OKIDATA ML172, ML182 Service Manual
Thank You for purchasing this
Click Here for more Factory Service
Manuals for other Computer and
Printer / Copier Manufacturers
from PCTECHINFO!

Page: 1
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 0 About This Manual
ML172/ML182 Series
Dot Matrix Printers
Adobe Acrobat printable reference
copy of the OKIDATA Service Training Manual.
09/17/97
Note: This Adobe Acrobat version of the Okidata Service Training Manual was built with the
pictures rendered at 300 dpi, which is ideal for printing, but does not view on most
displays well.
Okidata is a registered trademark, and OkiPage is a trademark of Oki Electric Industry Co., Ltd. HP,
LaserJet and PCL5e are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Co. Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe
Systems Incorporated.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Table of Contents Page
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
0 About This Manual
Front Cover 1
Copyright 2
1 General Description & Specifications
1.1 General Description 3
....1.1.1 ML172 4
....1.1.2 ML182 5
....1.1.3 ML182-PLUS 6
....1.1.4 ML182-TURBO 7
1.2 Specifications 8
2 Principles of Operation
2.1 Electrical Principles Of Operation 9
....2.1.1 Power Supply 10
....2.1.2 Control PCB 11
....2.1.3 Interconnect Board 12
....2.1.4 Operator Board 13
2.2 Mechanical Principles Of Operation : Printhead 14
....2.2.2 Head Gap Adjusting Mechanism 15
....2.2.3 Space Mechanism / Operation 16
....2.2.4 Ribbon Feed Mechanism / Operation 17
....2.2.5 Paper Feed Mechanism / Operation 18
....2.2.6 Paper-end Detection Mechanism 19
....2..2.7 Semi-Automatic Sheet Feed (SASF) 20
3 Printer Maintenance
3.1 General Information 21
....Figure 3-1a - ML172 22
....Figure 3-1b - ML182 23
....Figure 3-1c - ML182-PLUS/ML182-TURBO 24
3.2 Maintenance Procedures 25
....3.2.1 Upper Cover 26
....3.2.2 Control Board 27
....3.2.3 Transformer Assembly 28
....3.2.4 Power Supply Board 29
....3.2.5 Operation Board 30
....3.2.6 Printhead 31
....3.2.7 Ribbon Feed Gear Assembly 32
....3.2.8 Space Motor Assembly 33
....3.2.9 Space Rack 34
....3.2.10 Carriage Cable 35
....3.2.11 Printer Mechanism 36
....3.2.12 Linefeed Motor Assembly 37
....3.2.13 Column Indicator Bar 38

Table of Contents Page
....3.2.14 Platen Assembly 39
....3.2.15 Interconnect Board 40
....3.2.16 Paper Chute Assembly 41
....3.2.17 Bottom Paper Guide Assembly 42
....3.2.18 Near-end Lever And Bracket 43
....3.2.19 Bottom Near-end Lever 44
3.3 Adjustments 45
....3.3.2 Space Rack and Roller Gap Adjustment 46
3.4 Printer Self-Tests 47
3.5 Preventive Maintenance 48
4 Interfacing Techniques
4.1 Interfacing Techniques 49
5 Failure Analysis Procedures
5.1 Failure Analysis Procedure 50
....RAP Index 51
........Board layout and Wiring - ML182Plus and ML182Turbo 52
........Board layout and Wiring - ML172 and ML182 53
........Pin Numbers and Signals 54
........Check Points for Printed Circut Boards - 172 55
........Check Points for Printed Circuit Boards - ML182 56
........Check Points for Printed Circuit Boards - ML182Plus and
ML182Turbo
........RAP #1: Power is on but carriage does not move 58
........RAP #2: Power LED lights, but the carriage does not
move
........RAP #3: Carriage movement is abnormal when power is
turned on
........RAP #4: Homing operation is normal, but the indicators
(LED1 to LED9) are abnormal when power is turned on.
........RAP #5: Fuse F1 on power supply board (SLPB) blows
when power is turned on.
........RAP #6: Fuse F1 on the control board blows when power
is turned on.
........RAP #7: Neither spacing nor printing performed while
receiving data.
........RAP #8: Spacing is normal, but nothing is printed while
receiving data.
........RAP #9: Printer stops printing. 66
........RAP #10: Wrong characters are printed or some
characters are missing.
........RAP #11: Some dots are missing. 68
........RAP #12: Print is light. 69
........RAP #13: Line feed is not performed. 70
........RAP #14: Fuse F1 on power supply board blows while
receiving data and printing.
57
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
67
71

Table of Contents Page
........RAP #15: Switch on the operator panel does not work
(Carriage returns to home position when power is turned on).
........RAP #16: Paper not fed properly (SASF function). 73
A PCB Referance Charts
Power Supply Board (SLPB) 74
ML172 Control Board (SLMR-51 & SLMR-52) and Operator
Board
ML182 Control Board (SLMC) 76
ML182 Control Board (SLMR) and Operator Board 77
ML182-PLUS & ML182-TURBO Control Board (SLMX) and
Operator Boards
A PCB Reference Charts
RS232-D Super Speed Serial I/F Board 79
B Parts Compatability Chart
Parts Compatability Chart 80
72
75
78

Page: 2
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 0 About This Manual
Copyright
All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form without the prior written
permission of OKIDATA.
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document is complete, accurate and up
to date. We do not assume responsibility for errors beyond our control.
© Copyright 1989 by OKIDATA
First Edition May 1989
CENTRONICS is a registered trademark of Centronics Inc.
EPSON is a registered trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation
OKIDATA and MICROLINE are registered trademark of Oki America Inc.
IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines, Inc.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 3
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 1 General Description & Specifications
1.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Microline 172, 182, 182-PLUS and 182-TURBO Printers are reliable, compact, dot matrix printers
using a 9-wire printhead. These printers use a re-inking cartridge ribbon.
Although these printers are similar in appearance, there are differences in the features that each printer
offers. Lets take a closer look at each printer.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 1 General Description & Specifications
1.1.1 ML172
Emulates the IBM Graphics Printer.
Pitch, page length and print mode are set through a MENU.
Switches on the Control Board select default Menu settings. Settings return to default values when
the printer is powered off.
Pull tractor is standard.
Available in two models:
1. Centronics parallel interface, this model will not accept a serial board.
2. RS232-D serial interface. This model can be configured for parallel operation by removing the
Serial Board from the Control Board.
Page: 4
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 5
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 1 General Description & Specifications
1.1.2 ML182
Two models are available, IBM emulation, or Microline emulation.
Available with two interfaces, Centronics Parallel, or RS232-C Serial (9600 Baud, Ready Busy
Protocol). An optional Super Speed Serial board (19.2 Baud, Ready Busy and X-On, X-Off
Protocols) is available.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 6
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 1 General Description & Specifications
1.1.3 ML182-PLUS
The ML182-PLUS is an enhanced version of the ML182, with the following features:
Push-button front panel which allow the setting of Pitch (10,12 or 17 CPI), and Mode (Near Letter
Quality, Utility and High Speed Draft).
SASF (Semi-Automatic Sheet Feed), which allows single sheets of paper to be automatically loaded
using the bail arm lever.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 7
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 1 General Description & Specifications
1.1.4 ML182-TURBO
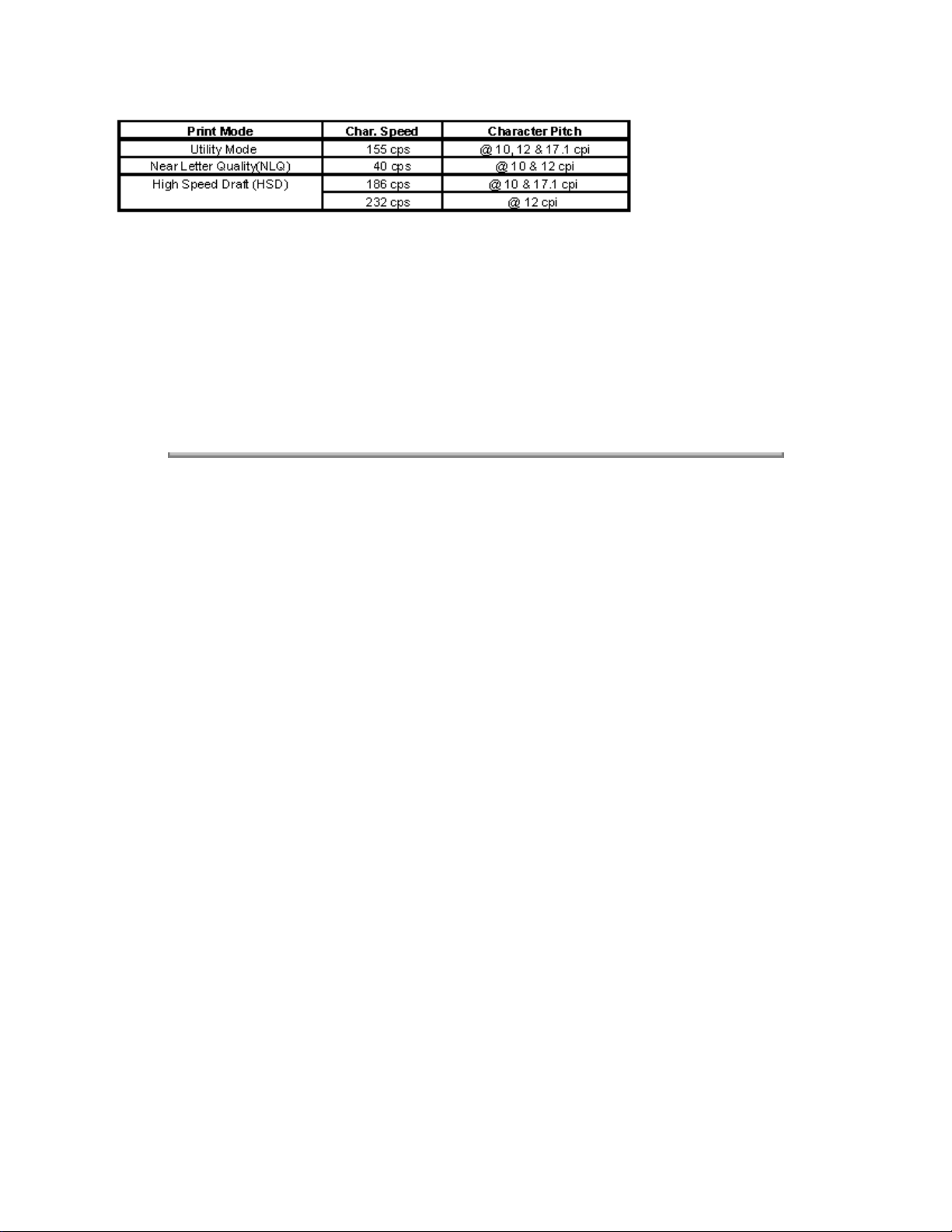
The ML182-Turbo is a faster version of the ML182-PLUS, but does not provide SASF capability. Print
speed at 10 CPI is 155 CPS in Utility mode, and 186 CPS in HSD mode. Super Speed Draft at 232 CPS is
available at 12 CPI.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 1 General Description & Specifications
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS
1.2.1 Paper-end Detection
· Paper-end is detected when the end of the paper is about 1 inch from the printing position.
1.2.2 Input Power
· 120 VAC +/- 10% 50/60 Hz +/- 2%
· 220 VAC +/- 10% 50/60 Hz +/- 2%
· 240 VAC +/- 10% 50/60 Hz +/- 2%
1.2.3 Ribbon
· Type: Re-Inking Cartridge
· Ribbon Life: Approximately 3 million characters
1.2.4 Line Feed Selection
· 6 lpi (.167 inch)
· 8 lpi (.125 inch)
· n/72 inch
· n/144 inch (Microline emulation)
· n/216 inch (IBM emulation)
Page: 8
NOTE:
1.2.5 Number Of Copies
· Original plus three copies (16 to 20 lb. weight paper)
NOTE:
1.2.6 Paper Feed Methods
· Bottom Feed
· Rear Feed
· Top feed (single sheets)
· Semi-Automatic Sheet Feeder (SASF) - ML182-Plus only
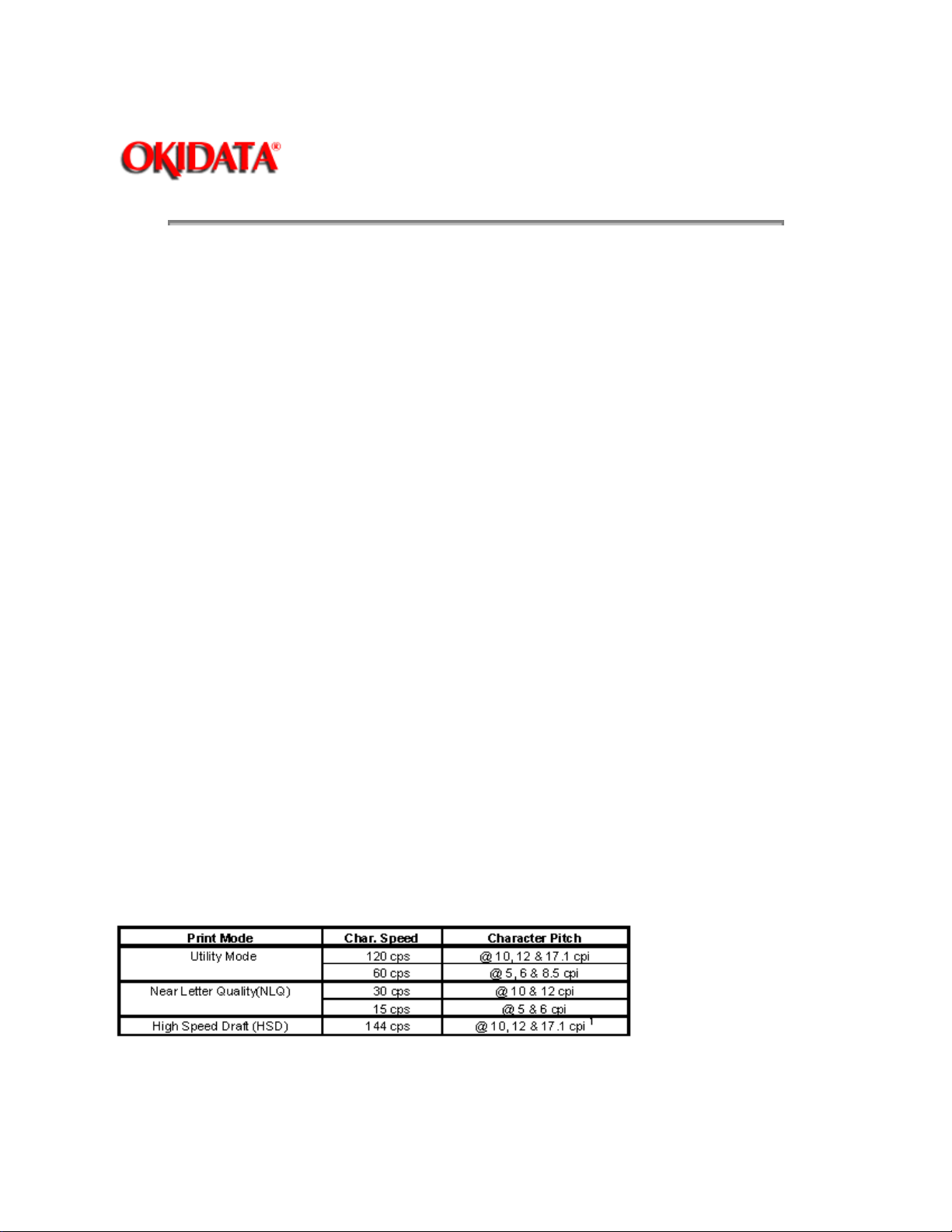
1.2.7 Print Speed
· ML172, ML182, ML182-PLUS
Refer to your Printer Handbook for applicability to your specific printer model.
The ML172 is capable of printing an original plus two copies
1 - Applies to ML172 & ML182-PLUS only
· ML182-TURBO
1.2.8 Reliability
· Printhead Life: Approximately 200 million characters
· MTBF: 4000 hours @ 25% duty cycle/35% page density
· MTTR: 15 minutes @ major sub-assembly level
1.2.9 Available Options
· Tractor Feed Assembly 1
· Super-speed Serial Interface (RS232-C)
· Roll Paper Stand
1 - Standard on the ML172
2 - Not available for ML172
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
2.1 ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
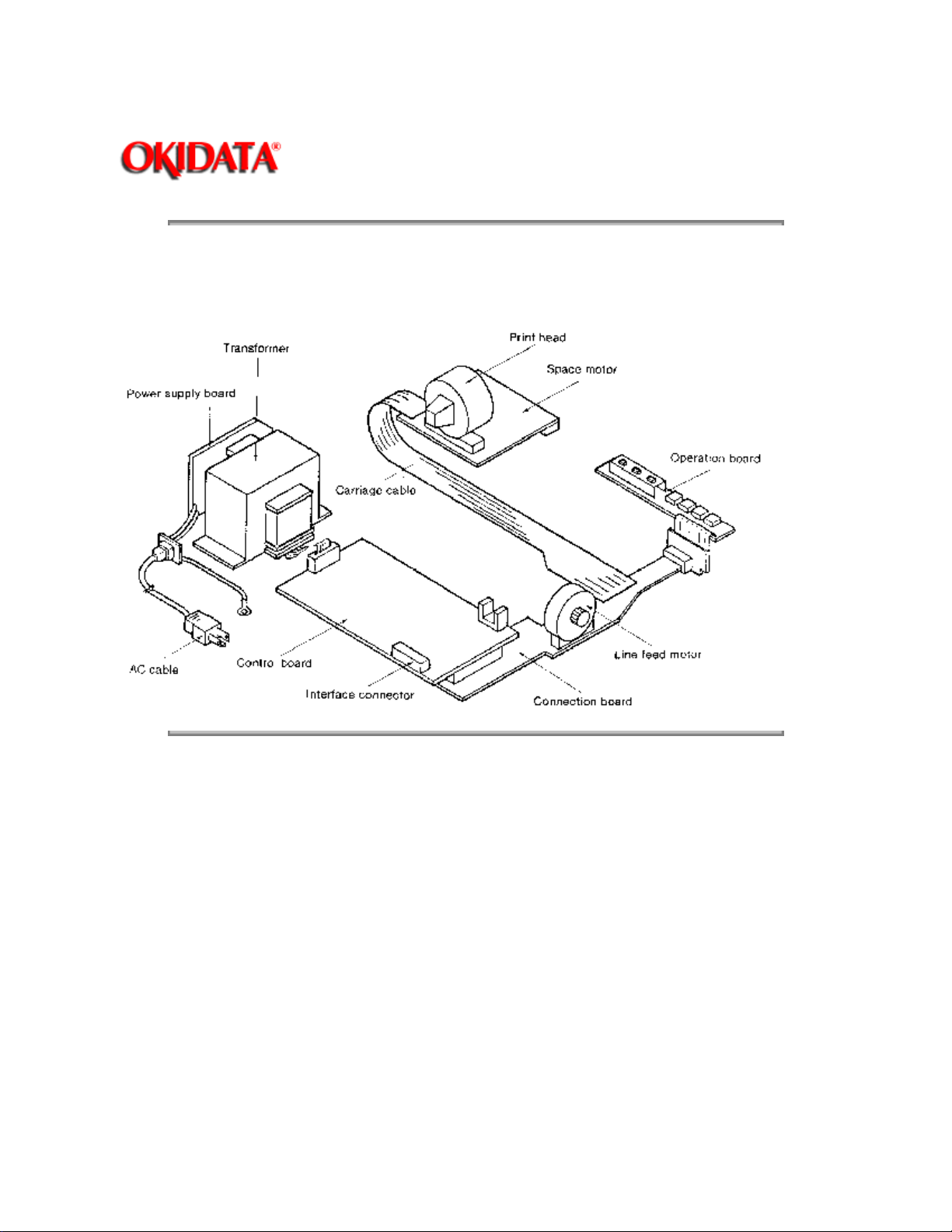
The printers major electrical assemblies are shown in Figure 2-1.
Page: 9
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 10
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
2.1.1 Power Supply
The Power Supply consists of the power supply board and the transformer. The Power Supply Board,
which contains the ON/OFF Switch, Line Filter and related circuits, uses a 1 amp fuse for over-current
protection. This circuit board transforms the AC input voltage into 7.6 VAC, 24 VAC and 10 VAC for use
on the Control PCB. The Transformer contains a thermal fuse for protection against overheating. If the
thermal fuse opens, the transformer must be replaced.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 11
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
2.1.2 Control PCB
The Control PCB contains the microprocessor and related circuits, DC power circuit, motor drive circuits,
paper end sensor and interface connector(s). If a serial interface is installed, it will be connected to the
Control PCB. The DC power circuit converts the AC input from the power supply board into +8 VDC, +5
VDC and +30 VDC to be used throughout the printer.
The Control PCB also contains the following two protective circuits:
a) Driver Fault - Alarm Circuit
This circuit causes the AC fuse (on the power supply board) to open when a fault occurs in the printhead
drive circuit, linefeed motor drive circuit or the spacemotor drive circuit. If the drive time of any drive circuit
exceeds a pre-determined time, an alarm condition will exist as follows:
HDALM - Printhead drive circuit alarm
SPALM - Spacemotor drive circuit alarm
LFALM - Linefeed motor drive circuit alarm
When any of the above signals become active, the Driver Fault - Alarm Circuit will output the ALM signal.
This signal then turns ON an SCR (which is located on the Control Board). When the SCR turns ON, the
secondary winding (30V) of the transformer is short-circuited. This induces an over-current condition
through the primary winding of the transformer causing the AC fuse (F1) to open.
b) Head Overheat - Alarm Circuit
In order to protect the printhead coils, this circuit monitors the head temperature using the printheads
built-in thermistor. When the temperature of the printhead exceeds 100 degrees Celsius, a head overheat
alarm (HEAD TEMP) is generated. This alarm causes the printing operation to stop until the printhead
cools. Once the printhead temperature returns below the alarm detection threshold, the printing operation
is restarted.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 12
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
2.1.3 Interconnect Board
The Interconnect Board is nothing more than a BUS, used to connect the printhead, operator panel,
spacemotor, linefeed motor and semi-automatic sheet feeder (SASF) Switch (ML182 PLUS only) to the
Control PCB.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 13
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
2.1.4 Operator Board
The Operator Board contains switches and indicators which allow the printer operator to control and
monitor the printers operation. The ML172 and ML182 use the same type Operator Board (SLSQ) while
the ML182-PLUS and ML182-TURBO use the same type Operator Board (SLSX). For specific information
on the capabilities and use of each of these Boards, please refer to the appropriate Printer Handbook.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 14
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
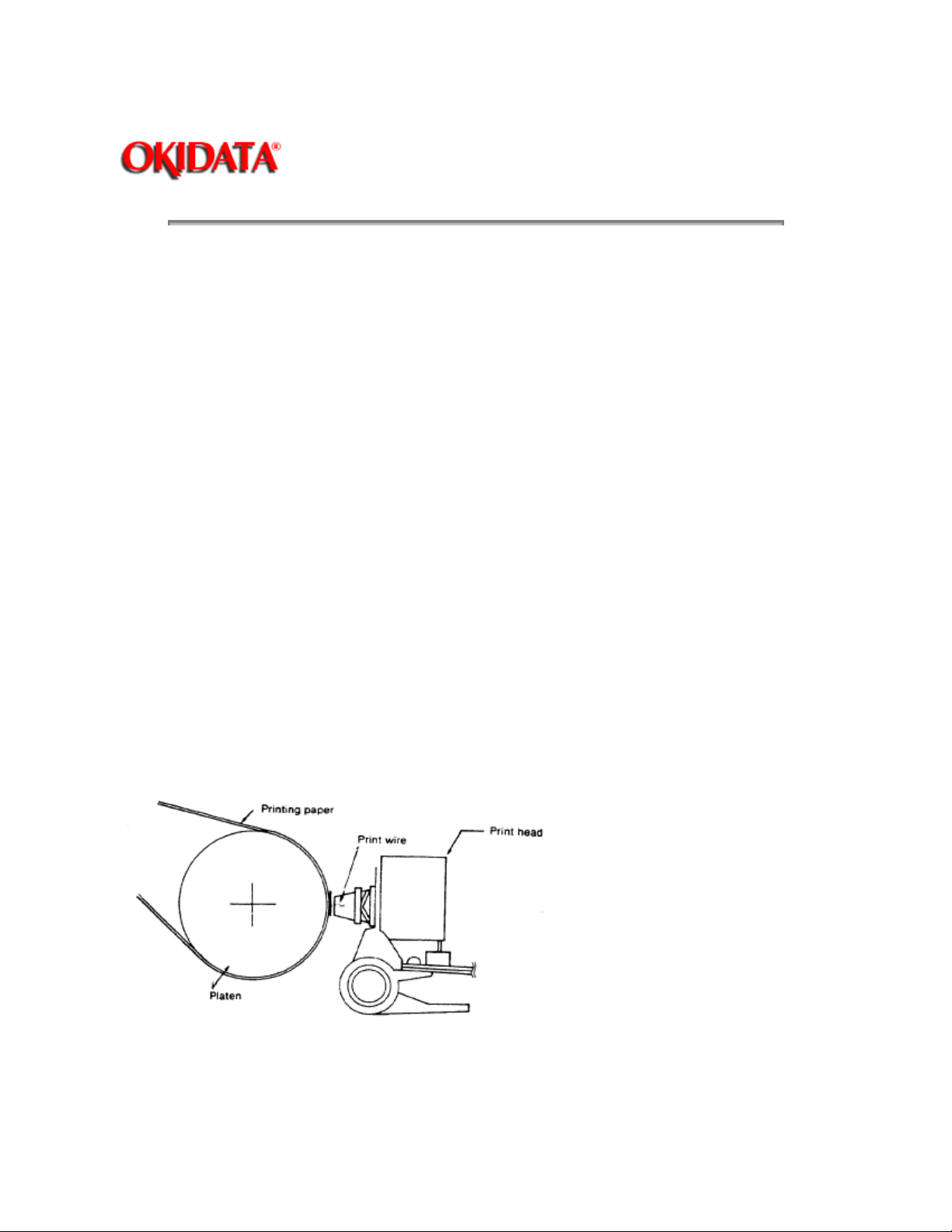
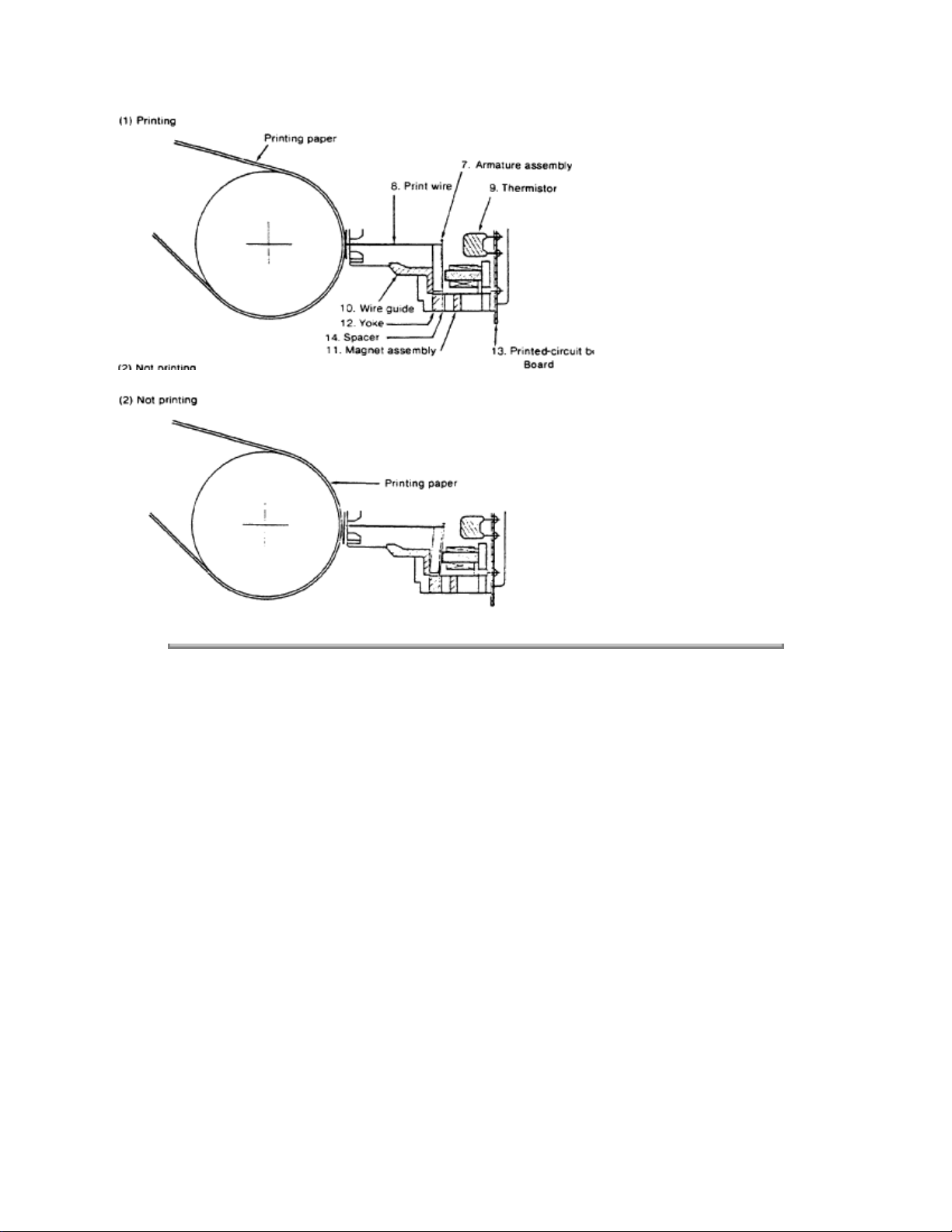
2.2 MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION : Printhead
The Printhead used by the ML172, ML182, ML182-PLUS and ML182-TURBO is a highly efficient Stored
Energy type. Power is not consumed until a printwire is activated, thereby extending the printhead life to
approximately 200 million characters.
The printhead is designed with nine (9) vertically aligned wires. Each wire is welded to an armature ring.
Behind this armature ring is a spacer ring.
Each of the nine print wire armatures on the ring has a permanent magnet behind it. The magnets attract
the armatures, keeping the print wires inside the printhead. Because of the spacer ring behind the
armature ring, the armature is attracted toward the permanent magnet at a cocked angle. There is also a
coiled wire, wrapped around each of the nine permanent magnets.
When a dot is to be printed, current passes through the coiled wire, creating a magnetic field which
counters the magnetic field of the permanent magnet. This causes the armature and print wire to spring
forward and imprint a dot onto the paper.
When the current is removed from the coiled wire, the magnetic field of the permanent magnet attracts the
armature, causing the print wire to retract into the printhead.
This printhead contains a built-in thermistor (rated at 100 degrees Celsius) to monitor the head
temperature. When the printhead temperature exceeds the 100 degree setting, the thermistor generates
an output signal to the Control PCB.
The printer then stops printing and sends a BUSY signal to the host computer. Data remains in the print
buffer until the printhead temperature is below 100 degrees Celsius. At this time, the BUSY signal to the
host computer becomes inactive and printing is resumed.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 15
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
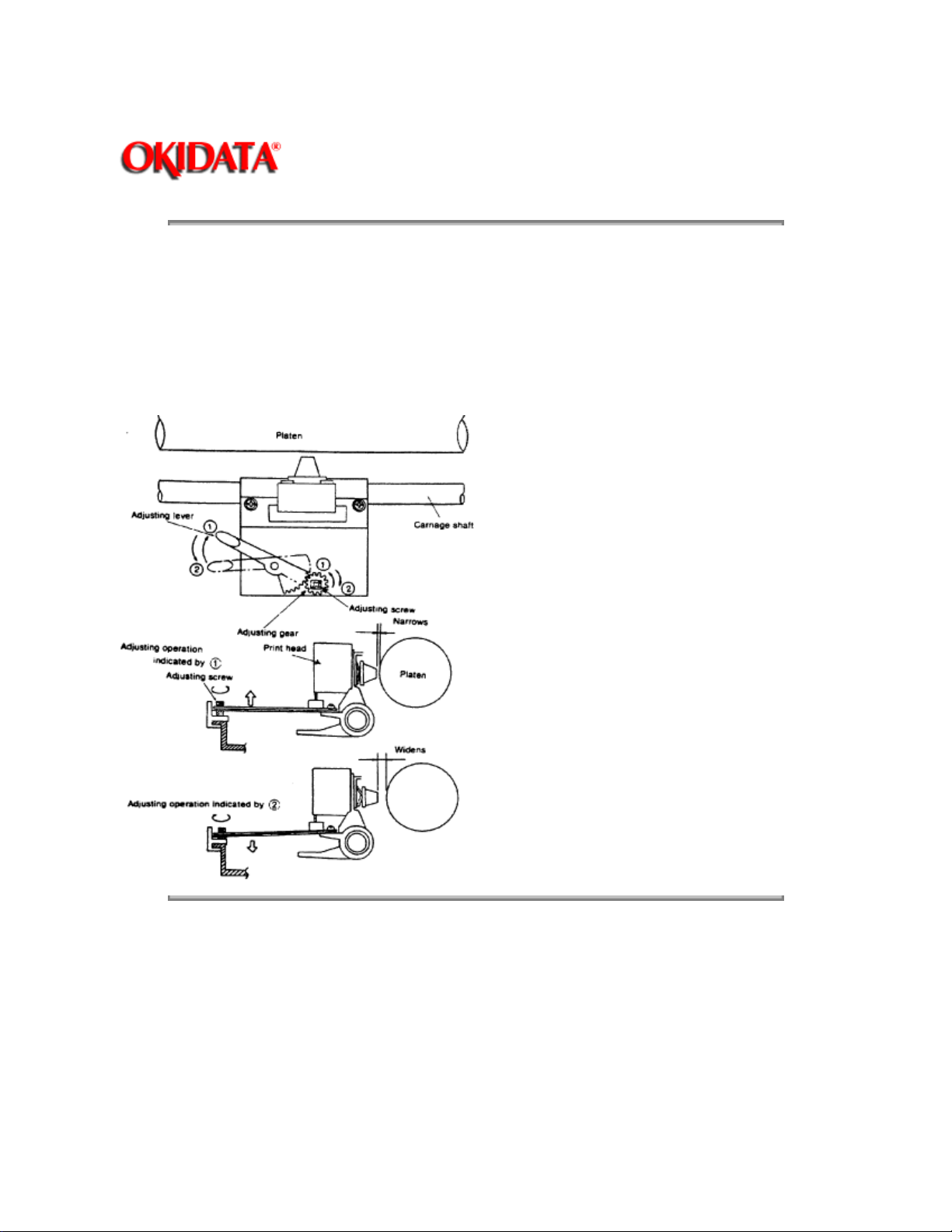
2.2.2 Head Gap Adjusting Mechanism
The head-gap adjusting mechanism adjusts the gap between the platen and printhead by changing the tilt
angle of the carriage frame. This is accomplished by using the adjusting lever.
When the adjusting lever is operated, the adjusting screw, which is interlocked with the lever via a gear,
rotates and changes the position of the carriage frame around the carriage shaft. The printhead, mounted
vertically on the carriage frame, moves closer to or farther away from the platen with the change in the
carriage frame tilt angle.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 16
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
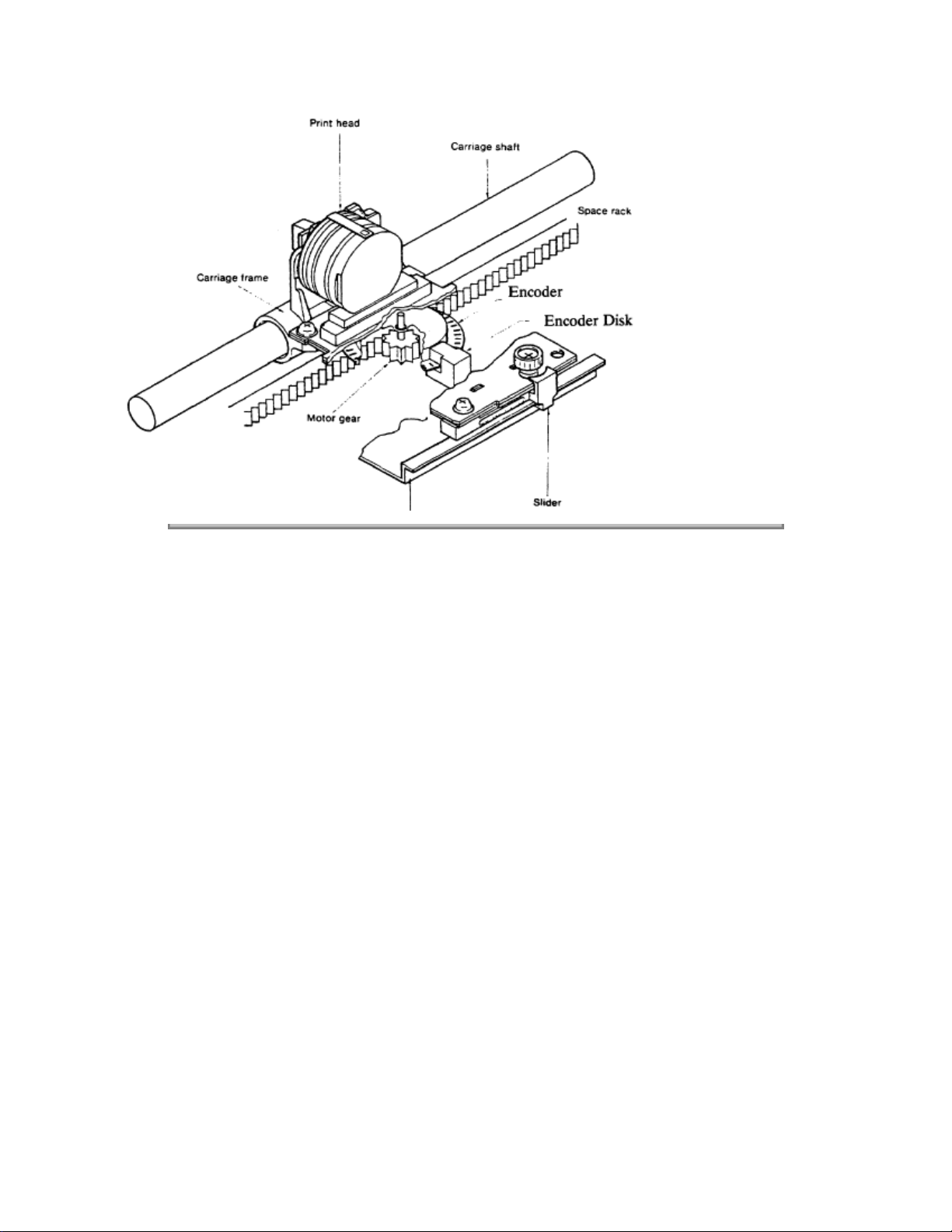
2.2.3 Space Mechanism / Operation
The spacing operation is performed by applying power to the DC Spacemotor. This drives the Carriage
Frame along the Carriage Shaft, which is mounted parallel to the platen.
The Spacemotor Assembly consists of :
DC Motor with Motor Gear
Carriage Frame (includes Stator Yoke & Motor Board)
Carriage Shaft
Space Rack
Encoder Disk Sensor
Encoder Disk
Slider
SPACING OPERATION
The Carriage Frame, with the Printhead and Spacemotor mounted on it, moves parallel to the platen
along the Carriage Shaft. As the Spacemotor rotates counterclockwise, the Carriage is driven to the
right, along the Space Rack.
The spacing mechanism is designed so when the Spacemotor rotates one turn, the Carriage Frame
moves 0.8 inch (20.56 mm).
Motor rotation also turns the Encoder Disk, causing the timing windows on the disk to pass through the
Encoder Disk Sensor. The position of the Carriage Frame is obtained by counting the number of
windows detected by the Encoder Disk Sensor.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

2.2.4 Ribbon Feed Mechanism / Operation
Page: 17
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
NOTE:
The ribbon feed gear assembly is secured to the top of the spacemotor assembly by the four claw
tabs.
The ribbon feed mechanism feeds the ribbon synchronously with the spacing operation. The mechanism
is driven by the spacemotor.
The ribbon feed mechanism consists of :
Ribbon feed gear assembly
Ribbon gear (attached to the spacemotor)
Ribbon cartridge
RIBBON CARTRIDGE
A uni-directional feed, continuous ribbon is used. The ribbon is replenished by a built-in ink tank in the
ribbon cartridge so that quality printing is assured.
RIBBON FEED OPERATION
As the spacemotor rotates, the ribbon gear on the spacemotor shaft turns the drive gear in the ribbon
cartridge via the ribbon feed gear assembly. As a result, the ribbon is fed.
In bi-directional printing, the ribbon gear rotational direction reverses each time the direction of the
carriage movement reverses. In this case, the gears in the ribbon feed gear assembly switch the rotational
direction so as to feed the ribbon in a fixed direction.
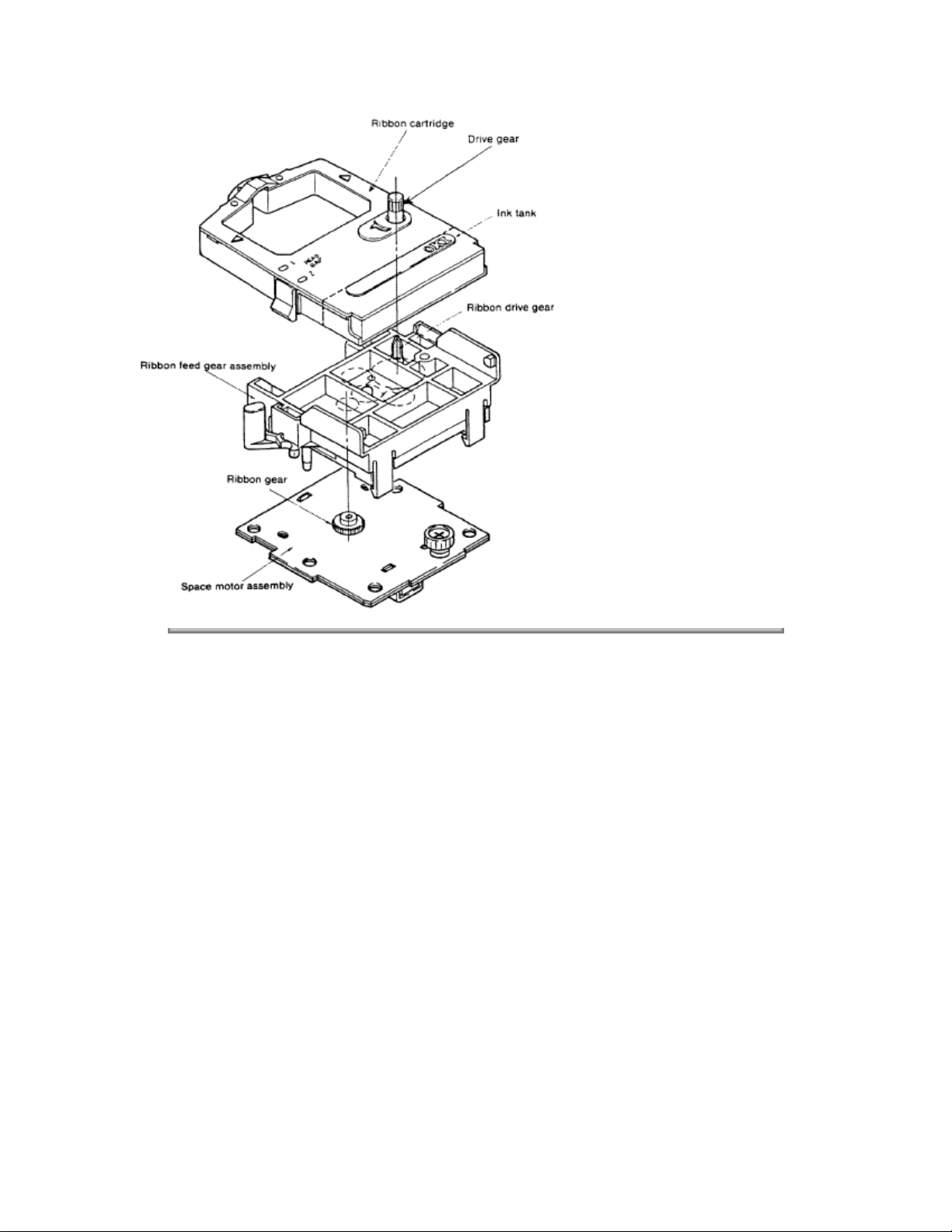
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 18
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
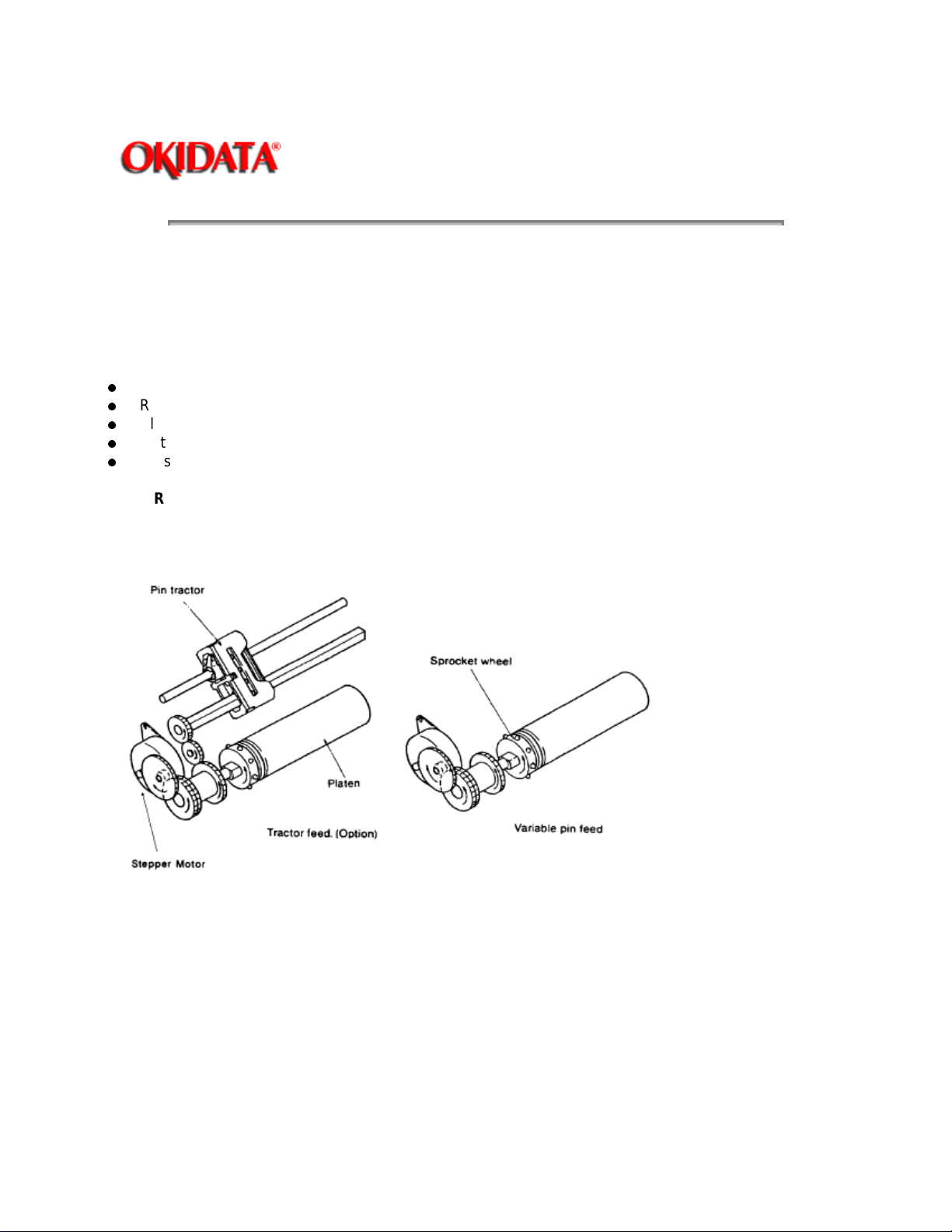
2.2.5 Paper Feed Mechanism / Operation
Paper Feed is performed by rotating the platen and pin tractors, which are driven by the linefeed stepper
motor.
The paper feed mechanism consists of :
Stepper motor with drive gear
Reduction gear
Platen - (no pins on ML172 Platen)
Optional Tractor unit (standard on ML172)
Pressure (friction feed) rollers - (no rear rollers on ML172)
PAPER FEED OPERATION
The paper feed stepper motor is mounted on the left side frame of the print unit, and it drives the platen via
the reduction gear. If the optional tractor unit is installed, platen rotation is also transmitted through the idle
gear to the tractor unit.
The paper feed mechanism is designed so when the stepper motor rotates 48 steps (360 degrees), paper
is fed 0.17 inch (4.23 mm).
PAPER CLAMP MECHANISM (FRICTION FEED)
When the release lever is set to the OPEN position, the release link moves backward, and the front and
rear release links rotate counter-clockwise.
At the same time, the release shaft (interlocked with them) rotates counter-clockwise and places a gap
between the pressure rollers and platen, allowing paper to be inserted.
When the release lever is set to the CLOSED position, the release link moves forward, and the front and
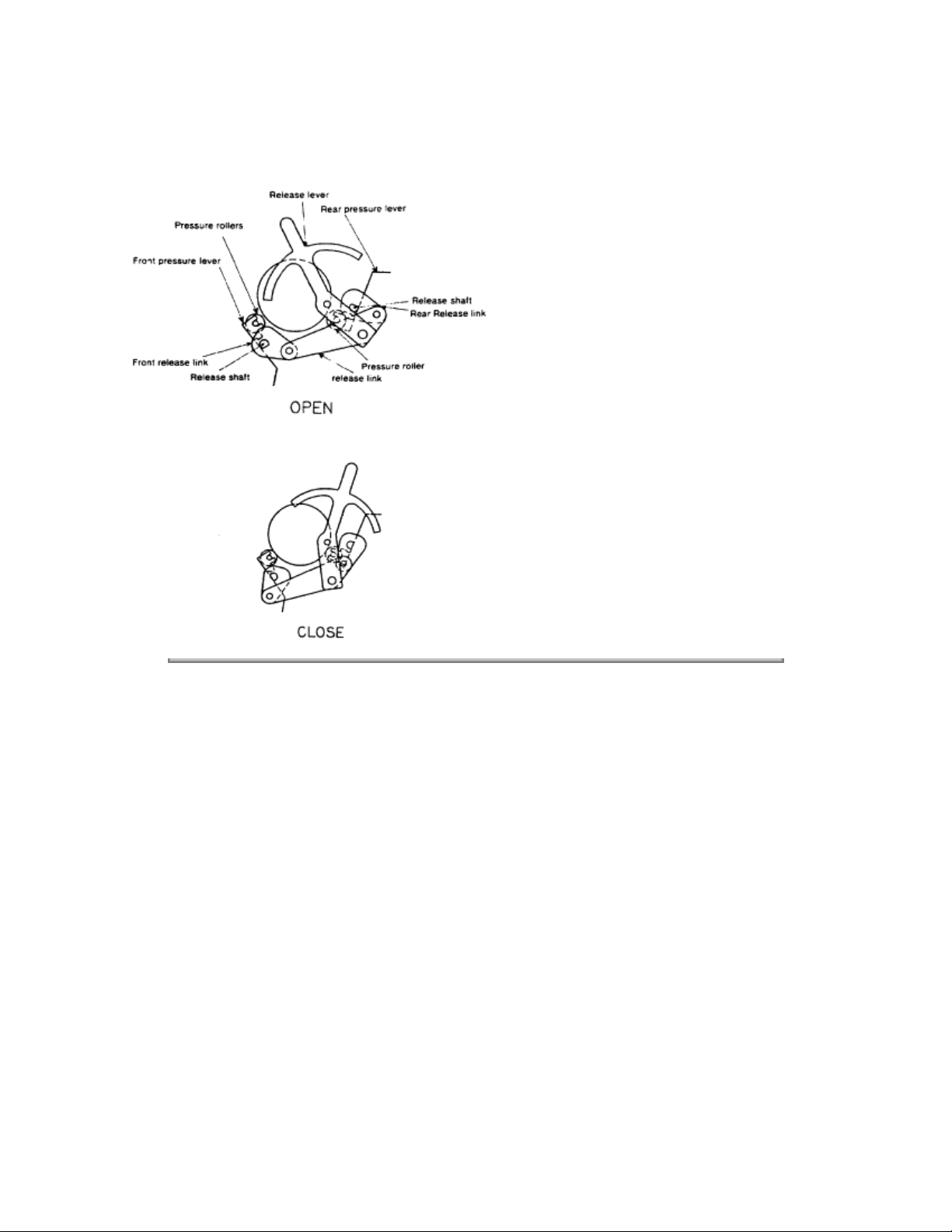
rear release links rotate clockwise. At the same time, the release shaft (interlocked with them) also rotates
clockwise so that the pressure rollers are pushed against the platen by the front and rear pressure levers,
allowing paper to be fed.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 19
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
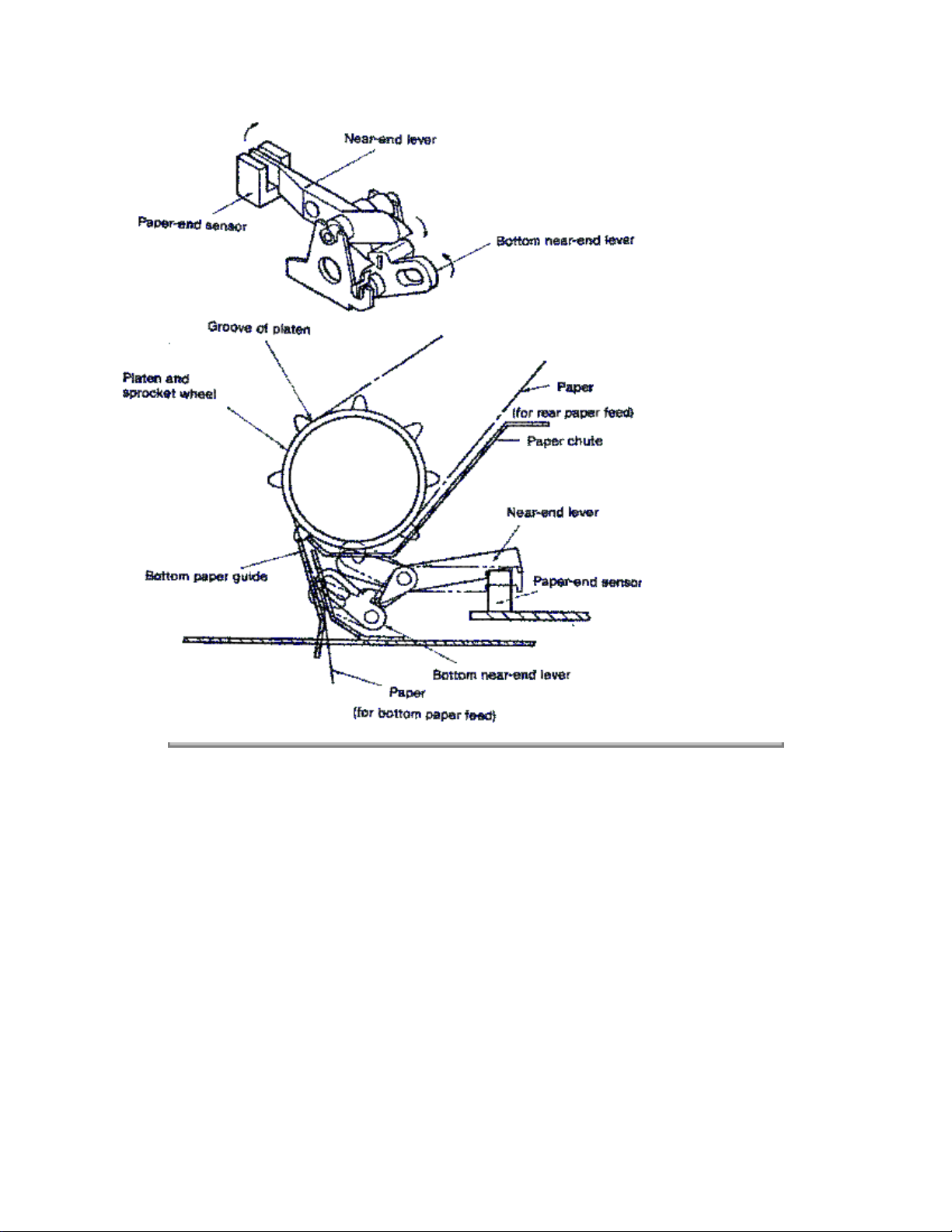
2.2.6 Paper-end Detection Mechanism
REAR PAPER FEED
When paper is installed in the printer, it prevents the near-end lever from falling into the groove of the
paper chute and platen, the paper-end sensor is on.
When the printer runs out of paper, the near-end lever falls into the groove of the paper chute and the rear
part of the near-end lever turns off the paper-end sensor, paper-end is detected.
Paper-end is detected when the end of the remaining paper is about 1 inch (25.4 mm) from the printhead
position.
BOTTOM PAPER FEED
When paper is installed in the printer, it prevents the bottom near-end lever from falling into the hole in the
bottom paper guide. That is, the wedge on the bottom near-end lever pushes down the projection of the
near-end lever, and the paper-end sensor is on.
When the printer runs out of paper, the tip of the bottom near-end lever falls into the hole in the bottom
paper guide so that the rear part of the near-end lever turns off the paper-end sensor, and thus paper-end
is detected.
Also in this case, paper-end is detected when the end of the remaining paper is about 1 inch (25.4 mm)
from the printhead position.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

2..2.7 Semi-Automatic Sheet Feed (SASF)
Page: 20
Service Guide ML172/ML182 Series
Chapter 2 Principles of Operation
NOTE:
Applies to ML182-PLUS only
The ML182-PLUS printer has a built in feature that allows you to automatically feed a single sheet of
paper into the printer.
The Semi-Automatic Sheet Feed operates as follows:
Place the printer OFF-LINE (Deselected) and set the Paper Release Lever for friction feed (rear
position).
Place the Sheet Separator in the upright position.
Insert the Cut Sheet Paper by placing it against the Sheet Separator and allowing it to rest against
the Platen. The ALARM LAMP should be ON, indicating that a PAPER-OUT condition exists.
Pull the Bail Arm toward the front of the printer. The Bail Arm will contact the SASF Switch (which is
mounted on the Interconnect Board) causing it to CLOSE. The signal SASF-N is then sent to the
Control Board. This causes the CPU to command the Carriage to move toward the center of the
Platen. At this time, approximately 1.1 inches of paper will be fed.
Place the Bail Arm back in its original position. As you do this, the SASF Switch will OPEN, causing
an additional 0.3 inch of paper to be fed.
NOTE:
As a result, the first line of printing will occur 1 inch below the top edge of the paper.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
 Loading...
Loading...