Omron VARISPEED G7 DATASHEET

VARISPEED G7
General purpose inverter (Advanced Vector Control)
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Manual No.
TOE-S616-60.2

YASKAWA
Varispeed G7
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
GENERAL PURPOSE INVERTER (ADVANCED VECTOR CONTROL)
MODEL: CIMR-G7C
200V CLASS 0.4 to 110kW (1.2 to 160kVA)
400V CLASS 0.4 to 300kW (1.2 to 460kVA)
Upon receipt of the product and prior to initial operation, read these instructions
thoroughly, and retain for future reference.
YASKAWA MANUAL NO. TOE-S616-60.2

Preface
This manual is designed to ensure correct and suitable
application of Varispeed G7-Series Inverters. Read
this manual before attempting to install, operate, maintain, or inspect an Inverter and keep it in a safe, convenient location for future reference. Before you
understand all precautions and safety information
before attempting application.
General Precautions
• The diagrams in this manual may be indicated without covers or safety shields to show details.
Be sure to restore covers or shields before operating the Units and run the Units according to the
instructions described in this manual.
• Any illustrations, photographs, or examples used in this manual are provided as examples only
and may not apply to all products to which this manual is applicable.
• The products and specifications described in this manual or the content and presentation of the
manual may be changed without notice to improve the product and/or the manual.
• When ordering a new copy of the manual due to damage or loss, contact your Yaskawa representatives or the nearest Yaskawa sales office and provide the manual number shown on the front
cover.
• If nameplates become warn or damaged, order new ones from your Yaskawa representatives or
the nearest Yaskawa sales office.
i

Safety Information
The following conventions are used to indicate precautions in this manual. Failure to heed precautions provided in this manual can result in serious or possibly even fatal injury or damage to
the products or to related equipment and systems.
WARNING
CAUTION
IMPORTANT
Indicates precautions that, if not heeded, could possibly result in loss of life or serious injury.
Indicates precautions that, if not heeded, could result in relatively serious or minor injury, damage
to the product, or faulty operation.
Failure to heed a precaution classified as a caution can result in serious consequences depending
on the situation.
Indicates important information that should be memorized.
ii
Safety Precautions
Confirmations upon Delivery
• Never install an Inverter that is damaged or missing components.
Doing so can result in injury.
Installation
• Always hold the case when carrying the Inverter.
If the Inverter is held by the front cover, the main body of the Inverter may fall, possibly resulting in injury.
• Attach the Inverter to a metal or other noncombustible material.
Fire can result if the Inverter is attached to a combustible material.
• Install a cooling fan or other cooling device when installing more than one Inverter in the same
enclosure so that the temperature of the air entering the Inverters is below 45°C.
Overheating can result in fires or other accidents.
CAUTION
CAUTION
Wiring
• Always turn OFF the input power supply before wiring terminals.
• Wiring must be performed by an authorized person qualified in electrical work.
• Be sure to ground the ground terminal. (200 V class: Ground to 100 Ω or less, 400 V class: Ground
• Always check the operation of any emergency stop circuits after they are wired.
• Never touch the output terminals directly with your hands or allow the output lines to come into con-
• Check to be sure that the voltage of the main AC power supply satisfies the rated voltage of the
• Do not perform voltage withstand tests on the Inverter.
• Connect braking resistors, Braking Resistor Units, and Braking Units as shown in the I/O wiring
• Tighten all terminal screws to the specified tightening torque.
• Do not connect AC power to output terminals U, V, and W.
• Do not connect phase-advancing capacitors or LC/RC noise filters to the output circuits.
WARNING
Otherwise, an electric shock or fire can occur.
Otherwise, an electric shock or fire can occur.
to 10 Ω or less)
Otherwise, an electric shock or fire can occur.
Otherwise, there is the possibility of injury. (Wiring is the responsibility of the user.)
tact with the Inverter case. Never short the output circuits.
Otherwise, an electric shock or ground short can occur.
CAUTION
Inverter.
Injury or fire can occur if the voltage is not correct.
Otherwise, semiconductor elements and other devices can be damaged.
examples.
Otherwise, a fire can occur.
Otherwise, a fire may occur.
The interior parts of the Inverter will be damaged if voltage is applied to the output terminals.
The Inverter can be damaged or internal parts burnt if these devices are connected.
iii
• Do not connect electromagnetic switches or contactors to the output circuits.
If a load is connected while the Inverter is operating, surge current will cause the overcurrent protection circuit inside the
Inverter to operate.
Setting User Constants
• Disconnect the load (machine, device) from the motor before performing rotational autotuning.
The motor may turn, possibly resulting in injury or damage to equipment. Also, motor constants cannot be correctly set
with the motor attached to a load.
• Stay clear of the motor during rotational autotuning.
The motor may start operating suddenly when stopped, possibly resulting in injury.
Trial Operation
• Check to be sure that the front cover is attached before turning ON the power supply.
An electric shock may occur.
• Do not come close to the machine when the fault reset function is used. If the alarmed is cleared,
the machine may start moving suddenly.
Also, design the machine so that human safety is ensured even when it is restarted.
Injury may occur.
• Provide a separate emergency stop switch; the Digital Operator STOP Key is valid only when its
function is set.
Injury may occur.
• Reset alarms only after confirming that the RUN signal is OFF.
Injury may occur.
CAUTION
CAUTION
WARNING
CAUTION
• Don't touch the radiation fins (heatsink), braking resistor, or Braking Resistor Unit. These can
become very hot.
Otherwise, a burn injury may occur.
• Be sure that the motor and machine is within the applicable ranges before starting operation.
Otherwise, an injury may occur.
• Provide a separate holding brake if necessary.
Always construct the external sequence to confirm that the holding brake is activated in the event
of an emergency, a power failure, or an abnormality in the Inverter.
Failure to observe this caution can result in injury.
• If using an Inverter with an elevator, take safety measures on the elevator to prevent the elevator
from dropping.
Failure to observe this caution can result in injury.
• Don't check signals while the Inverter is running.
Otherwise, the equipment may be damaged.
• Be careful when changing Inverter settings. The Inverter is factory set to suitable settings.
Otherwise, the equipment may be damaged.
iv
Maintenance and Inspection
• Do not touch the Inverter terminals. Some of the terminals carry high voltages and are extremely
dangerous.
Doing so can result in electric shock.
• Always have the protective cover in place when power is being supplied to the Inverter. When
attaching the cover, always turn OFF power to the Inverter through the MCCB.
Doing so can result in electric shock.
• After turning OFF the main circuit power supply, wait until the CHARGE indicator light goes out
before performance maintenance or inspections.
The capacitor will remain charged and is dangerous.
• Maintenance, inspection, and replacement of parts must be performed only by authorized personnel.
Remove all metal objects, such as watches and rings, before starting work. Always use grounded tools.
Failure to heed these warning can result in electric shock.
• A CMOS IC is used in the control board. Handle the control board and CMOS IC carefully. The
CMOS IC can be destroyed by static electricity if touched directly.
The CMOS IC can be destroyed by static electricity if touched directly.
• Do not change the wiring, or remove connectors or the Digital Operator, during operation.
Doing so can result in personal injury.
WARNING
CAUTION
Other
WARNING
• Do not attempt to modify or alter the Inverter.
Doing so can result in electrical shock or injury.
v
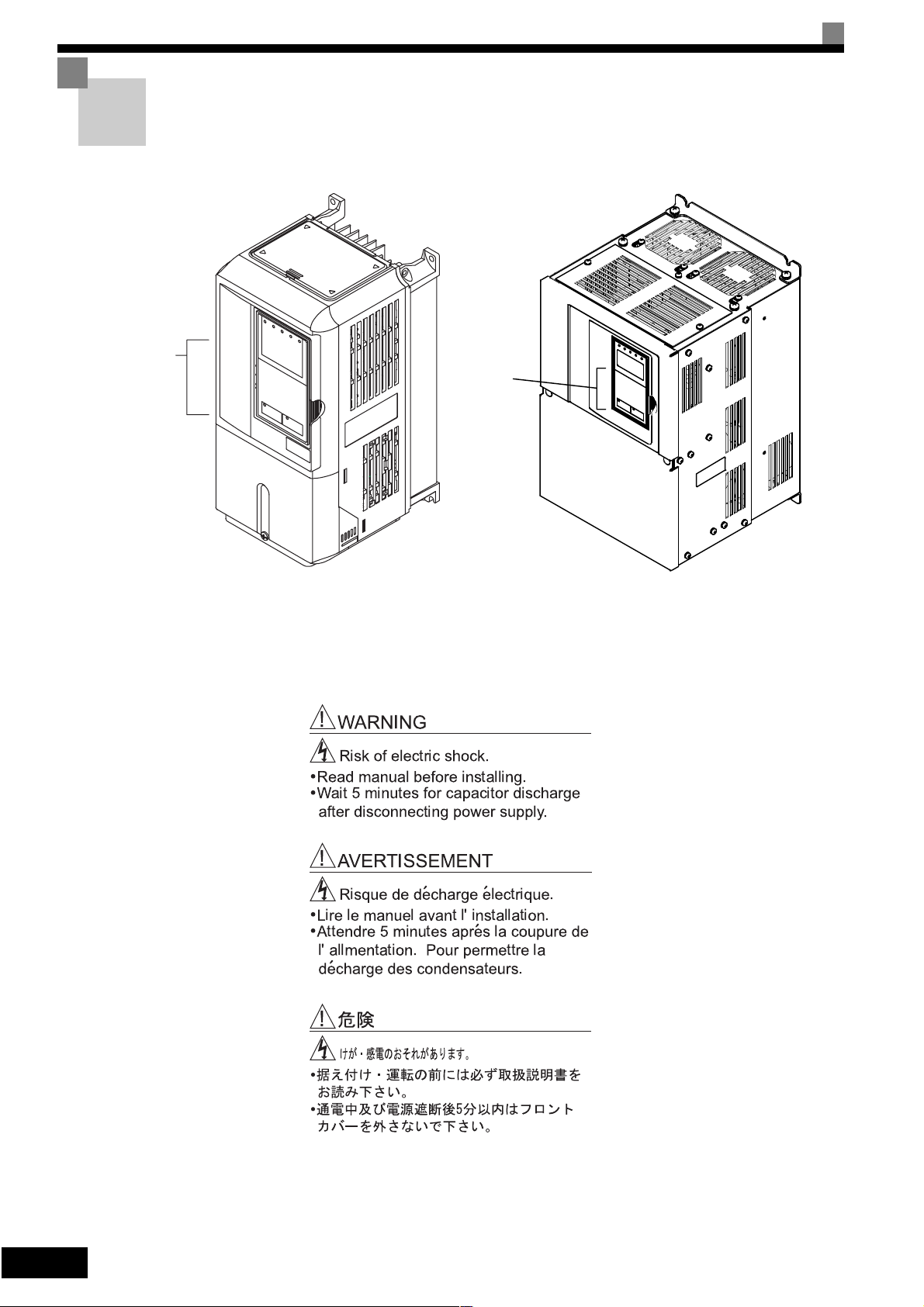
Warning Information and Position
There is warning information on the Inverter in the position shown in the following illustration.
Always heed the warnings.
Warning
information
position
Warning
information
position
Illustration shows the CIMR-G7C20P4
Warning Information
!
WARNING
Risk of electric shock.
Read manual before installing.
Wait 5 minutes for capacitor discharge
after disconnecting power supply.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Risque de decharge electrique.
Lire le manuel avant l' installation.
Attendre 5 minutes apres la coupure de
l' allmentation. Pour permettre la
'
decharge des condensateurs.
!
Illustration shows the CIMR-G7C2018
'
'
'
vi

Registered Trademarks
The following registered trademarks are used in this manual.
• DeviceNet is a registered trademark of the ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendors Association,
Inc.).
• InterBus is a registered trademark of Phoenix Contact Co.
• ControlNet is a registered trademark of ControlNet International, Ltd.
• LONworks is a registered trademark of the Echolon.
vii

viii

Contents
1 Handling Inverters .................................................................. 1-1
Varispeed G7 Introduction ............................................................................1-2
Varispeed G7 Models .....................................................................................................1-2
Confirmations upon Delivery ........................................................................1-3
Checks............................................................................................................................1-3
Nameplate Information ...................................................................................................1-3
Component Names.........................................................................................................1-5
Exterior and Mounting Dimensions...............................................................1-7
Open Chassis Inverters (IP00) .......................................................................................1-7
Enclosed Wall-mounted Inverters (NEMA1 Type 1) .......................................................1-7
Checking and Controlling the Installation Site ..............................................1-9
Installation Site ...............................................................................................................1-9
Controlling the Ambient Temperature .............................................................................1-9
Protecting the Inverter from Foreign Matter....................................................................1-9
Installation Orientation and Space..............................................................1-10
Removing and Attaching the Terminal Cover .............................................1-11
Removing the Terminal Cover ...................................................................................... 1-11
Attaching the Terminal Cover........................................................................................1-11
Removing/Attaching the Digital Operator and Front Cover ........................1-12
Inverters of 15 kW or Less............................................................................................1-12
Inverters of 18.5 kW or More ........................................................................................1-15
2 Wiring....................................................................................... 2-1
Connections to Peripheral Devices ..............................................................2-2
Connection Diagram.....................................................................................2-3
Terminal Block Configuration........................................................................2-5
Wiring Main Circuit Terminals.......................................................................2-6
Applicable Wire Sizes and Closed-loop Connectors ......................................................2-6
Main Circuit Terminal Functions ...................................................................................2-11
Main Circuit Configurations...........................................................................................2-12
Standard Connection Diagrams....................................................................................2-13
Wiring the Main Circuits................................................................................................2-14
Wiring Control Circuit Terminals .................................................................2-20
Wire Sizes and Closed-loop Connectors......................................................................2-20
Control Circuit Terminal Functions ...............................................................................2-22
Control Circuit Terminal Connections ...........................................................................2-26
Control Circuit Wiring Precautions................................................................................2-27
ix

Wiring Check.............................................................................................. 2-28
Checks ......................................................................................................................... 2-28
Installing and Wiring Option Cards............................................................. 2-29
Option Card Models and Specifications ....................................................................... 2-29
Installation ....................................................................................................................2-29
PG Speed Control Card Terminals and Specifications................................................. 2-30
Wiring ........................................................................................................................... 2-32
Wiring Terminal Blocks................................................................................................. 2-36
Selecting the Number of PG (Encoder) Pulses............................................................ 2-37
3 Digital Operator and Modes....................................................3-1
Digital Operator ............................................................................................ 3-2
Digital Operator Display ................................................................................................. 3-2
Digital Operator Keys .....................................................................................................3-2
Modes ..........................................................................................................3-4
Inverter Modes ............................................................................................................... 3-4
Switching Modes ............................................................................................................ 3-5
Drive Mode .....................................................................................................................3-6
Quick Programming Mode.............................................................................................. 3-7
Advanced Programming Mode....................................................................................... 3-9
Verify Mode .................................................................................................................. 3-12
Autotuning Mode .......................................................................................................... 3-13
4 Trial Operation .........................................................................4-1
Trial Operation Procedure ............................................................................4-2
Trial Operation Procedures .......................................................................... 4-3
Setting the Power Supply Voltage Jumper (400 V Class Inverters of 55 kW or Higher) 4-3
Power ON ....................................................................................................................... 4-3
Checking the Display Status .......................................................................................... 4-4
Basic Settings................................................................................................................. 4-5
Settings for the Control Methods.................................................................................... 4-7
Autotuning ......................................................................................................................4-9
Application Settings...................................................................................................... 4-14
No-load Operation ........................................................................................................ 4-14
Loaded Operation......................................................................................................... 4-14
Check and Recording User Constants ......................................................................... 4-15
Adjustment Suggestions ............................................................................ 4-16
5 User Constants ........................................................................5-1
User Constant Descriptions.......................................................................... 5-2
Description of User Constant Tables .............................................................................. 5-2
x
Digital Operation Display Functions and Levels...........................................5-3
User Constants Settable in Quick Programming Mode.................................................. 5-4

User Constant Tables ...................................................................................5-8
A: Setup Settings............................................................................................................5-8
Application Constants: b ...............................................................................................5-10
Autotuning Constants: C...............................................................................................5-20
Reference Constants: d ................................................................................................5-26
Motor Constant Constants: E........................................................................................5-32
Option Constants: F......................................................................................................5-38
Terminal Function Constants: H ...................................................................................5-45
Protection Function Constants: L..................................................................................5-57
N: Special Adjustments.................................................................................................5-67
Digital Operator Constants: o........................................................................................5-70
T: Motor Autotuning ......................................................................................................5-74
U: Monitor Constants ....................................................................................................5-75
Factory Settings that Change with the Control Method (A1-02) ...................................5-83
Factory Settings that Change with the Inverter Capacity (o2-04).................................5-86
6 Constant Settings by Function.............................................. 6-1
Frequency Reference ...................................................................................6-2
Selecting the Frequency Reference Source...................................................................6-2
Using Multi-Step Speed Operation .................................................................................6-5
Run Command .............................................................................................6-7
Selecting the Run Command Source .............................................................................6-7
Stopping Methods.........................................................................................6-9
Selecting the Stopping Method when a Stop Command is Sent.....................................6-9
Using the DC Injection Brake........................................................................................6-13
Using an Emergency Stop ............................................................................................6-14
Acceleration and Deceleration Characteristics...........................................6-15
Setting Acceleration and Deceleration Times...............................................................6-15
Accelerating and Decelerating Heavy Loads (Dwell Function).....................................6-19
Preventing the Motor from Stalling During Acceleration (Stall Prevention During
Acceleration Function)..................................................................................................6-20
Preventing Overvoltage During Deceleration (Stall Prevention During Deceleration
Function).......................................................................................................................6-22
Adjusting Frequency References ...............................................................6-24
Adjusting Analog Frequency References .....................................................................6-24
Operation Avoiding Resonance (Jump Frequency Function) .......................................6-27
Adjusting Frequency Reference Using Pulse Train Inputs ...........................................6-29
Speed Limit (Frequency Reference Limit Function) ...................................6-30
Limiting Maximum Output Frequency...........................................................................6-30
Limiting Minimum Frequency........................................................................................6-30
Improved Operating Efficiency ...................................................................6-32
Reducing Motor Speed Fluctuation (Slip Compensation Function)..............................6-32
Compensating for Insufficient Torque at Startup and Low-speed Operation
(Torque Compensation) ................................................................................................6-34
Hunting-prevention Function.........................................................................................6-36
xi

Stabilizing Speed (Speed Feedback Detection Function)............................................ 6-37
Machine Protection .................................................................................... 6-38
Reducing Noise and Leakage Current ......................................................................... 6-38
Limiting Motor Torque (Torque Limit Function) ............................................................ 6-41
Preventing Motor Stalling During Operation................................................................. 6-43
Changing Stall Prevention Level during Operation Using an Analog Input .................. 6-44
Detecting Motor Torque ................................................................................................ 6-44
Changing Overtorque and Undertorque Detection Levels Using an Analog Input ....... 6-48
Motor Overload Protection ........................................................................................... 6-49
Setting Motor Protection Operation Time ..................................................................... 6-51
Motor Overheating Protection Using PTC Thermistor Inputs ....................................... 6-52
Limiting Motor Rotation Direction .................................................................................6-54
Continuing Operation ................................................................................. 6-55
Restarting Automatically After Power Is Restored........................................................ 6-55
Speed Search............................................................................................................... 6-56
Continuing Operation at Constant Speed When Frequency Reference Is Lost ........... 6-62
Restarting Operation After Transient Error (Auto Restart Function) ............................ 6-63
Inverter Protection...................................................................................... 6-64
Performing Overheating Protection on Mounted Braking Resistors............................. 6-64
Reducing Inverter Overheating Pre-Alarm Warning Levels .........................................6-65
Input Terminal Functions ............................................................................ 6-66
Temporarily Switching Operation between Digital Operator and Control Circuit
Terminals ......................................................................................................................6-66
Blocking Inverter Outputs (Baseblock Commands)...................................................... 6-67
Stopping Acceleration and Deceleration (Acceleration/Deceleration Ramp Hold)....... 6-68
Raising and Lowering Frequency References Using Contact Signals (UP/DOWN) .... 6-69
Accelerating and Decelerating Constant Frequencies in the Analog References
(+/- Speed) ................................................................................................................... 6-72
Hold Analog Frequency Using User-set Timing ........................................................... 6-73
Switching Operations between a Communications Option Card and Control Circuit
Terminals ......................................................................................................................6-73
Jog Frequency Operation without Forward and Reverse Commands (FJOG/RJOG) . 6-74
Stopping the Inverter by Notifying Programming Device Errors to the Inverter
(External Fault Function) .............................................................................................. 6-75
Monitor Constants ......................................................................................6-76
Using the Analog Monitor Constants............................................................................ 6-76
Using Pulse Train Monitor Contents............................................................................. 6-79
Individual Functions ...................................................................................6-81
Using MEMOBUS Communications............................................................................. 6-81
Using the Timer Function .............................................................................................6-93
Using PID Control......................................................................................................... 6-94
Energy-saving ............................................................................................................ 6-103
Setting Motor Constants............................................................................................. 6-105
Setting the V/f Pattern ................................................................................................6-107
Torque Control ........................................................................................................... 6-114
Speed Control (ASR) Structure .................................................................................. 6-122
xii

Droop Control Function...............................................................................................6-127
Zero-servo Function....................................................................................................6-128
Digital Operator Functions ........................................................................6-132
Setting Digital Operator Functions..............................................................................6-132
Copying Constants .....................................................................................................6-135
Prohibiting Writing Constants from the Digital Operator .............................................6-139
Setting a Password.....................................................................................................6-140
Displaying User-set Constants Only...........................................................................6-141
Options .....................................................................................................6-142
Performing Speed Control with PG.............................................................................6-142
Using Digital Output Cards .........................................................................................6-146
Using an Analog Reference Card...............................................................................6-148
Using a Digital Reference Card ..................................................................................6-149
7 Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 7-1
Protective and Diagnostic Functions ............................................................7-2
Fault Detection................................................................................................................7-2
Alarm Detection ..............................................................................................................7-9
Operation Errors ...........................................................................................................7-13
Errors During Autotuning .............................................................................................7-15
Errors when Using the Digital Operator Copy Function................................................7-16
Troubleshooting..........................................................................................7-17
If Constant Constants Cannot Be Set...........................................................................7-17
If the Motor Does Not Operate......................................................................................7-18
If the Direction of the Motor Rotation is Reversed ........................................................7-19
If the Motor Does Not Put Out Torque or If Acceleration is Slow..................................7-20
If the Motor Operates Higher Than the Reference .......................................................7-20
If the Slip Compensation Function Has Low Speed Precision......................................7-20
If There is Low Speed Control Accuracy at High-speed Rotation in Open-loop Vector
Control Mode ................................................................................................................7-21
If Motor Deceleration is Slow........................................................................................7-21
If the Motor Overheats ..................................................................................................7-22
If There is Noise When the Inverter is Started or From an AM Radio...........................7-22
If the Ground Fault Interrupter Operates When the Inverter is Run..............................7-23
If There is Mechanical Oscillation.................................................................................7-23
If the Motor Rotates Even When Inverter Output is Stopped........................................7-24
If 0 V is Detected When the Fan is Started, or Fan Stalls.............................................7-24
If Output Frequency Does Not Rise to Frequency Reference ......................................7-24
8 Maintenance and Inspection.................................................. 8-1
Maintenance and Inspection.........................................................................8-2
Outline of Maintenance...................................................................................................8-2
Daily Inspection ..............................................................................................................8-2
Periodic Inspection .........................................................................................................8-2
xiii

Periodic Maintenance of Parts ....................................................................................... 8-3
Cooling Fan Replacement Outline ................................................................................. 8-4
Removing and Mounting the Control Circuit Terminal Card........................................... 8-6
9 Specifications ..........................................................................9-1
Standard Inverter Specifications .................................................................. 9-2
Specifications by Model.................................................................................................. 9-2
Common Specifications.................................................................................................. 9-4
Specifications of Options and Peripheral Devices ....................................... 9-5
10 Appendix ................................................................................10-1
Varispeed G7 Control Modes .....................................................................10-2
Control Modes and Features........................................................................................ 10-2
Control Modes and Applications................................................................................... 10-5
Inverter Application Precautions ................................................................ 10-7
Selection.......................................................................................................................10-7
Installation ....................................................................................................................10-8
Settings ........................................................................................................................10-8
Handling ....................................................................................................................... 10-9
Motor Application Precautions ................................................................. 10-10
Using the Inverter for an Existing Standard Motor...................................................... 10-10
Using the Inverter for Special Motors......................................................................... 10-11
Power Transmission Mechanism (Speed Reducers, Belts, and Chains) ................... 10-11
Conformance to CE Markings .................................................................. 10-12
CE Markings............................................................................................................... 10-12
Requirements for Conformance to CE Markings........................................................10-12
User Constants......................................................................................... 10-19
xiv

Handling Inverters
This chapter describes the checks required upon receiving or installing an Inverter.
Varispeed G7 Introduction ...........................................1-2
Confirmations upon Delivery........................................1-3
Exterior and Mounting Dimensions..............................1-7
Checking and Controlling the Installation Site .............1-9
Installation Orientation and Space .............................1-10
Removing and Attaching the Terminal Cover ............ 1-11
Removing/Attaching the Digital Operator
and Front Cover..........................................................1-12
Varispeed G7 Introduction
Varispeed G7 Models
The Varispeed-G7 Series of Inverters included two Inverters in two voltage classes: 200 V and 400 V. Maximum
motor capacities vary from 0.4 to 300 kW (41 models).
Table 1.1 Varispeed G7 Models
Voltage
Class
200 V class
400 V class
Maximum
Motor
Capacity
kW
0.4 1.2 CIMR-G7C20P4
0.75 2.3 CIMR-G7C20P7 20P71
1.5 3.0 CIMR-G7C21P5 21P51
2.2 4.6 CIMR-G7C22P2 22P21
3.7 6.9 CIMR-G7C23P7 23P71
5.5 10 CIMR-G7C25P5 25P51
7.5 13 CIMR-G7C27P5 27P51
11 19 CIMR-G7C2011 2011
15 25 CIMR-G7C2015 20151
18.5 30 CIMR-G7C2018 20181
22 37 CIMR-G7C2022 20220 20221
30 50 CIMR-G7C2030 20300 20301
37 61 CIMR-G7C2037 20370 20371
45 70 CIMR-G7C2045 20450 20451
55 85 CIMR-G7C2055 20550 20551
75 110 CIMR-G7C2075 20750 20751
90 140 CIMR-G7C2090 20900 -
110 160 CIMR-G7C2110 21100 -
0.4 1.4 CIMR-G7C40P4
0.75 2.6 CIMR-G7C40P7 40P71
1.5 3.7 CIMR-G7C41P5 41P51
2.2 4.7 CIMR-G7C42P2 42P21
3.7 6.9 CIMR-G7C43P7 43P71
5.5 11 CIMR-G7C45P5 45P51
7.5 16 CIMR-G7C47P5 47P51
11 21 CIMR-G7C4011 40111
15 26 CIMR-G7C4015 40151
18.5 32 CIMR-G7C4018 40181
22 40 CIMR-G7C4022 40220 40221
30 50 CIMR-G7C4030 40300 40301
37 61 CIMR-G7C4037 40370 40371
45 74 CIMR-G7C4045 40450 40451
55 98 CIMR-G7C4055 40550 40551
75 130 CIMR-G7C4075 40750 40751
90 150 CIMR-G7C4090 40900 40901
110 180 CIMR-G7C4110 41100 41101
132 210 CIMR-G7C4132 41320 41321
160 230 CIMR-G7C4160 41600 41601
185 280 CIMR-G7C4185 41850 -
220 340 CIMR-G7C4220 42200 -
300 460 CIMR-G7C4300 43000 -
Output
Capacity
kVA
Va risp ee d G 7
Basic Model Number
(Always specify through the protective structure when ordering.)
Open Chassis
(IEC IP00)
CIMR-G7
Remove the top and bottom cov-
ers from the Enclosed Wall-
mounted model.
Remove the top and bottom cov-
ers from the Enclosed Wall-
mount model.
Specifications
Enclosed Wall-mounted
(IEC IP20, NEMA 1)
CIMR-G7C
20P41
40P41
1-2

Confirmations upon Delivery
Checks
Check the following items as soon as the Inverter is delivered.
Table 1.2 Checks
Item Method
Has the correct model of Inverter been
delivered?
Check the model number on the nameplate on the side of the Inverter.
Confirmations upon Delivery
Is the Inverter damaged in any way?
Are any screws or other components
loose?
Inspect the entire exterior of the Inverter to see if there are any scratches or
other damage resulting from shipping.
Use a screwdriver or other tools to check for tightness.
If you find any irregularities in the above items, contact the agency from which you purchased the Inverter or
your Yaskawa representative immediately.
Nameplate Information
There is a nameplate attached to the side of each Inverter. The nameplate shows the model number, specifications, lot number, serial number, and other information on the Inverter.
Example Nameplate
The following nameplate is an example for a European standard Inverter: 3-phase, 200 VAC, 0.4 kW, IEC
IP20 and NEMA 1 standards
Inverter model
Input specifications
Input specifications
Output
specifications
Lot number
Serial number
GC
Inverter
specifications
Mass
Fig 1.1 Nameplate
1-3
Inverter Model Numbers
The model number of the Inverter on the nameplate indicates the specification, voltage class, and maximum
motor capacity of the Inverter in alphanumeric codes.
CIMR - G7 C 2 0P4
Inverter
Varispeed G7
No.
C
No.
2
4
Specification
European standard
Voltage Class
AC input, 3-phase, 200 V
AC input, 3-phase, 400 V
0P4
0P7
300
"P" indicates the decimal point.
Fig 1.2 Inverter Model Numbers
Max. Motor Capacity
No.
0.4 kW
to to
0.75 kW
300 kW
*
Inverter Specifications
The Inverter specifications (“SPEC”) on the nameplate indicate the voltage class, maximum motor capacity,
the protective structure, and the revision of the Inverter in alphanumeric codes.
2 0P4 1
No.
2
4
Voltage Class
AC input, 3-phase, 200 V
AC input, 3-phase, 400 V
TERMS
Max. Motor Capacity
No.
0P4
0P7
to
300
"P" indicates the decimal point.
0.4 kW
0.75 kW
to
300 kW
*
No.
0
1
Protective Structure
Open chassis (IEC IP00)
Enclosed wall-mounted (IEC IP20,
NEMA 1 Type 1)
Fig 1.3 Inverter Specifications
Open Chassis Type (IEC IP00)
Protected so that parts of the human body cannot reach electrically charged parts from the front when the
Inverter is mounted in a control panel.
Enclosed Wall-mounted Type (IEC IP20, NEMA 1 Type 1)
The Inverter is structured so that the Inverter is shielded from the exterior, and can thus be mounted to the
interior wall of a standard building (not necessarily enclosed in a control panel). The protective structure conforms to the standards of NEMA 1 in the USA.
Top protective cover must be installed to conform with IEC IP20 and NEMA 1 Type 1 requirements. Refer to
Fig. 1.4 for details.
1-4

Confirmations upon Delivery
NPJT31278-1-0
CAUTION
Component Names
Inverters of 15 kW or Less
The external appearance and component names of the Inverter are shown in Fig 1.4. The Inverter with the terminal cover removed is shown in Fig 1.5.
Top protective cover
Front cover
Digital Operator
Terminal cover
Fig 1.4 Inverter Appearance (15 kW or Less)
Mounting hole
Diecast case
Nameplate
Bottom protective cover
Control circuit terminals
CAUTION
NPJT31278-1-0
Fig 1.5 Terminal Arrangement (15 kW or Less)
Main circuit terminals
Charge indicator
Ground terminal
1-5
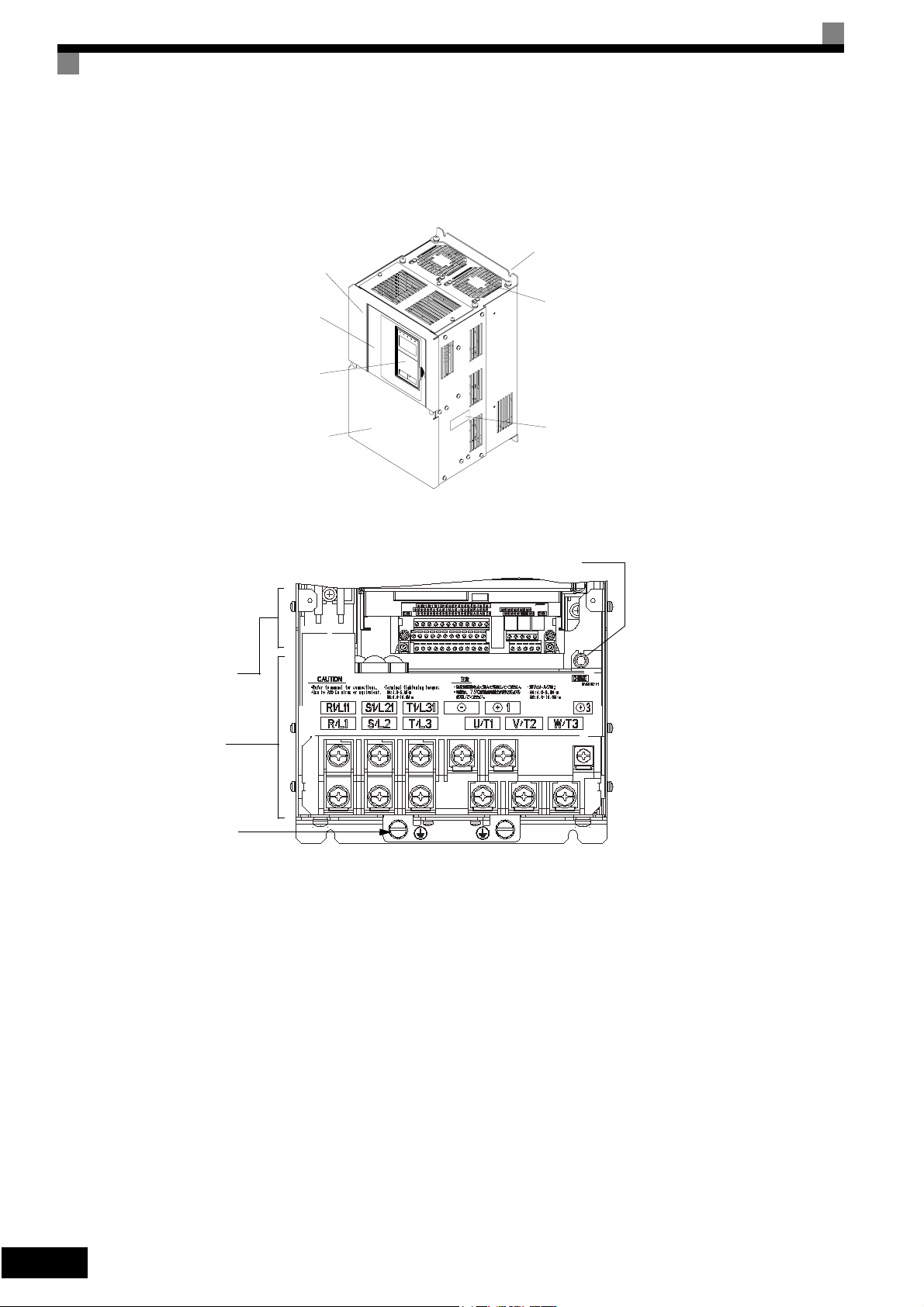
Inverters of 18.5 kW or More
The external appearance and component names of the Inverter are shown in Fig 1.6. The Inverter with the terminal cover removed is shown in Fig 1.7.
Mounting holes
Inverter cover
Control circuit
terminals
Main circuit
terminals
Front cover
Digital Operator
Terminal cover
Cooling fan
Nameplate
Fig 1.6 Inverter Appearance (18.5 kW or More)
Charge indicator
1-6
Ground terminal
Fig 1.7 Terminal Arrangement (18.5 kW or More)
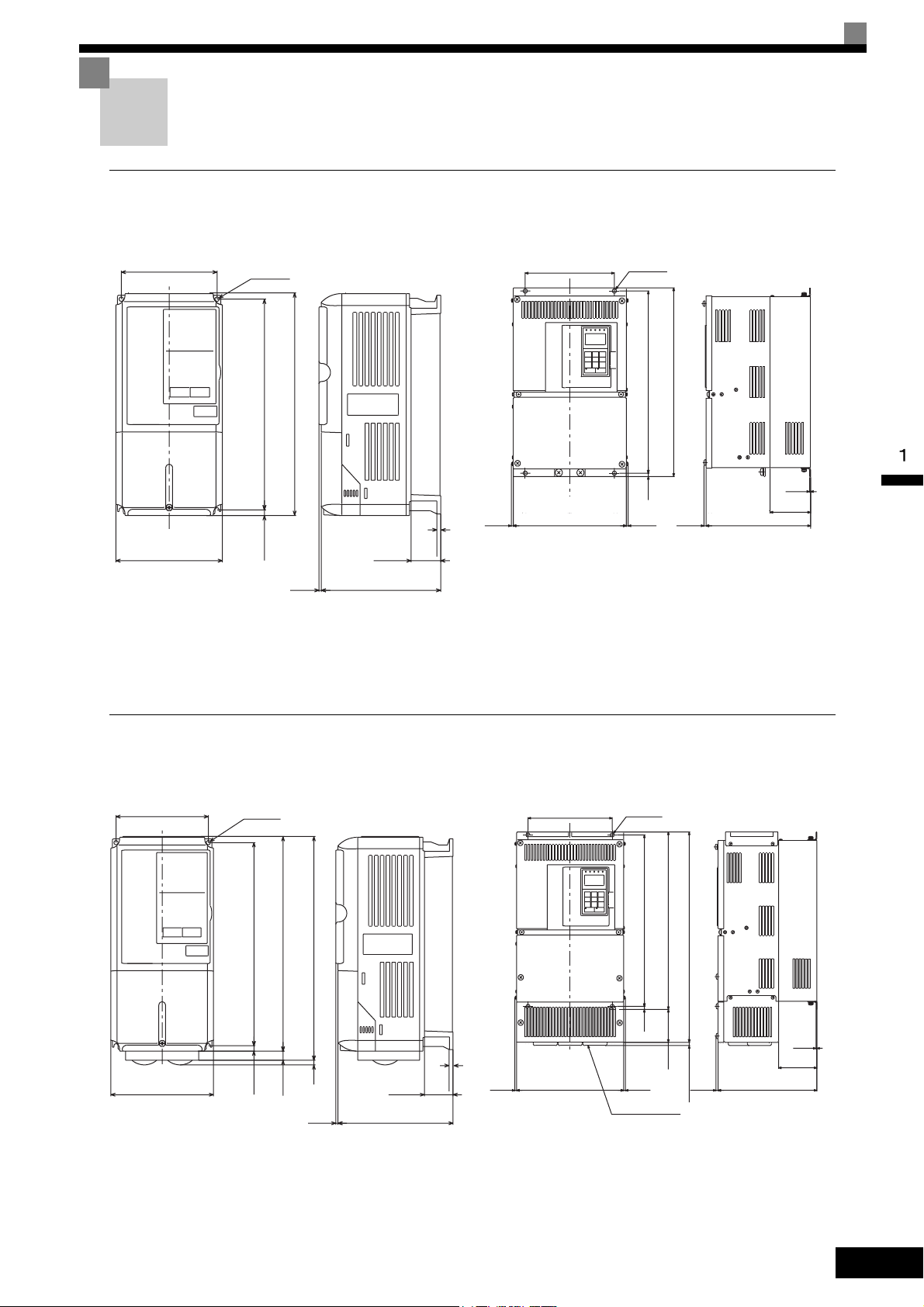
Exterior and Mounting Dimensions
Open Chassis Inverters (IP00)
Exterior diagrams of the Open Chassis Inverters are shown below.
Exterior and Mounting Dimensions
W1
W
200 V/400 V Class Inverters of 0.4 to 15 kW
4-d
H1H2DH
3
Fig 1.8 Exterior Diagrams of Open Chassis Inverters
D1
(5)
4-d
H1
H2
H
t1
(5)
D1
D
W1
t1
(5)
200 V Class Inverters of 18.5 or 22 kW
400 V Class Inverters of 30 to 45 kW
W
Enclosed Wall-mounted Inverters (NEMA1 Type 1)
Exterior diagrams of the Enclosed Wall-mounted Inverters (NEMA1 Type 1) are shown below.
W1
W
200 V/400 V Class Inverters of 0.4 to 15 kW
4-d
H1H2DH0
H3
4 H
3
D1
W1
t1
W
200 V Class Inverters of 18.5 or 22 kW
400 V Class Inverters of 30 to 45 kW
4-d
H1
H2
(5)(5)
Grommet
H0
H3
H
Max.10
t1
D1
D(5)
Fig 1.9 Exterior Diagrams of Enclosed Wall-mounted Inverters
1-7
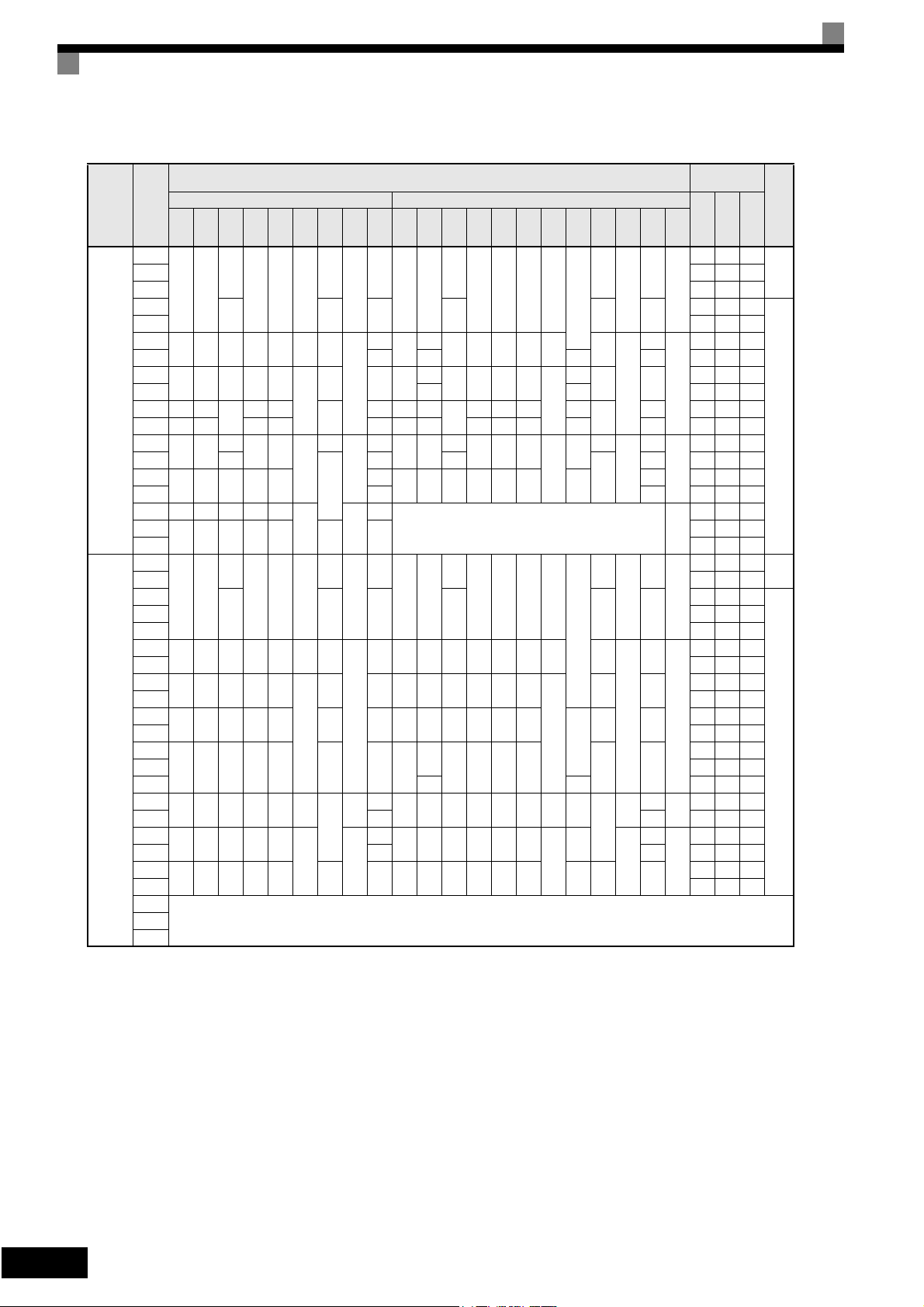
Table 1.3 Inverter Dimensions (mm) and Masses (kg)
Max.
Appli-
Voltage
cable
Class
Motor
Output
W H D W1 H1 H2 D1 t1
[kW]
0.4
0.75 27 42 69
140 280
1.5 50 50 100
2.2
3.7 11274186
5.5
200 300 197 186 285 8 65.5
7.5 7 310 10 7 219 113 332
11
240 350 207 216 335
200 V
(3-phase)
15 380 30 429 183 612
18.5 250 400
22 275 450 220 435 24 279 615 220 450 435 165 27 586 274 860
30
375 600
37 330
45
450 725 350 325 700
55 87 95 1588 619 2207
75 500 850 360 370 820
90
575 885 380 445 855 140 150
110 2733 1242 3975
0.4
0.75 17 41 58
1.5
140 280
2.2 59 56 115
3.7 80 68 148
5.5
200 300 197 186 285 8 65.5
7.5 193 114 307
11
240 350 207 216 335
15 326 172 498
18.5
275 450 258 220 435 100 21 279 535 258 220 450 435
400 V
(3-phase)
22 466 259 725
30
325 550 283 260 535 105 36 329
37 784 360 1144
45 715 165 901 415 1316
55
450 725 350 325 700 13
75 89 97 1399 575 1974
90
500 850 360 370 820
110 120 130 2097 853 2950
132
575 925 380 445 895 140 160 580 1325 380 445 925 895 400 140 170
160 2791 1147 3938
185
300
* Same for Open Chassis and Enclosed Wall-mounted Inverters.
Open Chassis (IP00) Enclosed Wall-mounted (NEMA1)
157
126 266 7
39
5
177 59 4 177 59 4
2.3
78 11 240
7.5
100
100
13
3.2
258
300
195 385
250 575
130
15 4.5
157
126 266 7
39
5
177 59 4 177 59 4
78 10 240 350 207 216 350 335
2.3
7.5
3.2
130
15 4.5
Dimensions (mm)
Ap-
prox.
W H D W1 H0 H1 H2 H3 D1 t1
Mass
3
140 280
6
200
21 254 535
57
380 890
63 330
86
455 1100 350 325 725 700 305
157
126 280 266 7
300
197 186 300 285 8 65.5
350
207 216 350 335
195 400 385 135
258
300
250 600 575
7.5
13
0
0
210
108
--- M12
3
140 280
157
126 280 266 7
0
6 200 300 197 186 300 285 8 65.5
7.5
85
635
283 260 550 535 105 40
88
455 1100 350 325 725 700 13 305
102
505 1245 360 370 850 820
395
15
Under development220
prox.
Mass
39
5
2.3
78 11
100
100
3.2
130
39
5
78 10
2.3
100 24
3.2
130
122
4.5
Heat Genera-
tion (W)
Tot a l
Exter
Mount-
Ap-
ing
Holes
d*
Heat
Inter-
Gen-
nal
nal
eration
20 39 59
3
M5
70 59 129
6
164 84 248
374 170 544
M6
24 501 211 712
62
68 1015 411 1426
94 1266 505 1771
865 352 1217
M10
2019 838 2857
2437 997 3434
14 39 53
3
36 48 84
M5
127 82 209
6
252 158 410
M6
426 208 634
678 317 995
96
1203 495 1698
M10
1614 671 2285
M12
2388 1002 3390
Cool-
ing
Method
Natu-
ral
Fan
Natu-
ral
Fan
1-8
Checking and Controlling the Installation Site
Checking and Controlling the Installation Site
Install the Inverter in the installation site described below and maintain optimum conditions.
Installation Site
Install the Inverter under the following conditions.
Table 1.4 Installation Site
Type Ambient Operating Temperature Humidity
Enclosed wall-mounted -10 to + 40 °C 95% RH or less (no condensation)
Open chassis -10 to + 45 °C 95% RH or less (no condensation)
Protection covers are attached to the top and bottom of the Inverter. Be sure to remove the protection covers
before installing a 200 or 400 V Class Inverter with an output of 15 kW or less in a panel.
Observe the following precautions when mounting the Inverter.
• Install the Inverter in a clean location free from oil mist and dust. It can be installed in a totally enclosed
panel that is completely shielded from floating dust.
• When installing or operating the Inverter, always take special care so that metal powder, oil, water, or other
foreign matter does not get into the Inverter.
• Do not install the Inverter on combustible material, such as wood.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from radioactive materials and combustible materials.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from harmful gasses and liquids.
• Install the Inverter in a location without excessive oscillation.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from chlorides.
• Install the Inverter in a location not in direct sunlight.
Controlling the Ambient Temperature
To enhance the reliability of operation, the Inverter should be installed in an environment free from extreme
temperature increases. If the Inverter is installed in an enclosed environment, such as a box, use a cooling fan
or air conditioner to maintain the internal air temperature below 45°C.
Protecting the Inverter from Foreign Matter
Place a cover over the Inverter during installation to shield it from metal power produced by drilling.
Always remove the cover from the Inverter after completing installation. Otherwise, ventilation will be
reduced, causing the Inverter to overheat.
1-9
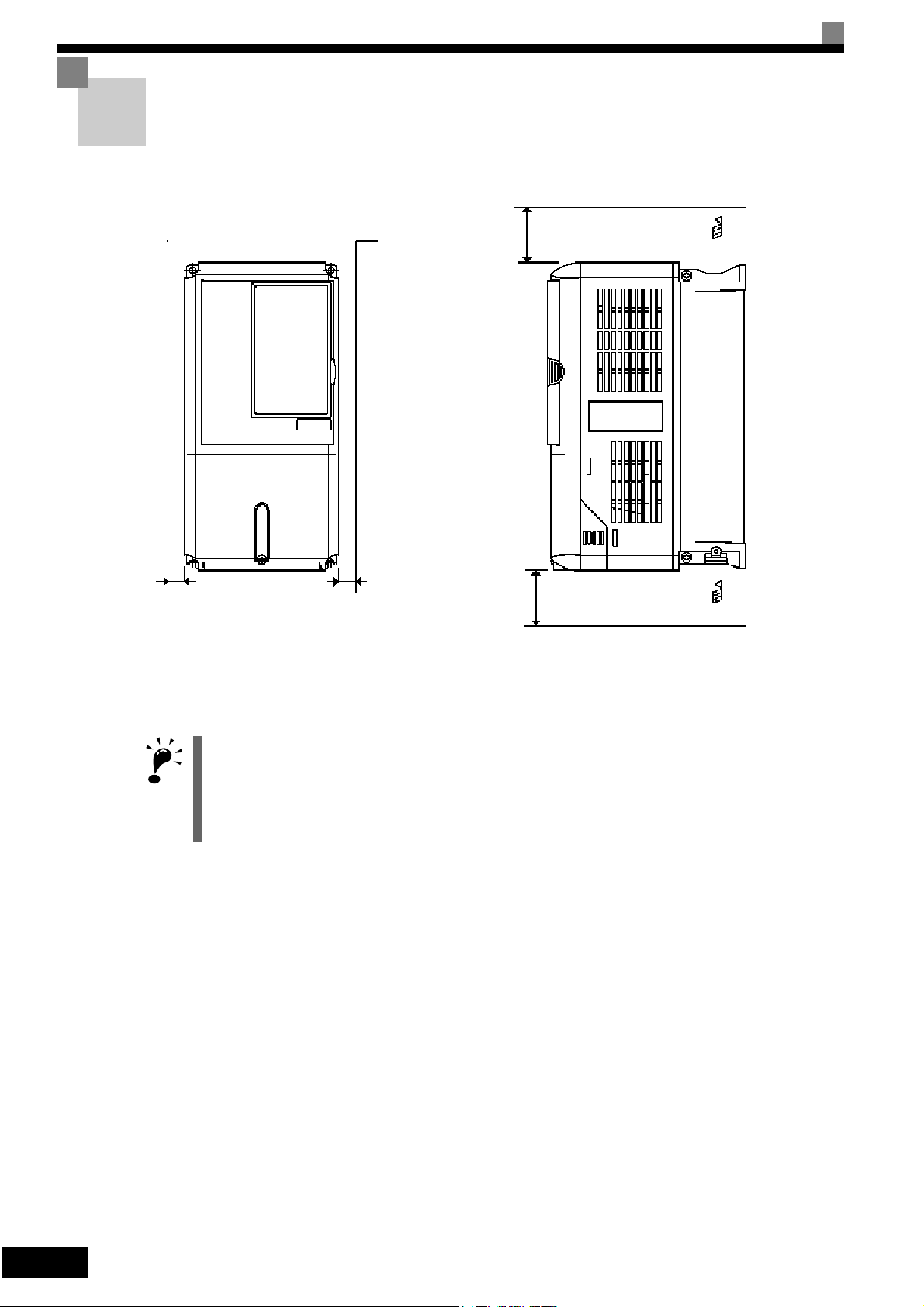
Installation Orientation and Space
Install the Inverter vertically so as not to reduce the cooling effect. When installing the Inverter, always
provide the following installation space to allow normal heat dissipation.
120 mm min.
Air
30 mm min.
IMPORTANT
30 mm min.
120 mm min.
Air
Vertical SpaceHorizontal Space
Fig 1.10 Inverter Installation Orientation and Space
1. The same space is required horizontally and vertically for both Open Chassis (IP00) and Enclosed Wallmounted (IP20, NEMA 1 Type 1) Inverters.
2. Always remove the protection covers before installing a 200 or 400 V Class Inverter with an output of
15 kW or less in a panel.
Always provide enough space for suspension eye bolts and the main circuit lines when installing a 200 or
400 V Class Inverter with an output of 18.5 kW or more in a panel.
1-10
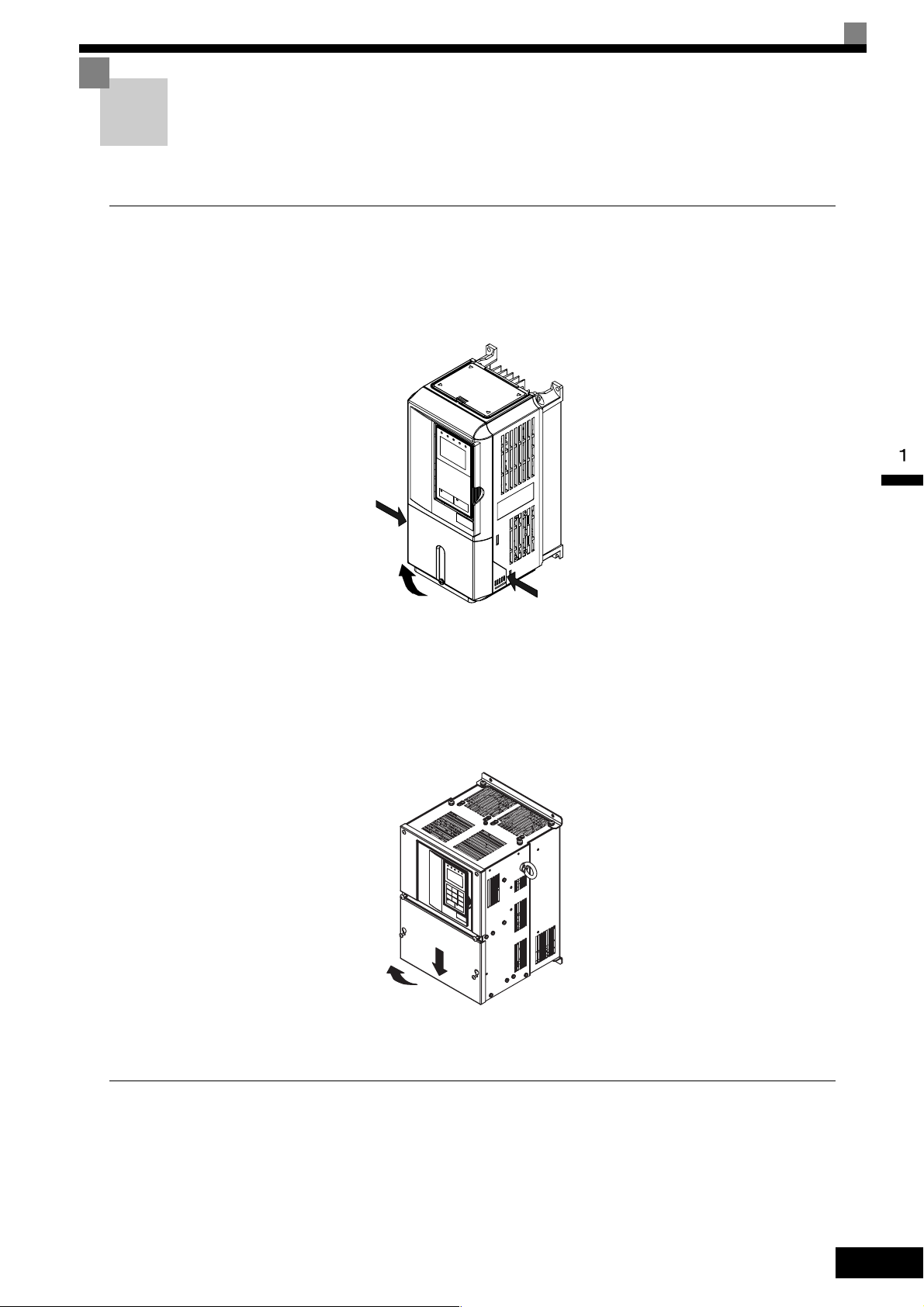
Removing and Attaching the Terminal Cover
Removing and Attaching the Terminal Cover
Remove the terminal cover to wire cables to the control circuit and main circuit terminals.
Removing the Terminal Cover
Inverters of 15 kW or Less
Loosen the screws at the bottom of the terminal cover, press in on the sides of the terminal cover in the direc-
tions of arrows 1, and then lift up on the terminal in the direction of arrow 2.
1
2
1
Fig 1.11 Removing the Terminal Cover (Model CIMR-G7C23P7 Shown Above)
Inverters of 18.5 kW or More
Loosen the screws on the left and right at the top of the terminal cover, pull out the terminal cover in the direction of arrow 1 and then lift up on the terminal in the direction of arrow 2.
1
2
Fig 1.12 Removing the Terminal Cover (Model CIMR-G7C2018 Shown Above)
Attaching the Terminal Cover
When wiring the terminal block has been completed, attach the terminal cover by reversing the removal procedure.
For Inverters with an output of 15 kW or less, insert the tab on the top of the terminal cover into the grove on
the Inverter and press in on the bottom of the terminal cover until it clicks into place.
1-11
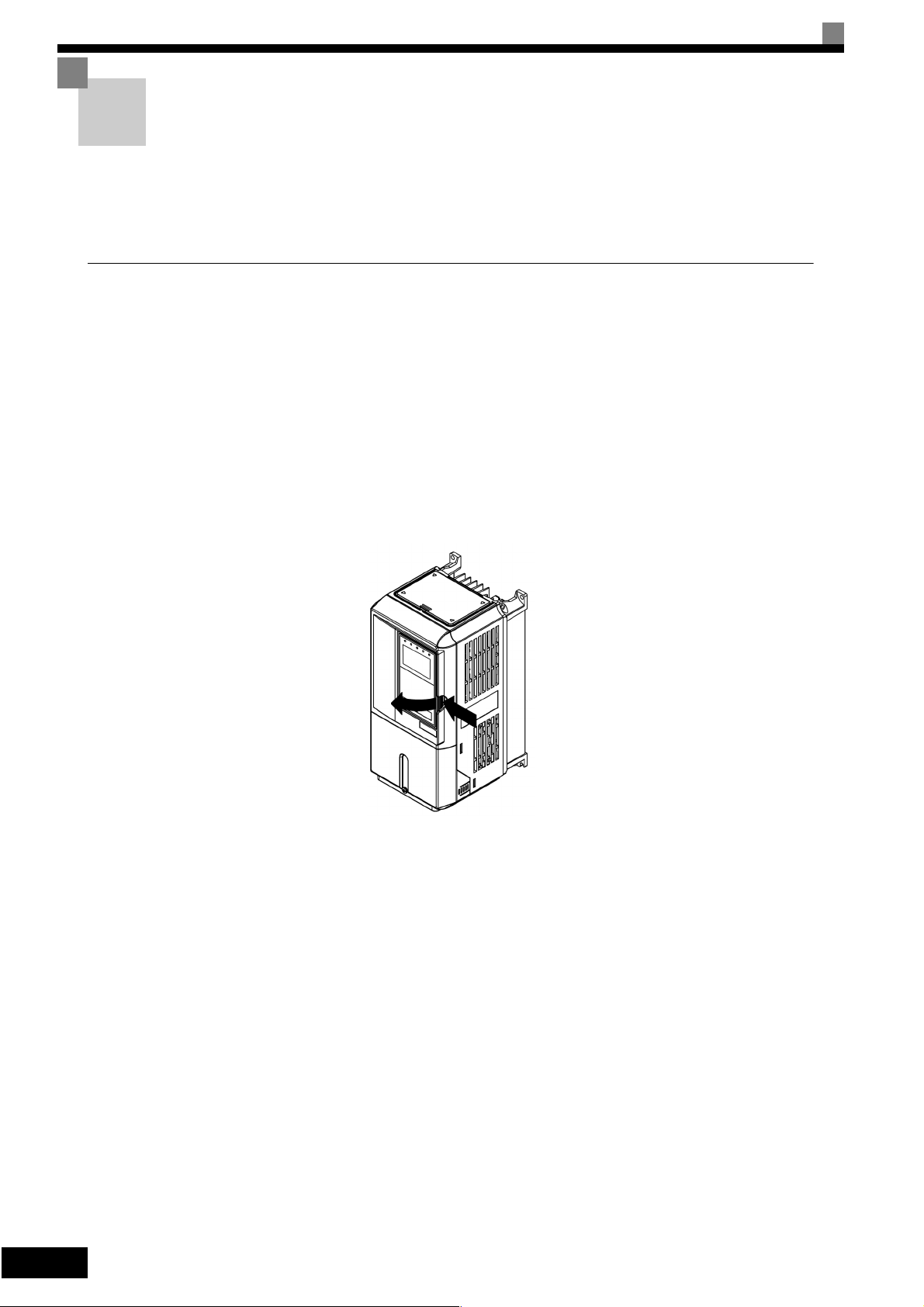
Removing/Attaching the Digital Operator and Front Cover
The methods of removing and attaching the Digital Operator and Front Cover are described in this section.
Inverters of 15 kW or Less
To attach optional cards or change the terminal card connector, remove the Digital Operator and front cover in
addition to the terminal cover. Always remove the Digital Operator from the front cover before removing the
terminal cover.
The removal and attachment procedures are given below.
Removing the Digital Operator
Press the lever on the side of the Digital Operator in the direction of arrow 1 to unlock the Digital Operator
and lift the Digital Operator in the direction of arrow 2 to remove the Digital Operator as shown in the following illustration.
2
Fig 1.13 Removing the Digital Operator (Model CIMR-G7C43P7 Shown Above)
1
1-12
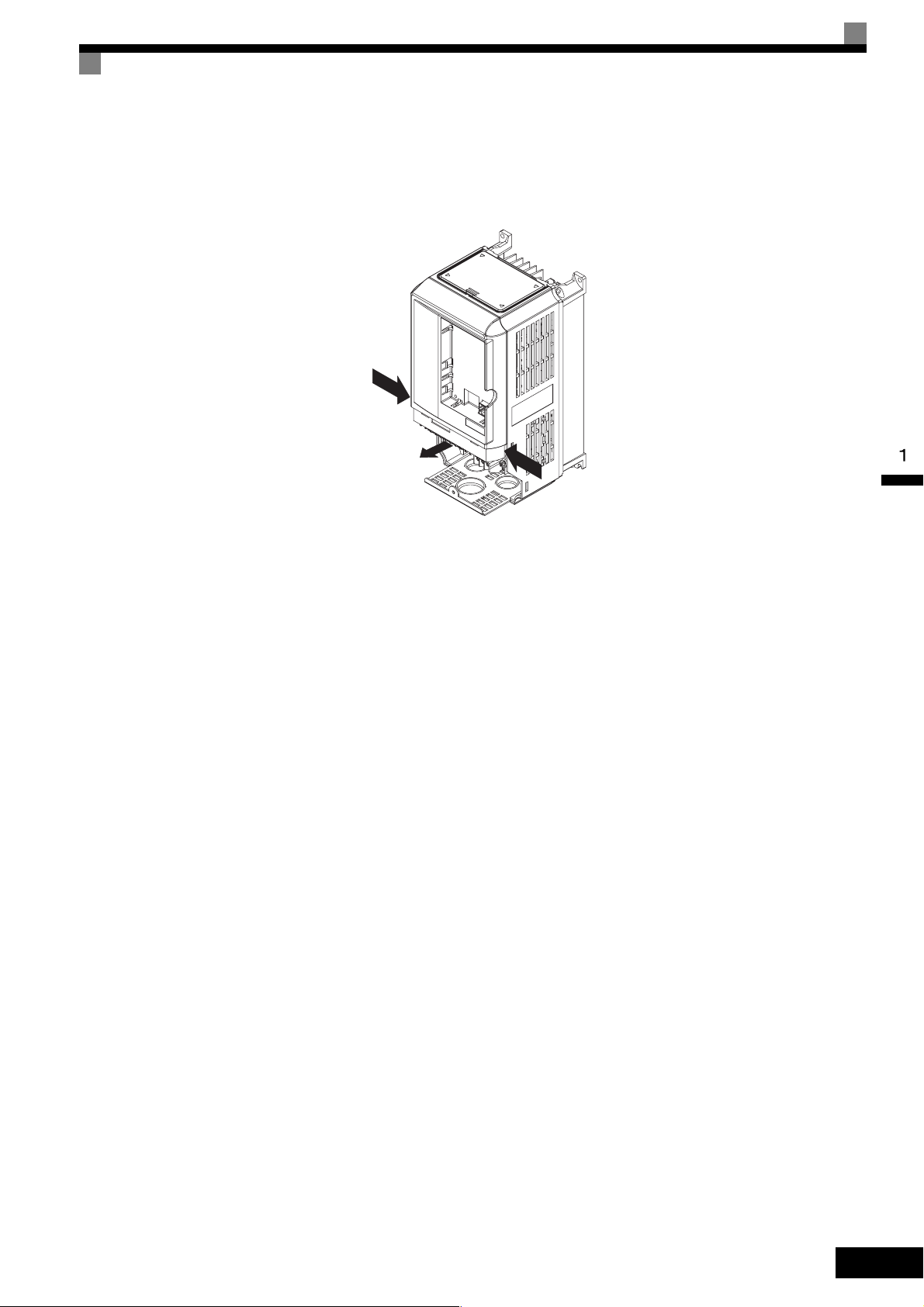
Removing/Attaching the Digital Operator and Front Cover
Removing the Front Cover
Press the left and right sides of the front cover in the directions of arrows 1 and lift the bottom of the cover in
the direction of arrow 2 to remove the front cover as shown in the following illustration.
1
1
2
Fig 1.14 Removing the Front Cover (Model CIMR-G7C43P7 Shown Above)
Mounting the Front Cover
After wiring the terminals, mount the front cover to the Inverter by performing in reverse order to the steps to
remove the front cover.
1. Do not mount the front cover with the Digital Operator attached to the front cover; otherwise, Digital
Operator may malfunction due to imperfect contact.
2. Insert the tab of the upper part of the front cover into the groove of the Inverter and press the lower part of
the front cover onto the Inverter until the front cover snaps shut.
Mounting the Digital Operator
After attaching the terminal cover, mount the Digital Operator onto the Inverting using the following procedure.
1. Hook the Digital Operator at A (two locations) on the front cover in the direction of arrow 1 as shown in
the following illustration.
2. Press the Digital Operator in the direction of arrow 2 until it snaps in place at B (two locations).
1-13
 Loading...
Loading...