
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 70
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
69
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Errors are indicated by the presence or absence of a response to an Amplifier Unit command, and by the
indicators.
List of Error Messages
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
Type
Host communications error
Communications
error between
the CIDRW Head
and ID Tag
CPU hardware
error
Response
code
14 Format error There is a mistake in the command format. (For example, the com-
70 Communications
71 Verification error Correct data cannot be written to an ID Tag.
72 No Tag error Either there is no ID Tag in front of the CIDRW Head, or the CIDRW
7B Outside write area
7E ID system error (1) The ID Tag is in a status where it cannot execute the command pro-
7F ID system error (2) An inapplicable ID Tag has been used.
9A Hardware error in
Name Description
mand portion is undefined, or the page or address specification is
inappropriate.)
Noise or another hindrance has occurred during communications with
error
error
CPU
an ID Tag, and communications cannot be completed normally.
Head is unable to detect the ID Tag due to environmental factors (e.g.,
noise).
The ID Tag is at a position where reading is possible but writing is not,
so writing does not complete normally.
cessing.
An error occurred when writing to EEPROM.
Amplifier Unit Indicators
Name Indications
RUN (green) Turns ON when the Amplifier Unit is in normal operation.
COMM (orange) Turns ON during communications with the host device or during communications with an ID Tag.
NORM (green) Turns ON when the communications finish with no error.
ERROR (red) Turns ON when an error occurs during communications with the host device, or during communications
with an ID Tag.
70
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
SECTION 6
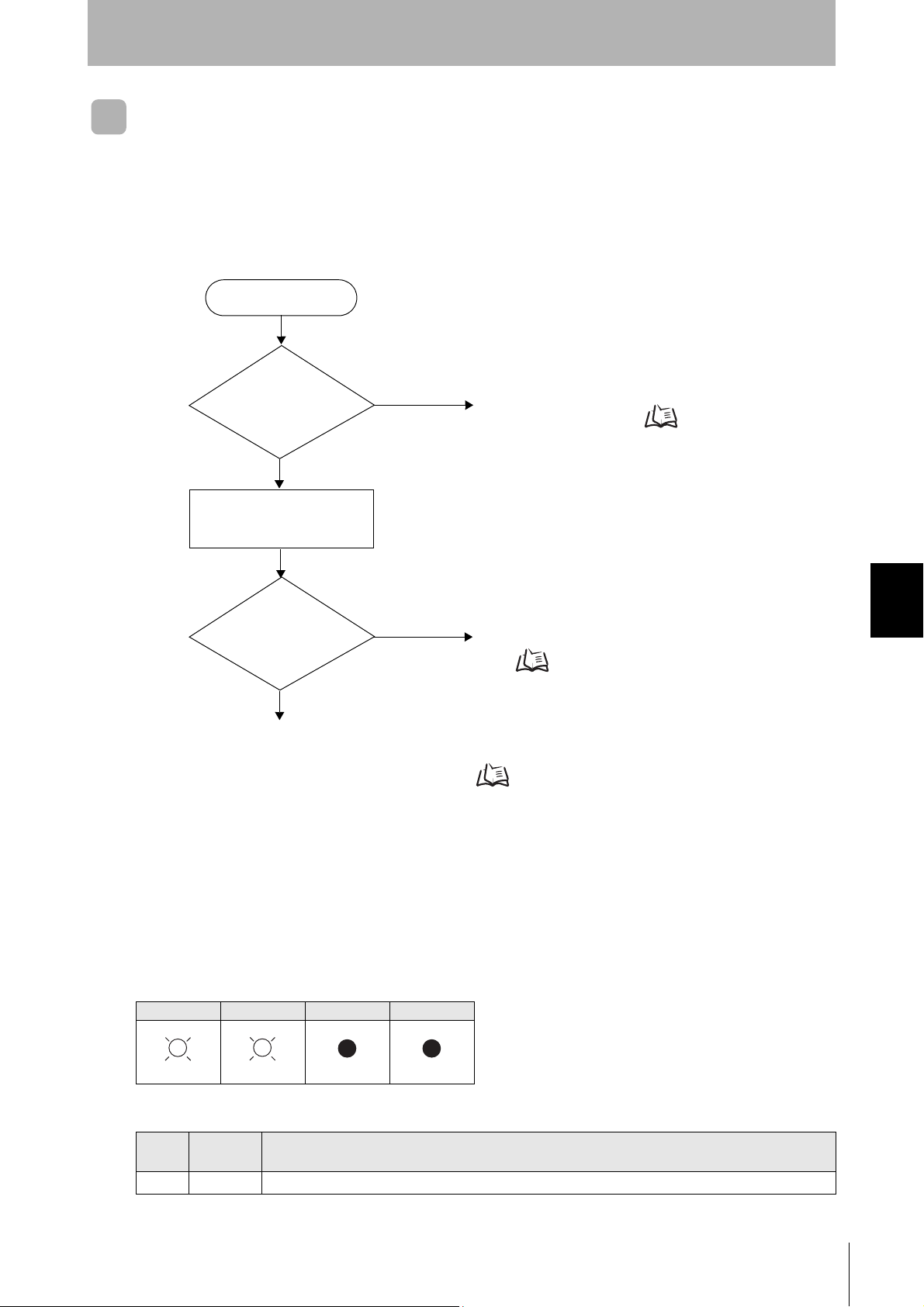
Error occurrence
Test command transmission
RUN indicator
OFF?
No
Yes
An error has occurred at the Amplifier Unit.
Amplifier Unit error Refer to page 72.
Check if the Amplifier Unit settings are correct.
If There Is No Response to the Command: Refer to page 72.
Response received?
Yes
Check the nature of the response.
If there is a response to the command
Refer to page 72.
No
(Lights once)
Troubleshooting
Operation Check Flowchart
■ From Installation to Trial Operation
Errors are indicated by whether or not a response to the test command is received and by the status of
the Amplifier Unit indicators.
• If the Test Command Was Received Normally:
Indicators
RUN COMM NORM ERROR
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
Response Code for the Response
Type
Normal 00 The command was received normally.
Response
code
Function
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
71
SECTION 6
(Lights once)
(Lights once)
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
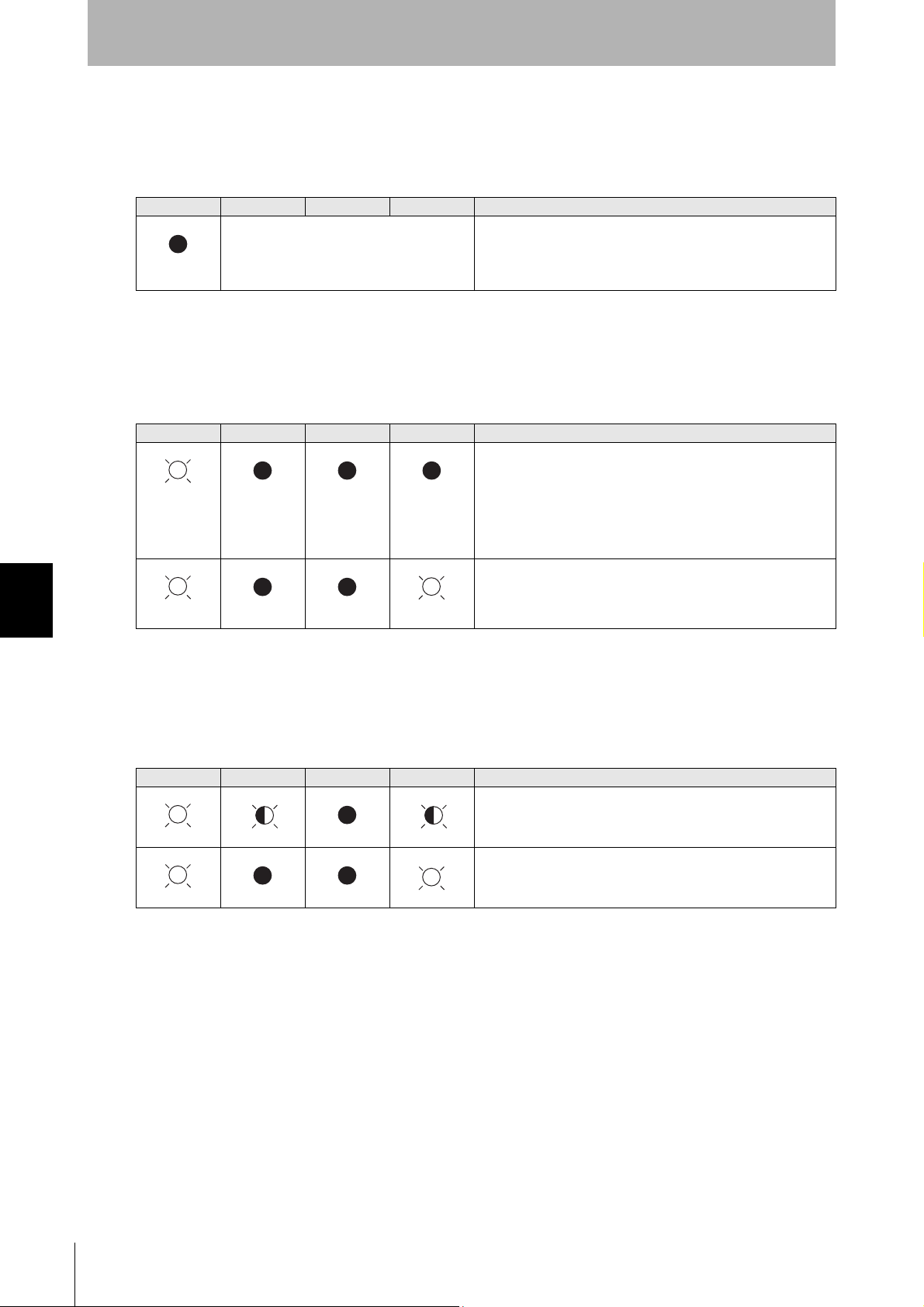
• Amplifier Unit Error
Check the status of the indicators after transmission of the test command.
After taking appropriate corrective action, restart the Amplifier Unit, send the test command again and
check again.
RUN COMM NORM ERROR Main check points
—
(If RUN is OFF, the status of the other indicators can be ignored.)
• Influence of background noise (change installation position)
• Amplifier Unit power supply
If the error cannot be resolved after checking, the Amplifier Unit
may be damaged.
• If There Is No Response to the Command:
Check the status of the indicators after transmission of the test command.
After taking appropriate corrective action, restart the Amplifier Unit, send the test command again and
check again.
RUN COMM NORM ERROR Main check points
• Amplifier Unit baud rate settings
• Node numbers of the Amplifier Units (do not match the node
number in the test command)
• Connection and wiring of the cable between the host device
and Amplifier Unit
• Routing of each cable (influence of background noise)
If the error cannot be resolved after checking, the Amplifier Unit
may be damaged.
• Amplifier Unit baud rate settings
• Connection and wiring of the cable between the host device
and Amplifier Unit
• Routing of the cables (influence of background noise)
Troubleshooting
• If There Is a Response to the Command:
Check the status of the indicators after transmission of the test command.
After taking appropriate corrective action, restart the Amplifier Unit, send the test command again and
check again.
RUN COMM NORM ERROR Main check points
• Node numbers of the Amplifier Units (The same number is set
for more than one Unit)
If the error cannot be resolved after checking, the Amplifier
Unit may be damaged.
There is a mistake in the command format (number of characters, character code, etc.).
72
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
SECTION 6
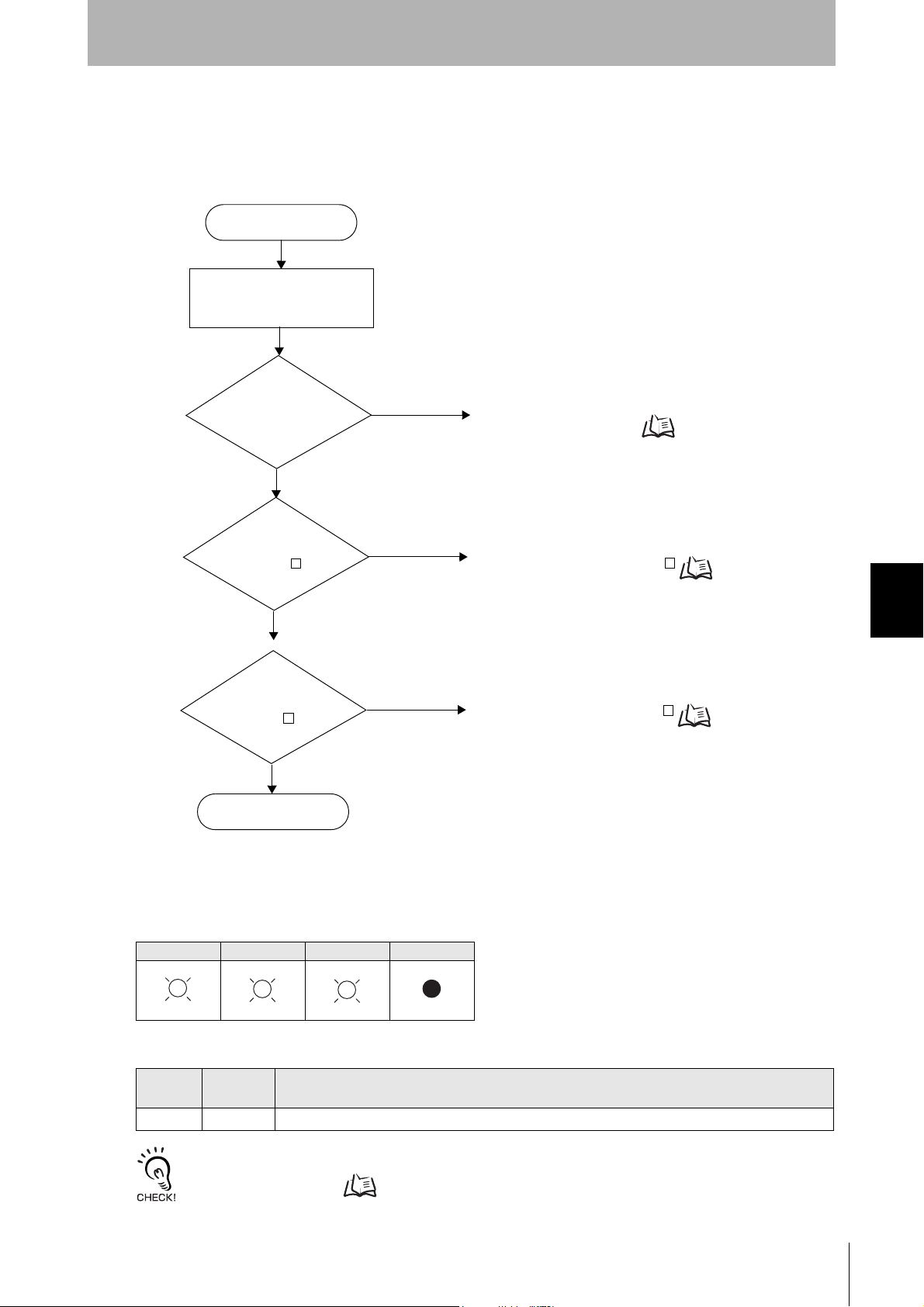
Error occurrence
Is the response
code 1 ?
No
Yes
Check the command format.
If the response code is 1 Refer to page 74.
Ye s
Communications with the ID Tag has failed.
If the response code is 7 Refer to page 74.
Write command sent
RUN indicator
OFF?
No
Yes
An error has occurred at the Amplifier Unit.
Amplifier Unit error Refer to page 74.
Is the response
code 7 ?
Communications OK
No
(Lights once)
(Lights once)
Troubleshooting
■ From Trial Operation to Communications
Errors are indicated by the status of the indicators after transmission of the write command, and by the
response code of the response.
• If the ID Tag Was Processed Normally:
Indicators
RUN COMM NORM ERROR
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
Response Code for the Response
Normal 00 The ID Tag was processed normally.
Type
Response
code
If there is no response to the write command, refer to the From Installation to Trial Operation,
Operation Check Flowchart. Refer to page 71.
Function
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
73
SECTION 6
(Lights once)
(Lights once)
(Lights once)
Troubleshooting
• Amplifier Unit Error
Check the status of the indicators after transmission of the command. After taking appropriate corrective action, send the write command again and check again.
RUN COMM NORM ERROR Main check points
—
(If RUN is OFF, the status of the other indicators can be ignored.)
• Influence of background noise (Change installation position)
• Amplifier Unit power supply
If the error cannot be resolved by checking the two points above,
the Amplifier Unit may be damaged.
• If the Response Code is 1 :
There is a host device communications error.
Check the status of the indicators and the response code of the response after transmission of the
command. After taking appropriate corrective action, send the write command again and check again.
RUN COMM NORM ERROR
SECTION 6
Troubleshooting
Response
code
14 Command format
(Command code, page designation, address designation, processed data volume, etc.)
Main check points
• If the Response Code is 7 :
There is a communications error in communications between the CIDRW Head and ID Tag.
Check the status of the indicators and the response code of the response after transmission of the
command. After taking appropriate corrective action, send the write command again and check again.
RUN COMM NORM ERROR
Response
code
70
71 • ID Tag overwrite life (Replace the ID Tag)
72 • Connection to the CIDRW Head
7B • Distance between the ID Tag and CIDRW Head
7E • Type/specifications of the ID Tags used
7F
• Background noise levels of the CIDRW Head (Check the surroundings with the environmental noise level measurement
function)
• Distance to another CIDRW Head
• Influence of background noise (Change installation position)
If the error cannot be resolved after checking, the Amplifier Unit may be damaged.
• Environment of use of the ID Tags (ID Tag breakage due to use in unanticipated ways)
• Distance between the ID Tag and CIDRW Head
• CIDRW Head background noise levels (Check the surroundings with the environmental noise level measurement function)
• Distance to another CIDRW Head
• Background noise levels of the CIDRW Head (Check the surroundings with the environmental noise level measurement
function)
• Distance to another CIDRW Head
• Influence of background noise (Change installation position)
• Settings of the ID Tags used (The ID Tag lock function is used.*)
• Environment of use of the ID Tags (ID Tag breakage due to use in unanticipated ways)
Main check points
74
* The ID Tag has a lock function, but the Amplifier Unit has no function for locking an ID Tag.
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

SECTION 7
Appendix
Specifications and Dimensions 76
Connection Examples 80
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use 81
ID Tag Memory Maps 111
Regular Inspection 112
ASCII Code Table 113
Protective Construction 114
SECTION 7
Appendix
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
75
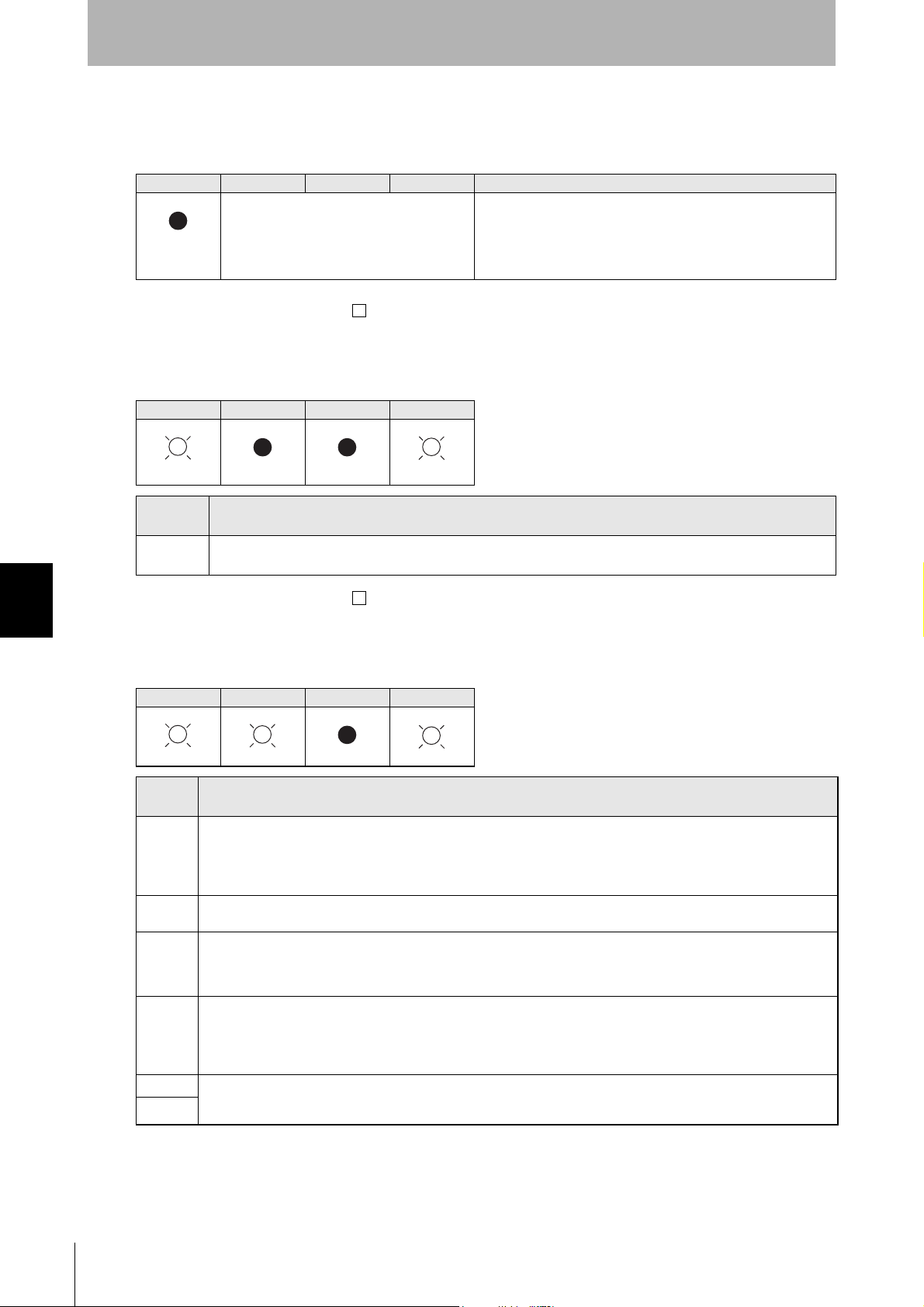
SECTION 7
DIP switch
(Unit: mm)
Mounting dimensions
Four, 4.5-dia. holes
DC power supply connector
MAC address label
Ethernet connector
Four operation indicators
Appendix
Specifications and Dimensions
Amplifier Units
V640-HAM11-ETN and V640-HAM11-L-ETN
SECTION 7
(15.8)
(31.95)
(13)
(18)
6.86.86.80.6
55.5
160
175
185
175±0.5
(11.5)
465680
(5.7)
5
(18.2)
(12)
(22.5)
43
(32.5)
Specifications and Dimensions
■ General Specifications
Item
Power supply voltage 24 VDC +10% -15%
Current consumption 150 mA max. 400 mA max.
Ambient temperature Operating: 0 to +40°C Storage: -15 to +65°C (with no icing)
Ambient humidity Operating/Storage: 35% to 85% (with no condensation)
Degree of protection IP20 (IEC60529 standard)
Insulation resistance 20 MΩ min. between power supply terminals and the frame ground terminal (100 VDC M)
Dielectric strength Leak current not to exceed 5 mA on application of 1000 VAC (50/60 Hz for 1 minute) between both
Vibration resistance Frequency: 10 to 150 Hz; double amplitude: 0.20 mm; acceleration: 15 m/s
Shock resistance Shock of 150 m/s
Ground Ground to 100 Ω or less.
Case material PC/ABS resin
Shape 80×185×43 mm (W×D×H)
Weight Approx. 250 g
CIDRW Head V640-HS61 V640-HS62
4-M4
Specifications
V640-HAM11-ETN V640-HAM11-L-ETN
power supply terminals and the frame ground terminal
8 minutes, 10 times each in X, Y, and Z directions
2
in X, Y, and Z directions, 3 times each for 18 repetitions
0.5
±
46
2
for
76
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

■ Host Communications Specifications
Item Description
Compliant standards 10Base-T and 100Base-TX
Protocol TCP/IP
Applicable port TCP/IP: port 7090
MTU 1,500 bytes
Access to an Amplifier Unit is possible from only one host device at a time. If a host device (A) is connected to an Amplifier Unit and another host device (B) connects to the Amplifier Unit, the connection between host device A and the
Amplifier Unit will be automatically broken and host device B will have the control right.
Communications with the ID Tag will be aborted if the Ethernet cable is disconnected or the connection is broken while
the Amplifier Unit is communicating with an ID Tag.
SECTION 7
Appendix
SECTION 7
Specifications and Dimensions
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
77
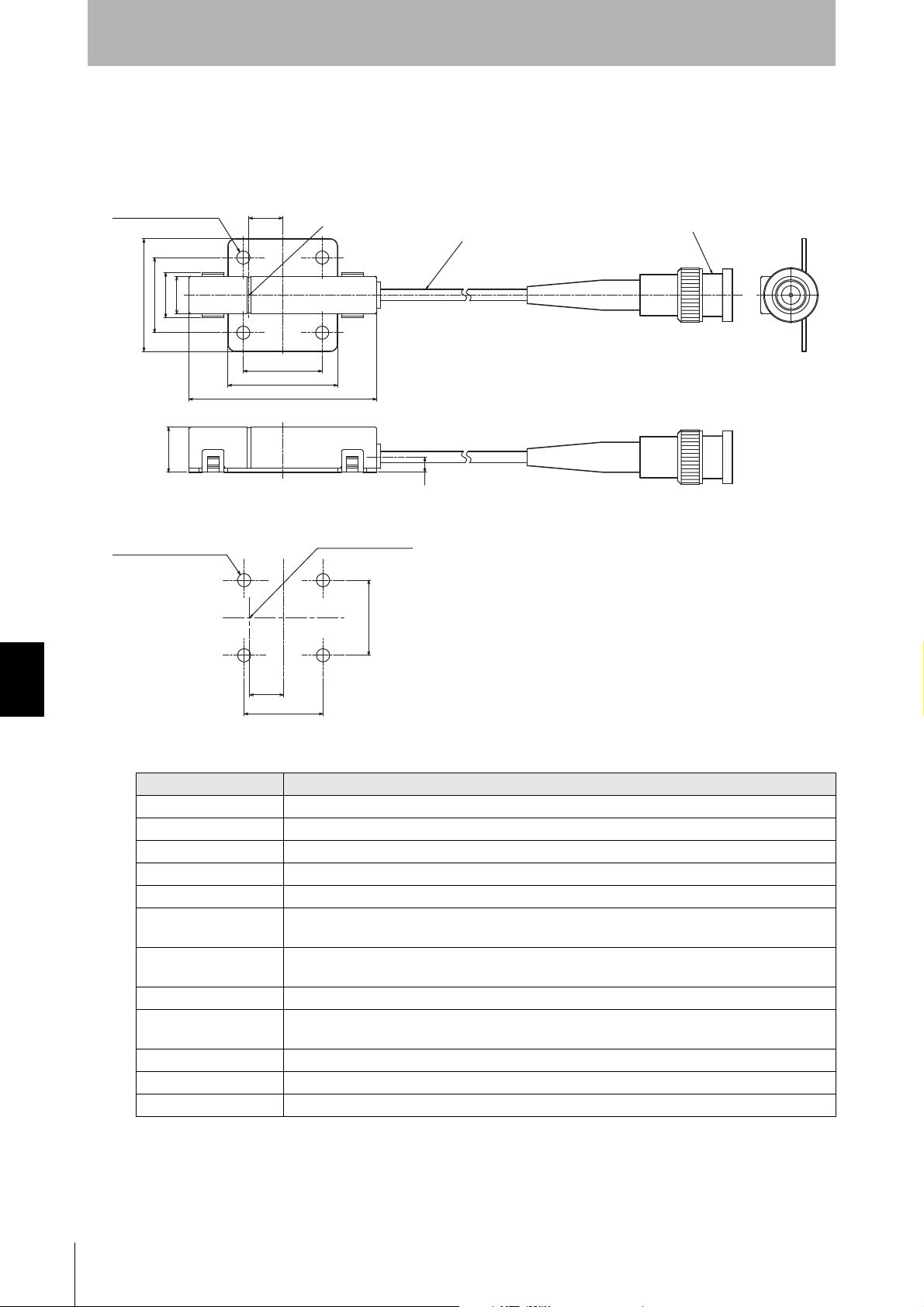
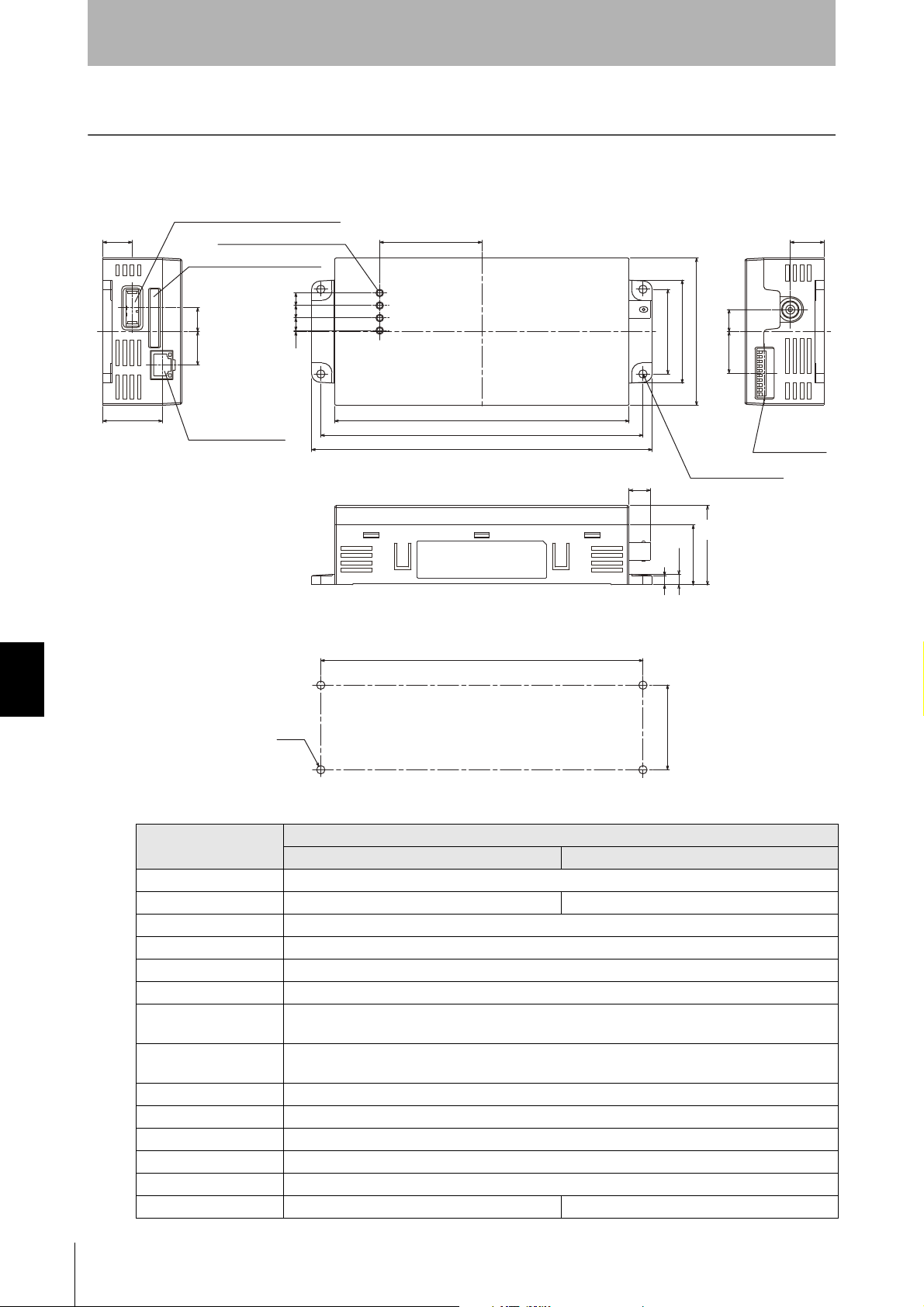
SECTION 7
Coaxial cable 3.0 dia., standard length 2 m
(Unit: mm)
Connector
Antenna center
Antenna center
Mounting dimensions
Four M3 or 3.5-dia. holes
Appendix
CIDRW Heads
V640-HS61
Four, 3.5-dia. holes
SECTION 7
Specifications and Dimensions
Transmission frequency 134 kHz
Ambient temperature Operating: 0 to +40°C Storage: -15 to +65°C (with no icing)
Ambient humidity Operating/Storage: 35% to 85% (with no condensation)
Degree of protection IP60 (IEC60529)
Insulation resistance 20 MΩ min. between all terminals and the case (100 VDC M)
Dielectric strength Leak current not to exceed 5 mA on application of 1000 VAC (50/60 Hz for 1 minute) between all
Vibration resistance Frequency: 10 to 150 Hz; double amplitude: 0.20 mm; acceleration: 15 m/s
Shock resistance Shock of 150 m/s
Casing material ABS/epoxy resin
Weight Approx. 70 g
Cable length 2 m
Cable specification 3-mm-dia. coaxial cable
Item Specifications
terminals and the case
8 minutes, 10 times each in X, Y, and Z directions
2
in X, Y, and Z directions, 3 times each for 18 repetitions
Stainless steel mount
2
for
78
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
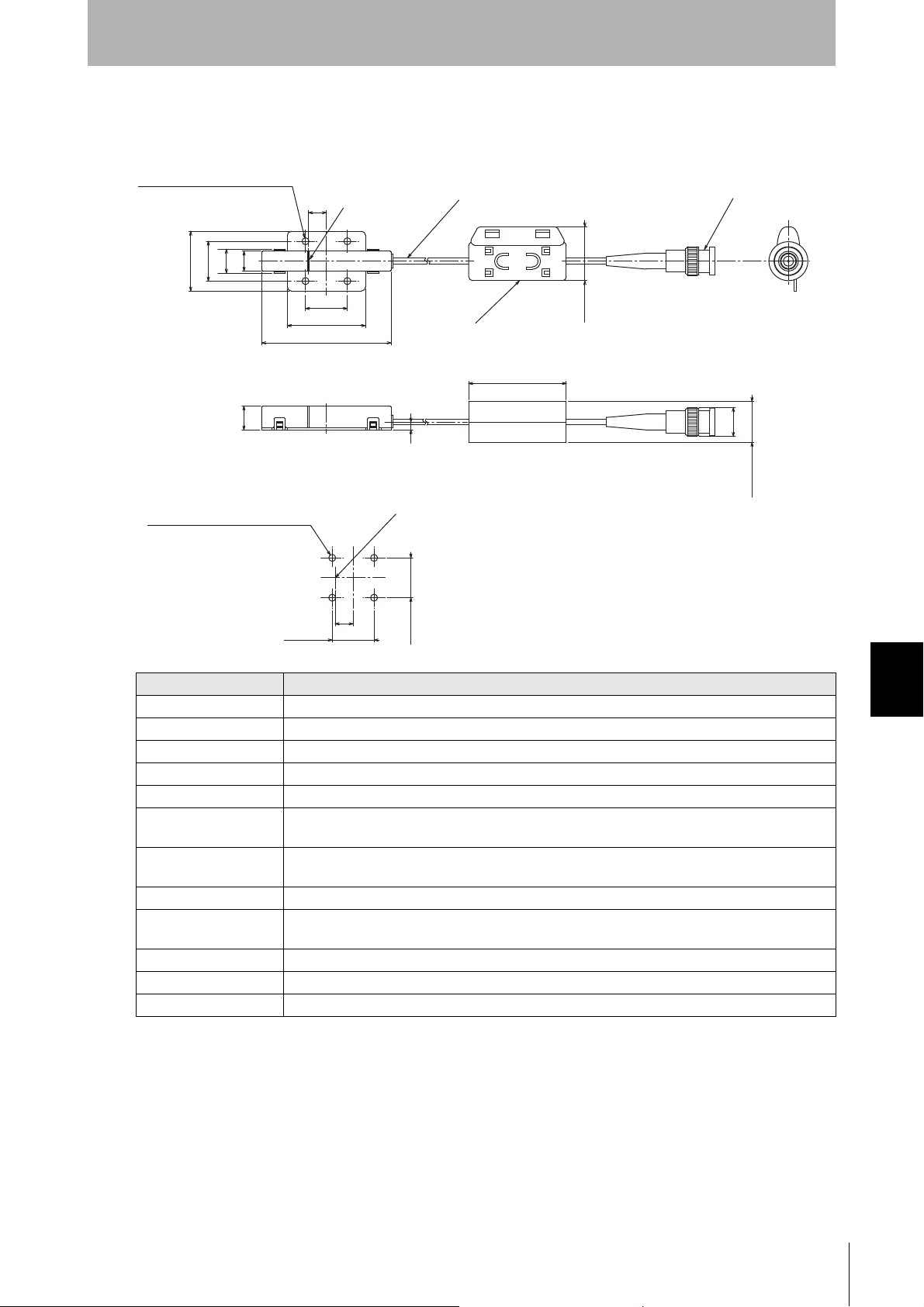
V640-HS62
302012
10
9
65
39.2
21
Max.28
12
4
49
14.5
Max.20.5
9
21
±0.2
20±0.2
Ferrite core
(Unit: mm)
Connector
Coaxial cable, Dia.: 3.0, Length: 1.9 m
Center of coil
Mounting Hole Dimensions
Four M3 or 3.5-dia. holes
Four 3.5-dia. (mounting holes)
Center of coil
SECTION 7
Appendix
Item Specifications
Transmission frequency 134 kHz
Ambient temperature Operating: 0 to +40°C Storage: -15 to +65°C (with no icing)
Ambient humidity Operating/Storage: 35% to 85% (with no condensation)
Degree of protection IP60 (IEC60529)
Insulation resistance 20 MΩ min. between all terminals and the case (100 VDC M)
Dielectric strength Leak current not to exceed 5 mA on application of 1000 VAC (50/60 Hz for 1 minute) between all
Vibration resistance Frequency: 10 to 150 Hz; double amplitude: 0.20 mm; acceleration: 15 m/s
Shock resistance Shock of 150 m/s
Casing material ABS/epoxy resin
Weight Approx. 100 g
Cable length 1.9 m
Cable specification 3-mm-dia. coaxial cable
terminals and the case
8 minutes, 10 times each in X, Y, and Z directions
Stainless steel mount
2
in X, Y, and Z directions, 3 times each for 18 repetitions
2
SECTION 7
Specifications and Dimensions
for
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
79
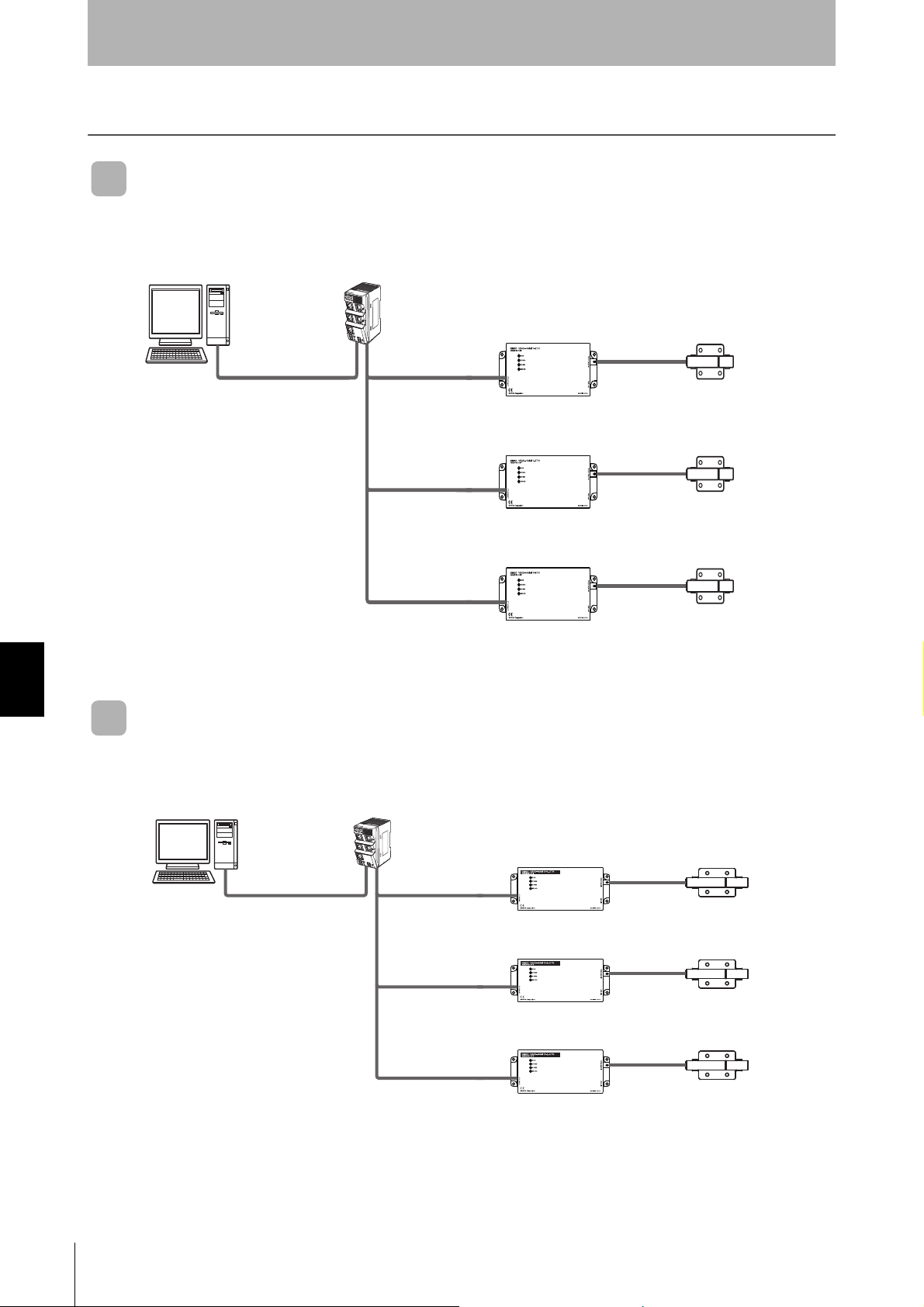
SECTION 7
Host device
Host computer,
device controller, etc.
CIDRW Head
V640-HS61
Amplifier Unit
V640-HAM11-ETN
Ethernet hub
LAN cable
LAN cable
CIDRW Head
V640-HS61
Amplifier Unit
V640-HAM11-ETN
LAN cable
CIDRW Head
V640-HS61
Amplifier Unit
V640-HAM11-ETN
LAN cable
The Amplifier Unit controls the
CIDRW Head. Up to 256 Amplifier Units can be connected.
The CIDRW Head is the
antenna. It reads and writes
carrier IDs and performs
other processing for ID Tags.
Host device
Host computer,
device controller, etc.
CIDRW Head
V640-HS62
Amplifier Unit
V640-HAM11-L-ETN
Ethernet hub
LAN cable
LAN cable
CIDRW Head
V640-HS62
Amplifier Unit
V640-HAM11-L-ETN
LAN cable
CIDRW Head
V640-HS62
Amplifier Unit
V640-HAM11-L-ETN
LAN cable
The Amplifier Unit controls the
CIDRW Head. Up to 256 Amplifier Units can be connected.
The CIDRW Head is the
antenna. It reads and writes
carrier IDs and performs
other processing for ID Tags.
Appendix
Connection Examples
V640-HAM11-ETN
Connect the host device and Amplifier Unit using a LAN cable.
SECTION 7
Connection Examples
V640-HAM11-L-ETN
Connect the host device and Amplifier Unit using a LAN cable.
80
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
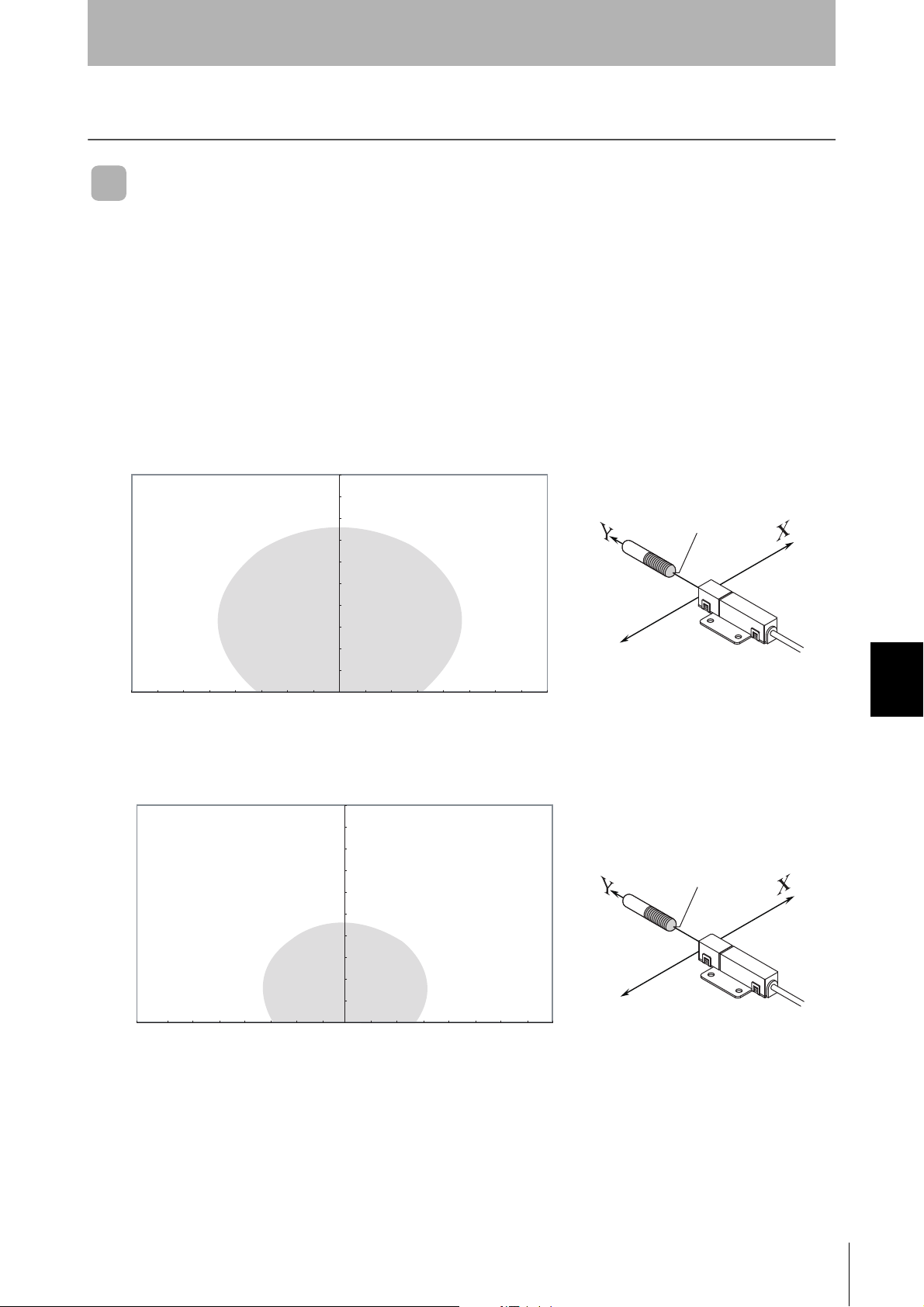
SECTION 7
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement point
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Communications Area (WRITE)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement point
Appendix
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
Maps of Communications Areas (Reference Only)
The figures given below for communications areas (communications distances) are reference values
only. The maps of communications areas will vary according to the ID Tags that you use, the background metals, the ambient noise, the effects of temperature and so on, and should be thoroughly confirmed on installation. The direction of the ID Tags will affect communications performance. Check the
direction of the coils in the ID Tags before using the ID Tags.
■ V640-HAM11-ETN
• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
• WRITE
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
81
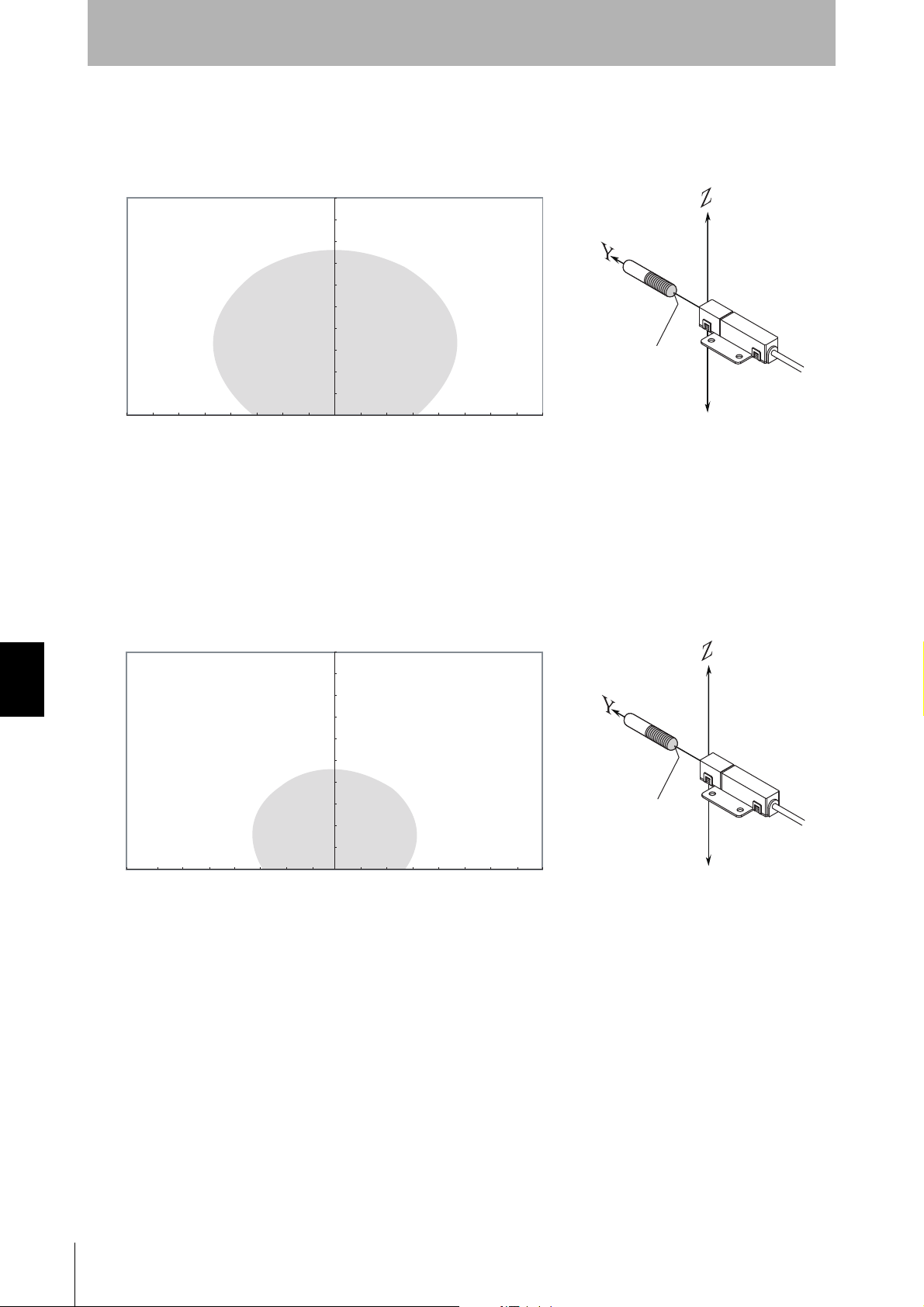
SECTION 7
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement point
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Communications Area (WRITE)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement point
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Appendix
• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
• WRITE
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
0
82
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
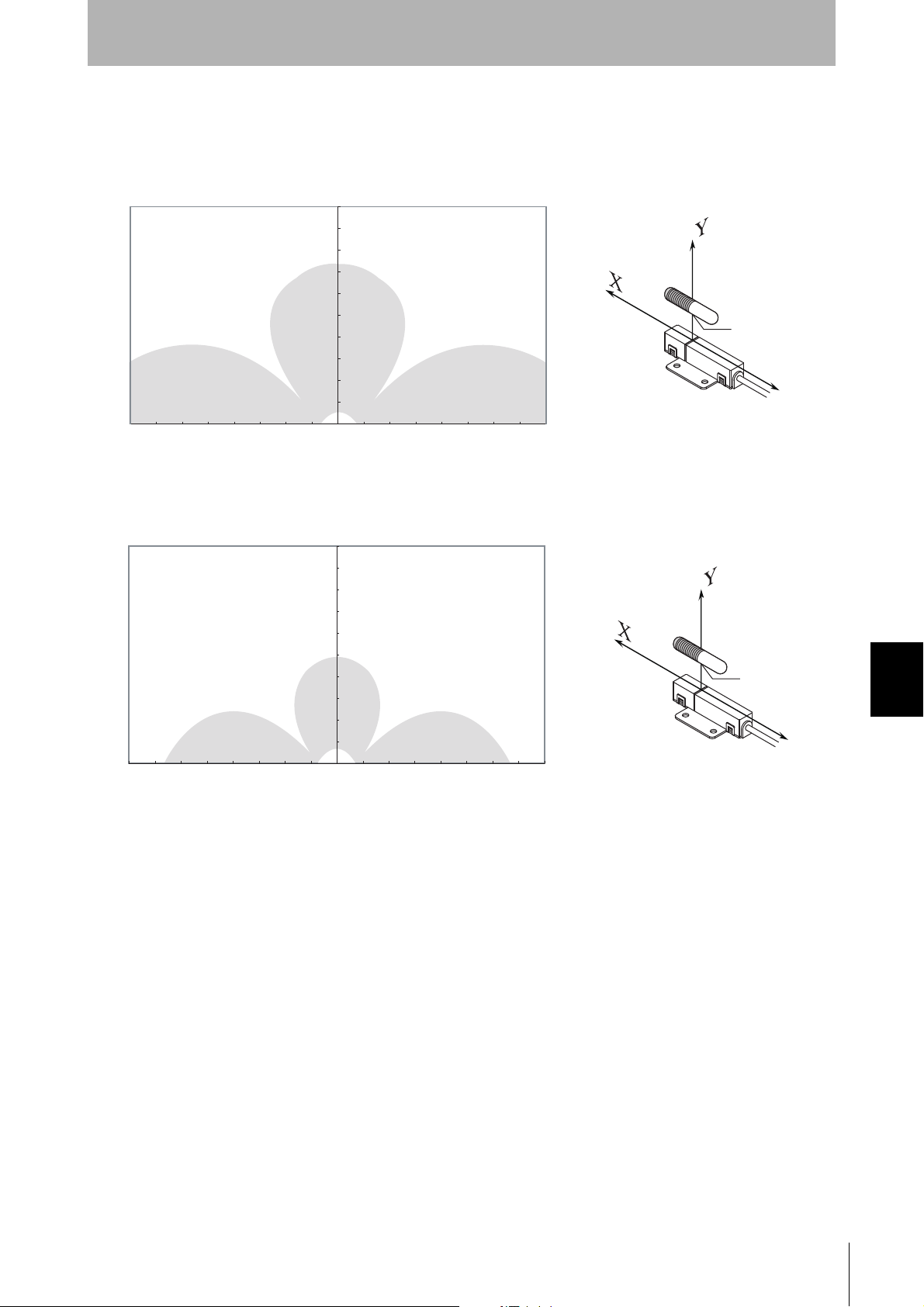
• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
0
Communications Area (WRITE)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
• READ
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Appendix
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
83

SECTION 7
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
010-10 20-20-30 30 40-40-50 50-60-70-80 60 70 80
Communications Area (WRITE)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Appendix
• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
010-10 20-20-30 30 40-40-50 50-60-70-80 60 70 80
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
84
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
-80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Communications Area (WRITE)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
• READ
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Appendix
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
85

SECTION 7
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (WRITE)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Appendix
• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
010-10 20-20-30 30 40-40-50 50-60-70-80 60 70 80
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
• WRITE
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
010-10 20-20-30 30 40-40-50 50-60-70-80 60 70 80
86
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 50 100 150 200-200 -150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 50 100 150 200-150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (WRITE)
• READ
SECTION 7
Appendix
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
87

SECTION 7
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 50 100 150 200-150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 50 100 150 200-150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (WRITE)
Appendix
• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
• READ
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
88
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 20050 100 150-150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (WRITE)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
SECTION 7
Appendix
-200 0 50 100 150 200-150 -100 -50
• WRITE
0
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
89

SECTION 7
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (WRITE)
Appendix
• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
-200 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 200
0
• WRITE
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
0 50 100 150 200-200 -150 -100 -50
90
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 20050 100 150-150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (WRITE)
• READ
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Appendix
-200 0 20050 100 150-150 -100 -50
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
91

SECTION 7
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
-200 0 20050 100 150-150 -100 -50
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Appendix
• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
• READ
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
180
150
120
90
60
30
-200 -150 -100 -50 50 100 150 2000
0
CIDRW System
92
User’s Manual

■ V640-HAM11-L-ETN
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement point
0-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement point
0-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
SECTION 7
Appendix
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
93

SECTION 7
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement point
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement point
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Appendix
• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
• WRITE
0-20
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
0-20
94
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
• READ
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
• WRITE
0-20
SECTION 7
Appendix
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
140
120
100
80
60
40
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
20
0
0-20
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
95

SECTION 7
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Appendix
• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
• WRITE
0-20
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
0-20
96
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
• READ
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
• WRITE
0-20
SECTION 7
Appendix
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
0-20
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
97

SECTION 7
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Appendix
• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-DR2B)
• READ
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
0-20
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
• WRITE
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-40-60-80-100-120-140-160-180 18016014012010080604020
0-20
98
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
㪇
㪇
㪄㪌㪇
㪊㪇
㪌㪇
㪍㪇
㪐㪇
㪈㪉㪇
㪈㪌㪇
㪈㪏㪇
㪄㪈㪇㪇 㪈㪇㪇㪄㪈㪌㪇 㪈㪌㪇㪄㪉㪇㪇 㪉㪇㪇
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
0
50
SECTION 7
Appendix
• WRITE
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
99

SECTION 7
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Appendix
• Coaxial Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
0
• WRITE
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
50
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
0
50
100
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
0
50
SECTION 7
Appendix
• WRITE
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
0
50
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
101

SECTION 7
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Appendix
• Parallel Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
0
• WRITE
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
50
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
180
150
120
90
60
30
0
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
0
50
102
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in X direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
SECTION 7
Appendix
• WRITE
180
150
120
0
0
90
60
30
0
0
50
50
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
-50
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
103

SECTION 7
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Distance in Y direction (mm)
Distance in Z direction (mm)
Measurement
point
Communications Area (READ)
Appendix
• Vertical Mounting (RI-TRP-WR2B)
• READ
180
150
120
90
60
30
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
• WRITE
180
150
120
0
0
90
60
30
0
0
50
50
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-100 100-150 150-200 200
-50
-50
CIDRW System
104
User’s Manual

SECTION 7
1 m min.
• V640-HS61
• V640-HS62
2 m min.
1 m min.
• V640-HS61
• V640-HS62
2 m min.
1 m min.
• V640-HS61
• V640-HS62
2 m min.
Appendix
Mutual Interference Distances (Reference Only)
If Amplifier Units are connected using multidrop connections and multiple CIDRW Heads are used, the
CIDRW Heads will not process commands simultaneously. In this case, install the CIDRW Heads at
least 0.1 m apart from each other.
Distance between Antennas and Changes in Communications Distances (Reference Only)
• V640-HS61 • V640-HS62
Distance between Antennas Change in communications distance Distance between Antennas Change in communications distance
1,000 mm 100% 2,000 mm 99%
900 mm 100% 1,600 mm 99%
800 mm 100% 1,400 mm 95%
700 mm 99% 1,200 mm 84%
600 mm 90% 1,000 mm 68%
500 mm 74% 800 mm 53%
400 mm 55% 600 mm 34%
300 mm 40% 400 mm 15%
200 mm 15% 200 mm 0%
If CIDRW Heads in separate CIDRW systems process commands simultaneously when the CIDRW
Systems are installed close to each other, mutual interference between the Heads can result in malfunctions. If this is a problem, install the CIDRW Heads separated at least by the distances shown in
the following illustrations.
■ For Coaxial Installation
■ For Parallel Installation
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
■ For Face-to-Face Installation
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
105

SECTION 7
Metal body (material: AL, SUS)
(Thickness: 1 mm)
10 mm min.
10 mm min.
20 mm min.
20 mm min.
Metal body (material: AL, SUS)
• V640-HS61
• V640-HS62
20 mm min.
20 mm min.
30 mm min.
30 mm min.
Metal body (material: AL, SUS)
Appendix
Influence of Background Metals (Reference Only)
The CIDRW Head can also communicate from an opening in a ceiling panel (metal body).
However, ensure the distances indicated below between the CIDRW Head and the metal body. If you
do not ensure these distances the communications distance will be substantially shortened.
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
V640-HS62
CIDRW HEAD
MADE IN JAPAN
CIDRW System
106
User’s Manual

SECTION 7
Host
Amplifier Unit
Command
Response
Communications time
TAT
Rounding up
Transmission time (ms) =
Number of bits per character (bits)
Baud rate (bps)
× total number of characters of command and response
TAT ( ms) =
10
9600
× (A + B) + Communications time (ms)
Appendix
Communications Time
Regardless of whether SECS is used or not, take the time required for processing between the host
device and Amplifier Units into account when designing the system.
Time Description
Communications time This is the time required for communications between an ID Tag and the CIDRW Head.
TAT This is the time required for processing at the Amplifier Unit, seen from the host device.
Communications time calculation formula (unit: ms)
READ: 150.5 × (number of pages) + 6.1
SAME WRITE: 468.6 × (number of pages) + 80.3
BYTE WRITE: 468.6 × (number of pages/8) + 229.9
TAT calculation formula (units: ms)
TAT = command and response transmission time + communications time
The command and response transmission time differs depending on the number of characters
sent and the communications conditions.
This calculation applies to continuous transmission in which the Controller uses no spaces
between command characters.
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
Example of TAT calculation:
Number of command characters: A; number of response characters: B
Baud rate: 9600 bps, data length: 8 bits, non parity, 1 stop bit
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
107

SECTION 7
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
Read
Number of pages processed
Communications time
Communications time (ms)
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
5000
5500
6000
6500
7000
7500
8000
8500
1246810121416
Communications time (ms)
Write (SAME WRITE)
Number of pages processed
Communications time
Appendix
The graph for communications time for communications between the ID Tag and CIDRW Head, and
TAT (when the baud rate is 9600 bps), is shown below.
The communications time and TAT, however, may increase substantially according to the conditions of
use.
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
108
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

SECTION 7
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
5000
5500
6000
6500
7000
7500
8000
8500
1 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128
Communications time (ms)
BYTE WRITE
Number of bytes processed
Communications time
Appendix
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
109

SECTION 7
Noise level
Communications distance (mm)
Relationship between noise level and communications distance (reference values)
(Max.)
Noise level
Communications distance (mm)
Relationship between noise level and communications distance (reference values)
(Max.)
Appendix
Communications Distance Characteristics vs. Ambient Noise
The graph below compares the results of measurement using the noise measurement function with
communications distances.
At installation implement measures in regard to metal in the vicinity of the CIDRW Head, power supply
noise, and atmospheric noise, to ensure that the noise level does not exceed 10.
NOISE MEASUREMENT command (applies only when SECS is not used) Refer to page 49.
■ V640-HAM11-ETN
90
80
70
60
SECTION 7
Characteristic Data According to Conditions of Use
50
40
30
20
10
0
02040608099
■ V640-HAM11-L-ETN
140
120
100
(MAX)
110
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
80
60
40
20
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
(MAX)

ID Tag Memory Maps
Page 8 bytes/1 page
1 00h 01h 02h 03h 04h 05h 06h 07h
2 08h 09h 0Ah 0Bh 0Ch 0Dh 0Eh 0Fh
3 10h 11h 12h 13h 14h 15h 16h 17h
4 18h 19h 1Ah 1Bh 1Ch 1Dh 1Eh 1Fh
5 20h 21h ••• ••• 27h
6 28h 29h ••• ••• 2Fh
7 30h 31h ••• ••• 37h
8
9 :
10 : :
11 :
12
13
14 68h 69h ••• ••• 6Fh
15 70h 71h ••• ••• 77h
16 78h 79h ••• ••• 7Fh
17 80h 81h ••• ••• 87h
DATASEG LENGTH
Carrier
ID
16
"S01" 8
"S02" 8
"S03" 8
"S04" 8
"S05" 8
"S06" 8
"S07" 8
"S08" 8
"S09" 8
"S10" 8
"S11" 8
"S12" 8
"S13" 8
"S14" 8
"S15" 8
Carrier ID
(16 byte)
Data area
(Total of 120
bytes)
■ RI-TRP-DR2B
ID Tag Memory Map
Example of data
segment settings
Page 8 bytes/1 page
1 00h 01h 02h 03h 04h 05h 06h 07h
DATASEG LENGTH
Carrier ID 8
Carrier ID
(8 byte)
■ RI-TRP-WR2B
ID Tag Memory Map
Example of data
segment settings
The memory maps of the RI-TRP-DR2B and RI-TRP-WR2B ID Tags are given below.
SECTION 7
Appendix
• The carrier ID memory area starts from page 1 (fixed).
• 00h to 87h in the table are addresses.
• The RI-TRP-WR2B has a memory capacity of 136 bytes.
• The RI-TRP-WR2B has a memory capacity of 8 bytes.
SECTION 7
ID Tag Memory Maps
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
111

Regular Inspection
In order to maintain optimum performance of the functions of the CIDRW system, daily and periodic
inspections are necessary.
Supply voltage fluctuation Check that the supply voltage fluctuation
Environment Ambient tem-
I/O power
supply
SECTION 7
Regular Inspection
Mounting condition Check that each device is securely
SECTION 7
Appendix
Inspection item Detail Criteria Tools required
To be within supply voltage rating. Multimeter
at the power supply terminal block is
within the permissible range.
Check that there are no frequent instantaneous power failures or radical voltage
drops.
Check that the ambient temperature and
perature
Ambient
humidity
Vibration and
shock
Dust Check that the system is free of dust
Corrosive gas Check that no metal part of the system is
Voltage fluctuation
Ripple
humidity are within specified range.
Check that no vibration or shock is transmitted from any machines.
accumulation.
discolored or corroded.
Check on the I/O terminal block that the
voltage fluctuation and ripple are within
the permissible ranges.
mounted.
Check that each connector is securely
connected.
Check that no wire is broken or nearly
broken.
Check if grounding to 100 Ω or less has
been done.
To be within permissible voltage fluctua-
tion range.
To be within the specified range. Maximum and
To be none.
To be within the specified range. Multimeter
There must be no loose screws. —
Each connector must be locked or
securely tightened with screws.
There must be no wire that is broken or
nearly broken.
To be grounded to 100 Ω or less.
Power supply
analyzer
minimum thermometer
Hygrometer
Oscilloscope
112
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

ASCII Code Table
Leftmost
bits
Rightmost bits
b8 to b5
0000 1001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 110 1 1010 1011 11 00 1101 1110 1111
b4 to b1
Row
Line
0 1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
0000 0
NUL TC7(DLE)
(SP) 0 @ P ` p
Undefined Undefined Undefined
0001 1
TC1(SOH) DC
1
!1AQaq
0010 2
TC2(STX) DC
2
"2BRbr
0011 3
TC3(ETX) DC
3
#3CScs
0100 4
TC4(EOT) DC
4
$4DTd t
0101 5
TC5(NEQ) TC8(NAK)
%5EUe u
0110 6
TC6(ACK) TC9(SYN)
&6FV f v
0111 7
BEL TC10(ETB)
'7GWgw
1000 5
FE0(BS) CAN
(8HXhx
1001 9
FE1(HT) EM
)9IYiy
1010 10
FE2(LF) SUB
*:JZjz
1011 11
FE3(VT) ESC
+;K[k{
110 0 12
FE4(FF) IS4(FS)
,<L\ l |
110 1 13
FE5(CR) IS3(GS)
-=M]m}
1110 14
S0 IS2(RS)
.>N^nÅP
1111 15
S1 IS1(US)
/?O_oDEL
SECTION 7
Appendix
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
SECTION 7
ASCII Code Table
113

SECTION 7
Appendix
Protective Construction
IP- is governed by the test methods described below. Check in advance the seal characteristics under
the actual environment and conditions of use.
IP is the abbreviation of International Protection.
■ IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
Standard (IEC60529: 1989-11)
(A) First numeral in code: Class of protection against entry of solid foreign material
Class Degree of protection
0 No protection
SECTION 7
Protective Construction
1 Protected against access by solid objects with a diameter of 50 mm or greater (e.g., human hands).
2 Protected against access by solid objects with a diameter of 12.5 mm or greater (e.g., fingers).
3 Protected against access by wires and solid bodies with a diameter of 2.5 mm or greater.
4 Protected against access by wires and solid bodies with a diameter of 1 mm or greater.
5 Entry of volumes of dust that would cause difficulties in normal operation of devices or compromise
safety is prevented.
6 Entry of dust is prevented.
(B) Second numeral of code: Class of protection against the entry of water
Class Degree of protection Outline of test methods (tests using water)
0 No special protection No protection against the
1 Protection against droplets
of water
entry of water.
The product suffers no ill
effects from droplets of water
falling vertically onto it.
No test
Water droplets are
sprayed onto the product
from directly above for 10
minutes by water droplet
exposure test apparatus.
114
2 Protection against droplets
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
of water
The product suffers no ill
effects from droplets of water
directed at it at an angle of up
to 15° to vertical.
The water droplet exposure test apparatus is set
to 15° from vertical and
water droplets sprayed
onto the product for 10
minutes (total of 25 minutes in each direction).

SECTION 7
0.07 L/min.
per hole in the
spray nozzle
0.07 L/min.
per hole in the
spray nozzle
Diameter of spray
nozzle head: 6.3
Diameter of spray
nozzle head: 12.5
Appendix
Class Degree of protection Outline of test methods (tests using water)
3 Protection against spraying
water
4 Protection against splashing
water
The product suffers no ill
effects from a water spray
directed at it at up to 60° from
vertical.
The product suffers no ill
effects from water splashed
on it from all directions.
Using the test apparatus
shown in the figure to the
right, water is sprayed
from both directions, onto
both sides of the product,
at angles up to 60° from
vertical for 10 minutes.
Using the test apparatus
shown in the figure to the
right, water is splashed
onto the product from all
directions for 10 minutes.
5 Protection against water
jets
6 Protection against powerful
jets of water
7 Protection against immer-
sion in water
8 Protection against
immersion in water
The product suffers no ill
effects from a water jet aimed
directly at it from all directions.
Water does not enter the
product when a powerful jet of
water is directed at it from all
directions.
No entry of water on
immersion in water at the
stipulated pressure for the
stipulated time.
The product can be used
while continually immersed in
water.
Using the test apparatus
shown in the figure to the
right, a water jet is directed
at the product from all
directions for 1 minute per
square meter of outer casing, with a minimum total
exposure of 3 minutes.
Using the test apparatus
shown in the figure to the
right, a water jet is directed
at the product from all
directions for 1 minute per
square meter of outer casing, with a minimum total
exposure of 3 minutes.
Immerse in water for 30
minutes at a depth of 1
meter (when the height of
the apparatus is less than
850 mm).
Depends on arrangements made between the
manufacturer and the user
of the product.
SECTION 7
Protective Construction
CIDRW System
User’s Manual
115

SECTION 7
Appendix
SECTION 7
Protective Construction
116
CIDRW System
User’s Manual

Revision History
Cat. No. Z308-E1-01
Revision code
A manual revision code appears as a suffix to the catalog number on the front cover of the manual.
The following table outlines the changes made to the manual during each revision. Page numbers refer to the previous
version.
Revision code Date Revised content
01 September 2010 Original production

OMRON Corporation Industrial Automation Company
Tokyo, JAPAN
Contact: www.ia.omron.com
Regional Headquarters
OMRON EUROPE B.V.
Sensor Business Unit
Carl-Benz-Str. 4, D-71154 Nufringen, Germany
Tel: (49) 7032-811-0/Fax: (49) 7032-811-199
OMRON ASIA PACIFIC PTE. LTD.
No. 438A Alexandra Road # 05-05/08 (Lobby 2),
Alexandra Technopark,
Singapore 119967
Tel: (65) 6835-3011/Fax: (65) 6835-2711
OMRON ELECTRONICS LLC
One Commerce Drive Schaumburg,
IL 60173-5302 U.S.A.
Tel: (1) 847-843-7900/Fax: (1) 847-843-7787
OMRON (CHINA) CO., LTD.
Room 2211, Bank of China Tower,
200 Yin Cheng Zhong Road,
PuDong New Area, Shanghai, 200120, China
Tel: (86) 21-5037-2222/Fax: (86) 21-5037-2200
Authorized Distributor:
© OMRON Corporation 2010 All Rights Reserved.
In the interest of product improvement,
specifications are subject to change without notice.
Cat. No. Z308-E1-01
Printed in Japan
0910
 Loading...
Loading...