Smoothing capacitor Approx. 5 years
Cooling fan
Aluminum electrolytic
capacitor of PC board
Part name Standard replacement
period (hrs)
2〜3 years
(1〜30,000 hrs)
Approx. 5 years
Remarks
Standard replacement period gives
a number of years for reference
only. If a part becomes fault y it must
be replaced even if the standard
replacement period has not yet
been reached.
‑29‑
Page 30

Troubleshooting
Inspection to determine cause of problem
When a prob lem occurs , perform th e inspe ctions and t ake the m easures pre scribed in the
following table. If you cannot determine the cause of the problem, if you suspect that the
inverter is not working properly, if a part is damaged, or there are any other problems you
cannot solve, contact your Panasonic dealer.
Problem Description of inspection Corrective measures, etc.
Motor doesn’t work.
Motor turns in
reverse.
Is there anything wrong with the
wiring?
Is power being supplied to the power
input terminals?
Is the LED on the operation panel lit? Recheck the above.
Is the voltage of the power in put
terminals normal?
Is an error being displayed? See “protective function”.
Has free-run been commanded? Cancel free-run.
Are both the forward AND reverse
switches on?
Is there anything wrong with the
frequency setting?
Is the motor locked? (Is the load too
heavy?)
Is phase interruption operation being
carried out?
Is there a mistake in the phase order
of the output terminals (U/T1, V/T2,
W/T3)?
Wire correctly.
Turn on the power.
Turn off the power once, and then turn
back on.
Check power source voltag e.
Turn either the forward OR reverse
switch on, and the other off.
Check the frequency sett ing.
Cancel the motor lock. (Reduce the
load.)
Recheck the wiring between the
inverter and motor.
Match the phase order of the output
terminals (U/T1, V/T2, W /T3) with the
motor.
The motor runs but
speed doesn’t change.
Motor speed is not
correct.
Motor speed is
unsteady.
Is the load too heavy? Reduce the load.
Are the number of poles and volt age
of the motor correct?
Is voltage of the power input
terminals (R/L1, S/L2, T/L3) c orrect ?
Is the frequency setting range
normal?
Has motor terminal voltage dropped
excessively?
Is the load too heavy? Reduce the load.
Is load variation too large? Reduce load variation. Raise the
Check the specificat ion manual and
name plate.
Check power source voltag e.
“
lower limit frequency”
upper limit frequency”
“
“
base frequency”
max. output voltage adjustment”
“
V/F reduction characteristics”
“
capacity of the inverter and motor.
‑30‑
Page 31

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
Parameter functions
No. Parameter name
Setting frequency
(0 speed)
1st speed frequency
nd
speed frequency
2
rd
speed frequency
3
th
speed frequency
4
th
speed frequency
5
th
speed frequency
6
th
speed frequency
7
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Run command
selection
Explanation
Sets the frequency with which you want to run the machine.
Valid when “
This sets the frequency when running in multi-speed mode.
Valid when “
Allows you to set 4
running mode for “
Operation Mode
8 Speed Operation Mode Frequency Setting Selections
This selects the run command from the following.
●
frequency command se lect” is
Running mode select” is higher than 4th speed operation.
th
speed frequency to 7th speed frequency when you select 8 speed
Running Mode Select.”
Input Terminal
I 3 I 4 I 5
(PANEL) :
RUN
switch on the operation panel.
.
(TERMINAL) : Input terminals “I1” and “I2”
(BOTH): Both operation panel and input terminals are
valid.
is selected, you cannot use the input terminal as the run
setting frequency
" setting frequency (0 speed)"
Analog Command “F1”
(Voltage Command) DC 0 to 5 V
Analog Command “F1”
(Voltage Command) DC 0 to 10 V
Volume on Main Unit *
Frequency command
selection
■
V alues set at ex-factory.
●
■
When
※
command.
This selects whether to set the 0 speed frequency using “
(0 speed), ” the input terminal for Frequency Setting Selections “F1” or the switch on
the main unit.
■
●
●
●
* You cannot operate inverters without volume under the 0 speed frequency when
selected.
is
‑31‑
Page 32

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
No. Parameter name
Operation mode
selection
Torque control
Explanation
These are the parameters that select the operation mode.
●
■
●
●
This adjusts the voltage output of the inverter at a low frequency region.
Be aware that as the settings are
※
increased, excessive current will
flow which will cause a trip.
●
●
2nd Speed mode
4th Speed mode
8th Speed mode
〜
: Auto-boost Controls for the optimum auto-torque for the
inverter and motor with the same capacity.
: Controls slip frequency compensation.
Controls compensation of the slip frequency for the motor
selected by “
Manual torque boost
:
Maximum output voltage
Large
Output voltage
0
Small
motor selection.”
Base frequency
Output frequency
<Precautions regarding the selection of Auto-boost and slip frequency compensation>
Select parameters when the motor is stopped.
・
Do not use when running in serial.
・
There are cases in which the system will be unstable depend ing on th e c ond itions of
・
the load. If that should occur, set the manual torque boost.
When running at a high power supply voltage, adjust to lower the output voltage of
・
the inverter using “
adjustment.”
Jogging frequency This sets the frequency for operating in the jogging mode.
Acceleration time
No. 2 Acceleration
time
This determines the rate of change of the output frequency during acceleration.
Sets the time that changes in 50 Hz.
・
When set to 0 seconds, ac celerati on is at its op timum sp eed and deceler ation w ill b e
・
0.01 second.
When less than 3 seconds set to 0.01 sec intervals; When 3 to 9 seconds set to 0.1
・
sec intervals; When 10 seconds or more set t o 1 sec interv als.
This sets the acceleration time of the No. 2 Acceleration.
This is valid when you select “
No. 2 Acceleration.
Base frequency” or “ Maximum output voltage
I5 Function Selection” in the
■ Values set at ex-factory.
‑32‑
Page 33

No. Parameter name
Not used
Not used
DC brake volume
DC brake time
DC braking time This selects the type of DC brake.
Starting brake time This runs the inverter after applying the DC brake to the motor for the amount of time
Brake start frequency This adjusts the frequency for starting to apply the positioning DC brake.
This adjusts the DC brake time and the DC brake volume when shifting from inverter
drive to a stopped state.
- The machine will enter a free-run when either or both the time and volume are set to
0 (zero).
※ The DC brake time when you select a sudden brake (all regions) will be twice the
time of the positioning brake.
■
set when you are starting up. This does not function when you set to 0 (zero).
・ The strength (torque) of the DC brake (torque) is the “
but be careful because it does not operate when set to 0.
・ The DC brake will be applied when the output frequency is lower than “Brake start
frequency” when you cause a soft-stop using the stop command and stop from
normal operation.
: Position
Explanation
●
: Sudden stop (all regions)
DC brake volume”
Carrier frequency
variable
■ Values set at ex-factory.
・ The DC brake will be applied when lower than 1 Hz regardless of the settings of
“Brake start frequency” when it stops because the frequency settings are low while
in normal operation.
This is the parameter that selects the carrier frequency. This selects the following 8.
Change the carrier frequency when the motor is stopped.Do not change while it is
operating.
Setting value Carrier frequency Setting value Carrier frequency
0 1.2kHz 4 8.0kHz
1 2.6kHz 5 10.1kHz
■
2 3.9kHz 6 12.0kHz
3 6.0kHz 7 14.9kHz
‑33‑
Page 34

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
A
e
(
)
No. Parameter name
Explanation
Deceleration time This determines the rate of change of the output frequency when decelerating.
・ Sets the time that changes in 50 Hz.
・ When set to 0 seconds, acceleration is at its optimum speed and deceleration will
be 0.01 second.
・ When less than 3 seco nds set to 0.01 sec intervals; When 3 to 9 se conds set to 0.1
sec intervals; When 10 or more seconds set t o 1 sec interv als.
No. 2 deceleration
time
This sets the deceleration time of the No. 2 Deceleration.
This is valid when you selec t “
I5 Function Selectio n” in the
Acceleration.
Not used
Not used
Base frequency
This sets the base frequency (maximum
Maximum output voltage
frequency of the torque region) to any
frequency within the range of 30 to 400 Hz
that matches the motor rating.
Output voltage
0
Output frequency
Adjustment range
(30 ~ 400Hz)
Base frequency
No. 2
Max. Output voltage
adjustment
V/F reduction
characteristics
■: Values set at ex-factory.
This adjusts the maximum output voltage
(base frequency voltage). The range of
adjustment is 0 to 100%.
Maximum output voltage
100 :
Power supply
voltage
Output voltage
0
Output frequency
djustment rang
0 ~ 100%
Base frequency
This adjusts the V/F characteristics to match
the load characteristics.
●
Rated torque load
●
Reduction torque load
1.0
Output voltage
0
Large
Base frequency
Output frequency
You can make fine adjustments between 1.0
and 2.0.
Note: This is valid only when you have selected “torque control” in the manual boost.
‑34‑
Page 35

0
No. Parameter name
No. 2 V/F selection
No. 2 V/F base
frequency
No. 2 V/F boost
Explanation
This sets the special V/F pattern using “No. 2 V/F selection.”
This selects the No. 2 V/F upper pattern
set using the normal V/F and “No. 2 V/F base frequency” and “No. 2 V/F boost.”
■
●
●
Normal pattern
Upper pattern
Lower pattern
Note: This is valid only when you have selected “torque control” in the manual boost
or the lower pattern
No. 2 V/F
Output voltage
Normal V/F
0
Output frequency
Upper selection
Output voltage
0
Output frequency
Lower selection
Output voltage
0
Output frequency
.
Jump frequency width
Jump frequency 1
Jump frequency 2
Jump frequency 3
Jump frequency 4
This creates areas that cannot set the
frequency in a range set by “
Jump
frequency width” above and below as the
center of the frequency set by “
frequency 1” to “
Jump frequency 4”
Jump
Set frequency
Frequency Frequency Frequency
1 2 3
Frequency command (Between F IN and G)
in order to avoid mechanical resonance.
・
Acceleration time outputs the frequency even in the jump region.
・ If jump frequency ranges are overlapped, it jumps all overlapping ranges.
I1/I2 function selection This switches the input terminals “I1” and “I2” in the following manner.
Input terminal
■
(
:
Fwd-Stop/Rev-Stop
Between “I1” and “G” Between “I2” and “G”
Short Open Short Open
Forward
Operation
Stop
Operation Stop
Reverse
Operation
Reverse Forward
:
Run-Stop/Fwd-Rev)
Jump frequency width
Stop
■: Values set at ex-factory.
‑35‑
Page 36

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
No. Parameter name
I5 function selection
Not used
Multi-speed input
selection
Explanation
This selects the input terminals “I5” functions in the following manner.
●
:
“Terminal” – “G” Short
●
:
“Terminal” – “G”
●
:
selection
“Terminal” – “G” short
■
※
This selects the type of frequency setting for multi-speed operation.
●
“Terminal” – “G” short
Set the status of the short “Terminal” – “G” before selecting “
When open, a trip occurs.
(FREE)
(THeRmal)
→
(UpーDown)
(ReSeT)
(1bit):1 bit input
→
Free-run Stop
External forced trip command
No. 2 acceleration and deceleration time
→
→
Trip reset command
.”
Not used
■: Values set at ex-factory.
This selects 1 type of multi-speed frequency for 1 terminal of the “Frequency setting
selection terminals.” This runs the inverter in 3 speeds in 4 speed operation mode
and 4 speeds in 8 speed operation mode.
Ex.) With 8 speed mode operation
Input terminals
I3 I4 I5
Open Open Open
Short
Open Short
Open Open Short
■
This selects the frequency by setting “Frequency setting selection terminals” in
binary.
××
×
(Binary):Binary input
Frequency setting
No. 0 speed
frequency
No. 1 speed
frequency
No. 2 speed
frequency
No. 3 speed
frequency
・ Open and short
are related to “G”
and terminals.
・× means there
is no relationship
between short
and open.
‑36‑
Page 37

No. Parameter name
Output signal 1
selection
Not used
Explanation
This selects the output signal between output terminals “O1” to “O2” in the following
manner.
■
:
●
:
Trip output signal (When trip: ON*)
Arrival signal (When arrival: ON*)
●
:
●
:
Run/Stop signal (When run: ON*)
Free-run singnal (While Free-run: ON*)
●
:
Forward operation signal (While forward operation: ON*)
●
:
●
:
→
Reverse operation signal (While reverse operation: ON*)
Output frequency detection signal
Refer to:
(TRIP)
(STaBLe)
(RUN)
(FREE)
(Fwd)
(Rev)
(CheckーF)
Compare frequency A” and “
Compare frequency B”
●
:
→
●
:
●
:
Motor current detection signal
Refer to “
DC brake signal (While DC brake: ON*)
Trip cause detection signal
(CheckーC)
Motor current detection level”*
(DC-Brake)
(CAUS)
The following signals are output when a trip occurs.*
Trip contents
Normal over-current
Acceleration over-current
Deceleration over-current
Over-voltage
External forced trip
Electronic thermal
CPU error
ON time
Continuous
3 seconds
1 second
1 second
0.25 second 0.25 second
0.9 second
0.1 second
OFF time
1 second
3 seconds
1 second
0.1 second
0.4 second
■: Values set at ex-factory.
* “
selection.”
Self-diagnosis
output signal 1 selection” can invert “
‑37‑
0.5 second
output signal 1 polarity
0.5 second
Page 38

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
No. Parameter name Explanation
Relay output selection
This selects the output signal when the relay output between “NC,” “C2” and “NO” is
used. Trip output signal
●
●
●
●
●
●
(TRIP):Trip output signal
(When trip: Between “NC” and “C2”: Open, Between “NO”
and “C2”:Closed)
(STaBLe):Arrival signal
(When arrival: Between “NC” and “C2”: Open, Between “NO”
and “C2”: Closed)
(RUN):Run/stop signal
(When run: Between “NC” and “C2”: Open Between “NO”
and “C2”: Closed)
(FREE):Free-run signal
(When free-run: Between “NC” and “C2”: Open, Between
“NO” and “C2”: Closed)
(Fwd):Forward operation signal
(When forward operation: Between “NC” and “C2”: Open,
Between “NO” and “C2”: Closed)
(Rev):Reverse operation signal
(When reverse operation: Between “NC” and “C2”: Open,
Between “NO” and “C2”: Closed)
Motor current
detection level
Output signal 1
polarity selection
Current limit operating
point
■ Values set at ex-factory.
●
●
Set the current level you want to detect using a percentage for the rated current of the
inverter when you selected “
selection” in
exceeds the detection level you set and it will turn “OFF” when it is below.
This function inverts the polarity of the output signal between output terminals “O1” and
“C1.”
■
●
This limits the operating point for the motor current that was set.
Numbers are percentages for the inverter rated current.
(NORmal): When operation: transistor “ON”
(REVerse): When operation: transistor “OFF
(Check-F):Output frequency detection signal
→"
Refer to “
(Check ー C):Motor current detection signal
→Refer to “
. The output terminal will operate when the motor current
Compare frequency A,” and
Compare frequency B."
Motor current detection level.”
Output signal 1 selection” and “
Relay output
‑38‑
Page 39

No. Parameter name Explanation
Stall deceleration
magnification
Acceleration mode
switch
Deceleration mode
switch
This adjusts the decelerat ion tim e when the stall prevention function of the decelerati on
is operating.
・Set in percentages for the deceleration time of the normal setting.
This selects the straight line acceleration/deceleration or curved line (S) acceleration/
deceleration independently.
■
Output frequency
0
This is a general
acceleration mode to
accelerate and decelerate
on a straight line up to the
set frequency.
Straight line ● S Shape 1 ● S Shape 2
Time
utput frequency
Base frequency
0
Time
With large output of the
motor torque, the incline is
steep and when the output
torque is small, the incline
is gentle.
Output frequency
f2
f1
0
Time
This shows an S
characteristic between
running frequencies f1 t o f2.
This is a smooth acceleration and deceleration
characteristic.
* This changes using the acceleration and deceleration time set when under the base
frequency if you select
S shape 1, but when over the base frequency,
the incline is gentler than the set time.
Monitor mode switch This selects the content that displays in the 4 digit LED.
Display magnification This sets the magnification of the value that displays in the 4 digit LED. This displays
■ Values set at ex-factory.
The value to which the “
display magnification” was applied is displayed with the
frequency display.
■
●
Output frequency ●
Set frequency ● Converter unit DC voltage
Output current
the motor synchronized rotation or the line speed.
* The parameters related to frequency (below) display the value to which the display
magnification was applied when you change the display magnification.
〜〜〜〜 0 to 8th speed frequency” " 〜〜〜〜 Compare frequency"
"
Jogging frequency" "Matching detection width"
"
Brake start frequency" " Instantaneous drop frequency"
"
" 〜〜〜〜 Jump frequency" "Lower limit frequency"
Frequency meter full scale indication" " Upper limit frequency"
"
‑39‑
Page 40

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
No. Parameter name Explanation
Frequency meter
adjustment
Frequency meter full
scale indication
This calibrates the frequency meter. Adjust using the △ ▽ switches so that
the needle on the frequency meter points at the full scale.
This indicates the frequency when using the frequency meter full scale. This is set to
60 Hz full scale at ex-factory so adjust to be used higher than 60 Hz.
“FOUT” switch This selects the frequency signal to output to the frequency output terminal “FOUT.”
■
●
Frequency analog output
Frequency digital output
● Current analog output
Compare frequency A
Compare frequency B
This sets the frequency to detect when you selected “ output signal 1 selection”
and “
relay output selection” in the output frequency detection signal
.
- The output signal is ON when the outp ut fre que ncy exceeds*1 “compare frequency A”
and is OFF when it is less
Output frequency
0
ON
Between “01” and “COM”
*1
than “compare frequency B.”
Output frequency
A
B
0
ON
ON ON
Between “01” and “COM”
A
B
Match detection width
■ Values set at ex-factory.
When A ≧ B
When A < B
* It does not turn ON or OFF if the difference of the output frequency and compare
frequency does not exceed 1 Hz.
This adjusts the timing to output the arrival signal during acceleration and deceleration
when you selected “ output signal 1 selection” and “ relay output selection” in
the
arrival signal.
- The arrival signal is output when the difference of the output frequency and the set
frequency is smaller than “match detection width.”
- The arrival signal is not output when 0 is set.
- The arrival signal is not output when forward/reverse are switched when stopped
or during DC brake.
- The arrival signal is output until immediately before stopping when “ brake
start frequency” < “match detection width.”
‑40‑
Page 41

No. Parameter name Explanation
Instantaneous drop
frequency
Instantaneous freerun time
Restart prevention
when power is
restored
Retry selection
Retry start time
This adjusts the output frequency after instantaneous stop or after the power is
restored.
- This starts the output from the value that subtracted “Instantaneous drop
frequency” from the output frequency of the instantaneous detection when power
was restored.
- It starts running from 0.5 Hz in the same way as when turning on the power under
normal conditions even though power is restored and the control circuit was reset
when the power cut was long.
This adjusts the free-run time after instantaneous stop or restoring power.
This prevents restarting after an instantaneous stop or after power was restored by
setting
.
You can try to continue running by automatically canceling the trip after “Retry start
time” even when a trip occurs. This will retry (re-execute) the set number of times but
if a trip does not occur in over approximately 120 minutes, the retry count will be
initialized.
■
(NO): Does not retry
● 〜 :Retries the set number of times
・Outputs a trip signal and stops when the set number of retries is reached but does
not output the trip signal (when trip is “ output signal 1 selection” and “
relay output selection”) during a retry.
* The retry function is invalid when Restart prevention when power is restored is set
.
Set frequency
Frequency setting
bias
to
This sets the “0 V input frequency” of
the frequency setting input terminal
“FI.”
0V
0 V input frequency Frequency setting voltage
Lower limit frequency This sets the lower limit of the inverter output frequency.
Upper limit frequency This sets the upper limit of the inverter output frequency.
Constant for input
filter
This sets the constant for input filter of the voltage or the current’s frequency setting
signal from an external source.
* Increase the constant of the filter if you cannot attain stable operation because of
the effects of noise. As you increase the setting value, response will worsen.
5 V input fr e que nc y
5V
(Between “FIN” and “G”)
■ Values set at ex-factory.
‑41‑
Page 42

Detailed Explanation of Parameters
No. Parameter name Explanation
Over-voltage trip retry
when power is turned
on
Reverse prevention
Electronic thermal
relay
This displays the
on the power when you set to
Also, the trip is automatically canceled at the point the DC voltage falls below
approximately 400 V on the converter.
※ The display will change from to and it will consider the
normal over-voltage trip when you continue the over-voltage beyond a prescribed
amount of time after turning on the power supply.
This prevents the trouble caused by reversing when you set to
This adjusts the amount that the electronic
thermal relay functions.
・ Set the percentage for the inverter’s rated
current.
・ The operation panel display unit will flash
when the motor current exceeds the set
value.
※ It is necessary to check the ambient
temperature when the setting is higher
than the ex-factory setting.
and trips when an over-voltage trip occurs when turning
.
.
1 min.
50 100 150
Operating time
0
100% 150%
Parameter value
200%
Motor current
Trip cause clear This clears the cause of the trip.
<How to clear>
Trip cause 1
Trip cause 2
Trip cause 3
Trip cause 4
Trip cause 5
Parameter
initialization
①
Use the △
is.
② After the display extinguishes, it will be cleared when the power is turned back on.
③ Switch the power supply again if the inverter does not operate in this state and use
after turning on the power again.
This remembers the latest 5 trips.
Refer to “Monitor” for details regarding the content of the display.
This initializes and returns all parameters to our standard ex-factory settings.
<How to initialize>
① Use the △
is.
② After the display extinguishes, it will be init ializ ed w hen the power i s turned bac k on.
switch to switch the power supply with the setting
will be displayed in the 4 digit LED.
switch to switch the power supply with the setting as it
will be displayed in the 5 digit LED.
as it
③ Switch the power supply again if the inverter does not operate in this state and use
after turning on the power again.
‑42‑
Page 43

No. Parameter name Explanation
Motor selection
Start-up starting
frequency
Automatic voltage
regulation reference
voltage
Automatic voltage
regulation selection
Parameter extraction This extracts the parameter. Refer to “How to Extract Parameters” for details.
Parameter lock This locks the parameters that you set.
Set the motor volume and polarity to use when you selected
compensation control) using “
* Select the motor when it is stopped.
This sets the inverter output starting frequency.
※ This increases the starting torque but it is close to a direct startup and is not
appropriate for a shock-less start. Also, there are cases of a trip occurring
depending on the load.
This selects the motor’s rated voltage when using automatic voltage regulation.
This corrects the output voltage and suppresses the variations in the output voltage for
the variations of the input power supply voltage.
However, you cannot output the value higher than the maximum output voltage or the
input power voltage.
Does not lock parameters
torque control.”
(slip frequency
Locks all parameters.
Locks parameters for which setting is unnecessary.
・ Setting to
switches become invalid. None of the parameters can then be set.
( RUN
・
Setting to
parameter extraction.”
Parameter copy This copies parameters.
Reads parameters to panel.
Writes parameters to main unit.
Checks the content of parameters.
Motor rated current This sets the motor rated current when using the slip frequency compensation control.
*1
Motor current without
load
This sets the motor current without load when using the slip frequency compensation
control. *1
and STOP switches are valid)
Does not copy parameters.
locks all parameters and the MODE △ ▽
allows setting of only the parameters selected by the “
‑43‑
Page 44

No. Parameter name Explanation
Motor 1 primary
resistance
Slip correction gain Adjusts the slip correction gain when using slip frequency compensation control.
Sets the motor 1 primary resistance w hen using slip frequency compe ns atio n c ontro l.
*1
Slip correction
response time
*1
Because slip frequency compensation control requires a motor constant, set to our standard motor constant that was
set at ex-factory. Set the motor constant to use when driving another motor.
Sets the slip correction res pons e t ime w hen us ing sl ip frequency compensati on control.
‑44‑
Page 45

Specifications
)
)
y
y
)
y
(
)
y
)
g)
Part Number
Applicable motor (kW)
Output capacity (kVA
Rated output current (A
Rated output voltage
Rated output
M1S02
*1
*2
For 3-phase power source: 3-phase AC 200 to 230 V
*4
Single phase power source: Single phase AC 200 to 240 V
2
*** M1S04
3
0.2 0.4 0.75
0.6 1.2 1.6
*3
1.4
2
*** M1S08
3
*3
2.5
For 3-phase power source: 3-phase AC 200 to 230 V
Voltage
Frequenc
Allowable voltage fluctuation
Power source
Allowable frequency fluctuation
Single phase power source: Single phase AC 200 to 240 V
50/60Hz
-15%, +10%
± 5%
Control method Low noise sine wave PWM style
Output frequenc
Frequency accurac
Frequency setting resolution
Frequency setting signal
Voltage/Frequency
characteristics
・
Digital: 0.01 Hz
・
Analog: Setting frequency range/1000 Hz (minimum 0.05 Hz)
Base frequency:30 to 400 Hz (1 Hz step), with reduced
0.5 to 400 Hz (Start and stop from 0.5 Hz
± 0.5%(25°C ± 10°C
DC0 to +5V, 0 to +10V
torque pattern
Rated overload current 150%/minute
Regenerative brake
torque
Control method
DC brake Brake start frequency/break operating time/break volume
Short time average reduced torque: 100% min.
Continuous regenerative torque: 20% min.
With optional braking resistor: continuous regenerative torque 100% min.
0 to 3600 s(seconds)
Acceleration/deceleration
time
0 to 3s: 0.01s step, 3 to 10s: 0.1s step, 10s or more: 1s step
*Time that changes in 50 Hz. Adjustable to a maximum of 4
kinds of acceleration/deceleration speeds.
Jogging frequenc
Operation mode
Others
2-speed operation mode, 4-speed ope ration mo de, 8-spee d operation mode
Automatic boost, AVR function/retry function selectable
RS-485 communication function (factory-set option), parameter lock available
0 to 30Hz
Insufficient voltage protection, over-current protection,
overvoltage protection, instantaneous power failure
Protective functions
protection, stall prevention, over-load limitation (current
limiter), overload trip (electric thermal relay), restart
prevention when power is restored, sel f-di agnosis trip (the last
5 causes of trips are stored)
Protective structure Built-in the panel (IP20
Cooling method Self-cooling method
Weight (k
0.7 0.7 0.9
)
4.0
2
3
*3
***
*1
Applicable motor: For Panasonic 3-phase induction motor (4 poles)
When using another motor, select the motor within inverter ratings.
*2
Output capacity: If the rated output voltage is 240V.
*3
Rated current is 90% if carrier frequency of 3 or 4 is selected.
Rated current is 80% if carrier frequency of 5, 6 or 7 is selected.
*4
Output voltage does not bec ome higher than the power source v olt age.
‑45‑
Page 46

Outer Dimensions
■
No. 1 frame
(Unit: mm) Dimensional tolerances: ±2 mm
■
No. 2 frame
Inverter part
number
M1S022**** 0.2 37.5 112
M1S023**** 0.2 37.5 112
M1S042**** 0.4 55.5 130
M1S043**** 0.4 37.5 112
M1S083**** 0.75 55.5 130
Inverter
capacity
kW
L1 L
mm mm
‑46‑
Inverter
capacity
kW mm mm
M1S082**** 0.75 55.5 130
L1 L
Page 47

Parameter Setting
Parameter overview
Inverters of this series hav e vari ous parameters th at adjust /set charact eristics and functions,
etc. The objectives and functions of various parameters are described herein. Get a good
understanding of the parameters and use to adjust inverter to the best condition for the
customer’s operating conditions.
Parameter configuration and list of parameters
Parameter settingNo. Parameter name
*1
Setting frequency
(0 speed)
1st speed frequency
2nd speed frequency
3rd speed frequency
4th speed frequency
5th speed frequency
6th speed frequency
7th speed frequency
Adjustment range Min. unit Factory setting Check
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0、 0.50〜upper limit frequency
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
0.01Hz
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
0Hz
50Hz
30Hz
15Hz
0Hz
0Hz
0Hz
0Hz
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Run command
selection
Frequency command
selection
Operation mode
selection
- 0〜10V
Operation panel
Terminal block,
Both
Operation panel
Volume
- 0〜5V
2、4、8、speed operation mode
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
4 speed
operation mode
*1
Parameters marked by in the Check column are tripped for safety if modified or memorized. Release the trip
to use.
*2
The minimum unit is 0.05 Hz when the setting frequency is min. 160 Hz.
‑47‑
Page 48

Parameter settingNo. Parameter name
Adjustment range Min. unit
0 〜 100
Torque control
. Automatic boost (standard)
Slip correction control
Jogging frequency
0、 0.5〜30 Hz
Acceleration time 5 sec
No. 2 acceleration
time
Not used
0〜3600 sec 3
10
3
sec : 0.01 sec interval
〜
sec〜10 sec : 0.1 sec interval
sec〜 :1 sec interval
Not used
DC brake volume
DC brake time
Case of
0〜3 sec
Case of -
0 〜 100%
:
:
0〜6 sec
DC brake selection
Starting brake time
Brake start frequency
Carrier frequency
variable
-
Positioning
Sudden stop
0 〜 3 sec
0.50 〜 400 Hz
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
∗2
Deceleration time 5 sec
2
0.01 Hz 7 Hz
294
0.05 sec
0.1 sec
0.05 sec
0.01 Hz
Factory setting
5 sec
−
−
0.5 sec
1.0 sec
0 (nonoperational)
*2
3 Hz
40
2
Check
*1
Not used 5 sec
Not used
0〜3600 sec 3
No. 4 deceleration
10
time
Base cycle
Max. output voltage
adjustment
V/F reduction
characteristics
No. 2 V/F selection
No. 2 V/F base
frequency
No. 2 V/F boost
30 〜 400 Hz
0 〜 100%
1.0 〜 2.0 squared
No selected
(usually V/F pattern)
Upper selection
Lower selection
30 〜 400 Hz
0 〜 100%
3
sec : 0.01 sec interval
〜
sec〜10 sec : 0.1 sec interval
sec〜 :1 sec interval
1 Hz 60 Hz
1 100
0.1 1.0
1 Hz 60 Hz
20
−
−
*1
Parameters marked by in the Chec k colu mn are trip pe d for saf ety if modifie d or me morized. Rele ase the trip
to use.
*2
The minimum unit is 0.05 Hz when the setting frequency is min. 160 Hz.
∗2
Rated current is 90% if carrier frequency of 3 or 4 is selected.
Rated current is 80% if carrier frequency of 5,6 or 7 is selected.
‑48‑
Page 49

Parameter Setting
Adjustment range Min. unit
Jump frequency
width
Jump frequency① 0、 0.50〜400 Hz
Jump frequency② 0、 0.50〜400 Hz
Jump frequency③ 0、 0.50〜400 Hz
Jump frequency④ 0、 0.50〜400 Hz
I1: Forward/Stop、
I1/I2 function
selection
0、 0.50〜400 Hz
I2: Reverse/Stop
I1: Run/Stop、
I2: Forward/Reverse
Parameter settingNo. Parameter name
*1
0.01 Hz
0.01 Hz
0.01 Hz
0.01 Hz
0.01 Hz
Factory setting
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
Check
0 Hz
0 Hz
0 Hz
0 Hz
0 Hz
I5 function selectio n
Not used
Multi-speed input
selection
Not used
Output signal ①
selection
Not used
Relay output signal
selection
*Effective only when
relay output
terminals NC, C2 or
NO are used.
Free-run、
External forced
- No. 2 acceleration/deceleration
Trip reset
1 bit
Binary
Trip、 Arrival
Running
Free-run
Forward、 Reverse
- O ut put frequency detection
- Mot or current det ection
Trip cause
- DC brake
Trip、 Arrival
Running
Free-run
Forward、 Reverse
- O ut put frequency detection
- Mot or current det ection
Motor current
detection level
Output signal polarity
selection
50〜150%
Forward polarity,
Reverse polarity
5% 100%
*1
Parameters marked by in the Chec k colu mn are trip pe d for saf ety if modifie d or me morized. Rele ase the trip
to use.
*2
The minimum unit is 0.05 Hz when the setting frequency is min. 160 Hz.
‑49‑
Page 50

Current limit operation
point
Stall time deceleration
power
Acceleration mode
switching
Deceleration mode
switching
Monitor mode
switching
Display power
Frequency meter
adjustment
Frequency meter full
scale indication
FOUT switching
Comparison
frequency A
Comparison
frequency B
Agreement detection
width
Reduced frequency at
instantaneous stop
Instantaneous stop
free-run time
Restart prevention
when power is
restored
Retry selection
Retry start time
Frequency setting
bias
Lower limit frequency
Upper limit frequency
Constant for input filter
Over-current trip retry
when power is turned
on
Reverse prevention
Electronic thermal relay
Parameter settingNo. Parameter name
Adjustment range Min. unit
50〜200%
1、2、4、8、16
Straight line - S-curve
- S-curve
- Set frequency
- Output frequency
- DC voltage
Output current
0.1 〜 60.0
---
0 〜 400 Hz
Digital
Analog
0、0.50〜400 Hz
0、0.50〜400 Hz 0.01 Hz
0、0.50〜400 Hz
0、0.50〜400 Hz
1、2、3、4、5
Restart
Restart prevention
No retry
〜
0〜120 sec
0〜-50 Hz
0、0.5〜400 Hz
0、0.5〜400 Hz
No retry
Retry
Reverse
Reverse prevention
30〜150%、
Retry No. of set times
1、2、3、4、5
Factory setting
10% 180%
8
①
②
0.1 1.0
1 Hz 60 Hz
0.01 Hz
0.01 Hz
0.01 Hz
2 sec 4 sec
0.01 Hz 0 Hz
0.1 Hz 0 Hz
0.1 Hz 60 Hz
*2
*2
*2
*2
11
5% 115%
-
0 Hz
0 Hz
3 Hz
3 Hz
1
Check
*1
*1
Parameters marked by in the Chec k colu mn are trip pe d for saf ety if modifie d or me morized. Rele ase the trip
to use.
*2
The minimum unit is 0.05 Hz when the setting frequency is min. 160 Hz.
‑50‑
Page 51

Parameter Setting
Adjustment range Min. unit
Trip cause clear
Trip cause①
Trip cause②
Trip cause③
Trip cause④
Trip cause⑤
Parameter
initialization
Motor selection
Start-up starting
frequency
Automatic voltage
adjustment reference
voltage
Automatic voltage
adjustment selection
Parameter lock
Parameter copy
Motor rated current
Motor current
without load
Motor primary
resistance
Slip correctio n gain
Slip correction
response time
Parameter extraction Parameter No. - -
---
---
---
---
---
Motor capacity
No. of motor poles
0.50〜10 Hz
200,220,230,240V 200
No automatic voltage adjust-
ment
- Automatic voltage adjustment
- No automatic voltage adjustment only when decelerating
No parameter lock
All parameters locked
Parameters that don’t need to
be set locked
Parameters not copied
Parameters read-out to panel
side
Parameters written in inverter
side
Parameter contents checked
0 〜100A
0 〜100A
0 〜100Ω
0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7
0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7
Parameter settingNo. Parameter name
Factory setting
Check
4 poles,
*2
inverter
capacity
*3
0.01 Hz 1
0.1 *
0.1 *
0.01 *
4
1
*1
*1
Parameters marked by in the Chec k colu mn are trip pe d for saf ety if modifie d or me morized. Rele ase the trip
to use.
*2
Motor capacity is : 0.2kW, : 0.4kW, : 0.75kW.
*3
4-pole motor of same capacity as inverter rating set when shipped from the factory.
‑51‑
Page 52

Optional Parts
Operation panel
Operation panel
■
Optional part number
DV0P20704 Standard
DV0P20702 With volume
Specifications
Operation panel cut dimensions
■
2-M3 orφ3.7
Operation panel remote cable
Optional part number Length (m)
DV0P20801 0.5
DV0P20802 1.5
DV0P20803 3.0
Regenerative brake resistor
Optional part number Specifications Power source voltage
DV0P23501
DV0P23502
60 W/200 Ω
60 W/50 Ω
200 V
100 V
‑52‑
Page 53

Optional Parts
AC reactor
Products of the 200 V class 3.7kW or lower are the products subjected to the "Home
appliances and general purpose product harmonic restriction guide line" announced by the
Ministry of International Trade and Industry on September, 1994. In accordance with this
guideline, the regulating levels have been set by Japanese Electric Industry Association.
A harmonic restriction reactor must be connected to the inverter to make it comply with this
standard.
Reactorconnectiondiagram
Harmonic restriction
Commercial Po w er
source
reactor
R
S
T
Optional part number
X
Y
Z
DV0P142-1
DV0P142-2
DV0P142-3
DV0P142-4 2.2
Inverter
Motor
Inverter capacity
kW
0.2/0.4
0.75
1.5
DV0P142-5
DV0P142-6
DV0P142-7
3.7
5.5
7.5
‑53‑
Page 54

Servicing (Repair)
Repair
● Consult your Panasonic dealer for repairs of your Panasonic inverter.
Consult your machine or device manufacturer when the inverter is installed in a
machine or device.
For your convenience: (Please fill in the blank when you need to consult for repairs.)
Date purchased
Shop purchased
Year/Month/Date
Phone number
Model number
Industrial and Appliance Motor Division, Motor Company,
Matsushita Electric Industrial Co. , Ltd.
7-1-1 Morofuku, Daito-shi, Osaka, 574-0044 Japan
Phone: 072-871-1212
IMAZZ S0796‑0
‑54‑
 Loading...
Loading...