Page 1

4-Channel VoIP Gateway Card
Getting Started
KX-TDA3480
Model
KX-TDA0484
Thank you for purchasing a Panasonic 4-Channel VoIP Gateway Card.
Please read this manual carefully before using this product and save this manual for future use.
Page 2

Table of Contents
1 Overview..................................................................................................5
1.1 Example Network Diagram...............................................................................................6
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan ...........................................................................7
1.2.1 Network Application ............................................................................................................8
1.2.2 Numbering Plan Example ...................................................................................................9
1.2.3 Numbering Plan Summary................................................................................................12
2 Installing in the KX-TDA30 PBX ..........................................................13
2.1 Installation.......................................................................................................................14
2.1.1 Names and Locations .......................................................................................................14
2.1.2 Installing the VoIP Gateway Card in the PBX....................................................................15
2.2 Cable Connection............................................................................................................17
2.2.1 Connection for Programming............................................................................................17
2.2.2 Connection to the LAN......................................................................................................18
3 Installing in the KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200/KX-TDA600 PBX................19
3.1 Installation.......................................................................................................................20
3.1.1 Names and Locations .......................................................................................................20
3.1.2 Installing the VoIP Gateway Card in the PBX....................................................................21
3.2 Cable Connection............................................................................................................23
3.2.1 Connection for Programming............................................................................................23
3.2.2 Connection to the LAN......................................................................................................24
4 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card ................................................25
4.1 Preparations....................................................................................................................26
4.1.1 Preparing the PC ..............................................................................................................26
4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office...............................29
4.2.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility..........................................................................29
4.2.2 Changing the Status of the VoIP Gateway Card...............................................................31
4.2.3 Assigning the IP Address..................................................................................................32
4.2.4 Assigning the Hunt Pattern ...............................................................................................33
4.2.5 Programming the Address Translation Table.....................................................................34
4.2.6 Downloading the Address Translation Table from the VoIP Gateway Card.......................37
4.2.7 Rebooting the VoIP Gateway Card ...................................................................................38
4.2.8 Confirming the IP Address Assignment ............................................................................39
4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office......................................40
5 Programming the PBX..........................................................................45
5.1 Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office........................................................46
5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office...............................................................49
A Guidance for VoIP Installation.............................................................53
A1 VoIP Requirements .........................................................................................................54
A1.1 Bandwidth Assessment.....................................................................................................54
A1.2 Network Configuration.......................................................................................................56
A1.3 Network Devices...............................................................................................................59
A1.4 QoS (Quality of Service) ...................................................................................................60
A2 VoIP Requirements Checklist.........................................................................................61
2 Getting Started
Page 3

B Alternative Numbering Plan Example.................................................63
B1 Extension Number Method............................................................................................ 64
B1.1 Example Network.............................................................................................................64
B1.2 Numbering Plan Example................................................................................................. 65
B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method ....................................................... 67
B2.1 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card.............................................................................. 67
B2.2 Programming the PBX...................................................................................................... 68
C Initialisation of the VoIP Gateway Card...............................................73
C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card................................................................................ 74
D Using the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 and KX-TDA0480 in One
Network..................................................................................................77
D1 Considerations in Installation....................................................................................... 78
Getting Started 3
Page 4

4 Getting Started
Page 5

Section 1
Overview
Panasonic PBX with VoIP Gateway Card will allow
organisations to route both voice and fax communications
over digital data net works.
The V oIP Gateway Card, designed to be easily integrated into
existing IP networks, seamlessly bridges Public Switched
Telephone Network (PSTN) and analogue telephones with
digital data networks without interrupting pre-existing data
communications. Because comm unications do not take place
over con ventional telephone networks, the high cost of long
distance communications is virtually eliminated.
Getting Started 5
Page 6
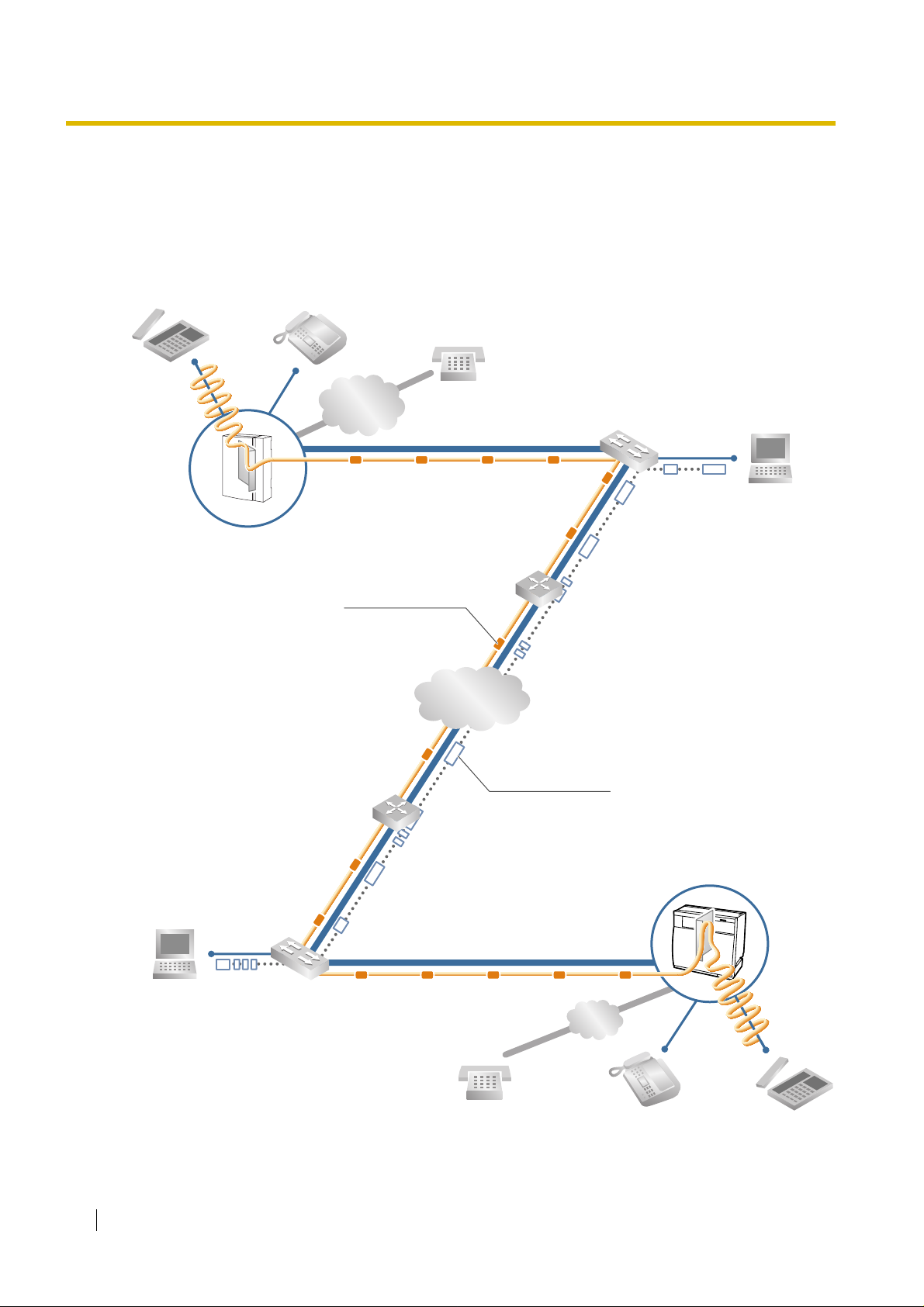
1.1 Example Network Diagram
1.1 Example Network Diagram
The following diagram illustr ates a simple VoIP network connecting PBXs at 2 locations. The VoIP
Gateway Card converts outgoing voice or fax signals into IP packets for transmission. On the
incoming side, it reverses this process and translates the packets back into appropriate voice or fax
signals.
PSTN
(Public Switched
Telephone Network)
Voice signals are converted
into IP packets.
KX-TDA30 PBX
with KX-TDA3480 VoIP Gateway Card
Voice data packets
Switching Hub
Router
IP Network
Other data packets
KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200/KX-TDA600 PBX
with KX-TDA0484 VoIP Gateway Card
IP packets are converted
back into voice signals.
PSTN
6 Getting Started
Page 7
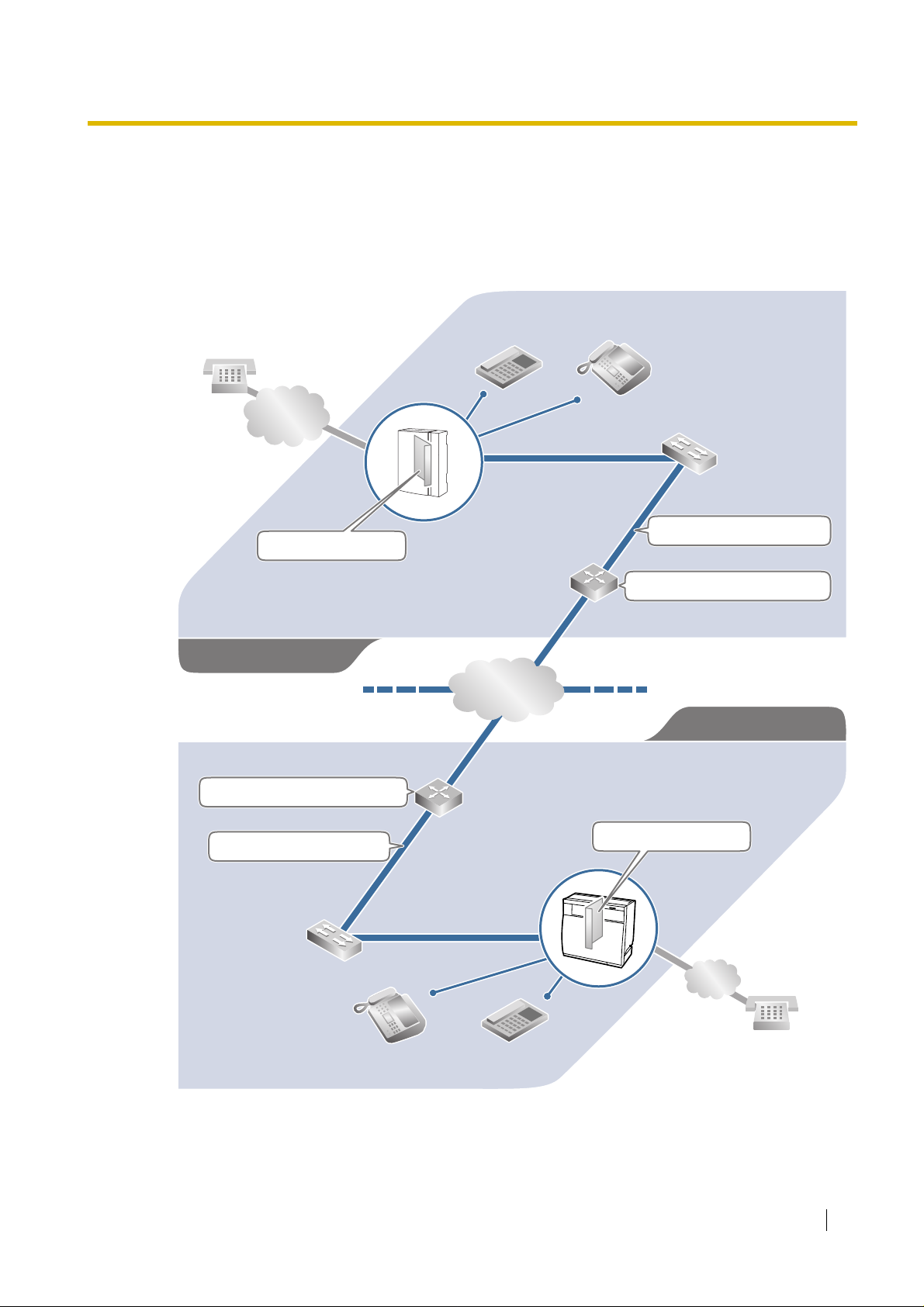
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
You will need to have network configuration information available to install VoIP Gateway Cards.
Referring to this example diagram, consult your network administrator to obtain necessary
information to configure yo ur own VoIP network.
Local Telephone
456-7890
PSTN
(Public Switched
Telephone Network)
Card IP: 200.45.11.35
PBX Code: 35
PSTN Trunk Number: 9
TIE Line Access Number: 7
Los Angeles Office
Default Gateway IP: 199.176.64.1
Extn. 201
(200-299)
IP Network
G3 Fax Extn. 501
(500-599)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway IP: 200.45.11.1
Chicago Office
PBX Code: 41
PSTN Trunk Number: 9
TIE Line Access Number: 7
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
G3 Fax Extn. 601
(600-699)
Extn. 301
(300-399)
Card IP: 199.176.64.41
PSTN
Local Telephone
123-4567
Getting Started 7
Page 8

1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
1.2.1 Network Application
QSIG Network Interface
QSIG is a protocol based on ISDN (Q.931) that offers enhanced PBX features in a private network.
The QSIG network supports private communications by the TIE line service method. Implementation
of VoIP Gateway Cards provides a VoIP interface to employ a QSIG network between PBXs at
different locations by using an IP network instead of conventional telephone networks.
Types of IP Network
The V oIP Gatew ay Card's quality o f performance depends on the t ype of IP network in use. Manage d
IP networks provide better quality of service compared to unmanaged networks, wher e quality of
service is not guaranteed.
Examples of recommended IP networks
• Digital Leased Line
• IP-VPN (Virtual Private Network)
•Frame Relay
Notice
The performance of the VoIP Gateway Card may deteriorate when it is used on the Internet.
Delays and loss in data transmission can degrade speech quality, and impair the card's capability
to use the enhanced networking features of the PBX (for more inf ormation about these features,
refer to the relevant sections of the Hybrid IP-PBX documentation.)
Using the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 with Other KX-TDA Series VoIP
Gateway Cards
When using the KX-TDA348 0/KX-TDA0484 in a network that contains other KX-TDA series VoIP
Gateway Cards, keep in mind the following points:
1. Making and Receiving Calls
Calls can be made and received between the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 and other KX-TDA
series VoIP Gateway Cards. However, the KX-TDA0480 requires a special setting to be able to
communicate with the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 on the network. Refer to "D1 Considerations
in Installation" for more details.
2. Using QSIG Services
All QSIG services available with the PBX can be used between the KX-TD A3480/KX-TDA0484
and KX-TDA0490. However, CLIP service is the only available QSIG service between the KXTDA3480/KX-TDA0484 and KX-TDA0480.
Firewall
A firewall protects the internal networks of an organisation against unauthorised penetration from
outside. When routing a VoIP network through a firewall, some perf ormance degradation may result.
If for practical reasons you must route the VoIP network through a firewall, refer to "A1.3 Network
Devices" for more details.
8 Getting Started
Page 9

1.2.2 Numbering Plan Example
There are 2 methods to plan your numbering system, as follows:
In addition to the destination number , the caller dials the unique PBX code of the
PBX code
method
Extension
number method
This section provides a network numbering mechanism using the PBX code method based on the
previous example diagram. Configure your network referring to this example.
Note
An example using the extension number method is provided in "B Alternative Numbering Plan
Example".
PBX to which the called party is connected. Therefore, extension numbers at
separate PBXs in the network can overlap. For example, each PBX in the
network can have an extension whose number is 201.
The caller dials only the destination number of the called party to call through
PBXs at different locations (hence there are fe wer digits to dial than with the PBX
code method). To employ the extension number method, no 2 PBXs can have
extensions sharing the same number. For example, if one PBX in the network
has an extension whose number is 201, no other PBX can have an extension
with the same number (201).
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
IP Addressing Information
IP addressing information is typically supplied by a network administrator. Consult your network
administrator for specific values.
Los Angeles
Office
Card IP Address 200.45.11.35 199.176.64.41
Default Gateway
Address
Subnet Mask
Address
200.45.11.1 199.176.64.1
255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Chicago
Office
Description
Identifies the location of each VoIP Gateway
Card in the network during VoIP
communications. A unique IP addre ss must
be assigned to each card.
Identifies the IP address of the primary
gatewa y (typically a router or similar de vice)
that exchanges IP packets with the other
gateways on the VoIP network.
Defines which digits of an IP address are
used for the network address and the host
address at each network location. A card IP
address must fall within th e same subnet as
that of the default ga tew ay (e .g., router) that
is connected to the card.
Getting Started 9
Page 10
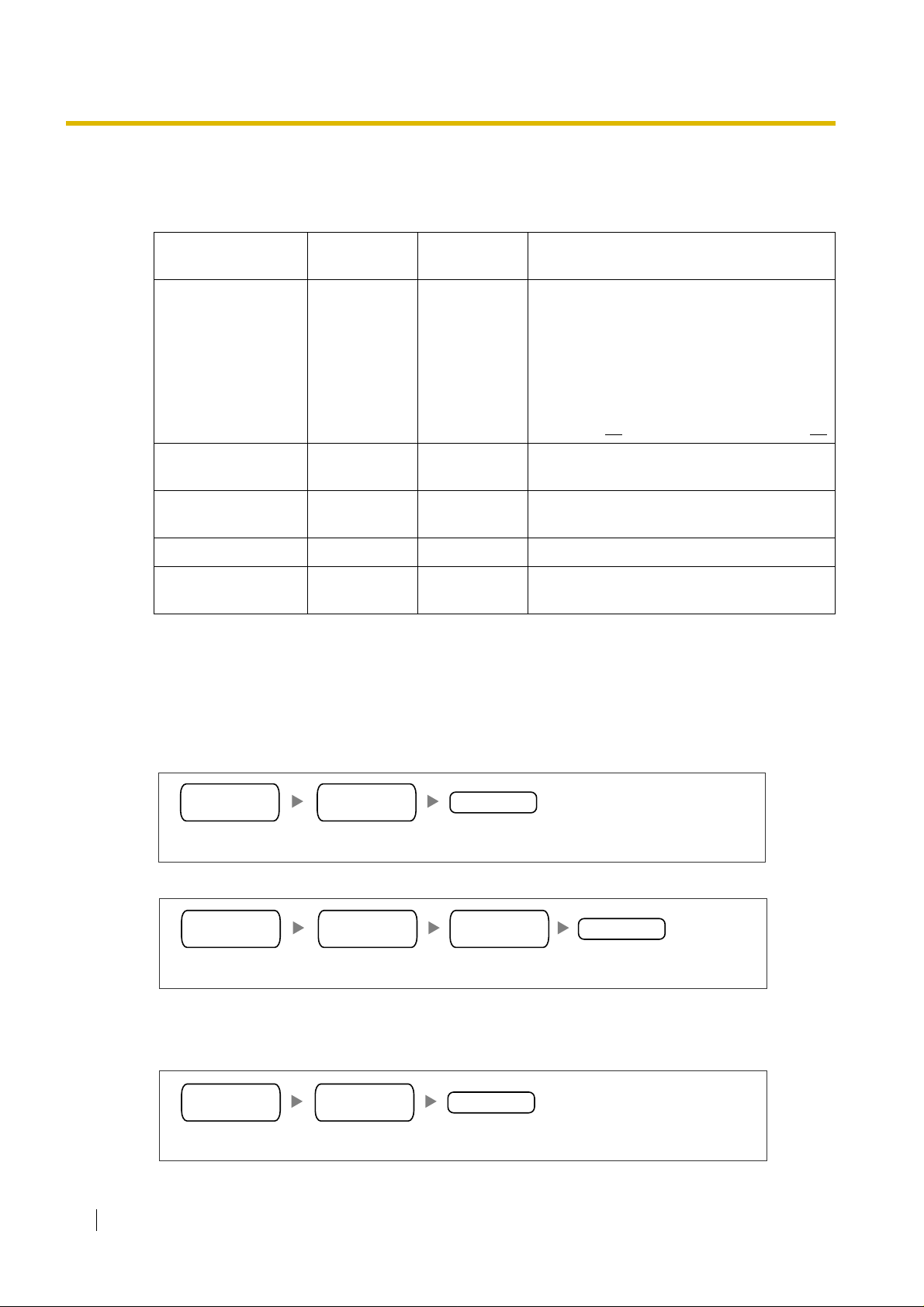
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
PBX Numbering Information
PBX numbering information is necessary to set up phone numbers for a VoIP network. Set the
numbers conforming to existing PBX numbering systems.
PBX Code 35 41
TIE Line Access
Number
PSTN Trunk Number 9 9
Extension Number 200 to 299 300 to 399 A number assigned to each extension.
Fax Extension
Number
Dialling Examples
The VoIP network allows you to access the PBX at one location from another to establish: (1) an
extension call, or (2) an outside call throu gh the local PSTN as if y o u are calling fro m the same area .
Los Angeles
Office
Chicago
Office
Description
A unique number (ranging from 1 to 7 digits)
assigned to identify each PBX within a
network.
In this example, for convenience, each PBX
code corresponds to the last portion of the
IP address of its card; that is, because the
Los Angeles office card has the IP address
200.45.11.35
77
An access number to use the TIE line
service.
, Los Angeles PBX code is 35.
An access number to seize a local PSTN
trunk.
500 to 599 600 to 699 A number assigned to each fax extension.
Calling from Los Angeles to Chicago
To extension 301 via VoIP network
TIE line
access no.
Chicago
PBX code
Dial 41.Dial 7. Dial 301.
To local telephone 123-4567 via VoIP network through local PSTN
TIE line
access no.
Chicago
PBX code
Dial 41. Dial 9.Dial 7. Dial 123-4567.
Calling from Chicago to Los Angeles
To extension 201 via VoIP network
TIE line
access no.
Los Angeles
PBX code
Dial 35.Dial 7. Dial 201.
extension no.
Chicago PBX
PSTN trunk no.
extension no.
phone no.
10 Getting Started
Page 11
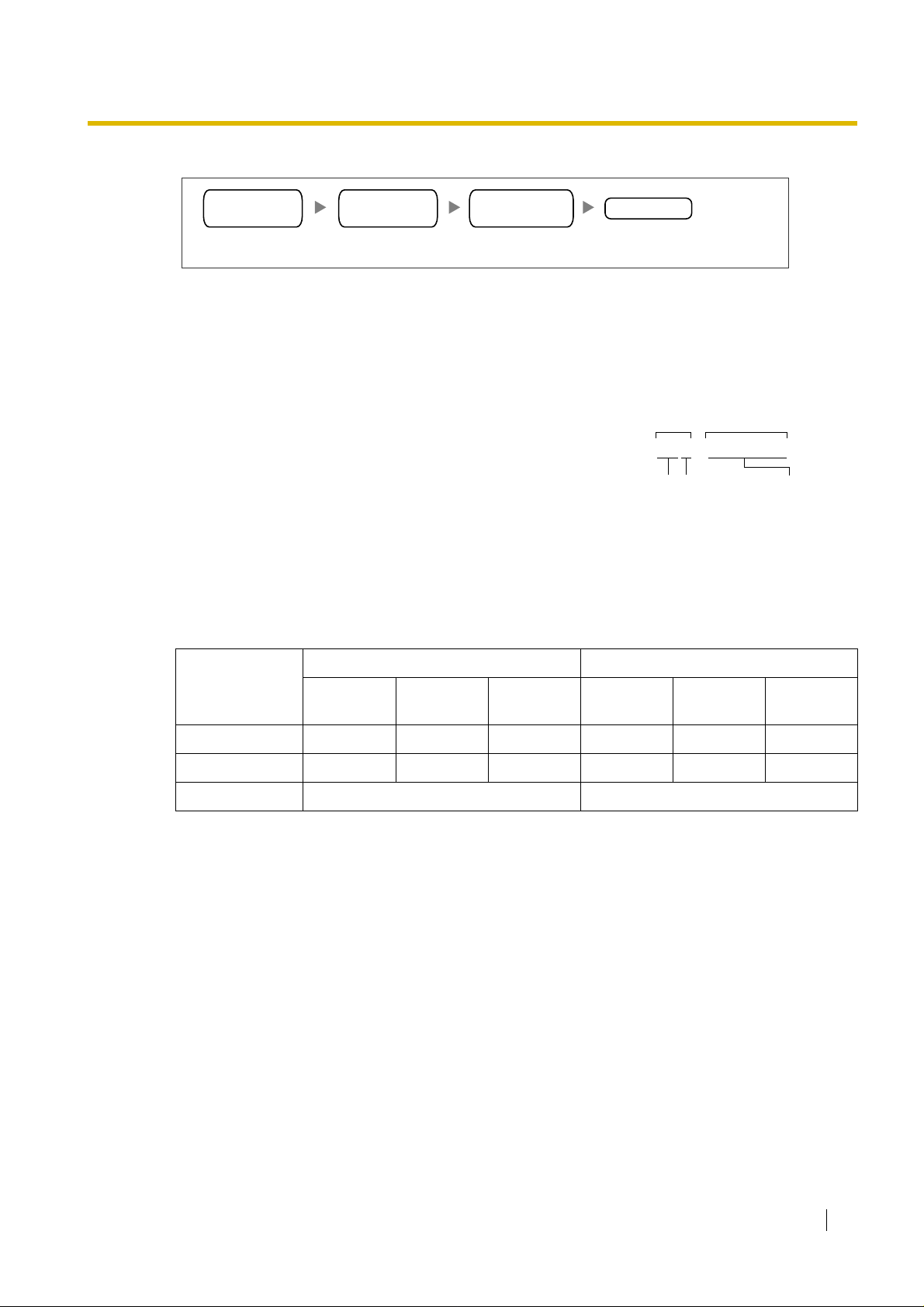
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
To local telephone 456-7890 via VoIP network through local PSTN
TIE line
access no.
Los Angeles
PBX code
Dial 35. Dial 9.Dial 7. Dial 456-7890.
PBX Connection Information
PBX connection information is created by combining IP Addressing Inf ormation and PBX Numbering
Information. Referring to the sample below, create your own PBX connection information.
Leading Number:
A number composed of the PBX code followed by the first digit
of the destination number. See the example on the right.
Remaining Digits:
The maximum number of digits to be dialled following the
leading number to access the destination. (However, for
example, sett ing the remaining digits to 7 does not mean that
the user must dial all 7 digits when making a call.) See the
example on the right.
Card IP Address:
The IP address of each card in the network (as the access destination).
Los Angeles PBX
PSTN trunk no.
phone no.
Los Angeles extensions
Remaining DigitsLeading No.
352+00 to 99
PBX Code
First digit of
the extension
number
Remaining digits
of the extension
number
Los Angeles Office (PBX Code: 35) Chicago Office (PBX Code: 41)
Extn. FAX Extn. PSTN
Access
Extn. FAX Extn. PSTN
Access
Leading Number 352 355 359 413 416 419
Remaining Digits227227
Card IP Address 200.45.11.35 199.176.64.41
Getting Started 11
Page 12
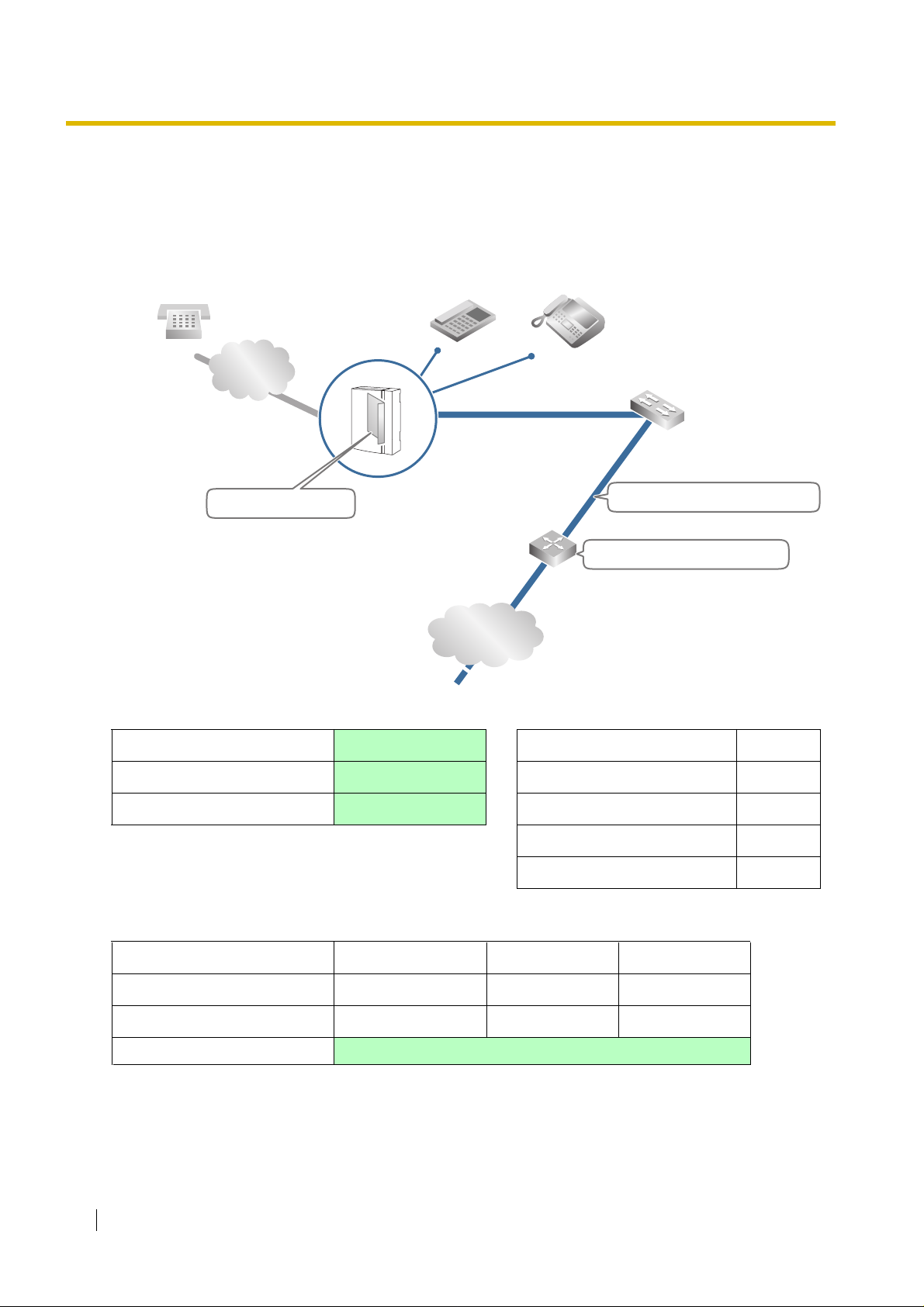
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan
1.2.3 Numbering Plan Summary
Print this page and write down your netw ork information in the space pr ovided belo w f or each card in
the network. Consult your network administrator to fill in the shaded entries.
Local Telephone:
PSTN
(Public Switched
Telephone Network)
Card IP:
PBX Code:
PSTN Trunk Number:
TIE Line Access Number:
IP Address
Extension Number:
IP Network
G3 Fax Extension Number:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway IP:
PBX Numbering
Card IP Address
Default Gateway IP Address
Subnet Mask Address
PBX Connection
Leading Number
Remaining Digits
Card IP Address
Extensions
PBX Code
TIE Line Access Number
PSTN Trunk Number
Extension Number
Fax Extension Number
PSTN AccessFax Extensions
12 Getting Started
Page 13

Section 2
Installing in the KX-TDA30 PBX
This section describes the physical installation process o f the
KX-TDA3480 VoIP Gateway Card covering the following
topics: (1) installing the card in the KX-TDA30 PBX, and (2)
connecting the card to a network device using a Category 5
(CAT5) Ethernet cable.
Getting Started 13
Page 14
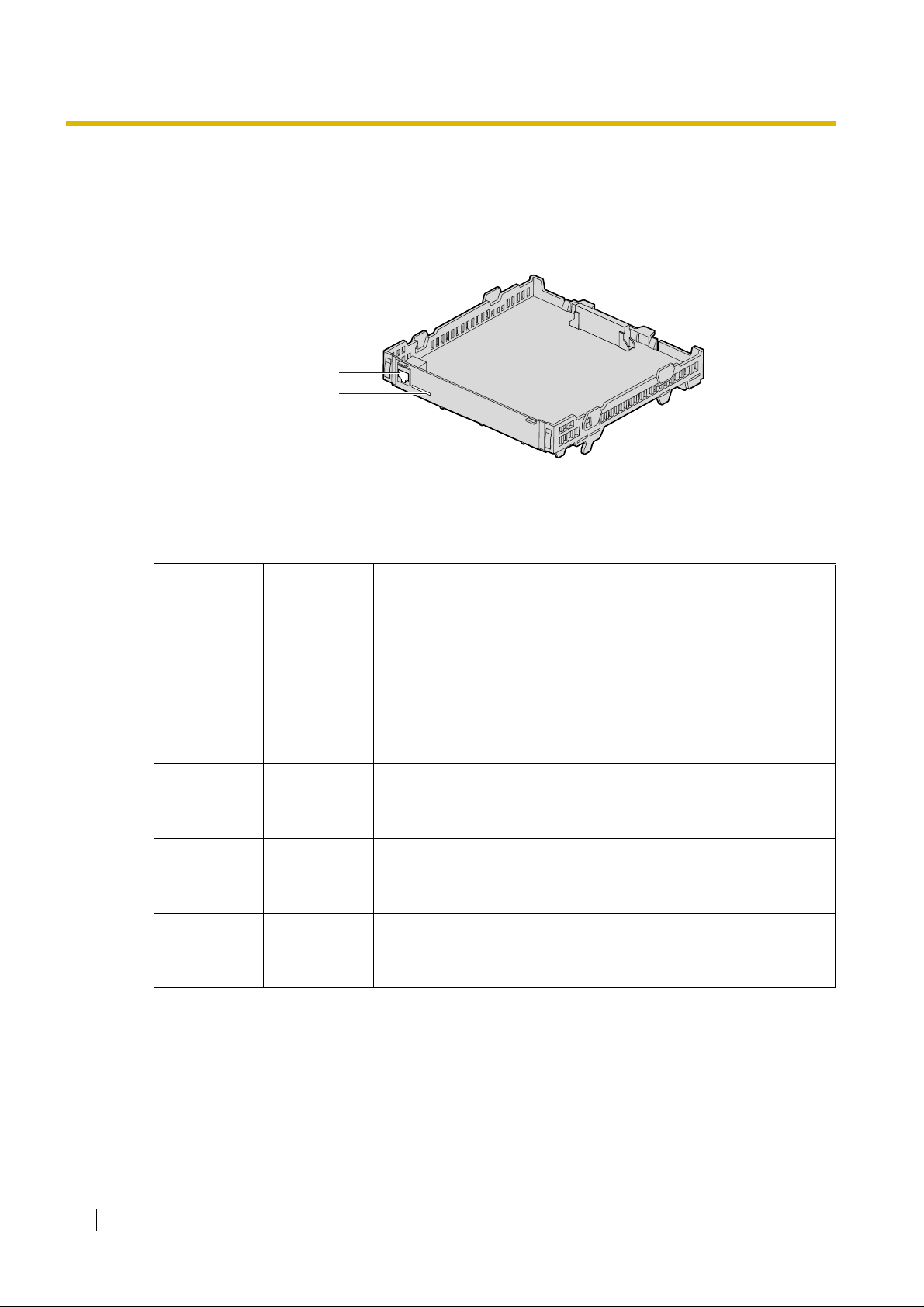
2.1 Installation
2.1 Installation
2.1.1 Names and Locations
RJ45
(10BASE-T/100BASE-TX)
LEDs
Indication Light (LED)
When the VoIP Gatewa y Card is oper ating, each LED should sho w the st atus identified in bold-face
letters under normal conditions.
Indication Colour Description
On-line status indication
• ON: On-line mode
• OFF: Off-line mode
ONLINE Green
ALARM Red
LINK Green
DA TA Green
• Flashing: Maintenance mode
Note
If the LINK indicator is OFF, the ONLINE indicator will also be
OFF.
Alarm indication
•ON: Alarm
• OFF: Normal
Link status indication
• ON: Normal connection
• OFF: Connection error
Data transmission indication
• ON: Data transmitting
• OFF: No data transmitted
14 Getting Started
Page 15
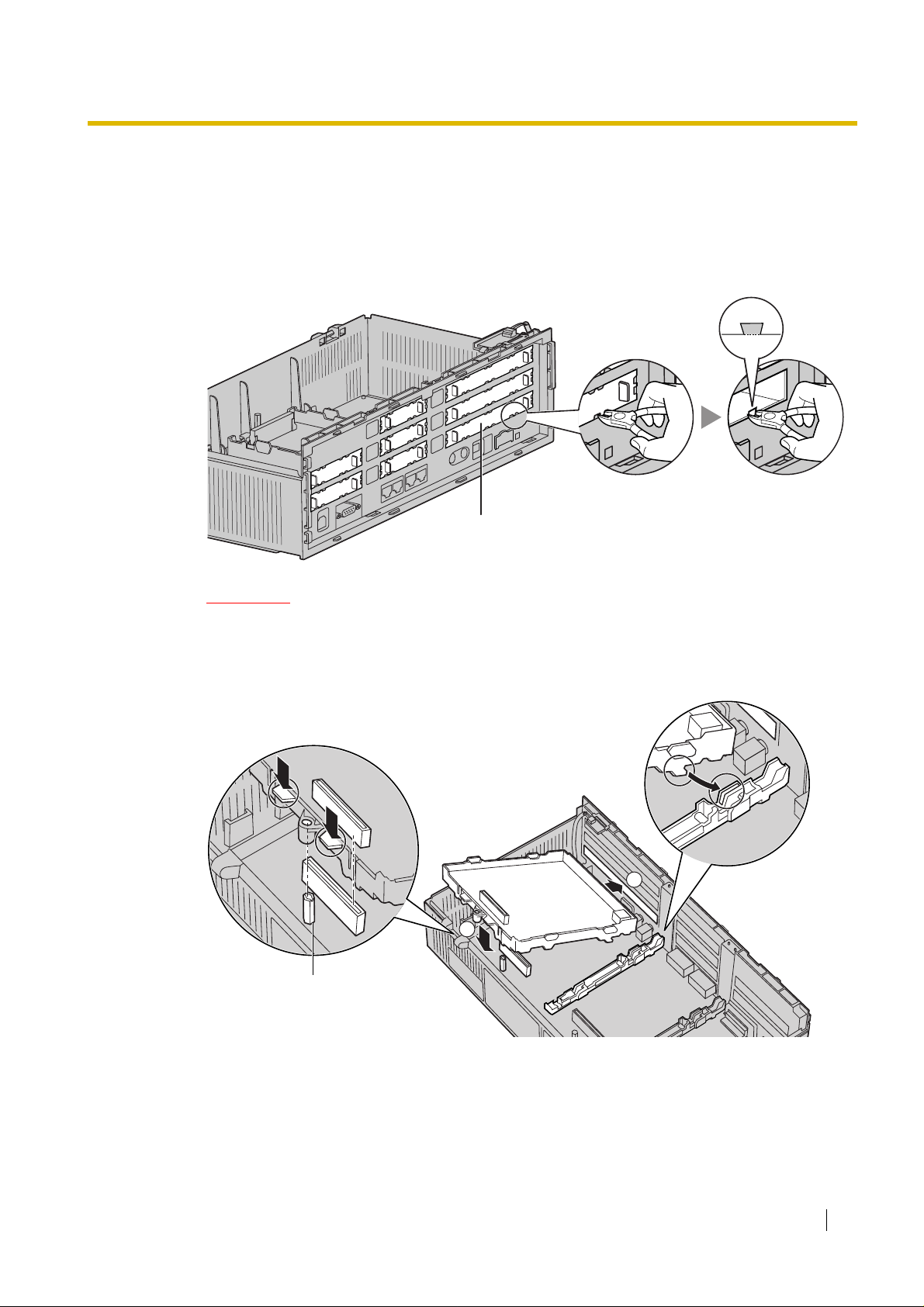
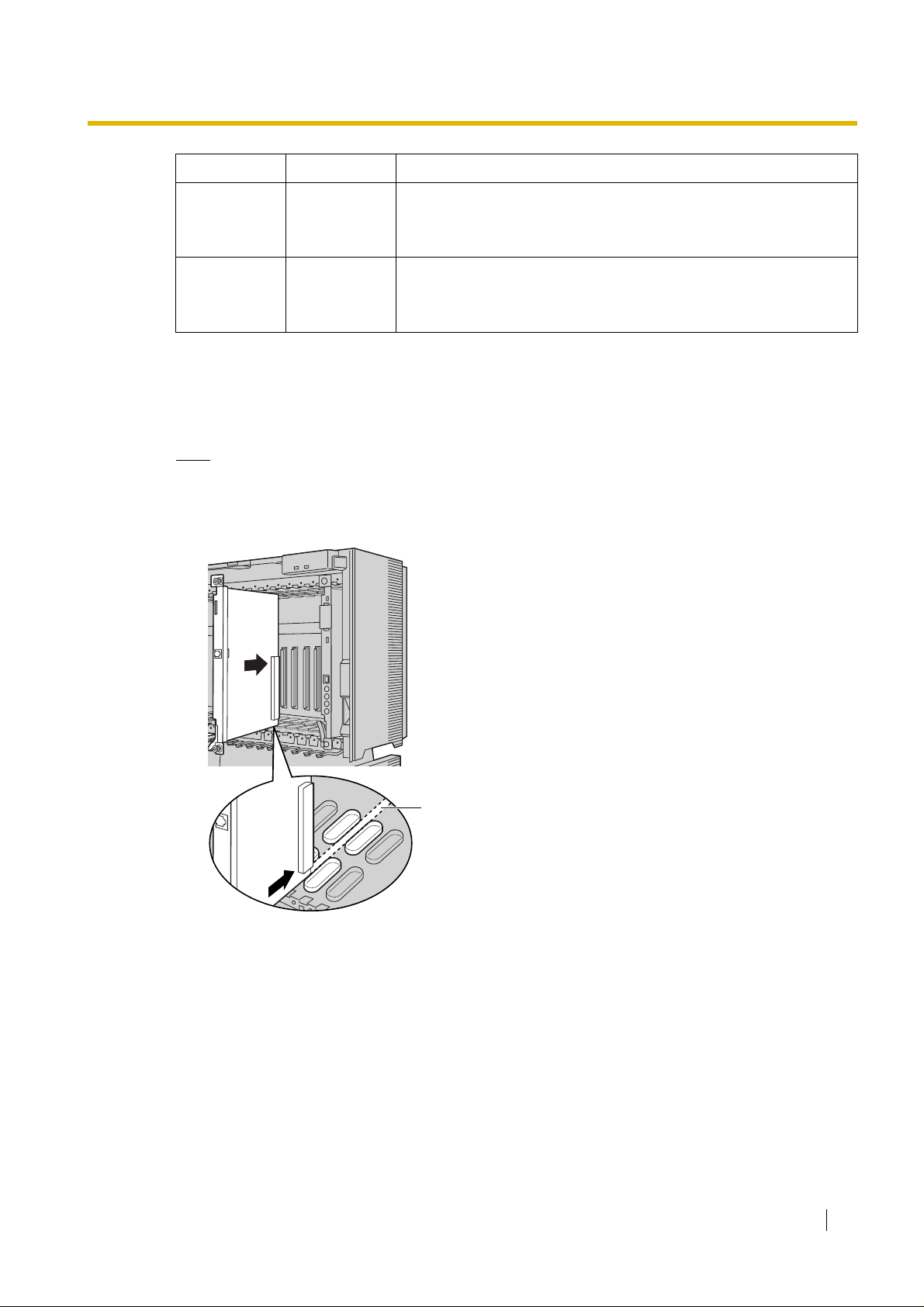
2.1.2 Installing the VoIP Gateway Card in the PBX
Install the VoIP Gateway Card in slot 05, 06, or 07 of the KX-TDA30 PBX.
1. Before installing the card, cut and remove the dummy cover plate for the appropriate slot from
the main unit.
Dummy Cover Plate
2.1 Installation
CAUTION
For safety reasons, smooth the cut edges after removing the dummy cover plate.
2. Position the card in the open slot, making sure that the tabs on both sides of the card fit into place.
Then, holding the card firmly in place, lower t he rear end so that the hole of th e card fits ov er the
extension bolt.
1
2
Extension Bolt
Getting Started 15
Page 16
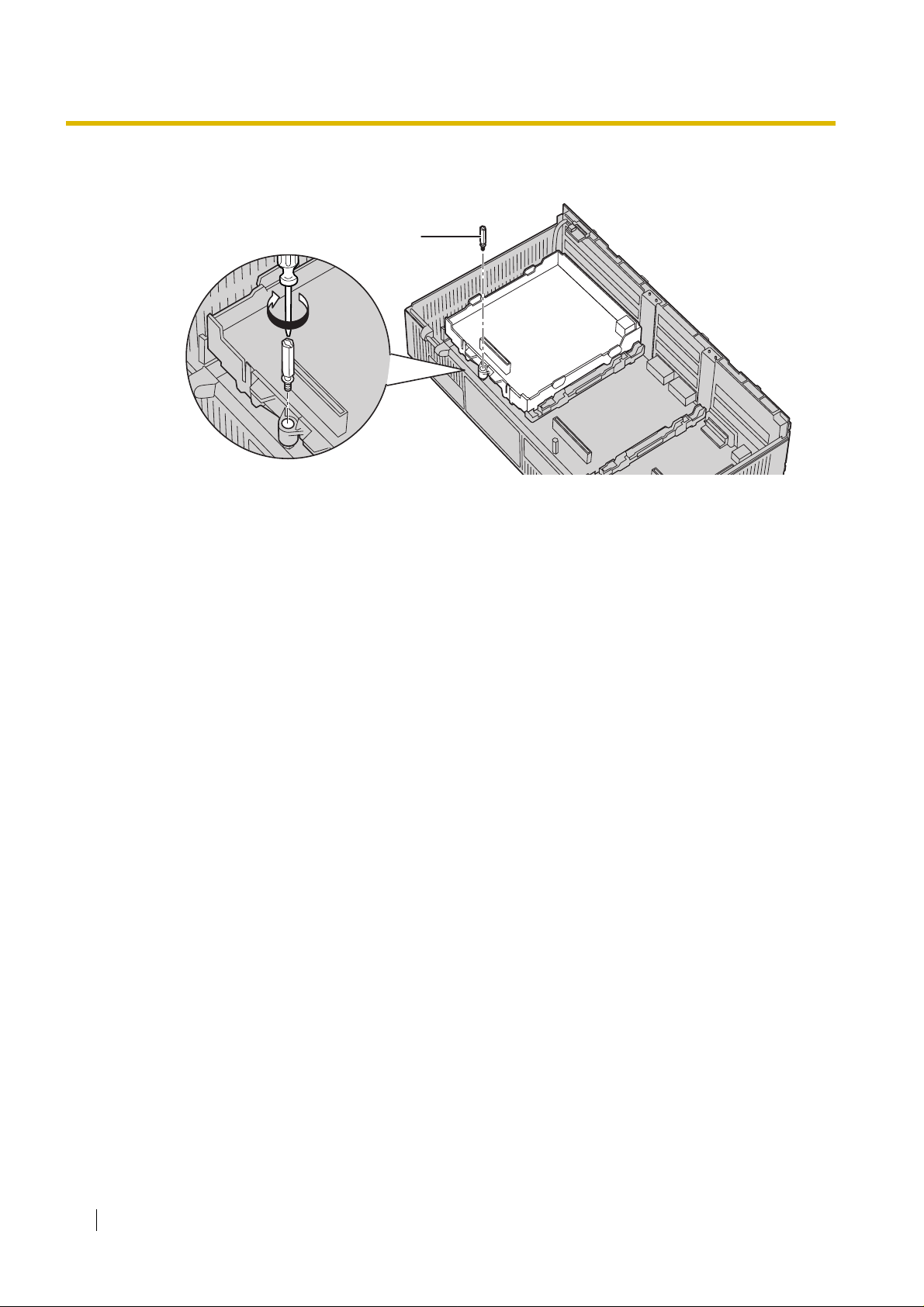
2.1 Installation
3. Insert the new extension bolt (included with the card) into the hole on the card, and tighten it to
secure the card.
Extension Bolt
16 Getting Started
Page 17

2.2 Cable Connection
Use a Category 5 (CAT5) Ethernet cable (10BASE-T/100BASE-TX) with an RJ45 connector to
connect the VoIP Gateway Card to a network device.
When connecting the card to a switching hub, use an Ethernet straight cable; when connecting
directly to a router or PC, use an Ethernet cross cable.
Note
Use only CAT5 Ethernet cable for connection.
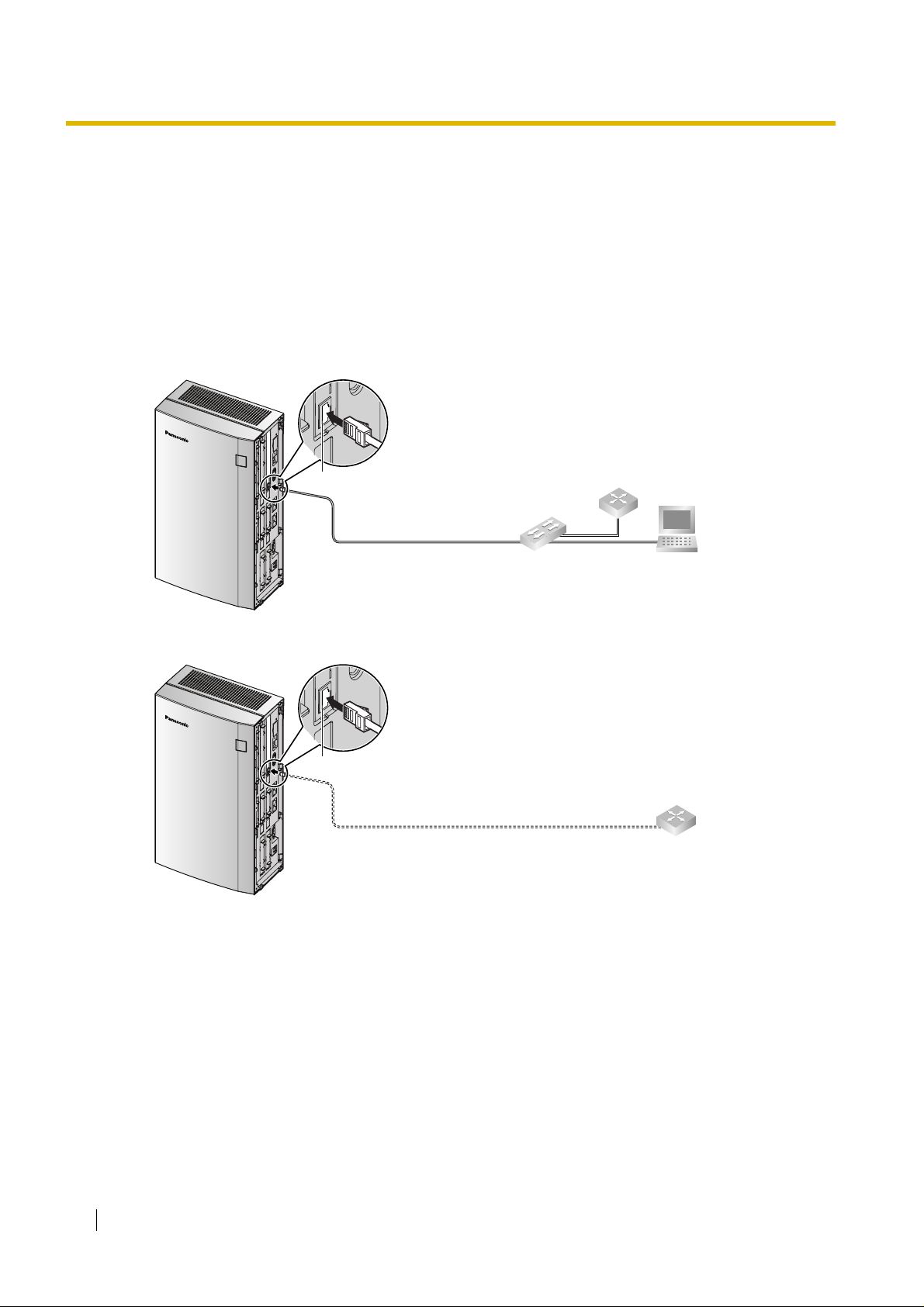
2.2.1 Connection for Programming
When assigning a new IP address t o th e VoIP Gateway Ca rd for the first time, connect a PC dir ectly
to the card using an Ethernet cross cable.
1. Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ45 connector of the card.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the PC.
2.2 Cable Connection
RJ45
Ethernet Cross Cable
PC
Getting Started 17
Page 18
2.2 Cable Connection
2.2.2 Connection to the LAN
Do not connect the VoIP Gateway Card to the LAN unless it has been assigned an IP address for
actual VoIP operations on the network. Doing so may result in the default IP address of the card
overlapping with an existing IP address on the LAN, or cause network failure.
1. Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ45 connector of the card.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the remote LAN equipment.
Connecting to a switching hub
RJ45
Ethernet Straight Cable
Connecting directly to a router
RJ45
Switching Hub
Ethernet Cross Cable
Router
PC
Router
18 Getting Started
Page 19

Section 3
Installing in the KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200/KX-
TDA600 PBX
This section describes the physical installation process o f the
KX-TDA0484 VoIP Gateway Card covering the following
topics: (1) installing the card in the KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200/
KX-TDA600 PBX, and (2) connecting the card to a network
device using a Category 5 (CAT5) Ethernet cable.
Getting Started 19
Page 20

3.1 Installation
3.1 Installation
3.1.1 Names and Locations
LEDs
RJ45
(10BASE-T/100BASE-TX)
Indication Light (LED)
When the VoIP Gatewa y Card is oper ating, each LED should sho w the st atus identified in bold-face
letters under normal conditions.
Indication Colour Description
CARD
STATUS
ONLINE Green
ALARM Red
Green/Red
Card status indication
• OFF: Power Off
• Green ON: Normal (all ports are idle)
• Green Flashing (60 times per minute): Normal (a port is in use)
• Red ON: Fault (includes reset)
• Red Flashing (60 times per minute): Out of Service
On-line status indication
• ON: On-line mode
• OFF: Off-line mode
• Flashing: Maintenance mode
Note
If the LINK indicator is OFF, the ONLINE indicator will also be
OFF.
Alarm indication
•ON: Alarm
• OFF: Normal
VoIP BUSY Green
20 Getting Started
VoIP (H.323) process indication
• OFF: VoIP process inactive
• ON: VoIP process active
Page 21
Indication Colour Description
Link status indication
LINK Green
DA TA Green
• ON: Normal connection
• OFF: Connection error
Data transmission indication
• ON: Data transmitting
• OFF: No data transmitted
3.1.2 Installing the VoIP Gateway Card in the PBX
Install the VoIP Gateway Card in a free slot of the KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200/KX-TDA600 PBX.
Note
The illustrations of the PBX shown in the installation procedure are based on the KX-TDA600.
1. Insert the card along the guide rails.
3.1 Installation
Guide Rail
Getting Started 21
Page 22
3.1 Installation
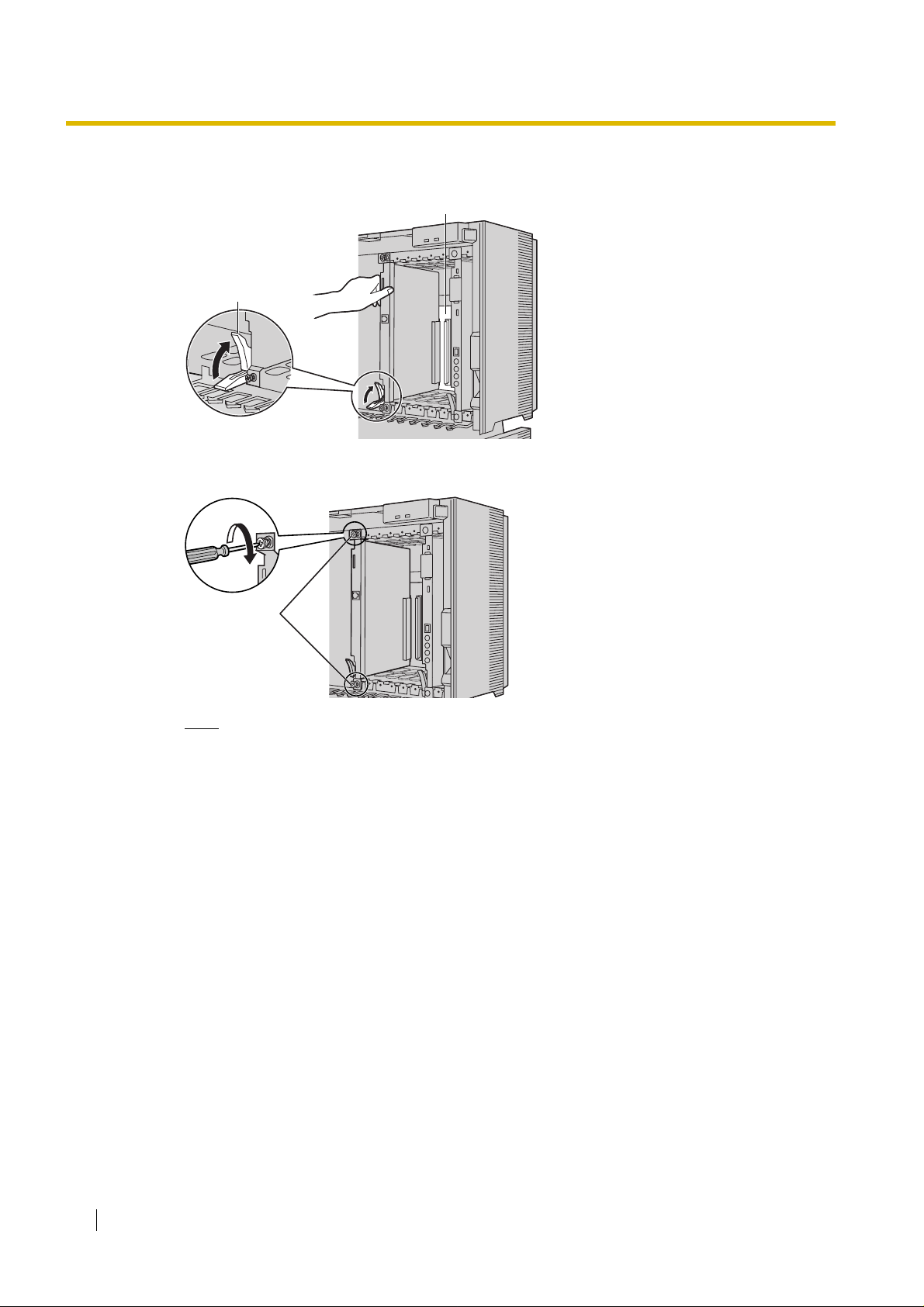
2. Holding the card as shown below, push the release lever in the direction of the arrow so that the
card engages securely with the connector on the back board.
Back Board
Release Lever
3. Turn the 2 screws clockwise to fix the card in place.
Screws
Note
Make sure the screws are tightened to earth the card securely.
22 Getting Started
Page 23

3.2 Cable Connection
Use a Category 5 (CAT5) Ethernet cable (10BASE-T/100BASE-TX) with an RJ45 connector to
connect the VoIP Gateway Card to a network device.
When connecting the card to a switching hub, use an Ethernet straight cable; when connecting
directly to a router or PC, use an Ethernet cross cable.
Note
Use only CAT5 Ethernet cable for connection.
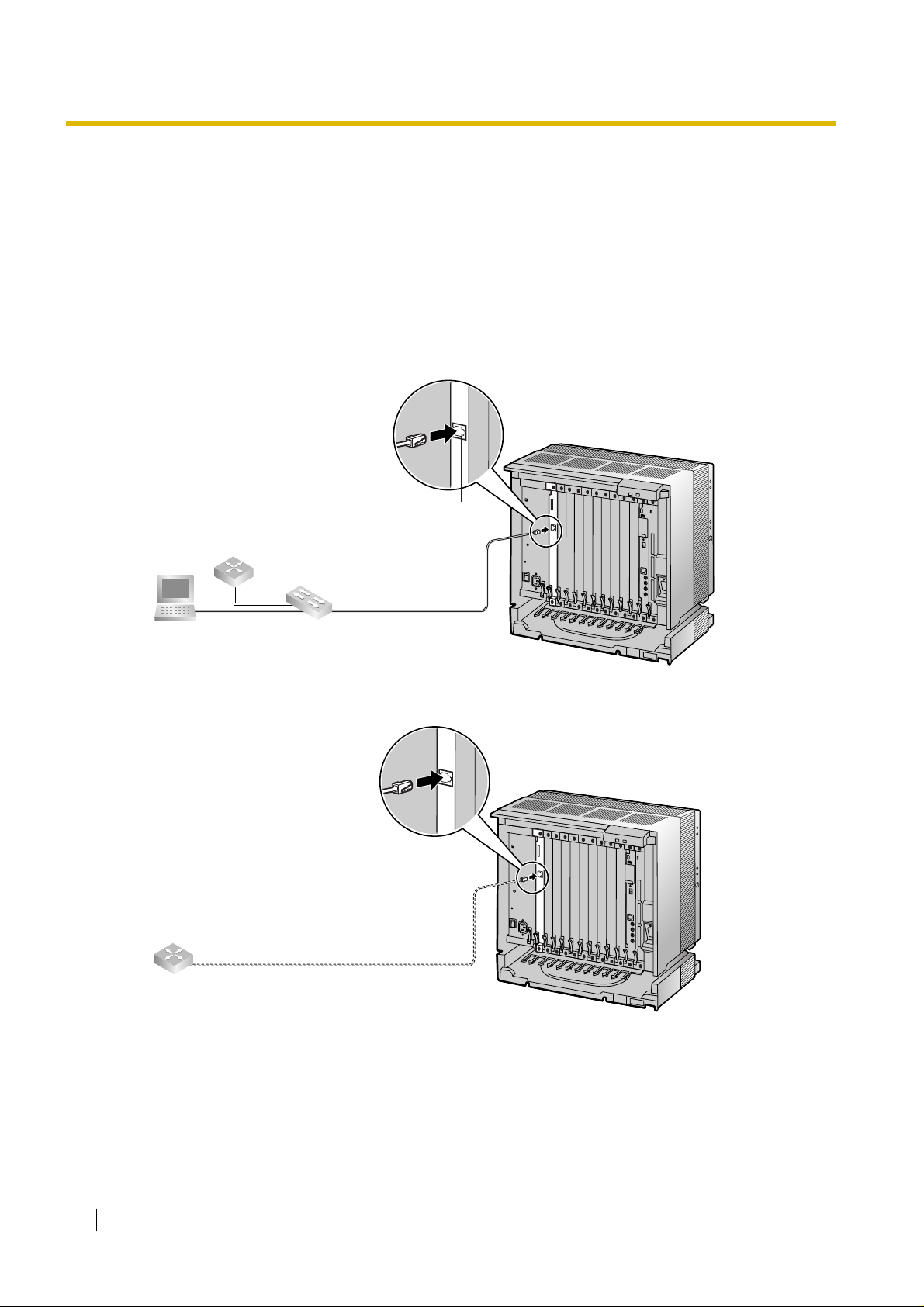
3.2.1 Connection for Programming
When assigning a new IP address t o th e VoIP Gateway Ca rd for the first time, connect a PC dir ectly
to the card using an Ethernet cross cable.
1. Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ45 connector of the card.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the PC.
3.2 Cable Connection
PC
RJ45
Ethernet Cross Cable
Getting Started 23
Page 24
3.2 Cable Connection
3.2.2 Connection to the LAN
Do not connect the VoIP Gateway Card to the LAN unless it has been assigned an IP address for
actual VoIP operations on the network. Doing so may result in the default IP address of the card
overlapping with an existing IP address on the LAN, or cause network failure.
1. Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ45 connector of the card.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the remote LAN equipment.
Connecting to a switching hub
Router
RJ45
Switching Hub
PC
Ethernet Straight Cable
Connecting directly to a router
Router
Ethernet Cross Cable
RJ45
24 Getting Started
Page 25

Section 4
Programming the VoIP Gateway Card
One way of setting up a V oIP network for the first time is to go
through the whole programming process of a VoIP Gateway
Card at one location in the network, then start progra mming
the other cards at different locations.
Based on the theoretical network illustrated previously in this
manual, this section demonstrates the procedure to
programme the cards in the Los Angeles and Chicago offices .
Getting Started 25
Page 26

4.1 Preparations
4.1 Preparations
A web programming utility called the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility is availab le for programming of the
VoIP Gateway Card.
For a complete discussion of w eb programming, ref er to the VoIP Gateway Card Progr amming Guide.
System Requirements
• The IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility requires Microsoft® Internet Explorer 5.0 or above.
Trademarks
• Microsoft is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
• All other trademarks identified herein are the property of their respective owners.
• Screen shots reprinted with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
4.1.1 Preparing the PC
To prepare for programming using the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility, configure your PC by (1)
assigning an IP address that belongs to the sa me network as that of t he VoIP Gateway Card, and (2)
choosing the appropriate options for the Internet properties.
Note
The procedure below is based on the Windows XP operating system as an example.
1. Open Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties from
the Start menu.
2.
a. Click Use the following IP address.
b. In the IP address box, type 192.168.1.100.
This is an example entry for t he case when the
card has the default IP address
(192.168.1.200).
c. In the Subnet mask box, type 255.255.255.0.
d. Click OK.
26 Getting Started
3.
a. Start Internet Explorer from the Star t menu.
b. Click Internet Options from the Tools menu.
Page 27
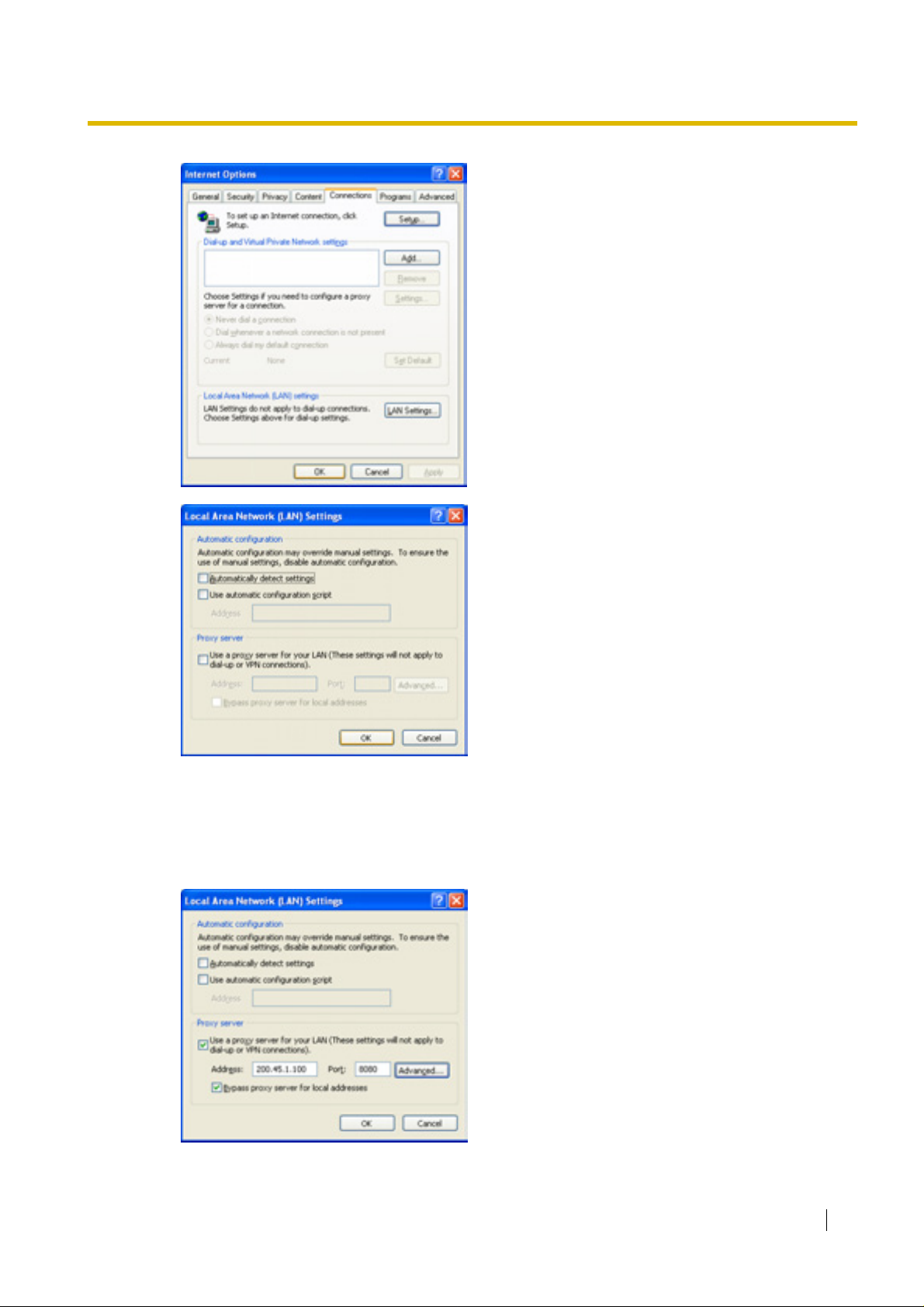
4.
a. Click the Connections tab.
b. Click Never dial a connection.
c. Click LAN Settings.
5.
a. Click to clear all check boxes.
b. Click OK.
4.1 Preparations
Your PC is now ready for programming through
direct access to the card.
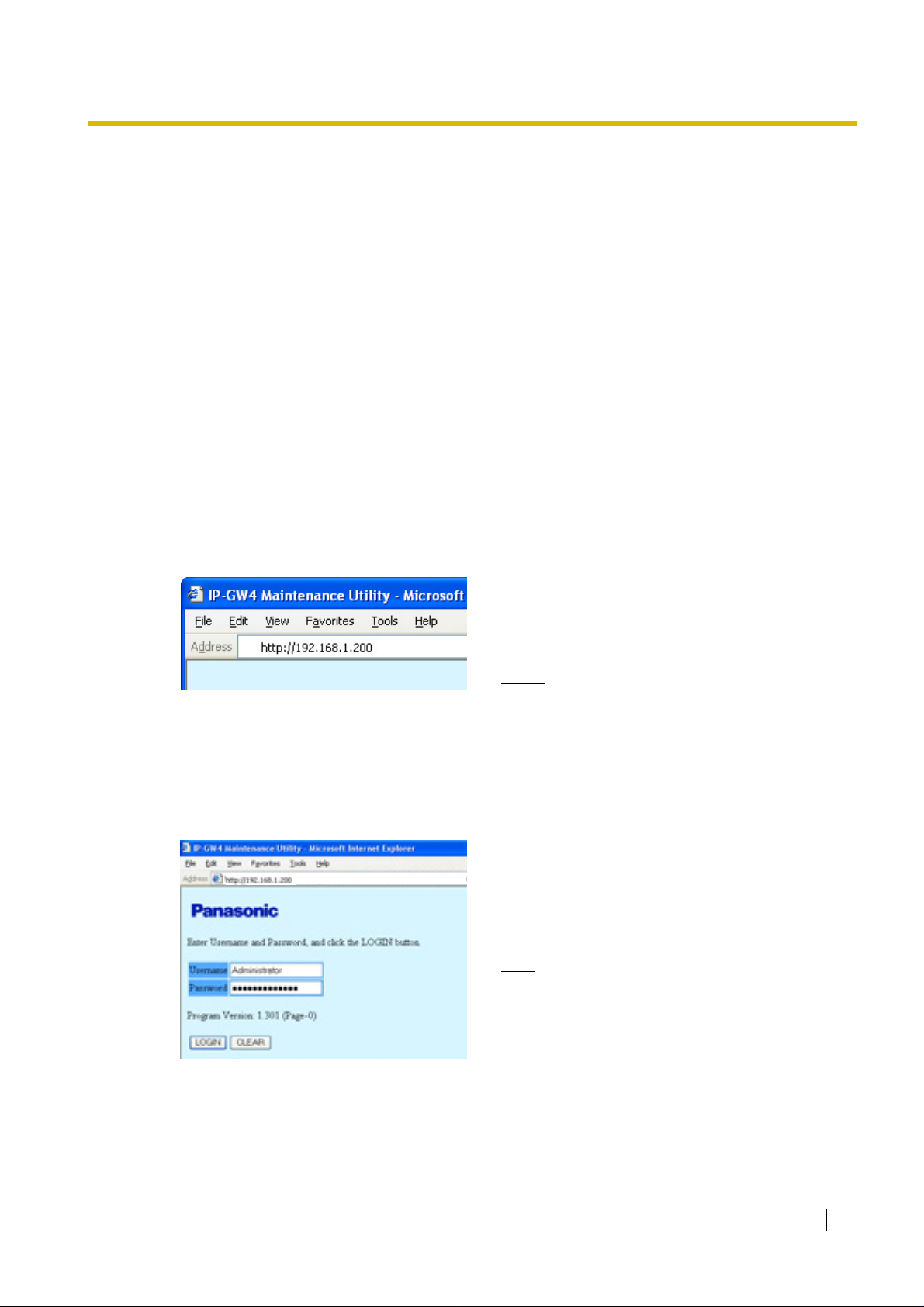
Notice When Programming the Card through an IP Network
When the card is put in actual operation on an IP netw ork, y ou can access and pr ogr amme the ca rd
through the network. Howe ver , if the network has a pro xy server installed, you must apply appro priate
proxy settings to your PC. In this case, follow the steps below in substitution for step 5 above:
5. Click Advanced.
Getting Started 27
Page 28
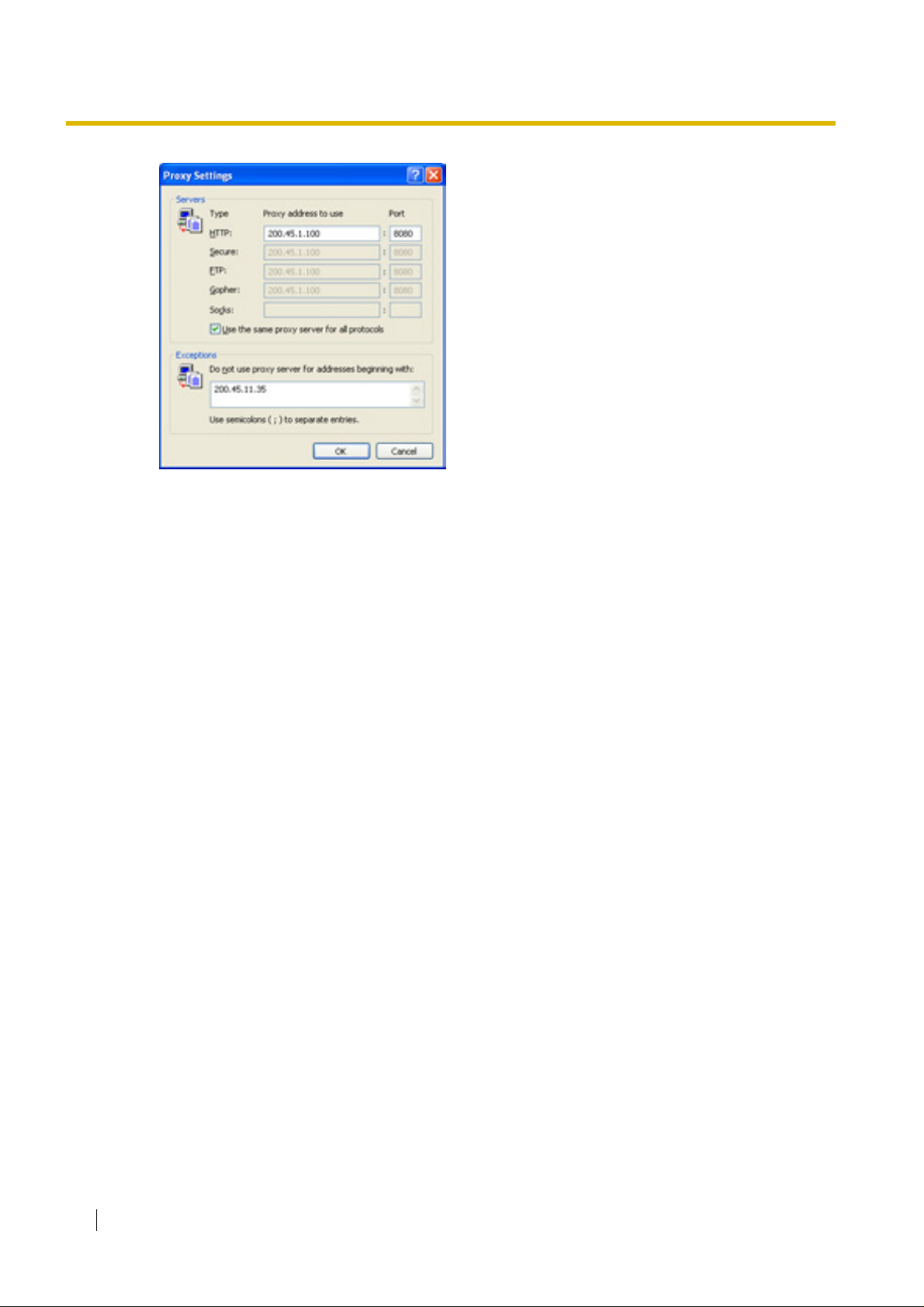
4.1 Preparations
6.
a. Under Do not use pro xy server for
addresses beginning with:, type the IP
address of the card.
b. Click OK.
Your PC is now ready for programming the card
through an IP network.
28 Getting Started
Page 29
4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the
Los Angeles Office
Based on the example network in "1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan", this section
demonstrates the procedure to programme a VoIP Gateway Card for use in the Los Angeles office,
as the first step of setting up a VoIP network. VoIP communications between the 2 offices will be
possible when the cards, as well as the PBXs, in both offices are fully programmed.
The procedure to programme the card in the Chicago office is given in "4.3 Prog ramming the VoIP
Gatewa y Card in th e Ch icago Offi ce". In add ition, the pro cedu re to pro g ramme the PBXs is given in
"5 Programming the PBX".
4.2.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility
Make sure that a PC is connected directly to the VoIP Gateway Card with an Ethernet cross cable
(see "2.2.1 Connection for Programming" or "3.2.1 Connection for Programming").
The card should not be connected to the LAN at this point.
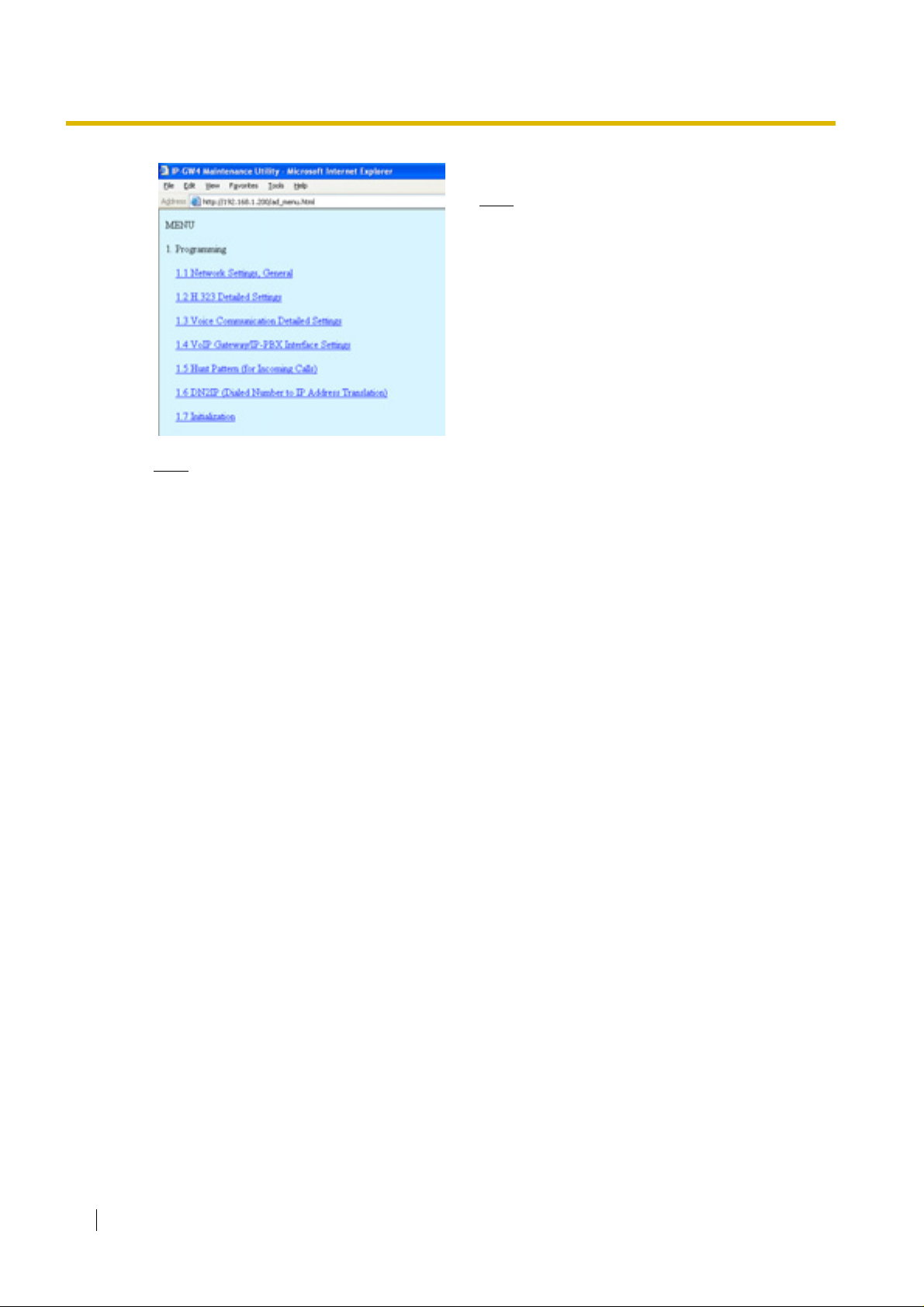
1. Start Internet Explorer from the Start menu.
2.
a. In the Address box of Internet Explorer, type
http://192.168.1.200 (default IP address of the
card).
b. Press the ENTER key on the keyboard.
Notes
• If you cannot see the log-in scree n, return
to "4.1.1 Preparing the PC" and confirm
that your PC has been configured
appropriately.
• If you forget the IP address, you must
initialise the card to the default setting (see
"C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card").
3.
a. In the Username box, type Administrator
(default user name).
b. In the Password box, type Administrator
(default password).
c. Click LOGIN.
Note
If you f orget the user name or password, you
must initialise the card to the default setting
(see "C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card").
Getting Started 29
Page 30
4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
The main menu appears.
Note
Note
If you finish a programming session without logging out from the card (e.g., quitting Internet
Explorer, or r eturning to the log-in screen with the "Back" button of Internet Explorer), you cannot
log in again for the period of time specified by the parameter Programming Auto Disconnect
Time (default: 10 min).
For the log-out procedure and Programming Auto Disconnect Time setting, refer to "2.5.2 Log
Out" and "2.3.2 Maintenance Settings" of the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide,
respectively.
For readability of the text on the screen, it is
recommended that you adjust the text size of
Internet Explorer to below medium.
30 Getting Started
Page 31

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.2 Changing the Status of the VoIP Gateway Card
When programming the VoIP Gateway Card, place the card in the "STOP" status.
1. Click 2.1 Change RUN/STOP status in the main
menu.
2.
a. Click STOP for Status after changing.
b. Click OK.
3. Click OK.
4. Click OK.
Getting Started 31
Page 32

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.3 Assigning the IP Address
When programming the VoIP Gateway Card for the first time, a new IP address must be assigned.
Once this is done and the card is on-line, it will be able to communicate with the other cards ov er the
VoIP network.
The specific setting values are based on the table under "IP Addressing Information" in "1.2.2
Numbering Plan Example" .
1. Click 1.1 Network Settings, General in the main
menu.
2.
a. In the IP Address box, type 200.45.11.35.
b. In the Subnet Mask box, type 255.255.255.0.
c. In the Default Gateway box, type 200.45.11.1.
d. Click OK.
3. Confirm your entry, and then click OK.
Note
For more details about IP addr ess assignm ent, re fer to "2.2.1 Network P ar a meter s" of th e VoIP
Gateway Card Programming Guide.
32 Getting Started
Page 33

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.4 Assigning the Hunt Pattern
The hunt pattern determines how to route incoming calls through the VoIP Gatewa y Card to the PBX.
1. Click 1.5 Hunt Pattern (for Incoming Calls) in the
2.
main menu.
a. In the Hunt Pattern No. box, type 1.
A hunt pattern will be created with this
numbering.
b. In the Receive Leading Number box, type 35
(PBX code).
c. Click ENTRY.
d. Click OK.
3. Confirm your entry, and then click OK.
Note
For more details about hun t patte rn assignment, ref er t o "2.2.5 Hu nt Pattern Parameters" of the
VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
Getting Started 33
Page 34

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.5 Programming the Address Translation Table
The function of an address translation table in a VoIP network is to provide 2-way tra nslation of
telephone numbers and IP addresses
Gateway Cards in the network. Therefore, whenever the address translation table is changed, it is
important to update all the cards in the network with the latest information; othe rwise VoIP
communications cannot be established.
It is possible, at one location in the network, to prog ramme the address tr anslation tabl e that contains
information for the ent ire network. The completed address translation table can then be distributed
across the network, so that all the cards share the same information (see "4.2.6 Downloading the
Address Translation Table from the VoIP Gateway Card", and "Uploading Address Translation Table
to the VoIP Gateway Card" in "4.3 Programming the VoIP Gatewa y Card in the Chicago Office").
Note
The address translation table created for the KX-TDA0484 or KX-TDA3480 can be shared with
the KX-TDA0490.
The procedure below demonstrates the process of programming the address translation table
necessary for VoIP communications between the Los Angeles and Chicago offices.
The specific setting values are based on the table under "PBX Connection Information" in "1.2.2
Numbering Plan Example" .
*1
. The address translation tab le is owned jointly by all VoIP
1. Click 1.6 DN2IP (Dialed Number to IP Address
Translation) in the main menu.
2. Click 1.6.1 GW Entry.
*1
IP address-to-telephone number translation can also be handled by using an H.323 Gatekeeper device. To configure Gatekeeper devices,
refer to the manufacturer's documentation. This manual f ocuses on the method using the V oIP Gatewa y Card's internal address translation
capabilities.
34 Getting Started
Page 35

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
3. Do the following to configure the gateway entry for
the Los Angeles office:
a. In the GW No. box, type 0.
A gateway entry for the card will be created with
this numbering.
b. In the Comment box, type Los Angeles (a
unique identifier of the card in the VoIP
network).
c. In the IP Address box, type 200.45.11.35.
d. In the Group No. box, type 0.
Note
Having the value 0 for Group No. means that
the card does not belong to an y gatewa y group .
Grouping is useful when installing multiple
cards at one location. For details, refer to "2.2.6
Address Translation Table—GW Entry" of the
VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
e. Click ENTRY.
4. Do the following to configure the gateway entry for
the Chicago office:
a. In the GW No. box, type 1.
b. In the Comment box, type Chicago.
c. In the IP Address box, type 199.176.64.41.
d. In the Group No. box, type 0.
e. Click ENTRY.
f. Click OK.
5. Confirm your entry, and then click OK.
The gateway entries for the Los Angeles and
Chicago offices are now configured.
Getting Started 35
Page 36

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
6. Click PREVIOUS.
7. Click 1.6.2 DN2IP Entry.
8. Do the following to confi gure the Los Angeles
extensions:
a. In the Leading Number box, type 352 (PBX
code [35] + extension starting digit [2]).
b. In the Remaining Number of Digits box, type
2 (2 digits to dial [00 to 99] follo wing the leading
number).
c. Click GW for GW No/Group No. Selection.
d. In the GW No/Group No. box, type 0 (the
gateway entry for the card).
e. Click ENTRY.
9.
a. Referring to step 8, complete the address
translation table as shown on the left.
b. Click OK.
c. Confirm your entry, and then click OK.
Note
For more details about address translation programming, refer to "2. 2.6 Address Translation
Table—GW Entry" and "2.2.7 Address Translation Table—DN2IP Entry" of the VoIP Gateway
Card Programming Guide.
36 Getting Started
Page 37

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.6 Downloading the Address Translation Table from the VoIP
Gateway Card
After the address translation table has been fully programmed, download the data from the VoIP
Gateway Card.
The downloaded data can be uploaded to the other cards on the VoIP network (see "Uploading
Address Translation Table to the VoIP Gateway Card" in "4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card
in the Chicago Office"), so that all the cards can communicate with each other over the network.
1. Click 3.4 Download of DN2IP data (VoIP Gateway
→ PC) in the main menu.
2.
a. Click DOWNLOAD.
b. Sp ecify the f ile name and the f older in which to
save the file.
Note
For more details about downloading the address translation table, refer to "2.2.4 VoIP Gateway/
IP-PBX Interface Parameters" of the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
Getting Started 37
Page 38

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.7 Rebooting the VoIP Gateway Card
For all the changes to the parameters to become effe ctive, you must reboot the VoIP Gatew ay Card.
1. Click REBOOT in the main menu.
2. Click REBOOT.
38 Getting Started
Page 39

4.2 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
4.2.8 Confirming the IP Address Assignment
After programming of the VoIP Gateway Card is finished, try to access the card with the new IP
addressing information. If you can connect to the card witho ut pr oblems, the card can be plac ed on
the LAN for VoIP operations (see "2.2.2 Connection to the LAN" or "3.2.2 Connection to the LAN").
Follow the procedure below, referring to "4.1.1 Preparing the PC" and "4.2.1 Starting the IP-GW4
Maintenance Utility".
1. Set the IP address settings of the PC to the following values:
• IP address: 200.45.11.100
• Subnet Mask address: 255.255.255.0
2. Start Internet Explorer from the Start menu.
3. In the Address box of Internet Explorer, type http://200.45.11.35 (the new IP address of the
card).
4. Press the ENTER key on the keyboard.
If you can log in, then the card has been successfully programmed.
After you have confirmed that the card has been successfully programmed, it is strongly
recommended that you download the configuration data from the card and save it on your PC for
backup and archive purposes.
The procedure for downloading the configuration data is provided in "2.4.2 Download of Configuration
Data" of the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
Getting Started 39
Page 40

4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office
4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the
Chicago Office
This section details the procedure to prog ramme the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago office, which
for the most part is a duplication of tha t f or the Los Ange les office . F o r gener al inf ormation that is no t
discussed here, ref er to the relev ant sections in "4.2 Prog ramming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los
Angeles Office".
There are difference s in the procedur e where distinct set ting v alues are re quired f or par ameters t hat
are dependent on the specific netw ork configuration of the Chicago office. Also, the address
translation table does not need to be pro grammed, beca use the one downlo aded from the card in the
Los Angeles office already contains the inf ormation for the entire net work. You can simply upload the
address translation tabl e from the Los Angeles office, and the cards can communicate with each
other on the network.
Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility
1. Start Internet Explorer from the Start menu.
2.
a. In the Address box of Internet Explorer, type
http://192.168.1.200 (def a ult IP addr ess of the
card).
Make sure that the PC has the appropriate IP
address setting to access the card (refer to
"4.1.1 Preparing the PC").
b. Press the ENTER key on the keyboard.
3.
a. In the Username box, type Administrator
(default user name).
b. In the Password box, type Administrator
(default password).
c. Click LOGIN.
The main menu appears.
Changing the Status of the VoIP Gateway Card
1. Click 2.1 Change RUN/STOP status in the main
menu.
2.
a. Click STOP for Status after changing.
b. Click OK.
c. Click OK.
d. Click OK.
40 Getting Started
Page 41

Assigning the IP Address
Note that the card in the Chicago office requires diff erent IP address setting s from the card in the Los
Angeles office.
4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office
1. Click 1.1 Network Settings, General in the main
menu.
2.
a. In the IP Address box, type 199.176.64.41.
b. In the Subnet Mask box, type 255.255.255.0.
c. In the Default Gateway box, type
199.176.64.1.
d. Click OK.
3. Confirm your entry, and then click OK.
Assigning the Hunt Pattern
Note that the card in the Chicago office require s a different PBX code from the card in the Lo s Angeles
office.
1. Click 1.5 Hunt Pattern (for Incoming Calls) in the
main menu.
2.
a. In the Hunt Pattern No. box, type 1.
b. In the Receive Leading Number box, type 41
(PBX code).
c. Click ENTRY.
d. Click OK.
3. Confirm your entry, and then click OK.
Getting Started 41
Page 42

4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office
Uploading Address Translation Table to the VoIP Gateway Card
For the VoIP Gateway Cards in the Los Angeles and Chicago offices to communicate properly over
the VoIP network, the cards must share the same address translation table.
Follow the procedu re belo w t o upload the addr ess tr anslati on table downloaded from the card in the
Los Angeles office (see "4.2.6 Downloading the Address Translation Table from the VoIP Gateway
Card") to the card in the Chicago office.
1. Click 3.3 Upload of DN2IP data (PC → VoIP
Gateway) in the main menu.
2.
a. Click Browse and choose a file to upload.
b. Click UPLOAD(PC→VoIP Gateway).
3. Click REBOOT.
4. Click REBOOT.
42 Getting Started
Page 43

4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office
Note
For more details about uploading t he address transl ation table , refe r to "2.4.3 Upload of Address
Translation Table" of the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
Confirming the IP Address Assignment
Note that the card in the Chicago has been assigned a different IP address from the card in the Los
Angeles office.
1. Set the IP address settings of the PC to the following values:
• IP address: 199.176.64.100
• Subnet Mask address: 255.255.255.0
2. Start Internet Explorer from the Start menu.
3. In the Address box of Internet Explorer, type http://199.176.64.41 (the new IP address of the
card).
4. Press the ENTER key on the keyboard.
If you can log in, then the card has been successfully programmed.
After you have confirmed that the card has been successfully programmed, it is strongly
recommended that you download the configuration data from the card and save it on your PC for
backup and archive purposes.
The procedure for downloading the configuration data is provided in "2.4.2 Download of Configuration
Data" of the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
Getting Started 43
Page 44

4.3 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office
44 Getting Started
Page 45

Section 5
Programming the PBX
For successful operation of a VoIP network using the VoIP
Gatewa y Card as a QSIG network interf ace , the PBX at each
location in the network must be programmed appropriately.
For a detailed discussion of related features, refer to the
Hybrid IP-PBX Feature Guide.
This section details the procedure to programme the PBX to
use the card.
Getting Started 45
Page 46

5.1 Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office
5.1 Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles
Office
This section details the procedure to programme the PBX in the Los Angeles office using the
Maintenance Console (PC programming software of the PBX). After the PBX in the Los Angeles
office has been fully programmed, programme the PBX in the Chicago office with the appropriate
setting values (see "5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office").
Notes
• It is assumed that you have already installed the KX-TDA30 Maintenance Console (PC
programming software of the KX-TD A30 PBX) in your PC.
• The contents and design of the software are subject to change without notice.
1. Start the KX-TDA30 Maintenance Console from the
Start menu.
2.
a. Type the Installer Level Programmer Code
(default: INSTALLER).
b. Click OK.
3.
a. Click Connect → RS-232C or USB.
b. On the ne xt screen, type the system password
for installer (default: 1234).
c. Click OK.
The system menu appears.
4.
a. Under Configuration, click Slot.
b. Mo ve the mouse pointer ov er the installed V oIP
Gateway Card to display the menu of options.
c. Click Port Property.
Confirm that ports 1 and 2 are in service (INS).
46 Getting Started
Page 47

5.1 Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office
5.
a. From the System Menu, click CO & Incoming
Call.
b. Click CO Line Settings.
c. Type the CO Name and assign an unused
Trunk Group Number to be used for all VoIP
gateway trunks (CO lines).
d. Click OK.
6.
a. From the System Menu, click System.
b. Click Numbering Plan.
c. Click Main.
d. Click the Features tab.
e. In the TIE Line Access bo x, t ype the preferred
dial number.
f. Click OK.
7.
a. From the System Men u, clic k Priv ate Netw ork.
b. Click TIE Table.
c. In the Own PBX Code box, type 35 (the PBX
code of the local PBX in the network).
d. In the first unused Leading Number box, type
41 (the PBX code of the remote PBX in the
network).
e. In the corresponding Trunk Group list, select
the number of the trunk group to be used wh en
making calls.
f. Set the number modification pattern, if
necessary.
g. Click OK.
8.
a. From the System Menu, click Configuration.
b. Click Slot.
c. Move the mouse pointer o ver the installed VoIP
Gateway Card to display the menu of options.
d. Click OUS.
You will see a confirmation message.
e. Click OK.
f. Move the mouse pointer o ver the installed VoIP
Gateway Card to display the menu of options.
g. Click Card Property.
9.
a. Select the preferred En-bloc Dialling setting
(Overlap [default] or En-bloc
*1
).
b. Click OK.
Getting Started 47
Page 48

5.1 Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office
*1
When "En-bloc" is selected, users need to press "#" after dialling the phone number to send the dialled digits.
Note
For details about network parameter settings, refe r to the relev ant sections of the Hybrid IP-PBX
PC Programming Manual.
10.
a. Move the mouse pointer ov er the installed VoIP
Gateway Card to display the menu of options.
b. Click INS.
48 Getting Started
Page 49

5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office
5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office
This section details the procedure to programme the PBX in the Chicago office using the
Maintenance Console (PC programmin g software of the PBX). Mak e sure to enter the setting v alues
as appropriate for the Chicago office.
Notes
• It is assumed that you have already installed the Maintenance Console (KX-TDA100/KXTDA200: KXTD A Maintenance Console; KX-TD A600: KX-TDA600 Maintenance Console) in
your PC.
• The screenshots shown in the installation procedure are based on the KX-TDA600
Maintenance Console.
• The contents and design of the software are subject to change without notice.
1. Start the Maintenance Console from the Start
menu.
2.
a. Type the Installer Level Programm er Code
(default: INSTALLER).
b. Click OK.
3.
a. Click Connect → RS-232C or USB.
b. On the ne xt screen, type the system password
for installer (default: 1234).
c. Click OK.
The system menu appears.
4.
a. Under Configuration, click Slot.
b. Move the mouse pointer over the installed
VoIP Gateway Card to display the menu of
options.
c. Click Port Property.
Confirm that ports 1 and 2 are in service (INS).
Getting Started 49
Page 50

5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office
5.
a. From the System Menu, click CO & Incoming
Call.
b. Click CO Line Setting.
c. Type the CO Name and assign an unused
Trunk Group Number to be used for all VoIP
gateway trunks.
d. Click OK.
6.
a. From the System Menu, click System.
b. Click Numbering Plan.
c. Click Main.
d. Click the Features tab.
e. In the TIE Line Access bo x, type the dialling
number.
f. Click OK.
7.
a. From the System Menu, click Private
Network.
b. Click TIE Table.
c. In the Own PBX Code box, type 41 (the PBX
code of the local PBX in the network).
d. In the first unused Leading Number box, type
35 (the PBX code of the remote PBX in the
network).
e. In the corr esponding Trunk Group list, select
the number of the trunk group to be used
when making calls.
f. Set the number modification pattern, if
necessary.
g. Click OK.
50 Getting Started
8.
a. From the System Menu, click Configuration.
b. Click Slot.
c. Move the mouse pointer over the installed
VoIP Gateway Card to display the menu of
options.
d. Click OUS.
You will see a confirmation message.
e. Click OK.
f. Move the mouse pointer over the installed
VoIP Gateway Card to display the menu of
options.
g. Click Card Property.
Page 51

5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office
9.
a. Select the preferred En-bloc Dialling setting
(Overlap [default] or En-bloc
*1
.
b. Click OK.
10.
a. Move the mouse pointer over the installed
VoIP Gateway Card to display the menu of
options.
b. Click INS.
*1
When "En-bloc" is selected, users need to press "#" after dialling the phone number to enter the dialled digits.
Note
For details about netw ork parameter settings, refer to the relev ant sections of t he Hybrid IP-PBX
PC Programming Manual.
Getting Started 51
Page 52

5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office
52 Getting Started
Page 53

Appendix A
Guidance for VoIP Installation
Getting Started 53
Page 54

A1 VoIP Requirements
A1 VoIP Requirements
A1.1 Bandwidth Assessment
When using the VoIP Gateway Card, you must ensure that the IP network in use has enough
bandwidth to support VoIP communications. If the amount of bandwidth required for VoIP
communications is larger than what the network can accommodate, speech quality will be
compromised. In addition, there ma y be some adverse eff ect on the performance of other applicati ons
(e.g., email or web applications) that use the same network. Therefore, care must be taken when
assessing bandwidth requirements.
Inform your network administrator of the required bandwidth, and make sure that the network can
support VoIP communications even under conditions of maximum network traffic.
Bandwidth Calculation
Provided below is the f ormula to find o ut the amount of bandwidth required f or VoIP communications:
Required Bandwidth
= (No. of Fax Machines × Required Bandwidth for Fax Communication) +
[(4 - No. of Fax Machines) × Required Bandwidth for Voice Communication]
Required bandwidth for fax and voice communications for one VoIP channel is shown in the tables
below (for more details, refer to "2.2.3 V oice Communication Par ameters" in the VoIP Gateway Card
Programming Guide).
Required Bandwidth for Voice Communication
The required bandwidth depends on what combination of CODEC and packet sending interval is
used. Keep in mind the following points about the type of CODEC and packet sending interval, in
terms of the speech quality:
• The speech quality of the CODECs varies as follows: (High) G.711, G.729A, G.723.1 (Low )
• The shorter the packet sending interval, the higher the speech quality.
• The higher the speech quality the VoIP Gateway Card provides, the more bandwidth the
card requires.
Via LAN
CODEC
20 ms 30 ms 40 ms 60 ms 90 ms
G.711 87.2 kbps 79.5 kbps 75.6 kbps — —
G.729A 31.2 kbps 23.5 kbps 19.6 kbps — —
G.723.1 5.3 kbps — 20.8 kbps — 13.1 kbps 10.5 kbps
G.723.1 6.3 kbps — 21.9 kbps — 14.1 kbps 11.6 kbps
Packet Sending Interval
54 Getting Started
Page 55

Via WAN (PPP: Point-to-Point Protocol)
A1 VoIP Requirements
CODEC
20 ms 30 ms 40 ms 60 ms 90 ms
G.711 84 kbps 77.3 kbps 74 kbps — —
G.729A 28 kbps 21 kbps 18 kbps — —
G.723.1 5.3 kbps — 18.7 kbps — 12 kbps 9.8 kbps
G.723.1 6.3 kbps — 19.7 kbps — 13.1 kbps 10.8 kbps
Required Bandwidth for Fax Communication
Via LAN
FAX High Reliable Method
Don't Use 87.2 kbps 79.5 kbps 75.6 kbps
Use 224.8 kbps 213.9 kbps 208.4 kbps
Via WAN (PPP: Point-to-Point Protocol)
FAX High Reliable Method
Packet Sending Interval
G.711 Packet Sending Interval
20 ms 30 ms 40 ms
G.711 Packet Sending Interval
20 ms 30 ms 40 ms
Example
Don't Use 84 kbps 77.3 kbps 74 kbps
Use 221.6 kbps 211.7 kbps 206.8 kbps
Consider the following case as an example:
• Communication: via LAN
• No. of Fax Machines: 1
• G.711 Packet Sending Interval for Fax Communication (not using the FAX High Reliable
Method): 40 ms (requiring 75.6 kbps per channel)
• G.729A Packet Sending Interval for Voice Communication: 30 ms (requiring 23.5 kbps per
channel)
In this case, the required bandwidth will be as follows:
Required Bandwidth
= (1 × 75.6) + [(4 - 1) × 23.5]
= 146.1
Therefore, inform your network administrator and make sure that the network can support a
bandwidth of 146.1 kbps even when the network is under conditions of maximum traffic.
Note
It is recommended that all cards in a VoIP network have the same packet sending interval.
Getting Started 55
Page 56

A1 VoIP Requirements
A1.2 Network Configuration
You must evaluate the structure of the e xisting network to see if a VoIP network can be implemented.
Below are the points that should be taken into your evaluation.
Is it possible to have static IP addressing?
Because the maintenance of the VoIP Gateway Card is carried out from a personal computer (PC)
through an IP network, the card must be assigned a static IP address.
Static IP addressing must be made possible e v en when the DHCP feature is used. For more details,
refer to "2.2.1 Network Parameters" in the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
Is network address translation (NAT/NAPT) disabled?
In a network where address translation tech niq ue s (e.g., NAT/NAPT) are used to conver t bet ween
global and local IP addresses, VoIP communications based on the H.323 protocol cannot be carried
out appropriately. Generally, NA T/NAPT are features that are available with routers.
IP Network
Global IP Address Domain
(NAT/NAPT enabled)
Note
If the router on the network supports the "H.323 NAT" feature, it may be possible to have VoIP
communications over the network. For more information, consult your network administrator.
Router
Local IP Address Domain
56 Getting Started
Page 57

A1 VoIP Requirements
Does only a single router provide access to the IP network?
In a dual network, 2 routers provide access to the IP netw ork as shown in the diagram below.
However, the VoIP Gateway Card cannot tak e the advantage of having 2 routers as access point s to
the IP network.
For exam ple, if router A, whose IP address is assigned as the def ault gate wa y IP address of the card,
fails, VoIP communications are no longer possible; the card is not able to switch its default gateway
from router A to router B to access the IP netwo rk. For more details about the def ault gatew ay setting,
refer to "2.2.1 Network Parameters" of the VoIP Gateway Card Programming Guide.
IP Network
Router A Router B
Default gateway
of the card:
Router A
Getting Started 57
Page 58

A1 VoIP Requirements
Is there only a single IP network between 2 ends of a call?
A huge degradation in speech quality will be produced when calls are made through multiple IP
networks as shown below; therefore, it is recommended that you avoid establishing a VoIP network
in this fashion.
PSTN/
BRI QSIG, etc.
IP Network 1 IP Network 2
IP Network 1 IP Network 2
58 Getting Started
Page 59

Is the card located appropriately?
Transmission delays can cause pauses and loss in V oIP comm unications. The more netw ork devices
(e.g., routers and s witches) there ar e betwee n the communicat ing cards , the larger the transmission
delays, be cause a certain amount of delay is inevitab le when packets go thr ough each network device
(hop).
One preventative measure is to install the card so that the number of transmission hops is kept to a
minimum. In the diagram below, the card is located as close to the IP network interface as possible.
A1 VoIP Requirements
Too many hops
Router
Switch
Switch
Hub
A1.3 Network Devices
You must evaluate the network de vices that are used in the e xist ing netwo rk to see if a VoIP network
can be implemented. Below are the points that should be taken into your evaluation.
Better
(PBX located nearest IP network access point)
Router
Switch
Switch
Hub
Can the firewall pass packets from the VoIP Gateway Card?
If the VoIP network contains a firewall, the firewall must be configured appropriately to allow VoIP
packets, which are listed in the table below, to pass through the network without being blocked by
filtering.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
Protocol TCP/UDP Default Port No.
*1
HTTP
RTP/RTCP
H.225.0 Call Signalling
H.245
H.225.0 RAS
*2
*2
*2
*2
QSIG Connectionless Tunnelling
TCP 80
UDP 5004 to 5011
TCP 1720
TCP 1712 to 1724
UDP 1719
*1
TCP 1718
Getting Started 59
Page 60

A1 VoIP Requirements
*1 For the actual setting values, refer to "2.2.1 Network Parameters" in the VoIP Gateway Card
Programming Guide.
*2 For the actual setting values, refer to "2.2.2 H.323 Parameters" in the VoIP Gateway Card
Programming Guide.
Are layer 2 or higher switches used?
Use of repeater hubs can increase the network load, and th erefore will result in degr adation in speech
quality.
To ensure high speech quality, it is strongly recommended that you use layer 2 or higher switches.
Are Category 5 (CAT5) cables used?
When connecting network de vices, make sure to use CAT5 cables. If other types of cabl es are used,
communications may not be carried out normally.
A1.4 QoS (Quality of Service)
Some routers permit the configuration of priority control f eatures. This allo ws the router to give h igher
priority to voice packe ts and low er the ra te of loss and d ela ys during transmissions , hence impr oving
speech quality. It is strongly recommended that you use this feature, especially in networks where
traffic is heavy.
Typically, a router identifies what packets to pass in priority by checking the value in the ToS field of
the header of IP packets. The VoIP Gateway Card has the ability to set the ToS field of outgoing voice
packets (see "2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters" in the VoIP Gateway Card Programming
Guide). When the card is appropriately configured, the router can give voice packets from the card
higher priority.
Consult your network administrator when setting the ToS field, as the setting value must conform to
the router's specifications.
Note
Some switches also permit the configuration of priority control features. For more information,
consult your network administrator.
60 Getting Started
Page 61

A2 VoIP Requirements Checklist
A2 VoIP Requirements Checklist
Use the following checklists to see if you can implement a VoIP network. The answers identified in
underlined bold-face letters
Bandwidth Assessment
No. Question Answer Memo Ref.
are the required answers for the corresponding questions.
Does the network have enough bandwidth
to support VoIP communications?
1
Make sure that there is more bandwidth
available for Vo IP communications than the
amount actually required.
Yes
No
• IP network bandwidth
= kbps
• Available bandwidth for VoIP
= kbps
• Required bandwidth for VoIP
= kbps
p. 54
Network Configuration
No. Question Answer Memo Ref.
2-a Is it possible to have static IP addressing?
Is network address translation (NAT/NAPT)
2-b
disabled?
Does only a single r outer provide access to
2-c
the IP network?
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
p. 56
p. 56
p. 57
Is there only a single IP network between 2
2-d
ends of a call?
2-e Is the card located appropriately?
Yes
No
Yes
No
No. of hops (routers/switches)
within one location:
p. 58
p. 59
Network Devices
No. Question Answer Memo Ref.
Can the firewall pass packets f r om the VoIP
Gateway Card?
When a firewall is used, make sure to configure
3-a
the firewall appropriately to allow VoIP packets
to pass through the network without being
block ed by filtering.
Yes
No
Model of the firewall:
p. 59
Getting Started 61
Page 62

A2 VoIP Requirements Checklist
No. Question Answer Memo Ref.
Are layer 2 or higher switches used?
3-b
Do not use repeater hubs as they can incre ase
the network load.
3-c Are Category 5 (CAT5) cables used?
Yes
No
Yes
Model of the switch:
p. 60
p. 60
No
QoS (Quality of Service)
No. Question Answer Memo Ref.
Model of the router/switch:
Can the router or switch be configured to
4
use priority control features?
Yes
No
VoIP Gateway Card's ToS field
setting:
p. 60
62 Getting Started
Page 63

Appendix B
Alternative Numbering Plan Example
Getting Started 63
Page 64

B1 Extension Number Method
B1 Extension Number Method
This section provides a numbering plan example using the extension number method, as
supplementary information to the PBX code method discussed in "1.2.2 Numbering Plan Example".
B1.1 Example Network
The following diagr am illustrates a simple VoIP network configured for the extension number method.
Local Telephone
456-7890
PSTN
(Public Switched
Telephone Network)
Card IP: 200.45.11.35
PSTN Trunk Number: 92
VoIP Gateway Trunk Access Number: 802
Los Angeles Office
Default Gateway IP: 199.176.64.1
Extn. 201
(200-299)
IP Network
G3 Fax Extn. 501
(500-599)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway IP: 200.45.11.1
Chicago Office
PSTN Trunk Number: 93
VoIP Gateway Trunk Access Number: 803
64 Getting Started
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
G3 Fax Extn. 601
(600-699)
Extn. 301
(300-399)
Card IP: 199.176.64.41
PSTN
Local Telephone
123-4567
Page 65

B1.2 Numbering Plan Example
IP Addressing Information
The following table is a duplication of the table used for the PBX code method.
B1 Extension Number Method
Los Angeles
Office
Card IP Address 200.45.11.35 199.176.64.41
Default Gateway
Address
Subnet Mask
Address
200.45.11.1 199.176.64.1
255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
PBX Numbering Information
The following tab le contains "VoIP Gateway Trunk Access Number", instead of "PBX Code" and "TIE
Line Access Number" as used in the PBX code method.
Los Angeles
Office
Chicago
Office
Chicago
Office
Description
Identifies the location of each VoIP Gateway
Card in the network during VoIP
communications. A unique IP address m ust be
assigned to each card.
Identifies the IP address of the primary gateway
(typically a router or similar device) that
exchanges IP packets with the other gateways
on the VoIP network.
Defines which digits of an IP address are used
for the netw ork address and the host address at
each network location. A card IP address must
fall within the same subnet as that of the default
gateway (e.g., router) that is connected to the
card.
Description
VoIP Gateway
Trunk Access
Number
PSTN Trunk
Number
Extension
Number
Fax Extension
Number
802 803
92 93 An access number to seize a local PSTN trunk.
200 to 299 300 to 399 A number assigned to each extension.
500 to 599 600 to 699 A number assigned to each fax extension.
An access number to seize a VoIP gateway
trunk.
Getting Started 65
Page 66

B1 Extension Number Method
Dialling Examples
With the extension number method, the caller dials only the destination number of the called party to
call through PBXs at different locations.
Calling from Los Angeles to Chicago
To extension 301 via VoIP network
extension no.
Dial 301.
To local telephone 123-4567 via VoIP network through local PSTN
VoIP Gateway
trunk access no.
Chicago PBX
PSTN trunk no.
Dial 93.Dial 802. Dial 123-4567.
Calling from Chicago to Los Angeles
To extension 201 via VoIP network
extension no.
Dial 201.
To local telephone 456-7890 via VoIP network through local PSTN
VoIP Gateway
trunk access no.
Los Angeles PBX
PSTN trunk no.
Dial 92.Dial 803. Dial 456-7890.
PBX Connection Information
Los Angeles Office Chicago Office
phone no.
phone no.
Leading Number 2 5 92 3 6 93
Remaining Digits227227
Card IP Address 200.45.11.35 199.176.64.41
66 Getting Started
Extn. FAX Extn. PSTN
Access
Extn. FAX Extn. PSTN
Access
Page 67

B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method
B2 Programming for the Extension Number
Method
When programming the VoIP Gateway Cards and PBXs for use in a network configured for the
extension number method instead of the PBX code method, some of the steps in the programming
procedures require different setting values.
The following 2 sections provide specific steps that require different setting values. The steps other
than those provided here have common setting values, and are therefore omitted from this
explanation.
B2.1 Programming the VoIP Gateway Card
The hunt patterns and address translation table need different setting values for the extension
number method, as shown in the screen shots provided below.
Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Los Angeles Office
Create hunt patterns with the setting values sho wn below , follo wing the procedure in "4.2.4 Assigning
the Hunt Pattern".
Programme an address tr anslation table with the setting values shown belo w , following th e procedure
in "4.2.5 Programming the Addre ss Translation Table".
Getting Started 67
Page 68

B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method
Programming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office
Create hunt patterns with the setting values shown below, following the procedure in "Assigning the
Hunt Pattern" under "4.3 Progr amming the VoIP Gateway Card in the Chicago Office".
B2.2 Programming the PBX
The steps below are provided in substitution for steps 6 and 7 of the procedure detailed in "5.1
Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office" and "5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago
Office". Programme the PBXs in both offices using the extension number method, following these
steps.
Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office
Step 6
Assign the PSTN trunk access number:
In the Idle Line Access (Local Access) box, type 92 (for Los Angeles office PSTN access).
68 Getting Started
Page 69

Step 7
Step 8
B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method
Assign the leading number used to reach the extensions of the remote PBX:
In the Other PBX Extension Numbering (TIE) box (01 and 02), type 3 (for the Chicago office
extensions) and 6 (for the Chicago office fax extensions).
Assign the routing information to route calls to the remote PBX:
In the Leading Number box, type 3 (for the Chicago office extensions), 6 (for the Chicago off ice fax
extensions), and 93 (for Chicago office PSTN access).
Note
Do not set any value in the Own PBX Code box.
After the above step, follow the procedure in "5.1 Programming the PBX in the Los Angeles Office",
starting from step 8.
Getting Started 69
Page 70

B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method
Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office
Step 6
Assign the PSTN trunk access number:
In the Idle Line Access (Local Access) box, type 93 (for Chicago office PSTN access).
Step 7
Assign the leading number used to reach the extensions of the remote PBX:
In the Other PBX Extension Numbering (TIE) box (01 and 02), type 2 (for the Los Angeles office
extensions) and 5 (for the Los Angeles office fax extensions).
70 Getting Started
Page 71

Step 8
B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method
Assign the routing information to route calls to the remote PBX:
In the Leading Number box, type 2 (for the Los Angeles office extensions), 5 (for the Los Angeles
office fax extensions), and 92 (for Los Angeles office PSTN access).
Note
Do not set any value in the Own PBX Code box.
After the above step, follow the procedure in "5.2 Programming the PBX in the Chicago Office",
starting from step 8.
Getting Started 71
Page 72

B2 Programming for the Extension Number Method
72 Getting Started
Page 73

Appendix C
Initialisation of the VoIP Gateway Card
Getting Started 73
Page 74

C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card
C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card
In case you have forgotten, for example, the IP address or log-in password you set to the VoIP
Gateway Card, follow the procedure below to return the settings of the card to the factory default.
Note
Resetting the card will restore all settings, not just the IP address and log-in password, to the
factory default.
KX-TDA3480
1. Install the card to the KX-TDA30 PBX, and then turn on the power to the PBX.
Power Switch
2. Using the KX-TDA30 Maintenance Console, confirm that the card is in service (INS).
3. Set the System Initialise Switch to the "SYSTEM INITIALIZE" position.
Reset Button
System Initialise Switch
74 Getting Started
CAUTION
Do not press the Reset Button nor turn the power off then on while the System Initialise
Switch is in this position. Doing so will initialise the PBX.
Page 75

4. Using the KX-TDA30 Maintenance Console, set the status of the card to OUS, then set it back
to INS.
5. Return the System Initialise Switch to the "NORMAL" position.
KX-TDA0484
1. Install the card to the KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200/KX-TDA600 PBX, and then turn on the power to
the PBX.
Power Switch
2. Using the Maintenance Console, confirm that the card is in service (INS).
C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card
3. Set the System Initialise Switch to the "SYSTEM INITIALIZE" position.
Reset Button
RESET
SYSTEM
INITIALIZE
NORMAL
System Initialise Switch
CAUTION
Do not press the Reset Button nor turn the power off then on while the System Initialise
Switch is in this position. Doing so will initialise the PBX.
4. Using the Maintenance Console, set the status of the card to OUS, then set it back to INS.
5. Return the System Initialise Switch to the "NORMAL" position.
Getting Started 75
Page 76

C1 Initialising the VoIP Gateway Card
76 Getting Started
Page 77

Appendix D
Using the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 and KX-
TDA0480 in One Network
Getting Started 77
Page 78

D1 Considerations in Installation
D1 Considerations in Installation
Provided below are the po ints to consider when the VoIP network contains both the KX-TDA3480/KXTDA0484 and KX-TDA0480 VoIP Gateway Cards.
Adding the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 to the Network Using the KX-TDA0480 Maintenance
Console Software
For the KX-TD A04 80 to recognise the KX-TDA3480/KX-TD A0484 in the net work, y ou must add it as
an "Other Unit" in a Unit Group (network) when programming with the MCS as shown below:
Note
For progra mming instructions and other information about the KX-TDA0480, refer to the
documentation for the KX-TDA0480.
Restrictions on Feature Compatibility
Some restrictions exist when using the KX-TD A3480/KX-TD A0484 with the KX-TDA0480, as d etailed
below:
• CLIP service is the only QSIG service available between the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484
and KX-TDA0480. There is no compatibility for other QSIG services.
• Fax communications cannot take place between the KX-TDA3480/KX-TDA0484 and KXTDA0480.
78 Getting Started
Page 79

D1 Considerations in Installation
Getting Started 79
Page 80

Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd.
1-62, 4-chome, Minoshima, Hakata-ku, Fukuoka 812-8531, Japan
Copyright:
This material is copyrighted by Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd., and may be reproduced for internal
use only. All other reproduction, in whole or in part, is prohibited without the written consent of Panasonic
Communications Co., Ltd.
© 2005 Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
PSQX3951YA
KK0805AH1076
Page 81

4-Channel VoIP Gateway Card
Programming Guide
KX-TDA3480
Model
KX-TDA0484
Thank you for purchasing a Panasonic 4-Channel VoIP Gateway Card.
Please read this manual carefully before using this product and save this manual for future use.
Page 82

Table of Contents
1 IP-GW4 Main t ena nc e Uti lit y ..... ... .......................... .......................... ... ....3
1.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility ........................................................................4
2 Administrator Functions........................................................................7
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator.....................................................................................8
2.2 Programming...................................................................................................................10
2.2.1 Network Parameter s .... ...................... .. ...................... .. ...................... ... ...................... .. ....10
2.2.2 H.323 Parameters.................................. .. ...................... ... ...................... .. ........................14
2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters....................................................................................18
2.2.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Parameters............... ......................................................25
2.2.5 Hunt Pattern Parameters...................................................................................................27
2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry . ...................... .. ...................... ... ...................... .. .... 3 2
2.2.7 Address Translation Table—DN2IP E n try ......... ...................... .. ....................... .. ...............35
2.2.8 Initialisation.......................................................................................................................39
2.3 Maintenance ....................................................................................................................40
2.3.1 Status Control...................................................................................................................40
2.3.2 Maintenance Settings .......................................................................................................41
2.3.3 Diagnosis ..........................................................................................................................43
2.3.4 Log Information.................................................................................................................44
2.4 Data Management ...........................................................................................................45
2.4.1 Upload of Co nfiguration Data............... ...................... .. ...................... ... ...................... .. .... 4 5
2.4.2 Download of Configuration Data.......................... ........................................... ..................47
2.4.3 Upload of Add r e s s Translat i o n Table....................................... .. ....................... .. ...............48
2.4.4 Download of Address Translation Table............... .......................................................... .. .50
2.5 Others...............................................................................................................................51
2.5.1 Reboot ..............................................................................................................................51
2.5.2 Log Out ................................................... .................. ........................................................52
3 Installer Functions................................................................................53
3.1 Main Menu for the Installer.............................................................................................54
3.2 Maintenance ....................................................................................................................55
3.2.1 Status Control...................................................................................................................55
3.2.2 Maintenance Settings .......................................................................................................56
3.3 Data Management ...........................................................................................................58
3.3.1 Upload of Firmware Data ..................................................................................................58
3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page...............................................................................................61
3.4 Others...............................................................................................................................63
3.4.1 Reboot ..............................................................................................................................63
3.4.2 Log Out ................................................... .................. ........................................................64
Index............................................................................................................65
2 Programming Guide
Page 83

Section 1
IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility
Programming of the VoIP Gatewa y Card is carried out through
a web programming utility called the IP-GW4 Mai nten ance
Utility. This section provides the start-up procedure for the IPGW4 Maintenance Utility.
Programming Guide 3
Page 84

1.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility
1.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Mainte nance Uti lit y
The IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility is a web programming utility for the VoIP Gateway Card. There are
2 different log-in levels available: Administrator level and Installer lev el. These levels provide different
programming options.
For full discussions of Administrator-level programming and Installer-level programming, refer to "2
Administrator Functions" and "3 Installer Functions", respectively.
System Requirements
• The IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility requires Microsoft® Internet Explorer 5.0 or above.
Trademarks
• Microsoft is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
• All other trademarks identified herein are the property of their respective owners.
• Screen shots reprinted with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
1. Run Internet Explorer from the Start menu.
2. In the Address box of Internet Explorer, type http://192.168.1.200.
192.168.1.200 is the default IP address of the VoIP Gateway Card.
3. Press the ENTER key on the keyboard.
4. In the Username box, type the user name.
• Default Administrator-level user name: Administrator
• Default Installer-level user name: Installer
5. In the Password box, type the password.
• Default Administrator-level password: Administrator
• Default Installer-level password: Installer
6. Click LOGIN.
4 Programming Guide
Page 85

1.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility
To clear your entry, click CLEAR.
Notes
• If another user is already logged in, you will be rejected.
• For readability of the text on the screen, it is recommended that you adjust the text size
of Internet Explorer to below medium.
• If you finish a programming session without logging out from the card (e.g., quitting
Internet Explorer, or returning to the log-in screen with the "Back" button of Internet
Explorer), you cannot log in again for the period of time specified by the parameter
Programming Auto Disconnect Time (default: 10 min).
For the log-out procedure and Programming Auto Disconnect Time setting, refer to
"2.5.2 Log Out"/"3.4.2 Log Out" and "2.3.2 Maintenance Settings", respectively.
Programming Guide 5
Page 86

1.1 Starting the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility
6 Programming Guide
Page 87

Section 2
Administrator Functions
This section provides operating instructions for the IP-GW4
Maintenance Utility when logged in as the Administrator.
Programming Guide 7
Page 88

2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator
The IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility provides the following menu to a user logged in as the Administrator.
8 Programming Guide
Page 89

Programming
Menu Section Reference
1.1 Network Settings, General 2.2.1 Network Parameters
1.2 H.323 Detailed Settings 2.2.2 H.323 Parameters
1.3 Voice Communication Detailed Settings 2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters
1.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Settings 2.2.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Parameters
1.5 Hunt Pattern (for Incoming Calls) 2.2.5 Hunt Pattern Parameters
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator
1.6 DN2IP (Dialed Number to IP Address
Translation)
1.7 Initialization 2.2.8 Initialisation
Maintenance
Menu Section Reference
2.1 Change RUN/STOP status 2.3.1 Status Control
2.2 Maintenance Settings 2.3.2 Maintenance Settings
2.3 Diagnosis 2.3.3 Diagnosis
2.4 Log Information 2.3.4 Log Information
Data Management
Menu Section Reference
3.1 Upload of Configuration data (PC → VoIP
Gateway)
3.2 Download of Configuration data (VoIP
Gateway → PC)
2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry
2.2.7 Address Translation Table—DN2IP Entry
2.4.1 Upload of Configuration Data
2.4.2 Download of Configuration Data
Others
3.3 Upload of DN2IP data (PC → Vo IP
Gateway)
3.4 Download of DN 2IP data (VoIP Gateway
→ PC)
Menu Section Reference
REBOOT 2.5.1 Reboot
LOGOUT 2.5.2 Log Out
2.4.3 Upload of Address Translation Table
2.4.4 Download of Address Translation Table
Programming Guide 9
Page 90

2.2 Programming
2.2 Programming
2.2.1 Network Parameters
1. Click 1.1 Network Settings, General in the main menu.
Current IP Address, Current Sub net Mask, and Current Default Gateway show the current
IP address settings of the VoIP Gateway Card.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
•Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
•Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
•Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
10 Programming Guide
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
Page 91

2.2 Programming
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "#" must be changed while the card is in the "STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status
Control"). The changes must be followed by a reboot to become effective (see "2.5.1 Reboot").
IP Address Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the card.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
#
Subnet Mask
Specifies the subnet mask address of the card.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
#
Default Gatewa y
Specifies the default gateway IP address of the card.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
192.168.1.200 The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
• Addresses with
host number all 0s
or 1s
255.255.255.0 Any address is valid.
0.0.0.0 Same as the parameter
IP Address, except that
the address 0.0.0.0. is
allowed.
DHCP Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
DHCP Server
Specifies the use of a DHCP server.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
#
DHCP Server Port No.
Specifies the port number for DHCP communications by the
DHCP server.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
DHCP Client Port No.
Specifies the port number for DHCP communications by the
card (the DHCP client).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
DHCP Lease Time (min) 1-1440min
This parameter is provided for engineer use only.
Don't use Use,
Don't use
67 1 to 65535
68 1 to 65535
1440 0 (disable),
1 to 1440
Programming Guide 11
Page 92

2.2 Programming
HTTP Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
HTTP Port No.
Specifies the port number for HTTP communications by the
card.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
80 1 to 65535
QSIG Connectionless Tunneling Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
QSIG Connectionless Tunneling Port No.
Specifies the port number for connectionless tunnelling
between cards at different locations in a QSIG network.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
Notes
• Connectionless tunnelling enables the PBXs on a
QSIG network to use enhanced networking
features. (For more information about these
features, refer to the relevant sections of the Hybrid
IP-PBX documentation.)
• If you are using a gatekeeper, and enhanced
networking features of the PBX are being used,
overall performance of the card may deteriorate
when network traffic is heavy.
• If you are using a gatekeeper, and "Routed" is
specified for the parameter Call Signaling Model
(see "2.2.2 H.323 Parameters"), connectionless
tunnelling is not possible. In this case, the PBX
cannot use the enhanced networking features.
1718 1 to 65535
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Host Name
This parameter is provided for engineer use only.
#
LAN Disconnect Threshold Time (s)
Specifies the time (in seconds) until disconnection from the
LAN is recognised.
For example, even if a LAN cable is disconnected during a
call, reconnecting the cable within this time period maintains
the call.
12 Programming Guide
VoIP + lower 3
bytes of the MAC
address
5 1 to 10
Max. 255 characters
Page 93

Detailed Explanations
DHCP Server
When using the DHCP feature, the IP address settings of the card (IP address, subnet mask, and
default gatewa y) will be assigned by a DHCP server.
However, k eep in mind that the maintenance of the card is performed through a web browser from a
PC; hence you must know the IP address of the card. Therefore, it is necessary to set up the DHCP
server to assign a static IP address to the card from a pool of IP addresses that is defined in advance.
For more information about DHCP server settings, consult your network administrator.
In addition, it is also necessary to specify the values for the parameters under IP Address Settings
as they will be assigned by the DHCP server.
2.2 Programming
Programming Guide 13
Page 94

2.2 Programming
2.2.2 H.323 Parameters
1. Click 1.2 H.323 Detailed Settings in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
•Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
•Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
•Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
14 Programming Guide
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
Page 95

2.2 Programming
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "#" must be changed while the VoIP Gatewa y Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes must be followed by a reboot to become effective (see "2.5.1 Reboot").
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the card is in the "STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status
Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
Port Number Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
H.225 Port No.
Specifies the port number for the H.225 protocol (call control)
in an H.323 protocol suite.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
H.245 Port No.
Specifies the port number for the H.245 protocol (negotiation
of channel usage and capabilities) in an H.323 protocol suite.
4 consecutive ports, starting with the specified port, will be
used (by default, 1721 to 1724).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
RAS Port No.
Specifies the port number for the H.225 protocol (RAS) in an
H.323 protocol suite.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
RTP/RTCP Port No.
Specifies the port number for RTP/RTCP. 8 consecutive
ports, starting with the specified port, will be used (by default,
5004 to 5011).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
1720 1 to 65535
1721 1 to 65532
1719 1 to 65535
5004 1 to 65528
Voice CODEC Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Voice CODEC Priority 1st–4th
Specifies the type of CODEC for voice communications.
Choose the appropriate CODEC for the network environment
(e.g., bandwidth, CODEC conditions of the remote terminal).
When using multiple CODECs, set them in an appropriate
priority order.
Prior to establishing a call, a negotiation takes place over the
network and the CODEC to be used will be decided
depending on the setting of this parameter.
For details about relations between bandwidth and CODEC,
refer to "Detailed Explanations" in "2.2.3 Voice
Communication Parameters".
1st: G.729A
2nd: No default
3rd: No default
4th: No default
G.723.1,
G.729A,
G.711Mu,
G.711A
Programming Guide 15
Page 96

2.2 Programming
Gatekeeper Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
Gatekeeper
Specifies the use of a gatekeeper.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
*
Primary Gatekeeper IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the primary gatekeeper.
*
Primary Gatekeeper Port No.
Specifies the port number of the primary gatekeeper.
*
Secondary Gatekeeper IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the secondary gatekeeper.
Set this parameter when setting up a secondary gatekeeper
as a redundant backup system.
*
Secondary Gatekeeper Port No.
Specifies the port number of the secondary gatekeeper.
Set this parameter when setting up a secondary gatekeeper
as a redundant backup system.
Don't use Use,
Don't use
192.168.1.3 The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
1719 1 to 65535
192.168.1.4 The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
1719 1 to 65535
*
Gatekeeper Connection Checking Interval (min) 01440min
Specifies the time (in minutes) between periodic checks of
connection to the gatekeeper.
When the primary gatekeeper fails, these checks can detect
the failure. In this case, the connection automatically switches
to the secondary gatekeeper if it is available, so that the
network remains functional.
*
Call Signaling Model
Specifies whether to carry out a call control (H.225) process
directly between the cards or through a gatekeeper.
Direct call control is typically preferred because it involves
less network load.
0 0 (disable),
1 to 1440
Direct Direct,
Routed (via
Gatekeeper)
16 Programming Guide
Page 97

2.2 Programming
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
Fast Connect
Specifies the use of the Fast Connect feature.
Using Fast Connect simplifies the communication process so
that calls can be established quickly.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
Detailed Explanations
Gatekeeper
The following are the general functions of a gatekeeper:
• Dialled number-to-IP address translation
• Authentication
• Bandwidth control
It is possible to employ a VoIP network without the use of a gatekeeper , because the card is equipped
with internal address translation capabilities. However, should the network contain dozens of cards,
maintenance of address translation tables in individual cards can become a strain.
A gatekeeper is useful in this case, because with the gatekeeper it is possible to consolidate the
maintenance. (However, you still need to programme each card on the network with its own address
translation information. For details, refer to "2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry" and "2.2.7
Address T ranslation T able—DN2IP Entry".) For more information about gatekeeper functions, consult
the documentation of the gatekeeper.
When using a gatekeeper, make sure to choose a compatible model. For more information about
gatekeeper compatibility with the card, consult a certified dealer.
Use Use,
Don't use
Programming Guide 17
Page 98

2.2 Programming
2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters
1. Click 1.3 Voice Communication Detailed Settings in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
•Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
•Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
•Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW4 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
18 Programming Guide
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
Page 99

2.2 Programming
Parameter Descriptions
QoS Field Settings
The parameters below are used to set the ToS (Type of Service) field in the header of IP packets to control
QoS of VoIP communications.
For more information about QoS, refer to "A1.4 QoS (Quality of Service)" of the VoIP Gateway Card Getting
Started. For the actual setting values, consult your network administrator.
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
ToS
Specifies the value in the ToS field by a generic term.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
DSCP
Specifies the value in the ToS field by a DSCP for DiffServ.
HEX
Specifies the value in the T oS field by a hexadecimal number.
Priority: 0 0 to 7
Normal Normal,
Monetary Cost,
Reliability,
Throughput,
Delay
No default 0 to 63
No default 00 to FF
Jitter buff er Settings
When voice signals are packetised and transmitted, individual packets can take different paths through the
network and arrive at the destination at varied timings. This is referred to as "jitter", and it can cause
degradation in speech quality. To compensate for jitter problems, the "jitter buffer" accumulates the packets
temporarily for processing.
The parameters below are used to adjust the size of the jitter buffer. However, in general, there is no need to
change the default values.
Parameter Default Value Range
G.711/G.729A Jitter Buffer Minimum (ms)
G.711/G.729A Jitter Buffer Maximum (ms)
G.711/G.729A Jitter Buffer Default Value (ms)
G.711/G.729A Jitter Buffer Adjustme nt Interval (s) 1-
5s
G.723.1 Jitter Buffer Minimum (ms)
G.723.1 Jitter Buffer Maximum (ms)
G.723.1 Jitter Buffer Default value (ms)
G.723.1 Jitter Buffer Adjustment Interval (s) 1-5s
10 10 × n (n = 1–40)
400 10 × n (n = 1–40)
10 10 × n (n = 1–40)
51 to 5
30 30 × n (n = 1–40)
1200 30 × n (n = 1–40)
30 30 × n (n = 1–40)
51 to 5
Programming Guide 19
Page 100

2.2 Programming
CODEC Frame Settings
The parameters below are used to set the interval between packet transmissions for each type of CODEC. It
is recommended that all VoIP Gatew a y Cards in a V oIP network have the same settings for these parameters.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
Parameter Default Value Range
G.723.1 Packet Sending Interval (ms)
G.729A Packet Sending Interval (ms)
G.711 Packet Sending Interval (ms)
30 30, 60, 90
20 20, 30, 40
20 20, 30, 40
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Echo Canceller
Specifies the use of the echo cancellation feature (G.168).
Echo is the audible duplication of a caller's voice on the return
path; when echo exists, the caller hears his or her own voice
after some delay. The echo canceller eliminates this echo.
Note
There are various factors that may cause an echo. In
some cases, this feature does not eliminate the echo
entirely.
G.723.1 VAD (Voice Activity Detection)
Specifies the use of the VAD feature (G.723.1).
The VAD conserves bandwidth by detecting silent periods
during a call and suppressing the packets of silence from
being sent to the network.
Use Use,
Don't use
Use Use,
Don't use
Note
T o use this feature , both the local and remote cards must
have this parameter set to "Use".
G.723.1 Rate
Specifies the rate of the G.723.1 CODEC.
DTMF Detection
Specifies the use of the DTMF detection feature.
DTMF detection enables end-to-end DTMF relay over the
network.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
FAX Signal Detection
Specifies the use of the fax signal detection feature.
Fax signal detection enables end-to-end fax signal relay over
the network.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
20 Programming Guide
6.3Kbps 5.3Kbps,
6.3Kbps
Use Use,
Don't use
Don't use Use,
Don't use
 Loading...
Loading...