Page 1

Manual No.
TOEP-C71080603-01-OY
OMRON YASKAWA Motion Control B.V.
JUNMA SERIES SERVO DRIVE
Mechatrolink-II communications type
Model: SJDE- ANA-OY
USER´ S MANUAL
Page 2

Copyright © 2006 YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted, in any form, or by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Yaskawa. No
patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein.
Moreover, because Yaskawa is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products,
the information contained in this manual is subject to change without notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, Yaskawa
assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for
damages resulting from the use of the information contained in this publication.
Page 3
Introduction
This instruction manual describes the JUNMA series AC SERVOPACKs. To properly use the JUNMA
series AC SERVOPACKs, read these instructions thoroughly and retain for easy reference for inspections,
maintenance, and so on. Make sure that the end user receives this manual.
Related Manuals
Refer to the following manuals as required.
Manual Name Manual Number
JUNMA series AC SERVOMOTOR
INSTRUCTIONS
TOMPC23026100
or
TOEPC23026101
Safety Information
The following conventions are used to indicate precautions in this manual. Failure to heed these precautions can result in serious or possibly even fatal injury or damage to the products or to related equipment
and systems.
WARNING
CAUTION
PROHIBITED
MANDATORY
Indicates precautions that, if not heeded, could possibly result in loss of life or serious injury.
Indicates precautions that, if not heeded, could result in relatively serious or minor
injury, damage to the product, or faulty operation.
In some situations, the precautions indicated could have serious consequences if
not heeded.
Indicates prohibited actions that must not be performed. For example, this symbol
would be used as follows to indicate that fire is prohibited: .
Indicates compulsory actions that must be performed. For example, this symbol
would be used as follows to indicate that grounding is compulsory: .
Visual Aids
The following aids are used to indicate certain types of information for easier reference.
• Indicates important information that should be memorized, including precautions
IMPORTANT
INFOINFO
such as alarm displays to avoid damaging the devices.
• Indicates supplemental information.
Trademarks
MECHATROLINK is a trademark of the MECHATROLINK Members Association.
1
Page 4

Notes for Safe Operation
Read these instructions thoroughly before checking products on delivery, storage and transportation,
installation, wiring, operation and inspection, and disposal of the AC SERVOPACK.
WARNING
• Be sure to correctly connect the SERVOPACK connectors.
Incorrect wiring may result in electric shock, fire, or damage to the equipment. For the wir-
ing method, refer to 3.4 Main Circuit Wiring.
• Use the emergency stop signal input E-STP to forcibly turn OFF the servo from an external
sequence, such as host controller, at occurrence of servo alarm or system emergency stop.
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has
been turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to completely stop the motor by turning OFF the servo using the emergency stop.
• Configure the circuit’s power supply to be automatically cut off if E-STP signal is OFF at
occurrence of emergency stop
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has
been turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to completely stop the motor by turning OFF the servo using the emergency stop.
Position information is not stored in the SERVOPACK, so this information will be lost if the
power supply is turned OFF. This information cannot be read again if the power supply is
turned OFF.
• Never touch any rotating motor parts while the motor is running.
Failure to observe this warning may result in injury.
• Before starting operation with a machine connected, make sure that an emergency stop can
be applied at any time. Also, configure the circuit’s power supply to be automatically cut off if
E-STP signal is OFF at occurrence of emergency stop.
Failure to observe this warning may result in injury.
• Never touch the inside of the SERVOPACK.
Failure to observe this warning may result in electric shock.
• Do not touch terminals for five minutes after the power is turned OFF.
Residual voltage may cause electric shock.
• Follow the procedures and instructions for trial operation precisely as described in this man-
ual.
Malfunctions that occur after the servomotor is connected to the equipment not only damage the equipment, but may also cause an accident resulting in death or injury.
• Do not remove cables, connectors, or optional items while the power is ON.
Failure to observe this warning may result in electric shock.
• Installation, wiring, advice on inspection and malfunction must be performed only by autho-
rized personnel.
Failure to observe this warning may result in fire, electric shock, or injury.
• Do not damage, press, exert excessive force or place heavy objects on the cables or the
cables between other objects where they might be pinched.
Failure to observe this warning may result in electric shock, stopping operation of the product, or burning.
2
Page 5

WARNING
• Provide an appropriate stopping device on the machine side to ensure safety.
A holding brake for a servomotor with brake is not a stopping device for ensuring safety.
Failure to observe this warning may result in injury.
• Do not come close to the machine immediately after resetting momentary power loss to
avoid an unexpected restart.
Take appropriate measures to ensure safety against an unexpected restart. Failure to
observe this warning may result in injury.
• Never modify the product.
Failure to observe this warning may result in injury or damage to the product.
• Be sure to correctly ground the SERVOPACK and the servomotor.
• Connect the SERVOPACK’s ground terminal to electrical codes (ground resistance: 100 Ω
or less).
Improper grounding may result in electric shock.
Checking on Delivery
CAUTION
• Always use the servomotor and SERVOPACK in one of the specified combinations.
Failure to observe this caution may result in fire or malfunction.
Storage and Transportation
CAUTION
• Do not store or install the product in the following places.
Failure to observe this caution may result in damage to the product.
• Locations subject to direct sunlight.
• Locations subject to temperatures outside the range specified in the storage or installation temperature conditions.
• Locations subject to humidity outside the range specified in the storage or installation
humidity conditions.
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of extreme changes in temperature.
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
• Locations subject to dust, salts, or iron dust.
• Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals.
• Locations subject to shock or vibration.
• Do not hold the product by the cables or motor shaft while transporting it.
Failure to observe this caution may result in injury or malfunction.
• Do not place any load exceeding the limit specified on the packing box.
Failure to observe this caution may result in injury or malfunction.
3
Page 6
Installation
CAUTION
• Make sure to follow the conditions on 2.1 Installation Conditions.
Failure to observe this caution may result in electric shock, fire, or SERVOPACK’s malfunc-
tion.
• Do not step on or place a heavy object on the product.
Failure to observe this caution may result in injury.
• Do not cover the inlet or outlet parts of the SERVOPACK and prevent any foreign objects,
such as metallic fragment, or combustibles from entering the product.
Failure to observe this caution may cause internal elements to deteriorate resulting in malfunction or fire.
• Be sure to install the product in the correct direction.
Failure to observe this caution may result in malfunction.
• Provide the specified clearances between the SERVOPACK and the control panel or with
other devices.
Failure to observe this caution may result in fire or malfunction.
• SERVOPACK and servomotor are precision equipment. Do not apply any strong impact.
Failure to observe this caution may result in malfunction.
4
Page 7
Wiring
WARNING
• Be sure to correctly ground the SERVOPACK and the servomotor.
• Wiring must be performed by an authorized person qualified in electrical work.
• When using the servomotor for a vertical axis, install safety devices to prevent workpieces
from falling off because of alarms. Workpiece’s falling off may result in injury or malfunction.
• Configure the interlock circuit so that the system is interlocked to avoid injury whenever the
protective cover on the machine is opened or closed.
• Use the emergency stop signal input E-STP to forcibly turn OFF the servo from an external
sequence, such as host controller, at occurrence of servo alarm or system emergency stop.
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has
been turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to completely stop the motor by turning OFF the servo using the emergency stop.
• When executing the JOG operation and the home position search operation using CX-Drive,
the E-STP signal will be ignored. Alternative measures must be taken in case an emergency stop is needed.
• Configure the circuit’s power supply to be automatically cut off if E-STP signal is OFF at
occurrence of emergency stop.
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has
been turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment.
Position information is not stored in the SERVOPACK, so this information will be lost if the
power supply is turned OFF. This information cannot be read again if the power supply is
turned OFF.
• When executing JOG operation and the home position search operation using CX-Drive, the
P-OT and N-OT signals will be ignored. Alternative measures must be taken in case of
overtravel.
5
Page 8
CAUTION
• Do not connect a three-phase power supply to the U, V, or W output terminals.
Failure to observe this caution may result in injury or fire.
• Securely connect the power supply terminals, regenerative unit connection terminal, and
motor main circuit cable terminals.
Failure to observe this caution may result in fire.
• Do not bundle or run power and signal lines together in the same duct. Keep power and sig-
nal lines separated by at least 300 mm. (11.81 in).
Failure to observe this caution may result in malfunction.
• Use twisted-pair shielded wires or multi-core twisted pair shielded wires for I/O signal cable
and encoder cable.
The maximum length is 3 m (118.11 in) for I/O signal cable and is 20 m (787.40 in) for
encoder cable.
• Do not touch the power terminals for five minutes after turning the power supply LED (PWR)
are OFF because high voltage may still remain in the SERVOPACK.
• Avoid frequently turning power ON and OFF. Do not turn power ON or OFF more than once
per minute.
Since the SERVOPACK has a capacitor in the power supply, a high charging current flows
when power is turned ON. Frequently turning power ON and OFF causes main power
devices such as capacitors and fuses to deteriorate, resulting in unexpected problems.
• Observe the following precautions when wiring connector for power supply/regenerative
unit.
• Remove the connector for power supply/regenerative unit from the SERVOPACK prior to
wiring.
• Insert only one wire per terminal on the connector for power supply/regenerative unit.
• Make sure that the core wire is not electrically shorted to adjacent core wires.
• Be sure to wire correctly and securely.
Failure to observe this caution may result in motor overrun, injury, or malfunction.
• Always use the specified power supply voltage of single-phase 200 V to 230 V without con-
necting directly to the power supply of 400 V.
The SERVOPACK will be destroyed.
• Take appropriate measures to ensure that the input power supply is supplied within the
specified voltage fluctuation range.
An incorrect power supply may result in damage to the product.
• Install external breakers or other safety devices against short-circuit in external wiring.
Failure to observe this caution may result in fire.
• Take appropriate and sufficient countermeasures for each when installing systems in the fol-
lowing locations.
Failure to observe this caution may result in damage to the product.
• Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise.
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields and magnetic fields.
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radioactivity.
• Locations close to power supplies, including power supply lines.
• Do not reverse the polarity of the battery when wiring with regenerative unit.
Failure to observe this caution may result in damage to the product.
6
Page 9

Operation
CAUTION
• Conduct trial operation on the servomotor alone with the motor shaft disconnected from
machine to avoid any unexpected accidents.
Failure to observe this caution may result in injury.
• During the JOG operation and the home position search operation using CX-Drive, the forward run prohibited (P-OT), reverse run prohibited (N-OT), and emergency stop (E-STP)
signals will be ignored. Alternative measures must be taken in case of overtravel and emergency stop.
• When using the servomotor for a vertical axis, install safety devices to prevent workpieces
from falling off because of alarms.
Workpiece’s falling off may result in injury or malfunction.
• Do not touch the SERVOPACK heat sinks, regenerative unit, or servomotor while power is
ON or soon after the power is turned OFF.
Failure to observe this caution may result in burns due to high temperatures.
• When an alarm occurs, remove the cause, turn OFF the power and ON again after confirming safety, and then resume operation.
Failure to observe this caution may result in injury.
• Do not use the holding brake of the servomotor for ordinary braking.
Failure to observe this caution may result in malfunction.
Maintenance and Inspection
CAUTION
• Do not open the SERVOPACK case for 5 minutes after the power supply indicator (PWR
LED) goes out. High voltage may remain in the SERVOPACK after the power supply has
been turned OFF.
• After turning OFF the power supply, wait 15 minutes before replacing the cooling fan.
Failure to observe this caution may result in burns because the heat sink is hot.
• Mount the cooling fan in the correct way explained in 9.3 Replacement of Cooling Fan.
Improper mounting may result in the breakdown of the SERVOPACK.
• Do not attempt to change wiring while the power is ON.
Failure to observe this caution may result in electric shock or injury.
• Do not touch the SERVOPACK heat sinks, regenerative unit, or servomotor while power is
ON or soon after the power is turned OFF.
Disposal
CAUTION
• When disposing of the products, treat them as general industrial waste.
7
Page 10

General Precautions
Note the following to ensure safe application.
• The drawings presented in this manual are sometimes shown without covers or protective guards.
Always replace the cover or protective guard as specified first, and then operate the products in
accordance with the manual.
• The drawings presented in this manual are typical examples and may not match the product you
received.
• This manual is subject to change due to product improvement, specification modification, and manual improvement. When this manual is revised, the manual code is updated and the new manual is
published as a next edition.
• If the manual must be ordered due to loss or damage, inform your nearest Omron Yaskawa representative or one of the offices listed on the back of this manual.
• Omron Yaskawa will not take responsibility for the results of unauthorized modifications of this
product. Omron Yaskawa shall not be liable for any damages or troubles resulting from unauthorized modification.
8
Page 11

CONTENTS
Introduction - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1
Related Manuals - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1
Safety Information - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1
Visual Aids- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1
Trademarks - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1
Notes for Safe Operation- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2
1 Before Use- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13
1.1 Checking Products - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13
1.2 Warning Label- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13
1.3 Model Designation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14
1.4 SERVOPACKs and Applicable Servomotors- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14
1.5 Part Names and Functions- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15
1.6 Applicable Standards- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
1.6.1 North American Safety Standards (UL, CSA) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
1.6.2 European Directives - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
2 Installation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -17
2.1 Installation Conditions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 17
2.2 Installation Method - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 18
3 Wiring - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
3.1 System Configuration - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
3.2 Standard Connection- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 20
3.3 Precautions on Wiring - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 21
3.3.1 Protection for Power Supply Line - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 21
3.3.2 Caution for Grounding - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 21
3.3.3 Caution for Cable - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
3.3.4 Power Loss- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
3.3.5 SERVOPACKs and Applicable Peripheral Devices - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
3.3.6 Noise Prevention- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 23
3.3.7 Installation and Wiring Conditions on CE Marking - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 26
3.3.8 Other Precautions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 27
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 27
3.4.1 SERVOPACK Main Circuit Cables - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 27
3.4.2 Wiring Connector for the Power Supply/Regenerative Unit (CNA) - - - - - - - - - - - - 32
3.4.3 Wiring Connector for the Servomotor Main Circuit Cable (CNB)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - 34
3.4.4 Wiring the Encoder Connector (CN2) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 38
3.4.5 Wiring the I/O Signal Connector (CN1) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 39
3.4.6 Wiring the MECHATROLINK-II Communication Connectors (CN6A and CN6B) - - 41
9
Page 12

3.4.7 Wiring the Personal Computer Connector (CN9)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 43
3.5 Connection Examples of Input Signal - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 44
3.6 Connection Example of Output Signal- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 45
3.7 I/O Signals - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 46
3.7.1 Homing Deceleration Signal Input - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 46
3.7.2 External Latch Signal Input - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 46
3.7.3 Emergency Stop Signal Input - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 47
3.7.4 Forward/Reverse Run Prohibited Inputs (Overtravel Inputs) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 49
3.7.5 Servo Alarm Output - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 50
3.7.6 Brake Interlock Output - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 50
3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II Communications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 52
3.8.1 MECHATROLINK-II Communications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 52
3.8.2 Wiring Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 52
3.8.3 Setting Communications Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 53
3.8.4 Transmission Cycle and Number of Stations- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 54
3.8.5 MECHATROLINK-II Communications Status Indicator COM LED- - - - - - - - - - - - - 54
4 MECHATROLINK-II Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 55
4.1 Lists of Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 55
4.1.1 Main Commands List - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 55
4.1.2 Subcommands List - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 57
4.2 Main Commands- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 58
4.2.1 Communication Phases- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 58
4.2.2 No Operation (NOP: 00H)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 60
4.2.3 Read Parameter (PRM_RD: 01H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 61
4.2.4 Write Parameter (PRM_WR: 02H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 62
4.2.5 Read ID (ID_RD: 03H)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 63
4.2.6 Setup Device (CONFIG: 04H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 64
4.2.7 Read Alarm or Warning (ALM_RD: 05H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 65
4.2.8 Clear Alarm or Warning (ALM_CLR: 06H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 66
4.2.9 Start Synchronous Communication (SYNC_SET: 0DH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 67
4.2.10 Establish Connection (CONNECT: 0EH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 68
4.2.11 Release Connection (DISCONNECT: 0FH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 69
4.2.12 Write Stored Parameter (PPRM_WR: 1CH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 69
4.2.13 Set Coordinates (POS_SET: 20H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 70
4.2.14 Apply Brake (BRK_ON: 21H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 70
4.2.15 Release Brake (BRK_OFF: 22H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 72
4.2.16 Turn Sensor ON (SENS_ON: 23H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 73
4.2.17 Turn Sensor OFF (SENS_OFF: 24H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 73
4.2.18 Stop Motion (HOLD: 25H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 74
4.2.19 Request Latch Mode (LTMOD_ON: 28H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 75
4.2.20 Release Latch Mode (LTMOD_OFF: 29H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 76
4.2.21 Status Monitoring (SMON: 30H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 77
4.2.22 Servo ON (SV_ON: 31H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 78
4.2.23 Servo OFF (SV_OFF: 32H)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 79
4.2.24 Interpolation Feed (INTERPOLATE: 34H)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 80
4.2.25 Positioning (POSING: 35H)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 81
10
Page 13

4.2.26 Constant Speed Feed (FEED: 36H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 82
4.2.27 Interpolation Feeding with Position Detection (LATCH: 38H)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 83
4.2.28 External Input Positioning (EX_POSING: 39H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 84
4.2.29 Homing (ZRET: 3AH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 85
4.2.30 Adjusting (ADJ: 3EH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 87
4.3 Subcommands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 90
4.3.1 No Operation (NOP: 00H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 90
4.3.2 Read Parameter (PRM_RD: 01H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 90
4.3.3 Write Parameter (PRM_WR: 02H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 91
4.3.4 Read Alarm or Warning (ALM_RD: 05H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 91
4.3.5 Write Stored Parameter (PPRM_WR: 1CH) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 92
4.3.6 Request Latch Mode (LTMOD_ON: 28H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 92
4.3.7 Release Latch Mode (LTMOD_OFF: 29H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 93
4.3.8 Status Monitoring (SMON: 30H) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 93
4.4 Combination of MECHATROLINK-II Main Commands and Subcommands - - - - - - - - - 94
4.5 Command Data Field- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 95
4.5.1 Latch Signal Field Specifications: LT_SGN - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 95
4.5.2 Option Field Specifications: OPTION - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 95
4.5.3 Status Field Specifications: STATUS - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 96
4.5.4 Monitor Selection and Monitor Information Field Specifications:
SEL_MON1/2/3/4, MONITOR1/2/3/4- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 101
4.5.5 IO Monitor Field Specifications: IO_MON - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 103
4.5.6 Substatus Field Specifications: SUBSTATUS - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 104
4.5.7 Alarm/Warning Field Specifications: ALARM- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 105
4.6 Command and Response Timing - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 108
4.6.1 Command Data Execution Timing - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 108
4.6.2 Monitor Data Input Timing- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 108
4.7 Operation Sequence - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 109
4.7.1 Operation Sequence for Managing Parameters Using a
Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 109
4.7.2 Operation Sequence for Managing Parameters
Using SERVOPACK- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 110
4.7.3 Operation Sequence to Turn the Servo ON- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 111
4.7.4 Operation Sequence When OT (Overtravel Limit Switch) Signal is Input - - - - - - - 111
4.7.5 Operation Sequence When E-STP Signal is Input - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 111
5 Trial Operation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 113
6 Functions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 118
6.1 Filter Setting - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 118
6.2 Switching Servomotor Rotation Direction - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 119
6.3 Electronic Gear - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 120
6.3.1 Setting the Electronic Gear - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 120
6.4 Position Management - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 123
6.5 Motion Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 124
11
Page 14

6.5.1 INTERPOLATE Related Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -124
6.5.2 POSING Related Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -124
6.6 Software Limit Function - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -125
6.6.1 Conditions Needed to Enable the Software Limit Function - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -125
6.6.2 Parameters Related Software Limit Function - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -125
6.6.3 Monitoring Software Limit - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -126
6.7 Latching Area - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -127
7 Parameters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 128
7.1 Parameter Editor- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -128
7.2 List of Parameters- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -129
8 Troubleshooting- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 134
8.1 Alarm Displays - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -136
8.2 Warning Displays - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -138
8.3 Alarm/Warning Display and Troubleshooting - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -139
8.3.1 Alarm Display and Troubleshooting - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -139
8.3.2 Warning Display and Troubleshooting - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -149
8.4 Troubleshooting for Malfunction without Alarm Display - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -151
9 Inspections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 156
9.1 Regular Inspections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -156
9.2 Part’s Life Expectancy - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -156
9.3 Replacement of Cooling Fan - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -157
10 Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 163
10.1 Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -163
10.2 Allowable Moment of Inertia - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -165
10.3 Overload Characteristics - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -166
Revision History
12
Page 15
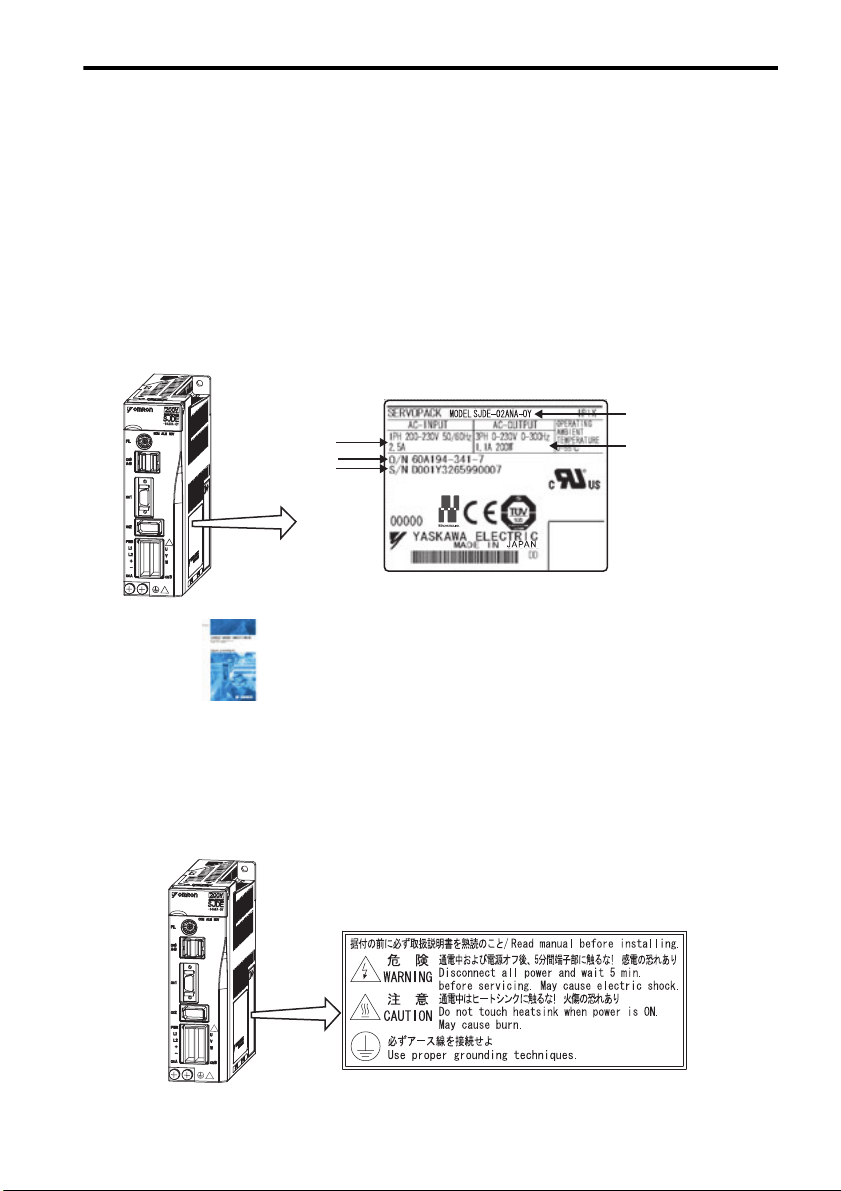
1.1 Checking Products
1 Before Use
1.1 Checking Products
Confirm that the following items have been delivered together with the SERVOPACK. Verify that the
ordered product as received by the model number marked on the nameplate on the SERVOPACK.
If you find any irregularities such as incorrect SERVOPACK model, damages, and missing parts or
items, contact your Omron Yaskawa representative or the dealer from whom you purchased the products.
SJDE
SERVOPACK
Nameplate
Applicable
power supply
Order number
Serial number
One copy of this Instruction Manual 1 Connector Part Number JZSP-CHG9-1
SERVOPACK
model
Applicable motor
capacity
1.2 Warning Label
A warning label is located on the side of the SERVOPACK.
SJDE
SERVOPACK
13
SERVOPACK's Warning Label
Page 16
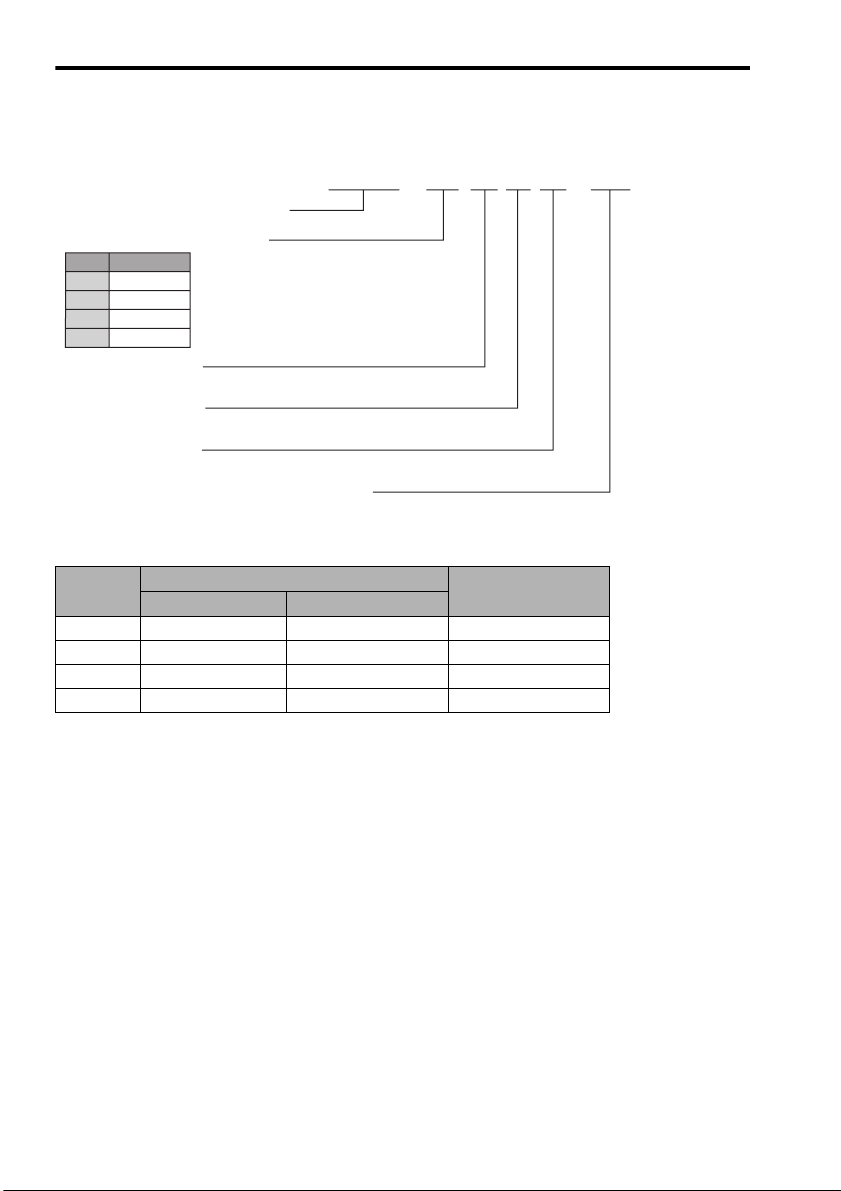
1.3 Model Designation
1.3 Model Designation
SJDE—02 A N A - OY
JUNMA series SJDE SERVOPACK
Applicable servomotor capacity
Code
Output (W)
100
01
200
02
400
04
750
08
Power supply voltage
A: 200 VAC
Interface specification
N: MECHATROLINK-II
Design revision order
A
Sold by OMRON YASKAWA Motion Control B.V.
1.4 SERVOPACKs and Applicable Servomotors
Rated
Output
100 W SJME-01AM41-OY SJME-01AM4C-OY SJDE-01ANA-OY
200 W SJME-02AM41-OY SJME-02AM4C-OY SJDE-02ANA-OY
400 W SJME-04AM41-OY SJME-04AM4C-OY SJDE-04ANA-OY
750 W SJME-08AM41-OY SJME-08AM4C-OY SJDE-08ANA-OY
Without Brakes With Brakes
Servomotors SERVOPACKs
14
Page 17
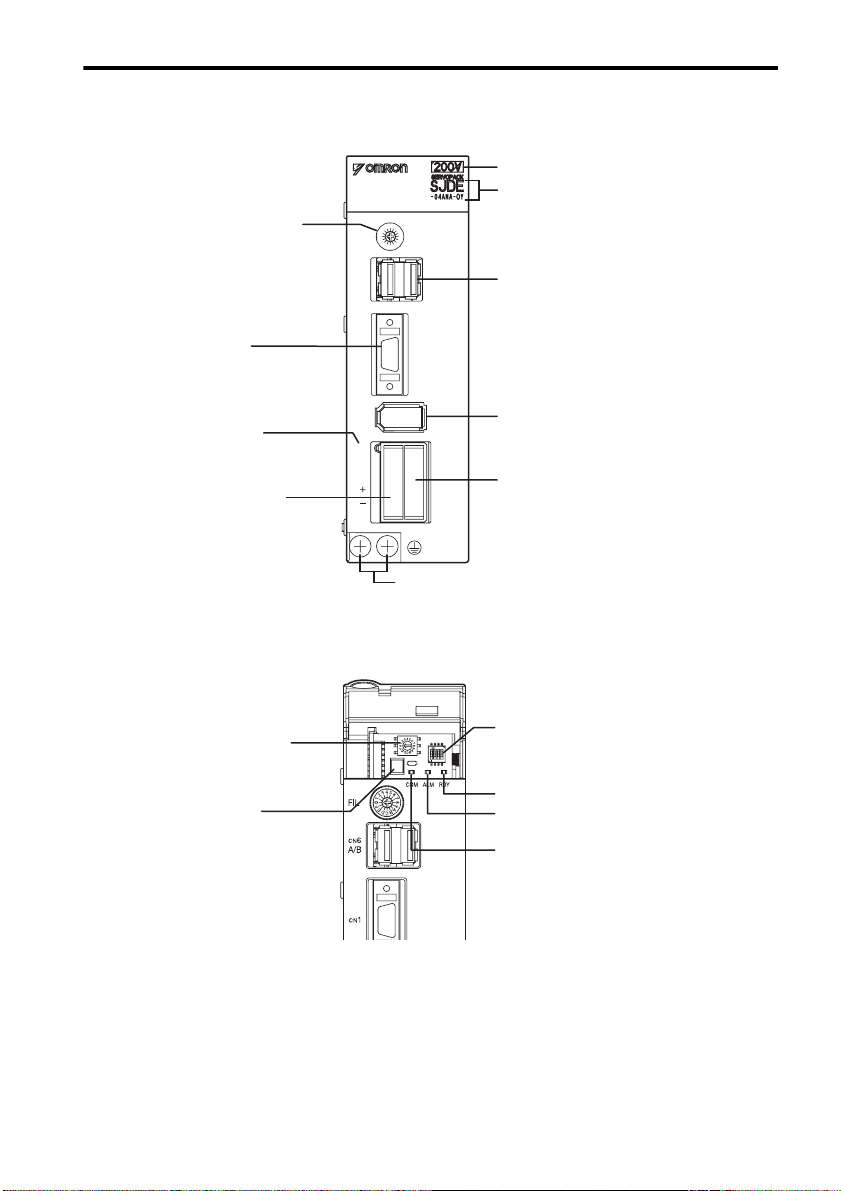
1.5 Part Names and Functions
Rotary switch for reference filter
setting(FIL)
Refer to 6.1 Filter Setting.
I/O signal connector (CN1)
Refer to 3.4 Main Circuit Wiring.
4
5
3
6
2
7
1
8
0
9
FIL
F
A
E
B
D
C
CN6
A/B
CN1
1.5 Part Names and Functions
Input voltage
Model
COM
ALM
RDY
Connector for MECHATROLINK-II
communications (CN6)
Refer to 3.4.6 Wiring the MECHATROLINK-
II Communication Connectors (CN6A and
CN6B).
Power supply indicator (PWR)
Connector for power supply/
regenerative unit (CNA)
Refer to 3.4.2 Wiring Connector for the
Power Supply/Regenerative Unit
(CNA).
CN2
PWR
L1
L2
U
V
W
CNBCNA
Encoder connector (CN2)
Refer to 3.4.4 Wiring the Encoder Connec-
tor (CN2).
Connector for servomotor main circuit
cable (CNB)
Refer to 3.4.3 Wiring Connector for the Ser-
vomotor Main Circuit Cable (CNB).
Ground terminal
MECHATROLINK-II Communications Settings
The SW1 and the SW2 switches set the MECHATROLINK-II communications settings. Settings that
have been changed are enabled when the power is turned OFF and then ON again.
DIP switch for MECHATROLINK-II
Rotary switch for MECHATROLINK-II
station address setting (SW1)
Refer to 3.8 Setting for
MECHATROLINK-II Communications.
Connector for personal
computer (CN9)
communications setting (SW2)
Refer to 3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II
Communications.
Servo status indicator (RDY)
Alarm indicator (ALM)
Refer to 8 Troubleshooting.
Indicator for MECHATROLINK-II
communications status (COM)
Refer to 3.8.5 MECHATROLINK-II
Communications Status Indicator COM LED
and 8 Troubleshooting.
15
Page 18
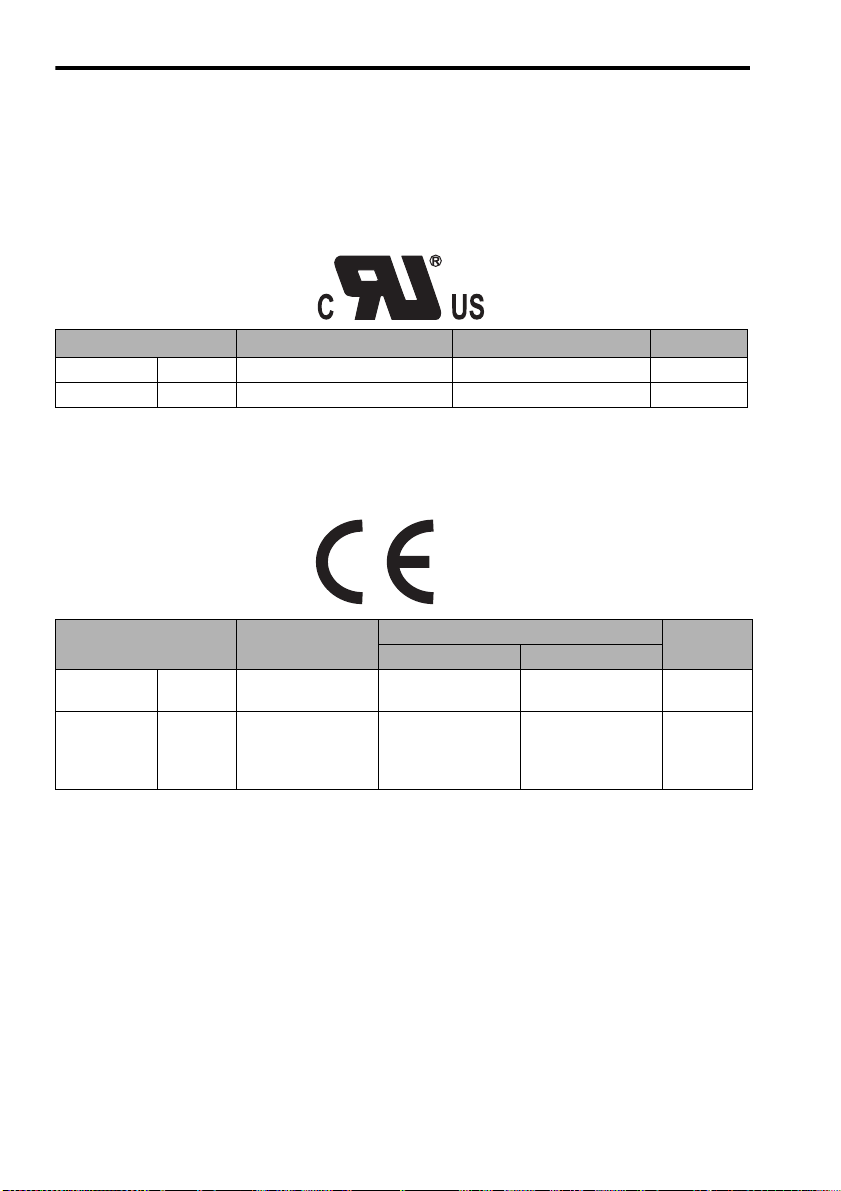
1.6 Applicable Standards
1.6 Applicable Standards
JUNMA series SERVOPACKs comply with the following standards.
1.6.1 North American Safety Standards (UL, CSA)
Model
SERVOPACK SJDE
Servomotor SJME
* 1. Underwriters Laboratories Inc.
* 2. Canadian Standards Association.
UL∗1 Standards (UL File No.) CSA∗2 Standards
UL508C (E147823) CSA C22.2 No.14 UL
UL1004 (E165827) CSA C22.2 No.100 UL
1.6.2 European Directives
Model Low Voltage
SERVOPACK
Servomotor
* TÜV Product Services GmbH
Note: 1. Because SERVOPACKs and servomotors are built-in type, reconfirmation is
required after being installed in the final product.
SJDE EN50178 EN55011
SJME IEC60034-1
Directive
IEC60034-5
IEC60034-8
IEC60034-9
class A, group 1
class A, group 1
EMC Directive Certification
EMI EMS
EN61000-6-2 TUV PS*
EN55011
EN61000-6-2 TUV PS*
Certification
16
Page 19
2 Installation
The following shows the installation location and method of the SERVOPACK.
2.1 Installation Conditions
Item Specifications
Operating temperature 0 ° C to +55 °C
Operating humidity 90% RH or less (with no condensation)
Storage temperature -20 ° C to +70 °C
Storage humidity 90% RH or less (with no condensation)
Installation site Free of corrosive gases
Altitude 1000 m or below
Vibration resistance
Shock resistance
Operating conditions Installation category (overvoltage category): II
Installation in a control
panel
Installation near a
Installation
Site
heating unit
Installation near a
source of vibration
Installation at a site exposed to corrosive gas
Free of dust and iron powder
Not subjected to moisture or lubrication oil such as cutting oil.
2
4.9m/s
2
19.6m/s
Pollution degree: 2
Protection class: IP1X (EN50178)
Design the control panel size, unit layout, and cooling method so that
the temperature around the SERVOPACK does not exceed 55 °C.
Note: To extend product life and maintain reli-
ability, keep the temperature inside the
control panel under 45 ° C.
Minimize the heat radiating from the heating unit as well as any
temperature rise caused by natural convection so that the temperature
around the SERVOPACK does not exceed 55 ° C.
Install a vibration isolator beneath the SERVOPACK to avoid subjecting
it to vibration.
Corrosive gas does not have an immediate effect on the SERVOPACK
but will eventually cause the electronic components and contactor-
related devices to malfunction. Take appropriate action to avoid corrosive gas.
2.1 Installation Conditions
17
Page 20
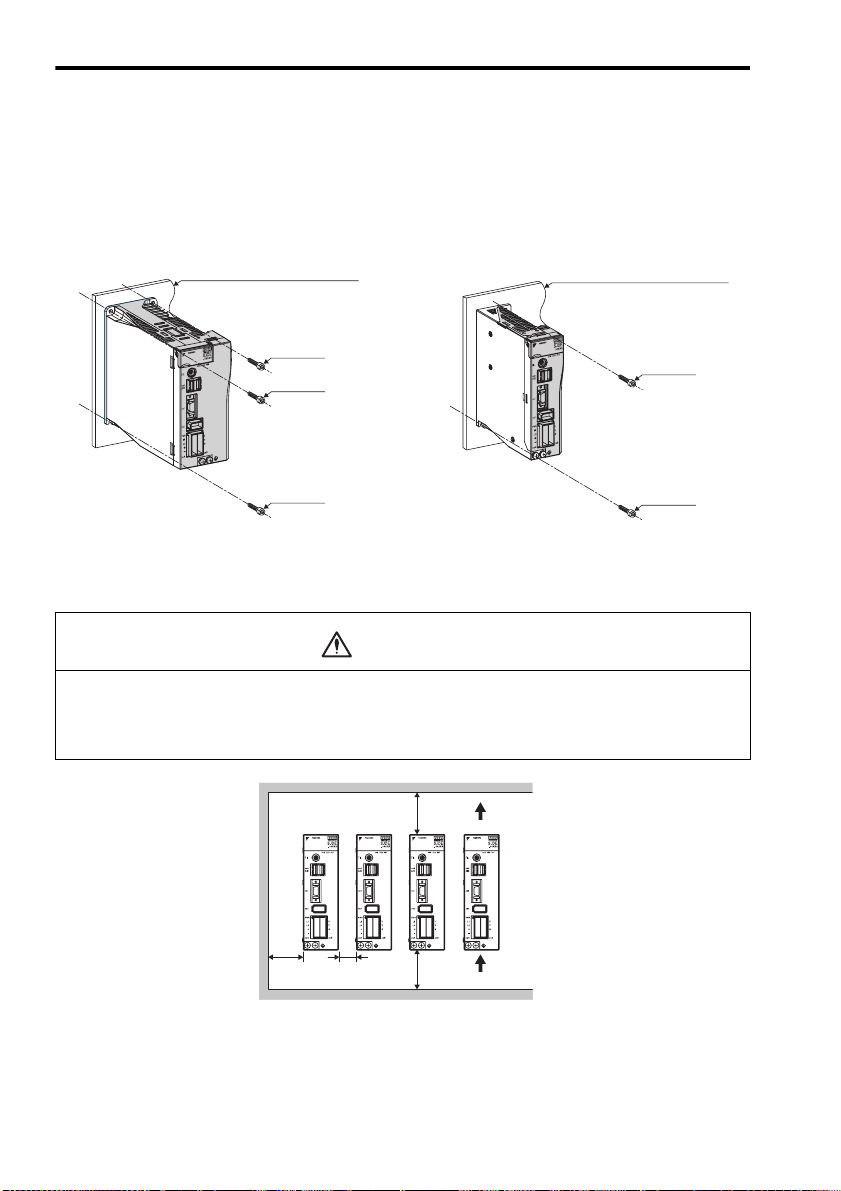
2.2 Installation Method
2.2 Installation Method
Installation Method and Direction
• Install the SERVOPACK perpendicular to the wall.
• Connect the mounting holes securely to the mounting surface with M4 screws.
SJDE-08ANA-OY: Three mounting holes SJDE-01 to 04ANA-OY: Two mounting holes
SERVOPACK installation plate
M4 screw
M4 screw
M4 screw
SERVOPACK installation plate
M4 screw
M4 screw
Space between SERVOPACK Units
• Be sure to keep a space between adjacent SERVOPACK units as shown the following figure if they
are mounted inside the control panel. This allows the units to cool.
CAUTION
• Do not cover the inlet or outlet parts of the SERVOPACK and prevent any foreign objects, such as
metallic fragment, or combustibles from entering the product.
Failure to observe this caution may cause internal elements to deteriorate resulting in malfunction
or fire.
50 mm
min.
Air outlet
direction
30 mm
min.
10 mm
min.
18
50 mm
min.
Air inlet
direction
Page 21
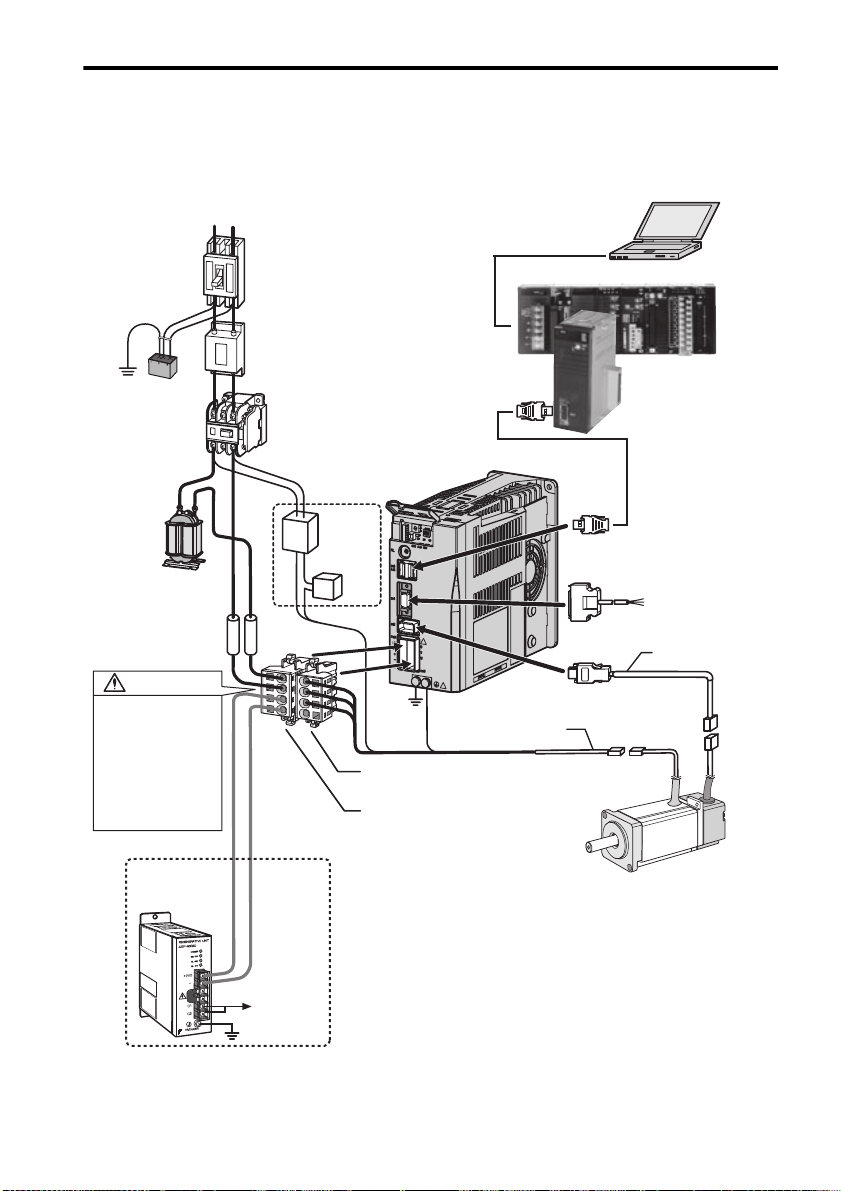
3 Wiring
3.1 System Configuration
Power supply
Single-phase 200 VAC
L1 L2
Molded-case circuit breaker
To protect the equipment and wiring,
always connect a molded-case circuit
breaker.
Noise filter
Used to eliminate suppress noise
from power lines.
Surge protector
Protects the
system from
lightening surge.
AC reactor
Used for a power
supply harmonic
suppression.
Fuse
To protect the
equipment, always
install fuses.
WARNING
Correctly connect the
connectors CNA and CNB.
Incorrect wiring may result in
electric shock, injury, or
damage to the equipment.
After wiring, install the
connectors as explained in
3.8 Wiring the Power
Supply/Regenerative Unit
Connector (CNA) and 3.9
Wiring the Servomotor Main
Circuit Cable Connector
(CNB).
Used for a
regenerative unit.
Regenerative unit
Used if regenerative
energy is high.
Magnetic contactor
Used to turn OFF the servo
power supply when using a
regenerative unit or a
emergency stop.
Used for a
servomotor
with a brake.
24-VDC
power
supply
Brake relay
n
SJDE
SERVOPACKs
*1
*
Servomotor main circuit
cable (for relay)
Connectors for servomotor
main circuit cable (CNB
Connectors for power
supply/regenerative unit
(
)
CNA
Personal computer
software: CX-One
)
SJME
Servomotors
3.1 System Configuration
CJ-series PLC
CJ1 series
Position control unit
CJ1W-NCF71
MECHATROLINK-II
connection
I/O Signal cable
Connects to
CJ-Series PLC
To the control
circuits of
magnetic
contactor
* 1. Prepare a 24-VDC power supply for the brake separately from the sequence power supply.
19
Page 22

3.2 Standard Connection
3.2 Standard Connection
Power supply
Single-phase 200 VAC to 230 VAC
50/60Hz
L1 L2
Molded-case circuit breaker
Surge protector
AVR 2
24 VDC power
supply
Noise
filter
200 VAC
to
230 VAC
+24V 0V
MC1
SW1 SW2
MC1
Regenerative unit
Controller
130Ω
MC1
Spark
killer
C1 C2
JUSP-
RG08D
MECHATROLINK-II
cable
Shielded wire
MC1
Ry1
Flywheel
diode
Shielded wire
AVR 1*
24 VDC
power supply
200 VAC to
230 VAC
CNA CNB
Fuse
1
L1
Reactor
Fuse
L2
2
3
/TXD
/RXD
GND
/S
Ter m i nator
130Ω
24VIN
/EXT1
/DEC
N-OT
P-OT
E-STP
ALM
/BK
SG_COM
+
4
-
CN9
1
2
3,4
CN6A
A2
S
A3
Shell
CN6B
B2
B3
CN1
5
1
2
3
4
6
12
13
7
+
Y4
Y5
+
24V
0V
SERVOPACK
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
Ry1
CN2
Shell
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Varistor
PG5V
PG0V
U
V
W
Shielded wire
A+
A-
B+
B-
/Z
U
V
W
Shielded wire
5
6
1
2
V
3
4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
Brake
U
Servomotor
W
FG
Encoder
Note: 1. AVR1:24 VDC
power supply for
brake
AVR2:24 VDC power supply for sequence
PB1:Power OFF switch
PB2:Power ON switch
MC1:Magnetic contactor
Ry1:Brake relay
• Parts example
Spark killer Okaya Electric Industries
Flywheel
diode
Co., Ltd.
Toshiba Corporation 1NH42
CRE-50500
Brake relay OMRON Corporation MY series
Varistor NIPPON CHEMI-CON
CORPORATION
TNR7V121K
20
Page 23
3.3 Precautions on Wiring
2. The ground protection circuit is designed for ground fault inside the motor
windings while the motor is running. Therefore, it may not protect the system
under the following conditions.
• A low-resistance ground fault occurs between the main circuit cable and connector for the servomotor.
• The power supply is turned ON during a ground fault.
To configure a safer system, install an earth leakage breaker for protection
against overloads and short-circuit, or install an earth leakage breaker for
ground protection combined with a wiring circuit breaker.
3. Position information is not stored in the SERVOPACK, so this information will be
lost if the power supply is turned OFF. If this information is required for the
operation of the host controller, make sure that the system has an emergency
stop signal (E-STP) that will stop operations without turning OFF the power
supply.
* 1. Prepare a 24 VDC power supply for sequence separately from the 24 VDC power supply for brake.
3.3 Precautions on Wiring
WARNING
• Be sure to correctly ground the SERVOPACK and the servomotor.
• Wiring must be performed by an authorized person qualified in electrical work.
• Configure the circuit’s power supply to be automatically cut off if E-STP signal is OFF at occurrence of emergency stop. (Refer to 3.7.3 Emergency Stop Signal Input.)
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has been
turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to completely stop the
motor by turning OFF the servo using the emergency stop.
Position information is not stored in the SERVOPACK, so this information will be lost if the power
supply is turned OFF. This information cannot be read again if the power supply is turned OFF.
• When using the servomotor for a vertical axis, install safety devices to prevent workpieces from falling off because of alarms. Workpiece’s falling off may result in injury or malfunction.
• Configure the interlock circuit so that the system is interlocked to avoid injury whenever the protective cover on the machine is opened or closed.
3.3.1 Protection for Power Supply Line
• Use a molded-case circuit breaker and fuse to protect the power supply line. The SERVOPACK connects directly to a commercial power supply without a transformer, so always use a circuit breaker
and fuse to protect the servo system from accidental high voltage.
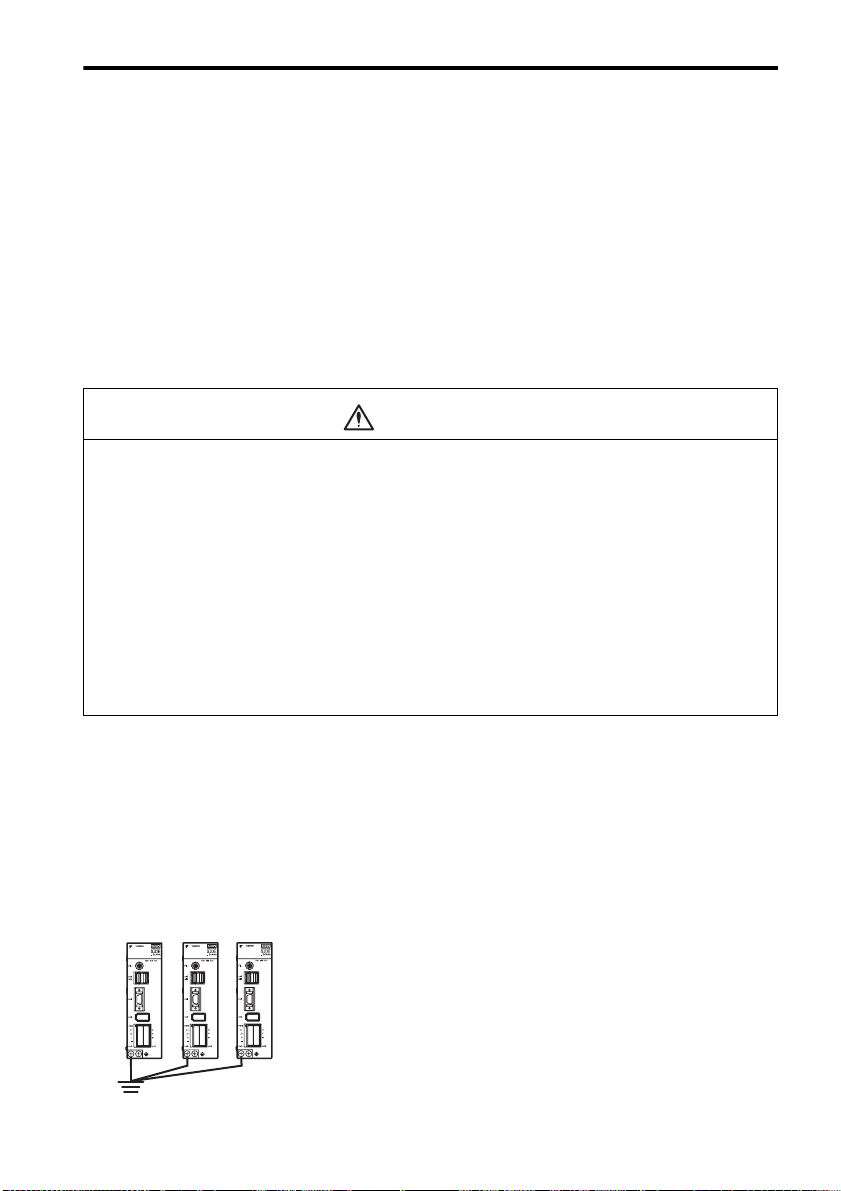
3.3.2 Caution for Grounding
Consider the following conditions when grounding the SERVOPACK.
• For a ground wire, use as thick a cable as possible (2.0 mm2 or thicker).
• A ground resistance of 100 (Ω) or less is recommended.
• Ground to one point only.
21
Page 24

3.3 Precautions on Wiring
3.3.3 Caution for Cable
• For wiring, use the specified cables. Use cables that are as short as possible.
• Do not bend or apply tension to cables. The conductor of a signal cable is thin (0.08 to 0.12 mm
so handle the cables carefully.
2
),
3.3.4 Power Loss
Power Loss with SERVOPACK Rated Output
Main
Circuit
Powe r
Supply
Single-
phase
200 V
Note: Values obtained with the servomotor rated output.
SERVOPACK Output Current
Model Capacity
SJDE-01ANA-OY 100 W 0.84 6 9 15
SJDE-02ANA-OY 200 W 1.1 8 17
SJDE-04ANA-OY 400 W 2.0 16 25
SJDE-08ANA-OY 750 W 3.7 27 36
(Effective
Val ue)
A
Main Circuit
Power Loss
W
Control Circuit
Power Loss
W
Tot a l Powe r
Loss
W
3.3.5 SERVOPACKs and Applicable Peripheral Devices
SERVOPACK Power
Ty pe Capa-
SJDE01ANA-OY
SJDE02ANA-OY
SJDE04ANA-OY
SJDE08ANA-OY
Manufacturer
Note: It is recommended to use a general-purpose circuit breaker of the sensed current 200 mA or more, or a cir-
* 1. Nominal value at the rated load. The specified derating is required to select the appropriate molded-case
circuit breaker.
* 2. Cut-off characteristics (25 °C): 200 % two seconds min. and 700 % 0.01 seconds min.
100 W
200 W
400 W
750 W
cuit breaker for inverters (for high-frequency).
city
Supply
Capacity
SERVO-
PAC K
Power sup-
ply
Capacity of
per
kVA
0.40 4 0KLK
0.75 X5053
1.2 8 X5054
2.2 16 0KLK
Molded-
case
Circuit
Breaker
Arms
--Littelfuse
*1 *2
Power
supply
Capacity
and
Model of
External
Fuse
015.T
(15 Arms)
030.T
(30 Arms)
Inc.
Inrus
Mag-
h
netic
Cur-
Contac-
rent
A0-p
tor
30 HI-11J R7A-
60 HI-15J R7A-
-Yaskawa
Controls
Co., Ltd.
Noise
Filter
FIZN105
-BE
FIZN109
-BE
Block
Elek-
tronik
Surge
Protector
xCxM-
R
601BQZ-4
Okaya
Electric
Industries
Co., Ltd.
AC
Reactor
X5052
X5056
Yaskawa
Controls
Co., Ltd.
IMPORTANT
Ground Fault
The ground protection circuit is designed for ground fault inside the motor windings while the
motor is running. Therefore, it may not protect the system under the following conditions.
• A ground fault occurs between the main circuit cable and connector for the servomotor.
• The power supply is turned ON during a ground fault.
To configure a safer system, install an ground fault detector for protection against overloads
22
Page 25
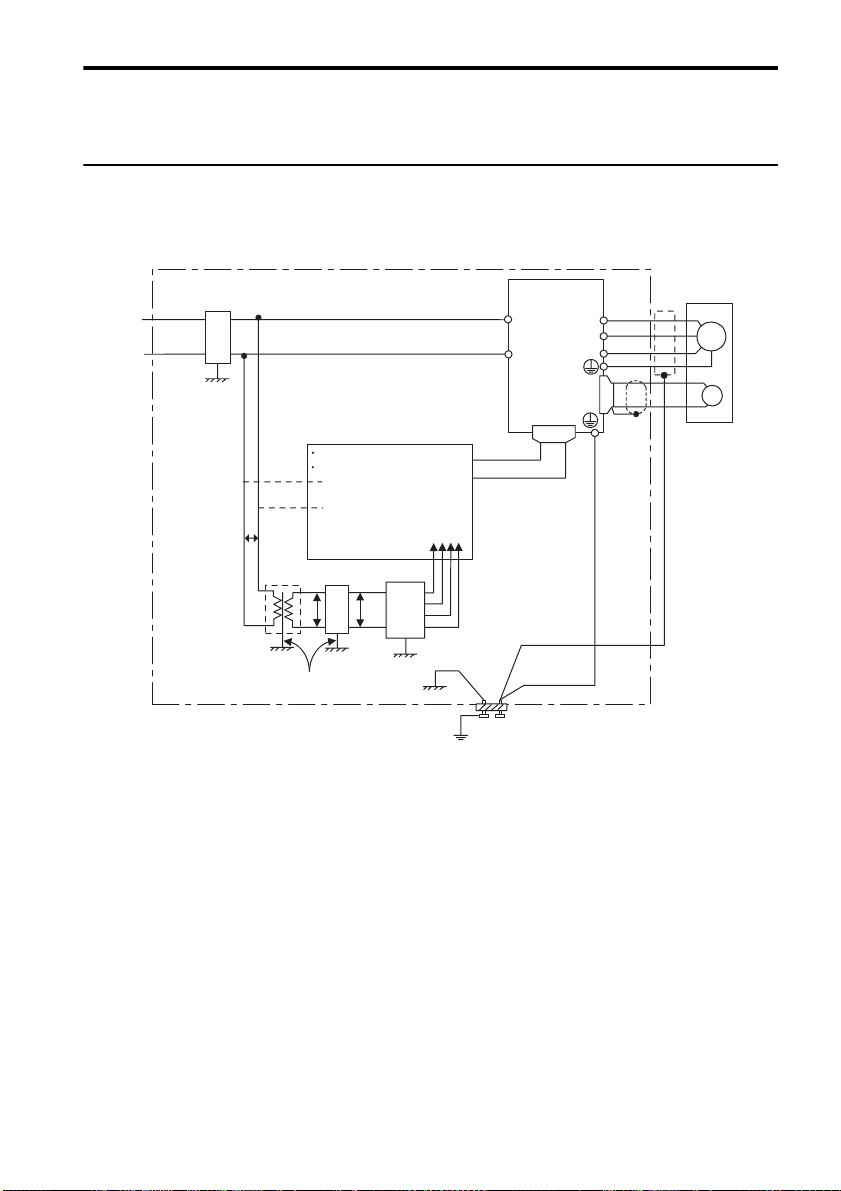
and short-circuit, or install an ground fault detector combined with a wiring circuit breaker for
ground protection.
3.3.6 Noise Prevention
Example of Wiring for Noise Prevention
3.3 Precautions on Wiring
Noise filter
Min. wire
size
: 3.5 mm
*
1.
2LF
Casing
2
P
Operation relay sequence
User signal generating circuit
1LF
P
Casing
Casing
Min. wire size: 3.5 mm
*2.
P
2
*1.
AVR
(Grounding)
Casing
2 mm2 or larger
Min. wire size:
3.5 mm
Casing
200 VAC
* 1. For the wires connected to the casings for installation purposes, use wires with a diameter of 3.5 mm2 or
larger. Flat braided copper wires are recommended.
* 2. Use twisted pair wires for section P.
SJDE
SERVOPACK
L1
L2
2
*1.
Grounding plate
Groudning: Ground to one point only.
Min. grounding resistance: 100 Ω
CN1
CN2
U
V
W
Min. wire
size
: 3.5 mm
Min. wire
size
: 3.5 mm
2
2
Servomotor
M
(FG)
PG
Correct Grounding
• Servomotor frame grounding:
Be sure to connect the FG grounding terminal on the frame of the servomotor to the grounding terminal on the SERVOPACK.
• Be sure to ground the grounding terminal of the SERVOPACK.
• If the wires of the servomotor’s main circuit are laid in a metal conduit, ground the conduit and the
grounding box.
One-point grounding must be used.
23
Page 26
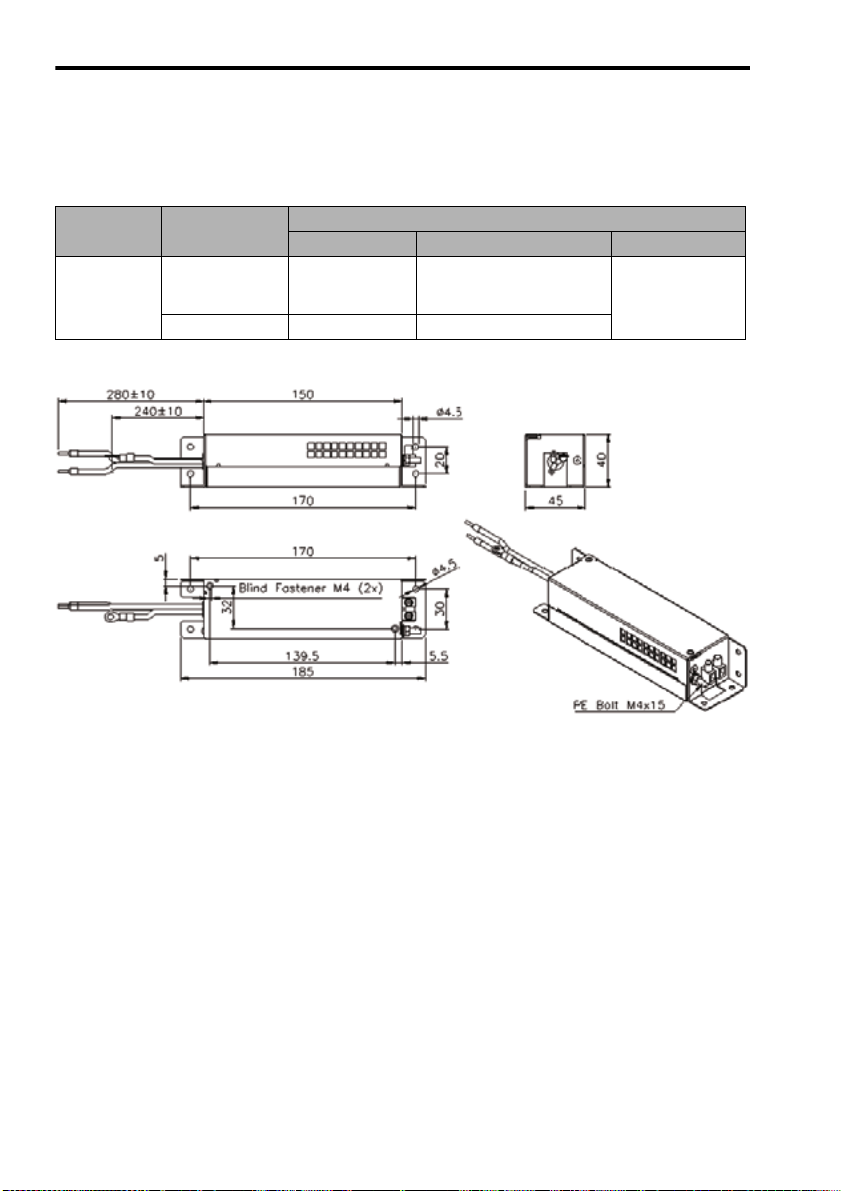
3.3 Precautions on Wiring
Noise Filters
Use a block type noise filters to prevent any noise interference from the power-supply line.
The following table lists the recommended noise filters for several SERVOPACK models.
Application of Noise Filters
Power-Supply
Voltage
Single-
phase
230 V +10%
50-60 Hz
Filter dimensions for model R7A-FIZN105-BE
SERVOPACK
Model
SJDE-01ANA-OY
SJDE-02ANA-OY
SJDE-04ANA-OY
SJDE-08ANA-OY
Recommended Noise Filters
Model Specifications Manufacturer
R7A-FIZN105-BE Single-phase 250 VAC, 5A
R7A-FIZN109-BE Single-phase 250 VAC, 9A
Block
Transformatoren
Elektronik
GmbH & Co. KG.
24
Page 27
Filter dimensions for model R7A-FIZN109-BE
3.3 Precautions on Wiring
25
Page 28
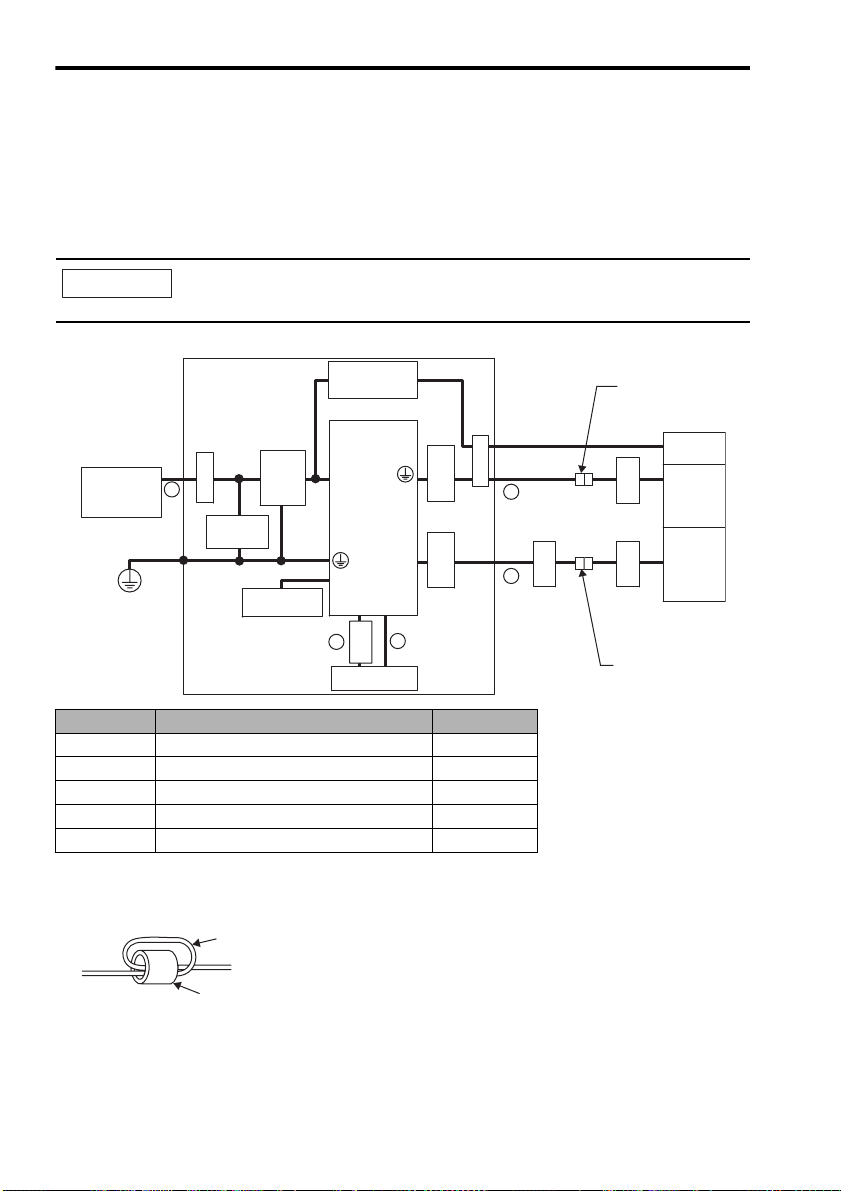
3.3 Precautions on Wiring
3.3.7 Installation and Wiring Conditions on CE Marking
Installation Conditions of EMC Directives
To adapt a combination of a SJME servomotor and a SJDE SERVOPACK to EMC Directives
(EN55011, group 1, class A and EN61000-6-2), the following conditions must be satisfied.
Because SERVOPACKs are built-in type, reconfirmation is required after being installed in the final
product.
IMPORTANT
Power supply
Single-phase
200 VAC
PE
The actual EMC level may differ depending on the actual system’s configuration, wiring, and
other conditions.
Ground Plate
Brake power
supply
SERVOPACK
Noise
Surge
protector
filter
Regenerative
unit
5
Clamp
U, V, W
L1, L2
CN2
+,–
CN1CN6
2
1
core
Ferrite
Host controller
Clamp
core
Ferrite
Ferrite
core
3
core
4
Ferrite
Cable joint
core
Ferrite
core
Ferrite
Cable joint
Servomotor
Encoder
Symbol Cable Name Specifications
A I/O Signals cable Shielded wire
B MECHATROLINK-II Communication cable Shielded wire
C Servomotor Main circuit cable Shielded wire
D Encoder cable Shielded wire
E AC Line cable Shielded wire
Attaching the Ferrite Core
Coil the servomotor main circuit cable (as a connection) around the ferrite core with two turns, then
attach them by the SERVOPACK. Refer to the diagram in the previous page.
Cable (two turns)
Brake
Ferrite core
Note: Recommended Ferrite-core
Model: ESD-SR-25 (Tokin. Corp.)
26
Page 29
Fixing the Cable
Fix and ground the cable shield using a piece of conductive metal (cable clamp).
• Example of Cable Clamp
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Host
controller
side
Ground plate
Cable
Cable
clamp
Shield (cable sheath stripped)
Fix and ground the cable shield
using a piece of conductive metal.
Remove paint on mounting surface.
Shield Box
A shield box, which is a closed metallic enclosure, should be used for shielding magnetic interference
(EMI). The structure of the box should allow the main body, door, and cooling unit to be attached to the
ground. The box opening should be as small as possible.
3.3.8 Other Precautions
• Whether the electricity is served or not to the motor, do not use the motor being rotated from the
outside.
• When restarting the power supply soon after turning OFF, alarm may occur to the SERVOPACK.
Refer to the power supply holding time in the following table to restart the power supply correctly.
SERVOPACK Min. Waiting Time
Model Capacity
SJDE-01ANA-OY 100 W
SJDE-02ANA-OY 200 W
SJDE-04ANA-OY 400 W
SJDE-08ANA-OY 750 W
before Restarting
(s)
20
30
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
• SJDE SERVOPACKs are suitable where the power supply is less than 5000 Arms (230 V max.).
• SERVOPACKs must be used with UL-listed fuses or molded-case circuit breakers, in accordance
with the National Electrical Code (NEC).
•Use 75 ° C heat-resistant copper wires or an equivalent.
3.4.1 SERVOPACK Main Circuit Cables
Cable Types
Symbol Name Allowable Conductor Temperature
PVC Normal vinyl cable
IV 600 V vinyl cable
HIV Temperature-resistant vinyl cable
• Wire sizes are selected for three cables per bundle at 40 ° C ambient temperature with the rated
current.
• Use cables with a minimum withstand voltage of 600 V for main circuits.
• If cables are bundled in PVC or metal ducts, consider the reduction ratio of the allowable current.
• Use heat-resistant cables under high ambient or panel temperatures where normal vinyl cables will
rapidly deteriorate and will not be able to use in a short period of time.
• Do not use cables under continuous regenerative state.
27
−
60 ° C
75 ° C
Page 30
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Wire Size and Allowable Current
The following table shows the wire size and allowable current for three cables. Use a cable whose
specifications meet or are less than allowable current in the table.
• 600 V Heat-resistant Vinyl Cables (HIV)
AWG
Note: The values in the table are only for reference.
Nominal Cross
Size
Section Diameter
20 0.5 19/0.18 39.5 6.6 5.6 4.5
- 0.75 30/0.18 26.0 8.8 7.0 5.5
18 0.9 37/0.18 24.4 9.0 7.7 6.0
16 1.25 50/0.18 15.6 12.0 11.0 8.5
14 2.0 7/0.6 9.53 23 20 16
mm
2
Configuration
Number of
2
wires/mm
Conductive
Resistance
2
Ω/mm
Allowable Current at Ambient Temperature
A
30 ° C 40 ° C 50 ° C
Power Supply Input Terminals (L1, L2), Motor Connection Terminals (U, V,
W), and Regenerative Unit Connection Terminals (+, -)
CapacityWSERVOPACK Type Terminal Symbol
L1, L2 U, V, W +, 100
200
400
750
Note: Connectors are used for all wiring.
SJDE-01ANA-OY
SJDE-02ANA-OY
SJDE-04ANA-OY
SJDE-08ANA-OY
HIV1.25 mm
HIV2.0 mm
2
2
HIV1.25mm
Wiring length:
20 m max.
2
HIV1.25mm
Wiring length:
0.5 m max.
2
Ground Terminal ( )
Wire Size Terminal Screw Size Tightening Torque
HIV 2.0 mm
2
min.
M4 1.2 to 1.4 Nxm
28
Page 31

Peripheral Devices List
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Name Specifications Ty p e Length Appearance Manufac-
Powe r cable
for Junma
servomotors without
brake
SJME0@AMB41OY
Powe r cable
for Junma
servomotors with
brake
SJME0@AMB4COY
Connector
Kit for Servomotor
Main
Circuit Cable
*1
Flexible cables
(standard)
UL/CSA listed
Shielded cable
Bending radius
(dynamic) >
10x diameter
Cycles > 10
million
Flexible cables
(standard)
UL/CSA listed
Shielded cable
Bending radius
(dynamic) >
10x diameter
Cycles > 10
million
Motor end
crimp type
(Common for
servomotors
with or without
brakes)
SERVOPACK
end (CNB)
JZSP-CHM000-01-5E
JZSP-CHM000-03-E
JZSP-CHM000-05-E
JZSP-CHM000-10-E
JZSP-CHM000-15-E
JZSP-CHM000-20-E
JZSP-CHM030-01-5E
JZSP-CHM030-03-E
JZSP-CHM030-05-E
JZSP-CHM030-10-E
JZSP-CHM030-15-E
JZSP-CHM030-20-E
JZSP-CHM9-1
JZSP-CHM9-2
∗2
∗3
1.5 m
3 m
5 m
10 m
15 m
20 m
1.5 m
3 m
5 m
10 m
15 m
20m
—
—
spring type
(Common for
servomotors
with or without
brakes)
SERVOPACK
end (CNB)
crimp type
Refer to Page 35.
—
14
(Common for
servomotors
with or without
brakes)
Connector
Kit for Power
Supply/
Regenera-
1
tive Unit*
SERVOPACK
end (CNA)
spring type
(Common for
servomotors
with or without
brakes)
JZSP-CHG9-1
∗3
—
turer
Omron
Ya s k aw a
Motion
Control,
* 4
BV.
J.S.T.
Mfg
Co.,Ltd.
*5
Omron
Ya s k aw a
Motion
Control,
*4
BV.
29
Page 32

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Name Specifications Ty pe Length Appearance Manufac-
Encoder
Cable for
Junma servomotors
SMJE0@AMB4@OY
Flexible cables
(standard)
UL/CSA listed
Shielded cable
Bending radius
(dynamic) >
10x diameter
Cycles > 10
million
Non flexible
cables
JZSP-CHP800-01-5E
JZSP-CHP800-03-E
JZSP-CHP800-05-E
JZSP-CHP800-10-E
JZSP-CHP800-15-E
JZSP-CHP800-20-E
R7A-CRZ003C
R7A-CRZ005C
R7A-CRZ0010C
Connector
Kit for
Encoder
1
Cable*
Motor end
crimp type
SERVOPACK
end (CN2)
soldered type
JZSP-CHP9-1
JZSP-CHP9-2
∗2
(black)
SERVOPACK
end (CN2)
soldered type
(gray)
JZSP-CHP9-3
I/O Signal Cable JZSP-CHI003-01
JZSP-CHI003-02
JZSP-CHI003-03
R7A-CPZ001S
R7A-CPZ001S
Connector
Kit for I/O
Signal Cable
1
(CN1)*
SERVOPACK
end soldered
type
JZSP-CHI9-1
1.5 m
3 m
5 m
10 m
15 m
20 m
3 m
5 m
10 m
—
—
—
1 m
2 m
3 m
1m
2m
—
(cont’d)
turer
Omron
Yaskawa
Motion
Control,
BV. *4
30
Page 33

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Name Specifications Ty p e Length Appearance Manufac-
-E
-E
—
—
*7
—
∗7
—
*7
—
—
2 m
(6.56 ft)
MECATROLINK-II
Communication Cable
Cable for
Personal
Computer
Cable with connectors at both
6
ends*
(Without ferrite
core)
Cable with connectors at both
*6
ends
(With ferrite
core)
JEPMC-W6002-
JEPMC-W6002(Compliant with RoHS
Directive)
JEPMC-W6003-
JEPMC-W6003(Compliant with RoHS
Directive)
Terminators JEPMC-W6022
JEPMC-W6022-E
(Compliant with RoHS
Directive
Cables JZSP-CPS00-02
∗7
(cont’d)
turer
Omron
Ya s k aw a
Motion
Control
BV. *4
To ol J -F AT-O T
Cooling Fan JZSP-CHF08-01 for
SJDE-04ANA-OY SER-
—
—
VOPACKs
JZSP-CHF08-02 for
SJDE-08ANA-OY SER-
—
VOPACKs
Note: Contact the manufacturer for more detailed information such as external diameter.
* 1. Connectors for CNB, CN1, and CN2 are not provided with the SERVOPACK. The servomotor-end
connectors are not provided with the servomotor. These connector kits must be purchased.
* 2. Refer to pages that provide details for the applicable crimping tool type. The crimping tool must be ordered
separately.
* 3. With an opening tool (lever for wire)
* 4. Omron Yaskawa Motion Control BV. URL: http://www.omronyaskawa.com
* 5. J.S.t.Mfg co., Ltd. URL: http://www.jst-mfg.com
* 6. The total cable length must be 50 m (164 ft) max. and the cable length between stations 0.5 m (1.64 ft) min.
* 7. Specify the cable length in when ordering as shown in the table below. .
Cable Length m (ft)
A5 0.5 (1.64)
01 1 (3.28)
03 3 (9.84)
05 5 (16.4)
07 7 (30.0)
Cable Length m (ft)
10 10 (32.8)
20 20 (65.6)
30 30 (98.4)
40 40 (131)
50 50 (164)
31
Page 34

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
3.4.2 Wiring Connector for the Power Supply/Regenerative Unit (CNA)
CAUTION
• Observe the following precautions when wiring main circuit connector.
• Remove the connector from the SERVOPACK prior to wiring.
• Insert only one wire per terminal opening on the connector.
• Make sure that the exposed wire is not electrically shorted to adjacent exposed wires.
Use the following procedure when connecting the SERVOPACK to the spring type connector for the power
supply/regenerative unit.
1. Remove the connector from the SERVOPACK.
Be sure to remove the connector from the SERVOPACK when wiring.
2. Strip the outer coating.
Straighten the exposed wire with your fingers to prevent the wires from unwinding.
9 to 10 mm
3. Open the wire terminal on the power supply connector housing (plug) with the tool (lever for wiring)
using the procedure shown in Fig. A or B.
• Insert the connection hook end of the provided tool into the slot as shown in Fig. A.
Tool must be purchased by the customer.
• Use a standard flat-blade screwdriver (blade width of 2.5 to 3.0 mm (0.09 to 0.12 in)). Put the blade
into the slot, as shown in Fig. B, and press down firmly to open the wire terminal.
Either the procedure shown in Fig. A or B can be used to open the wire insert opening.
Fig. A Fig.B
Tool Type: J-FAT-OT
(J.S.T. Mfg Co., Ltd.)
4. Insert the exposed wire into the opening.
Insert the exposed wire into the opening and then close the opening by releasing the tool hook or
removing the screwdriver.
Wire Size
Item Wire Size
Conductor
Size
Sheath Diameter
Twisted wire
Single wire
AWG14 to AWG22
φ1.6 mm to φ0.65 mm
φ3.8 mm to φ1.7 mm
32
Page 35

5. Attach the connector to the SERVOPACK.
After wiring the connector, attach the connector to the SERVOPACK.
Single-phase, 200 VAC
Molded-case circuit breaker
Regenerative Unit
+(Y3)
—
Y4
Y5
C1
C2
Power supply
L2 L1
Noise filter
Magnetic contactor
AC reactor
FuseFuse
A
N
4321
At the occurrence of alarms such as those for
regenerative resistor disconnection, regenerative
transistor (Tr) faults, and overvoltage, the contact
between terminals C1 and C2 will be open. Use
this contact signal to turn OFF the SERVOPACK
power supply.
YASKAWA
COM
4
5
3
6
2
7
1
8
0
9
FIL
F
A
E
B
D
C
CN6
A/B
CN1
CN2
PWR
L1
L2
1
Power supply/Regenerative Unit connector
JZSP-CHG9-1
2
(Is supplied with the Servopack)
3
4
200V
SERVOPACK
SJDE
- 04ANA
ALM
RDY
U
V
W
CNBCNA
CNA connector
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Note: 1. Pull lightly on the wires to confirm that they are securely connected.
2. Make sure that none of the insulating sheaths of the wires are caught in the
springs.
Connector for Power Supply/Regenerative Unit (CNA)
Pin No. Symbol Signal Name
1L1
2L2
3+
4 −
Power supply input terminals
Regenerative unit connection
terminals
33
Page 36

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
3.4.3 Wiring Connector for the Servomotor Main Circuit Cable (CNB)
Wire the connector for the servomotor main circuit cable (CNB) in the same way as the connector for
the power supply/regenerative unit (CNA). Refer to 3.4.2 Wiring Connector for the Power Supply/
Regenerative Unit (CNA) for details and the procedure.
Controller
Separate by 300 mm or more
Power Supply
IMPORTANT
• The distance between the servomotor main circuit and the encoder cable as well as the I/
O cable and MECHATROLINK-II cable is 300 mm or more.
• Do not bundle or run the servomotor main circuit cable in the same duct with other cables.
• Be sure that the maximum wiring length of the servomotor main circuit cable is 20 m.
34
Page 37

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Servomotors without Brakes
Connector for servomotor
main circuit cable
JZSP-CHG9-1
(Is supplied with the servopack.)
1
Connector provided with
servomotor main circuit cable
Motor
Red
White
Blue
Green/Yellow
Phase U
Phase V
Phase W
FG
1
2
3
4
5
6
Servomotor main circuit cable
(for relay)
Green/Yellow
Note: Confirm pin numbers on the connector as well.
Connection Diagram for Standard Servomotor Main Circuit Cable
The connection diagram for the standard cable (JZSP-CHM000- cable with connectors on both
ends) is shown below. If the servomotor main circuit cable is prepared by the customer, refer to the
diagram below and wire the cable correctly.
Motor end
L
50 mm
1
2
2
3 4
3
4
SERVOPACK end
CNB connector
Connector (crimp type)
Receptacle: 5557-06R-210
Terminal: 5556T (Chain) or
5556TL (Loose wires)
(Molex Japan Co., Ltd.)
Servomotor End Connector
(Viewed from cable insertion side)
456
123
Phase U
Phase V
FG
—
—
Lead ColorSignal Name
Red
White
Blue
Green/Yellow
—
—
Pin No.
1
2
Phase W
3
4
5
6
Connect the FG pin to the grounding terminal of the SERVOPACK.
∗:
Shielded wire
M4 crimped terminal
Connector (crimp type)
Receptacle: F32FSS-04V-KY
Receptacle contact: SF3F-01GF-P2.0 or SF3F-41GF-P2.0
(JST. Mfg. Co., Ltd.)
35
SERVOPACK End Connector
(Viewed from cable insertion side)
14
Lead ColorSignal NamePin No.
Phase U
1
Phase V
2
Phase W
3
4
Crimped terminal
—
∗
Green/Yellow
FG
Red
White
Blue
—
Page 38

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Servomotors with Brakes
Connector for servomotor
main circuit cable
JZSP-CHG9-1
(Is supplied with the servopack.)
Connector provided with
servomotor main circuit cable
Motor
Note: 1. A 24-VDC power supply must be prepared.
2. Connect the varistor in parallel with the 24-VDC power supply terminal and the
GND terminal to suppress the surge voltage caused by turning the holding brake
ON and OFF.
3. Confirm pin numbers on the connector as well.
4. If using the servomotor to drive a vertical axis, configure a circuit to turn the
holding brake ON and OFF so that the movable section will not be pulled down
by gravity when the power supply of the SERVOPACK is turned OFF.
5. Turn the holding brake on the secondary side ON and OFF as shown in the
figure above. A varistor must be connected.
Red
White
Blue
Green/Yellow
Black
Black
Phase U
Phase V
Phase W
FG
Brake
Brake
Servomotor main circuit cable
(for relay)
Green/Yellow
Black
Black
1234
1
2
3
4
Varistor
CNB connector
Relay
24 VDC
DC power
supply
36
Page 39

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Connection Diagram for Standard Servomotor Main Circuit Cable
The connection diagram for the standard cable (JZSP-CHM030- cable with connectors on both
ends) is shown below. If the servomotor main circuit cable is prepared by the customer, refer to the
diagram below and wire the cable correctly.
Motor end
Connector (crimp type)
Receptacle: 5557-06R-210
Terminal: 5556T (Chain) or
5556TL (Loose wires)
(Molex Japan Co., Ltd.)
Servomotor End Connector
(Viewed from cable insertion side)
456
123
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Connect the FG pin to the grounding terminal of the SERVOPACK.
∗1:
2: No polarity for connection to the brake.
∗
Phase U
Phase V
Phase W
FG
Brake
Brake
Lead ColorSignal Name
Red
White
Blue
Green/Yellow
Black
Black
L 50 mm
M4 crimped terminal
Connector (crimp type)
Receptacle: F32FSS-04V-KY
Receptacle contact: SF3F-01GF-P2.0 or SF3F-41GF-P2.0
(J.S.T. Mfg. Co., Ltd.)
Shielded wire
Crimped terminal
Crimped terminal
Crimped terminal
SERVOPACK end
SERVOPACK End Connector
(Viewed from cable insertion side)
14
Lead ColorSignal NamePin No.
—
∗1
∗2
∗2
Red
White
Blue
—
Green/Yellow
Black
Black
1
Phase U
2
Phase V
3
Phase W
4
FG
Brake
Brake
37
Page 40

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
3.4.4 Wiring the Encoder Connector (CN2)
Controller
Separate by
300 mm or more
Power Supply
IMPORTANT
• Separate the encoder cable at least 300 mm from power lines (i.e., high-voltage lines
such as the power supply line and servomotor main circuit cable).
• Do not bundle or run the encode cable in the same duct with power lines.
• Be sure that the maximum wiring length of the encoder cable is 20 m.
Connection Diagram for Standard Encoder Cable
The connection diagram for the standard cable (JZSP-CHP800- cable with connectors on both
ends) is shown below. If the encoder cable is prepared by the customer, refer to the diagram below
and wire the cable correctly.
Applicable wires
SERVOPACK end
Crimp type (Gray)
Plug and Cable Cover Set: 54599-1005
Plug Housing: 51209-1001
Crimp Terminals: 59351-8087(Chain) or
59351-8187 (Loose wires)
(Molex)
SERVOPACK End Connector
T(Viewed from soldered side)
9 7531
Pin No. Signal Name
Shell
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
PG5V
PG0V(GND)
Phase A (+)
Phase A (-)
Phase B (+)
Phase B (-)
Phase /Z
Phase U
Phase V
Phase W
—
Yellow/White
Soldered type (Black)
Shell Kit: 36310-3200-008
Receptacle: 36210-0100FD (3M)
246810
Lead Color
Red
Black
Blue
Blue/White
Yellow
Purple
Gray
Green
Orange
Shield
Note: Confirm pin numbers on the connector as well.
Motor end
Shield wire
38
For encoder power supply: AWG22 (0.33 mm
For other signal wires: AWG26 (0.12 mm
Cable Finished Diameter: φ9 mm max.
Receptacle: 5557-12R-210
Terminals: 5556T2 (Chain) or
5556T2L(Loose wires)
(Molex)
Servomotor End Connector
(Viewed from cable insertion side)
12 11 10 8 79
654321
Lead ColorPin No. Signal Name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PG5V
PG0V(GND)
Phase A (+)
Phase A (-)
Phase B (+)
Phase B (-)
Phase /Z
Phase U
Phase V
Phase W
—
FG
Red
Black
Blue
Blue/White
Yellow
Yellow/White
Purple
Gray
Green
Orange
—
Shield
2
)
2
)
Page 41

3.4.5 Wiring the I/O Signal Connector (CN1)
Controller
Separate by
300 mm or more
Power supply
Note: Do not pull or apply excessive force on the cable. Damage to the cable or con-
nectors may cause the product to stop operating or malfunction.
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
IMPORTANT
• Separate the I/O cable at least 300 mm from power lines (i.e., high-voltage lines, such as
the power supply line and servomotor main circuit cable).
• Be sure that the maximum wiring length of the I/O cable is 3 m.
Connection Diagram for Standard I/O Cable (Supplied by Yaskawa Electric )
The connection diagram connection diagram for the standard cable (JZSP-CHI003- cable with
connector) is shown below. If the I/O signal cable is prepared by the customer, refer to the diagram
below and wire the cable correctly.
Host controller endSERVOPACK end
Plug (14P): 10114-6000EL
Shell Kit: 10314-52A0-008
3M
Applicable Wires:
SERVOPACK Connector (Plug)
(Viewed from soldered side)
8 9 10 11 13 1412
5432761
(φ5.6)
AWG24 (0.2 mm
AWG26 (0.12 mm
AWG28 (0.08 mm
Pin
I/O Code Signal Name Lead
No.
1 Input /EXT1 External_Latch Orange 1 Black
2 Input /DEC Homing Decelaration Red
3 Input N-OT Reverse run prohibit Light gray Black
4 Input P-OT1 Forward run prohibit Red
5 Input +24VIN External input power supply White Black
6 Input E-STP Emergency stop Red
7 Output SG-COM Output signal ground Yellow Black
8 Red
9 Pink Black
10 Red
11 Orange 2 Black
12 Output ALM Servo alarm Red
13 Output /BK Brake Light gray Black
14 Red
Shell −− FG −−
2
Color
)
2
2
)
)
Number Color
Dot Mark
39
Page 42

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
Note: Confirm pin numbers given on the connector as well.
Connection Diagram and Description for the General-purpose control cables
(R7A-CPZ@@@S) supplied by OMRON Company.
A General-purpose Control Cable connects to the Servo Driver’s Control I/O Connector (CN1). There
is no connector on the controller end. Wire a connector to match the controller if you are connecting to
a Position Control Unit and a compatible cable is not available, or if the drive is connected to a controller manufactured by another company.
Cable Models
Model Length (L) Outer Diameter of the
R7A-CPZ001S 1 m
R7A-CPZ002S 2m
cable
5,6 mm Approx. 0.1 kg
5,6 mm Approx. 0.2 kg
Weight
Connection Configuration and Dimensions
Controller end Servo Driver end
Wiring
No. Wire Color/Mark Color Signal Name
1 Orange/Red (-)
2 Orange/Black (-)
3 Gray/Red (-)
4 Gray/Black (-)
5 White/Red (-)
6 Yellow/Black (-)
7 White/Black (-)
8 Pink/Red (-)
9 Pink/Black (-)
10 Orange/Red (--)
11 Orange/Black (--)
12 Gray/Red (--)
13 Gray/Black (--)
14 Yellow/Red (-)
Connector plug: 10114-3000VE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector case: 10314-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Wires with the same wire color and the same number of marks are twisted pairs
40
/EXT1 External Latch
/DEC Homing Deceleration
N-OT Reverse run prohibited
P-OT Forward run prohibited
+24VIN
RUN
OGND
/ALM
BKIR
Page 43

Connector Pin Arrangement
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
2
4
6
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
8
10
12
14
3.4.6 Wiring the MECHATROLINK-II Communication Connectors (CN6A and CN6B)
Number of Stations
A maximum of 30 slave stations can be connected when a repeater is connected. The maximum number of slave stations that can be connected is determined by the MECHATROLINK-II communications
settings. Refer to 3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II Communications for details.
Communication Cables
Use the cables specified in the table below.
Ty pe Model Length
MECHATROLINK Communication
Cable
(with connectors at both ends, without
ferrite core)
MECHATROLINK Communication
Cable
(with connectors at both ends, with
ferrite core)
Cable Length
The total cable length must be 50 m max. The cable length between stations must be 0.5 m min.
Terminator
Install a terminator on the SERVOPACK connected at the end of communication cable.
JEPMC-W6002- Specify the length in .
JEPMC-W6002--E
(Compliant with RoHS
Directive)
JEPMC-W6003-
JEPMC-W6003--E
(Compliant with RoHS
Directive)
Refer to Page 31 for details.
Ter m in a t or Ty p e Connector Type
MECHATROLINK-II Terminator JEMPC-W6022
JEMPC-W6022-E (Compliant with RoHS Directive)
41
Page 44

3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
L1+L2+···+Ln O 50 m
Cable length between stations: 0.5 m min.
Max. number of slaves: 30 (with repeaters connected)
CJ1 series
Position control unit
CJ1W-NCF71
LnL1 L2
SERVOPACK SERVOPACK SERVOPACK
Terminator
IMPORTANT
Keep a distance 300 mm min. between power lines (high-voltage circuit such as power supply line and servomotor main circuit cable) and MECHATROLINK-II cable.
42
Page 45

3.4.7 Wiring the Personal Computer Connector (CN9)
Prepare the specified cable to connect the SERVOPACK to a personal computer.
Communication Cable
Use the specified twisted-pare and shielded twisted cable.
Ty pe Model Length
Personal Computer
Cable
JZSP-CPS00-02
Applicable Wires (Tin coated annealed copper wires)
Conductor Size
(Configuration of
exposed wire)
AWG24 (0.16 mm)
AWG26 (0.16 mm)
AWG28 (0.127 mm)
Sheath Outer Diameter
φ0.9 to φ1,45 mm
Recommended Wires
UL1061 and UL1007
Cable Configuration
Remove the sheath to 1.7 to 2.3 mm from the cable configuration.
Cable Form
D-sub connector
17JE-13090-02 (D8A)
Manufactured by DDK, Ltd.
Cable
2 m
Connector
Socket: DF11-4DS-2C
Terminals: DF11-2428SCF
Manufactured by Hirose Electric Co., Ltd.
3.4 Main Circuit Wiring
2 × M2.6 screws
Connector Specifications
SJDE SERVOPACK End
Signal Pin No. Pin No. Signal
/TXD 1 2 RXD
/RXD 2 3 TXD
GND 3 5 GND
GND 4 7 RTS
Label
Heat shrinkable tube
Shielded wire
43
DOS/V (PC/AT compatible)
Personal Computer End
(D-SUB 9pin)
8 CTS
Case FG
Page 46

3.5 Connection Examples of Input Signal
3.5 Connection Examples of Input Signal
Connection Examples
Input current is 7 mA per point.
AVR 2
24VDC
Powe r
Supply
+24V 0V
IMPORTANT
Host Controller SERVOPACK
24VIN
/EXT1
Emergency
Stop
Shield wire
E-STP
/DEC
N-OT
P-OT
CN1
5
1
2
3
4
6
Photocoupler
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
3.3kΩ
∗ Twisted-pair wires
Prepare an external 24-VDC power supply. The 24-VDC power supply is not built into the
SERVOPACK.
• Specifications of the external power supply for sequence input signals:
24 VDC ± 1 V, 50 mA min.
The same power supply as that of the output circuit should be used.
44
Page 47

3.6 Connection Example of Output Signal
3.6 Connection Example of Output Signal
Set the load so that the output current will fall within 50 mA or less.
Photocoupler output (Per output signal)
Max. voltage: 30 VDC
Max. current: 50 m ADC
24 VDC
Load
Power Supply
+24V 0V
SERVOPACK
CN1
12
ALM
13
7
/BK
SG-COM
Load
45
Page 48

3.7 I/O Signals
3.7 I/O Signals
3.7.1 Homing Deceleration Signal Input
The usual connection for homing deceleration signal /DEC is shown below. A deceleration signal is
input when the homing function (ZRET command) of MECHATROLINK-II communications specifications is used.
24-VDC
power supply
24V
+24VIN
/DEC
0V
Signal Name Signal Function
Homing Deceleration
Signal Input
/DEC ON (low level) The signal turns ON.
OFF (high level) The signal turns OFF.
3.7.2 External Latch Signal Input
The usual connection for external latch signal input /EXT1 is shown below. This input signal is used for
the homing (ZRET command) and the external signal input positioning (EX_POSING) functions of
MECHATROLINK-II communications specifications.
24-VDC
power supply
24V
+24VIN
CN1-5
CN1-2
CN1-5
SERVOPACK
3.3 kΩ
7 mA
SERVOPACK
Photocoupler
Photocoupler
/EXT1
0V
Signal Name Signal Function
External Latch Signal
Input
/EXT1 ON (low level) The external signal is ON.
OFF (high level) The external signal is OFF.
CN1-1
46
3.3 kΩ
7 mA
Page 49

3.7 I/O Signals
3.7.3 Emergency Stop Signal Input
The usual connection for emergency stop signal input E-STP is shown below. When the signal turns
OFF while the servomotor is rotating, the servomotor will be stopped by the dynamic brake.
WARNING
• Use the emergency stop signal input E-STP to forcibly turn OFF the servo from an external
sequence, such as host controller, at occurrence of servo alarm or system emergency stop.
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has been
turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to completely stop the
motor by turning OFF the servo using the emergency stop.
• When executing the JOG operation and the home position search operation using CX-Drive, the ESTP signal will be ignored. Alternative measures must be taken in case an emergency stop is
needed.
Note: For the emergency stop signal, the SERVOPACK processing for stopping is exe-
cuted by the software. As the safety specifications of some applications may not
satisfy local safety requirements, add external safety circuits as required.
24-VDC
power supply
24V
+24VIN
Emergency stop
E-STP
0V
CN1-5
CN1-6
SERVOPACK
Photocoupler
3.3 kΩ
7 mA
Signal Name Signal Function
Emergency Stop
Signal Input
• The command warning 1 (A.95A) will occur if a SV_ON command is sent while the SERVOPACK is in
emergency stop status.
• The emergency stop alarm (A.280) will occur if the emergency stop signal turns ON while the power is
being supplied to the servomotor.
E-STP ON (low level) Releases the emergency stop.
OFF (high level) Emergency stop (Forced servo OFF)
47
Page 50

3.7 I/O Signals
Sequence at Occurrence of Emergency Stop
WARNING
• Configure the circuit’s power supply to be automatically cut off if E-STP signal is OFF at occurrence of emergency stop.
The residual voltage rotates the servomotor for a few seconds after the power supply has been
turned OFF, and may result in injury or damage to the equipment.
Position information is not stored in the SERVOPACK, so this information will be lost if the power
supply is turned OFF. This information cannot be read again if the power supply is turned OFF.
IMPORTANT
• Do not frequently start or stop the servomotor by turning ON or OFF the power supply or
by using the servo ON (SV-ON) or servo OFF (SV-OFF) signal. Failure to observe this
warning will cause deterioration of the SERVOPACK internal element.
Power supply
Single-phase 200 VAC to 230VAC
50/60 Hz
L2
L1
Noise Filter
24 VDC
Servo power
ON
MC1
MC1
Servo power
OFF
MC1
Emergency stop
Emergency
stop
CNA
1 (L1)
2 (L2)
CN1
5 (+24VIN)
6 (E-STP)
MC1
SUP
SERVOPACK
Set the following parameter to disable the emergency stop input signal if it is absolutely necessary.
Parameter Descriptions
Pn 515 n.4 Emergency stop when CN1-6 input signal is OFF (H-level) (factory set-
ting)
n.8 Always sets the input signal ON to disable the emergency stop.
48
Page 51

3.7 I/O Signals
3.7.4 Forward/Reverse Run Prohibited Inputs (Overtravel Inputs)
WARNING
• When executing JOG operation and the home position search operation using CX-Drive, the P-OT
and N-OT signals will be ignored. Alternative measures must be taken in case of overtravel.
The usual connection for forward/reverse run prohibited inputs P-OT and N-OT is shown below.
Connect these signals to limit switches to forcibly stop the servomotor when the machine movable part
travels beyond the allowable motion range. The servomotor will decelerate to a stop, and then the zero
clamp is performed. The maximum torque during deceleration to a stop will be the servomotor maximum torque.
Note: For forward/reverse run prohibited inputs, the SERVOPACK processing for stop-
ping is executed by the software. As the safety specifications of some applications may not satisfy local safety requirements, add external safety circuits as
required.
24-VDC
power supply
24V
0V
0V
+24VIN
P-OT
N-OT
SERVOPACK
CN1-5
3.3 k
CN1-4
3.3 k
CN1-3
Photocoupler
Ω
7 mA
Photocoupler
Ω
7 mA
Signal Name Signal Function
Forward Run
Prohibited Input
Reverse Run
Prohibited Input
P-OT
N-OT
ON at low (L) level Forward run allowed (normal status)
OFF at high (H) level Forward run prohibited (reverse run is
ON at low (L) level Reverse run allowed (normal status)
OFF at high (H) level Reverse run prohibited (forward run is
Related Parameters
Parameter Descriptions
Pn.50A
Pn.50B
n.2
n.8
n.4
n.4
Forward run permitted when CN1-4 input signal is ON (L level)
Always forward run allowed
Reverse run permitted when CN1-3 input signal is ON (L level)
Always reverse run allowed
49
allowed)
allowed)
Page 52

3.7 I/O Signals
3.7.5 Servo Alarm Output
The usual connection for alarm related output signals is shown below.
These signal is output when the SERVOPACK detects an error.
24-VDC power supply
0V
+24V
Photocoupler output
Max. operating voltage:
30 VDC per output
Max. output current:
50 mA DC per output
SERVOPACK
Photocoupler
CN1-12
50 mA max.
CN1-7
ALM
SG-COM
A 24-VDC power supply must be connected externally.
Signal Name Signal/Meaning Function
Servo Alarm Outputs ALM Servo alarm output Normal status when ON (close)
SG-COM Output signal ground
Note: Open collector outputs are used for output signals.
• At alarm occurrence, an alarm code is output to the host controller through MECHATROLINK-II
transmission. Take care that the SERVOPACK power supply is not turned OFF when the alarm output signal turns ON.
• Configure the system so that the SERVOPACK power supply is turned OFF by the contact signal
between C1 and C2 of the regenerative unit or the contact signal of the thermometal cut-out for the
external resistor.
The power supply must be turned OFF and the emergency stop input signal must be open when
using the system emergency stop.
Alarm output when OFF (open)
3.7.6 Brake Interlock Output
The usual connection for brake interlock signal /BK is shown below.
These signal turns ON when the servo turns ON, and OFF when the servo turns OFF. They are used
to control the brake. The brake can also be released by sending a release brake (BRK_OFF) command using MECHATROLINK-II communications.
24-VDC power supply
+24V
0V
Photocoupler output
Max. operating voltage:
30 VDC per output
Max. output current:
50 mA DC
SERVOPACK
Photocoupler
CN1-13
50 mA max.
CN1-7
/BK
SG-COM
Signal Name Signal/Meaning Function
Brake Interlock
Output
/BK Brake interlock output Releases the brake when ON (close)
SG-COM Output signal ground
Applies the brake when OFF (open)
50
Page 53

/BK Signal Timing
When the servo is turned OFF while the servomotor stops.
Servo OFF (SV_OFF)
command
Brake (/BK)
Servo ON Servo OFF
Brake ONBrake OFF
3.7 I/O Signals
Motor power
Motor power ON
Motor power OFF
Approx. 130 ms
When the servo is turned OFF while the servomotor is running.
Servo OFF (SV_OFF)
command
Motor speed
-1
)
(min
Approx. 100 min
Brake (/BK)
/BK Signal Output Conditions While the Servomotor is Rotating
/BK signal turns ON when either of the following is satisfied.
· The servomotor speed decreases to a value 100 min
· 500 ms elapses after the servo has been turned OFF.
-1
Servo ON
Servo OFF
Brake ONBrake OFF
Approx. 500 ms
-1
or less after the servo has turned OFF.
51
Page 54

3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II Communications
3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II Communications
3.8.1 MECHATROLINK-II Communications
Outline
MECHATROLINK-II is a field network that makes it possible for one factory automation controller (C1
master station) to control decentralized multiple factory automation devices (slave stations) such as
servo drives, inverters, and I/O modules.
Configuration
• Bus connection with one C1 master station and a maximum of 30 slave stations
• Install terminators at both ends of the network cable to reduce signal reflection.
• Connect repeaters for a network with a total distance exceeding 30 m, regardless of whether the
number of slaves is 17 or more or 16 or less.
C1 Master
station
(FA controller)
Slave station
(FA device)
#1 #2 #30
Slave station
(FA device)
Slave station
(FA device)
3.8.2 Wiring Specifications
Terminators
Install terminators at both ends of the network cable to reduce signal reflection, some Mechatrolink
controllers already have a terminating resistor built-in.
Model External Appearance
JEPMC-W6022
JEPMC-W6022-E
(Compliant with
RoHS Directive)
Repeaters
A repeater is needed in the network, when the total distance between stations exceeds 30 m, or when
the number of slave stations is 17 or more.
Ty pe External Appearance
JEPMC-REP2000
52
Page 55

Repeater Connection Example
Master side network distance
3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II Communications
Total distance
Total extended distance
C1 Master
station
Slave station
#1
Master side network Extended network
Slave station#mRepeater Slave station
#m+1
Slave station
#n-1
Slave station
3.8.3 Setting Communications Specifications
Setting Transmission Bytes
The SW2 bit 2 switch sets the MECHATROLINK-II transmission bytes, as shown below. Settings that
have been changed are enabled when the power is turned OFF and ON.
4
5
3
6
2
7
1
8
0
9
A
F
B
E
C
D
SW1 (factory setting) SW2 (factory setting)
SW2 Name Setting Description Factory
Bit 1 Reserved
Bit 2 Transmission bytes
Bit 3 Station address
Bit 4 Selection of filter
setting method
ON
OFF
1234
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Do not set
Fixed
17 bytes
32 bytes
Station address = 40H+SW1
Station address = 50H+SW1
Sets by using the FIL rotary switch (invalid
setting by Pn00A).
Sets by Pn00A (invalid setting by using the
FIL rotary switch).
Setting
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
#n
Setting Station Address
The SW1 and SW2 bit 3 switches set the MECHATROLINK-II station address.
SW2 Bit 3 Station Address
OFF 40H + SW1
ON 50H + SW1
53
Page 56

3.8 Setting MECHATROLINK-II Communications
3.8.4 Transmission Cycle and Number of Stations
The transmission cycle and number of stations that can be set with the SERVOPACK are shown
below.
Transmission Bytes Transmission Cycle
1.0 ms
17 14
32 8
Note: 1. If connecting more than 16 stations, use the repeater.
2. The number of stations indicated in the above table is the maximum number
of stations that can be connected through MECHATROLINK communications. The actual number of stations may differ depending on the Machine
Controller. Refer to the relevant Machine Controller’s manual.
1.5 ms 2.0 ms 3.0 ms 4.0 ms
23 30 30 30
14 20 30 30
3.8.5 MECHATROLINK-II Communications Status Indicator COM LED
The LED indicator COM (green) on the front of SERVOPACK lights up when MECHATROLINK-II communications with the host controller is established.
Status Indicator LED SERVOPACK Operation Status
Standby for establishment of communications
COM ALM RDY
2 seconds after the
power turns ON
COM ALM RDY
COM
COM ALM RDY
: Unlit
: Lit
: Blinking
MECHATROLINK-II communications are busy.
Servo ON status (Power is being supplied)
54
Page 57

4.1 Lists of Commands
4 MECHATROLINK-II Commands
4.1 Lists of Commands
4.1.1 Main Commands List
The MECHATROLINK-II main commands are classified into three types: Common commands, common motion commands, and servo standard commands.
Classifica-
tions
Common
Commands
Common
Motion
Commands
Command
Code
0DH SYNC_SET Start Synchro-
1CH PPRM_WR Write Stored
Command
Name
00H NOP No Operation N Asynchro-
01H PRM_RD Read Parameter D Asynchro-
02H PRM_WR Write Parameter D Asynchro-
03H ID_RD Read ID D Asynchro-
04H CONFIG Setup Device C Asynchro-
05H ALM_RD Read Alarm or
06H ALM_CLR Clear alarm or
0EH CONNECT Establish Con-
0FH DISCON-
NECT
20H POS_SET Set Coordinates D Asynchro-
21H BRK_ON Apply Brake C Asynchro-
22H BRK_OFF Release Brake C Asynchro-
23H SENS_ON Turn Sensor ON C Asynchro-
24H SENS_OFF Turn Sensor OFF C Asynchro-
25H HOLD Stop Motion M Asynchro-
Functions Process-
ing Classi-
Warning
warning
nous Communication
nection
Release Discon-
nection
Parameter
Synchroni-
fications
D Asynchro-
C Asynchro-
N Asynchro-
N Asynchro-
N Asynchro-
D Asynchro-
zation Clas-
sifications
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
Subcom-
mand
Can be
used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Can be
used
Remarks
55
Page 58

4.1 Lists of Commands
Classifica-
tions
Common
Motion
Commands
Servo
Standard
Commands
<Processing Classifications>
N: Network command
D: Data communication command
C: Control command
M: Motion command
X: Compound command
Command
Code
28H LTMOD_ON Request Latch
29H LTMOD_
30H SMON Status Monitoring D Asynchro-
31H SV_ON Servo ON C Asynchro-
32H SV_OFF Servo OFF C Asynchro-
34H INTERPO-
35H POSING Positioning M Asynchro-
36H FEED Constant Speed
38H LATCH Interpolation
39H EX_
3AH ZRET Homing M Asynchro-
3EH ADJ Adjustment D Asynchro-
Command
Name
OFF
LATE
POSING
Functions Process-
Mode
Release Latch
Mode
Interpolation
Feed
Feed
Feeding with
Position Detection
External Input
Positioning
ing Classi-
fications
C Asynchro-
C Asynchro-
M Synchro-
M Asynchro-
M Synchro-
M Synchro-
Synchroni-
zation Clas-
sifications
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
nous
Subcom-
mand
Cannot
be used
Cannot
be used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Can be
used
Cannot
be used
Remarks
IMPORTANT
If an unsupported command is received, the warning A.95b will occur, and the command will
be ignored.
The servo is not OFF and the servomotor is not stopped if an unsupported command is
received.
56
Page 59

4.1.2 Subcommands List
4.1 Lists of Commands
Command
Code
00H NOP No Operation
01H PRM_RD Read Parameter
02H PRM_WR Write Parameter
05H ALM_RD Read Alarm or Warning
1CH PPRM_WR Write Stored Parameter
28H LTMOD_ON Request Latch Mode
29H LTMOD_OFF Release Latch Mode
30H SMON Status Monitoring
Command
Name
Functions Remarks
57
Page 60

4.2 Main Commands
4.2 Main Commands
The following sections describe main command specific items that are unique to the SJDE-ANA-
OY.
The MECHATROLINK-II main commands use the first to the sixteenth bytes of the command and
response data.
4.2.1 Communication Phases
The table below shows the relationship between communication phases and device-level operations in
the MECHATROLINK-II during normal operations. The C1 master station phases described here indicate the communication state of the C1 master station in relation to the slave stations, but do not indicate the state of the C1 master station device.
Relationship between Communication Phase and Device level Operation
C1 Master Station Phase Transition between
Phase Device Operation Command Device Operation Phase
0 Power ON - Power ON 0
C1 Master and Slave Stations
Slave Station
1 Initialization state CONNECT Prepared for
2, 3 Normal operation
state
4 Operate
communication
5 Power OFF - Power OFF 5
Normal
operation
commands
DISCONNECT
CONNECT
Normal operation state
Stop
communication
1
2, 3
4
58
Page 61

4.2 Main Commands
Descriptions
The communication state of the C master station in each phase is explained.
Phase 0
When the C1 master and slave stations are turned ON, operation switches to phase 1.
Phase 1
The C1 master station completes the internal initialization including the communication system, and confirms the response state of all the connected slave stations that have no error. Then, the C1 master station sends a CONNECT command to all the connected slave stations to establish communication.
The slave station completes the internal initialization including the communication system, and then
awaits the CONNECT command.
The slave station establishes the communication with the C1 master station and then switches to the
phase specified by command.
Phase 2 (Asynchronous Communication Phase)
The C1 master station uses only asynchronous commands supported by MECHATROLINK-II-compatible
devices to exchange data needed for the operation and control of the devices. The timing for the execution of each command is controlled by the C1 master station.
The slave stations exchange data and the control of devices by the commands sent from the C1 master
station. The transition to phase 3 or phase 4 is performed by commands from the C1 master station to the
slave stations.
Phase 3 (Synchronous Communication Phase)
The C1 master station can use all commands supported by MECHATROLINK-II-compatible devices to
exchange data needed for the operation and control of devices. Each command is updated in a constant
cycle (communication cycle) and its timing for the execution is controlled by the C1 master station.
The slave stations exchange data and the control of devices by the commands sent from the C1 master
station. If there are any errors in communication synchronization, the slave station automatically switches
to phase 2. Synchronous communication is started again by sending SYNC_SET command from the C1
master station.
Phase 4
If the C1 master station is turned OFF, the C1 master station sends a DISCONNECT command to all
slave stations. The DISCONNECT command is also sent to any slave stations involved if there is a need
to change the system configuration.
When the slave station receives the DISCONNECT command from the C1 master station, they execute
the reinitialization processing and then shift to connection wait state (phase 1).
Phase 5
When the C1 master and slave stations are turned OFF, they switch to phase 5. The following two state
changes depend on which station is turned OFF first.
• C1 Master Station Turned OFF First
The C1 master station sends the DISCONNECT command to all slave stations before turning OFF the
power supply (Recommended Sequence).
A slave station receiving this command executes the reinitialization processing and then switches to
connection wait state (phase 1).
When the DISCONNECT command has not been sent, or has not been received by the slave station,
the slave station detects a communication error and shifts to an alarm state.
• Slave Station Turned OFF First
After the C1 master station sends the DISCONNECT command to the slave station to be turned OFF,
the power supply of the slave station is turned OFF (Recommended Sequence).
The slave station receiving the command executes the necessary initialization processing and then
switches to connection wait state (phase 1).
If a slave station is turned OFF without using the above procedure, the C1 master station detects a
communication error.
The operations in alarm state and recovery from alarm state depend on the specifications of the device
or application.
59
Page 62

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.2 No Operation (NOP: 00H)
Byte NOP Description
Command Response
1 00H 00H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Returns the status of the ALM, WARNG, and CMDRDY in STATUS
4
5 −
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub-
commands.
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within transmis-
bytes only. All other bits are not used. The response will be NOP when
the power is turned ON until initialization has been completed, and during this time, the following status will be returned: CMDRDY: 0.
• Can be used during any phase.
Network command group
sion cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Asynchronous
60
Page 63

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.3 Read Parameter (PRM_RD: 01H)
Byte PRM_RD Description
Command Response
101H 01H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Reads current operating parameters. The latest set value, however, is
4
5NO NO
6
7 SIZE SIZE
8 − PA R AM E -
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
TER
Processing classifications
Processing time 100 ms Subcommand Cannot be used
read for offline parameters. (The set value is enabled with the Setup
Device command (CONFIG).)
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases. If a warning occurs, PARAMETER will not be dependable.
-If NO is not within range: Data setting warning 1 (A.94A)
-If SIZE does not match: Data setting warning 4 (A.94D)
• For details on NO and SIZE, refer to 7.2 List of Parameters.
Data communications command group
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
61
Page 64

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.4 Write Parameter (PRM_WR: 02H)
Byte PRM_WR Description
Command Response
1 02H 02H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Writes a parameter and does not store them in non-volatile memory.
4
5NO NO
6
7 SIZE SIZE
8 PARAME-
TER
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
PA R AM E -
TER
Processing classifications
Processing time 100 ms Subcommand Cannot be used
A written parameter is enabled with the Setup Device command (CONFIG) transmission after setting.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If a parameter is changed mid-operation with CX-Drive: Command
warning 1 (A.95A)
-If NO is not within range: Data setting warning 1 (A.94A)
-If SIZE does not match: Data setting warning 4 (A.94D)
-If PARAMETER is not within range: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
For details on NO, SIZE, and PARAMETER, refer to 7.2 List of Parame-
ters.
Data communications command group
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
62
Page 65

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.5 Read ID (ID_RD: 03H)
Byte ID_RD Description
Command Response
103H 03H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Reads the ID. The corresponding DEVICE_CODE is shown in the table
4
5 DEVICE_
CODE
6 OFFSET OFFSET
7 SIZE SIZE
8 − ID
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
DEVICE_
CODE
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
below.
Data communications command group
nication cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
Details of DEVICE_CODE
Type/Name OFFSET
SERVOPACK Model
Software
Encoder Software Ver.
Motor Model
Reserved
Note: 1. Model numbers appear in ASCII code, with the last section as “00.”
2. Spaces indicate unspecified data.
3. The version number of the encoder software is set to 00 (binary) and cannot be
changed.
* 1. Rated output.
* 2. : Power supply voltage specifications.
DEVICE_
CODE
00H S J D E
02H Ver.
Ver .
12H Ver.
20H * * * * * 00
50H
52H
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A
63
∗1∗1∗
NA00
2
Page 66

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.6 Setup Device (CONFIG: 04H)
Byte CONFIG Description
Command Response
1 04H 04H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Recalculates all currently set parameters and initializes positions, output
4
5 −
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
* +α is setting of the Brake reference-Servo off delay time.
Status and Output Signal during CONFIG Command Execution
Status and
Output Signal
ALM (status) Current status Current status Current status
CMDRDY (status) 1 0 1
Other status Current status Not specified Current status
ALARM (code) Alarms currently
ALM
(CN1 output signal)
Other output signals Current status Not specified Current status
Processing classifications
Processing time
signals, etc.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• The SERVOPACK will change to Servo OFF if this command is received
when the SERVOPACK is Servo ON.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If parameters are changed mid-operation with CX-Drive: Command
warning 1 (A.95A)
Before CONFIG During CONFIG After CONFIG
occurred
Current status Current status Current status
Control command group
Within 4 s + α
Alarms currently
occurred
∗
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
Alarms currently
occurred
64
Page 67

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.7 Read Alarm or Warning (ALM_RD: 05H)
Byte ALM_RD Description
Command Response
1 05H 05H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Reads the following alarm or warning status.
4
5 ALM_RD_
MOD
6 − ALM_DATA
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
* Alarm occurrence history is saved in non-volatile memory, and will not be lost if power goes OFF.
ALM_RD_
MOD
Processing classifications
Processing time Refer to
-Current alarm/warning status
-Alarm status history* (warning history is not preserved.)
• The ALM_RD_MOD specifications are shown in the following table.
• Alarm and warning codes are set in ALM_DATA from byte 6 in their order
of detection, and 0 is set in the bytes that are blank in the table. Accordingly, the data in byte 6 is for the latest alarm or warning codes.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If ALM_RD_MOD is not within range: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
Details of ALM_RD_MOD
ALM_RD_MOD Description Processing Time
0 Read current alarm/warning status
1 Read alarm status history
2 Gets the detailed information of current alarm or warning one by one.
3 Gets the detailed information of alarm status history one by one.
10 items max. (sixth to fifteenth byte)
10 items max. (sixth to fifteenth byte)
(Warning history is not preserved.)
Set the occurrence order from 0 (the latest) to 9 for the alarm index.
Byte
6
7-8
Set the occurrence order from 0 (the latest) to 9 for the alarm index.
Byte
6
7-8
Command
Alarm index
0
Command
Alarm index
0
Data communications command group
Details of
ALM_RD_MOD.
Response
Alarm index
Alarm code
Response
Alarm index
Alarm code
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
Within communication cycle
Within 60 ms
Within 12 ms
65
Page 68

4.2 Main Commands
Each alarm code of the JUNMA-series SERVOPACK is 2-byte long. The data format of alarm code is as
follows.
D15-D12 D11-D4 D3-D0
Reserved (0) Alarm code Detailed information
Note: 1. When ALM_RD_MOD = 0 or 1, the alarm code (1-byte long) is returned.
2. When ALM_RD_MOD = 2 or 3, the alarm code (2-byte long) is returned.
4.2.8 Clear Alarm or Warning (ALM_CLR: 06H)
Byte ALM_CLR Description
Command Response
1 06H 06H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Clears the following alarm or warning status.
4
5 ALM_CLR_
MOD
6 −−
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
* Alarm occurrence history is saved in non-volatile memory, and will not be lost if power goes OFF.
ALM_CLR_
MOD
Details of ALM_CLR_MOD
ALM_CLR_MOD Description Processing Time
0 Clear current alarm/warning status Within 200 ms
1 Clear alarm status history Within 2 s
Processing classifications
Processing time Refer to
-Current alarm/warning status
-Alarm status history * (warning history is not preserved.)
• The ALM_CLR_MOD specifications are shown in the following table.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If parameters are changed mid-operation with CX-Drive: Command
warning 1 (A.95A)
-If ALM_CLR_MOD is not within range: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
Control command group
Details of
ALM_CLR_MO
D
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
66
Page 69

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.9 Start Synchronous Communication (SYNC_SET: 0DH)
Byte SYNC_SET Description
Command Response
10DH 0DH
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Starts synchronous communications. Switches from phase 2 to phase
4
5 −
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
Processing classifications
Processing time Transmission
3.
• Synchronization is established as values of each WDT in command and
response is detected.
• During phase 3, the command will be ignored (without a warning).
• During Servo ON in phase 2, the SERVOPACK will change to Servo
OFF if this command is received.
• At the occurrence of the following alarms, this command must be transmitted to restart synchronous communications.
-MECHATROLINK-II Synchronization Error (A.E50)
-MECHATROLINK-II Synchronization Failure (A.E51)
-MECHATROLINK-II Communications Error (A.E60)
-MECHATROLINK-II Transmission Cycle Error (A.E61)
• In the following case, a warning will occur and the command will be
ignored.
-During operation using CX-Drive: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
Network command group
cycle or more
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
67
Page 70

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.10 Establish Connection (CONNECT: 0EH)
Byte CONNECT Description
Command Response
10EH 0EH
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Establishes a MECHATROLINK-II connection. Sets the communications
4
5 VER VER
6 COM_MOD COM_MOD
7COM_TIMCOM_TIM
8 −−
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
Processing classifications
Processing time Communica-
mode according to COM_MOD.
• VER: Version
• Set VER to 21H (Ver. 2.1).
• COM_MOD: Communications mode. Refer to the following table.
• COM_TIM: Communications cycle
Set the multiple number of transmission cycle in the range of 1 to 32.
1 [ms] ≤ transmission cycle [ms] × COM_TIM ≤ 32 [ms]
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If COM_MOD is not within range: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
-If COM_TIM is not within range: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
-If the transmission bytes is 17, and SUBCMD is 1: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
-If VER is not equal to 21H in the MECHATROLINK communications
mode: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
-During operation using CX-Drive: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
• The only commands that will be accepted are CONNECT, DISCONNECT, and NOP. If any other command is issued, NOP will be sent as a
response.
Network command group
tions cycle or
more
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
Details of COM_MOD
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SUBCMD −−− DTMOD SYNCMOD −
• SYNCMOD:
0: Asynchronous communication (Transition to phase 2)
1: Synchronous communication (Transition to phase 3)
• DTMOD: Data transfer method
00, 11: Single transfer
01: Consecutive transfer
• SUBCMD:
0: Subcommand not used
1: Subcommand used
• Set the 0 in the other bits.
68
Warning/alarm
Phase 1
Phase 2
SYNC_SET
Phase 3
SYNCMOD=0
SYNCMOD=1
Page 71

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.11 Release Connection (DISCONNECT: 0FH)
Byte DISCONNECT Description
Command Response
10FH 0FH
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Releases the MECHATROLINK-II connection. The SERVOPACK
4
5 −
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
Processing classifications
Processing time Communica-
changes communication to phase 1.
• Can be used during any phase.
• When this command is received, the following operations will be performed.
-The SERVOPACK changes communication to phase 1.
-The SERVOPACK changes to Servo OFF.
-The reference point setting will become invalid.
-The position data will be initialized.
Network command group
tions cycle or
more
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
4.2.12 Write Stored Parameter (PPRM_WR: 1CH)
Byte PPRM_WR Description
Command Response
11CH 1CH
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Saves a parameter in non-volatile memory. If a parameter is online
4
5NO NO
6
7 SIZE SIZE
8 PARAME-
TER
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
PA RA M E -
TER
Processing classifications
Processing time Within 200 ms Subcommand Cannot be used
parameters, those parameters will become effective.
Offline parameters are enabled with the Set Up Device command (CONFIG) transmission communication after setting.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the
following cases.
-If parameters are changed mid-operation with CX-Drive: Command
warning 1 (A.95A)
-If NO is not within range: Data setting warning1 (A.94A)
-If SIZE does not match:Data setting warning 4 (A.94D)
-If PARAMETER is not within range: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
• For details on NO, SIZE and PARAMETER, refer to 7.2 List of Parame-
ters.
Data communications command group
69
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
Page 72

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.13 Set Coordinates (POS_SET: 20H)
Byte POS_SET Description
Command Response
1 20H 20H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Sets coordinates. REFE can also enable home position (ZPOINT) and
4
5 PS_SUBCMDPS_SUBC
6 POS_DATA POS_DATA
7
8
9
10 −−
11
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
MD
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
software limits.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• PS_SUBCMD: Refer to the following table for coordinate setting modes.
• Set position in POS_DATA.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If a number not within the range is set for PS_SUBCMD: Data setting
warning 2 (A.94B)
Data communications command group
nication cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
Details of PS_SUBCMD
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
REFE −−− POS_SEL
• REFE: Sets reference point.
0: Does not set reference point.
1: Sets reference point.
Decides the coordinates, and ZPOINT (home position) and software limits are enabled.
• POS_SEL: Selects coordinates.
3: Sets POS_DATA to the reference point and the coordinate system (POS, MPOS, APOS, IPOS, and
TPOS) if APOS (machine coordinate system feedback position) is selected (The “3: APOS” can only
be selected for POS_SEL.).
• Set all other bits to 0.
4.2.14 Apply Brake (BRK_ON: 21H)
Byte BRK_ON Description
Command Response
1 21H 21H
Processing classifications
Control command group
70
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
Page 73

4.2 Main Commands
Byte BRK_ON Description
Command Response
2 − ALARM Processing time Within commu-
3 STATUS • Turns OFF the brake signal and locks the brake. This command is
4
5 MONITOR
6
7
8
9 MONITOR
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
1/2
1
2
SEL_MON
1/2
enabled only while the servo is OFF.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• Brake signal output timing
BK
nications cycle
BRK_ON received
Within 3 ms
Subcommand Cannot be used
71
Page 74

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.15 Release Brake (BRK_OFF: 22H)
Byte BRK_OFF Description
Command Response
1 22H 22H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Turns ON the brake signal and releases the brake.
4
5 MONITOR
6
7
8
9 MONITOR
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
1/2
SEL_MON
1/2
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• Brake signal output timing
1
BRK_OFF received
2
BK
Control command group
nications cycle
Within 3 ms
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
IMPORTANT
BRK_ON and BRK_OFF become always valid as commands unless a warning occurs.
If a BRK_OFF command is sent while power is being supplied to the servomotor, the servomotor continues running.
However, if a Servo OFF command is sent later, the brake will remain released because the
BRK_OFF command is valid and may cause a critical situation.
When using a BRK_ON or BRK_OFF command, always keep in mind the status of the command.
72
Page 75

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.16 Turn Sensor ON (SENS_ON: 23H)
Byte SENS_ON Description
Command Response
123H 23H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Obtains the initial position data and creates the present position.
4
5 MONITOR
6
7
8
9 MONITOR
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
1/2
SEL_MON
1/2
Processing classifications
Processing time Within 1 s Subcommand Cannot be used
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
1
2
Control command group
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
4.2.17 Turn Sensor OFF (SENS_OFF: 24H)
Byte SENS_OFF Description
Command Response
124H 24H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • The reference point, home position (ZPOINT), and software limits will be
4
5 MONITOR
6
7
8
9 MONITOR
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
1/2
SEL_MON
1/2
Processing classifications
Processing time Within 1 s Subcommand Cannot be used
disabled.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
1
2
case.
-While the SERVOPACK is servo ON: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
Control command group
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
73
Page 76

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.18 Stop Motion (HOLD: 25H)
Byte HOLD Description
Command Response
1 25H 25H
2 − ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Stops the servomotor for positioning according to the stop method set in
4
5HOLD_
MOD
6 −
7
8
9 MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
MONITOR1
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
HOLD_MOD.
• From current motion status, performs a deceleration stop and positioning according to the deceleration speed set in the parameters.
• The stop method can be selected using HOLD_MOD.
0: Decelerate to a stop according to the deceleration parameter.
1: Stop immediately (output stop).
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• Use DEN (output complete) to confirm position data output completion.
• Latch processing, which is dependent on LATCH, EX_POSING will be
cancelled.
• ZRET latch processing and ZRET home position alignment will be cancelled.
• Upon completion of this command, the reference position (POS) must
be read, and the controller coordinate system must be set up.
• The modal latch mode set by LTMOD_ON command stays effective.
Motion command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Asynchronous
Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn80E Linear Deceleration Parameter
74
Page 77

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.19 Request Latch Mode (LTMOD_ON: 28H)
Byte LTM O D_ O N Description
Command Response
128H 28H
2LT_SGN ALARM
3 − STATUS • Sets the modal latch mode. If a latch signal is input during modal latch
4
5 MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
mode, position latching will be performed.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A latch signal can be selected using LT_SGN. Refer to Latch Signal
Field Specifications (LT_SGN).
• Use CMDRDY = 1 to confirm that the Request Latch Mode command
has been received.
• Confirm that L_CMP is 1 in STATUS at the completion of latching.
-When there is monitor data such as SMON or POSING appended to
the command response, LPOS is forcefully returned to MONITOR2.
-When there is no monitor data such as PRM_RD or ALM_RD
appended to the command response, confirm that L_CMP is 1 in STATUS, then use a command that has monitor data such as SMON in the
response and select LPOS to confirm.
• Once the latch operation has been performed, it will not be performed
again even if a latch signal is input. Send a LTMOD_OFF command and
then send a new LTMOD_ON command.
• Interference with another latch mode command
-During the execution of a command such as LATCH, ZRET, or
EX_POSING, the LTMOD_ON command cannot be used. If this command is used during the execution of these commands, the Command
warning 4 (A.95D) will occur.
Control command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn820 Latching Area Upper Limit
Pn822 Latching Area Lower Limit
75
Page 78

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.20 Release Latch Mode (LTMOD_OFF: 29H)
Byte LTM OD _ OF F Description
Command Response
1 29H 29H
2 − ALARM
3 − STATUS • Releases the modal latch mode.
4
5 MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• Check that CMDRDY is 1 to confirm that the Release Latch Mode command has been received.
• Interference with another latch mode command
-During the execution of a command such as LATCH, ZRET, or
EX_POSING, the LTMOD_OFF command cannot be used. If this command is used during the execution of these commands, the Command
warning 4 (A.95D) will occur.
Control command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
76
Page 79

4.2.21 Status Monitoring (SMON: 30H)
Byte SMON Description
Command Response
130H 30H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Reads the current status of the SERVOPACK.
4
5 MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
Data communications command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
4.2 Main Commands
Asynchronous
77
Page 80

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.22 Servo ON (SV_ON: 31H)
Byte SV_ON Description
Command Response
1 31H 31H
2 − ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Turns ON the power to the motor.
4
5 − MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For sub-
commands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within 50 ms Subcommand Can be used
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-During alarm occurrence (when ALM of STATUS is 1): Command
warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the main power supply turns OFF (when PON of STATUS is 0): Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the emergency stop switch input turns ON (when E-STP of IO_MON
is 1): Command warning 1 (A.95A)
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• Upon completion of this command, the reference position (POS) must
be read, and the controller coordinate system must be set up.
• If a SV_ON command is sent when the servo has been already turned
ON from CX-Drive, the Servo ON Reference Invalid Alarm (A.0b0) will
occur.
Control command group
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
78
Page 81

4.2.23 Servo OFF (SV_OFF: 32H)
Byte SV_OFF Description
Command Response
132H 32H
2 − ALARM
3 STATUS • Turns OFF the power to the motor.
4
5 MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within 50 ms Subcommand Can be used
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
Control command group
4.2 Main Commands
Synchronization
classifications
Asynchronous
79
Page 82

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.24 Interpolation Feed (INTERPOLATE: 34H)
Byte INTERPOLATE Description
Command Response
1 34H 34H
2 − ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Starts interpolation feeding every communications cycle.
4
5 TPOS MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 VFF MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For sub-
commands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
• Can be used during phase 3.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-During phase 2: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the SERVOPACK is Servo OFF: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the output speed [Target position (TPOS) - Current position (IPOS)]
exceeds the maximum speed: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• The target position (TPOS) is indicated by signed 4 bytes.
• Use DEN (output complete) to confirm the completion of position reference output.
• For details on interpolation, refer to 6.5.1 INTERPOLATE Related Com-
mands.
• Speed Feed Forward (VFF) cannot be used.
If a VFF is input, no compensation for speed feed forward will be
applied.
Motion command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Synchronous
80
Page 83

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.25 Positioning (POSING: 35H)
Byte POSING Description
Command Response
135H 35H
2 − ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Performs positioning at the target position (TPOS) using the target
4
5 TPOS MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 TSPD MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
speed (TSPD).
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the following
cases.
-If the SERVOPACK is Servo OFF: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the target speed (TSPD) exceeds the maximum speed: Data setting
warning 2 (A.94B)
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• The target position (TPOS) is a signed 4 bytes. It is sent by using an
absolute position in the reference coordinate system.
• The target speed (TSPD) is an unsigned 4 bytes. It is sent in the range
from 0 to the maximum speed [reference unit/s].
• Changes can be made to the target position and target speed during
movement.
• Use DEN (output complete) to confirm the completion of position reference output.
• For details on posing commands, refer to 6.5.2 POSING Related Com-
mands.
Motion command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Asynchronous
Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn80B Linear Acceleration Parameter
Pn80E Linear Deceleration Parameter
81
Page 84

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.26 Constant Speed Feed (FEED: 36H)
Byte FEED Description
Command Response
1 36H 36H
2 − ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Performs constant speed feeding using the target speed (TSPD). The
4
5 − MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 TSPD MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For sub-
commands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
servo performs constant speed feeding by position control. Use the Stop
Motion command (HOLD: 25H) to stop the constant speed feeding.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A command warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the
following cases.
-If the SERVOPACK is Servo OFF: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the target speed (TSPD) exceeds the maximum speed: Data setting
warning 2 (A.94B)
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• The target speed (TSPD) is a signed 4 bytes. The direction is determined by the sign. The target speed is sent in the range from a negative
maximum speed to a positive maximum speed [reference unit/s].
• Changes can be made to the target speed during movement.
• Use DEN (output complete) to confirm the completion of position reference output.
• For details on posing commands, refer to 6.5.2 POSING Related Com-
mands for details on the operation.
Motion command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Asynchronous
Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn80B Linear Acceleration Parameter
82
Page 85

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.27 Interpolation Feeding with Position Detection (LATCH: 38H)
Byte LATCH Description
Command Response
138H 38H
2LT_SGN ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Performs interpolation feeding and latches the position using the latch
4
5 TPOS MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 VFF MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For sub-
commands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
signal specified in LT-SGN.
• If the latch signal is input, the position when the signal is received is
recorded as the feedback latch position (LPOS) of the machine coordinate system, and the LPOS will forcibly be indicated as the MONITOR2
for one communications cycle.
• Can be used during phase 3.
• A command warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the
following cases.
-During phase 2: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the SERVOPACK is Servo OFF: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the output speed [the target position (TPOS) - the current position
(IPOS)] exceeds the maximum speed: Data setting warning 2 (A.94B)
• LT_SGN can be used. Refer to 4.5.1 Latch Signal Field Specifications:
LT _S G N (LT_SGN).
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• Speed Feed Forward (VFF) cannot be used.
If a VFF is input, no compensation for speed feed forward will be
applied.
• Use DEN (output complete) to confirm the motion completion.
• For details on interpolation, refer to 6.5.1 INTERPOLATE Related Com-
mands.
Motion command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Synchronous
Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn820 Latching Area Upper Limit
Pn822 Latching Area Lower Limit
83
Page 86

4.2 Main Commands
4.2.28 External Input Positioning (EX_POSING: 39H)
Byte EX_POSING Description
Command Response
1 39H 39H
2LT_SGN ALARM
3 OPTION STATUS • Moves toward the target position (TPOS) at the target speed (TSPD).
4
5 TPOS MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 TSPD MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − I/O_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
When a latch signal is input midway, positioning is performed according
to the final travel distance for external position specified in the parameter from the latch signal input position. When no latch signal is input,
positioning is performed for the target position (TPOS).
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A command warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the
following cases.
-If the SERVOPACK is Servo OFF: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the target speed (TSPD) exceeds the maximum speed : Data setting
warning 2 (A.94B)
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• The target position (TPOS) is a signed 4 bytes [reference unit]. It is sent
by using an absolute position in the reference coordinate system.
• The target speed (TSPD) is an unsigned 4 bytes. It is sent in the range
from 0 to the maximum speed [reference unit/s].
• After the latch is input, any changes to the target position during motion
will be ignored.
• Use DEN (output complete) to confirm the completion of position reference output.
• For details on posing commands, refer to 6.5.2 POSING Related Com-
mands.
Motion command group
nications cycle
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Asynchronous
84
Page 87

Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn80B Linear Acceleration Parameter
Pn80E Linear Deceleration Parameter
Pn814 Final Travel Distance for External Positioning
Pn820 Latching Area Upper Limit
Pn822 Latching Area Lower Limit
Operation
If a latch signal is input, positioning is
performed for the position calculated with the
following equation: latch signal input position
(LPOS) + final travel distance for external
positioning specified in Pn814.
When no latch signal is input, positioning is
performed for the target position (TPOS).
Latch signal
4.2.29 Homing (ZRET: 3AH)
Byte ZRET Description
Command Response
13AH 3AH
2LT_SGN ALARM
Processing classifications
Processing time Within commu-
Motion command group
nications cycle
4.2 Main Commands
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Can be used
Asynchronous
85
Page 88

4.2 Main Commands
Byte ZRET Description
Command Response
3 OPTION STATUS • Perform a homing using the following sequence.
4
5 − MONITOR1
6
7
8
9 TSPD MONITOR2
10
11
12
13 SEL_MON
14 − IO_MON
15
16 WDT RWDT
17 For sub18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
1/2
commands.
SEL_MON
1/2
For subcommands.
1. Accelerates to the target speed (TSPD) in the direction specified in
the parameter (Pn816) and continues to move at the target speed.
2. Decelerates to homing approach speed 1 (Pn817) at the DEC = 1.
3. Latch operation will start at the DEC = 0.
4. When a latch signal is input, positioning is performed to define the
target position at the homing approach speed 2 (Pn818). The target
position is calculated by adding the homing final travel distance
(Pn819). After the completion of positioning, the coordinate system is
set so that the position reached is 0.
• Can be used during phases 2 and 3.
• A command warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the
following cases.
-If the SERVOPACK is Servo OFF: Command warning 1 (A.95A)
-If the target speed (TSPD) exceeds the maximum speed: Data setting
warning 2 (A.94B)
• OPTION field cannot be used. Set all bits to 0.
• The target speed (TSPD) is an unsigned 4 bytes. It is sent in the range
from 0 to the maximum speed [reference unit/s].
• Before DEC is input, the target speed during motion can be changed.
• Use DEN (output complete) and ZPOINT (home position) to confirm the
completion of position reference output.
86
Page 89

Related Parameters
Parameter No. Description
Pn80B Linear Acceleration Parameter
Pn80E Linear Deceleration Parameter
Pn816 Homing Direction
Pn817 Homing Approach Speed 1
Pn818 Homing Approach Speed 2
Pn819 Final Travel Distance for Homing
Pn820 Latching Area Upper Limit
Pn822 Latching Area Lower Limit
Operation
4.2 Main Commands
Reference speed
Homing Approach Speed 1 (Pn817)
Homing Approach Speed 2 (Pn818)
Final Travel Distance
DEC
for Homing (Pn819)
Latch signal
4.2.30 Adjusting (ADJ: 3EH)
Byte ADJ Description
Command Response
13EH 3EH
2 SUBCODE ALARM
Processing classifications
Processing time Depends on
Data communications command group
processing
Synchronization
classifications
Subcommand Cannot be used
Asynchronous
87
Page 90

4.2 Main Commands
Byte ADJ Description
Command Response
3 − STATUS • This command is for maintenance. Parameter initialization can be done.
4
5CCMD CANS
6
7CAD-
DRESS
8
9 CSIZE CSIZE/
10
11 CDATA CDATA
12
13
14
15
16 WDT RWDT
CAD-
DRESS
ERRCODE
• Use as SUBCODE = 01H.
• Refer to the next page, for the way to use set this command.
• A command warning will occur and the command will be ignored in the
following cases.
-If parameters are changed mid-operation with CX-Drive: Command
warning 1 (A.95A)
-If CADDRESS is out of the range: Parameter setting warning (A.94A)
-If CSIZE does not match: Parameter setting warning (A.94D)
-If CCMD or CDATA is out of the range: Parameter setting warning
(A.94B)
88
Page 91

4.2 Main Commands
Setting Parameter Initialization Mode Using ADJ Commands
Use the following procedure to select an operation mode.
1. Set to “Parameter Initialization” mode.
Set the command fields to the following settings.
SUBCODE = 01H (fixed)
CCMD = 0004H (data setting: fixed)
CADDRESS = 2000H (operation mode address = 2000H: fixed)
CSIZE = 0002H (size = 2H: fixed)
CDATA = 1005H (operation mode = 1005H: fixed)
After sending the data, wait until CMDRDY of STATUS is equal to 1, and check ERRCODE to confirm
that no error occurred.
2. Execute the parameter initialization.
Set the command fields to the following settings.
SUBCODE = 01H (fixed)
CCMD = 0004H (data setting: fixed)
CADDRESS = 2001H (operation mode address = 2001H: fixed)
CSIZE = 0002H (size = 2H: fixed)
CDATA = 0001H (operation mode execution 0001H: fixed)
After sending the data, wait until CMDRDY of STATUS is equal to 1, and check ERRCODE to confirm
that no error occurred.
3. Set to “Normal mode” after execution.
Set the command fields to the following settings.
SUBCODE = 01H (fixed)
CCMD = 0004H (data setting: fixed)
CADDRESS = 2000H (operation mode address = 2000H: fixed)
CSIZE = 0002H (size = 2H: fixed)
CDATA = 0000H (normal mode: fixed)
When CMDRDY of STATUS changes to 1, the execution is completed.
89
Page 92

4.3 Subcommands
4.3 Subcommands
This section describes the MECHATROLINK-II subcommands applicable with SJDE-ANA-OY
SERVOPACK.
The MECHATROLINK-II subcommands can be used by specifying them with the CONNECT command when MECHATROLINK-II communications starts.
They use the seventeenth to the twenty-ninth bytes of the command and response data.
4.3.1 No Operation (NOP: 00H)
Byte NOP Description
Command Response
17 00H 00H
18 − SUBSTATUS • Not operation command.
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
Processing
classifications
Network command group
Processing time Within commu-
nications cycle
4.3.2 Read Parameter (PRM_RD: 01H)
Byte PRM_RD Description
Command Response
17 01H 01H
18 - SUBSTATUS • Reads a parameter.
19 NO NO
20
21 SIZE SIZE
22 - PARAME23
24
25
26
27
28
29
TER
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command
PRM_RD.
Data communications command group
90
Processing time Within 100 ms
Page 93

4.3.3 Write Parameter (PRM_WR: 02H)
Byte PRM_WR Description
Command Response
17 02H 02H
18 − SUBSTATUS • Writes a parameter.
19 NO NO
20
21 SIZE SIZE
22 PARAME23
24
25
26
27
28
29
TER
PA RA M E -
TER
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command
PRM_WR.
Data communications command group
4.3.4 Read Alarm or Warning (ALM_RD: 05H)
Byte ALM_RD Description
Command Response
17 05H 05H
18 - SUBSTATUS • Reads the alarm or warning.
19 ALM_RD_
20 - ALM_DATA
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
MOD
ALM_RD_
MOD
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command
ALM_RD.
Data communications command group
4.3 Subcommands
Processing time Within 100 ms
Processing time 6 ms to 2 s
91
Page 94

4.3 Subcommands
4.3.5 Write Stored Parameter (PPRM_WR: 1CH)
Byte PPRM_WR Description
Command Response
17 1CH 1CH
18 - SUBSTATUS • Writes a parameter.
19 NO NO
20
21 SIZE SIZE
22 PARAME23
24
25
26
27
28
29
TER
PA RA M E -
TER
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command
PPRM_WR.
Data communications command group
4.3.6 Request Latch Mode (LTMOD_ON: 28H)
Byte LT MO D _O N Description
Command Response
17 28H 28H
18 LT_SGN SUBSTATUS • Sets the modal latch mode.
19 SEL_MON
20 - MONITOR3
21
22
23
24 MONITOR4
25
26
27
28 - 29
3/4
SEL_MON
3/4
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command
LT MO D _O N .
Control command group
Processing time Within 200 ms
Processing time Within commu-
nications cycle
92
Page 95

4.3 Subcommands
4.3.7 Release Latch Mode (LTMOD_OFF: 29H)
Byte LT MO D_ O FF Description
Command Response
17 29H 29H
18 - SUBSTATUS • Releases the modal latch mode.
19 SEL_MON
3/4
20 - MONITOR3
21
22
23
24 MONITOR4
25
26
27
28 - 29
SEL_MON
3/4
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command
LT MO D _O FF.
Control command group
Processing time Within commu-
4.3.8 Status Monitoring (SMON: 30H)
Byte SMON Description
Command Response
17 30H 30H
18 - SUBSTATUS • Reads the monitoring information specified in SEL_MON3/4.
19 SEL_MON
20 - MONITOR3
21
22
23
24 MONITOR4
25
26
27
28 - 29
3/4
SEL_MON
3/4
Processing
classifications
This command has the same function as the main command SMON.
Data communications command group
Processing time Within commu-
nications cycle
nications cycle
93
Page 96

4.4 Combination of MECHATROLINK-II Main Commands and Subcommands
4.4 Combination of MECHATROLINK-II Main Commands and
Subcommands
MECHATROLINK-II subcommands can be used by combining as listed below.
Code Main
Command
00 NOP
01 PRM_RD
02 PRM_WR
03 ID_RD
04 CONFIG
05 ALM_RD
06 ALM_CLR
0D SYNC_SET
0E CONNECT
0F DISCON-
1C PPRM_WR
20 POS_SET
21 BRK_ON
22 BRK_OFF
23 SENS_ON
24 SENS_OFF
25 HOLD
28 LTMOD_ON
29 LTMOD_
30 SMON
31 SV_ON
32 SV_OFF
34 INTERPO-
35 POSING
36 FEED
38 LATCH
39 EX_POSING
3A ZRET
Note: 9: Can be combined.
NECT
OFF
LATE
× : Cannot be combined.
NOP PRM_RDPRM_ WRALM_ RDPPRM_WRLT MO D
99999999
9
9
99999999
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
99999999
9
9
99999999
99999999
99999999
99999999
99999999
99999999
99999
99999
99999
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
× × × × × × 9
Subcommand
LT MO D
_ON
_OFF
× × 9
× × 9
× × 9
SMON
IMPORTANT
If a command with a subcommand that cannot be combined is received, the warning A.95d
or A.95E (see 8.3.2 Warning Display and Troubleshooting for details.) will occur, and the
command will be ignored.
The servo is not OFF and the servomotor is not stopped if a command with a subcommand
that cannot be combined is received during operation.
94
Page 97

4.5 Command Data Field
4.5 Command Data Field
This section describes command data in main commands and subcommands.
4.5.1 Latch Signal Field Specifications: LT_SGN
The latch signal field specifications (LT_SGN) can be designated using the following commands:
LATCH, EX_POSING, ZRET, LTMOD_ON
The latch signal field is used to select latch signals for position data, with the second byte of the above
main commands, or the eighteenth byte reserved area of the subcommands.
Refer to the following table for details on bit allocation.
Latch Signal Field
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
−−−−−− LT _ SG N
Latch Signal Selection
D1 D0 Latch Signal
0 0 Phase Z
01 /EXT1
10 Reserved
11 Reserved
INFOINFO
Set 0 for unused bits.
4.5.2 Option Field Specifications: OPTION
The option field cannot be used. Set 0 for all bits.
Refer to the following table for details on bit allocation.
Option Field
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00000000
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
00000000
95
Page 98

4.5 Command Data Field
4.5.3 Status Field Specifications: STATUS
The status field is used to monitor the Servo status with the third to fourth byte reserved area of the
main commands.
Refer to the following table for details on bit allocation.
Status Field
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PSET ZPOINT − PON SVON CMDRDY WARNG ALM
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
−−N_SOT P_SOT NEAR L_CMP T_LIM DEN
Alarm (ALM)
Indicates alarm occurrence.
D0 Status
0
No alarm (Normal)
1
Alarm occurred.
Warning (WARNG)
Indicates the warning occurrence.
D1 Status
0
No warning (Normal)
1
Warning occurred.
Command ready (CMDRDY)
Indicates whether the command can be received or not.
No command can be received if the SERVOPACK is in busy status. The SERVOPACK will continue exe-
cuting the previously received command.
D2 Status
0
Command cannot be received (busy).
1
Command can be received (ready).
Servo ON (SVON)
Indicates the servo ON/OFF status.
D3 Status
0
Servo OFF
1
Servo ON
96
Page 99

Main power supply ON (PON)
Indicates the status of the main power supply.
D4 Status
0
Main power supply OFF
1
Main power supply ON
4.5 Command Data Field
INFOINFO
D4 will remain set to 0 and the main power supply will be turned OFF for a maximum of 300 ms.
Home position (ZPOINT)
Indicates if the feedback position (APOS) is within or outside the home position range.
Home position
range
Machine coordinate
system APOS
Home position (0)
D6 Status
0
The feedback position (APOS) is within the home position range.
1
The feedback position (APOS) is outside the home position range.
The home position range can be set in the following parameter.
The setting will be immediately written in the SERVOPACK.
Parameter
No.
Pn803 Home posi-
INFOINFO
Name Data Size Min.
tion range
After completion of the following operations, a ZPOINT signal should be detected. If not, the operation was not successfully completed.
1. Homing (ZRET) operation
2. Coordinates setting by having set the reference point (REFE=1) by using POS_SET (coordinates setting)
2 bytes 0 250 Reference
Set Value
Within range.
Home position
width (Pn803)
Max.
Set Value
Units Factory
unit
Setting
10
97
Page 100

4.5 Command Data Field
Positioning completion (PSET)
Indicates the completion of positioning.
Positioning complete
range
Machine coordinate
system APOS
Target position
D7 Status
0
Other than the status 1.
1
Output completion (DEN = 1) and the feedback position (APOS) are within the
positioning complete range.
The positioning complete width can be set in the following parameter.
The setting will be immediately written in the SERVOPACK.
Parameter
No.
Pn522 Positioning
Name Data Size Min.
complete
width
4 bytes 0 1073741824 Reference
Set Value
Positioning complete
width (Pn522)
Max.
Set Value
Within range.
Units Factor y
unit
Setting
10
98
 Loading...
Loading...