Page 1

ORDER NO. KM41401789CE
Telephone Equipment
Model No. KX-TGE210B
KX-TGE212B
KX-TGE232B
KX-TGE233B
KX-TGE234B
F13
KX-TGEA20
(Handset)
KX-TGE230
(Base Unit)
Configuration for each model
Model No
KX-TGE210
KX-TGE212
KX-TGE232
KX-TGE233
KX-TGE234
KX-TGEA20*
*KX-TGEA20 is also an optional accessory, which contains a
handset and a charger.
Base Unit Handset
1 (TGE210) 1 (TGEA20)
1 (TGE210) 2 (TGEA20) 1
1 (TGE230) 2 (TGEA20) 1
1 (TGE230) 3 (TGEA20) 2
1 (TGE230) 4 (TGEA20) 3
1 (TGEA20) 1
KX-TGE210
(Base Unit)
(Charger Unit)
Charger Unit Expandable
Up to 6
Up to 6
Up to 6
Up to 6
Up to 6
KX-TGEA20B
Digital Cordless Phone
Digital Cordless Answering System
B: Black Version
(for U.S.A.)
© Panasonic System Networks Co., Ltd. 2014
Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation
of law.
Page 2

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
WARNING
This service information is designed for experienced repair technicians only and is not designed for use by the general
public. It does not contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in attempting
to service a product. Products powered by electricity should be serviced or repaired only by experienced professional
technicians. Any attempt to service or repair the product or products dealt with in this service information by anyone
else could result in serious injury or death.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety. These parts are marked by
in the Schematic Diagrams, Circuit Board Diagrams, Exploded Views and Replacement Parts List. It is essential that
these critical parts should be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT LEAD FREE, (PbF), SOLDERING
If lead free solder was used in the manufacture of this product, the printed circuit boards will be marked PbF.
Standard leaded, (Pb), solder can be used as usual on boards without the PbF mark.
When this mark does appear, please read and follow the special instructions described in this manual on the
use of PbF and how it might be permissible to use Pb solder during service and repair work.
L When you note the serial number, write down all 11 digits. The serial number may be found on the bottom of the unit.
L The illustrations in this Service Manual may vary slightly from the actual product.
2
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Safety Precautions ----------------------------------------------- 5
1.1. For Service Technicians --------------------------------- 5
2 Warning-------------------------------------------------------------- 5
2.1. Battery Caution--------------------------------------------- 5
2.2. About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)-------------- 5
2.2.1. Suggested PbF Solder ------------------------------ 6
2.3. Discarding of P. C. Board-------------------------------- 6
3 Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 7
4 Technical Descriptions ----------------------------------------- 8
4.1. US-DECT Description ------------------------------------ 8
4.1.1. TDD Frame Format ---------------------------------- 8
4.1.2. TDMA system------------------------------------------ 8
4.1.3. Signal Flowchart in the Radio Parts-------------- 9
4.2. Block Diagram (Base Unit_Main)---------------------10
4.3. Tel Interface Circuit--------------------------------------- 11
4.4. Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part) -----------------12
4.5. Circuit Operation (Base Unit) --------------------------13
4.5.1. BBIC (Base Band IC: IC501) ---------------------13
4.5.2. Flash Memory (IC502)------------------------------13
4.5.3. Flash Memory (IC601)------------------------------13
4.5.4. EEPROM (IC611)------------------------------------13
4.5.5. Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit--------------14
4.5.6. Telephone Line Interface---------------------------16
4.5.7. Parallel Connection Detect Circuit/Auto
Disconnect Circuit -----------------------------------17
4.5.8. Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)/Call
Waiting Caller ID -------------------------------------18
4.6. Block Diagram (Handset)-------------------------------20
4.7. Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)-------------------21
4.8. Circuit Operation (Handset)----------------------------22
4.8.1. Outline --------------------------------------------------22
4.8.2. Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit--------------22
4.8.3. Charge Circuit ----------------------------------------23
4.8.4. Battery Low/Power Down Detector--------------23
4.8.5. Speakerphone ----------------------------------------23
4.9. Behavior of Electric Power Failure -------------------24
4.10. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit) ----------------------24
5 Location of Controls and Components ------------------25
6 Installation Instructions ---------------------------------------25
7 Operating Instructions-----------------------------------------25
8 Test Mode ----------------------------------------------------------26
8.1. Engineering Mode ----------------------------------------26
8.1.1. Base Unit ----------------------------------------------26
8.1.2. Handset ------------------------------------------------28
9 Service Mode -----------------------------------------------------30
9.1. How to Clear User Setting (Handset Only)---------30
10 Troubleshooting Guide ----------------------------------------31
10.1. Troubleshooting Flowchart -----------------------------31
10.1.1. Check Power------------------------------------------32
10.1.2. Check Record ----------------------------------------33
10.1.3. Check Playback -------------------------------------36
10.1.4. Check Battery Charge ------------------------------36
10.1.5. Check Link---------------------------------------------37
10.1.6. Check the RF part -----------------------------------39
10.1.7. Registering a Handset to the Base Unit--------43
10.1.8. Deregistering a Handset ---------------------------43
10.1.9. Check Handset Transmission --------------------44
10.1.10. Check Handset Reception-------------------------44
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
PAG E PAG E
10.1.11. Check Caller ID ------------------------------------- 44
11 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions--------------- 45
11.1. Disassembly Instructions------------------------------- 45
11.1.1. Base Unit ---------------------------------------------- 45
11.1.2. Handset------------------------------------------------ 49
11.1.3. Charger Unit ------------------------------------------ 50
11.2. How to Replace the Handset LCD------------------- 51
12 Measurements and Adjustments -------------------------- 52
12.1. Equipment Required ------------------------------------ 52
12.2. The Setting Method of JIG----------------------------- 52
12.2.1. Connections (Base Unit) -------------------------- 52
12.2.2. Connections (Handset) ---------------------------- 53
12.2.3. How to install Batch file into P.C. ---------------- 54
12.2.4. Commands-------------------------------------------- 55
12.3. Adjustment Standard (Base Unit) -------------------- 56
12.3.1. Bottom View ------------------------------------------ 56
12.4. Adjustment Standard (Handset)---------------------- 57
12.4.1. Component View ------------------------------------ 57
12.5. Things to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal------------ 58
12.5.1. How to download the data ------------------------ 58
12.6. Frequency Table------------------------------------------ 59
13 Miscellaneous ---------------------------------------------------- 60
13.1. How to Replace the LLP (Leadless Leadframe
Package) IC ----------------------------------------------- 60
13.1.1. Preparation-------------------------------------------- 60
13.1.2. Caution------------------------------------------------- 60
13.1.3. How to Remove the IC ----------------------------- 60
13.1.4. How to Install the IC -------------------------------- 61
13.2. How to Replace the Flat Package IC --------------- 62
13.2.1. Preparation-------------------------------------------- 62
13.2.2. How to Remove the IC ----------------------------- 62
13.2.3. How to Install the IC -------------------------------- 63
13.2.4. How to Remove a Solder Bridge ---------------- 63
13.3. Terminal Guide of the ICs, Transistors and
Diodes ------------------------------------------------------ 64
13.3.1. Base Unit ---------------------------------------------- 64
13.3.2. Handset ------------------------------------------------ 64
14 Schematic Diagram -------------------------------------------- 66
14.1. For Schematic Diagram -------------------------------- 66
14.1.1. Base Unit (Schematic Diagram (Base
Unit_Main)) ------------------------------------------- 66
14.1.2. Handset (Schematic Diagram
(Handset_Main))------------------------------------- 66
14.2. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Main)-------------- 67
14.2.1. KX-TGE210 ------------------------------------------- 67
14.2.2. KX-TGE230 ------------------------------------------- 69
14.3. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Operation) ------- 71
14.3.1. KX-TGE230 ------------------------------------------- 71
14.4. Schematic Diagram (Handset_Main) --------------- 73
15 Printed Circuit Board ------------------------------------------ 76
15.1. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main) ---------------------- 76
15.1.1. Component View ------------------------------------ 76
15.1.2. Bottom View ------------------------------------------ 77
15.2. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Operation)---------------- 78
15.2.1. KX-TGE230 ------------------------------------------- 78
15.3. Circuit Board (Handset_Main) ------------------------ 80
15.3.1. Component View ------------------------------------ 80
15.3.2. Bottom View ------------------------------------------ 81
3
Page 4

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
16 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List -----------82
16.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Base Unit) ----------- 82
16.1.1. KX-TGE210 ------------------------------------------- 82
16.1.2. KX-TGE230 ------------------------------------------- 83
16.2. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Handset) ------------- 84
16.3. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Charger Unit) ------- 85
16.4. Accessories and Packing Materials ----------------- 86
16.4.1. KX-TGE210B ----------------------------------------- 86
16.4.2. KX-TGE212B ----------------------------------------- 87
16.4.3. KX-TGE232B ----------------------------------------- 88
16.4.4. KX-TGE233B ----------------------------------------- 89
16.4.5. KX-TGE234B ----------------------------------------- 90
16.5. Replacement Parts List --------------------------------- 91
16.5.1. Base Unit ----------------------------------------------91
16.5.2. Handset ------------------------------------------------ 94
16.5.3. Charger Unit ------------------------------------------95
16.5.4. Accessories and Packing Materials------------- 95
16.5.5. Screws ------------------------------------------------- 96
16.5.6. Fixtures and Tools ----------------------------------- 96
4
Page 5
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Component
Component
pin
Solder
Remove all of the
excess solder
(Slice View)
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. For Service Technicians
• Repair service shall be provided in accordance with repair technology information such as service manual so as to
prevent fires, injury or electric shock, which can be caused by improper repair work.
1. When repair services are provided, neither the products nor their parts or members shall be remodeled.
2. If a lead wire assembly is supplied as a repair part, the lead wire assembly shall be replaced.
3. FASTON terminals shall be plugged straight in and unplugged straight out.
• ICs and LSIs are vulnerable to static electricity.
When repairing, the following precautions will help prevent recurring malfunctions.
1. Cover plastic parts boxes with aluminum foil.
2. Ground the soldering irons.
3. Use a conductive mat on worktable.
4. Do not grasp IC or LSI pins with bare fingers.
2Warning
2.1. Battery Caution
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Dispose of used batteries according to the instructions.
Attention:
A nickel metal hydride battery that is recyclable powers the product you have purchased.
Please call 1-800-8-BATTERY (1-800-822-8837) for information on how to recycle this battery.
2.2. About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)
Note:
In the information below, Pb, the symbol for lead in the periodic table of elements, will refer to standard solder or solder that
contains lead.
We will use PbF solder when discussing the lead free solder used in our manufacturing process which is made from Tin (Sn),
Silver (Ag), and Copper (Cu).
This model, and others like it, manufactured using lead free solder will have PbF stamped on the PCB. For service and repair
work we suggest using the same type of solder.
Caution
• PbF solder has a melting point that is 50 F ~ 70 F (30 C ~ 40 C) higher than Pb solder. Please use a soldering iron with
temperature control and adjust it to 700 F ± 20 F (370 C ± 10 C).
• Exercise care while using higher temperature soldering irons.:
Do not heat the PCB for too long time in order to prevent solder splash or damage to the PCB.
• PbF solder will tend to splash if it is heated much higher than its melting point, approximately 1100 F (600 C).
• When applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side for excess which may flow onto the
opposite side (See the figure below).
5
Page 6
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
0.3 mm X 100 g
0.6 mm X 100 g 1.0 mm X 100 g
2.2.1. Suggested PbF Solder
There are several types of PbF solder available commercially. While this product is manufactured using Tin, Silver, and Copper
(Sn+Ag+Cu), you can also use Tin and Copper (Sn+Cu), or Tin, Zinc, and Bismuth (Sn+Zn+Bi). Please check the
manufacturer's specific instructions for the melting points of their products and any precautions for using their product with other
materials.
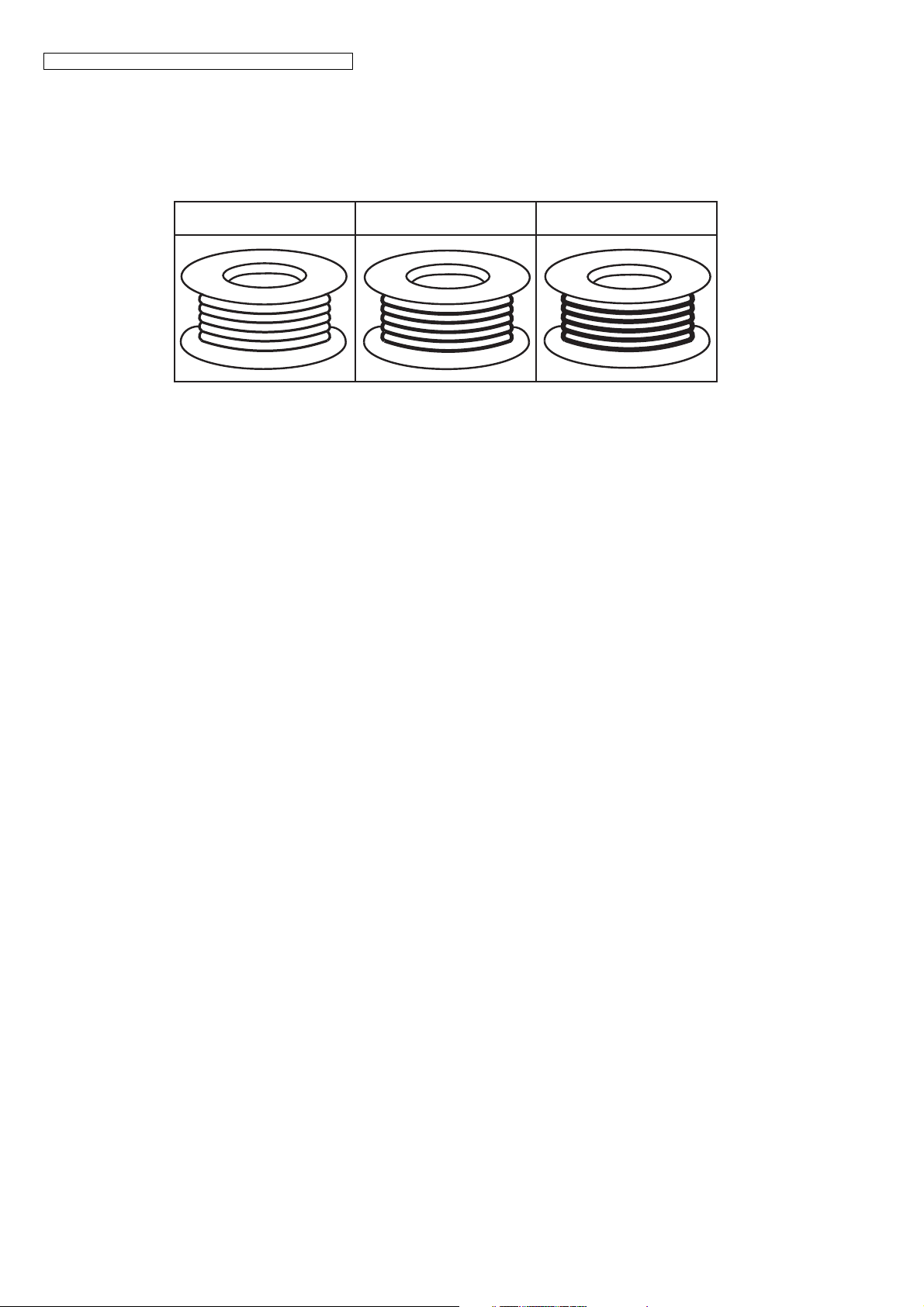
The following lead free (PbF) solder wire sizes are recommended for service of this product: 0.3 mm, 0.6 mm and 1.0 mm.
2.3. Discarding of P. C. Board
When discarding P. C. Board, delete all personal information such as telephone directory and caller list or scrap P. C. Board.
6
Page 7
3 Specifications
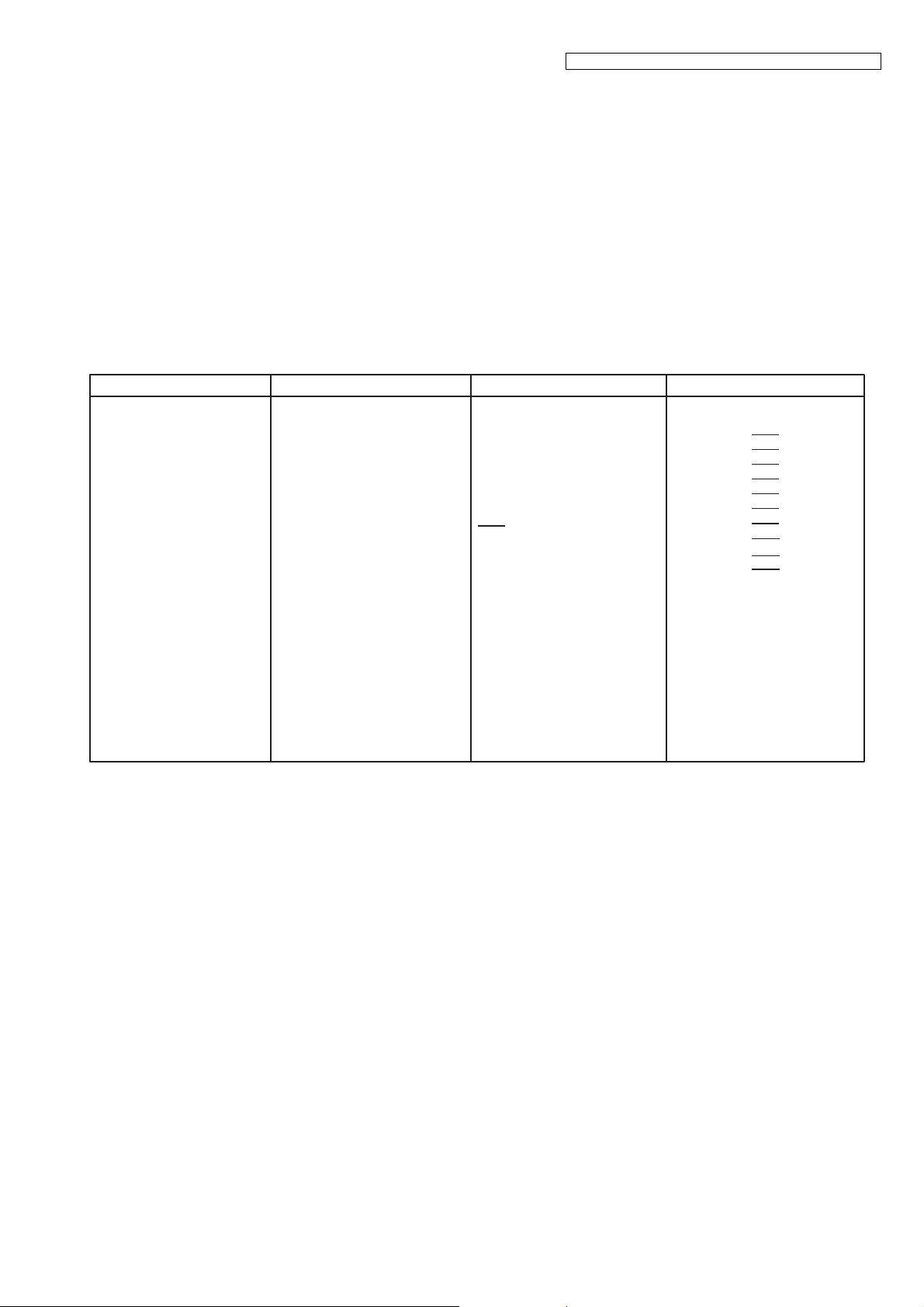
Rechargeable Ni-MH battery
AAA (R03) size (1.2 V 400 mAh)
Super Heterodyne
PLL synthesizer
Quadrature Discriminator
13.824 MHz ±100 Hz
Frequency Modulation
40 bit
Tone (DTMF)/Pulse
Up to 48 digits
Up to 24 digits
(Phonebook)
8 days at Standby,
10 hours at Talk
8 days at Standby,
10 hours at Talk
Approx. 130
0 °C - 40 °C (32 °F – 104 °F)
20 % – 80 % relative air humidity
(dry)
Approx. 54
mm x 31 mm x
171
mm
Approx. 130 g
Power source
Receiving Method
Oscillation Method
Detecting Method
Tolerance of OSC Frequency
Modulation Method
ID Code
Ringer Equivalence No. (REN)
Dialing Mode
Redial
Speed Dialer
Power Consumption
Operating Conditions
Dimensions (W x D x H)
Mass (Weight)
AC Adaptor
(PNLV226Z, 120 V AC, 60 Hz)
Super Heterodyne
PLL synthesizer
Quadrature Discriminator
10.368 MHz ±41 Hz
Frequency Modulation
40 bit
0.1B
Tone (DTMF)/Pulse
Up to 48 digits
Up to 24 digits (Phonebook)
Base Unit*1
Standby: Approx. 1.0 W
Maximum: Approx. 4.3 W
Base Unit*2
Standby: Approx. 1.0 W
Maximum: Approx. 4.3 W
0 °C - 40 °C (32 °F – 104 °F)
20 % – 80 % relative air humidity
(dry)
Approx. 197 mm x 88 mm x 83 mm
Approx. 270 g
Base Unit
Handset
Charger
AC Adaptor
(PNLV233AZ, 120 V AC, 60 Hz)
Standby: Approx 0.1 W
Maximum: Approx 1.8 W
Standby: Approx 0.1 W
Maximum: Approx 1.8 W
0 °C - 40 °C (32 °F – 104 °F)
20 % – 80 % relative air humidity
(dry)
Approx. 72 mm x 72 mm x 38 mm
Approx. 90 g
*1 KX-TGE210 series
*2 KX-TGE230 series
Duplex procedure:
TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
█ Channel spacing:
1.728MHz (DECT 6.0)
█ Bit rate:
1.152Mbit/s (DECT 6.0)
Modulation:
GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying)
RF transmission power:
115 mW (max/DECT6.0)
Voice coding:
ADPCM 32 kbit/s (DECT 6.0)
█
█
█
█
█
█
█ Standard:
DECT 6.0 (Digital Enhanced Cordless
Telecommunications 6.0)
█ Number of channels:
60 Duplex Channels (DECT 6.0)
█ Frequency range:
1.92 GHz to 1.93 GHz (DECT 6.0)
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Note:
Design and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Note for Service:
• Operation range: Up to 300 m outdoors, Up to 50 m indoors, depending on the condition.
• Analog telephone connection: Telephone Line
• Optional headset: KX-TCA60, KX-TCA93, KX-TCA400, KX-TCA430
• Optional Range extender: KX-TGA405
• Optional Key detector: KX-TGA20
• T-adaptor: KX-J66
7
Page 8
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4 Technical Descriptions
4.1. US-DECT Description
The frequency range of 1.92 GHz-1.93 GHz is used. Transmitting and receiving carrier between base unit and handset is same
frequency. Refer to Frequency Table (P.59).
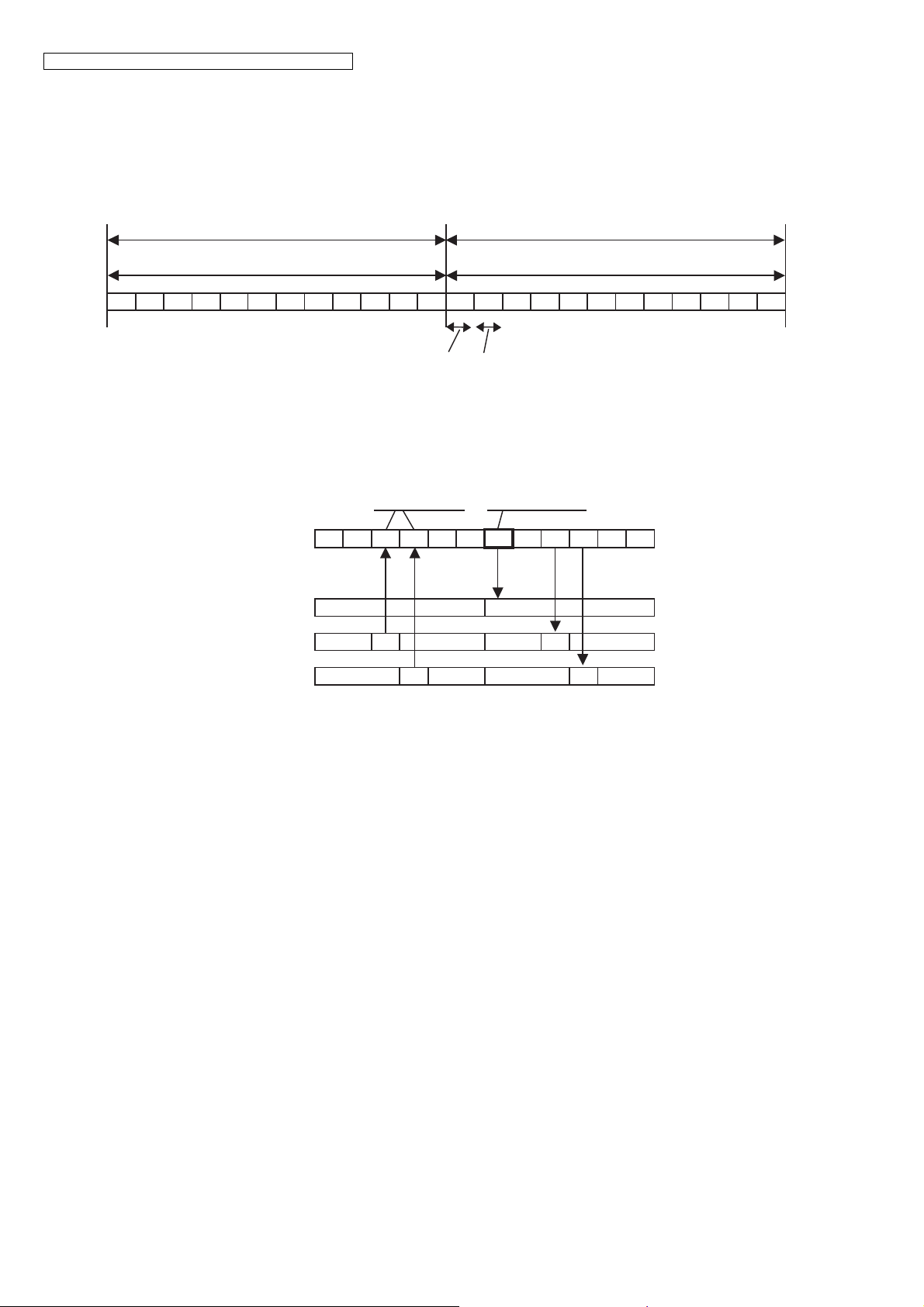
4.1.1. TDD Frame Format
5 ms 5 ms
Up Link ( Handset -> Base Unit ) Down Link ( Base Unit -> Handset )
RX1 RX2 RX3 RX4 RX5 RX6 TX1 TX2 TX3 TX4 TX5 TX6
DATA rate : 1.152 Mbps
417 μs (available) 417 μs (blind)
4.1.2. TDMA system
This system is the cycles of 10 ms, and has 6 duplex paths, but maximum duplex communication path is 5 because of dummy
bearer use.
In 1 slot 417 s, the 10 ms of voice data is transmitted.
• 2 - Handsets Link
Traffic Bearer Dummy bearer
Base unit
Handset 1
(Stand by)
Handset 2
(Link)
Handset 3
(Link)
Traffic Bearer
A link is established between base unit and handset.
The state where duplex communication is performed.
Handset doesn't make up duplex in no free RF channels because of interference. (*1)
Dummy Bearer
Base unit sends Dummy-data to the all stand-by state handsets.
Handsets receive that data for synchronization and monitoring request from the base unit.
Base unit doesn't send Dummy bearer in no free RF channels because of interference. (*1)
Note:
(*1) It is a feature under FCC 15 regulation and for interference avoidance.
In the case of checking RF parts, it is better in least interference condition.
RX1 RX2 RX3 RX4 RX5 RX6 TX1 TX2 TX3 TX4 TX5 TX6
TX RX
RXTX
8
Page 9

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.1.3. Signal Flowchart in the Radio Parts
Reception
Base unit:
A voice signal from TEL line is encoded to digital data and converted into a 1.9GHz modulated radio signal by BBIC(IC501).
The RF signal, after which is amplified in BBIC, is fed to selected antenna.
Handset:
As for a handset RF, RF signal is received in one antenna.
BBIC down-converts to 864 kHz IF signal from RX signal and demodulates it to digital data "RXDATA".
BBIC (IC1) converts RXDATA into a voice signal and outputs it to speaker.
Transmission
Handset:
A voice signal from microphone is encoded to digital data and converted into a 1.9GHz modulated radio signal by BBIC(IC1).
The RF signal, after which is amplified in BBIC, is fed to an antenna.
Base unit:
As for a base unit RF, RF signal is received in two antennas.
BBIC (IC501) compares RF signal levels and selects the antenna to be used. Then BBIC down-converts to 864 kHz IF signal
from RX signal in the selected antenna, and demodulates it to digital data "RXDATA".
BBIC (IC501) converts RXDATA into a voice signal and outputs it to TEL line.
9
Page 10
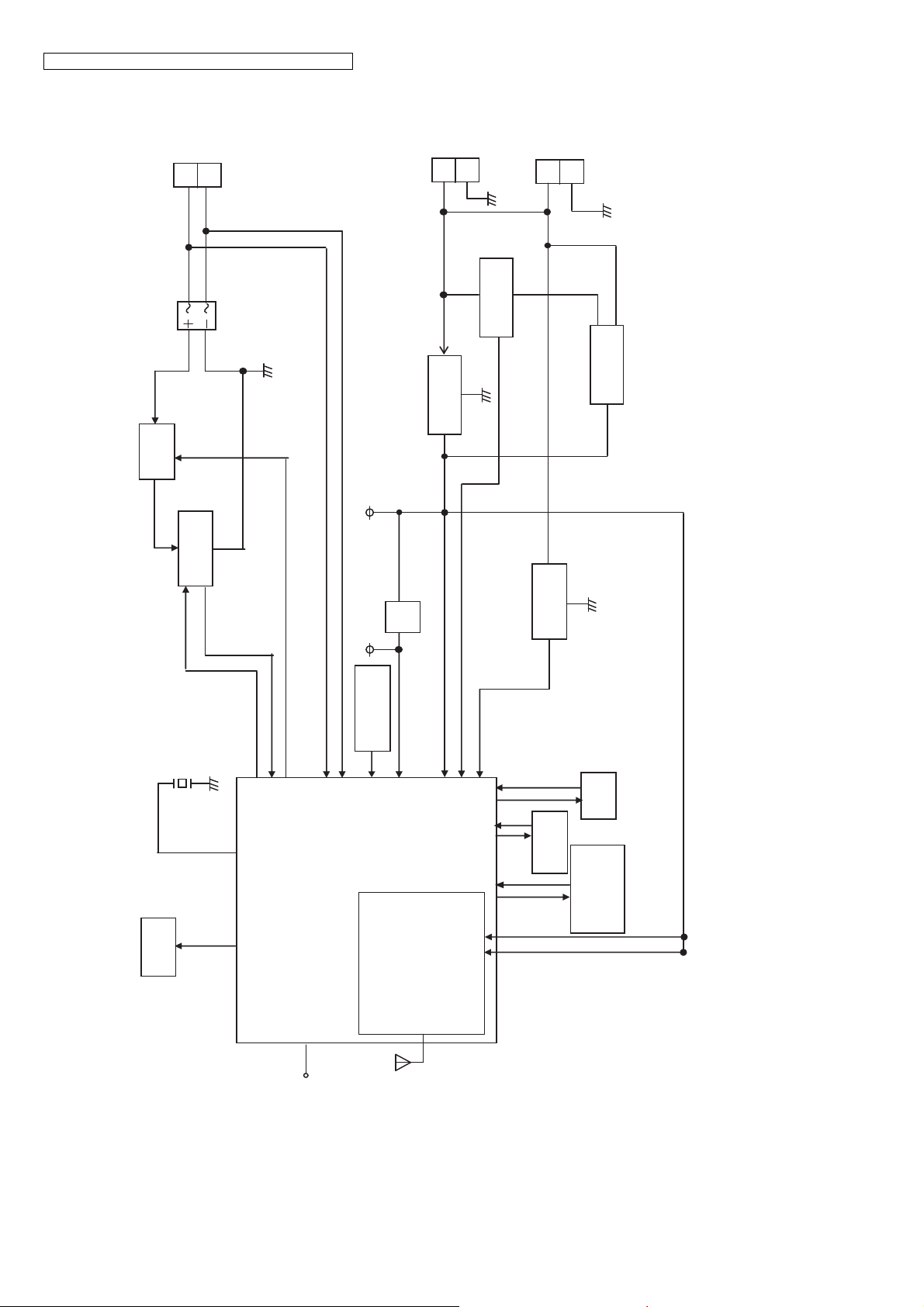
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
KX-TGE210/212/232/233/234 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Base Unit_Main)
SIDE_TONE
CIRCUIT
Crystal
10.368MHz
TR_RLY
TIP
RING
RF_Block
IC501
BBIC
DC5.5V+
GND
DC_JACK
+
-
CHARGE
3
4
2
D101
CHARGE
DETECT
Q701
REGULATOR
IC302
Power Down
DET
Power supply
at AC failure
KEY
PAD
LED
VBAT
PDN_DET
CHARGE_DET
IC611
Q301
+1.8V
+3.0V
AVD/VDD
QSPI
CIDINp
CIDINn
P3_6
MICh
LSRp
RF_VDD
VDD_PA
ANT1
IC502
Flash(Program)
IC601
Flash
(Voice prompt)
EEPROM
4.2. Block Diagram (Base Unit_Main)
10
Page 11

4.3. Tel Interface Circuit
TX AMP
SIDE TONE
RX AMP
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
CALLER ID
DETECT
BELL
DETECT
P101
R142
4
C101
Q141
C102
SA101
TIP
R141
REGULATOR
C104
R102
C106
R104
C103
R101
C105
R103
D101
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
11
Page 12
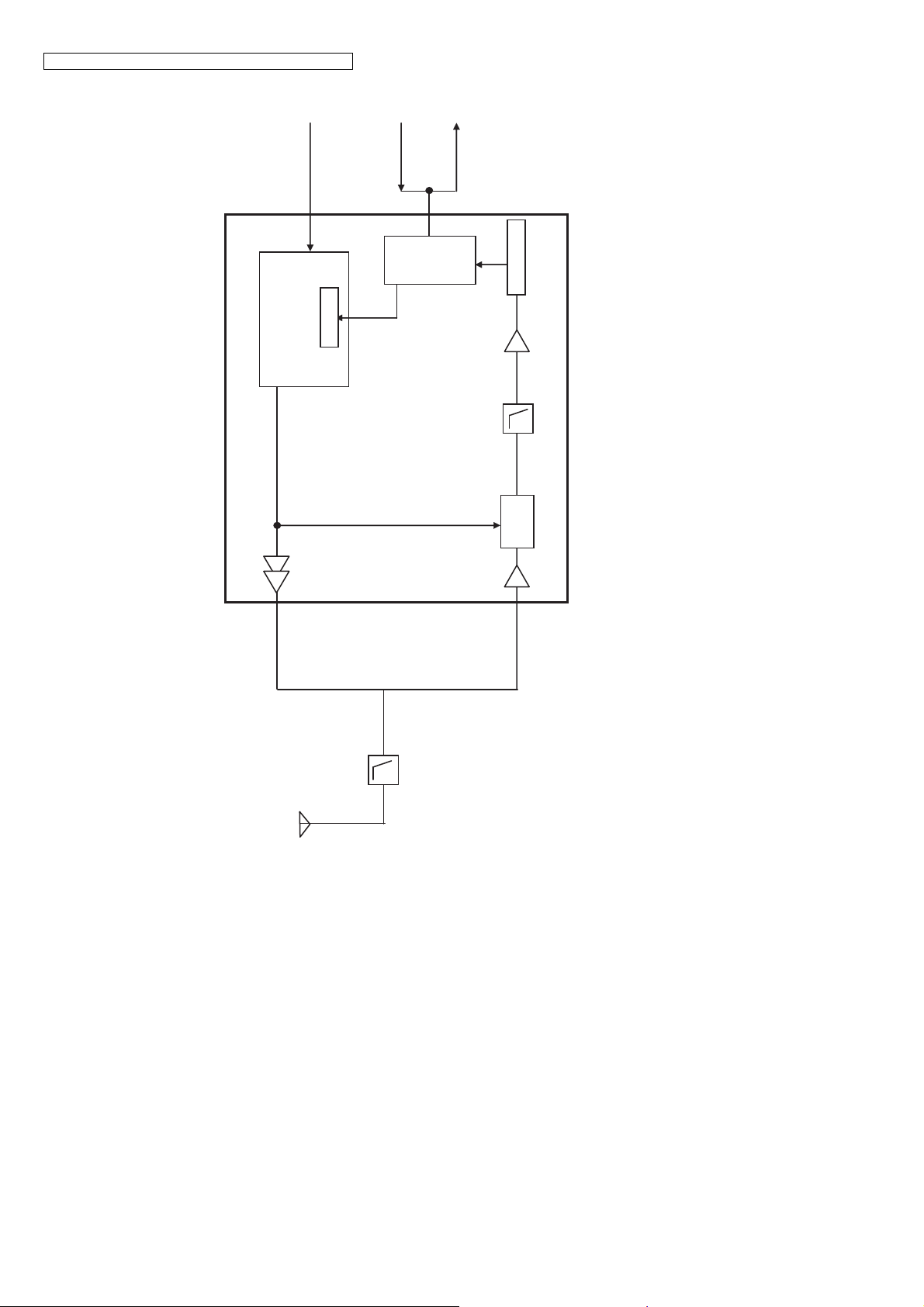
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
10.368
MHz
IC501 RF block
TXDATA
RF_TXp
RF_TXn
RF_RXp
RF_RXn
Control
Logic
RXDATA
Mixer
Demodulator
PLL
3856-3843MHz
/3859-3845MHz
Modulator
KX-TGE210/212/232/233/234 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Base Unit_RF Part)
4.4. Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part)
12
Page 13
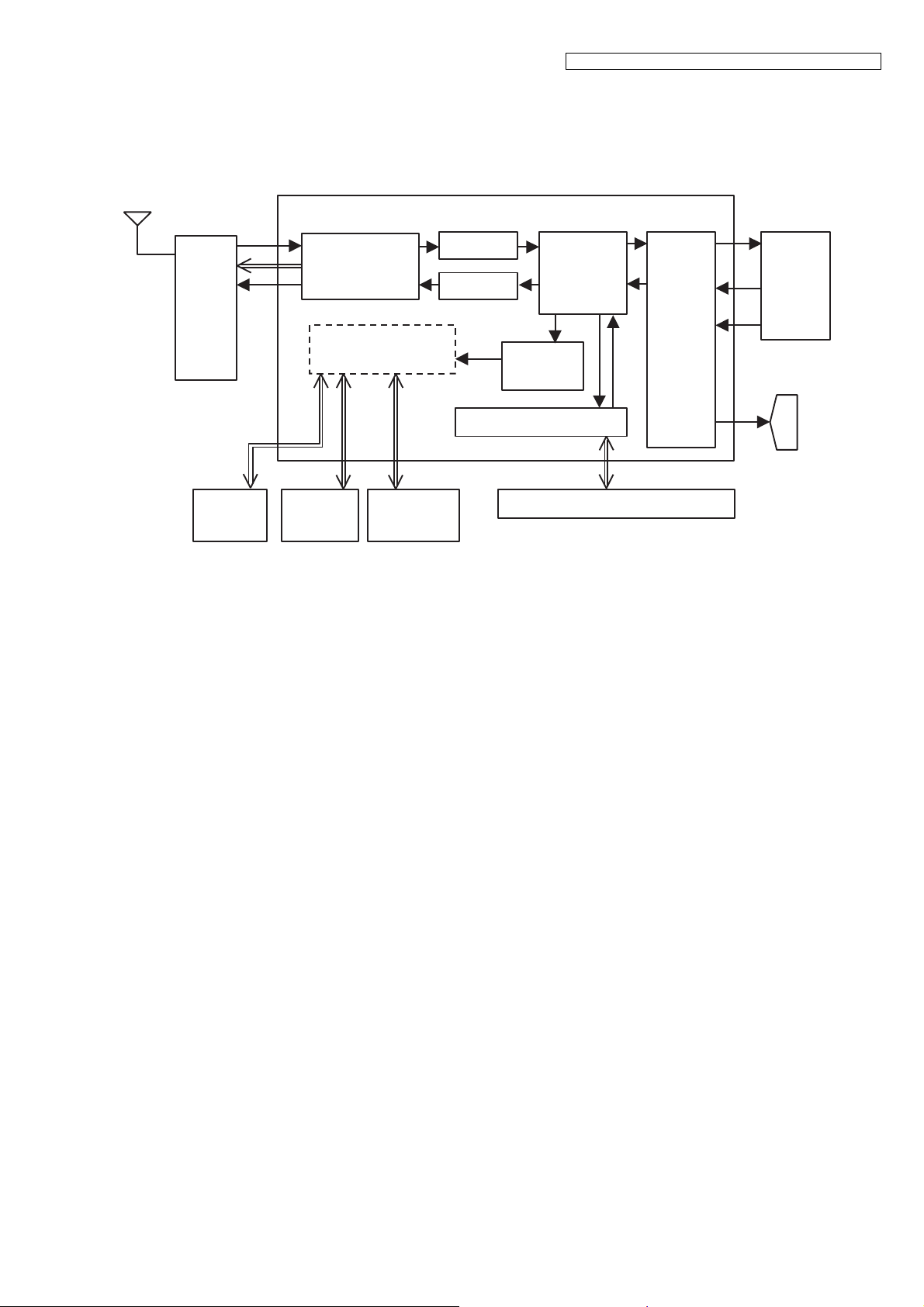
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.5. Circuit Operation (Base Unit)
General Description:
(BBIC, Flash Memory, EERROM) is a digital speech/signal processing system that implements all the functions of speech
compression, record and playback, and memory management required in a digital telephone answering machine.
The BBIC system is fully controlled by a host processor. The host processor provides activation and control of all that functions
as follows.
ADPCM
ADPCM
Caller ID
Modem
Digital TAM System
Flash Memory IC601
Digital
Speech
Processor
Analog
Front
End
&
Multiplexer
TEL
Line
Interface
SP
RF part
EEPROM
IC611
TDD & TDMA
with FHSS
Processor
Keys/ LEDs
/ Charge
Host CPU
BBIC (IC501)
Flash Memory
(Program)
IC502
4.5.1. BBIC (Base Band IC: IC501)
• Voice Message Recording/Play back
The BBIC system uses a proprietary speech compression technique to record and store voice message in Flash Memory.
An error correction algorithm is used to enable playback of these messages from the Flash Memory.
• DTMF Generator
When the DTMF data from the handset is received, the DTMF signal is output.
• Synthesized Voice (Pre-recorded message)
The BBIC implements synthesized Voice, utilizing the built in speech detector and a Flash Memory, which stored the vocabulary.
• Caller ID demodulation
The BBIC implements monitor and demodulate the FSK/DTMF signals that provide CID information from the Central Office.
• Digital Switching
The voice signal from telephone line is transmitted to the handset or the voice signal from the handset is transmitted to the
Telephone line, etc. They are determined by the signal path route operation of voice signal.
• Block Interface Circuit
RF part, LED, Key scan, Speaker, Telephone line.
4.5.2. Flash Memory (IC502)
Main program data is stored.
4.5.3. Flash Memory (IC601)
Following information data is stored.
• Voice signal
ex: Pre-recorded Greeting message, Incoming message
4.5.4. EEPROM (IC611)
Following information data is stored.
• Settings
ex: message numbers, ID code, Flash Time, Tone/Pulse
13
Page 14
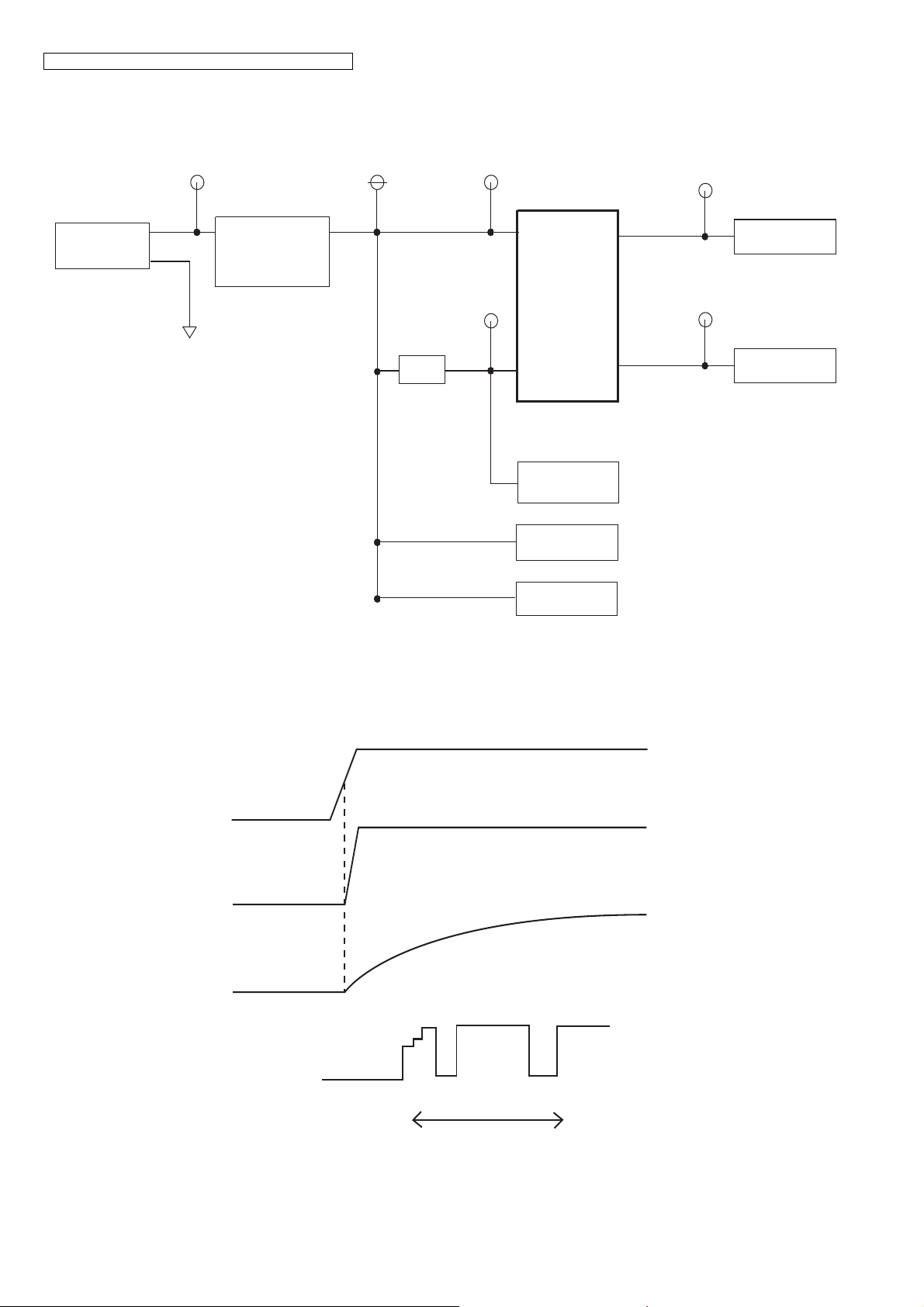
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
+5.5V
+5.5V +3.0V
+3.0V
+1.8V
+3.0V_CP
IC501
IC302
IC611
BBIC
AC Adaptor
3.0V
REGULATOR
EEPROM
VDD3
VDD1
VDD4
+3.0V_CP2
IC601
TAM FLASH
VDD5
RF Part
LEDs
Q301
QSPI FLASH
IC502
Startmonitor
(IC501 57pin)
VDD1 (1.8 V)
VBAT
Reset (RSTN)
(IC501_77pin)
BBIC chip initialize
(CKM/STM)
4.5.5. Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit
The power supply voltage from AC adaptor is converted to VBAT (3.0V) in IC302. And +3.0V for peripherals and analog part is
insulated from VBAT by Doubler of BBIC.
Circuit Operation:
14
Page 15
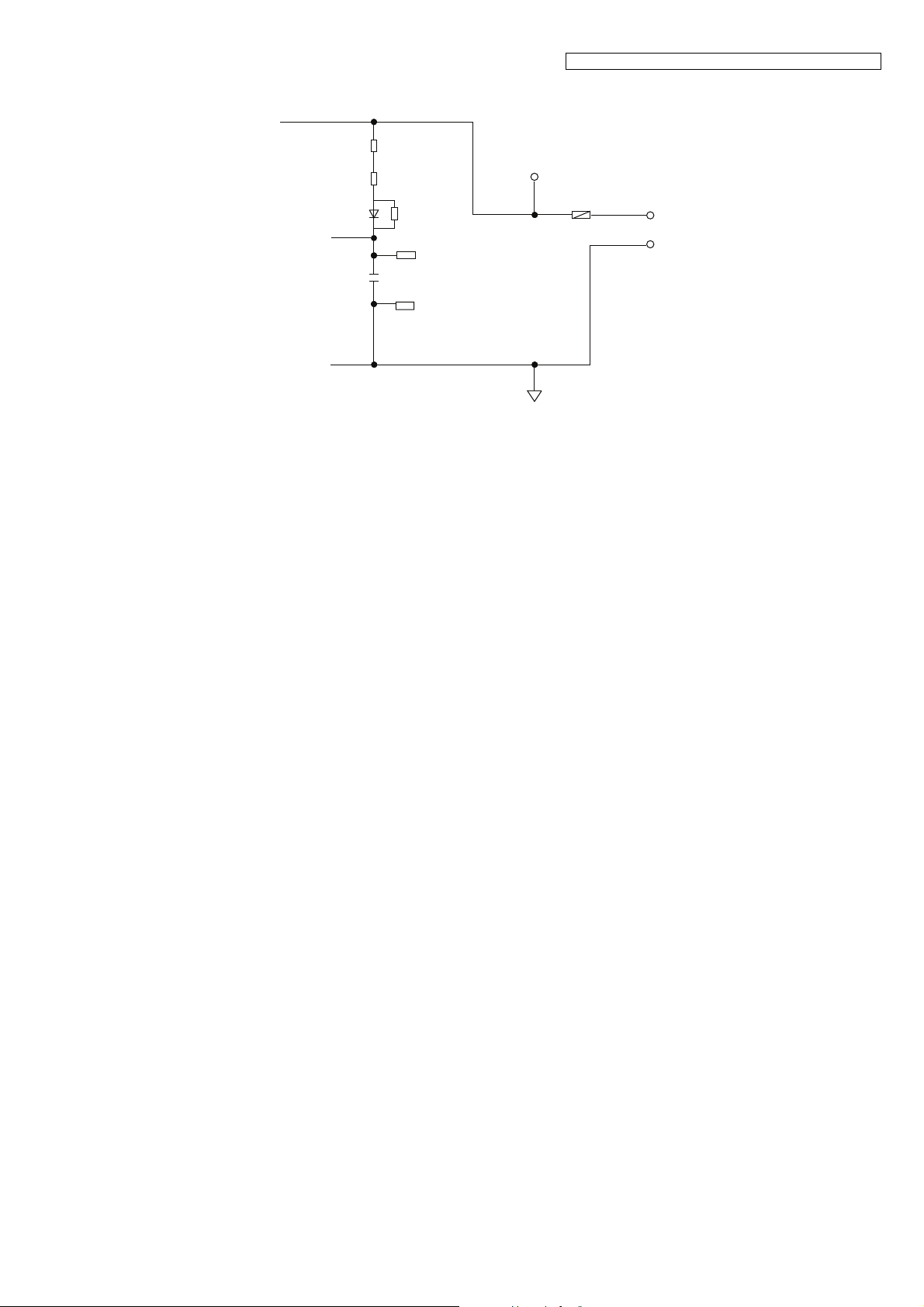
4.5.5.1. Charge Circuit
R372
D362
R371
CHARGE+
R373
C351
F301
DCP
CHARGE-
+5.5V
DCM
K A
The voltage from the AC adaptor is supplied to the charge circuits.
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
15
Page 16
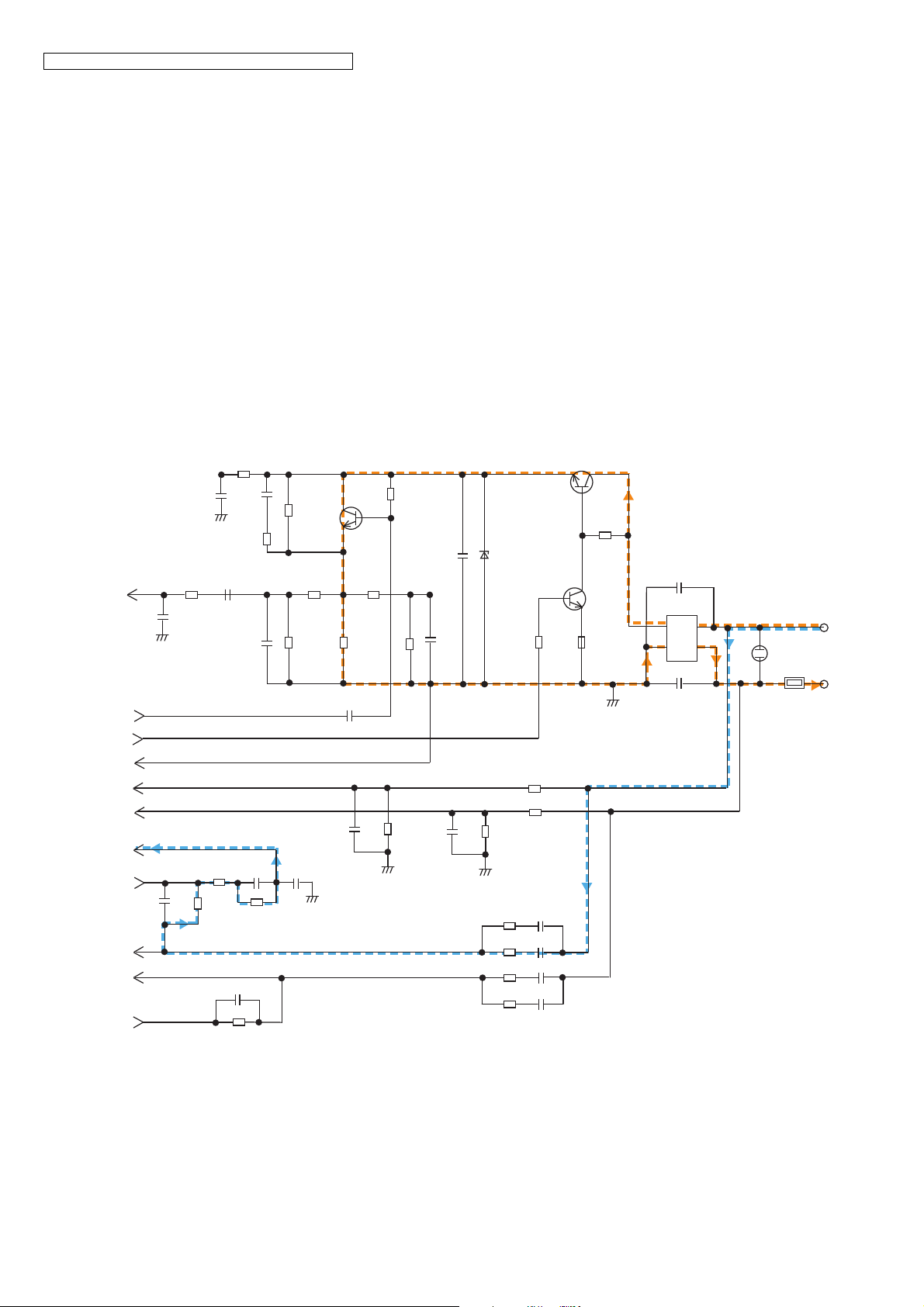
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
OFF Hook
BELL signal detection
C174
C171
R166
R178
RX
Pin25 of IC501
TX
Pin27 of IC501
R160
+
C161
C167
R165
R162
C173
R151R164
C184
C103
C111
Q161
E
B
C
R163
R117
C115
R109
C109
Q141
Q142
C101
P101
L1T
L1R
D101
C102
1
2
3
+
~~
_
4
R145
C142
C152
R152
A
K
D142
R141
B
E
C
E
B
C
R142
SA101
R111
R101
HOOK
Pin19 of IC501
CIDOUT
Pin24 of IC501
LSRn
Pin28 of IC501
RINGING
Pin18 of IC501
CIDINn
Pin23 of IC501
CIDINp
Pin21 of IC501
R168
PARADET
Pin17 of IC501
ADC1
Pin33 of IC501
ADC0
Pin32 of IC501
R118
C116
R115
R116
R110
C110
R112
C113
C105
R103
C104
R102
C106
R104
4.5.6. Telephone Line Interface
Telephone Line Interface Circuit:
Function
• Bell signal detection
• ON/OFF hook and pulse dial circuit
• Side tone circuit
Bell (RINGING) signal detection and OFF HOOK circuit:
In the idle mode, Q141 is open to cut the DC loop current and decrease the ring load. When ring voltage appears at the Tip (T)
and Ring (R) leads (When the telephone rings), the AC ring voltage is transferred as follows:
L1T C105 R103 R110 R11 1 R112 BBIC pin18(RINGING)
When the CPU (BBIC) detects a ring signal, Q141 turns on, thus providing an off-hook condition (active DC current flow through
the circuit). Following signal flow is the DC current flow.
T D101 Q141 Q161 R163 D101 P101 R
ON HOOK Circuit:
Q141 is open, Q141 is connected as to cut the DC loop current and to cut the voice signal. The unit is consequently in an onhook condition.
Pulse Dial Circuit:
Pin 19 of BBIC turns Q141 ON/OFF to make the pulse dialing.
Side Tone Circuit:
Basically this circuit prevents the TX signal from feeding back to RX signal. As for this unit, TX signal feed back from Q161 is
canceled by the canceller circuit of BBIC.
16
Page 17
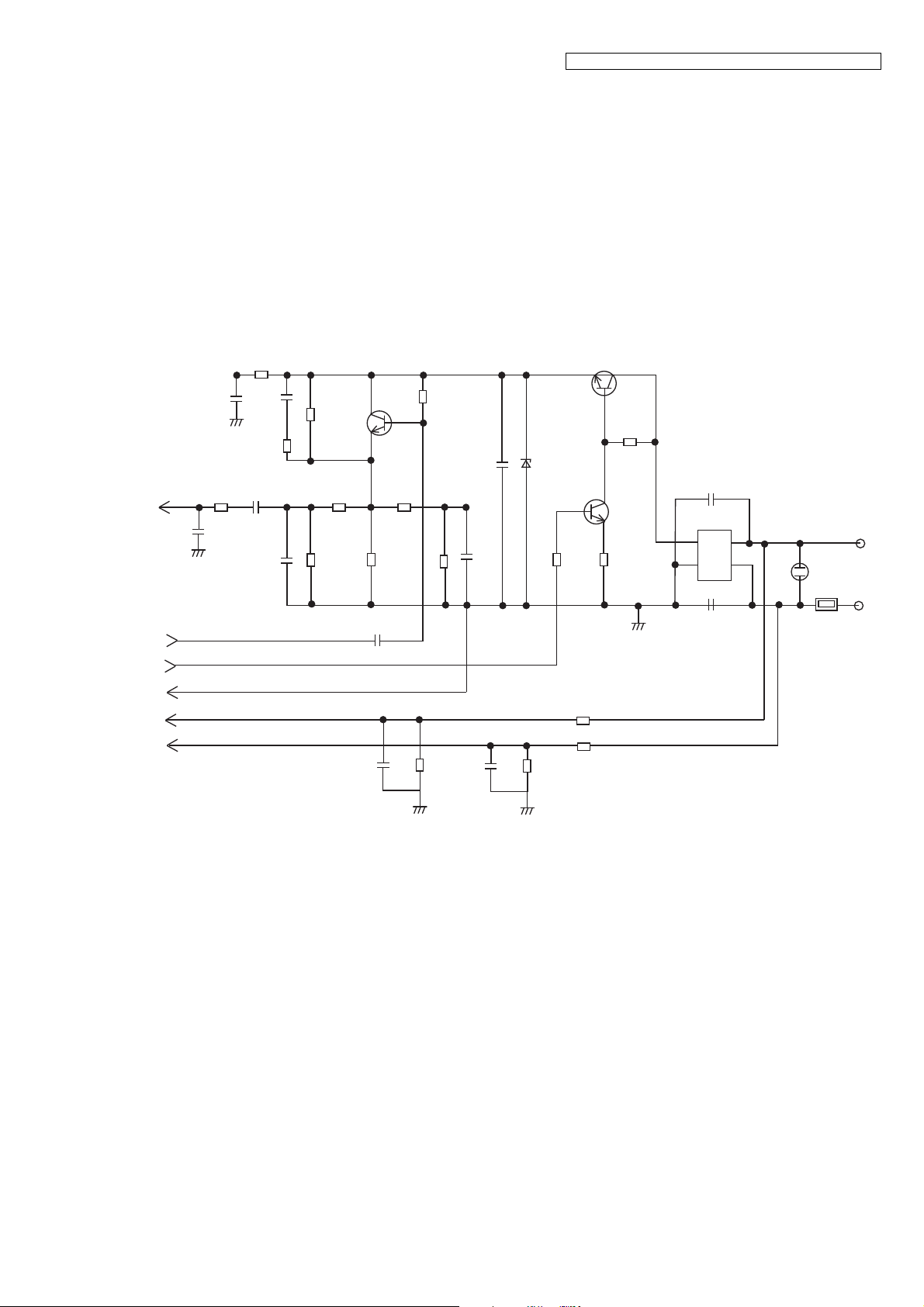
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
C174
C171
R166
R178
RX
Pin25 of IC501
TX
Pin27 of IC501
R160
+
C161
C167
R165
R162
C173
R151R164
C184
Q161
E
B
C
R163
R117
C115
Q141
Q142
C101
P101
L1T
L1R
D101
C102
1
2
3
+
~~
_
4
R145
C142
C152
R152
A
K
D142
R141
B
E
C
E
B
C
R142
SA101
HOOK
Pin19 of IC501
R168
PARADET
Pin17 of IC501
ADC1
Pin33 of IC501
ADC0
Pin32 of IC501
R118
C116
R115
R116
4.5.7. Parallel Connection Detect Circuit/Auto Disconnect Circuit
Function:
In order to disable call waiting and stutter tone functions when using telephones connected in parallel, it is necessary to have a
circuit that judges whether a telephone connected in parallel is in use or not. This circuit determines whether the telephone
connected in parallel is on hook or off hook by detecting changes in the T/R voltage.
Circuit Operation:
Parallel connection detection when on hook:
When on hook, the voltage is monitored at pin 32 of IC501. There is no parallel connection if the voltage is
0.54 V or higher, while a parallel connection is deemed to exist if the voltage is lower.
Parallel connection detection when off hook:
When off hook, the voltage is monitored at pin 17 of IC501; the presence/absence of a parallel connection is determined by
detecting the voltage changes.
If the Auto disconnect function is ON and statuses are Hold, receiving ICM, OGM transmitting, BBIC disconnects the line after
detecting parallel connection is off hook.
17
Page 18
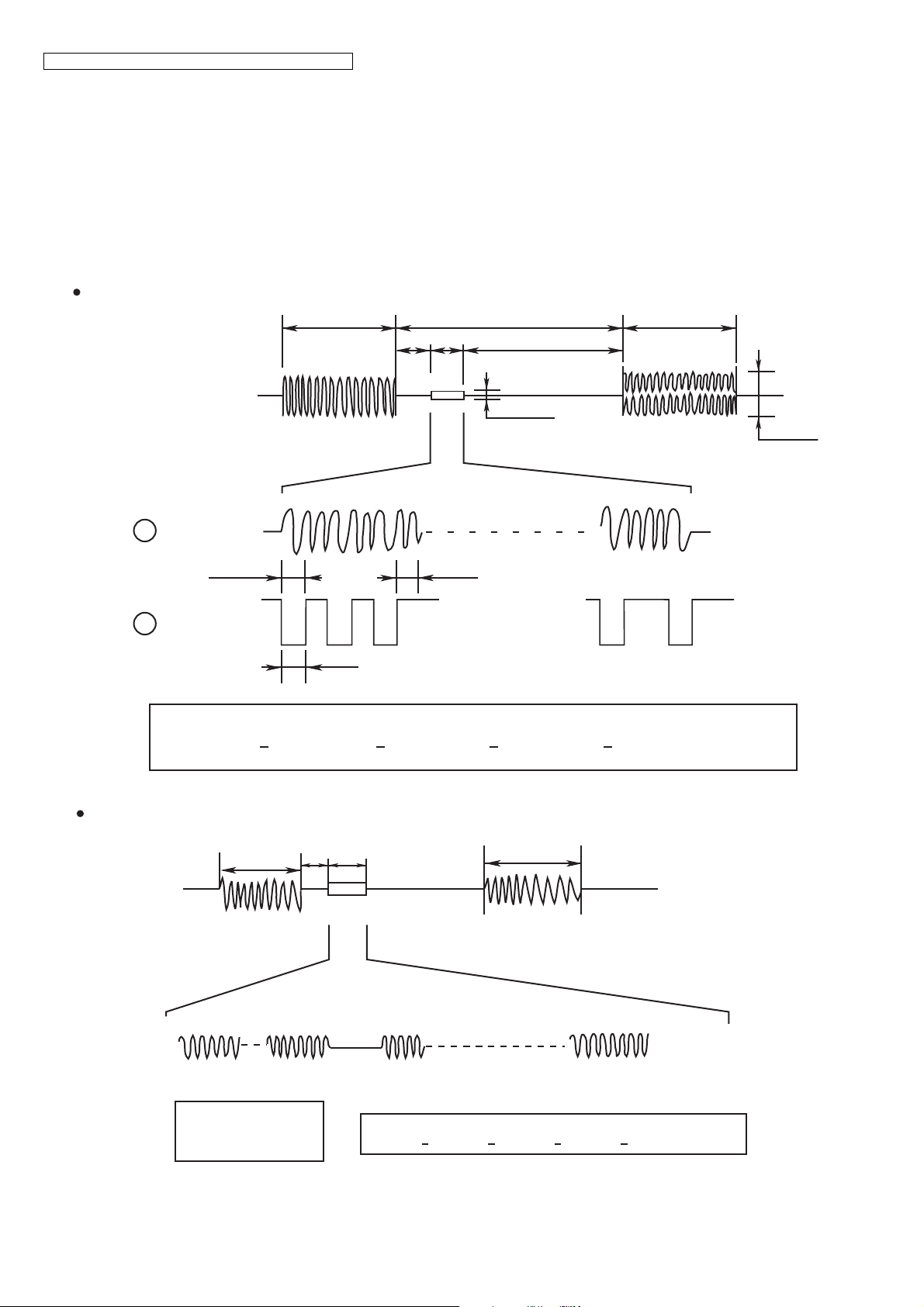
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
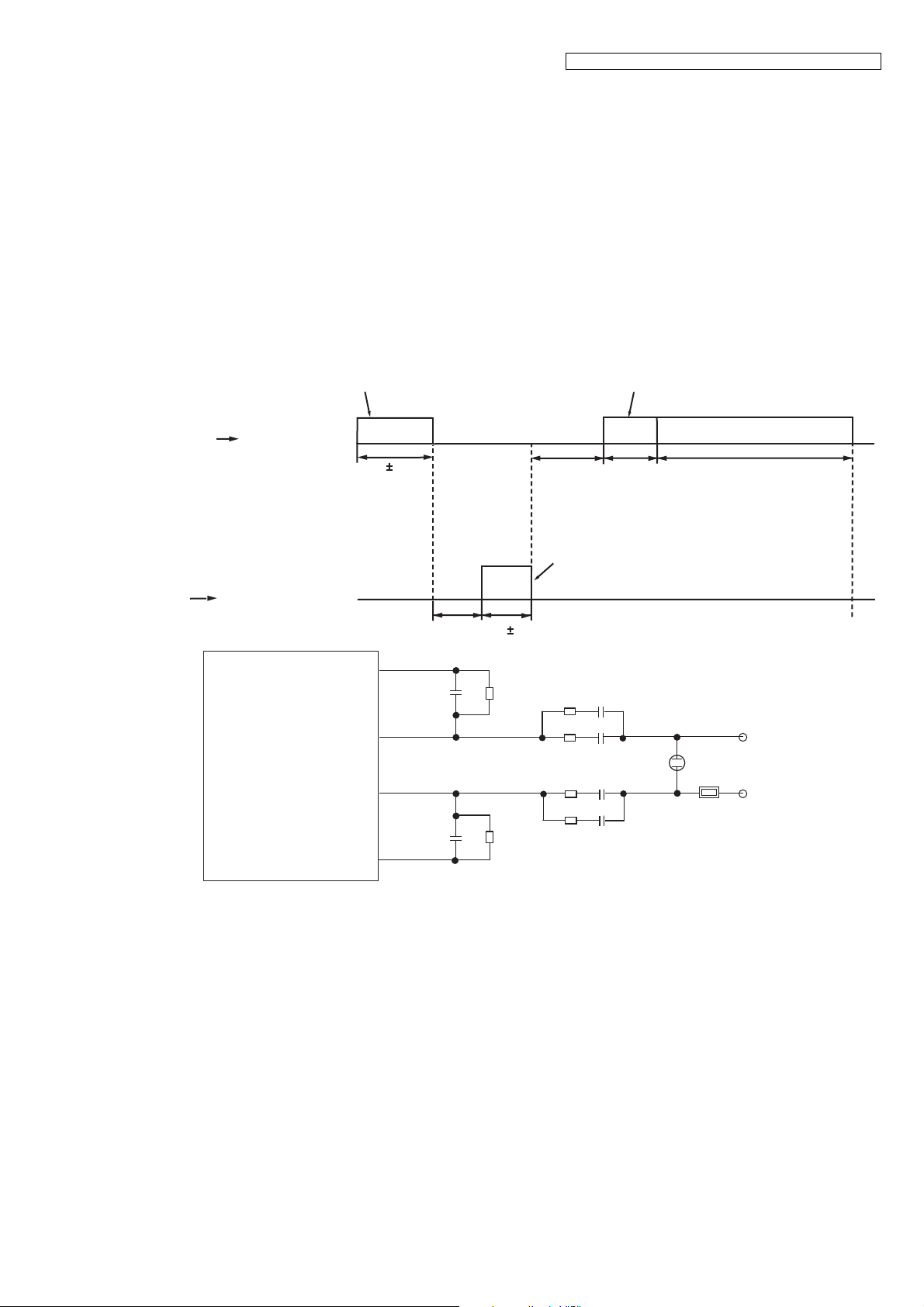
4.5.8. Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)/Call Waiting Caller ID
Function:
Caller ID
The caller ID is a chargeable ID which the user of a telephone circuit obtains by entering a contract with the telephone company
to utilize a caller ID service. For this reason, the operation of this circuit assumes that a caller ID service contract has been
entered for the circuit being used. The data for the caller ID from the telephone exchange is sent during the interval between the
first and second rings of the bell signal. The data from the telephone exchange is a modem signal which is modulated in an FSK
(Frequency Shift Keying) * format. Data
the message format which can be received: i.e. the single message format and plural message format. The plural message
format allows to transmit the name and data code information in addition to the time and telephone number data.
*: Also the telephone exchange service provides other formats.
Single message format
"1" is a 1200 Hz sine wave, and data "0" is a 2200 Hz sine wave. There are two types of
1st Ring
2 sec
0.5 s 575 ms
Silent interval 4 sec
min 0.5 s
2nd Ring
2 sec
STD Ring / 20 Hz
Tip-Ring
DATA in
A
1200 Hz
=DATA "1"
DATA out
B
month day hour minute number
Plural message format
DATA
0.1 Vrms
70 Vrms
2200 Hz
=DATA "0 "
1 bit=833 µs
201348700035161504
1st Ring
2 sec
0.5 s
DATA CODE NAME
201 John Smith
718 ms
DATA
month
04
18
day
2nd Ring
hour
16
minute
number
20134870003516
Page 19
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
CAS
CAS: CPE Alerting Signal
Dual Tone of 2130 Hz, 2750 Hz
-15 dBm (900 ohm load)
80 5 ms
MARK
DATA
0~500 ms
58~75 ms about 300 ms
(be changed by
Information Volume)
Continuance Signal
of 1200 Hz (Data "1")
"FSK"
ACK: Acknowledged Signal
DTMF
"D"
ACK
0~100 ms
60 5 ms
Telephone Exchange
Cordless phone
Cordless phone
Signal Flow
Signal Flow
Telephone Exchange
Call Waiting Format
Call Waiting Caller ID
Calling Identity Delivery on Call Waiting (CIDCW) is a CLASS service that allows a customer, while off-hook on an existing call,
to receive information about a calling party on a waited call. The transmission of the calling information takes place almost
immediately after the customer is alerted to the new call so he/she can use this information to decide whether to take the new
call.
Function:
The telephone exchange transmits or receives CAS and ACK signals through each voice RX/TX route. Then FSK data and
MARK data pass the following route.
Telephone Line P101 C105, C104 R103, R104 RA101 IC501(23, 21).
If the unit deems that a telephone connected in parallel is in use, ACK is not returned even if CAS is received, and the
information for the second and subsequent callers is not displayed on the portable handset display.
IC501
CIDOUT
Pin 24
CIDINn
Pin 23
CIDINp
Pin 21
LSRn
Pin 28
C110
C109
R110
R109
R101
R103
R102
R104
C103
C105
C104
C106
SA101
P101
L1T
L1R
19
Page 20
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
IC1
IC3
MIP
MIN
HSSPOUTP
LOUT
HSMIP
HEADSET_DET
SPOUTP
SPOUTN
CKM//STM
CKM/STM
BBIC
RESET
CHG_CTL
BATTERY_ON
CHG_DET
WP, CLK, DATA
KEYSTOROBE_A~E
KEYIN_1~5
CHARGE
MIC
Receiver
Headset Jack
CN4
Monitor SP
LCD
CHARGE
PUMP
IC4
KEYS
RF part
ANT1
X1
13.824 MHz
EEPROM
3V
BATTERY
LED
(LCD)
RSTN
VBAT
VBAT
3V
4.0V
VBAT
RXn
RXp
TXp
TXn
KX-TGEA20 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Handset)
KEY_LED
CP_OFF
Q6
LED
(KEY)
4V
CHARGE
CONTROL
POWER SUPPLY
CONTROL
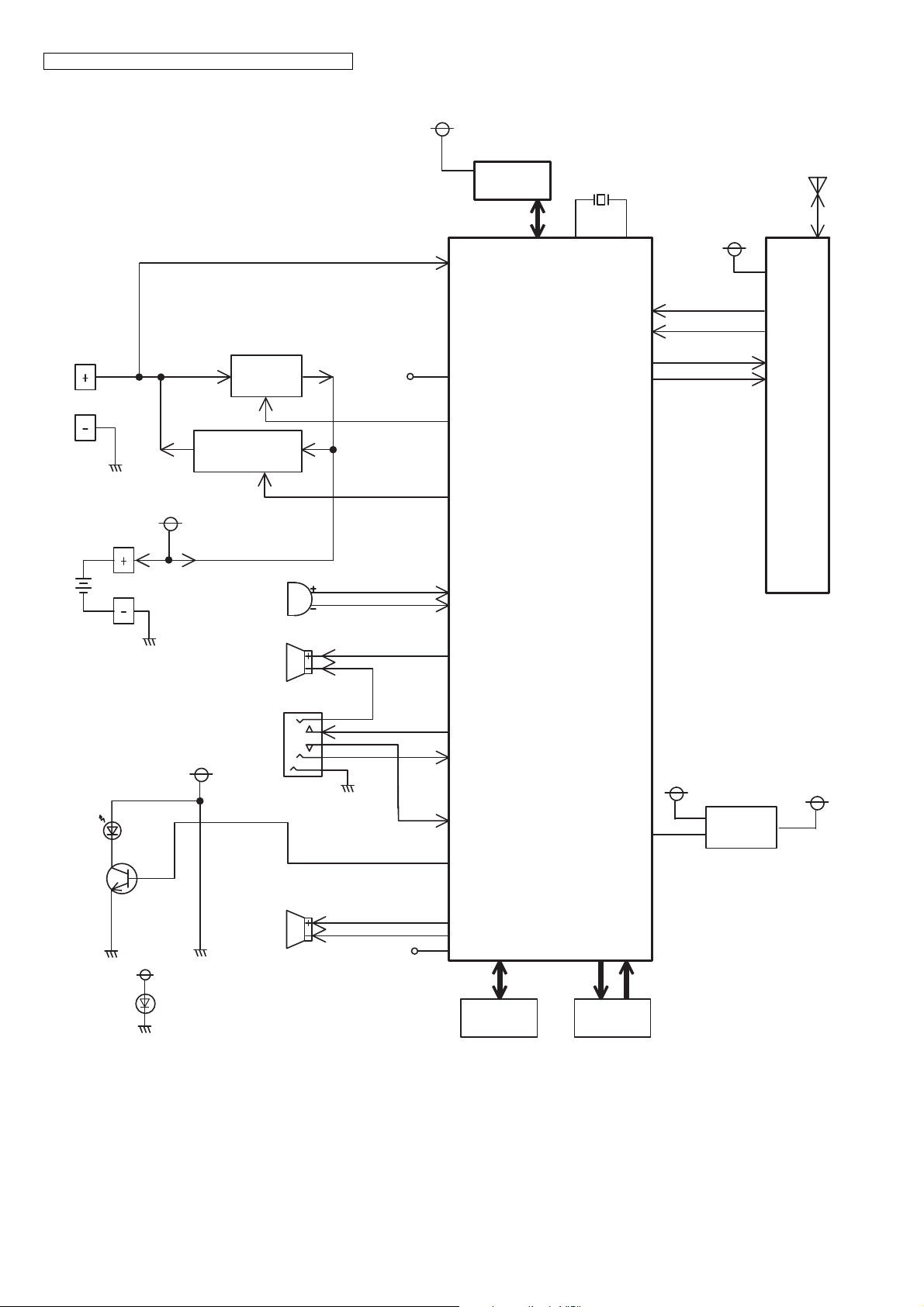
4.6. Block Diagram (Handset)
20
Page 21

4.7. Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)
ANT
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
TXp
TXn
RXp
RXn
KX-TGEA20 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Handset_RF Part)
21
Page 22

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.8. Circuit Operation (Handset)
4.8.1. Outline
Handset consists of the following ICs as shown in Block Diagram (Handset) (P.20).
• DECT BBIC (Base Band IC): IC1
- All data signals (forming/analyzing ACK or CMD signal)
- All interfaces (ex: Key, Detector Circuit, Charge, EEPROM, LCD)
• EEPROM: IC3
- Setting data is stored. (e.g. ID, user setting)
4.8.2. Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit
Circuit Operation:
When powering on the Handset, the voltage is as follows;
BATTERY(2.2 V ~ 2.6 V: BATT+) F1 BBC1 (IC1) 10 pin
The Reset signal generates IC1 (54 pin) and 1.8 V.
VBAT
VDDC (1.2 V)
GND
VBAT
External Charge Pump
Circuit or IC
Reset (RSTN)
(IC1_54 pin)
Start monitor
(IC1 57pin)
(CKM/STM)
BATTERY
2CELL
VDDC (1.2V)
VBAT
4.0V
BBIC
BBIC chip initialize
3.0V
3.0V
DOUBLER OUT (Charge Pump)
For all peripherals
3.0V3.0V
EEPROM
3.0V3.0V
LCD
4.0 output
LCD BACKLIT LED
3.0V
KEY LED
GND
22
Page 23
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
CHG +
Q4
R45
R4
47K
R6
10K
Q9
GND
R7 CHG DET (34)
CHG CTRL (32)
100K
CHG -
GND
BATT +
BATTERY
2CELL
BATT -
GND
BBIC
IC1
Q2
R8
Q3
C27
R2
R9
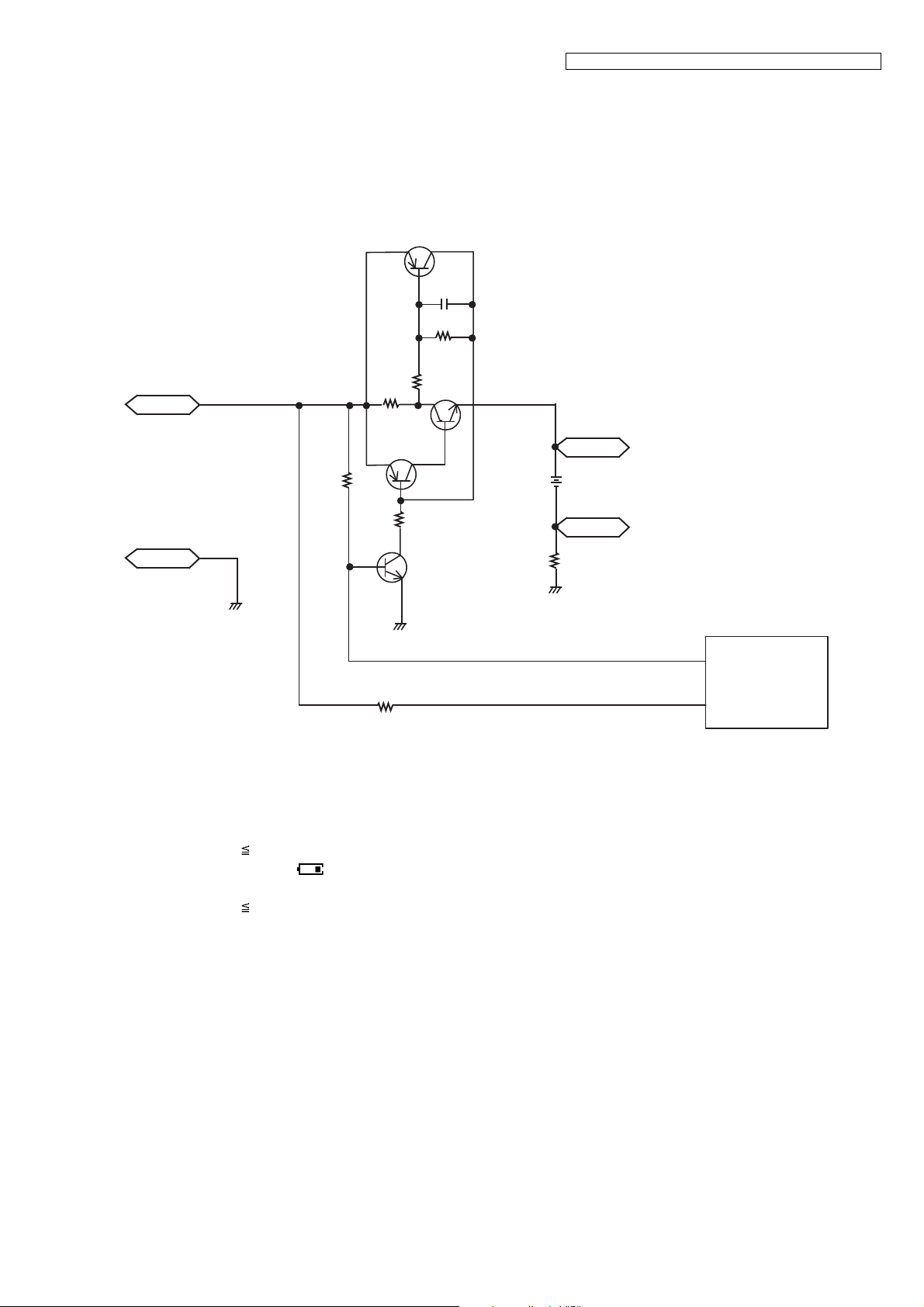
4.8.3. Charge Circuit
Circuit Operation:
When charging the handset on the Base Unit, the charge current is as follows;
DCP(5.5V) F301 R371 R372 D362 CHARGE+(Base) CHARGE+(Handset) R8 Q3 F1 BATTERY+...
Battery...
BATTERY- R45 GND CHARGE-(Handset) CHARGE-(Base) GND DC-(GND)
In this way, the BBIC on Handset detects the fact that the battery is charged.
The charge current is controlled by switching Q9 of Handset.
Refer to Fig.101 in Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.14).
4.8.4. Battery Low/Power Down Detector
Circuit Operation:
“Battery Low” and “Power Down” are detected by BBIC which check the voltage from battery.
The detected voltage is as follows;
• Battery Low
Battery voltage: V(Batt) 2.35 V ± 50 mV
The BBIC detects this level and " " starts flashing.
• Power Down
Battery voltage: V(Batt) 2.1 V ± 50 mV
The BBIC detects this level and power down.
4.8.5. Speakerphone
The hands-free loudspeaker at SP+ and SP- is used to generate the ring alarm.
23
Page 24
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
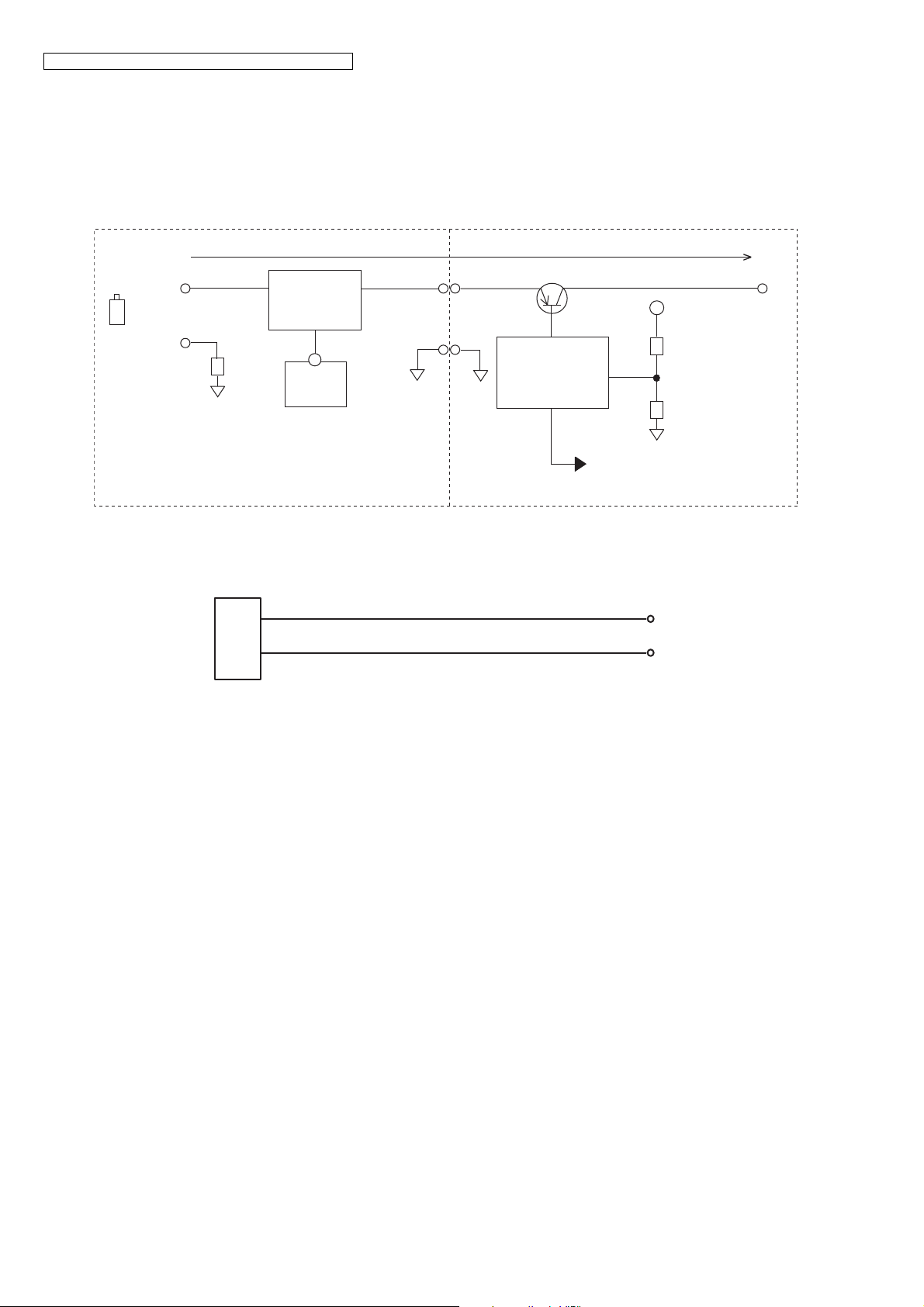
4.9. Behavior of Electric Power Failure
In case that the power from AC adaptor is lost and lose radio waves, BBIC (IC1) turns Q11 ON since handset presumes that
base unit's power is falied.
Base unit detects that power voltage of AC adaptor +5.5V is OFF, then turns Q351 ON.
It's possible to use the units during the power failure, supplying power to VBAT of base unit from battery of handset through
Q10, CHG terminal and Q351.
Handset
Base Unit
BATT+
BATT_
R45
CHG+
Power Supply
at AC failure
(Q10,Q11,Q12)
CHG-
3
BBIC
IC1
Q351
Power Down
DET
(Q352,Q353,Q354)
(pin101-IC501)
+5.5V
R351
R352
PDN_DET
4.10. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit)
Charge control is executed at handset side so that the operation when using charger is also controlled by handset.
Refer to Circuit Operation (Handset) (P.22)
TP1
J1
TP2
AC Adaptor
VBAT
The route for this is as follows: DC+pin of J1(+) CHARGE+pad Handset CHARGE-pad DC-pin of J1(-)
24
Page 25

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
5 Location of Controls and Components
Refer to the Operating Instructions.
Note:
You can download and refer to the Operating Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
6 Installation Instructions
Refer to the Operating Instructions.
Note:
You can download and refer to the Operating Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
7 Operating Instructions
Refer to the Operating Instructions.
Note:
You can download and refer to the Operating Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
25
Page 26
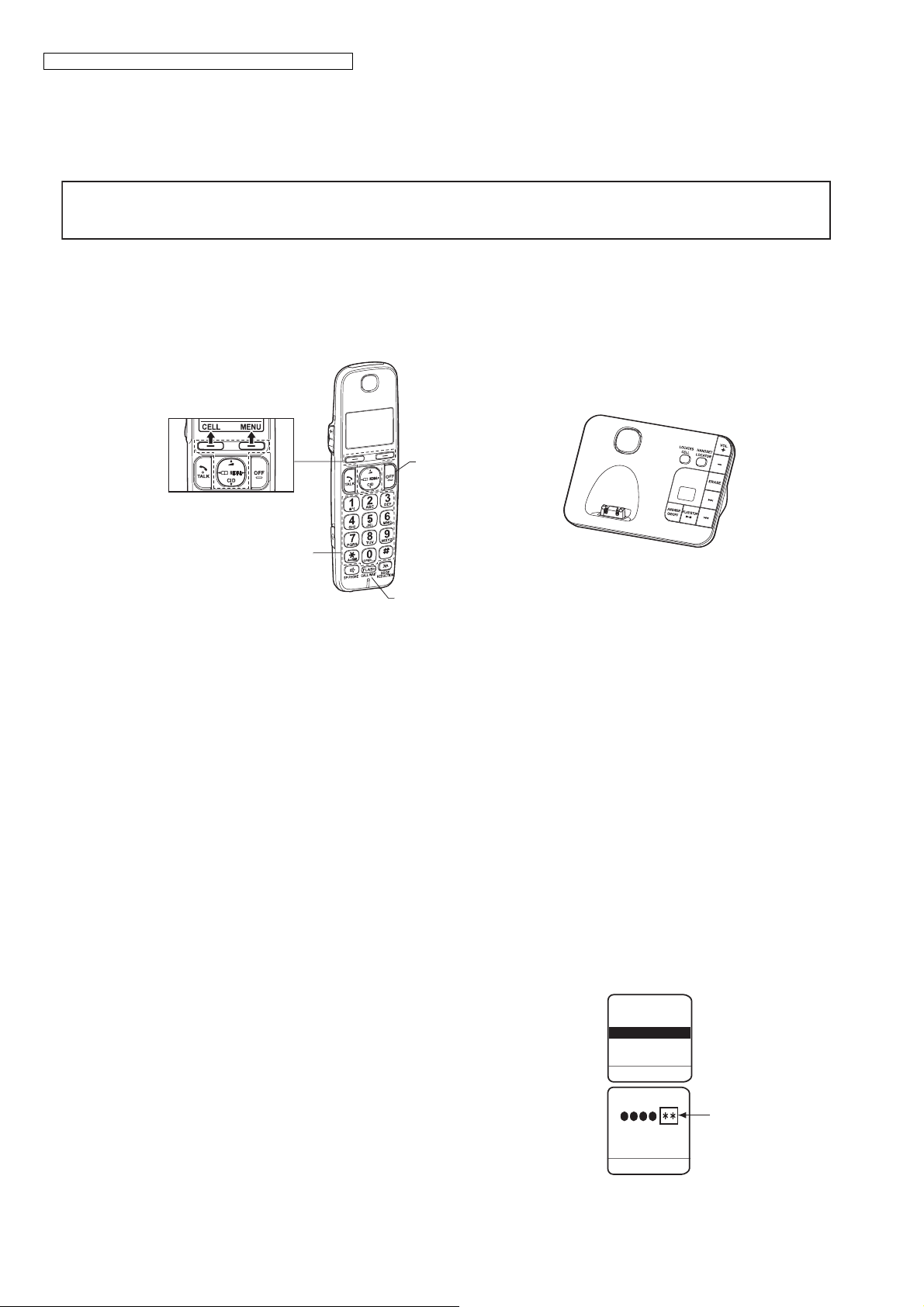
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
8 Test Mode
8.1. Engineering Mode
8.1.1. Base Unit
Important:
Make sure the address on LCD is correct when entering new data. Otherwise, you may ruin the unit.
Make sure the link between Base and Handset before that. Then in case using not original Handset,
you need to deregister Handset.
Note: Refer to Registering a Handset to a Base Unit in the Operating Instructions.
{OFF}
Dial keypad
{FLASH}
H/S key operation
{CALL WAIT}
1). Press {MENU}.
{^}
2). Select "Settings" using or
then press
{SELECT} or {>}.
Select "Set tel line" using or
then press
{SELECT} or {>}.
{V}
{^} {V}
3). Enter "7", "2", "6", "2", "7", "6", "6", "4".
Note: 7262 7664 = PANA SONI
(see letters printed on dial keys)
4). Select "Write EEP" using or
then press
{SELECT} or {>}.
{^} {V}
This pictured model is KX-TGE230.
H/S LCD
Service Mode
Read EEP
Write EEP
5). Enter "
6). Enter "
ە
", "ە", "ە", "ە" (Address). (*1)
㸨
", "㸨" (New Data). (*1)
26
BACK
Set Addr.:
CLEAR
SELECT
Default Data
OK
Page 27
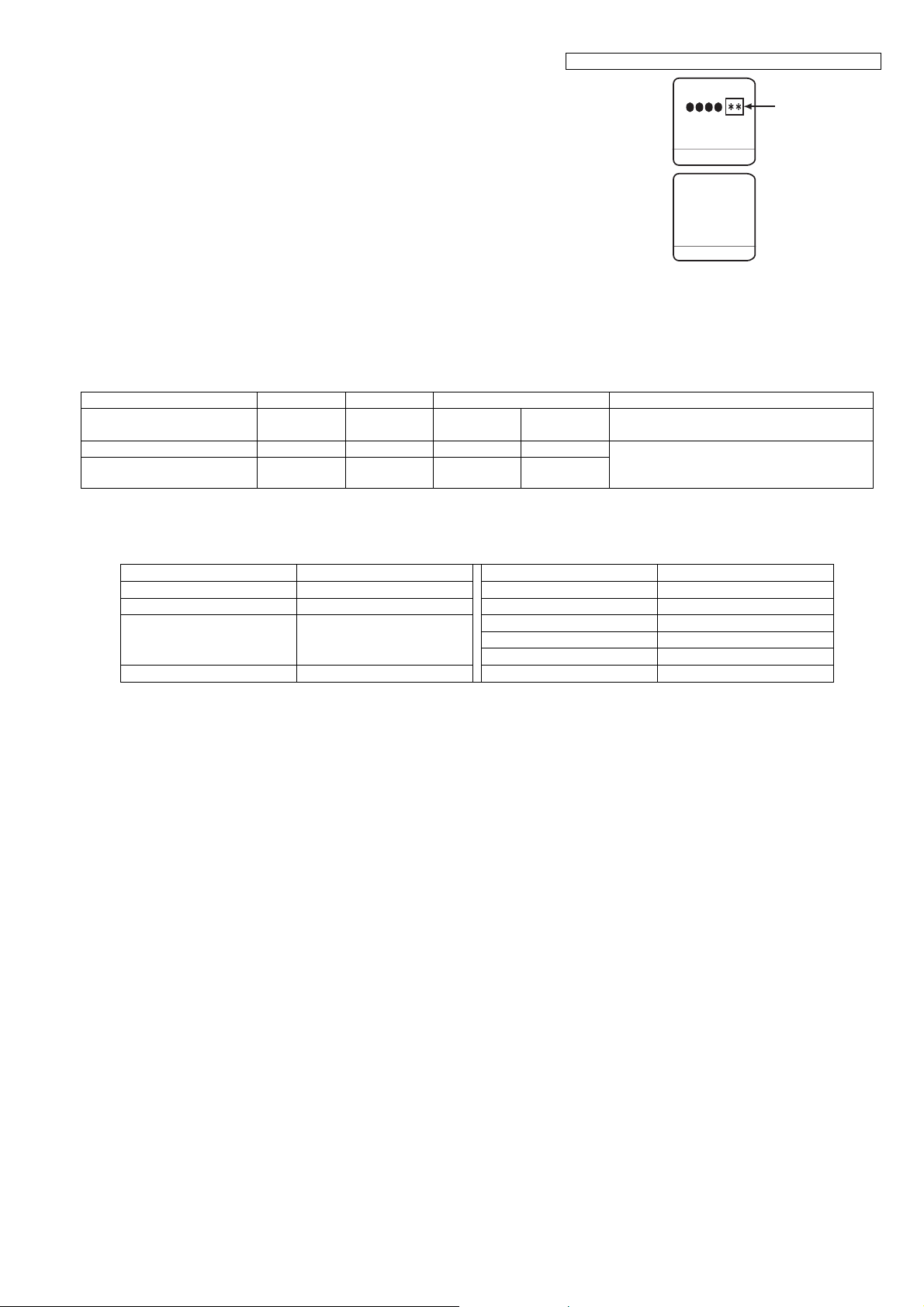
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
7). Press {OK} , a long confirmation beep
will be heard.
8).
Press to return to standby mode.
After that, turn the base unit power off and then power on.
Note:
New Data
_ _ _ _ _ _
Set Addr.:
Set Addr.:
{OFF}
CLEAR
OK
BACK
* "Set tel line" isn't displayed in Cell line only mode.
To return to normal mode, execute the following procedure:
1 {MENU} i {#}{1}{5}{7}
2 {V}/{^}: Select "off "i {SELECT}
3 {OFF}
Frequently Used Items (Base Unit)
ex.)
Items Address Default Data New Data Remarks
C-ID (FSK) sensitivity 06 0B 00 01 (6dB UP) 02 (12dB UP) When hex changes from"00" to "01" or "02"
gain increases by 6dB or 12dB.
Frequency 00 07 / 00 08 70/02 - - Use these items in a READ-ONLY mode to
ID 00 02 ~ 00 06 Given value - -
confirm the contents. Careless rewriting may
cause serious damage to the computer system.
Note:
(*1) When you enter the address or New Data, please refer to the table below.
Desired Number (hex) Input Keys Desired Number (hex) Input Keys
0 0 A [Flash] + 0
1 1 B [Flash] + 1
. . C [Flash] + 2
. . D [Flash] + 3
. . E [Flash] + 4
9 9 F [Flash] + 5
27
Page 28

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
8.1.2. Handset
Important:
Make sure the address on LCD is correct when entering new data. Otherwise, you may ruin the unit.
{OFF}
Dial keypad
{FLASH}
H/S key operation H/S LCD
1). Press {MENU}.
{CALL WAIT}
2). Select "Settings" using or
then press
{SELECT} or {>}.
{^} {V}
3). Enter "7", "2", "6", "2", "7", "6", "6", "4".
Note: 7262 7664 = PANA SONI
(see letters printed on dial keys)
4). Select "Write EEP" using or
then press
5). Enter "
6). Enter "
7). Press
{SELECT} or {>}.
ە
", "ە", "ە", "ە" (Address). (*1)
㸨
", "㸨" (New Data). (*1)
{OK} , a long confirmation beep
{^} {V}
will be heard.
Service Mode
Read EEP
Write EEP
BACK
SELECT
Set Addr.:
CLEAR
Set Addr.:
CLEAR
Set Addr.:
_ _ _ _ _ _
Default Data
OK
New Data
OK
8).
{OFF}
Press to return to standby mode.
BACK
After that, remove and reinsert the batteries. Press the Power button for
about 1 second if the power is not turned on.
28
Page 29
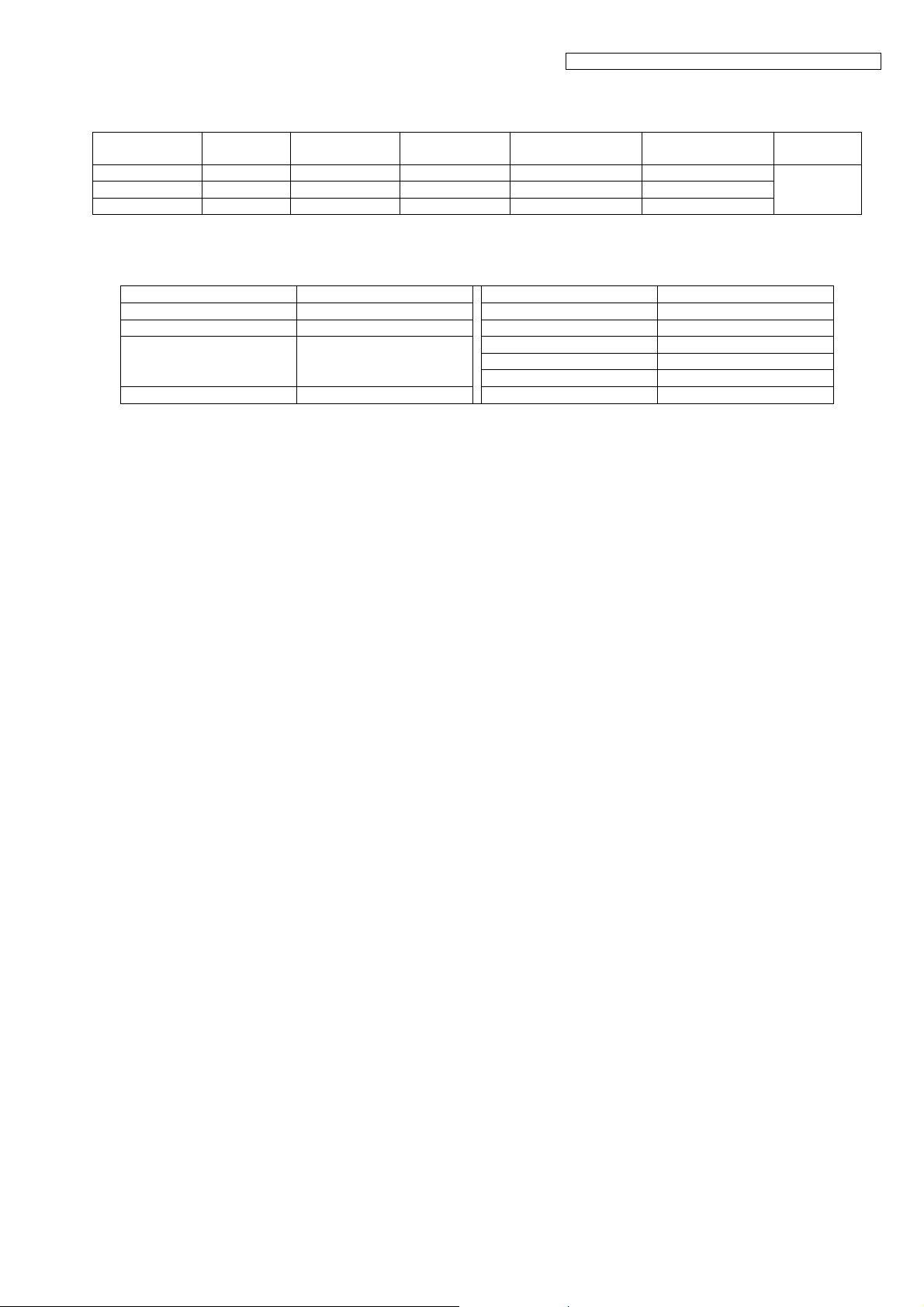
Frequently Used Items (Handset)
ex.)
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Items Address Default Data New Data Possible Adjusted
Value MA X (hex)
Battery Low 00 12/00 13 00 / 00 - - -
Frequency 00 07 / 00 08 00 / 01 - - -
ID 00 02 ~ 00 06 Given value - - -
Possible Adjusted
Value MIN (hex)
Remarks
(*2)
Note:
(*1) When you enter the address or New Data, please refer to the table below.
Desired Number (hex.) Input Keys Desired Number (hex.) Input Keys
0 0 A [Flash] + 0
1 1 B [Flash] + 1
. . C [Flash] + 2
. . D [Flash] + 3
. . E [Flash] + 4
9 9 F [Flash] + 5
(*2) Use these items in a READ-ONLY mode to confirm the contents. Careless rewriting may cause serious damage to the
handset.
29
Page 30

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
9 Service Mode
9.1. How to Clear User Setting (Handset Only)
Handset
Press ,,, simultaneously until a beep sound is heard. Then single handset is initialized.
(The contents of user setting are reset to factory default)
*Usage time is not cleared.
30
Page 31

10 Troubleshooting Guide
10.1. Troubleshooting Flowchart
FLOW CHART
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Power ON Base Unit
OK
Record
OK
Playback Pre-Message Check Playback
OK
Link
No link
Battery Charge
OK
Range Check the RF part
Handset Voice Transmission Check Handset Transmission
Handset Voice Reception
Caller ID function Check Caller ID
OK
OK
OK
OK
Not working
Not recording (*1)
No playback
Not charged
NG
No voice
No voice
Caller ID Error
Check Power
Check Record
Check Battery Charge
Check Link
Check Handset Reception
Cross Reference:
Check Power (P.32)
Check Record (P.33)
Check Playback (P.36)
Check Battery Charge (P.36)
Check Link (P.37)
Check the RF part (P.39)
Check Handset Transmission (P.44)
Check Handset Reception (P.44)
Check Caller ID (P.44)
Note:
(*1) When a user claims that the unit disconnects a call right
after the greeting message and no incoming messages can
be recorded, this symptom can not reappear with TEL
simulator in the service center. In this case, try to change
the Auto disconnect activation time and Vox level.
<How to change the Auto Disconnect activation time
and VOX level> (P.34) item (A) and (B).
31
Page 32

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
10.1.1. Check Power
10.1.1.1. Base Unit
Is the AC Adaptor inserted into AC outlet? (*1)
Is output voltage of AC adaptor 5.5 V?
YES
Check VDD1(1.8V) :Test point (VDD1)
OK
RSTN: Reset = "High"?
YES
Check Xtal CLK=10.368MHz?
YES
Check BBIC.
Cross Reference:
Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.14)
10.1.1.2. Handset
Is the battery inserted to BATT+ and BATT-?
YES
Is the voltage of TP-VBAT 2.3 V more?
YES
Is the voltage of TP 3.0 V about 3.0 V?
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
Check AC Adaptor.
Check Power Supply Circuit.
Check Reset Circuit.
Check X501.
Note:
BBIC is IC501.
(*1) Refer to Specifications (P.7) for part number and
supply voltage of AC adaptor.
(*2) Refer to Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main) (P.76).
Check the battery and around BATT+ and
BATT- are not shorted.
YES
Is the voltage of TP VDDC about 1.2 V?
YES
Does BBIC (IC1: 36) oscillate at 13.824 MHz?
YES
Check BBIC (IC1).
Cross Reference:
Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.22)
Check Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit.
NO
NO
Check X1, C52, C53.
32
Page 33

10.1.2. Check Record
10.1.2.1. Base Unit
Not record Incoming Message
Check Bell signal.
Does the unit catch line?
Check Line In: Pin 25 of BBIC. Check ICM Recording in Signal Route.
Check Auto Disconnect Circuit.
Check Parallel Connection Detection
Circuit.
Check BBIC and Flash Memory.
OK
YES
OK
OK
OK
NO
NO
NO
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Check Telephone Line Interface
[Bell].
Check Telephone Line Interface
[OFF HOOK].
Cross Reference:
Telephone Line Interface (P.16)
Parallel Connection Detect Circuit/Auto Disconnect
Circuit (P.17)
Note:
Flash Memory is IC601.
BBIC is IC501.
33
Page 34

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
1) Press "MENU " key at standby Mode and "#" key.
Note: The set must power on and be linked.
2) Press "9", "0", "0", "0"," " .
3) Press "7","3","1".
4) Then enter the below last digit;
5) Back to "standby" mode automatically after step 4).
You can hear beep sound which is a confirmation tone.
Service ready
:731
Service ready
:
LCD (H/S)
last digit
"0"
Auto disconnect & CPC
: enable
㨇default㨉
(*1)
(*1)
Auto disconnect & CPC
: disable
(*2)
"1"
"2"
Auto disconnect : enable
CPC : disable
Note:
(*1) Both Auto Disconnect and CPC don't detect for the first 2 seconds.
(*2) If the "Disable" is selected, even if the parallel-connected telephone is OFF HOOK,
the line isn't disconnected.
CLEAR
BACK
<How to change the Auto Disconnect activation time and VOX level>
A) Auto Disconnect activation time:
Some Telephone Company lines (fiber or cable) ON Hook and OFF Hook voltages are lower than conventional lines, which may
cause a malfunction of Auto Disconnect detection. To solve this problem, try changing the Auto Disconnect activation through
the procedures below.
34
Page 35

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
B) Vox level:
It makes easier to detect a small voice (caller) by raising the sensitivity of VOX level. Therefore, the recording of TAM is not
turned off during detection.
1) ~ 2) are same as (A).
3) Press "5","1","1".
Service ready
:511
CLEAR
4) Then enter the below last digit;
last digit
default setting
"0"
: normal
6dB up
"1"
5) Back to "standby" mode automatically after step 4.
You can hear beep sound which is a confirmation tone.
35
Page 36

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Check Charge Circuit of Base Unit.
Check Handset.
Plug in the AC Power source.
Charge Handset on Base Unit.
Is the voltage of two charge contacts about
3 V or more?
OK
NO
Check Charge Contacts at
Base Unit from mechanical point of view.
YES
Is BBIC (IC1: 34) high at charge state?
Check Charge Circuit.
Check Power of Handset.
Is Check Power OK?
NO
NO
YES
Check Charge Circuit of Charger Unit.
Check Handset.
Plug in the AC Power source.
Charge Handset on Charger Unit.
Is the voltage of two charge contacts about
5.5 V or more?
OK
NO
Check Charge Contacts at Charger Unit
from mechanical point of view.
YES
10.1.3. Check Playback
10.1.3.1. Base Unit
Check VDD1(1.8V) :Test point (VDD1)
OK
Check output of BBIC (Pin 41,43).
OK
Check Speaker and its surroundings.
NO
NO
Check Power Supply Circuit.
Check BBIC and Flash Memory.
Cross Reference:
Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.14)
Note:
Flash Memory is IC601.
10.1.4. Check Battery Charge
10.1.4.1. Base Unit
Cross Reference:
Charge Circuit (P.15)
10.1.4.2. Handset
BBIC is IC1.
(*1) Refer to Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main) (P.76).
Cross Reference:
Check Power (P.32)
Charge Circuit (P.23)
10.1.4.3. Charger Unit
Cross Reference:
Charge Circuit (P.23)
36
Page 37

10.1.5. Check Link
Check around Power Supply Circuit.
Does Base Unit connect to the properly working
Handset?
Check around X501 and RF module and adjust
clock frequency.
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
Is the voltage of VDD3 about 3.0V?
Check the RF part
Does the RF clock (CLK) oscillate at 10.368 MHz in
Base Unit Test Mode?
YES
Is the voltage of VDD1 about 1.8V?
YES
Base Unit is OK. Check Handset.
*1
10.1.5.1. Base Unit
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Cross Reference:
Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.14)
Check the RF part (P.39)
Note:
Refer to Things to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal (P.52)(P.58) for Base Unit.
*1 How to adjust the frequency of X501.
37
Page 38

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Check around Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit.
Does Handset link with Base Unit?
(Properly working unit)
Check around X1 and RF module and adjust
clock frequency.
NO
NO
NO
NO
Is the voltage of TP VBAT about 2.2~2.8 V?
Is the voltage of TP VDDC about 1.2 V?
YES
YES
YES
YES
Is the voltage of TP 3.0 V about 3.0 V?
Does the RF clock (CLK) oscillate: 13.824 MHz
in Handset Test Mode?
Handset is OK. Check Base Unit.
YES
Check the RF part
Check the batteries.
*1
10.1.5.2. Handset
Cross Reference:
Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.22)
Check the RF part (P.39)
Note:
Refer to Things to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal (P.53)(P.58) for Handset.
*1 How to adjust the frequency of X1.
38
Page 39

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
1. Prepare Regular HS(*1) and Regular BU(*2).
2. a. Re-register regular HS (Normal mode) to base unit (to be checked).
If this operation fails in some ways, the base unit is defective.
b. Re-register handset (to be checked) to regular BU (Normal mode).
If this operation fails in some ways, the handset is defective.
Base unit is defective Handset is defective
START
Registration of
Regular HS to
base unit
Registration of
handset to
Regular BU
(other checkings)
Registration of handset to base unit
(checked ones)
Registration of Regular HS to Regular BU
Yes
No No
Yes
10.1.6. Check the RF part
10.1.6.1. Finding out the Defective part
After All the Checkings or Repairing
1. Re-register the checked handset to the checked base unit, and Regular HS to Regular BU.
Note:
(*1) HS: Handset
(*2) BU: Base Unit
39
Page 40

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
10.1.6.2. RF Check Flowchart
Each item (1 ~ 5) of RF Check Flowchart corresponds to Check Table for RF part (P.41).
Please refer to the each item.
Start
1
confirmation
Normal
OK
Link
NG
2
Control
signal
confirmation
OK
3
X'tal
Frequency
confirmation
OK
4
TX confirmation
OK
NG
NG
NG
Check BBIC interface parts.
(RF Block <->BBIC on BU/HS P.C.B)
Adjust X'tal Frequency. (*1)
Check TX Block.
5
Range
confirmation
Normal
OK
GOOD
Note:
(*1) Refer to Check Link (P.37).
NG
TEST RANGE Check.
40
Page 41

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
10.1.6.3. Check Table for RF part
No. Item BU (Base Unit) Check HS (Handset) Check
1 Link Confirmation Normal
HS, BU Mode [Normal Mode]
2
X
'tal Frequency confirmation
HS, BU Mode: [Adjustment]
3 TX confirmation
HS Mode:
HS_Burst Mode] (*1)
BS Mode:
BS_Burst Mode] (*1)
4 Range Confirmation Normal
HS, BU Mode: [Normal Mode]
Note:
(*1) Refer to Commands (P.55)
(*2) Adjustment Standard (Base Unit) (P.56)
(*3) Adjustment Standard (Handset) (P.57)
1. Register Regular HS to BU (to be
checked).
2. Press [Talk] key of the Regular HS to
establish link.
Check X'tal Frequency.
(10.368 MHz ± 41Hz)
1. Remove wire antenna 2 and connect
spectrum analyzer to TP. (*2)
2. Confirm TX power whether spec. is
satisfied.
Power >=13.5dBm
1. Register Regular HS to BU (to be
checked).
2. Press [Talk] key of the Regular HS to
establish link.
3. Compare the range of the BU (being
checked) with that of the Regular BU.
1. Register HS (to be checked) to Regular
BU.
2. Press [Talk] key of the HS to establish link.
Check X'tal Frequency.
(13.824 MHz ±100 Hz)
1. Connect spectrum analyzer to TP. (*3)
2. Confirm TX power whether satisfied spec.
Power >=16.0dBm
1. Register HS (to be checked) to Regular
BU.
2. Press [Talk] key of the HS to establish link.
3. Compare the range of the HS (being
checked) with that of the Regular HS.
41
Page 42

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
10.1.6.4. TEST RANGE Check
Circuit block which range is defective can be found by the following check.
Item BU (Base Unit) Check HS (Handset) Check
Range Confirmation TX TEST
(TX Power check)
HS, BU setting
Checked unit: Low TX power (*1)
Regular unit: High TX power (*1)
Range Confirmation RX TEST
(RX sensitivity check)
HS, BU setting
Checked unit: High TX power (*1)
Regular unit: Low TX power (*1)
1. Register Regular HS to BU (to be checked).
2. Set TX Power of the BU and the Regular HS
according to CHART1.
3. At distance of about 20m between HS and BU,
Link OK = TX Power of the BU is OK.
No Link = TX Power of the BU is NG.
1. Register Regular HS to BU (to be checked).
2. Set TX Power of the BU and the Regular HS
according to CHART1.
3. At distance of about 20m between HS and BU,
Link OK= RX Sensitivity of the BU is OK.
No Link = RX Sensitivity of the BU is NG.
CHART1: Setting of TX Power and RX Sensitivity in Range Confirmation TX TEST, RX TEST
BU (to be checked) Regular_HS
TX Power TX Power
BU (Base Unit) TX Power Check Low Hig h
BU (Base Unit) RX Sensitivity Check High Low
1. Register HS (to be checked) to Regular BU.
2. Set TX Power of the HS and the Regular BU
according to CHART1.
3. At distance of about 20m between HS and BU,
Link OK = TX Power of the HS is OK.
No Link = TX Power of the HS is NG.
1. Register HS (to be checked) to Regular BU.
2. Set TX Power of the Checking HS and the Regular BU according to CHART1.
3. At distance of about 20m between HS and BU,
Link OK= RX Sensitivity of the HS is OK.
No Link = RX Sensitivity of the HS is NG
HS (Handset) TX Power Check Low High
HS (Handset) RX Sensitivity Check High Low
Note:
(*1) Refer to Commands (P.55).
HS (to be checked) Regular_BU
TX Power TX Power
42
Page 43

10.1.7. Registering a Handset to the Base Unit
L
{OFF}
{ }
A handset can cancel its own registration to the base unit, or other handsets
registered to the same base unit. This allows the handset to end its wireless
connection with the system.
1
All handsets registered to the base unit are displayed.
2 : Select the handset you want to cancel. i {SELECT}
3 : “Yes” i {SELECT}
4
{MENU} i # 1 3 1
{ }
The supplied handset and base unit are pre-registered. If for some reason the
handset is not registered to the base unit, re-register the handset.
1 Handset:
{MENU} i # 1 3 0
2 Base unit:
Press and hold {LOCATOR} for about 5 seconds until the registration tone
sounds.
If all registered handsets start ringing, press {LOCATOR} again to stop, then
L
repeat this step.
The next step must be completed within 90 seconds.
L
3 Handset:
Press {OK}, then wait until a long beep sounds.
Note:
While registering, “Base in registering” is displayed on all registered
L
handsets.
When you purchase an additional handset, refer to the additional handset’s
L
installation manual for registration.
10.1.8. Deregistering a Handset
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
43
Page 44

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Check MIC of handset.
Check handset Tx in Signal Route.
Check speaker of handset.
Check handset Rx in Signal Route.
YES
Did bell ring?
(Message indicator
blinks)
Check Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)/
Call Waiting Caller ID.
Check bell signal detection in
Telephone Line Interface.
BASE UNIT
NO
10.1.9. Check Handset Transmission
10.1.10. Check Handset Reception
Note:
When checking the RF part, Refer to Check the RF part
(P.39).
10.1.11. Check Caller ID
Cross Reference:
Telephone Line Interface (P.16)
Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)/Call Waiting Caller
ID (P.18)
Note:
• Make sure the format of the Caller ID service of the
Telephone company that the customer subscribes to.
• It is also recommended to confirm that the customer is really
a subscriber of the service.
44
Page 45

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
11 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions
11.1. Disassembly Instructions
11.1.1. Base Unit
11.1.1.1. KX-TGE210
Remove the 2 screws to remove
ձ
the cabinet cover.
Cabinet
cover
ձ
2 screws
ղ
Remove the solders.
ղ
Solders
45
Page 46

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
ճ
Screw
Main P.C.Board
Jack holder
Remove the screw to remove the Jack Holder and
Main P.C.Board.
ճ
46
Page 47

11.1.1.2. KX-TGE230
Remove the 5 screws to remove
ձ
the cabinet cover.
Remove the solders.
ղ
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4 screws
Cabinet cover
Solders
Main P.C. board
Remove the screw to remove the
ճ
Jack Holder.
screws
Jack holder
47
Page 48

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Remove the pararell wire to remove the
main P.C. board.
Main P.C. board
Remove the 5 screws to remove
յ
the operational P.C.B board.
Pararell wire
2 screws
Operational P.C.B board
48
Page 49

11.1.2. Handset
Remove the 2 screws.
Insert a plastic card.
(Ex. Used SIM card etc.)
between the cabinet body
and the cabinet cover, then
pull it along the gap to open
the cabinet.
Likewise, open the other
side of the cabinet.
Remove the cabinet cover
by pushing it upward.
Remove the solders.
Remove the solders to remove
the 2 charge terminals.
Remove the screw to remove
the main P. C. board.
Cabinet body
Cabinet cover
2 screws
Cabinet cover
Screw
Solders
Main P.C. board
2 charge terminals
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
49
Page 50

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
11.1.3. Charger Unit
Unhook the click of one side.
ձ
Then unhook the other one.
ղ
2 charge terminals
50
Page 51

11.2. How to Replace the Handset LCD
Peel off the FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) from
the LCD, in the direction of the arrow. Take
care to ensure that the foil on the P.C. board
is not damaged.
Fit the heatseal of a new LCD.
Heatweld with the tip of the soldering
iron about 5 to 8 seconds
(in case of 60W soldering iron).
0.2 mm
0.2 mm
P. C . board
New LCD
Tip of Soldering Iron
(Part No. PQZZ430PIR)
Rubber of Soldering Iron
(Part No. PQZZ430PRB)
If interval tolerance between center lines
is less than 0.2 mm, it is o.k.
Horizontal Interval
Tolerance
Vertical Interval
Tolerance
OK
NG
NG
NG
(Horizontal interval tolerance is
more than 0.2 mm.)
(Vertical interval tolerance is
more than 0.2 mm.)
(Inclined)
Note:
The illustrations are simplified in this page.
They may differ from the actual product.
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
51
Page 52

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Base unit P. C. board
AC adaptor
1
DC JACK
UTX (yellow)
3
2
3
GND (black)
URX (red)
To Serial Port
(COM port 1*)
JIG Cable
PC
GND
UTX
URX
12 Measurements and Adjustments
This chapter explains the measuring equipment, the JIG connection, and the PC setting method necessary for the measurement in
Troubleshooting Guide (P.31)
12.1. Equipment Required
• Digital multi-meter (DMM): it must be able to measure voltage and current.
• Oscilloscope.
• Frequency counter: It must be precise enough to measure intervals of 1 Hz (precision; ±4 ppm)
Hewlett Packard, 53131A is recommended.
• DECT tester: Rohde & Schwarz, CMD 60 is recommended.
This equipment may be useful in order to precisely adjust like a mass production.
12.2. The Setting Method of JIG
<Preparation>
• Serial JIG cable: PQZZ1CD300E*
• PC which runs in DOS mode
• Batch file CD-ROM for setting: PNZZTGE230M
12.2.1. Connections (Base Unit)
Connect the AC adaptor.
Connect the JIG Cable GND (black).
Connect the JIG Cable RX (red) and TX (yellow).
Note:
*: If you have the JIG Cable for TCD500 series
(PQZZ1CD505E), change the following values of
resistance. Then you can use it as a JIG Cable for both
TCD300 and TCD500 series. (It is an upper compatible JIG
Cable.)
Resistor Old value (k) New value (k)
R2 22 3.3
R3 22 3.3
R4 22 4.7
R7 4.7 10
Note:
*: COM port names may vary depending on what your PC calls it.
52
Page 53

12.2.2. Connections (Handset)
DC Power
or Battery
2
GND
(black)
3
To Serial Port
(com port 1*)
JIG Cable
PC
URX (red)
3
UTX (yellow)
Handset P. C. board
1
BATT-BATT+
GND
UTX
URX
Connect the DC Power or Battery to BATT+ and BATT-.
Connect the JIG cable GND (black) to GND.
Connect the JIG cable UTX (yellow) to UTX and URX (red) to URX.
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Note:
*: COM port names may vary depending on what your PC calls it.
53
Page 54

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
1. Insert the Batch file CD-ROM into CD-ROM drive and
copy PNZZTG**** folder to your PC (example: D drive).
2. Open an MS-DOS mode window.
3. At the DOS prompt, type "D:" (for example) to select the
drive, then press the Enter key.
4. Type "CD 㪳PNZZTG****", then press the Enter key.
5. Type "SET_COM=X", then press the Enter key
(X: COM port number used for the serial connection on your PC).
6. Type "READID", then press the Enter key.
䊶If any error messages appear, change the port number or
䇭check the cable connection.
䊶If any value appear, go to next step.
7. Type "DOSKEY", then press the Enter key.
<Example>
C: >Documents and Settings>D:
D: >>CD >PNZZTG****
D: >PNZZTG**** >SET_COM=X
D: >PNZZTG****>READID
00 52 4F A8 A8
D: >PNZZTG****>DOSKEY
D: >PNZZTG****>
<Example: error happens>
C: >Documents and Settings>D:
D: >>CD >PNZZTG****
D: >PNZZTG**** >SET_COM=X
D: >PNZZTG****>READID
ޓCreateFile error
ERROR 10: Can't open serial port
D: >PNZZTG ****>
<Example for Windows>
On your computer, click [Start], select Programs
(All Programs for Windows XP/Windows Server 2003),
then click
MS-DOS Prompt. (for Windows 95/Windows 98)
Or
Accessories-MS-DOS Prompt. (for Windows Me)
Or
Command Prompt. (for Windows NT 4.0)
Or
Accessories-Command Prompt.
(for Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003)
12.2.3. How to install Batch file into P.C.
Note:
• “*****” varies depending on the country or models.
54
Page 55

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
12.2.4. Commands
See the table below for frequently used commands.
Command name Function Example
rdeeprom Read the data of EEPROM Type “rdeeprom 00 00 FF”, and the data from address
“00 00” to “FF” is read out.
readid Read ID (RFPI) Type “readid”, and the registered ID is read out.
writeid Write ID (RFPI) Type “writeid 00 18 E0 0E 98”, and the ID “0018 E0 0E
hookoff Off-hook mode on Base Type “hookoff”.
hookon On-hook mode on Base Type “hookon”.
getchk (Base unit) Read checksum Type “getchk”.
How to use of
"getchk"
in Handset
wreeprom Write the data of EEPROM Type “wreeprom 01 23 45”. “01 23” is address and “45”
bursttx Burst TX mode Type “bursttx”
testrx Burst RX mode Type “testrx”
tph Keep TX power high Type"tph"
tpl Keep TX power low Type"tpl"
1.rdeeprom Read EEPROM Type “RdEeprom 03 7D 04”, and the data from address
2.sendchar epw Write EEPROM Type “sendchar epw 03 7D 04 FF FF FF FF”
3.sendchar RST Reset baseset Type “sendchar RST”
4.getchk Read checksum Type “getchk”.
5.sendchar epw Write EEPROM Type “sendchar epw 03 7D 04 WW XX YY ZZ”
98” is written.
"03 7D" to "03 80" is read out
*This command gets 4 byte "WW", "XX", "YY", "ZZ".
*Please NEVER forget these 4 byte data!
*"WW", "XX", "YY", "ZZ" is 4 byte data that already read
from same address.
is data to be written.
55
Page 56

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
+
-
+
-
GRY
PUR
BRN/RED
BLU
ORG
+
-
YLW/BLK
PNLB2278ZP N L B 2 2 7 8 Z
PC
URX
UTX
GND
UART
JIG
A
PbF
RSTN
DCM
DCP
STM/P15
C611
CHARGE+
CHARGE-
F301
SPN
SPP
R477
ANT1-S-GND
URX
R891
C661
C662
C857
C663
C664
C477
ANT1_TP
C478
Q901
Q902
Q903
Q904
Q905
Q906
Q907
UTX
Q909
Q910
Q913
Q914
Q144
IC611
JTAG
Q351
Q352
Q353
R115R116
R117
Vcap
R125
D472
ANT2_TP
R901
R902
R903
R904
R906
R907
GAP
R143
VDD1
R146
VDD3
R917
R147
R918
VDD4
R148
R919
VDD5
R920
R151
C115
R152
C116
R924
R925
R926
L1R
L1T
R351
R352
R354
R355
R163
R167
C518
C519
+5.5V
RA611
R178
ANT1-Short
R371
R372
R373
R951
R952
R953
R954
R956
R957
R958
C152
R960
R961
R965
R966
C351
C174
CKM
C962
D132
C963
D133
C964
IC502
IC901
GND
D362
C901
C870
C511
R478
D473
R923
R118
Frequency Counter (*1)
Oscilloscope (*2)
Send command "SFR", then
the frequency output on this TP.
STM/CKM/P15
DC
5.5V
ANT_1
Spectrum
Analyzer
12.3. Adjustment Standard (Base Unit)
When connecting the simulator equipment for checking, please refer to below.
12.3.1. Bottom View
Note:
(*1) refers to No.2 of Check Table for RF part (P.41)
(*2) refers to Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.14)
56
Page 57

12.4. Adjustment Standard (Handset)
When connecting the simulator equipment for checking, please refer to below.
12.4.1. Component View
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Oscilloscope (*2)
* Start Monitor
ANT
Spectrum Analyzer
PNLB2282Z
PbF
TDI
GND_J
CKM/STM
3.0V
TMS
TCK
O
TD
the frequency output on this TP.
* Send command "SFR", then
Frequency Counter (*1)
IC3
RA5
C3
C2
C1
ANT1
ANT-Short
CKM/STM
RA1
C69
C40
R18
C19
ANT-Short-GND
C44
C807
C46
D30
RA2
RA3
RSTN
RTCK
C41
Q6
CS
RESET
ATSTP
ATSTN
C79
CD
SCL
C4
5
C51
C32
CHG_CUR
R72
R33
C92
SID
L801
C43
IC1
C30
C29
L3
R31
C36
VBAT_MON
21DEL11DEL
Q5
R70
R51
R50
C81
RECEIVER
C71
Blue
R16
R73
Q7
C42
C70
U_LOV
P
D13
D14
V
O
WD_L
X1
C16
R81
R55
R56
Q13
C93
C91
S
P
P
H
NO
E
S_
AEP
EK
R
Orange
C72
C73
C802
C801
C80
6
C22
C25
C24
C26
C52
C99
C68
C98
C97
C96
C53
C17
C89
C88
C39
R24
C20
C21
C31
C18
R22
R26
RA4
C14
C13
C11
C34
C80
Oscilloscope
VOLT METER
40
Oscilloscope
VOLT METER
8
VBG/CHG_MON
R21
R10
R20
Q12
Q11
CHG+
Q10
Q9
CHG_CTRL
C35
R4
Q2
R8
Q4
Q3
C56
IC4
C58
BAT+
Note:
(*1) refers to No.2 of Check Check Table for RF part (P.41)
(*2) refers to Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.22)
R7
R6
R2
C27
R9
C57
F1
C33
R11
R13
R12
C90
CHG_DET
C6
R71
47
MIC+
MIC-
GND
VBAT
+
+
47
SPM
MIC+
SPP
MIC-
C85
R80
C84
C12
R32
R34
R23
R28
C83
R27
C37
R25
C78
R54
Q8
CN4
C82
C86
C15
R45
C10
URX
UTX
VBAT
GND
CHG-
BAT-
MIC Load
1.1 kHz
OSC
DC POWER SUPPLY
2.6 V 2.34 V
DC VOLT METER
R3
C5
A
57
Page 58

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
12.5. Things to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal
If repairing or replacing EEPROM and X'tal, it is necessary to download the required data such as Programming data or adjustment
data, etc. in memory.
The set doesn't operate if it is not executed.
12.5.1. How to download the data
12.5.1.1. Base Unit
First, operate the PC setting according to The Setting Method of JIG (P.52).
Then download the appropriate data according to the following procedures.
Items How to download/Required adjustment
BBIC(IC501) Programming data is stored in memory. 1) System Clock adjustment.
EEPROM (IC611) Adjusted parameter data is stored in memory.
(country version batch file, default batch file,
etc.)
X'tal (X1) System clock Clock adjustment data is in EEPROM, adjust the data again
1) Change the address “0001” of EEPROM to “AA” to download
the data.
2) Default batch file: Execute the command “default.bat”.
3) Country version batch file: Execute the command
“TG49WW_US_US_RevXXX_YYY.bat”. (*1)
4) System Clock adjustment
after replacing it.
1) Apply 5.5V between DCP ad DCM with DC power.
2) Input Command "sendchar sfr", then you can confirm the
current value.
3) Check X'tal Frequency.(10.368MHz ± 41Hz).
4) If the frequency is not 10.368MHz ±41Hz, adjust the
frequency of CLK executing the command "sendchar sfr xx xx
(where xx is the value)" so that the reading of the frequency
counter is 10.368MHz ±5Hz.
Note:
(*1) WW: model number, XXX_YYY: revision number, ZZZ:Voice prompt, AA: Baud rate(9600/19200/57600/115200)
"XXX_YYY” and "ZZZ" vary depending on the country version. You can find them in the batch file, PNZZ- mentioned in The
Setting Method of JIG (P.52).
12.5.1.2. Handset
First, operate the PC setting according to The Setting Method of JIG (P.52).
Then download the appropriate data according to the following procedures.
Items How to download/Required adjustment
BBIC(IC1) Programming data is stored in memory. 1) System Clock adjustment.
EEPROM (IC3) Adjusted parameter data is stored in memory.
(country version batch file, default batch file,
etc.)
X'tal (X1) System clock 1) Apply 2.6V between BATT+ and BATT- with DC power.
1) Default batch file: Execute the command “default.bat”.
2) Default batch file (remaining): Execute the command
“TGEA20_US_DEF_RevXXX_YYY.bat”. (*2)
3) Country version batch file: Execute the command
“TGEA20_US_US_RevXXX_YYY.bat”. (*2)
4) System Clock adjustment
5) 2.35 V setting and battery low detection
2) Input Command " sendchar sfr", then you can confirm the
current value.
3) Check X'tal Frequency.(13.824 MHz ± 100 Hz).
4) If the frequency is not 13.824 MHz ± 100 Hz, adjust the frequency of CLK executing the command "sendchar sfr xx xx
(where xx is the value)" so that the reading of the frequency
counter is 13.824000 MHz ± 5 Hz.
Note:
(*2) XXX_YYY: revision number
"XXX_YYY" vary depending on the country version. You can find them in the batch file, PNZZ- mentioned in The Setting
Method of JIG (P.52).
58
Page 59

12.6. Frequency Table
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Ch. (hex) TX/RX Frequency (MHz)
Channel 0 00 1928.448
Channel 1 01 1926.720
Channel 2 02 1924.992
Channel 3 03 1923.264
Channel 4 04 1921.536
59
Page 60

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
13 Miscellaneous
13.1. How to Replace the LLP (Leadless Leadframe Package) IC
Note:
This description only applies to the model with Shield case.
13.1.1. Preparation
• PbF (: Pb free) Solder
• Soldering Iron
Tip Temperature of 700 F ± 20 F (370 C ± 10 C)
Note:
We recommend a 30 to 40 Watt soldering iron. An expert may be able to use a 60 to 80 Watt iron where someone with less
experience could overheat and damage the PCB foil.
• Hot Air Desoldering Tool
Temperature: 608 F ± 68 F (320 C ± 20 C)
13.1.2. Caution
• To replace the IC efficiently, choose the right sized nozzle of the hot air desoldering tool that matches the IC package.
• Be careful about the temperature of the hot air desoldering tool not to damage the PCB and/or IC.
13.1.3. How to Remove the IC
1. Heat the IC with a hot air desoldering tool through the P.C.Board.
IC
P.C.Board
Hot Air Desoldering Tool
2. Pick up the IC with tweezers, etc. when the solder is melted completely.
Note:
• Be careful not to touch the peripheral parts with tweezers, etc. They are unstable.
Tweezers, etc.
IC
P.C.Board
When it is hard to melt the solder completely, heat it with a hot air desoldering tool through the IC besides through the
P. C .B o ar d .
P.C.Board
Hot Air Desoldering Tools
3. After removing the IC, clean the P.C.Board of residual solder.
60
Page 61

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Solder
Soldering Iron
P.C.Board
Land
IC
Solder
Soldering Iron
P.C.Board
Land
13.1.4. How to Install the IC
1. Place the solder a little on the land where the radiation GND pad on IC bottom is to be attached.
2. Place the solder a little on the land where IC pins are to be attached, then place the IC.
Note:
• When placing the IC, the positioning should be done very carefully.
3. Heat the IC with a hot air desoldering tool through the P.C.Board until the solder on IC bottom is melted.
Note:
• Be sure to place it precisely, controlling the air volume of the hot air desoldering tool.
IC
P.C.Board
Hot Air Desoldering Tool
4. After soldering, confirm there are no short and open circuits with visual inspection.
61
Page 62

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
13.2. How to Replace the Flat Package IC
Even if you do not have the special tools (for example, a spot heater) to remove the Flat IC, with some solder (large amount), a
soldering iron and a cutter knife, you can easily remove the ICs that have more than 100 pins.
13.2.1. Preparation
• PbF (: Pb free) Solder
• Soldering Iron
Tip Temperature of 700 F ± 20 F (370 C ± 10 C)
Note: We recommend a 30 to 40 Watt soldering iron. An expert may be able to use a 60 to 80 Watt iron where someone with
less experience could overheat and damage the PCB foil.
•Flux
Recommended Flux: Specific Gravity 0.82.
Typ e RMA (lower residue, non-cleaning type)
Note: See About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free) (P.5)
13.2.2. How to Remove the IC
1. Put plenty of solder on the IC pins so that the pins can be completely covered.
Note:
If the IC pins are not soldered enough, you may give pressure to the P.C. board when cutting the pins with a cutter.
2. Make a few cuts into the joint (between the IC and its pins) first and then cut off the pins thoroughly.
3. While the solder melts, remove it together with the IC pins.
When you attach a new IC to the board, remove all solder left on the board with some tools like a soldering wire. If some solder is
left at the joint on the board, the new IC will not be attached properly.
62
Page 63

13.2.3. How to Install the IC
1. Temporarily fix the FLAT PACKAGE IC, soldering the two marked pins.
*Check the accuracy of the IC setting with the corresponding soldering foil.
2. Apply flux to all pins of the FLAT PACKAGE IC.
3. Solder the pins, sliding the soldering iron in the direction of the arrow.
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
13.2.4. How to Remove a Solder Bridge
1. Lightly resolder the bridged portion.
2. Remove the remaining solder along the pins using a soldering iron as shown in the figure below.
63
Page 64

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
13.3. Terminal Guide of the ICs, Transistors and Diodes
13.3.1. Base Unit
5
4
1
2
3
C0DBEYY00102
1
(Reverse View)
25
48
49
72
24
1
96
73
C1CB00003663
8
4
1
PNWI1TGE230H
PNWI2TGE230H
PNWI3TGE230H
B1ACGP000008
C
B
DSC7003S0L
E
B1ABDM000001, B1ADGE000012
B1ADNB000003, 2SC6054JSL
2SA1576S, B1GBCFYY0020
Ѝ
Ѝ
Anode
B0DDCD000001
13.3.2. Handset
(Reverse View)
88
1
22
23
C2HBCY000142
B
Cathode
67
66
45
44
E
Cathode
C
Anode
B3AAB0000347
5
8
4
1
PNWITGEA20R
B0EDER000009
4
5
6
3
2
1
C0DBZYY00357
Cathode
DY2J25000L
C
B
E
B1ADCF000040
DRC9113Z0L
2SC6054JSL
B1ADNB000003
Anode
Cathode
B0ECKM000008
B1ABGE000011
Anode
Cathode
B0BC4R3A0006
Anode
(Reverse View)
Cathode
B3ACB0000190
Anode
64
Page 65

Memo
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
65
Page 66

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Important Safety Notice:
Components identified by mark have special characteristics important for
safety. When replacing any of these components, use only the manufacture's
specified parts.
14 Schematic Diagram
14.1. For Schematic Diagram
14.1.1. Base Unit (Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Main))
Notes:
1. DC voltage measurements are taken with voltmeter from the negative voltage line.
2. The schematic diagrams may be modified at any time with the development of new technology.
14.1.2. Handset (Schematic Diagram (Handset_Main))
Notes:
1. DC voltage measurements are taken with an oscilloscope or a tester with a ground.
2. The schematic diagrams may be modified at any time with the development of new technology.
66
Page 67

14.2. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Main)
14.2.1. KX-TGE210
11
ANT1-Short
ANT1-S-GND
Shield
12
810
34
GND
NC
ANT1_TP
OJ6
GND
12
GND
SHORT SHORT
OJ5
GND
79
6
521
C851
10p
W 0.15mm
L 22+/-4mm
1st or 4th layer
C857
ANT1
GND
1
2
NC
DA802
3
NC
C855
GND
ANT2_TP
GND
C853
NC
W 0.15mm
L 22+/-4mm
1st or 4th layer
NC
ANT2
12
SHORT
OJ9
GND
CL1
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
RF
C859
10p
SL
W=0.2mm
L=20.0mm
OJ3
SHORT
open-stub
SL
W=0.6mm
L=20.0mm
SL
W=0.3mm
L=6.95mm
open-stub
SL
W=2.9mm
L=2.8mm
VBAT
GND
50 ohm line
L=4mm
50ohm Line
9g7W
L=4mm
LPF
NC
C870
SL
W=0.3mm
L=6.5mm
open-stub
SL
W=2.0mm
L=10.8mm
GND
NC
C863
open-stub
SL
W=2.2mm
L=5.0mm
open-stub
SL
W1=0.2mm
L1=3.0mm(
W2=0.7mm
L2=4.3mm
%9%k!<%[!<%k
RX-balun
MSL
W=0.175mm
L=3.6mm
S=0.125mm
-0.3mm)
SHORT
OJ4
GND
TX-balun
SL
W=0.3mm
L=39.0mm
*open-stub
$N>l9g
SLx2
W1=0.2mm
L1=3.3mm
MSL
W2=0.7mm
W=0.25mm
L2=5.0mm
L=2mm
C862
2.4p
MSL
W=0.25mm
C860
1.1p
L=2mm
MSL
W=0.25mm
L=5mm
MSL
W=0.25mm
L=5mm
OJ1
SHORT
OJ2
SHORT
RF_RXn
RF_Rx
RF_RXp
RF_TXn
RF_Tx
RF_TXp
*WBX02 NC
PARALLEL WIRE
CNT_RST
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
CNT_VDD
CNT_GND
MSG_LED
LED_VDD
KEYIN1
KEYS_D
KEYS_C
KEYS_E
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
*WBX01 NC
PARALLEL WIRE
5
1
C665
8
1
SP Phone Rx
VBAT
NC
*C661 NC
C662 NC
*C663 NC
C664 NC
VBAT
C655 NC
C654 NC
C651 NC
C652 NC
C653 NC
+3.0_CP
NC
*R661
Q651
NC
*R653
NC
NC
*SW601
12
.
R654
C657 NC
C656 NC
C658 NC
R651 1k
*RA651 NC
1
2
3
45
*R652 NC
CNT_RST
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
MSG_LED
KEYIN1
KEYIN2
8
KEYIN3
7
KEYS_C
6
KEYS_D
KEYS_E
SPP
VDD4: 3.0V
VDD5: 3.0V
CHARGE_DET
QSPI_IO3
KEYS_E
KEYIN1
QSPI_SCK
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
QSPI_IO0
KEYS_C
KEYS_D
PDN_DET
SPI_DI
QSPI_IO2
SPI_DO
SPI_CLK
QSPI_CS
TAM_CSn
QSPI_IO1
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
CKM
UTX
URX
GND
JTAG
IC901
4
3
NC
1
*CS
2
DO/IO1
3
*WP/IO2
4
GND5DI/IO0
*R478NC*R477
AK
D473 NCAKD472 NC
*C478NC*C47
VDD4
VDD5
C507 1u
NC
R961
1
OUT
VSS
2
VDD
NC
NC
NC
C964
+3.0_CP2
*IC601
8
VCC
7
*HOLD/IO3
6
CLK
NC
7
NC
+3.0_CP
1u
C509
+3.0_CP2
1u
C512
C505 0.1u
RA501
2
1
220
VBAT
NC
R958
R965
NC
NC
R956
*C601
3
4
*RA601
NC
123
44
CP_VOUT2
45
PON/P1_6
46
VDD1
47
QSPI_IO3
48
P2_7/BXTAL
49
P1_5/INT5/RDI/VDDE
50
QSPI_SCK
51
P1_4/INT4/TDOD
52
P1_3/INT3/SIO
53
QSPI_IO0
54
P1_2/INT2/SK
55
P1_1/INT1/LE
56
QSPI_VDDIO
57
P2_6/WTF_IN
58
P0_7/SPI_DI/PWM1
59
QSPI_IO2
60
P0_6/SPI_DO
61
P0_5/SPI_CLK
62
QSPI_CS
63
P0_4/SPI_EN
64
P0_3/SCL2/URX2
65
QSPI_IO1
66
67
R505 1k
VBAT
Q909
NC
Q910
NC
NC
678
NC
*R601
45
SPI_CLK
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
TAM_CSn
*C473 NC
*C472 NC
C506
2.2u
C508
1u
36
37
38
39
42
43
VDD_PA
CP_C1X40CP_C2X41CP_C1Y
CP_C2Y
CP_VBAT1
CP_VBAT2
CP_VOUT1
DP0/PAOUTn/P3_0
IC501
P2_4/SCL1/PCM_DO/DP3
P0_2/SDA2/UTX2
P0_1/URX/PWM0
68
69
RSTN
P2_3/SDA1/PCM_DI/DP2
P0_0/UTX70VDD271*RST72JTAG73P2_5/PCM_FSC/SF
74
75
C504
0.1u
C513
0.1u
EEP_WP
CAP_CHG
CAP_SW
IC611
C611
0.1u
1
A0
2
A1
3
A2
4
GND5SDA
VBAT
C501
0.1u
3.3k
R502
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
SOCn
DC_I
VBAT
DC_CTRL
DC_SENSE
CHARGE_CTRL
P1_7/CHARGE
DP1/PAOUTp/P3_1
GND
P2_2/PCM_CLK/CLK100
WLED_CUR_0
WLED_CUR_179P2_1/ECZ2/PWM1/LED4
P2_0/ECZ1/PWM0/LED3
VDD3
LDORF_CTRL
76
77
RFP0N
78
80
818283
C516
0.1u
0.1u
VBAT
C312
MSG_LED
CNT_RST
HS_SUPPLY_DET
+3.0_CP
8
VCC
7
WP
6
SCL
27
RF_SUPPLY2
84
(10)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
SPN
67
Page 68

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
VDD1: 1.8V
+1.8V
VDD1
Q301
1u
C311
+1.8V
0.1u
C517
25
26
23
24
AVD
SOCp
LDO_CTRL
ADC0/P3_3
LSRn
22
LSRp
VREFM
MICH
CIDOUT/MICn
CIDINn/MICp
VREFP
CIDINp/P3_2
RINGp/P3_7
RINGn/P3_6
PARADET/P3_4
RF_SUPPLY1
AVD_XTAL
XTAL1
XTAL2
AVS_XTAL
REF_RES
RFP0
RFP1
RF_RXp
RF_RXn
RF_TXp
RFP2
88
89
10p
RA611
3.3k
123
678
EEP_WP
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
ADC1/INT0/P1_0
RINGOUT/RINGING/P3_5
RF_SUPPLY_PA
RF_TXn
858687
C514
45
Rx
R125
270
NC
C166
VBAT
R311
NC
R170
NC
C162
RX
10k
R178
3.3k
2200p
R501 56k
R891 NC
Tx
C174
R
0
61
28
0
C164 NC
C161 10u
371C
1.0
u
TX
C109
820p
R109
82k
C511 NC
10p
25
C503
C502 1u
F
R892
NC
QSPI_CS
QSPI_IO1
QSPI_IO2
C167
1000p
4.7k
R168
8.2k
C171 0.022u
R166
C181
R110
C110 820p
X501
10p
C518
1
*CS
2
DO/IO1
3
*WP/IO2
4
GND5DI/IO0
C
E
R165 27k
461R
.2
k7
R163 39
C184
1u
NC
BELL
R111
3.9k
82k
C111
3
1
2
10.368M
ANT1
RF_RXp
RF_RXn
RF_TXp
RF_TXn
ANT2
IC502
C3FBMY000312
VCC
*HOLD/IO3
CLK
(0.5W)
Q161
8
7
6
47k
R162
B
R167 NC
D133
120k
R112
0.033u
+1.8V
QSPI_IO3
QSPI_SCK
QSPI_IO0
1C
C5190.1u
R151
100k
NC
31
u280.0
R169 NC
+1.8V
D132
100k
0.01u
C152
R152
NC
CAP_SW
CAP_CHG
25V
NC
C142 K0.01u
D142
D141
STM/P15
Caller ID
+1.8V
+1.8V
R923
R925
NC
D143
R148 NC
C115
NC
NC
R143 NC
R146 NC
Q144
NC
R147 NC
R117
150k
C116
100n
R101 5.6M
R103 180k
R102 5.6M
R104 180k
CHARGE_DET
PDN_DET
HS_SUPPLY_DET
+3.0_CP
NC
R926
R903
NC
Q906
NC
Q901
NC
R145 2.2k
100n
+1.8V
R957
C143 NC
R115 8.2M
R116 8.2M
R118
150k
C103 0.01u
C105 680p
C104 0.01u
C106 680p
10k
Q907
Q351
680
R355
Q352
R901
Vcap
C901
Q141
C
R142
Q142
R144 NC
C141 NC
+5.5V
VBAT
22k
R964
R962
Q908
R963
R952
R960
NC
R954
Power Supply
from Handset
0
NC
R906
(0.5W)
Q902
NC
R917
NC
R902
R907
1000u
Q903
NC
56k
10k
NC
B
NC
E
R141
100k
2.7k
NC
Q913
NC
NC
Q905
NC
+1.8V
R702
R918
Q702
NC
10k
R951
Q914
NC
R953
VBAT
NC
C101 680p
D101
1
2
43
C102 680p
NC
Q701
E
B
C
+1.8V
NC
R904
Q904
NC
1k
R920
R924
NC
NC
Q353
NC
R
3
VDD3
R
09
D901
NC
330u
6.3
@Doub
C342 0.1u
C341
C121 NCR120
NC
NC
R119
+5.5V
R371
R372
AK
D362
R701
NC
R919
NC
+5.5V
33k
R351
NC
C352
6.8k
R352
45
k21
VDD3: 3.0V
05
R322
NC
C902
R321
HAK_CL1
L2T
(BLACK)
L1T
NC
CHG+
C351
L1R
L2R
CHARGE+
1u
CHARGE-
(YELLOW)
(BROWN)
(RED)
DCP
DC_IN
DCM
+5.5V
21
21
C120 NC
SA102
SA101
1
P101
GAP
2
REFERENCE
1XX : TEL LINE
3XX : POWER, CHARGE
4XX : MIC, SP
5XX : BBIC
6XX : FLASH, EEPROM, KEY, LCD
7XX : FOR DK/BT
8XX : RF
9XX : BACKUP
5.5V
+5.5V
F301
3.0A
1
NC
R966
1
680
R373
C962 NC
C963 NC
IC302
3
2
IN
OUT1
4
OUT2
ADJ
100F
140F
1u
1
C321
NC: No Components
KX-TGE210/212 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (Base Unit (Main))
68
Page 69

14.2.2. KX-TGE230
ANT1_TP
OJ6
GND
12
GND
ANT1-Short
11
*WBX02 5pin
PARALLEL WIRE
CNT_RST
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
CNT_VDD
CNT_GND
MSG_LED
LED_VDD
KEYIN1
KEYS_D
KEYS_C
KEYS_E
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
*WBX01 8pin
PARALLEL WIRE
ANT1-S-GND
GND
Shield
NC
PNMC1091ZA/Z1
810
79
12
34
VBAT
5
1
C665
NC
VBAT
8
1
6
521
*C661 0.1u
C651 NC
C652 NC
*C663 1000p
C653 NC
SHORT SHORT
OJ5
GND
C662 NC
C664 NC
C656 NC
C655 NC
C654 NC
W 0.15mm
L 22+/-4mm
1st or 4th layer
C657 NC
C658 NC
C851
10p
+3.0_CP
*R661
R654
*R653
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
SP Phone Rx
CNT_RST
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
MSG_LED
KEYIN1
KEYIN2
1
8
KEYIN3
2
7
KEYS_C
3
6
KEYS_D
45
KEYS_E
RF
C859
10p
SL
W=0.2mm
L=20.0mm
CHARGE_DET
QSPI_IO3
KEYS_E
KEYIN1
QSPI_SCK
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
QSPI_IO0
KEYS_C
KEYS_D
PDN_DET
SPI_DI
QSPI_IO2
SPI_DO
SPI_CLK
QSPI_CS
TAM_CSn
QSPI_IO1
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
OJ3
SHORT
open-stub
SL
W=0.6mm
L=20.0mm
SPN
SPP
VDD4: 3.0V
VDD5: 3.0V
SL
W=0.3mm
L=6.95mm
open-stub
SL
W=2.9mm
L=2.8mm
VBAT
GND
50 ohm line
L=4mm
50ohm Line
9g7W
L=4mm
open-stub
SL
W=2.0mm
L=10.8mm
LPF
NC
C870
CKM
UTX
URX
GND
JTAG
4
3
1
*CS
2
DO/IO1
3
*WP/IO2
4
GND5DI/IO0
NC
GND
SL
W=0.3mm
L=6.5mm
AK
D473 NCAKD472 NC
VDD5
IC901
1
OUT
VSS
2
VDD
NC
NC
8M FLASH
*IC601
*HOLD/IO3
open-stub
SL
W1=0.2mm
L1=3.0mm(
W2=0.7mm
C863
L2=4.3mm
open-stub
SL
W=2.2mm
L=5.0mm
*R4781*R477
2200p
*C478
+3.0_CP
VDD4
+3.0_CP2
C507 1u
NC
R961
NC
C964
+3.0_CP2
8
VCC
7
6
CLK
%9%k!<%[!<%k
1
*C4772200p
1u
C509
1u
C512
C505 0.1u
RA501
2
1
220
VBAT
NC
R958
R965
NC
NC
R956
*C601
3
4
0.1u
RX-balun
MSL
W=0.175mm
L=3.6mm
S=0.125mm
OJ4
GND
TX-balun
SL
W=0.3mm
L=39.0mm
VBAT
*RA601
123
*open-stub
SLx2
W1=0.2mm
L1=3.3mm
W2=0.7mm
L2=5.0mm
-0.3mm)
OJ1
SHORT
SHORT
OJ2
SHORT
44
CP_VOUT1
CP_VOUT2
45
PON/P1_6
46
VDD1
47
QSPI_IO3
48
P2_7/BXTAL
49
P1_5/INT5/RDI/VDDE
50
QSPI_SCK
51
P1_4/INT4/TDOD
52
P1_3/INT3/SIO
53
QSPI_IO0
54
P1_2/INT2/SK
55
P1_1/INT1/LE
56
QSPI_VDDIO
57
P2_6/WTF_IN
58
P0_7/SPI_DI/PWM1
59
QSPI_IO2
60
P0_6/SPI_DO
61
P0_5/SPI_CLK
62
QSPI_CS
63
P0_4/SPI_EN
64
P0_3/SCL2/URX2
65
QSPI_IO1
66
P0_2/SDA2/UTX2
67
R505 1k
Q909
NC
Q910
NC
560
678
3.3k
*R601
45
SPI_CLK
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
TAM_CSn
$N>l9g
MSL
W=0.25mm
L=2mm
C862
2.4p
C860
1.1p
C508
1u
42
43
CP_C2Y
P0_1/URX/PWM0
68
69
RF_Rx
MSL
W=0.25mm
L=2mm
MSL
W=0.25mm
L=5mm
RF_Tx
MSL
W=0.25mm
L=5mm
*C473 10p
*C472 10p
C506
2.2u
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
VDD_PA
CP_C1X
CP_C2X
CP_C1Y
CP_VBAT1
CP_VBAT2
DP1/PAOUTp/P3_1
DP0/PAOUTn/P3_0
IC501
C1CB00004121
P2_2/PCM_CLK/CLK100
P2_4/SCL1/PCM_DO/DP3
C504
0.1u
P2_3/SDA1/PCM_DI/DP2
76
74
75
P0_0/UTX70VDD271*RST72JTAG73P2_5/PCM_FSC/SF
RSTN
C513
0.1u
EEP_WP
CAP_CHG
CAP_SW
HS_SUPPLY_DET
IC611
128K EEPROM
C611
0.1u
1
A0
2
A1
3
A2
4
GND SDA
RF_RXn
RF_RXp
RF_TXn
RF_TXp
VBAT
3.3k
R502
32
33
34
31
VBAT
DC_CTRL
CHARGE_CTRL
P1_7/CHARGE
GND
WLED_CUR_0
WLED_CUR_1
P2_1/ECZ2/PWM1/LED4
P2_0/ECZ1/PWM0/LED3
77
78
79
80
MSG_LED
CNT_RST
(5)
VCC
(6)
WP
SCL
(7)
(8)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
ANT2_TP
CL1
12
GND
C853
NC
W 0.15mm
L 22+/-4mm
1st or 4th layer
NC
C855
ANT2
GND
GND
SHORT
OJ9
ANT1
GND
C857
1
2
NC
DA802
3
NC
10k
Q651
NC
NC
0
R651 1k
*RA651 1k
*R652 1k
*SW601
12
NC
69
Page 70

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
C501
0.1u
26
27
29
30
SOCp28SOCn
DC_I
DC_SENSE
ADC1/INT0/P1_0
RINGOUT/RINGING/P3_5
VDD382LDORF_CTRL
RFP0N84RF_SUPPLY2
RF_SUPPLY_PA
81
83
85
C516
0.1u
C514
VBAT
0.1u
C312
+3.0_CP
45
678
8
7
6
5
VDD1: 1.8V
+1.8V
VDD1
1u
C311
+1.8V
C517
25
23
24
AVD
LDO_CTRL
ADC0/P3_3
LSRn
LSRp
VREFM
MICH
CIDOUT/MICn
CIDINn/MICp
VREFP
CIDINp/P3_2
RINGp/P3_7
RINGn/P3_6
PARADET/P3_4
RF_SUPPLY1
AVD_XTAL
XTAL1
XTAL2
AVS_XTAL
REF_RES
RFP0
RFP1
RF_RXp
RF_RXn
RF_TXn87RF_TXp
RFP2
86
88
89
10p
RA611
3.3k
123
EEP_WP
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
Q301
B1ADGE000012
0.1u
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Rx
R125
270
NC
C166
VBAT
R311
NC
R170
C162
RX
10k
R178
3.3k
R501 56k
R891 NC
NC
Tx
C174
2200p
R
06
1
28
0
C164 NC
C161 10u
371C
.0
1
u
TX
C109
820p
R109
82k
C511 NC
10p
C503
C502 1u
F
R892
NC
QSPI_CS
QSPI_IO1
QSPI_IO2
C167
1000p
4.7k
R168
8.2k
C171 0.022u
R166
C184
NC
C181
R110
C110 820p
3
X501
10.368M
H0J103500037
8
10p
C3FBMY000312
C51
1
*CS
2
DO/IO1
3
*WP/IO2
4
GND5DI/IO0
R165 27k
461R
.2
1u
R111
82k
1
2
ANT1
RF_RXp
RF_RXn
RF_TXp
RF_TXn
ANT2
IC502
*HOLD/IO3
k7
BELL
3.9k
VCC
CLK
C
E
39
(0.5W)
R163
C111
Q161
B
R167 NC
0.033u
+1.8V
8
QSPI_IO3
7
6
R162 47k
D133
2
120k
R11
1C
31
80.0
C5190.1u
QSPI_SCK
QSPI_IO0
R151
100k
NC
u2
9NC
R16
+1.8V
D132
100k
R152
NC
CAP_SW
CAP_CHG
0.01u
C152
NC
C142 K0.01u
D141
STM/P15
Caller ID
25V
D142
+1.8V
R923
+1.8V
R925
NC
D143
R148 NC
C115
NC
NC
(3216)
(3216)
R143 NC
R146 NC
Q144
NC
R147 NC
R117
150k
C116
100n
R101 5.6M
R103 180k
R102 5.6M
R104 180k
CHARGE_DET
PDN_DET
HS_SUPPLY_DET
+3.0_CP
NC
R926
R903
NC
Q906
NC
100n
Q901
NC
R145 2.2k
+1.8V
R957
C143 NC
R115 8.2M
R116 8.2M
R118
150k
C103 0.01u
C105 680p
C104 0.01u
C106 680p
10k
Q907
.
Q351
680
R355
Q352
.
R901
Vcap
C901
Q141
C
R142
Q142
R144 NC
C141 NC
VBAT
+5.5V
22k
R964
56k
R962
Q908
10k
.
R963
.
R952
R960
NC
R954
Power Supply
from Handset
0
NC
R906
(0.5W)
Q902
NC
R917
NC
R902
u
R907
1000
Q903
NC
E
2SA1972
B
R141
100k
(3216)
2.7k
NC
Q913
NC
NC
+1.8V
R702
NC
R918
Q702
NC
10k
R951
R953
NC
C101 680p
D101
1
2
43
C102 680p
E
C
+1.8V
NC
R904
Q904
NC
1k
R920
R924
NC
NC
Q353
Q914
NC
NC
VDD3
VBAT
R
09
D901
330u
6.3
@Doub
C342 0.1u
C341
NC
Q701
R701
B
NC
R919
NC
+5.5V
33k
.
R351
6.8k
R352
R
45
3
21
k
VDD3: 3.0V
05
NC
C902
21
C121 NCR120
R119
NC
NC
+5.5V
R371
R372
AK
D362
21
C120 NC
J0LE00000047
J0LY00000063
NC
.
SA102
SA101
1
P101
D4DAY220A022
GAP
2
REFERENCE
1XX : TEL LINE
3XX : POWER, CHARGE
4XX : MIC, SP
5XX : BBIC
6XX : FLASH, EEPROM, KEY, LCD
7XX : FOR DK/BT
8XX : RF
9XX : BACKUP
5.5V
+5.5V
F301
3.0A
1
NC
R966
1
680
R373
CHG+
C351
C962 NC
C963 NC
NC
C352
IC302
C0DBEYY00102
3
2
IN
OUT1
4
OUT2
ADJ
100F
R322
NC
R321
1
140F
L2T
L1T
L1R
L2R
CHARGE+
1u
CHARGE-
1u
C321
(BLACK)
(YELLOW)
(BROWN)
(RED)
DCP
DC_IN
DCM
+5.5V
NC
Q905
NC
HAK_CL1
KX-TGE232/233/234 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (Base Unit (Main))
70
Page 71

14.3. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Operation)
14.3.1. KX-TGE230
8
HS_LED
CELL1_LED
CELL2_LED
CNT_RST
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
CNT_VDD
CNT_GND
*LED906
*LED904
*LED905
1
GREEN
AK
GREEN
AK
GREEN
AK
C901
NC
NC
R901
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
DA901
1
*RESET
2
SDA
3
VDD
SCL
GND
5
4
MSG_LED
LED_VDD
KEYIN1
KEYS_D
KEYS_C
KEYS_E
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
8
1
LED901
KEYIN1
KEYS_D
KEYS_C
KEYS_E
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
AK
RED
SW903
2
1
3
4
ERASE
SW905
1
2
3
4
RPT
CELL_LOCAT
12
SW901
2
1
3
4
UP
SW906
1
2
3
4
PLAY/STOP
SW902
1
2
3
4
SW907
2
1
3
4
ANS
SW904
1
2
3
4
SKIP
HS_LOCAT
12
DOWN
KX-TGE232/233/234 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (Base Unit_Operation)
71
Page 72

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Memo
72
Page 73

14.4. Schematic Diagram (Handset_Main)
* Start Monitor
* When "SFR" command
is executed, 13.824MHz
frequency will be output.
1.2V
3.0V
NC: No Components
STB_D
KIN_4
CHG_CUR
STB_CSTB_C
EEP_WP
EEP_SCL
EEP_SDA
EEP_WP
STB_D
LCD_RESET
LCD_SID
LCD_SCL
LCD_CS
LCD_CD
KIN_1
KIN_2
KIN_3
KIN_4
STB_A
STB_B
URX
UTX
STB_C
NR_LED
KEY_LED
CHG_CTRL
CHG_DET
UTX
URX
CHG_CUR
KIN_2
HEADSET_DET
KIN_3
STB_B
KIN_1
STB_ASTB_A
CP_OFF
EEP_SDA
EEP_SCL
LCD_CS
LCD_RESET
LCD_CD
LCD_SCL
LCD_SID
BELL_LED
BELL_LED
KEY_LED
NR_LED
CHG_DET
STB_E
KIN_5
CP_OFF
KIN_5
STB_E
VBAT
GND
C35
NC
GND
GND
GND
C43
K0.1u
GND
C41
k0.1u
C5
K0.1u
GND
VDDC
GND
GND
GND
GND
VDDC
CP3V
C40
k0.1u
GND
R24
10
C44
K1u
GND
R4
47k
C45
K0.1u
VBAT
RA2
330
CP3V
CP3V
CP3V
GND
C69
0.1u
CKM/STM
3.0V
R3
1.5k
GND
GND
R7
100k
C46 10p
C31
10u
C51
10u
C15
39p
L3
F1
2.5A
RA5
3.3k
CP4V
IC4
1
VOUT
2
GND
4
CN
5
VCC
3
SHD
6
CP
C58
1u
CP3V
C1
NC
C32 1u
GND
C34
39p
Q2
C27
1000p
Q3
R9
30k
R2
30k
Q4
R6
10k
C56
1u
C57
1u
C33
0.1u
VBG/CHG_MON
CP4V
GND
C90
K0.1u
GND
C79
100p
GND
CHG+
VBAT
LED5
LED4
LED2
LED1
LED3
LED6
Q6
Q9
*R12
18k
*R11
680
*R10 1.0
*R13
10k
*Q12
GND GND
*Q11
*Q10
Battery_ON
CHG+
Battery_ON
C30
1u
C29
1u
TCK
TDO
TDI
GND_J
TMS
GND
UTX
GND
URX
VBAT
BAT-
BAT+
VBAT
C10
NC
RA3
330
CHG_CTRL
RTCK
ATSTN
ATSTP
CD
CHG_CUR
CHG_DET
CS
RESET
RSTN
SCL
SID
C2
22u
GND
C3
22u
R72
0
R71
NC
CP4V
CHG+
R8
4.3
R45
0.1
(1608)
CN3_C
3
CS
CN3_C
8
VDD
CN3_C
10
VSS
CN3_C
9
VDD
C93 1u
CN3_C
2
GND(OTP)
CN3_C
6
SCLK
CP3V
CN3_C
14
GND
CN3_C
7
SDA
CN3_C
12
XV0
CN3_C
4
RST
C92 K1u
CN3_C
15
GND
CN3_C
5
A0
CN3_C
1
GND
CN3_C
11
V0
GND
C91 1u
CN3_C
13
VG
VOL_UP
RE2
VOL_DW
RE2
2
SOFT_C
8
AST
5
SP
7
DOWN
SOFT_A
UP
FLASH
639
RIGHT
4
LEFT
TALK
1
0
SHARP
OFF
NR
C81
100p
GNDQ5GND
LED12
LED11
CP3V
Q7
NC
GND
R73
NC
R55
NC
LED13
CP3V
GND
Q8
CP4V
C78
100p
R56
0
GND
RA1
10k
LED20
*Q13
NC
VBAT
*R17
NC
*R16
NC
*R18
NC
*C19 NC
*D30
NC
CP3V
R20
30k
R21
10k
R70
47
R54
220
C6
68p
*IC1
3
GPIO[22]4GPIO[23]5GPIO[24]6GPIO[25]7GPIO[26]8VDDC29COREOUT10VBAT11DOUBCAPN1
49
TRSW_p
50
ANT_n
51
ATST_n
52
ATST_p
53
TEST
54
RSTN
55
NC
76
VDDIO1
77
GPIO[9]
78
GPIO[10]
79
GPIO[11]
80
GPIO[12]
81
GPIO[13]
82
GPIO[14]
83
GPIO[15]
84
GPIO[16]
1
GPIO[20]2GPIO[21]
12
DOUBCAPN13DOUBCAPP14DOUBCAPP1
56
VCC_VCO
57
GPIO[27]
58
VDDUSB
74
GPIO[7]
75
GPIO[8]
85
GPIO[17]
86
VDDIO2
87
GPIO[18]
15
DOUBOUT
59
DM_USB/GPI28
88
GPIO[19]
89
GND
16
DCIN0/LIN017DCIN1
18
DCIN2
60
DP_USB/GPI29
61
VDDC1
62
JTAG_TDO
63
JTAG_TDI
64
JTAG_TCK
65
JTAG_TMS
66
JTAG_RTCK
67
GPIO[0]/SCL_IIC
68
GPIO[1]/SDA_IIC
69
GPIO[2]
70
GPIO[3]
71
GPIO[4]
72
GPIO[5]
73
GPIO[6]
R51
220
R50
220
IC3
1
A0
2
A1
6
SCL
7
WP
3
A2
8
VCC
4
VSS
5
SDA
Battery
KEY BACKLIGHT
FLASH:1.8V / ROM:1.2V
(AMBER)
CHARGE
Terminal
LCD BACKLIGHT
(WHITE)
B/W LCD Unit
BELL LED
(AMBER) (AMBER)
NR LED
(POWER)
CHG-
Charge Current
!
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
When on Charge
1s
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
73
Page 74

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
(1)
(2)
TO RF BLOCK
TXn
TXp
RXp
RXn
(3)
(4)
47
48
RXn
GND_RF
DCIN3/LIN1
VREF
192021
VBAT_MON
R33
R31
C36
0.1u
45
TXp46RXp
VBAT_APU
HSSPOUTP
VCCA
MIN
22
C21 1u
GNDA
VBAT
100k
100k
GND
TRSW_n
VCC_FE
VDD_IF
VCC_IF
VDD_APU
XOUT
DCINS
PWM0
PWM1
SPOUTP
VCCPA
SPOUTN
LOUT
MPWR
HSMIP
HSMIN
C20 10u
SHORT1
SHORT
C806
Pre-matching
+
-
+
-
1
2
3
4
5
NC
RF BLOCK
MSL
W=0.25
L=2mm
1p
MSL
W=0.25
L=2mm
SP-PHONE_SPEAKER
RECEIVER
CN4
Headset Jack
SHORT2
SHORT
GNDA1
GNDA
RXn
RXp
TXp
TXn
ANT-Pattern
ANT-Short
STAR8
GND
ANT1
ANT-Short-GND
GND
44
TXn
43
C22
42
ANT
0.1u
C25
41
K2.2u
40
39
C26
38
37
10u
36
XIN
C24
35
1u
GND
K0.1u
C68
1u
GNDA
R26
C80
GNDA
CHG_CTRL
3.3k
0.039u
GND
CHG_DET
C88 NC
C89 NC
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
MIP
10p
C17
10p
C18
GNDA
RA4
3.3k
C11
C13
K0.1u
C96
10p
GNDA
HEADSET_DET
R32
GND
C52
X1
D10p
GND
C53
12p
GND
R22
3.3k
C98NCC99
R23
390
GND
NC
MIC POWER
C97
10p
100k
MSL L=11mm,W=0.2mm
Speakerphone_SP+
Speakerphone_SP-
C14
0.039u
R25
R27
C12
10u
R28
R34
GNDA
D=3mm
2.2k
2.2k
MIC+
MIC-
2.2k
0
C37
GNDA
D=3mm
10u
RECEIVERRECEIVER+
MIC+
MIC-
MSL
W=0.3mm
L=12.0mm
open-stub
SL
W=4.0mm
L=4.5mm
C16 22u
NC
C39
GNDA
Handset Tx
SP Phone Tx
VBAT
GND
SL
W=0.2mm
L=20mm
C807
STAR5
3p
R81
NC
1.5p
C802
open-stub
SL
W=0.6mm
L=20mm
SPM
Headset_RECEIVER
MSL
Wm=0.4mm
Lm=10mm
SL
W=0.3mm
L=5.0mm
SPP
GNDA GNDA
C85
MIC
C801
2p
L801
2.7n
GND
open-stub
SL
W=4.0mm
L=3.5mm
STAR9
GND
Tx-balun
SL
W=0.3
L=40mm
STAR7
SL
W=0.3mm
L=4.5mm
SL
W=0.3mm
L=4.5mm
open-stub
SL
W=2.0mm
L=2.25mm
SP Phone Rx
D13
NC
NC
D14
C72
C73
GNDGND
GND
GND
C42
NC
Handset Rx
C71
68p
C70
68p
GNDGND
R80
1000p
GNDA1
10
C86
C84
1000p
GND
GNDGND
NC
NC
C83
C82
AP1
*RF-SHIELD
74
HAK_CL1
NC
GND
NC: No Components
KX-TGEA20 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (Handset_Main)
Page 75

Memo
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
75
Page 76

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
IC302
IC601
MSG_LED
R601
P101
KEYS_D
KEYS_E
C601
RA501
SA101
SA102
R651
R652
R653
R654
I2C_SCL
R661
Q301
C651 C652
C653
C654
C655
C656C657
C658
C851
C853
C855
R892
C859
Q701
C472
Q702
C473
C860
C863
CNT_RST
Q908
LED_VDD
Q141
Q142
KEYIN1
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
R101
Q161
R102
R103
R104
I2C_SDA
R109
R110
R111
R112
R501
R119
R502
R311
R505
R120
R701
R702
CNT_GND
R321
R905
C101
C102
C103
C104
C105
R141
C106
R142
R144
C109
R145
C110
C111
C113
Shield
C501
C502
C503
C504
C505
C311
C506
C312
C507
C508
C120
C509
C121
R160
R162
R164
RA601
X501
R165
C512
R166
C513
R168
C514
C321
R169
C516
C517
HAK_CL1
C902
DA802
R170
C141
C142
C143
C862
C342
R962
R963
R964
C352
C161
D101
C162
C164
C166
C167
C171
C173
RA651
CL1
C181
C184
D901
D141
D142
D143
CNT_VDD
SW601
Q651
C341
C665
R322
KX-TGE2xx SerieK X - T G E 2 xx S e r i e s
PUR
GRY
-
+
PNLB2278Z
BLU
-
ORG
+
YLW
BRN
PbF
A
KEYS_C
IC501
15 Printed Circuit Board
15.1. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main)
15.1.1. Component View
KX-TGE210/212/232/233/234
CIRCUIT BOARD (Base Unit_Main (Component View))
76
Page 77

15.1.2. Bottom View
P N L B 2 2 7 8 Z
ANT1-Short
ANT_1
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
ANT
GND
ANT1_TP
ORG
SPP
SPN
BLU
ANT1-S-GND
D473
C478
R478
+
C477
R477
D472
-
ANT2_TP
PNLB2278Z
RA611
R167
C857
PbF
C611
R163
R151
R152
R891
C663
R178
C174
C662
IC611
R117
C116
D133
R125
C152
C511
Q906
Q905
C901
C664
C661
R147
R118
C115
D132
C518
STM/P15
JTAG
C870
R961
IC901
R926
R90
R923
R907
R116
Q144
R148
R953
VDD4
C519
R965
C964
3
R925
Q903
R115
VDD1
IC502
RSTN
R956
VDD3
Q901
R902
R917
Q914
Q913
R924
Q910
Q909
R958
R901
R143
R146
R951
R355
R952
Q904
R904
UTX
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
BRN/RED
YLW/BLK
L1R
L1T
GAP
-
Frequency Counter (*1)
Send command "SFR", then
the frequency output on this TP.
Oscilloscope (*2)
CKM
PC
UART JIG
UTX
VDD5
VDD3
DC
5.5V
Q351
R954
R354
R919
R920
CKM
VDD5
Q902
R918
Vcap
Q352
R960
Q353
R352
R351
R372
R957
URX
R906
CHARGE-
C351
D362
Q907
GND
R966
F301
+
C962
C963
R373
R371
+5.5V
-
DCP
+
CHARGE+
VDD1
VDD4
GND URX
DCM
GRY
PUR
STM/CKM/P15
A
KX-TGE210/212/232/233/234
CIRCUIT BOARD (Base Unit_Main (Bottom View))
77
Page 78

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
A
SW907
SW906
SW905
LED901
CT1
CT2
C A R B O N _ T E S T
SW904
SW903
DA901
R901
C901
SW902
HS_LOCAT
CELL_LOCAT
MSG_LED
LED_VDD
KEYIN1
KEYS_D
KEYS_C
KEYS_E
KEYIN2
KEYIN3
CNT_RST
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
CNT_VDD
CNT_GND
SW901
PNLB2286Z
PbF
15.2. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Operation)
15.2.1. KX-TGE230
KX-TGE232/233/234
CIRCUIT BOARD (Base Unit_Operation (Component View))
78
Page 79

Memo
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
79
Page 80

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
C20
C21
C22
C24
C25
C26
C27
C29
RESET
C30
C31
C32
C33
C34
C35
C36
C37
RTCK
3.0V
C40
C41
C42
C43
C44
ANT-Short-GND
C4
5
C46
RSTN
CHG+
GND_J
C51
C52
C53
C56
C57
C58
Q10
Q11
Q12
C68
C69
ATSTN
ATSTP
C70
C71
RA2
C72
RA3
C73
RA4
C801
RA5
C802
C79
C806
C80
C82
C83
C84
ANT1
C85
C88
SPM
C89
SPP
VBG/CHG_MON
C90
C91
C92
C96
C97
C98
C99
C1
C2
C3
C5
C6
CD
TCK
CS
URX
TDI
F1
TD
O
RECEIVER
UTX
R
E
K
A
EP
S
_
E
NO
H
P
-
P
S
MIC+
MIC-
D13
D14
L3
VBAT
IC1
IC3
CHG_CTRL
IC4
TMS
R10
R11
R12
R13
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
R25
R26
Q2
R27
Q3
R28
Q4
Q6
Q9
R31
R32
R33
R34
R2
R3
BAT+
R4
CKM/STM
BAT-
R6
R7
R8
R9
R45
SCL
R70
R71
R72
VBAT_MON
R80
R81
L801
CN4
CHG_CUR
CHG_DET
X1
SID
C10
C11
C12
C13
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
GND
C78
Q8
R54
Q13
R16
R55
R56
R18
C19
D30
W
D
_LOV
P
U
_
LOV
C93
Q7
R73
C81
Q5
R50
R51
21DEL11DEL
RA1
C39
C86
ANT-Short
C807
CKM/STM
(CLK:13.824MHz)
TP (3.0V)
CHG (+)
SP-
MIC+
MIC-
SP+
UTX
URX
VBAT
GND
for signal communication jig
CHG-
CHG (-)
A
PNLB2282Z
Blue
Orange
PbF
VDDC (1.2V)
15.3. Circuit Board (Handset_Main)
15.3.1. Component View
KX-TGEA20 CIRCUIT BOARD (Handset_Main (Component View))
80
Page 81

15.3.2. Bottom View
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
LED20
CN3_C
SOFT_A
UP
T
A
L
K
LEFT
1
4
LED2 LED3
7
DOWN
2
5
8
RIGHT
LED4LED5
SOFT_C
OFF
3
6
9
AST
LED
SHARP
1
LED13
NR
0
LED6
SP
FLASH
MIC
KX-TGEA20 CIRCUIT BOARD (Handset_Main (Bottom View))
81
Page 82

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
16 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List
16.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Base Unit)
16.1.1. KX-TGE210
10
1
3
A
4
6
2
5
PCB1
A
7
8
Ref.No. Figure
A
2.6 x 8mm
9
11
A
82
Page 83

16.1.2. KX-TGE230
Ref.No. Figure
A
2.6 x 8mm
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
PCB1
PCB2
A
15
16
17
A
A
A
18
19
A
20
21
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
83
Page 84

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
16.2. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Handset)
CUSHION RUBBER
*STICK IT WITH IN THE FRAME WORK ON P. C.B.
Note:
101
102
110
104
103
111
112
105
106
113
107
109
E104
E105
108
116
E106
PCB 100
E107
E108
MIC 100
122
E101
E102
E103
123
B
117
Ref.No.
B
118
106
115
114
B
Figure
119
2 8 mm
(*2)
(*1) This cable is fixed by heat-sealing. Refer to How to Replace the Handset LCD (P.51).
(*2) The rechargeable Ni-MH battery HHR-4DPA is available through sales route of Panasonic.
(*3) Attach the SPACER (No. 120) to the exact location described above.
84
120
Battery cover
Spacer (No.118)
Stick it between
ribs.
Put it in the center.
121
Page 85

16.3. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Charger Unit)
200
200-1
200-5
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
200-2
200-3
200-4
201
85
Page 86

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
A
16.4. Accessories and Packing Materials
16.4.1. KX-TGE210B
A1
A3
A2
4
P2
A5, A6, A7
P1
86
Page 87

16.4.2. KX-TGE212B
A
A102
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
A103
A101
104
P102
P102
A105, A106, A107
P101
87
Page 88

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
A
16.4.3. KX-TGE232B
A203
A202
P202
204
P202
A205, A206, A207
P201
A201
P202
88
Page 89

16.4.4. KX-TGE233B
A305, A306, A307
A302
A301
A303
P301
P302
P302
P302
P302
P302
A304
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
89
Page 90

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
A401
A402
A403
A404
A405, A406, A407
P401
P402
P402
P402
P402
16.4.5. KX-TGE234B
90
Page 91

16.5. Replacement Parts List
Type
ERC:Solid
ERDS:Carbon
ERJ:Chip
ERX:Metal Film
ERG:Metal Oxide
ER0:Metal Film
PQ4R:Chip
ERS:Fusible Resistor
ERF:Cement Resistor
Type
ECFD:Semi-Conductor
ECQS:Styrol
ECUV,PQCUV, ECUE:Chip
ECQMS:Mica
ECCD,ECKD,ECBT,F1K,ECUV:Ceramic
ECQE,ECQV,ECQG:Polyester
ECEA,ECST,EEE:Electlytic
ECQP:Polypropylene
Wattage
*Type & Voltage Of Capacitor
10,16:1/8W 14,25:1/4W 12:1/2W 1:1W 2:2W 3:3W
Voltage
ECQ Type ECQG
ECQV Type
05:50V
1:100V
2:200V
ECSZ Type
0J :6.3V
1A :10V
1C :16V
1E,25:25V
1V :35V
50,1H:50V
1J :16V
2A :100V
0F:3.15V
1A:10V
1V:35V
0J:6.3V
Others
1H:50V
2A:100V
2E:250V
2H:500V
1. RTL (Retention Time Limited)
Note:
The “RTL” marking indicates that its Retention Time is
Limited.
When production is discontinued, this item will
continue to be available only for a specific period of
time.
This period of time depends on the type of item, and
the local laws governing parts and product retention.
At the end of this period, the item will no longer be
available.
2. Important safety notice
Components identified by the mark indicates special
characteristics important for safety. When replacing any
of these components, only use specified manufacture's
parts.
3. The S mark means the part is one of some identical parts.
For that reason, it may be different from the installed part.
4. ISO code (Example: ABS-94HB) of the remarks column
shows quality of the material and a flame resisting grade
about plastics.
5. RESISTORS & CAPACITORS
Unless otherwise specified;
All resistors are in ohms () k=1000, M=1000k
All capacitors are in MICRO FARADS (F) p=F
*Type & Wattage of Resistor
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Safety Ref.
No.
8 PNKF1315X2 CABINET COVER PS-HB
9 PNHA1032Z RUBBER PARTS, FOOT
10 PNYM1065Z2 CABINET COVER ASS’Y
11 PNGT7986Z NAME PLATE
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
CUSHION
(for KX-TGE210B)(for
KX-TGE212B)
16.5.1.1.2. KX-TGE230B
Safety Ref.
1 PNGP1316Y2 PANEL, UPPER (for KX-
No.
3 PNMH1304Z HOLDER, SPEAKER POM-HB
4 L0AA02A00087 SPEAKER
5 PNKE1310Z2 CASE, CHARGE TERMINAL PS-HB
6 PNJT1176Z CHARGE TERMINAL
7 PNBC1523Z1 BUTTON, ANSWER
8 PNBC1524Z1 BUTTON, PLAY
9 PNJK1209Y KEYBOARD SWITCH, TAM
15 PNHR1919Z GUIDE, JACK (for KX-
16 PQJJ1T039L JACK, MODULAR
17 K2ECYZ000002 JACK, DC (for KX-
18 PNKF1315X2 CABINET COVER (for KX-
19 PNHA1032Z RUBBER PARTS, FOOT
20 PNYM1060Y2 CABINET COVER ASS’Y (for
21 PNGT7995Z NAME PLATE (for KX-
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KX-TGE234B)
TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KX-TGE234B)
TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KX-TGE234B)
TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KX-TGE234B)
CUSHION
KX-TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KX-TGE234B)
TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KX-TGE234B)
PC-HB
PS-HB
PS-HB
PS-HB
16.5.1. Base Unit
16.5.1.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts
16.5.1.1.1. KX-TGE210B
Safety Ref.
No.
1 PNKM1526Z1 CABINET BODY (for KX-
2 PNBC1531Z1 BUTTON, LOCATOR (for
3 PNKE1310Z2 CASE, CHARGE TERMINAL PS-HB
4 PNJT1176Z CHARGE TERMINAL
5 PNHR1919Z HOLDER, JACK
6 PQJJ1T039L JACK, MODULAR
7 K2ECYZ000002 JACK, DC PS-HB
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
TGE210B)
(for KX-TGE212B)
KX-TGE210B)
(for KX-TGE212B)
PS-HB
ABS-HB
16.5.1.2. Main P.C. Board Parts
Note:
(*1) When replacing IC501, IC611 or X501, make the
adjustment using PNZZTGE230B. Refer to How to
download the data (P.58) of Things to Do after Replacing
IC or X'tal.
(*2) When replacing IC501 or IC721, refer to How to
Replace the LLP (Leadless Leadframe Package) IC
(P.60).
16.5.1.2.1. KX-TGE210B
Safety Ref.
No.
PCB1 PNWP1TGE210H MAIN P.C.BOARD ASS'Y
(ICs)
IC302 C0DBEYY00102 IC
IC501 C1CB00004121 IC (*1)(*2)
IC502 PNWI2TGE230H IC(FLASH) (*1)
IC611 PNWI1TGE210H IC(EEPROM)(*1)(for KX-
(TRANSISTORS)
Q141 2SA1776P TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q142 B1ABDM000001 TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q161 DSC7003S0L TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q301 B1ADGE000012 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q351 B1ADNB000003 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q352 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q353 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q907 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
91
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
(RTL) (for KX-TGE210B)
(for KX-TGE212B)
TGE210B)(for KXTGE212B)
Page 92

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Safety Ref.
Q908 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
(DIODES)
D101 B0EDER000009 DIODE(SI) S
D142 DY2J25000L TRANSISTOR(SI)
D362 B0ECKM000008 DIODE(SI)
(RESISTOR ARRAYS)
RA501 EXB24V221JX RESISTOR ARRAY
RA611 EXB28V332JX RESISTOR ARRAY
(VARISTOR)
SA101 J0LE00000047 VARISTOR (SURGE
(RESISTORS)
R101 ERJ3GEYJ565 5.6M S
R102 ERJ3GEYJ565 5.6M S
R103 PQ4R10XJ184 180k S
R104 PQ4R10XJ184 180k S
R109 ERJ2GEJ823 82k S
R110 ERJ2GEJ823 82k S
R111 ERJ2GEJ392 3.9k S
R112 ERJ2GEJ124 120k S
R115 ERJ3GEYJ825 8.2M S
R116 ERJ3GEYJ825 8.2M S
R117 ERJ3GEYJ154 150k S
R118 ERJ3GEYJ154 150k S
R125 ERJ2GEJ271 270 S
R141 ERJ3GEYJ104 100k S
R142 PQ4R18XJ272 2.7k S
R145 ERJ2GEJ222 2.2k S
R151 ERJ2GEJ104 100k S
R152 ERJ2GEJ104 100k S
R160 ERJ3GEYJ821 820 S
R162 ERJ2GEJ473 47k S
R163 D0GG390JA007 39
R164 ERJ2GEJ272 2.7k S
R165 ERJ3GEYJ273 27k S
R166 ERJ3GEYJ822 8.2k S
R168 ERJ2GEJ472X 4.7k S
R178 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R311 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R321 ERJ2RKF1400 140 S
R322 ERJ2RKF1000 100 S
R351 ERJ2GEJ333 33k S
R352 ERJ2GEJ682 6.8k S
R354 ERJ2GEJ123 12k S
R355 ERJ2GEJ681 680 S
R371 ERJ8GEYJ1R0 1 S
R372 ERJ8GEYJ1R0 1 S
R373 ERJ2GEJ681 680 S
R501 ERJ2RKF5602 56k
R502 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R505 ERJ2GEJ102 1k S
R651 ERJ2GEJ102 1k S
R702 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R901 ERJ2GE0R00 S
R905 ERJ3GEY0R00 S
R924 ERJ2GEJ102 S
R957 ERJ2GEJ103 S
R962 ERJ2GEJ563 S
R963 ERJ2GEJ103 S
R964 ERJ2GEJ223 S
(CAPACITORS)
C101 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C102 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C103 ECUV1H103KBV 0.01
C104 ECUV1H103KBV 0.01
C105 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C106 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C109 ECUE1H821KBQ 820p
C110 ECUE1H821KBQ 820p
C111 ECUE1A333KBQ 0.033
C113 ECUE1A823KBQ 0.082
C115 ECUV1C104KBV 0.1
C116 ECUV1C104KBV 0.1
No.
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
ABSORBER)
Safety Ref.
C142 ECUV1H103KBV 0.01
C152 ECUE1C103KBQ 0.01
C161 F1K1E1060001 10
C167 ECUV1H102KBV 0.001
C171 ECUV1C223KBV 0.022
C173 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C174 ECUE1H222KBQ 0.0022
C184 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C311 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C312 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C321 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C341 F2G0J331A146 330
C342 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C351 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C501 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C502 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C503 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C504 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C505 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C506 ECUV0J225KBV 2.2
C507 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C508 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C509 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C512 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C513 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C514 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C516 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C517 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C518 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C519 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C611 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C851 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C859 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C860 F1G1H1R1A765 CERAMIC CAPACITOR
C862 F1G1H2R4A765 CERAMIC CAPACITOR
C901 F2A1A102B641 ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITOR
(OTHERS)
P101 D4DAY220A022 THERMISTOR
X501 H0J103500037 CRYSTALOSCILLATOR (*1)
No.
F301 K5H302Y00003 FUSE !
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
16.5.1.2.2. KX-TGE230B
Safety Ref.
PCB1 PNWP1TGE230H MAIN P.C.BOARD ASS'Y
(ICs)
IC302 C0DBEYY00102 IC
IC501 C1CB00004121 IC (*1)(*2)
IC502 PNWI2TGE230H IC(FLASH) (*1)
IC601 PNWI3TGE230H IC(FLASH) (*1)
IC611 PNWI1TGE230H IC(EEPROM)(*1)(for KX-
(TRANSISTORS)
Q141 2SA1776P TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q142 B1ABDM000001 TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q161 DSC7003S0L TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q301 B1ADGE000012 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q351 B1ADNB000003 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q352 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q353 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q907 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q908 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
(DIODES)
D101 B0EDER000009 DIODE(SI) S
D142 DY2J25000L TRANSISTOR(SI)
D362 B0ECKM000008 DIODE(SI)
(RESISTOR ARRAYS)
No.
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
(RTL) (for KX-TGE230B)
(for KX-TGE232B)(for
KX-TGE233B)(for KXTGE234B)
TGE232B)(for KXTGE233B)(for KXTGE234B)
92
Page 93

Safety Ref.
RA501 EXB24V221JX RESISTOR ARRAY
RA601 EXB28V561JX RESISTOR ARRAY
RA611 EXB28V332JX RESISTOR ARRAY
RA651 D1H810240004 RESISTOR ARRAY S
(VARISTOR)
SA101 J0LE00000047 VARISTOR (SURGE
(RESISTORS)
R101 ERJ3GEYJ565 5.6M S
R102 ERJ3GEYJ565 5.6M S
R103 PQ4R10XJ184 180k S
R104 PQ4R10XJ184 180k S
R109 ERJ2GEJ823 82k S
R110 ERJ2GEJ823 82k S
R111 ERJ2GEJ392 3.9k S
R112 ERJ2GEJ124 120k S
R115 ERJ3GEYJ825 8.2M S
R116 ERJ3GEYJ825 8.2M S
R117 ERJ3GEYJ154 150k S
R118 ERJ3GEYJ154 150k S
R125 ERJ2GEJ271 270 S
R141 ERJ3GEYJ104 100k S
R142 PQ4R18XJ272 2.7k S
R145 ERJ2GEJ222 2.2k S
R151 ERJ2GEJ104 100k S
R152 ERJ2GEJ104 100k S
R160 ERJ3GEYJ821 820 S
R162 ERJ2GEJ473 47k S
R163 D0GG390JA007 39
R164 ERJ2GEJ272 2.7k S
R165 ERJ3GEYJ273 27k S
R166 ERJ3GEYJ822 8.2k S
R168 ERJ2GEJ472X 4.7k S
R178 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R311 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R321 ERJ2RKF1400 140 S
R322 ERJ2RKF1000 100 S
R351 ERJ2GEJ333 33k S
R352 ERJ2GEJ682 6.8k S
R354 ERJ2GEJ123 12k S
R355 ERJ2GEJ681 680 S
R371 ERJ8GEYJ1R0 1 S
R372 ERJ8GEYJ1R0 1 S
R373 ERJ2GEJ681 680 S
R477 ERJ2GEJ1R0 1 S
R478 ERJ2GEJ1R0 1 S
R501 ERJ2RKF5602 56k
R502 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R505 ERJ2GEJ102 1k S
R601 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R651 ERJ2GEJ102 1k S
R652 ERJ2GEJ102 1k S
R653 ERJ2GE0R00 0 S
R661 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R702 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R901 ERJ2GE0R00 S
R905 ERJ3GEY0R00 S
R924 ERJ2GEJ102 S
R957 ERJ2GEJ103 S
R962 ERJ2GEJ563 S
R963 ERJ2GEJ103 S
R964 ERJ2GEJ223 S
(CAPACITORS)
C101 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C102 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C103 ECUV1H103KBV 0.01
C104 ECUV1H103KBV 0.01
C105 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C106 F1K2H681A008 680p S
C109 ECUE1H821KBQ 820p
C110 ECUE1H821KBQ 820p
C111 ECUE1A333KBQ 0.033
C113 ECUE1A823KBQ 0.082
No.
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
ABSORBER)
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Safety Ref.
C115 ECUV1C104KBV 0.1
C116 ECUV1C104KBV 0.1
C142 ECUV1H103KBV 0.01
C152 ECUE1C103KBQ 0.01
C161 F1K1E1060001 10
C167 ECUV1H102KBV 0.001
C171 ECUV1C223KBV 0.022
C173 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C174 ECUE1H222KBQ 0.0022
C184 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C311 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C312 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C321 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C341 F2G0J331A146 330
C342 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C351 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C472 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C473 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C477 ECUE1H222KBQ 0.0022
C478 ECUE1H222KBQ 0.0022
C501 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C502 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C503 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C504 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C505 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C506 ECUV0J225KBV 2.2
C507 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C508 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C509 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C512 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C513 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C514 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C516 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C517 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C518 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C519 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C601 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C611 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C661 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C663 ECUE1H102KBQ 0.001
C851 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C859 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C860 F1G1H1R1A765 CERAMIC CAPACITOR
C862 F1G1H2R4A765 CERAMIC CAPACITOR
C901 F2A1A102B641 ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITOR
(OTHERS)
P101 D4DAY220A022 THERMISTOR
X501 H0J103500037 CRYSTALOSCILLATOR (*1)
No.
F301 K5H302Y00003 FUSE !
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
16.5.1.3. Operational P.C. Board Parts
Safety Ref.
PCB2 PNWP2TGE230H OPERATIONAL P.C.BOARD
No.
DA901 B3CAT0000004 LED
LED901 B3AAB0000347 LED
SW901 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
SW902 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
SW903 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
SW904 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
SW905 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
SW906 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
SW907 K0H1BA000578 SPECIAL SWITCH
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
ASS'Y (RTL)
(LEDS)
(SWITCHES)
93
Page 94

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
16.5.2. Handset
16.5.2.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts
Safety Ref.
No.
101 PNGP1317Y2 PANEL, LCD PMMA-HB
102 PNYE1124Z TAPE, DOUBLE SIDED
103 PNKM1524Y2 CABINET BODY ABS-HB
104 PNHR1922Z LENS, LED
105 L0AD01A00026 RECEIVER
106 PNYE1125Z SPACER, CUSHION LCD
107 PNBC1491X6 BUTTON, NAVIGATOR KEY ABS-HB
108 PNJK1211Z KEYBOARD SWITCH
109 PNBC1530Z1 BUTTON, NR KEY
110 PNMH1308Z GUIDE, SPEAKER
111 L0AA02A00120 SPEAKER
112 PNHS1502Z SPACER, SPEAKER NET
113 PNJK1212Y COVER, VOLUME
114 PQJC10056W BATTERY TERMINAL
115 PNKE1311Z2 COVER, EP CAP
116 PNKF1314Z2 CABINET COVER ABS-HB
117 PNQT2006Z LABEL, ATTENTION
118 PNQT2859Z LABEL, BATTERY
119 PNGT7989Z NAME PLATE
120 PNHS1079Z SPACER, BATTERY
121 PNKK1094Z2 LID, BATTERY ABS-HB
122 PNYNTGEA20BR LID, BATTERY ASS'Y ABS-HB
123 PNHR1644Z SPACER
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
16.5.2.2. Main P.C. Board Parts
Note:
(*1) Reconfirm the model No. written on the handset's name
plate when replacing PCB100. Because the model No. of
the optional handset may differ from the included handset.
(*2) When replacing IC1, IC3 or X1, make the adjustment
using PNZZTGE230M. Refer to Handset (P.58) of Things
to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal.
(*3) When replacing the handset LCD, See How to
Replace the Handset LCD (P.51).
(*4) Backside of this IC has a ground plate. Refer to How to
Replace the Flat Package IC (P.62).
(*5) Supplied IC is Flat Package Type.
Safety Ref.
PCB100 PNWP1TGEA20R MAIN P.C.BOARD ASS'Y
(ICs)
IC1 C2HBCY000142 IC (*2)(*4)(*5)
IC3 PNWITGEA20R IC(EEPROM)(*2)
IC4 C0DBZYY00357 IC
(TRANSISTORS)
Q2 B1ADCF000040 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q3 B1ABGE000011 TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q4 B1ADCF000040 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q5 DRC9113Z0L TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q6 DRC9113Z0L TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q8 DRC9113Z0L TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q9 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q10 B1ADNB000003 TRANSISTOR(SI)
Q11 2SC6054JSL TRANSISTOR(SI) S
Q12 B1ADCF000040 TRANSISTOR(SI)
(DIODES)
D13 B0BC4R3A0006 DIODE(SI)
D14 B0BC4R3A0006 DIODE(SI) S
(LEDS)
LED1 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED2 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED3 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED4 B3ACB0000190 LED
No.
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
(RTL) (*1)
Safety Ref.
LED5 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED6 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED11 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED12 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED13 B3ACB0000190 LED
LED20 B3AFB0000370 LED
(IC FILTER)
L3 J0JDC0000045 IC FILTER
(COIL)
L801 G1C2N7Z00009 COIL
(RESISTOR ARRAYS)
RA1 EXB28V103 RESISTOR ARRAY
RA2 D1H83314A013 RESISTOR ARRAY S
RA3 EXB24V331J RESISTOR ARRAY
RA4 EXB24V332JX RESISTOR ARRAY
RA5 EXB28V332JX RESISTOR ARRAY
(RESISTORS)
R2 ERJ2GEJ303 30k S
R3 ERJ2GEJ152 1.5k S
R4 ERJ2GEJ473 47k S
R6 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R7 ERJ2GEJ104 100k S
R8 ERJ8GEYJ4R3V 4.3 S
R9 ERJ2GEJ303 30k S
R10 ERJ3GEYJ1R0 1 S
R11 ERJ2GEJ681 680 S
R12 ERJ2GEJ183 18k S
R13 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R20 ERJ2GEJ303 30k S
R21 ERJ2GEJ103 10k S
R22 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R23 ERJ2GEJ391 390 S
R24 ERJ2GEJ100 10 S
R25 ERJ2GEJ222 2.2k S
R26 ERJ2GEJ332 3.3k S
R27 ERJ2GEJ222 2.2k S
R28 ERJ2GEJ222 2.2k S
R31 ERJ2RKF1003X 100k S
R32 ERJ2GEJ104 100k S
R33 ERJ2RKF1003X 100k S
R34 ERJ2GE0R00 0 S
R45 D0GBR10JA113 0.1
R50 ERJ2GEJ221 220 S
R51 ERJ2GEJ221 220 S
R54 ERJ2GEJ221 220 S
R56 ERJ2GE0R00 0 S
R70 ERJ2GEJ470 47 S
R72 ERJ2GE0R00 0 S
R80 ERJ2GEJ100 10 S
(CAPACITORS)
C11 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C12 ECJ1VB0G106M 10 S
C13 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C14 ECUV1C393KBV 0.039
C15 ECUE1H390JCQ 39p
C16 F1J0J2260002 22
C17 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C18 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C2 F1J0J2260002 22
C20 ECJ1VB0G106M 10 S
C21 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C22 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C24 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C25 ECUV1A225KBV 2.2
C26 ECJ1VB0G106M 10 S
C27 ECUE1H102KBQ 0.001
C29 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C3 F1J0J2260002 22
C30 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C31 ECJ1VB0G106M 10 S
C32 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C33 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C34 ECUE1H390JCQ 39p
No.
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
94
Page 95

Safety Ref.
C36 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C37 ECJ1VB0G106M 10 S
C40 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C41 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C43 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C44 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C45 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C46 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p S
C5 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C51 ECJ1VB0G106M 10 S
C52 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C53 ECUE1H120JCQ 12p
C56 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C57 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C58 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C6 ECUE1H680JCQ 68p
C68 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C69 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C70 ECUE1H680JCQ 68p
C71 ECUE1H680JCQ 68p
C78 ECUE1H101JCQ 100p
C79 ECUE1H101JCQ 100p
C80 ECUV1C393KBV 0.039
C801 F1G1H2R0A765 2p
C802 F1G1H1R5A765 1.5p
C806 F1G1H1R0A765 1p
C807 F1G1H3R0A765 3p
C81 ECUE1H101JCQ 100p
C82 ECUE1H102KBQ 0.001
C84 ECUE1H102KBQ 0.001
C90 ECUE1A104KBQ 0.1
C91 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C92 ECUE0J105KBQ 1
C93 ECUV1C105KBV 1
C96 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
C97 ECUE1H100DCQ 10p
(OTHERS)
E101 PNVE1002Z BATTERY TERMINAL ABS-HB
E102 PNJT1184Z CHARGE TERMINAL (L)
E103 PNJT1185Z CHARGE TERMINAL (R)
CN4 K2HD103D0001 JACK
MIC100 L0CBAY000053 MICROPHONE
SW1 K0H1BB000094 PUSH SWITCH
SW2 K0H1BB000094 PUSH SWITCH
SW601 K0H1BA000259 PUSH SWITCH
X1 H0J138500003 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR(*2) S
No.
E104 L5DYBYY00043 LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
E105 PNHR1921Z TRANSPARENT PLATE, LCD PMMA-HB
E106 PNHR1920Z GUIDE, LCD ABS-HB
E107 PQHG10729Z RUBBER PARTS, RECEIVER
E108 PNJE1194Z SPECIAL SWITCH
F1 K5H252Y00002 FUSE !
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
(*3)
(for KX-TGE210B) (for
KX-TGE212B)
S
S
16.5.3. Charger Unit
16.5.3.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts
Safety Ref.
No.
200 PNLC1050ZB
200-1 PNKM1527Z1 CABINET BODY PS-HB
200-2 PNJT1177Z CHARGE TERMINAL
200-3 PNKF1279Z1 CABINET COVER PS-HB
200-4 PQHA10023Z RUBBER PARTS, FOOT CUSH-
200-5 PNLV233-AZ AC ADAPTOR
201 PNGT7990Z NAME PLATE
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
CHARGER UNIT ASS'Y
without NAME PLATE (RTL)
ION
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
16.5.4. Accessories and Packing Materials
Note:
(*1) You can download and refer to the Operating
Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
16.5.4.1. KX-TGE210B
Safety Ref.
No.
A1 PNLV226Z AC ADAPTOR
A2 PQJA10075Z CORD, TELEPHONE
A3 PNKE1312Z2 HANGER, BELT CLIP ABS-HB
A4 PNKL1044Z2 WALL MOUNT ADAPTOR ABS-HB
A5 PNQX6358Z INSTRUCTION BOOK (*1)
A6 PNQW2611Z LEAFLET,REPEATER
A7 PNQW3426Z LEAFLET, MINI-LOCATOR
P1 PNPK3779003Z GIFT BOX
P2 PNPD1826Z CUSHION
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
APPEAL
APPEAL
16.5.4.2. KX-TGE212B
Safety Ref.
No.
A101 PNLV226Z AC ADAPTOR
A102 PQJA10075Z CORD, TELEPHONE
A103 PNKE1312Z2 HANGER, BELT CLIP ABS-HB
A104 PNKL1044Z2 WALL MOUNT ADAPTOR ABS-HB
A105 PNQX6358Z INSTRUCTION BOOK (*1)
A106 PNQW2611Z LEAFLET,REPEATER
A107 PNQW3426Z LEAFLET, MINI-LOCATOR
P101 PNPK3770001Y GIFT BOX
P102 PNPD1827Z CUSHION
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
APPEAL
APPEAL
16.5.4.3. KX-TGE232B
Safety Ref.
No.
A201 PNLV226Z AC ADAPTOR
A202 PQJA10075Z CORD, TELEPHONE
A203 PNKE1312Z2 HANGER, BELT CLIP ABS-HB
A204 PNKL1044Z2 WALL MOUNT ADAPTOR ABS-HB
A205 PNQX6358Z INSTRUCTION BOOK (*1)
A206 PNQW2611Z LEAFLET,REPEATER
A207 PNQW3426Z LEAFLET, MINI-LOCATOR
P201 PNPK3770002Y GIFT BOX
P202 PNPD1827Z CUSHION
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
APPEAL
APPEAL
16.5.4.4. KX-TGE233B
Safety Ref.
No.
A301 PNLV226Z AC ADAPTOR
A302 PQJA10075Z CORD, TELEPHONE
A303 PNKE1312Z2 HANGER, BELT CLIP ABS-HB
A304 PNKL1044Z2 WALL MOUNT ADAPTOR ABS-HB
A305 PNQX6358Z INSTRUCTION BOOK (*1)
A306 PNQW2611Z LEAFLET,REPEATER
A307 PNQW3426Z LEAFLET, MINI-LOCATOR
P301 PNPK3772001Y GIFT BOX
P302 PNPD1828Z CUSHION
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
APPEAL
APPEAL
95
Page 96

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
16.5.4.5. KX-TGE234B
Safety Ref.
No.
A401 PNLV226Z AC ADAPTOR
A402 PQJA10075Z CORD, TELEPHONE
A403 PNKE1312Z2 HANGER, BELT CLIP ABS-HB
A404 PNKL1044Z2 WALL MOUNT ADAPTOR ABS-HB
A405 PNQX6358Z INSTRUCTION BOOK (*1)
A406 PNQW2611Z LEAFLET,REPEATER
A407 PNQW3426Z LEAFLET, MINI-LOCATOR
P401 PNPK3773001Y GIFT BOX
P402 PNPD1829Z CUSHION
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
APPEAL
APPEAL
16.5.5. Screws
Safety Ref.
A XTB26+8GFJ TAPPING SCREW
No.
B XTB2+8GFJ TAPPING SCREW
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
16.5.6. Fixtures and Tools
Note:
(*1) See Equipment Required (P.52), and The Setting
Method of JIG (P.52)
(*2) When replacing the Handset LCD, See How to
Replace the Handset LCD (P.51)
Safety Ref.
PQZZ1CD300E JIG CABLE (*1)
PNZZTGE230M BATCH FILE CD-ROM (*1)
PQZZ430PIR TIP OF SOLDERING IRON
No.
PQZZ430PRB RUBBER OF SOLDERING IRON
Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
(*2)
(*2)
96
ADDA
KXTGE210B
KXTGE212B
KXTGE232B
KXTGE233B
KXTGE234B
KXTGEA20B
KXTGA20B
 Loading...
Loading...