OKIDATA 4410 Service Manual

P ACEMARK 4410/
MICROLINE 4410
PRINTER
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
ODA/OEL/INT
1999. 3. 26 Rev.1
40496501TH Rev.1 1 / 214
Rev.No. Date Corrected items Person in
No. Page Description of change change
40496501TH Rev.1 2 /

PREFACE
This maintenance manual describes how to maintain the Pacemark 4410/Microline 4410 printer
in the field.
This manual is for customer engineers.
For further information, refer to the Users Manual for handling or operating the equipment.
40496501TH Rev.1 3 /

CONTENTS
1. CONFIGURATION..................................................................................... 6
1.1 Basic System Configuration............................................................... 6
1.2 Printer Specifications......................................................................... 7
1.3 Option Specifications......................................................................... 8
1.4 Basic Specifications........................................................................... 9
2. THEORY OF OPERATION........................................................................ 12
2.1 Electrical Operation ........................................................................... 12
2.1.1 Summary ................................................................................................. 12
2.1.2 Microprocessor and the peripheral circuit ............................................... 12
2.1.3 Initialization.............................................................................................. 21
2.1.4 Interface control....................................................................................... 22
2.1.5 Parallel Interface Control ......................................................................... 22
2.1.6 Serial Interface ........................................................................................ 23
2.1.7 Printing operation .................................................................................... 24
2.1.8 Printhead control ..................................................................................... 25
2.1.9 Print Compensation Control .................................................................... 27
2.1.10 Space motor control ................................................................................ 27
2.1.11 Line feed..................................................................................................28
2.1.12 Bail, tractor switching, AG, ribbon motor control ..................................... 29
2.1.13 Operation Panel ...................................................................................... 30
2.1.14 Alarm circuits ........................................................................................... 32
2.1.15 Power supply circuit ................................................................................ 34
2.2 Mechanical Operation........................................................................ 35
2.2.1 Printhead mechanism and operation (See Figure 2-13) ......................... 35
2.2.2 Spacing operation (See Figure.2-15) ...................................................... 37
2.2.3 Head gap adjusting ................................................................................. 38
2.2.4 Ribbon drive (See Figure) ....................................................................... 41
2.2.5 Paper Feed Mechanism .......................................................................... 42
2.2.6 Bail Feed Mechanism (See Figure ) ........................................................ 46
2.2.7 Paper End Detection Mechanism (See Figure ) ..................................... 48
3. PARTS REPLACEMENT........................................................................... 50
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement................................................... 50
3.2 Parts Layout....................................................................................... 53
3.3 How to Change Parts......................................................................... 54
3.3.1 Cover-Assy-Access / Cover-Assy-Side (R) / Cover-Assy-Side (L)
/Cover-Assy-Front / Frame-Assy-Rear / Plate-Front (stuck) .................. 55
3.3.2 Printer Unit .............................................................................................. 56
3.3.3 Control Block [Control Board (PMA Printed Board),
Driver Board (PDA Printed Board)] ......................................................... 57
3.3.4 Power Supply Assy ................................................................................. 58
3.3.5 PG Cooling Fan ....................................................................................... 59
3.3.6 I/F Board (PHA Printed Board) ................................................................ 60
3.3.7 AG Board (PGA Printed Board) / Connector Cord .................................. 61
3.3.8 AG Motor Assy ........................................................................................ 62
3.3.9 Mini Pitch Belt.......................................................................................... 63
3.3.10 Tractor Change Motor Assy .................................................................... 64
3.3.11 Bail Motor Assy ....................................................................................... 65
3.3.12 LF Motor Assy ......................................................................................... 66
3.3.13 Head Cooling Fan 1 ................................................................................ 67
3.3.14 Head Cooling Fan 2 ................................................................................ 68
3.3.15 Space Motor ............................................................................................ 69
40496501TH Rev.1 4 /

3.3.16 Operator Board (POA Printed Board) ...................................................... 70
3.3.17 Ribbon Feed Assy ................................................................................... 71
3.3.18 Printing Head........................................................................................... 72
3.3.19 Head Cable ............................................................................................. 73
3.3.20 Ribbon Protector ..................................................................................... 74
3.3.21 Space Motor Fan ..................................................................................... 75
3.3.22 Junction Board ........................................................................................ 76
3.3.23 Cover Open Switch Assy / Ribbon Rotation Sensor ............................... 77
3.3.24 Interlock Switch / Interlock Switch Cord Assy ......................................... 78
3.3.25 Knob Bracket Assy .................................................................................. 79
3.3.26 Space Belt ............................................................................................... 80
3.3.27 AG Sensor Frame / Start Searching Sensor ........................................... 81
3.3.28 Paper Jam Sensor Assy / Bail PE Sensor Assy ...................................... 82
3.3.29 Sprocket Assy (L) (R) (Front Tractor) ...................................................... 83
3.3.30 Sheet Feeder Assy (L) Rear / Sheet Feeder Assy (R) Rear ................... 84
3.3.31 Bail Assy.................................................................................................. 87
4. ADJUSTMENTS ........................................................................................ 88
5. CLEANIG AND LUBRICATION ................................................................ 95
5.1 Cleaning............................................................................................. 95
5.2 Lubrication ......................................................................................... 96
6. TROUBLESHOOTING AND REPAIR ....................................................... 104
6.1 Items to Check Before Repair............................................................ 104
6.2 Troubleshooting Table....................................................................... 104
6.3 Lamp and LCD Display...................................................................... 105
6.4 Part Layout ........................................................................................ 110
6.5 Connection......................................................................................... 113
6.6 Troubleshooting Flow Chart............................................................... 130
7. PARTS LIST .............................................................................................. 161
APPENDIX A PCB LAYOUT.......................................................................... 202
APPENDIX B RS-232C SERIAL INTERFACE BOARD (OPTION) ............... 205
1. GENERAL.......................................................................................... 205
2. OPERATION DESCRIPTION............................................................ 206
2.1 Element Description ................................................................................ 206
2.2 Circuit Description ................................................................................... 206
2.3 Local Test................................................................................................ 209
APPENDIX C MAINTENANCE-SUPPORT FUNCTION ................................ 211
1. Normal mode ..................................................................................... 211
2. Maintenance mode 1 ......................................................................... 212
3. Maintenance mode 2 ......................................................................... 213
40496501TH Rev.1 5 /
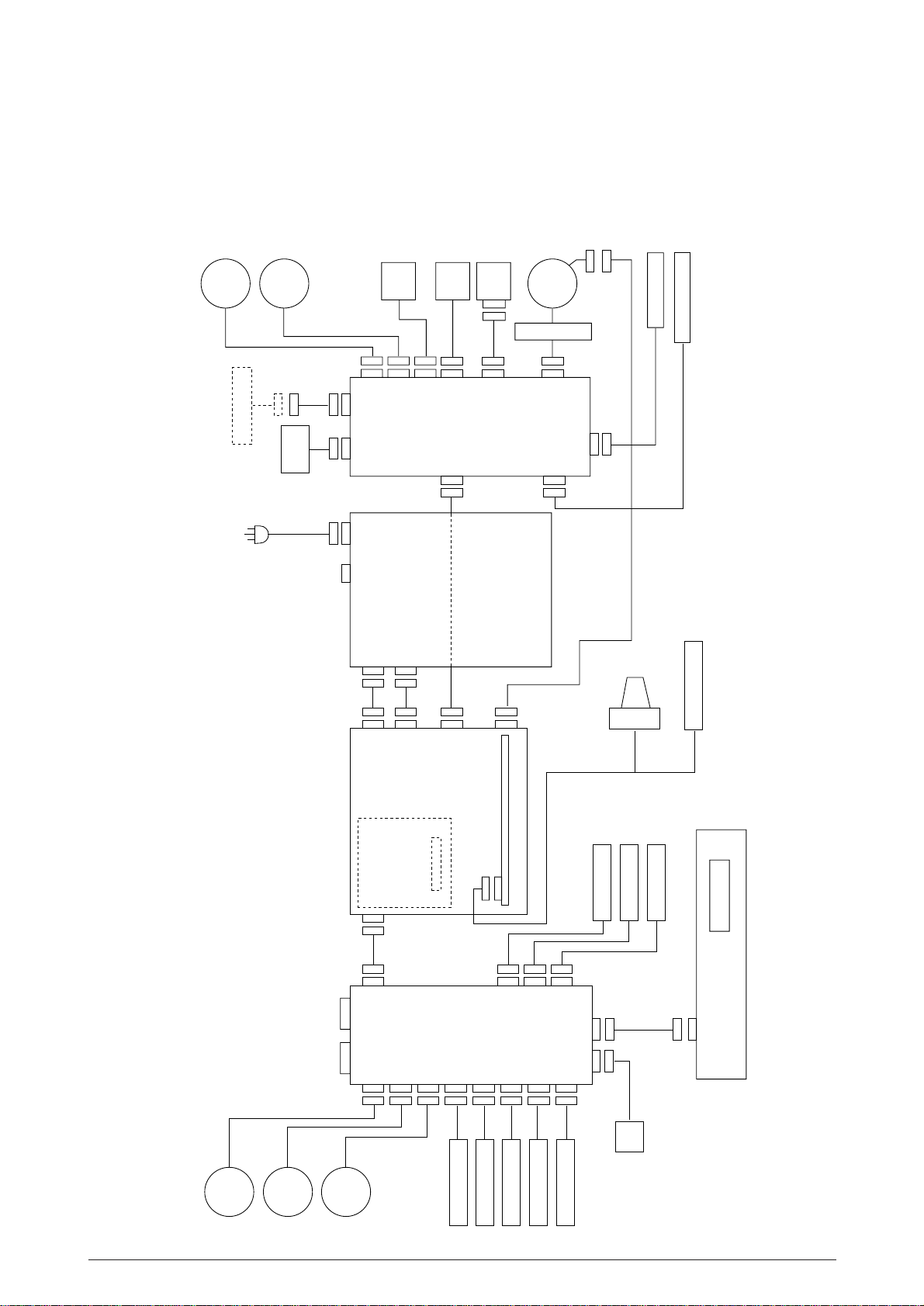
1. CONFIGURATION
1.1 Basic System Configuration
The basic system configuration of Pacemark 4410/ Microline 4410 is illustrated in Figure 1.1.
feed
motorAGmotor
Ribbon
FAN
HEAD
SP
FAN
AG
PCB
sensor
SP
motor
AC source
FAN
Power supply
Motor/Sensor PCB
FUSE holder
Power supply unit
Inter lock SW
Print head
Cover open SW
Ribbon jam sensor
Paper width sensor
Figure 1.1
Bail
motor
RS232C
IEEE 1284
motorLFmotor
Tractor
change
Main control/
I/F
I/F
Interface/Motor
Motor driver PCB
(Option)
Interface board
/Sensor PCB
Head driver PCB
Bail position SW
Front PE SW
Tractor change SW
Rear PE SW
Paper jam sensor
Bail PE sensor
AG sensor coil
Paper top sensor
FAN
Head
LCD
Operation panel PCB
40496501TH Rev.1 6
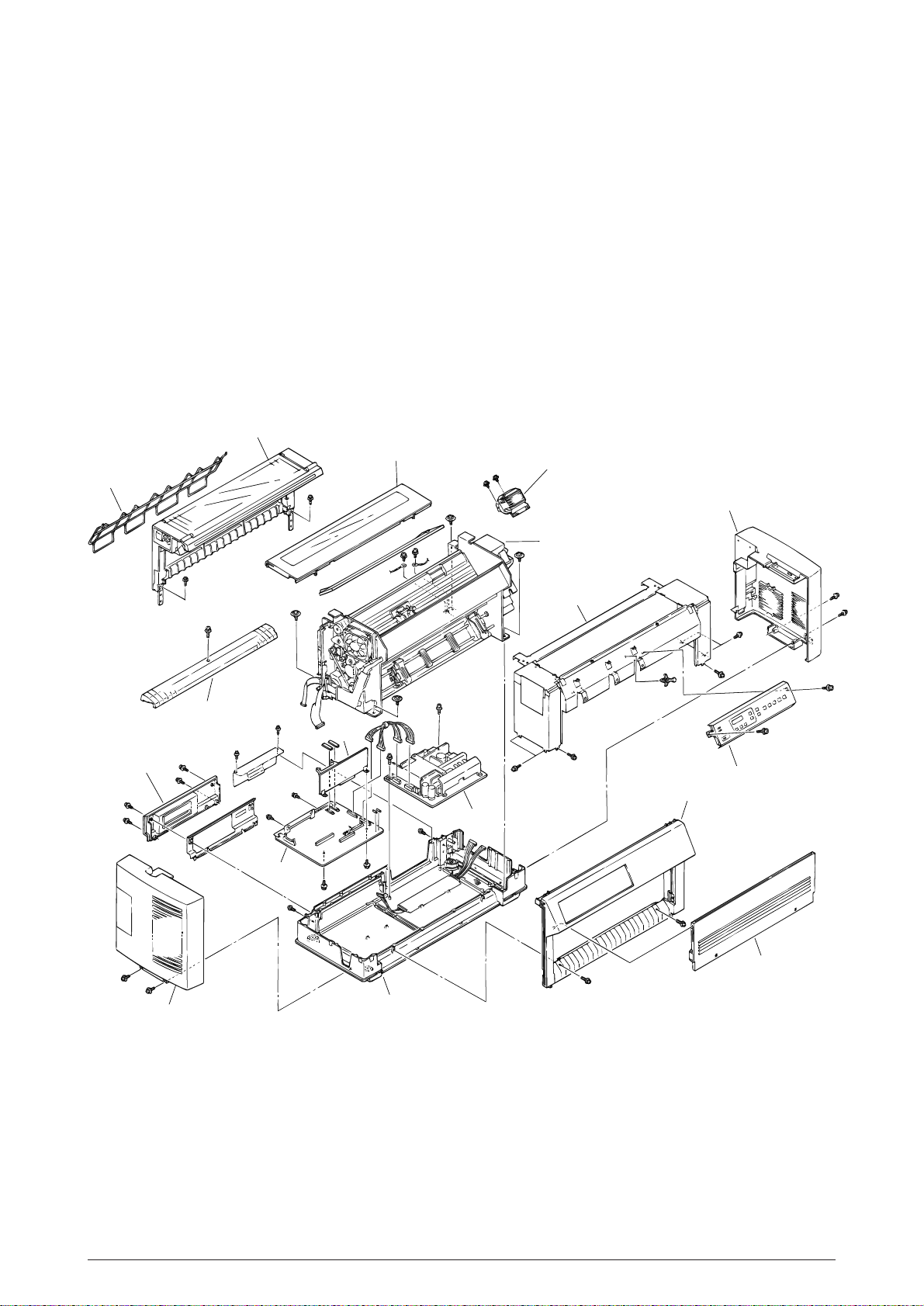
1.2 Printer Specifications
Sheet guide
Cover Assy Rear
Cover Assy Access
Print head
Printer Unit
Cover-Assy-Side(R)
Operation panel Assy
Cover Assy Front
Door Assy Front
Cover Assy Lower
Cover Assy Side(L)
Control Board
Cover Rear B
Guide Paper B
Driver Board
Power Supply Assy
Plate Front
(stuk)
This printer unit is composed with the following hardware.
• Printer mechanism
• Main control/Motor driver board
• Head driver board
• Interface/Motor/Sensor board (including IEEE 1284 bidirectional parallel interface and RS232C serial interface)
• Motor/Sensor and AG sensor boards
• Operation panel board
• Power supply unit
• Covers
Figure 1-2 show the printer unit configuration.
Figure 1.2
40496501TH Rev.1 7
1.3 Option Specifications
Options available for Pacemark 4410/ Microline 4410 are as follows.
(1) Interface boards
(a) Oki-HSP (MUPIS) Network card
(b) 300/500 Series Serial/ HSP Adapter
• RS232C
• RS422A
• Current Loop
40496501TH Rev.1 8

1.4 Basic Specifications
(1) Dimensions
Width: 768mm(30.24inches) Length: 385mm(15.16inches) Height: 358mm(14.09inches)
(2) Weight
Approx. 42kg (92.6lbs)
(3) Form
Continous Paper
One-part paper
Ream weight: 45 to 90g/m2 (12 to 24 lb)
Multiple-part paper Max.0.79mm(0.031inches)total thickness(with front feed)
Paper type Ream weight Number of sheet
Carbon-lined paper Ten sheet maximum including original
Pressure-senstive (9 to 11 lbs) Six sheet maximum including original
paper (with rear feed)
Interleaf paper (9 to 14 lbs) (with front feed)
Max.0.36mm(0.014inches)total thickness(with rear feed)
35 to 40 g/m
2
(with front feed)
Paper
35 to 52 g/m
2
Seven sheet maximum including original
Corbon paper Four sheet maximum including original
34 g/m2 (9 lbs) (with rear feed)
When 7p or more papers are used for the front tractor, "High Impact Copy" should be
selected in the menu mode to print these papers.
Continuous Envelope
Weight : Max. 90 g/m2 (24lb)
Thickness : Max. 0.36mm (0.014 inch)
Width : 76.2 - 254mm (3 - 10 inches)
Media supply :Front paper feed only
Card
Weight : Max. 375 g/m2 (100lb)
Thickness : Max. 0.20mm (0.008 inch)
Size : 5 x 8 inches (separated)
Media supply :Front paper feed only
Label
Thickness : Max 0.28mm (0.011 inch)
Size : Max. 381 x 83mm (15 x 3.25 inches)
Media supply :Front paper feed only
(4) Print speed
Print Mode Character Pitch
10 CPI 12 CPI 15 CPI 17.1 CPI 20 CPI
HSD 1066 CPS 1066 CPS 1066 CPS 1066 CPS 1066 CPS
NLQ 200 CPS 200 CPS 200 CPS 200 CPS 200 CPS
UTILITY 800 CPS 800 CPS 800 CPS 800 CPS 800 CPS
40496501TH Rev.1 9

(5) Maximum Number of Dot Columns per Line
a) Graphics
Single Density Double Density Quadruple Density
816 1,632 3,264
b) Text
Print Mode Character Pitch (CP)
10 CPI 12 CPI 15 CPI 17.1 CPI 20 CPI
ML, EPSON, IBM UTILITY 1,632 1,958 2,448 2,798 3,264
ML, EPSON, IBM NLQ 3,264 3,917 4,896 5,596 6,528
ML, EPSON, IBM HSD 1,224 1,468 1,836 2,098 2,448
(6) Maximun Number of Character per Line
Character Pitch (CPI) 5 6 7.5 8.5 10 12 15 17.1 20
ML EPSON IBM 68 81 102 116 136 163 204 233 272
(7) Printhead
Print method: Impact dot matrix
Number of dot wires: 9 wires x 2 rows
Dot wire diameter: 0.36mm(0.014inch)
(8) Line feed Speed
6 LPI spacing, one LF = 60 ms
8 LPI spacing, one LF = 52 ms
Continuous paper feed rate is 15 inches per second. (at head gap 1, 2)
(9) Line Feed Pitches
6 LPI 0.167 inch (4.23mm)
8 LPI 0.125 inch (3.175mm)
A variable line feed pitch of n/216 inch (integer n: 0 ≤ n ≤ 255) can also be specified. Also,
7/72 inch and n/72 inch can be specified.
PROPRINTER n : 1 ≤ n ≤ 255
EPSON n : 1 ≤ n ≤ 255 (Cannot specify MSB : 1≤ n ≤ 127)
(10) Power Requirements
a) Input power
Single-phase AC
Voltage : 120VAC +5.5%, -15%
230 VAC ±15%
Frequency : 50/60Hz ±2%
b) Power consumption
Local Test : Max. 295 W (Rolling ASCII, Utility)
Idle : Max. 15W (Energy Star compliant)
c) AC power cable
Length : Approximately 5.9 It (1.8 m)
Cable conforms to the UL, CSA, and European Standards.
40496501TH Rev.1 10

(11) Ambient temperature and relative humidity
Operating Non-operating Storage Transportation Unit
Temperature 41 to 95 32 to 109.4 14 to 122 -40 to 158 °F
(5 to 35) (0 to 43) (-10 to 50) (-40 to 70) (°C)
Relative 20 to 80 10 to 90 5 to 95 5 to 95 %RH
Humidity
Avoid condensation at all times.
(12) Vibration
Operating : Max. 0.3G (5 to 150 Hz) (except at resonant frequency)
Non-operating : Max. 1G (5 to 150 Hz) (except at resonant frequency)
(13) Impact (Drop Test)
Packing : 12" Drop
(14) Noise
The 8-second average noise is Max. 55 dBA in quiet utility mode. (ISO 7779)
(15) Ribbon
Genuine OKI cartridge ribbon
Ink color : Black
Ribbon life : Approximately 15 million characters (Characters in Utility mode)
(16) Reliability
a) MTBF (mean time between failures)
12,000 hours of power-on time at 25% duty cycle and 35% page density.
b) Printhead life
400 million characters (average) in 10 CPI Utility print mode at 25% duty cycle and 35%
page density.
c) Printer life
12,000 hours of power-on time at 25% duty cycle and 35% page density, or 5 years.
d) MTTR
30 minutes, major Sub-assembly level.
Definition of terms
• Duty cycle : Actual operation rate
• Page density : The proportion in area of characters and spaces within print head
PPmovable area.
• Power on Time : 8H/day, 25days/month and 12 months/year.
40496501TH Rev.1 11

2. THEORY OF OPERATION
2.1 Electrical Operation
The electrical operation of the printer circuit is described in this section.
2.1.1 Summary
Fig. 2-1 shows the block diagram of the printer.
The control board is made up of the microprocessors, peripheral circuits, drive circuits, sensors and
interface connectors.
The power to the control board is supplied by the power board through the connector cord.
The pwer to other electrical parts is also distributed through the connectors within the control board.
2.1.2 Microprocessor and the peripheral circuit
(1) Microprocessor (IC24: 80C186-16)
This processor is a CMOS single-chip computer with integrated peripheral device functions
and a 16 bit MPU core.
The processor has a 20 bit address bus and a 16 bit data bus.
It is capable of accessing up to 4M bit program memory and 4M bit of data memory.
The following characteristics are also provided:
• High-Speed DMA Channel x 2
• Programmable Interrupt Controller
• Programmable 16-bit Timer x 3
• Programmable Memory and Peripheral Chip-Select Logic
• Programmable Wait State Generator
• Local Bus Controller
And others.
The function of this microprocessor is to provide a central mechanism for the entire printer
by executing the control program through the LSI and driver circuits.
40496501TH Rev.1 12
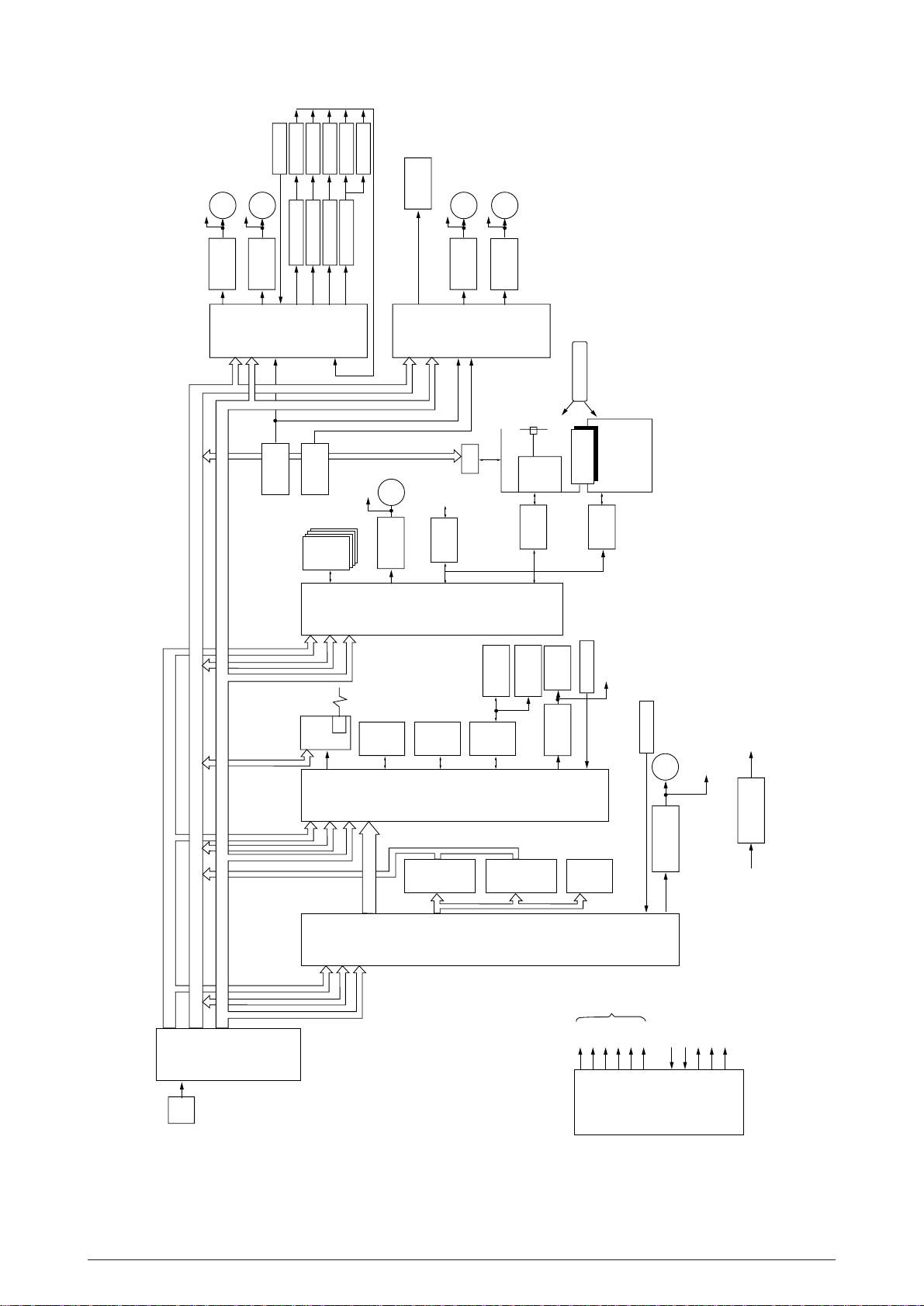
to ALM circuit
PM
LF motor
driver
Sub LSI #1
72V017
AG slit sensor
to ALM circuit
PM
AG motor
driver
P/S FANP/S FAN DV.
HD FAN 1
HD FAN 2
HD FAN DV.1
HD FAN DV.2
SP FAN
CB FAN
SP FAN DV.
FAN ALM
Continuous
paper cutter
(option)
Sub LSI #2
72V017
to ALM circuit
PM
Bail motor
driver
to ALM circuit
PM
Paper path
switching
motor driver
Either of them
LAN
Sensor, SW
DIP SW
SRAM
(1M)
2/2
NHDC LSI
RS232
LSI
1/2
NHDC LSI
D/R
to ALM
circuit
PM
Ribbon motor
driver
DRAM
(4M)
TFA. TFD.720S
PRG,
EEPROM
ROM
(4M)
IEEE1284
BUF
BUF
OPpanel
OPpanel
LSI
CG,
ROM
MUPIS
LCD
(4M)
card
BUF
(x1)
HEAD
Head driver
Extended slot
<OPTION>
ML300's/ 500's
BUF
to ALM circuit
AG sensor
FL ROM
(8M)
OPTION
RS232C, TWINAX,
COAX, etc
Slit sensor
to ALM circuit
SP motor
DC
SP motor driver
ALM circuit
Head/ motor driver POWEROFF-P
Main LSI
Each part
ALE/ RD/ WR/ CS/ CLK
AD0~AD15
A16~A19/ BHE
+44V
+12V
+ 5V
CPU
80C186
32
MHz
-12V0VEP
Unit
Power Supply
POWOFF-P
POWDOWN-P
AC DOWN-P
POW ONRST-N
POWALM-P
Figure 2.1
40496501TH Rev.1 13
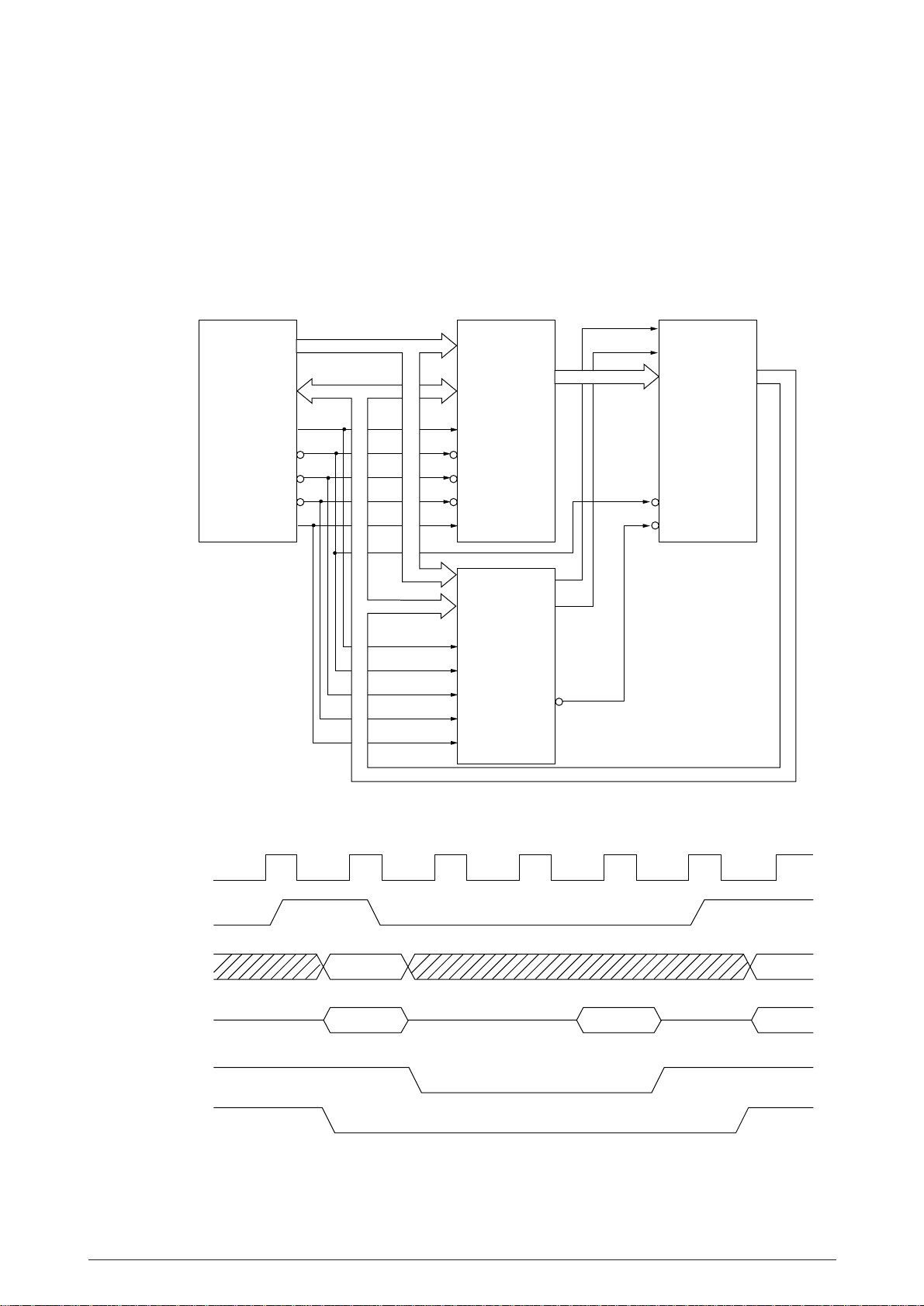
(2) PG ROM (IC46)
This is a 256 x16 bits (4M bit) EPROM with the control program for the printer stored. The MPU
executes instructions under this program.
The program ROM is assigned to the program memory area of the MPU and is fetched by the
RD signal of the MPU.
The following shows the operation of the memory access.
MPU
ALE
RD
WR
CS
CLK
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
Main LSI PG ROM
A17
A16
A1~A16
NHDC LSI
BANK0
BANKS
CS
A0~A15
OE
CE
MPU CLOCK
ALE
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
RD
CS
A16-BHE
A0–A15 D0–D15
Figure 2.2
40496501TH Rev.1 14
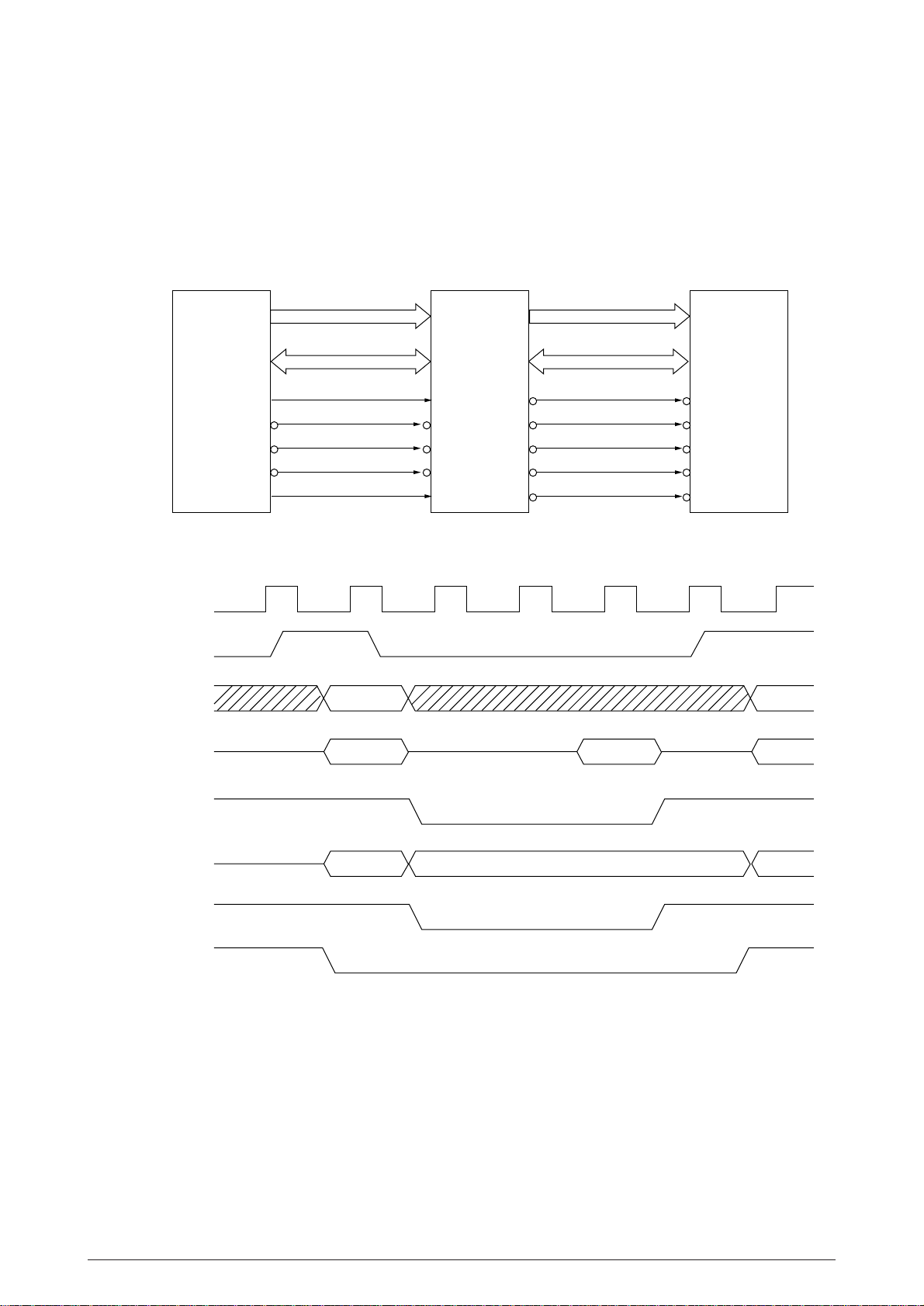
(3) DRAM(IC28)
The RAM is CMOS dynamic RAM with (256K x 16 bit) configuration, and used as buffers (such
as receiving buffer, printing buffer, DLL buffer and working buffer).
The following shows the examples of the memory access operation.
MPU CLOCK
ALE
A16~BHE
MPU NHDC LSI
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
ALE
RD
WR
CS
CLK
A16~BHE
RAS
CASU
CASL
WR
DRAM
DRAMA0~A9
DRAMD0~D15
RD
AD0~AD15
RD
AD0~AD15
WR
CS
A0–A15 D0–D15
A0–A15 D0–D15
Figure 2.3
40496501TH Rev.1 15

(4) CG ROM (IC48)
This is a 256K x 16 bits (4M bits) EPROM with the font data for the characters stored.
CG ROM is assigned to the program memory area of the MPU and is fetched by the RD signal
of the MPU.
The following shows the memory access operation.
MPU
ALE
RD
WR
CS
CLK
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
Main LSI CG ROM
A17
A16
A1~A16
NHDC LSI
BANK0
BANKS
CS
A0~A15
OE
CE
MPU CLOCK
ALE
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
RD
CS
A16-BHE
A0–A15 D0–D15
Figure 2.4
40496501TH Rev.1 16
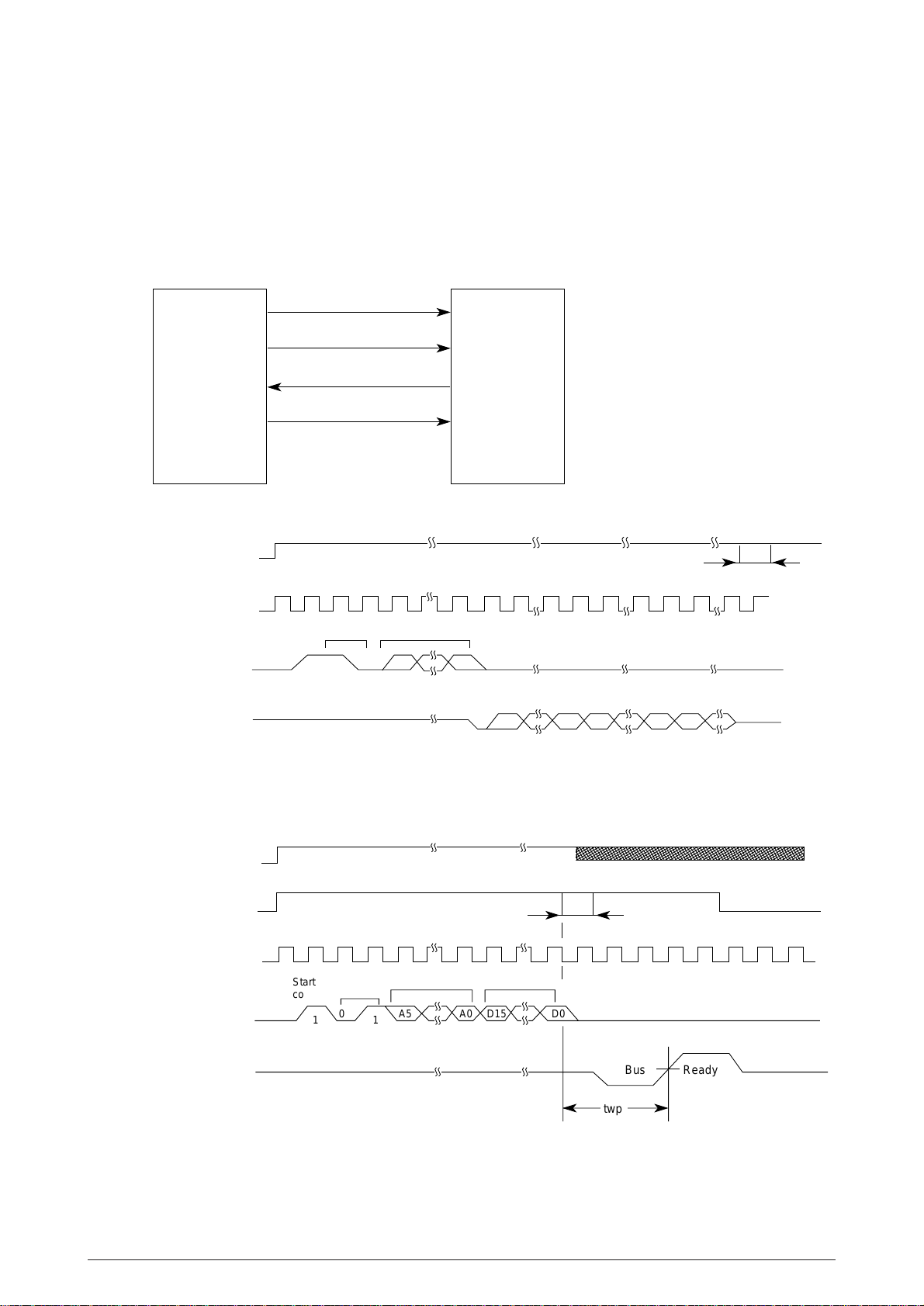
(5) EEPROM(IC40)
,
The EEPROM is a CMOS serial I/O type memory which is capable of electrically erasing and
writing 1,024 bits.
The EEPROM contains menu data.
The following shows the memory access operation.
NHDC LSI EEPROM
EEPROMWR-P
DI
EEPROMCS-P
CS
EEPROMRD-P
DO
EEPROMCLK-P
SK
PRE = O
PE = X
EEPROMCS-P
EEPROMCLK-P
EEPROMWR-P
EEPROMRD-P
PRE = O
PE
EEPROMCS-P
EEPROMCLK-P
EEPROMWR-P
Read cycle timing (READ)
Operation
Start
code
code
0
11
Write cycle timing (WRITE)
Operation
Start
code
code
0
11
Address
A0A5
0
D15 D0 D15 D0 D15
Address Data
t
CS
t
CS
D0D15A0A5
EEPROMRD-P
twp
ReadyBus
Figure 2.5
40496501TH Rev.1 17

(6) Main LSI (IC38: MSM91U036)
MSM91U036 is control LSI for head data, DC motor and modification of print data, which has
the following functions.
(a) Head data control
It distributes print data stored in the DRAM over wire arrangements of the print head and
outputs it as dot data in synchronism with print timing. In this time, the distribution
complies with each print mode which is specified by the MPU.
(b) Print timing control
It outputs the signals which control the print timing of ODD and EVEN pins on the print
head.
(c) Space motor speed control function
It controls the space motor with micro-programs to accelerate/decelerate it.
This LSI also controls the speed of the space motor in agreement with each print mode.
(d) I/O port
This printer has 8-bit output port which is used for controlling the SRAM.
(e) Head position count
It counts the outputs from slit sensors (SPPHASE A, B) located on the space motor to
keep monitoring the current position of the print head.
(f) Print data modifying function
It modifies the print data stored in the DRAM with command inputs from the MPU.
(h) DMA control function
It outputs a DMA request to the MPU, simultaneously controlling the DMA.
This LSI is connected in multiplex to the MPU.
40496501TH Rev.1 18
MPU CLOCK
ALE
MPU Main LSI
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
ALE
RD
WR
CS
CLK
A16~BHE
AD0~AD15
RD
AD0~AD15
WR
CS
A16~BHE
A0–A15 D0–D15
A0–A15 D0–D15
Figure 2.6
40496501TH Rev.1 19

(7) NHDC LSI(IC27: TC190G08CF-7036)
This LSI controls timer, interruption, memories, printing, external interface, motor drive
interface.
(a) Timer control
It controls the watchdog timer for detecting any out-of-control program, baud rate
generator for setting the baud rate of the serial interface, and pulse generation timer for
AG plus count.
(b) Interruption control
It controls LSI inside interruptions, external interruptions and interruptions from an
external interface as outputs for the MPU.
(c) Memory control
DRAM and SRAM control, chip select output control of ROM, flash memory and MUPIS,
and bank switch control for expanding their memory spaces.
(d) Print control
It creates a print timing corresponding to the print DPI to control the possition and print
correction for pins.
This also controls the print Mask and DMAC which reads print data from the memory and
transmits it to the print output buffer.
(e) External interface
It controls various interfaces for main LSI, IEEE1284, serial, MUPIS, OpePaneLSI,
EEPROM.
(f) Motor drive interface
Each control of OVDV pulse generation for AG motor, generation of pulse for switching
ribbon motor phase, and OVDV pulse generation for LF motor.
(8) Sub LSI (IC17, IC18: MSM72V017)
This LSI is the I/O port LSI which controls the input/output of various controlling signals with
command inputs from the MPU.
(a) Sub LSI #1 (IC17: MSM72V017)
Input/output control for controlling signals to various sensors, FAN controlling signals,
sensor slice level controlling signals, AG motor controlling signals, and LF motor
controlling signals.
(b) Sub LSI #2 (IC18: MSM72V017)
Input/output control for controlling signals to various sensors, SP motor current controlling signals, external interface controlling signals, TR motor controlling signals, bail motor
controlling signals, cutter motor (for optional connection) controlling signals.
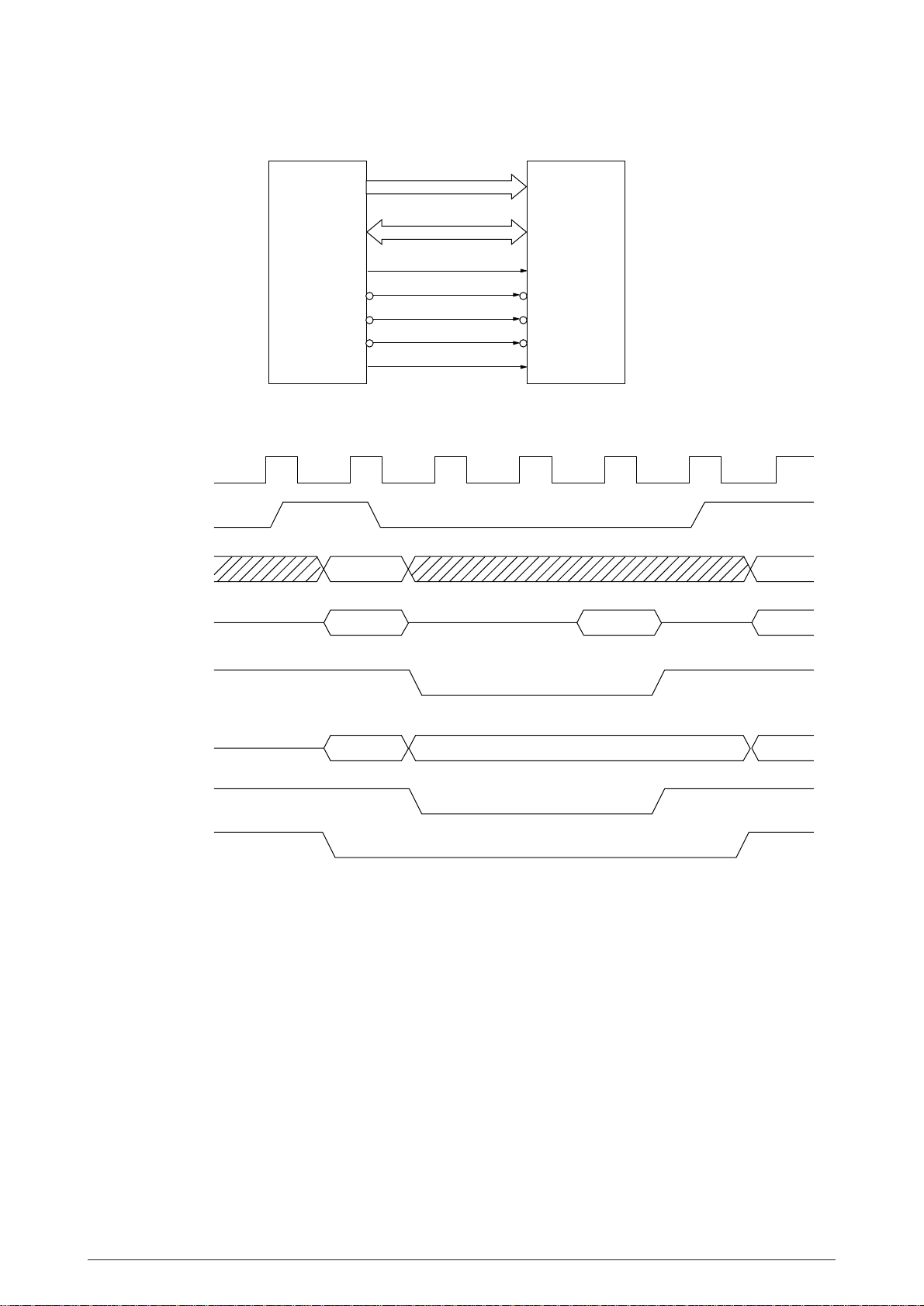
(9) Serial I/F LSI (IC35: 85L30)
This LSI is the serial I/F LSI which controls the input/output of serial I/F controlling signals with
command inputs from the MPU.
40496501TH Rev.1 20
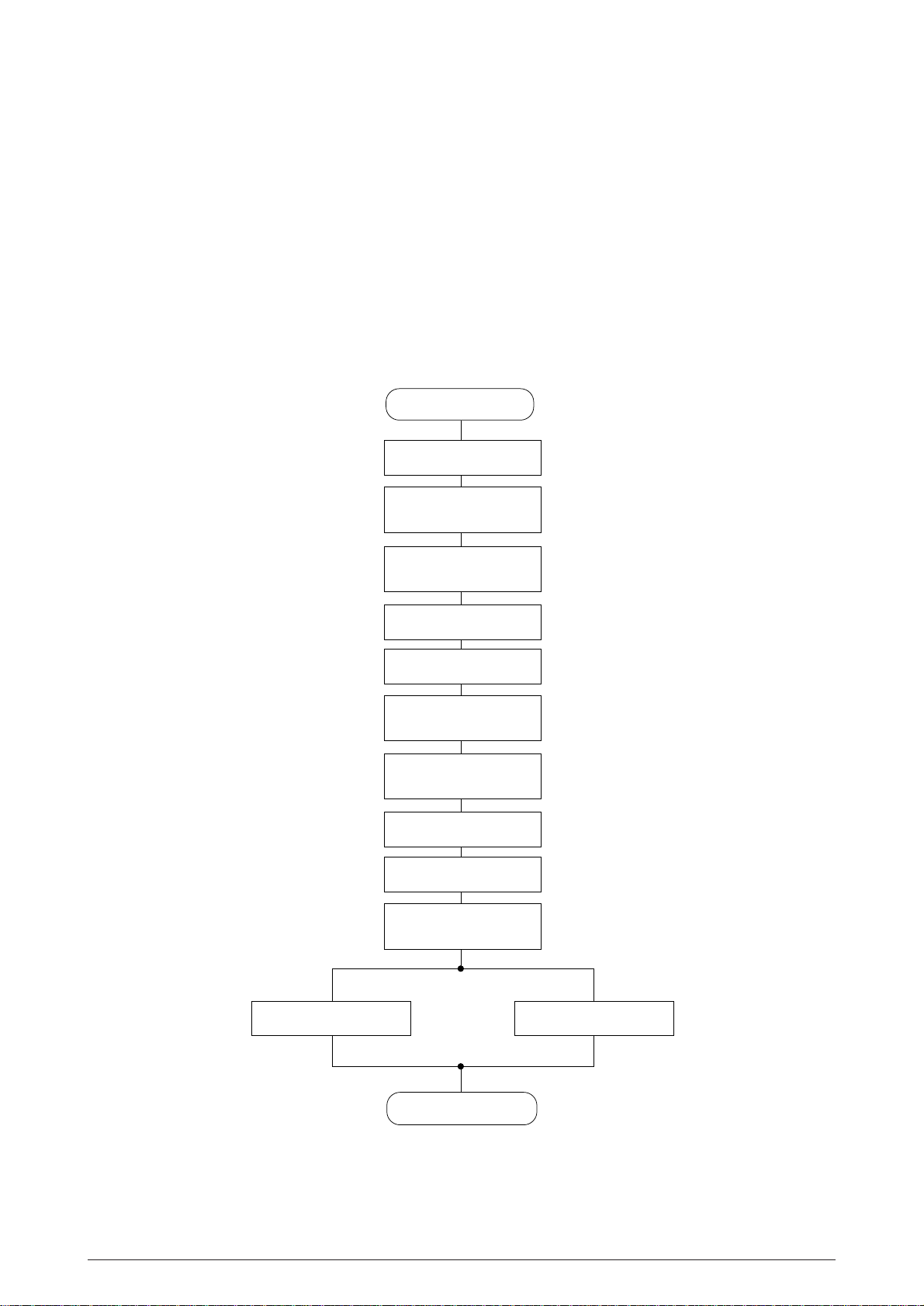
2.1.3 Initialization
This printer is initialized when the power is tumed on or when the I-PRIME-N signal is input from
the host side via the parallel interface.
For the initialize operation, the RESET-N signal is first output from the reset circuit to reset the MPU
and LSIs. When resetting ends, the program starts and the LSIs are reset by NHDC LSI via
LRESET-N. Reset operation by I-PRIME starts program to initialize, but does not reset the MPU.
The program here sets the mode of the LSI including the MPU, checks the memories (ROMs and
RAMs), then carries out carriage homing, and determines the LF motor phase.
Finally, the program establishes the interface signals (P-I/F: ACK-P signal sending, and S-I/F:
BUSY-N signal off) and lights the SELECT lamp to inform the ready state for receiving to the host
side and ends the initialize operation.
Start
MPU RESET
MPU
Initial Setting
Internal RAM
CHECK
Serial
I/F
I/F BUSY OFF
ROM CHECK
LSI RESET
External RAM
CHECK
LSI Initial Setting
and I/F Busy ON
RAM Clear
Carriage Homing
LF Motor Phase
Initialization
Parallel
I/F
I/F ACK Send
End
Figure 2.7
40496501TH Rev.1 21
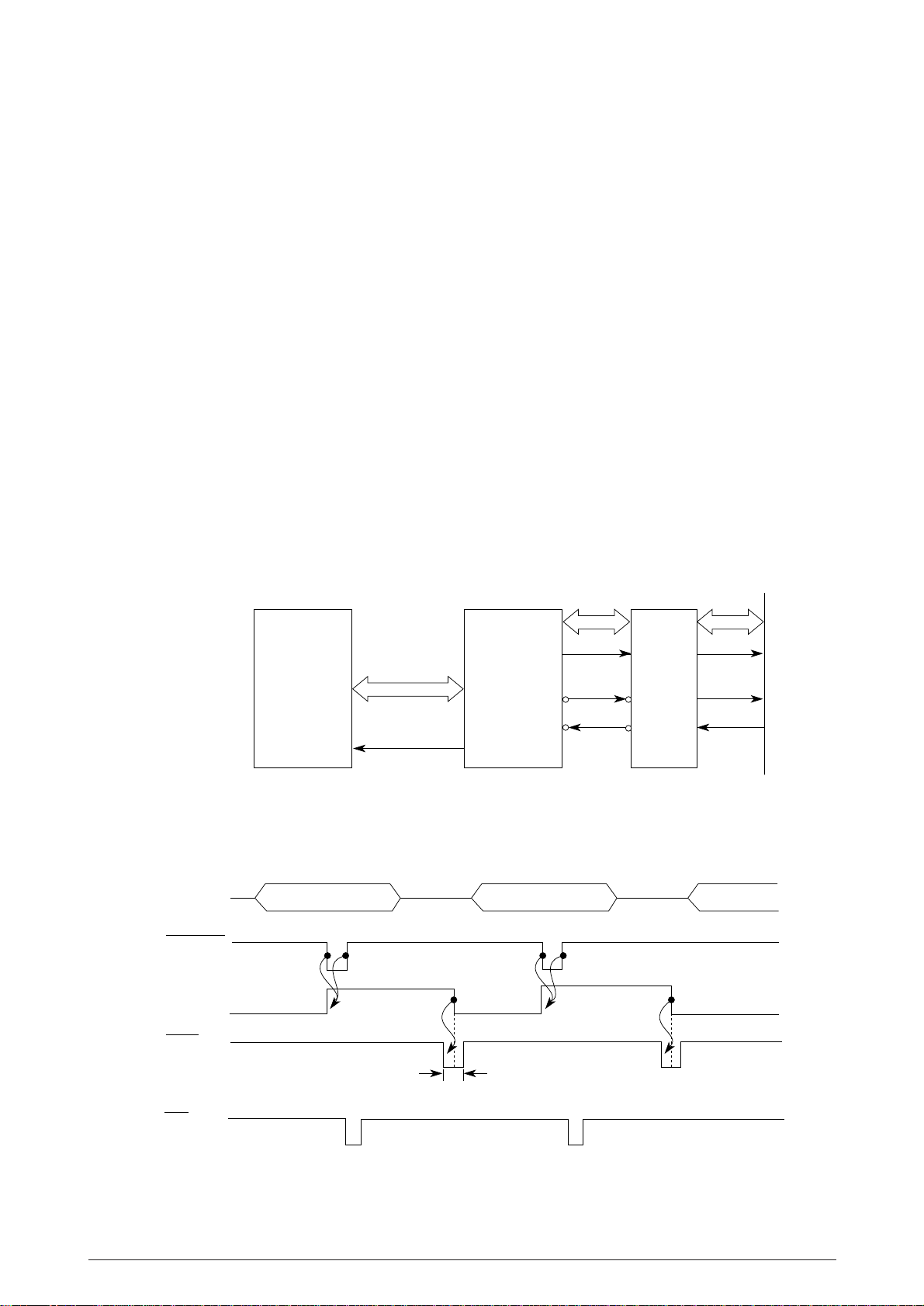
2.1.4 Interface control
The PM4410 is provided with the centronics parallel interface and RS-232C serial interface as
standard features.Also, it can be connected to option OKI HSP or Opt. Card. The interface cable
can be connected simultaneously with these interfaces.
These interfaces can be switched with the menu switch on the operation panel, in addition, you can
designate auto-select for them. The MPU communicates with hosts through the NHDC according
to the selected interface mode. The selected interface is stored to the EEPROM and can maintain
even after powering the printer off.
2.1.5 Parallel Interface Control
The Parallel data input from the host to the NHDC LSI is latched to its internal register at the falling
or rising edge of the STROBE-N signal.
At the same time, the LSI sets the BUSY signal to the high level to inform the host that the data
is being processed, and outputs the INT-P signal to inform the MPU of data reception. The data
is read upon receiving the RD-N signal from the MPU.
When the data processing ends, the BUSY signal is set to off and the ACK-N signal in sent to
request the next data. When reception is impossible because the buffer is full, the BUSY signal is
sent to request stopping of data transmission.
Data
1 to 8
STROBE
BUSY
MPU NHDC LSI
BSYP
A/D bus
ACKN
PSBN
INT-P
INT INT
or or
500ns max.
Line
driver
receiver
Parallel I/F
BUSY
ACK-N
STB-N
ACK
2~8µs
INT
Figure 2.8
40496501TH Rev.1 22
2.1.6 Serial Interface
The MPU sets the baud rate which is selected with the menu switch for the NHDC LSI and have
the serial I/F LSI to output the clock frequency of the baud rate.
Input signals from the serial I/F (DSR, CTS, CD and RD) are converted into TTL level ones by the
Line driver/receiver and input to the serial I/F LSI and NHDC LSI. The serial I/F LSI converts serial
data into parallel data to output it to the MPU.
Output signals (DTR, RTS, SSD and TD) to the serial I/F are output from the MPU to the NHDC
LSI and serial I/F LSI, and then converted through the Line driver/receiver into line voltage which
is output to the serial I/F.
AD0-AD7
MPU NHDC LSI
DSR
RD
ST SP
TCK0
RTSN
SSDN
DTRN
CTSN
DSRN
DCDN
Serial I/F LSI
CLK
RXDA
TXDA
Line
driver
receiver
Serial I/F
TD
RD
RTS
SSD
DTR
CTS
DSR
CD
SSD
Figure 2.9
40496501TH Rev.1 23
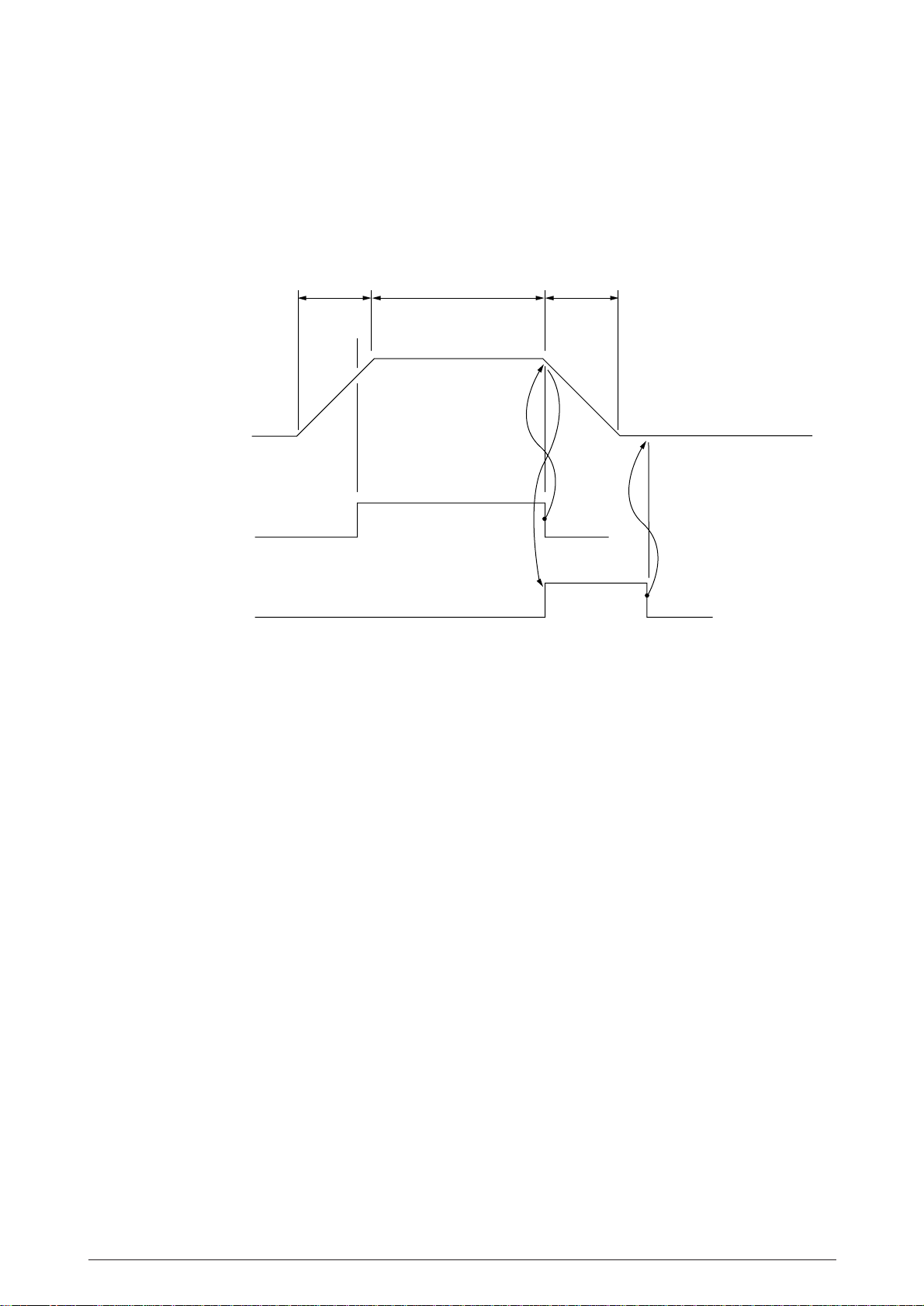
2.1.7 Printing operation
The time chart for the spacing and printing, line feed operations are as shown below.
The spacing, printing and line feed operations are controlled by the MPU. The MPU also controls
the entire timing of these operations.
Acceleration
Constant speed
Deceleration
SP Motor
Operation
Printing
Print
Line Feed
LF
Figure 2.10
When starting the printing operation, the MPU specifies the distance moved, print start position,
printing speed, etc. to the LSI, and activates the spacing motor. The MPU, when the carriage
arrives at the print position specified, activates the printer to start printing, and when printing
terminates, the MPU activates the line feed motor for line feed operation. During the line feed
operation, the MPU causes the carriage to decelerate. Upon termination of line feed operation, the
spacing operation is performed.
40496501TH Rev.1 24
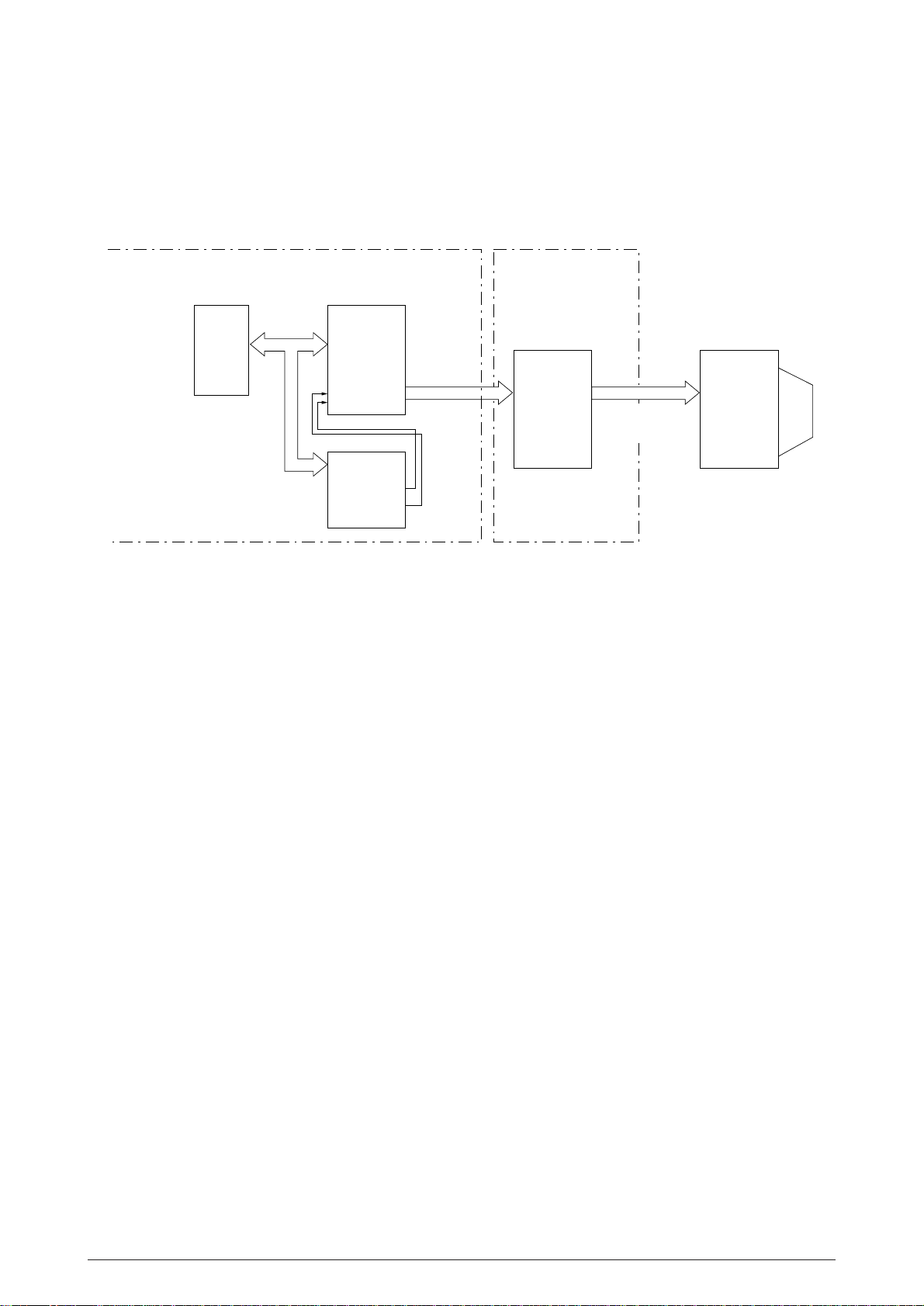
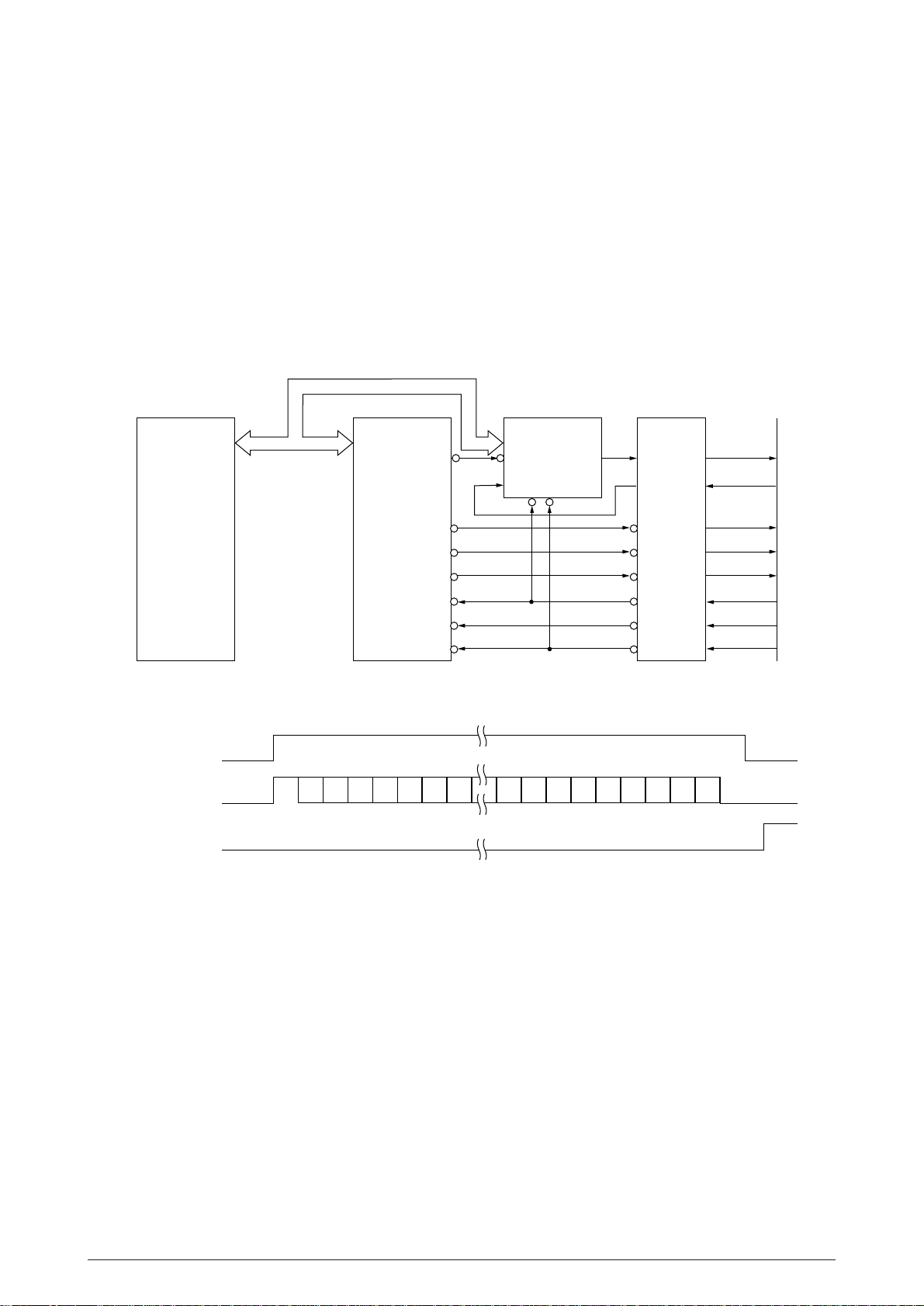
2.1.8 Printhead control
The printhead is controlled by the Main LSI and NHDC LSI.
Printing is synchronized with the ITOUT signal from the NHDC LSI.
Control Board
The NHDC LSI outputs the dot timing1 signals (DT1:1~18) and the dot timing2 signals (DT2:1~18),
and the driver IC drives each dot magnet. These signals are output from the NHDC LSI after the
following corrections for final driving time determination inside the LSI:
(1) Correction for the number of pins driven
MPU NHDC LSI
A/D bus
Main LSI
TFA-N
TFD-N
Print Data
HEAD1-P~
HEAD18-P
Figure 2.11
Driver Board
DRIVER
Print Data
HEAD1~
HEAD18
Print Head
The driving time is corrected according to the number of pins driven at the same time out of
18 pins.
(2) Correction according to adjacent pin drive timing
The driving time is adjusted by checking whether the pin adjacent to the pin to be driven is
driven on the previous timing.
(3) Correction for head gap
The driving time is corrected according to the head gap.
40496501TH Rev.1 25
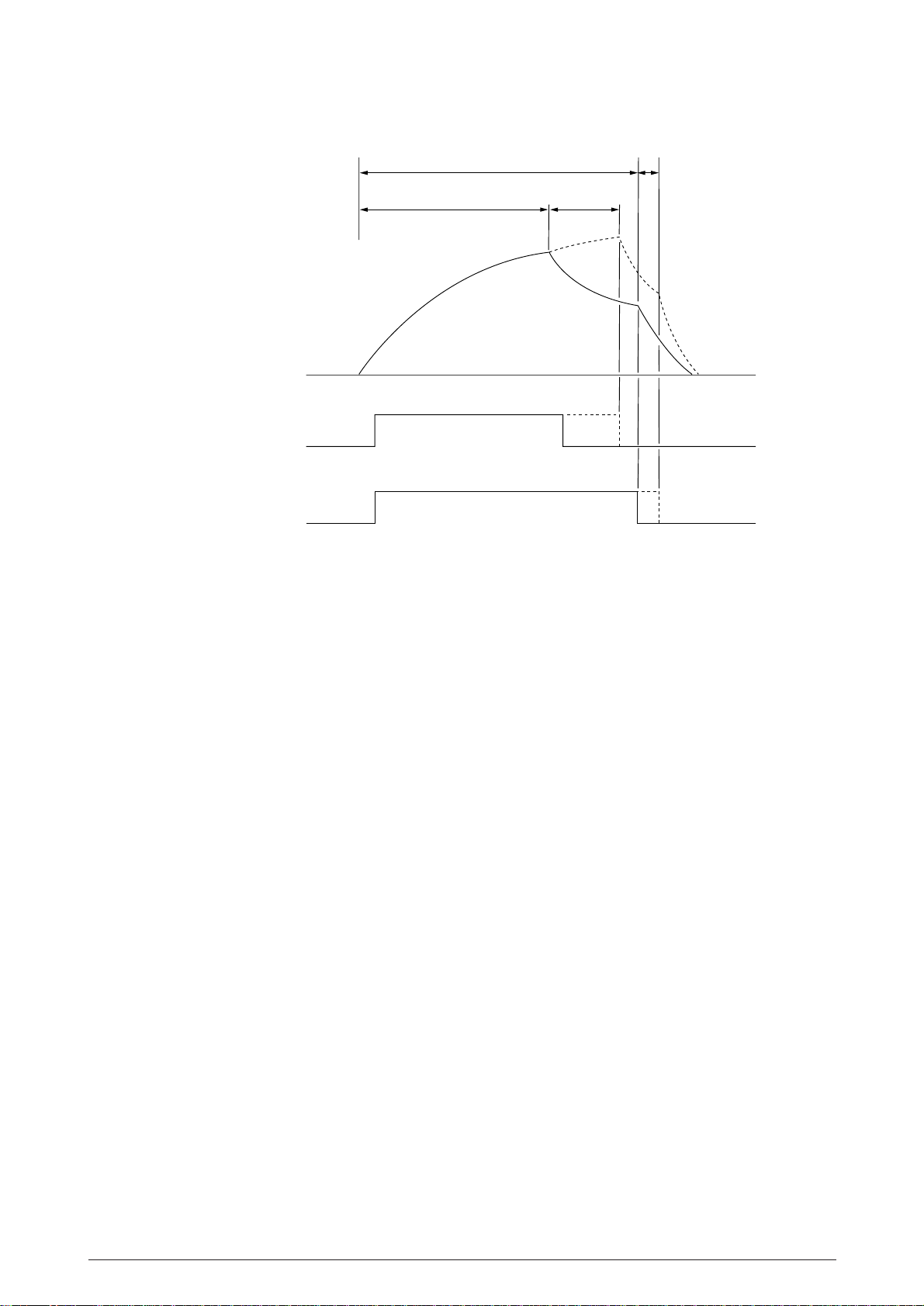
DT2 Basic drive time
(3)
Dot magnet drive
coil current
signals
DT
1
(D1–D18)
signals
DT
2
(D1–D18)
Basic drive time
DT
1
Figure 2.12
(1)+(2)+(3)
40496501TH Rev.1 26

2.1.9 Print Compensation Control
The print compensation can be made as shown below:
(a) Simultaneous Compensation of the number of impact pins
The NHDC LSI is provided with the compensation table for each pin to make necessary
compensation.
Number of impact pins Few Many
Drive time Short Long
(b) Duty control
1. If the number of the lines which exceeds 60% printing duty is continuous 8 lines, the printer
starts 2-path printing at the 8th line.
2. If the printer can activate 12 pins simultaneously in a line, it 2-path prints the line.
(c) Temperature compensation (See2.1.14 "Alarm Circuit.")
(d) Print mode compensation
According to the thickness of the printing medium, the print mode is compensated as shown
in the table below:
Head Gap Range 1 2 3 4 5
Print speed 100% 97% 95% 90% 89%
Drive time Short Long
(Drive time lengthens at each step.)
2.1.10 Space motor control
(1) The Main LSI generates the SPDV-P signal upon receiving the spacing command from the
MPU. This is a fixed cycle pulse signal.
The Main LSI varies the pulse duty according to the speed data from the MPU to control the
motor speed.
The SPFOW-P or SPREV-P signal from the Main LSI changes the current direction in the DC
motor to run the motor in the forward or reverse direction.
SPFOW-P
SPREV-P
SPDV-P
MotorCurrent
Figure 2.13
40496501TH Rev.1 27
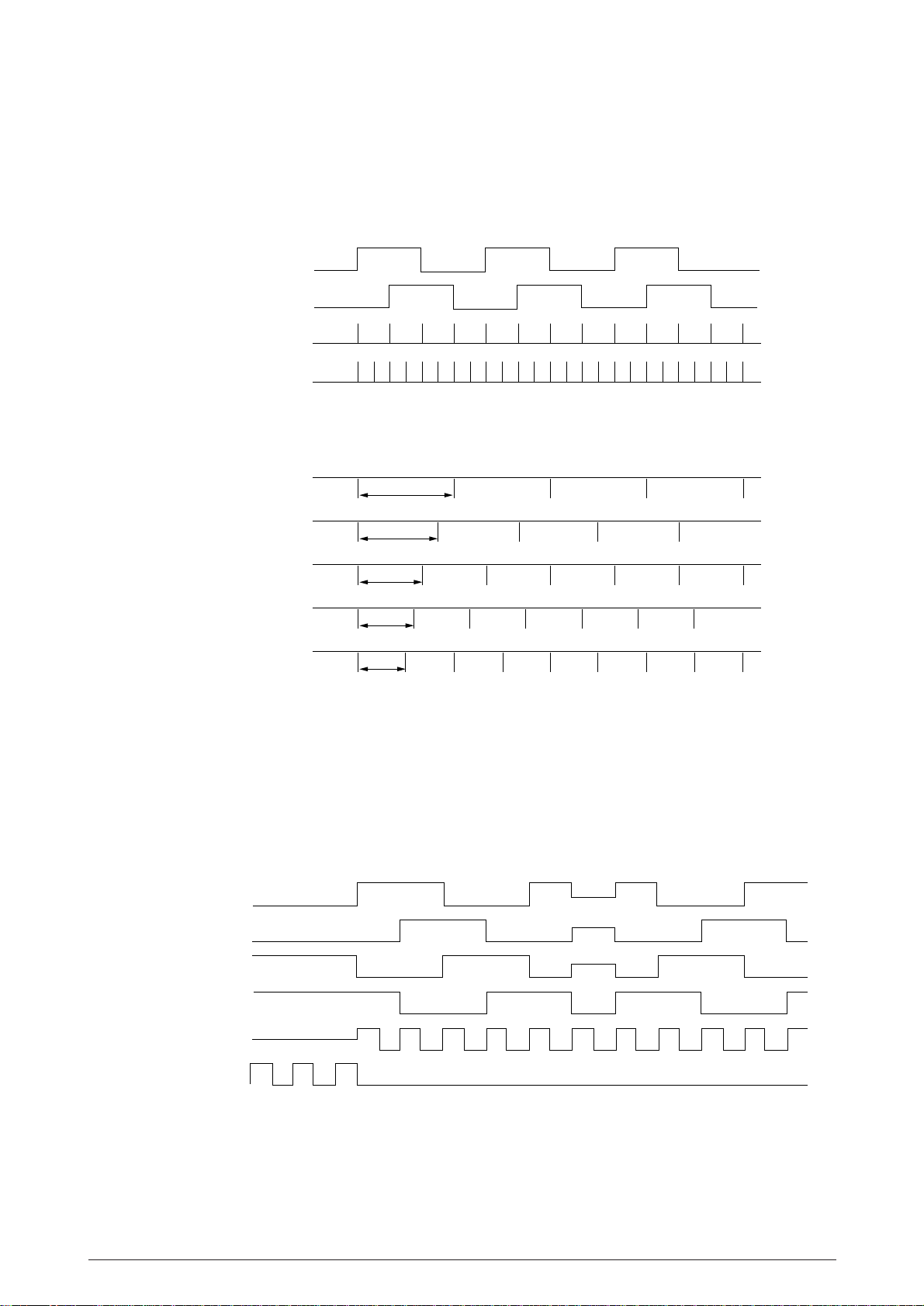
(2) Slit encoder
As the space motor rotates, it generates feedback pulse signals SPA-P and SPB-P. The Main
LSI detects the edge pulses from these signals and multiplies the frequency to output the
S720-P signals as the normalized timing to NHDC LSI to generate head drive timing.
SPA-P
SPB-P
Edge pulse
S720-P
UTILITY MODE
ITOUT 10CPI
ITOUT 12CPI
ITOUT 15CPI
ITOUT 17CPI
ITOUT 20CPI
2.1.11 Line feed
1/360"
1/120"
1/144"
1/180"
1/206"
1/240"
Figure 2.14
The LF motor is locked by the current supplied from +12V according to the pulse duty of the
LFCHOP-P signal during the stop period.
It is driven by +44V application by the LFOVDV-P signal for line feed operation.
LFø1
LFø2
LFø3
LFø4
LFOVDV-P
LFCHOP-P
Figure 2.15
40496501TH Rev.1 28
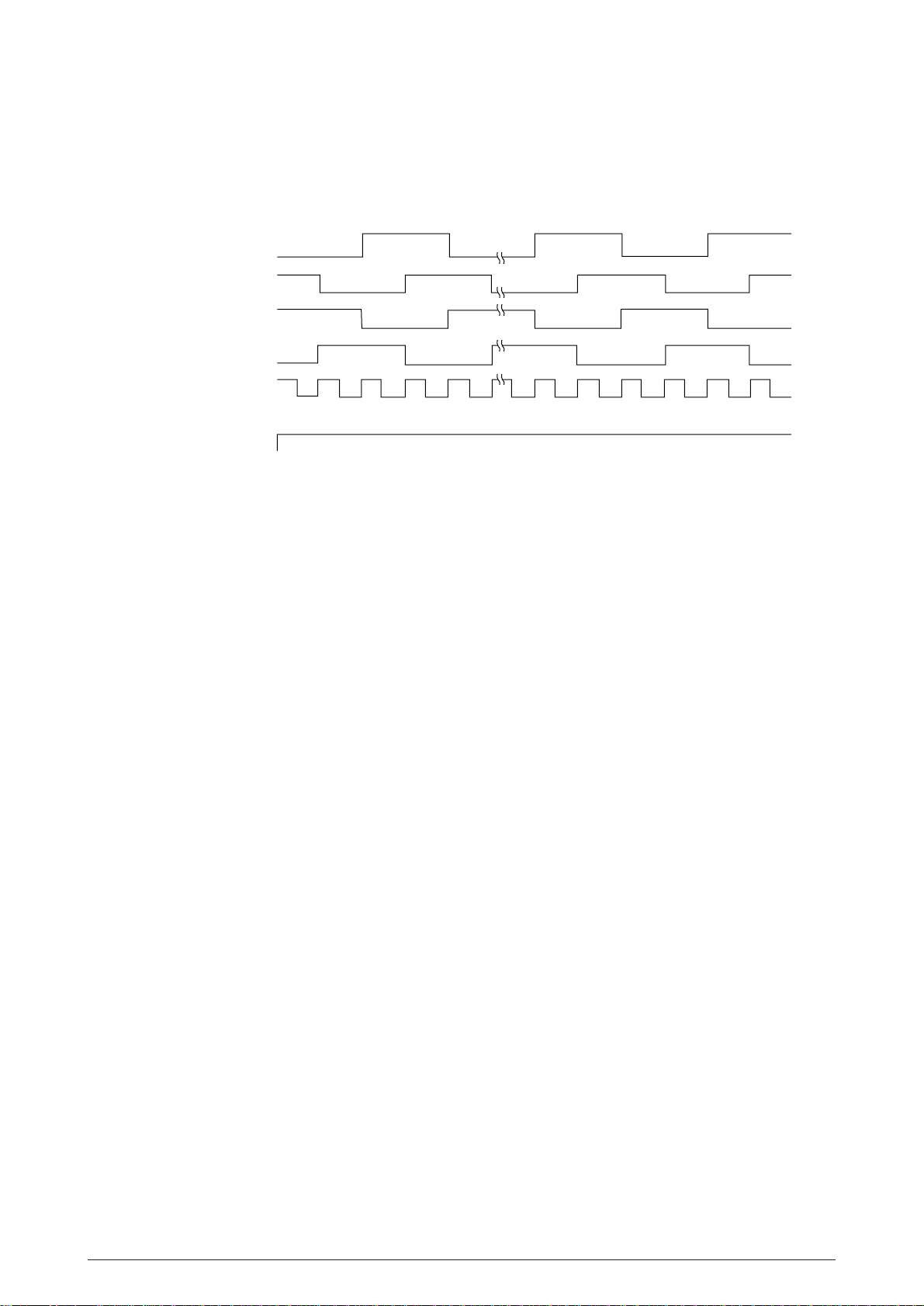
2.1.12 Bail, tractor switching, AG, ribbon motor control
Bail, tractor switching, AG and ribbon motor control is as shown below.
The AG motor is locked with AGHOLD-P.
MO ø1
MO ø2
MO ø3
MO ø4
MO OVDV
AGHOLD-P
Figure 2.16
40496501TH Rev.1 29
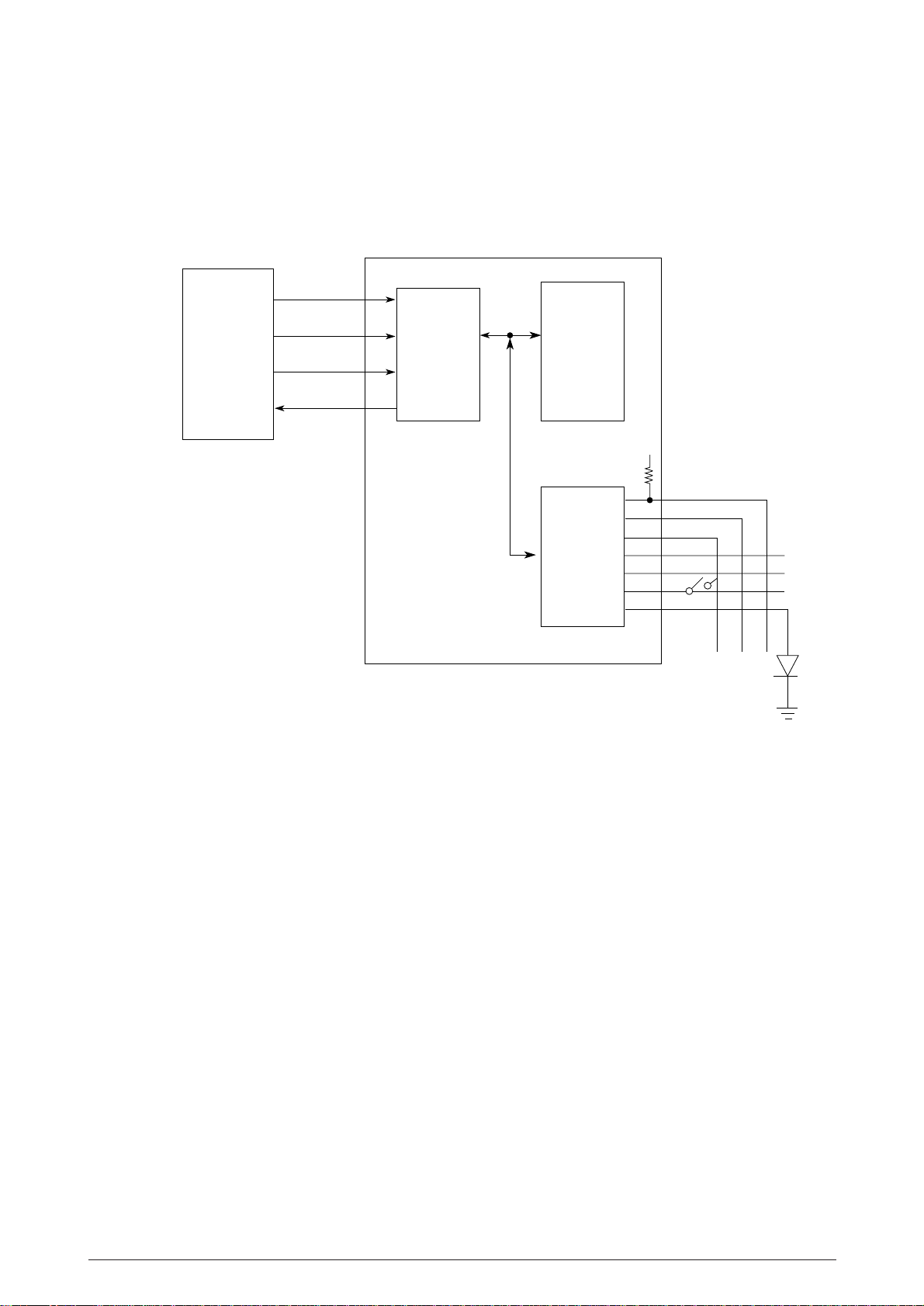
2.1.13 Operation Panel
The clock synchronization OPCLK of NHDC LSI is used to input the switch data and output the LED
data and LCD data through the operation panel control LSI (IC1: BU6152S).
NHDC LSI
SCKN
SCSN
SDO
SDI
OPDATAOUT-P
56
OPSCLK-N
59
OPSQCR-N
58
OPDATAIN-P
57
BU6152S
Command
and Data
latch
LED driver
+5V
Switch
controller
Figure 2.17
A 2-byte (15 bits + 1 even parity bit) command (OPDATAOUT-P) is transmitted to the LSI
(BU6152S) in synchronization with the OPSCLK-N signal. The LSI decodes this command and
when it is found to be legal, returns a 2-byte command response back to the NHDC LSI which
includes data on Switch information, LED status, LCD status receive command ACK/NAK and 1
odd parity bit.
Any transmission errors found cause the command to be reissued after the transmission of the
OPSQCR-N signal.
40496501TH Rev.1 30
 Loading...
Loading...