Okidata OKIPAGE 10ex Service Manual

Front Cover
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 0 Introduction
OKIPAGE 10ex
To propel your company into the future, you need technology that fits the way you work. You need the OKIPAGE® 10ex,
the best-featured desktop printer in its class. This digital LED printer combines professional performance with
excep-tional value, for years of high-quality documents and low ongoing operating costs.
Adobe Acrobat printable reference copy
of the OKIDATA Service Training Manual.
05/13/98
Note: This Adobe Acrobat version of the Okidata Service Training Manual was built with the pictures
rendered at 300 dpi, which is ideal for printing, but does not display well on most displays.
Table of Contents Page
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
0 Introduction
Introduction 1
1 Specifications
1.1 System Configuration 2
1.2 Printer Configuration 3
1.3 Optional Configuration 4
1.4 Specification 5
1.5 Safety Standards 6
....1.5.1 Certification Label 7
....1.5.2 Warning Label 8
....1.5.3 Warning/Caution Marking 9
2 Operation
Operation Description 10
2.1 Main Control Board 11
2.2 Power Supply/Sensor Board 12
2.3 Electrophotographic Process 13
....2.3.1 Electrophotographic Process Mechanism 14
....2.3.2 Electrophotographic Process 15
....2.3.3 Process Operation Descriptions 16
....2.3.4 Revision of LED Head Illumination 17
2.4 Paper Jam Detection 18
2.5 Cover Open 19
2.6 Toner Low Detection 20
3 Disassembly
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement 21
3.2 Parts Layout - [Lower base unit] 22
........[Upper cover unit] 23
........[Base unit] 24
3.3 How to Change Parts 25
....3.3.1 Upper Cover Assy 26
....3.3.2 IC Card Cover 27
....3.3.3 LED Head 28
....3.3.4 Operator Panel Assy 29
....3.3.5 Lower Base Unit 30
....3.3.6 Pulse Motor Main/Drum 31
....3.3.7 Pulse Motor (Registration) 32
....3.3.8 Face Up Stacker Assy 33
....3.3.9 Hopping Roller Assy 34
....3.3.10 Motor Assy 35
....3.3.11 Hopping Roller Shaft Assy 36
....3.3.12 Stacker Cover Assy 37
....3.3.13 Registration Roller 38
....3.3.14 Transfer Roller Assy 39
....3.3.15 Fusing Unit 40
....3.3.16 Back-up Roller 41
....3.3.17 Sensor Plate (Inlet) 42
....3.3.18 Sensor Plate (Outlet) 43
....3.3.19 Manual Feed Guide Assy 44
....3.3.20 Sensor Plate (Paper Supply) 45
Table of Contents Page
....3.3.21 Main Control M5B-PCB 46
....3.3.22 Transformer 47
....3.3.23 Power Supply/Sensor Board and Contact Assy 48
....3.3.24 Cassette Guide L Assy 49
....3.3.25 Cassette Guide R 50
....3.3.26 Spacer Bearing (L/R) 51
4 Adjustments
4. Adjustment 52
4.1 Maintenance Modes and Functions 53
....4.1.1 User Maintenance Mode 54
....4.1.2 System Maintenance Mode 55
....4.1.3 Engine Maintenance Mode 56
....4.1.4 EEPROM Initialization 57
4.2 Adjustment When Replacing a Part 58
4.2.1 Setting of LED Head Drive Time 59
4.2.2 Uploading/Downloading EEPROM data 60
5 Maintenance
5.1 Periodical Replacement Parts 61
5.2 Cleaning 62
....5.2.1 Cleaning of LED Lens Array 63
....5.2.2 Cleaning Page Function 64
6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Troubleshooting Tips 65
6.2 Points to Check before Correcting Image Problems 66
6.3 Tips for Correcting Image Problems 67
6.4 Preparation for Troubleshooting 68
6.5 Troubleshooting Flow 69
....6.5.1 LCD Status Message/Problem List 70
....6.5.2 LCD Message Troubleshooting 71
........(1) The printer does not work normally after the power is
turned on.
........(2) [JAM error] 73
............Paper input jam 74
............Paper feed jam 75
............Paper exit jam 76
........(3) Paper size error 77
........(4) Fusing unit error (ERROR 71) (ERROR 72) (ERROR
73)
........(5) SSIO error (ERROR 74) 79
........(6) Fan error (ERROR 70) 80
....6.5.3 Image Troubleshooting 81
........(1) Images are light or blurred entirely 82
........(2) Dark background density 83
........(3) Blank paper is output 84
........(4) Black vertical belts or stripes 85
........(5) Cyclical defect 86
........(6) Prints voids 87
........(7) Poor fusing 88
........(8) Vertical belts or streaks 89
........Figure 6-4 90
72
78
Table of Contents Page
........Figure 6-5 91
7 Wiring Diagram
7.1 Interconnect Signal Diagram 92
7.2 PCB Layout and Connector Signal List 93
7.3 Resistance Check 94
7.4 Short Plug Setting 95
8 Parts List
Lower Base Unit 96
Upper Cover Unit 97
Base Unit 98
A Centronics Parallel
Centronics Parallel Interface 99
B Loop Test (RS-232C Interface)
Loop Test (RS-232C Interface) 100
C Diagnostics Test
1. Maintenance Modes 101
....1.1 User Maintenance Mode 102
....1.2 System Maintenance Mode 103
....1.3 Engine Maintenance Mode 104
....1.4 User Factory Set Operation 105
Product Accessory 1: RS-232C Serial Interface (Option)
RS-232C Serial Interface (Option) 106
Product Accessory 2: Multi-Purpose Feeder Maintenance
1. PREFACE 107
....1.1 Functions 108
....1.2 External View and Component Names 109
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTION - General Mechanism 110
....2.2 Hopper Mechanism 111
3. PARTS REPLACEMENT 112
....3.1 Precautions Concerning Parts Replacement 113
....3.2 Parts Layout 114
....3.3 Parts Replacement Methods 115
........3.3.1 Link 116
........3.3.2 Separator 117
........3.3.3 OLEV-11 PCB 118
........3.3.4 Pulse Motor 119
........3.3.5 Planet Gear 120
........3.3.6 Roller-A and B 121
4. TROUBLESHOOTING - Precautions Prior to the
Troubleshooting
....4.2 Preparations for the Troubleshooting 123
....4.3 Troubleshooting Method 124
........4.3.1 LCD Status Message List 125
5. CONNECTION DIAGRAM - Interconnection Diagram 126
....5.2 PCB Layout 127
6. PARTS LIST 128
Product Accessory 3: High Capacity 2nd Paper Feeder
High Capacity Second Paper Feeder Maintenance 129
....1. OUTLINE - Functions 130
....1.2 External View and Component Names 131
122
Table of Contents Page
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTION - General Mechanism 132
....2.2 Hopper Mechanism 133
3. PARTS REPLACEMENT 134
....3.1 Precautions Concerning Parts Replacement 135
....3.2 Parts Layout 136
....3.3 Parts Replacement Methods 137
........3.3.1 Stepping Motor (Hopping) 138
........3.3.2 TQSB-2 PCB 139
........3.3.3 Hopping Roller Shaft Assembly and One-way Clutch
140
Gear
4. TROUBLESHOOTING - Precautions Prior to the
141
Troubleshooting
....4.2 Preparations for the Troubleshooting 142
....4.3 Troubleshooting Method 143
........4.3.1 LCD Status Message List 144
5. CONNECTION DIAGRAM 145
....5.1 Interconnection Diagram 146
....5.2 PCB Layout 147
6. PARTS LIST 148
....2nd Tray ASSEMBLY 149
....SECTION 1 CABINET & CASSETTE ASSEMBLY 150
....SECTION 2 MECHANICAL ASSEMBLY 151
....2nd Tray Parts List 152

Page: 1
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 0 Introduction
Introduction
This Service Handbook describes the field maintenance methods for OKIPAGE 10ex Digital LED Printer. This manual is
written for use by the maintenance personnel. Please note that you should refer to the Printer Handbook and Printer
Setup for the handling and operating methods of the equipment.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.1 System Configuration
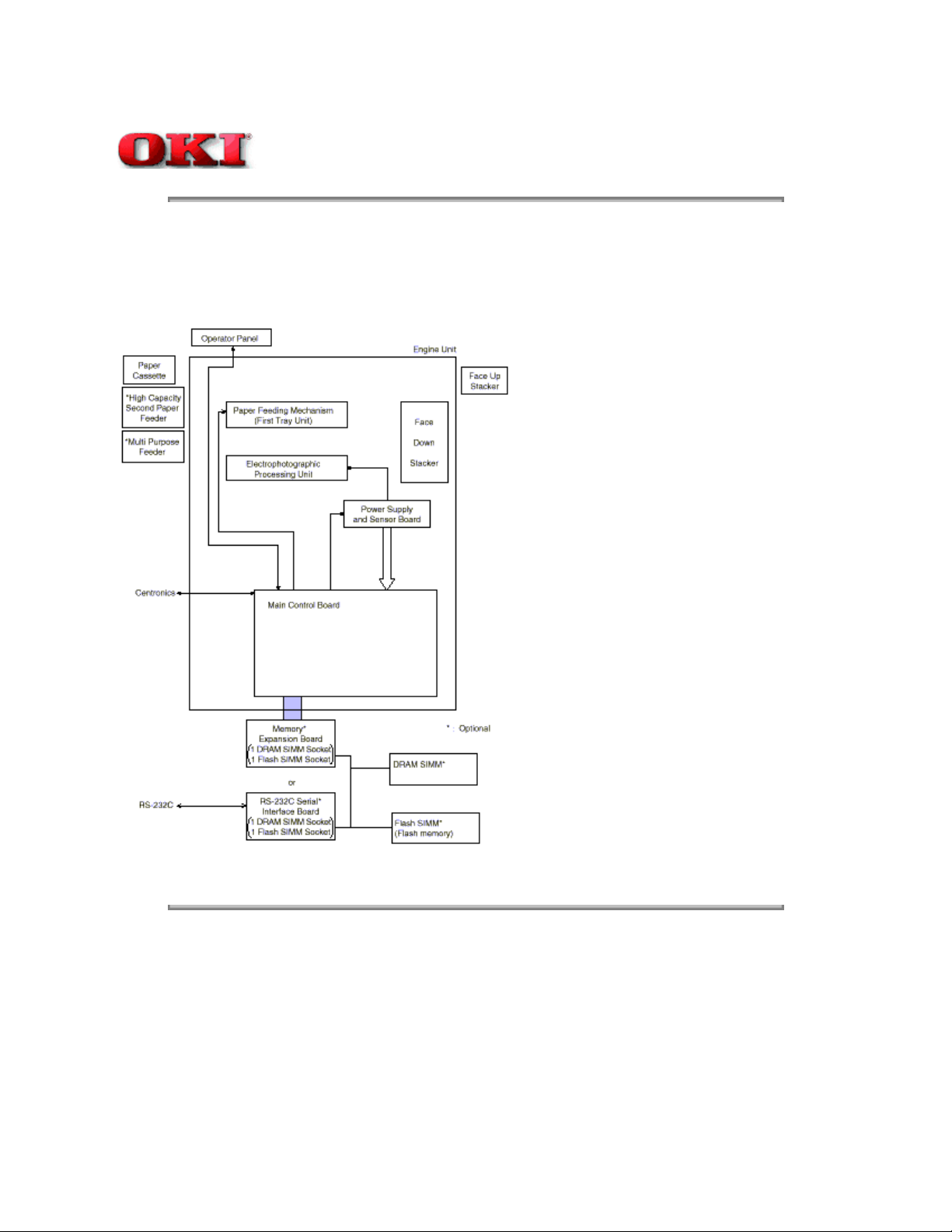
OKIPAGE 10ex consists of control and engine blocks in the standard configuration, as shown in Figure 1-1.
In addition, the options marked with asterisk (*) are available.
Page: 2
Figure 1-1
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
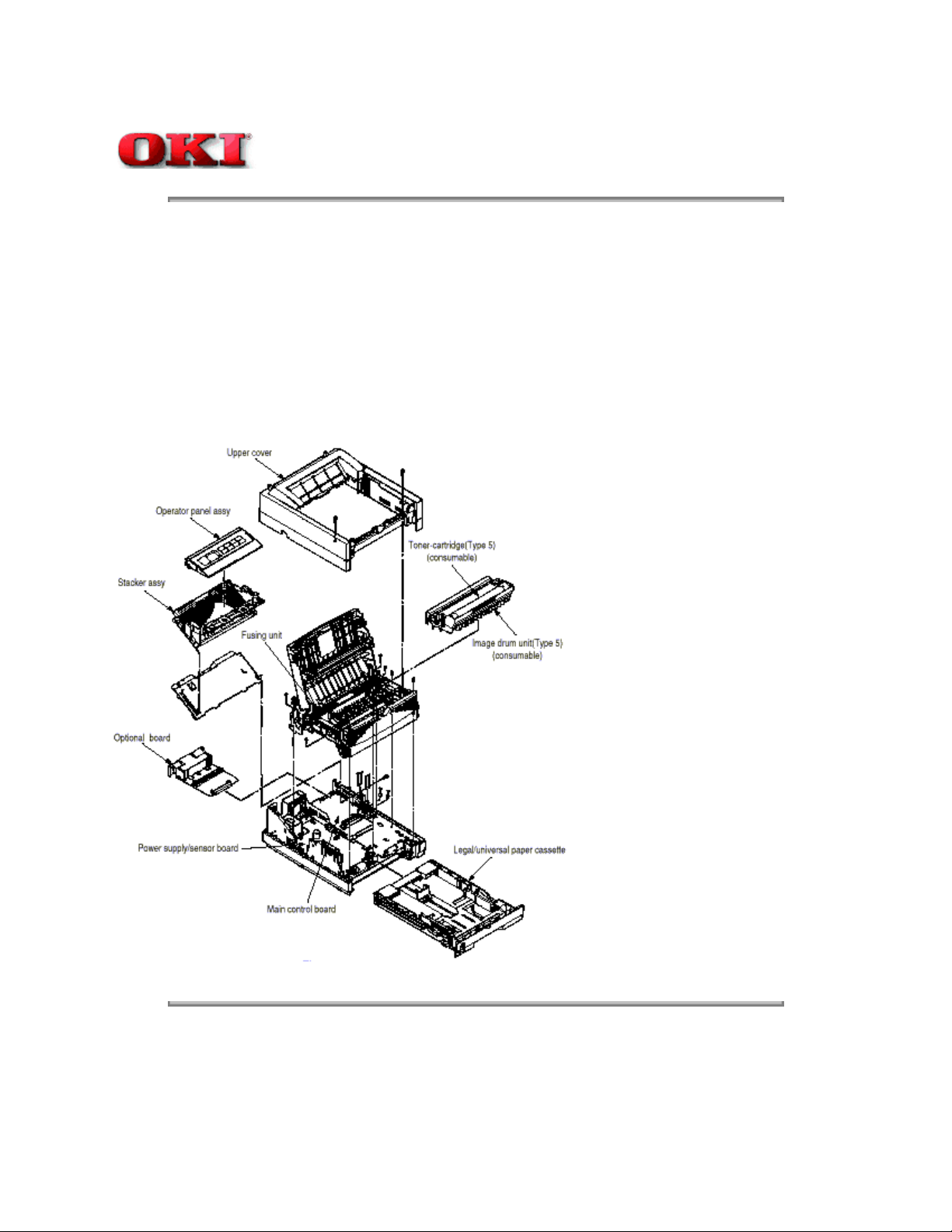
1.2 Printer Configuration
The printer unit consists of the following hardware components:
Electrophotographic Processorl
Paper Feederl
Controllerl
Operator Panell
Power Supply Unitl
The printer unit configuration is shown in Figure 1-2.
Page: 3
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 4
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.3 Optional Configuration
The options shown below are available for use with OKIPAGE 10ex. These are available separately from the printer unit.
(1) High Capacity Second Paper Feeder
(2) Multi-Purpose Feeder
(3) 1 MB Memory Expansion Board
(4) RS-232C Serial Interface Board
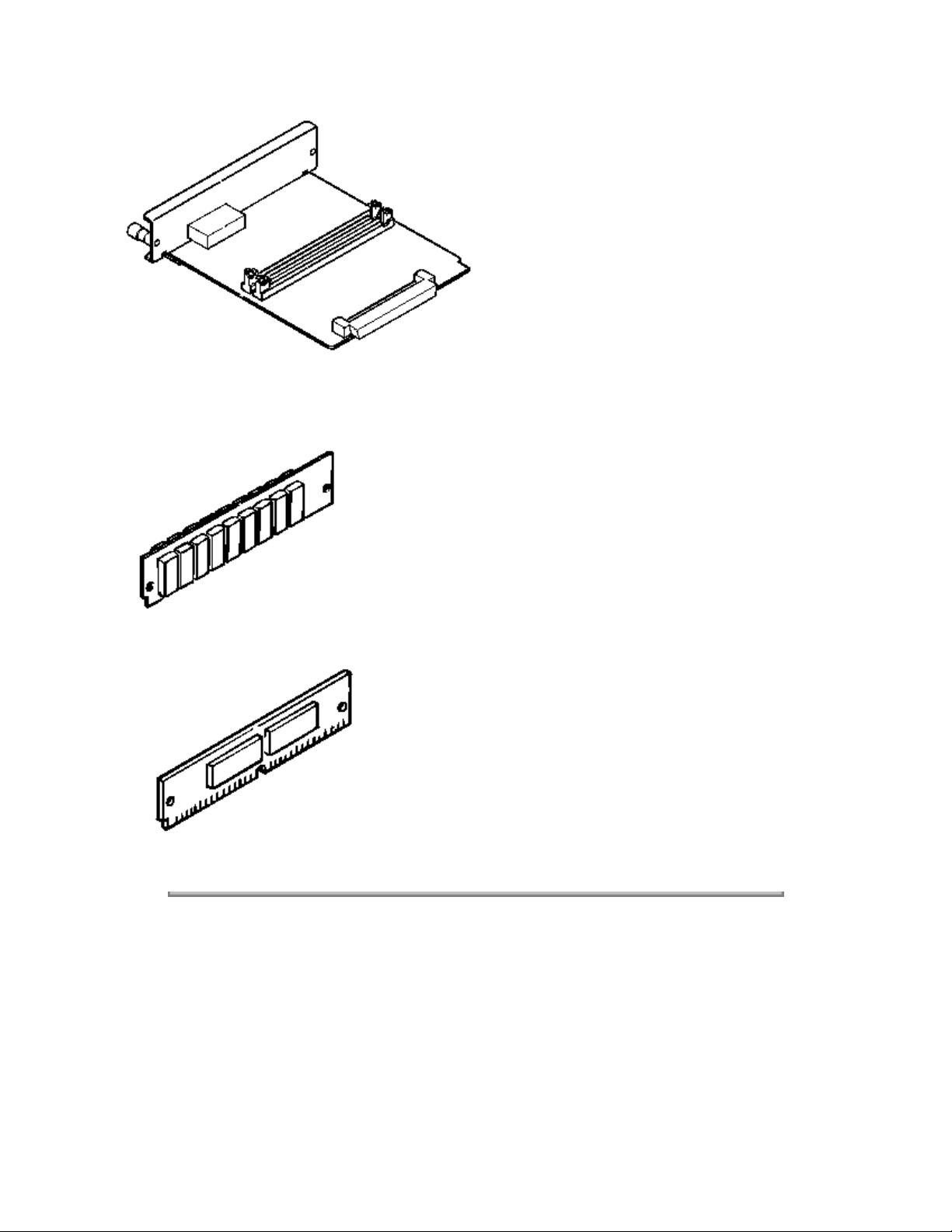
(5) DRAM SIMM Memory
DRAM SIMM memory is available with memory of 1 MB (min.) to 32 MB (max.). The access time of SIMM memories are
60ns, 70ns, 80ns, and 100ns.
(6) Flash SIMM
Flash SIMM is available with memory of 4 MB and 8 MB.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
1.4 Specification
(1) Type: Desktop
(2) Outside dimensions Height: 7.9" (200 mm)
Width 13.0" (330 mm)
Depth 15.6" (395mm)
(3) Weight 22 lbs. (10 kg)
Page: 5
Chapter 1 Specifications
(4) Development method
Exposure method
(5) Paper used <Type>
Dry electrophotography LED stationary head
Standard paperl
- Xerox 4200 (20 lbs)
Application paper (manual face-up feed)l
- Label
- Envelope
- OHP paper (Transparency)
<Size>
Standardl
Letter
Legal * [*Without Mutli-Purpose Feeder (Option)]
Legal-13*
Executive
-COM-10** [**manual feed and Multi-Purpose Feeder (Option)
only]
Monarch**
DL**
C5**
B5 (JIS)
A6
Applicable sizesl
- Width: 3.87" x 8.5" (116 to 216 mm)
- Length: 5.83" to 14" (148 to 355.6 mm)
<Thickness>
- Automatic feed: 16 to 28 lbs (60 to 135 g/m2)
- Manual feed: Label, OHP paper (transparency), Envelope (24 to
28 lbs.)
(6) Printing speed: First print: 12 seconds typical for the Letter size paper after
warm-up
Continuous print: 10 pages per minute with Letter size paper.
[Except Second Paper Feeder (8.8 PPM), Multi-Purpose Feeder
(8.3 PPM)]
Warm-up time: 60 seconds typical at room temperature [68o F (20o
C), AC 120/230 V].(120 VAC for ODA, 230 VAC for OEL/INT)
(7) Paper feeding method Automatic paper feed or manual paper feed
(8) Paper delivery
Face down/face up
method
(9) Resolution 600 dpi x 600 dpi (true)
600 x 1200 dots/inch graphics
(10) Power input 230 VAC +/-10%
120 VAC +/-15% for
(11) Power consumption Peak: Approx. 460W
Typical operation: Approx. 215W
Idle: Approx. 61W
Power save mode: Approx. 18W
(12) Temperature and
humidity
In operation Power off mode During Storage Unit
Temperature 50-90
(10-32)
32-110
(0-43)
14-110
(-10-43)
Humidity 20-80 10-90 10-90 %RH
Maximum wet bulb
temperature
Minimum difference
between wet and
77
(25)
35.6
(2)
80.4
(26.8)
35.6
(2)
-----
-----
dry bulb
o
F
o
C
o
F
o
C
o
F
o
C
temperatures
1. Storage conditions specified above apply to printers in packed condition.
2. Temperature and humidity must be in the range where no condensation occurs.
(13) Noise During operation: 50 dB (A) or less
Standby: 38 dB (A) or less
Quite mode: Back ground level
(14) Consumables Toner cartridge kit - 2,000 (5% duty) ---- 45g cartridge kit
Image drum cartridge - 20,000 (at continuous printing); 14,000 (3
page/job) without Power Save
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.5 Safety Standards
1.5.1 Certification Label
1.5.2 Warning Label
1.5.3 Warning/Caution Marking
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 6
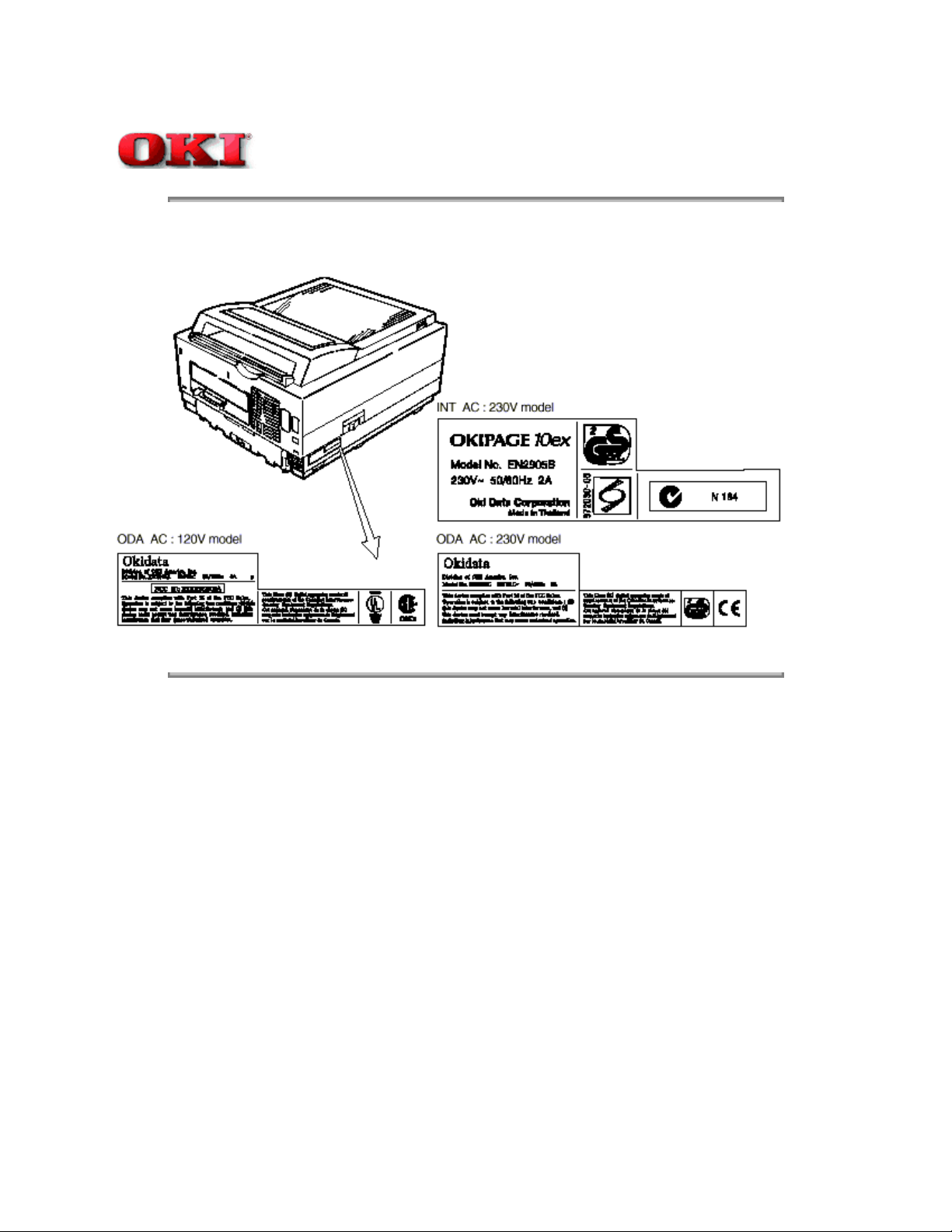
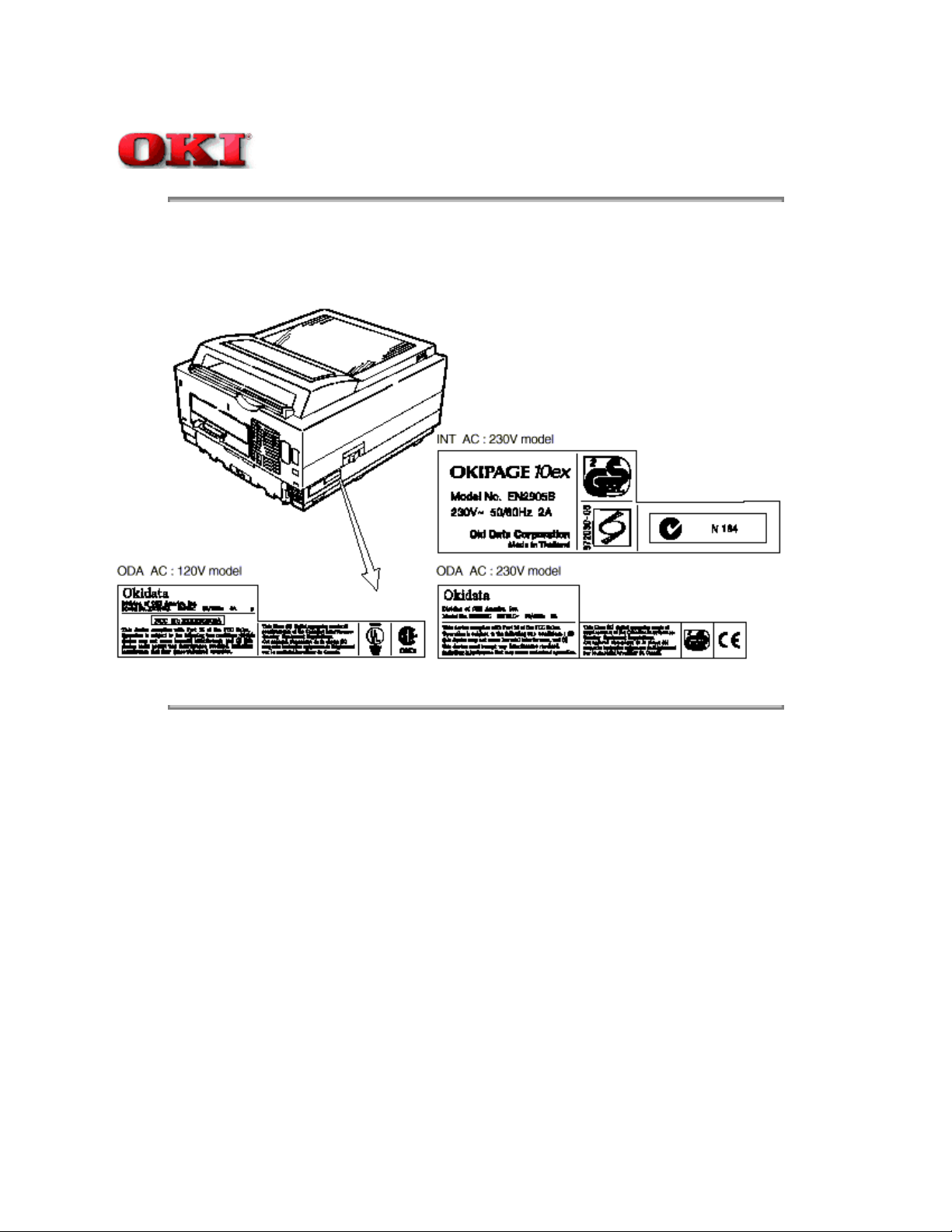
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.5.1 Certification Label
The safety certification label is affixed to the printer in the position described below.
Page: 7
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.5.2 Warning Label
The warning labels are affixed to the sections which may cause bodily injury.
Follow the instructions on warning labels during maintenance.
Page: 8
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
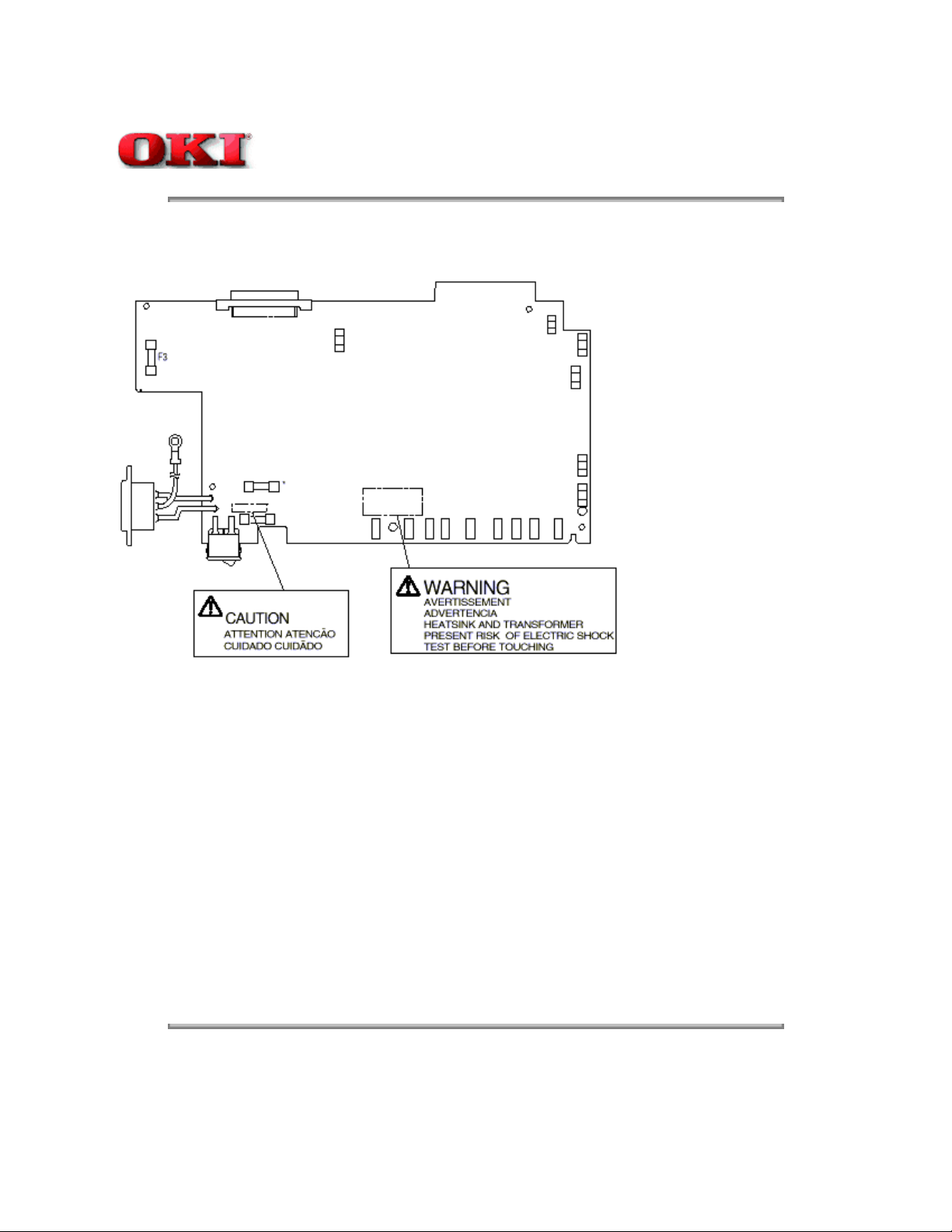
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.5.3 Warning/Caution Marking
The following warning and caution markings are made on the power supply/sensor board.
Page: 9
* No fuse is mounted here for 200V series.
ENGLISH - Heatsink and transformer core present risk of electric shock. Test before touching.
FRENCH - Le dissipateur thermique et le noyau du transformateur présentent des risques de choc électrique. Testez
avant de manipuler.
SPANISH - Las disipadores de color el núcel del transformador pueden producir un choque eléctrico. Compruebe antes
de tocar.
PORTUGUESE - O dissipador de calor e o núcleo do fransiormador apresentam risco de choque elétrico. Teste antes
de focar.
ENGLISH - Circuits maybe live after fuses open.
FRENCH - Il se peut que les circuits soient sous tension une fois que les fusibles ont éfé rerirés.
SPANISH - Las circuitos pueden estar activos una vez que se hayan abierio los fusibles.
PORTUGUESE - Os circuitos podem estar energizados após os fusiveis se queimarem.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 10
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
Operation Description
OKIPAGE 10ex consists of a main control board, a power supply/sensor board, an operator panel, an
electrophotographic process mechanism, and revision for illumination of LED head.
The main control board receives data via the host I/F, it then decodes, edits and stores the data in memory. After
completing the editing of a single page of data, it references the font memory and generates bit image data, which is
transferred to the LED head in one dot line units.
Through the electrophotographic process mechanism, the data is printed on the paper.
The operator panel is used for operations and status display.
OKIPAGE 10ex block diagram is shown in Figure 2-1.
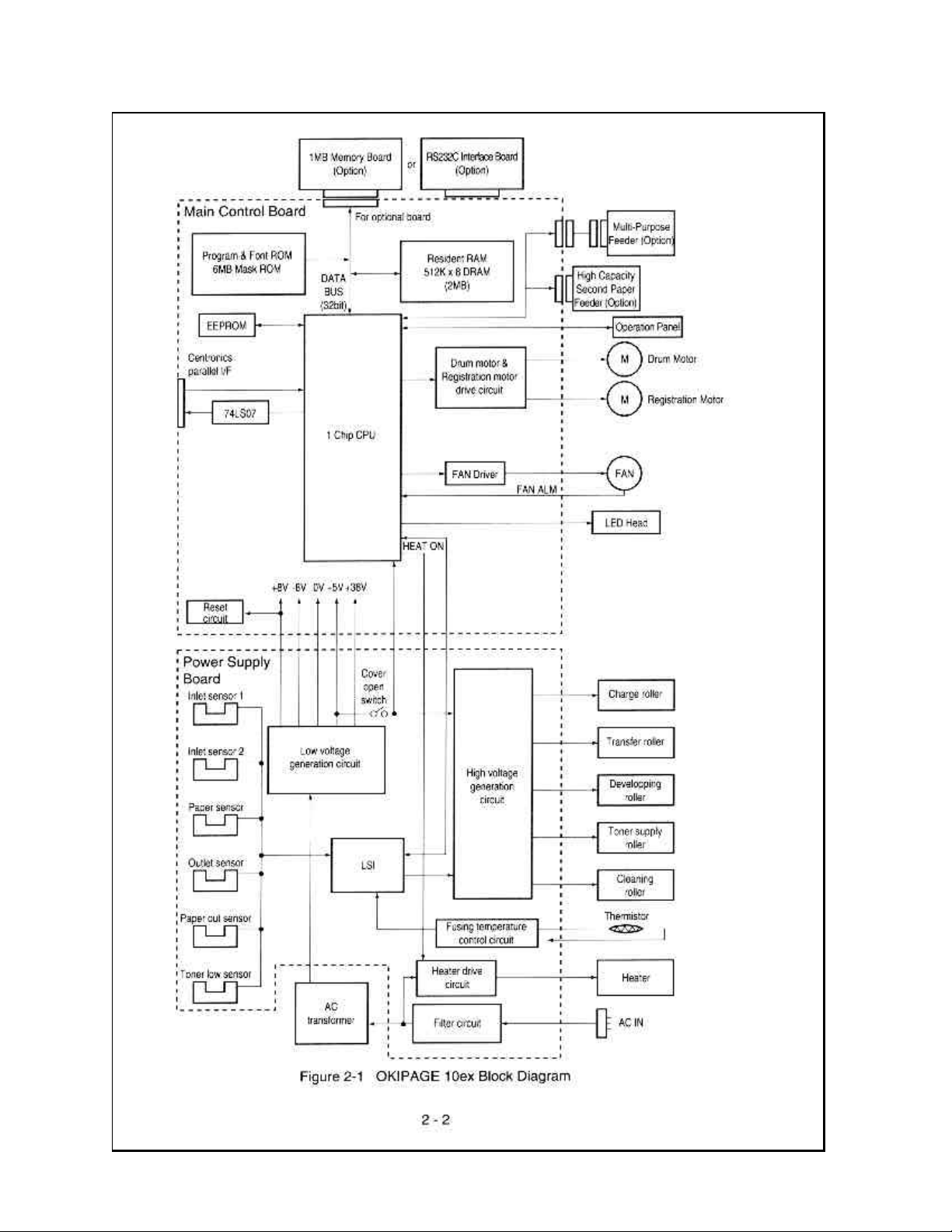

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 11
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
2.1 Main Control Board
The main control board consists of a single chip CPU, two program/font ROMs, four DRAMs, an EEPROM, a host
interface circuit, and a mechanism driving circuit.
(1) Single chip CPU
The single chip CPU is a custom CPU (32-bit internal bus, 32-bit external bus, 28.24-MHz clock, with input frequency
from a 7.06-MHz clock) which incorporates the RISC CPU and its peripheral devices, and has the following functions:
Built-in Device Function
Chip select controller
Control of ROM, DRAM and I/O device.
Bus controller
DRAM controller
DMA controller Transfer of image data from DRAM to video output port.
Parallel interface controller Control of Centronics parallel interface.
Serial interface controller Control of RS-232C serial interface.
Video output port
Controls LED head.
LED STB output port
Timer Generation of various control timing
Monitoring of paper running and paper size.
I/O Port Input and output of sensor and motor signals.
(2) Program and Font ROMs
The Program and Font ROMs store the equipment program and various types of fonts. Mask ROM is used as Program
and Font ROMs. The mounting locations of these Program and Font ROMs vary depending on the type of the ROMs.
(3) DRAM
The DRAM is a 2MB resident memory on the main control board that stores edited data, image data, DLL data and
macro data.
(4) EEPROM
1,024-bit Electrically Erasable PROM (EEPROM), is loaded with the following kinds of data:
Menu datal
Various counter data (page counter, drum counter)l
Adjusting parameters (LED head drive time, print start position, paper feed length)l
(5) Parallel Interface
Parallel data is received from a host system via parallel interface which conforms to the IEEE 1284 specification.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 12
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
2.2 Power Supply/Sensor Board
The power supply/sensor board consists of an AC filter circuit, a low voltage power supply circuit, a high voltage power
supply circuit, heater drive circuit, and photosensors.
(1) Low Voltage Power Supply Circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages.
Output voltage Application
+5 V Logic circuit supply voltage.
+38 V Motor and fan drive voltage and source voltage for high-voltage supply.
+ 8 V RS-232C line voltage.
- 8 V RS-232C line voltage and PS board supply voltage.
+ 3.3 V LED head supply voltage
(2) High Voltage Power Supply Circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages required for electrophotographic process from +5 V, according to the control
sequence from the main control board. When cover open state is detected, +5 V supply is interrupted automatically to
stop the supply of all high-voltage outputs.
Output Voltage Application
CH -1.3 KV Voltage to be applied to charge roller.
DB -265 V/+300 V Voltage to be applied to a developing roller.
SB -500 V/ 0 V Voltage to be applied to a sponge roller.
CB +400 V/+3.5 KV Voltage to be applied to a cleaning roller.
TR +500 V to +3.5 KV/-1100 V Voltage to be applied to a transfer roller. (Variable)
(3) Photosensor
The photosensor mounted on this power supply/sensor board monitors the status of paper being fed through the printer
during printing.
The sensor layout diagram is shown in Figure 2-2 below.
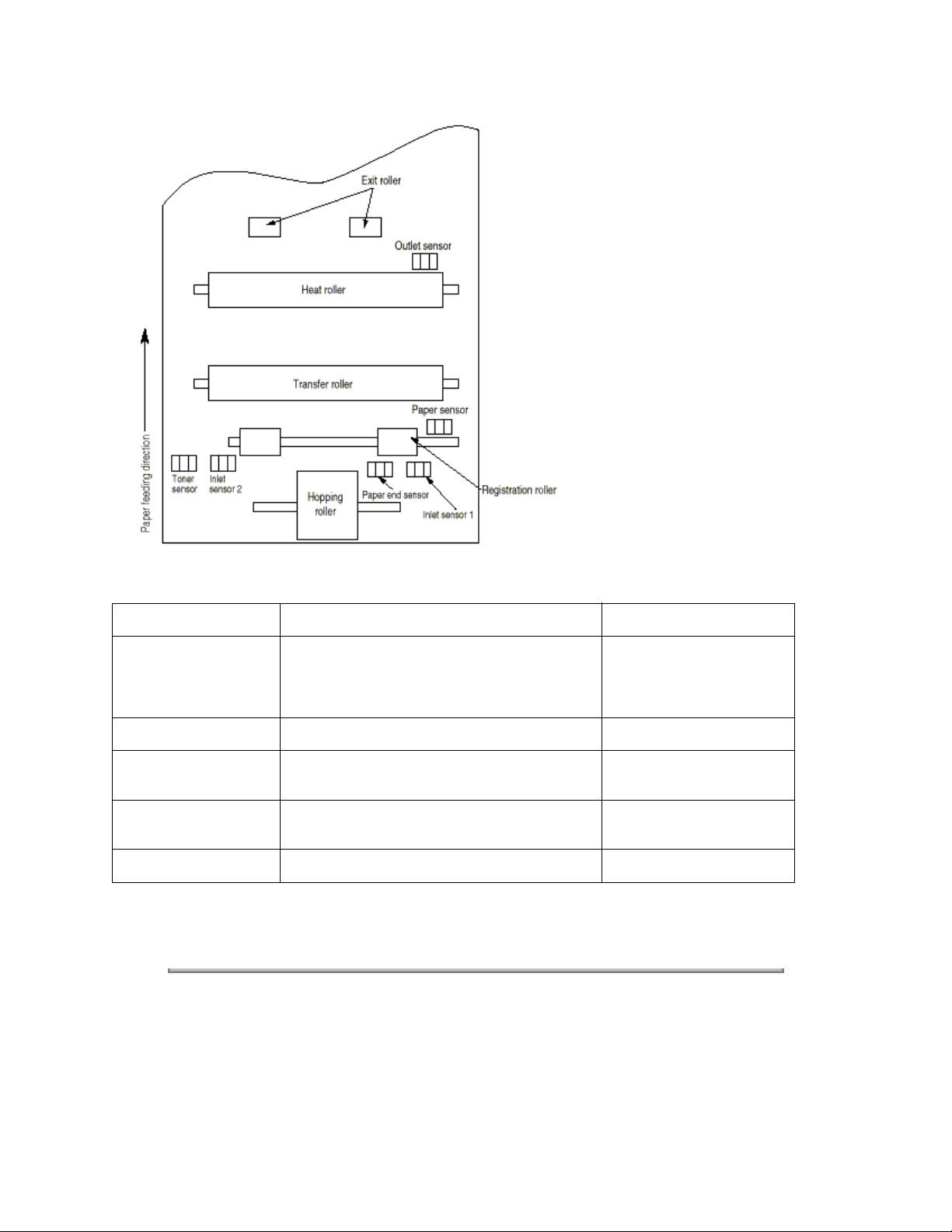
Figure 2-2
Sensor Function Sensing State
Inlet sensor 1 Detects the leading part of the paper and gives the
monitor timing for switching from hopping operation
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
to feeding operation. Monitors paper feeding
situation and paper size based on the paper arrival
time and running time.
Inlet sensor 2 Detects the paper width. ON: A4 or larger.
OFF: Smaller than A4.
Paper sensor Detects the leading portion of the paper. Monitors
paper feeding situation.
Output sensor Monitors paper feeding and size according to the
time of arrival to and leaving past the sensor.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
Toner sensor Detects the lack of toner. - - - - -
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
2.3 Electrophotographic Process
2.3.1 Electrophotographic Process Mechanism
2.3.2 Electrophotographic Process
2.3.3 Process Operation Descriptions
2.3.4 Revision of LED Head Illumination
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 13

Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
2.3.1 Electrophotographic Process Mechanism
This mechanism actuates the printing of image data supplied by the main control board on the paper by
electrophotographic process.
The layout of the electrophotographic process mechanism is shown in Figure 2-3.
Page: 14
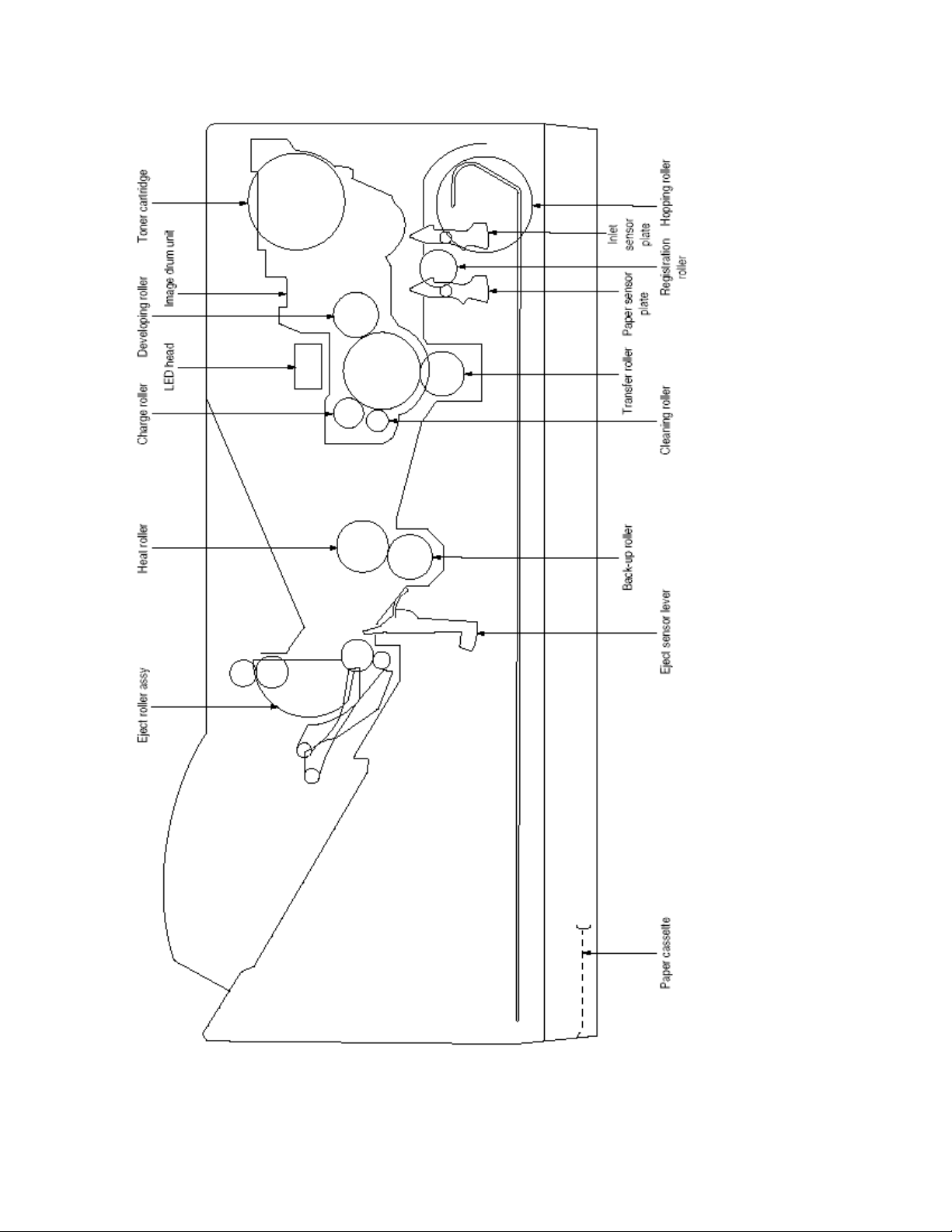
(1) Image Drum Unit

The image drum unit consists of a sensitive drum, a charger, and a developer. The unit forms a toner image on the
sensitive drum, using a electrostatic latent image formed by the LED head.
(2) Registration Motor
The registration motor is a pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation with two-phase excitement by the signal from the main
control board. It drives the hopping and registration rollers via two one-way clutches according to the direction of
rotation.
(3) Main (Drum) Motor
The main or drum motor is a pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation with two-phase excitement by the signal from the main
control board and is the main motor of this mechanism.
(4) LED Head
Image data for each dot line from the main control board is received by the shift register and latch register. The 4992
LED's are driven to radiate the image data on the image drum.
(5) Fuser
The fuser consists of a heater, a heat roller, a thermistor and a thermostat.
The AC voltage from the power supply/sensor board is applied to the heater controlled by the HEATON signal from the
main control board. This AC voltage heats the heater. The main control board monitors the heat roller temperature via
the thermistor, and regulates the heater roller to keep it at a designated temperature in the menu, depending on the
thickness of the paper (tray 1&2: light=165°C, medium light=170°C, medium=175°C, medium heavy and heavy=195°C;
manual feeding and power envelope feeder: light=175°C, medium light=180°C, medium=185°C, medium heavy=190°C,
heavy=195°C, transparency = 160°C) by connecting or disconnecting the AC voltage supply to the heater.
When an abnormal rise of the heater roller temperature takes place, the thermostat of the heater voltage supply circuit
becomes active and forcibly cuts the AC voltage supply.
The temperature setting of the fuser can be changed through operator panel setting.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 15
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
2.3.2 Electrophotographic Process
The electrophotographic processing is outlined below. The electrophotographic printing process is shown in Figure 2-4
(see below).
1 Charging
The surface of the image drum is charged uniformly with a negative charge by applying the negative voltage to the
charge roller.
2 Exposure
Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of the image drum. The surface potential of
the irradiated portion of the image drum surface becomes lower, forming the electrostatic latent image associated with
the print image.
3 Developing and toner recovery
When the negatively charged toner is brought into contact with the image drum, it is attracted to the electrostatic latent
image by static electricity, making the image visible. At the same time, the residual toner on the image drum is attracted
to the developing roller by static electricity.
4 Transfer
When paper is placed over the image drum surface, the positive charge which is opposite in polarity to that of the toner,
is applied to the reverse side of the paper by the transfer roller. The toner is attracted by the positive charge and is
transferred onto the paper. This results in the transfer of the toner image formed on the image drum onto the paper.
5 Temporary cleaning
Residual toner which remains on the image drum without being transferred is evened out by the cleaning roller and is
temporarily attracted to the cleaning roller by static electricity.
6 Fusing
The toner image transferred onto the paper is fused to the paper by heat and pressure.
An electrophotographic process timing chart is shown in Figure 2-5 (see last chart below).
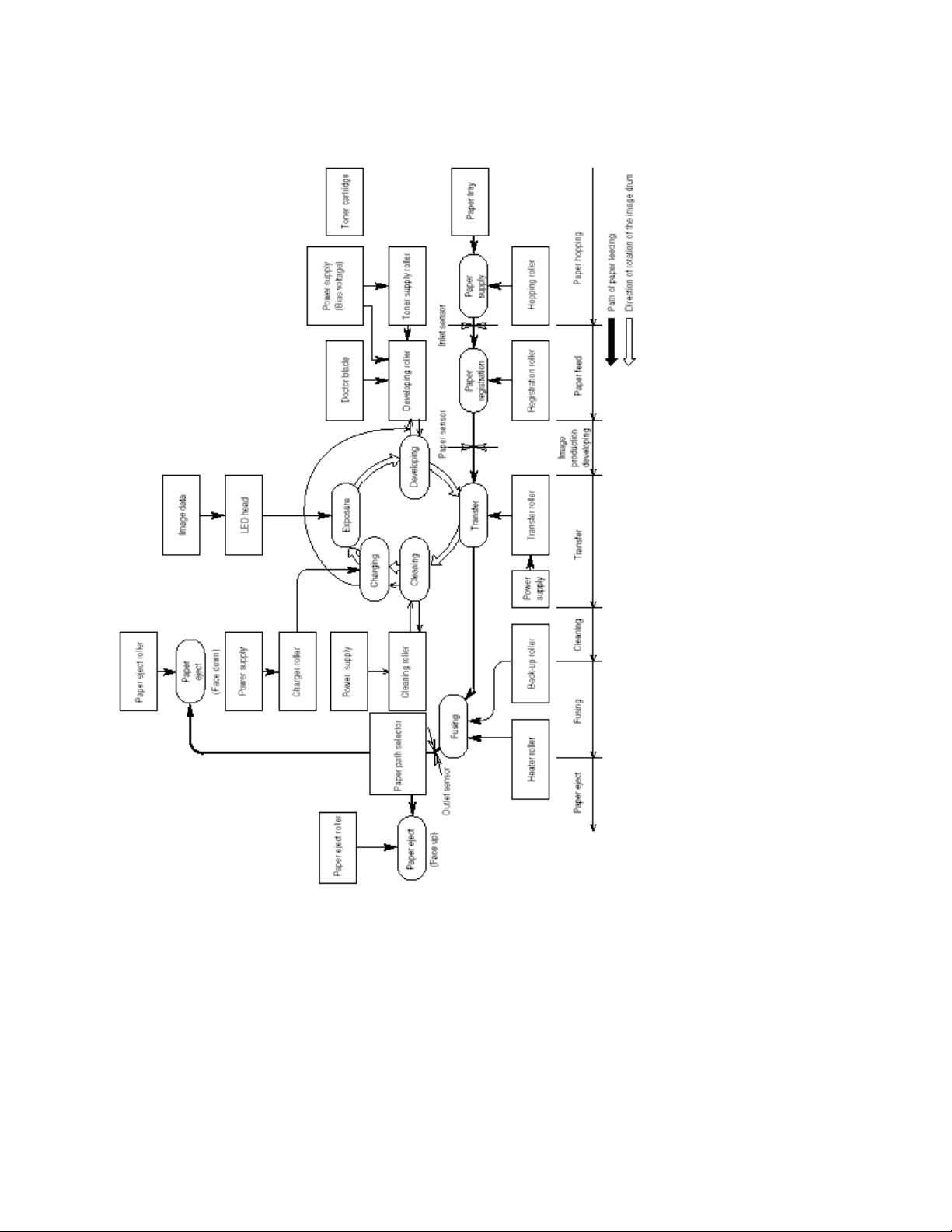
Figure 2-4
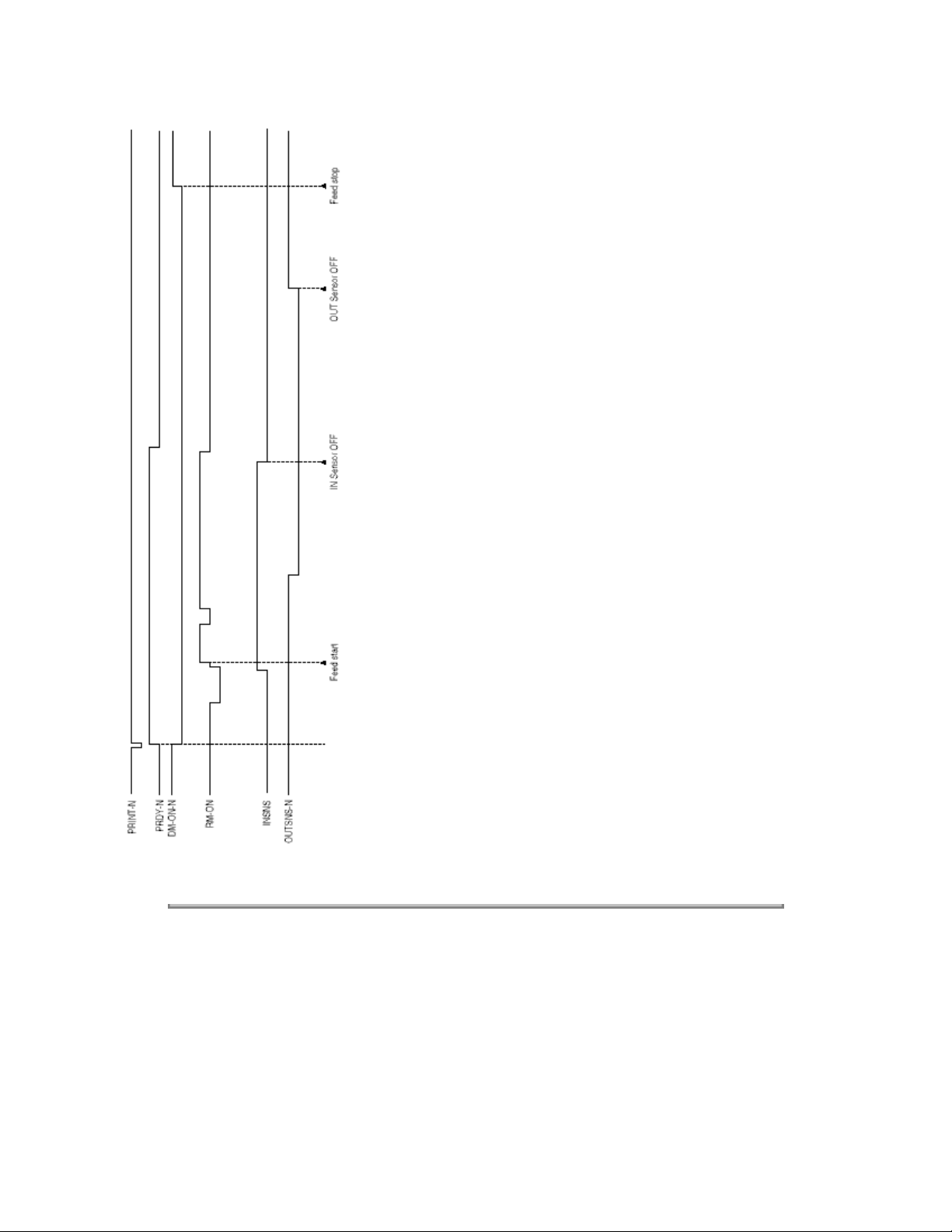
Figure 2-5
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OKIPAGE 10ex
Chapter 2 Operation
2.3.3 Process Operation Descriptions
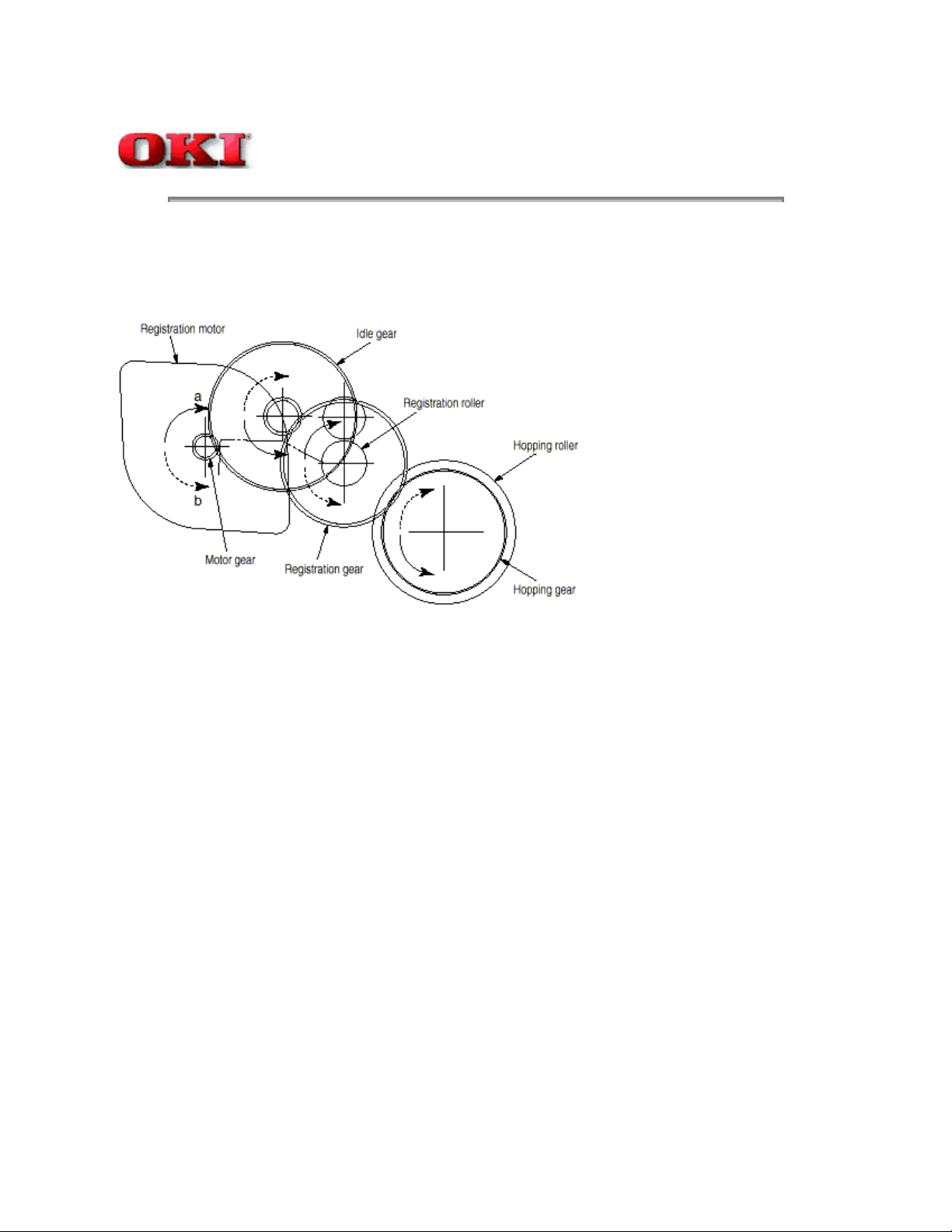
(1) Hopping and Feeding
Hopping and feeding motions are actuated by a single registration motor in the mechanism as shown below:
Page: 16
The registration motor turning in direction "a" drives the hopping roller. The registration motor turning in direction "b"
drives the registration roller. The registration and hopping gears have one-way bearing, so turning any of these gears in
the reverse direction will not transmit the motion to the corresponding roller.
(a) Hopping
1 For hopping, the registration motor turns in direction "a" (clockwise direction) and drives the hopping roller to advance
the paper until the inlet sensor turns on (in this case, the registration gear also turns, but the registration roller is
prevented from
turning by the one-way bearing).
2 After inlet sensor is turned on by the paper advance, the paper is further advanced to a predetermined distance until
the paper hits the registration roller (the skew of the paper can thus be corrected).
 Loading...
Loading...